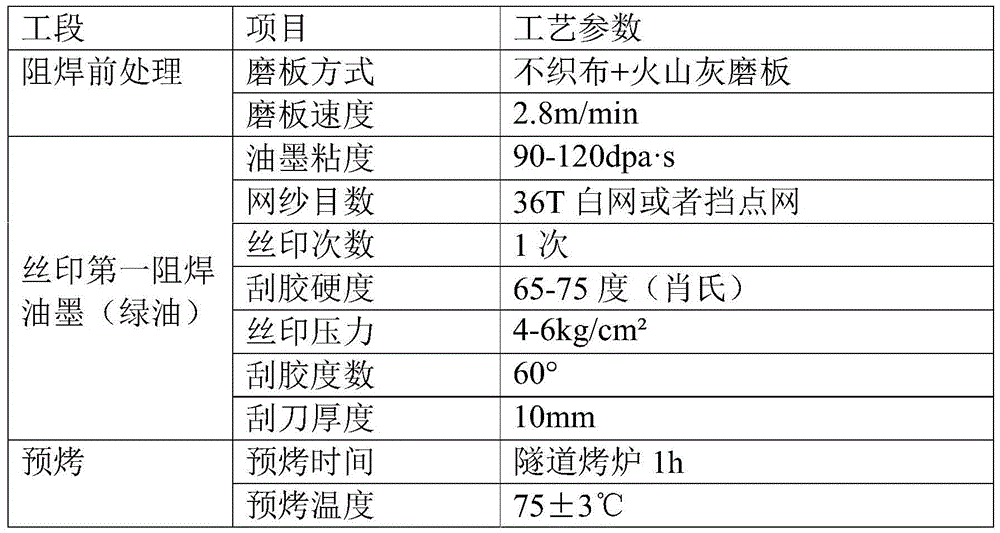
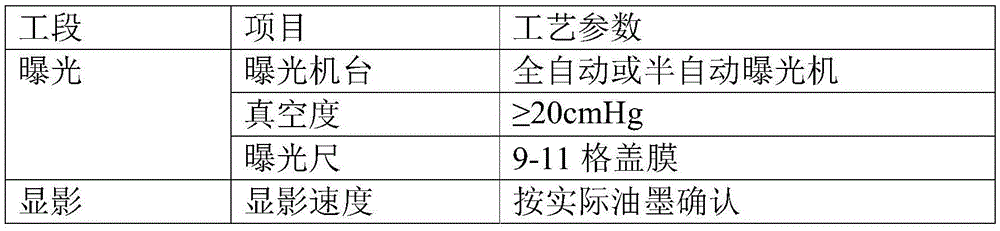
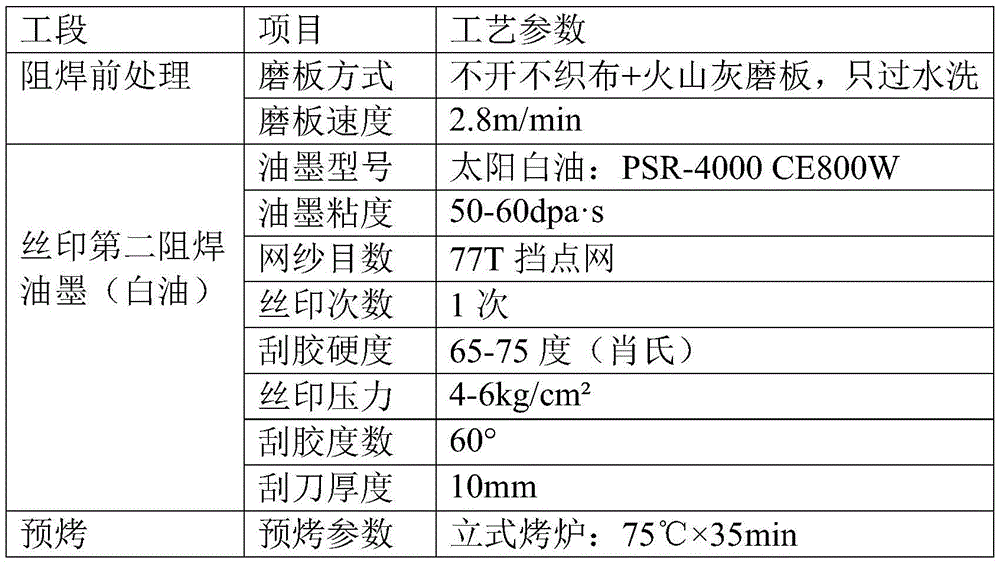
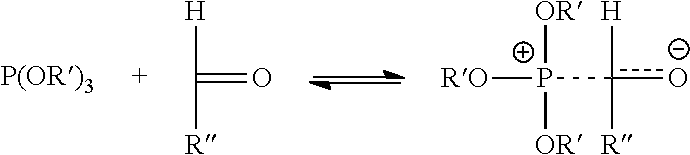Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
101results about "Circuit masks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molded waveguides
InactiveUS8012382B2Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsInorganic saltsActive agent
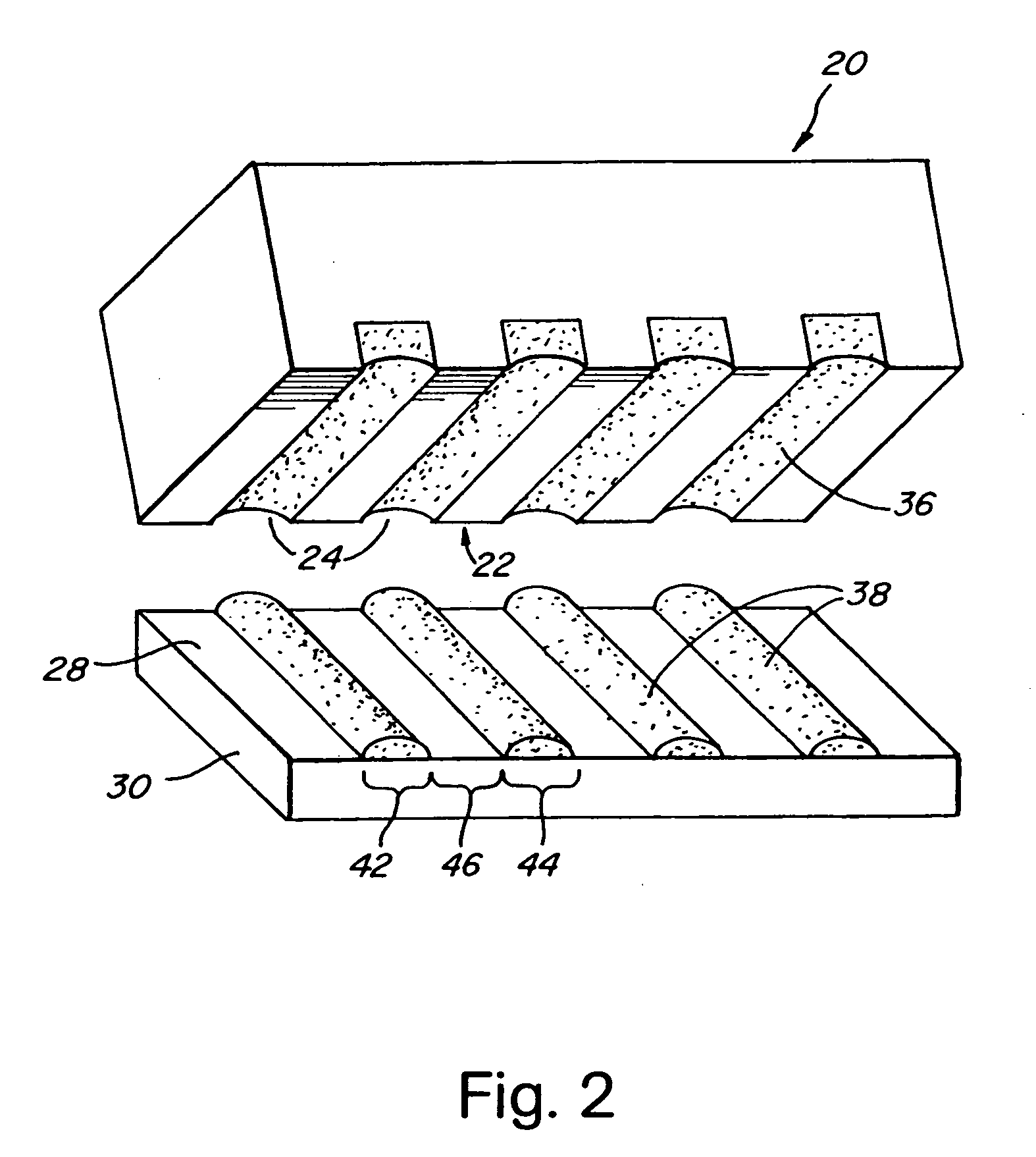
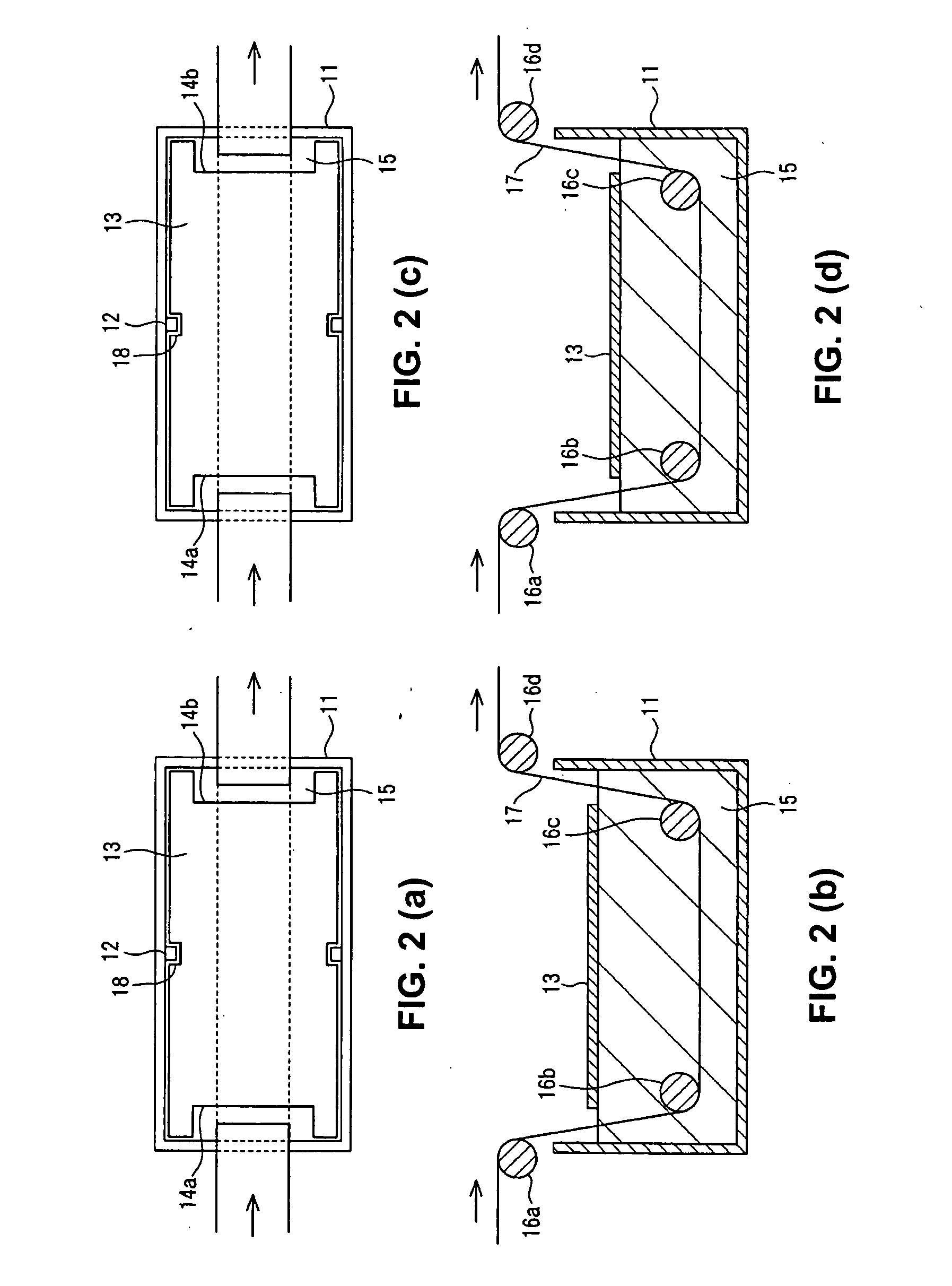
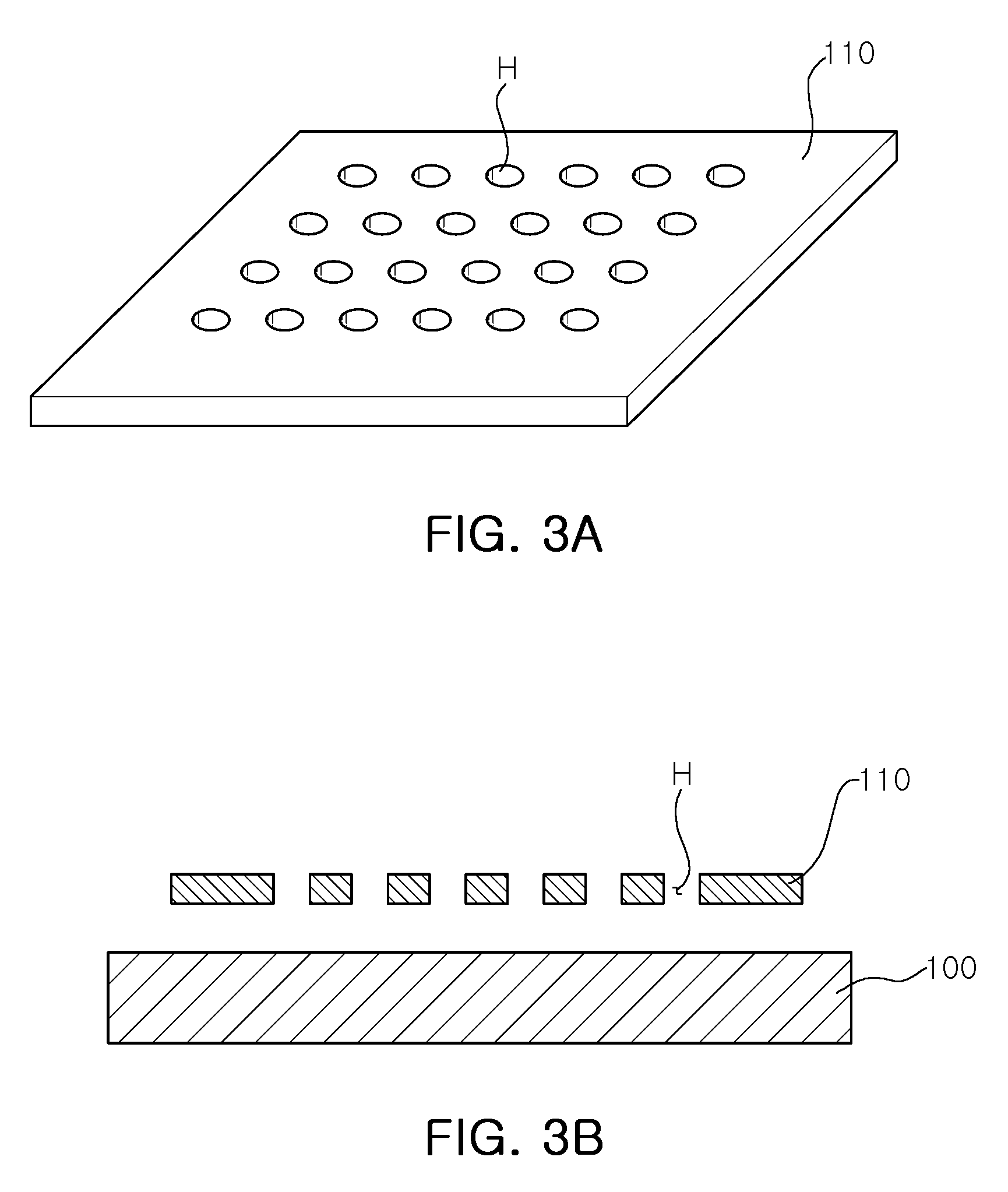
Chemically or biochemically active agents or other species are patterned on a substrate surface by providing a micromold having a contoured surface and forming, on a substrate surface, a chemically or biochemically active agent or fluid precursor of a structure. A chemically or biochemically active agent or fluid precursor also can be transferred from indentations in an applicator to a substrate surface. The substrate surface can be planar or non-planar. Fluid precursors of polymeric structures, inorganic ceramics and salts, and the like can be used to form patterned polymeric articles, inorganic salts and ceramics, reactive ion etch masks, etc. at the surface. The articles can be formed in a pattern including a portion having a lateral dimension of less than about 1 millimeter or smaller. The indentation pattern of the applicator can be used to transfer separate, distinct chemically or biochemically active agents or fluid precursors to separate, isolated regions of a substrate surface. Waveguide