Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Transport Protein Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transport Protein Genes encode a diverse group of proteins that function as carriers of ligands through solubility barriers such as aqueous body fluids or in active transport across cell membranes. (NCI)
Bacillus subtilis for producing N-acetylglucosamine as well as construction method and application of bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN104195094APrevent backflowAvoid consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationPhosphate
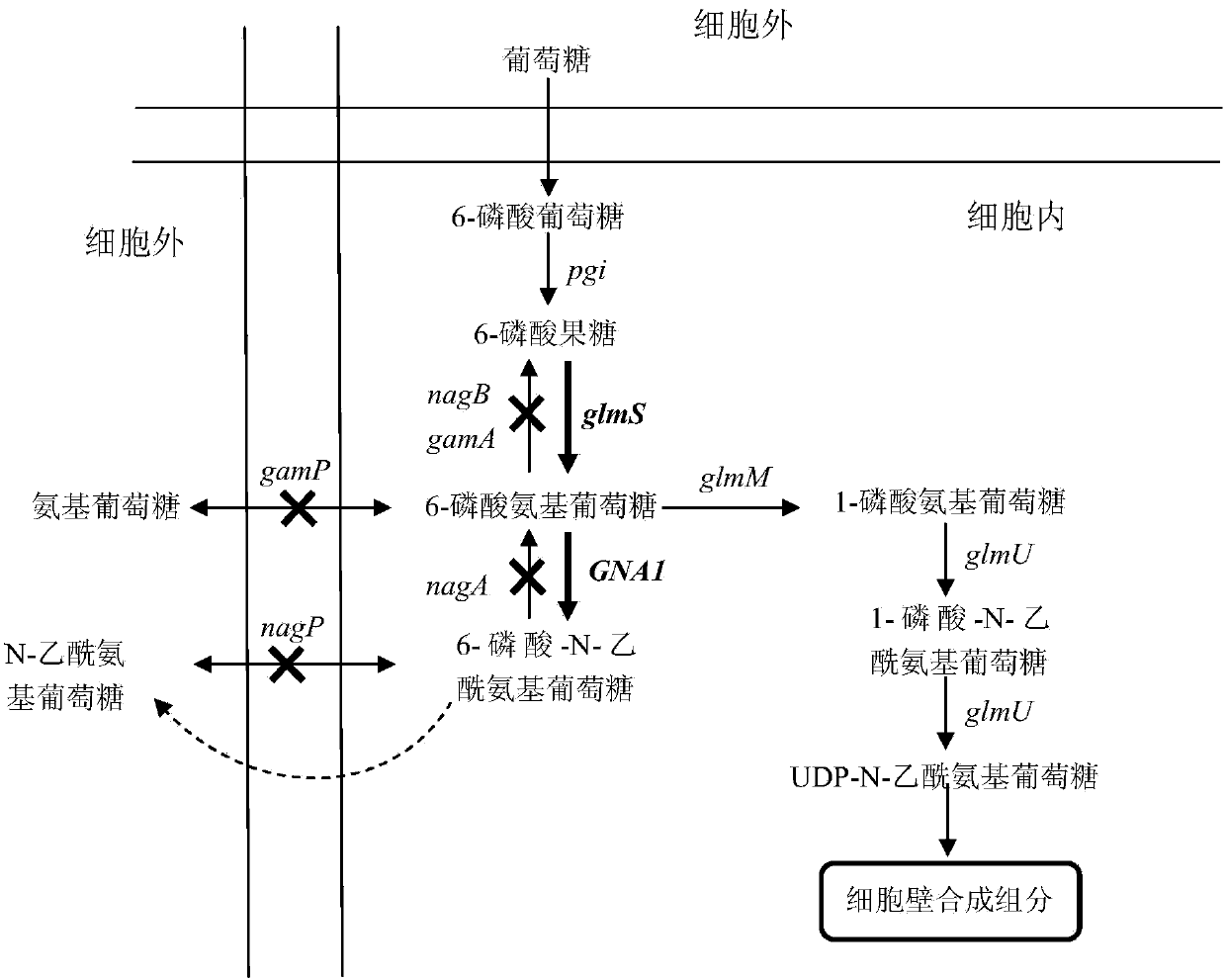
The invention belongs to the construction and the application of genetically engineered bacterium and particularly relates to bacillus subtilis for producing N-acetylglucosamine as well as a construction method and application of bacillus subtilis. The construction method for the genetically engineered bacterium (bacillus subtilis) comprises the following steps: expressing and coding 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase gene and 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene in bacillus subtilis to form a complete metabolic pathway from glucose to N-acetylglucosamine; knocking out or inactivating glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase genes nagB and gamA, an N-acetylglucosamine 6-phosphate deacetylase gene nagA, a glucosamine transport protein gene gamP and an N-acetylglucosamine transport protein gene nagP in an N-acetylglucosamine catabolism pathway in bacillus subtilis. The construction method can be used for solving the problem that N-acetylglucosamine produced in the prior art is poor in safety, low in yield and high in cost. The constructed genetically engineered bacterium has the advantage that N-acetylglucosamine with relatively high concentration can be accumulated, and the industrial utilization value is relatively high.
Owner:张帆
PDR transport protein gene promoter for controlling ginsenoside accumulation, and its application
InactiveCN103088027AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSecondary metaboliteSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a PDR transport protein gene promoter for controlling ginsenoside accumulation, and its application. A promoter ProPDR1 has a DNA sequence represented by SEQIDNo.1 or has a DNA sequence having a homology of above 99% to SEQIDNo.1. A PgPDR1 transport protein gene promoter sequence is obtained through cloning by adopting genome walker in the invention, and includes a TCA element and TCCACCT-Motif. A promoter expression vector pBI121-ProPDR1::GUS is constructed in the invention, and reporter gene GUS is strongly controlled by ginsenoside, salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in transgenic tobacco under the driving of the promoter ProPDR1, so the ginseng PgPDR1 gene expression promoted by the promoter is closely related to the ginsenoside accumulation. The promoter provided by the invention has very important application values in the medical plant secondary metabolite synthesis and accumulation control gene engineering.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Gene engineering application of rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2
InactiveCN101736014AEnhanced tillering abilityImprove utilization efficiencyFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses gene engineering application of rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2, which belongs to the field of gene engineering. The accession numbers of the nucleotide sequence of the rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2 and the expression OsPIN2 protein amino acid sequence thereof are AK101191 in an NCBI website (www. ncbi. nlm. nih. Gov / ). The engineering application of the gene is firstly reported in the rice, and participates in the transport of rice auxin so as to increase the rice roots, tiller number, tiller angle, nitrogen utilization efficiency and finial output.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Relevant gene combination, primer, probe and application used for detecting chemotherapeutic effect on acute myelogenous leukemia
InactiveCN101851683ASmall toxicityAdjusting the dose of chemotherapyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSide effectEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a relevant gene combination, a primer, a probe and application used for detecting a chemotherapeutic effect on acute myelogenous leukemia. The gene combination comprises four gene combinations closely relevant to pharmacotherapy of the acute myelogenous leukemia: medicament metabolism phase I enzyme gene CYP3A5, medicament metabolism phase II enzyme genes NAT2 and GSTO2, and medicament transport protein gene OATP1B1; and the gene combination comprises the following SNP loci: the locus rs776746 of the gene CYP3A5, the locus rs1799931 of the gene NAT2, the locus rs156697 of the gene GSTO2, and the locus rs4149056 of the gene OATP1B1. A method is performed by hybridizing a specific primer and probes which are subjected to fluorescence marks of different colors with target gene fragments in a nucleic acid sample after PCR amplification. The treatment effect of a leukemia medicament is detected and analyzed by mononucleotide extension technology so as to direct clinical medicament application, reduce a toxic or side effect of the medicament application for a patient, and increase a curative effect.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG +1
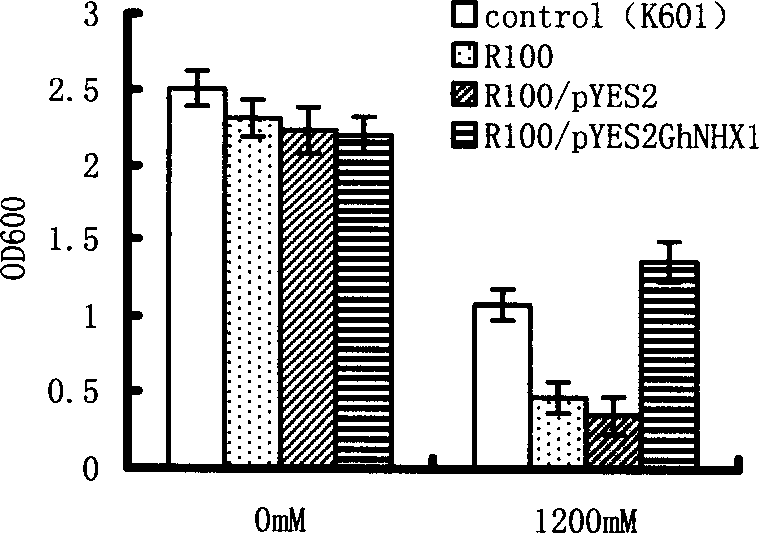
