Saccharomyces cerevisiae bacterial strain with high xylose transport capacity and application thereof
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the application field of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae, can solve problems such as plasma membrane incompatibility, correct expression of transport proteins, difficulty in membrane positioning, and differences in chemical composition, and achieve broad application prospects Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1: Construction of araE Saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector
[0029] Methods as below:
[0030] (1) Vector selection: pJFE3 (Yeplac195, TEFp-PGKt, Ura - , Amp + ) empty plasmid;
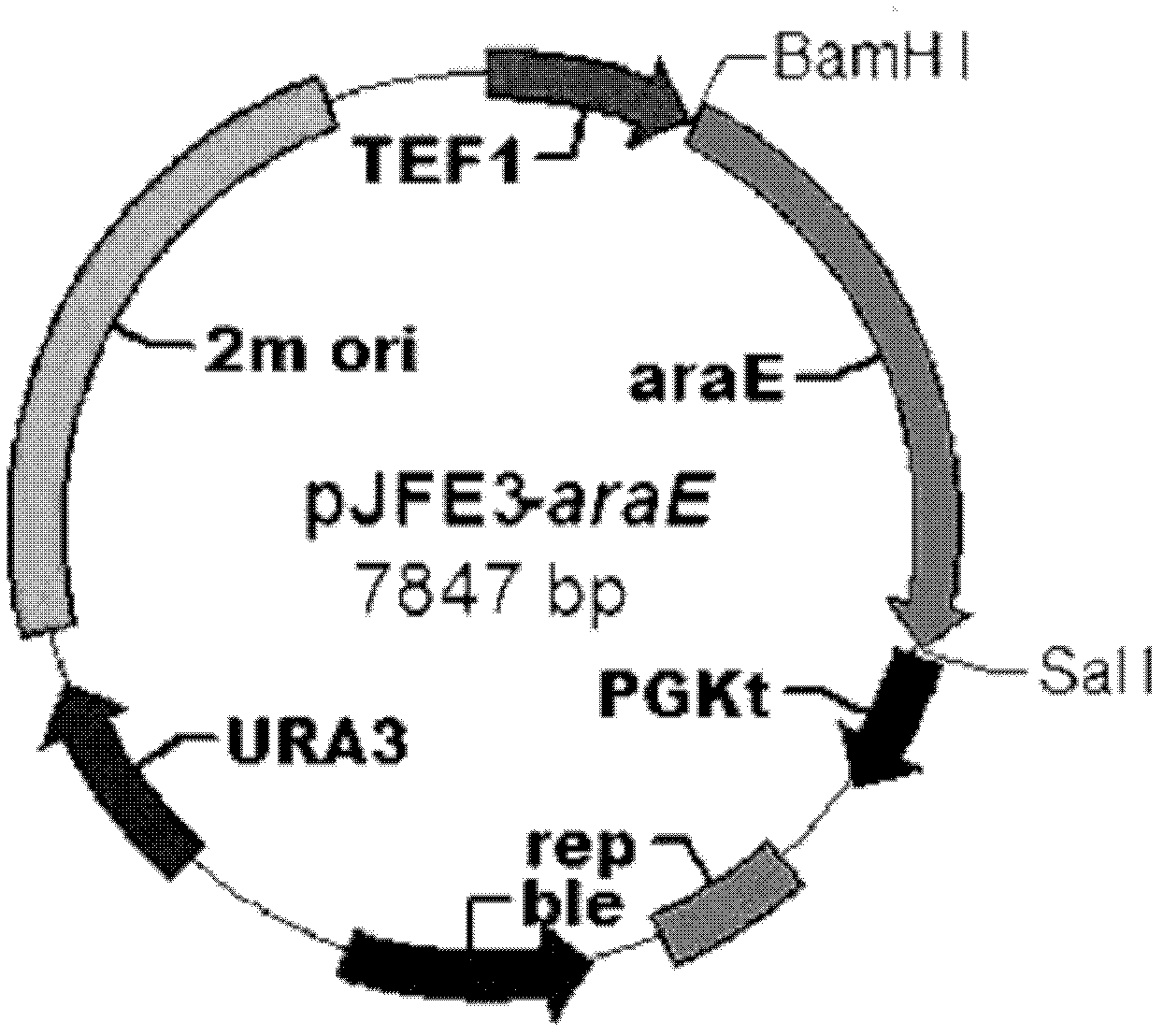
[0031] (2) Expression vector construction: use upstream and downstream primers AraE3up: 5'-ATCGC GGATCC ATGGCAGGGCACATCATCCGCTCAG-3' and AraEdown-His:5'-ACGC GTC GAC TTAGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGAGGCTAAGGAGTGTTTAAGAGC-3'Clone the transporter gene araE from the DNA of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 31831, and construct the Saccharomyces cerevisiae episomal shuttle plasmid on the plasmid in (1) using BamH I and Sal I restriction sites pJFE3-araE, see appendix figure 1 ;
