Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
120 results about "Spurious-free dynamic range" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
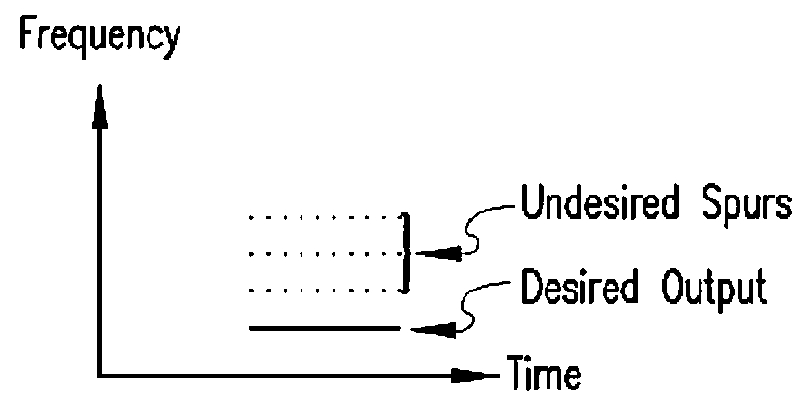
Spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) is the strength ratio of the fundamental signal to the strongest spurious signal in the output. It is also defined as a measure used to specify analog-to-digital and digital-to-analog converters (ADCs and DACs, respectively) and radio receivers. SFDR is defined as the ratio of the RMS value of the carrier wave (maximum signal component) at the input of the ADC or output of DAC to the RMS value of the next largest noise or harmonic distortion component (which is referred to as “spurious” or a “spur”) at its output.
System and method for generating analog transmission signals
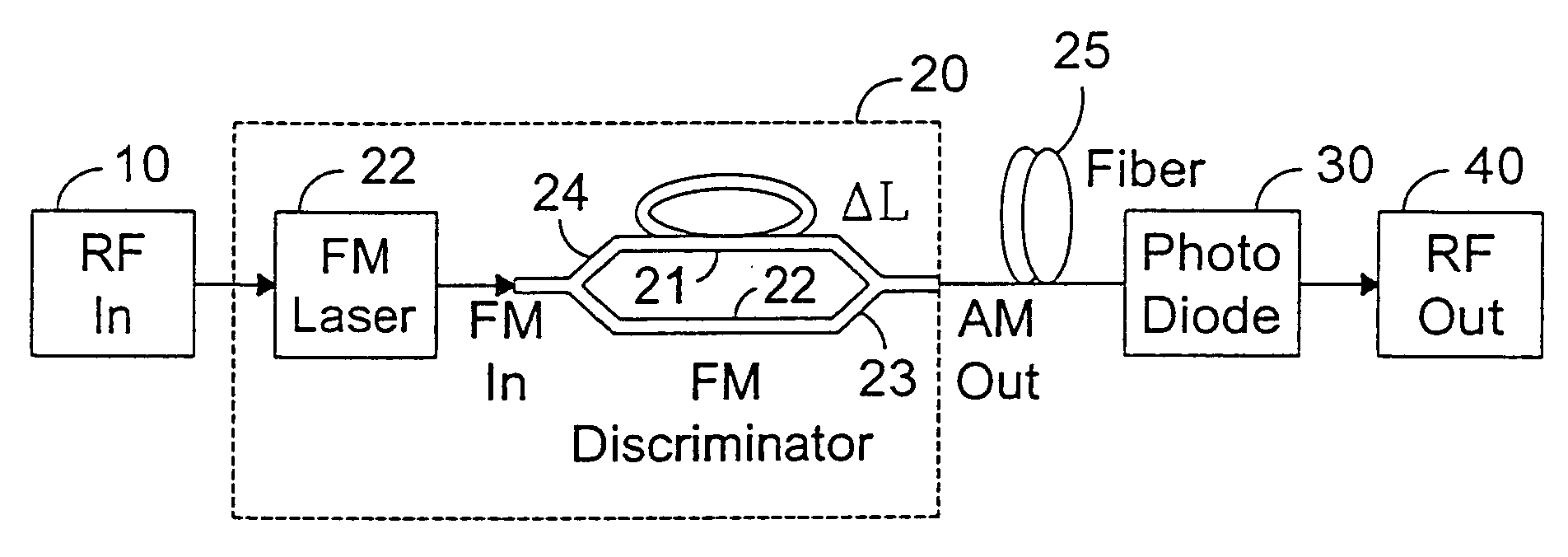
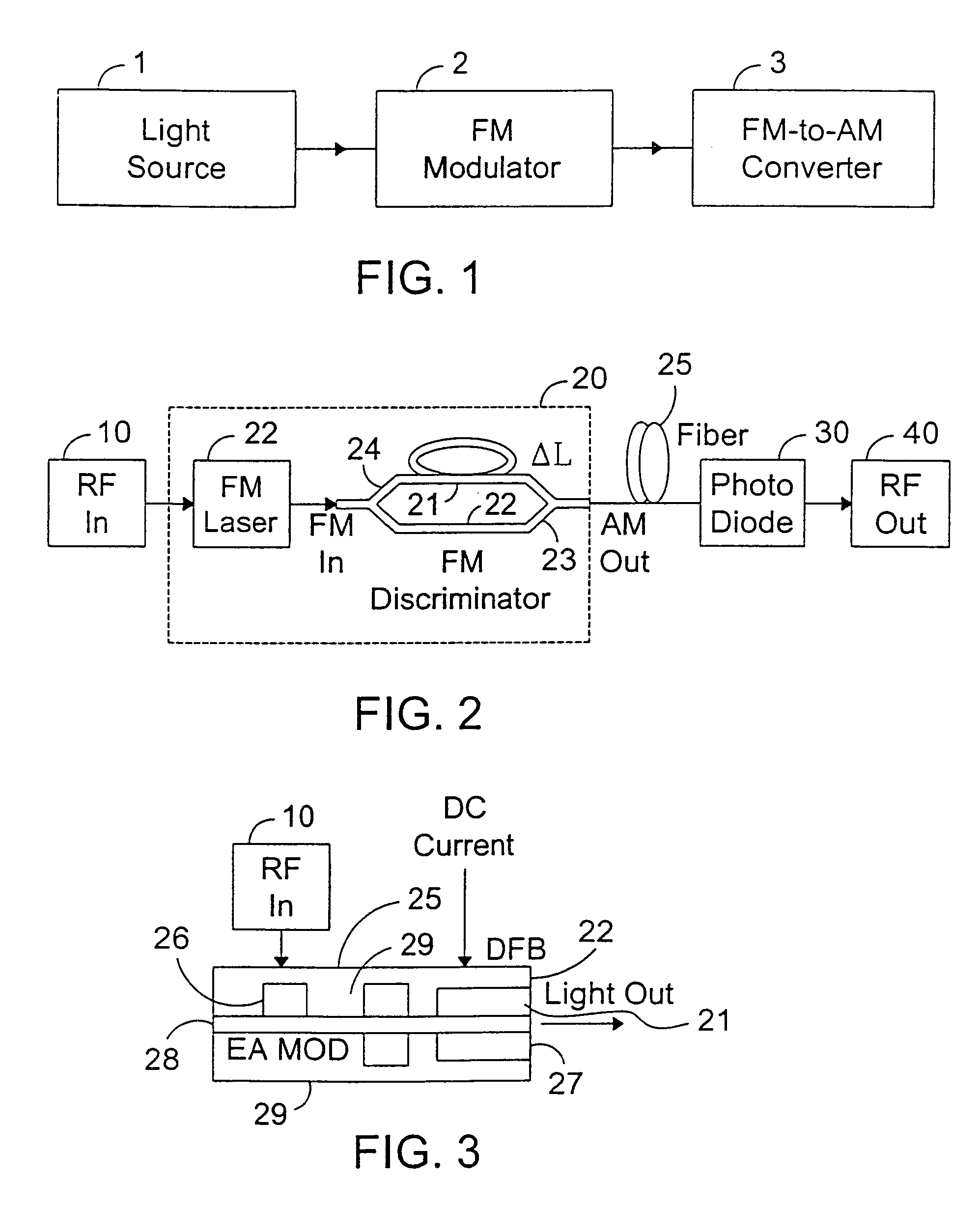
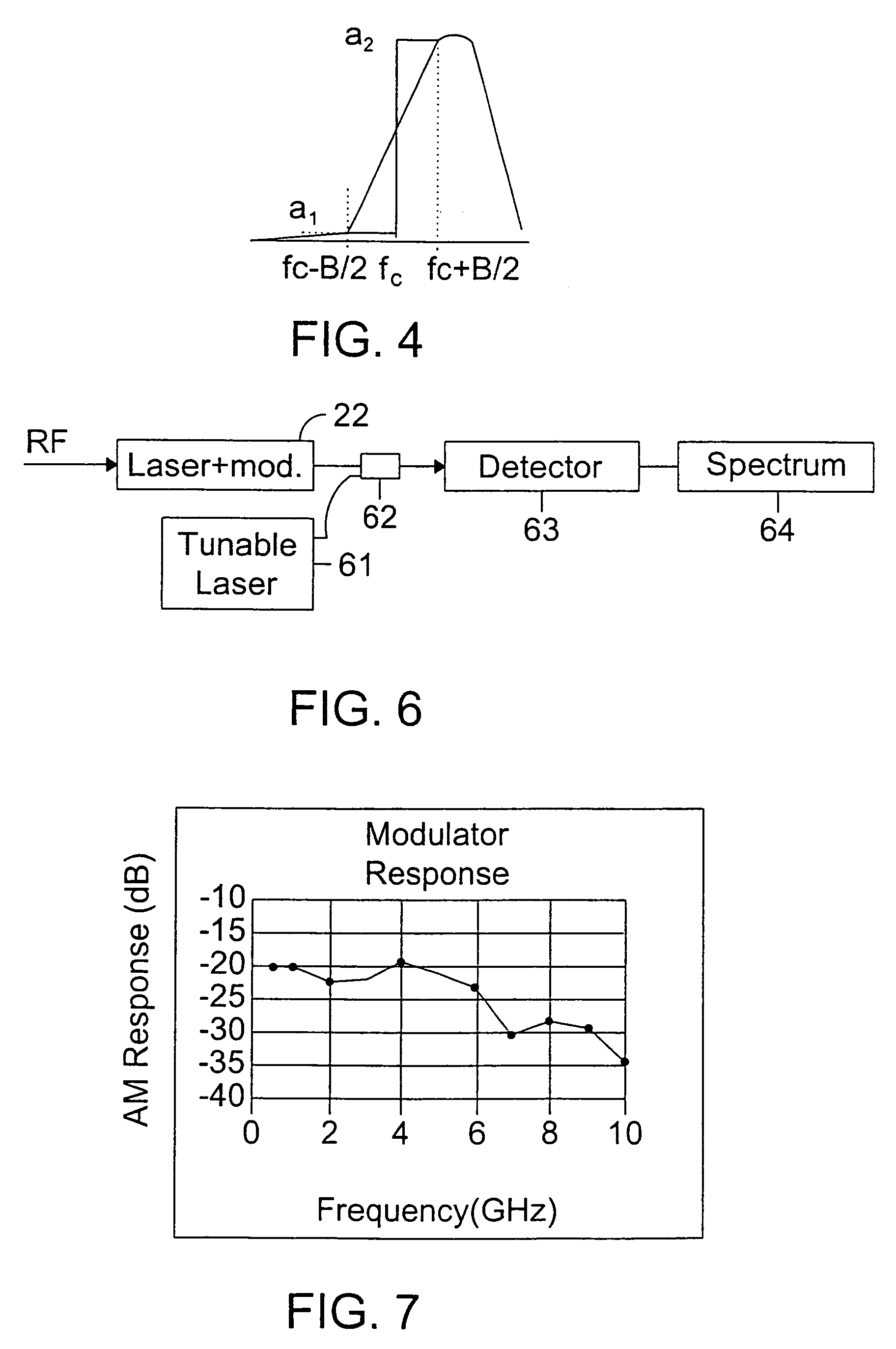
InactiveUS7076170B2Overcomes drawbackImprove dynamic rangeLaser detailsCoupling light guidesLow noiseDiscriminator
An RF-lightwave transmitter performs successive conversions of an information-bearing input signal in order to generate an output signal suitable for transmission in a wireless communications system. The transmitter includes a high-efficiency FM laser connected to a FM discriminator. In operation, the laser converts an RF signal into a frequency-modulated optical signal, and the discriminator converts this signal into an amplitude-modulated optical signal. The discriminator performs its conversion using a high slope-efficiency linear transfer function which ensures that the AM optical signal varies in accordance with a desired operational performance. The transmitter also includes a photodiode which converts the AM signal output from the optical discriminator back into an RF signal for transmission. Experimental results demonstrated that a transmitter of this type is able to realize greater than 10 dB RF insertion gain at less than 0 dBm optical power, with a high spurious-free dynamic range and low noise. A signal processor embodied within the transmitter may be used in a purely optical communication systems or may be used for other types of RF-photonics applications such as those expected for use in next-generation systems.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
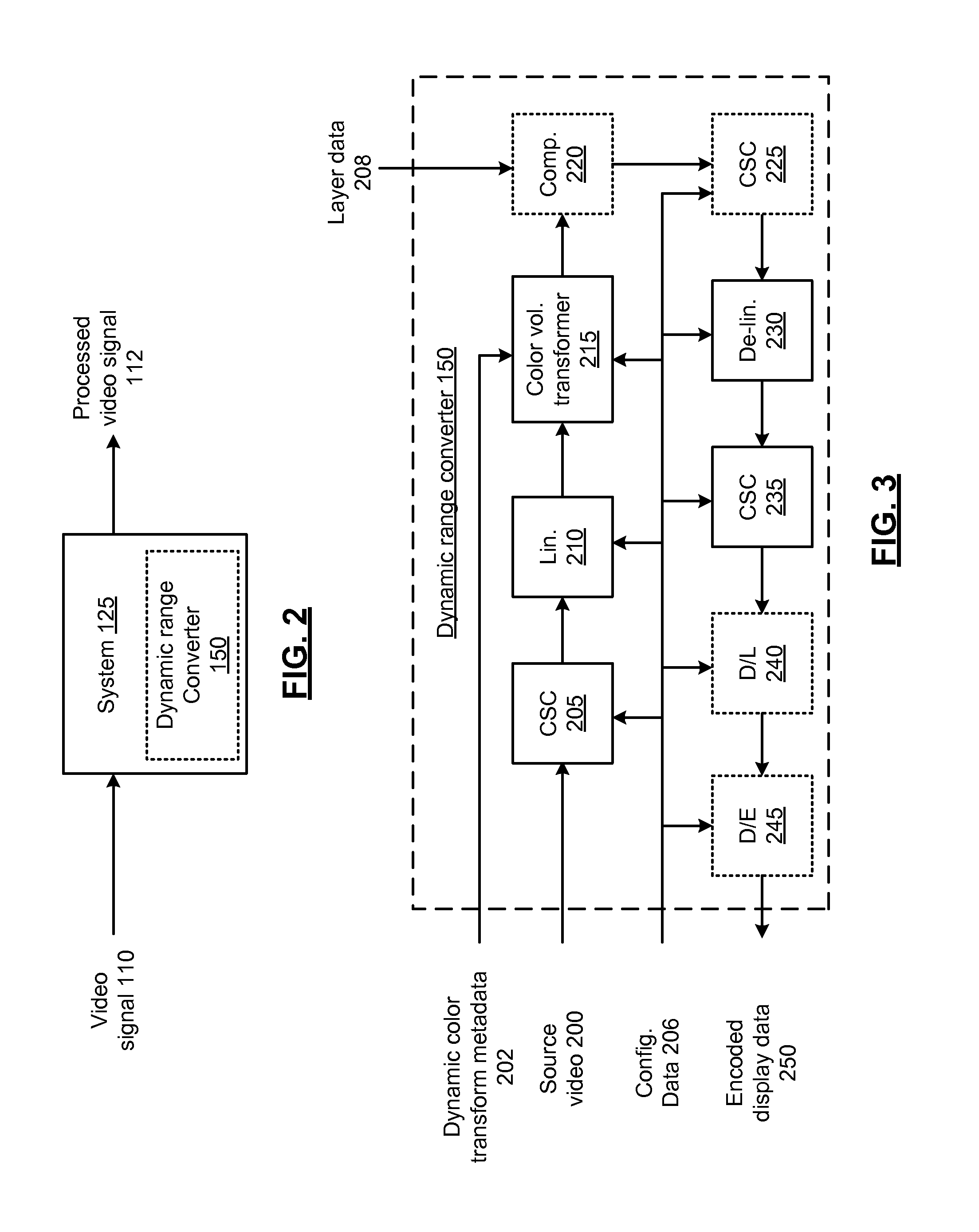
Dynamic range converter with generic architecture and methods for use therewith
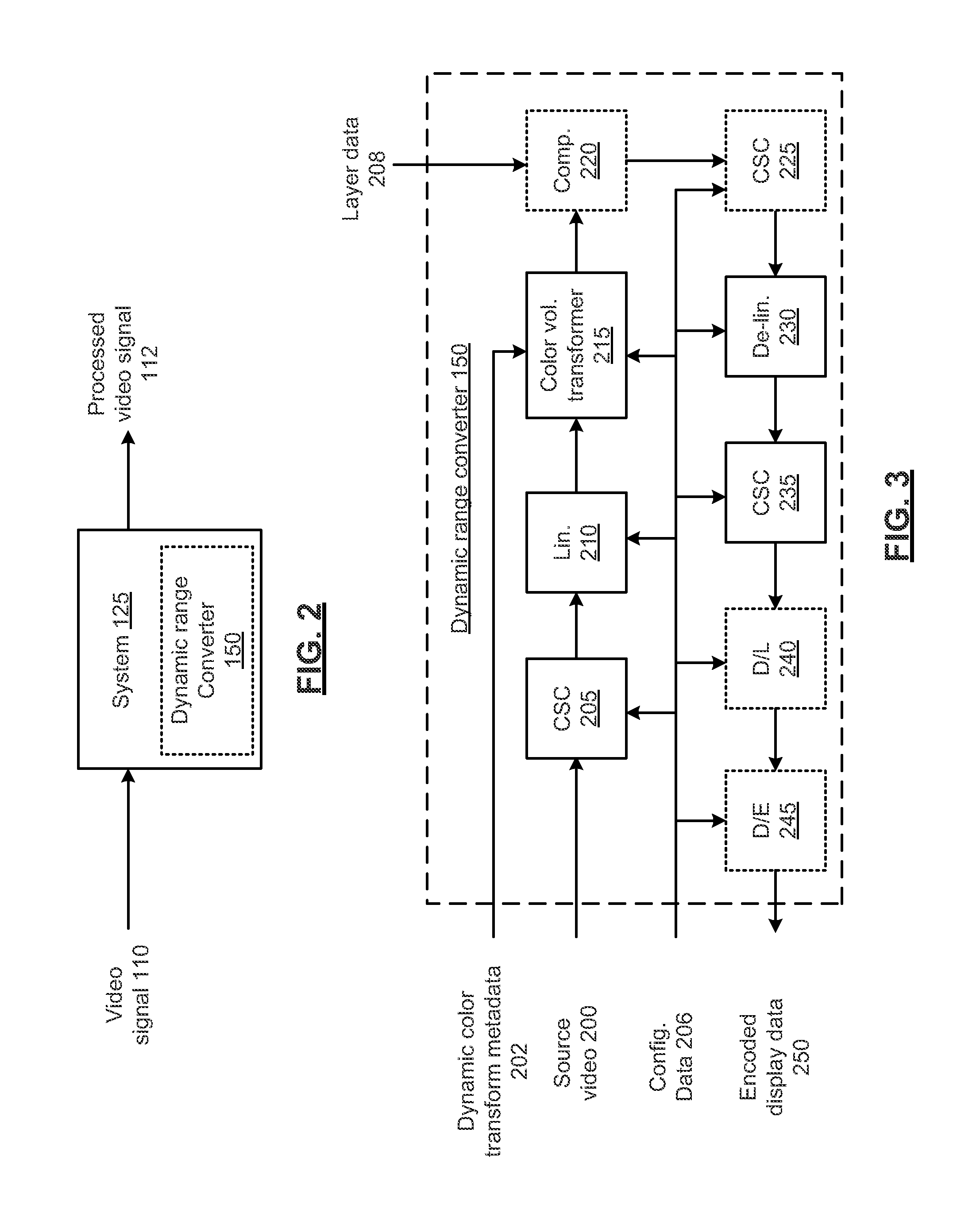
In various embodiments, a dynamic range converter includes a first color space converter to convert a source color space of a source video having a source dynamic range to nonlinear color space signals. A linearizer configured converts the nonlinear color space signals to linearized color space signals having a mastering dynamic range via a piecewise linear interpolation of a transfer function. A color volume transformer applies dynamic color transform metadata associated with the source video to generate master adjusted color space signals from the linearized color space signals. A delinearizer converts the master adjusted color space signals to nonlinearized color space signals via a piecewise linear interpolation of an inverse transfer function in accordance with a display dynamic range. A second color space converter converts the nonlinearized color space signals to display domain signals. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
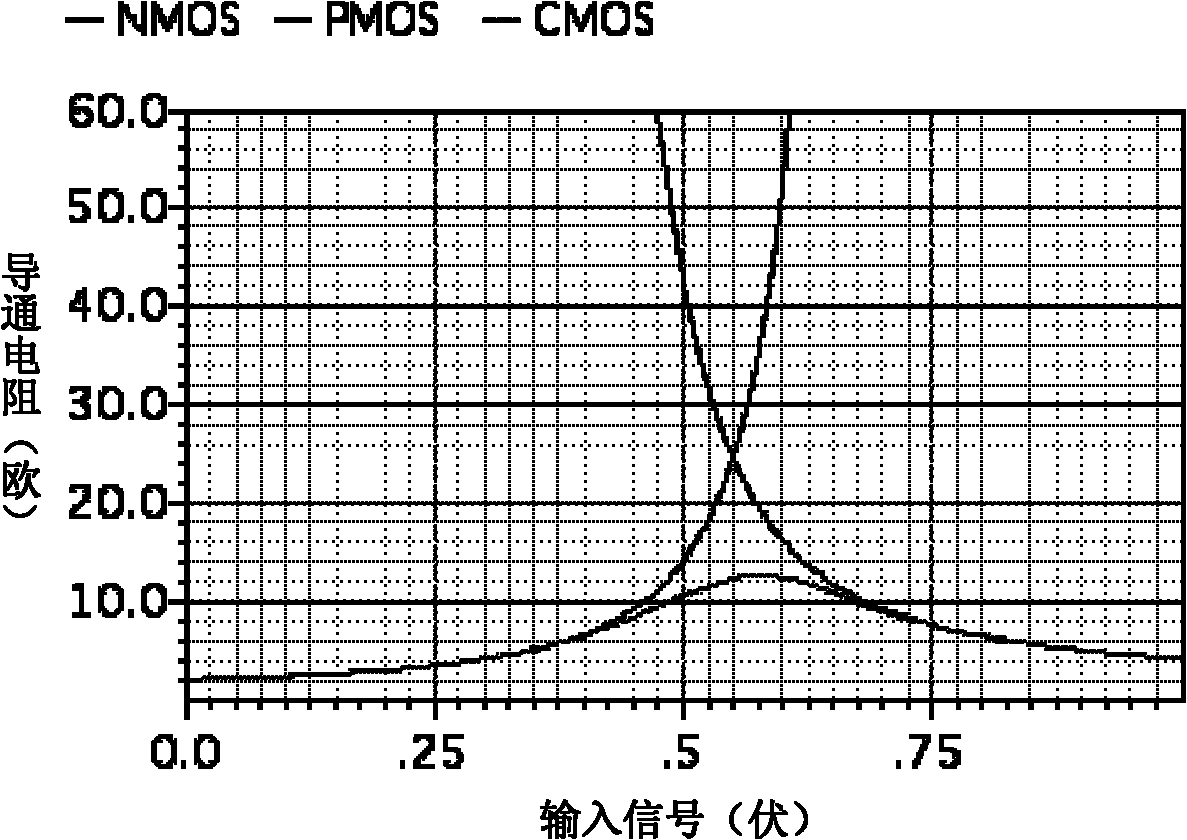
Method and structure for improving the linearity of MOS switches
InactiveUS6897701B2Improve dynamic rangeEliminate the effects ofTransistorPulse automatic controlCapacitanceLinearity
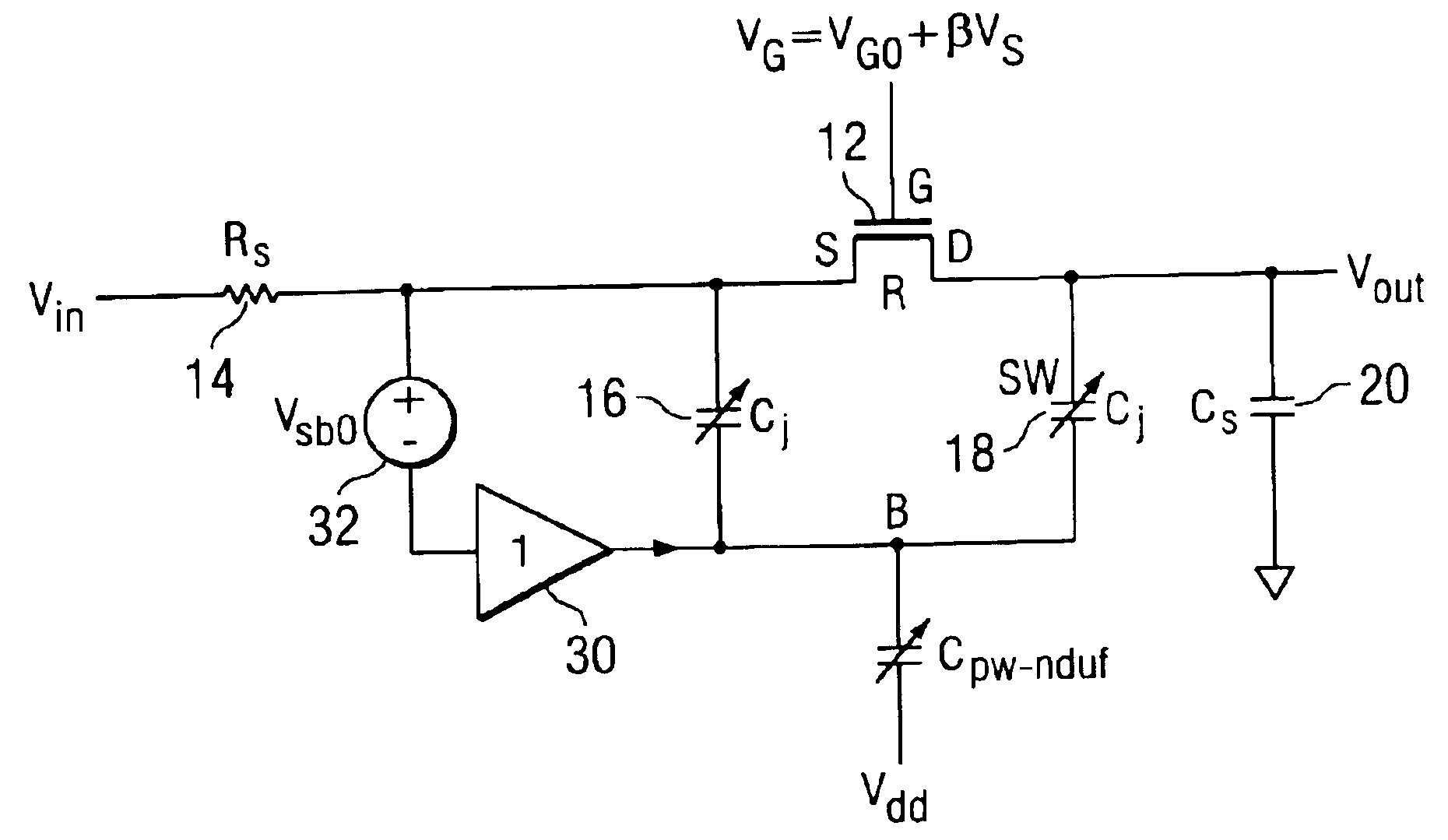
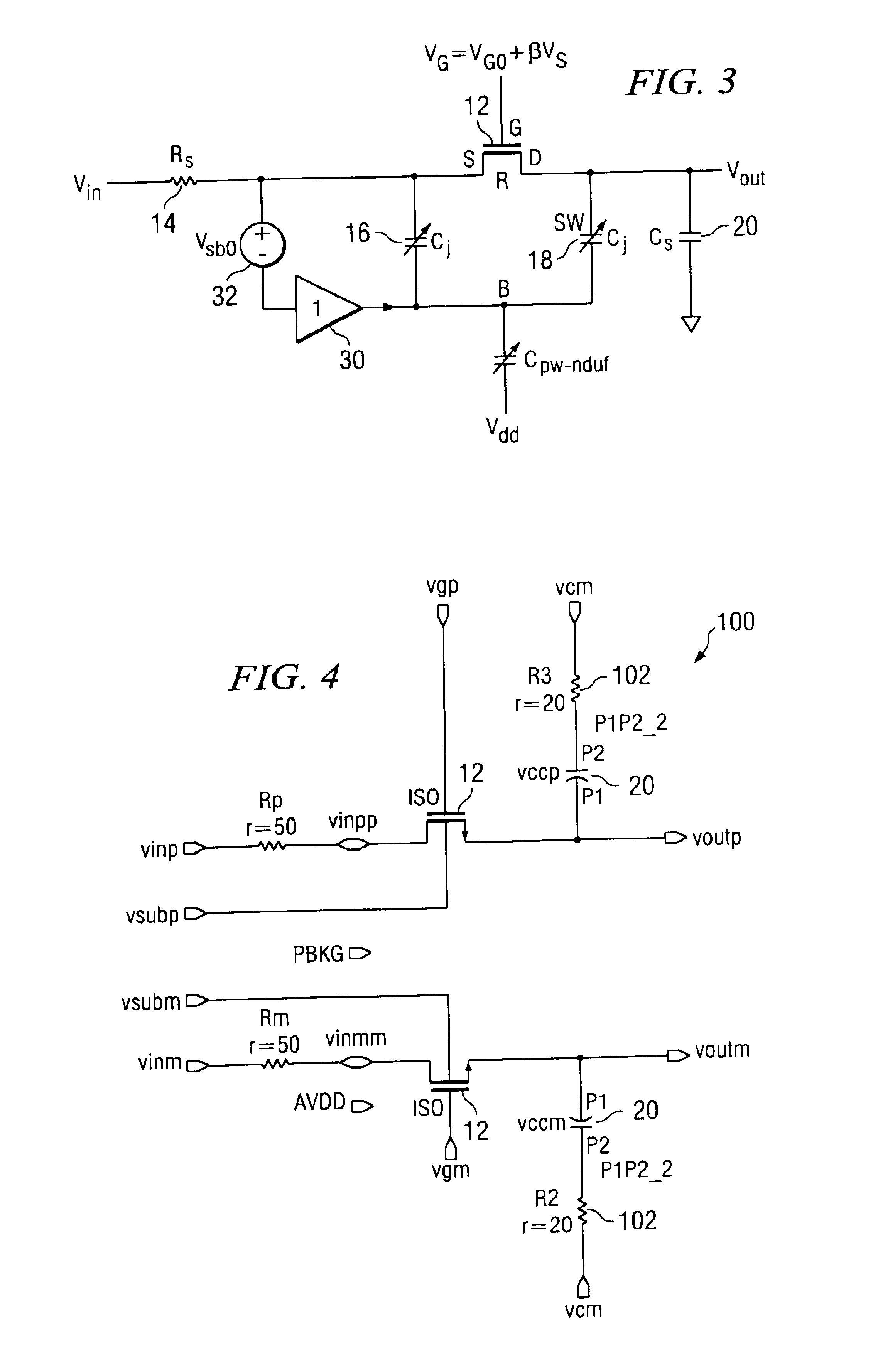
A technique is provided to linearize a MOS switch on-resistance and the nonlinear junction capacitance. The technique linearizes the sampling switch by using a buffer having substantially unity gain with proper DC shift to drive an isolated bulk terminal of the MOS well to improve the spurious free dynamic range (SFDR). In this way, the 2nd-order effect such as nonlinear body effect (VT(VSB)) and nonlinear junction capacitance (Cj(VSB)) can be substantially removed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Dynamic range converter with reconfigurable architecture and methods for use therewith
