Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
874 results about "Plasma Gases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compressed air, nitrogen, argon, hydrogen and oxygen, or blends of two or three of these components are the most popular plasma gases for plasma cutting.
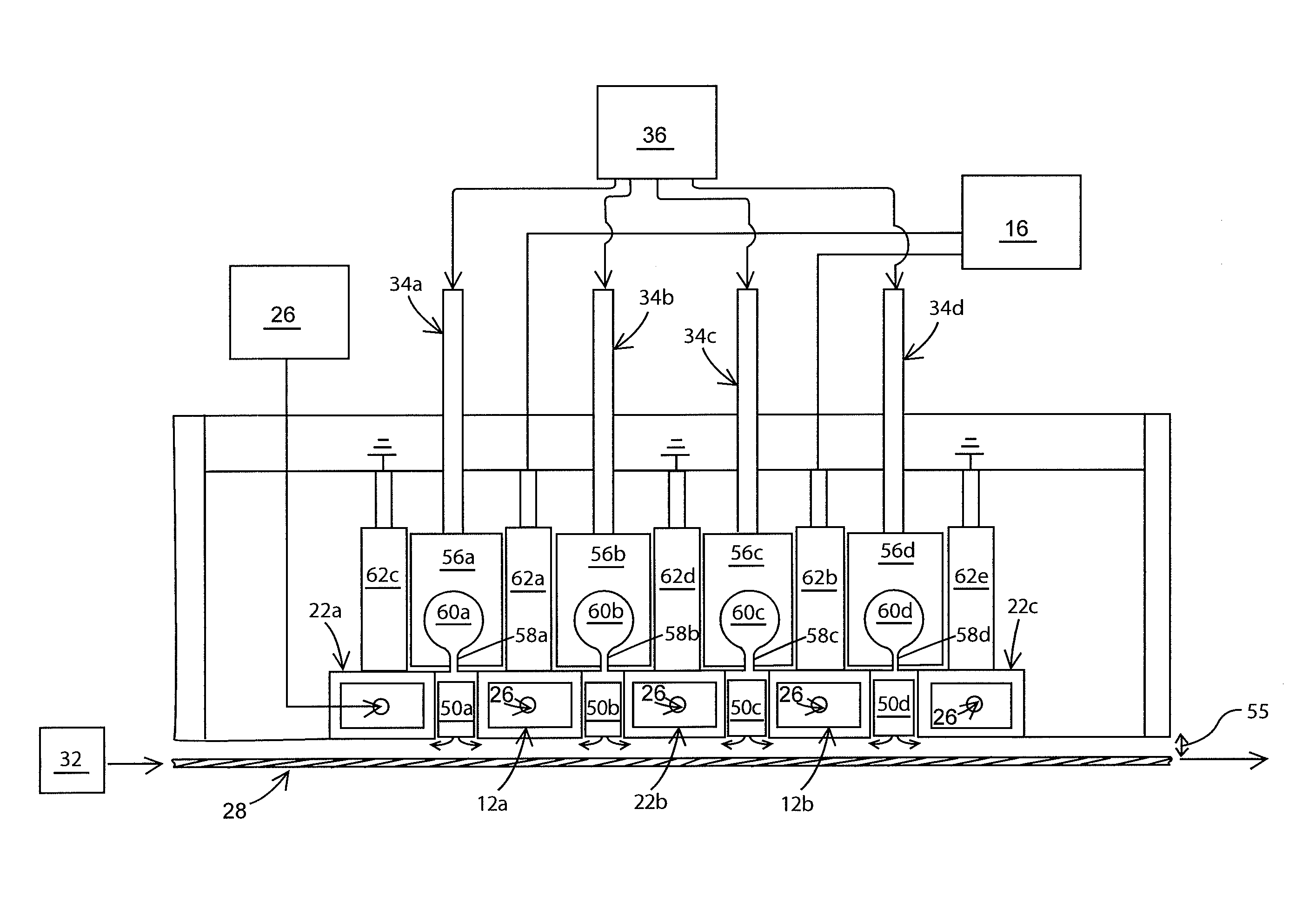
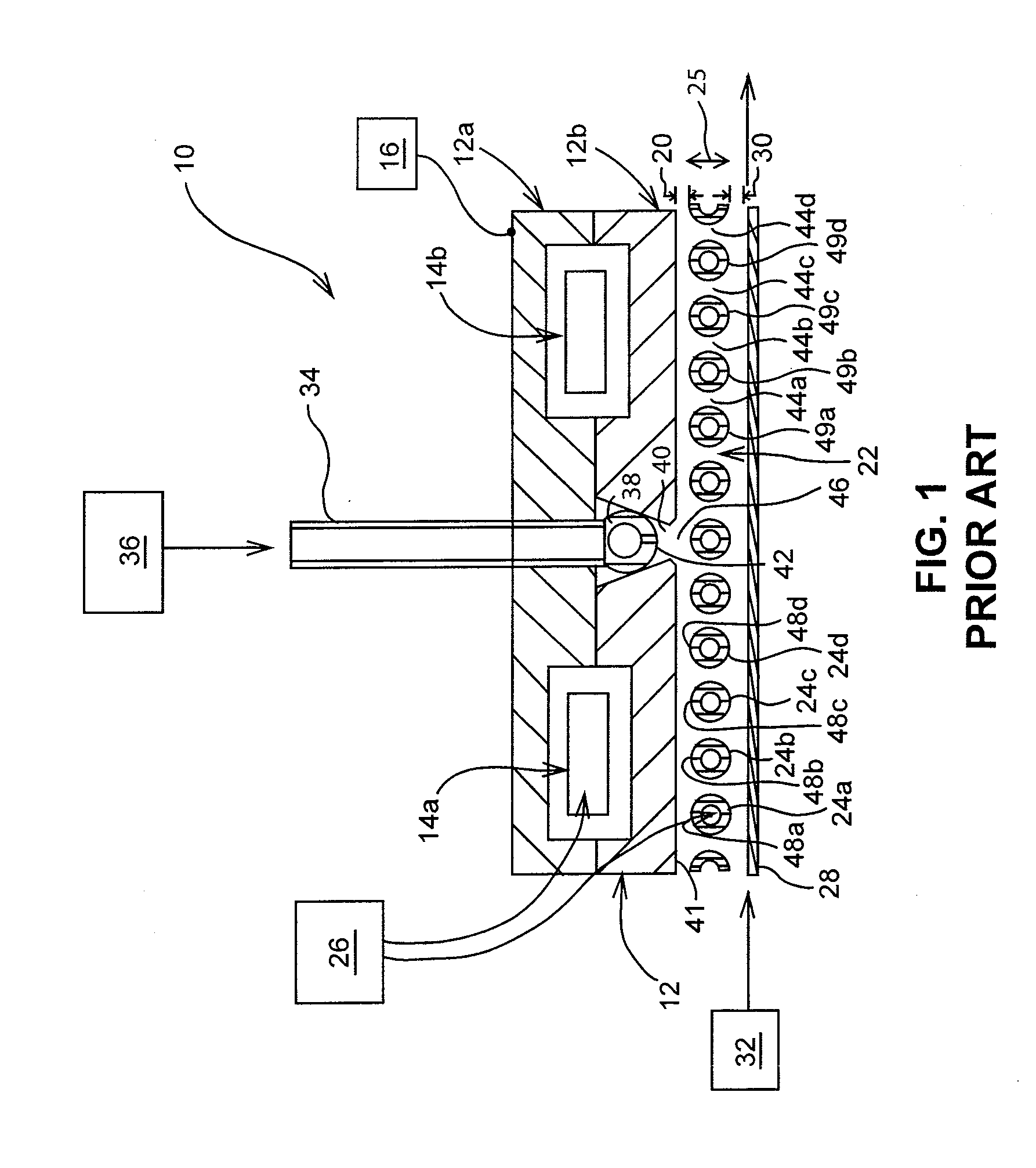
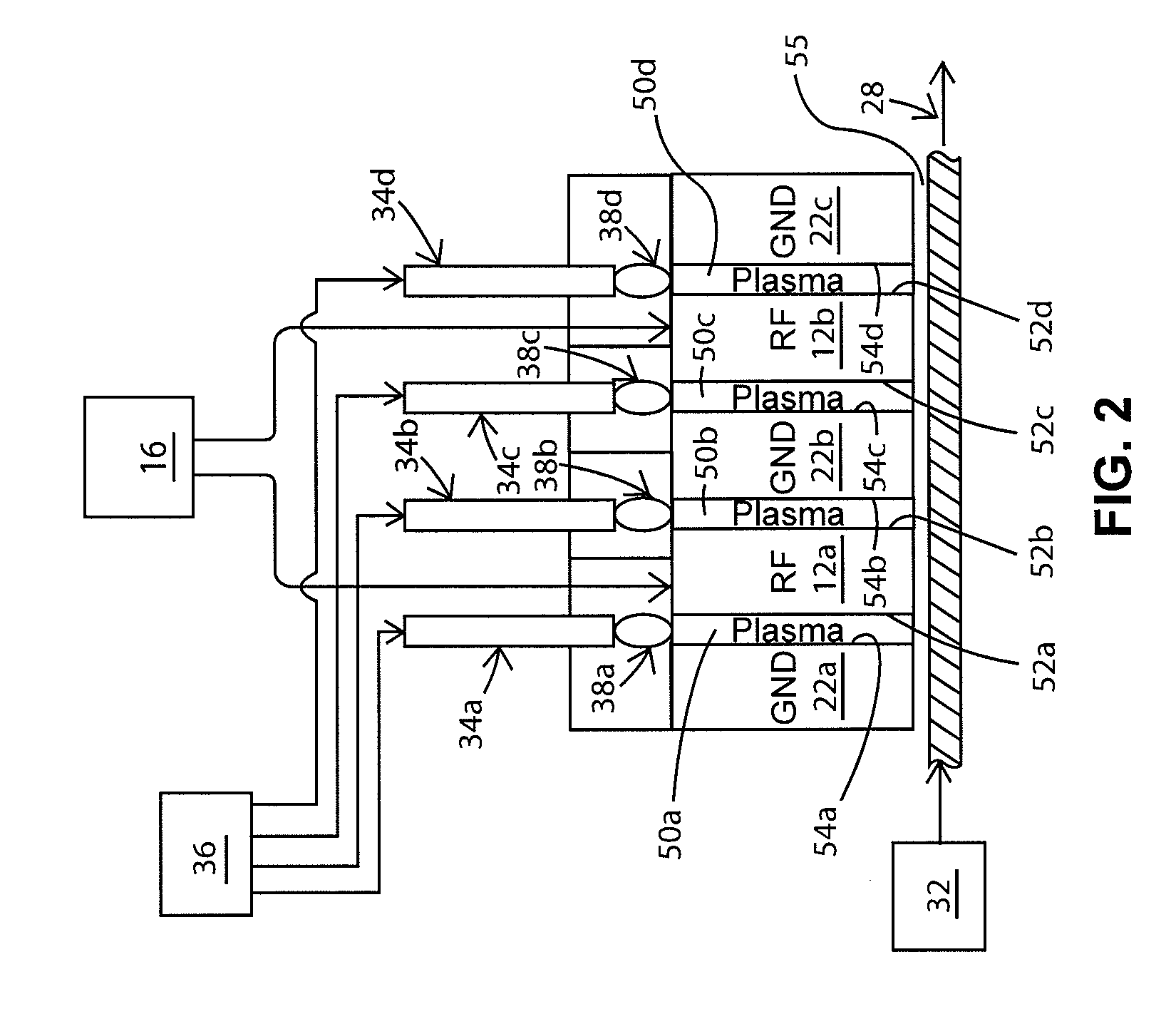
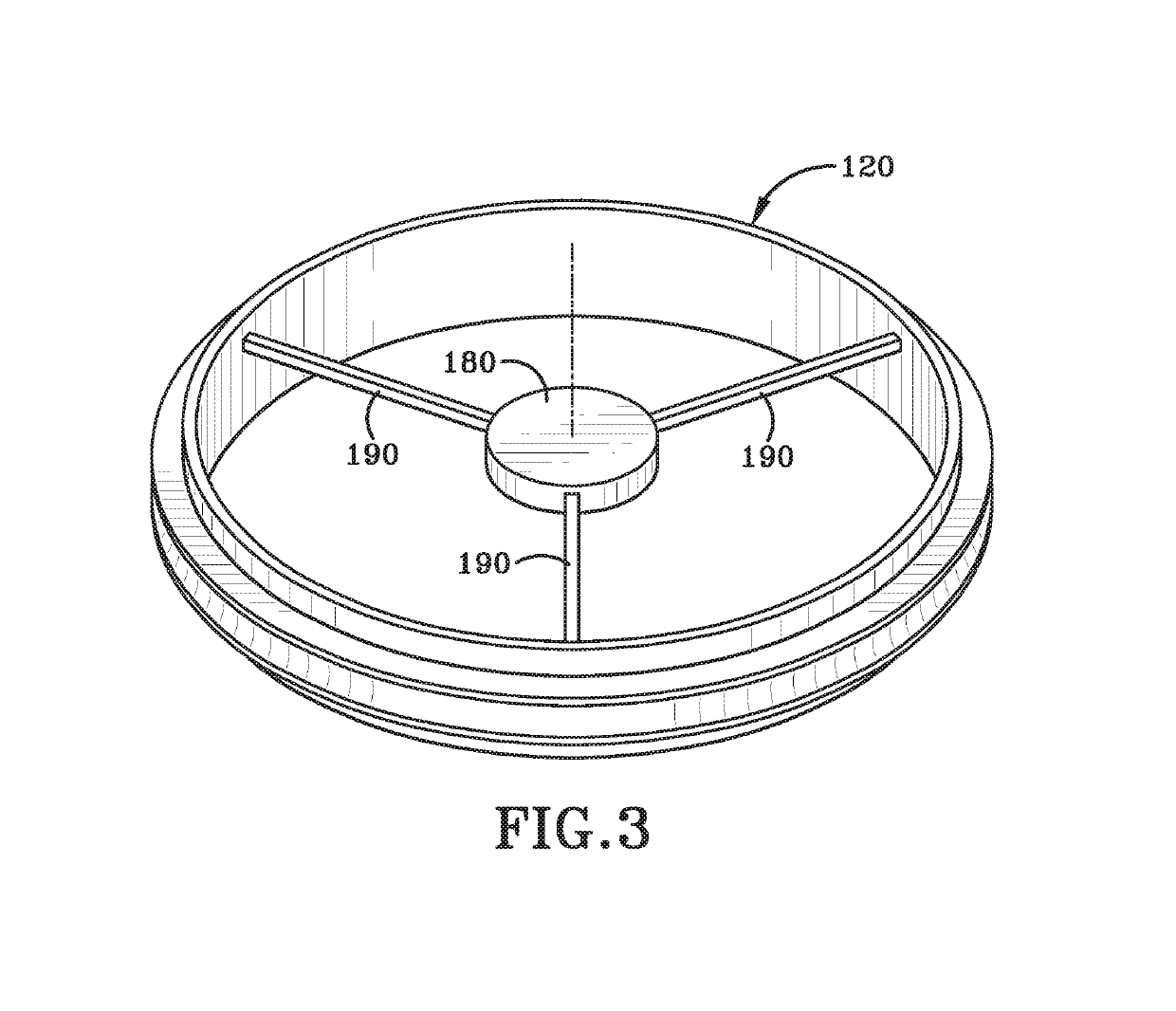
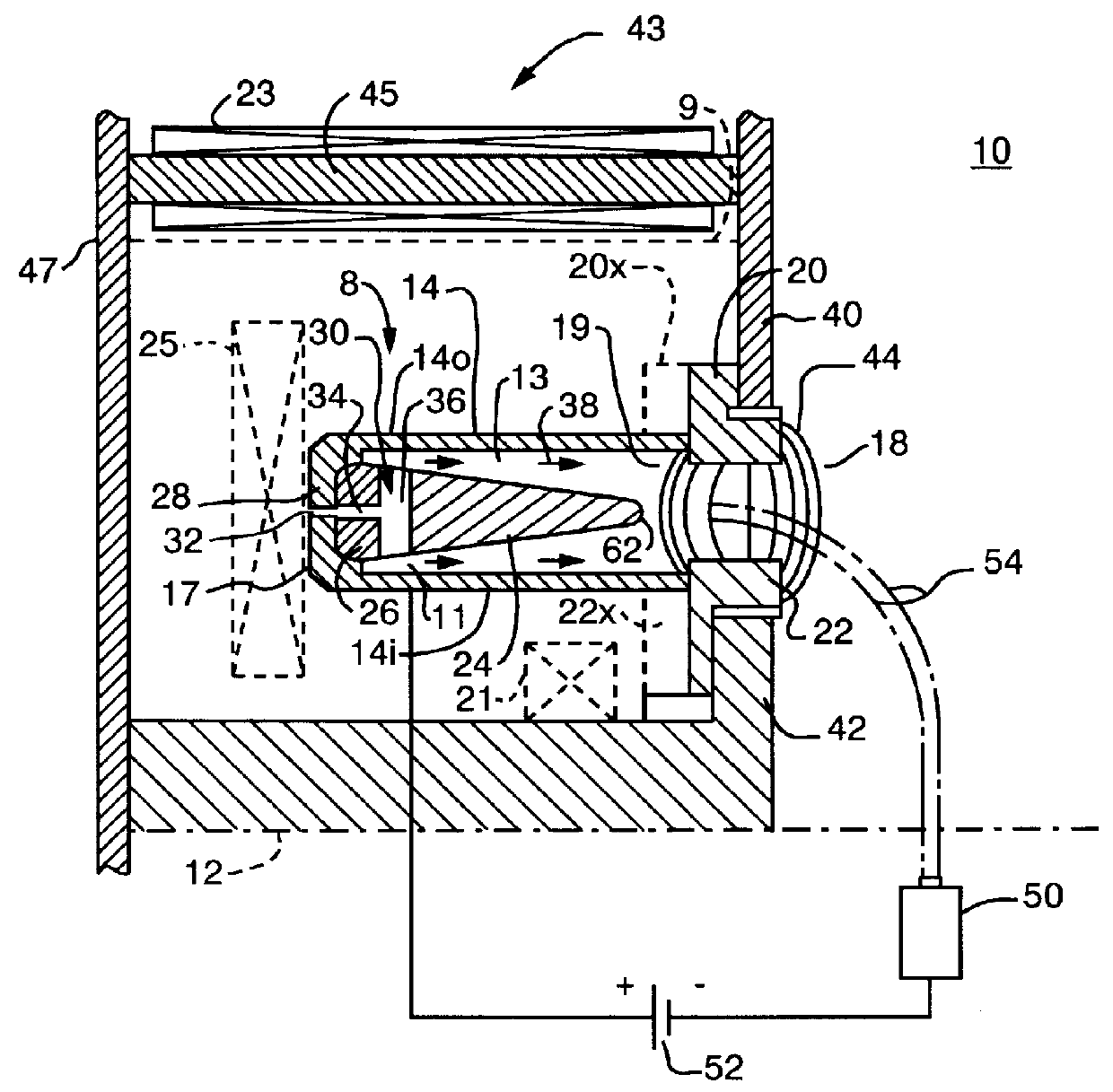
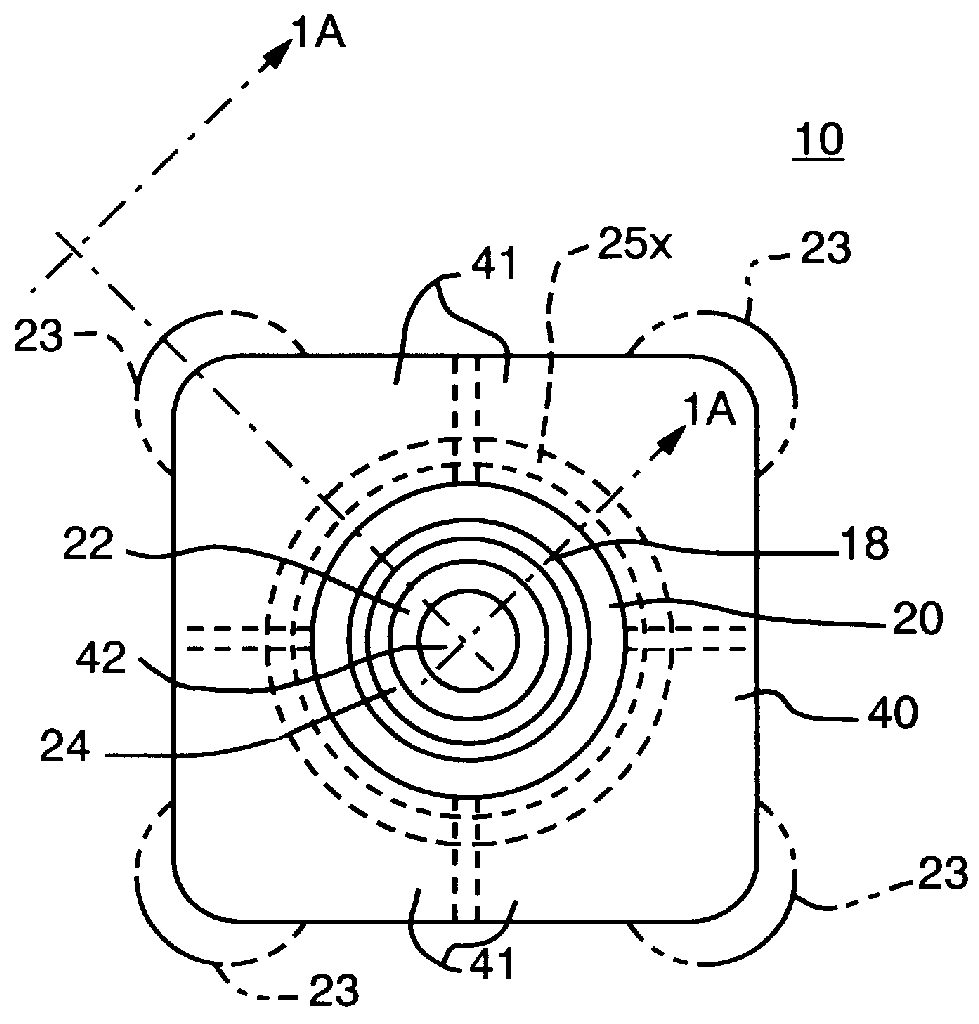
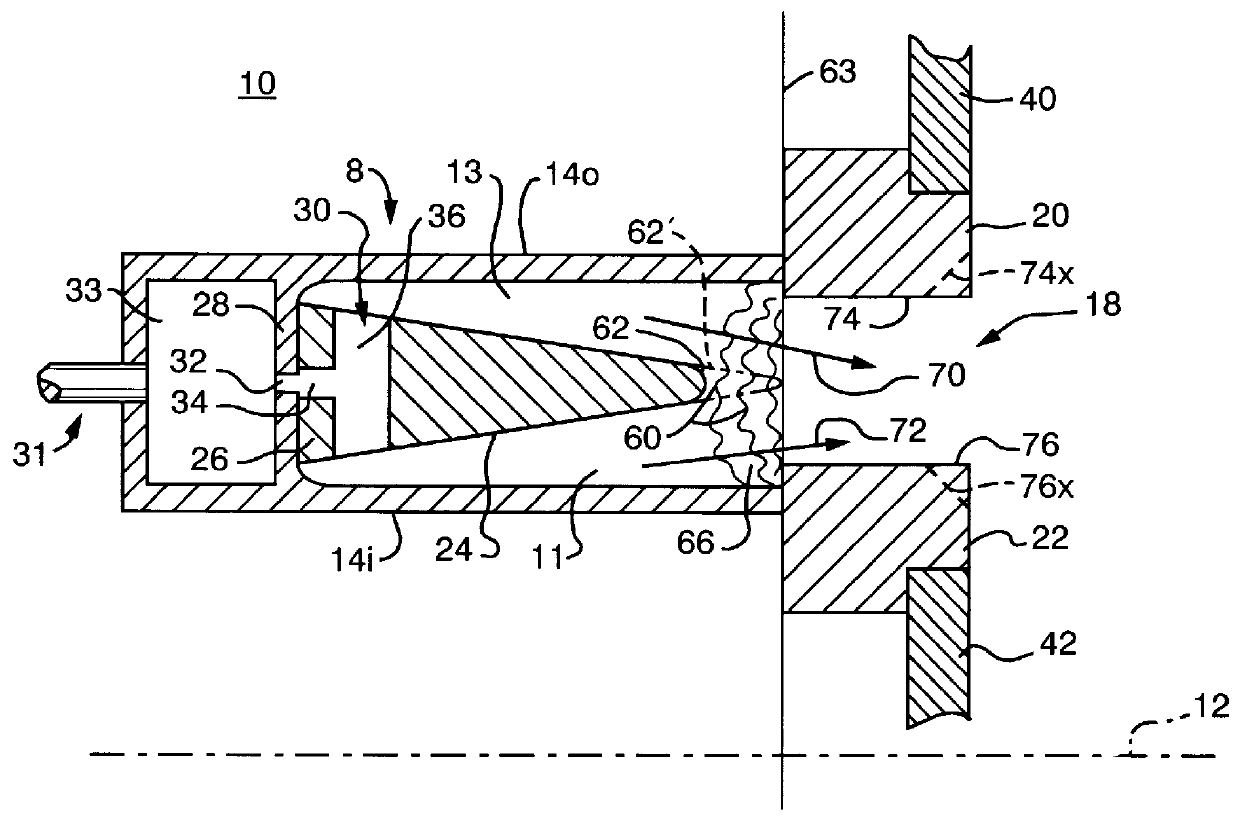
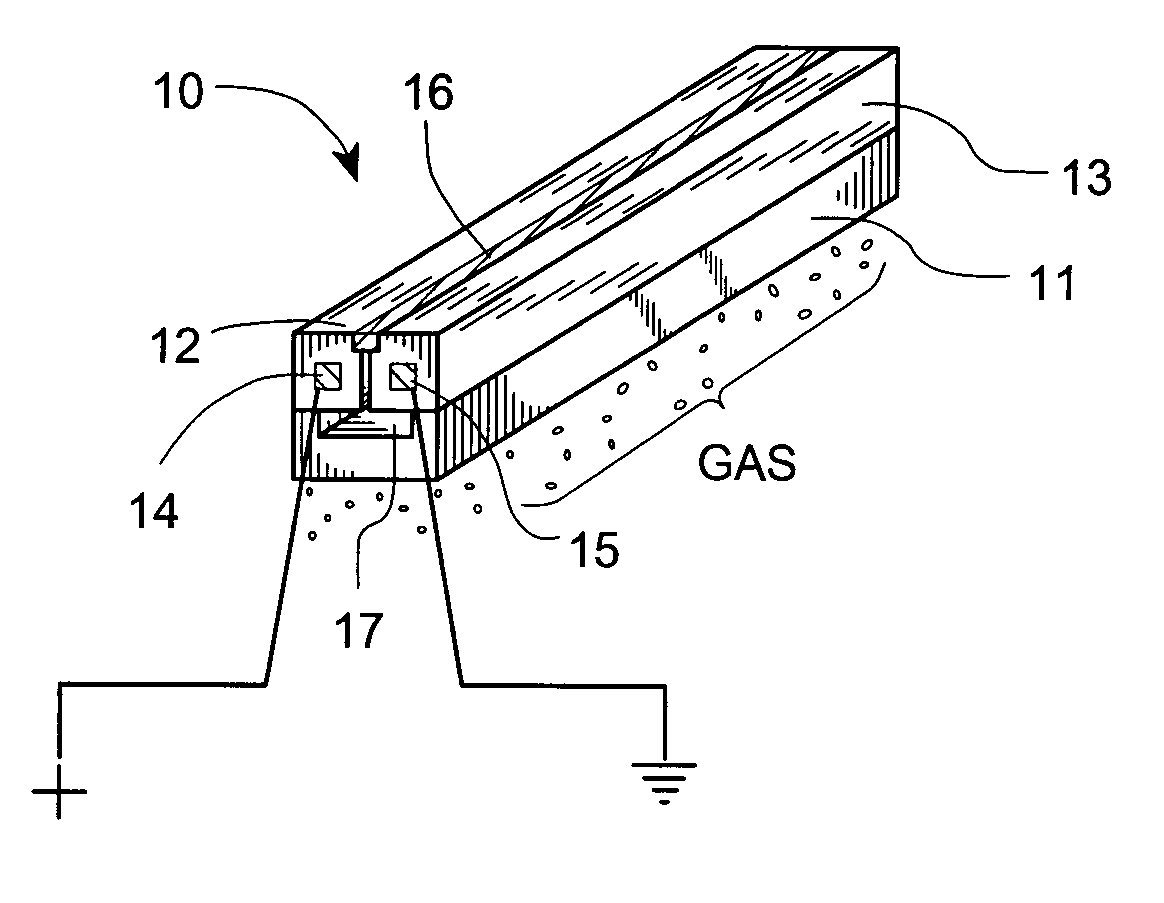
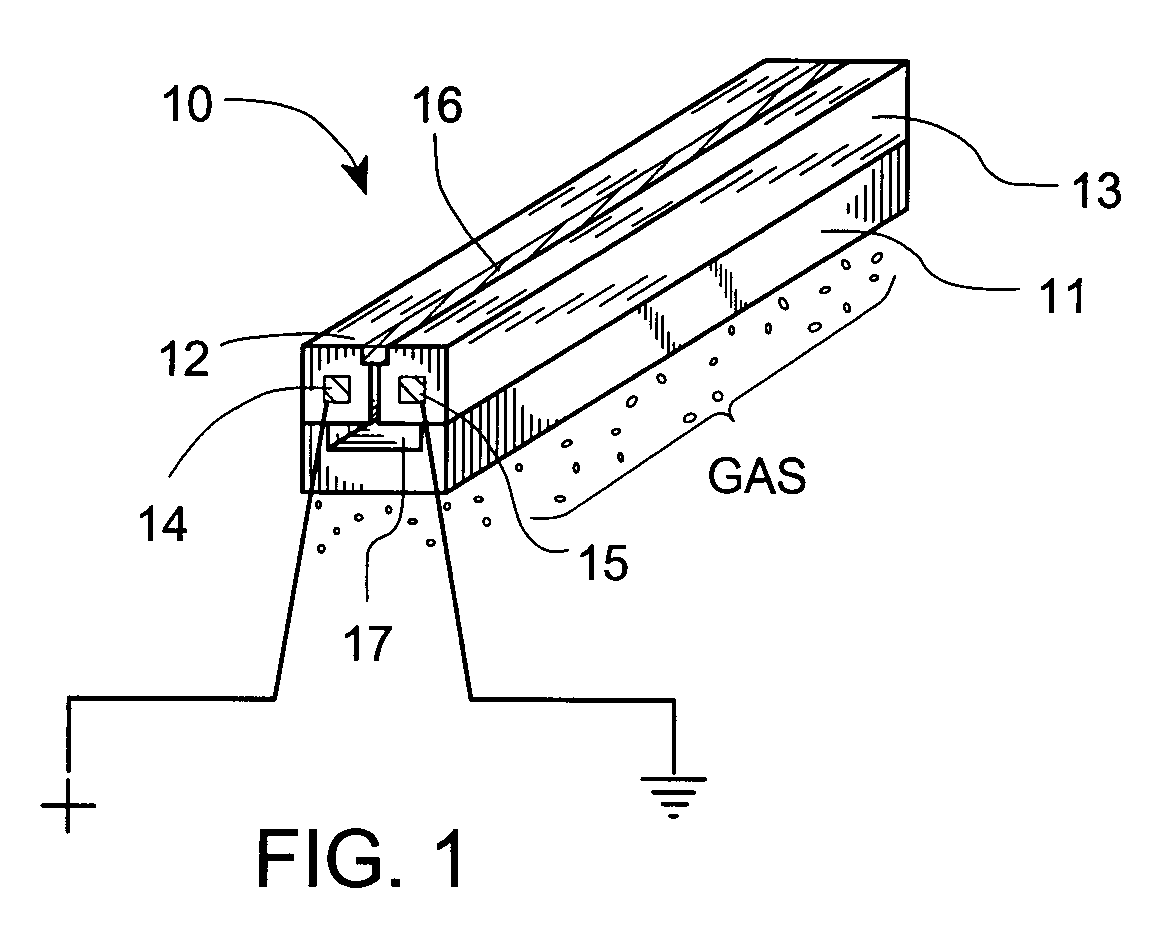
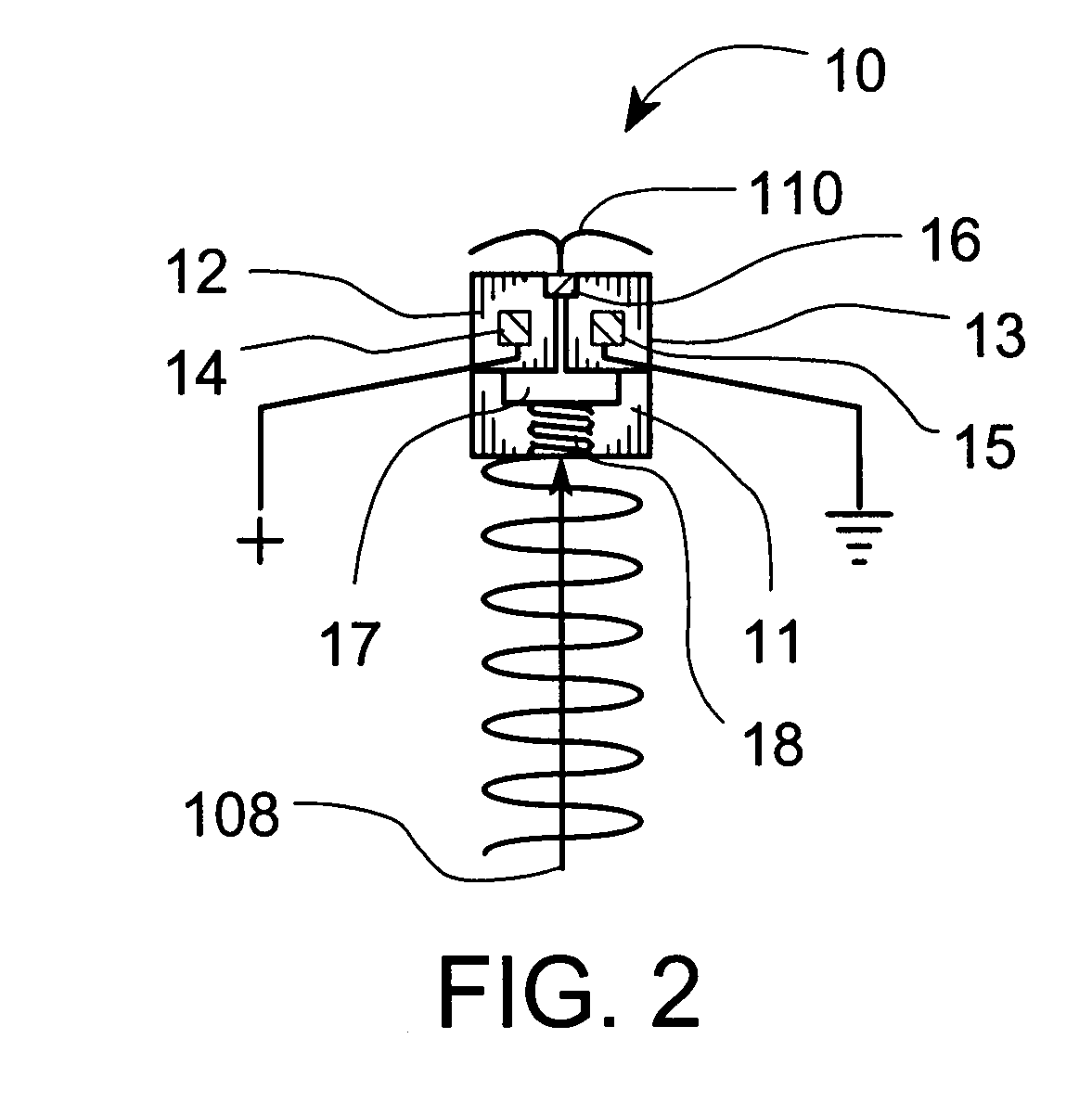
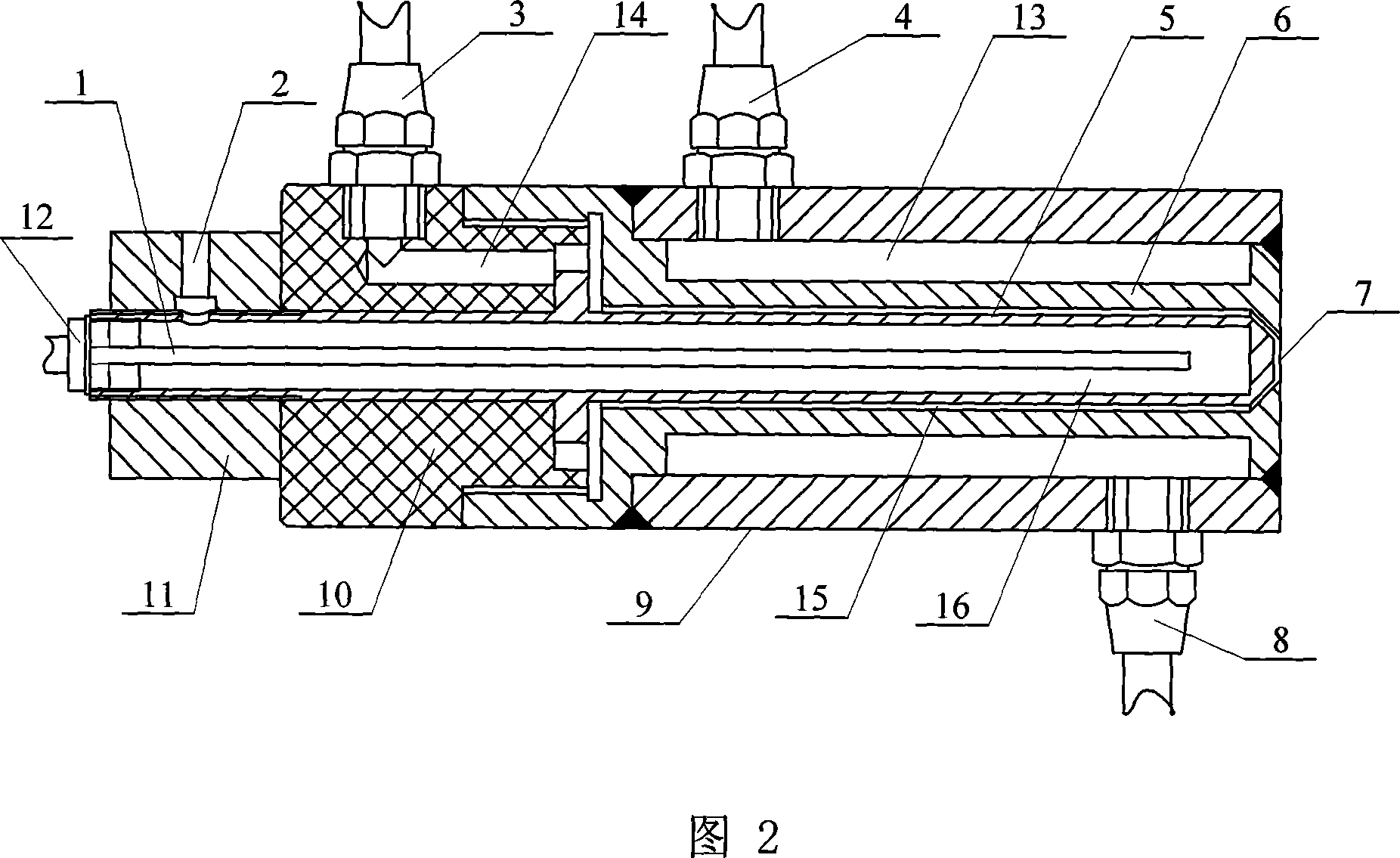
Atmospheric-pressure plasma processing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20140076861A1Faster plasma processing speedMinimum distanceChemical fixing of textilesArc welding apparatusEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
A plasma processing apparatus including powered electrodes having elongated planar surfaces; grounded electrodes having elongated planar surfaces parallel to and coextensive with the elongated surfaces of the powered electrodes, and spaced-apart a chosen distance therefrom, forming plasma regions, is described. RF power is provided to the at least one powered electrode, both powered and grounded electrodes may be cooled, and a plasma gas is flowed through the plasma regions at atmospheric pressure; whereby a plasma is formed in the plasma regions. The material to be processed may be moved into close proximity to the exit of the plasma gas from the plasma regions perpendicular to the gas flow, and perpendicular to the elongated electrode dimensions, whereby excited species generated in the plasma exit the plasma regions and impinge unimpeded onto the material.
Owner:APJET INC
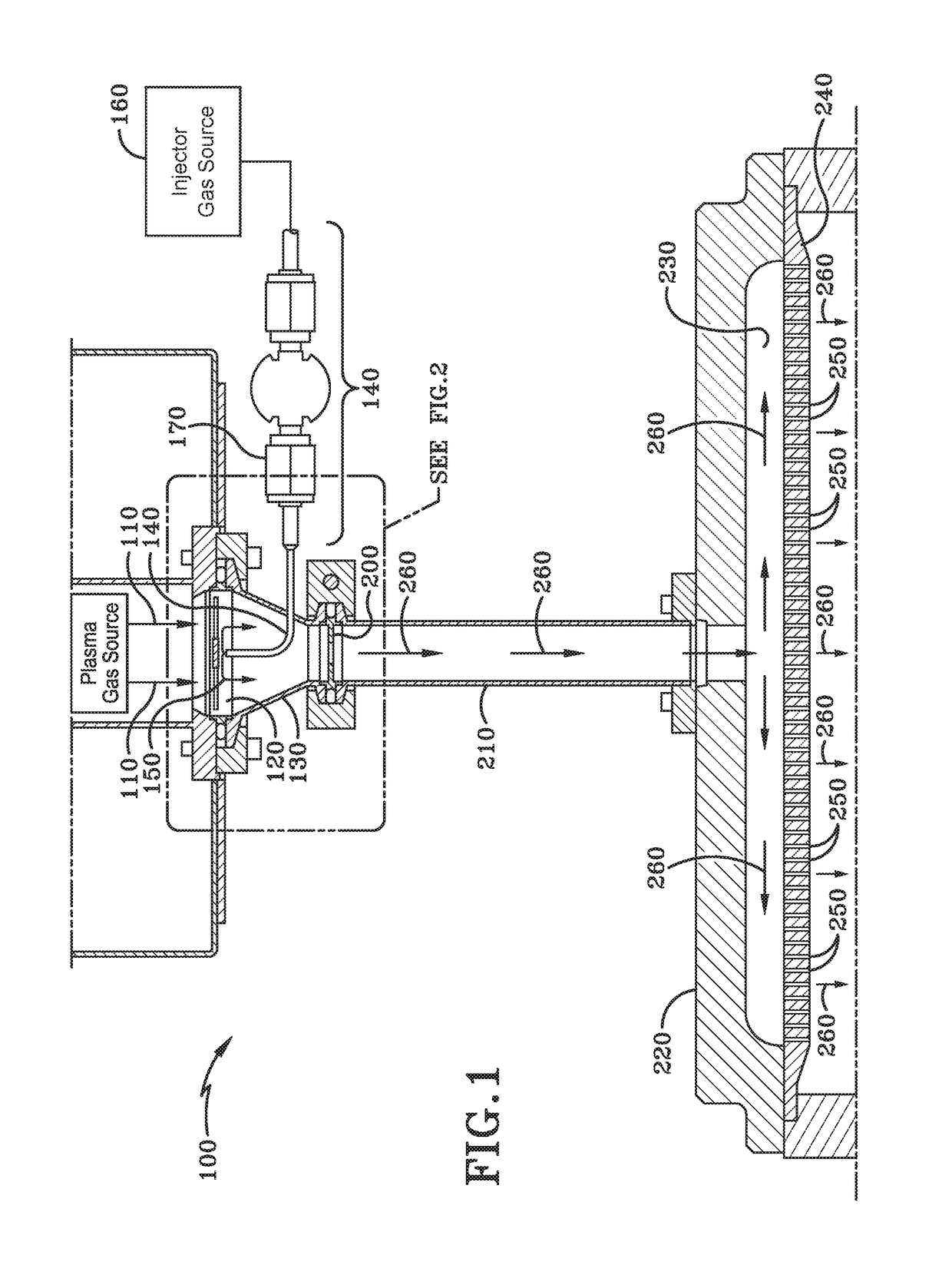
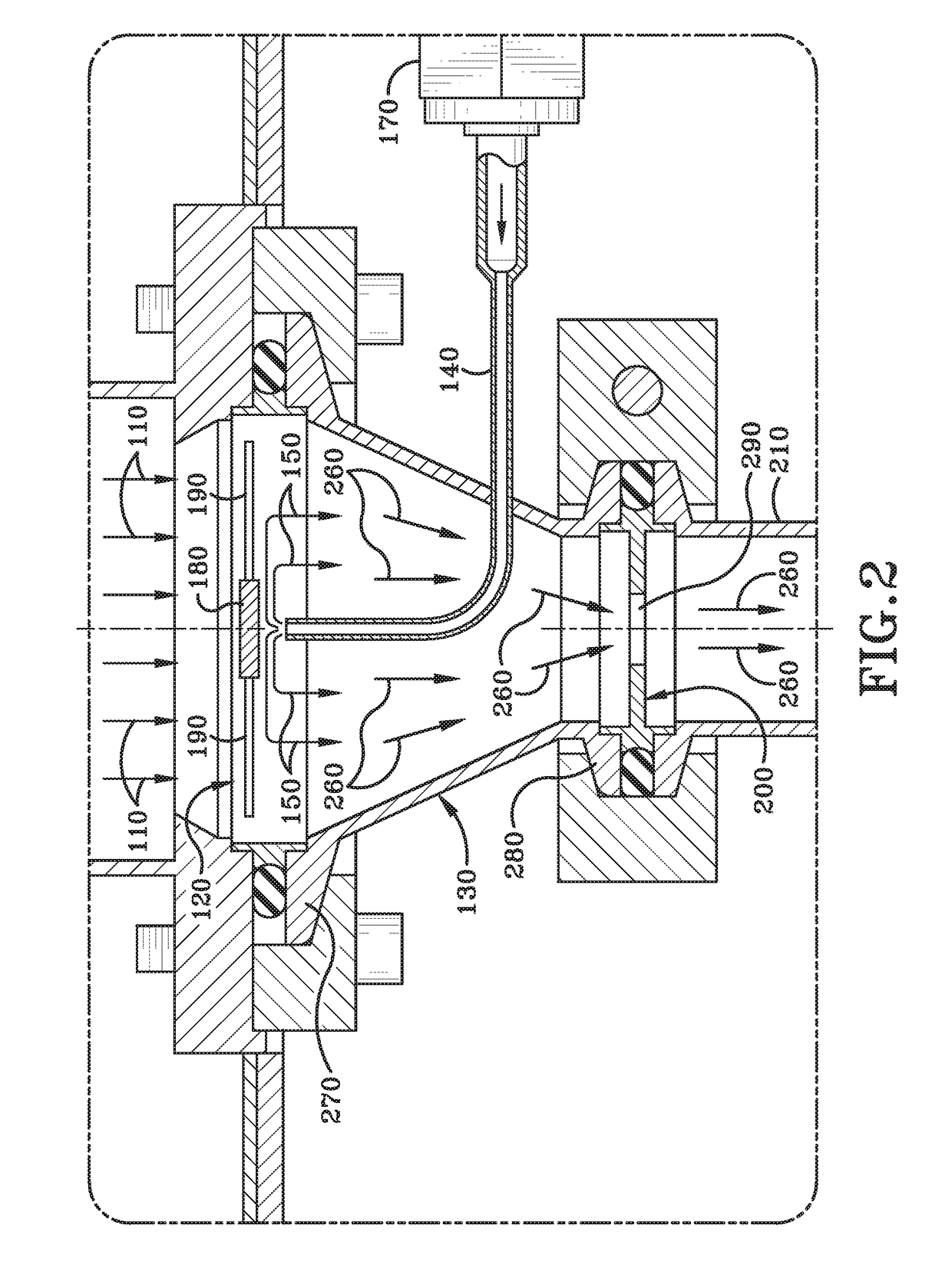
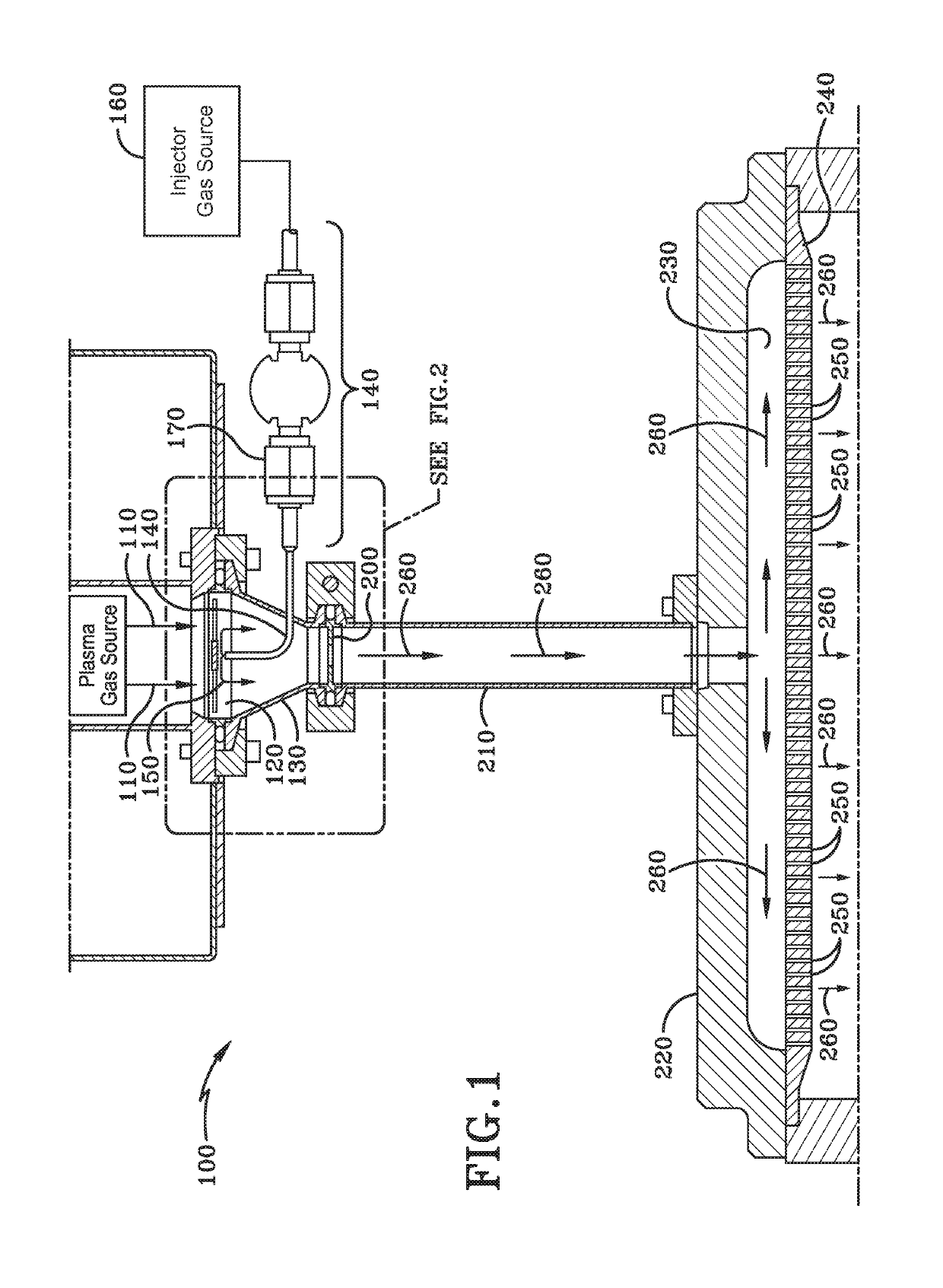
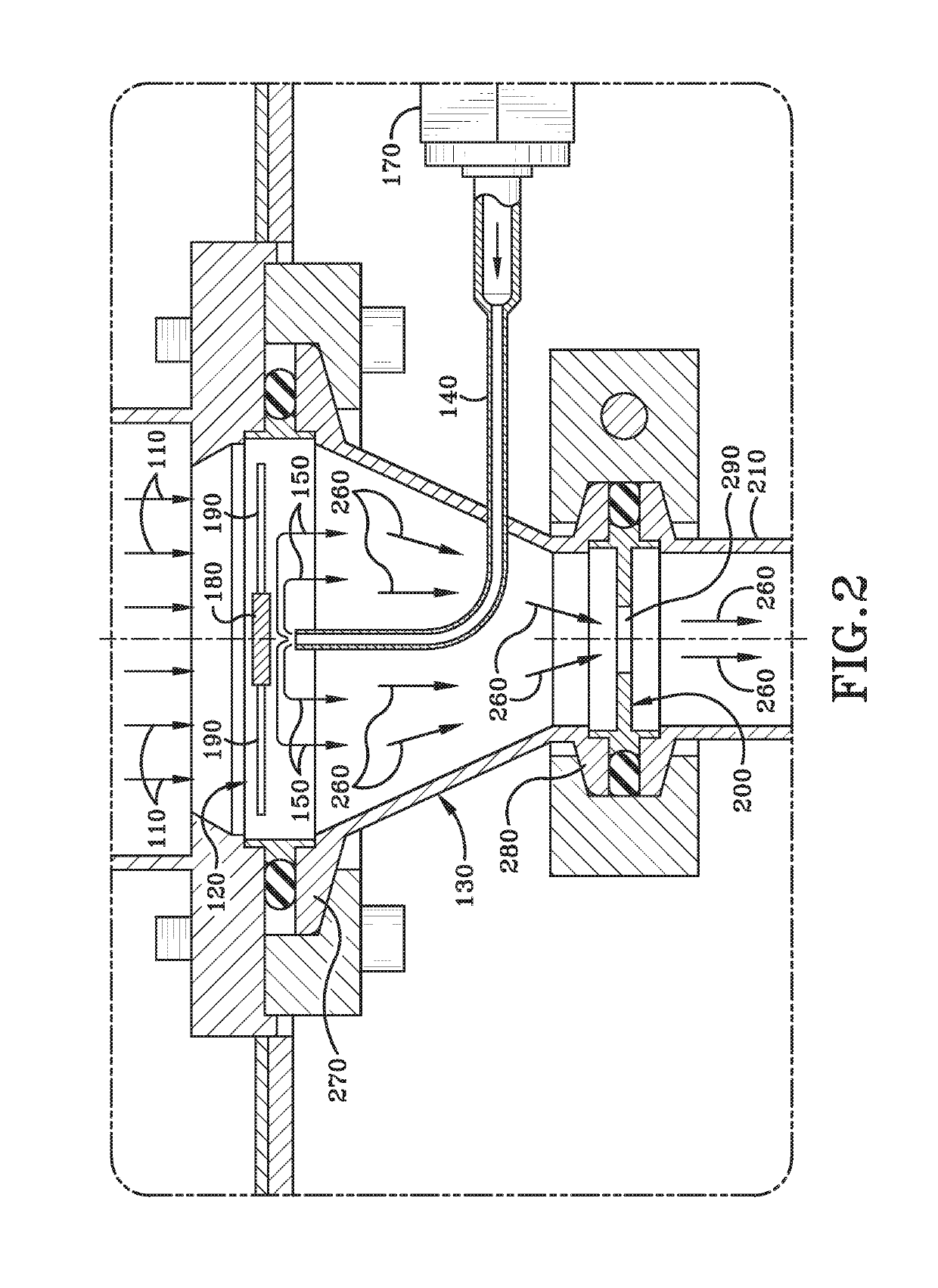
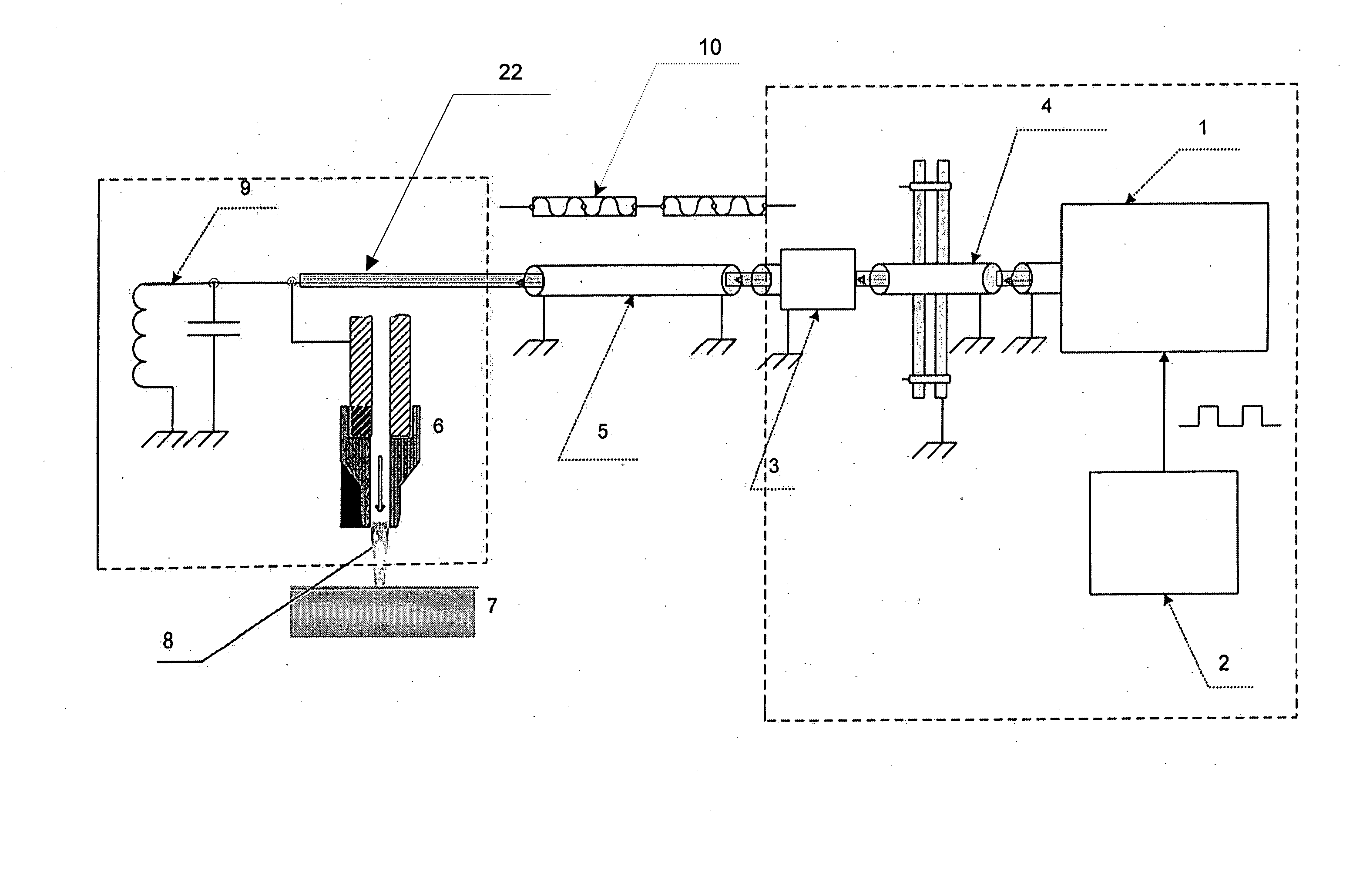
Counter flow mixer for process chamber
A counterflow mixing device for a process chamber is disclosed, comprising an injection tube that introduces a fluid in a manner counter to a flow of a post-plasma gas mixture traveling downward from a plasma source. The invention allows for proper mixing of the fluid as well as avoiding recombination of generated ions and radicals.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Counter flow mixer for process chamber