Embodiment 2
[0032] Embodiment 2: Construction of the bacterial strain BSW2ABE expressing AraE transporter
[0033] Methods as below:
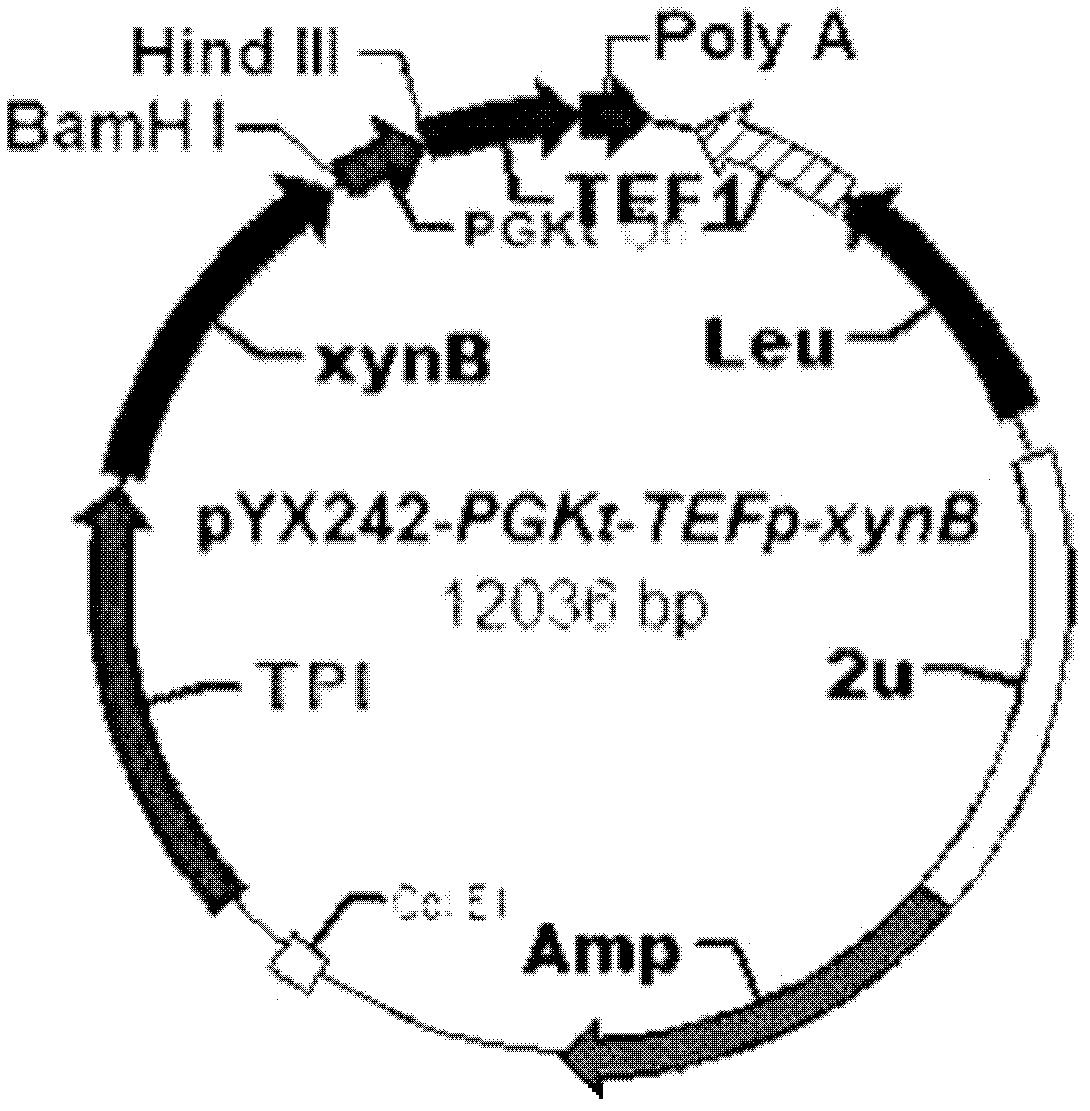
[0034] (1) Strain selection: select the constructed laboratory strain BSW2AB (CEN.PK102-3A derivative, MATa, leu2-3, ura3-52, pYX242-PGKt-TEFp TPIp-xynB) with intracellular heterologous expression of xylosidase -PGKt) as the recipient strain, which contains the constructed pYX242-PGKt-TEFp TPIp-xynB-PGKt heterologous expression vector, see figure 2 , the strain was deposited in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on November 17, 2011, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.5465;
[0035] (2) Strain construction: the plasmid pJFE3-araE constructed in Example 1 was transformed into the BSW2AB strain by the lithium acetate transformation method, and the correct transformant was screened with the fully synthetic auxotrophic medium SC-Leu-Ura added with 2% glucose;
[0036] (3) Bacterial strain v...