Cotton Na+/H+ reverse transport protein gene and its cloning method and use
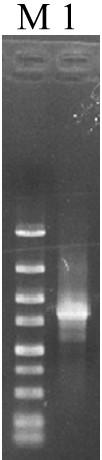
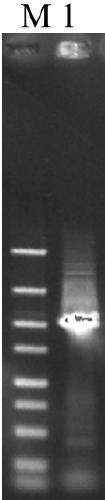
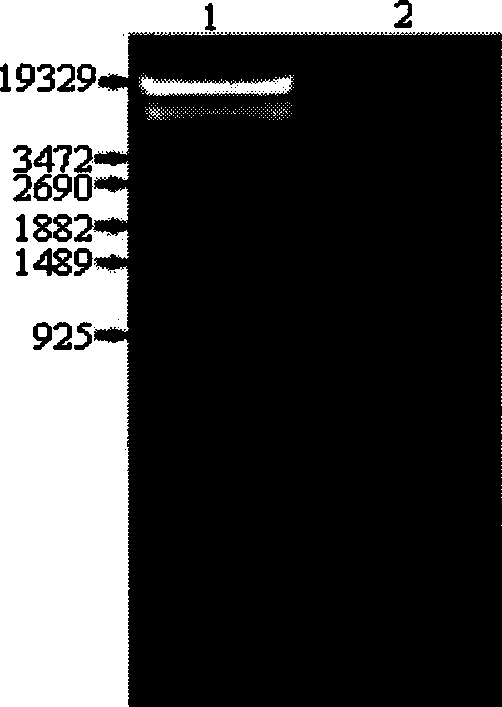
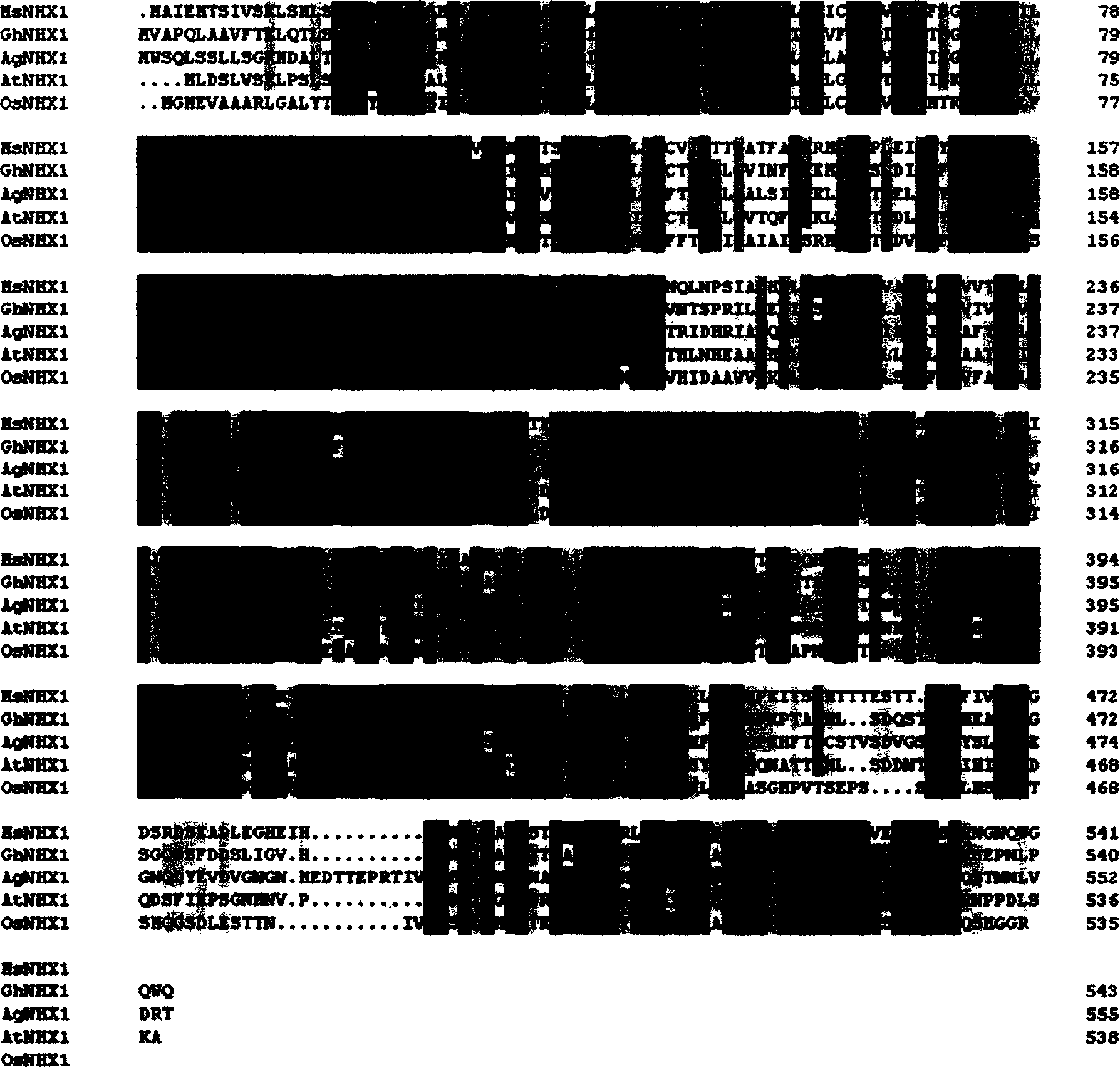
The present invention relates to the cloning, recombination and salt tolerance analysis of cotton Na+ / H+ reverse transport protein GhNHX1 gene, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and biological technology. Total RNA is extracted from cotton leaf treated with 0.4 mol / L NaCl solution and inversely transcribed into cDNA. Facultative primer is used for conventional PCR to obtain intermediate segment, and whole length cDNA is obtained through fast amplification in 3' and 5' ends. The gene is transformed to salt-sensitive yeast mutant to restore its salt tolerant capacity to some degree; and the gene is further transformed to tobacco to obtain transgenic plant capabl eof growing normally in salt concentration of 200 mmol / L. Therefore, the gene is one important salt tolerant gene and may be used in raising the salt tolerant capacity of plant for plantation in saline land.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for effectively improving L-malic acid production intensity of Aspergillus oryzae pp25
InactiveCN106222099AIncrease productionIncrease consumption rateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention discloses a method for effectively improving L-malic acid production intensity of Aspergillus oryzae pp25, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, Aspergillus oryzae pp25 is used as a starting strain, a C4-dicarboxylate transport protein gene C4T318 of the Aspergillus oryzae pp25 and a malic acid transport protein gene maeI of Schizosaccharomyces pombe are expressed to obviously reduce the intracellular accumulation of malic acid, and finally, the shake flask yield of the L-malic acid is up to 93.17+ / -2.10g / L and is increased by 47.4%; the concentration of succinic acid is 5.17+ / -0.49g / L and is reduced by 41.8%; and the conversion rate of the malic acid relative to glucose is 0.85g / g and is increased by 49.1%. Meanwhile, the fermentation period is shortened from 90 hours to 80 hours, and the production intensity is up to 1.16g / L.h and is increased by 65.7%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Application of rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN9 in gene engineering
ActiveCN107988236AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease nitrogen uptakePlant peptidesFermentationHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN9 in gene engineering, belonging to the field of gene engineering. The nucleotide sequence of the rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN9 and the amino acid sequence for expressing OsPIN9 protein have an accession number of AK059229 in an NCBI website (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov / ). The application of the rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN9 in gene engineering is reported for the first time in rice; the rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN9 is involved in the transport of auxin in both aspects of heterogenous frog eggs and rice, thus increasing rice tillers, biomass, nitrogen utilization rate and final yield.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Multiple PCR primer for expanding plasmodium falciparum drug resistance-related gene and method
ActiveCN101161822AImprove detection efficiencyReduce dosageMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenotype AnalysisMultiplex pcrs
The invention relates to a plasmodium falciparum drug resistance related gene multiple PCR amplification method, wherein, plasmodium falciparum genome DNA is adopted as template; a multiple PCR primer set designed by the invention is adopted for monotube PCR reaction to realize amplification of five specific gene (plasmodium falciparum chloroquine resistance transport protein gene Pfcrt, plasmodium falciparum multidrug-resistance gene Pfmdrl, plasmodium falciparum dihydropteroic synthetase gene Pfdhps, plasmodium falciparum dihyrofolate reductase gene Pfdhfr and plasmodium falciparum adenosine triphosphatase Sixth subunit gene PfATPase6) target sequences; moreover, the amplification product covers the currently known 21 plasmodium falciparum drug-resistance related SNP sites. With fewer operational procedures, the invention is quick and convenient and saves cost; moreover, the invention which is particularly suitable for high-throughput genotype analysis is sure to accelerate the wide application of plasmodium falciparum resistance related SNP in field monitoring.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Auxin transport protein gene of paddy rice and application thereof
InactiveCN102373224AWell developed root systemImprove drought resistancePlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceLateral root
The invention discloses an auxin transport protein gene of paddy rice and application thereof, and aims to provide an auxin transport protein gene of paddy rice, an encoding protein thereof and a method for improving the drought resistance of a plant by using the gene. The nucleotide sequence of the auxin transport protein gene of paddy rice provided by the invention is a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) in a sequence 1 in a sequence table; and an encoded amino acid sequence of the auxin transport protein gene is an amino acid residue sequence in a sequence 2 in the sequence table. As proved by experiments, the gene is overexpressed in paddy rice, so that the development of lateral roots and adventitious roots of paddy rice can be promoted, and the drought resistance of paddy rice can be improved under the action of drought stress. The auxin transport protein gene can be importantly applied to improving the drought resistance and abiotic stress resistance of paddy rice by adopting molecular breeding.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
