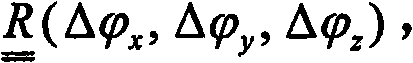Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
741 results about "Magnet resonance imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
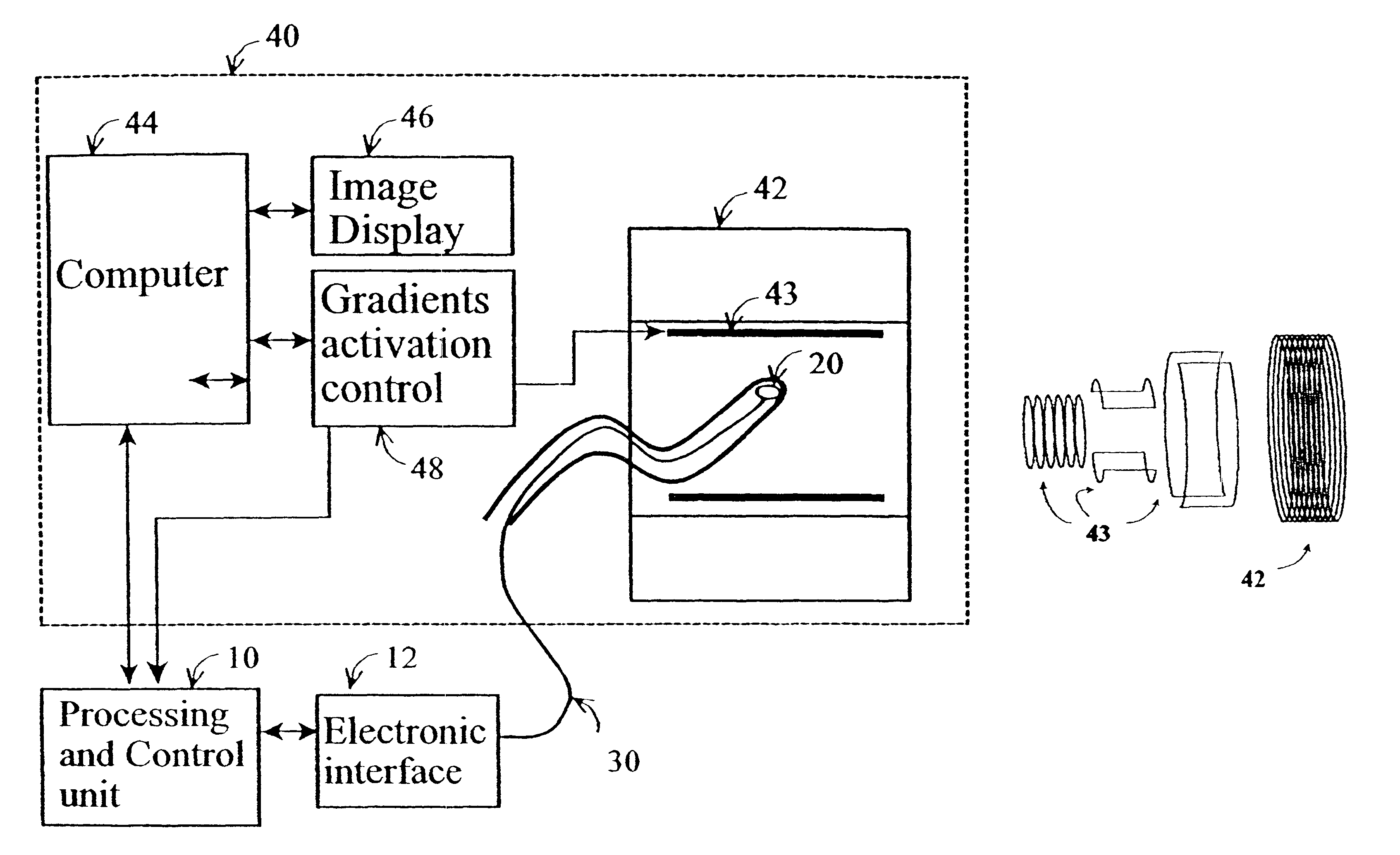
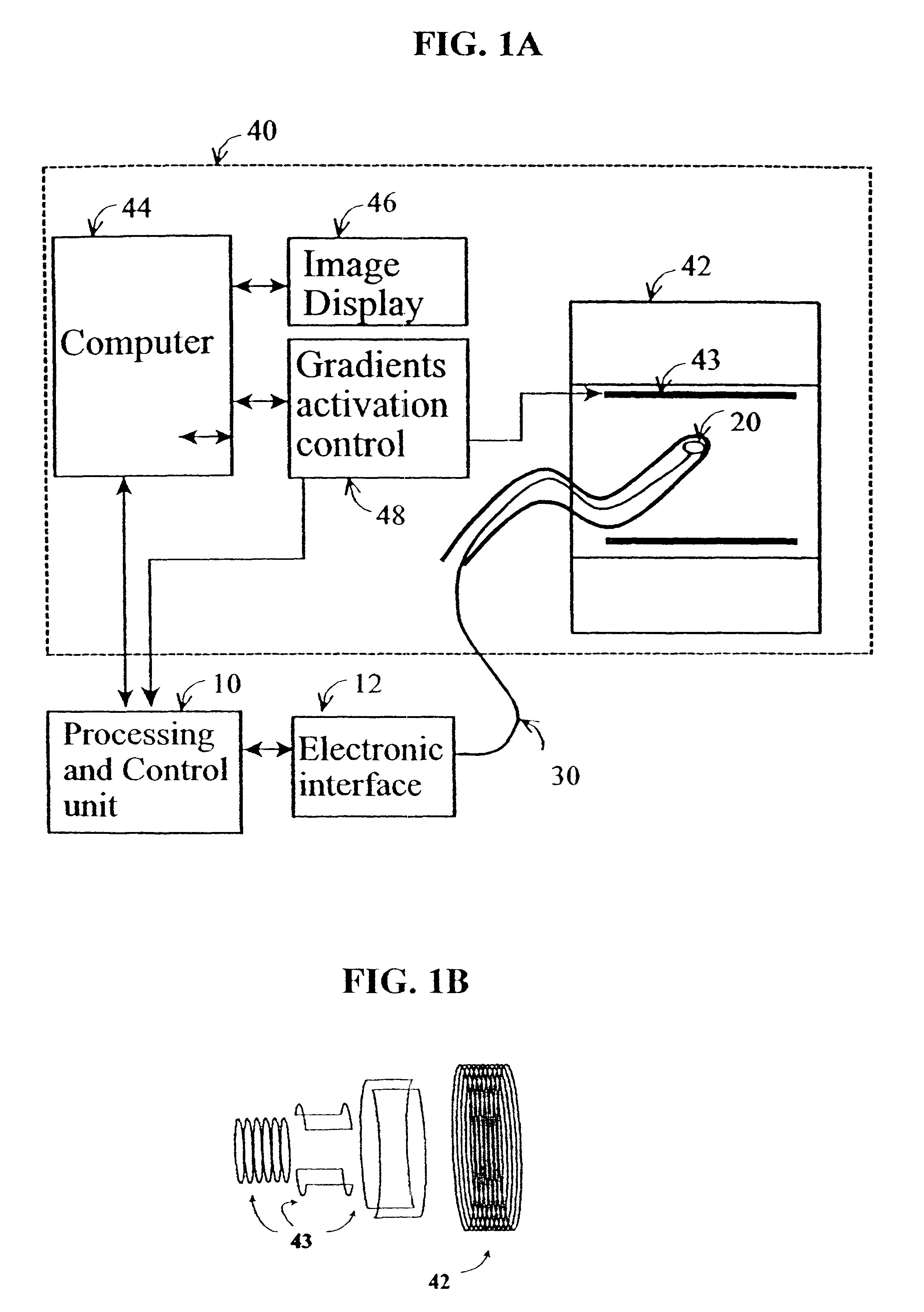
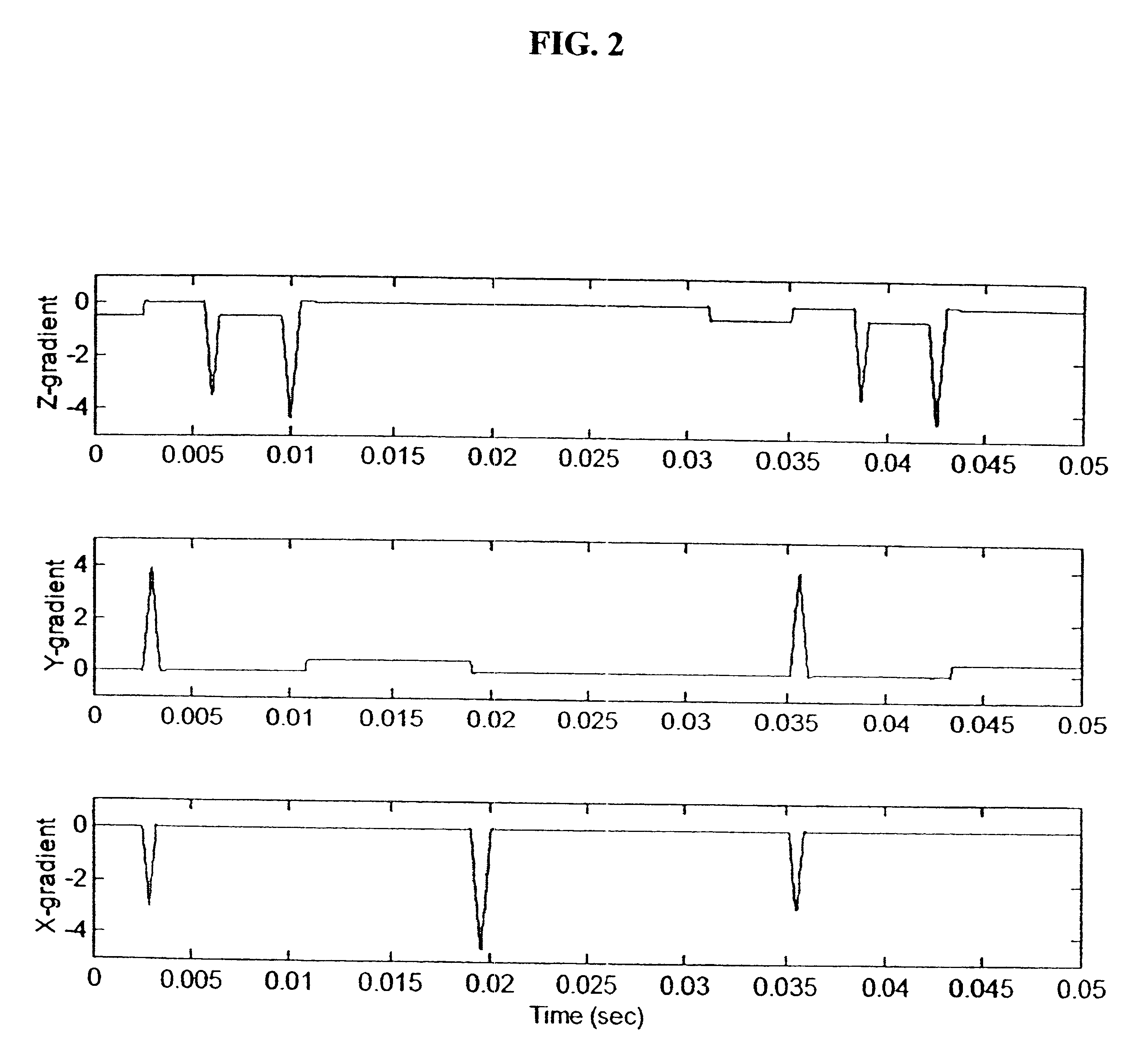
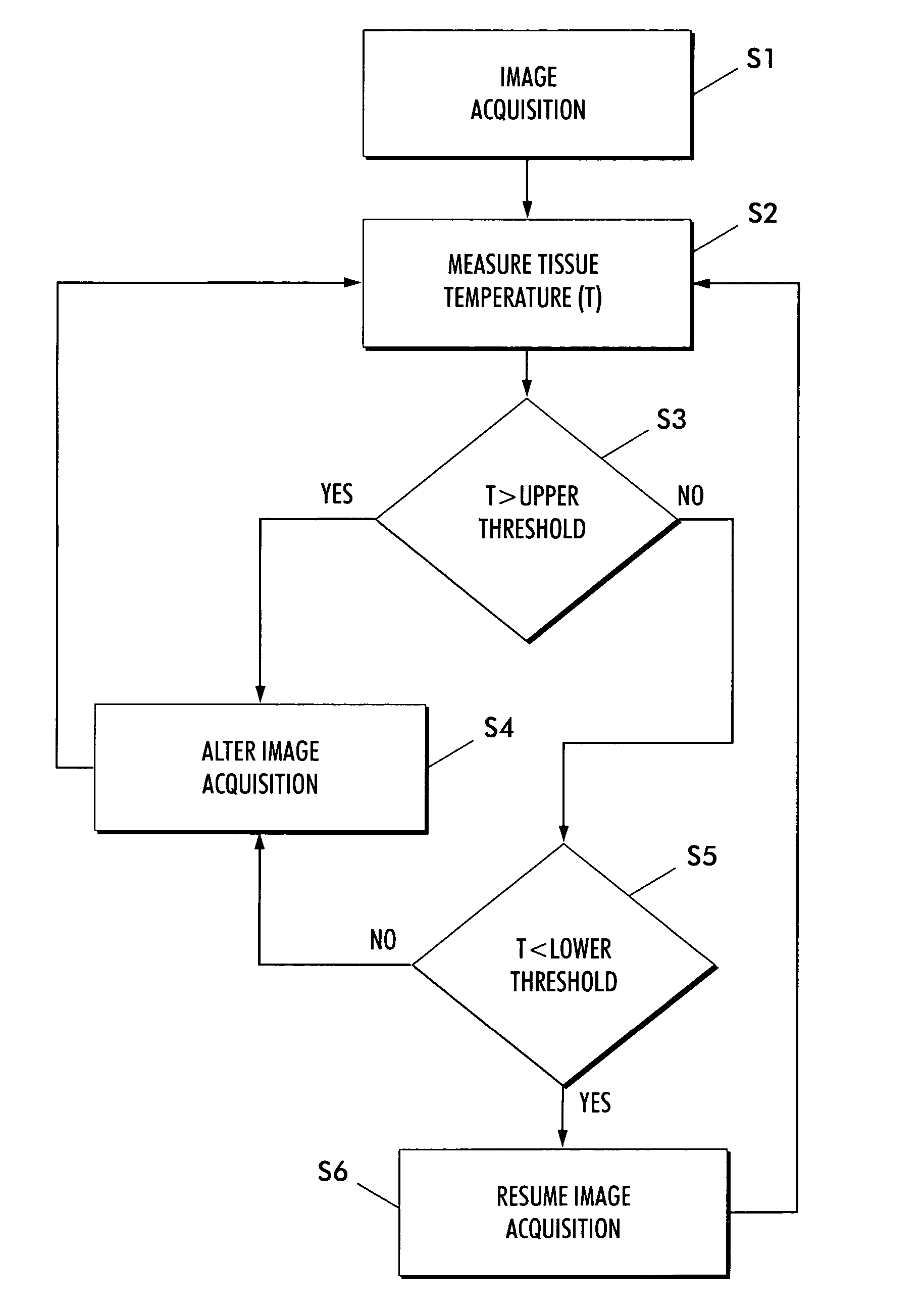
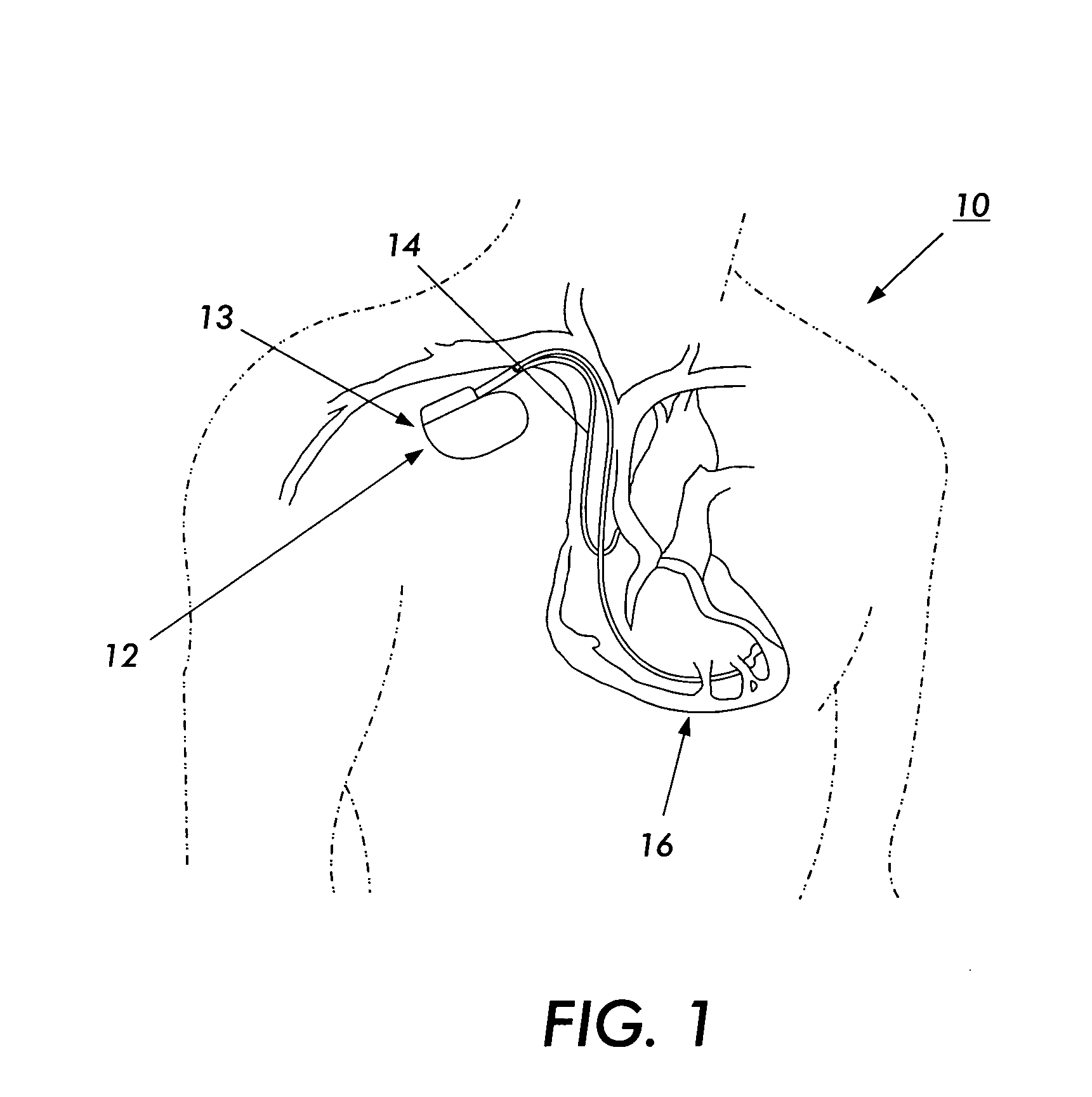
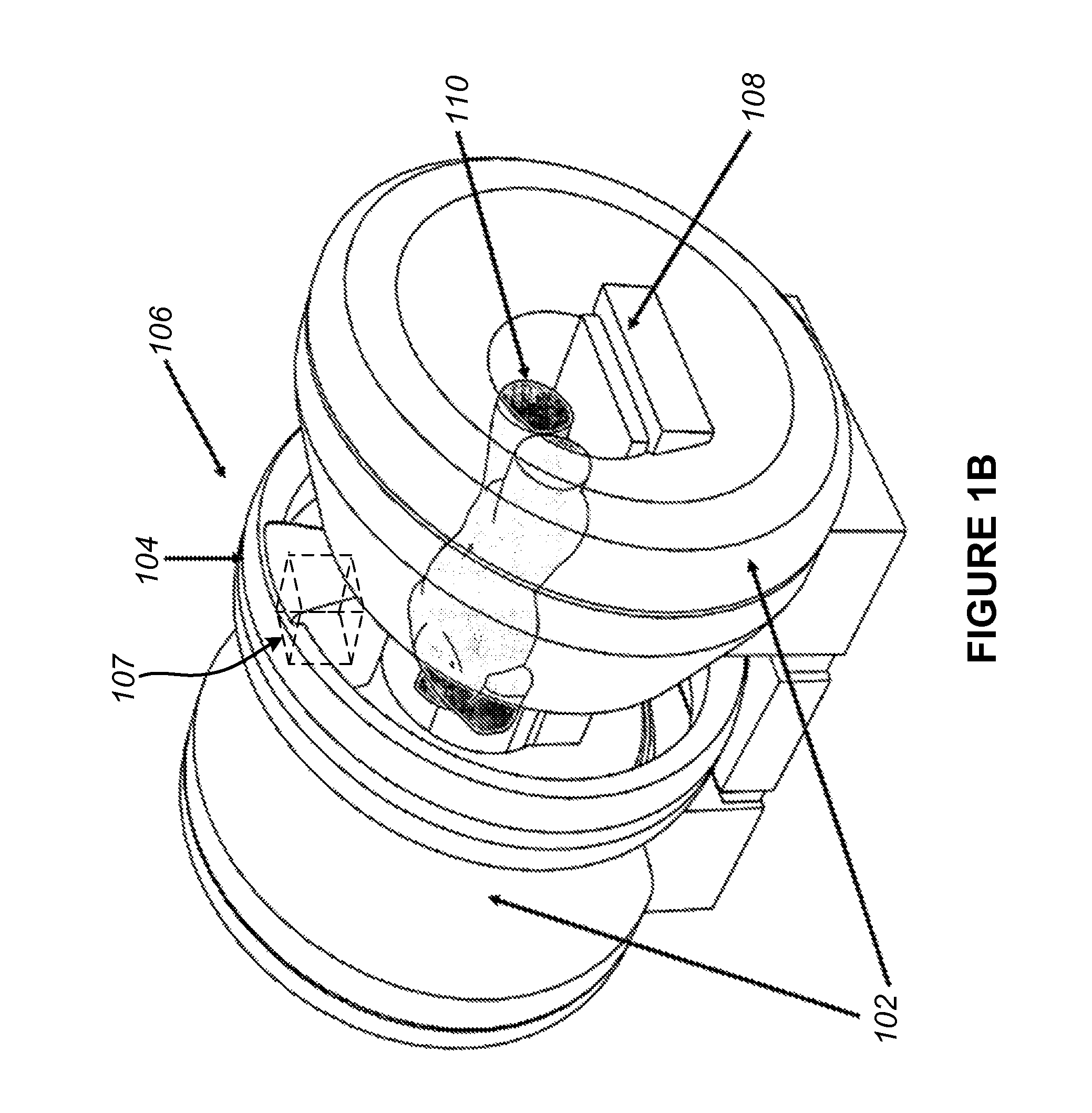
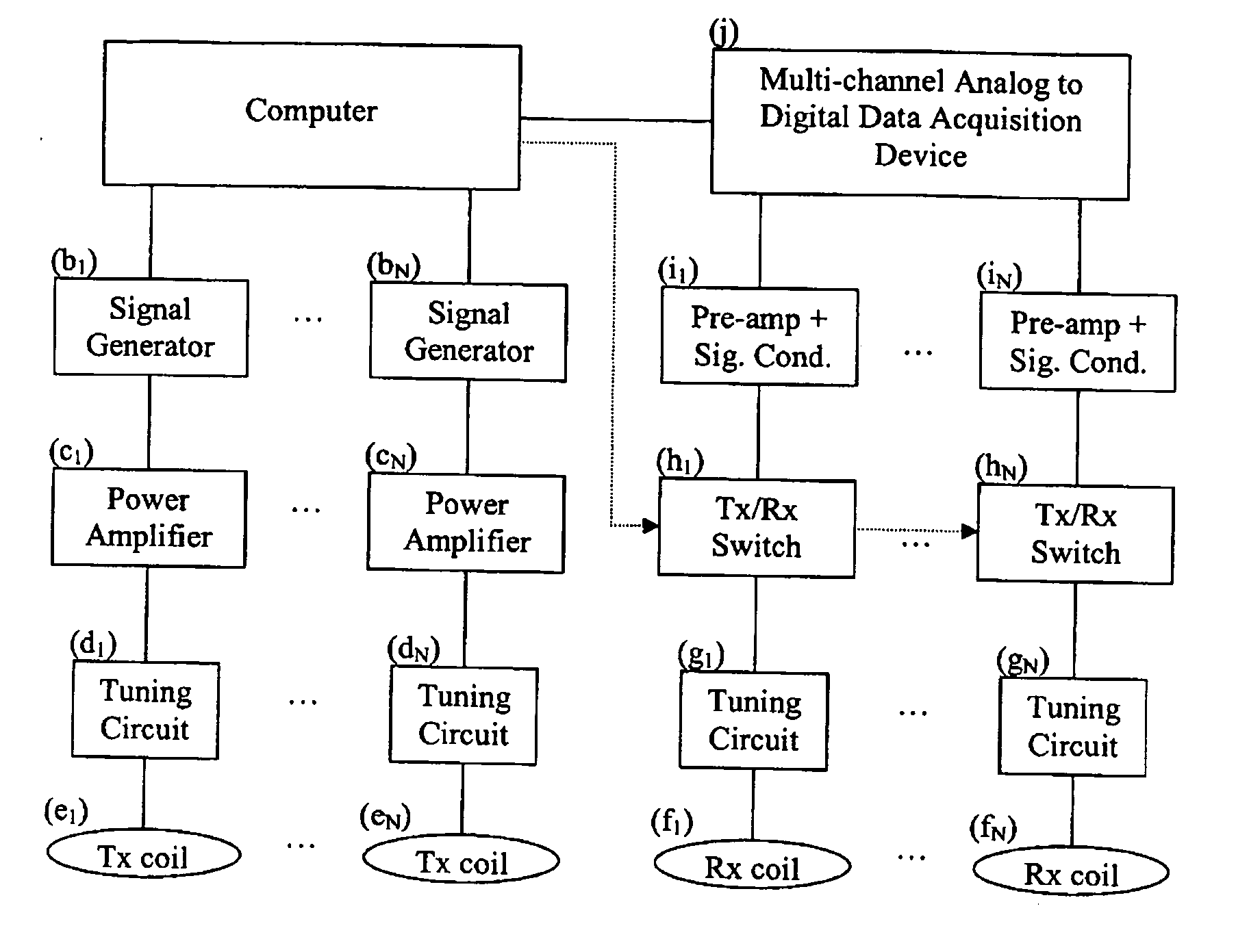
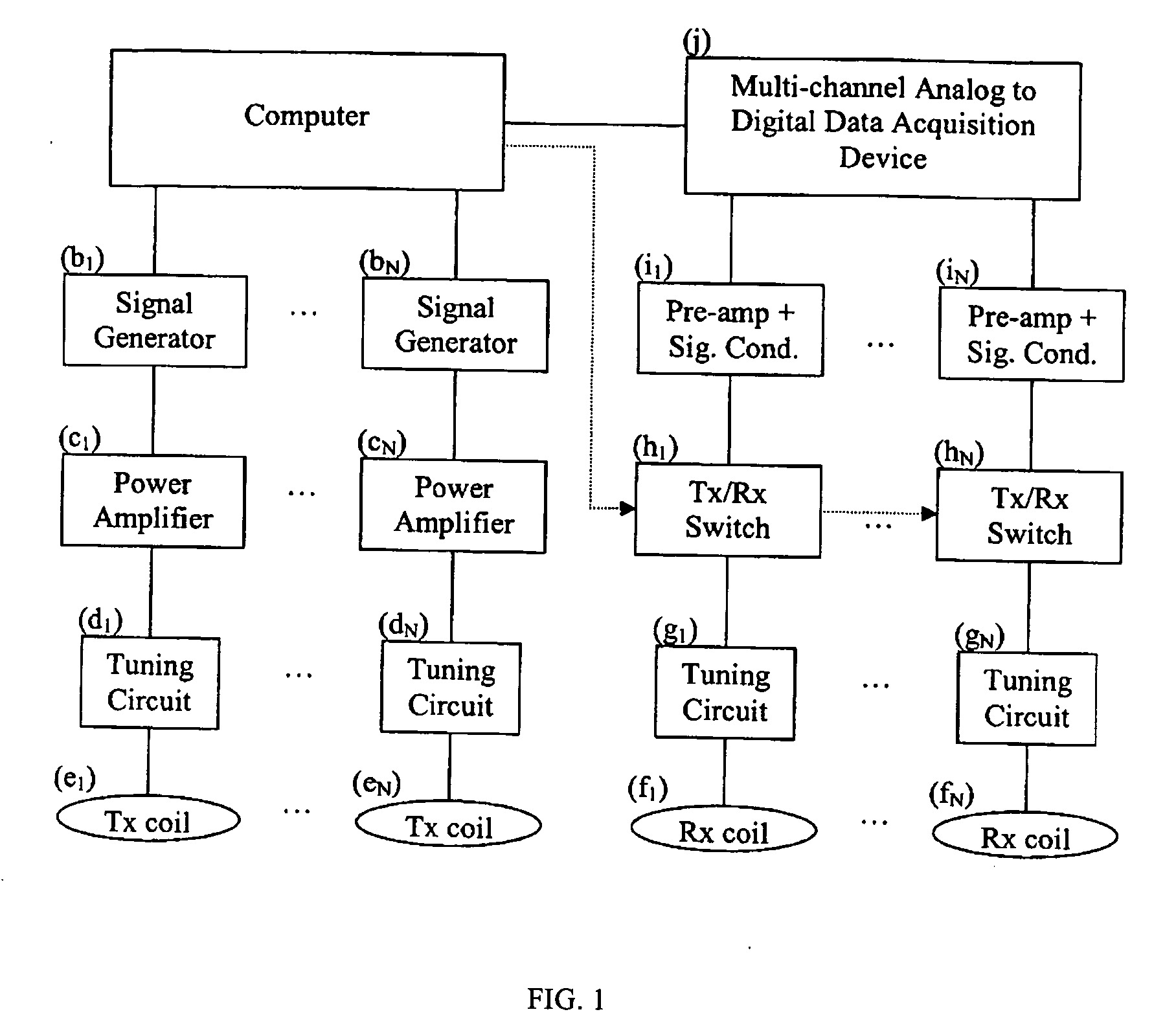
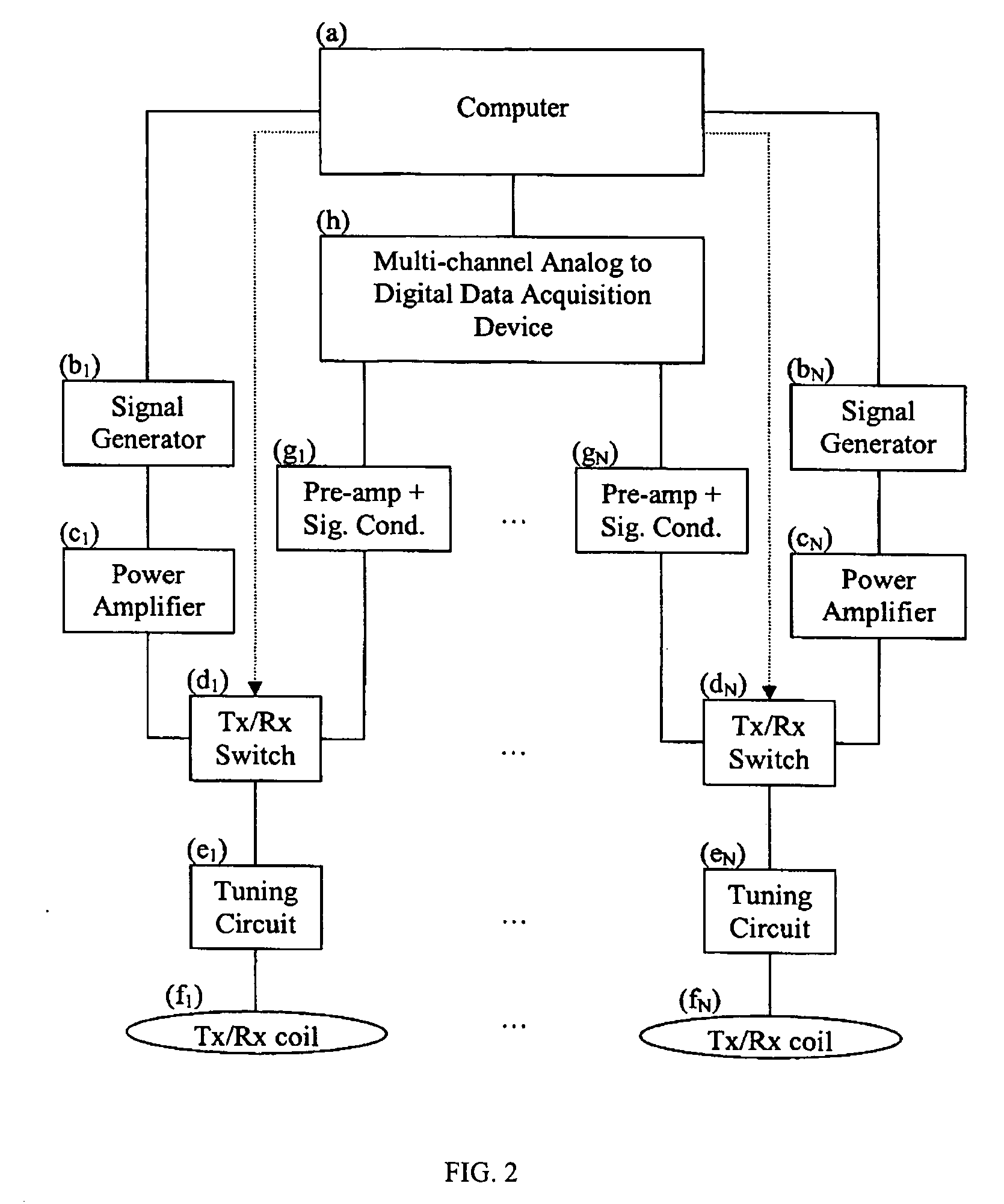
Method and apparatus to estimate location and orientation of objects during magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS6516213B1Limited accuracy of orientationSatisfies requirementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic field gradientThree-dimensional space
Method and apparatus for determining the instantaneous location, the orientation of an object moving through a three-dimensional space by applying to the object a coil assembly including a plurality of sensor coils (20) having axes of known orientation with respect to each other including components in the three orthogonal planes; generating a time-varying, three-dimensional magnetic field gradient having known instantaneous values of magnitude and direction; applying the magnetic field gradient to the space, and object moving therethrough to induce electrical potentials in the sensor coils; measuring the instantaneous values of the induced electrical potentials generated in the sensor coils; processing the measured instantaneous values generated in the sensor coils together with the known magnitude, direction of the generated magnetic field gradient, the known relative orientation of the sensor coils in the coil assembly to compute the instantaneous location, orientation of the object within the space.