Embodiment 3
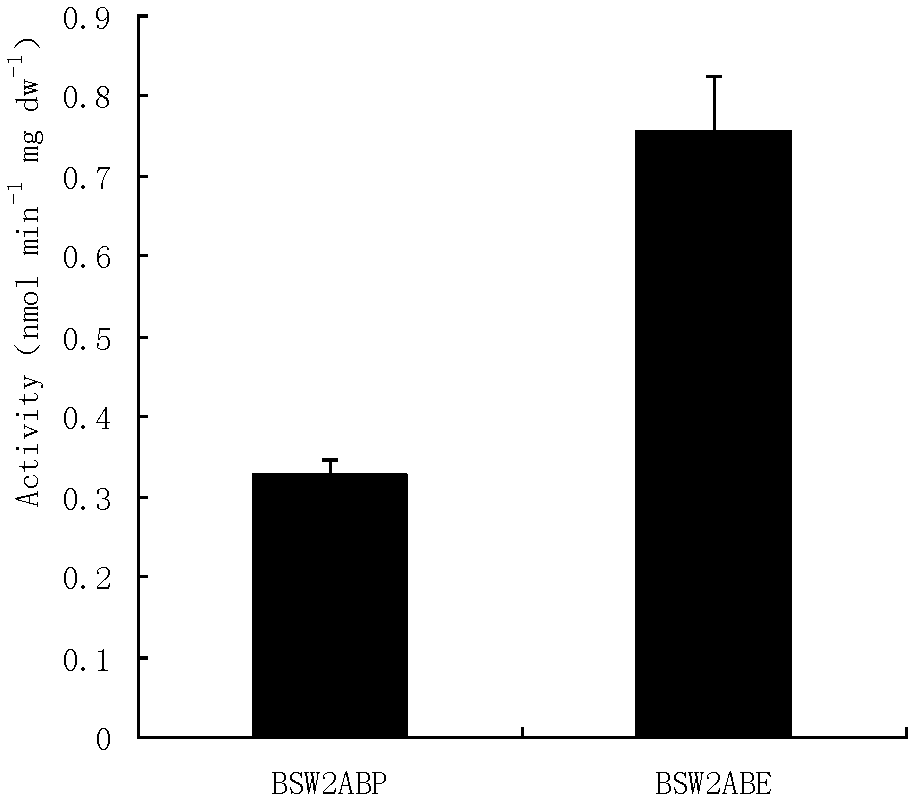
[0037] Example 3: Determination of the pNPX Transport Ability of the Bacterial Strain BSW2ABE
[0038] Methods as below:
[0039] (1) Routine strain selection: select the laboratory strain BSW2ABP (CEN.PK102-3A derivative, MATa, leu2-3, ura3- 52, pYX242-PGKt-TEFp TPIp-xynB-PGKt, pJFE3) as a conventional strain;
[0040] (2) Bacterial strain culture: the single bacterium colony of bacterial strain BSW2ABP and BSW2ABE is activated twice with the fully synthetic auxotrophic culture medium SC-Leu-Ura that adds 2% glucose, transfers 40ml to 100ml small Erlenmeyer flask, initial 600nm light absorption (expressed as OD 600 or OD 600nm ) was connected to 0.5, and the culture conditions were 30°C, 200r·min -1 ;
[0041] (3) Preparation of complete cell suspension: take the bacterium liquid cultivated in step (2) for 10 hours, centrifuge (3000r min -1 , 5min) resuspended with 50mmol / L PBS solution of pH 6.5 after removing the original culture medium;
[0042] (4) Determination of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com