arrays, combinatorial chemical or biochemical libraris, etc. can be made. Differences in refractive index of waveguide and cladding can be created by subjecting the waveguide and cladding, made of indentical prepolymeric material, to different polymerization or cross-linking conditions. Interferometers are defined by coupling arrays of waveguides, where coupling can be controlled by altering the difference in refractive index between cladding and waveguide at any desired location of the array. Alteration and refractive index can be created photochemically, chemically, or the like. Sensors also are disclosed, including biochemical sensors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
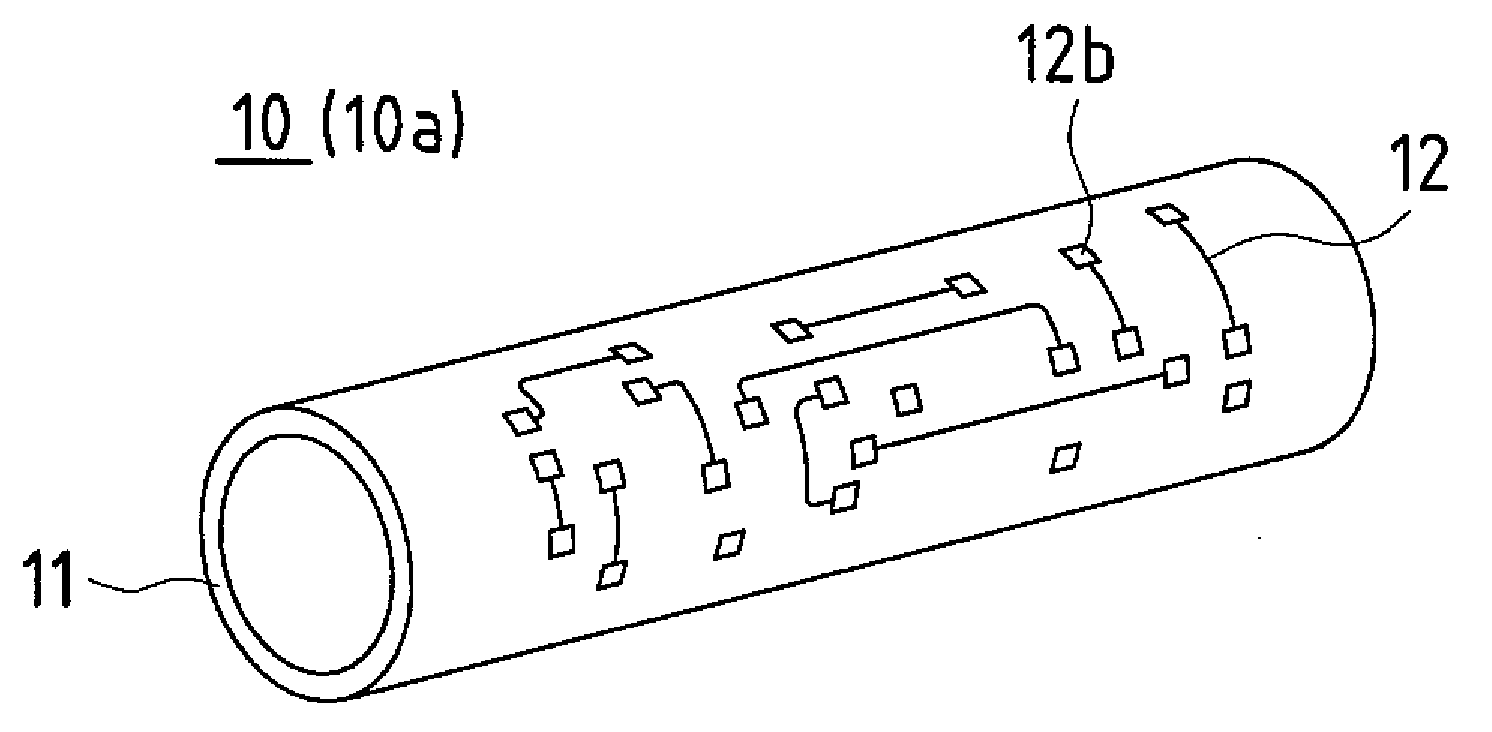
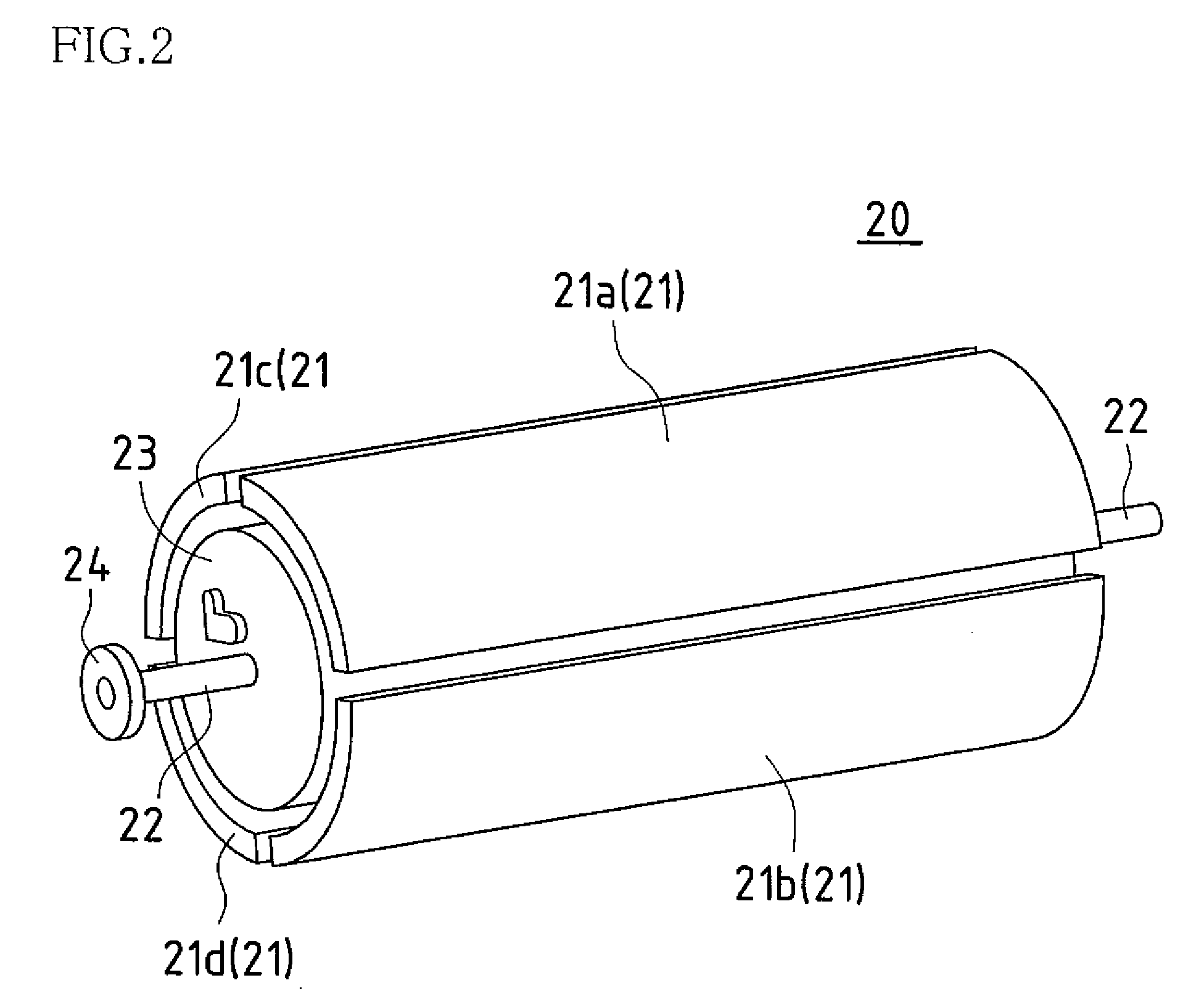
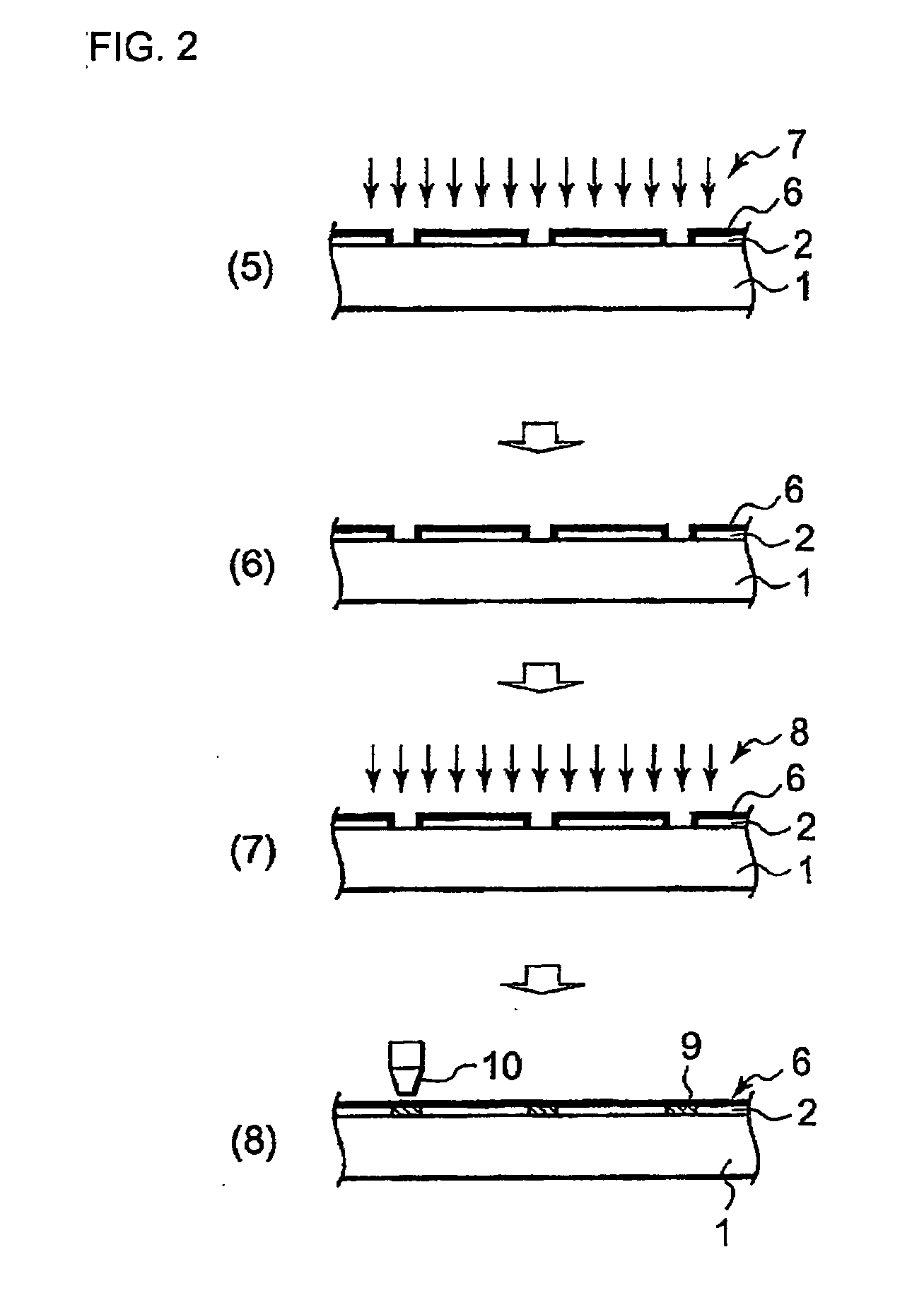
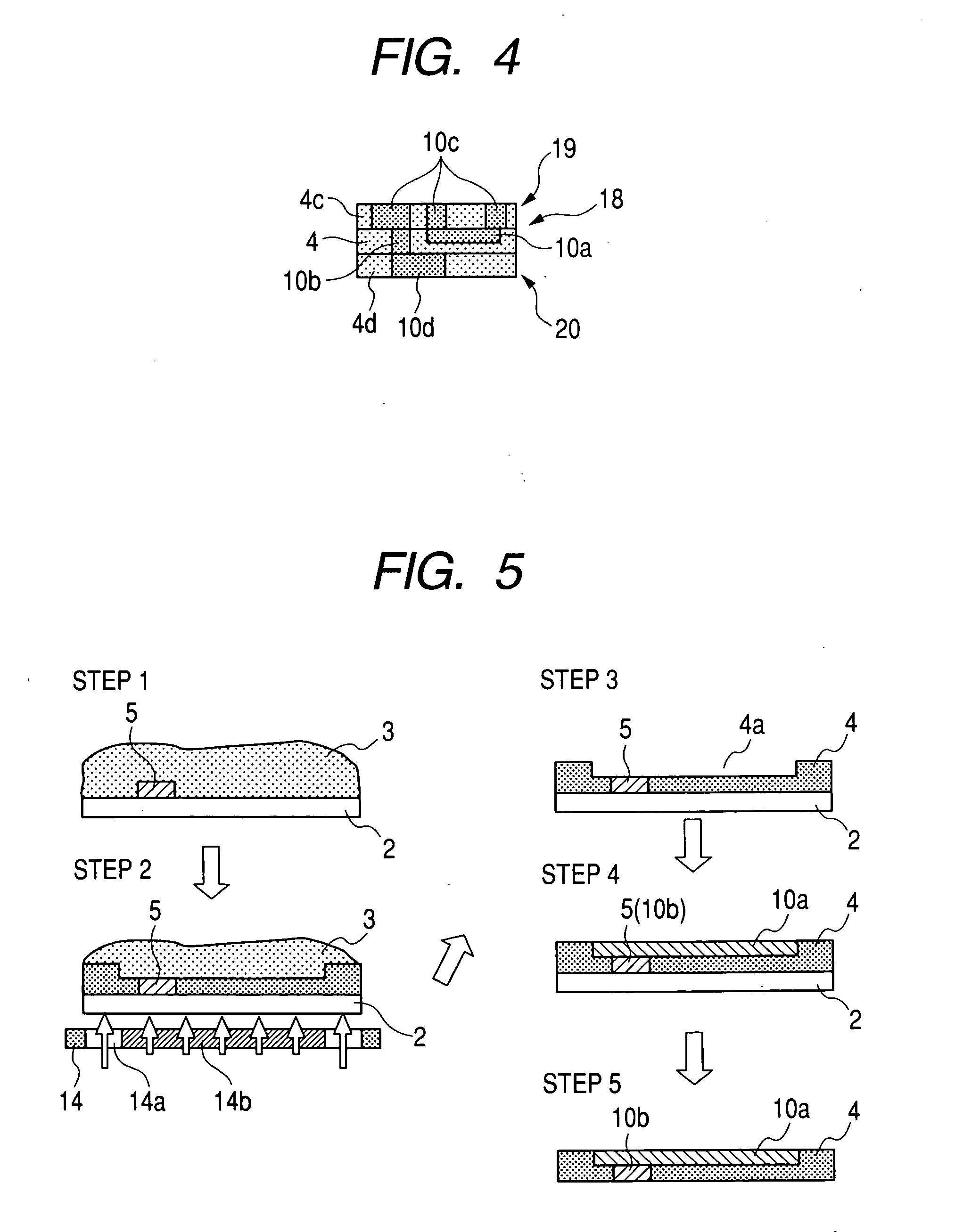
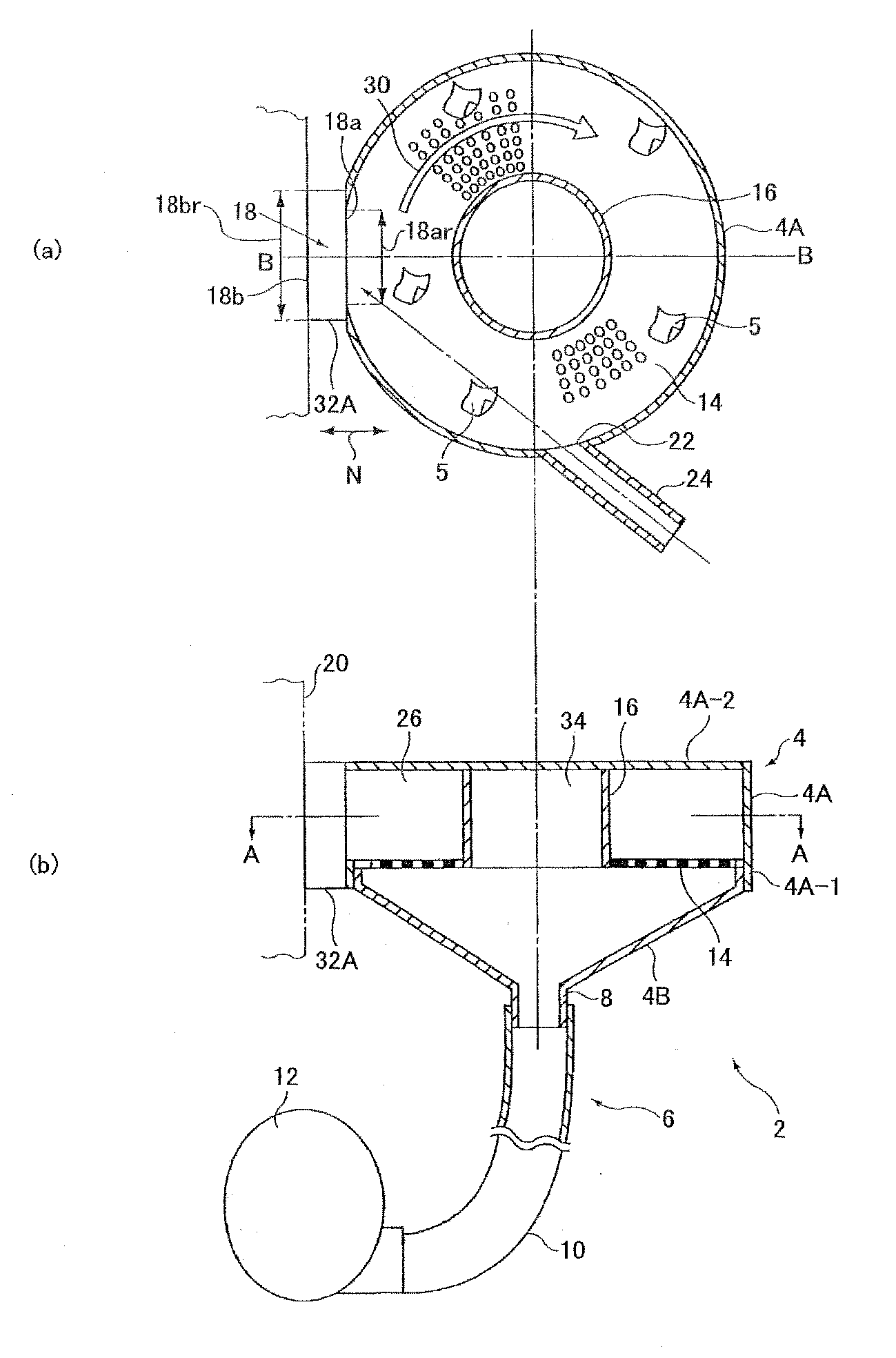
Printed wiring board manufacturing apparatus, printed wiring board, method for manufacturing printed wiring board, and electronic device
InactiveUS20080118681A1Easy to manufactureAdaptableMechanical working/deformationWelding/cutting auxillary devicesEngineeringElectronic equipment
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a printed wiring board manufacturing apparatus being provided with a drum unit having a processing cylinder that holds the printed wiring board material and comprises a cylinder outer circumference and a processing unit that performs processing on the printed wiring board material held by the processing cylinder.
