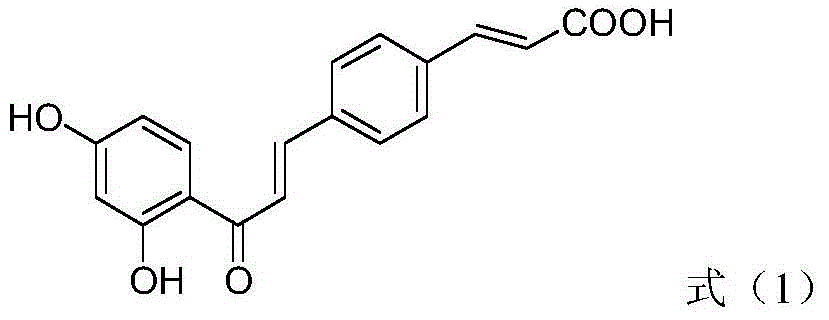
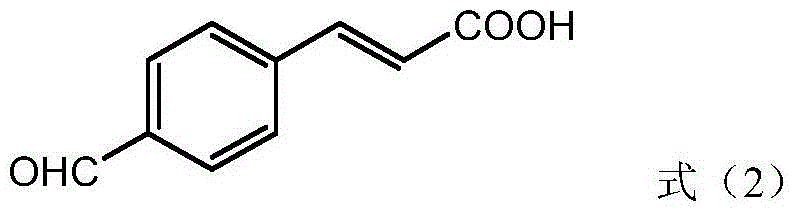
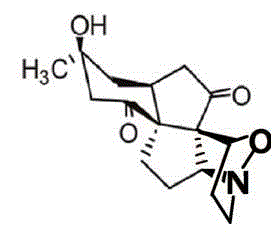
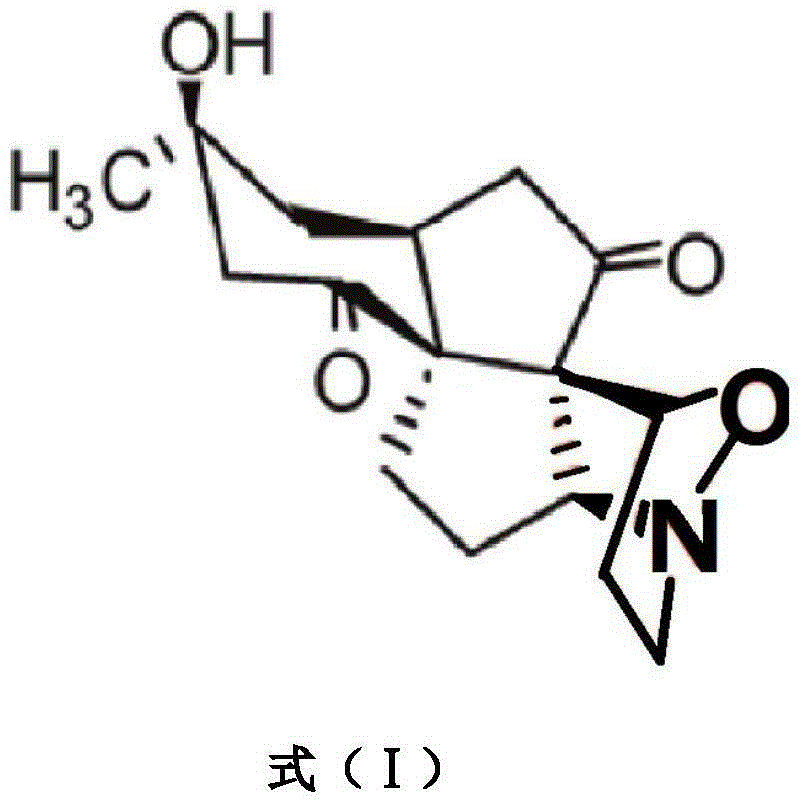
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Paenibacillus macerans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Paenibacillus macerans is a diazotroph bacterium found in soil and plants capable of nitrogen fixation and fermentation. This bacteria was originally discovered in 1905 by an Austrian biologist named Schardinger and thought to be a bacillus.
Technology for producing alpha-cyclodextrins by biological method
ActiveCN101712972AImprove conversion rateLow costTransferasesMicroorganism based processesGlycosyltransferaseAlpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
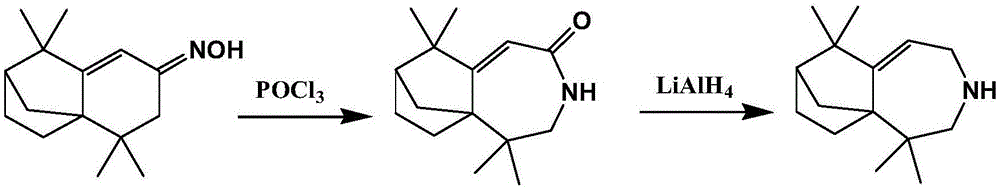
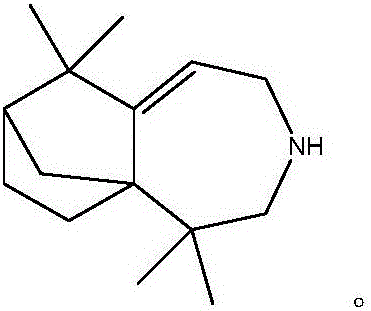
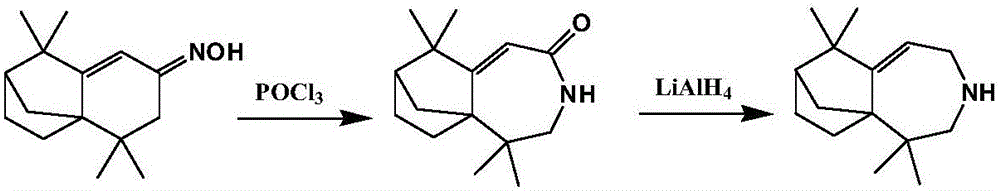
Heavy turpentine longifolene derivative, preparation thereof and application
The invention discloses a longifolene derivative (2, 2, 8, 8-tetramethyl-4-atrane [5. 4. 0. 11, 9] dodecane-6-alkene obtained by rearrangement and reduction reaction and by taking isolongifolene ketoxime as a raw material. Besides, bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumonia, Escherichia coli, bacillus proteus vulgaris and pseudomonas aeruginosa can be inhibited by the longifolene derivative, and particularly, the longifolene derivative has a superior insecticidal effect on pests such as aphids and rice planthopper.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
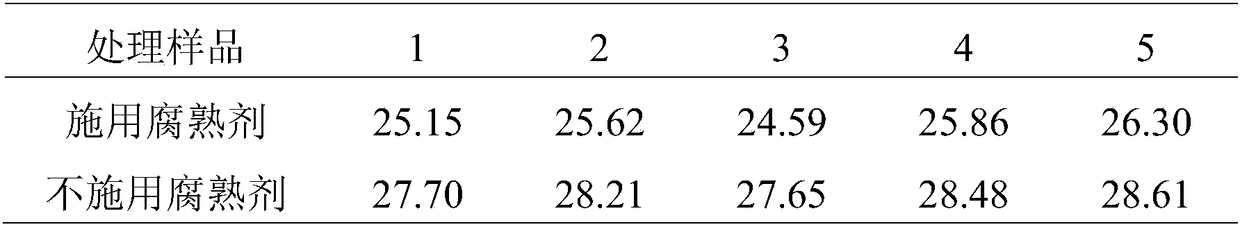
Bacillus series straw fast rotting agent and using method thereof
InactiveCN102876607ACorrupted Time ReductionShorten the durationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBacillus licheniformis
The invention relates to a bacillus series straw fast rotting agent and a using method thereof. The fast rotting agent comprises bacillus licheniformis, bacillus circulans, bacillus subtilis, clostridium pasteurianum, bacillus megatherium, jelly-like bacillus, clostridium acetobutylicum, bacteria macerans, bacillus polymyxa and nutrient solution and is used for treating straws to make biological organic fertilizer. The using method comprises the following steps: stacking the straws into a walkway with the width of 40 cm and the height of 30 to 50 cm; uniformly spraying 1.25 kilograms of the fast rotting agent into per ton of straws; controlling the water content of the straws to be 40 to 60 wt%; and rotting at normal temperature for 1 to 2 weeks, wherein when the straws change into brown or black brown, the wet straws are flexible and elastic when being held by hands and the dry straws are crisp and easy to break, a straw decomposition agent product with the nutrient substance content up to 59 weight percent is obtained and can direct serve as fertilizer. By adoption of the fast rotting agent, the straw rotting time is reduced from 15-20 days at present to 7-10 days.