In various embodiments, a dynamic range converter includes a plurality of circuits, including at least one configurable circuit that operates based on configuration data. The plurality of circuits include a first color space converter to convert a source color space of a source video having a source dynamic range to nonlinear color space signals. A linearizer configured converts the nonlinear color space signals to linearized color space signals having a mastering dynamic range via a piecewise linear interpolation of a transfer function. A color volume transformer applies dynamic color transform metadata associated with the source video to generate master adjusted color space signals from the linearized color space signals. A delinearizer converts the master adjusted color space signals to nonlinearized color space signals via a piecewise linear interpolation of an inverse transfer function in accordance with a display dynamic range. A second color space converter converts the nonlinearized color space signals to display domain signals. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
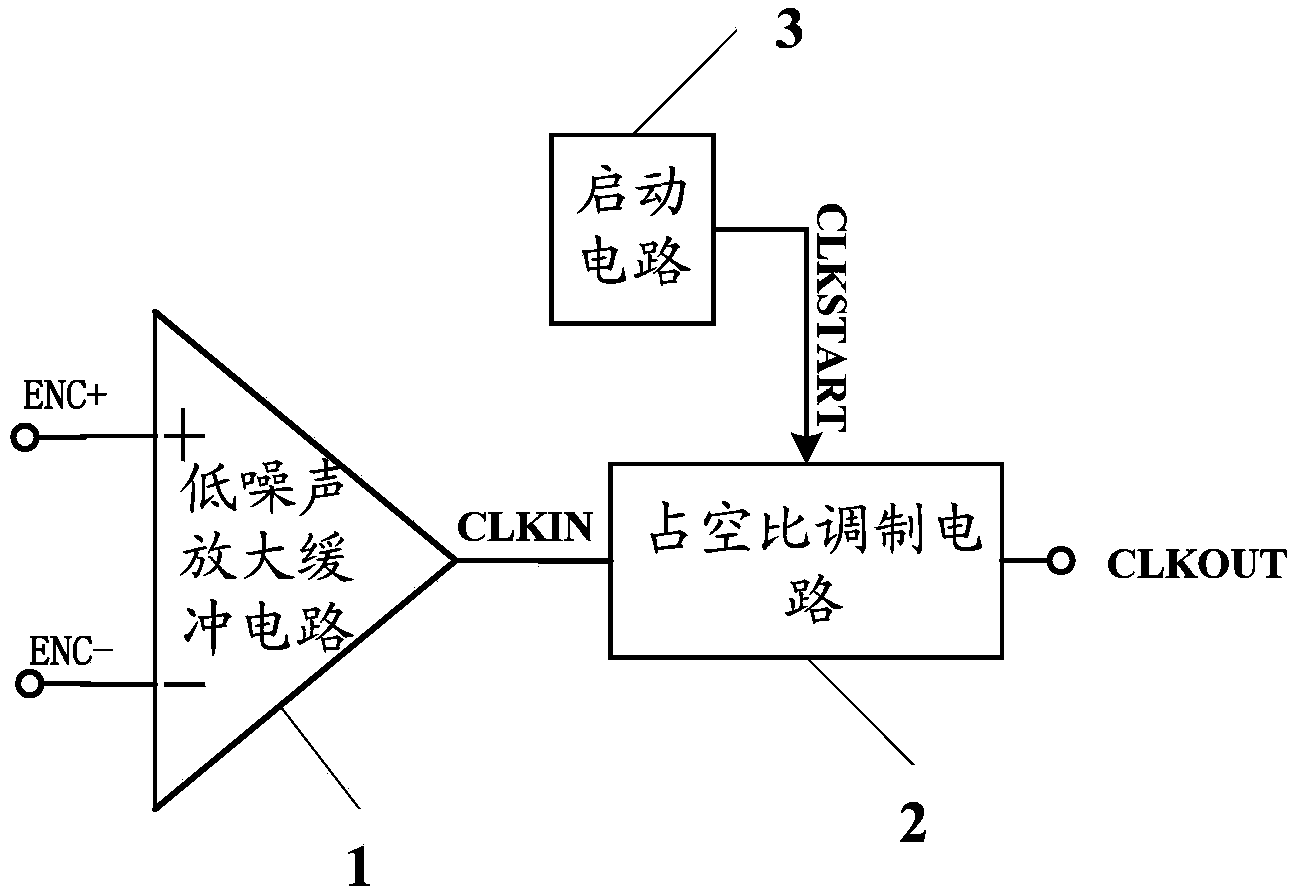
50% duty ratio clock generation circuit
ActiveCN104113303AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImproved clutter-free dynamic rangeElectric pulse generatorLow noiseEngineering
The invention provides a 50% duty ratio clock generation circuit, and relates to the field of digital-analog hybrid integrated circuit design. The circuit comprises a low-noise amplification buffer circuit and a duty ratio modulation circuit. The low-noise amplification buffer circuit is used for amplifying an externally inputted differential clock signal so that a single-end clock signal is generated and outputted to the duty ratio modulation circuit. The duty ratio modulation circuit is used for modulating duty ratio of the single-end clock signal so that a clock single with duty ratio of 50% is generated. The differential clock signal is converted into the single-end clock signal by the circuit via the low-noise amplification buffer circuit, duty ratio of the single-end clock signal is modulated and clock single with duty ratio of 50% is generated so that design difficulty and power consumption of a sampling and holding circuit in an analog-to-digital conversion circuit are reduced, and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and a spurious free dynamic range (SFDR) of an analog-to-digital conversion quantizer are enhanced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
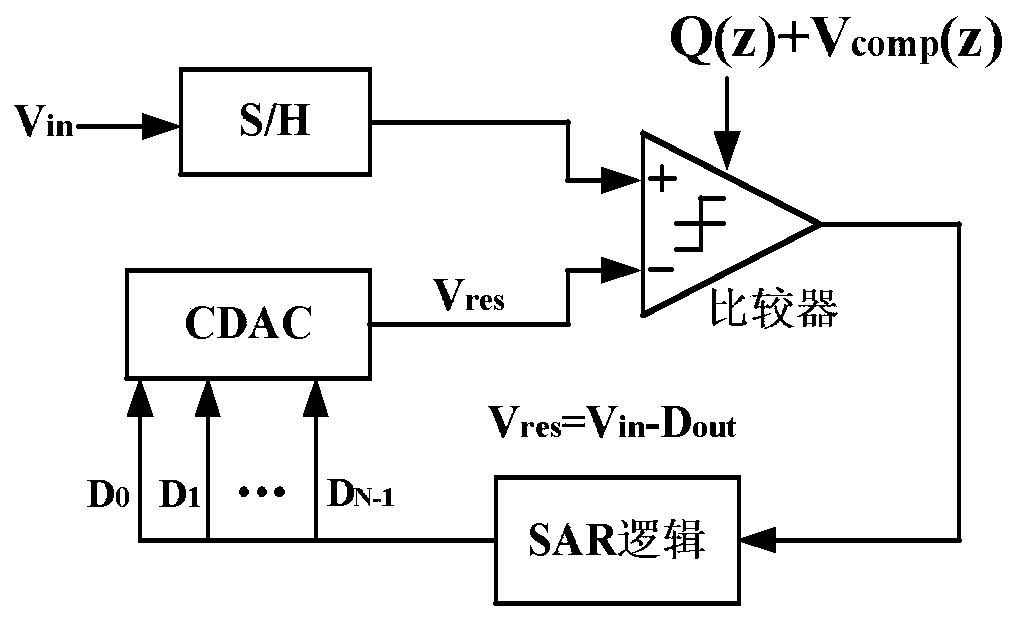
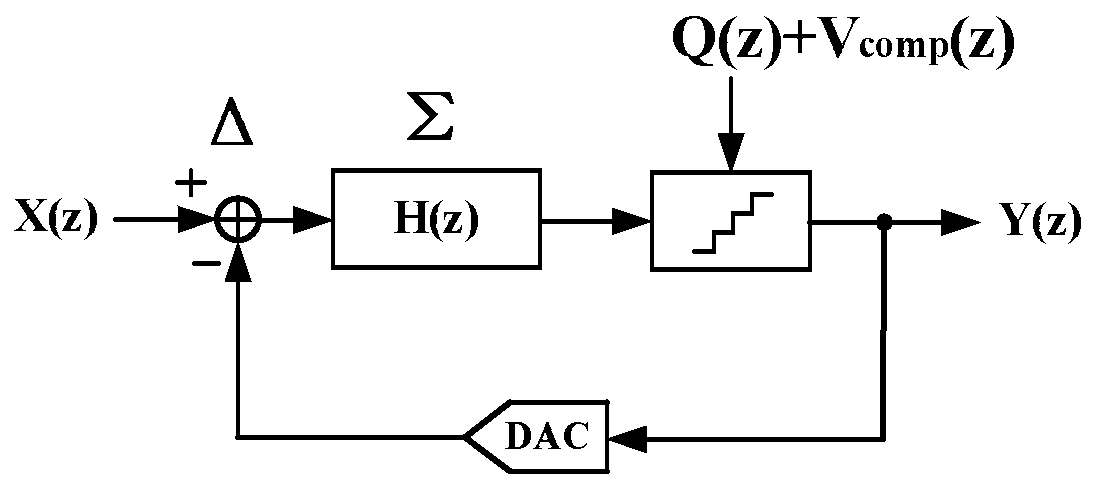
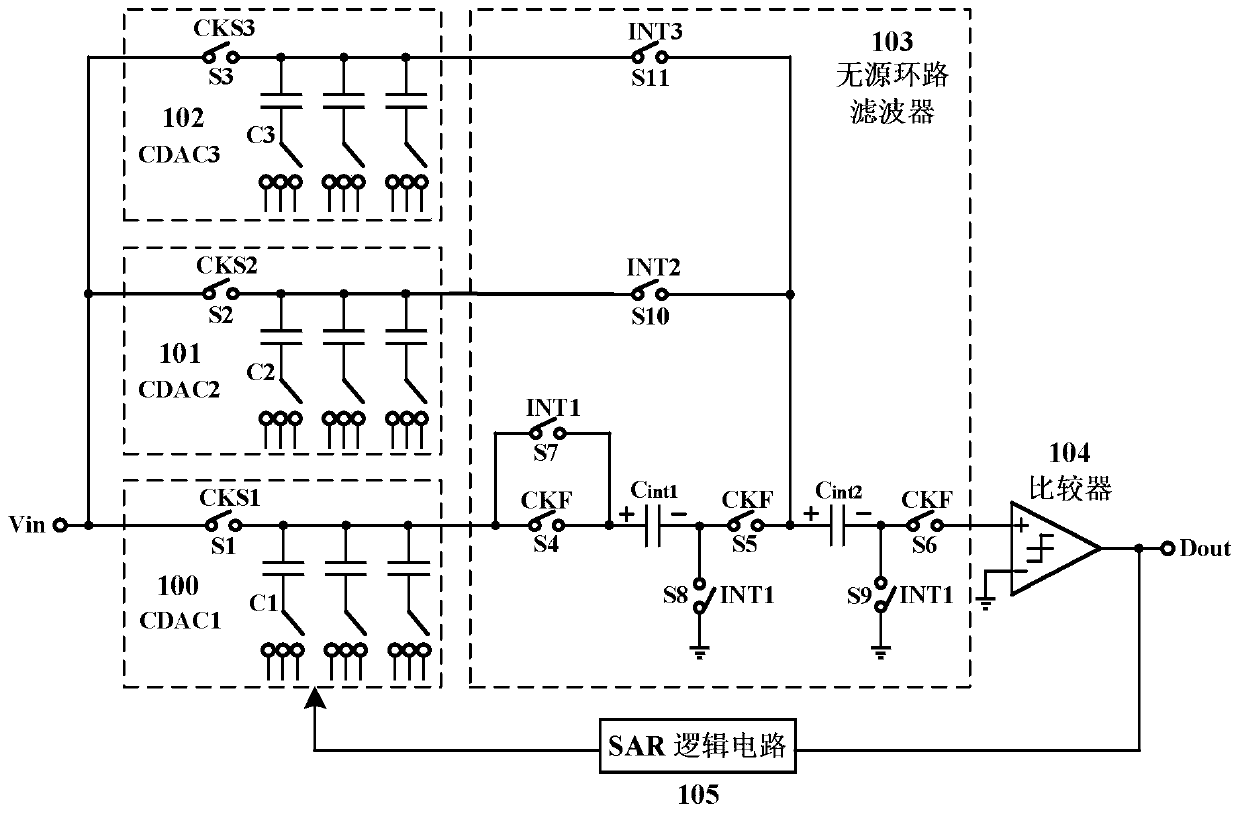
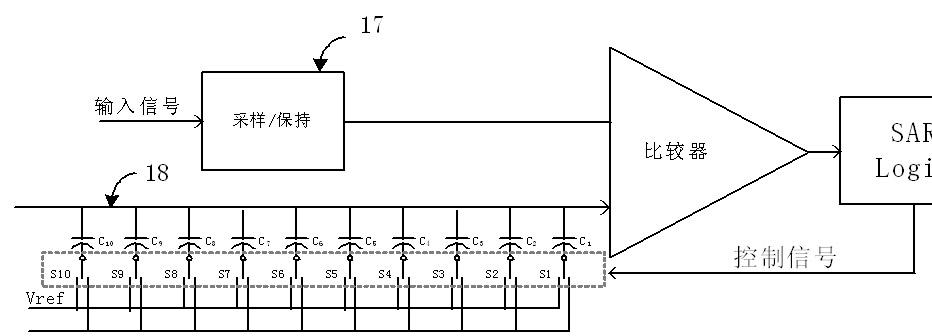
Passive noise shaping successive approximation SAR analog-to-digital converter
ActiveCN110492885AReduce capacitanceCancel noiseElectric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionCapacitanceLoop filter
The invention discloses a passive noise shaping successive approximation SAR analog-to-digital converter. The analog-to-digital converter comprises three capacitive digital-to-analog converters (CDACs), a passive loop filter, a comparator and an SAR logic circuit, wherein the three identical CDACs comprise a CDAC1 required by normal SAR conversion and two auxiliary CDAC2 and CDAC3 used for generating a margin voltage of a previous period. Two interlaced CDAC2 and CDAC3 are added, and KT / C noise and gain loss introduced by passive margin sampling are removed. Wherein the CDAC1 generates the margin voltage Vres (n) of the current period, and the CDAC2 and the CDAC3 alternately generate the margin voltage Vres (n-1) of the previous period. And the passive loop filter carries out noise shapingon the margin voltage and suppresses in-band noise of the signal. And the comparator quantizes the analog output of the passive loop filter into a digital code, the digital code toggles the next capacitor switch in the CDAC through the SAR logic circuit until the conversion is finished, and all the digital codes are sequentially spliced together to serve as the output code of the SAR ADC, which is the same as that of the common SAR ADC. According to the invention, the second-order noise shaping effect can be realized, the signal in-band quantization noise and the comparator noise are effectively suppressed, and the signal-to-noise ratio and the spurious-free dynamic range of the SAR ADC are obviously improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Radar echo processing with partitioned de-ramp
The spurious-free dynamic range of a wideband radar system is increased by apportioning de-ramp processing across analog and digital processing domains. A chirp rate offset is applied between the received waveform and the reference waveform that is used for downconversion to the intermediate frequency (IF) range. The chirp rate offset results in a residual chirp in the IF signal prior to digitization. After digitization, the residual IF chirp is removed with digital signal processing.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Apparatus and method for spurious-free signal range measurement for RF circuitry