Owner:SHARP KK
Fabrication process of stepped circuit board
InactiveUS20140304977A1Reduce gapSmall coefficientElectronic circuit testingPrinted circuit aspectsCopper platingSolder mask
A fabrication process of a stepped circuit board, comprises the following steps of: A) cutting a circuit board substrate, printing patterns on an inner layer thereof, performing etching, stepped groove grinding, washer milling, brownification and lamination processing on the inner layer, and then drilling holes on an outer layer thereof; B) depositing copper on the outer layer of the circuit board substrate with drilled holes, and then electroplating the entire circuit board substrate; C) performing pattern transfer; D) performing pattern copper plating on the circuit board substrate, and grinding the shape of a connecting piece (SET) on the circuit board substrate, and then etching the outer layer; E) printing a solder mask and texts in a silk-screen manner; F) depositing nickel immersion gold on the entire substrate, then printing characters in a silk-screen manner; and G) testing and inspecting the electrical performance and appearance of a finished board.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNTAK MULTILAYER PCB
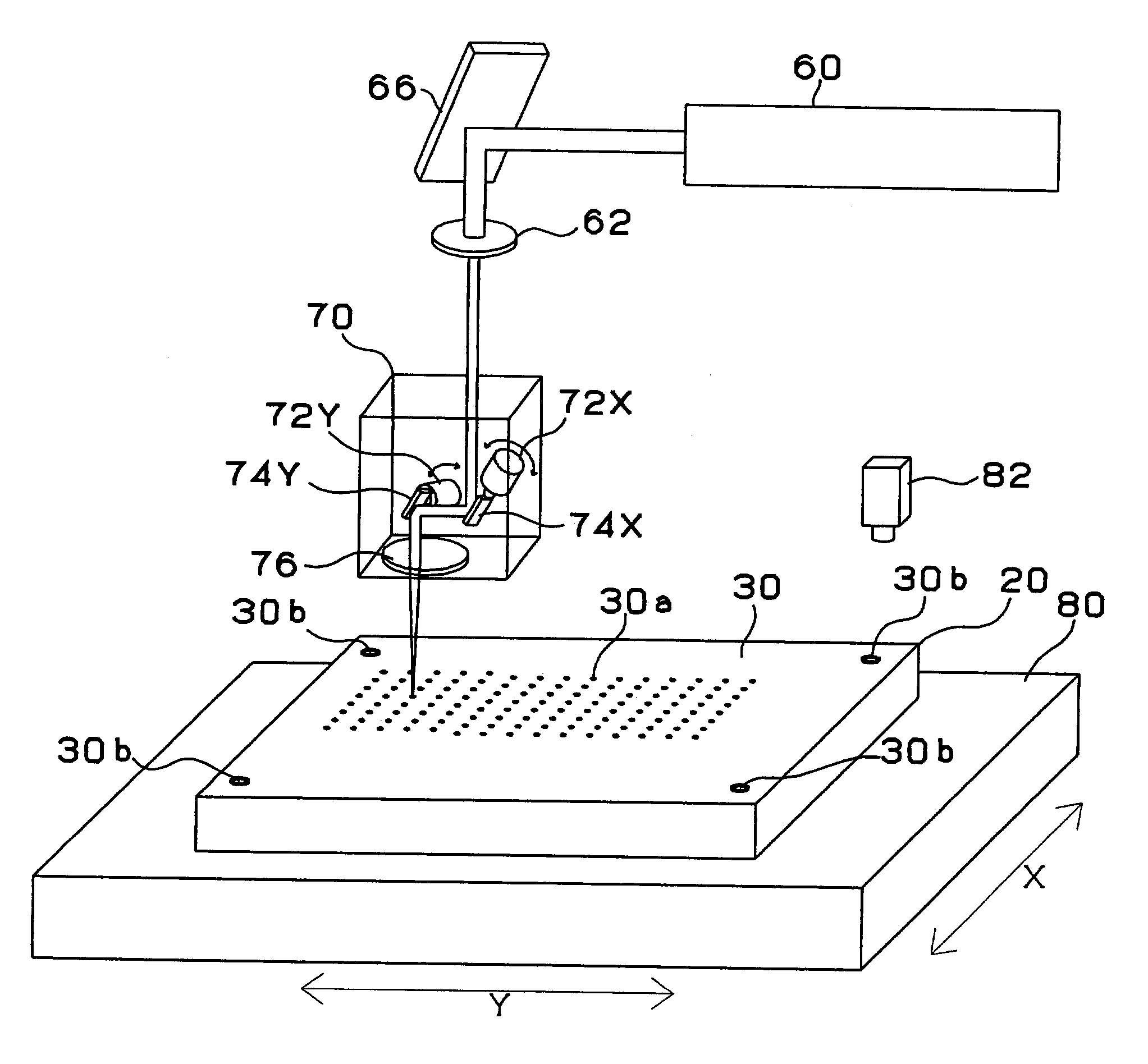
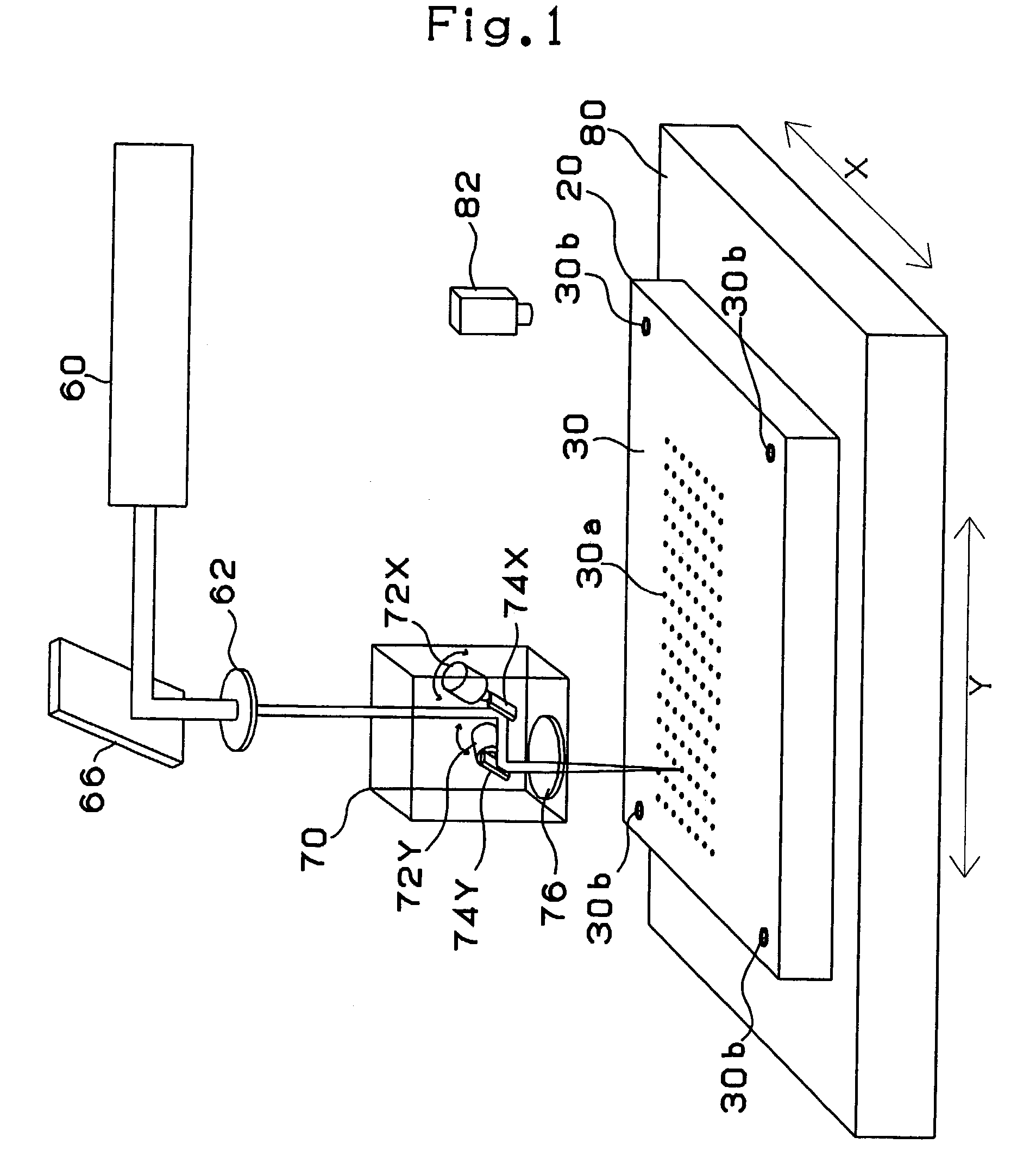
Process for producing a multi-layer printed wiring board
InactiveUS7127812B2Easy to disassembleNot to damageElectrical testingCircuit board tools positioningLaser beamsElectrical and Electronics engineering
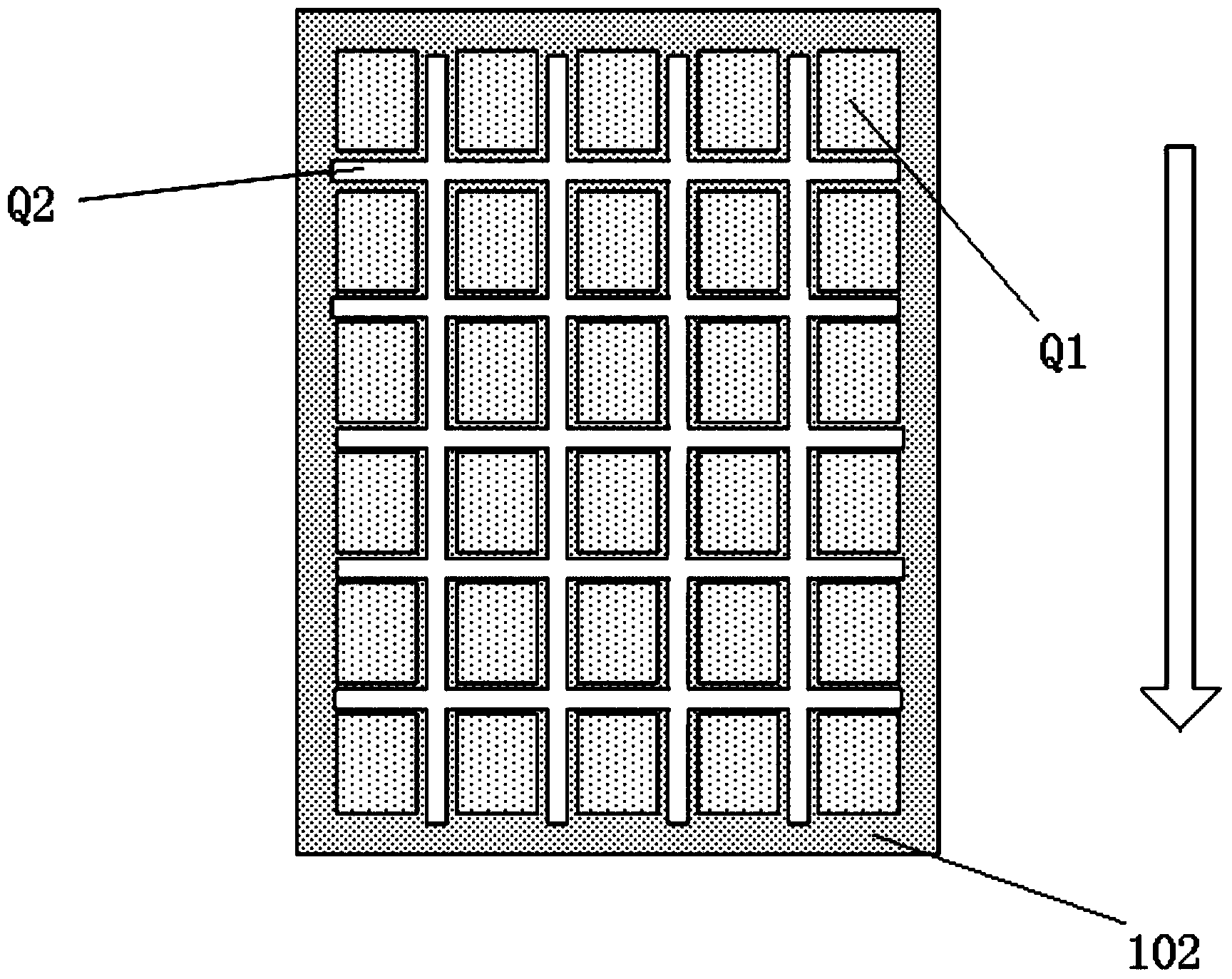
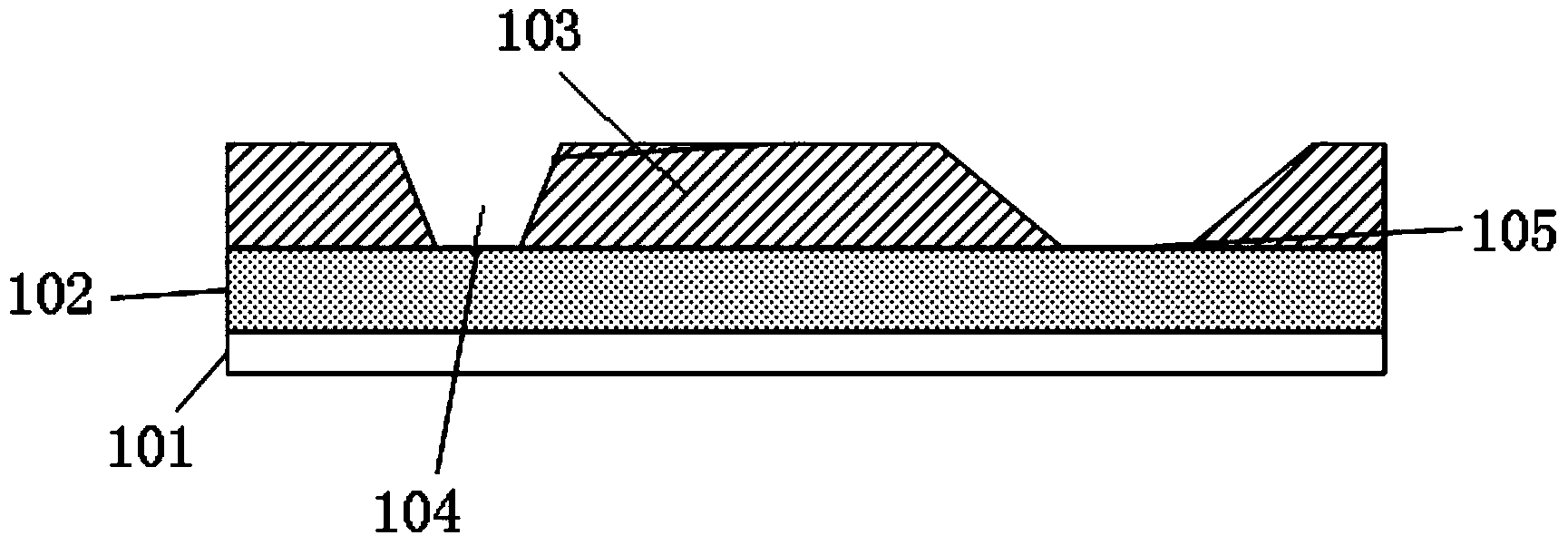
A board 20 is provided with a Cu film 30 as a conformal mask, in which are formed a register mark 30b and an opening 3a through which a via hole is formed. A camera senses this register mark 30b so that the position of the board 30 is determined. A laser beam is directed to the approximate position of the opening 30a, so that the opening 26a through which the via hole is drilled is formed. The accuracy of the position of the opening of the via hole depends on the accuracy of the position of the opening 30a in the Cu film 30 as the conformal mask. Therefore, the via hole can be formed at an adequate position despite the low accuracy of the position for laser irradiation.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Display panel mother board and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103779356ARelease internal stressAvoid influenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerComputer science
The invention provides a display panel mother board and a preparation method thereof, belongs to the field of display techniques and solves the problem that other graphs in the display panel mother board offset due to large inside stress of electrical insulation layers in the existing display panel mother board. The display panel mother board comprises a plurality of display panel regions arranged at intervals and precutting regions adjacent to the display panel regions, wherein at least parts of the electrical insulation layers arranged in the precutting regions in the display panel mother board are removed.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD +1
Conductive adhesive and circuit board bonding method
InactiveCN108882552AReduce manufacturing costEvenly distributedPorous dielectricsPrinted circuit assemblingAdhesiveElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides a conductive adhesive and circuit board bonding method, which comprises a substrate, an insulating portion and a conducting portion formed on the surface of the substrate. The insulating portion comprises insulating rubber retaining walls spaced apart in the same direction. The conductive portion is a conductive adhesive, and the conductive adhesive is filled in a space between the adjacent insulating rubber retaining walls. According to the conductive adhesive and circuit board bonding method, the longitudinal conduction and the lateral cutting of the conductive adhesive are realized by preparing the conductive portion and the insulating portion in steps in the conductive adhesive, uniform distribution of the conductive particles can be guaranteed, and the manufacturing costs of the conductive adhesive can be reduced.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS SEMICON DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
High-speed interconnects for printed circuit boards
ActiveUS20160174364A1Improve data transfer rateImprove adhesionInsulating substrate metal adhesion improvementDielectric materialsChemical treatmentSurface roughness
High-speed interconnects for printed circuit boards and methods for forming the high-speed interconnects are described. A high-speed interconnect may comprise a region of a conductive film having a reduced surface roughness and one or more regions that have been treated for improved bonding with an adjacent insulating layer. Regions of reduced roughness may be used to carry high data rate signals within PCBs. Regions treated for bonding may include a roughened surface, adhesion-promoting chemical treatment, and / or material deposited to improve wettability of the surface and / or adhesion to a cured insulator.