Aspergillus niger genetic engineering bacterial strain high in yield of malic acid under condition of low pH and application
ActiveCN110734865AIncrease productionIncreased capacity to produce malic acidFungiMicroorganism based processesMalate synthaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to an aspergillus niger genetic engineering bacterial strain high in yield of malic acid under condition of low pH. The aspergillus niger genetic engineering bacterial strain isprepared through the steps of obtaining a pexG gene knock-out bacterial strain S914; obtaining an expression Malate synthase gene mas* bacterial strain S1016; overexpressing aspergillus niger malic acid transport protein gene dct1, performing transformant screening and hygromycin resistant gene reorganization to obtain an overexpressing dct1 bacterial strain S1140 without a screening mark, namelythe aspergillus niger genetic engineering bacterial strain high in yield of malic acid under condition of low pH. The bacterial strain is based on the natural characteristics that the aspergillus niger resists acid and generates organic acid, through heredity reorganization, the physiological property of the aspergillus niger is reformed, and experiments confirm that the capacity of the aspergillus niger genetic engineering bacterial strain for generating malic acid at low pH can be notably improved. A good strain is provided for preparation of apples by a microbial fermentation method.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
Construction body for producing carbohydrate compound by virtue of synechococcus UTEX2973, strain and method
ActiveCN107236754ADoes not increase emissionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhylum Cyanobacteria
The invention relates to the bio-manufacturing field and particularly relates to a construction body for producing carbohydrate compound by virtue of synechococcus UTEX2973, a strain and a method. The construction body contains a promoter, a proton / saccharose synergetic transport protein gene, an antibiotic resistance gene and a homologous arm, wherein the promoter has activity in synechococcus UTEX2973, the proton / saccharose synergetic transport protein gene is controlled by the promoter, the antibiotic resistance gene is used for screening a transformant, and the homologous arm is used for homologously integrating genomes. The carbohydrate compound is synthesized by immobilizing carbon dioxide by virtue of solar energy in a photosynthetic microorganism, namely cyanobacteria, the energy for synthesizing carbohydrates is from the solar energy, and a carbon source is from carbon dioxide. Therefore, a biology base product prepared by virtue of the method is not restricted by insufficient raw materials, the carbon emission is not increased during the use of the biology base product, and the biology base product is a true zero-emission biology base product.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
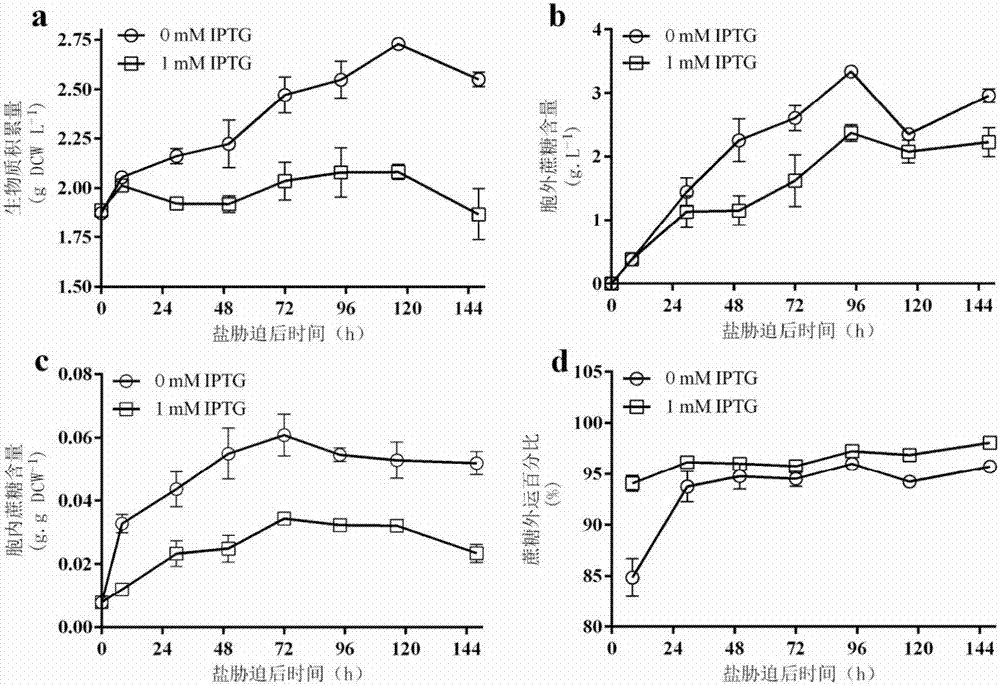
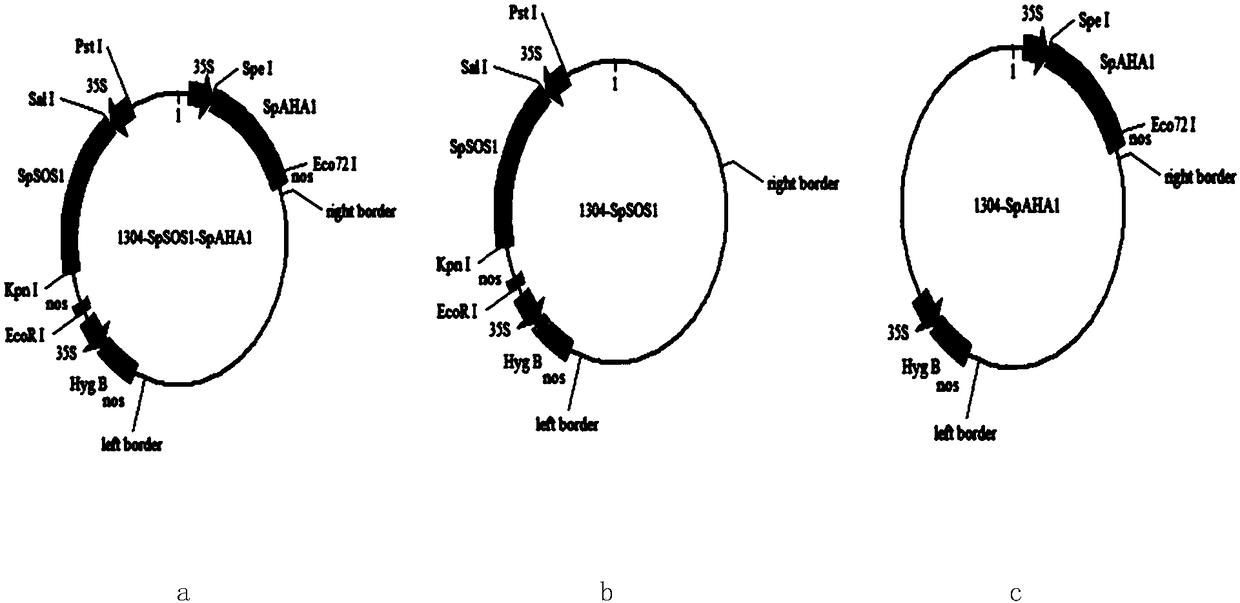
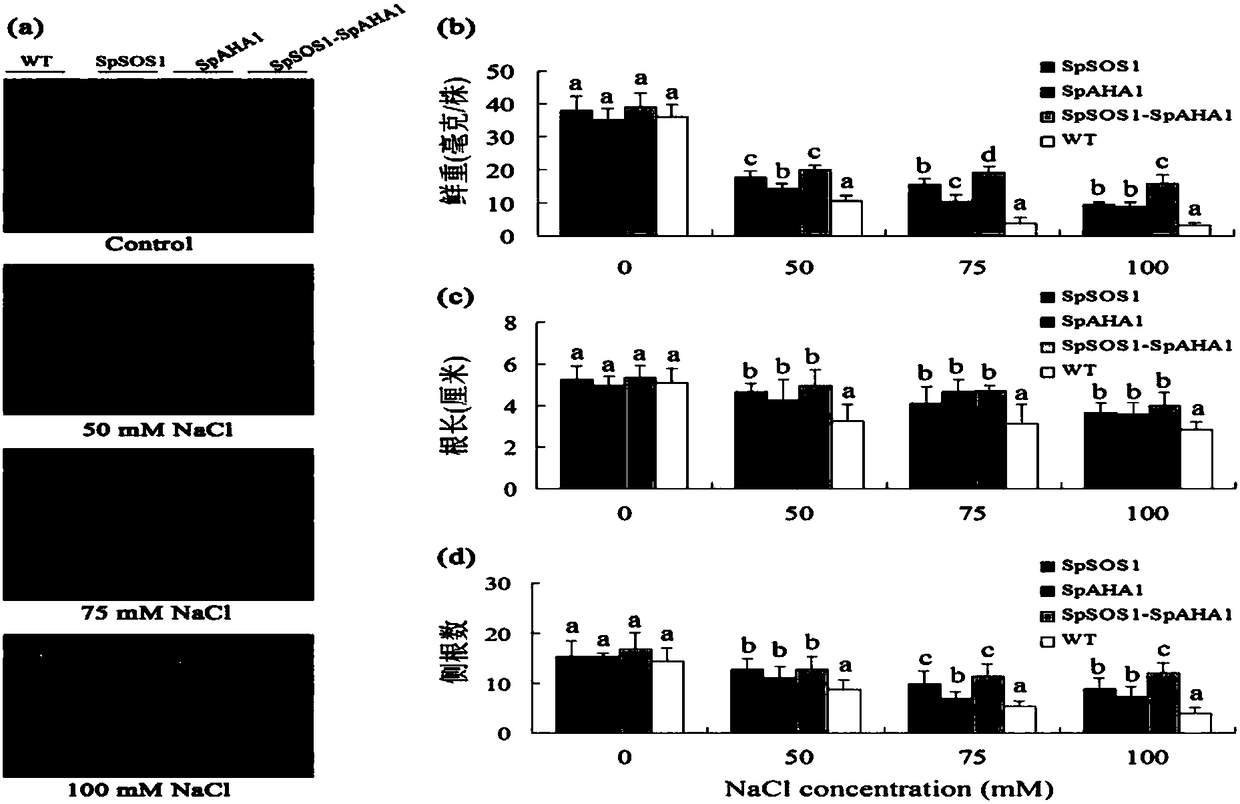
Method for improving salt tolerance of plants
InactiveCN108070028AImprove salt toleranceHigh expressionPlant peptidesFermentationTransport systemLateral root
The invention discloses a method for improving salt tolerance of plants. In the method for improving the salt tolerance of the plants, cell membrane Na+ / H+ reverse transport protein gene SpSOS1 and anH+-ATPase gene SpAHA1 are co-transformed into the plants, and the expression quantity and / or activity of SpSOS1 protein and SpAHA1 protein in the receptor plants is improved. Experiments prove that with the SpSOS1 protein and SpAHA1 protein, which is concretely embodied in that the salt tolerance of the plants can be improved, and the fresh weight, the root length, the number of lateral roots, the flowing speed of H+ ions, the flowing speed of Na+ ions and the content of K+ of the plants are increased, and the content of Na+ and malondialdehyde is decreased. With the method, the cell membraneNa+ / H+ reverse transport protein gene SpSOS1 and an H+-ATPase gene SpAHA1 are co-transformed into the plants to prove the salt tolerance for the first time, which directly proves that H+-ATPase can provide energy for an Na+ / H+ reverse transport system.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Bacillus licheniformis for enhancing expression of cysP and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides bacillus licheniformis for enhancing expression of cysP and a preparation method and application thereof. The bacillus licheniformis is prepared by transferring a plasmid carrier carrying a sulfur element transport protein gene cysP into bacillus licheniformis DW2, thereby realizing free expression of the sulfur element transport protein gene cysP in the bacillus licheniformis DW2, and achieving a purpose of enhancing the expression of the sulfur element transporter gene CysP. Compared with a strain obtained by directly transferring a blank plasmid vector without the cysP gene into the bacillus licheniformis DW2, the bacillus licheniformis for enhancing expression of cysP constructed by the invention has a large increase in bacitracin production.