InactiveUS20100052652A1Receivers monitoringResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
The present invention is directed to an apparatus and methodology for performing spurious-free dynamic range (SFDR) measurements on an RF circuit, such as a mixer, using a single analog input port. The present invention is designed for use when access to the intermediate frequency (IF) port in a radio frequency (RF) front-end circuit is not available, when the traditional two-port method for making an SFDR measurement is inadequate. Passing the analog input through a directional coupler between the RF combiner and the mixer facilitates the performance of the traditional third order intermodulation (IMD) test. Key differences between the single-port and traditional two-port setups are considered and examined, and experimental data obtained using the single-port setup is compared to data obtained using the traditional two-port set-up for different mixer models. Comparison of similar results yields confirmation and a calibration to account for the additional losses introduced by the directional coupler.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Quadrature mixture LO suppression via DSW DAC noise dither
A Quadrature Error Corrected Digital Waveform Synthesizer (QECDWS) employs frequency dependent phase error corrections to, in effect, pre-distort the phase characteristic of the chirp to compensate for the frequency dependent phase nonlinearity of the RF and microwave subsystem. In addition, the QECDWS can employ frequency dependent correction vectors to the quadrature amplitude and phase of the synthesized output. The quadrature corrections cancel the radars' quadrature upconverter (mixer) errors to null the unwanted spectral image. A result is the direct generation of an RF waveform, which has a theoretical chirp bandwidth equal to the QECDWS clock frequency (1 to 1.2 GHz) with the high Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) necessary for high dynamic range radar systems such as SAR. To correct for the problematic upconverter local oscillator (LO) leakage, precision DC offsets can be applied over the chirped pulse using a pseudo-random noise dither. The present dither technique can effectively produce a quadrature DC bias which has the precision required to adequately suppress the LO leakage. A calibration technique can be employed to calculate both the quadrature correction vectors and the LO-nulling DC offsets using the radar built-in test capability.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Calibration system and method suitable for current source array in multichannel sectional type current steering DAC (digital to analog converter)
ActiveCN104617953AImprove linearityIncrease the number of effective digitsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingProcess deviationsBit field
The invention discloses a calibration system and a calibration method suitable for a current source array in a multichannel sectional type current steering DAC (digital to analog converter). The calibration method suitable for the current source array in the multichannel sectional type current steering DAC includes steps: firstly, calibrating a channel, and then sequentially calibrating other channels, and enabling output among all the channels to tend to be uniform, wherein when the channels are calibrated, switches in a current source switch array are by selectively closed and calibrated, and an output amplitude adjustment circuit is adjusted so as to sequentially calibrate a low data bit segment and a high data bit segment of the current source array segment by segment. The calibration method suitable for the current source array in the multichannel sectional type current steering DAC can calibrate each current source at the low data bit segment of the sectional type current steering DAC, and thereby achieves high calibration accuracy, remedies deviation and a mismatch, among the current sources in the current source array of the sectional type current steering DAC, improves linearity of the single DAC, and then improves performance indexes such as the significant number of digits of the DAC and a spurious free dynamic range, and improves linear performance of the multichannel sectional type current steering DAC and amplitude consistency among all the channels.