Owner:AMPHENOL CORP
Molded waveguides
InactiveUS20090166903A1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsInorganic saltsCoupling
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Photoimprintable Low Dielectric Constant Material and Method for Making and Using Same
A process for preparing a photoimprinted film, a composition for forming a photoimprinted film and a photoimprinted film comprising a dielectric constant of less than about 3.5. The method includes providing a material film having a composition including at least one silica source capable of being sol-gel processed, at least one photoactive compound and at least one solvent; and water. The composition contains less than about 0.1% by weight of an added acid. A mold having mold features is provided. The mold is positioned in sufficient contact with the material film to allow the material to contact at least a portion of the mold features. The material film is then exposed to a radiation source and the film is cured to form a solidified material film. The mold is separated from the solidified material, wherein the material includes film features corresponding to the mold features.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Method of manufacturing resin multilayer substrate
ActiveUS20160044798A1Small sizePrecise positioningPrinted circuit assemblingSolid-state devicesEngineering
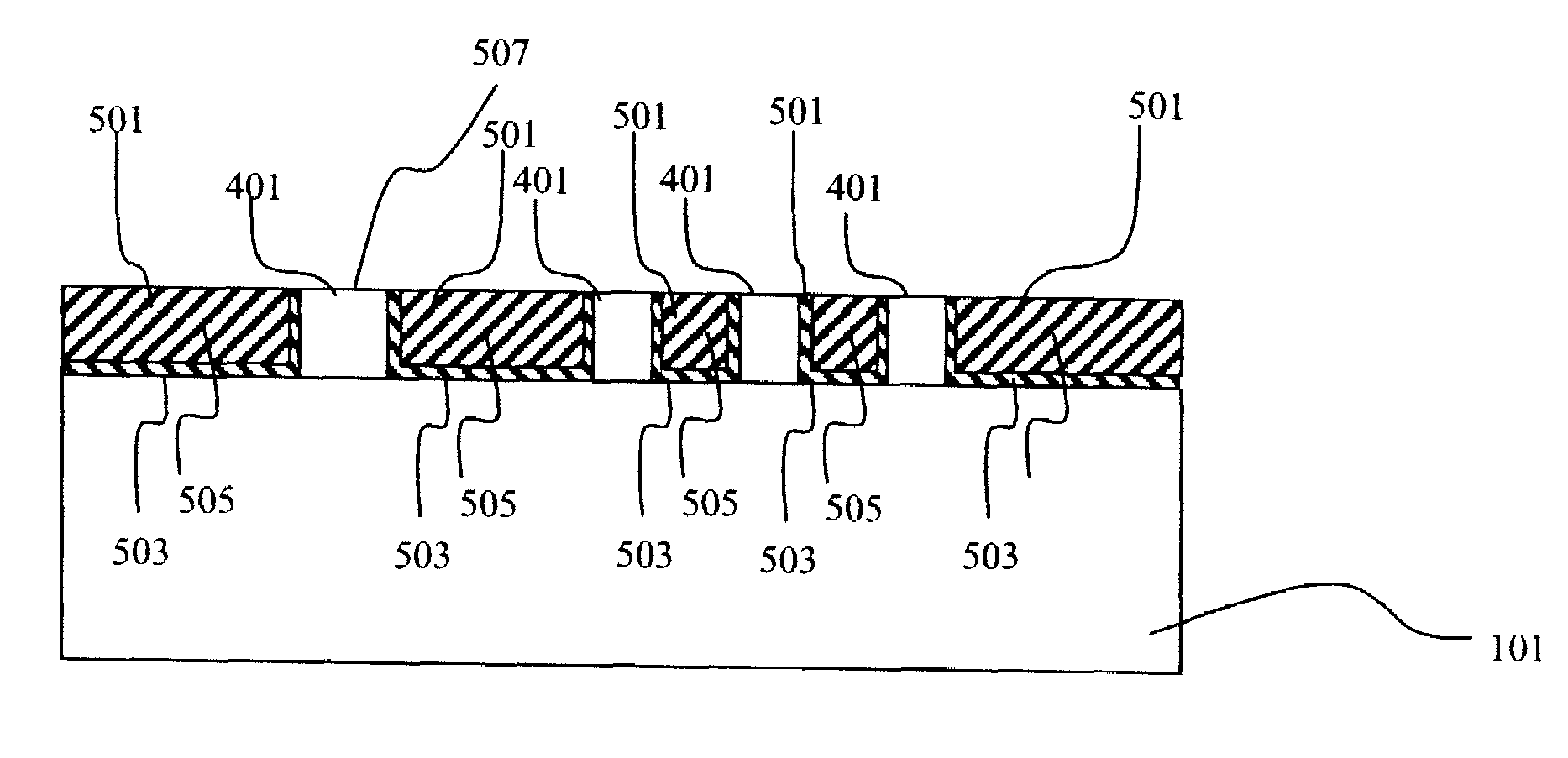
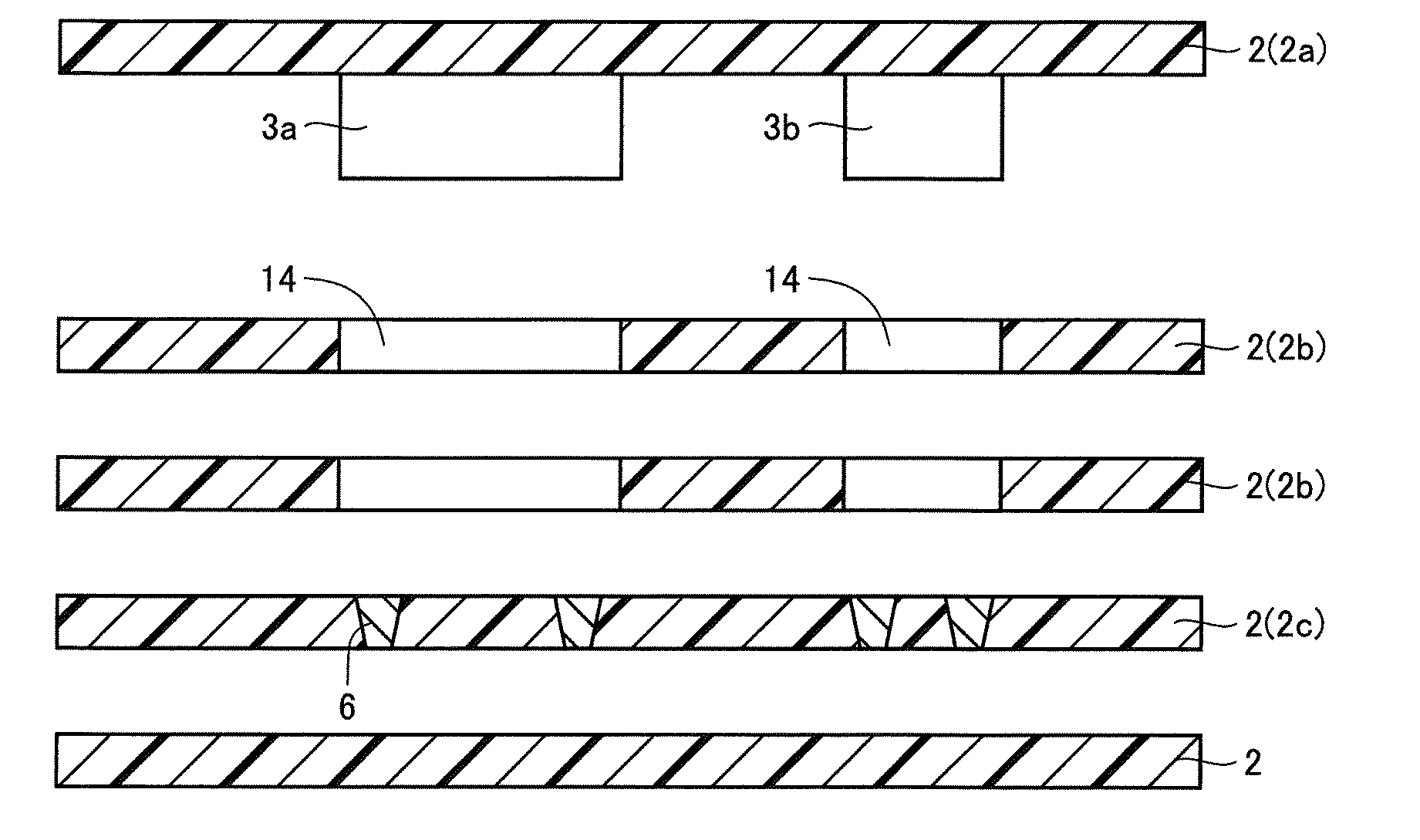
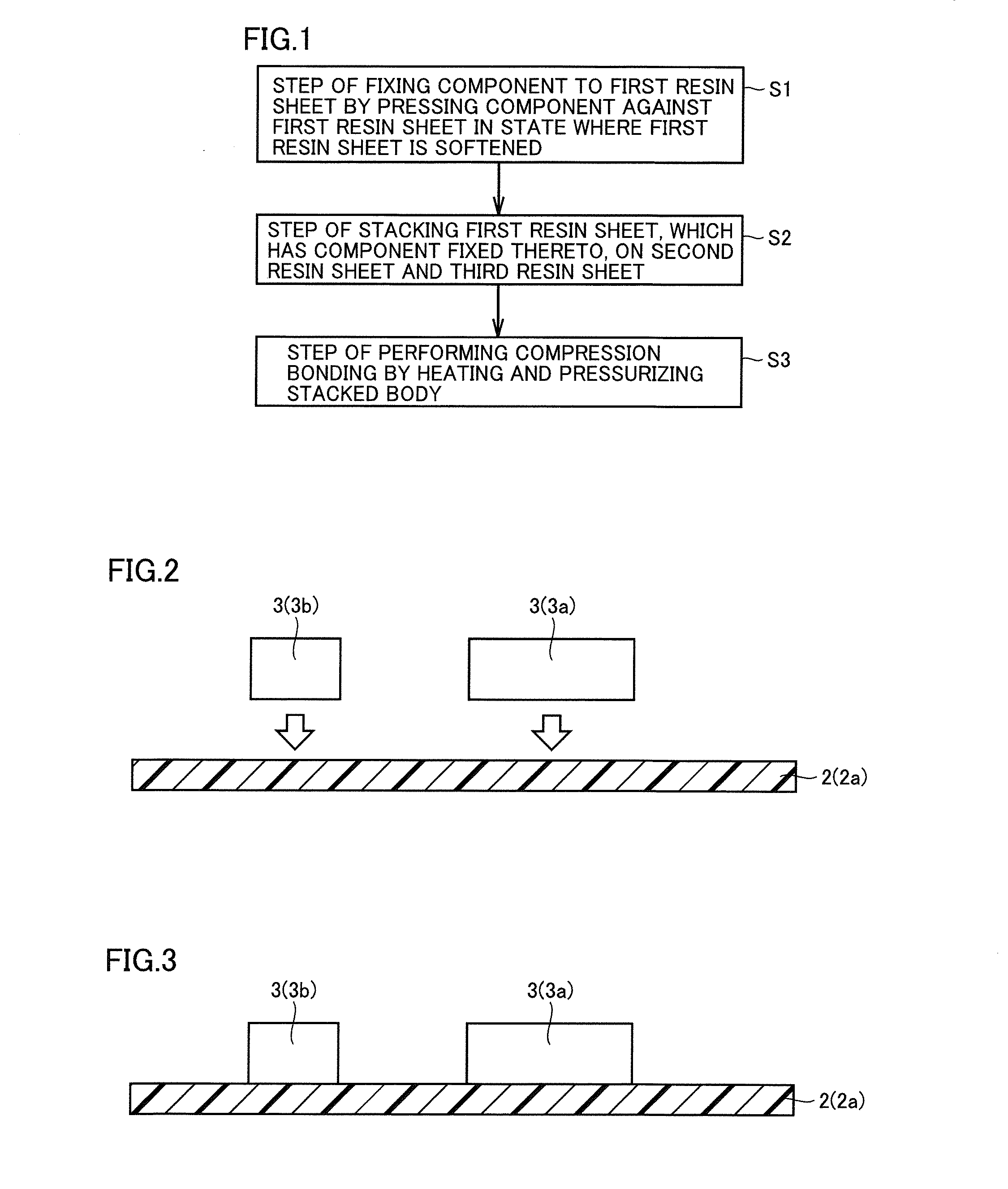
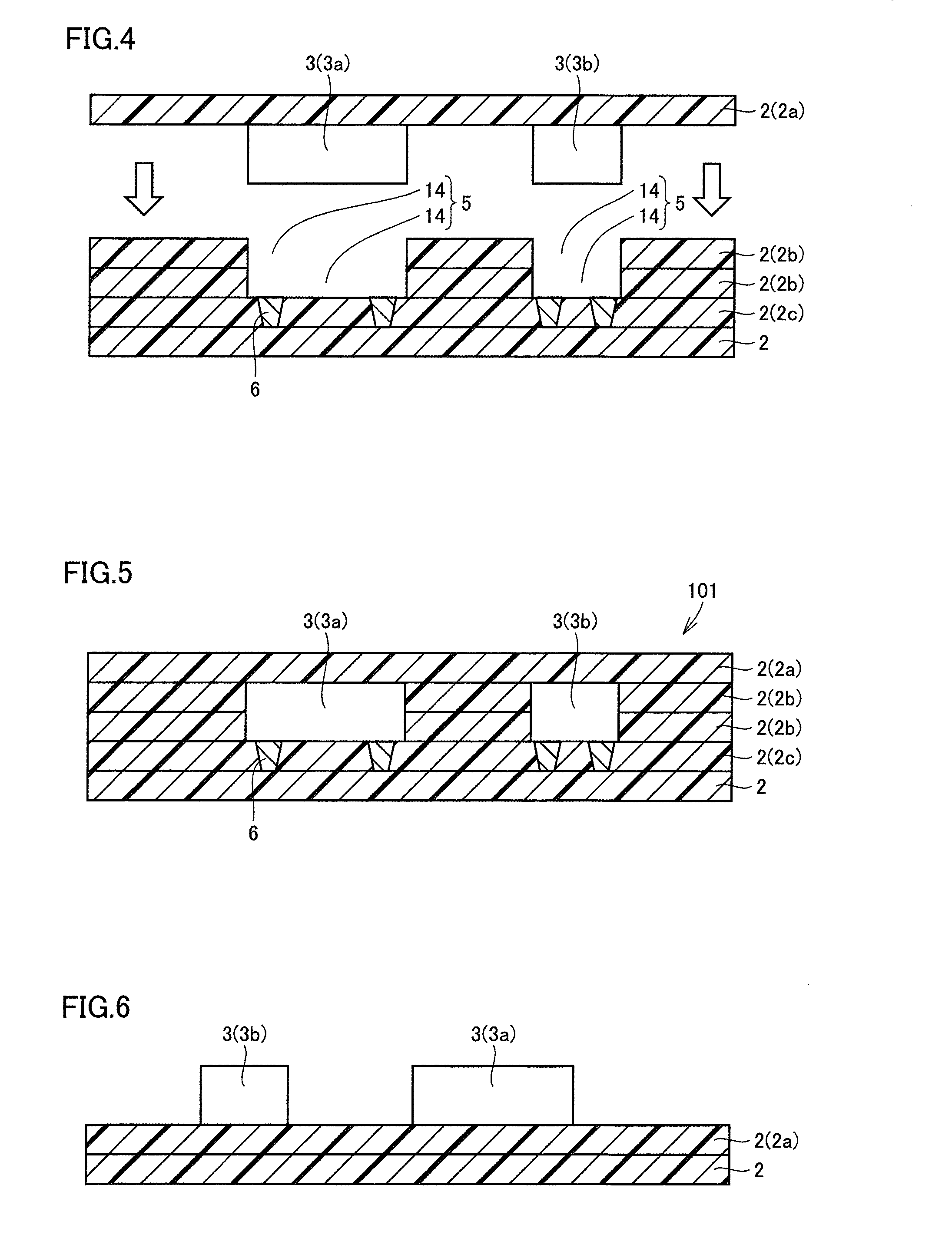
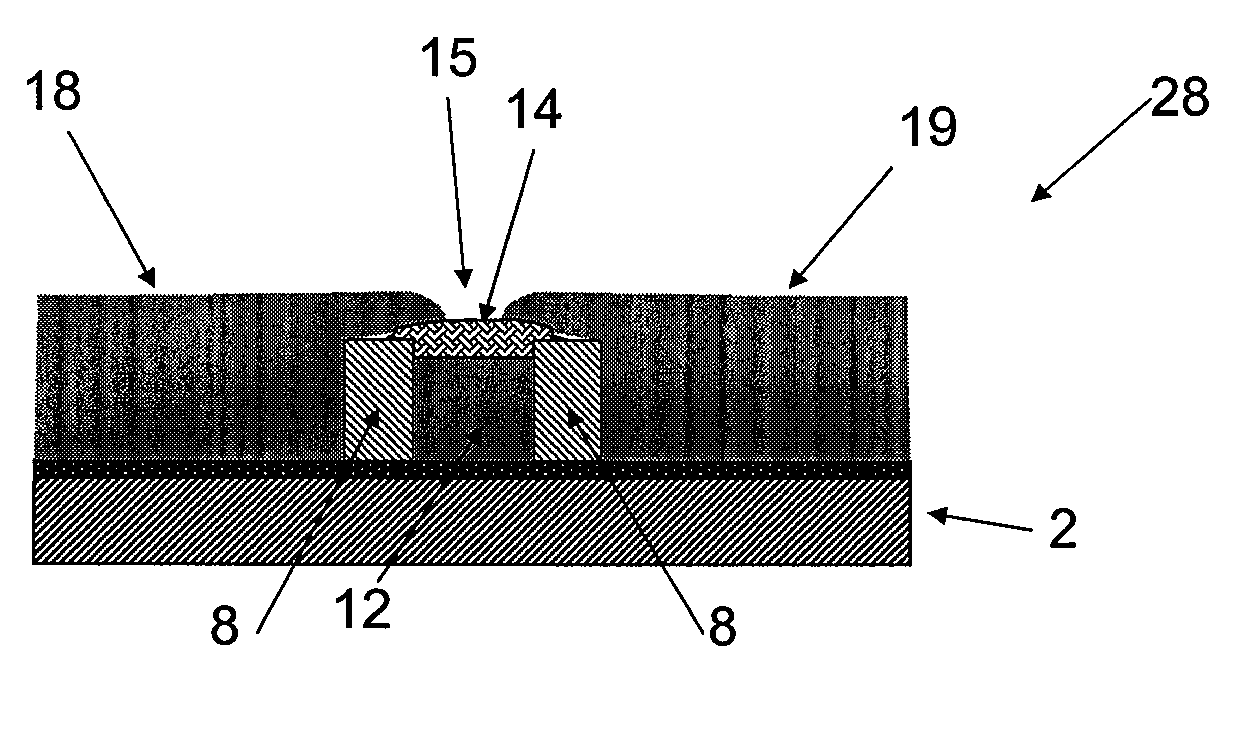
A method of manufacturing a resin multilayer substrate is provided in which a component (3) is incorporated in a stacked body obtained by stacking a plurality of thermoplastic resin sheets (2). The method includes the steps of: softening a first resin sheet (2a) by heating, and pressing the component (3) against the first resin sheet (2a), thereby fixing the component (3) to the first resin sheet (2a); stacking the first resin sheet (2a) on a second resin sheet (2b) having a through hole (14) receiving the component (3) and a third resin sheet (2c) located adjacent to a lower side of the component (3) such that the component (3) is inserted into the through hole (14) and the lower surface of the component (3) faces the third resin sheet (2c); and performing compression bonding by heating and pressurizing the stacked body including these resin sheets (2).
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Circuit Board, Method Of Manufacturing Circuit Board, And Display Device Having Circuit Board
InactiveUS20070209200A1Solve lack of contrastPromote formationElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaUltraviolet
A circuit board manufacturing method includes formation of a thermosetting photosensitive resin film on an insulating board by a spin coat method and the like, exposure of the photosensitive resin film to radiation rays such as ultraviolet rays, development with a developer or by etching, heat-hardening of the photosensitive resin film, oxygen plasma treatment or ultraviolet treatment if required, adjustment of a water quantity in the photosensitive resin film by drying the resin film, exposure in a fluorine gas atmosphere, anneal treatment, and then immersion of the resin film in a fluorinated acid chemical.