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and the application thereof and relates to an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene, an encoding enzyme, a carrier and an engineering bacterium which are extracted from paenibacillus macerans and the application thereof. The alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene can be connected with an expression vector to construct an expression recombinant plasmid (pET-20b(+) / cgt) containing the gene, the expression recombinant plasmid is then transferred into escherichia coli E.coil BL21, then recombinant escherichia coli is obtained, and the recombinant escherichia coli can secrete expression recombinant starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, so that cyclodextrin is prepared through biotransformation reaction with glucose polymer such as starch, glycogen and oligosaccharide as substrate.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
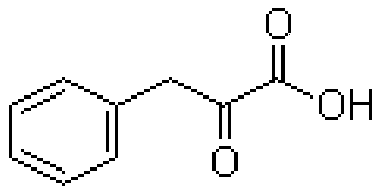
Method for efficiently producing phenylpyruvic acid
ActiveCN108841844AIncrease productionIncrease production intensityBacteriaHydrolasesPhenylpyruvic acidThallus
The invention discloses a method for high-yield production of phenylpyruvic acid, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the method provided by the invention, amino acid deaminase from proteus mirabilis is modified by a conformational dynamics engineering method, and the gene of the modified amino acid deaminase is connected to a pET 20b carrier and expressed in E. coliBL21 (DE3). A recombinant strain is cultured in a fermentation tank, and wet thallus converted alanine is collected to produce phenylpyruvic acid; and when the amount of wet thalli is 30g / L, the yield of phenylpyruvic acid can reach 72.5 g / L and the mol conversion rate of phenylalanine can reach 96.7% after 12h of conversion.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
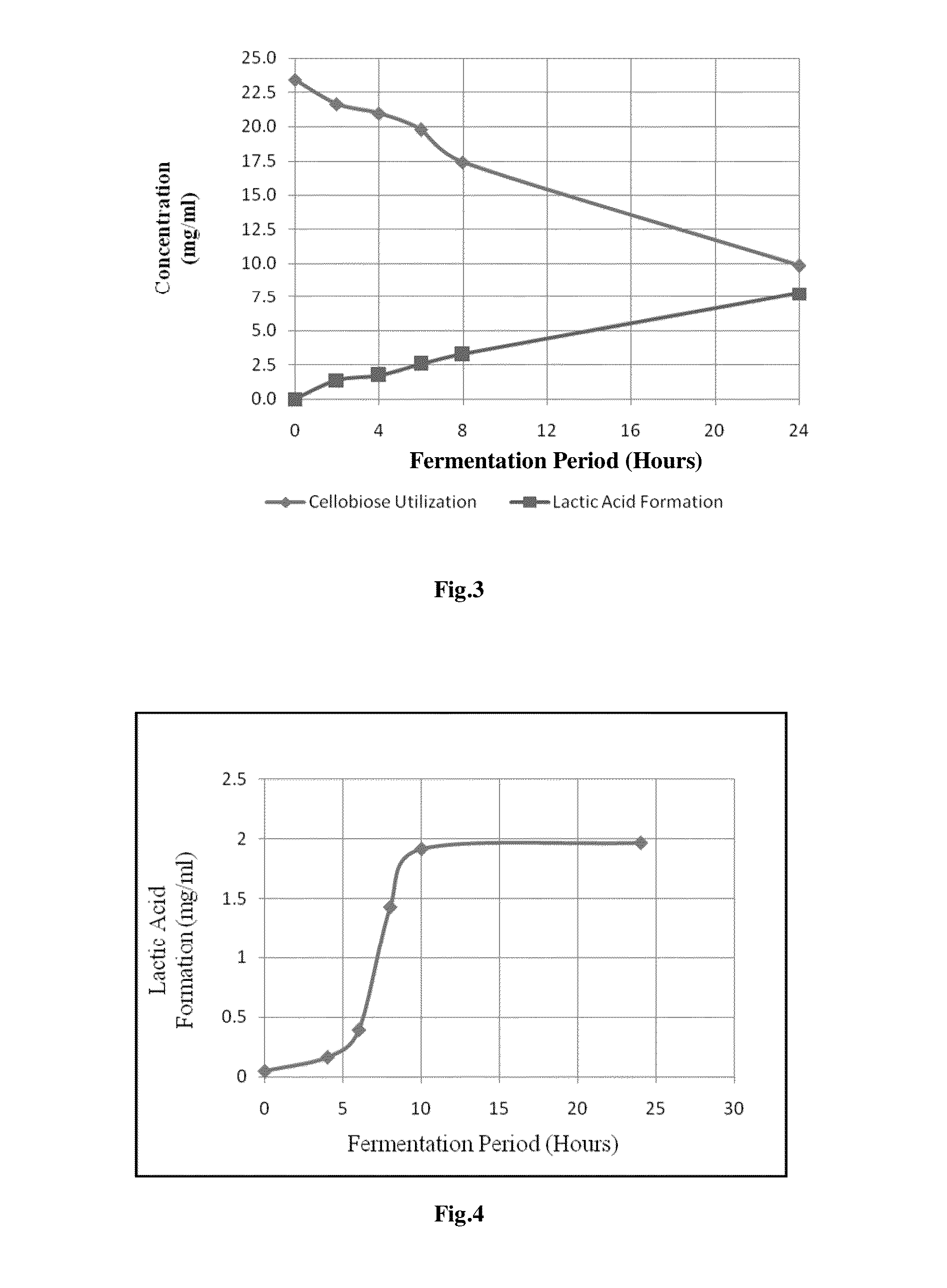
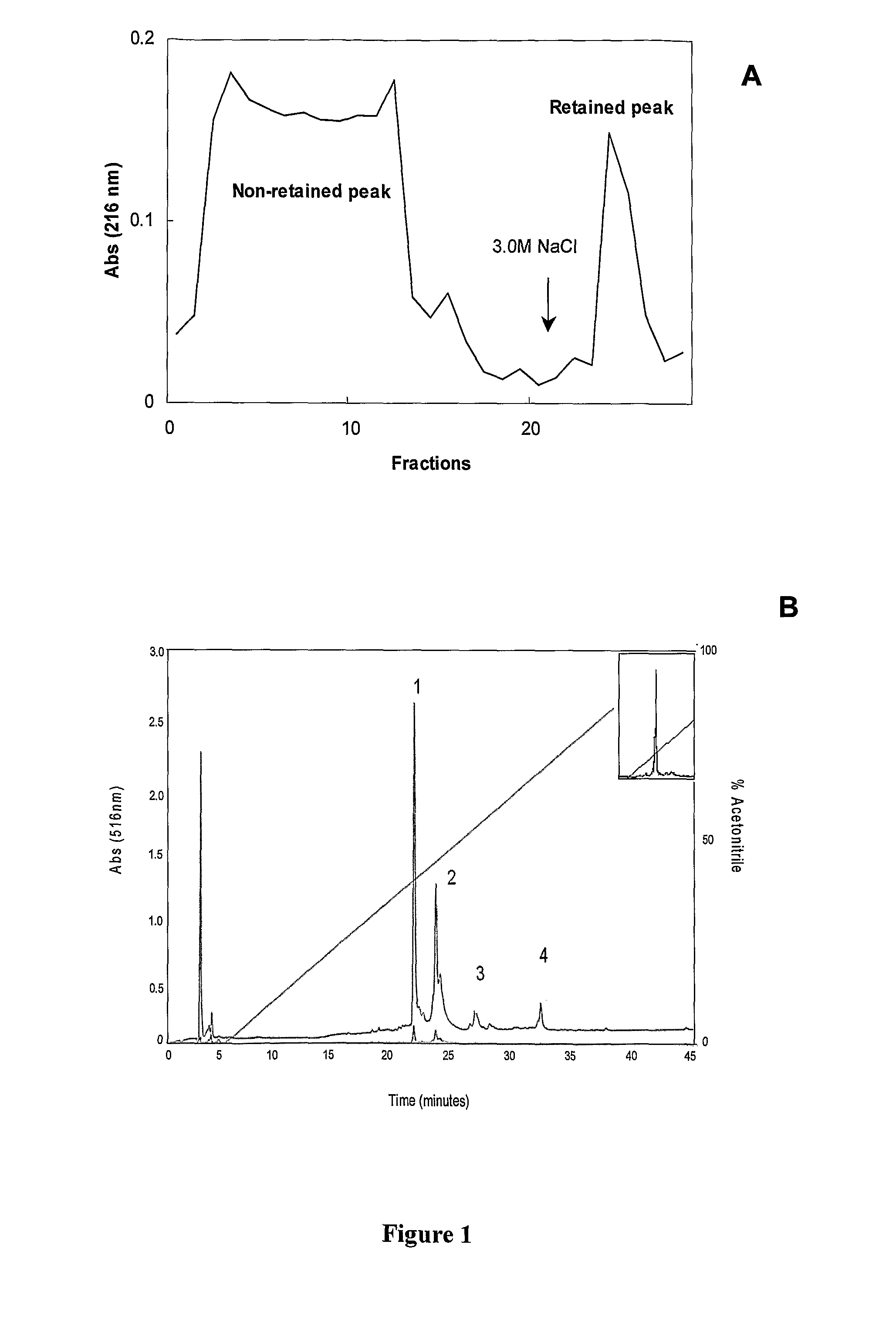
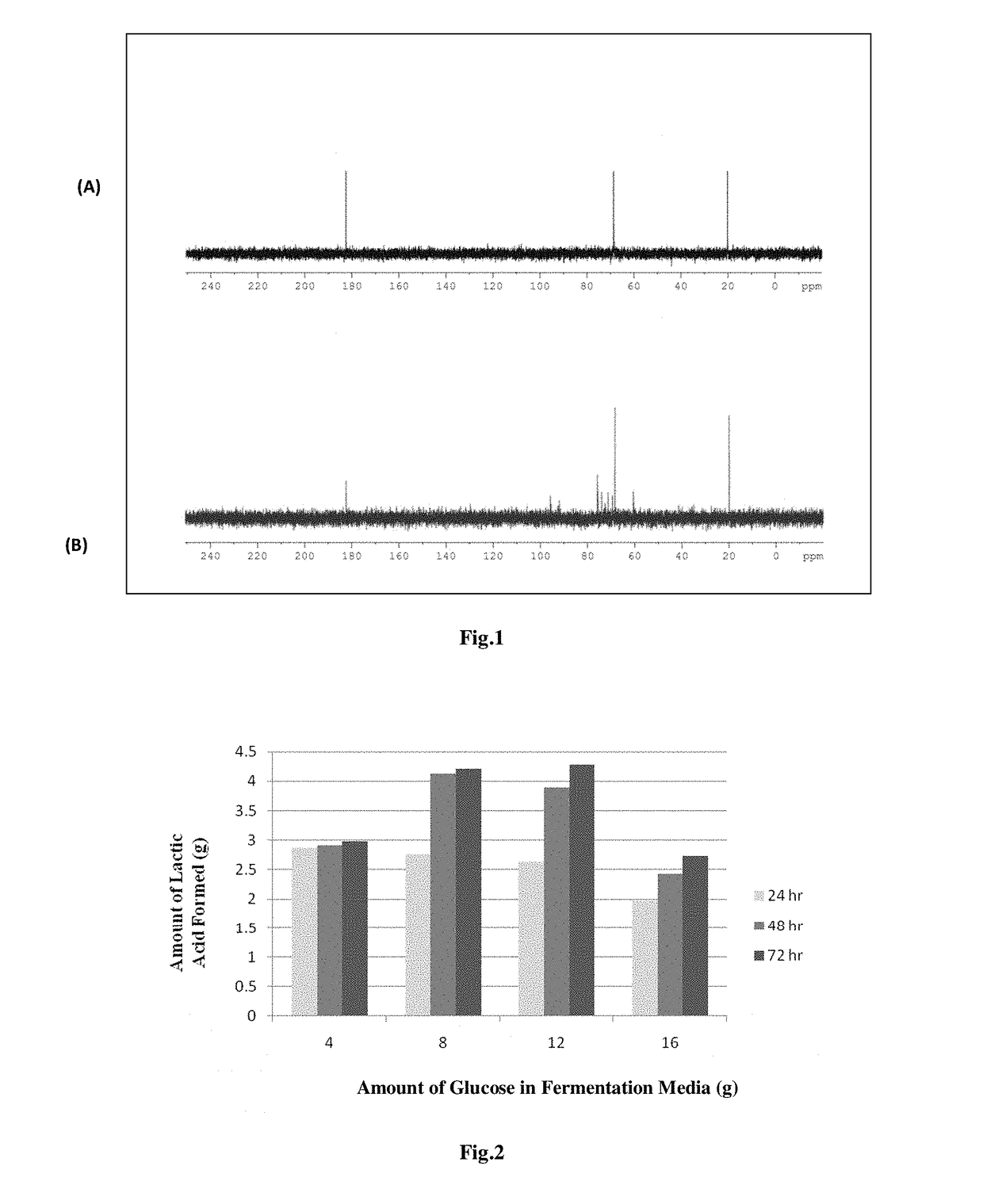
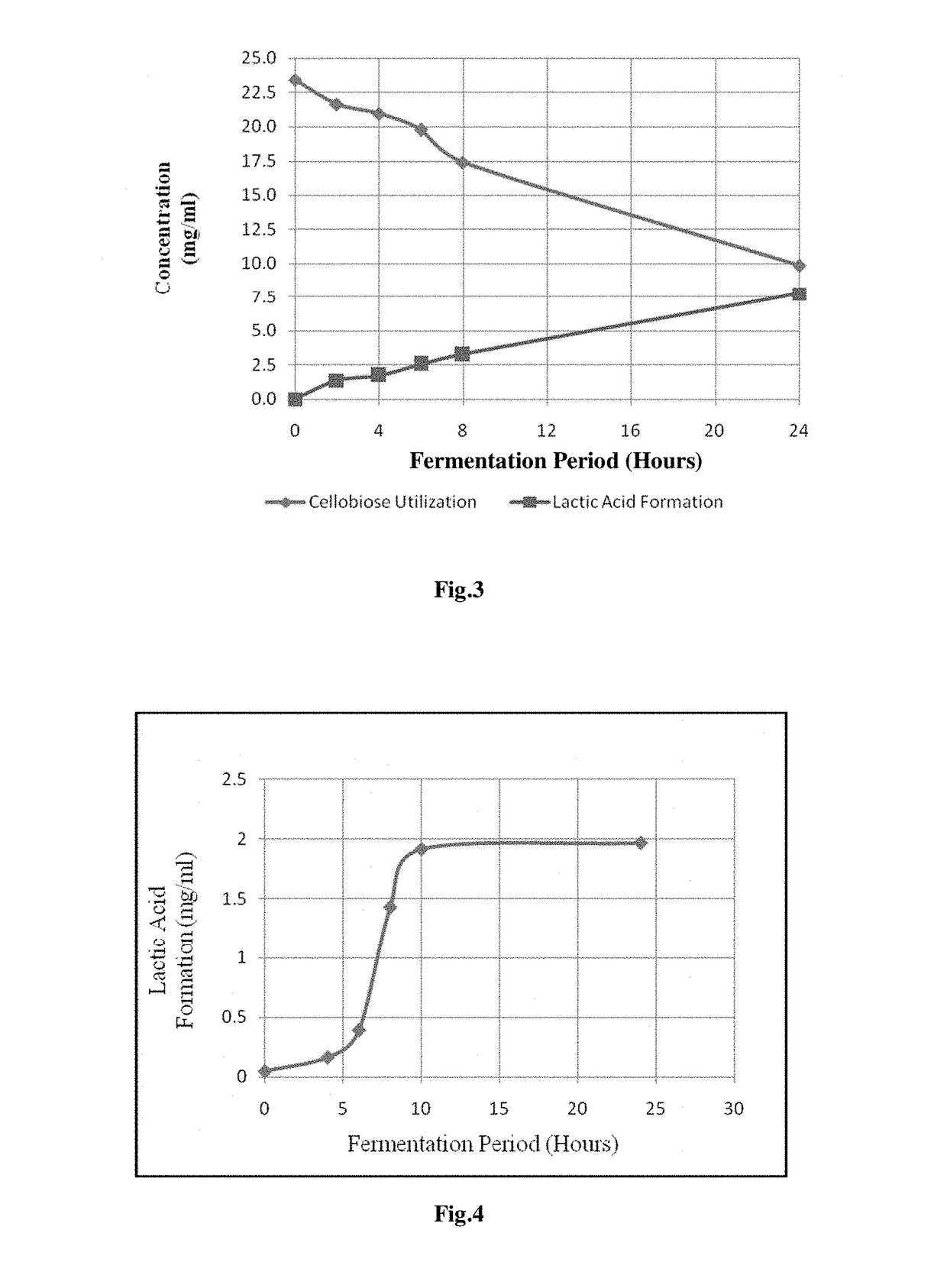
Consolidated bio processing of lignocellulosic biomass for l-lactic acid production
ActiveUS20150197777A1Simple efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
The present invention pertains to a method for consolidated bio processing of lignocellulosic biomass to L-Lactic acid. Particularly, the present invention relates to the production of L-Lactic Acid from low cost non edible feedstock lignocellulosic biomass. More particularly the present invention relates to the process for one step production of L-Lactic Acid from lignocellulosic biomass using thermophilic bacteria Paenibacillus macerans IIPSP3 (MTCC 5569), which is not only capable of hydrolysing cellulose to glucose but also further fermenting it to L-Lactic Acid under aerobic conditions, without any growth inhibition in presence of lignin. The present invention provides a process which has less chances of contamination, as the fermentation is carried out at higher temperatures and is economically attractive, as preferably no external enzyme loadings are required.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Monochloro substitution second type halogenated polyketone compound, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108017655ASatisfy growth metabolismGood against Gram-positive bacteriaAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsMonilinia laxaStaphylococcus epidermidis