Owner:LIFECOME BIOCHEM
Recombinant adenovirus of Survivin promoter regulated human NIS gene, construction method and use
InactiveCN101503677APromote generationImprove recombination efficiencyGenetic material ingredientsViruses/bacteriophagesNucleotideImage View
The invention provides a recombined adenovirus constructed by a human sodiumiodide symporter, NIS adjusted and controlled by a survivin promoter and a construction method and application thereof. The method connects nucleotide of a coding human NIS to the lower reach of the survivin promoter which is a broad spectrum tumor specificity promoter; the nucleotide of the coding human NIS and a polyadenylid acid form an expression cassette which is inserted into a non-coding region of the adenovirus so as to construct the recombined adenovirus; the characteristic of the recombined adenovirus which is specifically expressed in a tumor cell and is basically not expressed in a normal cell makes the tumor cell which does not express the protein be capable of taking in radionuclides of iodine and technetium; therefore, the method not only can lead the radionuclides to kill the tumor cell specifically, but also can conveniently and simply carry out quantitative monitoring on the positioning and expression of the gene through image viewing technology.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Alfalfa Na+/H+ reverse transport protein gene and its clone and use
InactiveCN1632122AImprove salt toleranceIncrease planting areaFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionTotal rnaGene conversion
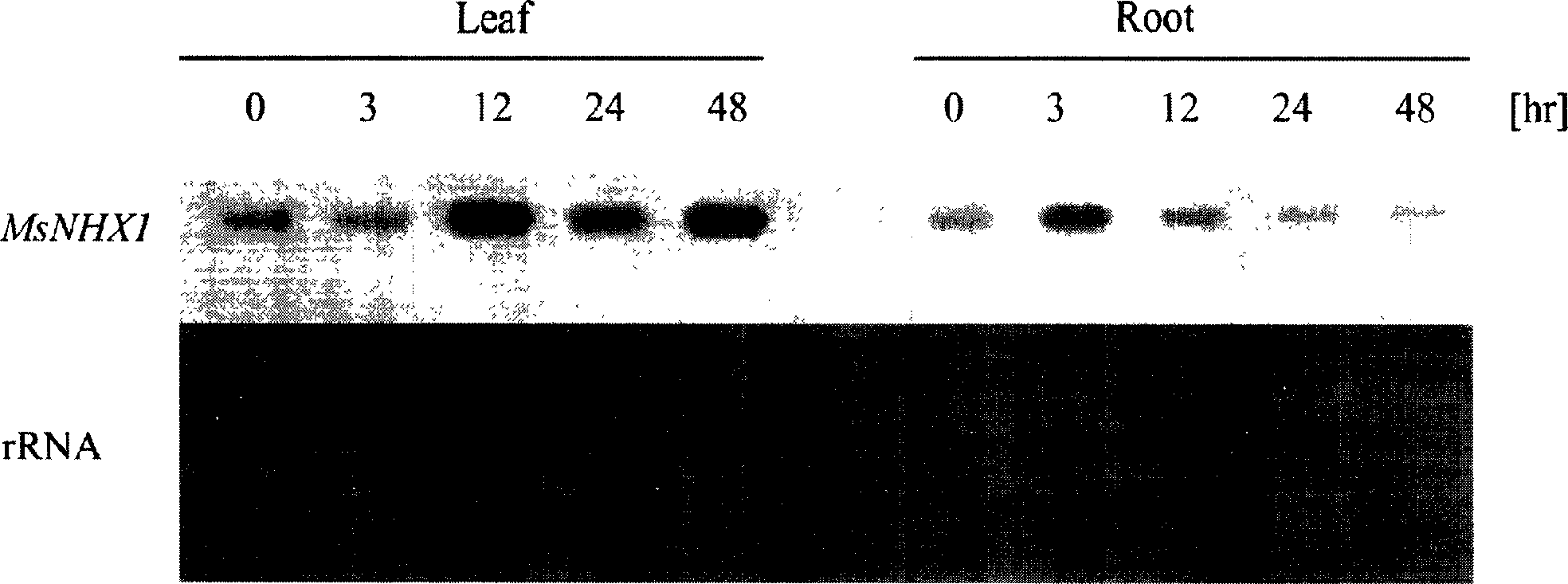
The invention relates to the cloning, recombination, salt tolerance function analysis and application of alfalfa Na+ / H+ antiporter MsNHX1 gene, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and biotechnology. Total RNA was extracted from alfalfa roots, and then 1 μg of total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNA. According to the conserved amino acid sequences of Na+ / H+ antiporters in other plants, a pair of degenerate primers were designed, and conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed. The PCR product was connected to the pGEM-T vector and transformed into DH5α cells. Perform sequence determination. The full-length cDNA was then obtained by rapid amplification of the 3' and 5' ends. Further construct the sense expression vector and transform Arabidopsis. Transgenic Arabidopsis has higher salt tolerance. Therefore, the gene transformation of dicotyledonous crops such as alfalfa will improve their salt tolerance, yield and quality, thereby expanding the planting area of dicotyledonous plants on saline-alkali land and generating huge economic and social benefits.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering probiotics for treating phenylketonuria
PendingCN112662606AEfficient degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses engineering probiotics for treating phenylketonuria and a preparation method of the engineering probiotics, the engineering probiotics are Escherichia coli Nissel 1917 derivative bacteria, and an exogenous Lphenylalanine ammonia lyase gene, an Lphenylalanine transport protein gene and an Lamino acid deaminase gene are integrated on a genome. The engineering probiotics disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing phenylketonuria treatment medicines.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI +1
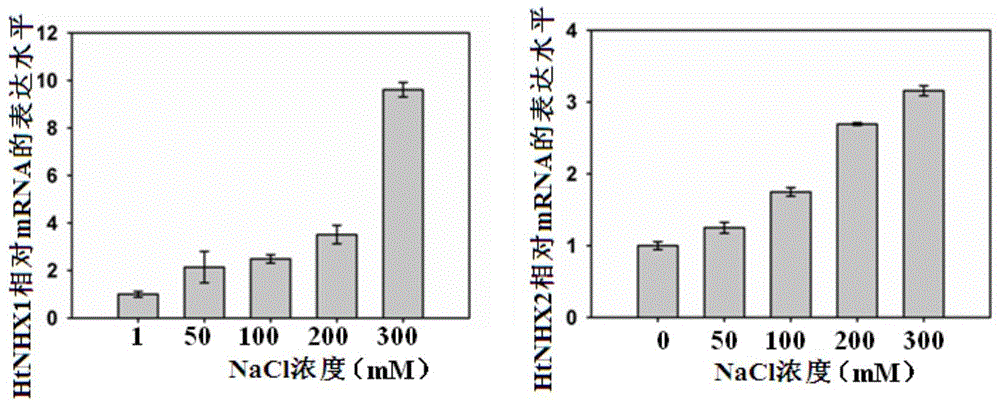
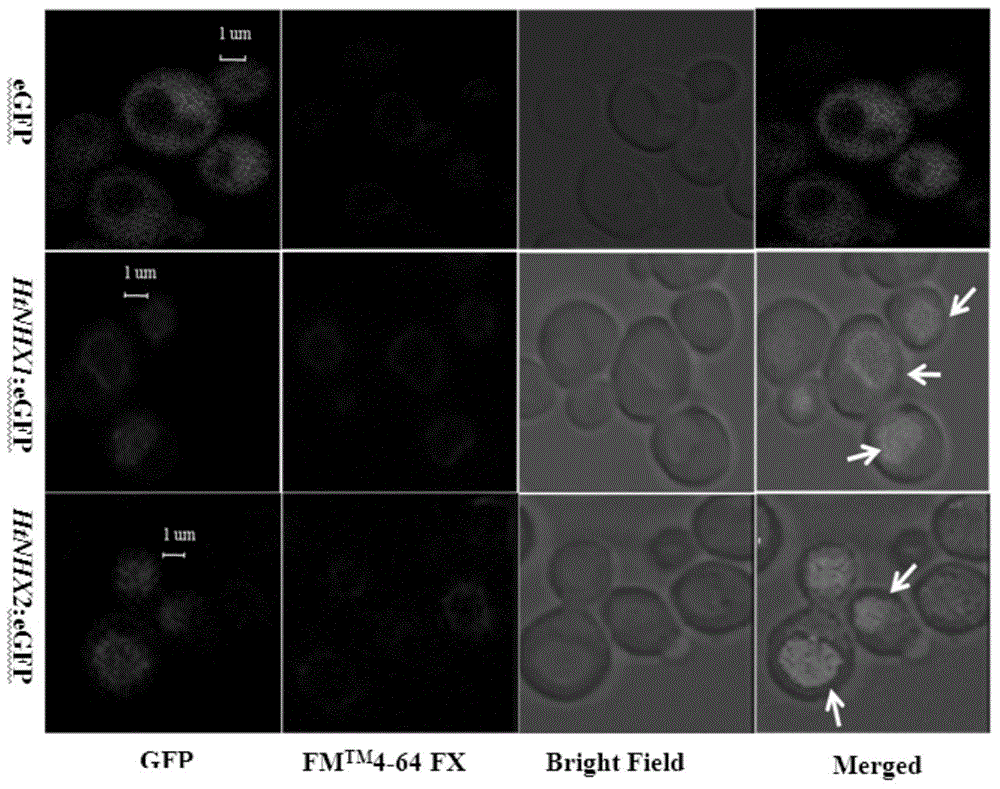
Helianthus tuberosus L. Na<+>/H<+> reverse transport protein genes HtNHX1 and HtNHX2 and use thereof
ActiveCN103602688AIncrease productionImprove salt toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceWild type
The invention discloses helianthus tuberosus L. Na<+> / H<+> reverse transport protein genes HtNHX1 and HtNHX2 and a use thereof. The helianthus tuberosus L. Na<+> / H<+> reverse transport protein genes HtNHX1 and HtNHX2 are first cloned from Nan helianthus tuberosus L. I having extreme resistance to salt and barren soil, and cDNA sequences of the helianthus tuberosus L. Na<+> / H<+> reverse transport protein genes HtNHX1 and HtNHX2 are respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.1. HtNHX1- and HtNHX2-overexpressed paddy rice materials are obtained by a transgenosis method. Compared with wild-type paddy rice materials, the HtNHX1- and HtNHX2-overexpressed paddy rice materials have bigger biomass after long-term and short-term NaCl stress. The trans-HtNHX2 paddy rice has stronger barren soil resistance, has bigger biomass in the low-K<+> content soil and can improve a paddy rice single-plant yield by more than 50%.