Owner:CHENGDU CORPRO TECH CO LTD
High spurious-free-dynamic-range (SFDR) multichannel time staggering successive approximation type analog to digital converter
InactiveCN102332920AGood randomizationEffective distributionAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceHarmonic
The invention belongs to the technical field of integration circuits and particularly relates to a high spurious-free-dynamic-range (SFDR) multichannel time staggering successive approximation (SAR) type analog to digital converter. A capacitor array for sampling and quantifying at the front end of each channel of the conventional multichannel time staggering SARADC is often relatively independent and fixed; and the own capacitor array of each channel at the front end is dismantled into a number of equal modules so as to form a 'capacitance pool'. Before sampling, the capacitance pool is randomly distributed to each channel, so a fixed error of each channel is reduced and randomized then; from an energy spectrum, energy of a harmonic component is changed into noise which is normalized to a noise base; therefore, the nonlinearity caused by capacitance mismatch is improved effectively.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
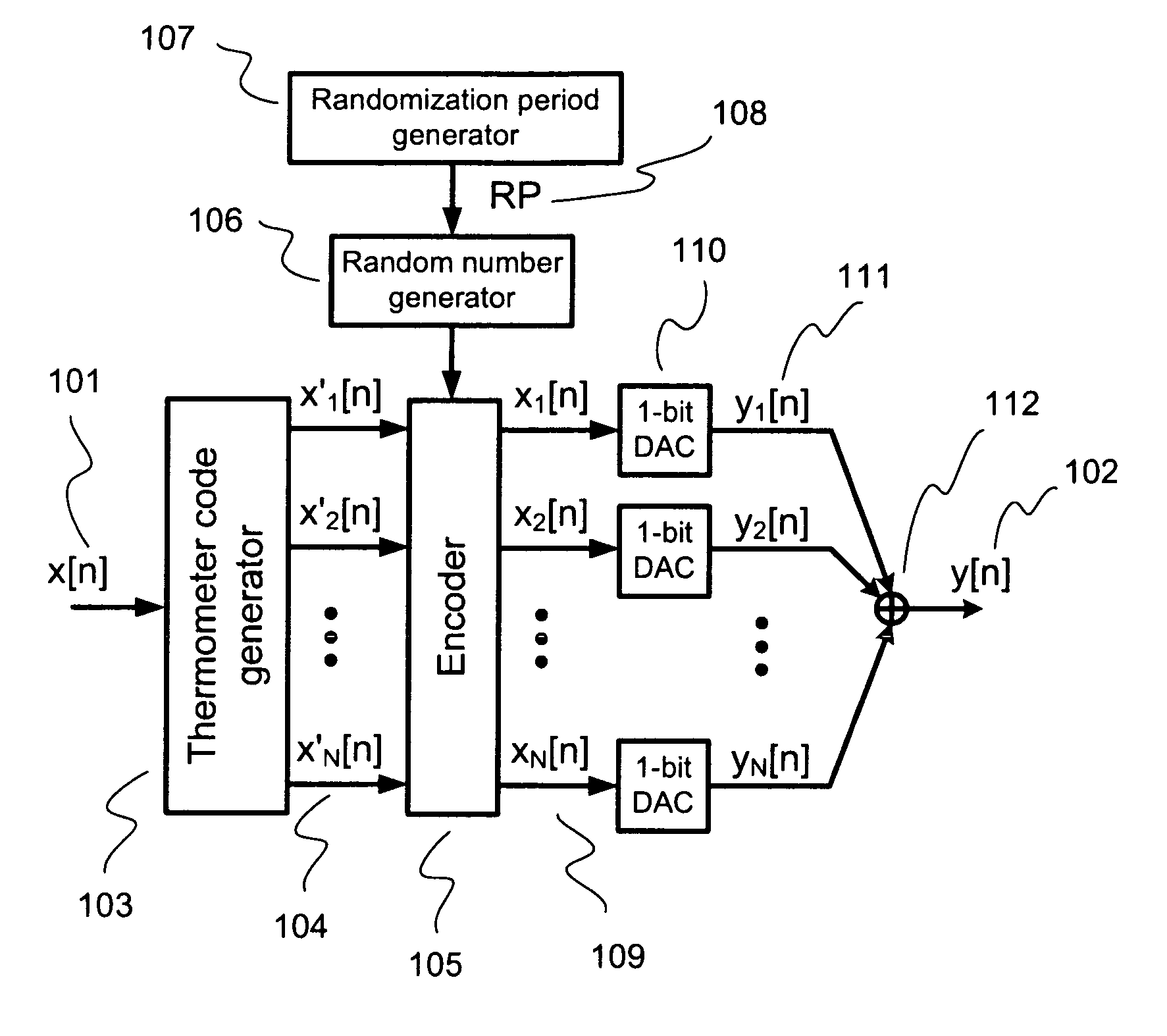
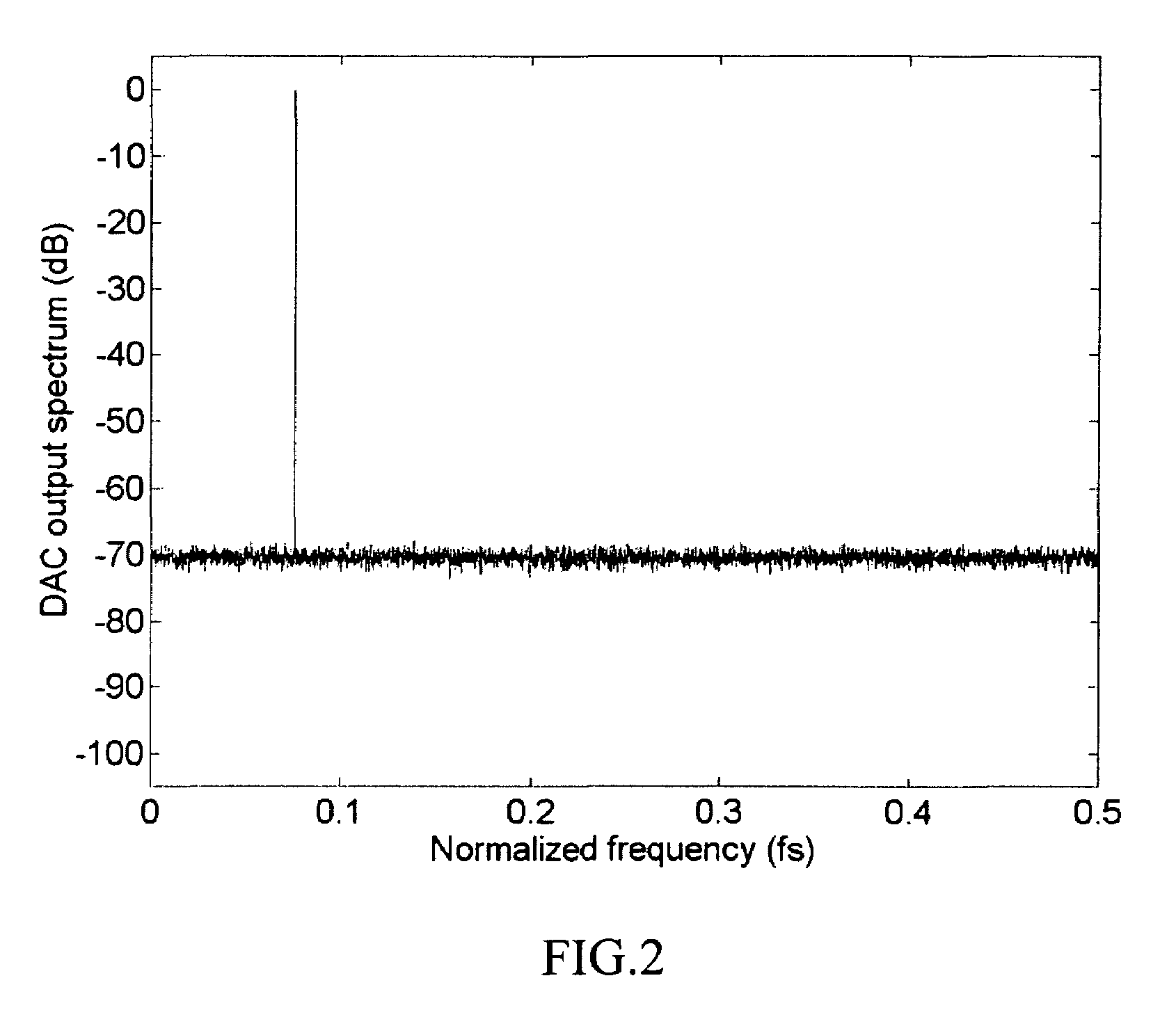
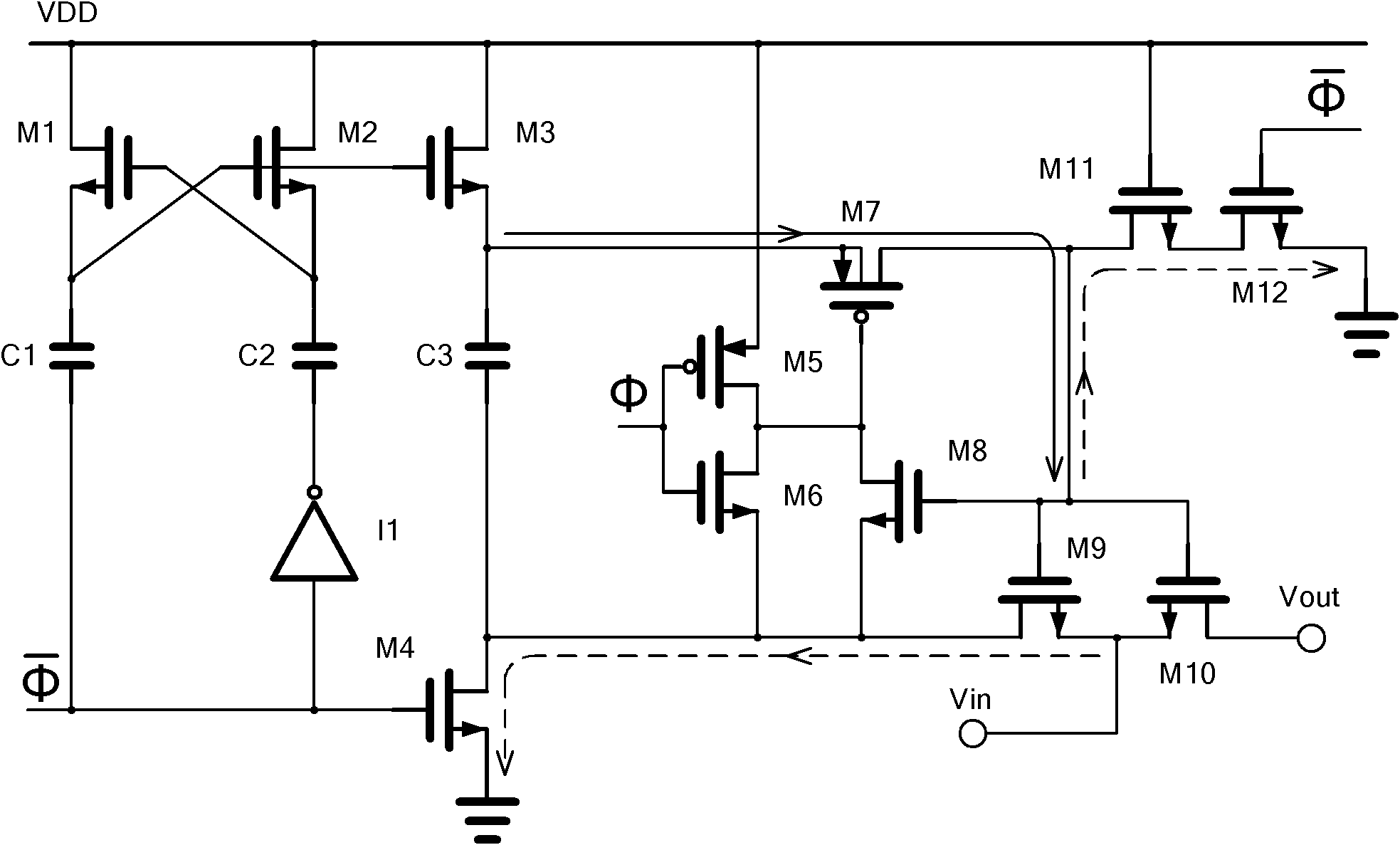
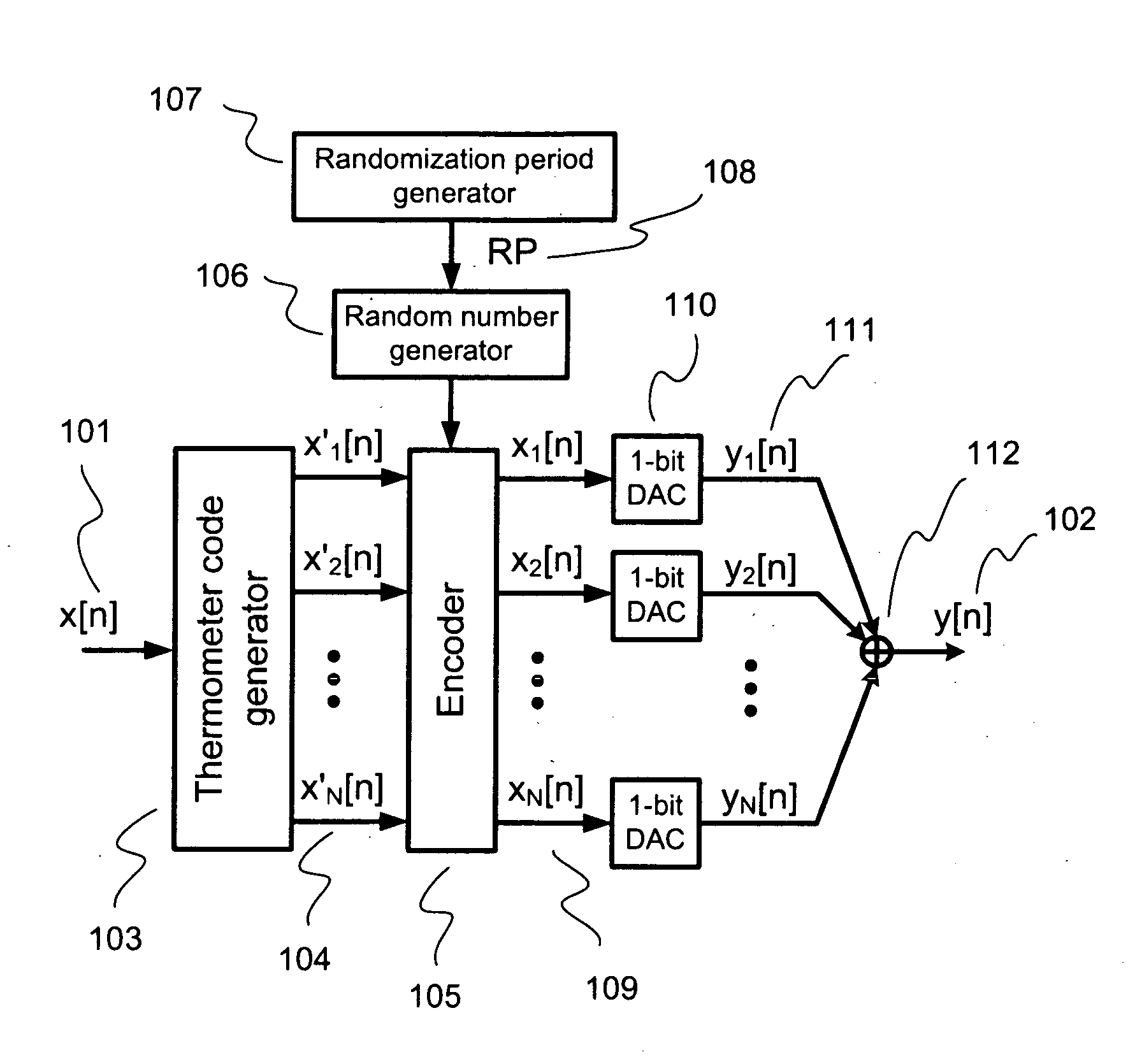
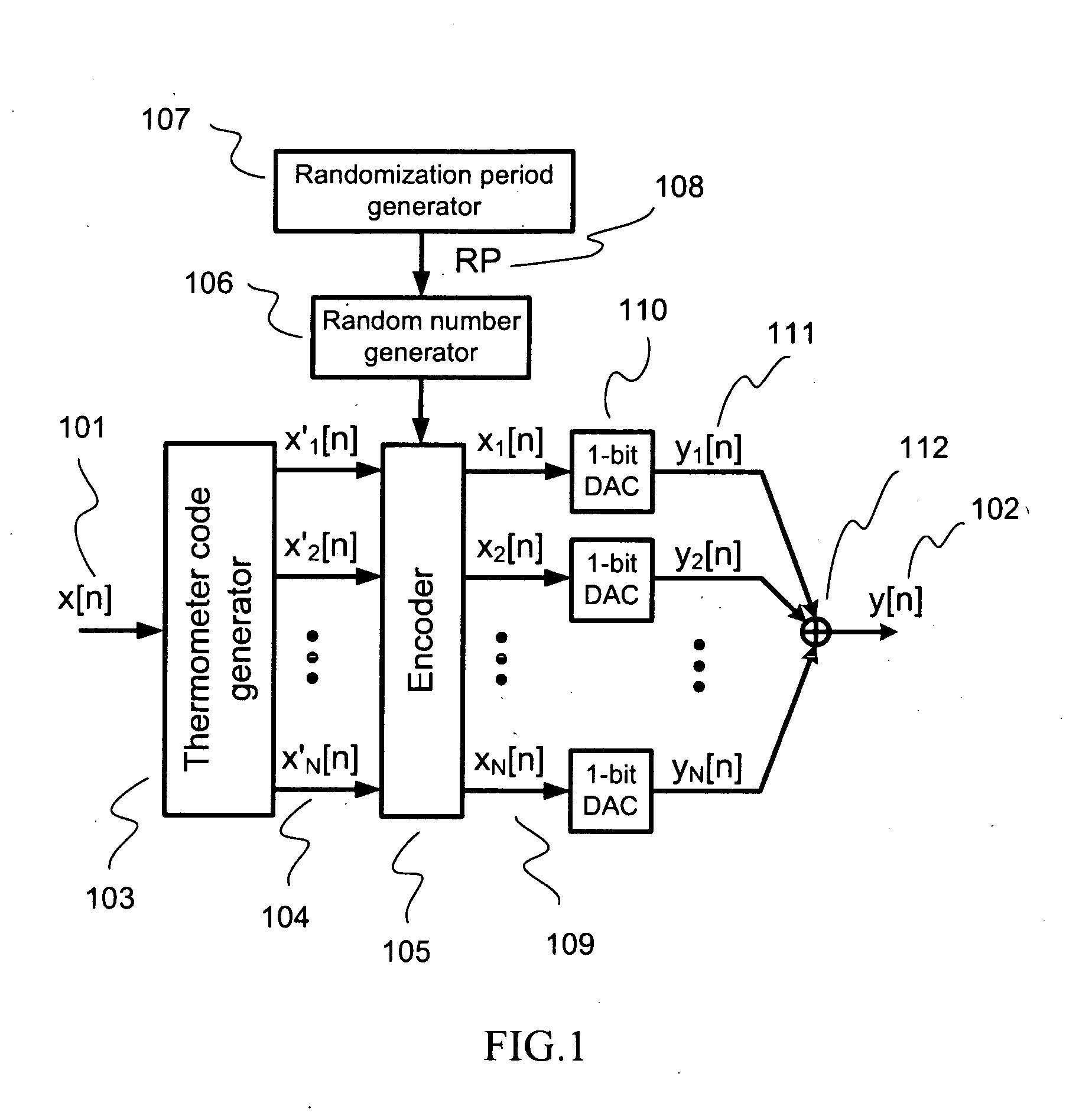
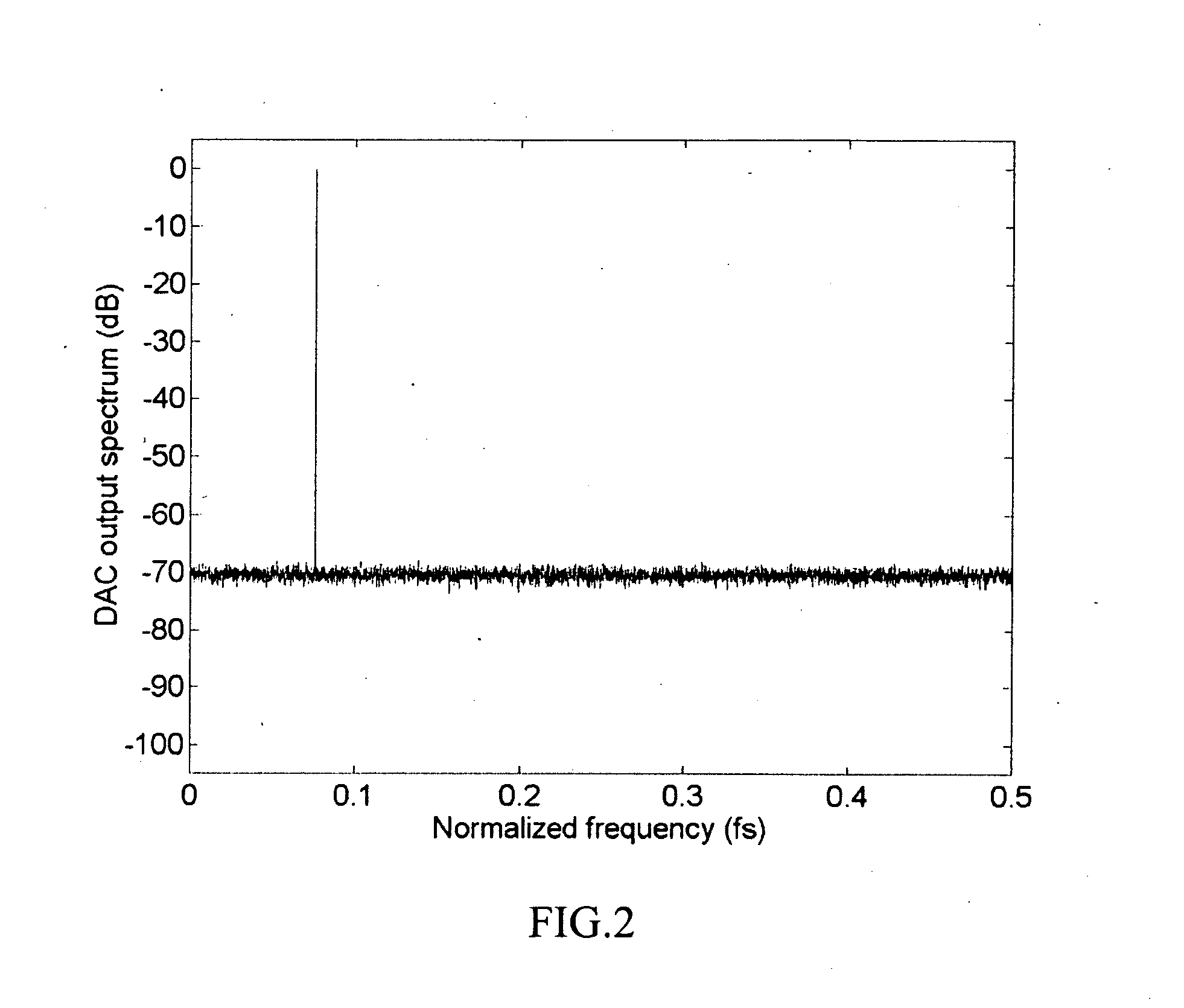
Randomized thermometer-coding digital-to-analog converter and method therefor
InactiveUS7679539B2Reduce errorsHigh spectral purityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterEngineering
A randomized thermometer-coding digital-to-analog converter (DAC) for the reduction of harmonic distortion due to non-ideal circuit mismatch is presented. The present invention introduces a new dynamic element matching technique that contains three properties of randomization, consecutive selection and less element switching activity to achieve good spurious-free dynamic range and small maximum output error. The topology uses a bank of 1-bit DAC elements, whose outputs are summed to produce a multi-level analog output. The binary digital input is encoded to be thermometer code. During a randomization period, the thermometer code is barrel-shifted to a specific starting position where the position is generated randomly. Thus, the DAC noise is randomized with less element switching activity and consecutive selection.