The invention discloses a monochloro substitution second type halogenated polyketone compound. The structural formula of the monochloro substitution second type halogenated polyketone compound is as shown in the description. The compound has antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria or fungi. More monochloro compounds are obtained by improving a preparation method, meanwhile the antibacterial activity of the compound is screened, and results show that the compound has spectrum antibacterial activity and has the antibacterial activity against the Gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and drug-resistance bacteria, staphylococcus epidermidis and bacillus subtilis thereof; the compound has the antibacterial activity against the Gram-negative bacteria such as escherichia coli (ESBL) capable of producing hyper spectrum beta-lactamase, proteusbacillus vulgaris and bacterium burgeri; the compound has the antibacterial activity against the fungi such as Candida albicans.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Composition and method for detecting and early and differentiated counting of gram-negative microorganisms
InactiveUS20030044882A1High diagnostic specificityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrobacter
The present invention is related with the Microbiology field and particularly with a composition and a method for early detection, identification, differentiation and count of microscopic organisms, concretely Gram-negative microorganisms. The composition described in the invention consist on a mixture of substances of protein origin with a total nitrogen content from 9 to 20% and in relationship between 2:1 to 24:1, concerning to the content of inhibitors of the Gram-positive organisms. It contains a mixture of organic and inorganic substances that facilitate the differentiation of the Gram-negative organisms, being this mixture in a relationship from 0.5:1 to 2:1 concerning to the mixture of substances of protein origin. The referred composition allows the detection and differentiated count of E. coli and other coliform organisms due to the blue-greenish color of the colonies of these microorganisms on the orange bottom of the medium; Salmonella not typhi for the red color of the centers of the colonies on rosy bottom of the medium; Salmonella typhi and Proteus for the transparency of the colonies; Citrobacter and Klebsiella for the violet color of the colonies on the pink to orange bottom of the medium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa for the orange color with darker center of the colony, taking greenish pigmentation after 24 hours and producing greenish fluorescence under low ultraviolet light.