Owner:ROBIN MEDICAL
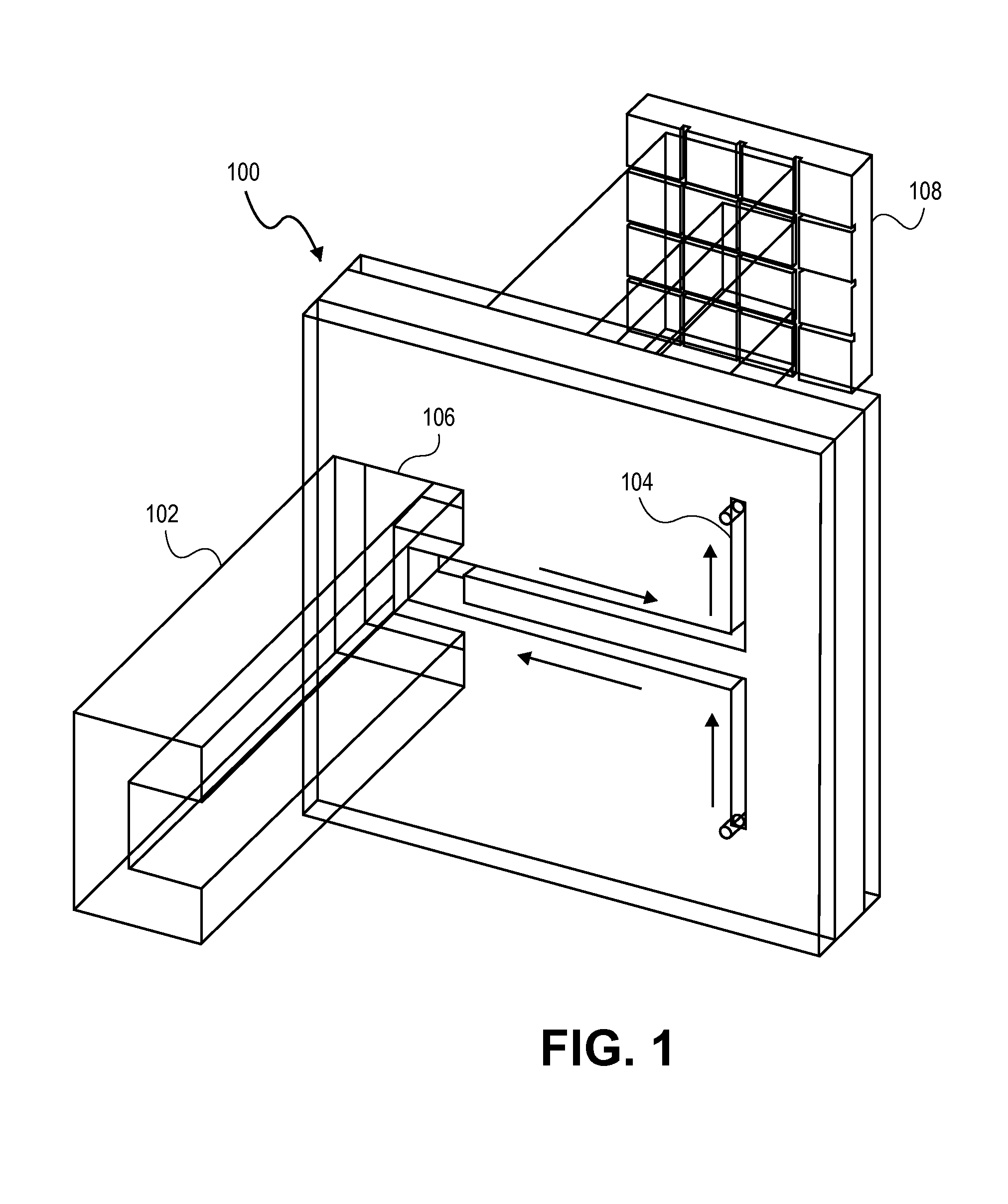
Device and method for preventing magnetic resonance imaging induced damage
An electromagnetic shield has a first patterned or apertured layer having non-conductive materials and conductive material and a second patterned or apertured layer having non-conductive materials and conductive material. The conductive material may be a metal, a carbon composite, or a polymer composite. The non-conductive materials in the first patterned or apertured layer may be randomly located or located in a predetermined segmented pattern such that the non-conductive materials in the first patterned or apertured layer are located in a predetermined segmented pattern with respect to locations of the non-conductive materials in the second patterned or apertured layer.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
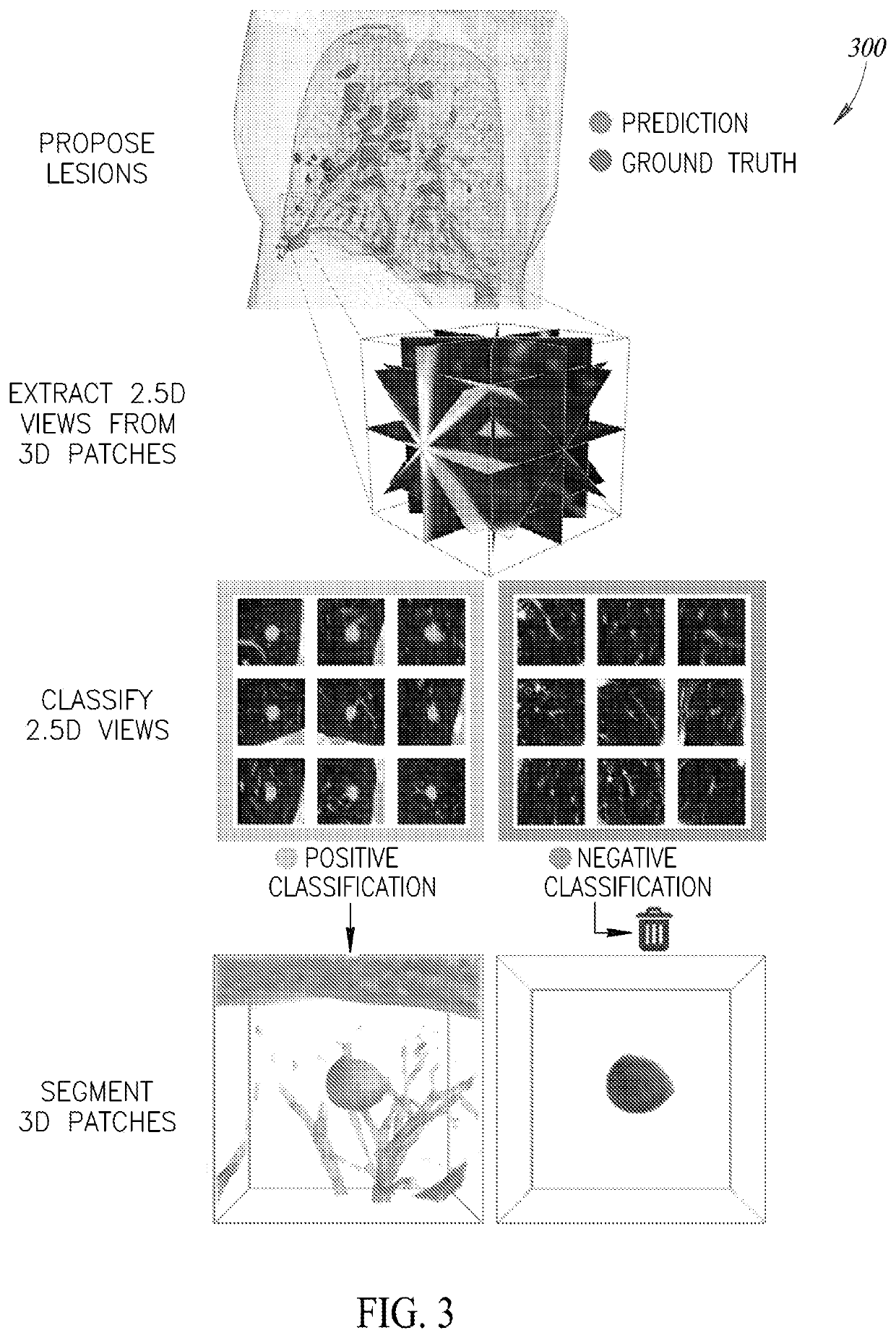
Automated lesion detection, segmentation, and longitudinal identification
InactiveUS20200085382A1Reducing penaltyImage enhancementQuantum computersComputed tomographyLesion detection
Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are commonly used to assess patients with known or suspected pathologies of the lungs and liver. In particular, identification and quantification of possibly malignant regions identified in these high-resolution images is essential for accurate and timely diagnosis. However, careful quantitative assessment of lung and liver lesions is tedious and time consuming. This disclosure describes an automated end-to-end pipeline for accurate lesion detection and segmentation.