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
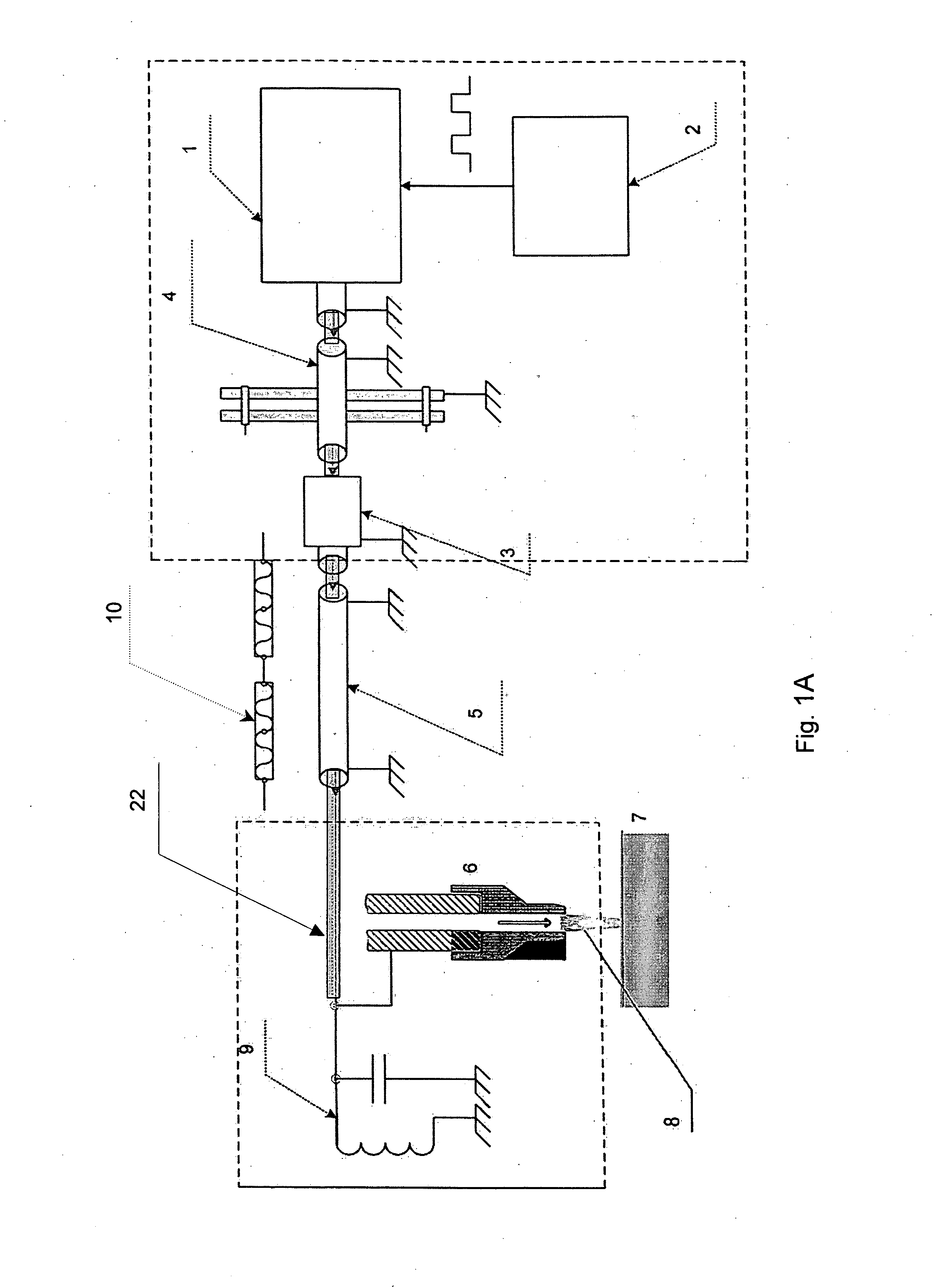
System and method for treating biological tissue with a plasma gas discharge
ActiveUS20060189976A1Effective treatmentSurgical instrument detailsPlasma techniqueMedicineProduct gas
Devices and methods for treating biological tissue using a plasma gas-discharge are disclosed herein. An electrode for igniting a gas flow to form a plasma gas-discharge, wherein the electrode is configured within the device such that upon encountering a surface of the biological tissue by the electrode, a path of current from the electrode to the surface of the biological tissue is formed, thereby igniting the gas flow and forming the plasma gas-discharge. In some embodiments, electromagnetic interactions between the treated biological tissue and the plasma gas discharge traversing the electromagnetic interaction gap shape the profile of the plasma gas discharge. According to some embodiments, the device includes an electrode for igniting gas of the gas flow, and electromagnetic interactions between the electrode and the skin determine, at least in part, the electromagnetic interactions that shape the profile of the plasma gas discharge. In some embodiments, the device further includes a housing for providing support for the electrode, wherein the electrode is disposed relative to the housing such that the electrode is substantially electrically unshielded by the housing, and the electrode is positioned to electromagnetically interact with a surface of the biological tissue to shape, at least in part, the plasma profile. According to some embodiments, the presently disclosed device includes a dual-purpose nozzle-electrode for gas delivery and for igniting the gas flow. A method of transdermal ion delivery of a plasma flux to biological tissue as a means of treating the biological tissue is also provided.
Owner:ALMA LASERS LTD
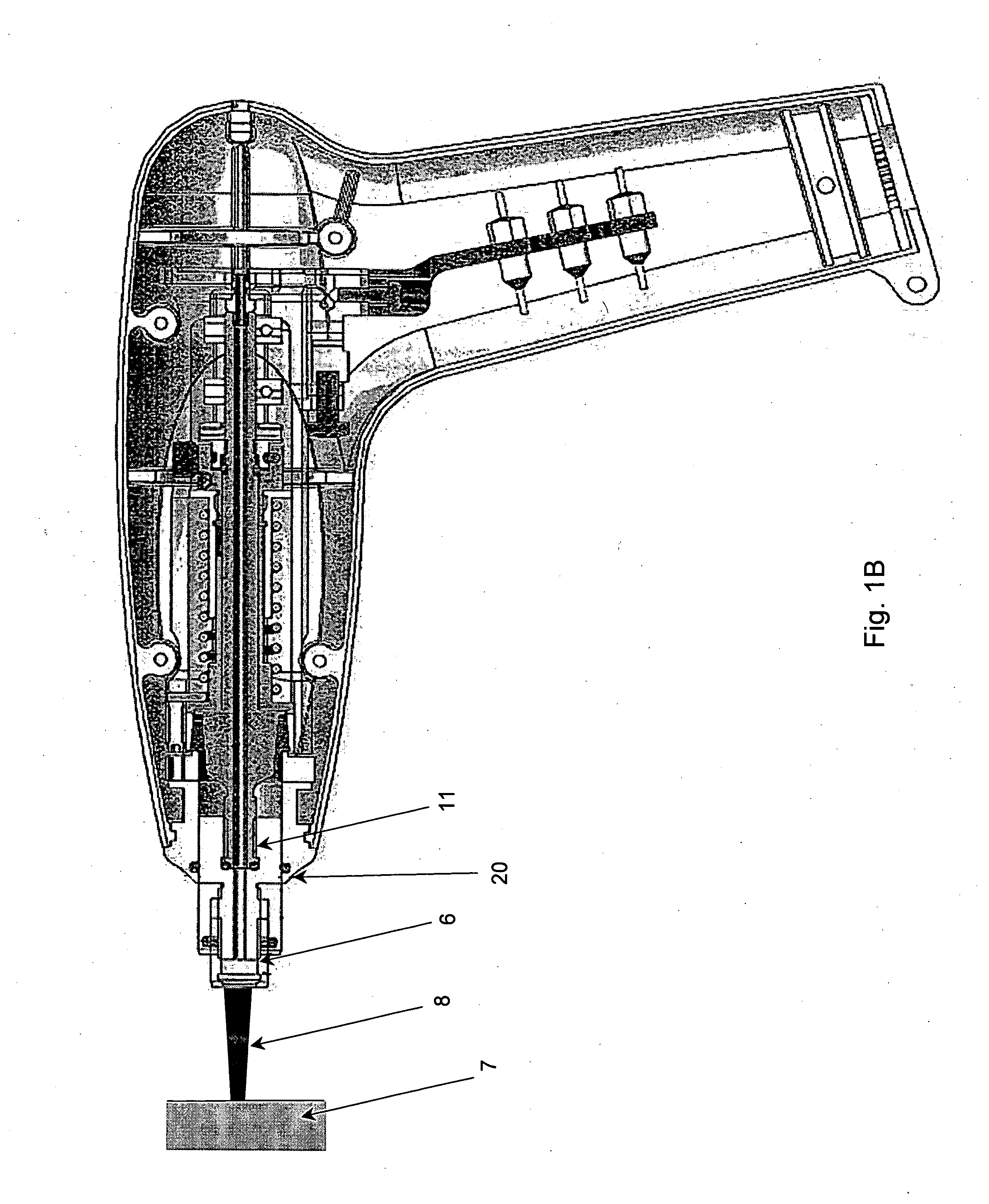
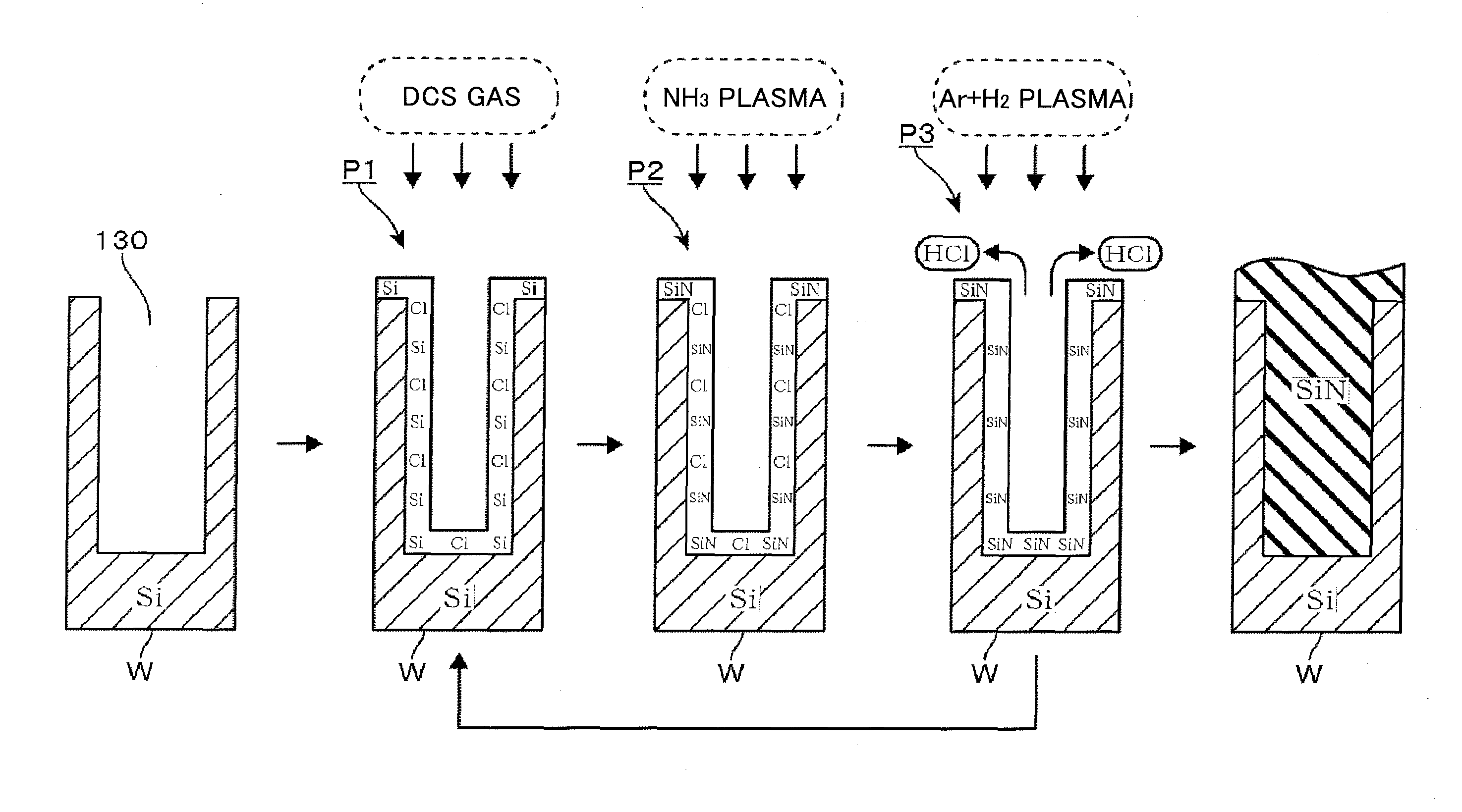
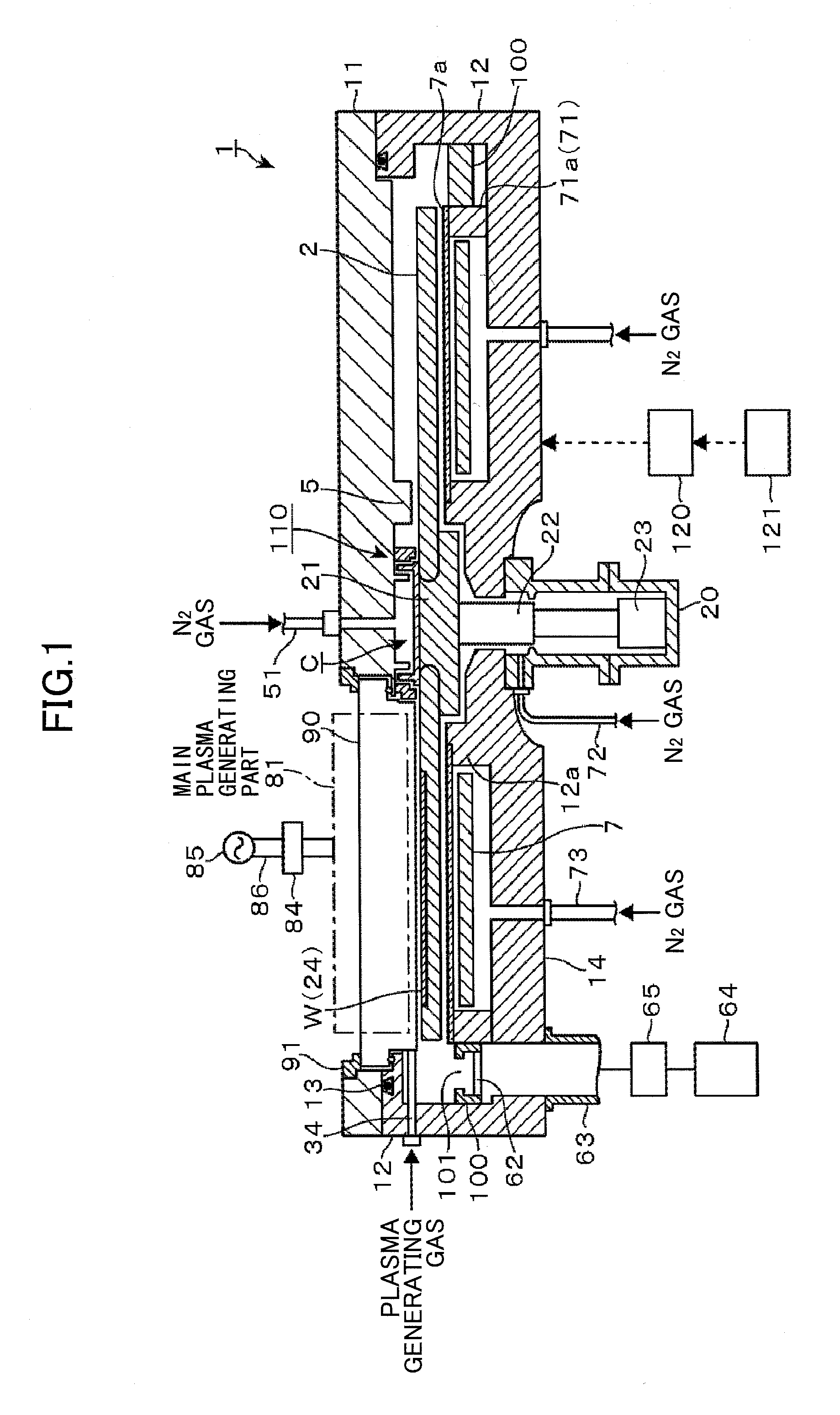
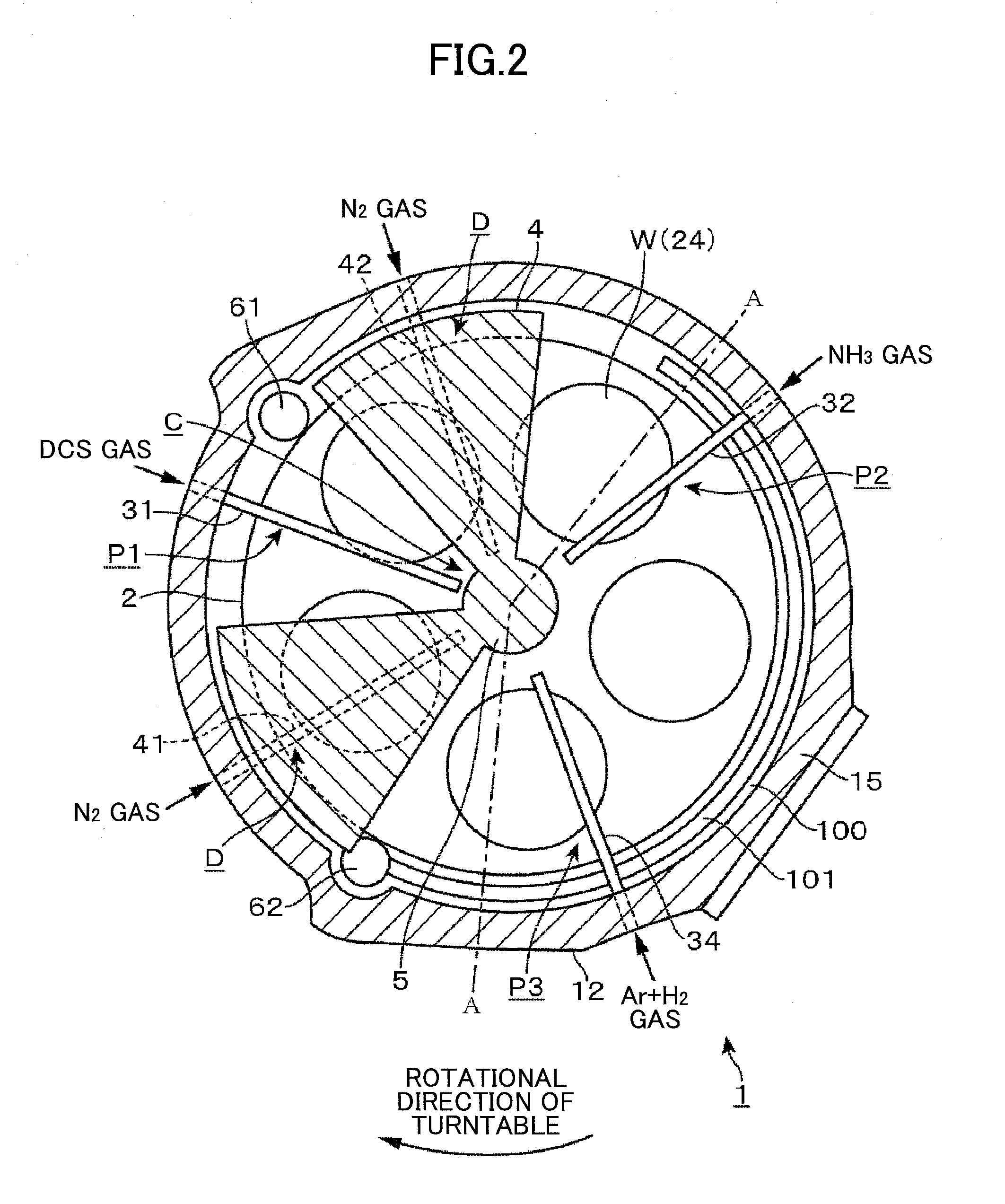
Film deposition apparatus, film deposition method and storage medium