Owner:CENT NACIONAL BIOPREPARADOS
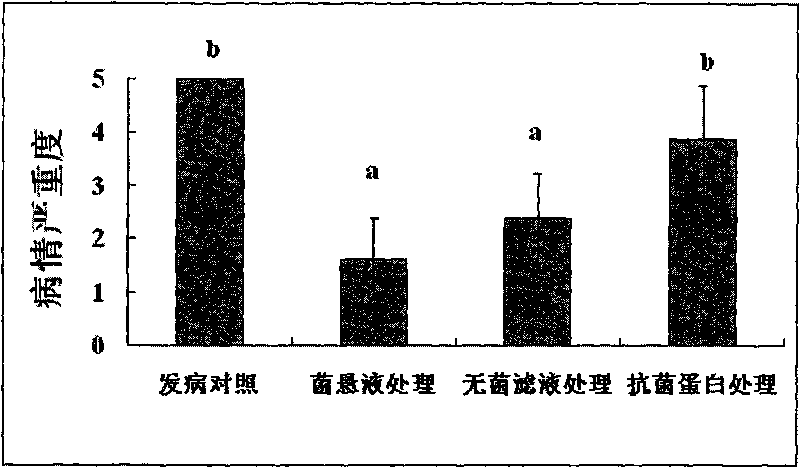
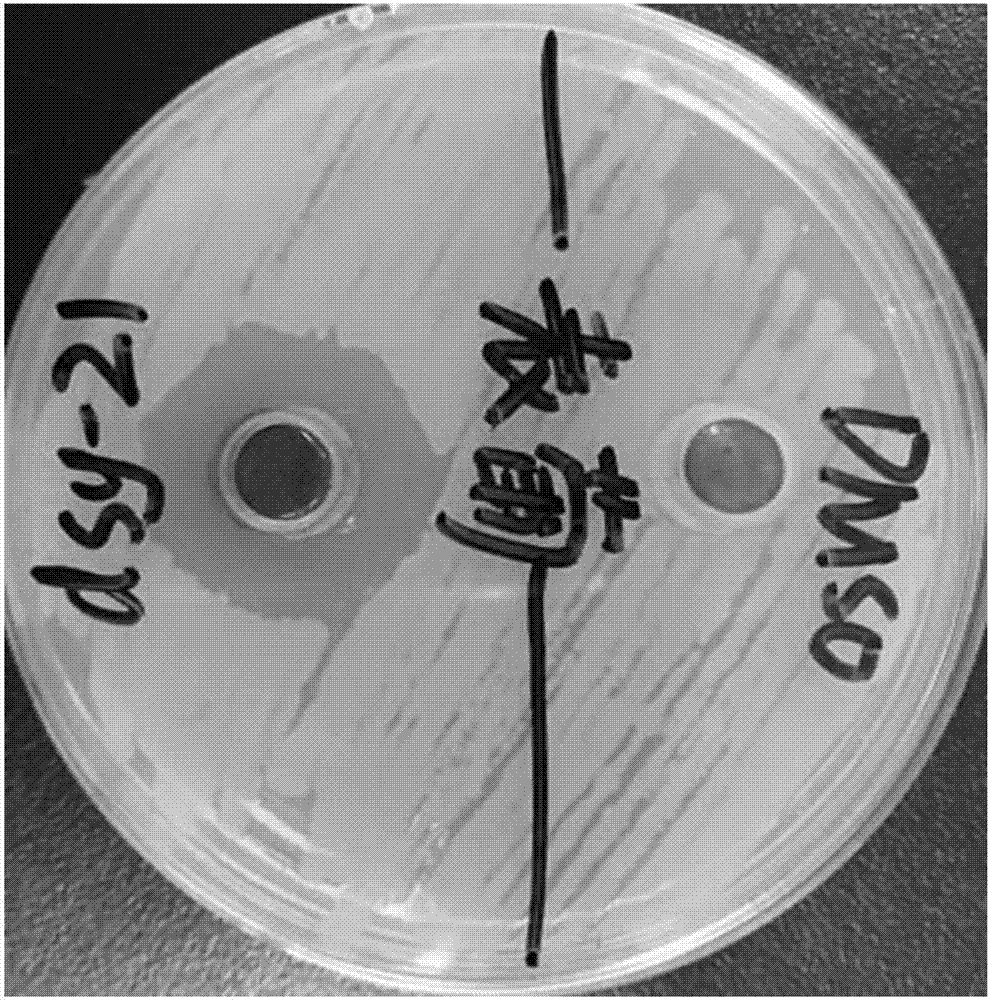
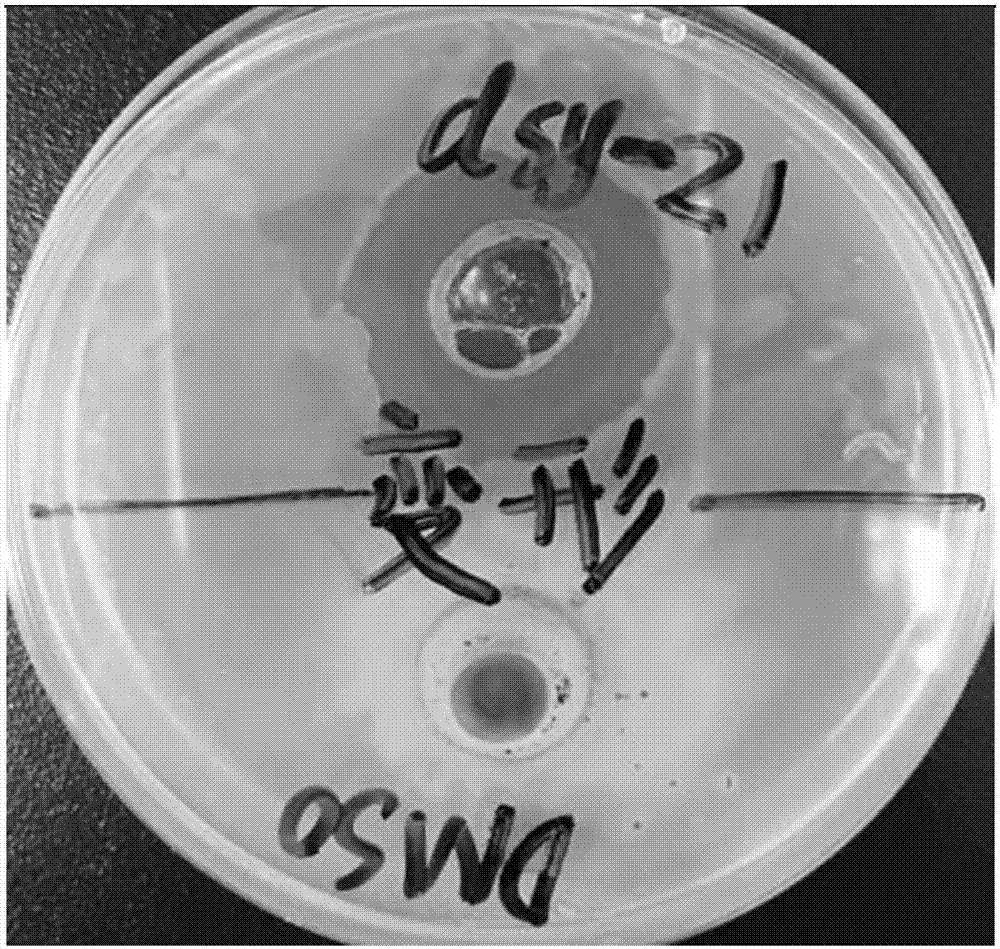
Paenibacillus macerans for preventing and controlling plant bacterial wilt and application thereof
The invention discloses a paenibacillus macerans strain for preventing and controlling plant bacterial wilt, which is named paenibacillus macerans ZJU0902 after being identified and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) of Wuhan University in Mount Luojia, Wuhan City, wherein the preservation data is on 19th July, 2009 and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M209158. The paenibacillus macerans of the invention can play a role in inhibiting the growth of different biochemical strains of ralstonia solanacearum under the condition in vitro, and can effectively prevent and control the plant bacterial wilt.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Application of trichlorine substituted II-type halogenated poly-ketone compound
ActiveCN107961233AHigh antibacterial activityHas broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMonilinia laxaCandida famata
The invention discloses an application of a trichlorine substituted II-type halogenated poly-ketone compound, which has the structural formula represented as follow. The compound has anti-Gram-positive bacteria, anti-Gram-negative bacteria or anti-fungus activities. Through modification of the preparation method, more trichlorine compounds can be produced. In addition, antibacterial functions of the modified compounds are screened; the results prove that the compound has wide-spectral antibacterial activities, and has the anti-Gram-positive bacteria activity, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and drug-resistant bacteria thereof, staphylococcus epidermidis and bacillus subtilis, and the anti-Gram-negative bacteria activity, such as escherichia coli generating extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBL), proteusbacillus vulgaris and bacterium burger, and anti-fungus activity, such as candida albicans.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gene sequence and amino acid constitution of (D)-specific carbonyl reduction enzyme of Morganella morganii proteus
InactiveCN101486998ASimple compositionOptimizationOxidoreductasesFermentationMicroorganismOxidoreductase
The invention discloses the gene sequence and the amino acid composition of a D-specific carbonyl reductase of Morganella morganii with the CMCC(B) number of 49208, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention determines that the D-specific carbonyl reductase of the Morganella morganii with the CMCC(B) number of 49208 has a gene nucleotide sequence with the SEQ ID NO of 1 and the amino acid composition with the SEQ ID NO of 2, the D-specific carbonyl reductase gene is used for decomposing recemic compounds with biological methods, and by utilizing the gene, a recombinant Morganella morganii bacteria can be used for racemic chiral separation and creating further research conditions of diversity, transforming ways and reaction mechanisms of a stereoselective microbial oxidoreductase that is used in chiral separation.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin
ActiveCN103484439ARaise the ratioSimplify the subsequent purification processFungiBacteriaWild typeGlucosyltransferases
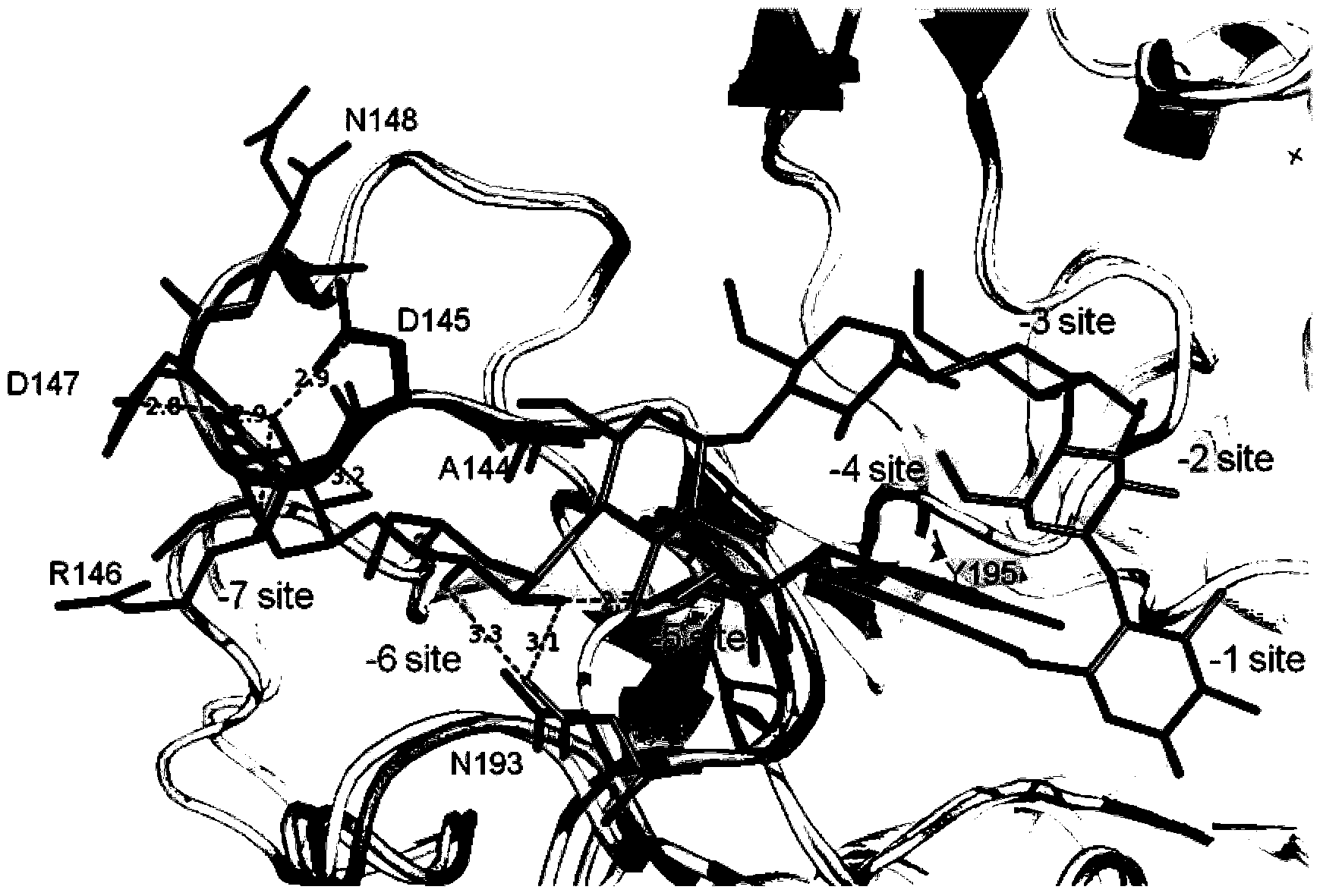
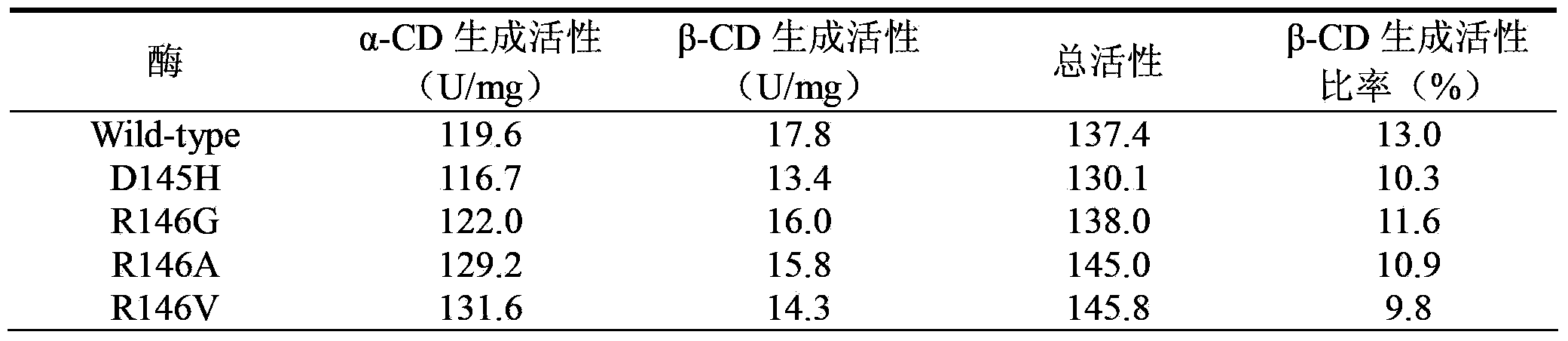