Owner:MEGAWIN TECH +1
Bootstrapping sampling switch applied to high-speed and high-linearity analog-to-digital converter
InactiveCN102185596ASimple structureFast switching speedElectric analogue storesElectronic switchingDigital down converterEngineering
The invention provides a bootstrapping sampling switch applied to a high-speed and high-linearity analog-to-digital converter. The bootstrapping sampling switch comprises a clock booster, a grid-source voltage follower, a conduction switch and a charging and discharging enhanced circuit, wherein several times of power voltage are generated by the clock booster and used for charging a capacitor; the grid-source voltage follower connects the capacitor between the grid and the source when the conduction switch is off, so that a relevantly constant grid-source voltage difference under different voltage input is ensured; the charging and discharging enhanced circuit is added in a charging or discharging loop during switching of the switch so as to shorten the off and on time, reduce a parasitic capacitance of the grid of the conduction switch and reduce the loss of the storage charge of the capacitor; the use of a high-voltage metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) tube is not needed; meanwhile, high-linearity sampling is realized (the sampling rate is more than 1 KMHz under 65-nano complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology and a stray-free dynamic range more than 95 decibels can be obtained). A complicated logic control circuit is absent in the structure, so the area of a chip cannot be increased; moreover, a requirement of the clock buffer is not needed to be enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
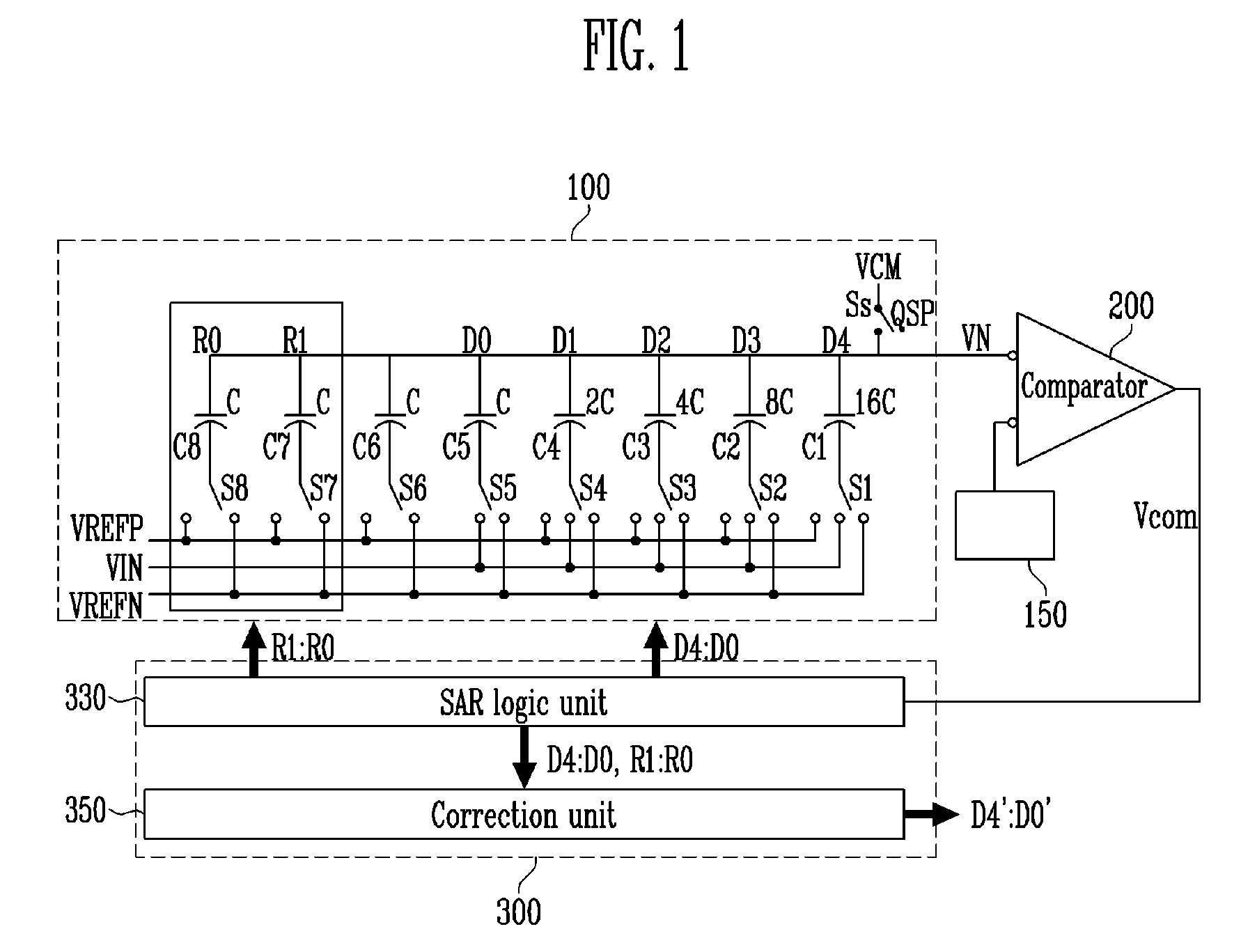
Successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter and calibration method
ActiveCN110880934AImprove linearityNo loss of accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersConvertersA d converter
The invention provides a successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter and a calibration method. The successive approximation type analog-to-digital converter comprises a sampling / holdingcircuit, a digital-to-analog converter, a comparator, a successive approximation logic circuit, a clock generation circuit and a digital pseudo-random signal generator. An analog input signal is connected to the sampling / holding circuit. Positive and negative input ends of the comparator are connected with the digital-analog converter and the sampling / holding circuit respectively, and the output end of the comparator is connected with the successive approximation logic circuit; the successive approximation logic circuit and the digital pseudo-random signal generator are connected to the inputof the adder, and the output of the adder is connected with the digital-to-analog converter; the successive approximation logic circuit and the digital pseudo-random signal generator are connected tothe input of a subtracter, and the output of the subtracter is a final output result; and the clock generation circuit is respectively connected with the comparator and the successive approximation logic circuit. Harmonic energy is reduced, the spurious-free dynamic range of the ADC is improved, and the linearity of the core ADC is effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
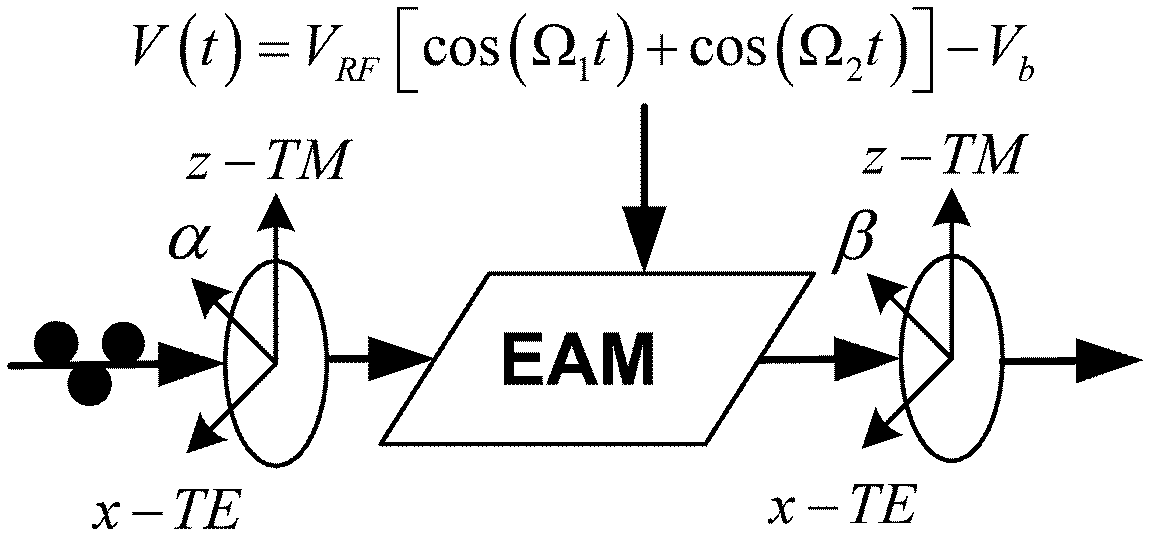
Method for improving radio over fiber link performance
InactiveCN102611504ASuppression of second-order nonlinear distortionDistortion/dispersion eliminationRadio-over-fibreNonlinear distortionRadio over fiber
The invention relates to a method for improving radio over fiber (RoF) link performance, which belongs to the technical field of electronics. According to the method, the RoF link performance is improved by a mixed-polarization electro-absorption modulator (EAM) or a mixed-polarization Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM). The improvement is as follows: the mixed-polarization EAM or the mixed-polarization MZM is composed of a linear polarizer with an angle of alpha, an EAM or MZM and a second linear polarizer with an angle of beta; the two linear polarizers are respectively placed at the front end and the rear end of the EAM or the MZM; and the values of the alpha and the beta are related with the characteristics of the modulators. The method has the following advantages: (1) third-order non-linear and second-order non-linear distortions can be inhibited, and the SFDR (spurious-free dynamic range) is improved by more than about 12dB for a 20km optical fiber transmission RoF system using the mixed-polarization EAM and is improved by about 12dB for the 20km fiber transmission RoF system using the mixed-polarization MZM; and (2) through an OFDM UWB (orthogonal frequency division multiplexing ultra wide band) signal test, the EVM (error vector magnitude) is improved by 3dB by using the mixed-polarization EAM and is improved by 8.7dB by using the mixed-polarization MZM.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Randomized thermometer-coding digital-to-analog converter and method therefor
InactiveUS20090243904A1Reduce errorsHigh spectral purityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital analog converterDigital input
A randomized thermometer-coding digital-to-analog converter (DAC) for the reduction of harmonic distortion due to non-ideal circuit mismatch is presented. The present invention introduces a new dynamic element matching technique that contains three properties of randomization, consecutive selection and less element switching activity to achieve good spurious-free dynamic range and small maximum output error. The topology uses a bank of 1-bit DAC elements, whose outputs are summed to produce a multi-level analog output. The binary digital input is encoded to be thermometer code. During a randomization period, the thermometer code is barrel-shifted to a specific starting position where the position is generated randomly. Thus, the DAC noise is randomized with less element switching activity and consecutive selection.
Owner:MEGAWIN TECH +1
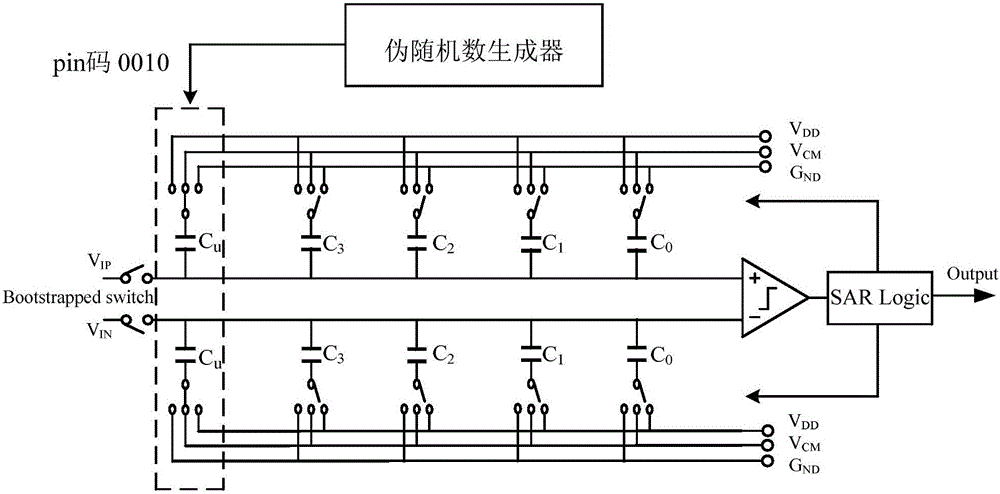
Digital weight average algorithm applied to successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter
InactiveCN106027049ARealize first-order shapingImproved scatter-free dynamic rangeAnalogue-digital convertersPhysical parameters compensation/preventionCapacitanceHarmonic
The present invention discloses a digital weight average algorithm applied to a successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter, characterized in that a pseudo-random number generator is added in a circuit of the successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter, a random pin code is generated by the pseudo-random number generator before each quantization of the successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter, and the connection of each unit capacitor is determined by the pin code through successive approximation register control logic, so that the unit capacitors form capacitors of different weights at random. In the present invention, the DWA algorithm is applied to a structure of the SAR ADC, so that the harmonic of an output signal is suppressed to the noise floor, to realize the first-order shaping of the noise of the output signal, thereby increasing the spurious-free dynamic range of the SAR ADC; and when the number of times of quantification of the SAR ADC reaches a certain number, the DWA algorithm enables capacitor mismatch to be allocated to each quantization, to average the capacitor mismatch, reduce the effect of the capacitor mismatch on the static characteristic and the dynamic characteristic of the SAR ADC, and improve the quantization accuracy of the SAR ADC.
Owner:西安电子科技大学昆山创新研究院 +1
Background calibration method for capacitance mismatch and interstage gain error of pipelined SAR ADC (Synthetic Aperture Radar Analog-to-Digital Converter)