Owner:安徽田间云生物科技有限公司
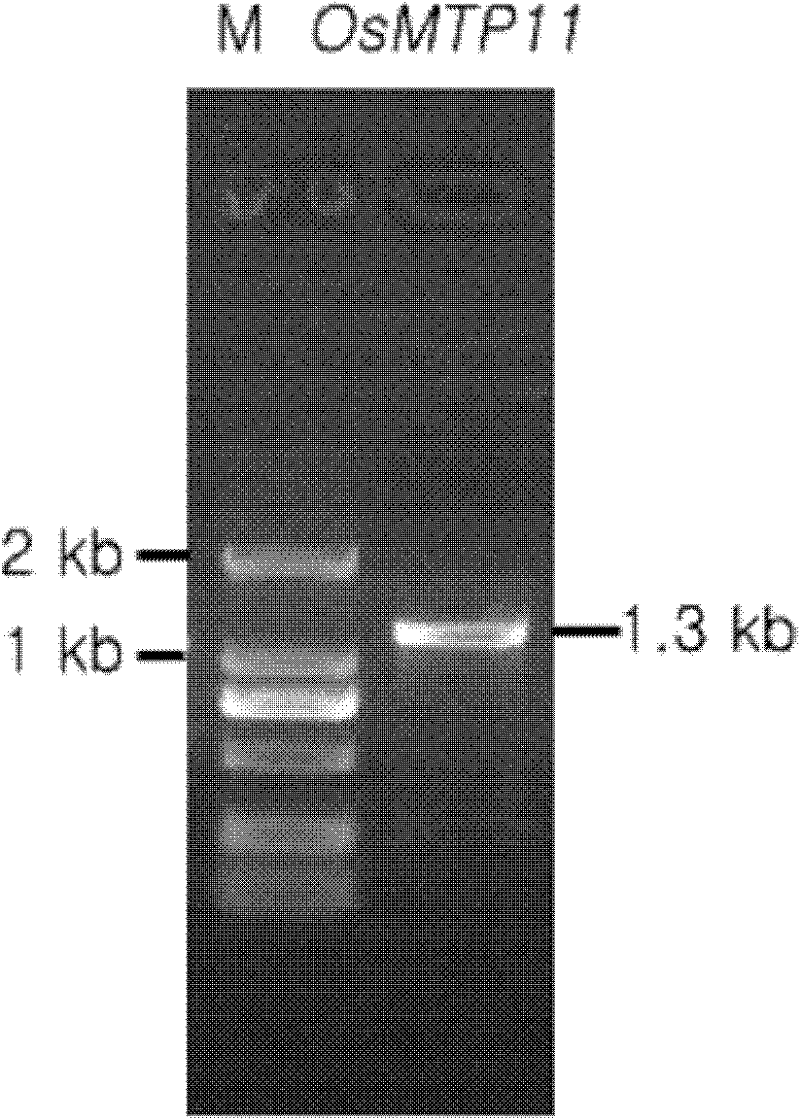
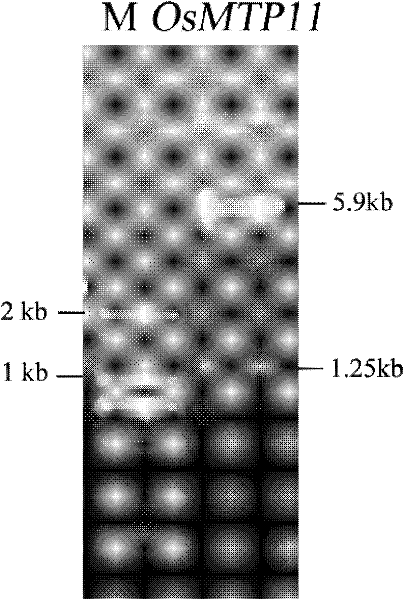
A rice heavy metal-inducible tissue-specific promoter mtp11p and its application
InactiveCN102296068AEasy to transportFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyVascular bundle
The invention discloses a paddy rice heavy metal inducible tissue specific promoter MTP11P and an application thereof. The promoter MTP11P nucleotide sequence is shown as a SEQ ID NO.1-1988 site, the whole length of the sequence is 1988 basic groups. According to the invention, the promoter MTP11P can mainly start the expression of gene in vascular bundle, and induced by a heavy metal. Accordingly, the paddy rice heavy metal inducible tissue specific promoter MTP11P can be used for controlling the expression of metal ions transport protein gene in paddy rice, thereby effectively adjusting theexpression of the metal ions transport protein gene in the vascular bundle and changing the absorption and accumulation of metal ions in plants, also can be used for regulating and controlling the specific expression of the transport protein certain in plant vascular bundle so that the transportation of nutrition, salinity, moisture and the like by plants can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Water-soluble biomass derived carbon dots as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114524428AWide source and green environmental protectionSimple processBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPlant rootsCytoplasm
The invention discloses a water-soluble biomass derived carbon dot and a preparation method and application thereof.The preparation method is characterized in that phenolic acid-containing biomass serves as a carbon source, the water-soluble carbon dot is prepared through a one-step hydrothermal reaction of the carbon source and distilled water, the preparation process is simple, operation is easy, the cost is low, the yield reaches up to 20-30%, pollution is avoided, and the preparation method can be used for industrial production. The surface of the carbon dot provided by the invention contains rich oxygen-containing functional groups, so that the carbon dot is endowed with excellent biological characteristics, Ca < 2 + > inflow of a plant root system is induced, a calcium signal is formed, and the expression of a corresponding defense gene is regulated. The carbon dots not only can activate the expression of a Na < + > / H < + > reverse transport protein gene SOS1 of a plant root system cytoplasmic membrane, reduce the absorption of the plant to Na < + > and remarkably relieve plant salt stress, but also can improve the overexpression of a plant low-iron response gene, improve the absorption and utilization efficiency of the plant to Fe < 2 + > and relieve plant low-iron stress. The prepared carbon dots can effectively relieve plant abiotic stress and improve plant stress resistance.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of peanut AhFRDL1 gene in improving aluminum toxicity stress resistance of plants
The invention provides an application of peanut citric acid transport protein gene AhFRDL1 in improving aluminum toxicity stress resistance of plants. The application comprises: transferring the peanut citric acid transport protein gene AhFRDL1 or a recombinant expression vector containing the peanut citric acid transport protein gene AhFRDL1 into plant cells, screening transgenic plants, and making the transgenic plants express the peanut citric acid transport protein gene so as to improve the aluminum toxicity stress resistance of the plants. In the invention, the fact that the peanut citric acid transport protein gene AhFRDL1 is gene for regulating and controlling secretion of citric acid in vitro of the plants and participates in the biological process of the aluminum toxicity stress resistance of plants is proved at first, and the peanut citric acid transport protein gene AhFRDL1 is used for improving the aluminum toxicity stress resistance of plants, which has long-term practical significance for further breeding aluminum toxicity resistant main crops on acid soil.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Couchgrass sodium ion reverse transport protein gene and its cloning method and use