ActiveUS20130059415A1Reduce plasma damageAvoid passingLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesEngineeringPlasma Gases
A film deposition apparatus includes a turntable having a substrate mounting area, a first plasma gas supplying part, a second plasma supplying part, a first plasma gas generating part to convert the first plasma generating gas to first plasma, and a second plasma generating part provided away from the first plasma generating part in a circumferential direction and to convert the second plasma generating gas to second plasma. The first plasma generating part includes an antenna facing the turntable so as to convert the first plasma generating gas to the first plasma, and a grounded Faraday shield between the antenna and an area where a plasma process is performed, and to include plural slits respectively extending in directions perpendicular to the antenna and arranged along an antenna extending direction to prevent an electric field from passing toward the substrate and to pass a magnetic field toward the substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Apparatus for generating remote plasma
ActiveUS20100096367A1Eliminate chargeImprove film qualityElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRemote plasmaPulsed DC
Provided is an apparatus for generating remote plasma, which can improve thin-film quality by preventing an arc at a bias electrode. The apparatus includes a radio frequency (RF) electrode installed inside an upper portion of a chamber, a bias electrode installed apart from the RF electrode, and including a plurality of through holes through which plasma passes, wherein a bias power is supplied to the bias electrode, a plasma generating unit formed between the RF electrode and the bias electrode, wherein a plasma gas is supplied to the plasma generating unit, and a ground electrode installed under and spaced apart from the bias electrode, and including plasma through holes corresponding to the through holes of the bias electrode, wherein a pulsed DC bias of a second voltage level, which has a first voltage level periodically, is applied to the bias electrode.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
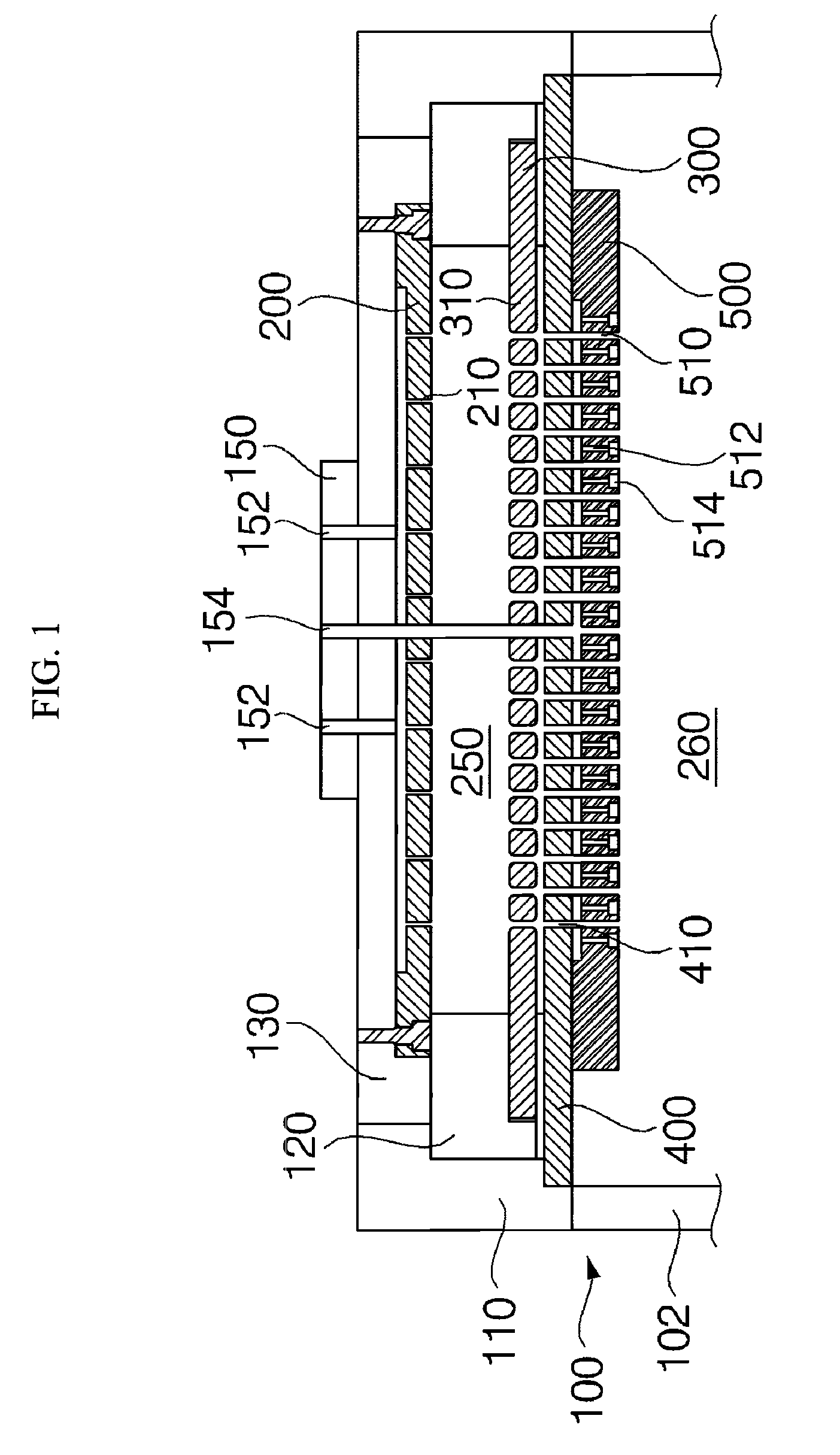
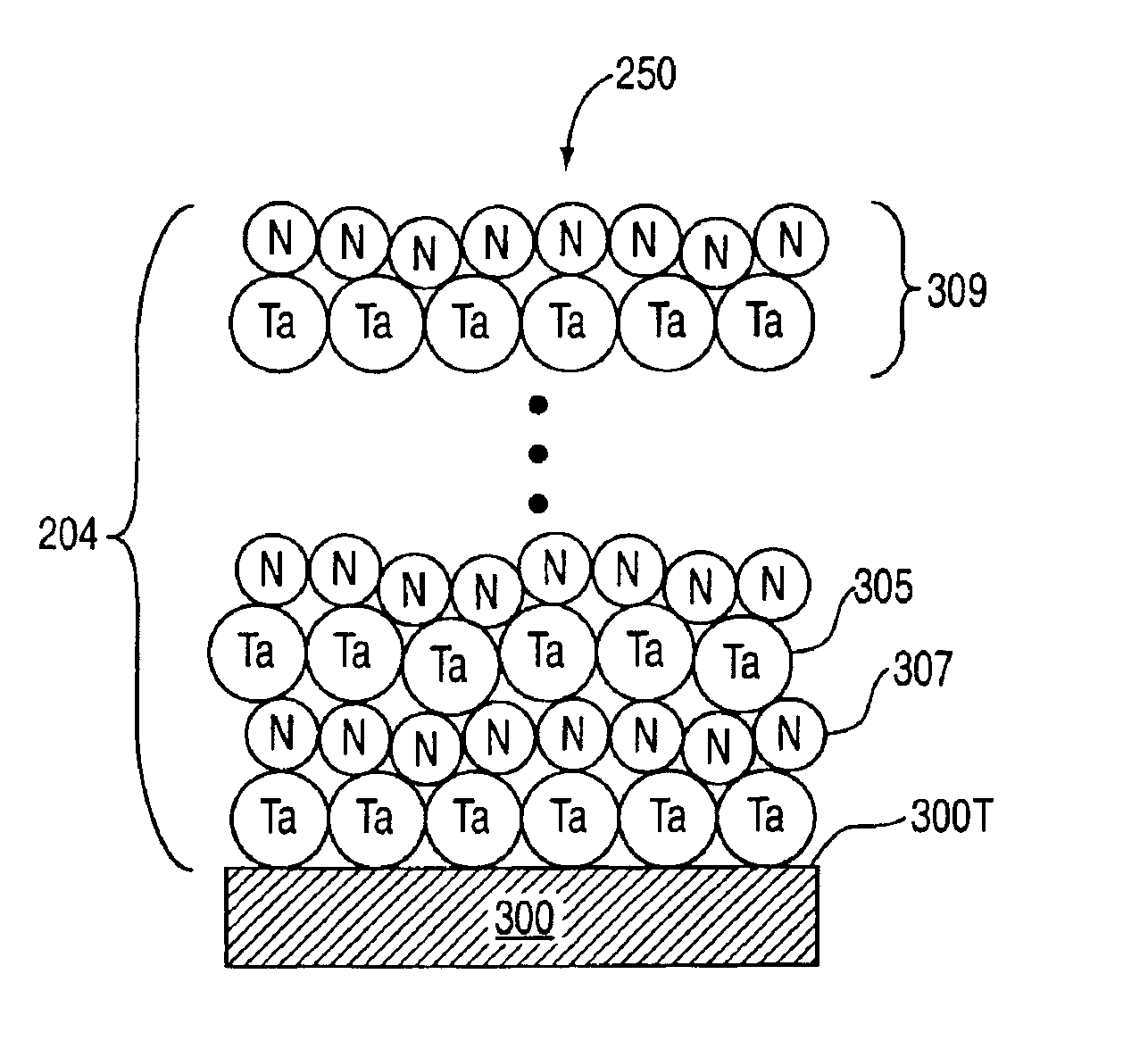
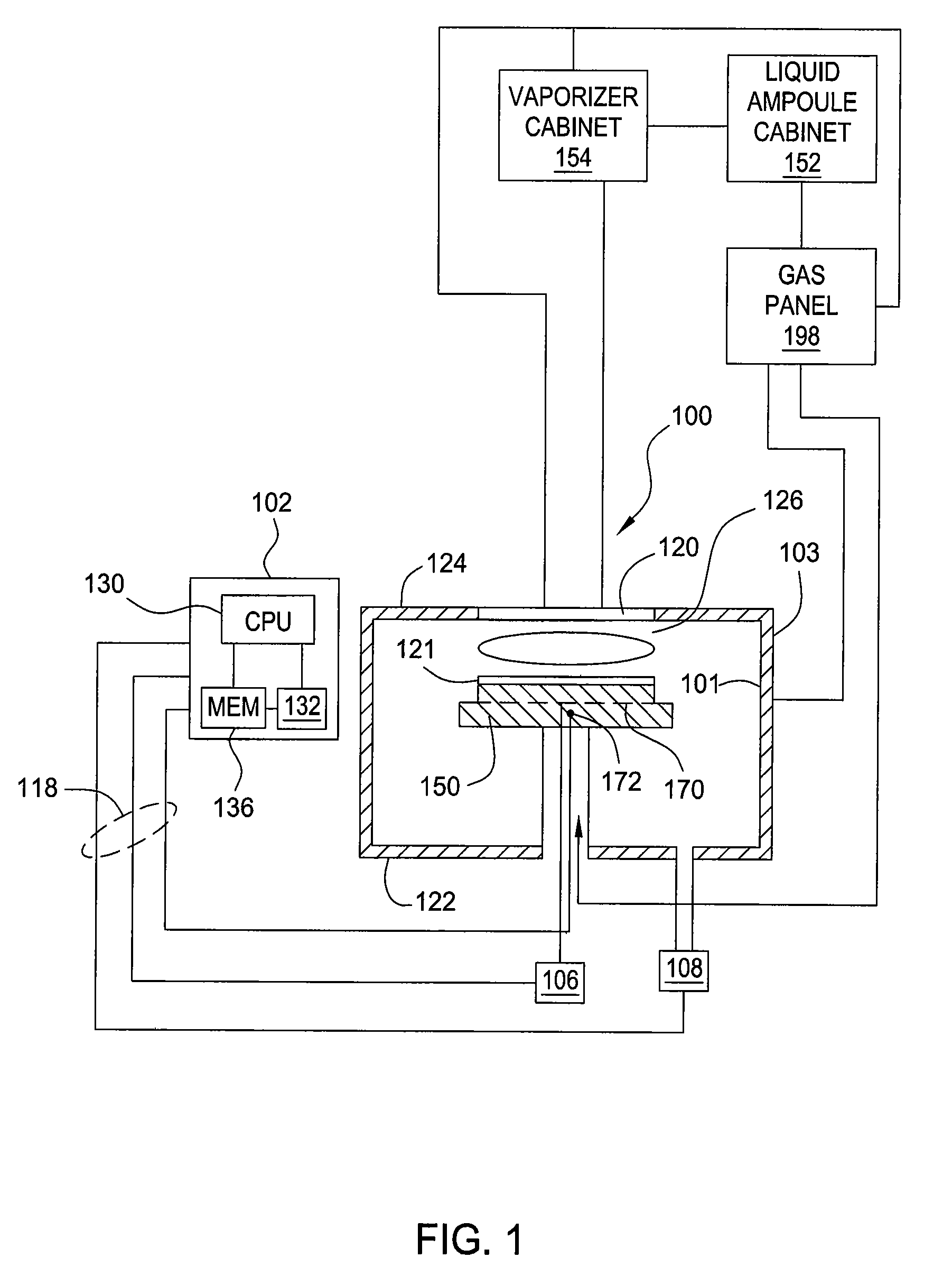
Formation of a tantalum-nitride layer