Owner:ARTERYS INC
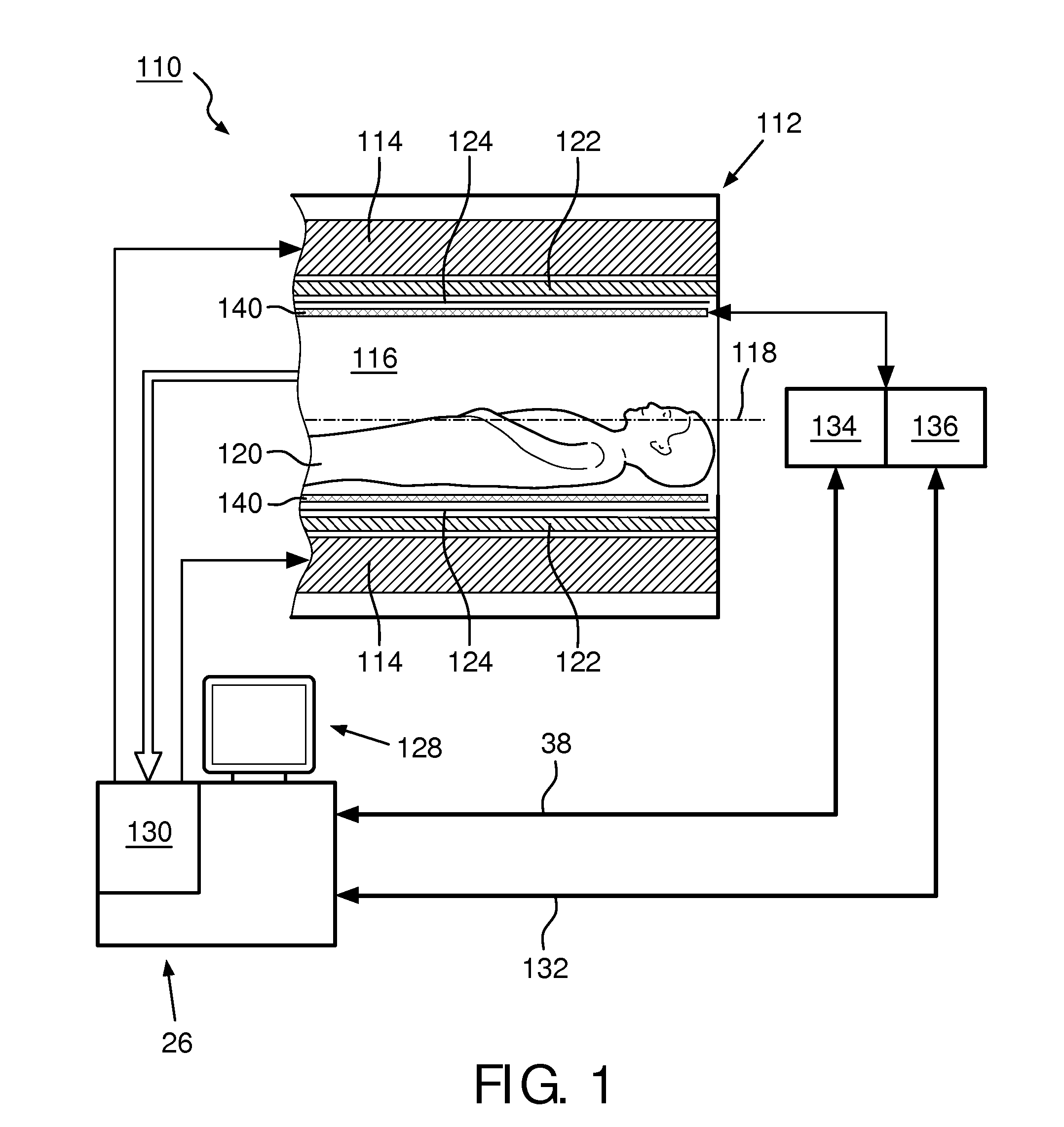
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS20110012593A1Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
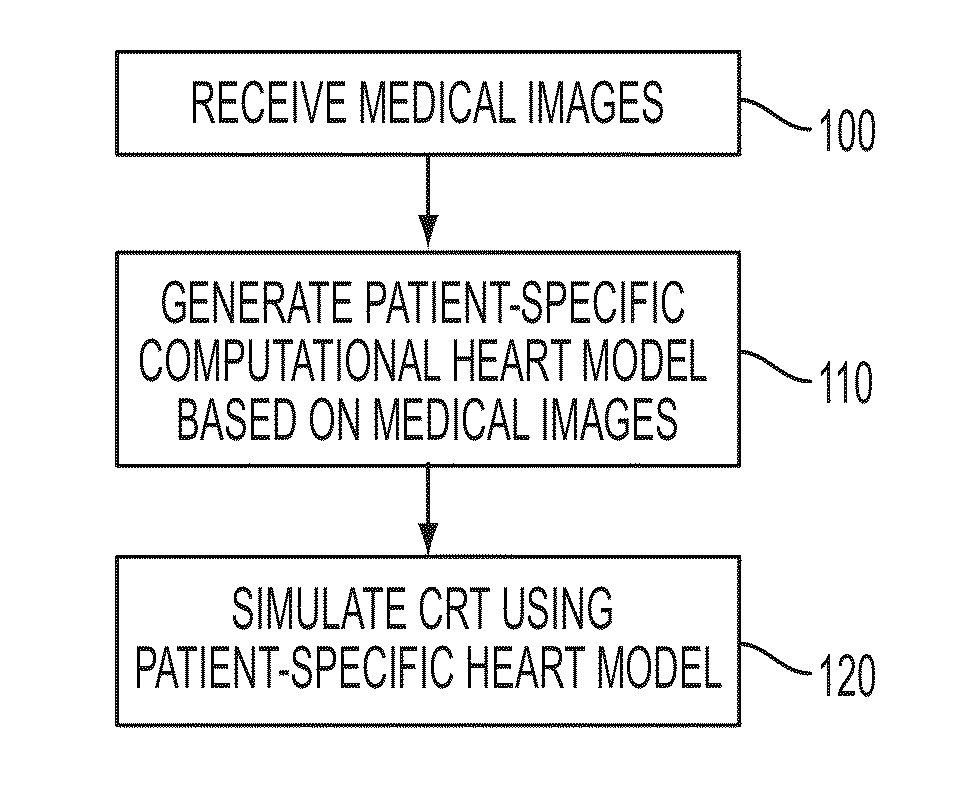
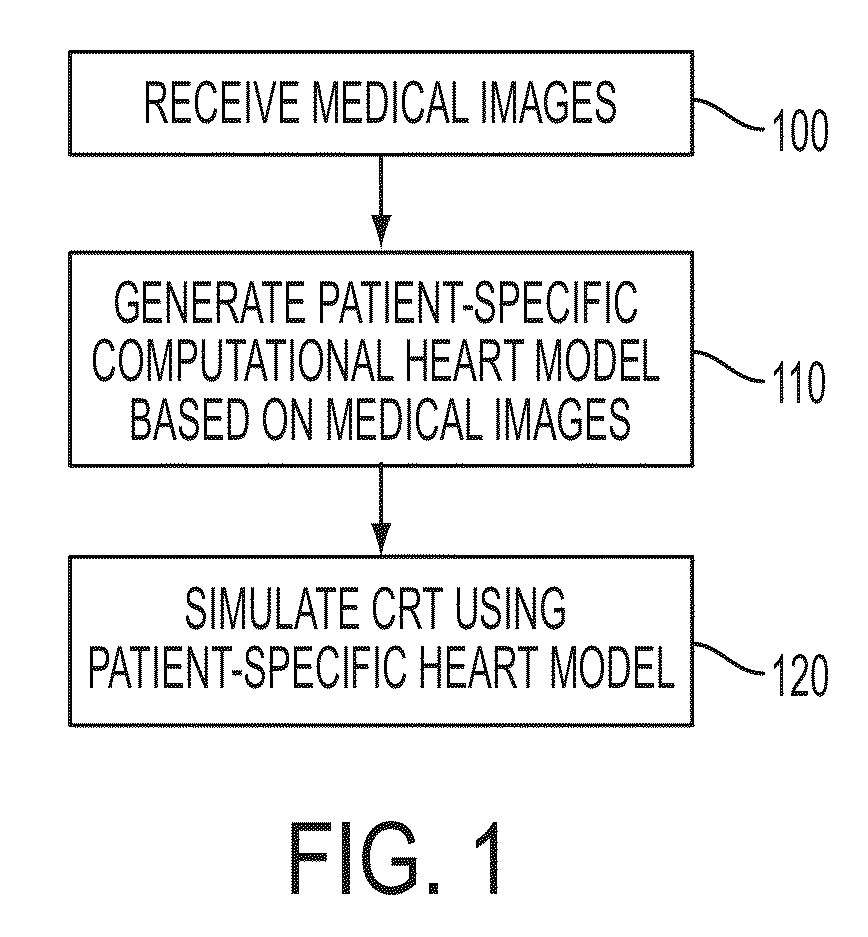
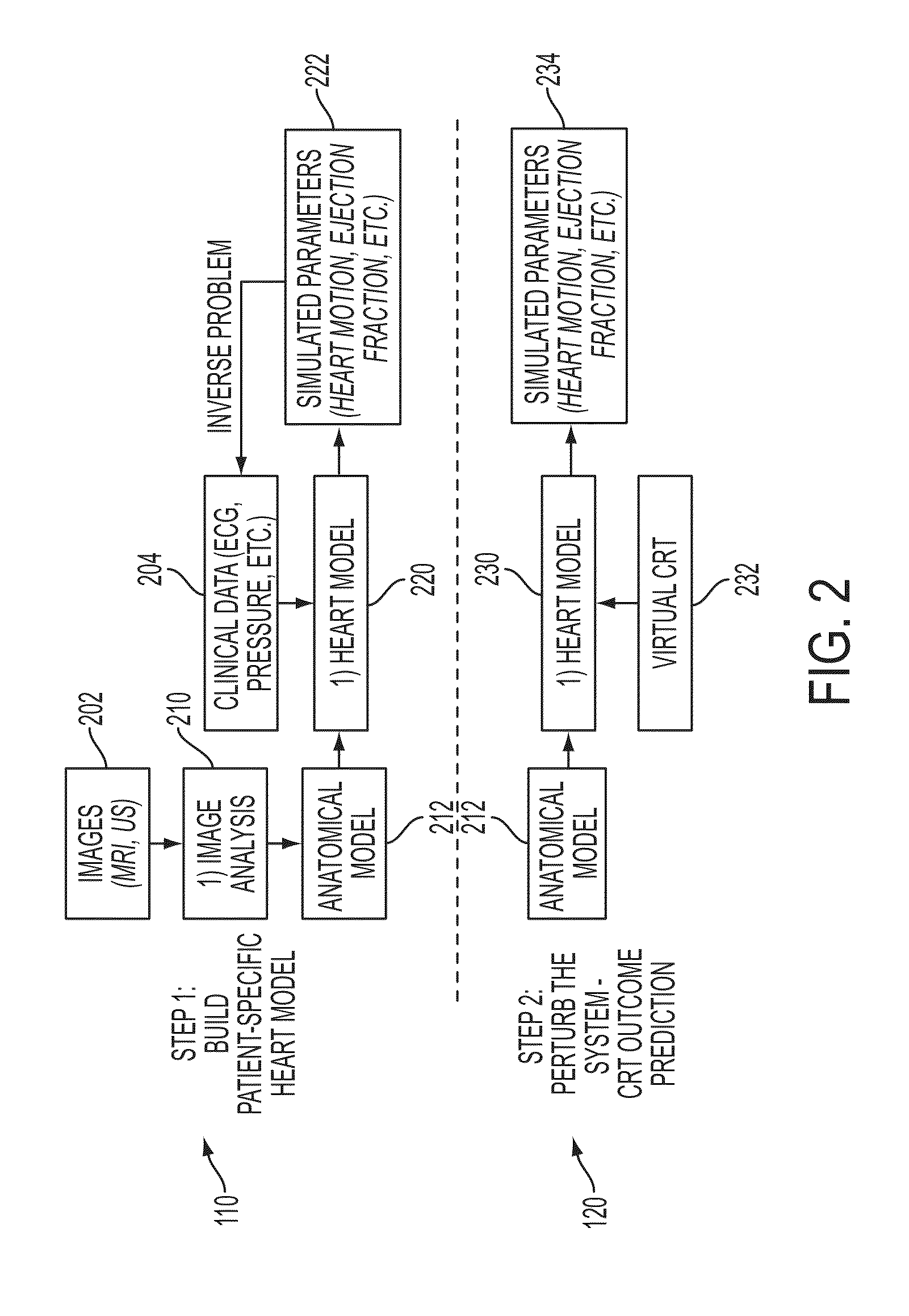
Method and System for Patient Specific Planning of Cardiac Therapies on Preoperative Clinical Data and Medical Images
ActiveUS20130197881A1Increase the number ofEasy to placeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMedical imagingSonificationBiomechanics
A method and system for patient-specific planning of cardiac therapy, such as cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT), based on preoperative clinical data and medical images, such as ECG data, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data, and ultrasound data, is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model, which comprises cardiac electrophysiology, biomechanics and hemodynamics, is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and clinical data. Simulations of cardiac therapies, such as CRT at one or more anatomical locations are performed using the patient-specific computational heart model. Changes in clinical cardiac parameters are then computed from the patient-specific model, constituting predictors of therapy outcome useful for therapy planning and optimization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Self-shielded gradient coil
ActiveUS20110121832A1Reduce eddy currentTotal current dropElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRElectrical conductorEddy current
Gradient coil assemblies for horizontal magnetic resonance imaging systems (MRIs) and methods of their manufacture. Some embodiments may be used with open MRIs and can be used with an instrument placed in the gap of the MRI. In general, concentrations of conductors or radially oriented conductors may be moved away from the gap of the MRI so as to reduce eddy currents that may be induced in any instrument placed within the gap. Systems for directly cooling primary gradient and shield coils may be utilized and various coil supporting structures may be used to assist in coil alignment or to facilitate use of an instrument in the MRI gap.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
Implantable or insertable medical devices visible under magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20070167735A1Shorten the relaxation timeStentsBalloon catheterPolymer coatingsMedical device
Disclosed is an implantable or insertable medical device comprising (a) a substrate and (b) a hydrogel polymer coating at a least a portion of the surface of the substrate, wherein the hydrogel polymer is adapted to render the medical device visible under magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) upon insertion or implantation of the medical device into a patient. Also disclosed is the use of such a hydrogel coated implantable or insertable medical device in a medical procedure, wherein during or after insertion or implantation of the medical device in a patient, the position of the medical device is viewed under MRI. The use of a hydrogel polymer for coating a medical device wherein the hydrogel polymer is adapted to render a medical device coated with the hydrogel polymer visible under MRI and a hydrogel polymer adapted to render a medical device coated therewith visible under MRI are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and apparatus for shielding a linear accelerator and a magnetic resonance imaging device from each other