ActiveCN110971235AFix mismatchCorrection errorAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a background calibration method for correcting capacitance mismatch and an interstage gain error in a pipelined SAR ADC (Synthetic Aperture Radar Analog-to-Digital Converter),which comprises the following steps of: injecting a pseudo random sequence PN (Pseudo-Noise) signal into a background, extracting the gain error of the capacitance mismatch and the interstage operational amplifier, and then correcting the gain error by a digital calibration engine. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a noise quantizer technology. During the first-stage SAR conversion, the inter-stage operational amplifier is multiplexed into an additional comparator, the two comparators compare the same input signal, and the comparison result is used for detecting whether the margin voltage is near the threshold of the comparator or not, thereby deciding whether to inject a pseudo random sequence PN signal or not. According to the method, capacitor mismatch and gain errors in the pipelined SAR ADC can be corrected without an additional analog circuit and time sequence overhead, harmonic components in a signal band can be effectively reduced, the signal-to-noise ratio is obviouslyimproved, and the spurious-free dynamic range is obviously enlarged.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Successive approximation register analog-digital converter and method of driving the same
InactiveUS7893860B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceDigital down converter
A successive approximation register (SAR) analog-digital converter (ADC) and a method of driving the same are provided. The SAR ADC includes a first converting unit including a bit capacitor array corresponding to the number of bits and a correction capacitor array, a comparator outputting a high or low voltage corresponding to each capacitor according to an output voltage of the converting unit, and a correction unit correcting the output of the bit capacitor according to the output of the correction capacitor array among the high or low output of the comparator. Therefore, two bits having the same capacitance as a least significant bit (LSB) enable a digital output error to be corrected, so that a spurious free dynamic range (SFDR) of the signal converter is increased, and a signal to noise and distortion ratio (SNDR) of an output signal is improved.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
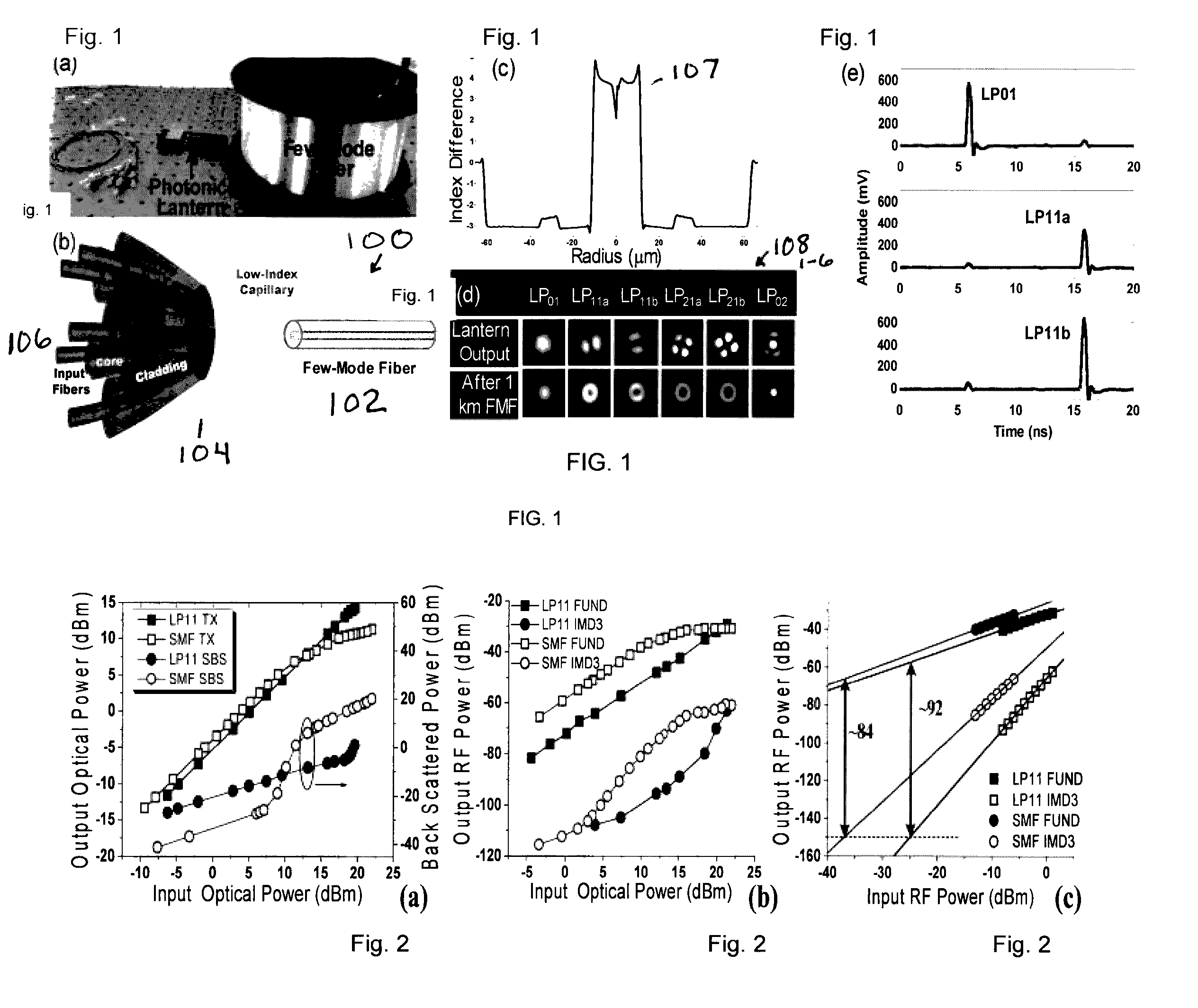
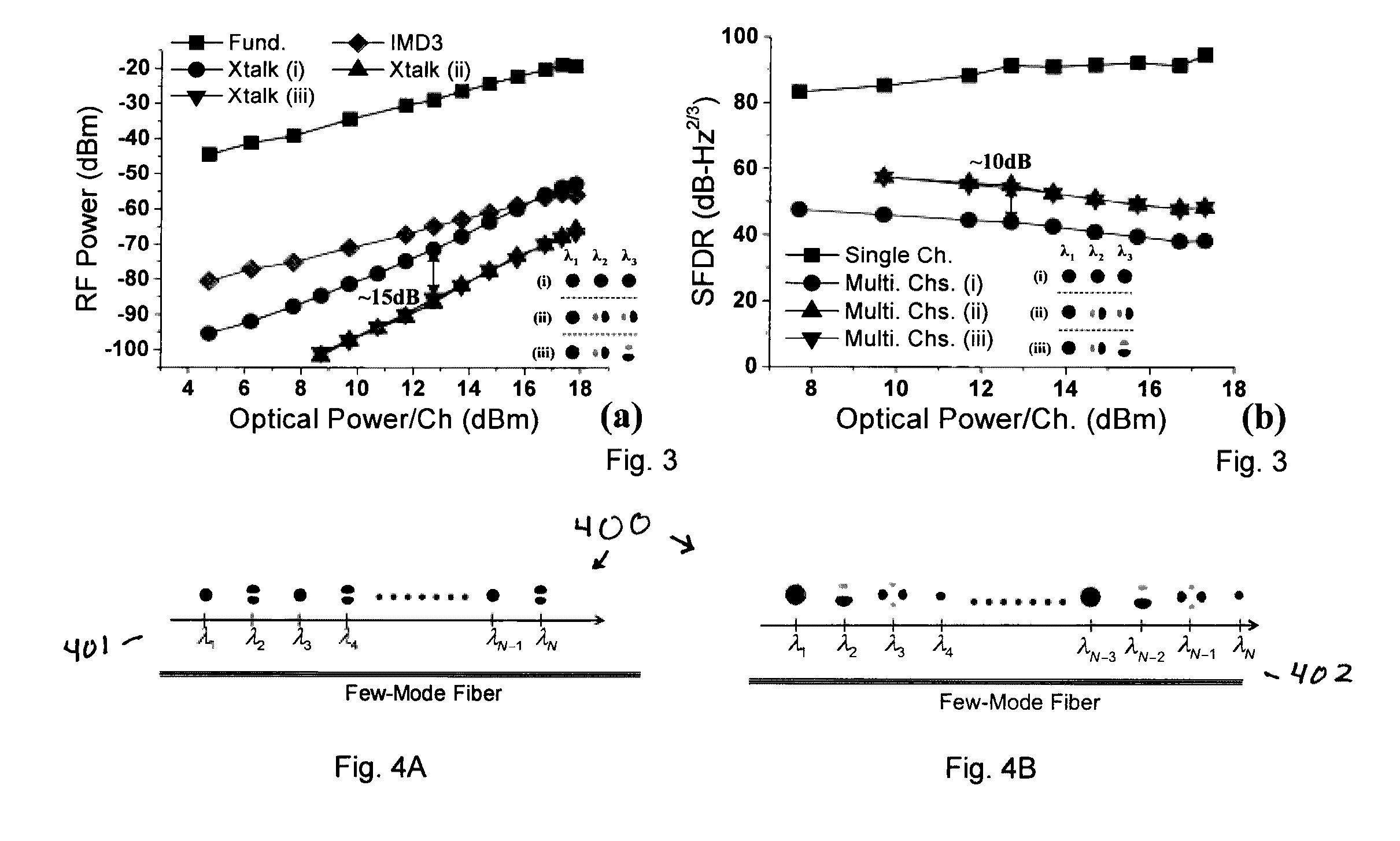
Optical Transmission Apparatus, Method, and Applications Thereof
InactiveUS20160285579A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsFew mode fiberTelecommunications link
Analog and digital fiber-optic telecommunication links using high-order modes in few-mode fibers (FMFs) to improve the Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR) and reduce wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) penalties due to fiber nonlinearities. Methods and applications.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
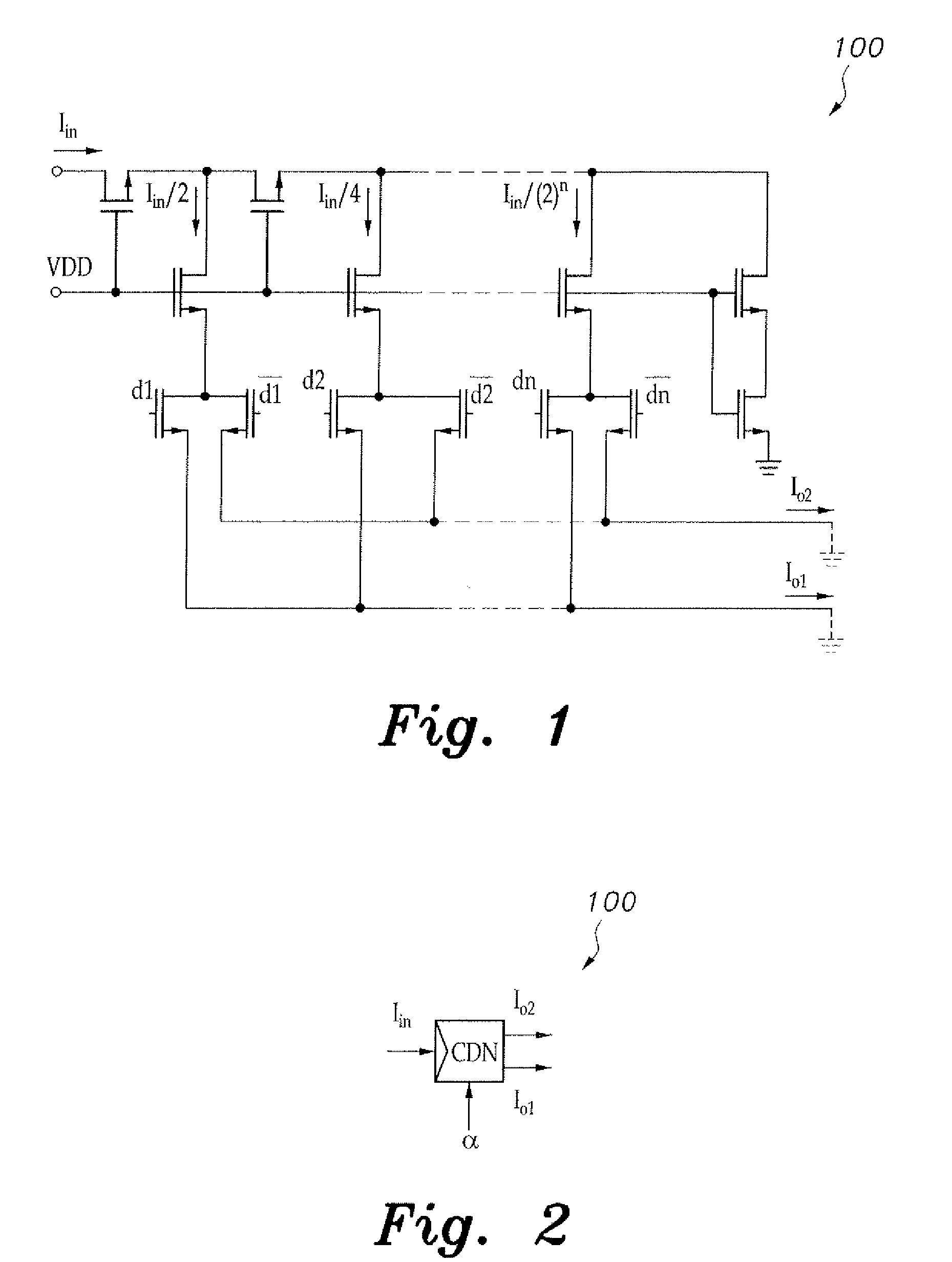
Digitally programmable active-RC filter
InactiveUS8508291B1Readily apparentActive element networkOscillations generatorsAudio power amplifierIntegrator
The digitally programmable active-RC filter provides an active-RC filter having programmable time constants. An inherently linear current division network (CDN) provides the programmable time constants while preserving a high linearity property of the active-RC filter. Using this approach, wide tuning characteristics are achieved. The programmable active-RC filter uses two op-amps per integrator. Cross-coupling two of the units configured with I and Q inputs provides the reconfigurable filter with a complex bandpass and normal lowpass response. One embodiment is formed as a fourth-order filter fabricated in a standard 0.18 μm CMOS process. The complex and lowpass filters achieve in-band spurious-free dynamic ranges (SFDRs) of about 70 dB and 71 dB for bandwidths of 1 MHz and 5.5 MHz, respectively.
Owner:KING ABDULAZIZ CITY FOR SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Frequency conversion and phase-shifting integrated photonic microwave mixing device
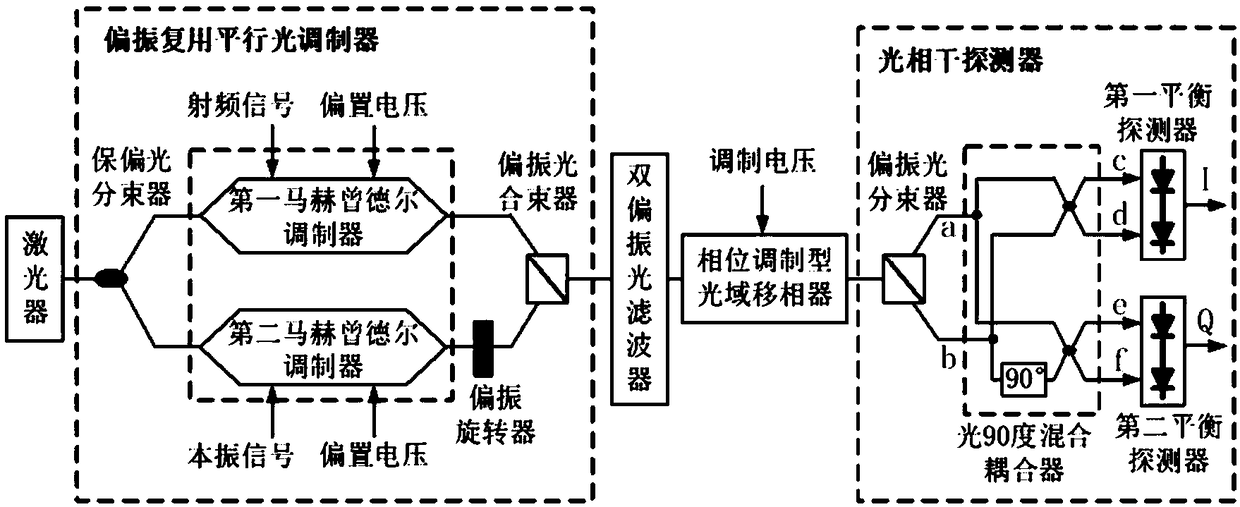
ActiveCN109150314ARelatively small disturbanceSmall group delay fluctuationElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversIntermediate frequencyPolarization multiplexed
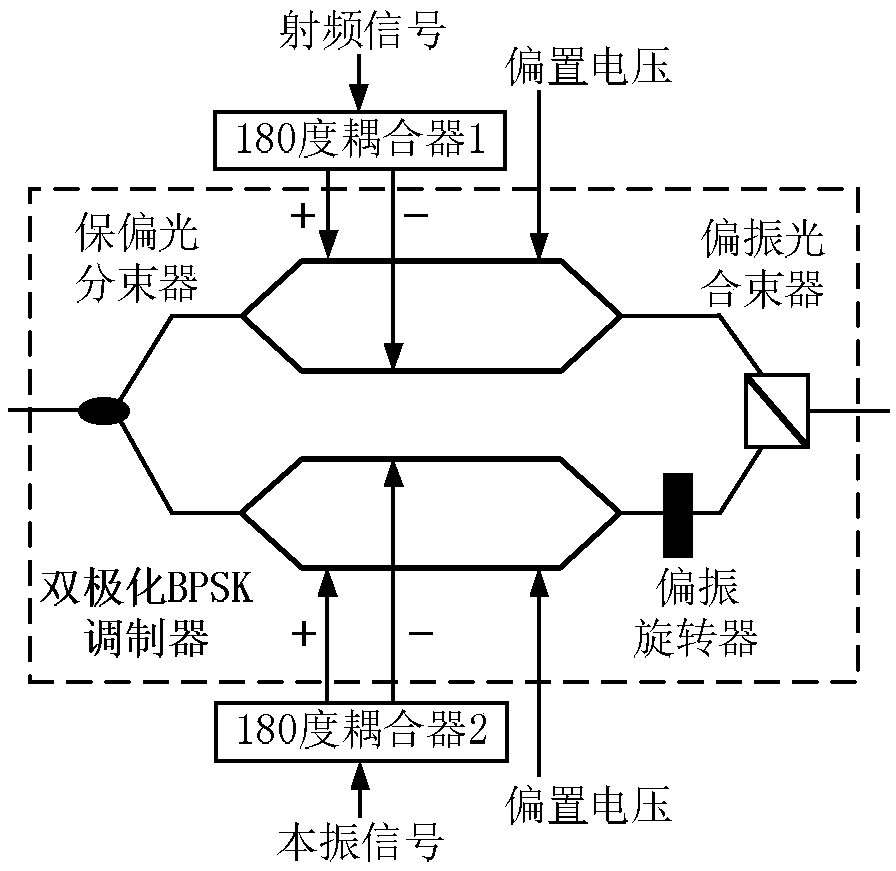
The invention provides frequency conversion phase-shifting integrated photonic microwave mixing device which comprises a laser, a polarization multiplexing parallel light modulator (also known as a dual polarization parallel light modulator, a polarization multiplexing I / Q modulator, a dual polarization I / Q modulator), a bipolarized light filter, an optical domain phase shifter, and an optical coherence detector. A parallel structure photonic mixer based on orthogonal polarization multiplexing technology is realized by the polarization multiplexing parallel optical modulator, which makes the RF modulated optical signal and the LO modulated optical signal in the orthogonal polarization state with phase coherence, and keeps the phase of the two parallel optical signals relatively stable allthe time, and realizes arbitrary phase shifting of the obtained intermediate frequency signal through the optical domain phase shifter. Compared with the traditional microwave mixer, the device has larger bandwidth, spurious-free dynamic range and smaller group delay fluctuation, and can realize the functional integration of frequency mixing and phase shifting.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Background calibration method based on related SAR ADC capacitor mismatch errors
ActiveCN111900983AImprove signal-to-noise ratioCapacitor Mismatch Error CorrectionElectric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionCapacitanceEngineering
The invention discloses a background calibration method based on related SAR ADC capacitor mismatch errors. Pseudo-random signal PN is injected into the margin voltage by using a detection skip algorithm and an alignment switching technology, and then the digital signal and the pseudo-random signal PN are subjected to related operation at the background, so that the capacitor mismatch error can beextracted. Because the weight error injected into the margin voltage is very small relative to the total capacitance, the margin increment caused by injection can be ignored. Therefore, the calibration algorithm does not need to increase the condition of extra circuit detection injection, and can also minimize the overhead of a redundancy range. Simulation results show that after correction, thesignal-to-noise distortion ratio is increased from 35.9 dB to 61.1 dB, and the spurious-free dynamic range is increased from 41.2 dB to 79.3 dB.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Radio-frequency signal A/D (Analog to Digital) conversion system and method based on multi-rate parallel sampling
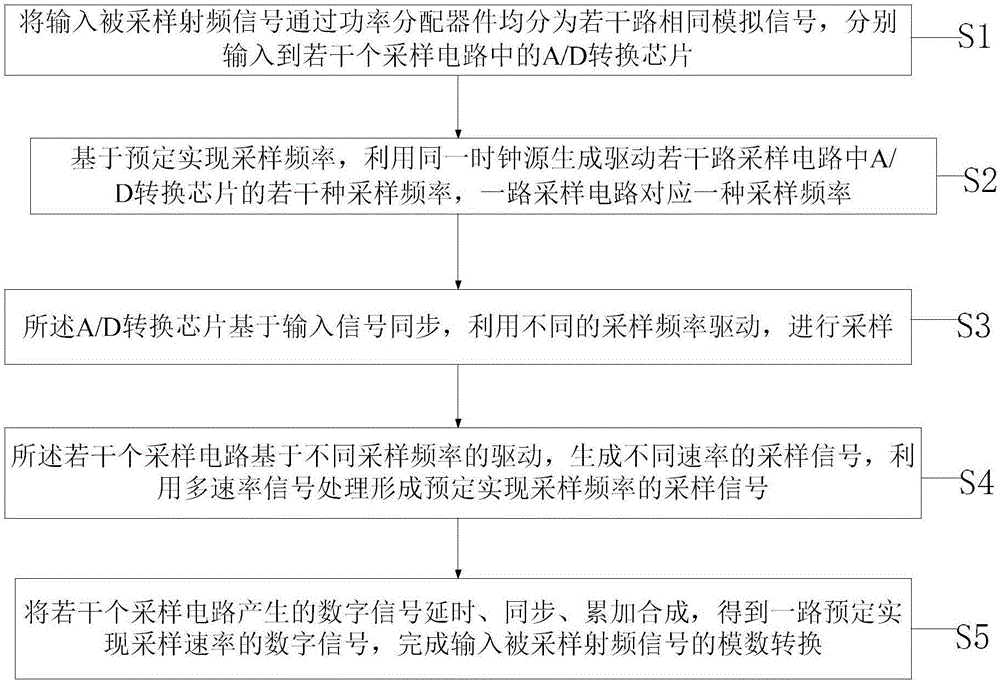
InactiveCN106849950AHigh resolutionExpand the scope ofAnalogue-digital convertersInformation processingImage resolution
The invention discloses a radio-frequency signal A / D (Analog to Digital) conversion system and method based on multi-rate parallel sampling. The system comprises a power distribution module, a first A / D conversion chip, a clock source module, a second A / D conversion chip and a digital information processing module; the first A / D conversion chip and the second A / D conversion chip both are connected with the power distribution module; the clock source module is positioned between the first A / D conversion chip and the second A / D conversion chip; the first A / D conversion chip is connected with the digital information processing module; and the second A / D conversion chip is connected with the digital information processing module. According to the radio-frequency signal A / D conversion system and method based on the multi-rate parallel sampling, the direct digitalization for receiving a radio-frequency signal in wireless communication can be realized, the resolution and the spurious-free dynamic range are improved, and the operation is simple.