InactiveUS6951804B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingMetal interconnectTantalum nitride
A method of forming a tantalum-nitride layer (204) for integrated circuit fabrication is disclosed. Alternating or co-reacting pulses of a tantalum containing precursor and a nitrogen containing precursor are provided to a chamber (100) to form layers (305, 307) of tantalum and nitrogen. The nitrogen precursor may be a plasma gas source. The resultant tantalum-nitride layer (204) may be used, for example, as a barrier layer. As barrier layers may be used with metal interconnect structures (206), at least one plasma anneal on the tantalum-nitride layer may be performed to reduce its resistivity and to improve film property.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Carbon nanostructures and process for the production of carbon-based nanotubes, nanofibres and nanostructures
InactiveUS20070183959A1Enhanced interactionImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesThermal insulationNanostructure
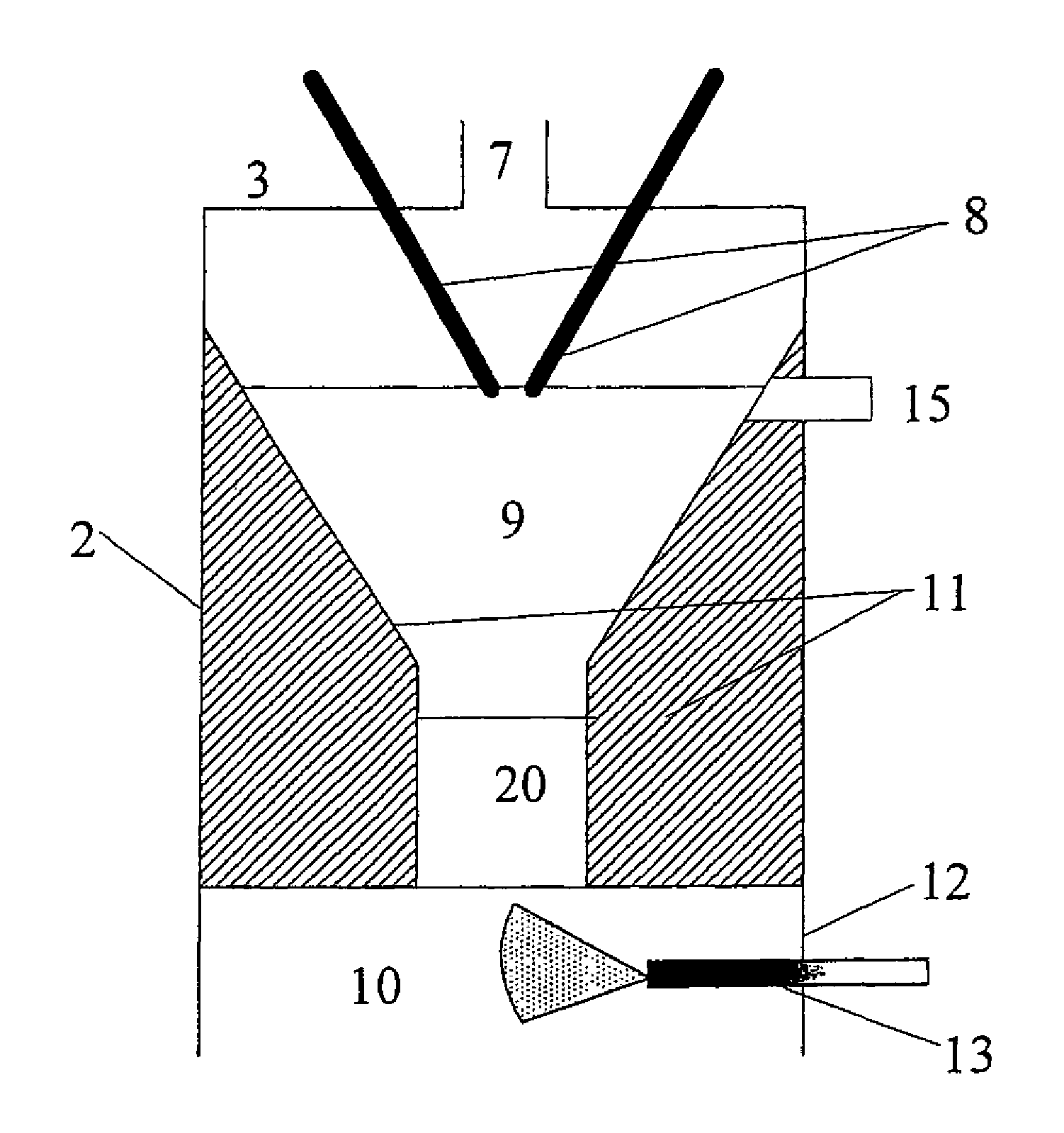
Continuous process for the production of carbon-based nanotubes, nanofibres and nanostructures, comprising the following steps: generating a plasma with electrical energy, introducing a carbon precursor and / or one or more catalysers and / or carrier plasma gas in a reaction zone of an airtight high temperature resistant vessel optionally having a thermal insulation lining, vaporizing the carbon precursor in the reaction zone at a very high temperature, preferably 4000° C. and higher, guiding the carrier plasma gas, the carbon precursor vaporized and the catalyser through a nozzle, whose diameter is narrowing in the direction of the plasma gas flow, guiding the carrier plasma gas, the carbon precursor vaporized and the catalyses into a quenching zone for nucleation, growing and quenching operating with flow conditions generated by aerodynamic and electromagnetic forces, so that no significant recirculation of feedstocks or products from the quenching zone into the reaction zone occurs, controlling the gas temperature in the quenching zone between about 4000° C. in the upper part of this zone and about 50° C. in the lower part of this zone and controlling the quenching velocity between 103 K / s and 106 K / s quenching and extracting carbon-based nanotubes, nanofibres and other nanostructures from the quenching zone, separating carbon-based nanotubes, nanofibres and nanostructures from other reaction products.
