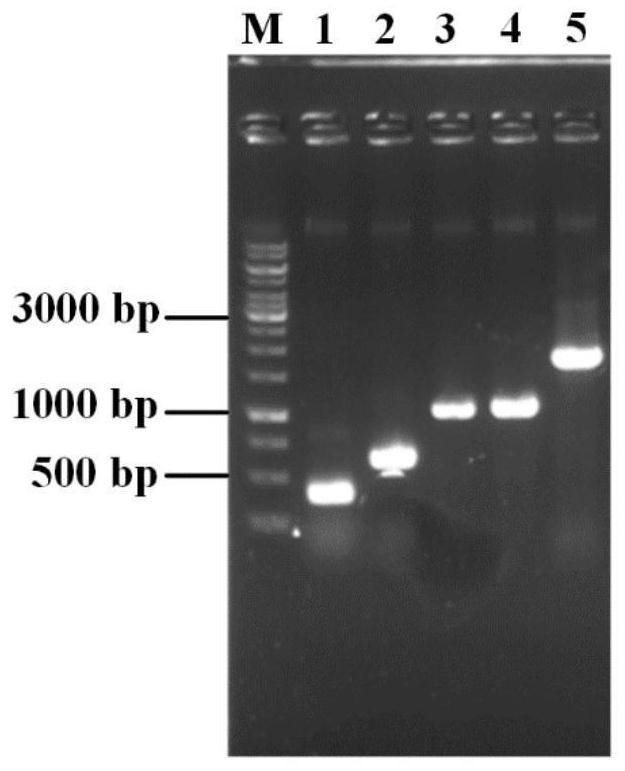
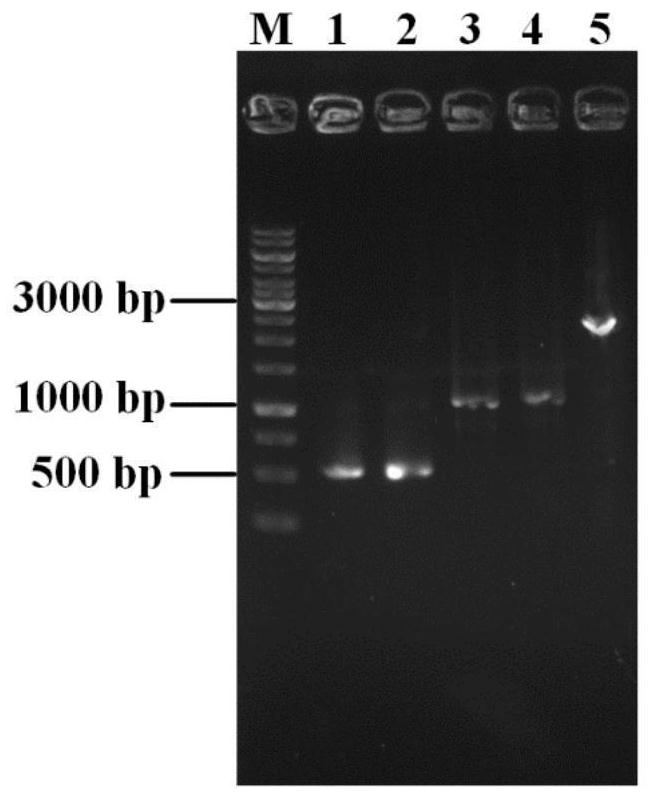
Genetic engineering strain for producing inosine as well as construction method and application thereof
A genetically engineered strain and gene technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of easily lost production of plasmids, increase of production costs, complex fermentation process, etc., and achieve good industrial application prospects, stable and efficient production, and clear genetic background effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0040] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the nucleoside transporter gene pbuE is connected with a promoter P trc and / or the purine operon mutant gene purEKBCSQLF K316Q MNHD-linked promoter P trc and / or the PRPP transamidase mutant gene purF K316Q linked with promoter P trc ; Preferably, the promoter P trc The nucleotide sequence of is shown in SEQ ID NO:5.
[0041] According to the present invention, the starting strain for constructing the E. coli genetic engineering strain may be any E. coli, and according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the starting strain is E. coli MG1655.
[0042] In a second aspect, the present invention provides a method for constructing the Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain as described above, comprising: introducing the nucleoside transporter gene pbuE into the starting strain Escherichia coli, the purine operon mutant gene purEKBCSQLF K316Q MNHD and PRPP transamidase mutant gene purF ...
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1: the construction of Escherichia coli genetic engineering strain E.coli INO4
[0060] 1. Blocking inosine decomposition pathway
[0061] 1.1 Knockout of deoD gene:
[0062] Using the E.coli MG1655 genome as a template, the upstream homology arm primers (UP-deoD-S, UP-deoD-A) and the downstream homology arm primers ( DN-deoD-S, DN-deoD-A), and its upstream and downstream homology arm fragments were amplified by PCR. The above fragments were fused by overlapping PCR to obtain a knockout fragment of the deoD gene (upstream homology arm-downstream homology arm). The DNA fragment containing the target sequence used in the construction of pGRB-deoD was prepared by annealing the primers gRNA-deoD-S and gRNA-deoD-A. The recombinant fragment and plasmid pGRB-deoD were electrotransformed into competent cells of E.coliMG1655, and the positive strains were screened, and then the plasmid was eliminated to obtain strain INO1-1. The construction of the deoD knockout f...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Embodiment 2: strain INO2-6, INO2-7, INO2-8 and INO2-9 shake flask fermentation to produce inosine experimental shake flask culture method is as follows:
[0107] Slant activation culture: Streak inoculation of -80°C preserved strains on the activation slant, culture at 37°C for 12 hours, and then passage again;
[0108] Seed culture: Scrape a ring of slanted seeds with an inoculation loop and inoculate in a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 30mL of seed medium, seal with nine layers of gauze, and incubate at 37°C and 200rpm for 7-10h;
[0109] Fermentation culture: Inoculate 10-15% of the volume of seed culture solution into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with fermentation medium (final volume is 30mL), seal with nine layers of gauze, 37°C, 200r / min shaking culture, fermentation process Maintain the pH at 7.0-7.2 by adding ammonia water; add 60% (m / v) glucose solution to maintain the fermentation; the fermentation period is 24 hours.
[0110] Incline medium: glucose 1-5g / L,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com