The present invention belongs to the cloning, recombination and salt endurance function analysis of couchgrass sodium ion reverse transport protein ENHX1 gene, and belongs to the field of molecular biology and biological technology. General RNA is first extracted from couchgrass root and then inverse transcripted into cDNA. A pair of facultative primer is designed based on the conservative amino acid sequence of other plant's sodium ion reverse transport protein CycD2 for conventional PCR, land the PCR product is connected to pGEM-The vector to convert DH5 alpha cell and determine sequence. Then, whole length cDNA is obtained via fast amplification in 3' and 5' ends. Further, positive-sense expression vector is constituted to convert pseudomustard.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving capacity of producing pyruvic acid with engineering bacteria by knocking out pyruvic acid transport protein genes
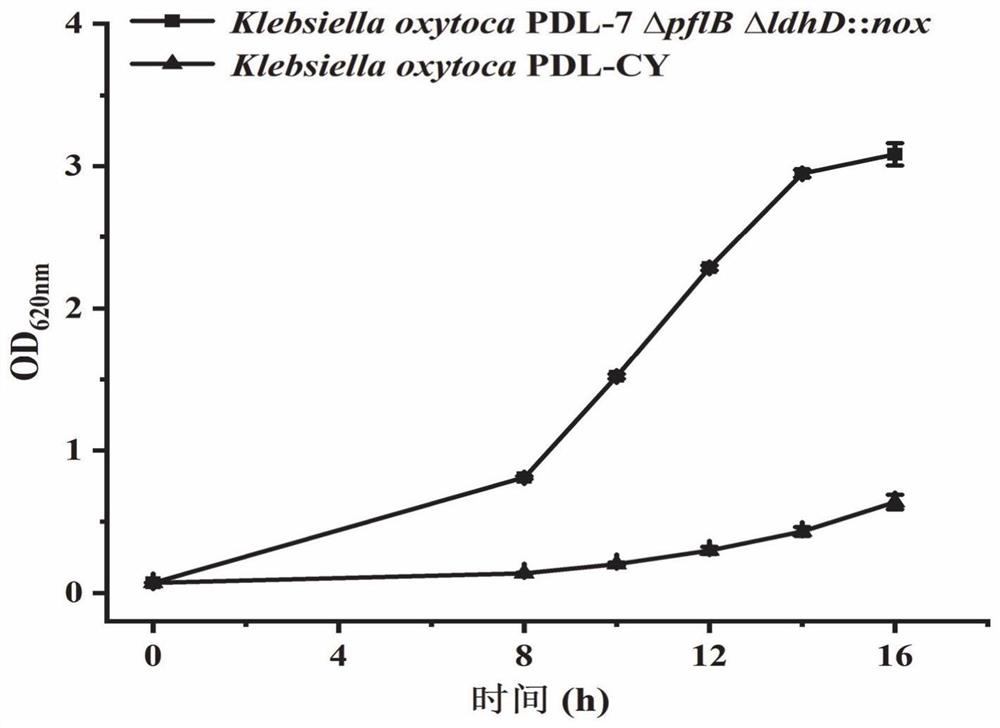
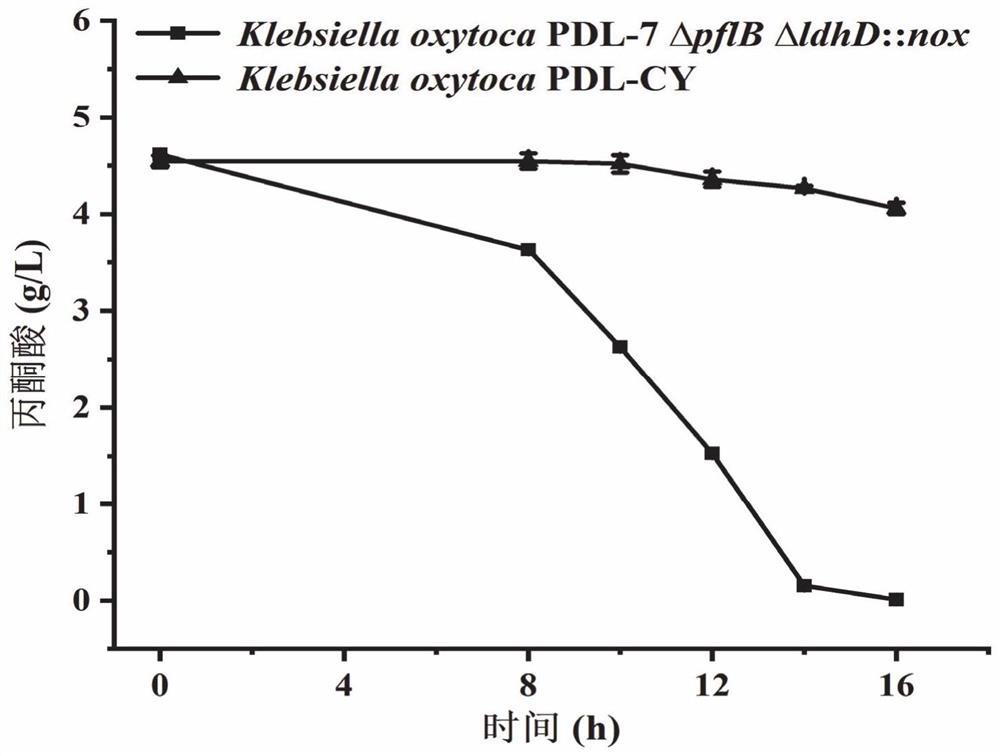
InactiveCN111718950ASolve the reuse problemHas pyruvate uptake functionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesKlebsiella oxytocaHigh pyruvate
The invention discloses a method for improving the capacity of producing pyruvic acid with engineering bacteria by knocking out pyruvic acid transport protein genes. Recombinant klebsiella oxytoca PDL-7 Delta pflB Delta ldhD::nox is taken as an original strain; the pyruvic acid transport protein genes cstA and yjiY of the original strain are knocked out to construct a klebsiella oxytoca engineering strain which can increase the fermentation production capacity of the pyruvic acid, and the klebsiella oxytoca engineering strain is named klebsiella oxytoca PDL-CY; experiments confirm that the yield of the pyruvic acid fermented-produced by the constructed engineering strain is 103.31g / L by taking glucose as a substrate, and the substrate conversion rate reaches 0.90g / g; and compared with theoriginal strain, the yield of the pyruvic acid and the substrate conversion rate of the constructed engineering strain are increased by 67.8% and 76.8% respectively. The method of the invention has asimple process; product components are single and are easy to separate; and the method has important economic benefits and social meaning.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Genetic engineering strain for producing inosine as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN114317386AClear genetic backgroundIncrease production capacityBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and relates to breeding of industrial microorganisms, in particular to a genetic engineering strain for producing inosine as well as a construction method and application of the genetic engineering strain. According to the genetic engineering strain, a nucleoside transport protein gene pbuE, a purine operon mutant gene purEKBCSQLFK316QMNHD and a PRPP transamidase mutant gene purFK316Q are subjected to heterologous overexpression, a gene purA is replaced by a heterologous adenosine succinate synthetase mutant gene purAP242N, and purine nucleoside phosphorylase genes deoD and ppnP and nucleoside hydrolase genes rihA, rihB and rihC are not expressed. Starting from the genome level of Escherichia coli, modules of an inosine decomposition pathway, an inosine synthesis pathway, an inosine transport system and a branch metabolic pathway are systematically and comprehensively combined and optimized mainly through a metabolic engineering technical means, and the inosine fermentation performance of the strain is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Gene engineering application of rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2