Owner:ТІМКАЛ SА +1
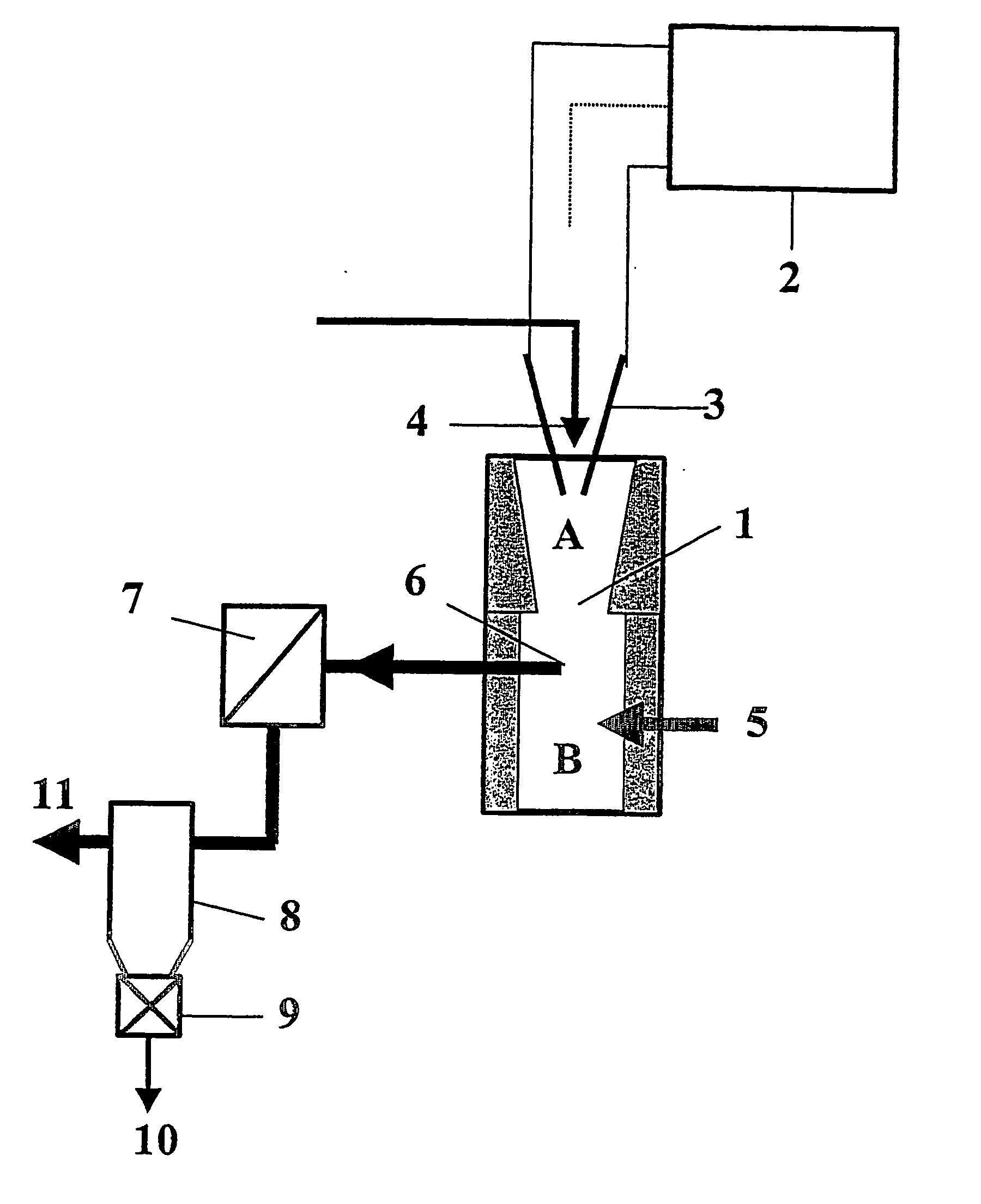
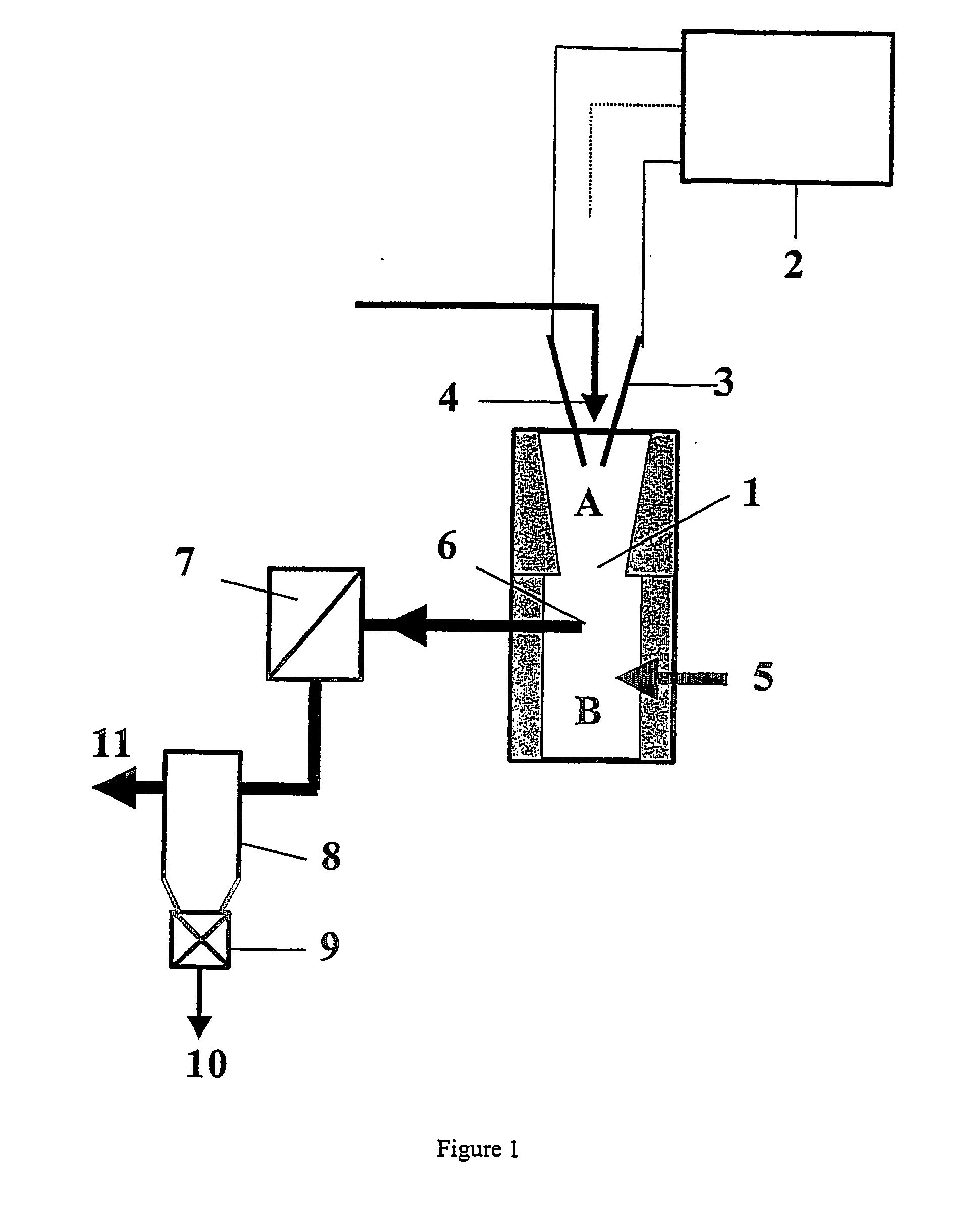
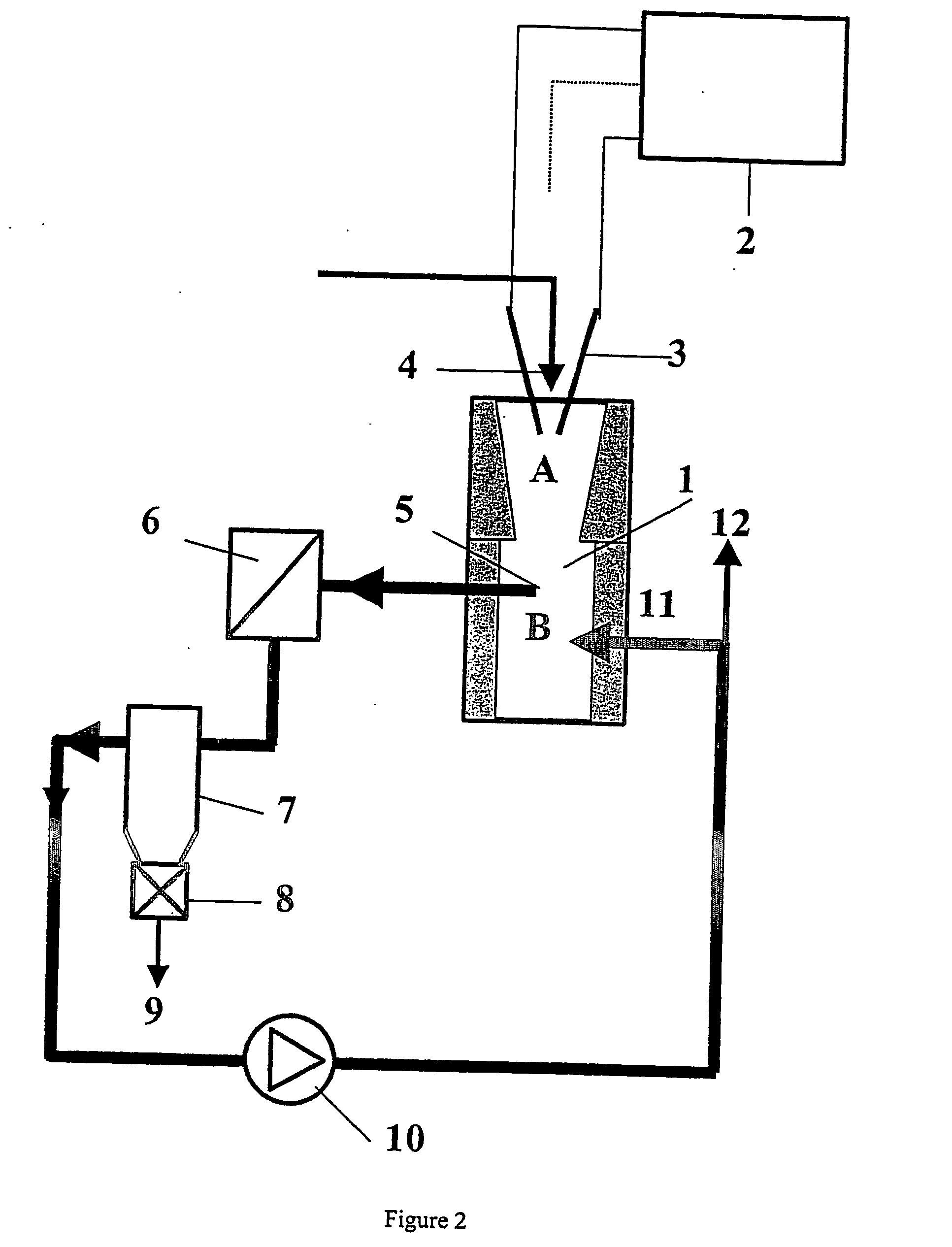
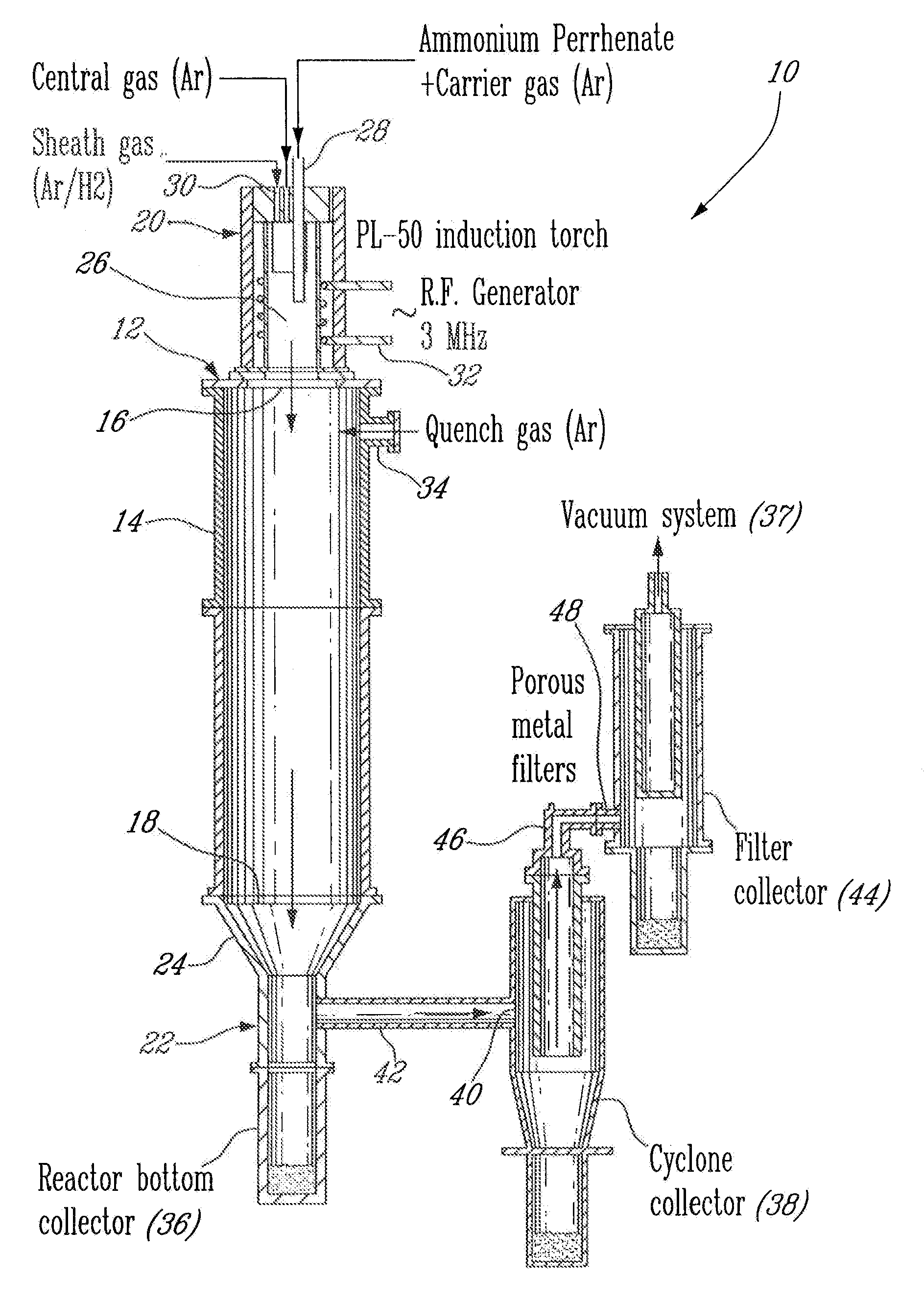
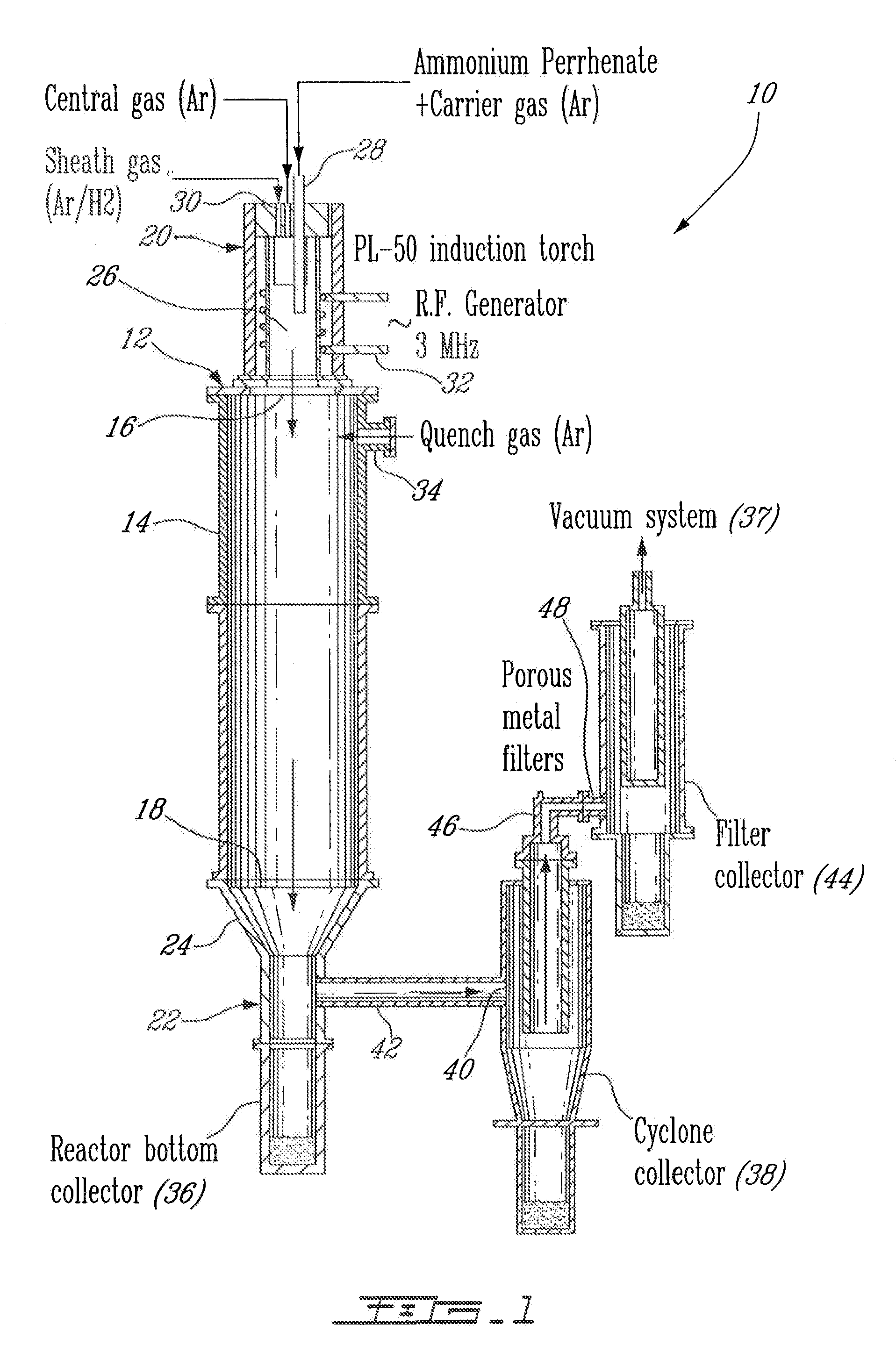
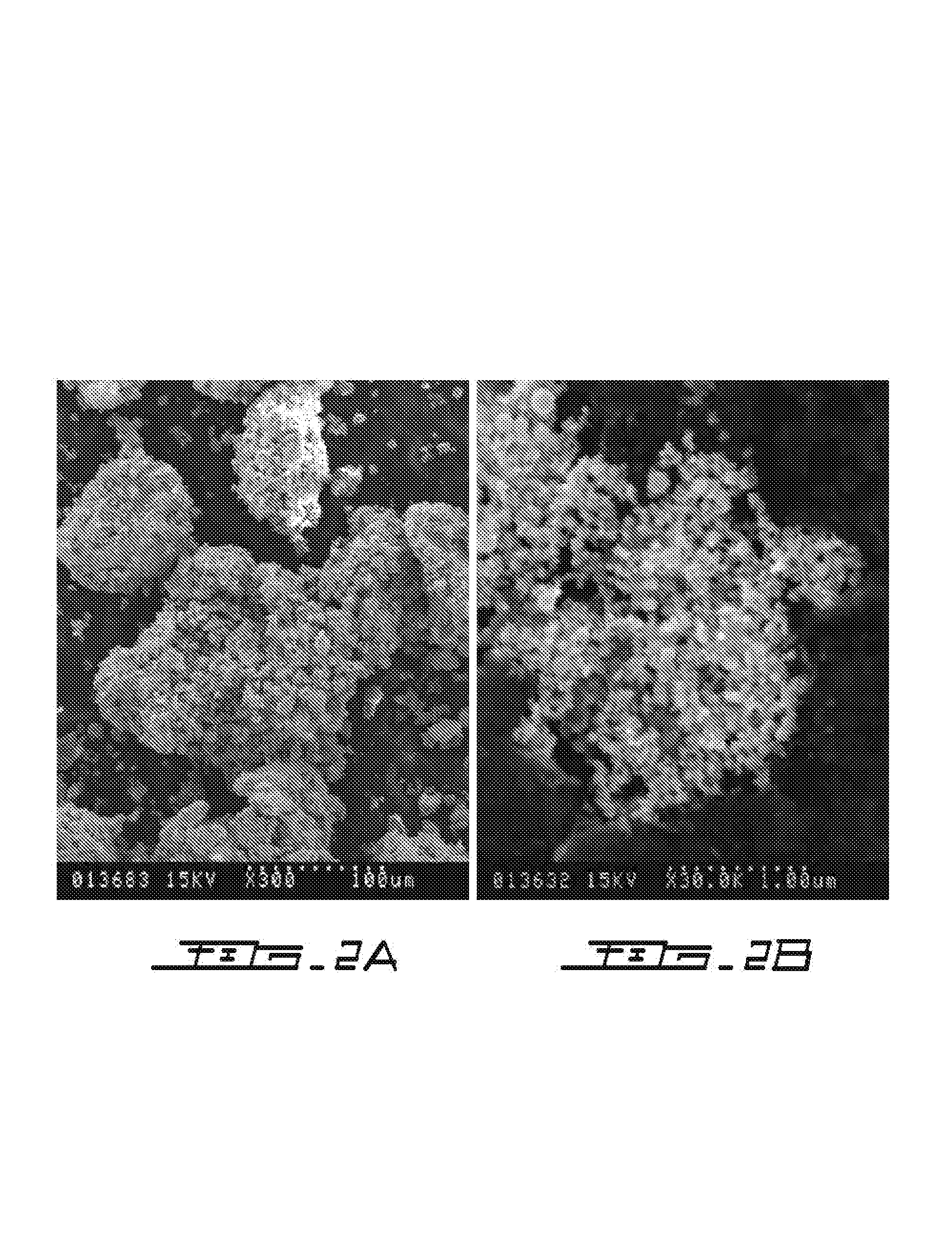
Process for plasma synthesis of rhenium nano and micro powders, and for coatings and near net shape deposits thereof and apparatus therefor
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
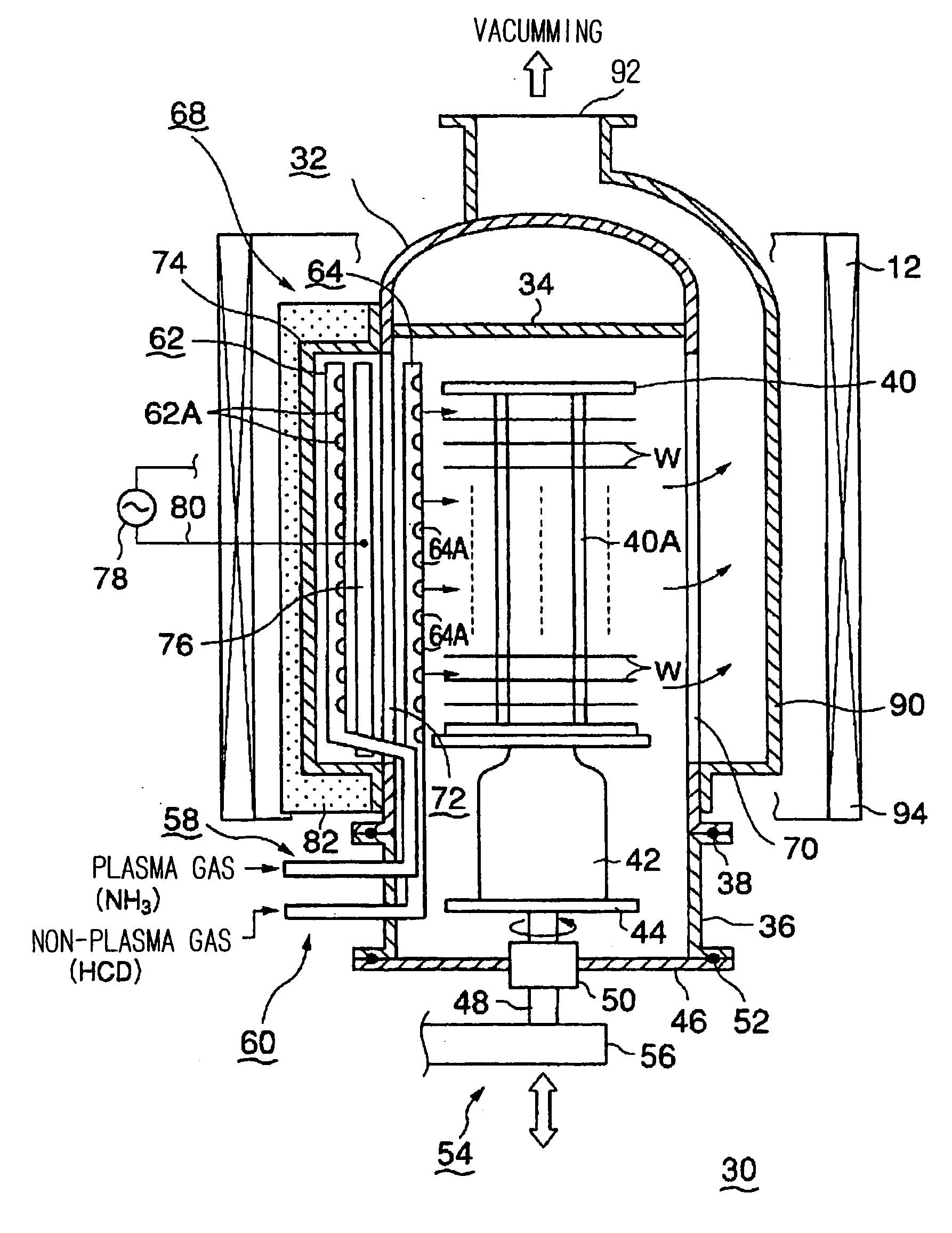
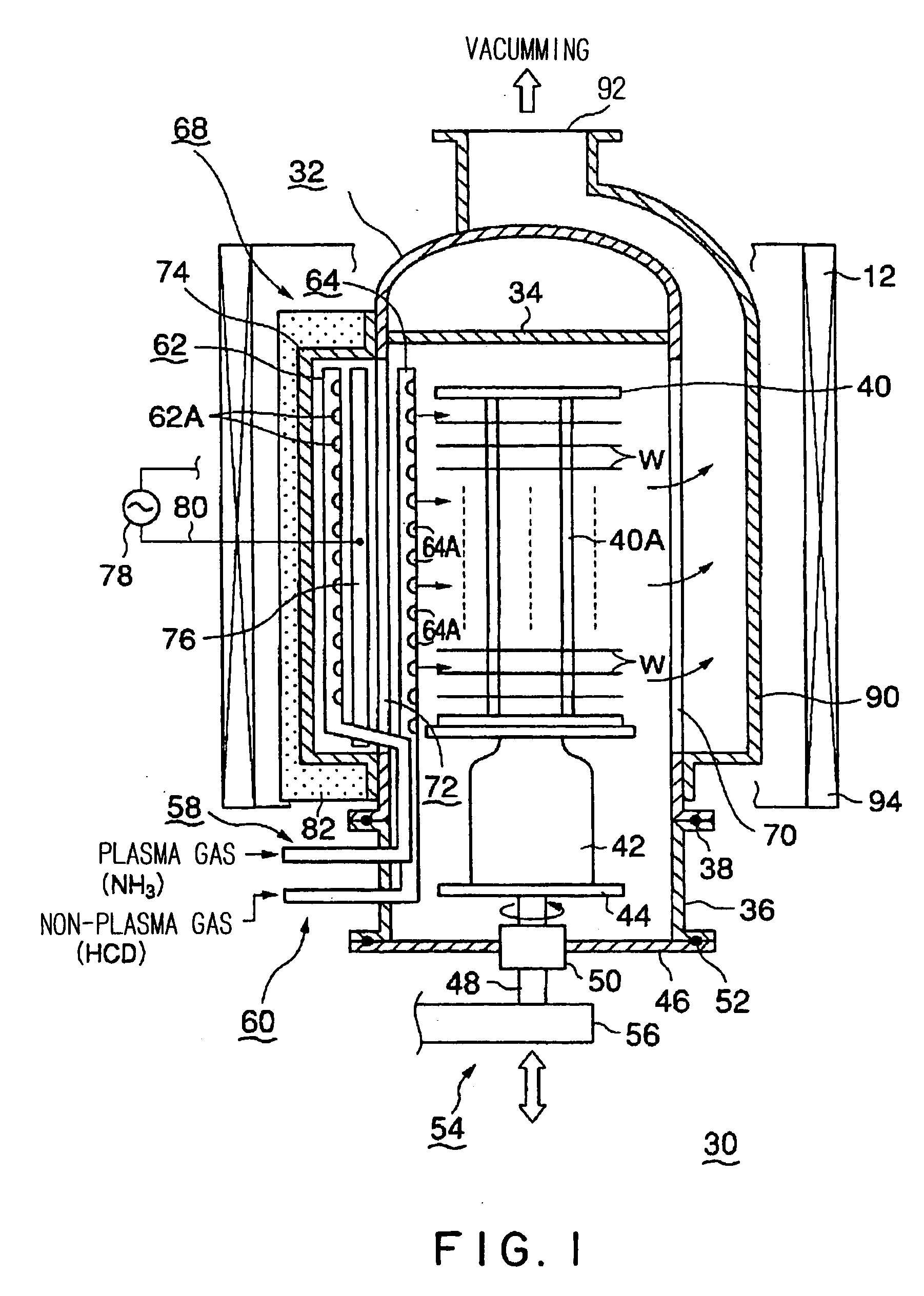
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20070137572A1Avoid damageEfficient use ofElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma Gases
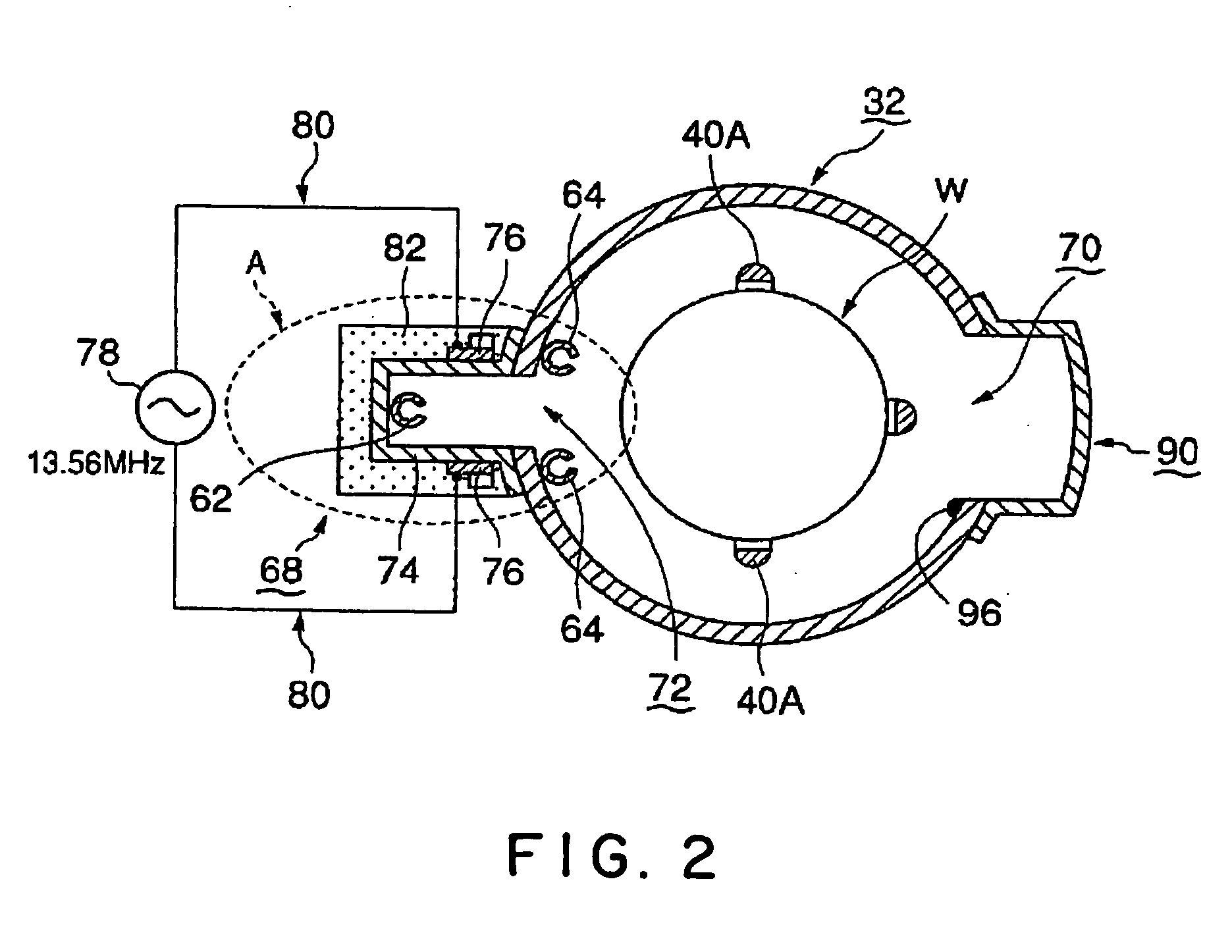
The invention is intended, in a vertical type plasma processing apparatus, to prevent damage to process objects due to a plasma, and to suppress the generation of sputter due to hollow cathode discharge and the plasma, without lowering the radical utilization efficiency. A part of the inner surface of the side wall of a processing vessel 32 is provided with a vertically extending recess 74. A plasma gas supplied from a plasma gas nozzle 62 disposed in the recess 74 is converted into a plasma in an area PS between plasma electrodes 76 in the recess 74, and leaves the recess 74 toward the process objects W.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
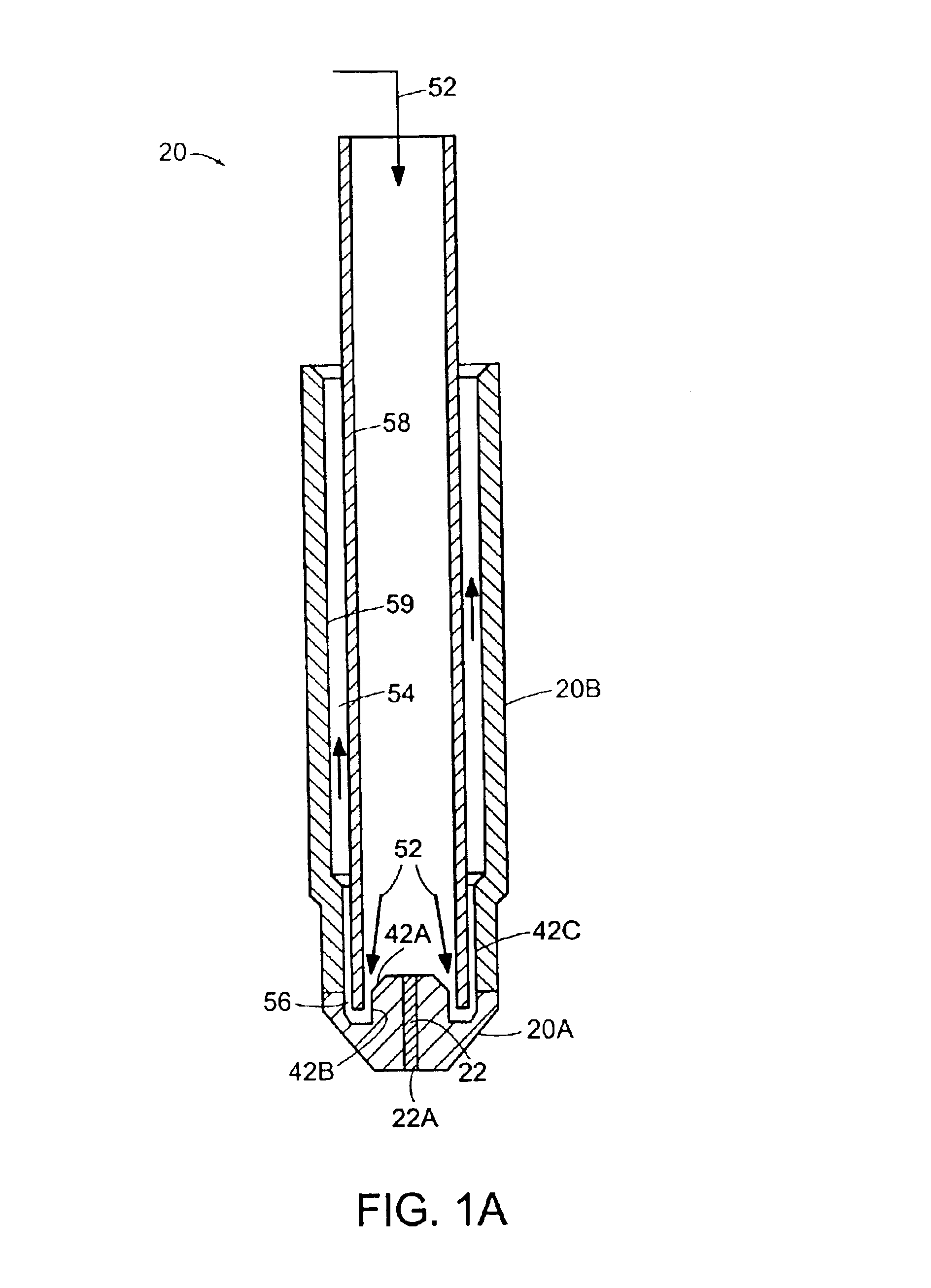
Plasma cutting apparatus and control unit thereof
ActiveUS20050035093A1Improve cut qualityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusEngineeringPlasma Gases
Cutting quality of the product, in particular, hole cutting quality, in plasma arc cutting is improved. A control unit, which controls a plasma cutting apparatus for cutting a product from a plate material by moving a plasma torch at a cutting speed along a cutting path corresponding to the product shape to cut the plate material, while supplying an arc current and a plasma gas to the plasma torch and forming a plasma arc from a nozzle of the plasma torch to the plate material, conducts control so that, when a hole is cut, a cutting speed is lower, a value of the arc current value is smaller, and a plasma gas flow rate or pressure is less than those when a contour is cut.