InactiveUS8836332B2Improve permeabilityReduce flux densityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSplit magnetResonance
A radiation therapy system comprises a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system combined with an irradiation system, which can include one or more linear accelerators (linacs) that can emit respective radiation beams suitable for radiation therapy. The MRI system includes a split magnet system, comprising first and second main magnets separated by gap. A gantry is positioned in the gap between the main MRI magnets and supports the linac(s) of the irradiation system. The gantry is rotatable independently of the MRI system and can angularly reposition the linac(s). Shielding can also be provided in the form of magnetic and / or RF shielding. Magnetic shielding can be provided for shielding the linac(s) from the magnetic field generated by the MRI magnets. RF shielding can be provided for shielding the MRI system from RF radiation from the linac.
Owner:VIEWRAY TECH
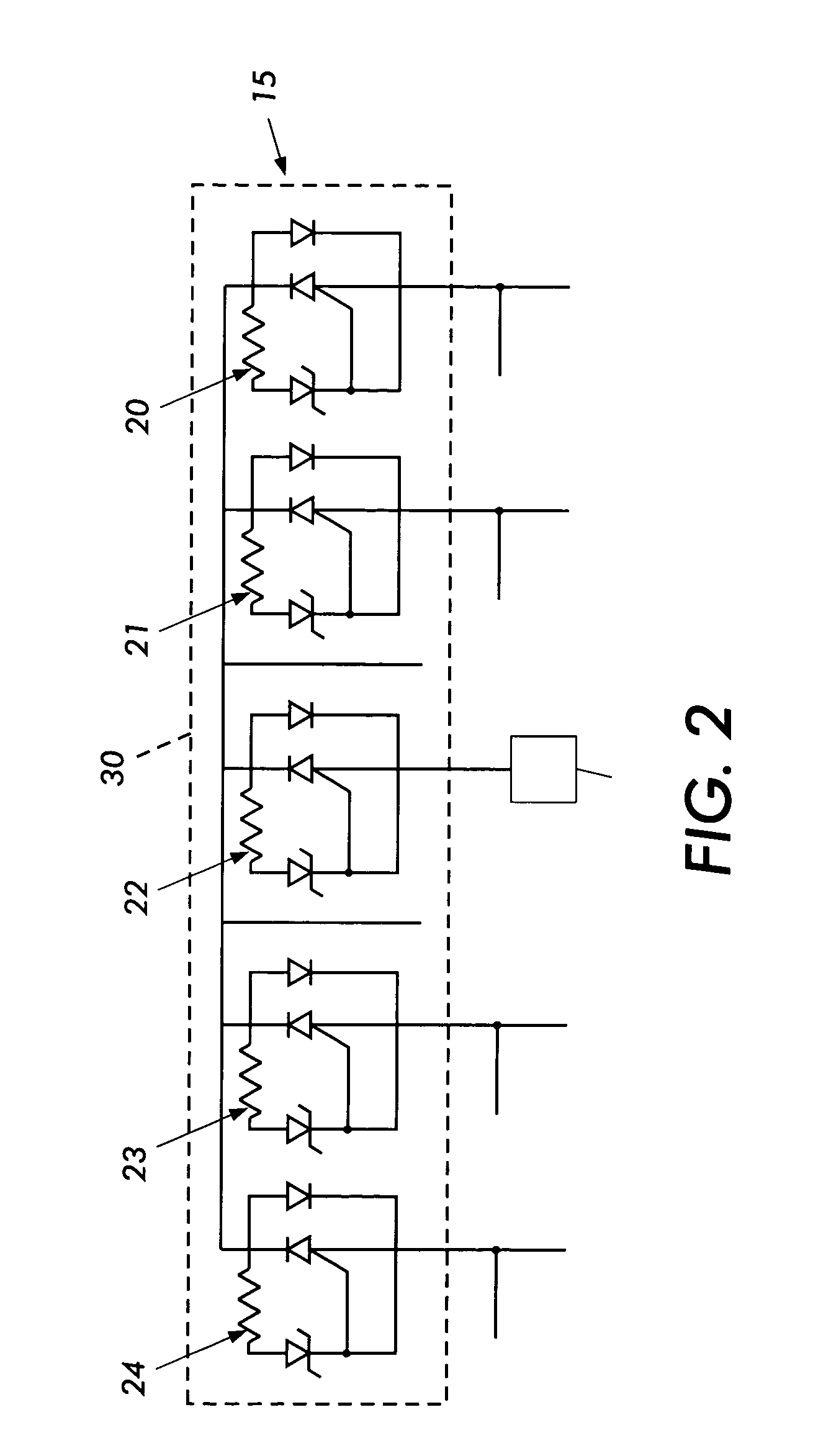
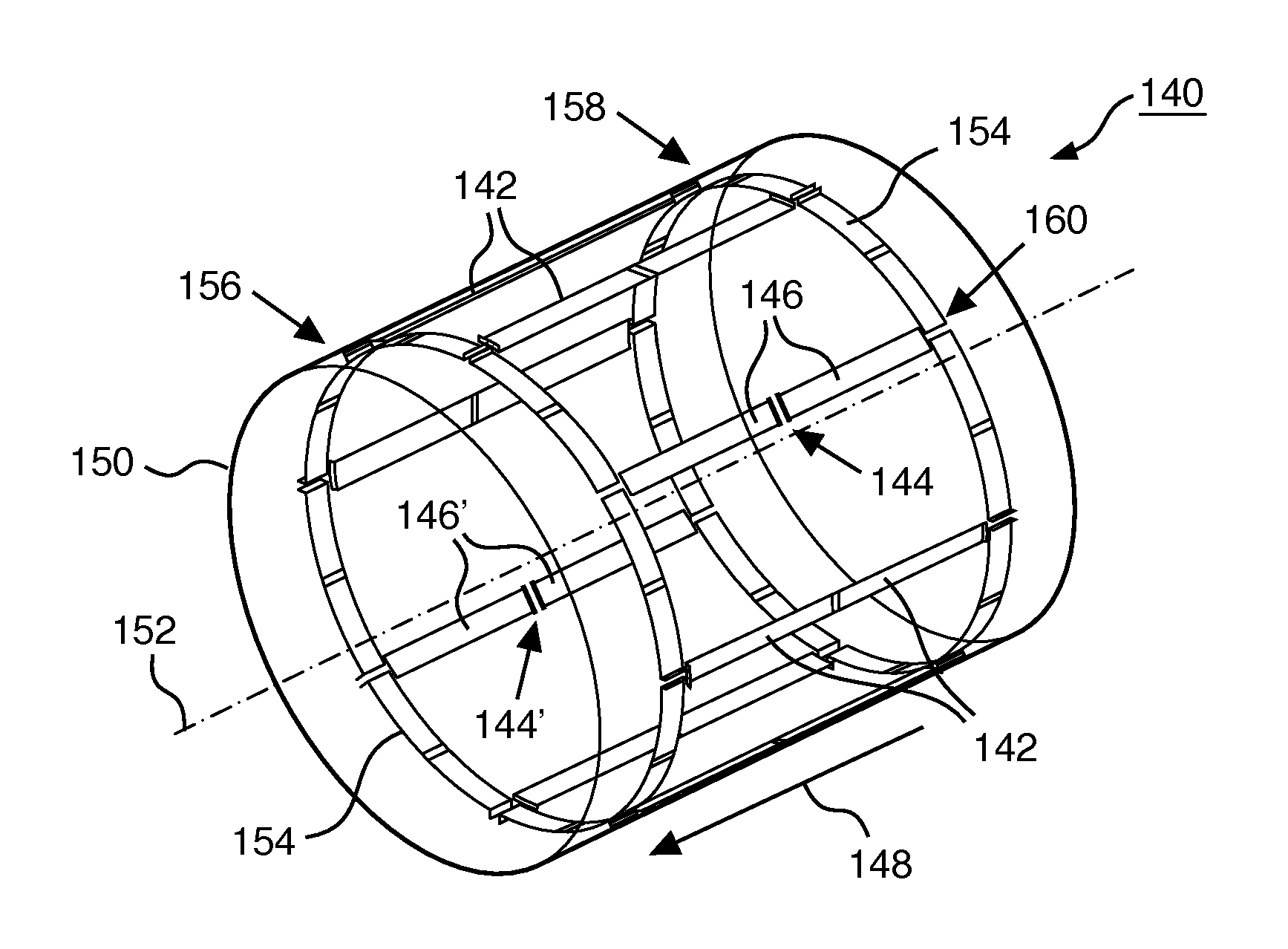
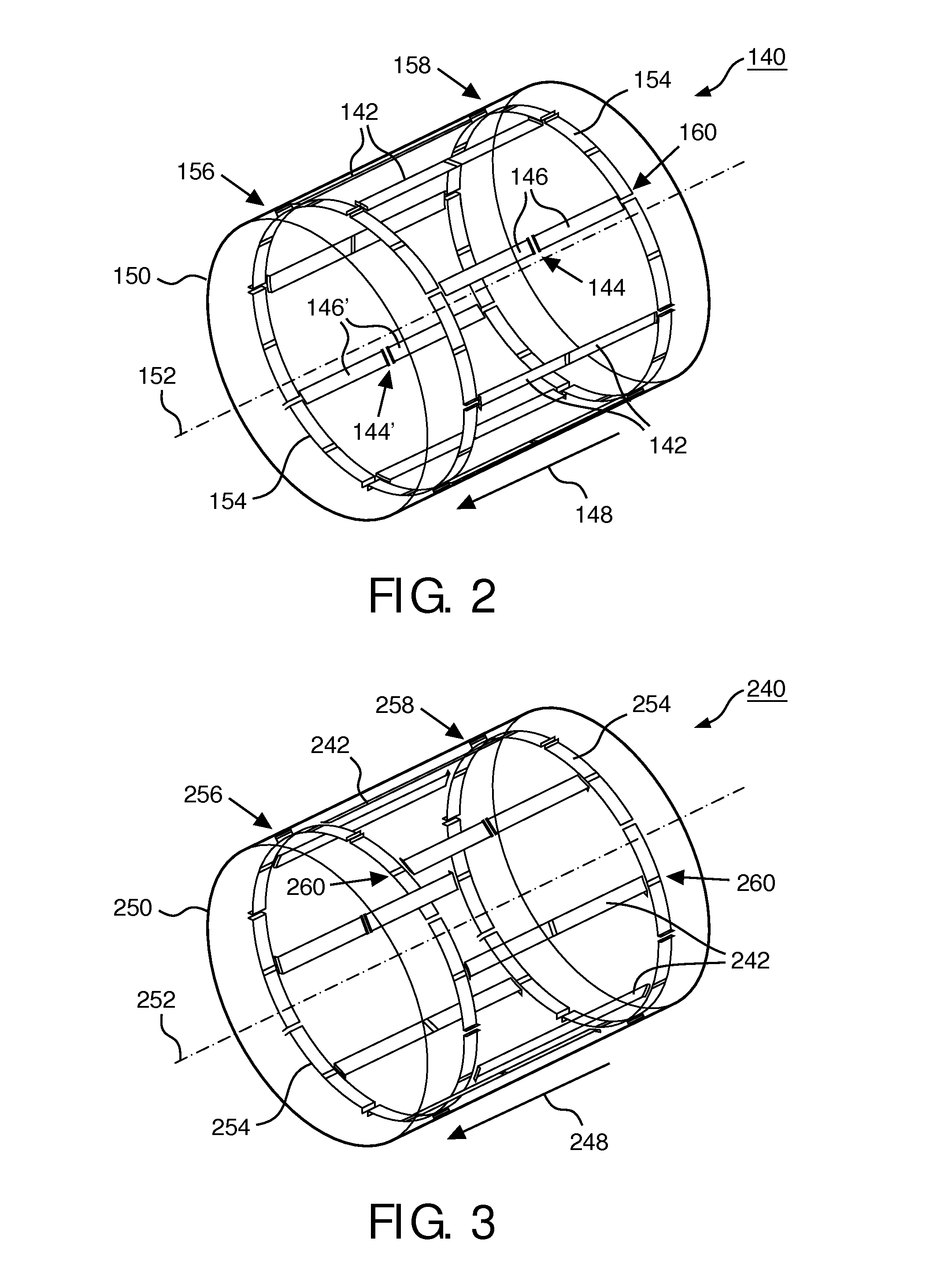
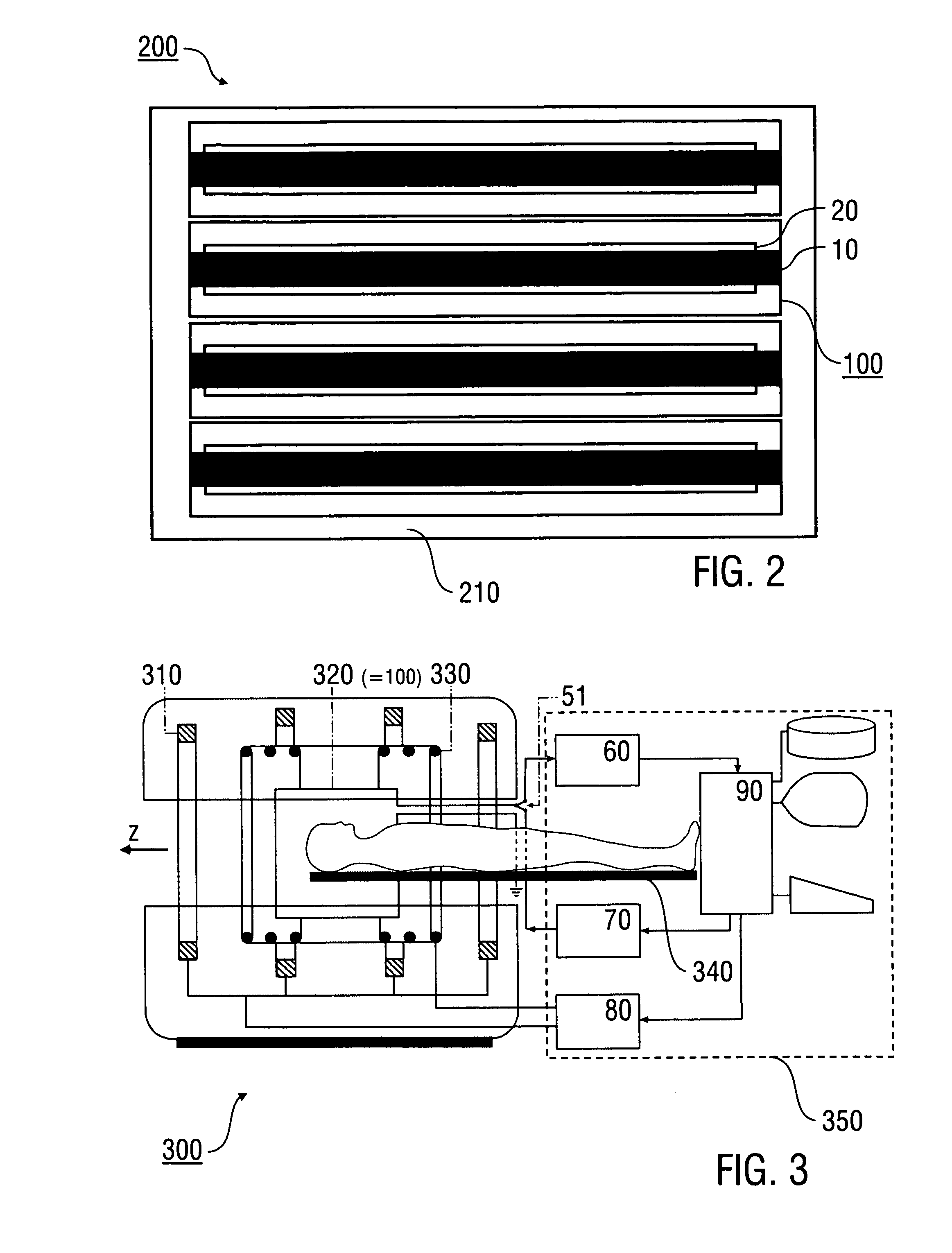
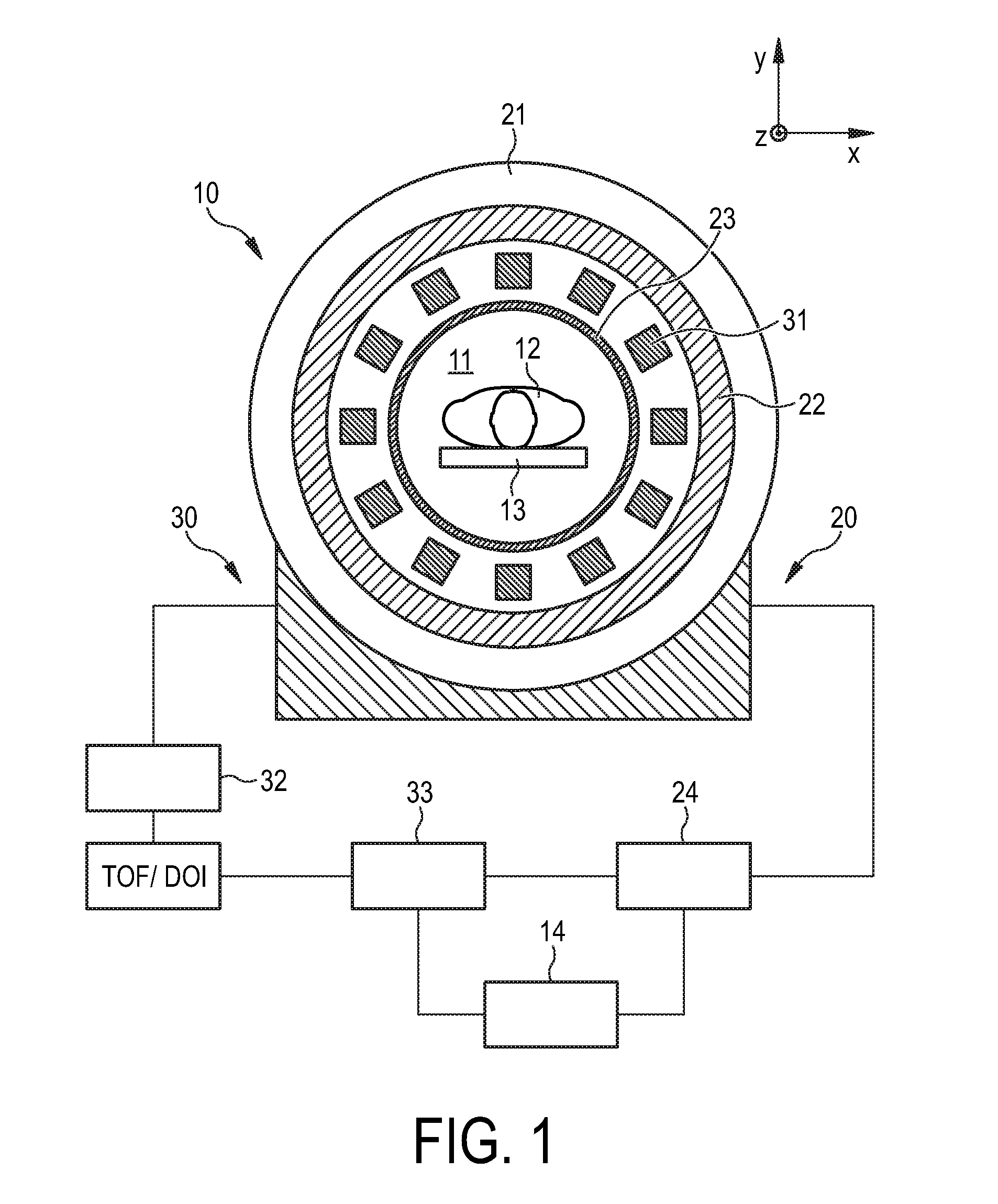
Radio frequency (RF) birdcage coil with separately controlled ring members and rungs for use in a magnetic resonance (MR) imaging system
ActiveUS20150276897A1Improve sar controlImprove rf shimming optionLoop antennasElectric/magnetic detectionElectron magnetic resonanceRf field
A radio frequency (RF) antenna device (40) for applying an RF field to an examination space (16) of a magnetic resonance (MR) imaging system (10), the RF antenna device (40) comprising a plurality of rungs (42, 44) arranged substantially parallel and in an azimuthally substantially equally spaced relationship along an outside of a virtual cylinder (50) with a cylinder axis (52) running parallel to main directions of extension (48); at least one transversal antenna member (54) electromagnetically coupled to at least one rung (42, 44) of the plurality of rungs (42, 44), wherein the at least one transversal antenna member (54) is arranged within a plane substantially perpendicular to the main directions of extension (48) of the plurality of rungs (42, 44); and a plurality of RF circuitries (62, 64, 66), wherein at least one RF circuitry (62, 64, 66) is provided for each rung (42, 44) of the plurality of rungs (42, 44) for mutual decoupling and for individually feeding RF power into and for the at least one transversal antenna member (54) for individually feeding RF power into.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for real-time noise reduction in MRI data acquisition
InactiveUS20140300358A1Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData acquisitionNoise reduction