Owner:OHMI +1
Rolled Copper Foil or Electrolytic Copper Foil for Electronic Circuit, and Method of Forming Electronic Circuit using same
InactiveUS20110300401A1Prevent saggingPrevent occurrencePrinted circuit aspectsConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalCopper foilAlloy
A rolled copper foil or electrolytic copper foil for an electronic circuit to be used for forming a circuit by etching, characterized in comprising a layer of metal of one or more types among a platinum group, gold and silver with an etching rate that is lower than the copper formed on an etching surface side of the rolled copper foil or the electrolytic copper foil, or alternatively comprising a layer of an alloy having the above-described metal as its main component. This invention aims to achieve the following upon forming a circuit by etching a copper foil of a copper clad laminate; specifically, to prevent sagging caused by the etching; to form a uniform circuit of the intended circuit width; to shorten the time of forming a circuit by etching as much as possible; to improve the etching properties in pattern etching; and to prevent the occurrence of short circuits and defects in the circuit width.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Photosensitive resin compsn., photosensitive element, prodn. method for resist pattern and prodn. method for printed circuit board
InactiveCN1432141AImprove reliabilityPrevent intrusionRadiation applicationsPhotosensitive material processingPolymer scienceSpray nozzle
A photosensitive resin composition is here disclosed which satisfies the following (1) and (2): (1) when a 1.0 wt % aqueous sodium carbonate solution is sprayed by a spray on a layer of the photosensitive resin composition having a thickness of 37 to 42 mum under the following conditions, the photosensitive resin composition layer being able to be removed within 20 seconds, the above conditions being that an internal diameter of a nozzle of the spray is 1.2 mm, a spraying pressure is 0.05 MPa, and a distance between a point of the spray nozzle which is closest to the photosensitive resin composition layer and the photosensitive resin composition layer is 50 mm; and (2) when the 1.0 wt % aqueous sodium carbonate solution is sprayed three times for 36 seconds under the above conditions on a cured film obtained by laminating a layer of the photosensitive resin composition having the above thickness on a copper-clad laminate having 18 three-continuous holes in which 3 holes each having a diameter of 6 mm are continuously integrated and which has a length of 16 mm, and then photo-curing the layer with an exposure capable of curing 24 steps in a 41-step tablet, the number of holes where the cured film is broken being 5 or less.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
Printed circuit board and method for manufacturing a printed circuit board
InactiveCN103582302AReduce areaPrinted circuit assemblingFinal product manufactureSolder maskCopper foil
A printed circuit board is disclosed. The printed circuit board includes a solder mask area and at least one chip attachment area. The at least one chip attachment area has an isolation solder mask layer such that the chip attachment area forms a plurality of chip sub-attachment areas to reduce an area of a solder paste smeared on the chip attachment area, and the isolation solder mask layer has at least one hole.
Owner:WISTRON CORP
Method for preventing printing ink in jack of single-side-windowed jack panel of PCB from attaching to welding pad
InactiveCN105916305ASolve the problem of residue on the pad of the apertureIncrease productivityCircuit masksSolder maskPrinting ink
The invention relates to a method for preventing printing ink in jacks of a single-side-windowed jack panel of a PCB from attaching to a welding pad. The method is used for manufacturing the PCB, and comprises the steps that the PCB is subjected to an exposure working procedure after solder mask printing, and then subjected to a development working procedure and an added empty exposure working procedure after the development working procedure. According to the method, the empty exposure working procedure is added, so that surface of the printing ink in the jacks at single-side-windowed positions are subjected to preliminary curing, a printing ink solvent in the jacks can volatilize towards two sides of the jacks evenly rather than volatilize towards jack surfaces at the single-side-windowed positions, since the solvent in the jacks volatilize towards two sides of the jack ports evenly, printing ink residues formed through volatilization towards one surface of the jack ports excessively cannot appear on the jack ports of the welding pad, the problem that the printing ink or printing ink solvent residues appear on the jack ports of the welding pad can be solved, thereby enhancing production efficiency.
Owner:LONGTENG ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Systems and methods for breadboard sytle printed circuit board
ActiveUS20160360613A1Printed circuit groundingCross-talk/noise/interference reductionEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The present invention relates generally to electric circuit testing, building, or implementing using a breadboard style PCB. Aspects of the present invention include eliminating the need to use hookup wires when building and testing electric circuits on PCBs. In embodiments, a PCB system having rows and columns of signal tie points connected in a breadboard layout and using an embedded wire and a solder bridge to form partial connections between signal tie points. In embodiments, the embedded wire and solder bridge is capable of connecting a column of signal tie points. In embodiments, the embedded wire and solder bridge is capable of connecting a power rail to a signal tie point. Thus, a circuit can be implemented and tested by applying a small amount of solder to the solder bridge without the need for hookup wires.
Owner:KHO SAMUEL P
Method for manufacturing ceramic green sheet and method for manufacturing electronic part using that ceramic green sheet