Owner:KOMATSU IND CORP
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the semiconductor device
InactiveUS20030193090A1The process steps are simpleRun at high speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceCooking & baking
A semiconductor device capable of high speed operation with a substantially small interlayer capacitance is produced by steps of using an insulating film comprising an organic insulating film and an insulating film composed of an organometallic polymer material as an interlayer insulating film formed by coating, patterning the insulating film in a semi-thermosetting state, etching the organic insulating film as the lower layer by means of the organometallic polymer as a mask, using a plasma gas containing oxygen as the main component, and then conducting ultimate baking treatment of these insulating films.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Composite electrode for a plasma arc torch
InactiveUS6841754B2Improve heat transfer performanceImprove thermal conductivityElectric discharge heatingArc welding apparatusMetallic materialsCopper electrode
A plasma arc torch that includes a torch body having a nozzle mounted relative to a composite electrode in the body to define a plasma chamber. The torch body includes a plasma flow path for directing a plasma gas to the plasma chamber in which a plasma arc is formed. The nozzle includes a hollow, body portion and a substantially solid, head portion defining an exit orifice. The composite electrode can be made of a metallic material (e.g., silver) with high thermal conductivity in the forward portion electrode body adjacent the emitting surface, and the aft portion of the electrode body is made of a second low cost, metallic material with good thermal and electrical conductivity. This composite electrode configuration produces an electrode with reduced electrode wear or pitting comparable to a silver electrode, for a price comparable to that of a copper electrode.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
Hall field plasma accelerator with an inner and outer anode
InactiveUS6075321AWeaken energyIncreased heat rejectionElectric arc lampsMachines/enginesElectricityPlasma acceleration
A Hall field plasma accelerator with closed electron drift includes a composite anode including a housing with inner and outer walls which form an outer anode and an inner anode forming inner and outer distribution zones; the housing is electrically conductive and has an upstream end and an exit port electrically insulated from the housing; the composite anode includes an input distribution system for introducing plasma gas into the distribution zones; poles establish a magnetic field across the exit port and a cathode establishes an electron flow through the magnetic field toward the composite anode and creates an electric field through the exit port; the electrons ionize the plasma gas that is accelerated by the electric field through the exit port.
Owner:BUSEK
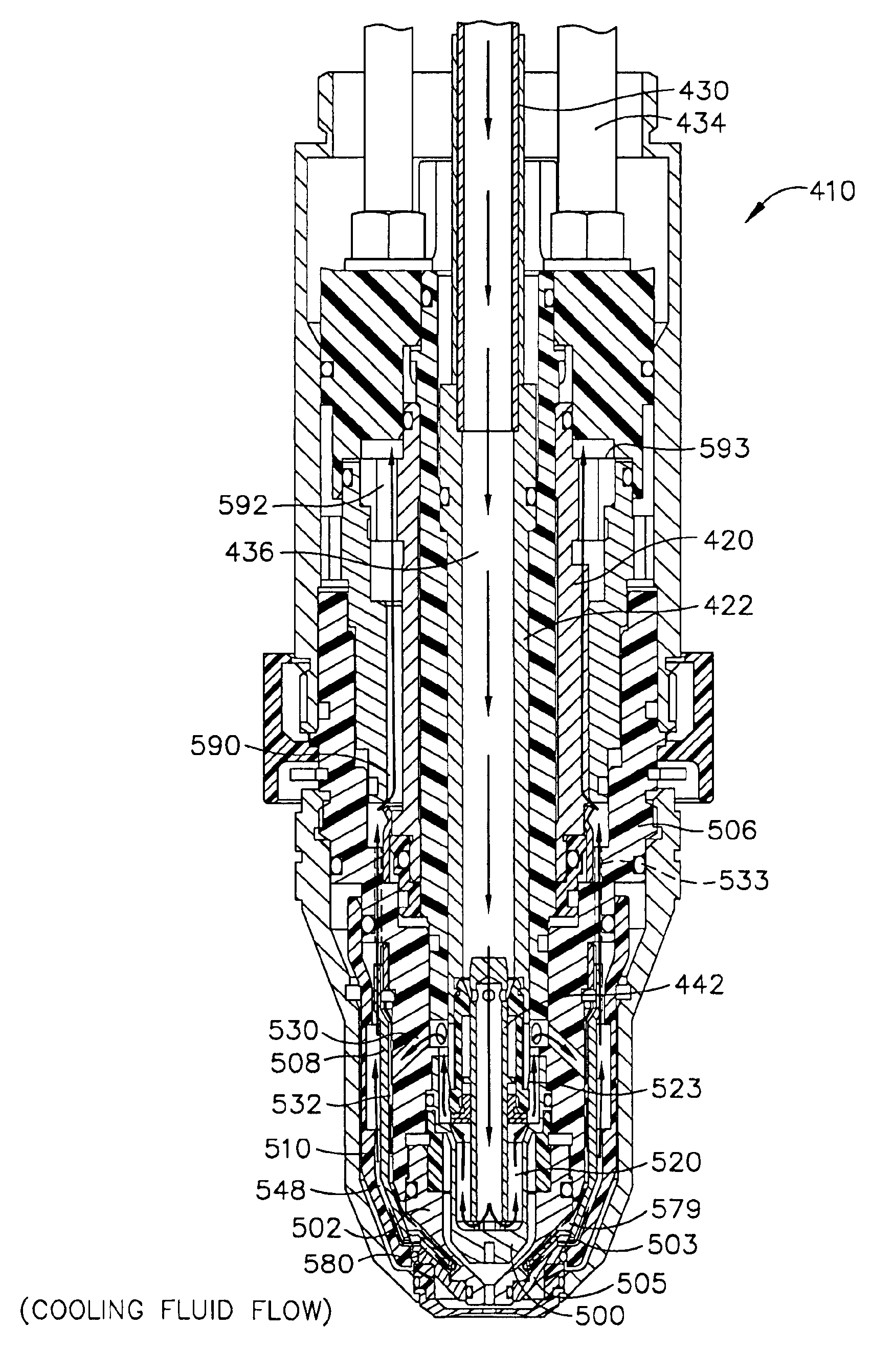
Plasma arc torch cooling system
InactiveUS6946616B2Precision coolingHigh trafficSupport devices with shieldingPlasma welding apparatusRadial positionEngineering
Owner:VICTOR EQUIP
Method and Apparatus for Applying Material to Glass
Abstract of Disclosure A method of applying a polymer to a glass surface includes applying atmospheric plasma to a glass surface, applying a film of polymerizable fluid to the surface and curing the film with high-energy radiation. Apparatus for applying atmospheric plasma includes positive and ground electrodes, and an emitter strip of porous material with a plasma gas diffusing between the electrodes and through the emitter strip onto the glass surface.
Owner:GLASSHIELD PATENT HLDG
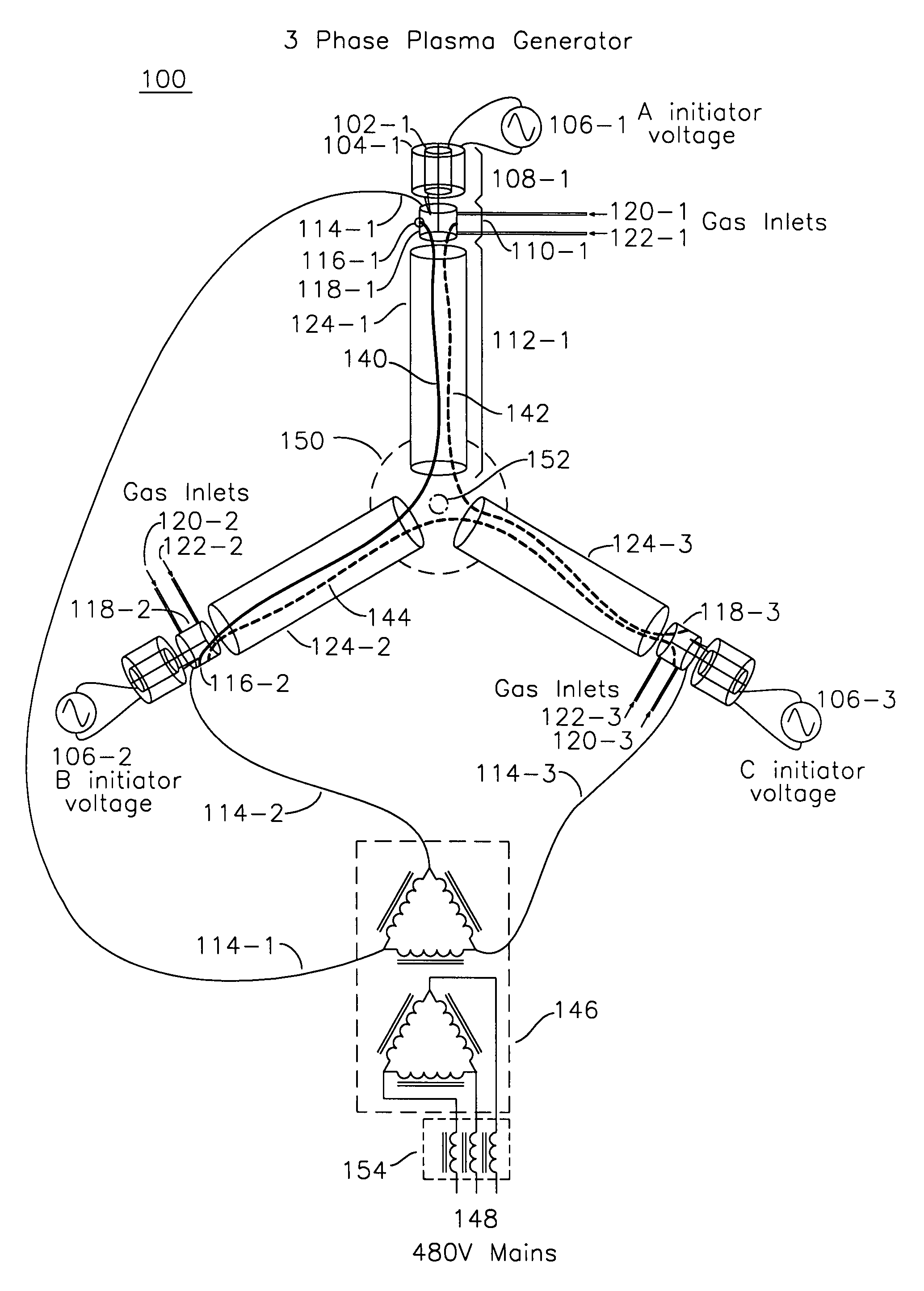
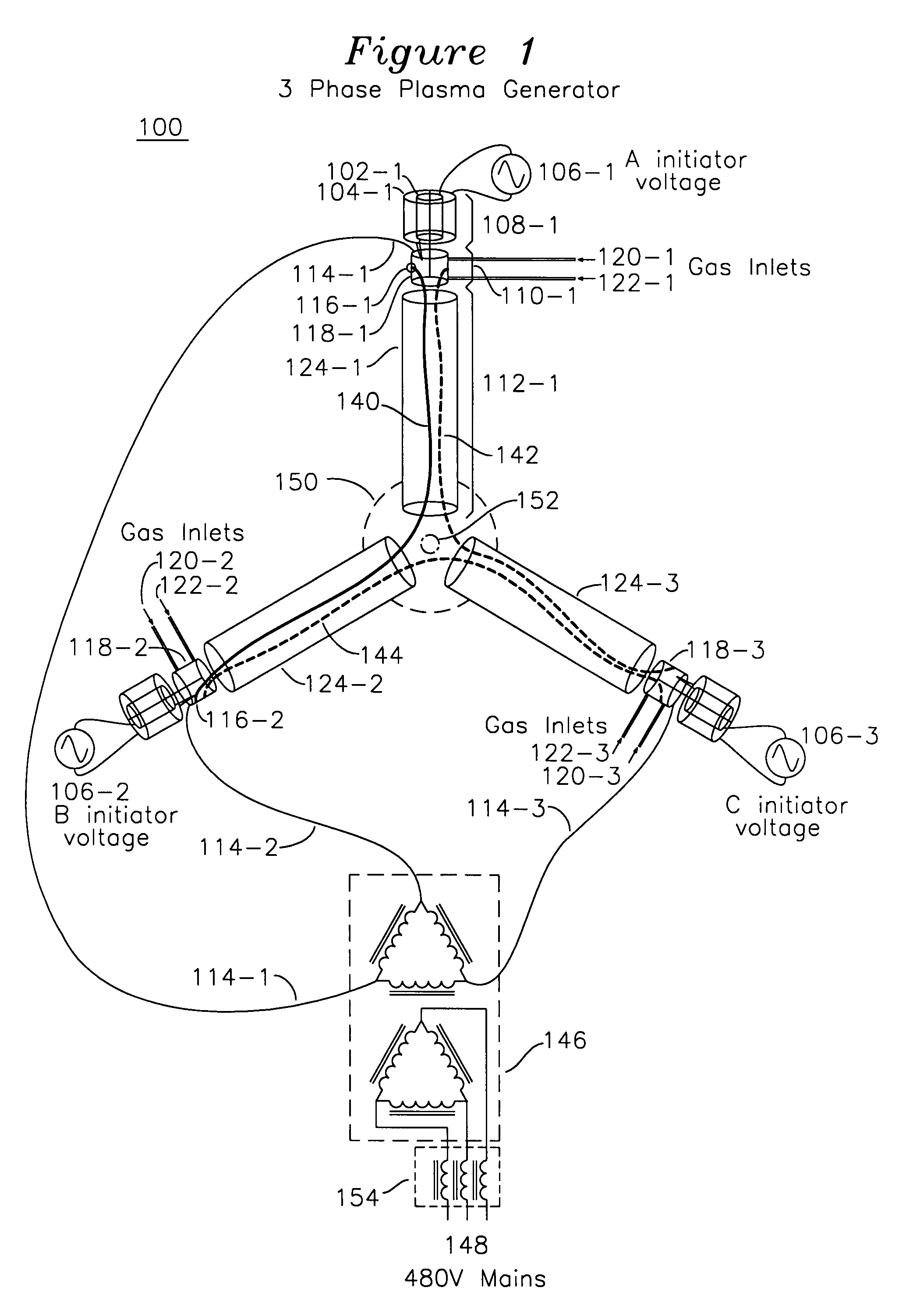
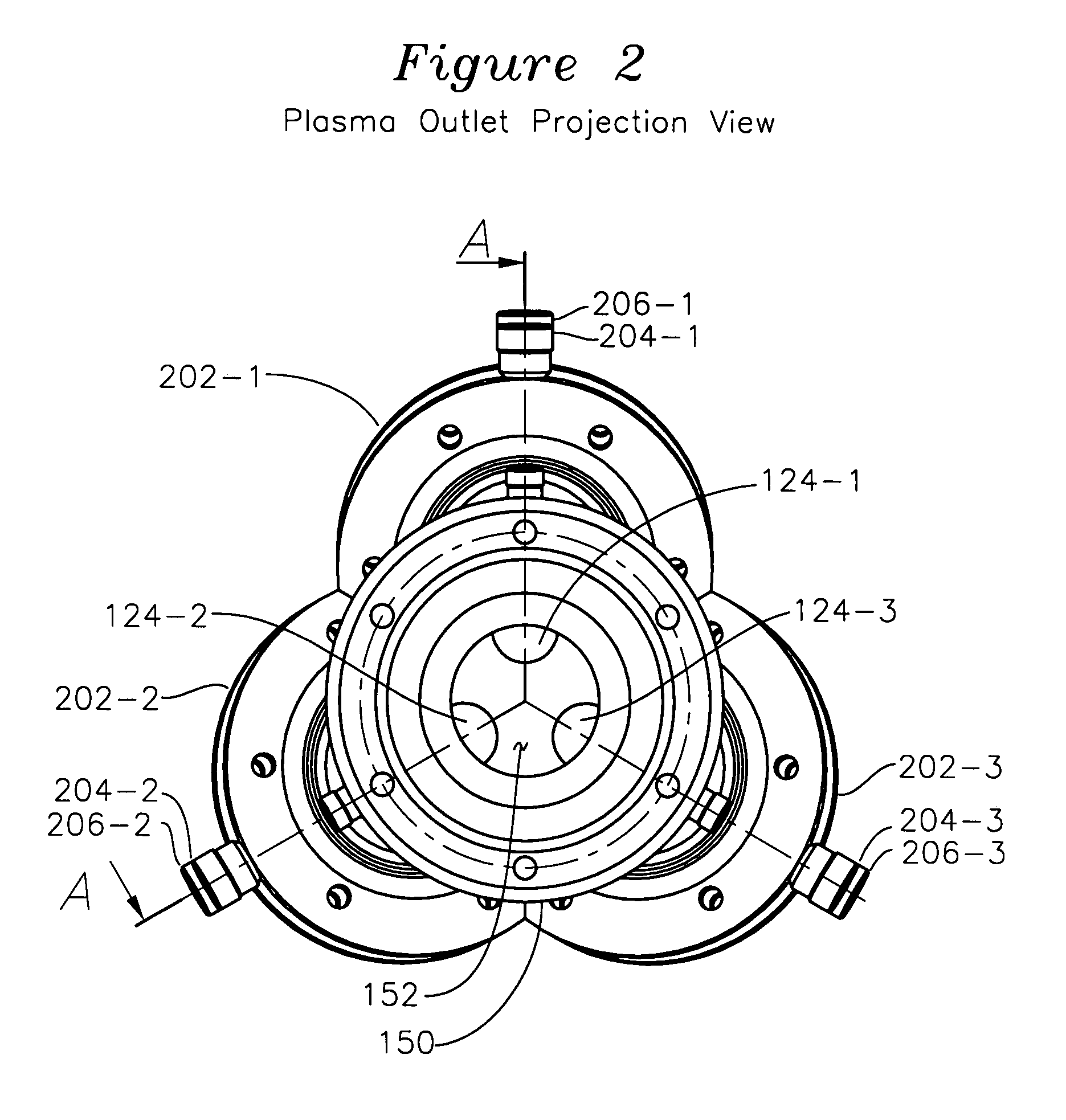
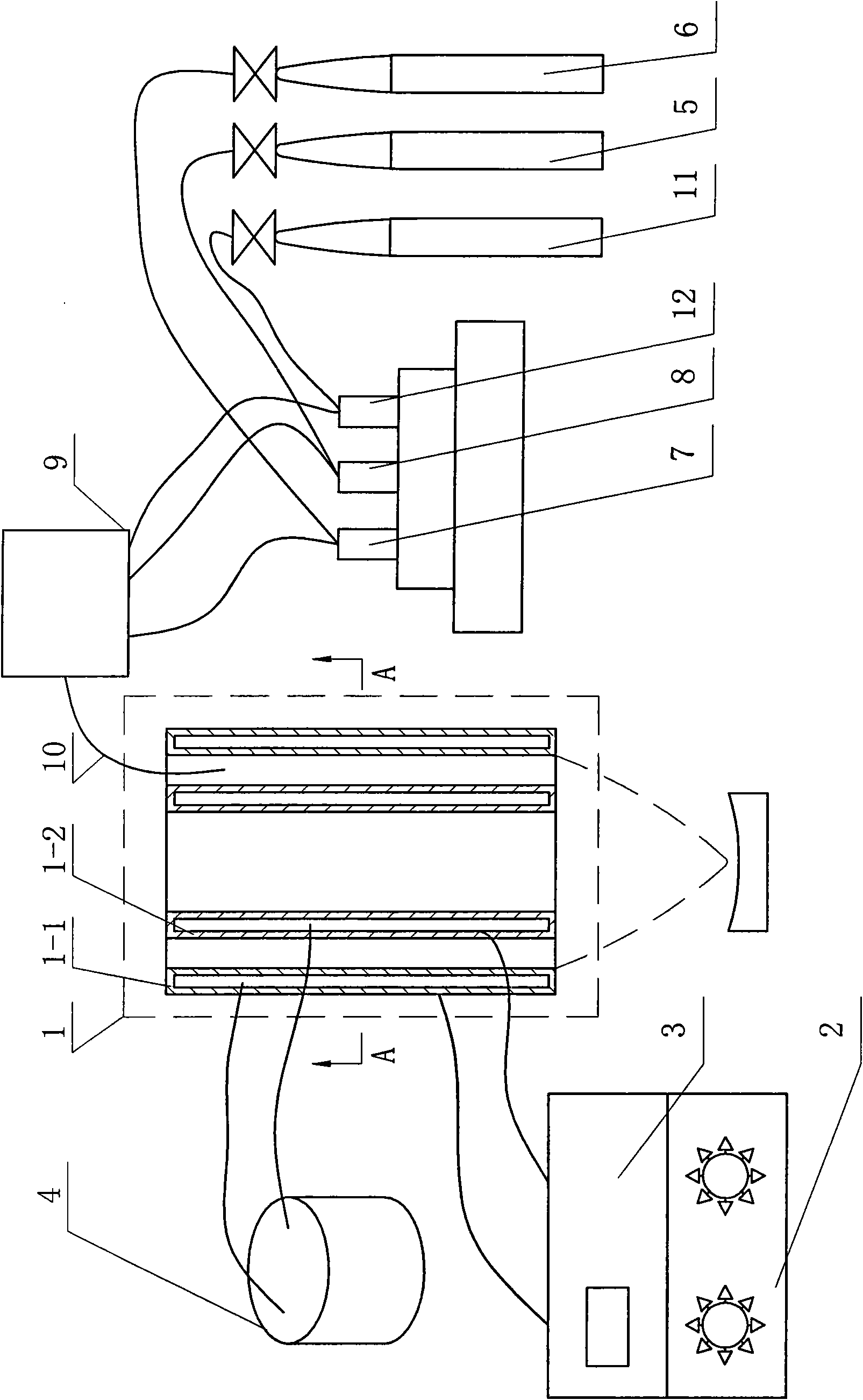
Alternating current multi-phase plasma gas generator with annular electrodes
InactiveUS7411353B1Preventing spot wearElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPlasma generatorThree-phase
A plasma generator for three phase mains alternating current operation has three plasma generation tubes interconnected with a nozzle, each plasma generation tube having a plasma initiator for forming a plasma into an electrode ring, the electrode ring including substantially tangential gas introduction orifices which cause gas entering the electrode ring to helically rotate. Each of the electrode rings is coupled to a unique one of the three phases of AC voltage supply, such that when the initiator plasma is introduced into one of the electrode rings, a plasma discharge occurs with a path from the electrode ring, through the plasma generation tube, and to a different electrode ring. Each electrode ring has gas introduced in a helically rotating manner such that the erosion of the surface of the electrode ring is uniform over the entire surface, and minimally erosive in a single arc attachment spot, since the arc spot is constantly moving as provided by the helical trajectory of the gas entering the electrode.