Owner:NO 50 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
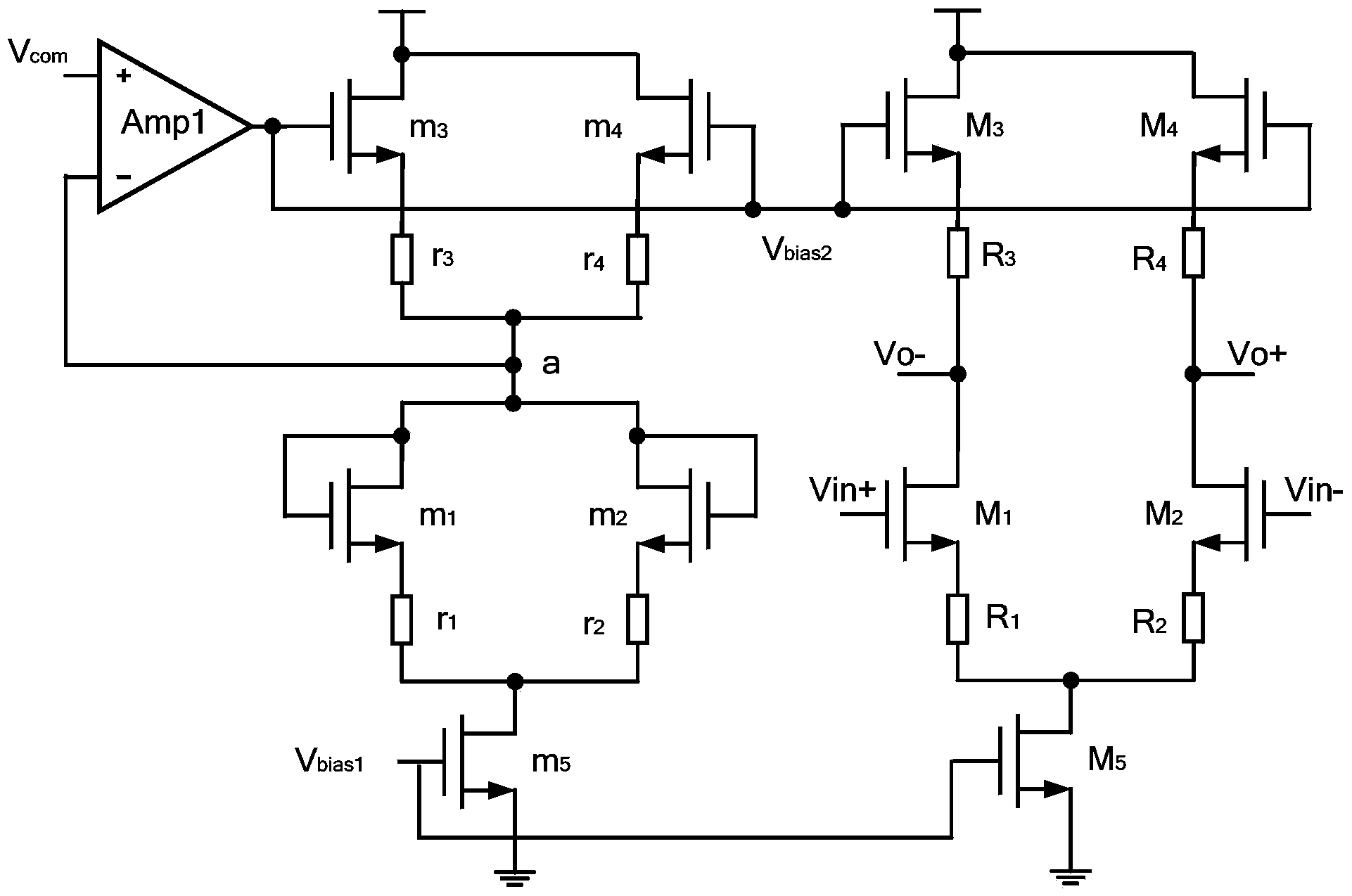
Open loop amplifier with stable output common-mode voltage
InactiveCN103414441AStable outputImprove job transition speedNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention relates to an open loop amplifier with stable output common-mode voltage. The open loop amplifier comprises a main amplifier unit and an auxiliary amplifier unit. Compared with a conventional negative feedback amplifier with stable output common-mode voltage, the open loop amplifier has the beneficial effects that the differential output common-mode voltage of the main amplifier unit under an open loop structure is stable; the differential output end of the main amplifier unit does not adopt a common-mode feedback circuit, so that the output load is lowered, the working conversion speed of the amplifier is increased, and the frequency of an analog input signal can exceed 1GHz when the dynamic indicator SFDR (Spurious Free Dynamic Range) of the main amplifier unit exceeds 70dB. The circuit provided by the invention is applied to the field of ultrahigh-speed sampling / retaining circuits in low-voltage CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Transistor) process circuits with a high dynamic performance requirement.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
High-precision and low-distortion digital-analog converter
InactiveCN104796145AReduce noise powerHigh precisionAnalogue-digital convertersLow distortionIntegrator
The invention relates to a high-precision and low-distortion digital-analog converter which comprises an analog adder / subtractor, first and second analog integrators, an analog adder, an analog-digital converter, first, second and fourth gain amplification stages, an analog gain stage and a feedback gain amplification stage. A signal output end OUTPUT is connected with an output end of the analog-digital converter, a second-order DEM (dynamic element matching) module is arranged between the analog-digital converter and the analog adder / subtractor, an input end of the second-order DEM module is connected with the output end of the analog-digital converter, and an output end of the second-order DEM module is connected with an input end of the analog adder / subtractor by a digital-analog converter. The high-precision and low-distortion digital-analog converter has the advantages that owing to a feedback factor adding mode, zero points are imported into noise transfer functions, accordingly, noise power in signal base bands can be reduced, the signal-to-noise ratio of the high-precision and low-distortion digital-analog converter can be increased, and the system precision of the high-precision and low-distortion digital-analog converter can be improved; second-order suppression can be carried out on mismatched noise by the aid of second-order sigma-delta DEM technologies, accordingly, the signal-to-noise distortion ratio of the integral sigma-delta analog-digital converter can be increased, and the spurious-free dynamic range of the integral sigma-delta analog-digital converter can be expanded.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
DA (Digital to Analog) converter
ActiveCN103281085AHigh impedanceReduce couplingAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsConvertersControl signal
The invention provides a DA (Digital to Analog) converter which comprises a switching unit. The switching unit comprises a first MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) tube, a second MOS tube, a third MOS tube, a fourth MOS tube, a fifth MOS tube, a sixth MOS tube, a first operational amplifier and a second operational amplifier. The operational amplifiers can increase impedances of the MOS tubes at the same side with the operational amplifiers and reduce coupling of a control signal on the output end so as to improve the SFDR (Spurious Free Dynamic Range); and the two operational amplifiers are respectively connected with one MOS tube, so that the effect that when the MOS tubes at one side of the switching unit are switched off, the operational amplifier at the same side with the MOS tubes is also simultaneously switched off without consuming additional power consumption is implemented, and thus, no more power consumption can be increased by the DA converter provided by the invention on the basis of implementing the high SFDR.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Narrow-ridge distributed feedback laser with mode field diffusion structure and application thereof
InactiveCN110957633ALarge model field areaReduce power densityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDistributed feedback laserGrating
The invention discloses a narrow-ridge distributed feedback laser with a mode field diffusion structure and application thereof. The distributed feedback laser comprises an N-surface electrode layer,a substrate layer, a buffer layer, a first waveguide layer, a multiple quantum well active layer, a second waveguide layer, a grating layer, an etching self-stop layer, a cladding layer, an ohmic contact layer, and a P-plane electrode layer; and the cladding layer and the ohmic contact layer are etched to form a ridge waveguide, and the ridge waveguide comprises a straight waveguide and a mode field diffusion structure. The ridge width in the horizontal direction is shrunk, disconnection of the end face ridges and deposition of a layer of low-refractive-index material film on the end face arerealized, the mode field area of output laser can be effectively increased, the power density of the end face of the laser is reduced, the damage threshold of the end face of the laser is improved, the maximum injection current is increased, the bandwidth is increased, the stray-free dynamic range is enlarged, the high-frequency response characteristic of the laser is improved, and the modulationrate is increased.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Suppressing digital-to-analog converter (DAC) error
ActiveUS20060022857A1Suppress errorLow profileElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionEngineeringDigital-to-analog converter
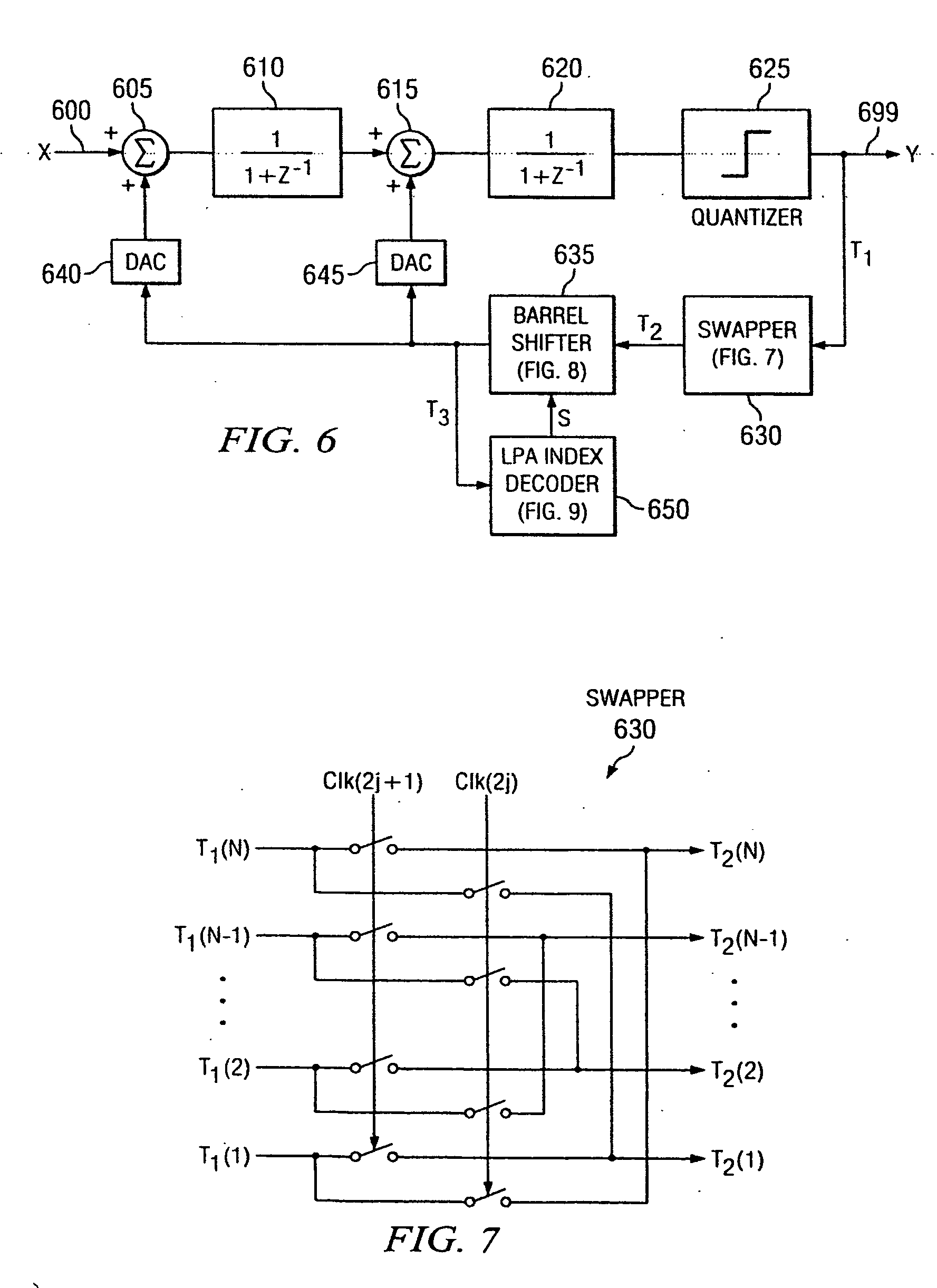
A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) error suppression arrangement suppresses DAC error arising from mismatched elements contained in a DAC (640 and / or 645) that is part of a modulator (FIG. 6). A low pass averaging (LPA) index decoder 650 controls a shifting arrangement 635 to shift a digital word T2 derived from modulator output Y so that the DAC error distribution constitutes a low pass profile (FIG. 5). Thus, DAC error is suppressed at higher frequencies (close to half the sampling rate), thereby providing improved spurious free dynamic range (SFDR). The LPA index decoder 650 causes the shifting arrangement 635 to shift the digital word T2 using only a single pointer per clock cycle.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Spurious free dynamic range in optical communications systems
InactiveUS7095960B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsRadio-over-fibreCommunications systemFrequency spectrum
The present invention is directed towards an optical transmitter including a noise generator. The noise generator provides noise signals that are filtered to below a frequency spectrum. The filtered noise signals are combined with RF signals to provide continuous modulation of a laser. The combined signals are converted to optical signals by the laser and transmitted over an optical link.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com