InactiveUS20050079450A1Quality improvementReduce variationConductive/insulating/magnetic material on magnetic film applicationFixed inductancesUltraviolet lightsTransmittance
There is provided a sheet used for manufacturing multilayer electronic parts in which accuracy in shape and formation position and uniformity in thickness of a complex configuration with recesses and projections of an insulating layer or the like are assured. A layer made of a photosensitive material containing a powder having a specific electric characteristic is formed on a light transmissive base member. A mask having a plurality of patterns with different transmittances for ultraviolet light is disposed on the back side of the base member. The photosensitive material is subjected to an exposure process in which it is irradiated with ultraviolet light or the like through the mask. The photosensitive material is subjected to development process after the exposure process.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
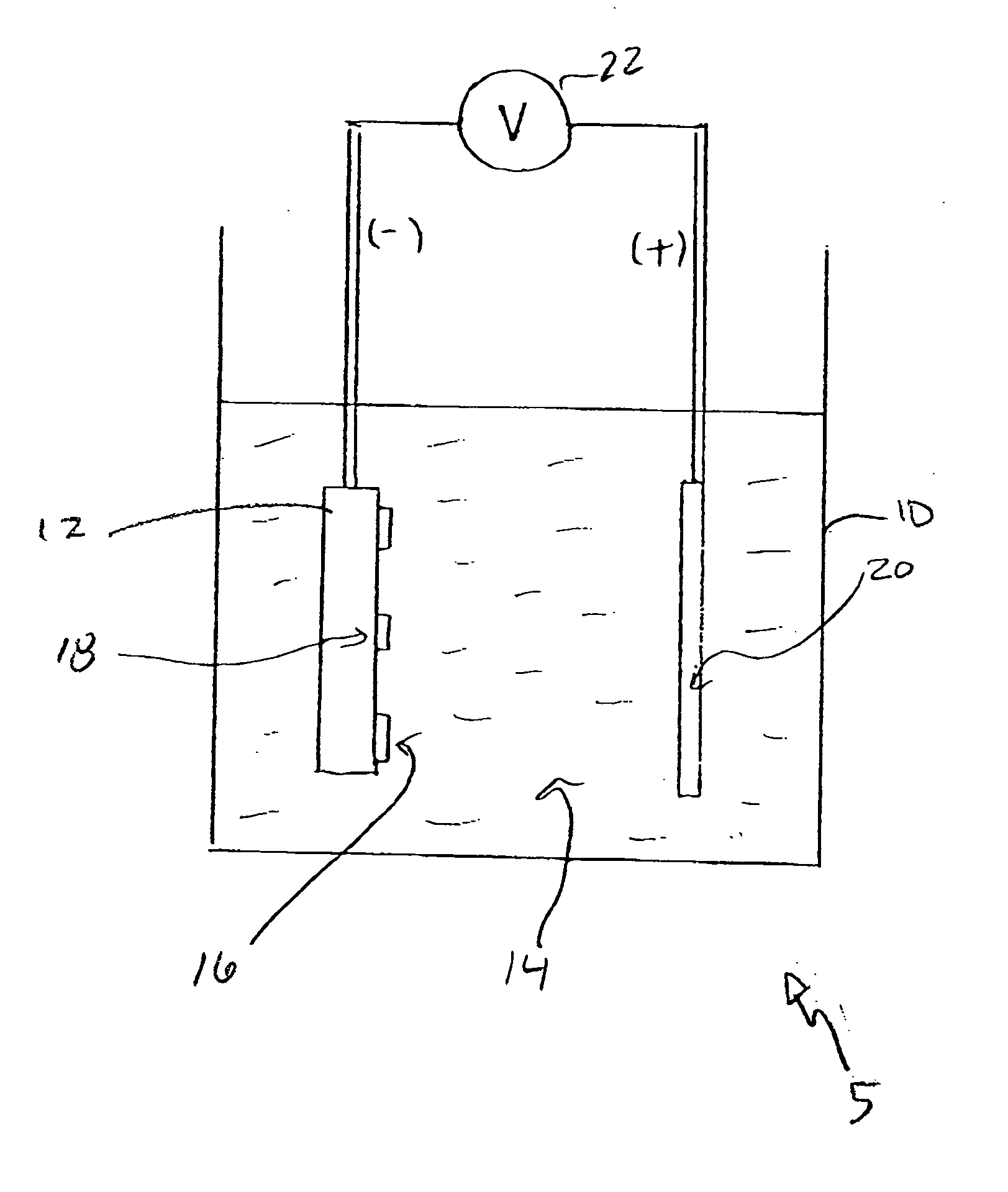
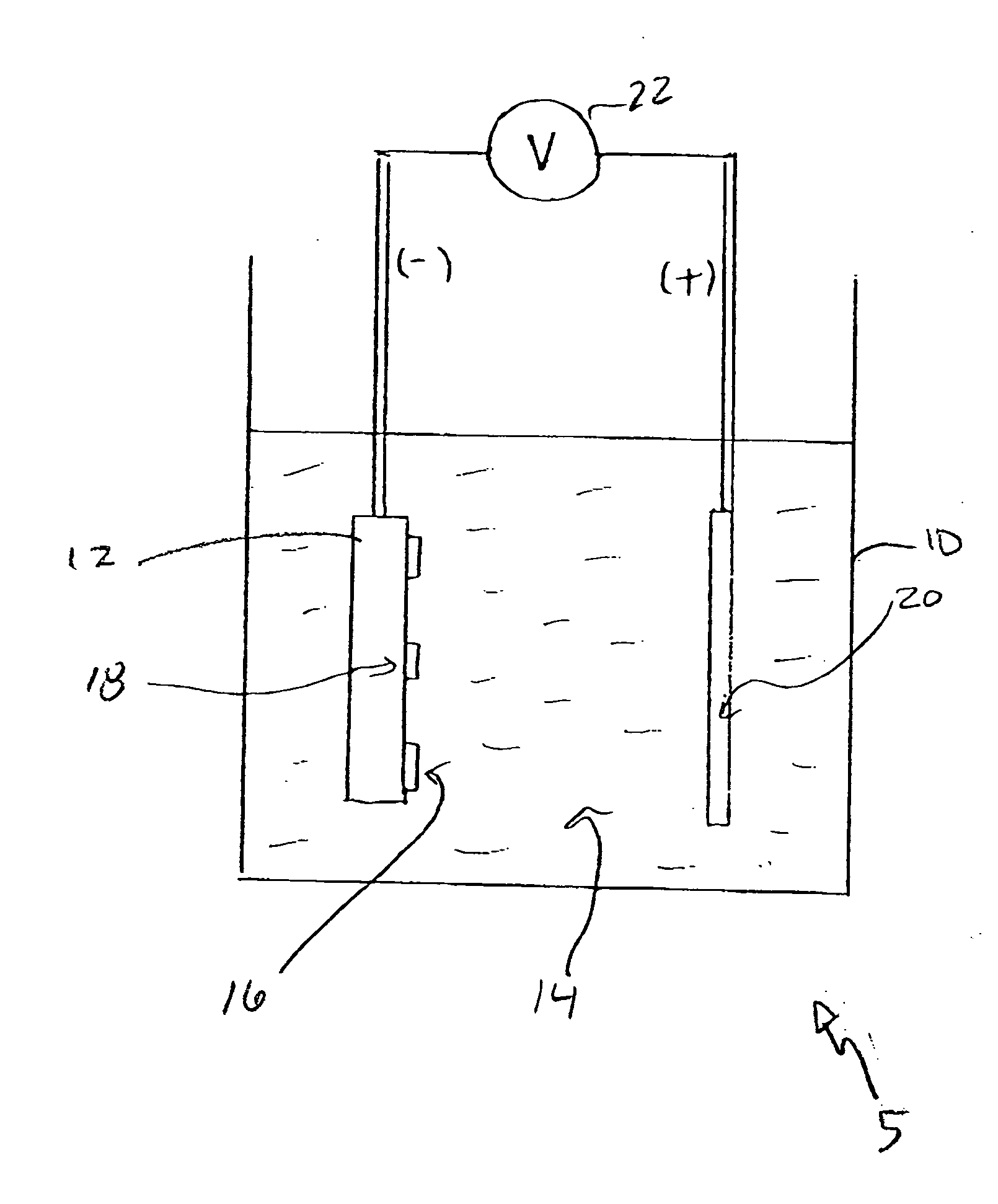
Electrolytic method for photoresist stripping
Photoresist stripping is performed by having a piecepart with a conductive layer that patterned by the photoresist immersed in a neutral solution. A voltage potential is applied to induce a current between the conductive layer and a counter electrode in neutral solution bath at a specified current density. After a short period of time, on the order of minutes, the photoresist is lifted off the piecepart. The piecepart is then removed from the bath, rinsed and dried.
Owner:IBM CORP
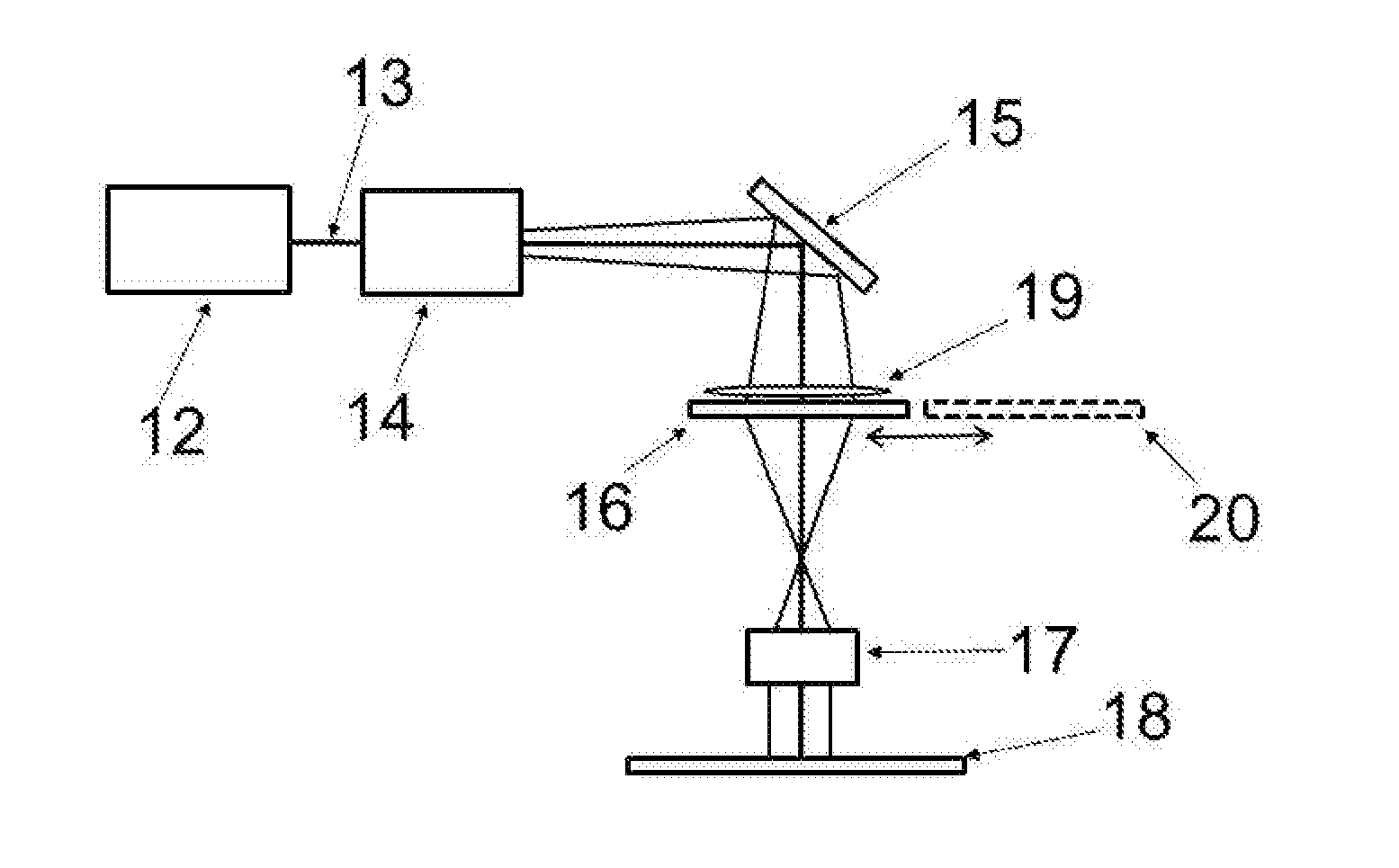
Method and apparatus for forming fine scale structures in dielectric substrate
ActiveUS20150230341A1Laser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingScale structure
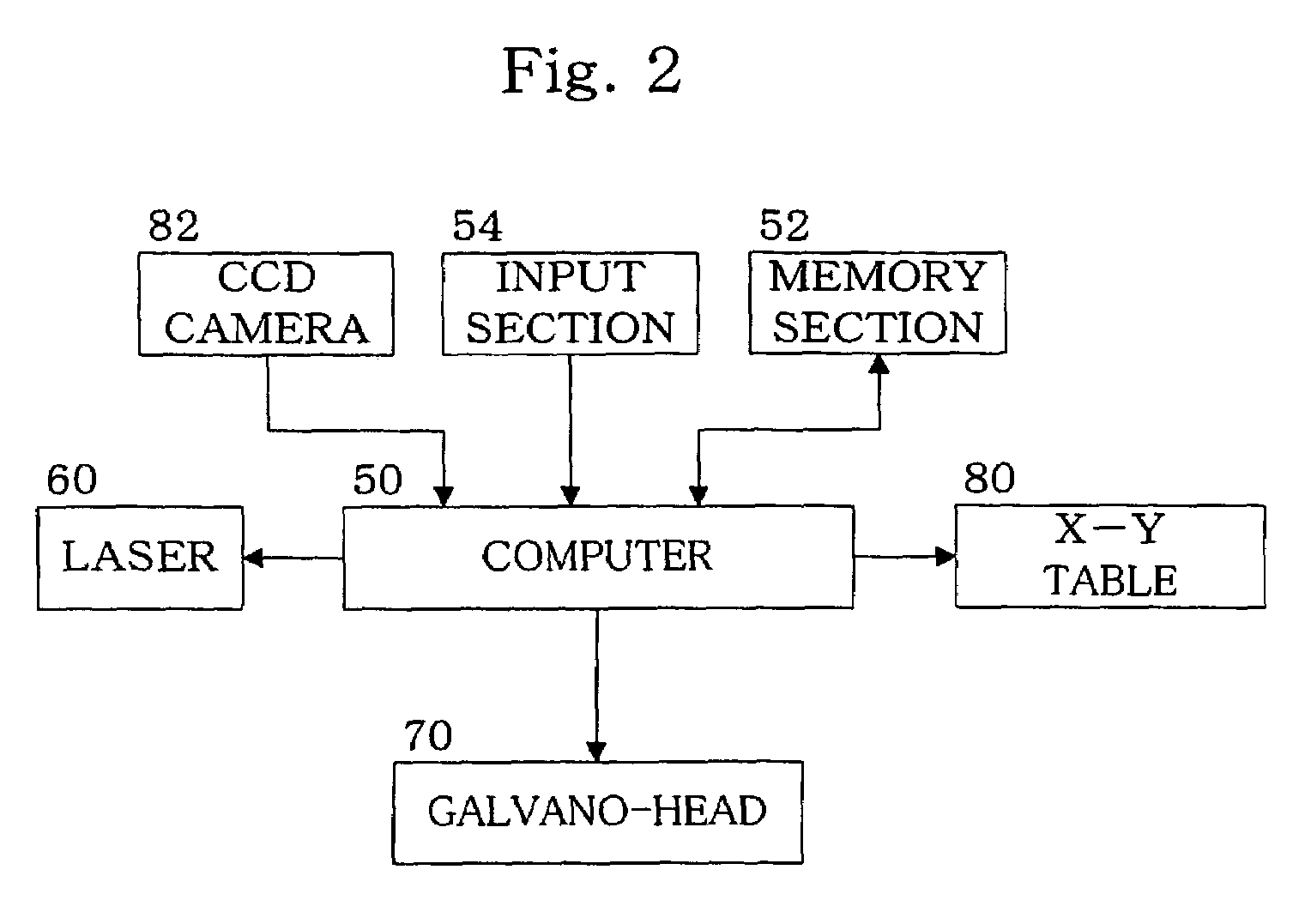
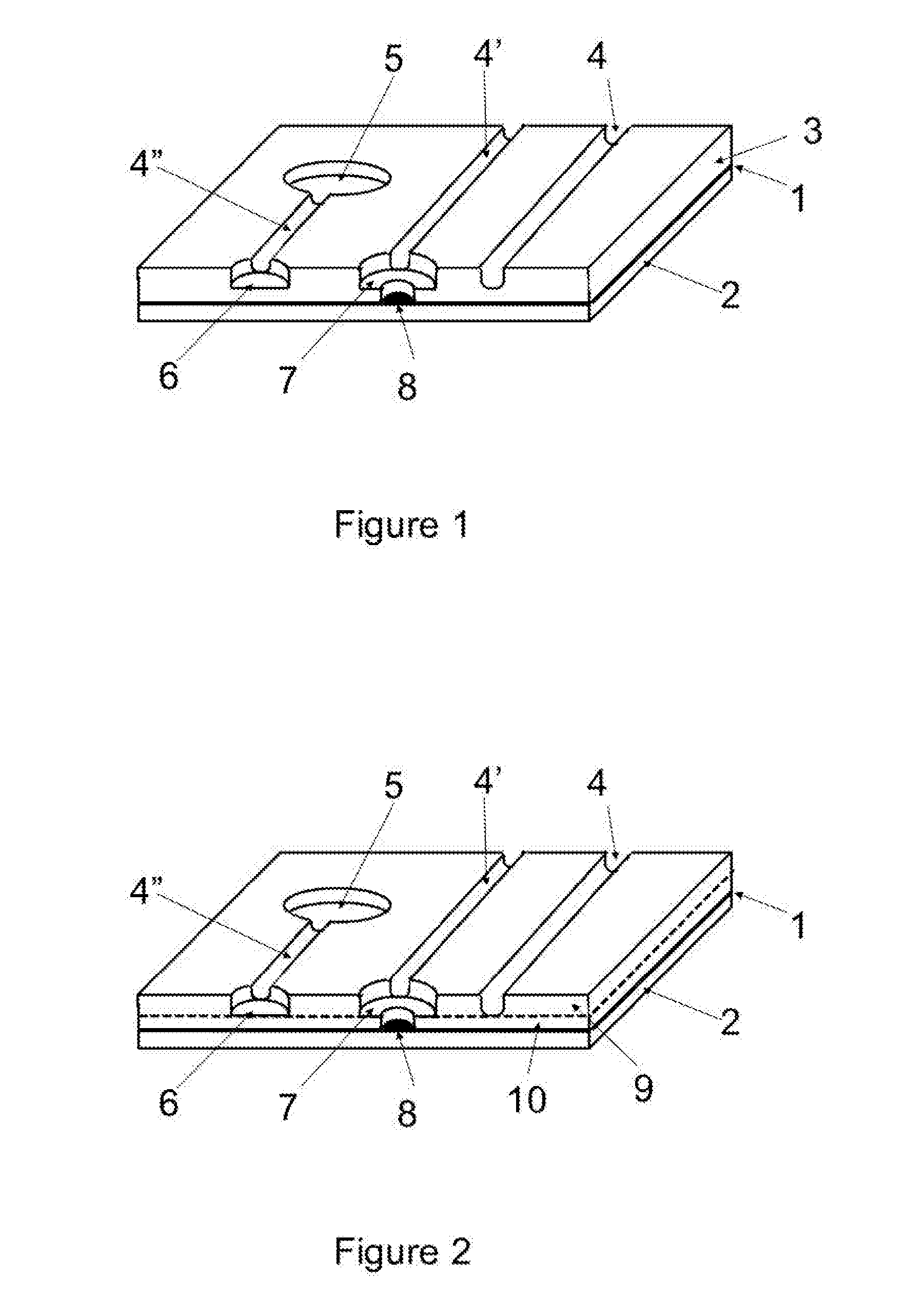
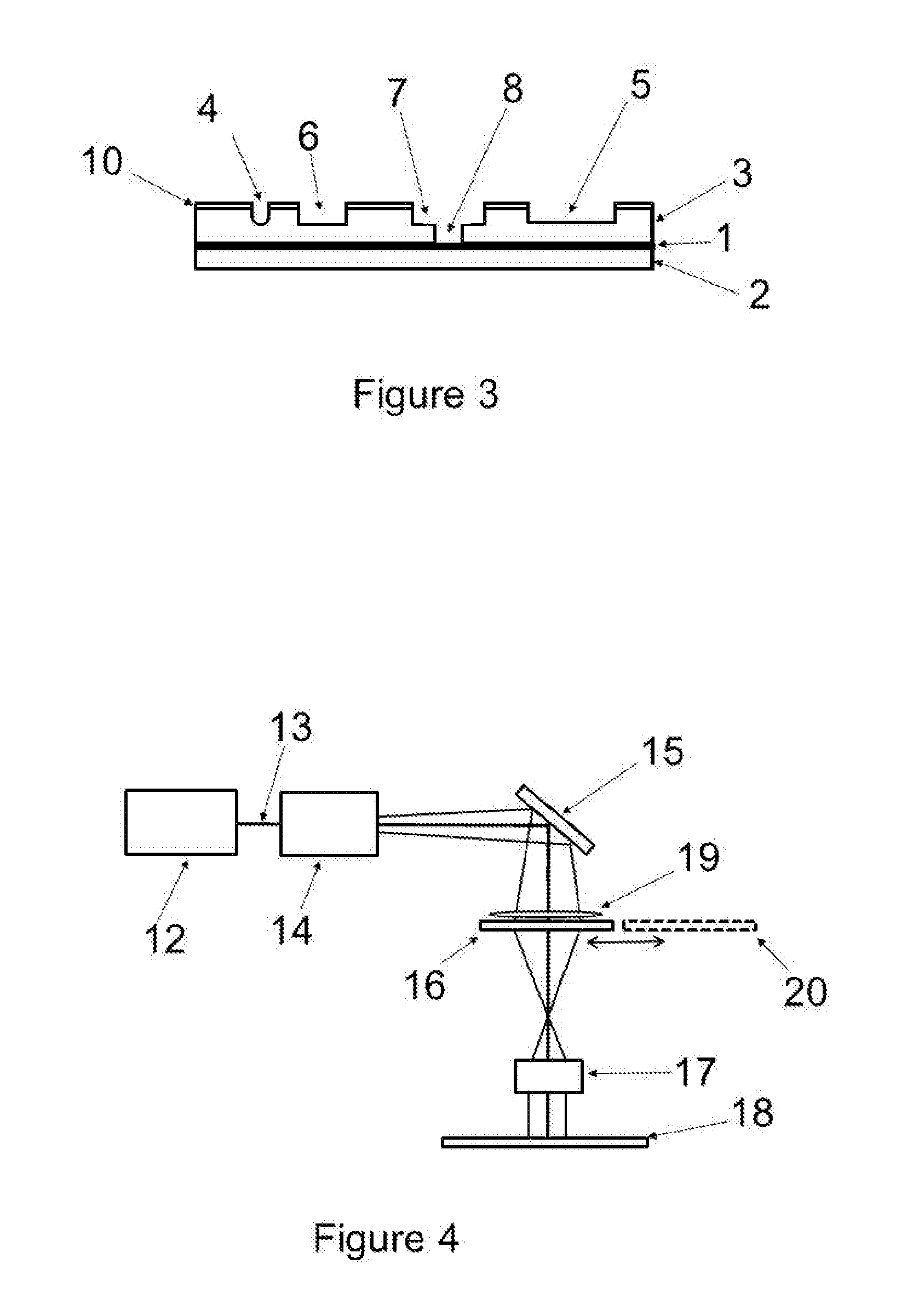
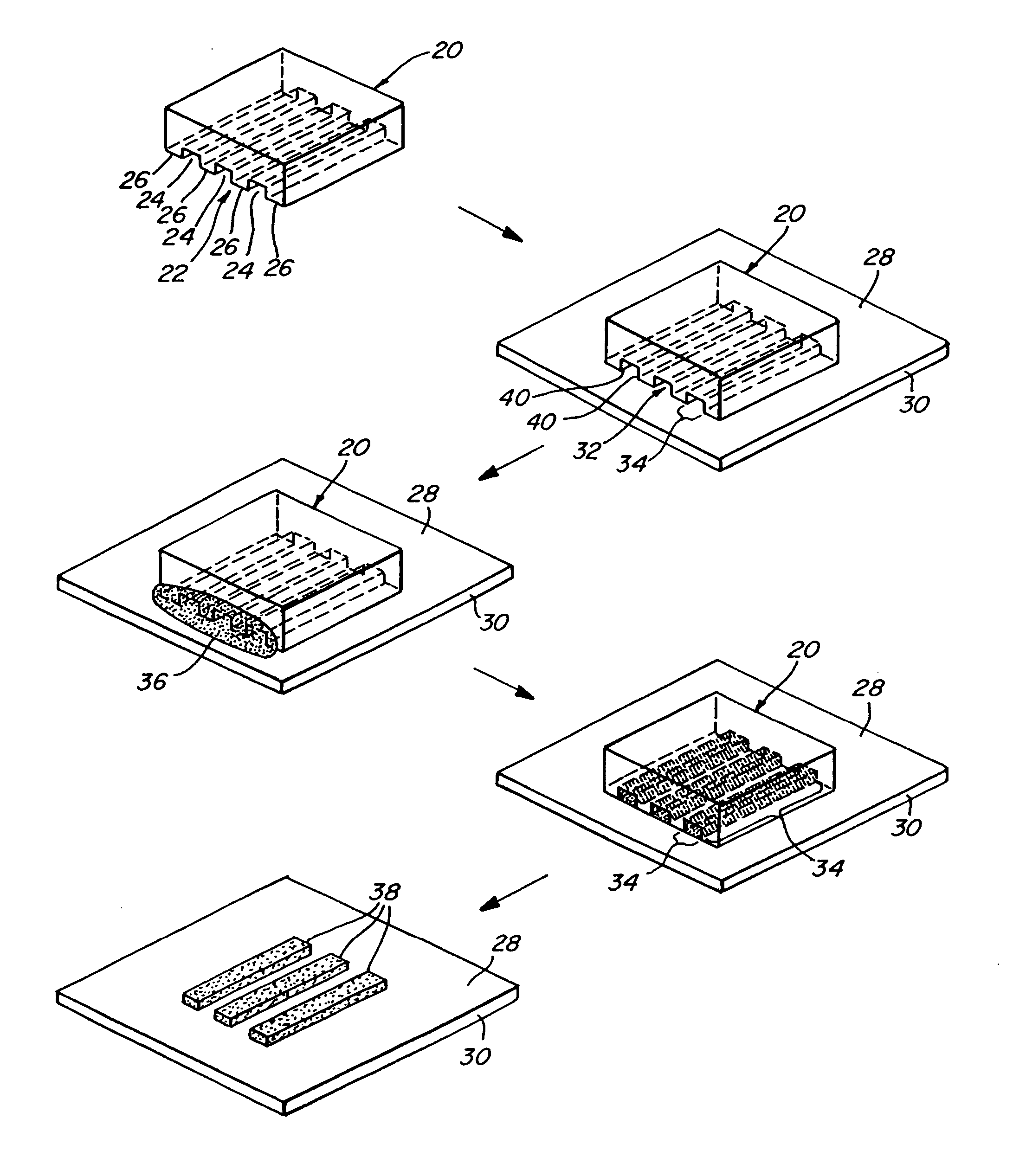
Apparatus and methods for forming fine scale structures (4, 4′, 4″, 5, 6, 7, 8) in the surface of a dielectric substrate (3) to two or more depths are disclosed. In an example, the apparatus 25 comprises a first solid state laser (12) arranged to provide a first pulsed laser beam (13), a first mask (16) having a pattern for defining a first set of structures (4, 6, 7, 8) at a first depth, a projection lens (17) for forming a reduced size image of said pattern on the surface (3) of the substrate and a beam scanner arranged to scan said first pulsed laser beam (13) in a two-dimensional raster scan relative to the first pattern to form a first set of structures (4, 6, 7, 5) at a first depth in the substrate, wherein the first or a further solid state laser is arranged to form a second set of structures (8) at a second depth in the substrate (3).
Owner:M SOLV LTD
Molded waveguides
InactiveUS20080116608A1Material nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsActive agentRefractive index
Chemically or biochemically active agents or other species are patterned on a substrate surface by providing a micromold having a contoured surface and forming, on a substrate surface, a chemically or biochemically active agent or fluid precursor of a structure. A chemically or biochemically active agent or fluid precursor also can be transferred from indentations in an applicator to a substrate surface. The substrate surface can be planar or non-planar. Fluid precursors of polymeric structures, inorganic ceramics and salts, and the like can be used to form patterned polymeric articles, inorganic salts and ceramics, reactive ion etch masks, etc. at the surface. The articles can be formed in a pattern including a portion having a lateral dimension of less than about 1 millimeter or smaller. The indentation pattern of the applicator can be used to transfer separate, distinct chemically or biochemically active agents or fluid precursors to separate, isolated regions of a substrate surface. Waveguide arrays, combinatorial chemical or biochemical libraris, etc. can be made. Differences in refractive index of waveguide and cladding can be created by subjecting the waveguide and cladding, made of identical prepolymeric material, to different polymerization or cross-linking conditions. Interferometers are defined by coupling arrays of waveguides, where coupling can be controlled by altering the difference in refractive index between cladding and waveguide at any desired location of the array. Alteration and refractive index can be created photochemically, chemically, or the like. Sensors also are disclosed, including biochemical sensors.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
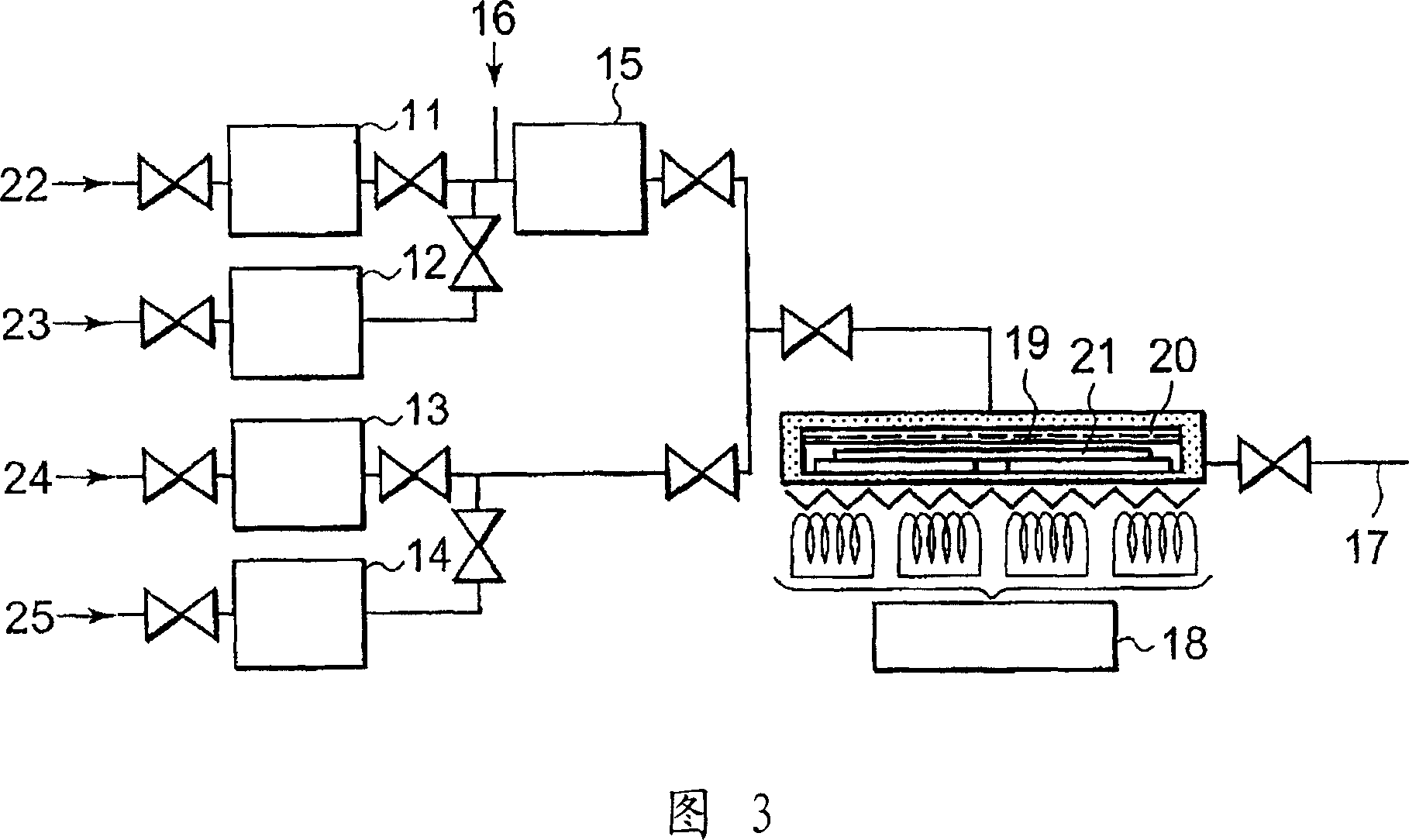
Chemical processing apparatus for manufacturing circuit substrates
InactiveUS7553457B2Extended service lifeMaintain qualityLiquid processingPrinted circuit liquid treatmentChemical treatmentCompound (substance)
A chemical processing apparatus includes a chemical tank that stores a chemical, means for transferring an object to be processed into the chemical and a lid disposed to cover a liquid surface of the chemical and to float on the chemical.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Circuit board, circuit board manufacturing method and display apparatus provided with circuit board
InactiveCN1947478AFull contrast ratioElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOxygen plasmaUltraviolet
A circuit board manufacturing method includes formation of a thermosetting photosensitive resin film on an insulating board by a spin coat method and the like, exposure of the photosensitive resin film to radiation rays such as ultraviolet rays, development with a developer or by etching, heat-hardening of the photosensitive resin film, oxygen plasma treatment or ultraviolet treatment if required, adjustment of a water quantity in the photosensitive resin film by drying the resin film, exposure in a fluorine gas atmosphere, anneal treatment, and then immersion of the resin film in a fluorinated acid chemical.