Owner:OAKS PLASMA +1
Method of polishing normal pressure plasma
The normal pressure plasma polishing method is provided. The normal pressure plasma polishing method includes providing plasma gas and reaction gas in the volume ratio of 4-1000; and starting RF power source and increasing power gradually while controlling the reflected power to zero, with the initial effective power being 180-240 W, normal power being 400-1200 W, and maximum power being 1500 W. The present invention realizes super smooth surface machining by means of plasma chemical reaction at normal pressure, and has no need of vacuum chamber, low cost, wide application range, high machining efficiency, no surface damage and contamination, and high surface smoothness up to 1nm Ra.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
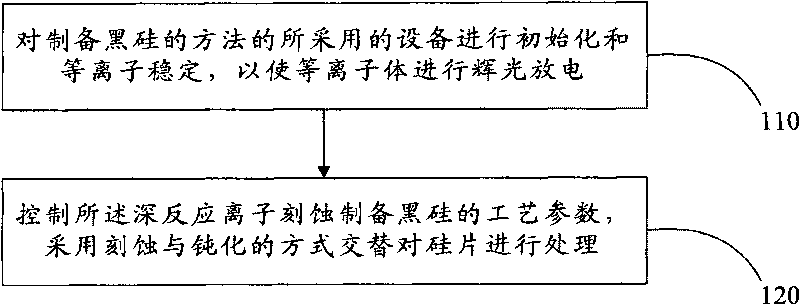
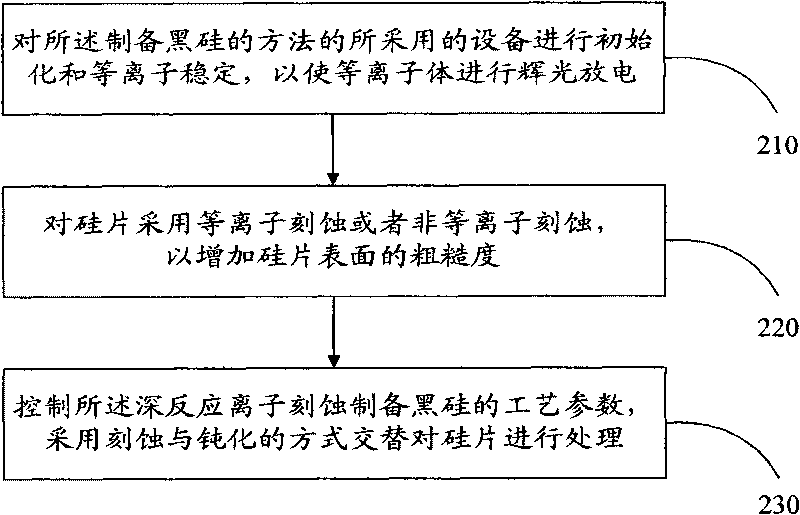
Maskless method for preparing black silicon by deep reactive ion etching
ActiveCN101734611AImprove efficiencyWon't breakNanostructure manufactureDecorative surface effectsNanostructureLarge range
The invention discloses a maskless method for preparing black silicon by deep reactive ion etching, which comprises the following steps: performing initialization and plasma stability on equipment adopted by the method for preparing the black silicon so as to make plasma perform glow discharge; and controlling technological parameters for preparing the black silicon by deep reactive ion etching, and adopting etching and passivating modes to alternately process a silicon chip, wherein the parameters comprise plasma gas flow, panel etching power, panel passivating power, coil power, and etching and passivating cycle and temperature. The maskless method directly performs plasma processing on the surface of the silicon chip, and can generate large-range high-intensity nanostructures on the surface of the silicon chip in case of no nano mask by adjusting and selecting proper etching technological parameters. Meanwhile, the method for preparing the black silicon has high efficiency and low cost, and can be integrated with other micro-fabrication technology.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
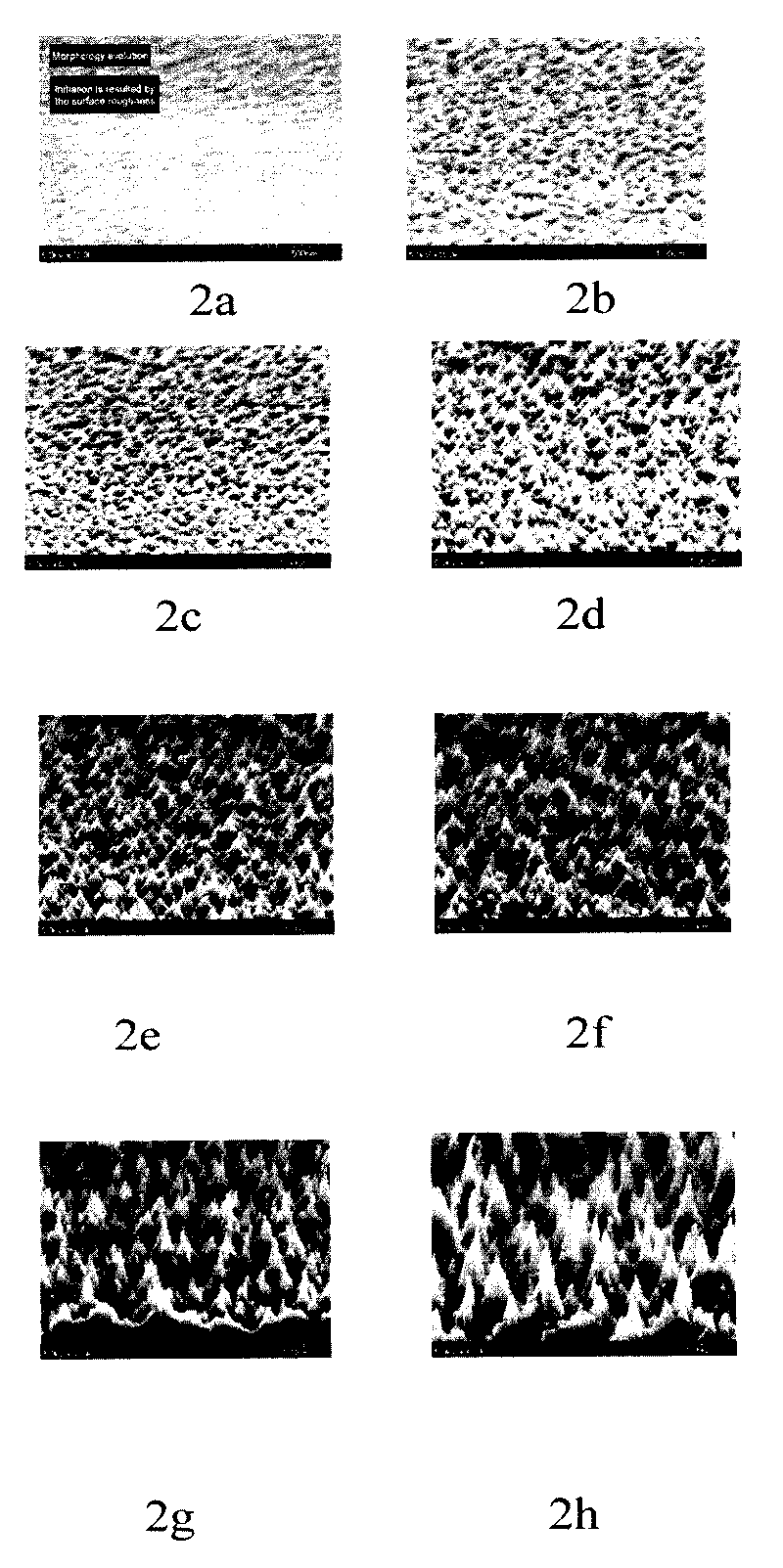
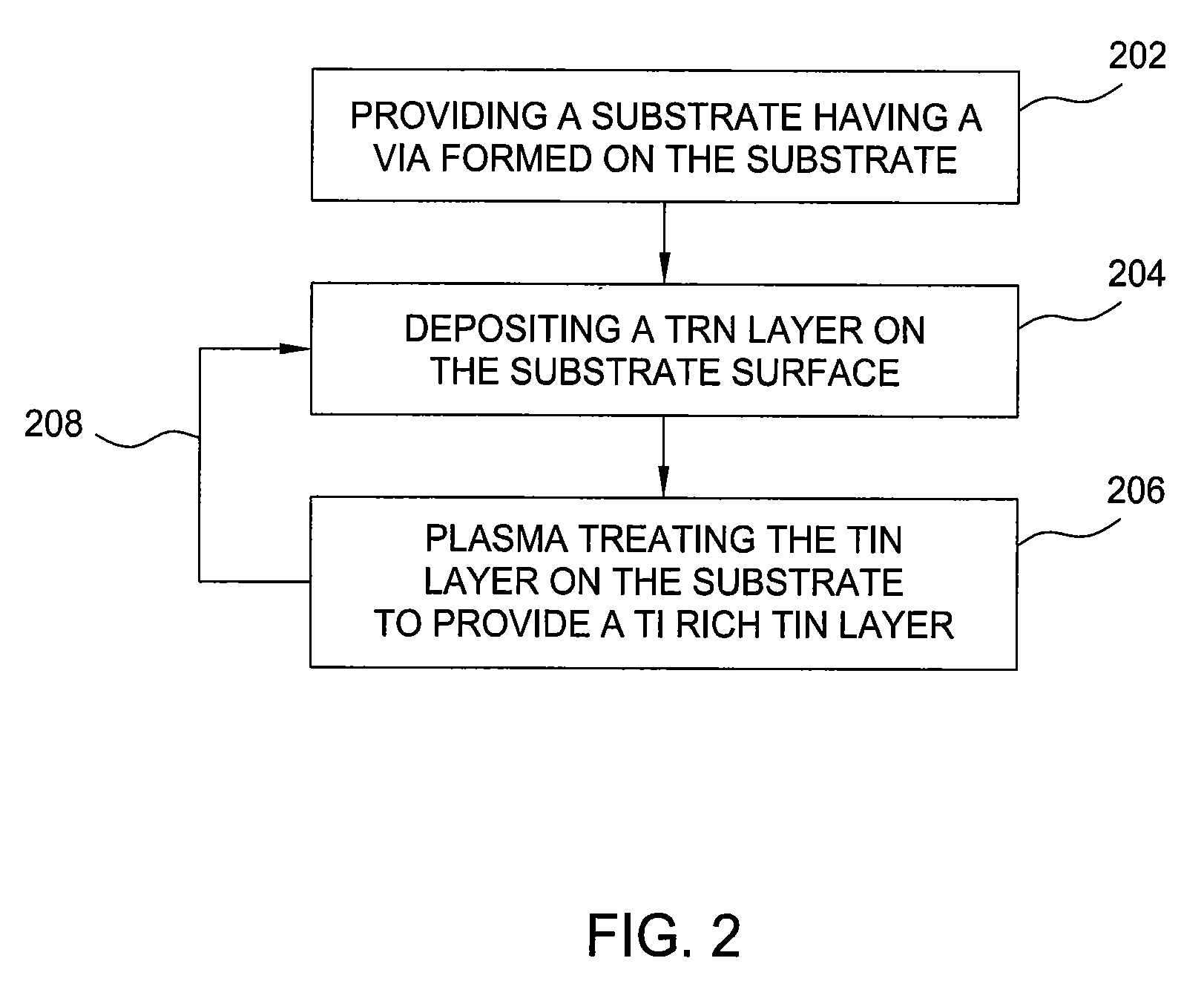
Densification process for titanium nitride layer for submicron applications
InactiveUS20100151676A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenGas phase
Embodiments of the present invention provide methods of forming and densifying a titanium nitride barrier layer. The densification process is performed at a relatively low RF plasma power and high nitrogen to hydrogen ratio so as to provide a substantially titanium rich titanium nitride barrier layer. In one embodiment, a method for forming a titanium nitride barrier layer on a substrate includes depositing a titanium nitride layer on the substrate by a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition process, and performing a plasma treatment process on the deposited titanium nitride layer, wherein the plasma treatment process operates to densify the deposited titanium nitride layer, resulting in a densified titanium nitride layer, wherein the plasma treatment process further comprises supplying a plasma gas mixture containing a nitrogen gas to hydrogen gas ratio between about 20:1 and about 3:1, and applying less than about 500 Watts RF power to the plasma gas mixture.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Atmospheric plasma chemical processing method of WC and SiC optical molding molds
ActiveCN101659568AIncreased durabilityEfficient removalGlass pressing apparatusPlasma jetChemical reaction
The invention relates to an atmospheric plasma chemical processing method of WC and SiC optical molding molds, which belongs to the atmospheric plasma chemical processing methods of the optical molding molds. The atmospheric plasma chemical processing method can solve the problems that the grinding and polishing technology which is used for processing after processing and forming of the optical molding molds made of SiC and WC materials has the disadvantages of low processing efficiency, poor surface quality, damage of a sub-surface layer and short service life of the molds. The method comprises the steps of: introducing a mixture of plasma gas, reaction gas and oxygen into space between a cathode and an anode of a plasma generator, imposing radio frequency power signals on the cathode andthe anode, producing the plasma discharge between the two electrodes, then placing the surface to be processed of the WC or SiC optical molding mold in a plasma jet region for carrying out chemical reaction and realizing the optical surface processing of the optical molding molds made of the SiC and WC materials. The method is used for carrying out the optical processing on the surfaces of the WCand SiC optical molding molds.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Plasma arc torch head connections
InactiveUS6919526B2Precision coolingHigh trafficSupport devices with shieldingPlasma welding apparatusElectrical connectionTorch
A plasma arc torch is provided that comprises torch head connections that are made between consumable components and a torch head independent of rotational alignment of the consumable components. Accordingly, connections for the flow of a cooling fluid, plasma gas, and / or a secondary gas are made independent of rotational alignment. Additionally, electrical connections are also provided that are independent of rotational alignment of the various plasma arc torch components.
Owner:THERMAL DYNAMICS
Plasma ashing process
InactiveUS6951823B2Electric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenPlasma Gases