InactiveCN101736014BEnhanced tillering abilityImprove utilization efficiencyFermentationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses gene engineering application of rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2, which belongs to the field of gene engineering. The accession numbers of the nucleotide sequence of the rice auxin transport protein gene OsPIN2 and the expression OsPIN2 protein amino acid sequence thereof are AK101191 in an NCBI website (www. ncbi. nlm. nih. Gov / ). The engineering application of the gene is firstly reported in the rice, and participates in the transport of rice auxin so as to increase the rice roots, tiller number, tiller angle, nitrogen utilization efficiency and finial output.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1 as well as encoding protein and application of strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1
InactiveCN103993020AImprove screening efficiencyImprove salt toleranceBacteriaPlant peptidesNicotiana tabacumSalt Tolerant Plants
The invention discloses a strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1 as well as an encoding protein and application of the strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1. The strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; a reverse Na<+> / H<+> transport protein for encoding the strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the strong-salt-tolerant plant gene SseNHX1 is applied to the aspect of culturing salt-tolerant plants. According to the invention, a strong-salt-tolerant gene (SseNHX1) obtained after two reverse Na<+> / H<+> transport protein genes (NHX1) with different sources in the same family are recombined is transplanted into tobacco in a genetic transformation way, therefore, after the tobacco is subjected to salt stress treatment, the salt tolerance of the transgenic tobacco can be further improved, and a basis is provided for culturing novel genetic materials with stronger salt tolerance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain with high xylose transport capacity and application thereof
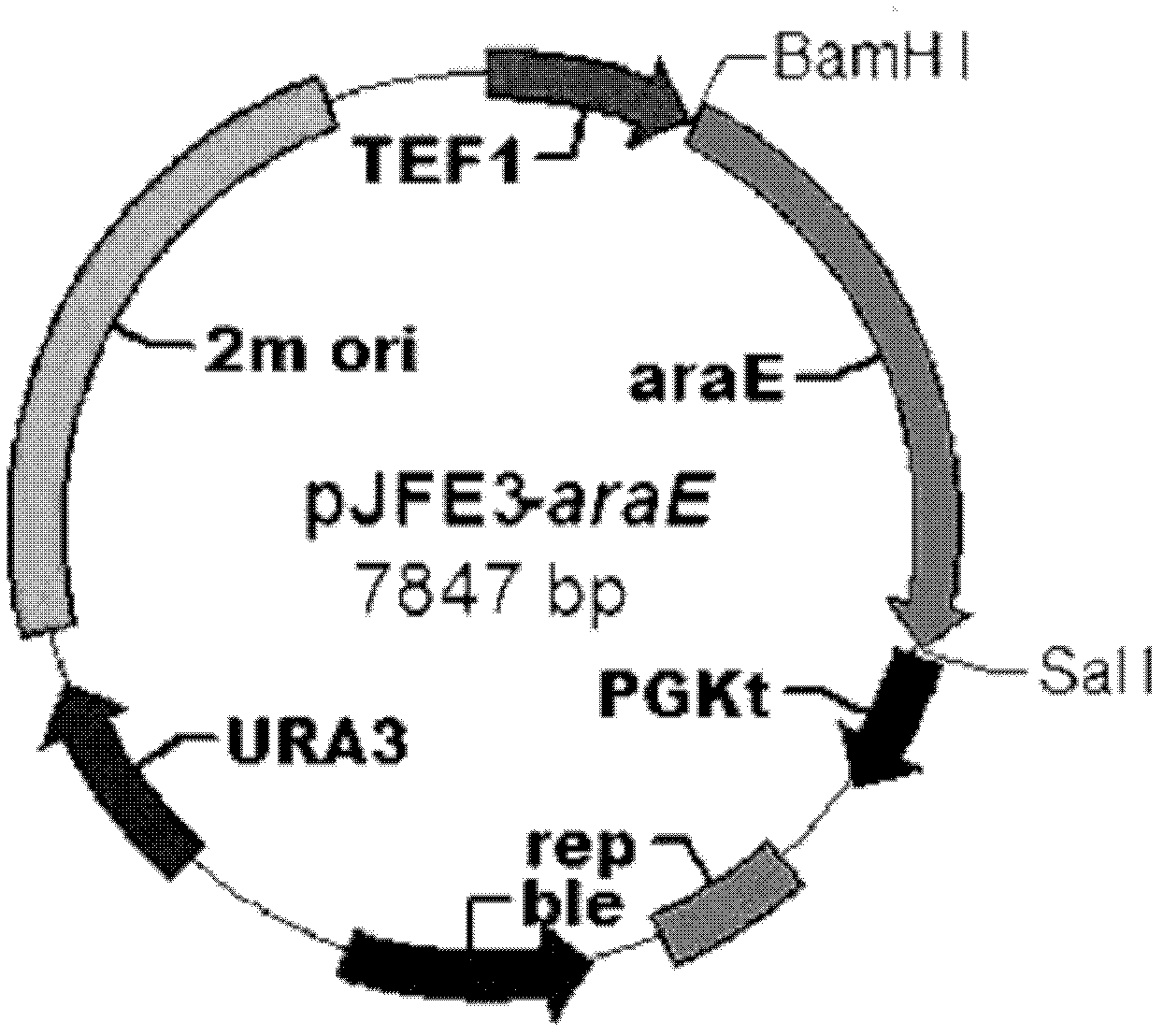
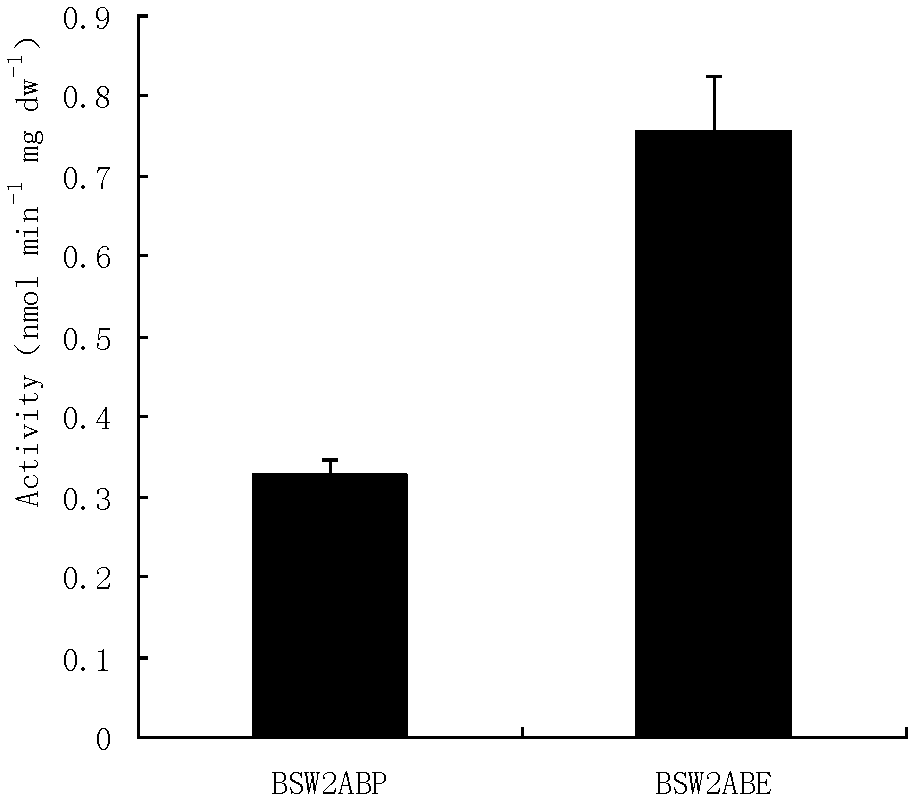
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain with high xylose transport capacity. The bacterial strain is BSW2ABE, is named as saccharomyces cerevisiae in a classified manner and is preserved at China General Microbiological Center Culture Collection Center on December, 27th, 2011, and the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No. 5658. The bacterial strain expresses a transport protein gene araE cloned from corynebacterium glutamicum and also expresses the detection on the saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain containing transport protein by utilizing a method for screening and expressing the saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain containing the active xylose transport protein (refer to an invention patent application with an application date of December, 15th , 2011 and an application number of 201110420908.4 submitted by a same applicant); and compared with an initial bacterial strain, the xylose transport speed of the saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain is improved by 1.9 times. The invention also relates to an application of the bacterial strain with improved xylose transport capacity in the construction of recombinant saccharymyces cerevisiae of metabolizable xylose.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Compositions and methods related to silicon transport
Based on our identification of silicon influx and efflux transporter genes in plants known to take up silicon efficiently, including wheat, horsetail, oat, sorghum, and barley, the present invention features polynucleotides encoding silicon transporters; vectors, cells, and plants including such polynucleotides, and methods for making such plants. The invention also features silicon transporter polypeptides and fragments thereof. Plants expressing heterologous silicon transporters may exhibit both increased silicon uptake and increased resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. In particular, plants such as soybean expressing silicon transporters may exhibit increased resistance to pathogens such as rust.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Paddy rice heavy metal inducible tissue specific promoter MTP11P and application thereof