Owner:ZEON CORP +1
Interconnect circuit methods and devices
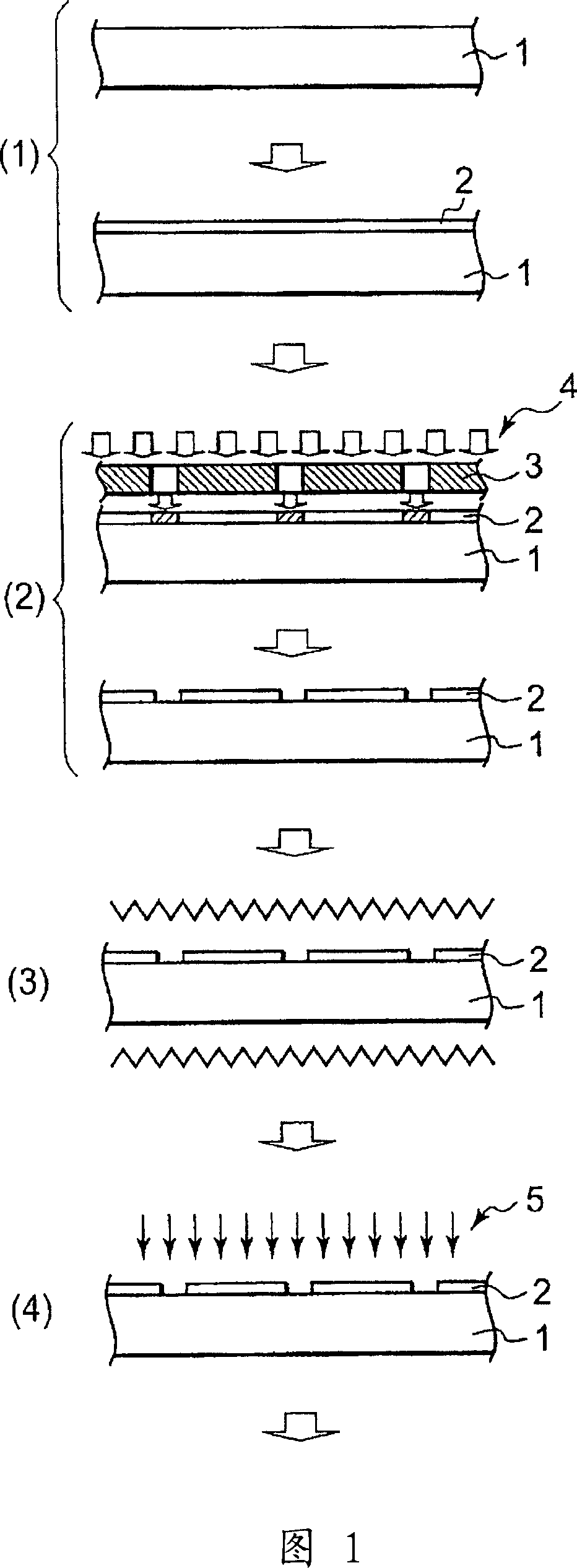
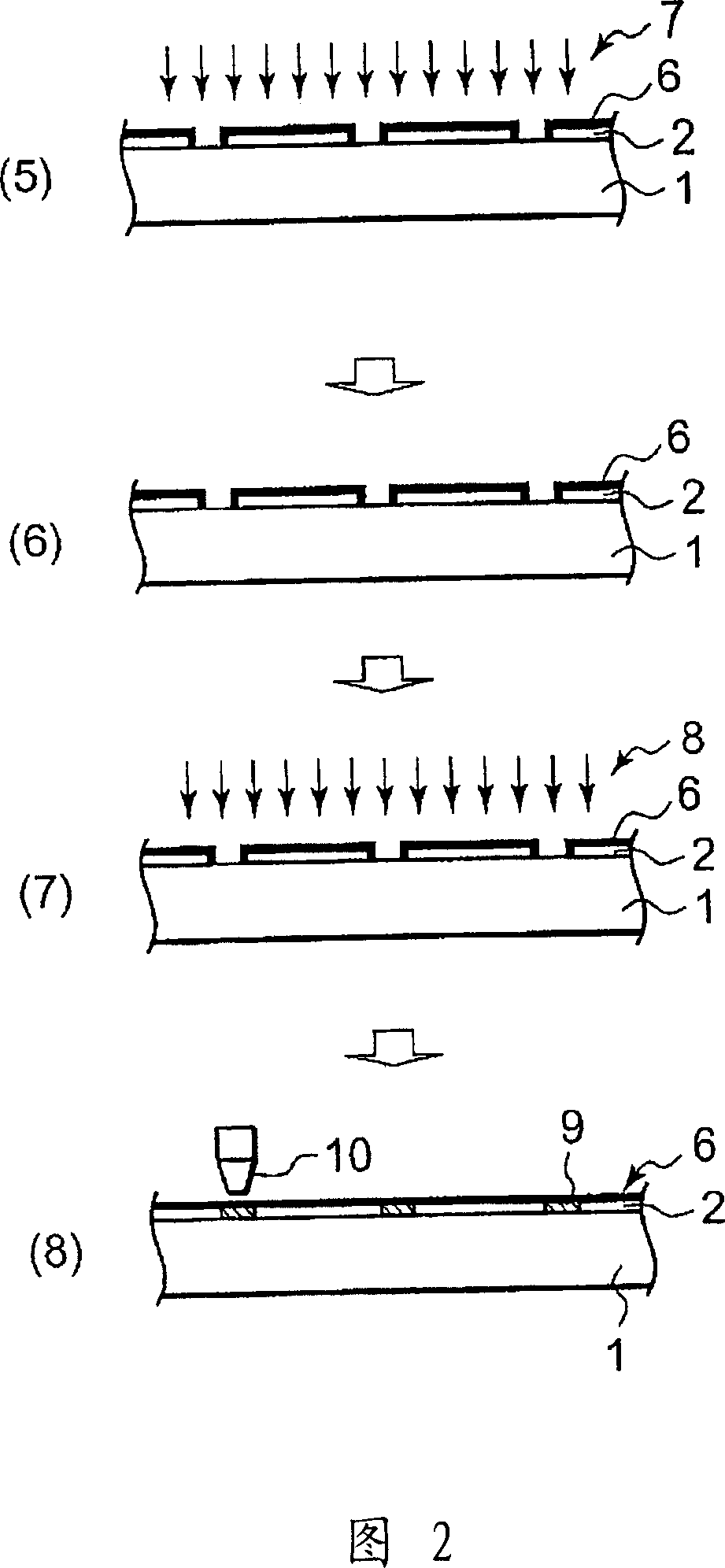
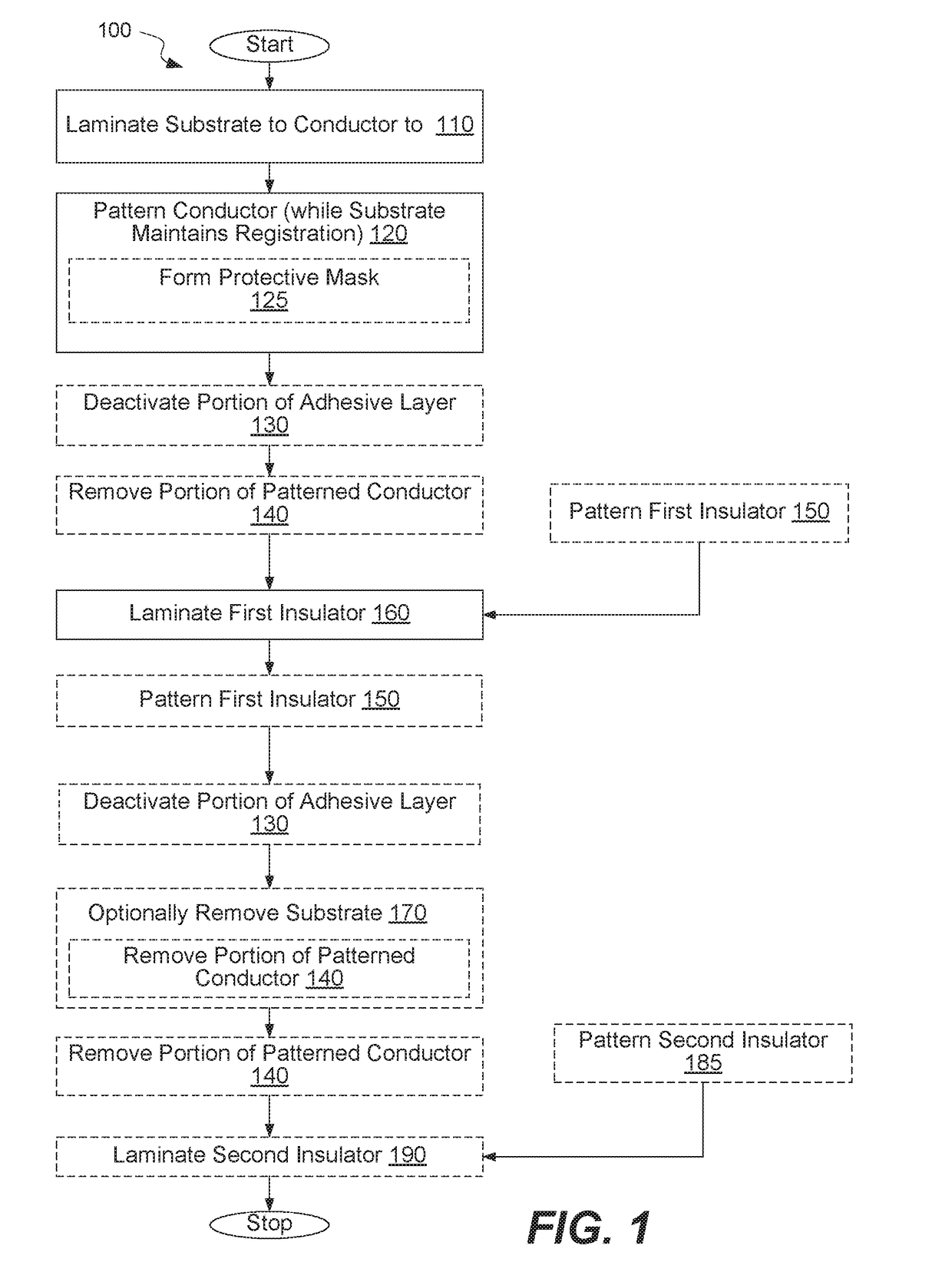
Provided are interconnect circuits and methods of forming thereof. A method may involve laminating a substrate to a conductive layer followed by patterning the conductive layer. This patterning operation forms individual conductive portions, which may be also referred to as traces or conductive islands. The substrate supports these portions relative to each other during and after patterning. After patterning, an insulator may be laminated to the exposed surface of the patterned conductive layer. At this point, the conductive layer portions are also supported by the insulator, and the substrate may optionally be removed, e.g., together with undesirable portions of the conductive layer. Alternatively, the substrate may be retained as a component of the circuit and the undesirable portions of the patterned conductive layer may be removed separately. These approaches allow using new patterning techniques as well as new materials for substrates and / or insulators.
Owner:CELLINK
Chemical processing apparatus, chemical processing method, and method for manufacturing circuit substrate
InactiveUS20050008360A1Maintain qualityOxidative deteriorationPrinted circuit liquid treatmentLiquid processingChemical treatmentCompound (substance)
A chemical processing apparatus includes a chemical tank that stores a chemical, means for transferring an object to be processed into the chemical and a lid disposed to cover a liquid surface of the chemical and to float on the chemical.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
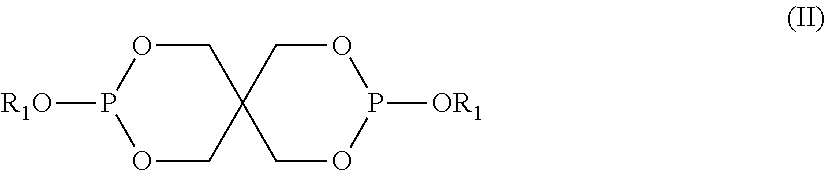
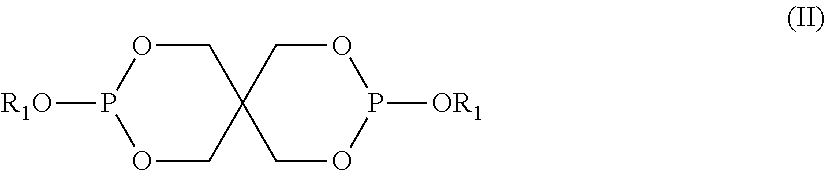
Articles with photocurable and photocured compositions
ActiveUS8816211B2Improve performanceReduced unpleasant odorsImpression capsPhotosensitive materialsOxygenPhotoinitiator
The photocuring efficiency of a photoinitiator is increased by mixing it with an organic phosphite and an aldehyde. This mixture or photoinitiator composition can be used to cure acrylates or other photocurable compounds, particularly in an oxygen-containing environment, and the photocurable compositions can be used to form various articles.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Method for fabricating line between two bonding pads of PCB
ActiveCN105555039AWill not shiftQuality assuranceCircuit masksPre-fabricated insulating pattern transferScreen printingEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of production of circuit boards, in particular to a method for fabricating a line between two bonding pads of a PCB. The line is fabricated between the two bonding pads in manners of screen printing, exposure and development. The minimal distance between the line and each bonding pad can be 0.035mm according to the exposure accuracy of the prior art; and the minimal width of the line can be 0.07mm. Therefore, the method provided by the invention can fabricate the line between the bonding pads between which the space is equal to or greater than 0.14mm; and the condition that the line is clear and intact and does not deviate to the bonding pads can be ensured, so that the quality of a PCB product is ensured. The problem that the line cannot be fabricated between the two bonding pads between which the space is smaller than 0.336mm under the premise of ensuring the quality in the prior art is solved.
Owner:大连崇达电子有限公司
Dry type cleaning case and dry type cleaning device
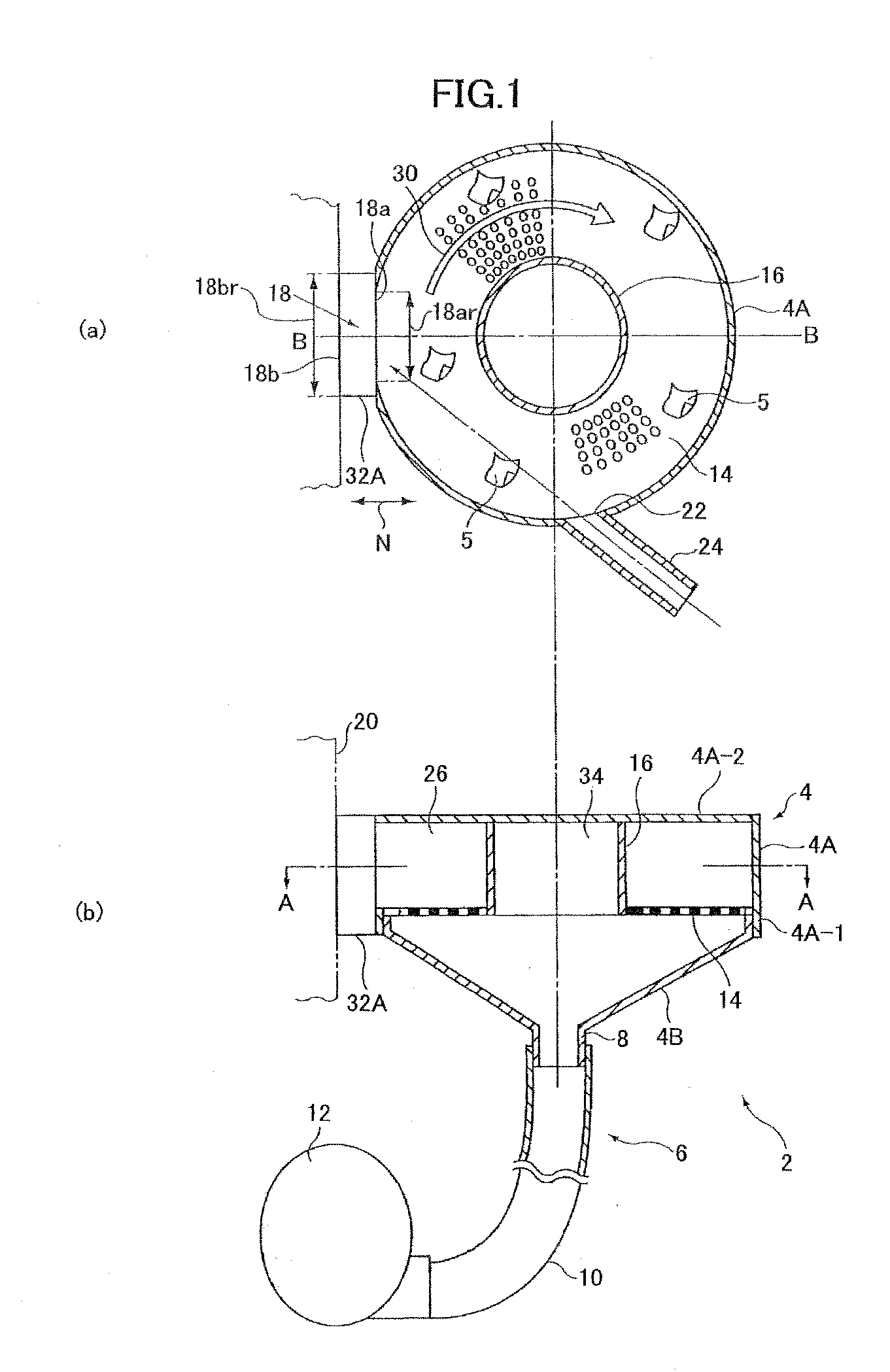
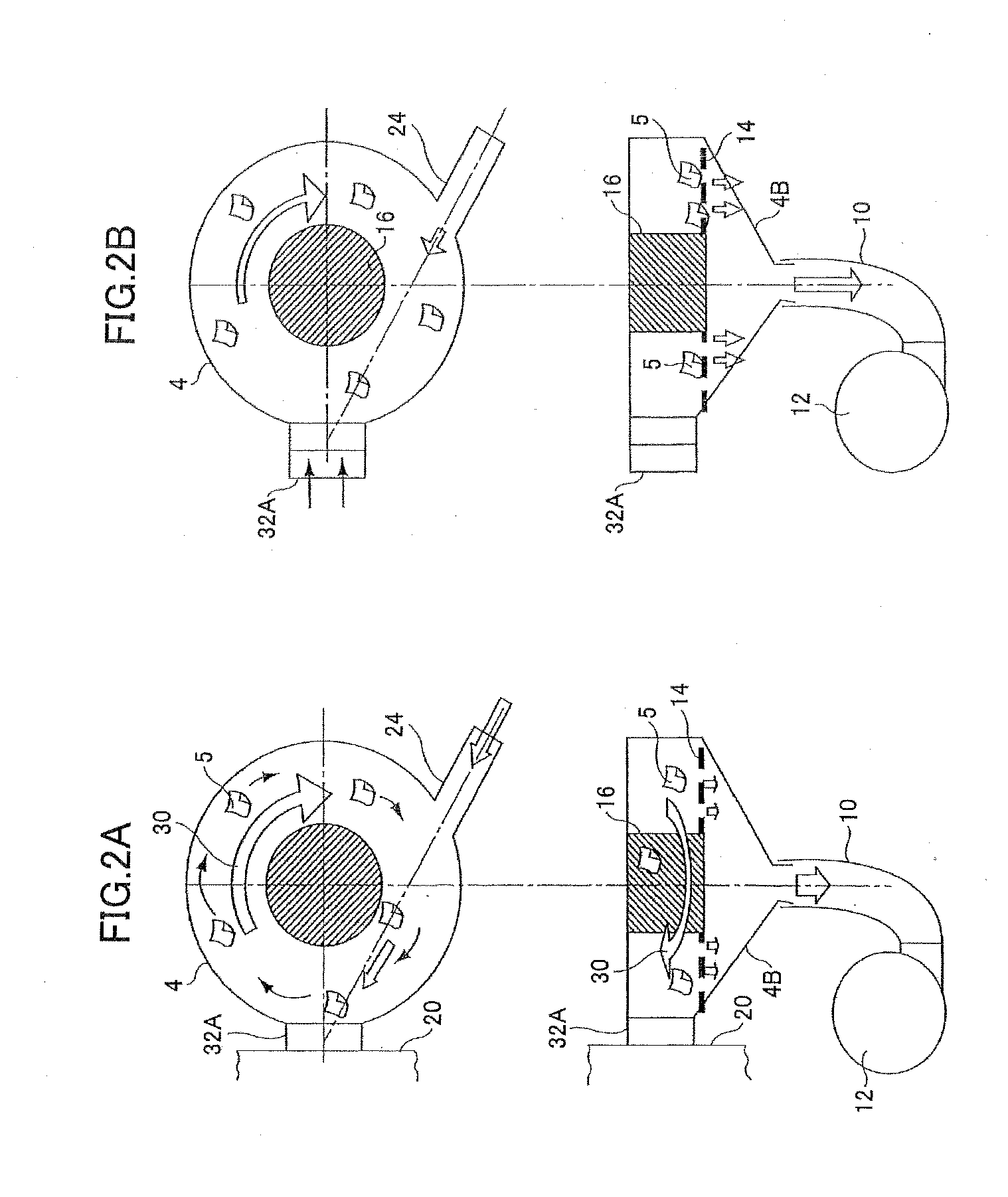
A dry type cleaning case is for cleaning an object with a medium that flies by a revolving airflow. The dry type cleaning case includes a case unit and a leakage prevention unit. The case unit includes a space in which the medium flies, an opening that contacts the object so that the medium collides with the object, a ventilation path through which air flows into the space from outside, a suction opening that suctions the air that has been guided into the space through the ventilation path, to generate the revolving airflow in the space, and a porous unit through which a substance removed from the object is passed to the suction opening. The leakage prevention unit prevents the medium from leaking outside through the opening from the space, by causing outer air to flow in when the case unit is separated from the object.