A substantially oxygen-free and nitrogen-free plasma ashing process for removing photoresist in the presence of a low k material from a semiconductor substrate includes forming reactive species by exposing a plasma gas composition to an energy source to form plasma. The plasma gas composition is substantially free from oxygen-bearing and nitrogen-bearing gases. The plasma selectively removes the photoresist from the underlying substrate containing low k material by exposing the photoresist to substantially oxygen and nitrogen free reactive species. The process can be used with carbon containing low k dielectric materials.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
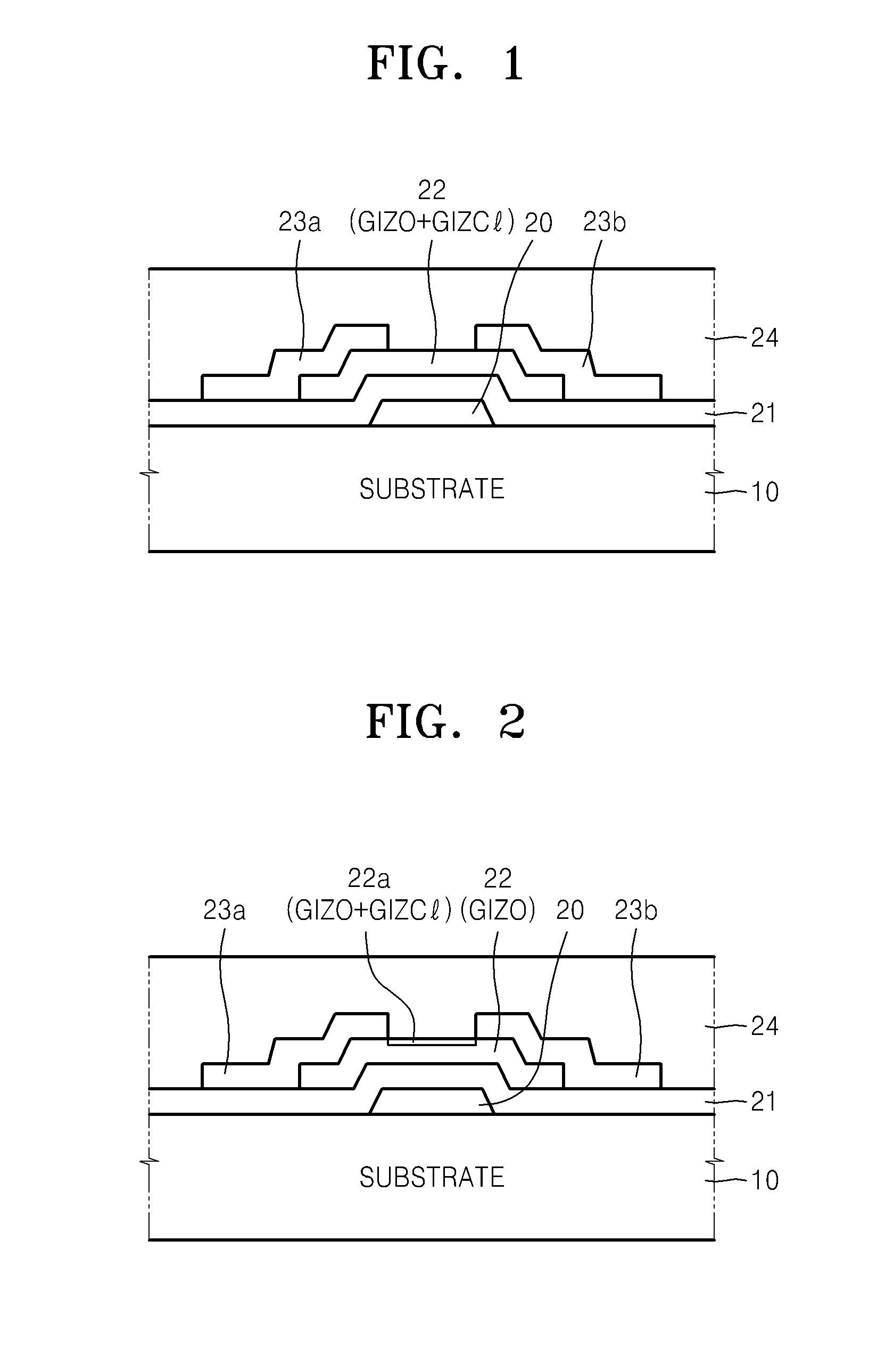
ZnO-BASED THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURING THE SAME
InactiveUS20080283831A1Avoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringPlasma Gases
A ZnO-based thin film transistor (TFT) is provided herein, as is a method of manufacturing the TFT. The ZnO-based TFT has a channel layer that comprises ZnO and ZnCl, wherein the ZnCl has a higher bonding energy than ZnO with respect to plasma. The ZnCl is formed through the entire channel layer, and specifically is formed in a region near THE surface of the channel layer. Since the ZnCl is strong enough not to be decomposed when exposed to plasma etching gas, an increase in the carrier concentration can be prevented. The distribution of ZnCl in the channel layer, may result from the inclusion of chlorine (Cl) in the plasma gas during the patterning of the channel layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Device and method for converting carbon containing feedstock into carbon containing materials, having a defined nanostructure
InactiveUS7452514B2Improve conversion efficiencyEasy to controlMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentPlasma GasesNanostructure
Apparatus and process for producing carbon black or carbon containing compounds by converting a carbon containing feedstock, comprising the following steps: generating a plasma gas with electrical energy, guiding the plasma gas through a venturi, whose diameter is narrowing in the direction of the plasma gas flow, guiding the plasma gas into a reaction area, in which under the prevailing flow conditions generated by aerodynamic and electromagnetic forces, no significant recirculation of feedstock into the plasma gas in the reaction area recovering the reaction products from the reaction area and separating carbon black or carbon containing compounds from the other reaction products.
Owner:ТІМКАЛ SА
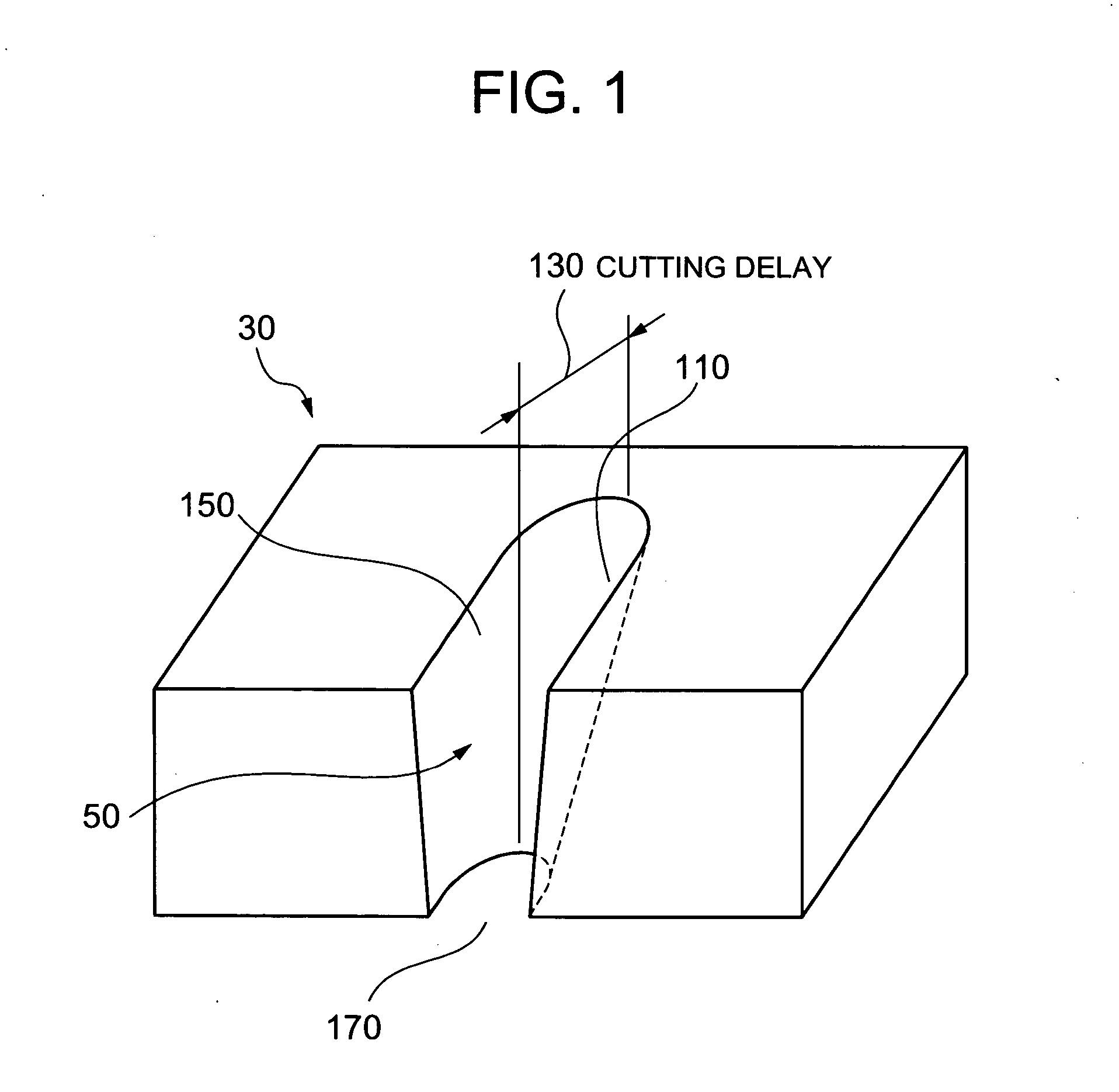
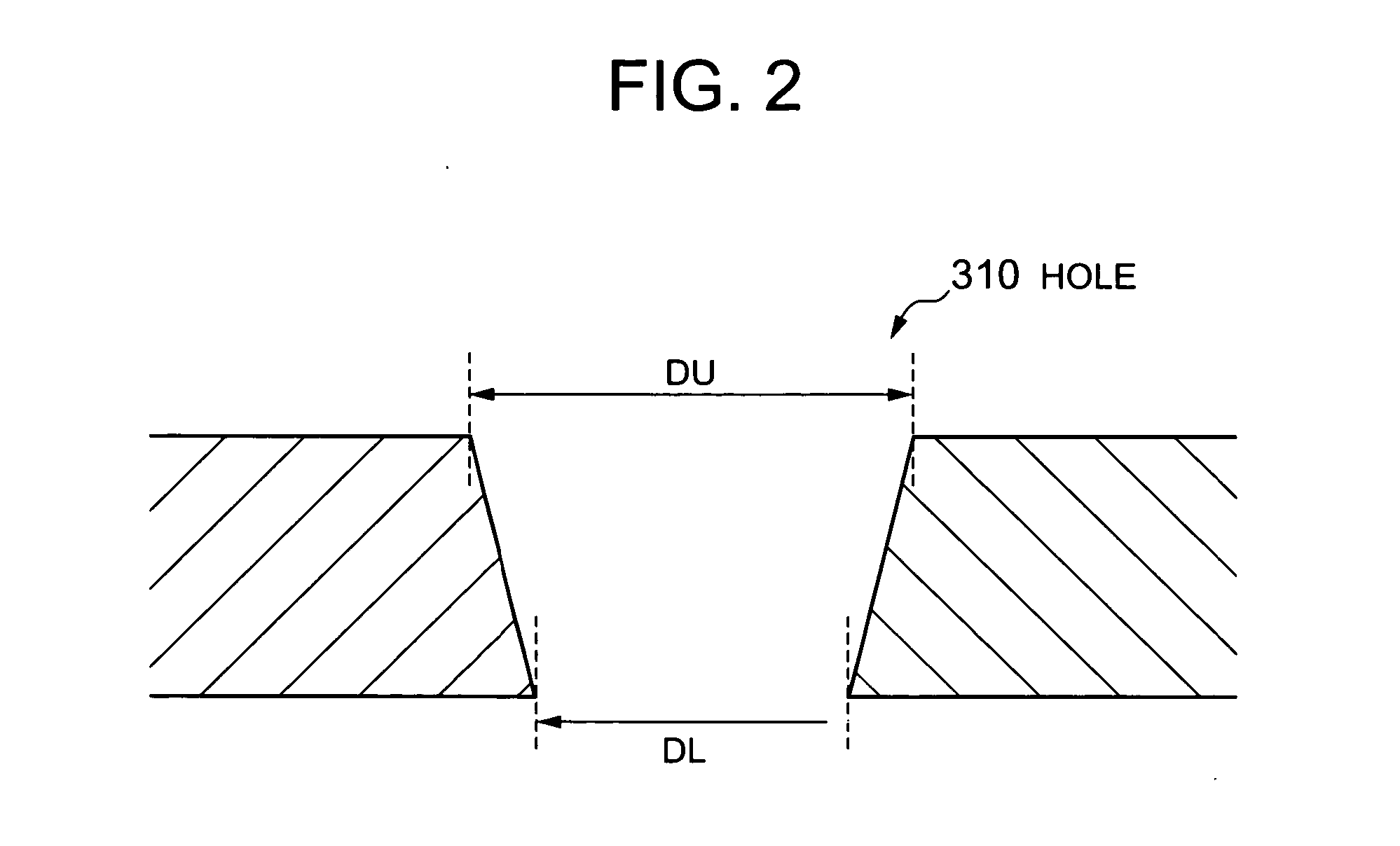
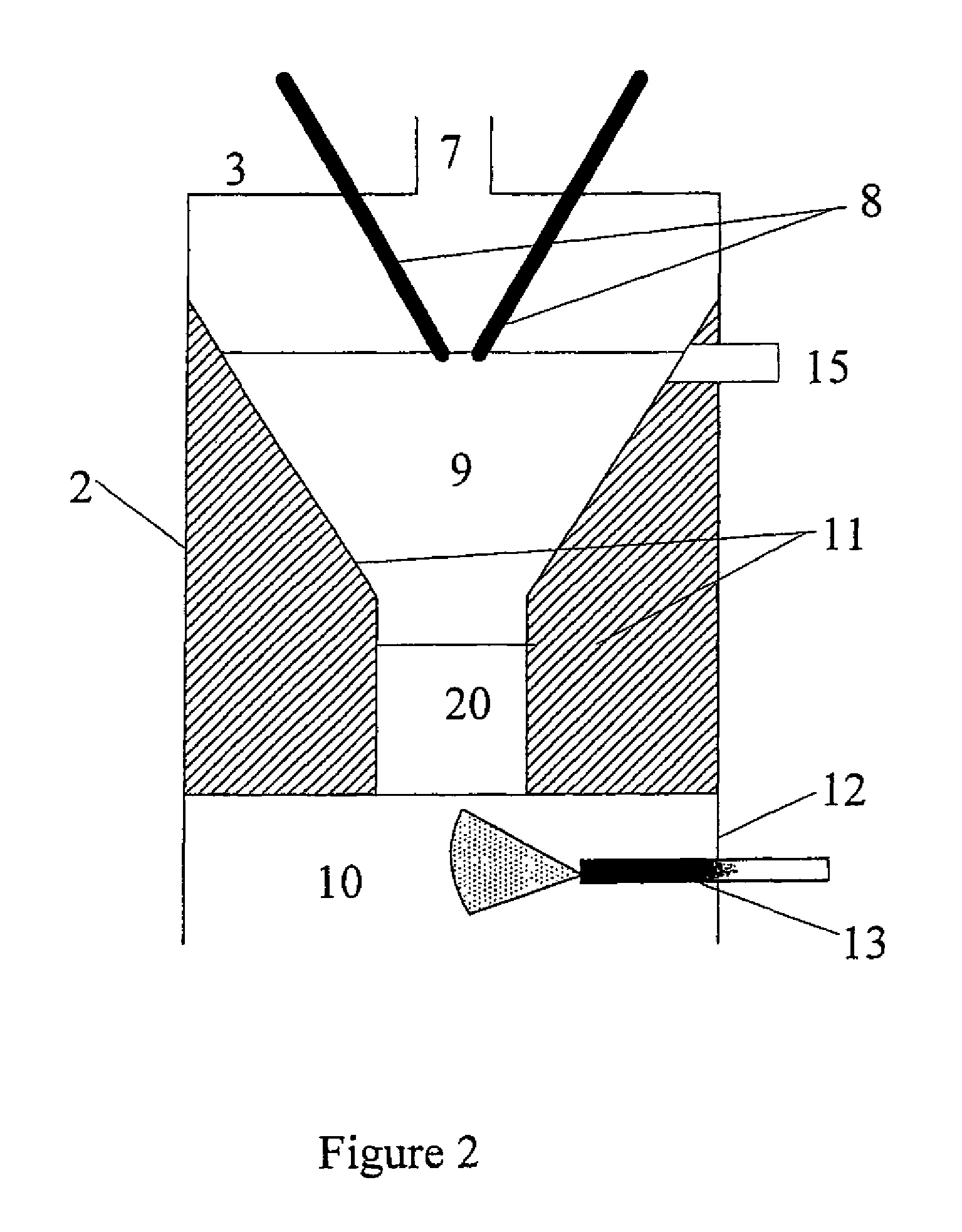
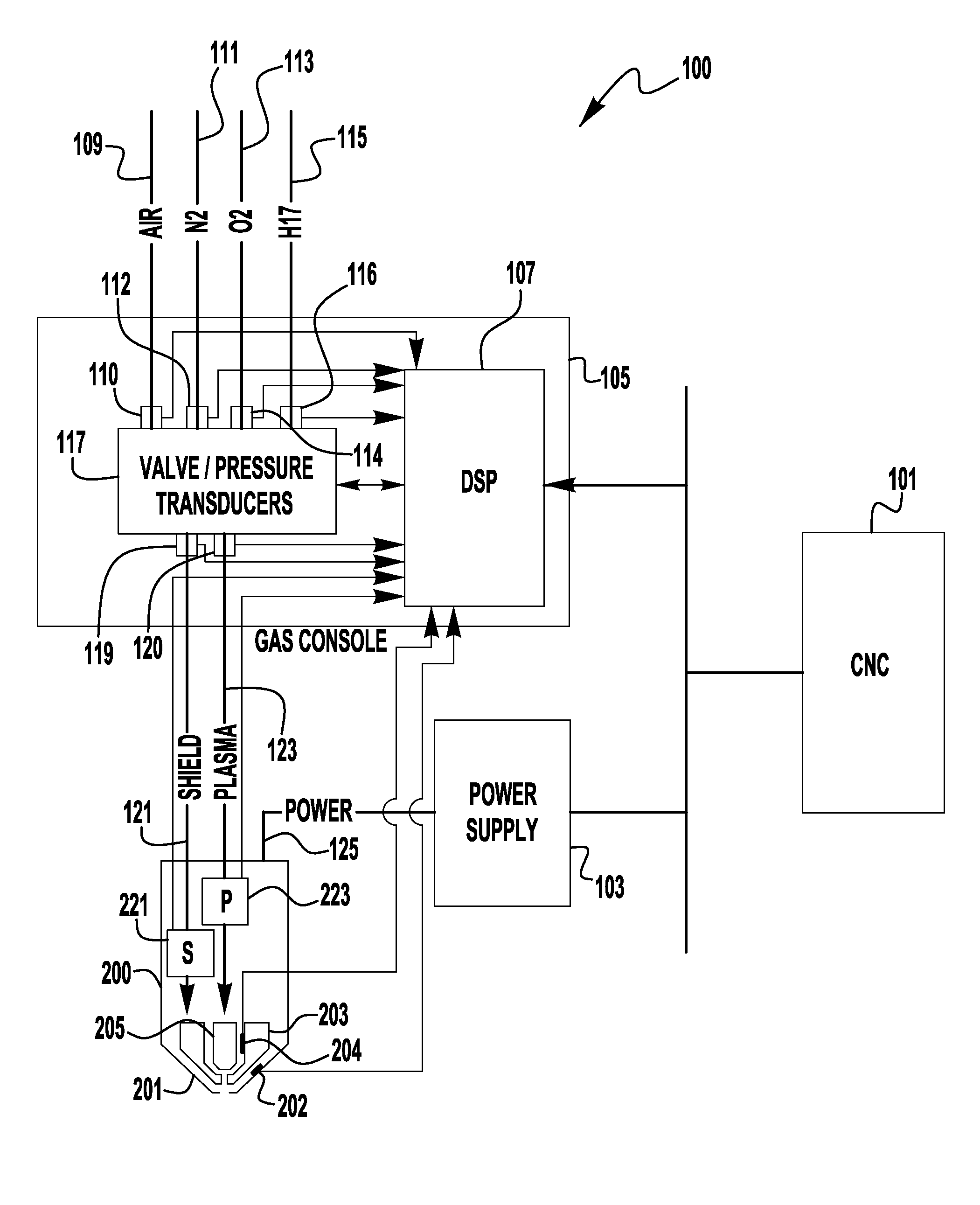
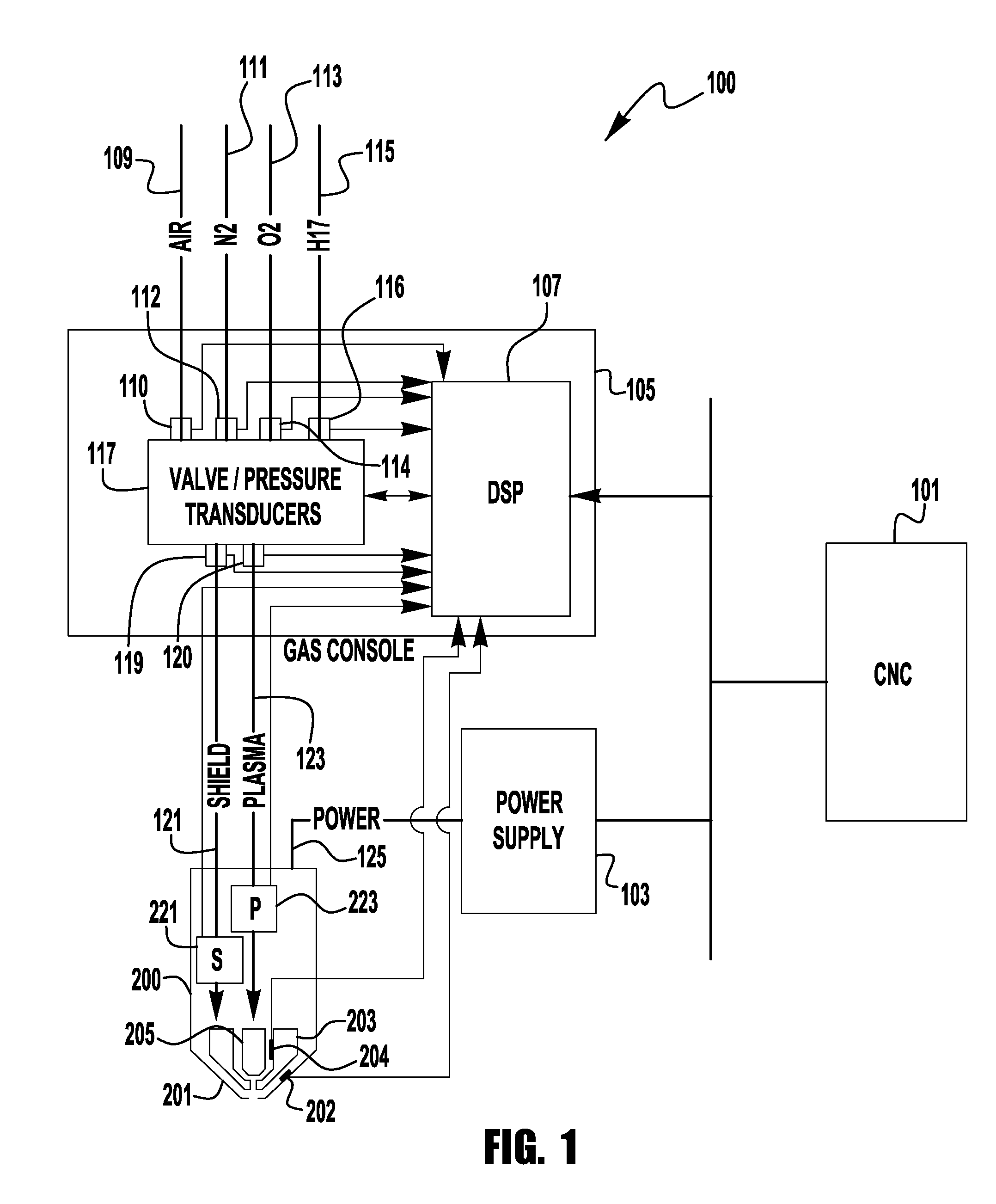
Adaptive plasma cutting system and method
A plasma torch system and method is provided, in which the system utilizes a number of pressure sensors throughout the system and the torch to detect the flow / pressure of shield and plasma gas during operation. The detected pressures are used by the system to dynamically control the system pressures to optimize the cutting operation.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Method and apparatus for improved plasma arc torch cut quality
InactiveUS20070181540A1Reduce entrainmentSimple interfaceArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusTorchPlasma Gases
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
Plasma spray apparatus
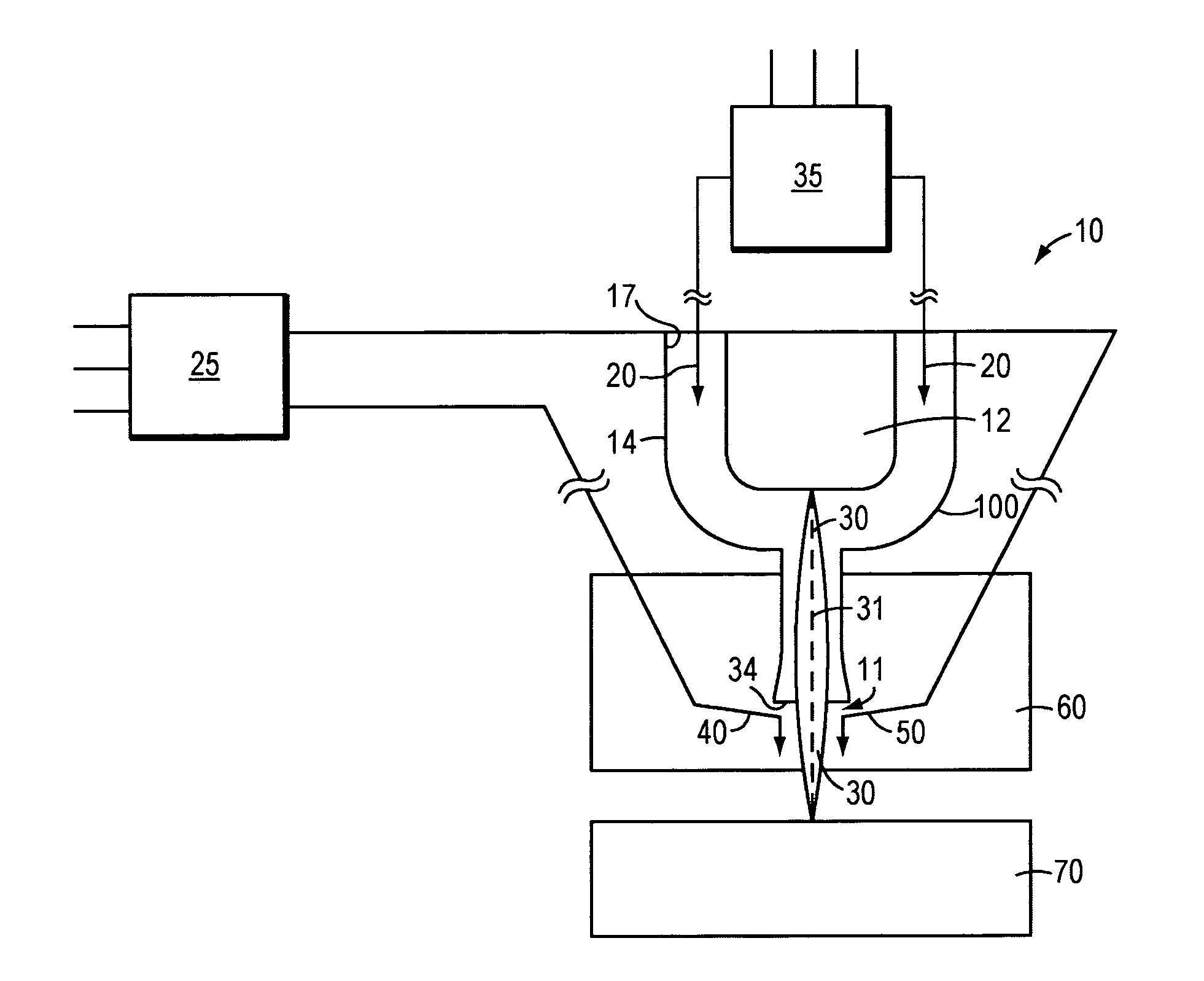
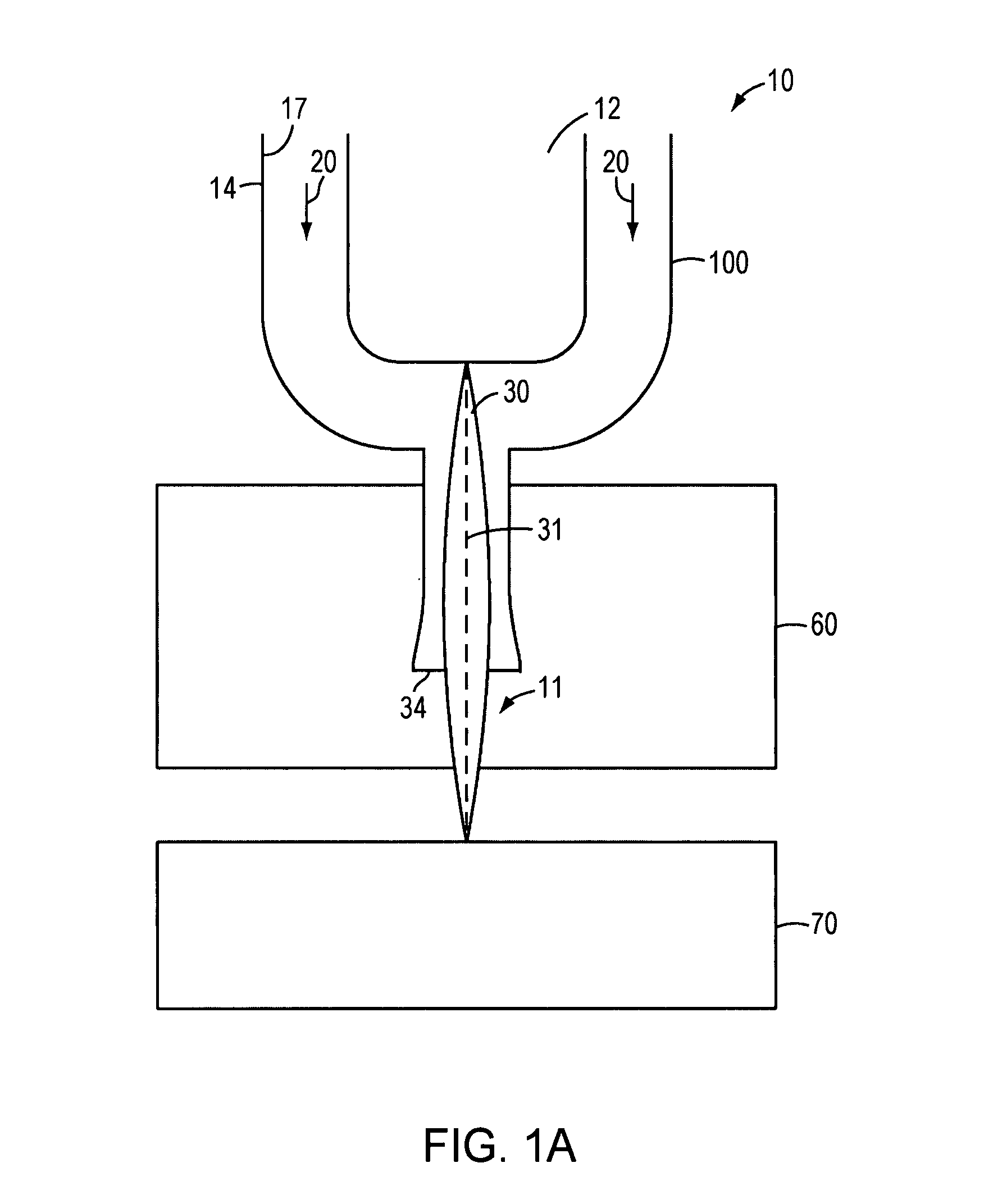
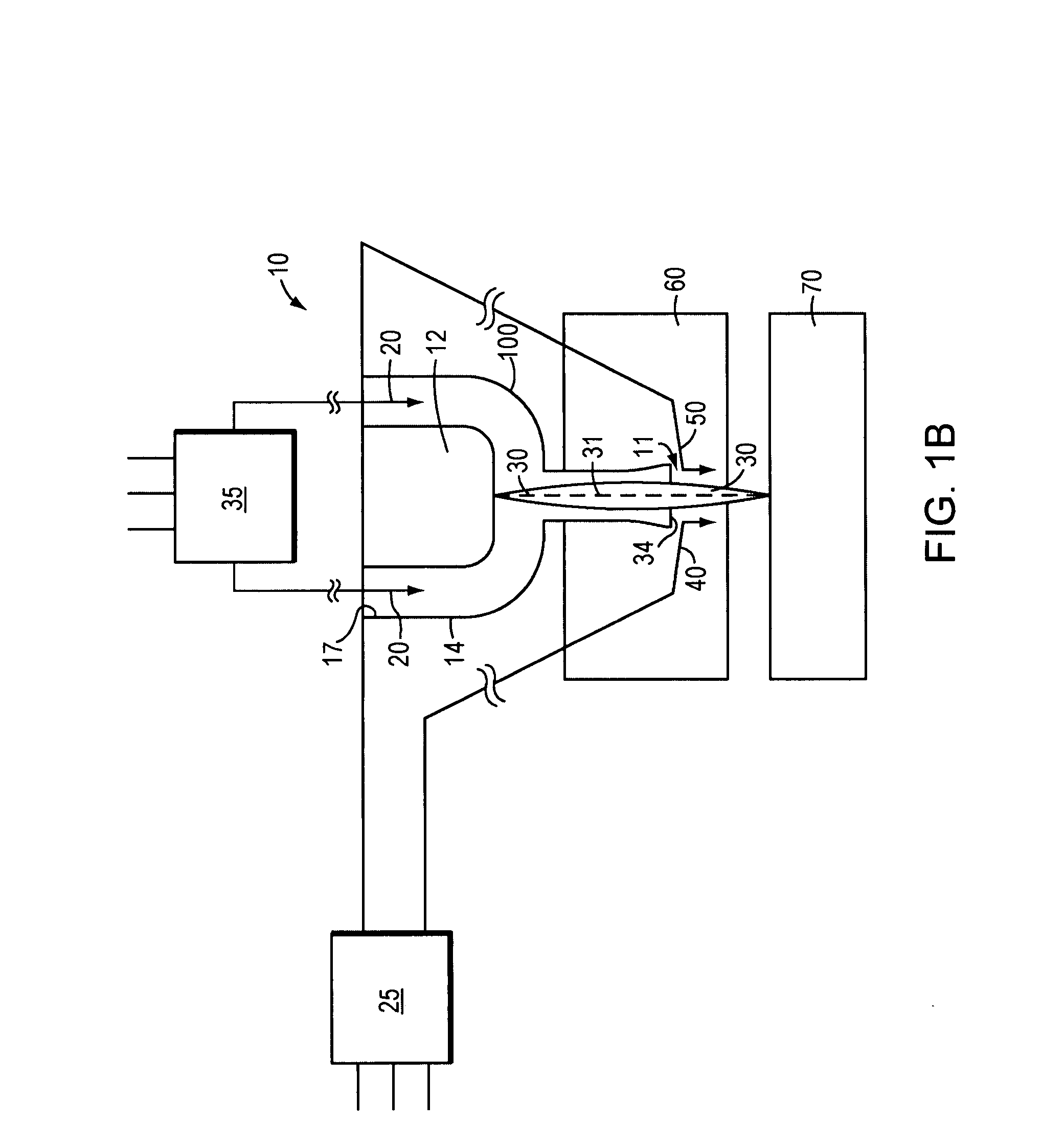
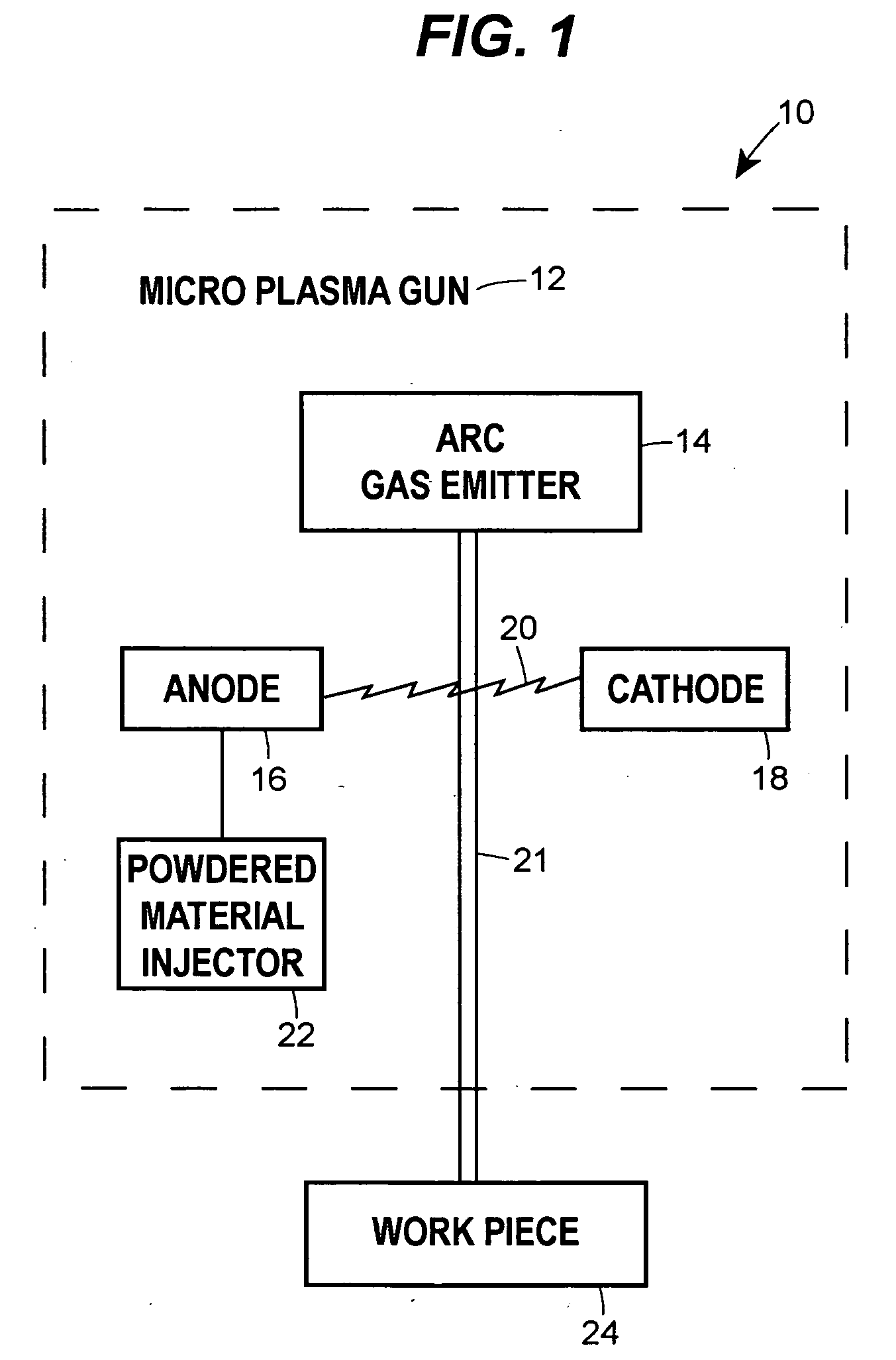
A microplasma spray coating apparatus includes a microplasma apparatus with an anode, cathode, and an arc generator for generating an electric arc between the anode and cathode. An arc gas emitter injects inert gas through the electric arc. The electric arc is operable for ionizing the gas to create a plasma gas stream. A powder injector nozzle extends through the anode and injects powdered material into the plasma stream for transfer to the workpiece.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Dry etching method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050048787A1Lower ionization energyImprovement in apparatus costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistNoble gas
A condition without using Ar as plasma gas is applied to processing of an organic anti-reflection-coating, which suppresses a spatter effect and decreases the cleavage of C—H and OC—O bonds in a resist. As a result, roughness of the resist after processing the anti-reflection-coating can be suppressed, and pitting and striations after processing a next film to be processed, that is an insulating film, can be prevented. For a rare gas to be used at the time of processing the insulating film, any one of Xe, Kr, a mixed gas of Ar and Xe, and a mixed gas of Ar and Kr is applied in place of Ar, giving rise to reduction in pitting and striations after etching. In addition, a dry etching method with less critical-dimension shift and excellence in both apparatus cost and throughput can be provided by performing resist modification and etching by turns.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Atmospheric glow discharge with concurrent coating deposition
InactiveUS7067405B2Improve adhesionImprove curingElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetallic electrodeGas phase
A plasma is produced in a treatment space by diffusing a plasma gas at atmospheric pressure and subjecting it to an electric field created by two metallic electrodes separated by a dielectric material, a precursor material is mixed with the plasma, and a substrate film or web is coated by vapor deposition of the vaporized substance at atmospheric pressure in the plasma field. The deposited precursor is cured by electron-beam, infrared-light, visible-light, or ultraviolet-light radiation, as most appropriate for the particular material being-deposited. Plasma pre-treatment and post-treatment steps are used to enhance the properties of the resulting coated products. Similar results are obtained by atomizing and spraying the liquid precursor in the plasma field.
Owner:SIGMA LAB OF ARIZONA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com