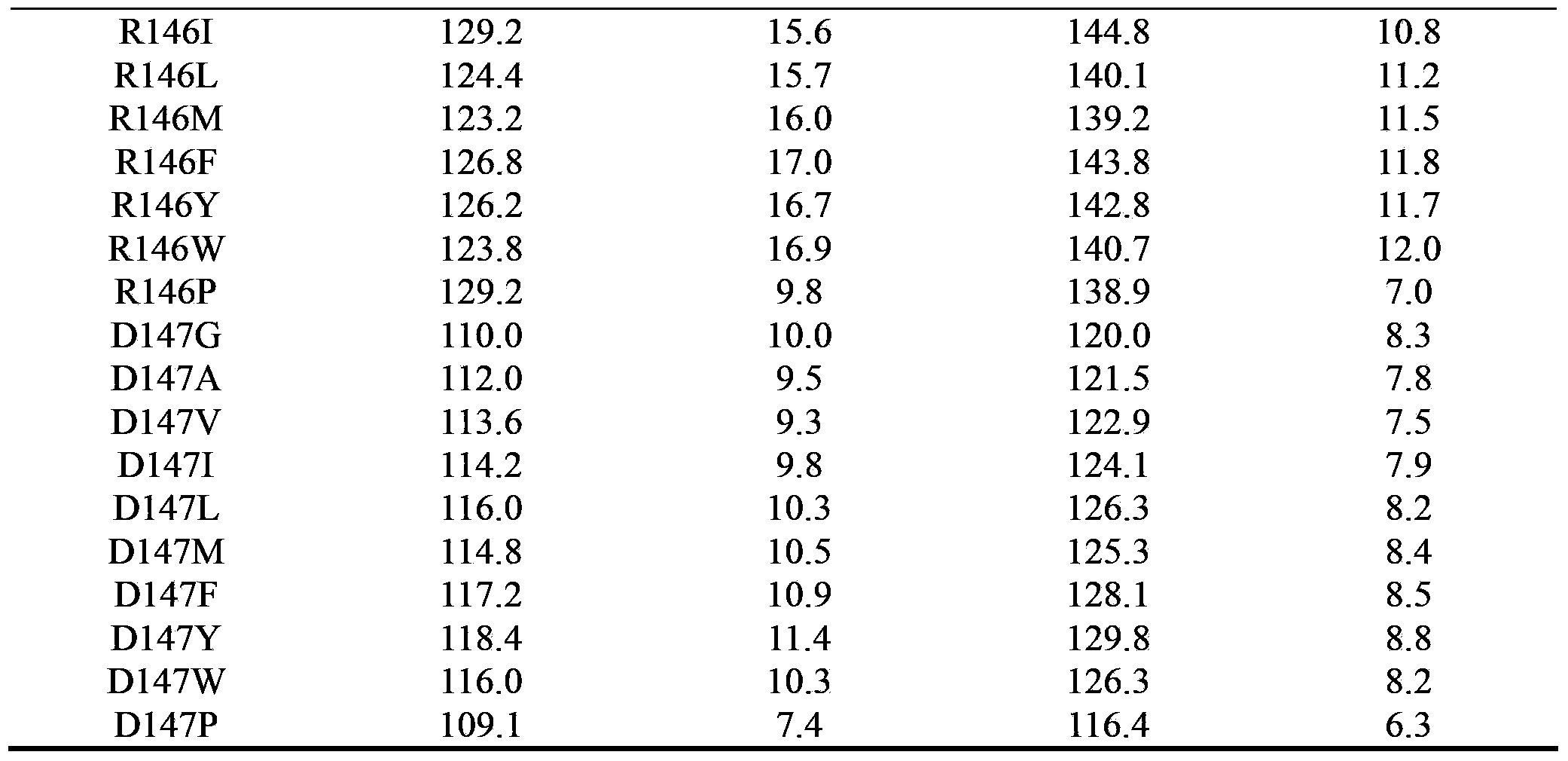
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. The cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant is prepared by transforming CGTase derived from Paenibacillus macerans JFB 05-01 and carrying out site-specific mutation on 145-site Asp,146-site Arg and 147-Asp of CGTase. The production capacity of beta-cyclodextrin of the prepared single mutant enzyme is lowered than that of wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly increased, and the specificity of a principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved; double mutants and three mutants are obtained through combined mutation at the mutation sites of the CGTase; compared with the wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of the beta-cyclodextrin of the mutants is remarkably lowered, the production capacity of the alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly improved, the specificity of the principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved, and therefore, the industrial production of the alpha-cyclodextrin is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for cultivating rosemary
InactiveCN102687634AHigh antibacterial activityAvoid planting difficultiesHorticultureEscherichia coliRosmarinus
The invnetion discloses a method for cultivating rosemary. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: 1), irrigating the rosemary from the end of October to the beginning of November in the north area, at the same time, erecting a plastic shelter, and covering coverings on the outer surface of the plastic shelter; 2), removing the coverings treated in the step 1) at the end of February in the next year; and 3), removing the plastic shelter treated in the step 2) at the end of March in the next year and irrigating the rosemary. Experimental results show that the method disclosed by the invention performs cold-proof cultivation in Beijing, and avoids the cultivation difficulty in the north area; the bacteriostatic activity of an essential oil extracted from the cultivated rosemary is high, so that the essential oil has inhibition effects on escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis and proteus.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
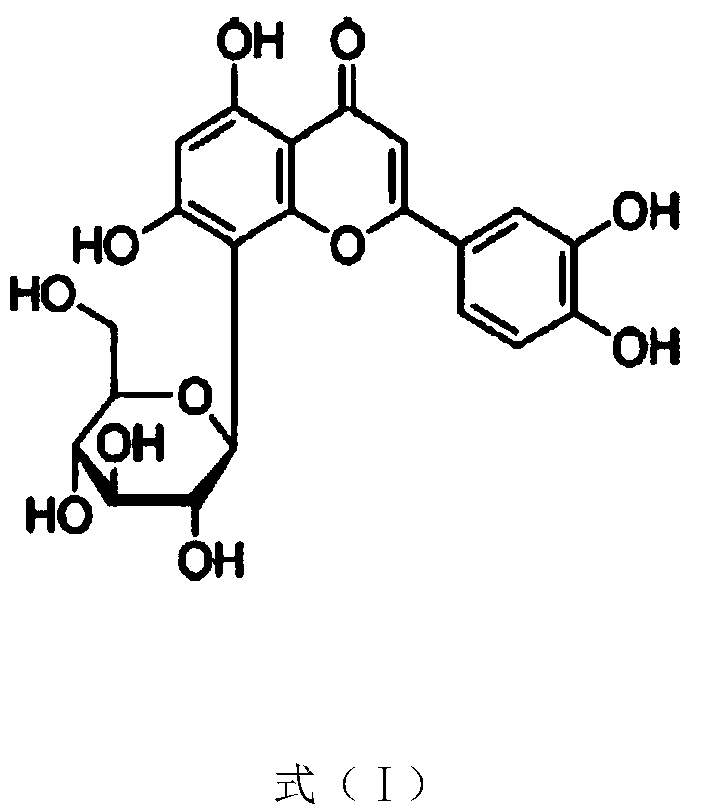
Application of dibenzimidazolamine compound to preparation of antimicrobial medicine
InactiveCN105287522ASimple structureStrong antimicrobial activity in vitroAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntifungalMonilinia laxa
The invention provides an application of a dibenzimidazolamine compound to preparation of an antimicrobial medicine. The dibenzimidazolamine compound has a structure shown as formula (I), and is simple in structure. The dibenzimidazolamine compound is relatively good in in-vitro antimicrobial activity, and performs quite high inhibitory activity of gram positive bacteria, such as staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis, and micrococcus luteus, gram negative bacteria, such as escherichia coli, proteus vulgaris, pseudomonas aeruginosa, and salmonella typhi, and fungi, such as candida utilis, aspergillus flavus, saccharomyces cerevisiae, candida albicans, and candida. The dibenzimidazolamine compound is used for preparing an antibacterial and / or antifungal medicine.
Owner:LINYI UNIVERSITY
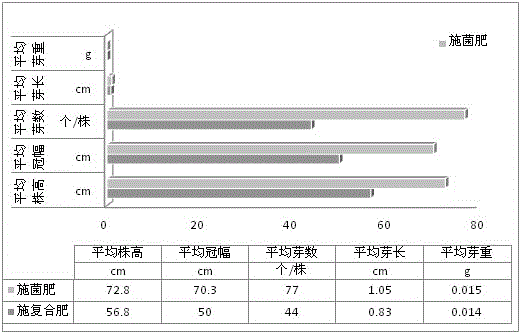
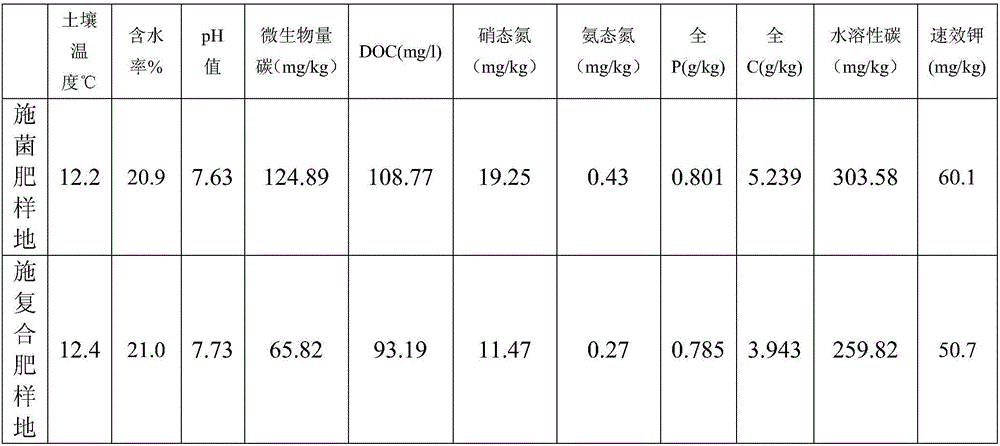