A system for determining the level of shielding in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus and for real-time reduction of noise produced during MRI data acquisition. The system includes: at least one antenna; data acquirer in communication with the at least one antenna and in communication with the RF pulse generator; and a synchronizer for synchronizing the acquisition of data by the data acquirer with MRI pulses being produced by the MRI apparatus.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Method For Image Reconstruction Using Low-Dimensional-Structure Self-Learning and Thresholding
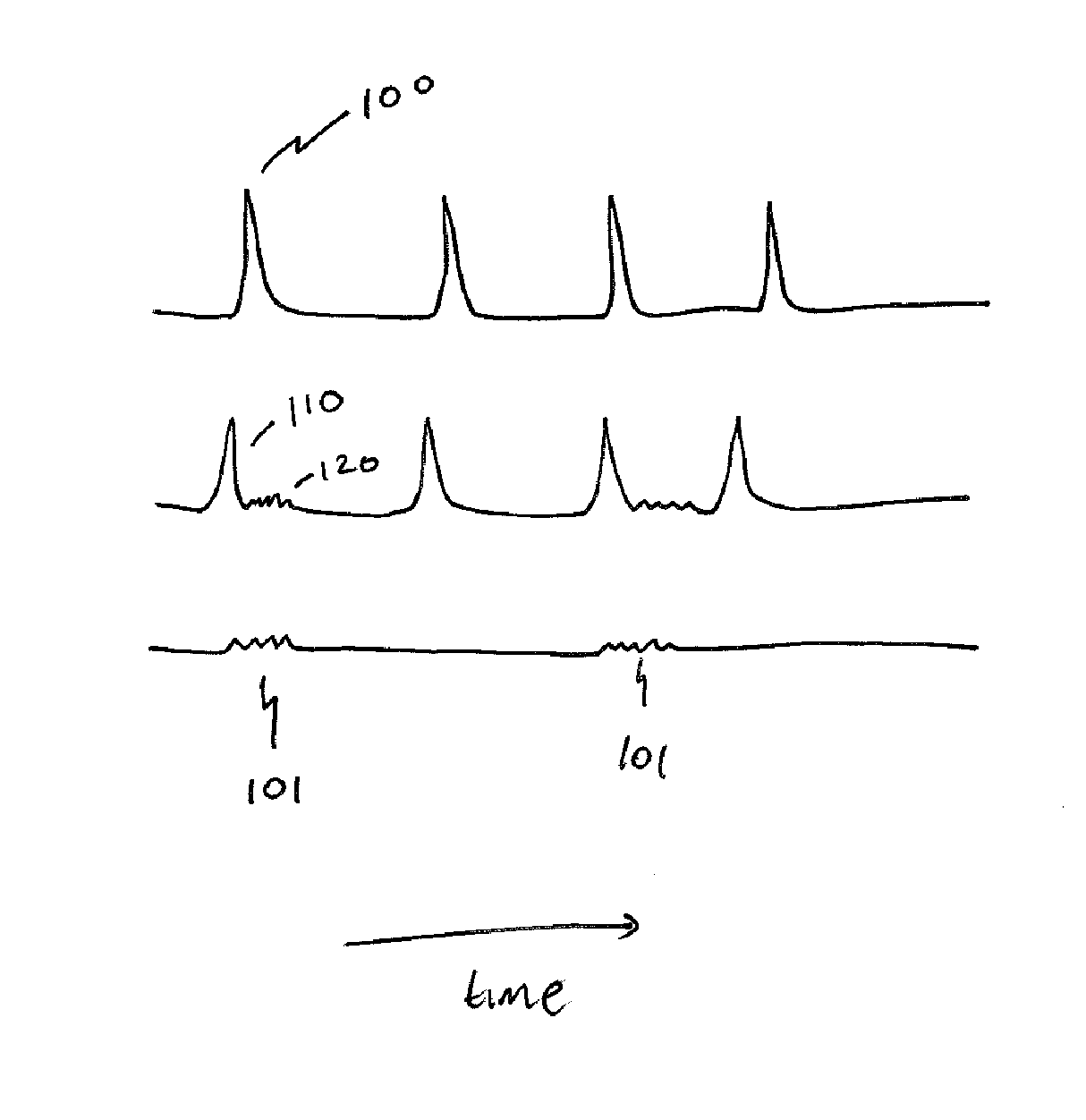
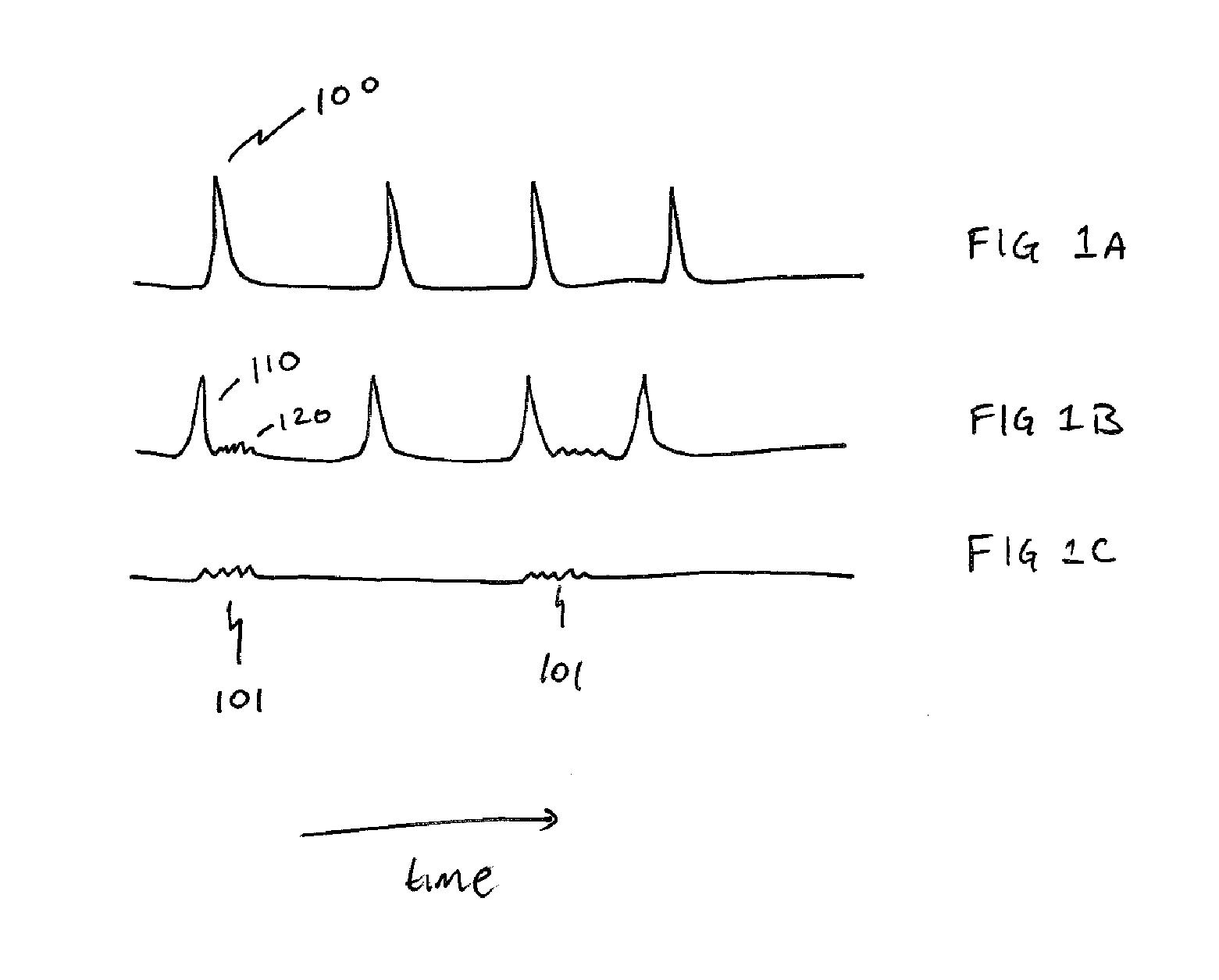
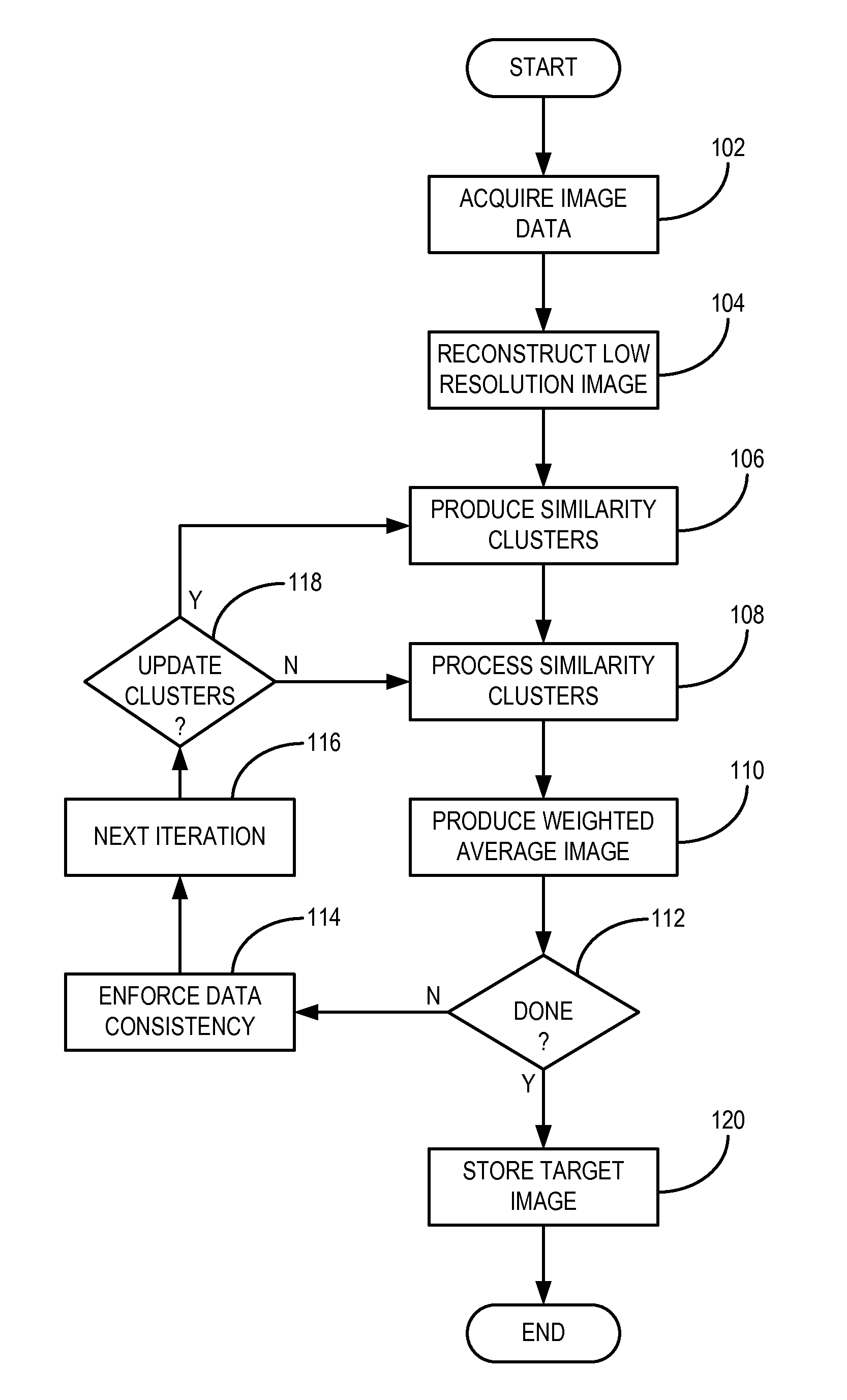
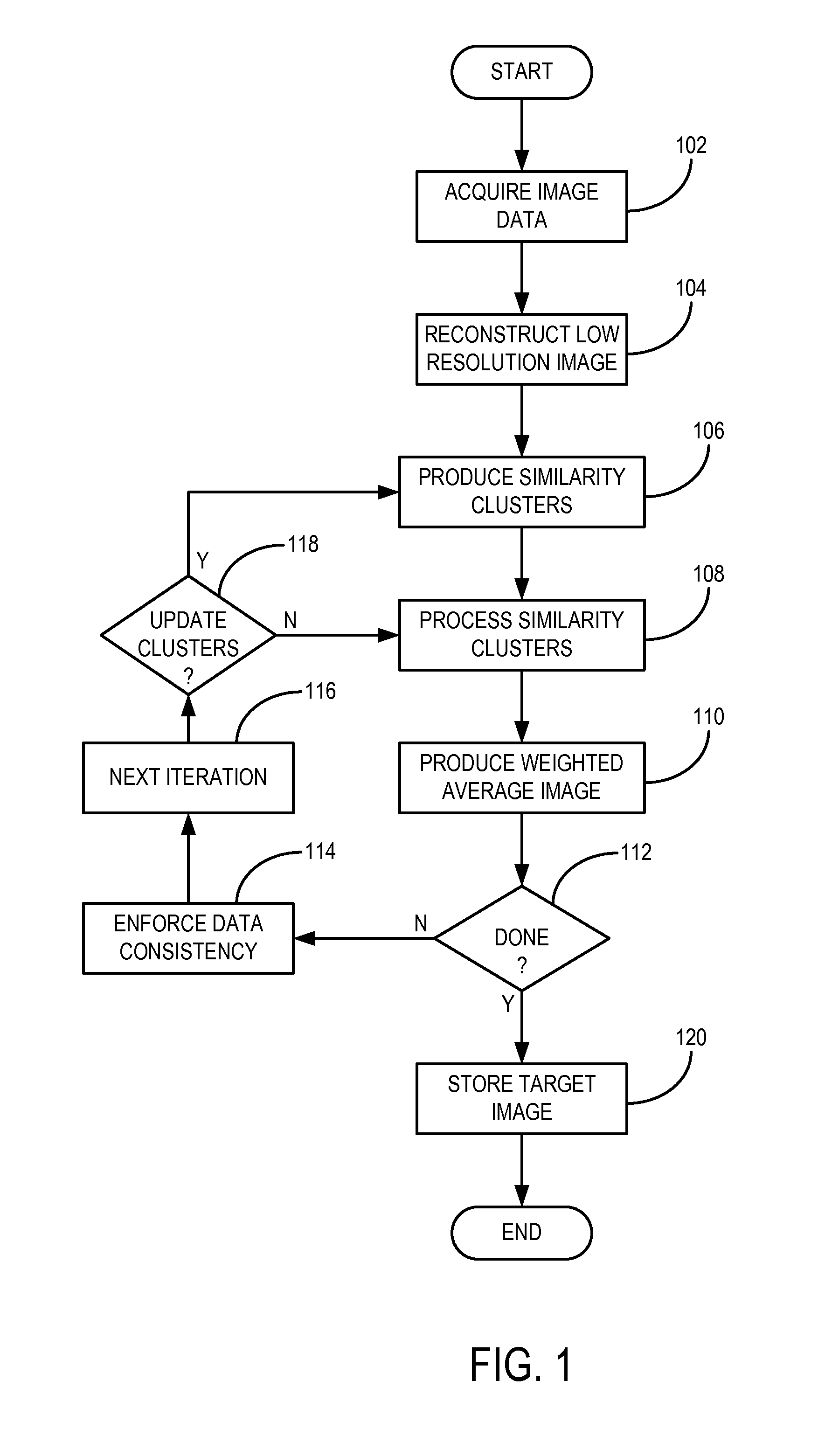
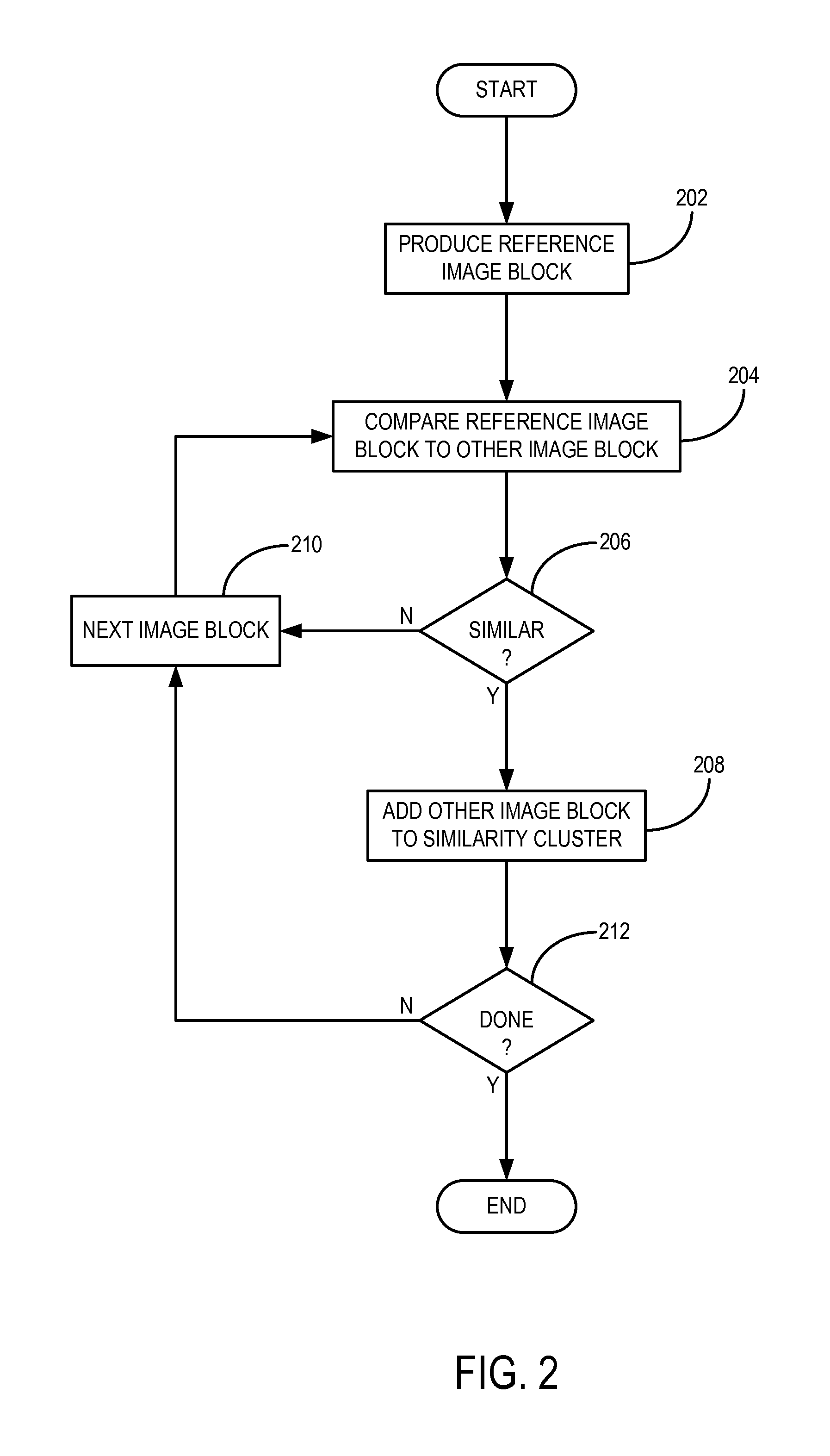
InactiveUS20120099774A1Improve reconstructionPromote reconstructionImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionImage resolutionPrincipal component pursuit
A method for reconstructing an image of a subject from undersampled image data that is acquired with an imaging system, such as a magnetic resonance imaging system or computed tomography system, is provided. From the acquired undersampled image data, an image of the subject is reconstructed and used to guide further image reconstruction. For example, a low resolution image is reconstructed from a portion of the undersampled image data, such as from a portion corresponding to the center of k-space when MRI is used. From this image, a number of similarity clusters are produced and processed. The processing may be by hard thresholding, Wiener filtering, principal component pursuit, or other similar techniques. These processed similarity clusters are then used to reconstruct a final, target image of the subject using, for example, a weighted average combination of the similarity clusters.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Apparatus and method for removing magnetic resonance imaging-induced noise from ECG signals
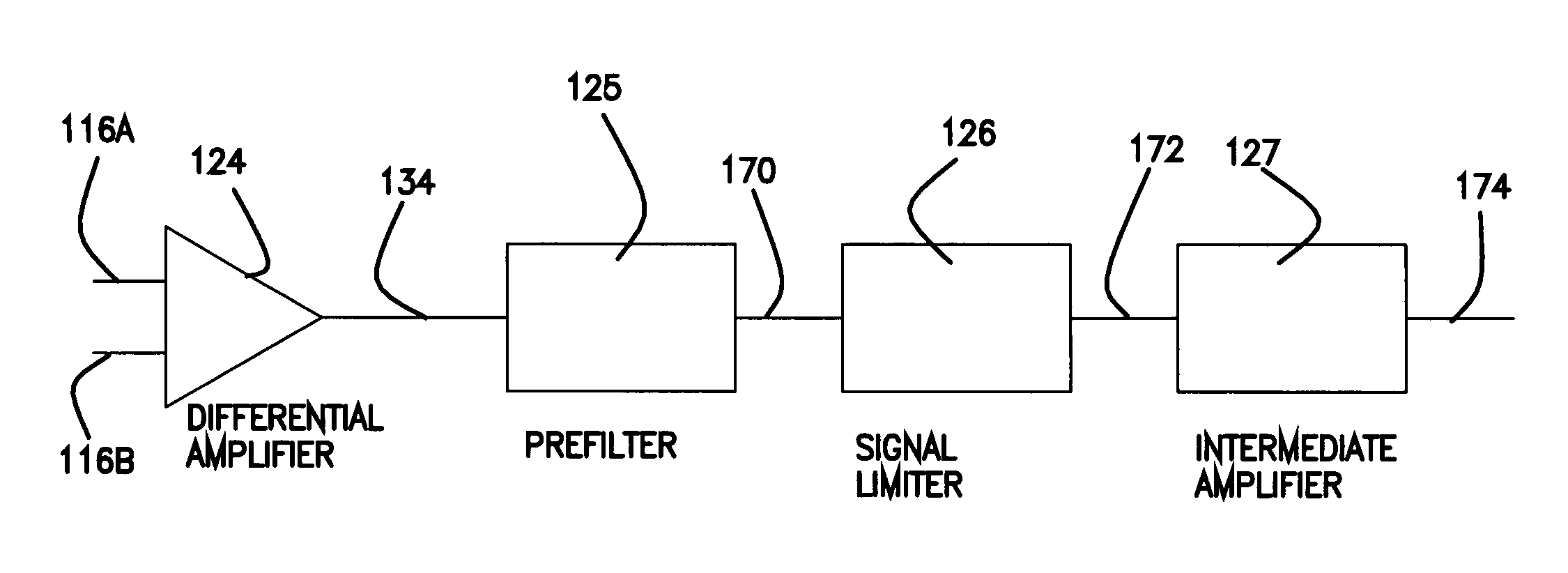
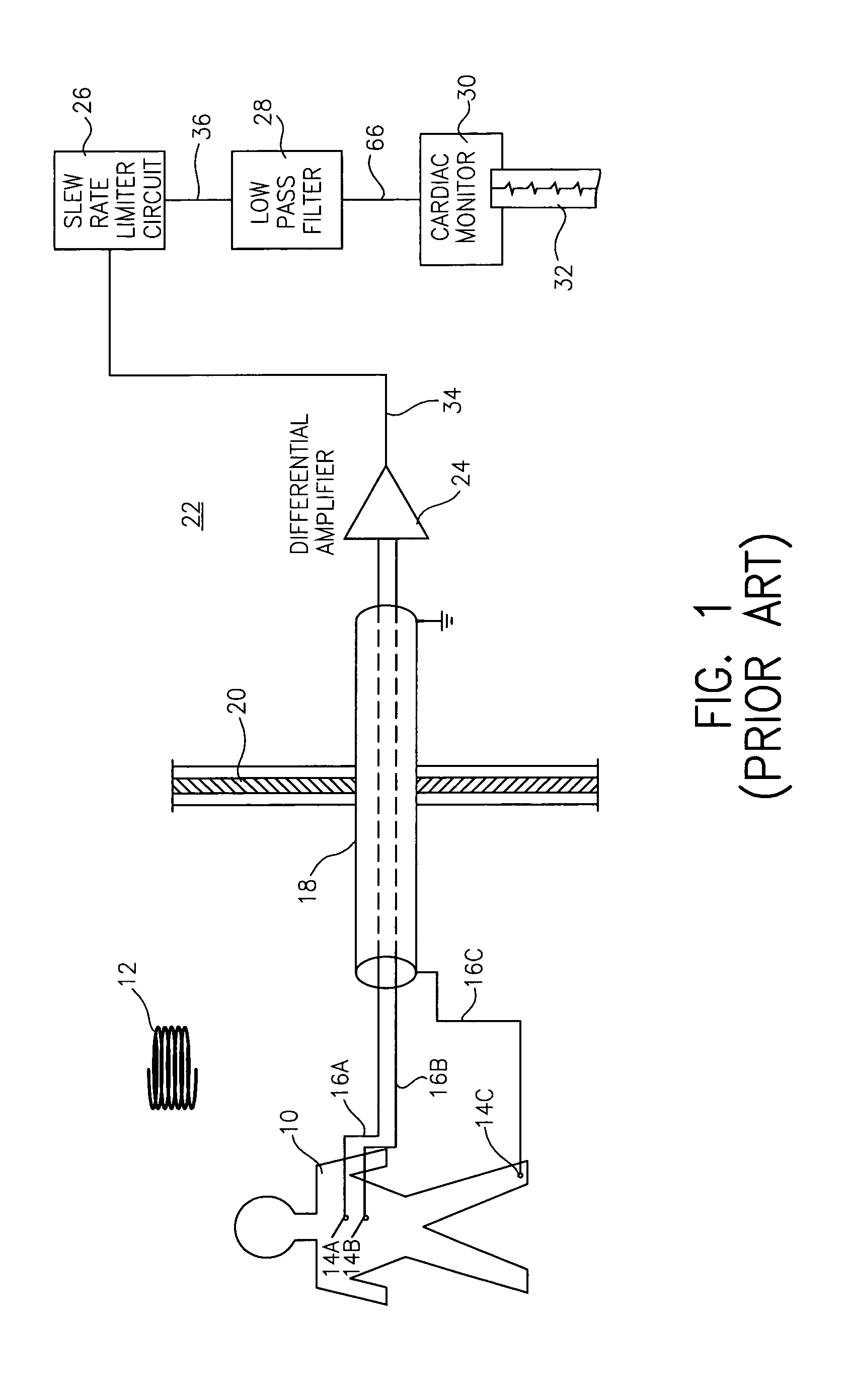
An apparatus and method is provided for improving the quality of electrocardiogram (ECG) signals obtained from a patient undergoing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) wherein the ECG signal has relatively high levels of noise or interference voltages induced on it by changing magnetic fields. The apparatus includes the arrangement of a differential amplifier, a prefilter, a signal limiter (SL) circuit and an intermediate amplifier with an integral low pas filter. The prefilter limits the rise time or high frequency component of the noise or interfering voltages induced on the ECG that are presented to the signal limiter.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
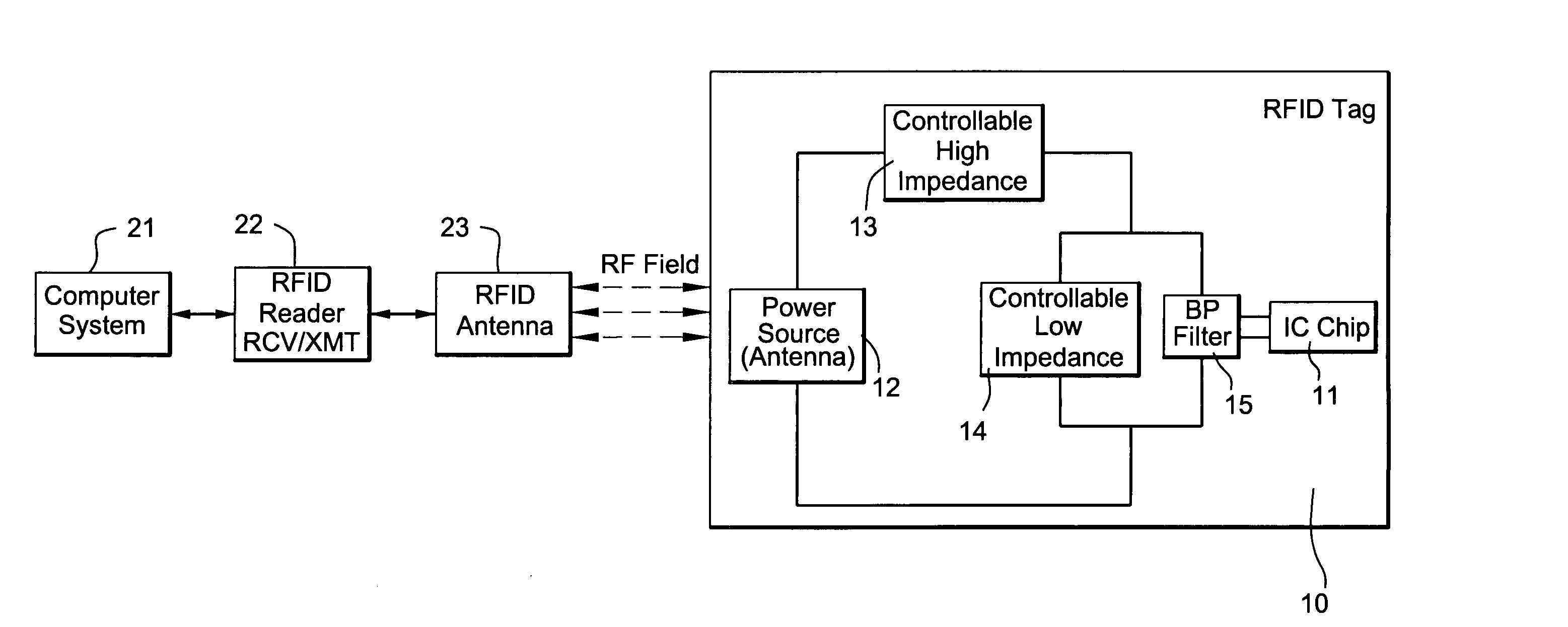
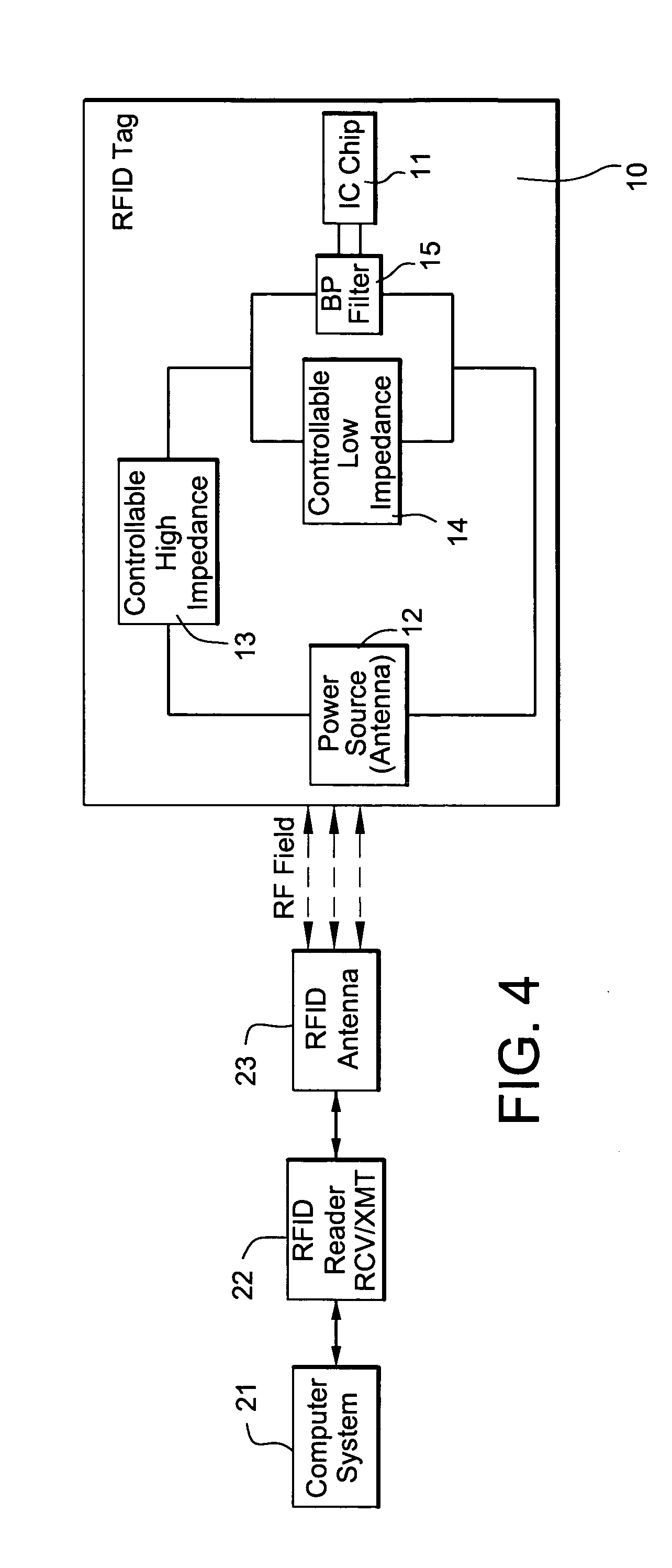
IC tags/RFID tags for magnetic resonance imaging applications
ActiveUS20070257800A1Protection from damageProtection from destructionElectrotherapyAntenna couplingsEngineeringRf filters
An RFID tag for use with an MRI machine has an integrated circuit and structure for protecting it from damage when exposed to an intense MRI RF transmitter field. The structure for protecting the integrated circuit may include a controllable low impedance device coupled across the integrated circuit, a controllable high impedance device coupled in series with the integrated circuit, and / or frequency selective RF filter.
Owner:QUALITY ELECTRODYNAMICS
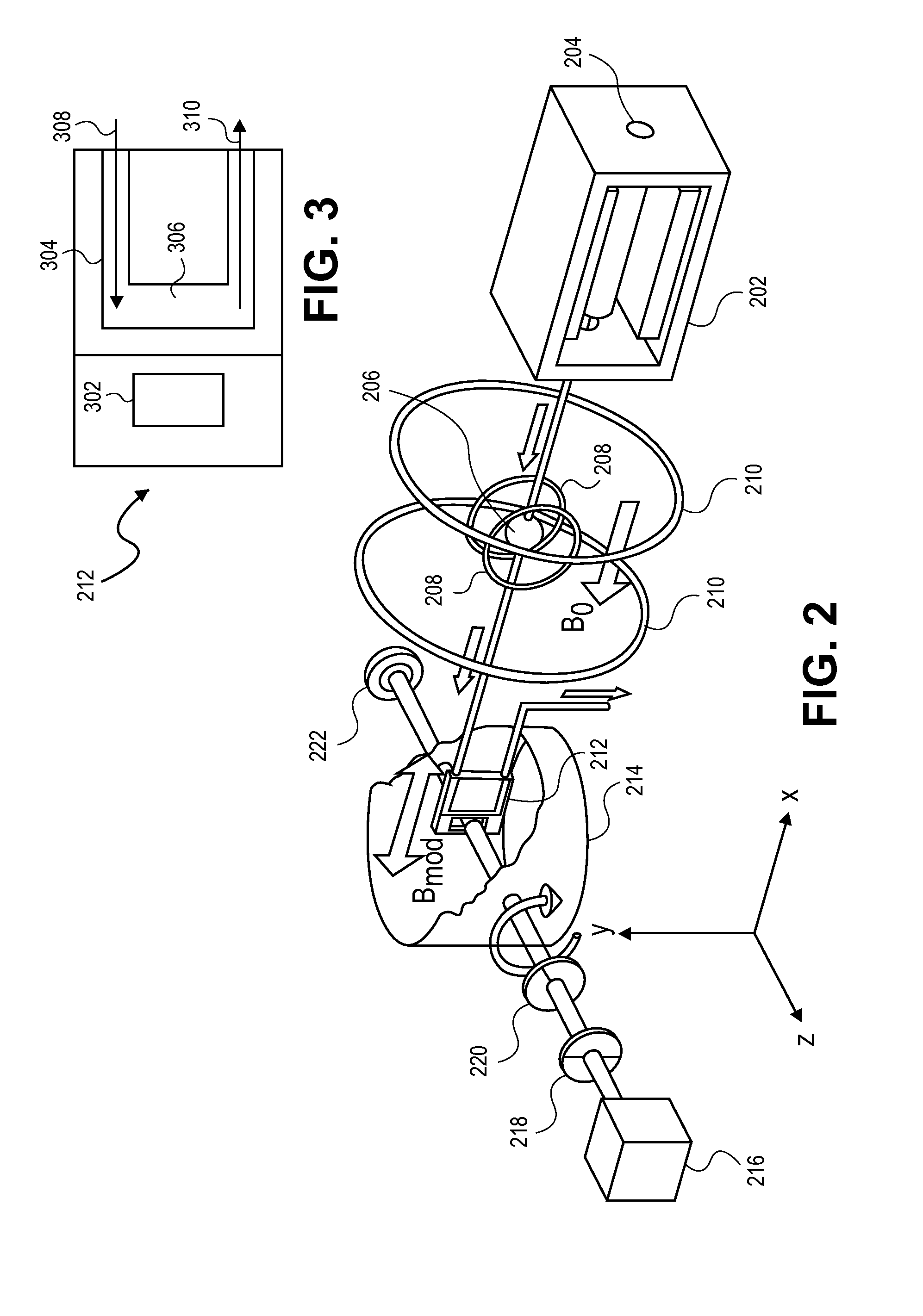
Pole piece for permanent magnet MRI systems