The invention discloses a paddy rice heavy metal inducible tissue specific promoter MTP11P and an application thereof. The promoter MTP11P nucleotide sequence is shown as a SEQ ID NO.1-1988 site, the whole length of the sequence is 1988 basic groups. According to the invention, the promoter MTP11P can mainly start the expression of gene in vascular bundle, and induced by a heavy metal. Accordingly, the paddy rice heavy metal inducible tissue specific promoter MTP11P can be used for controlling the expression of metal ions transport protein gene in paddy rice, thereby effectively adjusting theexpression of the metal ions transport protein gene in the vascular bundle and changing the absorption and accumulation of metal ions in plants, also can be used for regulating and controlling the specific expression of the transport protein certain in plant vascular bundle so that the transportation of nutrition, salinity, moisture and the like by plants can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
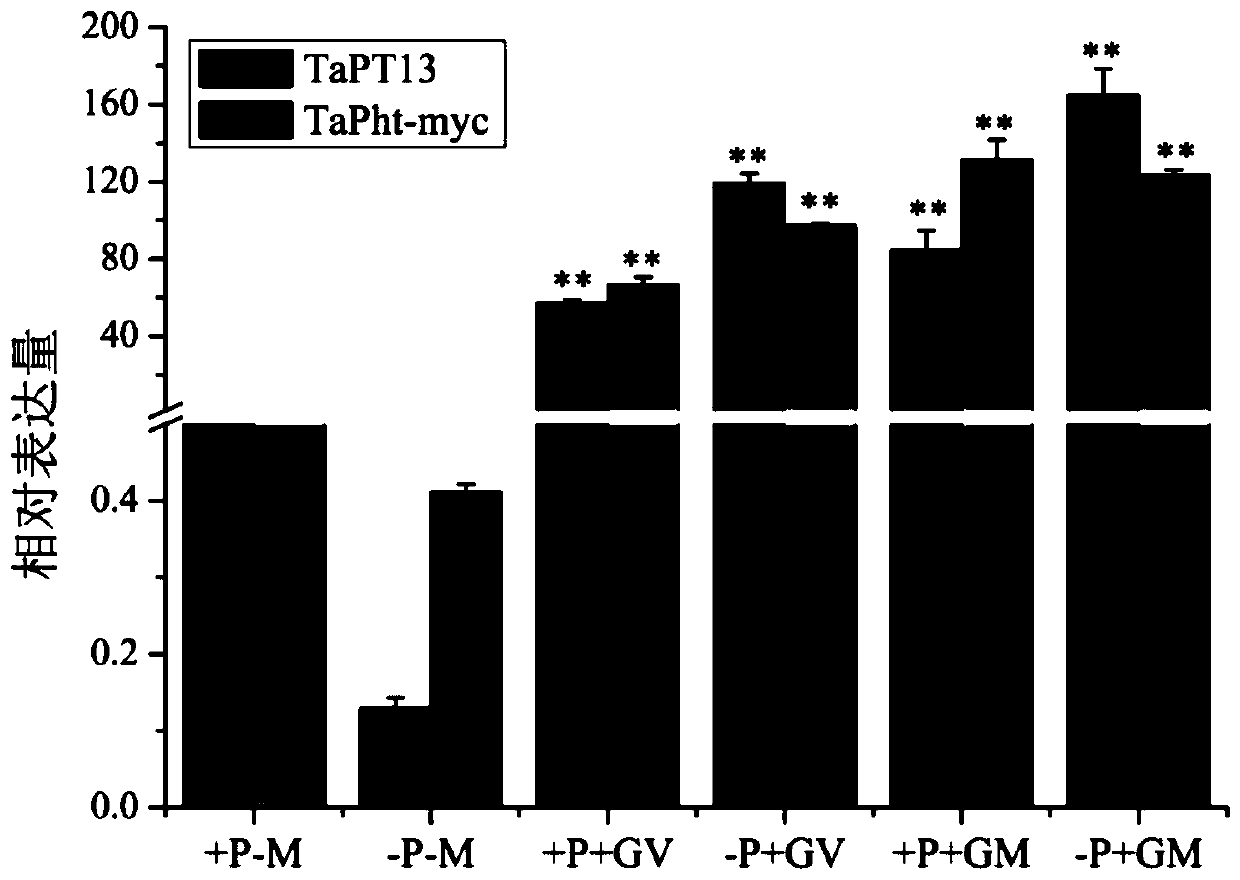
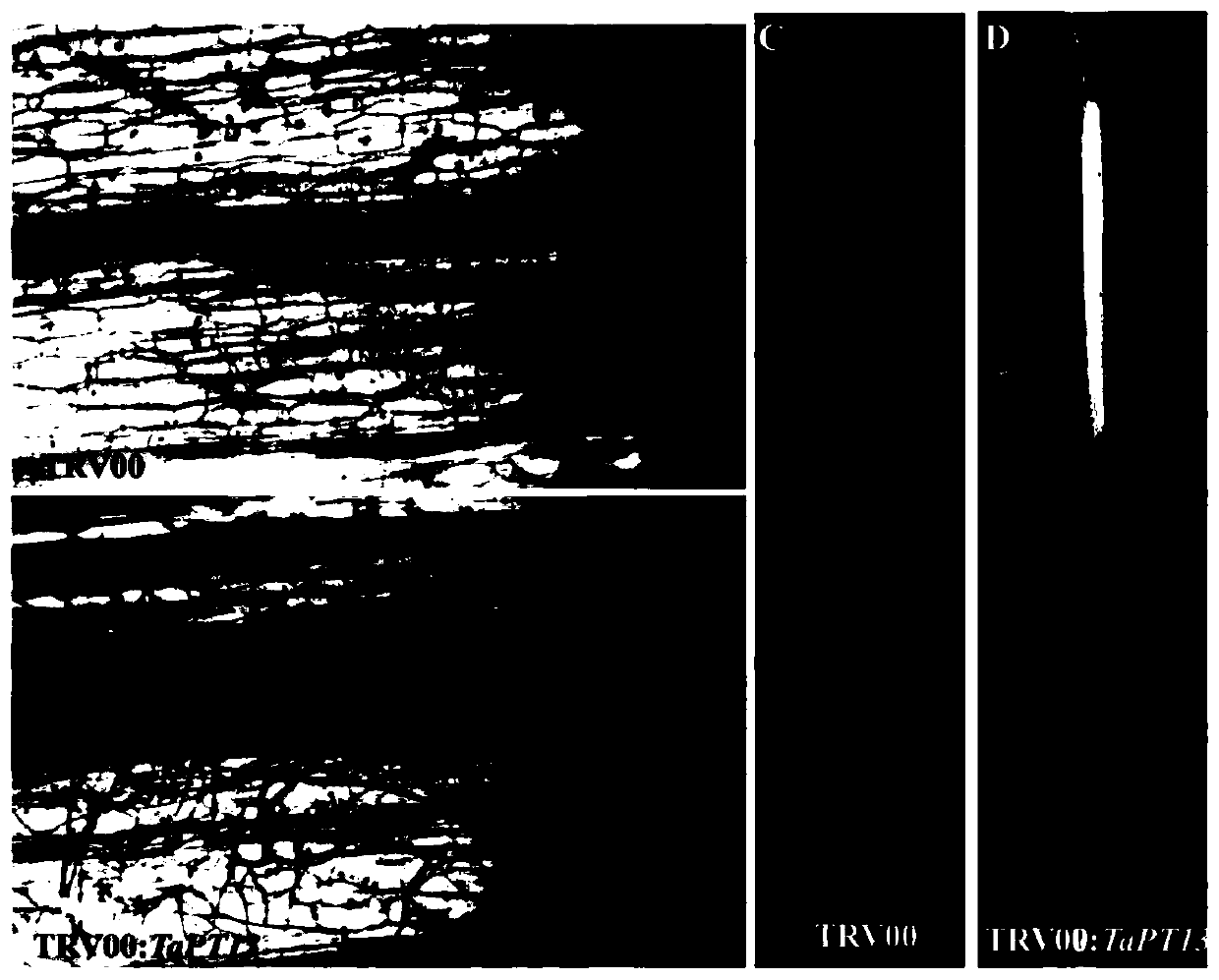
Application of TaPT13 gene in improving resistance of plants to Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici J. Walker
ActiveCN110714012AEffective absorptionImprove disease resistanceClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of agricultural biology, and particularly relates to application of a TaPT13 gene in improving the resistance of plants to Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici J. Walker. According to the invention, the arbuscular mycorrhiza-specific phosphorus transport protein gene TaPT13 can be used for improving plant disease resistance, with the nucleotide sequence shown asSEQ ID NO. 1. The invention determines that the TaPT13 gene is an arbuscular mycorrhiza-specific phosphorus transport protein gene, and the TaPT13 gene expression level is significantly increased after the plant is inoculated with the Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici J. Walker; and the susceptibility of the plant is increased, and the expression levels of disease-resistant marker genes are decreased after silencing the TaPT13 gene in the plant. Therefore, the TaPT13 gene can be used for improving the resistance of wheat to the Gaeumannomyces graminis var. tritici J. Walker, and has wide application space in plant breeding and cultivation.
Owner:ZHOUKOU NORMAL UNIV
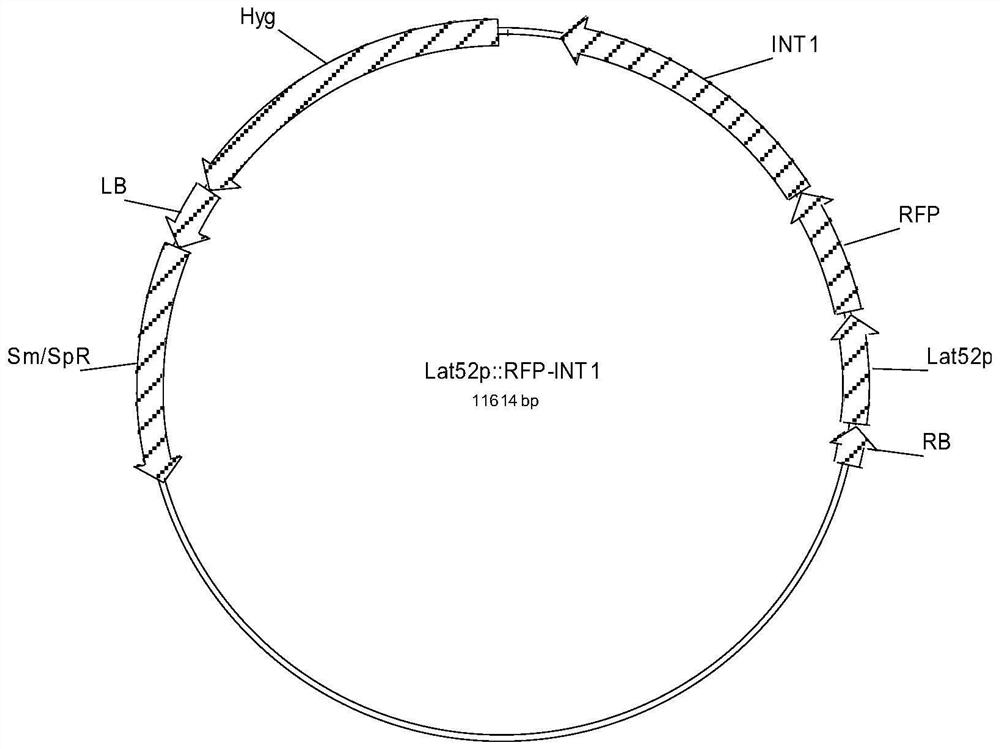
Construction method and application of fluorescence marker for pollen tube vacuole of plant
InactiveCN112852828AShow vacuolar dynamicsShow dynamicsPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to a construction method of a fluorescence marker for a pollen tube vacuole of a plant. The construction method comprises the following steps: cloning a CDS sequence of an inositol transport protein gene AT2G43330 INT1, wherein the sequence of the CDS sequence is represented by SEQ ID No. 1 or is a nucleotide sequence having the same function and formed by replacing, deleting or adding one or more basic groups to the CDS sequence of the inositol transport protein gene AT2G43330 INT1; linking INT1 to a Gateway expression vector of a red fluorescent protein (RFP) started by a pollen tube-specific promoter, and expressing fusion protein RFP-INT1 in plant pollen through the vector, wherein RFP is the red fluorescent protein, and INT1 is an amino acid sequence coded by arabidopsis AT2G43330; and transforming the plant, and conducting screening and identifying to obtain a transgenic plant with a fluorescence signal. The red marker constructed by the invention can be applied to scientific research and is used for determining subcellular localization of unknown proteins; and meanwhile, through instantaneous transformation, the dynamic state of the vacuole of the plant pollen can be rapidly displayed, pollen viability is indirectly reflected, and excellent germplasm and genetic materials are convenient to screen.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com