Bacterial fertilizer for increasing budding rate of tea trees and preparation method of same
InactiveCN106365703AImprove germination rateImprove fertilityOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesPaenibacillus polymyxaOrganic compound
The invention discloses a bacterial fertilizer for increasing budding rate of tea trees and a preparation method of same. The bacterial fertilizer includes microorganism compound bacterial powder, and one of an inorganic compound fertilizer, an organic compound fertilizer or an organic / inorganic mixed compound fertilizer containing nutrition elements of N, P and K, wherein the microorganism compound bacterial powder is composed of bacterial powders of bacillus megatherium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus, and paenibacillus. The paenibacillus bacterial powder is paenibacillus polymyxa bacterial powder or paenibacillus macerans bacterial powder. Mass ratio of the microorganism compound bacterial powder to the compound fertilizer is 0.05-1.0 kg : 100 kg. The bacterial fertilizer can improve fertility of soil and promote complete nutritional absorption of root systems of the tea trees. The invention also provides a method of preparing the bacterial fertilizer for increasing the budding rate of the tea trees, wherein the method is simple.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
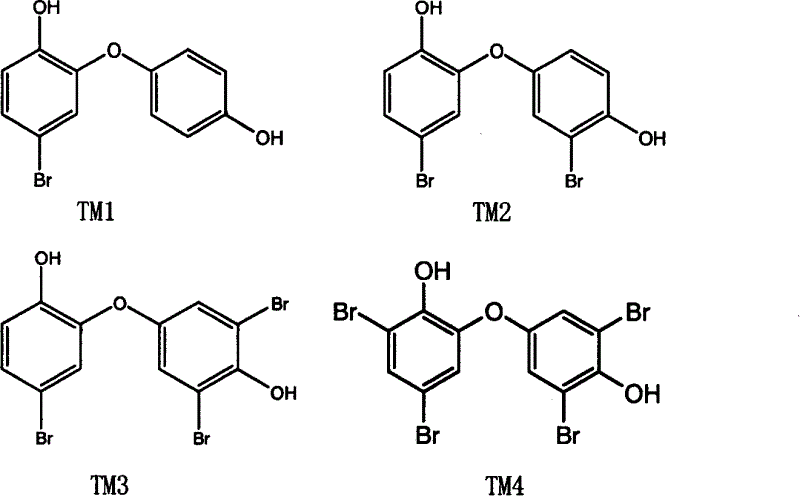
Bromo-2, 4'-dihydroxy diphenyl ether compound and its synthesizing method
The inventiona relates to bromo-2, 4í»-dihydroxyl diphenyl ether compound and its synthesizing method, using 2-methoxy phenol and 4-methoxy chlorobenzene as raw materials, and it is an antimicrobial obtained by three-step reaction, and has better antimicrobial activity to Escherichia coli, catarrh diplococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus Albus, bacillus proteus, etc. and avoids producing highly toxic dioxin compound in the producing and using course, avoiding environmental pollution and damaging human health; and also overcomes the shortages that natural bromic2, 4í»-dihydroxyl diphenyl ether antimicrobial can form highly toxic dioxin compound in use on certain conditions, and the natural bromic2, 4í»-dihydroxyl diphenyl ether antimicrobial has limited source, complex extracting course and high cost..
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Paenibacillus macerans and straw decomposing agent
ActiveCN108504586AShort degradation timeDecomposition is stableBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaMicrobiologyViable Cell Count
The invention discloses a straw decomposing agent which comprises components of Paenibacillus macerans CGMCC No. 14564 and Bacillus subtilis CICC No. 10089; the total effective viable cell count in the decomposing agent is 0.5*10<8>-2*10<8> / g, and the effective viable cell count of the Paenibacillus macerans is 65%-70% of the total effective viable cell count; the invention also discloses a preparation method of the straw decomposing agent, compared with use of various strains to prepare the decomposing agent in the prior art, the preparation method has a small variety of raw materials, and has a simple preparation process, the Bacillus subtilis whoch is not used in the prior art is used in the preparation method as one of the raw materials to interact with the Paenibacillus macerans, andthe use effect is remarkable, so that the preparation method can be promoted in related enterprises.