InactiveUS20110234347A1Improve stabilityMagnetic measurementsPermanent magnetsComputational physicsPole piece
A pole piece for a permanent magnet MRI system and a method for increasing the stability of a gradient field in an MRI system. The method includes: obtaining an MRI system comprising a magnet capable of providing a gradient magnetic field within an image volume in an air gap; and fixing a plurality of pole pieces within said MRI system, thereby defining the air gap, the raw material of construction of the pole piece being a material including a plurality of ferromagnetic particles coated with an electrically insulating substance. The fixing increases the stability of said gradient field by at least 10% relative to that of a gradient magnetic field in an MRI system identical except for the use of the material in the fabrication of the pole pieces.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
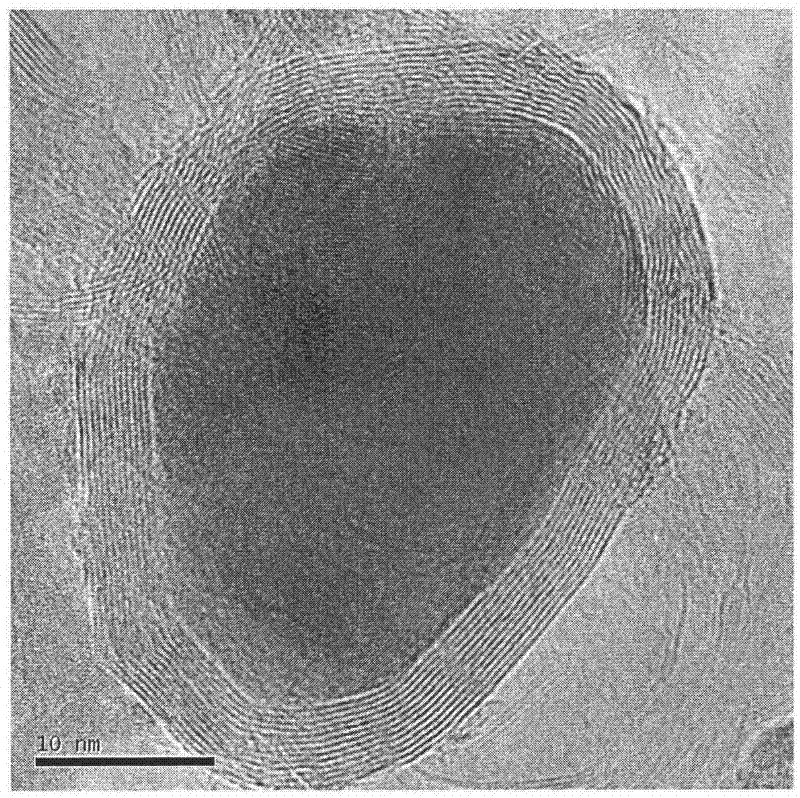
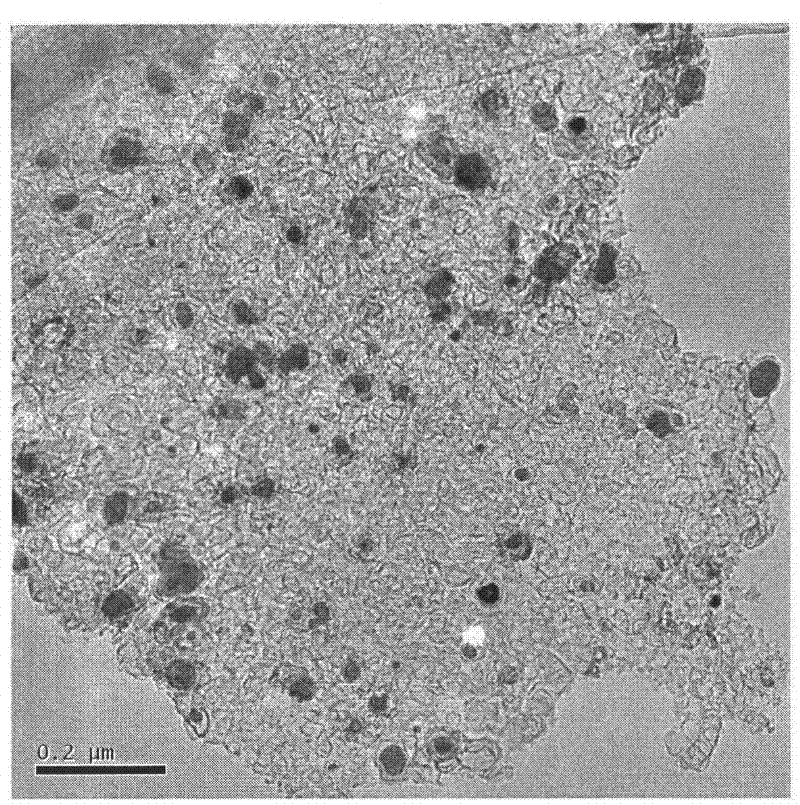
Preparation method of carbon-coated metallic nano-particles
InactiveCN102500295AEasy to operateHigh degree of graphitizationMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationTube furnaceCarbon coated
The invention discloses a preparation method of carbon-coated metallic nano-particles, which comprises the steps that: NaCl serves as dispersant and a carrier, and is fully mixed with a metal source and a solid carbon source; the mixed solution is dried under a vacuum condition, and mixture is obtained; the mixture is put into a tubular furnace and calcinated in the inertial / reduction atmosphere, and a calcinated product is obtained; and the calcinated product is washed and ground, and the carbon-coated metallic nano-particles are obtained. The method is safe, non-toxic, environmental-friendly and simple to operate, so that the grain sizes of the prepared carbon-coated nano-particles are controlled to be 0nm to 100nm, the graphitization degree of a carbon layer is high, the dispersion of the particles is good, and the yield is high. The carbon-coated metallic nano-particles which are prepared through the preparation method have better magnetism and larger specific surface areas, can be used for electronic and magnetic materials, and can be used for magnetic resonance imaging, targeted drug transportation and other fields through functionalization treatment and other steps.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Automated methods for pre-selection of voxels and implementation of pharmacokinetic and parametric analysis for dynamic contrast enhanced MRI and CT
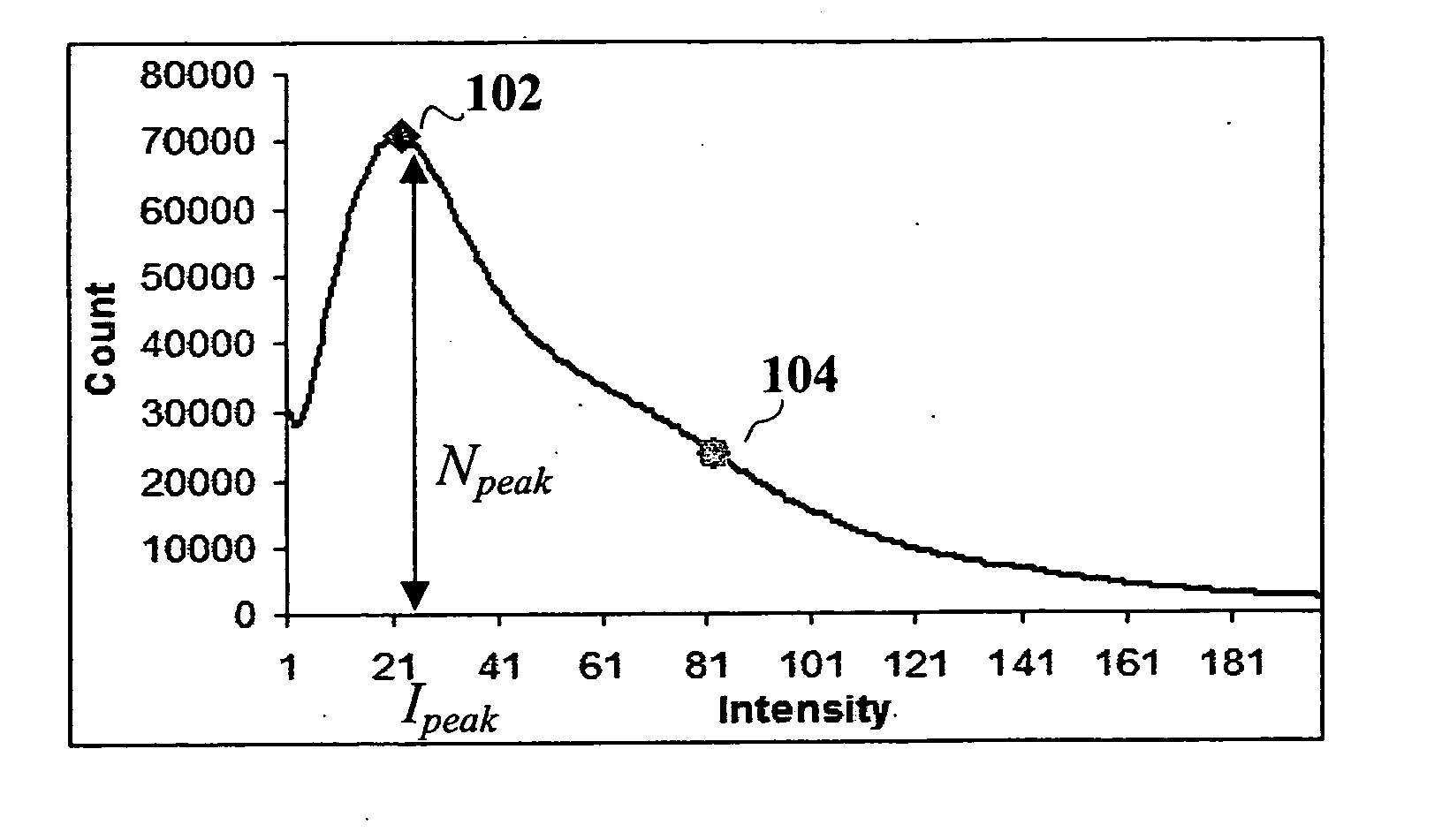
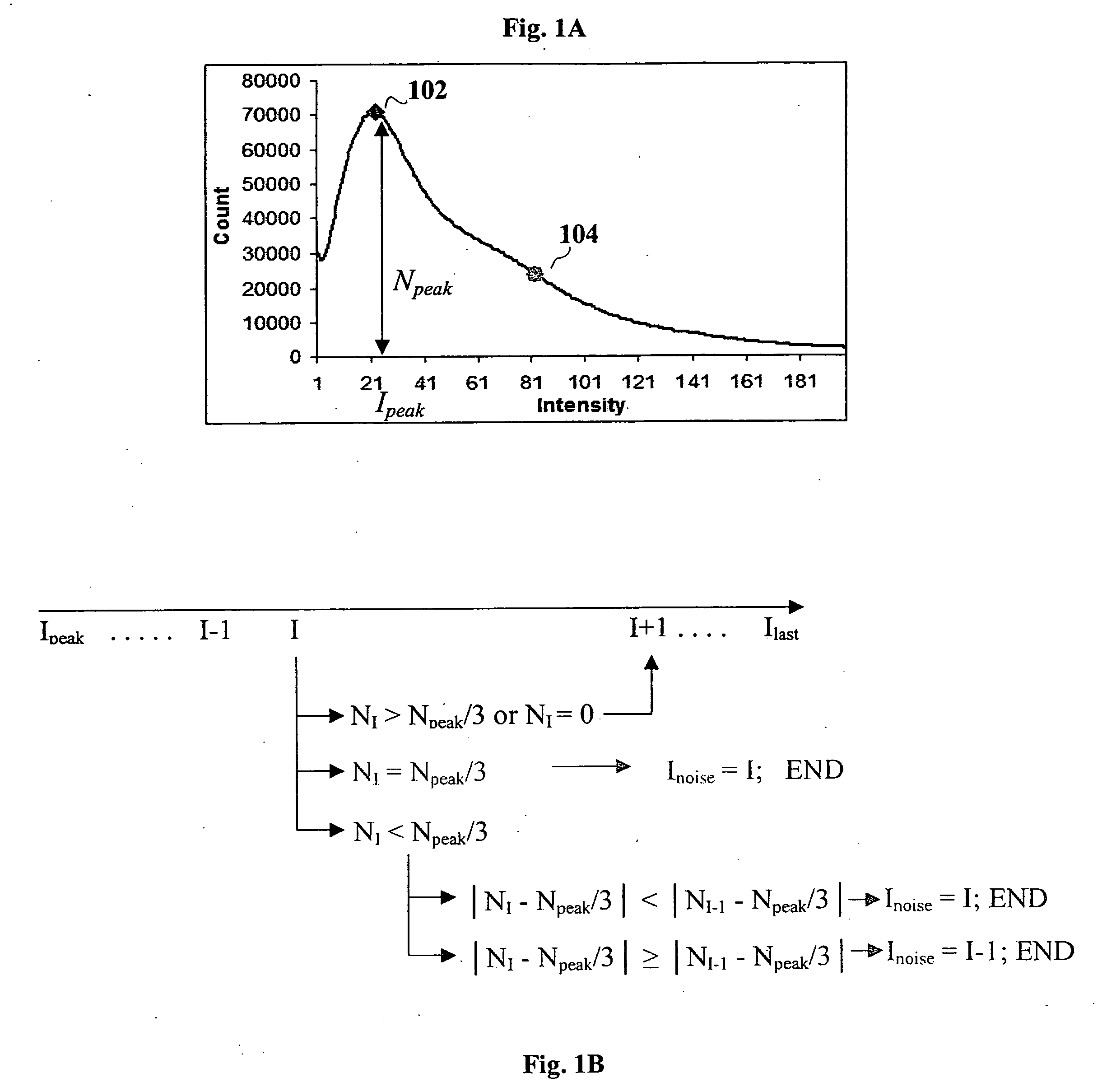
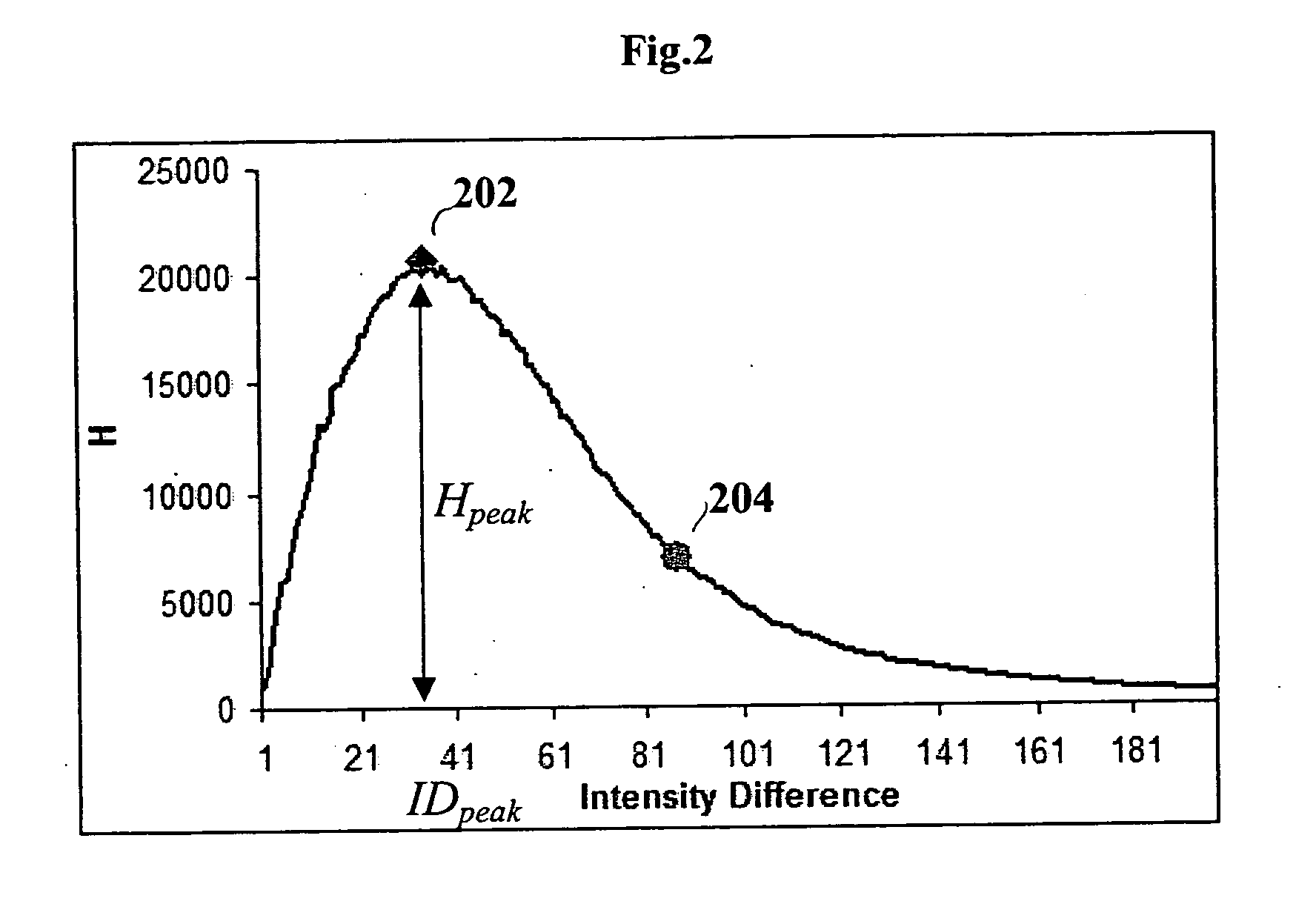
A method, system and computer-readable medium of filtering noise pixels and other extraneous data, including saturated fat tissue and air data in image data is provided. Examples of image data may include but are not limited to magnetic resonance imaging data and computed tomography data. The method includes receiving pixel count for each signal intensity value of the image data; determining a signal intensity value, Ipeak, corresponding to a pixel count of a greatest number of pixels, Npeak; setting a noise threshold at a signal intensity value, Inoise, corresponding to a pixel count, NI, such that NI, is determined based on Npeak; and filtering from the image data one or more pixels with signal intensity values below the noise threshold. NI, may be determined such that NI=Npeak / 3 or close to Npeak / 3.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