Owner:RICOH KK
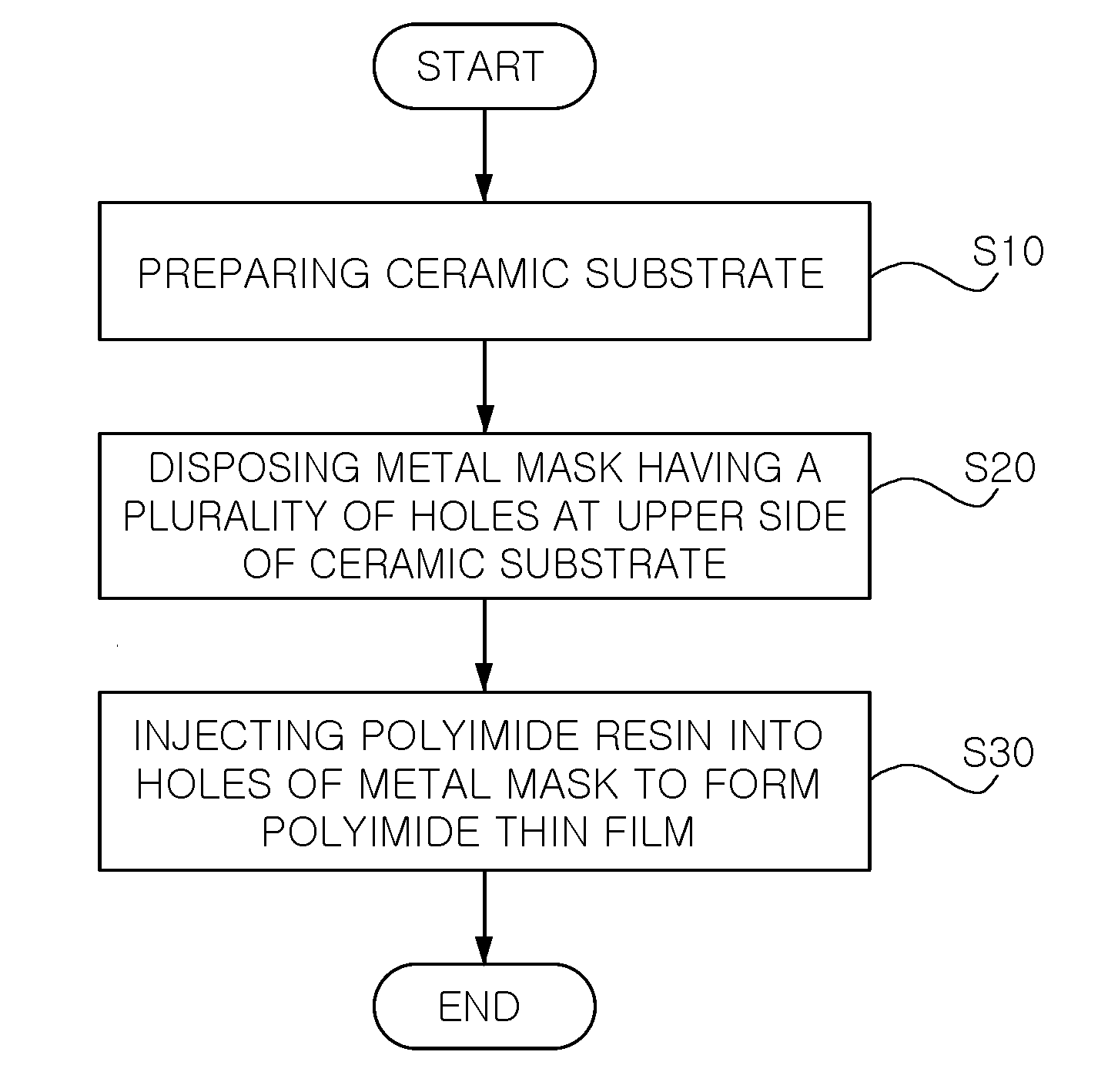
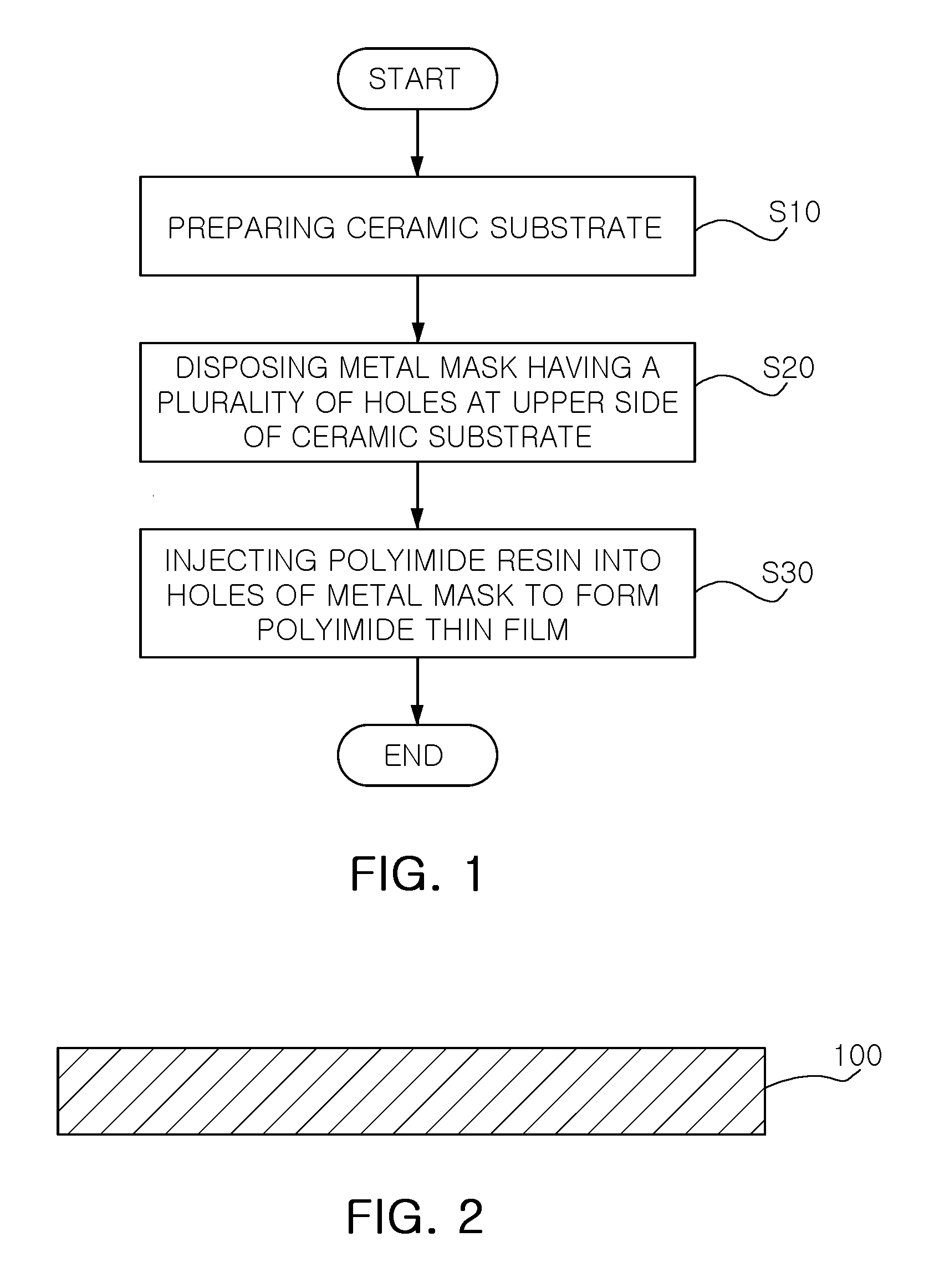
Method for fabricating ceramic substrate
ActiveUS20120047730A1Simple processPrinted circuit assemblingPrinted circuit aspectsManufacturing cost reductionMetal
A method for fabricating a ceramic substrate includes: preparing a ceramic substrate; disposing a metal mask having a plurality of holes at an upper side of the ceramic substrate; and injecting a polyimide resin into the holes of the metal mask to form a polyimide thin film on the ceramic substrate. A thin film is formed on a ceramic substrate in a simpler manner, so the fabrication cost can be reduced and a fixed time can be shortened, thus increasing the efficiency of a product.
Owner:SEMCNS CO LTD
Photosensitive resin composition, photosensitive element, production method of resist pattern and production method for printed circuit board
InactiveUS7517636B2Shorten development timeHigh stripping propertyPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsSpray nozzleCopper
A photosensitive resin composition is here disclosed which satisfies the following (1) and (2):(1) when a 1.0 wt % aqueous sodium carbonate solution is sprayed by a spray on a layer of the photosensitive resin composition having a thickness of 37 to 42 μm under the following conditions, the photosensitive resin composition layer being able to be removed within 20 seconds, the above conditions being that an internal diameter of a nozzle of the spray is 1.2 mm, a spraying pressure is 0.05 MPa, and a distance between a point of the spray nozzle which is closest to the photosensitive resin composition layer and the photosensitive resin composition layer is 50 mm; and(2) when the 1.0 wt % aqueous sodium carbonate solution is sprayed three times for 36 seconds under the above conditions on a cured film obtained by laminating a layer of the photosensitive resin composition having the above thickness on a copper-clad laminate having 18 three-continuous holes in which 3 holes each having a diameter of 6 mm are continuously integrated and which has a length of 16 mm, and then photo-curing the layer with an exposure capable of curing 24 steps in a 41-step tablet, the number of holes where the cured film is broken being 5 or less.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
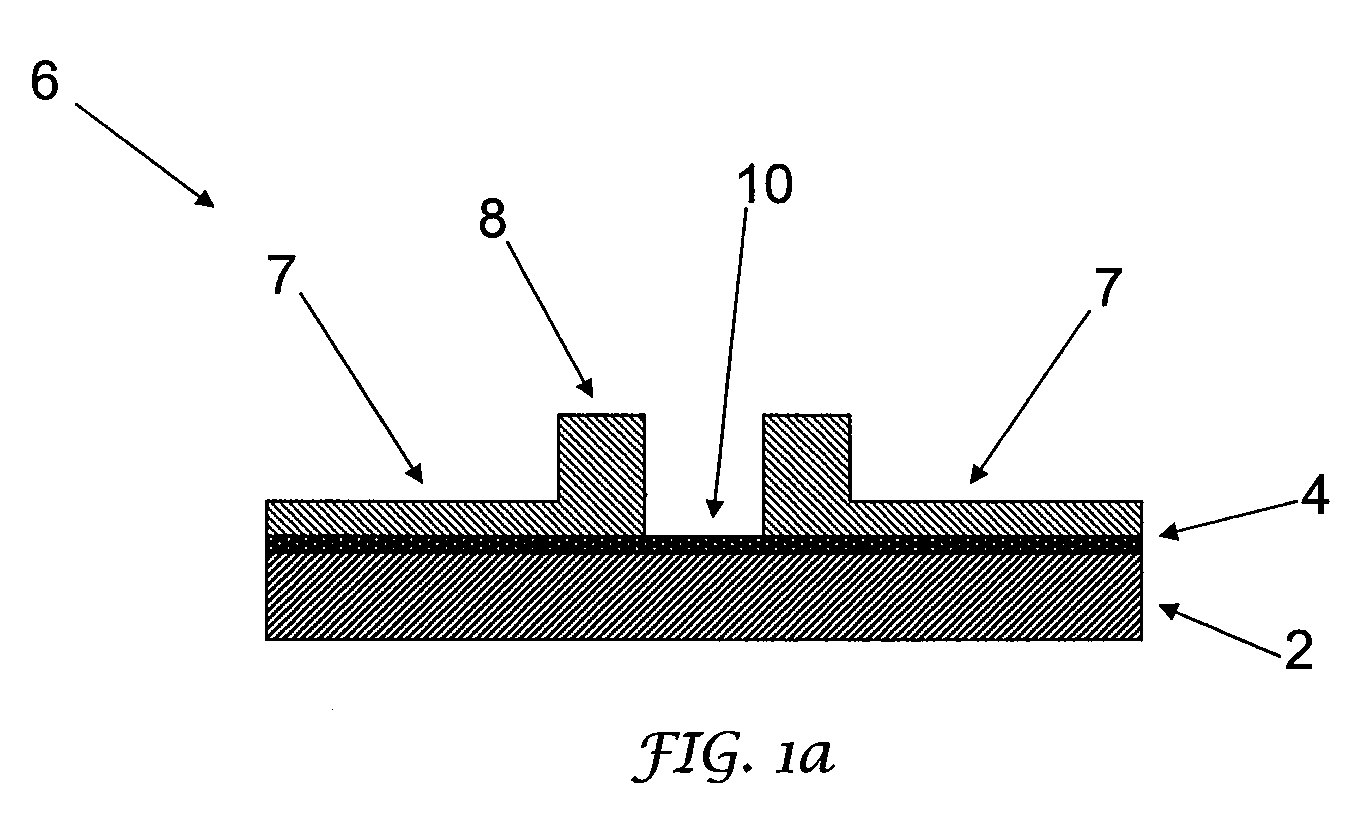
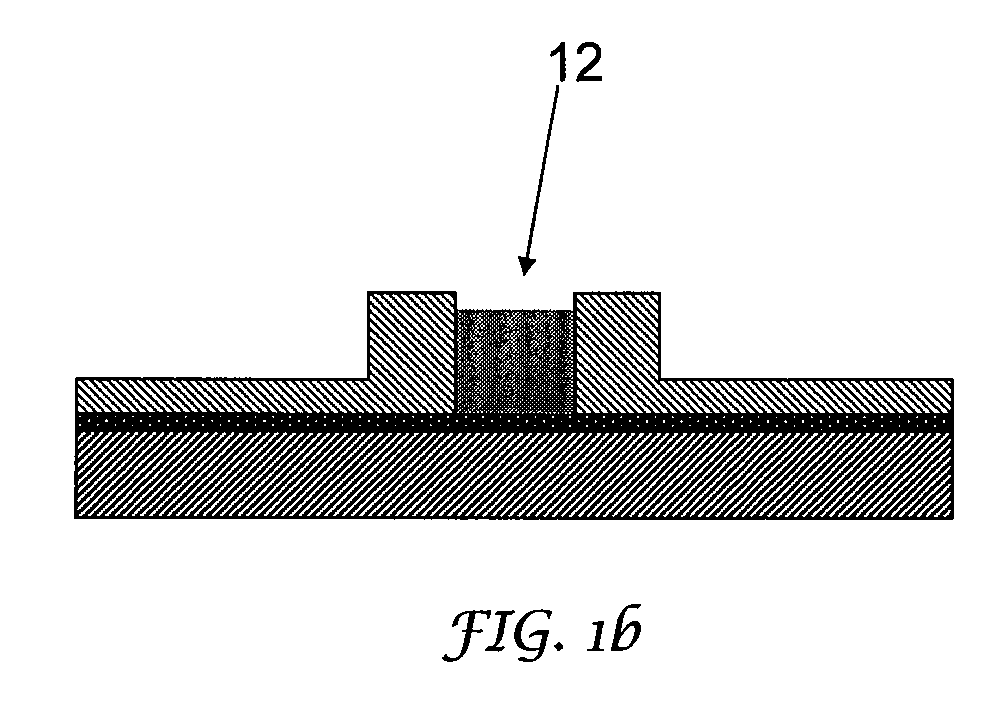
Conductive interconnects
InactiveUS8604604B2Improve manufacturing yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptoelectronicsMetal
A method of making a conductive interconnect structure includes the steps of: electrodepositing a metal on a conductive surface (4) of a carrier (2) to form a first elongate conductive interconnect (12); and electrodepositing a dielectric material (14) on said conductive interconnect (12) while the conductive interconnect (12) is in contact with the conductive surface (4).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com