Owner:四川明湖环保科技有限公司
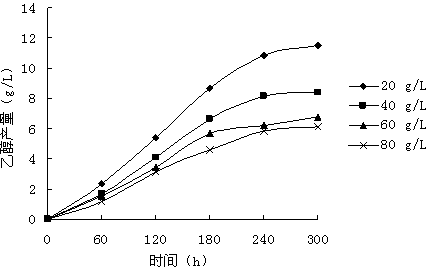
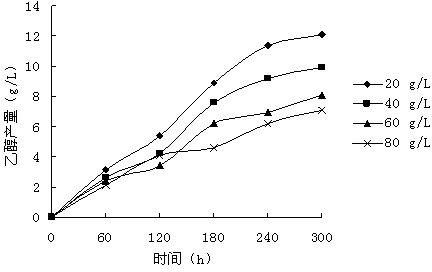
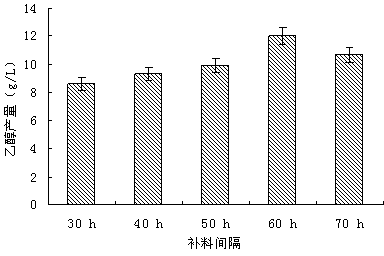
Method for producing ethanol by adopting mixed culture organism by means of glycerol fermentation
The invention provides a method for producing ethanol by adopting paenibacillus macerans and monasucs by means of glycerol mixed culture fermentation. According to the invention, the paenibacillus macerans and monasucs are taken as original strains and glycerol as raw materials, researches are carried out on initial glycerol concentration, glycerol concentration in feeding supplement, feeding supplement time interval, fermentation time and slurry quantity that influence the ethanol yield.
Owner:TAICANG ZHOUSHI CHEM PROD
Plant derived antibiotic peptide rich in glycine
The present invention relates to a novel peptide extracted from guava (Psidium guajava) seeds, that provides bactericide activity, Preferentially against Gram-negative bacteria which are known to cause urinary, hospital, and intestinal tract infections (Proteus sp. And Klebsiella sp.). The peptide, that has the amino acid sequence RESPSSRMEC YEQAERYGYG GYGGGRYGGG YGSGRGQPVG QGVERSHDDN RNQPR, belongs to the class of glycine rich proteins and has approximately 5 kDa of molecular weight. The invention also relates to antibiotic compositions for human, veterinary and plant treatments. Alternatively, the peptide, or a functionally similar derivative, subjects of the present invention, can be used for transforming organisms aiming pathogen resistance, other adaptive advantages, as well as various properties, specially for plants and animals.
Owner:UNIAO BRASILEIRA DE EDUCACAO CATOLICA UBEC +1
Application of Houttuynoid C in antibacterial medicine
ActiveCN102872105AStrong inhibitory activitySignificant progressAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesEscherichia coli
The invention relates to application of Houttuynoid C in preparing an antibacterial medicine, belonging to the field of medicines. The Houttuynoid C has a strong effect on suppressing escherichia coli, pseudomonas fluorescens, staphylococcus aureus, proteusbacillus vulgaris and cryptococcus neoformans, thus the Houttuynoid C can be used as an antibacterial compound and is expected to be used in preparing related medicines. The application of Houttuynoid C in preparing an antibacterial medicine is disclosed for the first time; and since the skeleton type is a brand new one and the activity in suppressing bacterial activity is unexpectedly strong, the possibility of any other compound offering any inspiration does not exist, outstanding substantial characteristics are obtained, and an obvious progress is made in preventing and treating bacterial infection.
Owner:如东文园投资开发有限公司
Method of consolidated bioprocessing of lignocellulosic biomass for production of L-lactic acid
The present invention pertains to a method for consolidated bio processing of lignocellulosic biomass to L-Lactic acid. Particularly, the present invention relates to the production of L-Lactic Acid from low cost non edible feedstock lignocellulosic biomass. More particularly the present invention relates to the process for one step production of L-Lactic Acid from lignocellulosic biomass using thermophilic bacteria Paenibacillus macerans IIPSP3 (MTCC 5569), which is not only capable of hydrolyzing cellulose to glucose but also further fermenting it to L-Lactic Acid under aerobic conditions, without any growth inhibition in presence of lignin. The present invention provides a process which has less chances of contamination, as the fermentation is carried out at higher temperatures and is economically attractive, as preferably no external enzyme loadings are required.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Application of shiitake mushroom volatile oil in preparation of antibacterial drugs or food preservatives
InactiveCN108338995ABroad spectrum antibacterialLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsFood preservationFood poisoningAntibacterial activity
The invention provides application of shiitake mushroom volatile oil in preparation of antibacterial drugs or food preservatives. Experimental results show that the shiitake mushroom volatile oil hasa wider antibacterial spectrum, has a better inhibitory effect on drug-resistant bacteria and especially methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus, is low in toxicity and convenient to extract, andhas great application prospects when being developed into drugs; and the shiitake mushroom volatile oil has certain antibacterial activity on the bacteria such as proteus species and typhoid bacilluscausing food deterioration, so that the shiitake mushroom volatile oil has certain application potential in the aspects of preventing food deterioration, preventing food poisoning and the like and hasdevelopment potential of serving as a natural preservative.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Toona sinensis endophytic fungus 56-50 and its secondary metabolites, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106520572BHigh antibacterial activitySimple methodAntibacterial agentsFungiMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbes, and discloses a Toona sinensis endophytic fungus 56-50. spore Alternaria mali ; Preservation unit: General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, preservation address: Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 3, No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, preservation date: September 30, 2016, preservation number: CGMCC No. 12980. The present invention isolates an endophytic fungus from the stem of Toona sinensis for the first time Alternaria mali , the secondary metabolites of the bacteria have good inhibitory effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Proteus. The preparation of Toona sinensis endophyte 56-50 ( Alternaria mali ) The method for secondary metabolites is simple and easy, and the cost is low.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of orientin in preparation of antibacterial drugs
InactiveCN107865881AStrong inhibitory activitySignificant progressAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention relates to application of orientin in preparation of antibacterial drugs. Orientin has strong inhibition effect on Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Staphylococcus aureus, Proteusbacillus vulgaris and Cryptococcus neoformans, and thus, orientin can be used as an antibacterial compound. The application of orientin in preparation of antibacterial drugs is disclosed for the first time; orientin has good bacteriostasis activity; the application of orientin has outstanding substantive distinguishing features; meanwhile, substantial progress is made as orientin is applied to prevention and treatment of bacterial infections.
Owner:ZIBO DINGLI PATENT INFORMATION CONSULTING CO LTD
Chinese and western compound disinfectant solution for disinfection in examination rooms and preparation method
InactiveCN107912468AGood treatment effectImprove the ingredients of traditional Chinese medicineBiocideDead animal preservationEscherichia coliDisinfectant
The invention discloses a Chinese-Western compound disinfectant used for laboratory disinfection and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of medicine; the ingredients of the disinfectant in the invention are composed of sassafras, amaranthus, purple back vegetable, yin xiangpi, oil Citrus leaves, garlic, salt bran, misty kudzu, sharp tail wind, sticky grass, wild chrysanthemum, willow root, scorpion tree lotus, chlorhexidine, povidone iodine and glutaraldehyde; the disinfectant of the present invention uses traditional Chinese and Western medicine The combined treatment method is more effective than the simple use of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine. With the principle of sterilization, insecticide, disinfection and anti-inflammation, it can maximize the efficacy of Chinese medicine ingredients and western medicine, play a complementary and enhancing role, and improve the medicinal effect , has antimicrobial effect, can destroy the permeability barrier of cell wall, reduce the enzyme activity, denature the bacterial protein, and thus play a bactericidal effect. It is effective against Staphylococcus aureus, E. Bacteria, common Proteus, etc. have good sterilization and disinfection effects.