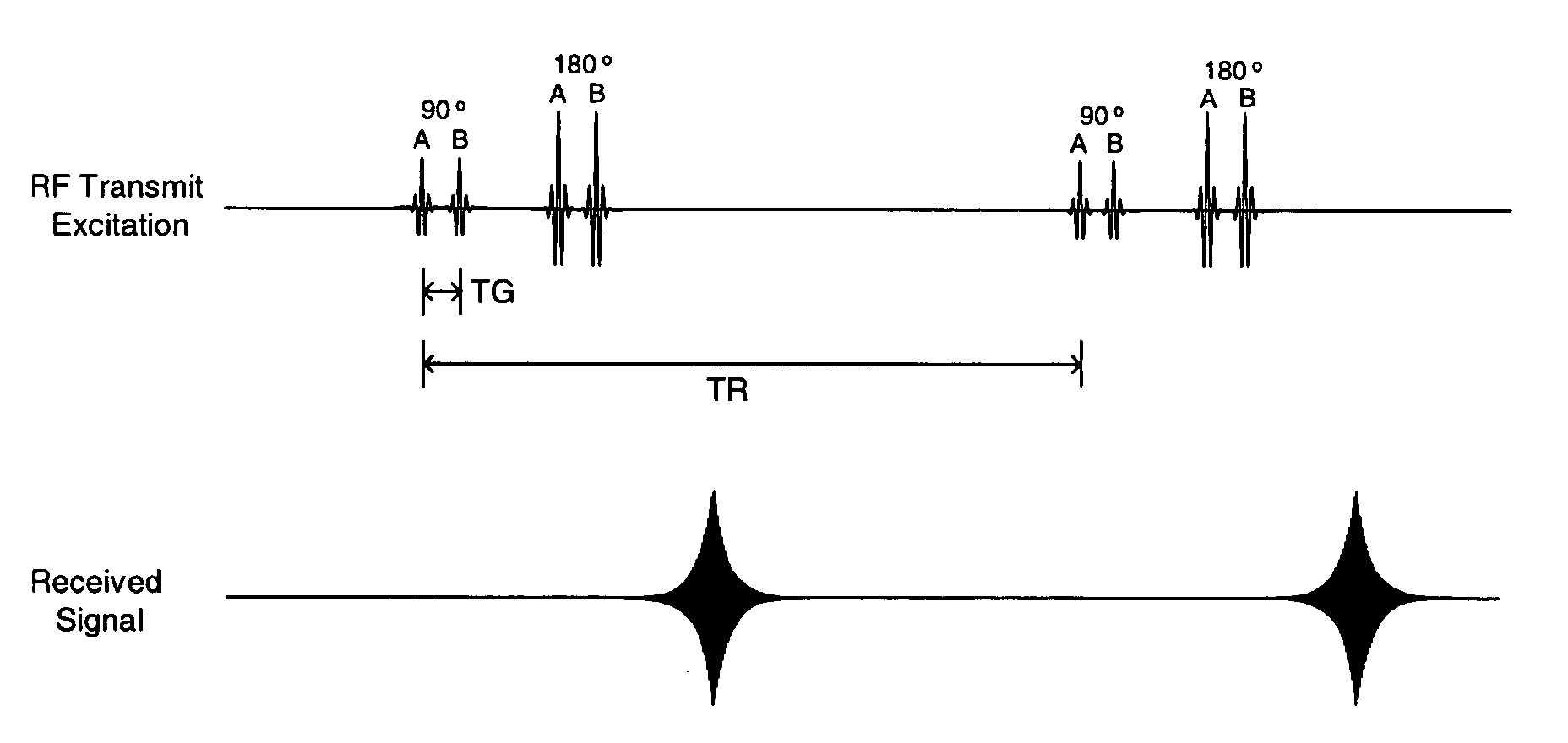
Methods for transmit excitation in magnetic resonance imaging using a transmit pulse with time varying spatial characteristics
ActiveUS6975114B1Optimize allocationEnhance excitationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSurface coilInductor
A method of inducing spin excitation by employing RF transmission fields of time-varying spatial characteristics in order to better control the overall distribution of spin excitation. The MRI transmit inductor system generates an RF transmission of particular spatial characteristics, followed by one or more additional RF transmissions with different spatial characteristics, where the additional RF transmissions alter the spin excitation produced by the first RF transmission. The spin excitation can be provided by a sequence of two or more discrete RF transmissions with different spatial characteristics, by a single RF transmission that has continuously varying spatial characteristics, by using successive RF transmissions of the primary and higher order modes of a volume coil, and / or by an RF transmission from a volume or surface coil followed by a second RF transmission from one or more local surface coils.
Owner:NOVA MEDICAL
Multicoil NMR data acquisition and processing methods
ActiveUS20060186882A1Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientAcquisition apparatus
A multicoil NMR data acquisition apparatus and processing method for performing three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging in a static magnetic field without the application of controlled static magnetic field gradients. A preferred application relates specifically to the detection and localization of groundwater using the Earth's magnetic field. Multicoil arrays are used in both transmit and receive modes, and coherent data processing algorithms applied to the data to generate three-dimensional NMR spin density estimates. Disclosed are methods for acquiring NMR data using an array of at least two transmit and receive coils, and for processing such multicoil data to estimate the three-dimensional NMR spin density distributions.
Owner:VISTA CLARA
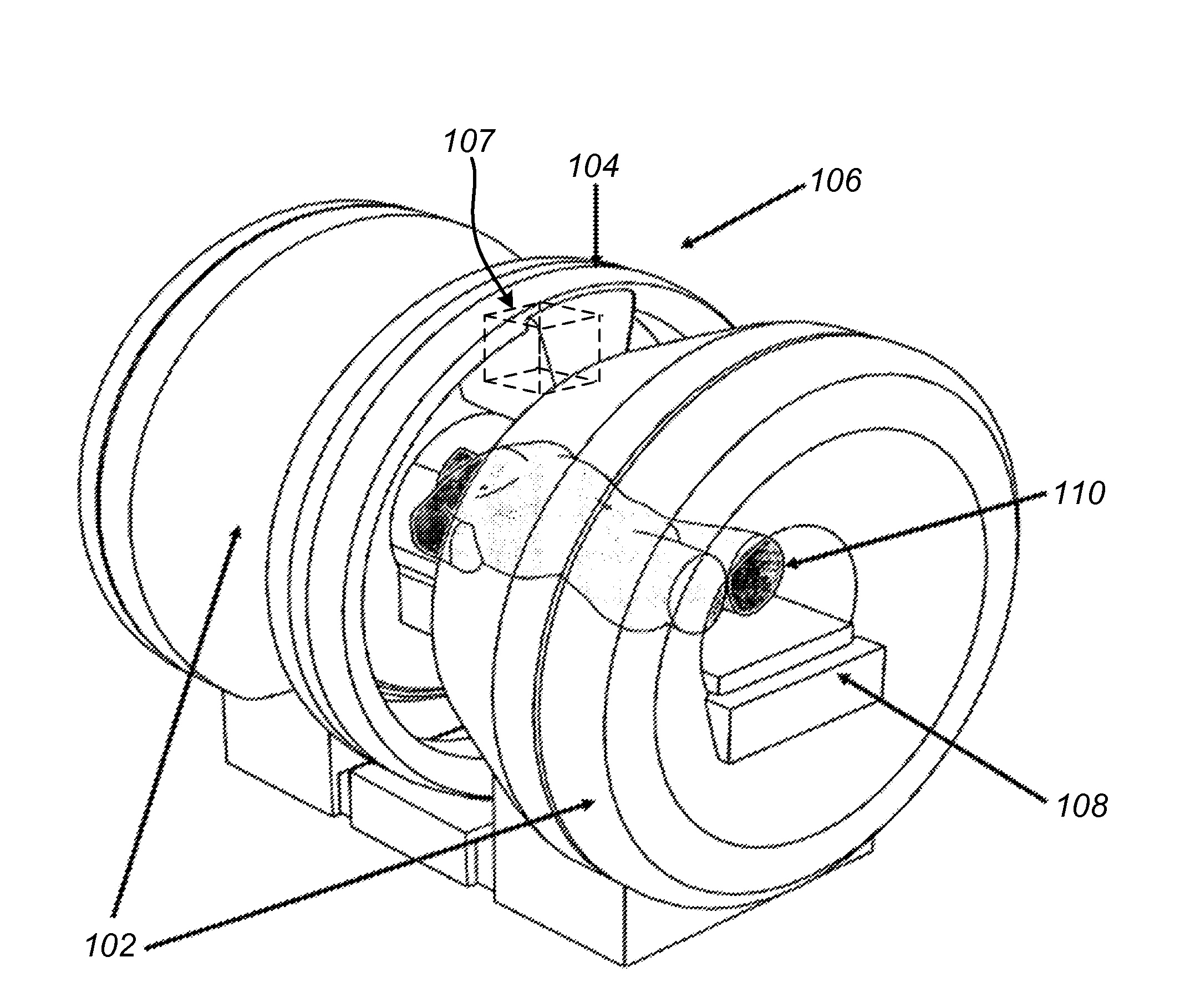
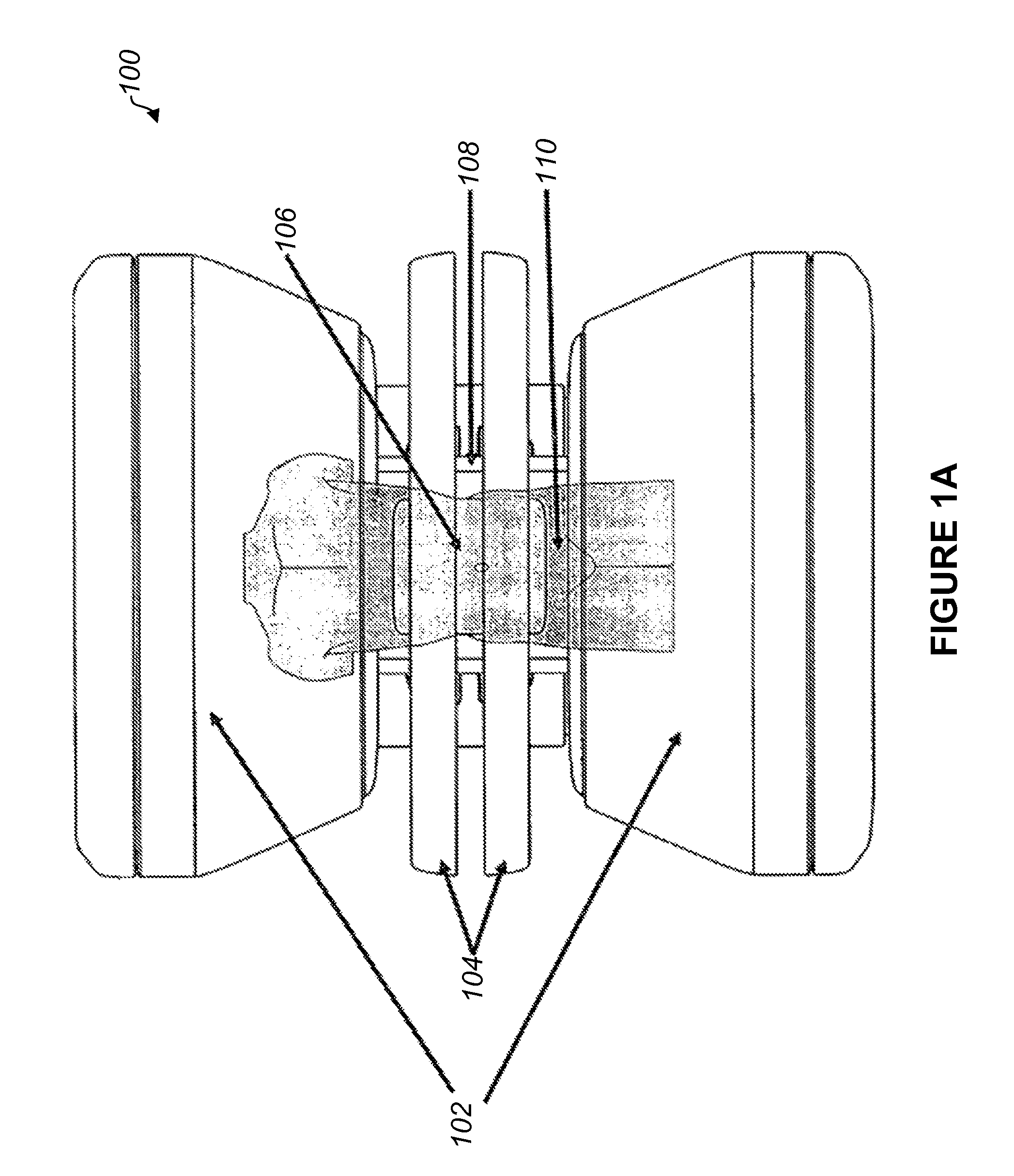
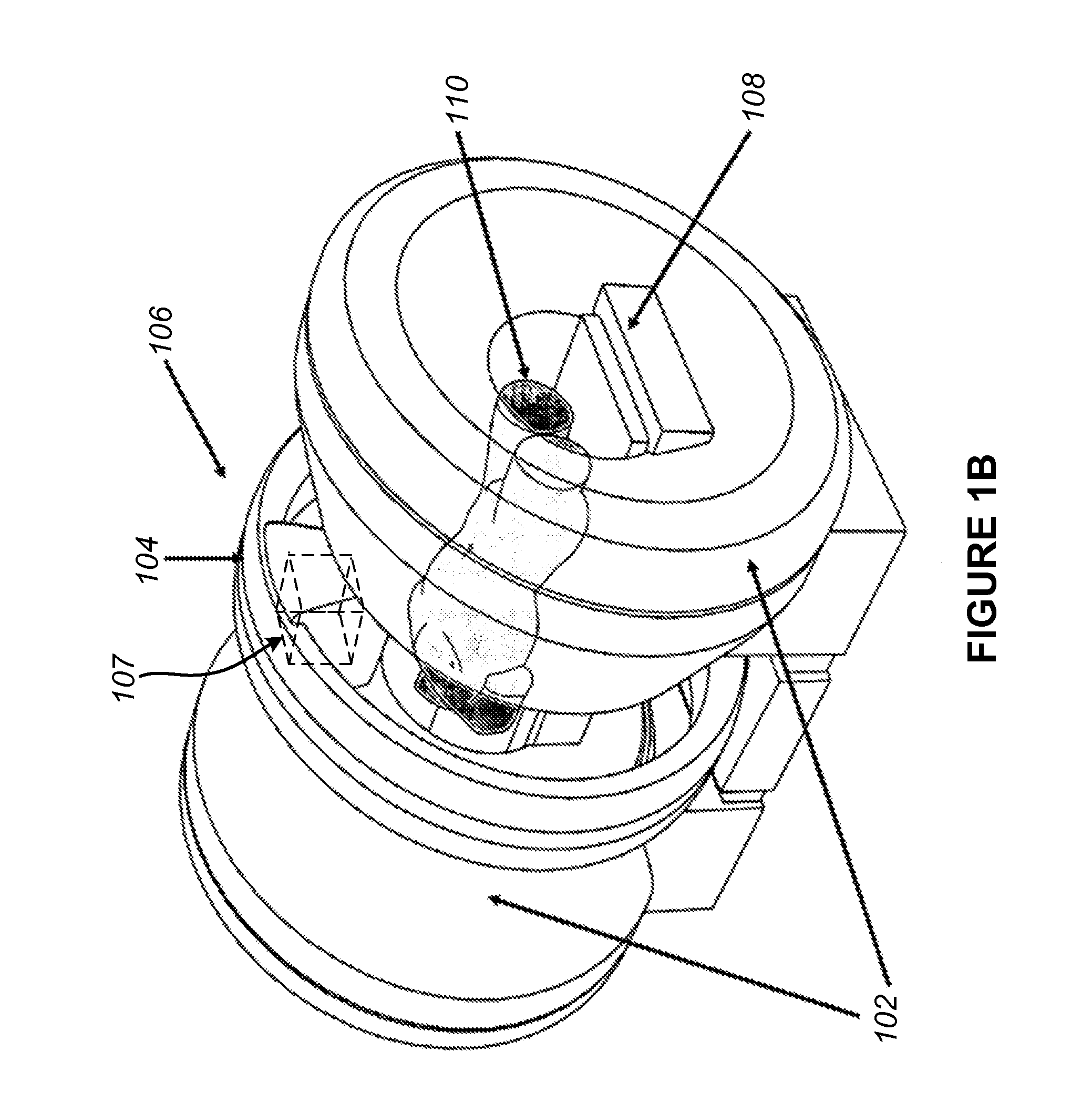
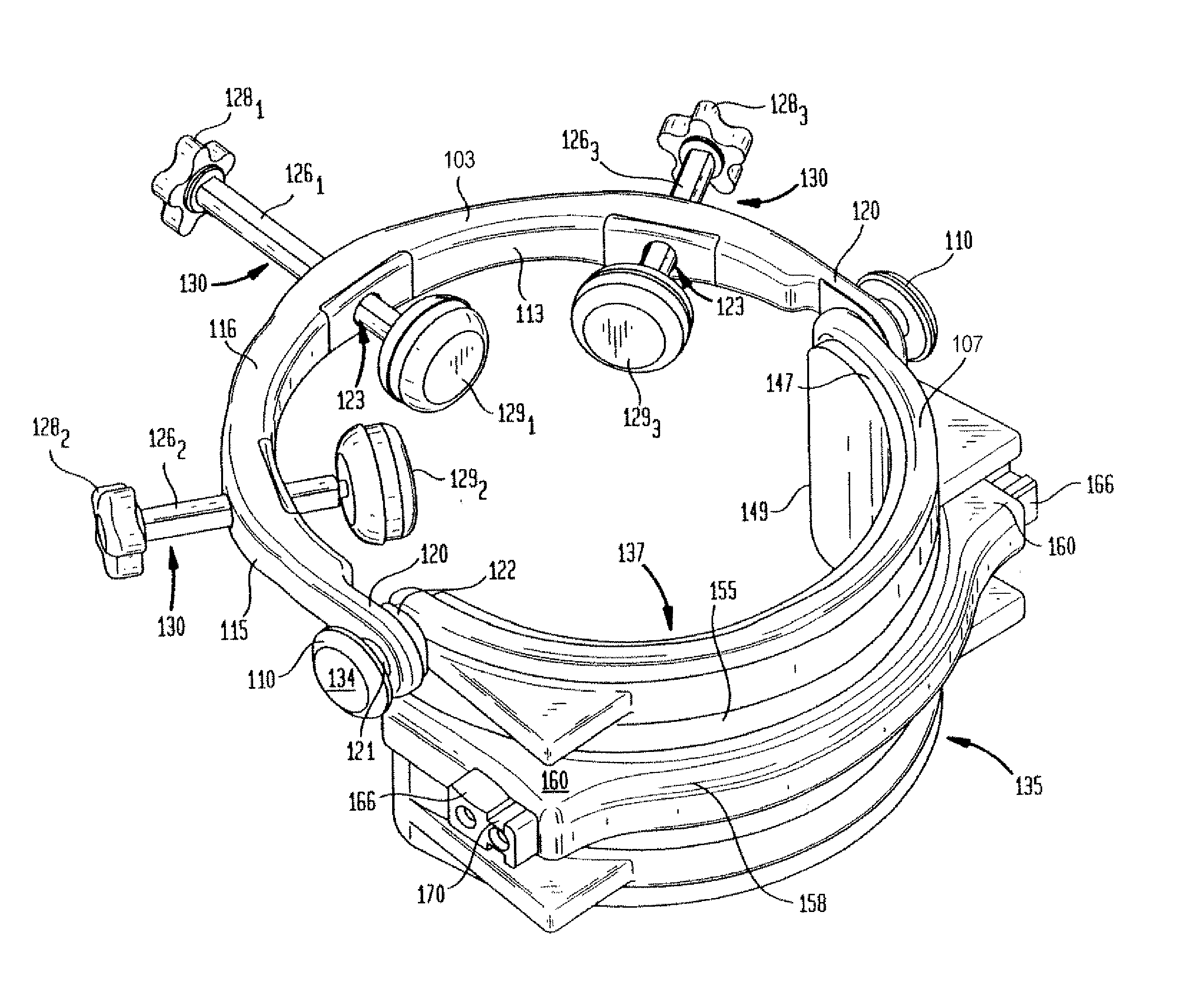
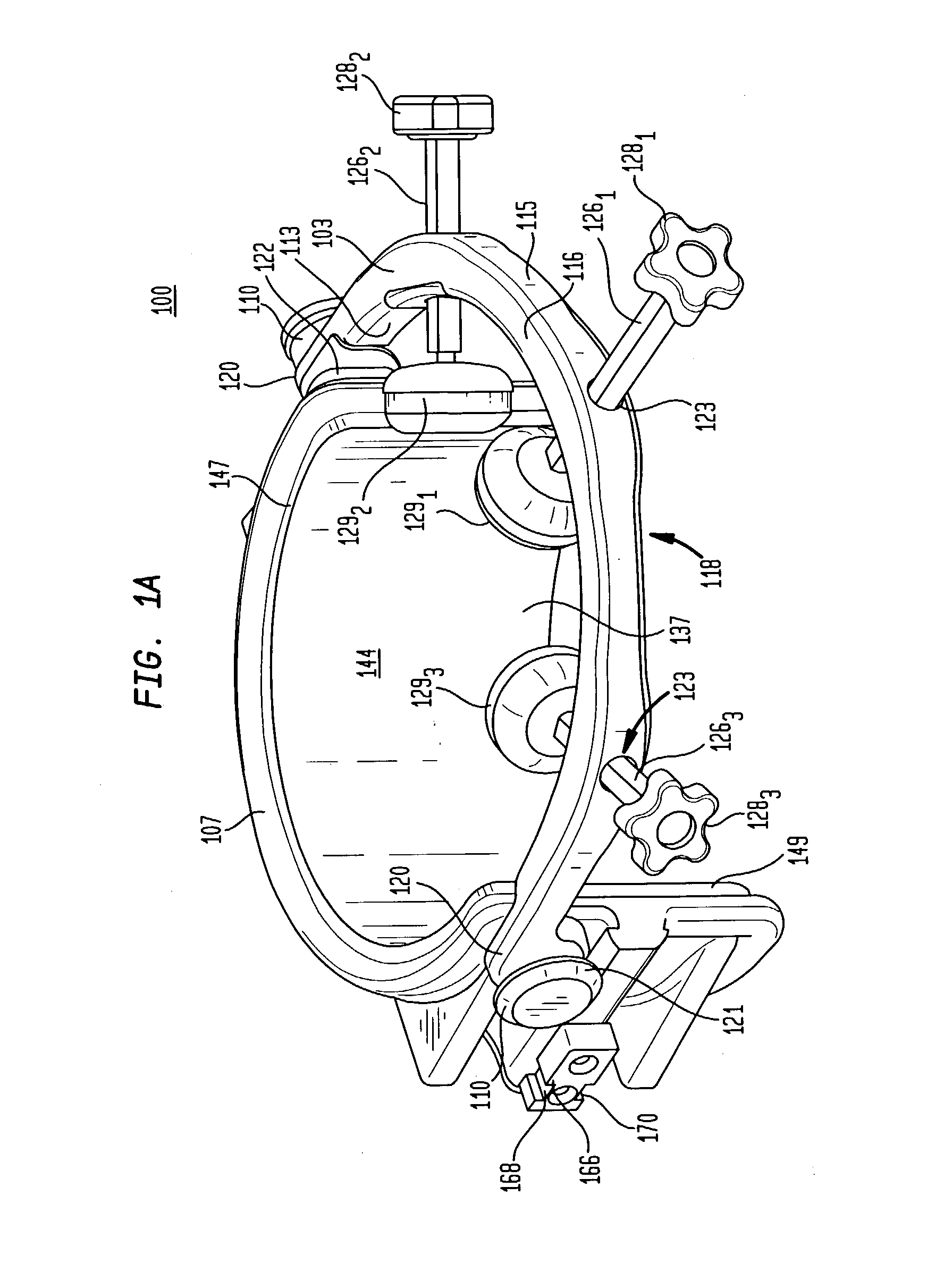
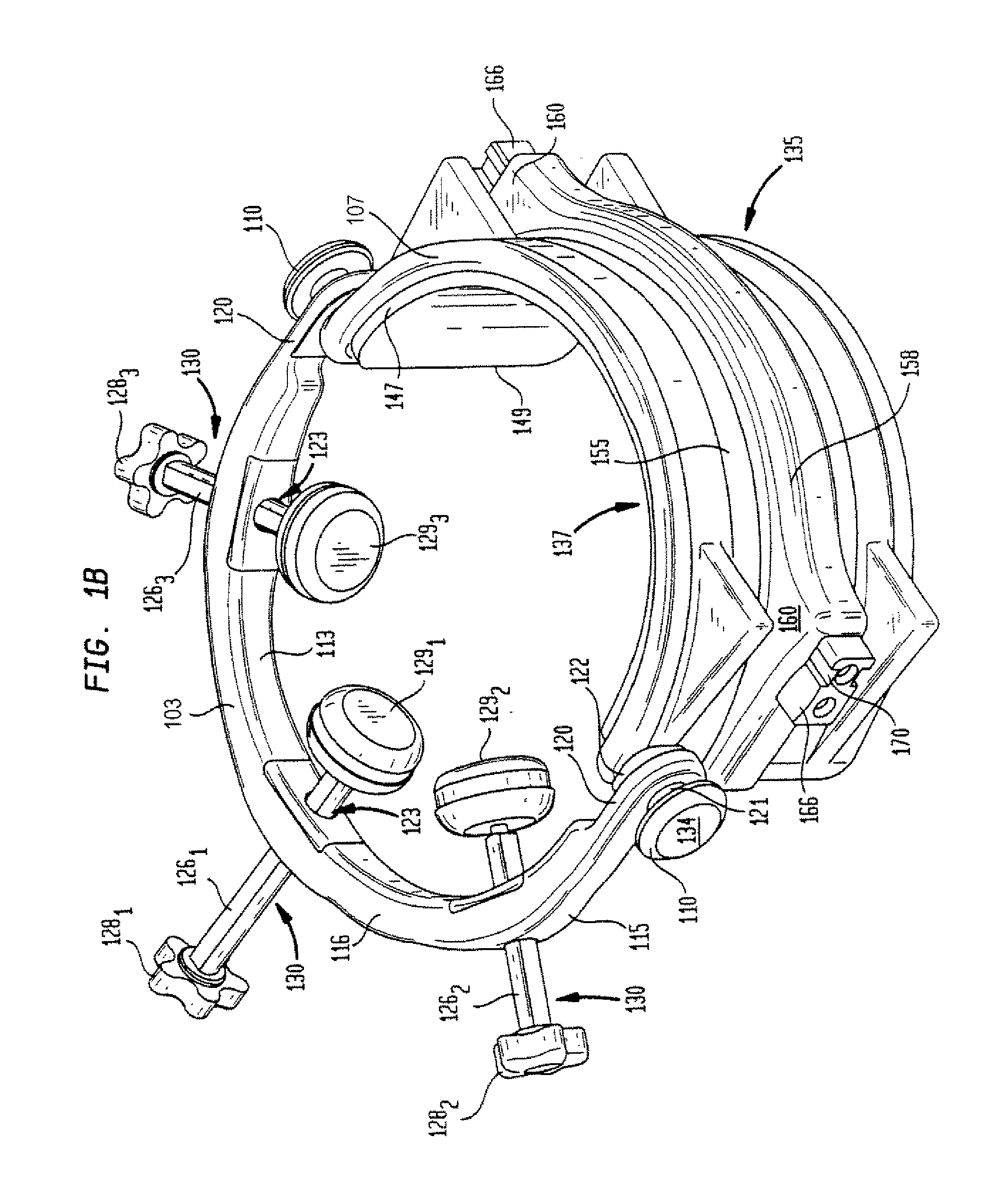
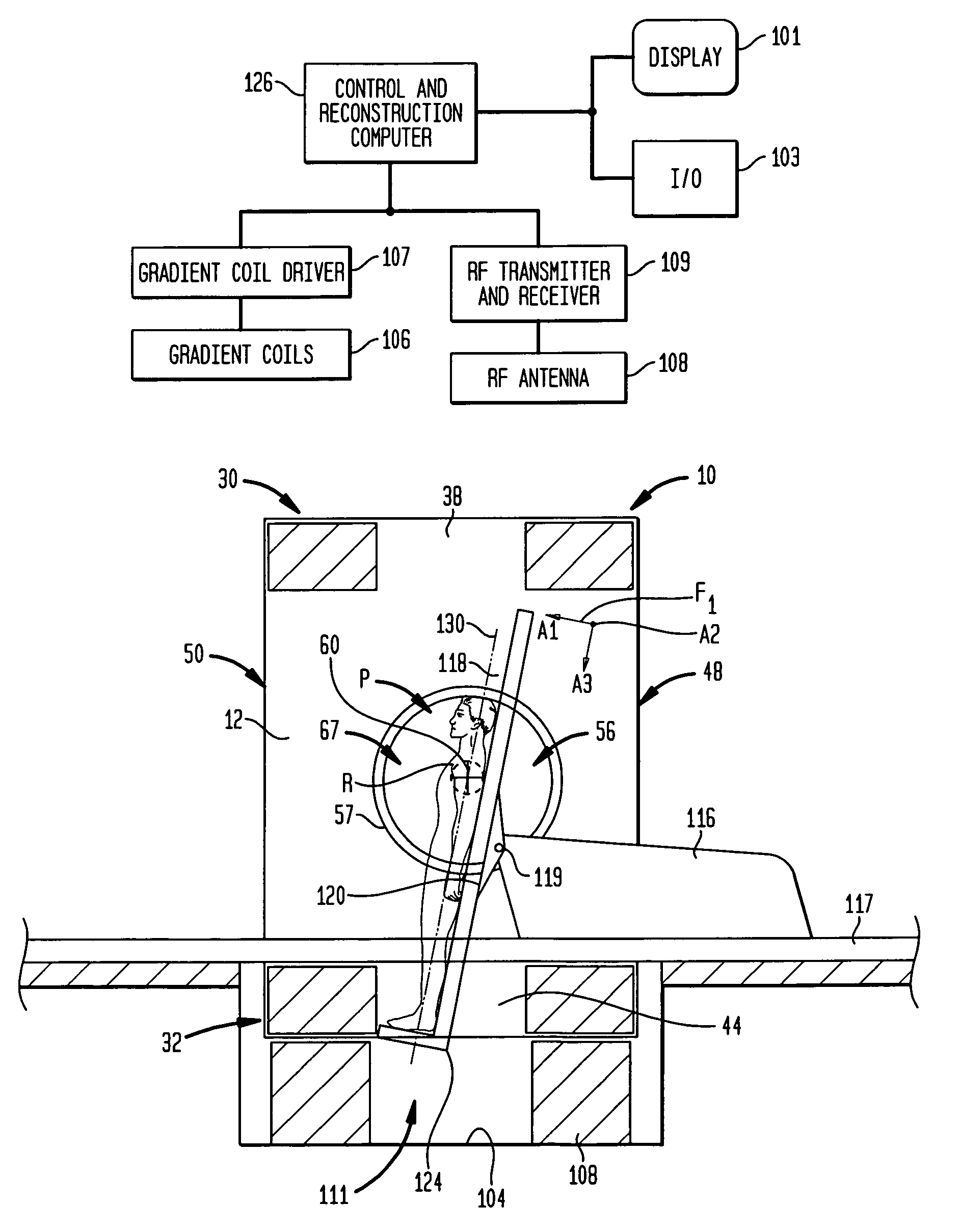
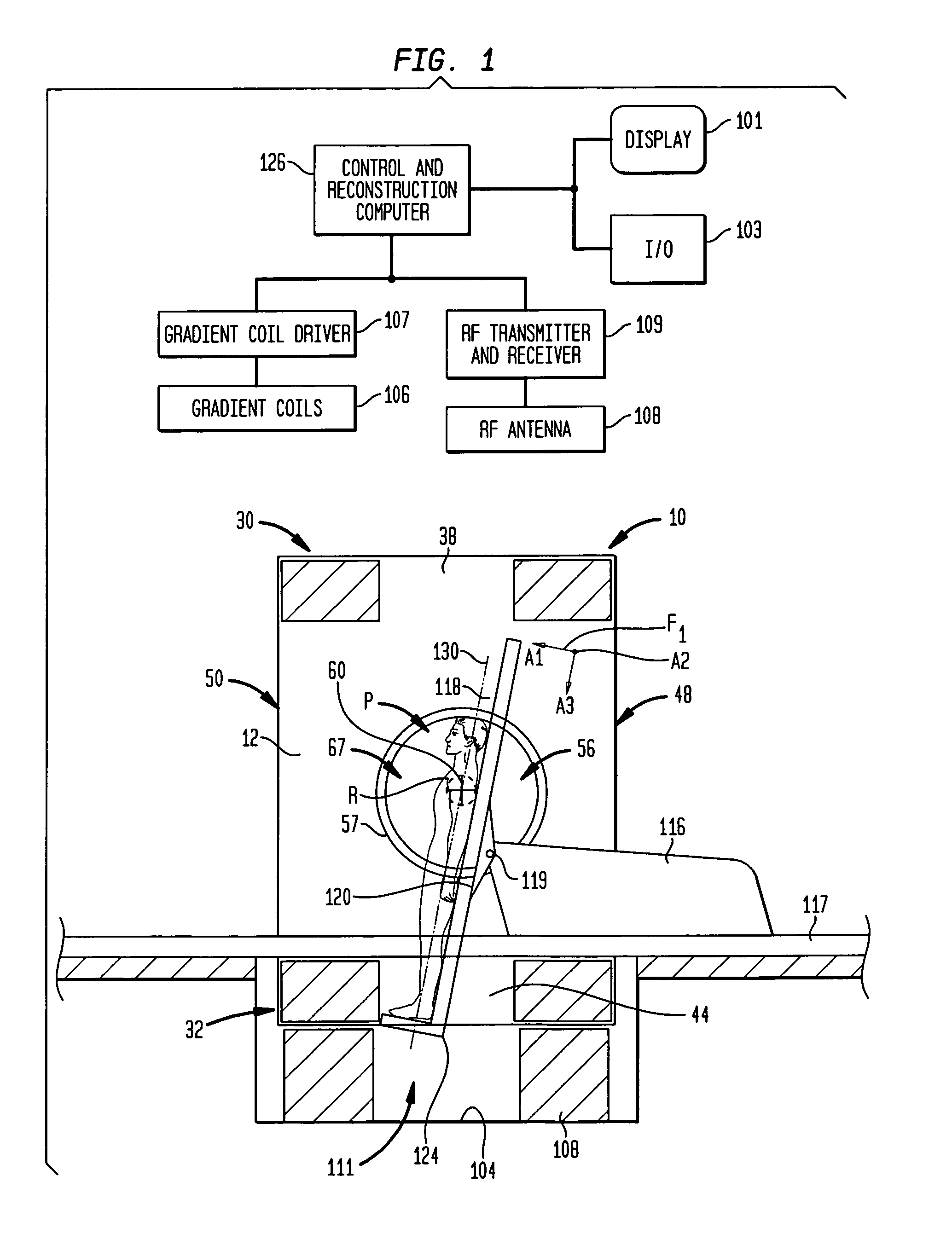
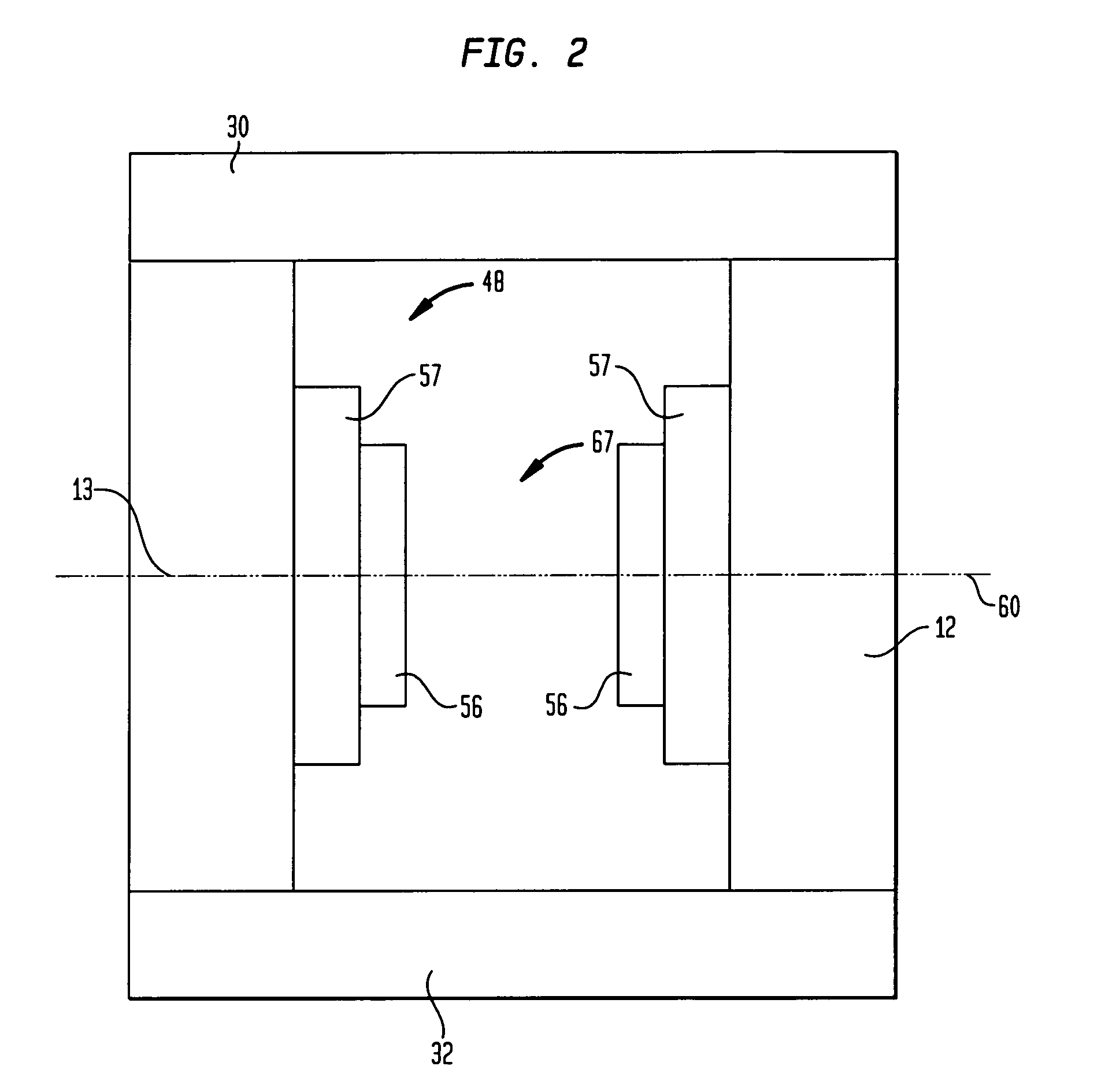
Head and neck immobilization in magnetic resonance imaging
Apparatus, system and method for immobilizing a patient's head during imaging. The apparatus includes two substantially C-shaped members that are pivotably mounted to each other. One C-shaped member includes at least one adjustable positioning rod for securing the patient's head during imaging. The apparatus is attached to a magnet resonance imaging apparatus to form a system. The system is used for imaging a patient whose head and neck is immobilized by the apparatus.