Owner:崔庆军
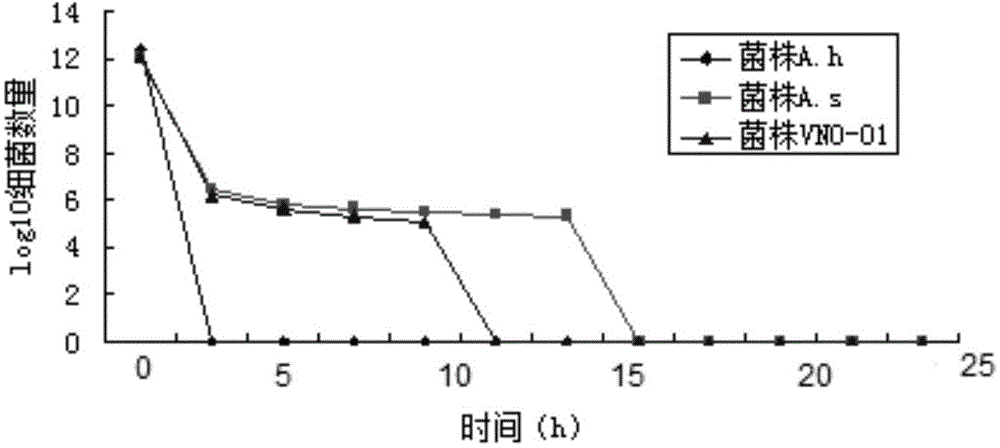
A novel bacteriostatic compound, a preparing method thereof and applications of the bacteriostatic compound in aquatic products
InactiveCN105777536ABroad spectrum antibacterialLow side effectsAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention relates to a novel bacteriostatic compound named as Butein-0908, a preparing method thereof and applications of the bacteriostatic compound in aquatic products. When the mass percentage is 0.06%, the bacteriostatic compound can inhibit staphylococcus aureus, bacillus subtilis, salmonella bacillus, bacillus proteus and escherichia coli, has strong inhibiting functions for common pathogenic bacteria of the aquatic products, has obvious and rapid sterilization functions for aeromonas hydrophila, aeromonas sobria and non-O1 group vibrio cholerae, and can kill all bacteria in 12 h. Accordingly, the bacteriostatic compound is wide in antibacterial spectrum, few in side and toxic effects and high in bacteriostatic activity, is especially suitable for the common pathogenic bacteria of the aquatic products, and can be widely used as an economical and environmental friendly bacteriostatic agent for aquatic product bacteriostasis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
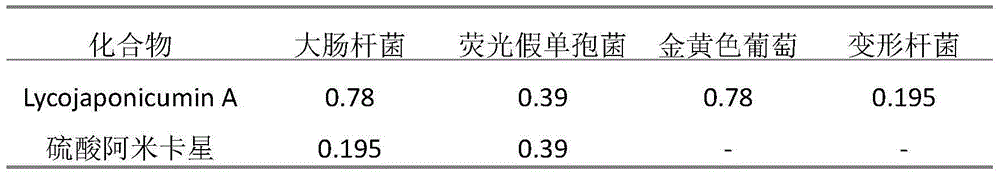
Application of lycojaponicumin A in the preparation of antibacterial drugs
ActiveCN103463037BStrong inhibitory activitySignificant progressAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBacteroidesEscherichia coli
Owner:FENGJIE DONGYANG BUILDING MATERIALS CO LTD
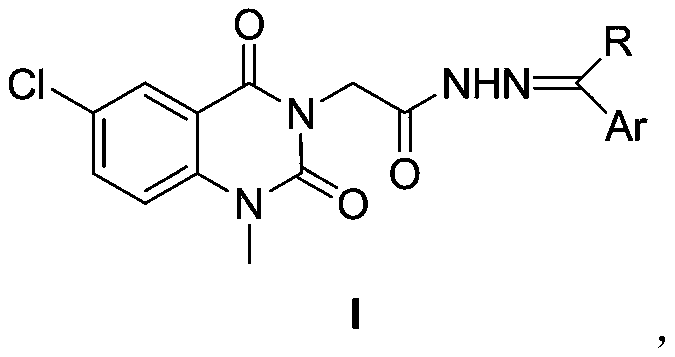
A kind of acetylhydrazone compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106279046BEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsEscherichia coliAntifungal drug
Owner:LIUPANSHUI NORMAL UNIV
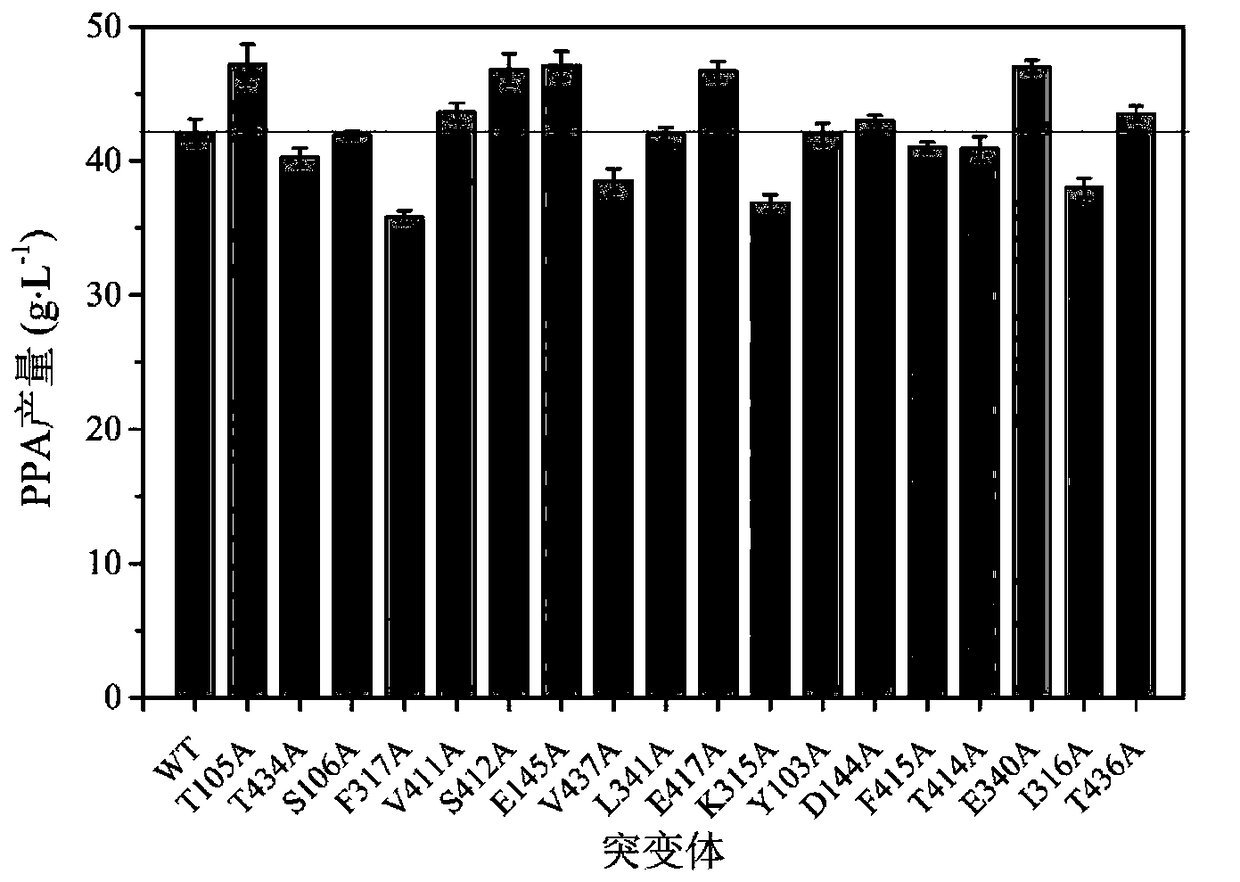
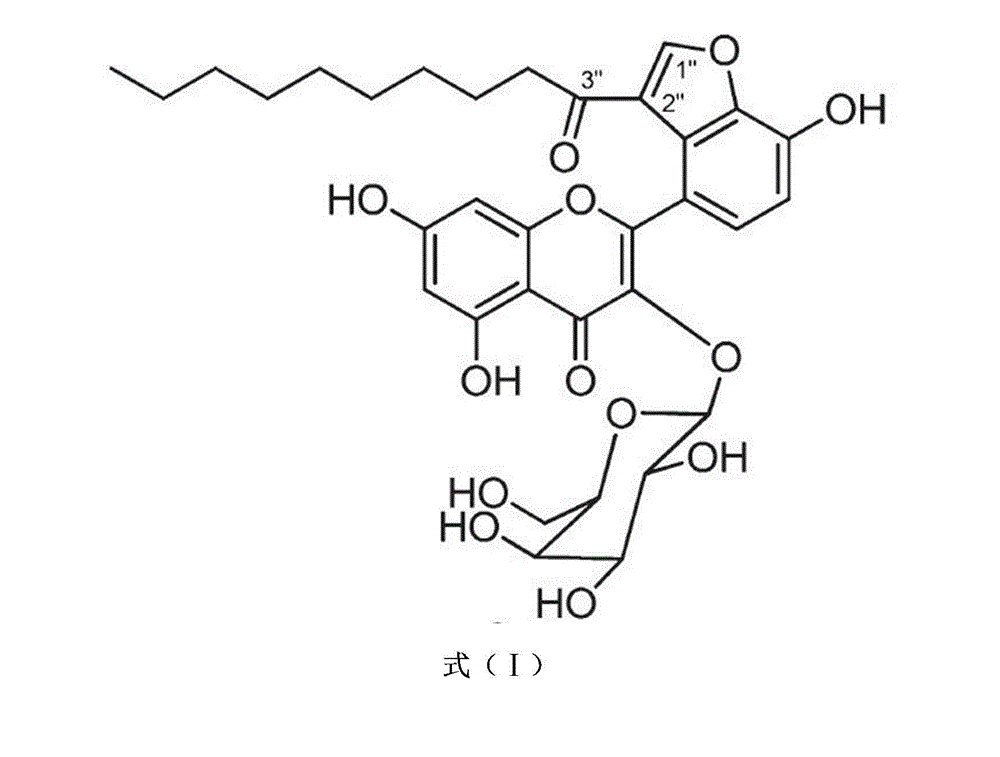
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutants with improved disproportionation specific activity and aa-2g production
ActiveCN111534498BIncreased disproportionation specific activityIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationCyclodextrinEngineered genetic
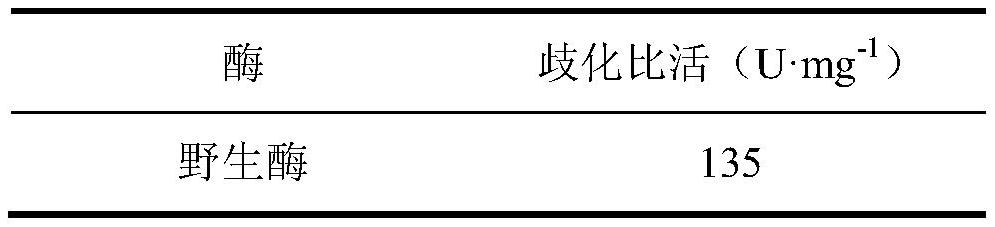
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with improved disproportionation specific activity and AA-2G yield, belonging to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The present invention mutates the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase derived from Paenibacillusmacerans JFB05-01, and the obtained mutant has significantly improved disproportionation specific activity, wherein, the yield of AA-2G produced by the mutant Y195F / Y260F is 22g / L, which is higher than that of the wild enzyme 46.7%, the conversion rate is improved, the production cost is reduced, and it is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Technology for producing alpha-cyclodextrins by biological method
ActiveCN101712972BImprove conversion rateLow costTransferasesMicroorganism based processesGlycosyltransferaseAlpha-cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
The invention discloses technology for producing alpha-cyclodextrins (alpha-CGT) by a biological method, belonging to the technical field of cyclodextrins production. The alpha-CGT is produced by adopting alpha-cyclodextrins glycosyltransferase (alpha-CGTase) derived from paenibacillus macerans (China Center for Type Culture Collection of Microbe, CCTCCM 208063). By applying the technology to produce alpha-CGT, the total conversion of starch is as high as 71%, and in the product, alpha-CGT accounts for 80% and beta-CGT accounts for 20%. The technology has the advantages of simple flow, short production cycle, high conversion and high purity of the obtained alpha-CGT, etc.
Owner:山东黄三角生物技术产业研究院有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com