Owner:FONAR
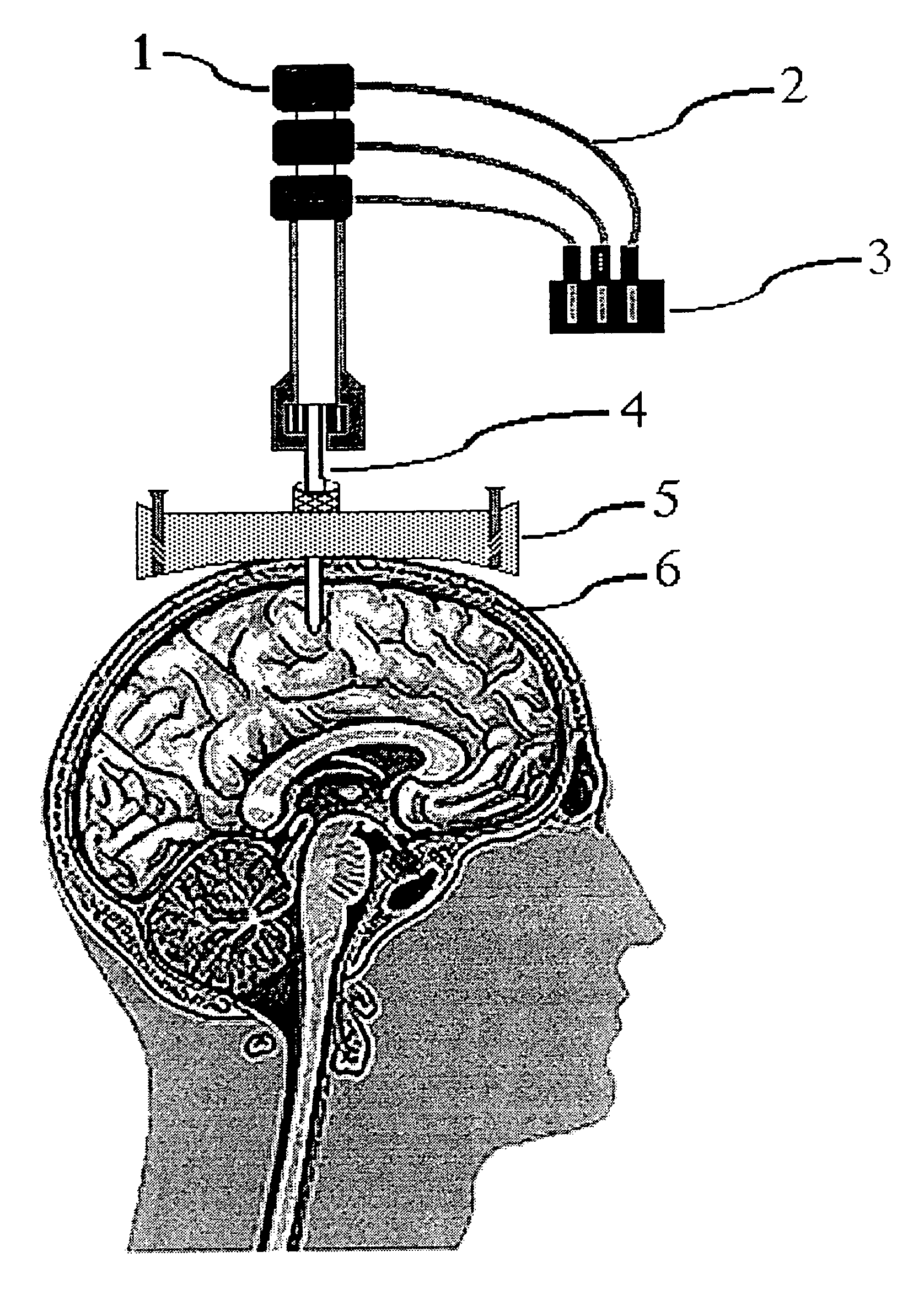
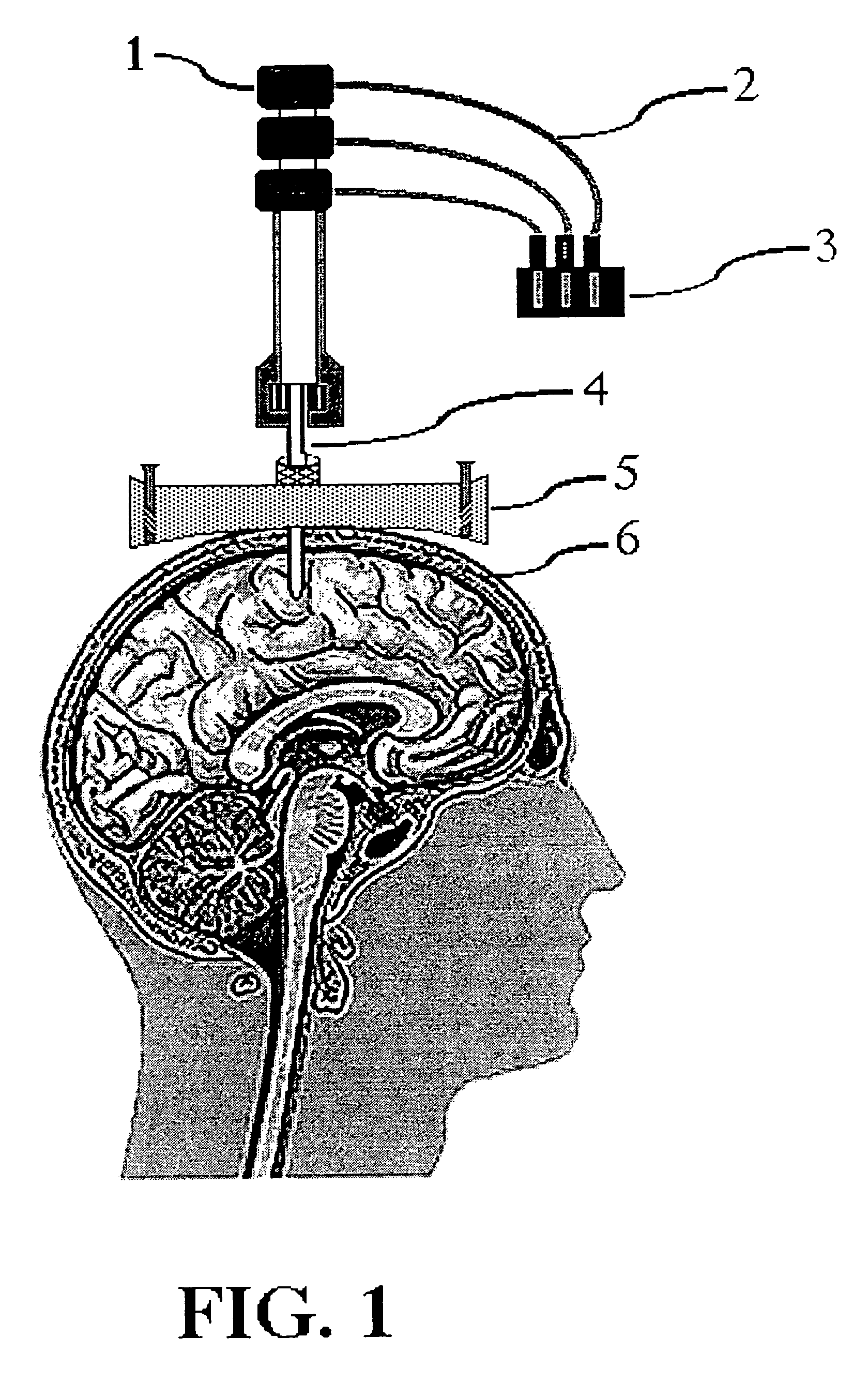
Magnetic resonance apparatus for use with active electrode and drug deliver catheter
InactiveUS7505807B1Altered growthImprove efficacyMagnetic measurementsCannulasDrugs solutionResonance
The invention is an apparatus and method for treatments and targeted drug delivery into a living patient, particularly but not exclusively using magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The apparatus and method are useful in delivery to all types of living tissue and uses MR Imaging to track the location of drug delivery and estimating the rate of drug delivery. An MR-visible drug delivery device positioned at a target site (e.g., intracranial delivery) delivers a diagnostic or therapeutic drug solution into the tissue (e.g., the brain). The spinal distribution kinetics of the injected or infused drug agent are monitored quantitatively and non-invasively using water proton directional diffusion MR imaging to establish the efficacy of drug delivery at a targeted location.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
Multicoil NMR data acquisition and processing methods
ActiveUS7466128B2Reduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsDetection using electron/nuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientAcquisition apparatus
Owner:VISTA CLARA
NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles with double effects and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102391874AUniform and controllable scaleIn-vivo testing preparationsLuminescent compositionsChemical physicsMagnet resonance imaging
The invention relates to NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles with double effects and a preparation method thereof. The NaYF4-based fluorescent nano particles at least comprise a kernel and a shell, wherein the kernel is NaYF4: Er / Yb / Gd or NaYF4: Er / Yb, and the shell is NaGdF4. By introducing different luminous ion pairs into different layers, the single-excitation multi-color luminescence function of the single fluorescent particles is realized, and the fluorescent particles have magnetic resonance imaging function; and meanwhile, by introducing a wrapping layer, surface defects of the particles are reduced, and the fluorescent strength of the particles is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic resonance imaging having patient video, microphone and motion tracking
ActiveUS8214012B2Efficient removalImprove diagnostic qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDigital videoProjection system
Critical needs for MRI patient instruction, testing, comfort, motion control, and speech communication are provided for better imaging which leads to more effective medical care. An MRI Digital Video Projection System is disclosed which provides better quality display to the patient to better inform, instruct, test, and comfort the patient plus the potential to stimulate the brain with microsecond onset times to better diagnose brain function. An MRI Motion Tracker and Patient Augmented Visual Feedback System enables monitoring patient body part motion, providing real time feedback to the patient and / or technician to substantially improve diagnostic yield of scanning sessions, particularly for children and mentally challenged individuals. An MR Forward Predictive Noise Canceling Microphone System removes the intense MRI acoustic noise improving patient communication, patient safety and enabling coding of speech output. These systems can be used individually but maximum benefit is from providing all three.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF +1
Detection and tracking of interventional tools
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Methods for spatial and spectral selectivity in magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS20160139222A1Provide spaceIncrease inhomogeneityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientResonance
The present invention provides magnetic resonance multidimensional selectivity based on spatiotemporal encoding (SPEN). In particular, multidimensional selectivity is achieved by the concurrent application of frequency-swept irradiation and magnetic field gradients for the sequential manipulation of spins in space in one dimension or more. Simultaneous spatial and spectral selectivity is disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Stripline antenna and antenna array for a magnetic resonance device
InactiveUS20100213941A1Antenna structure is simpleSimple structureElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance spectroscopicStripline resonator
An antenna (100) for a magnetic resonance device has a predetermined sensitivity and is designed to excite and / or detect a magnetic resonance in an object under test. The antenna (100) includes a stripline resonator (10) that is equipped with at least one stripline (11), and a conductor loop arrangement (20) that adjoins the stripline resonator (10) and forms at least one conductor loop (21, 22, 28) which is interrupted by at least one capacitor (23). The sensitivity of the antenna (100) is formed by overlapping sensitivity profiles of the stripline resonator (10) and the conductor loop arrangement (20). Also described are an antenna array (200) including a plurality of antennas (100), a magnetic resonance device (300) including at least one antenna (100) or antenna array (200), and methods for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Temporal magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8036730B1Accurately reflectSimple registrationMedical imagingMagnetic measurementsIndividual dataImaging data
A patient is subjected to magnetic resonance imaging at substantial intervals such as weeks, months or years, or after an interval sufficient for a therapeutic regimen to affect the anatomy, and the data acquired at different times is compared to show changes in the anatomy with time or due to the effects of the therapeutic regimen. Individual data elements or larger groups of plural data elements representing particular locations a set of image data acquired at one time can be automatically compared with data elements associated with the same locations in another set of image data acquired at another time to yield a set of comparison data.
Owner:FONAR
Apparatus for providing high resolution images in a mri-device
ActiveUS20090093705A1Static indicating devicesColor television detailsHigh resolution imageMri image
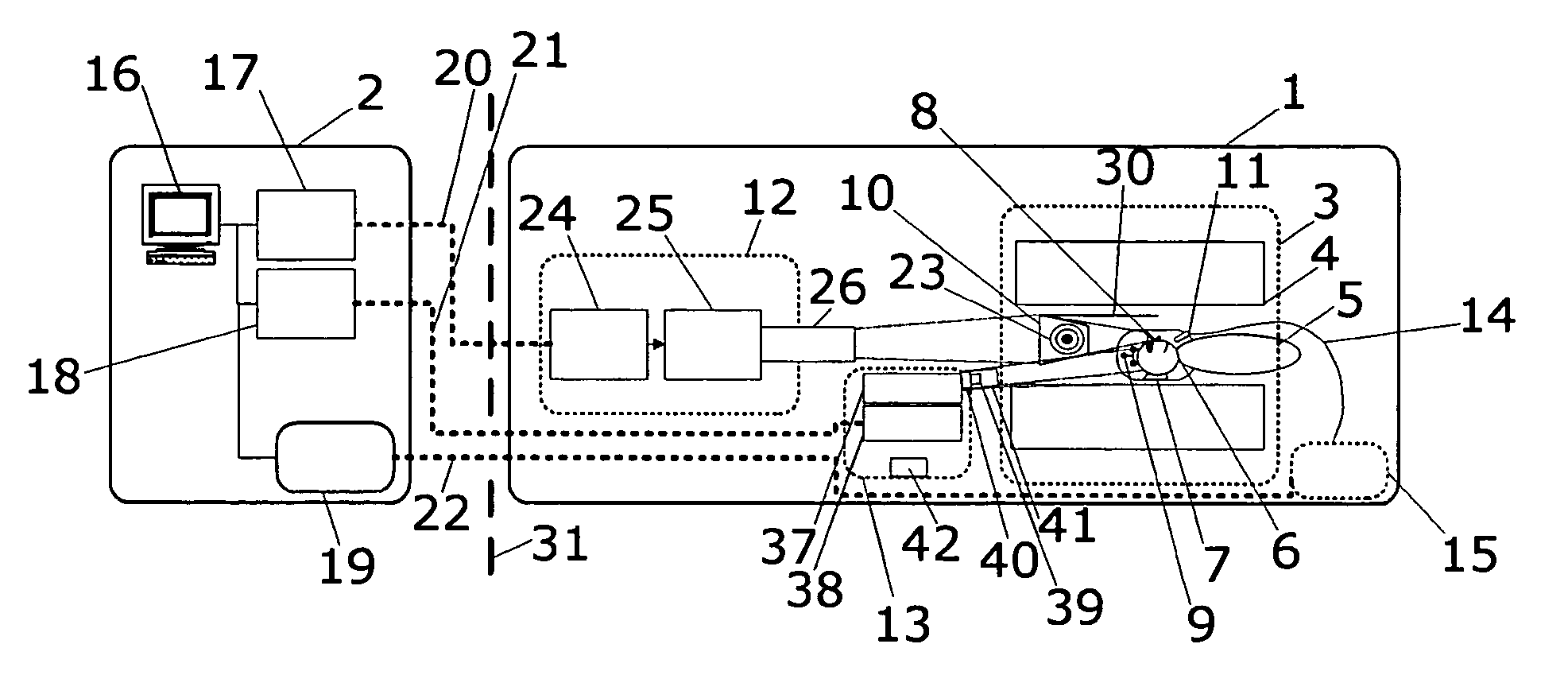
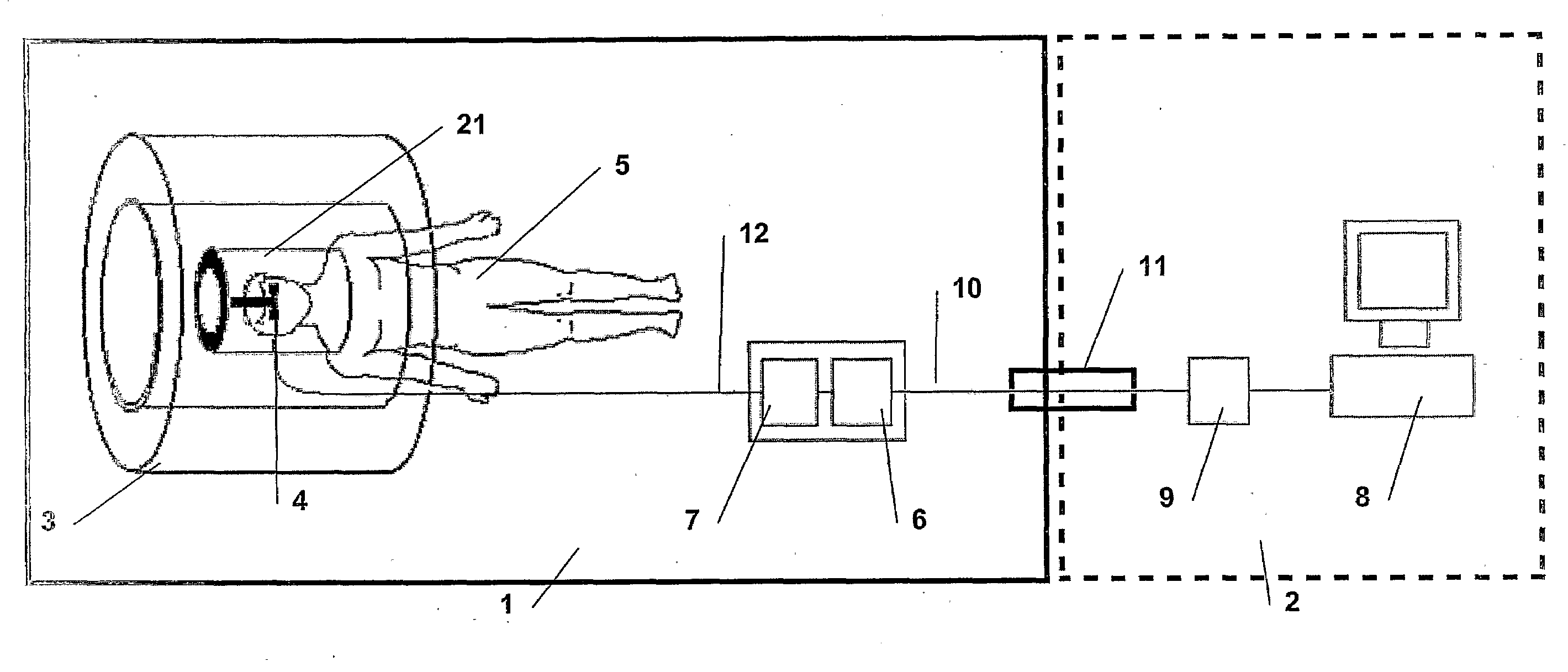
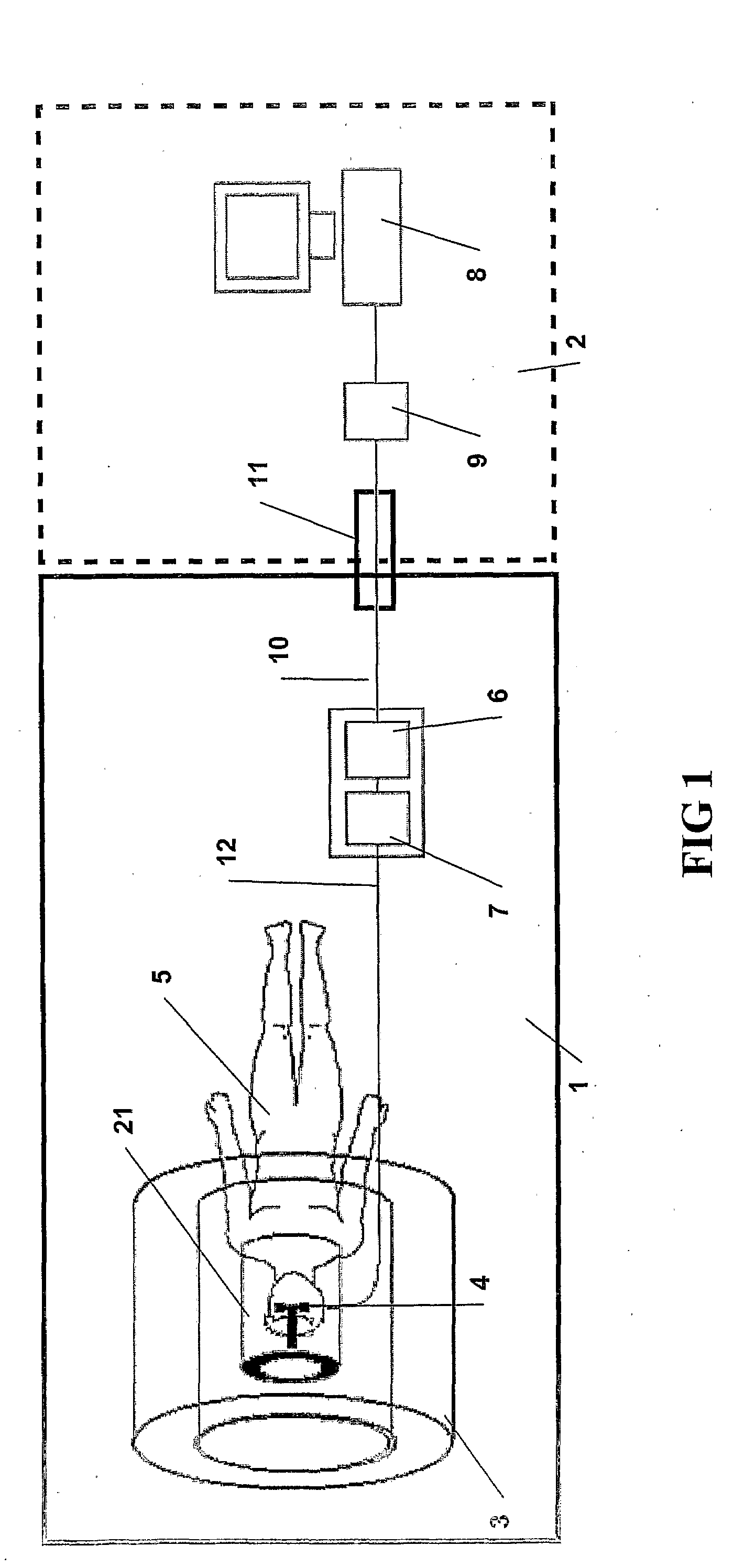
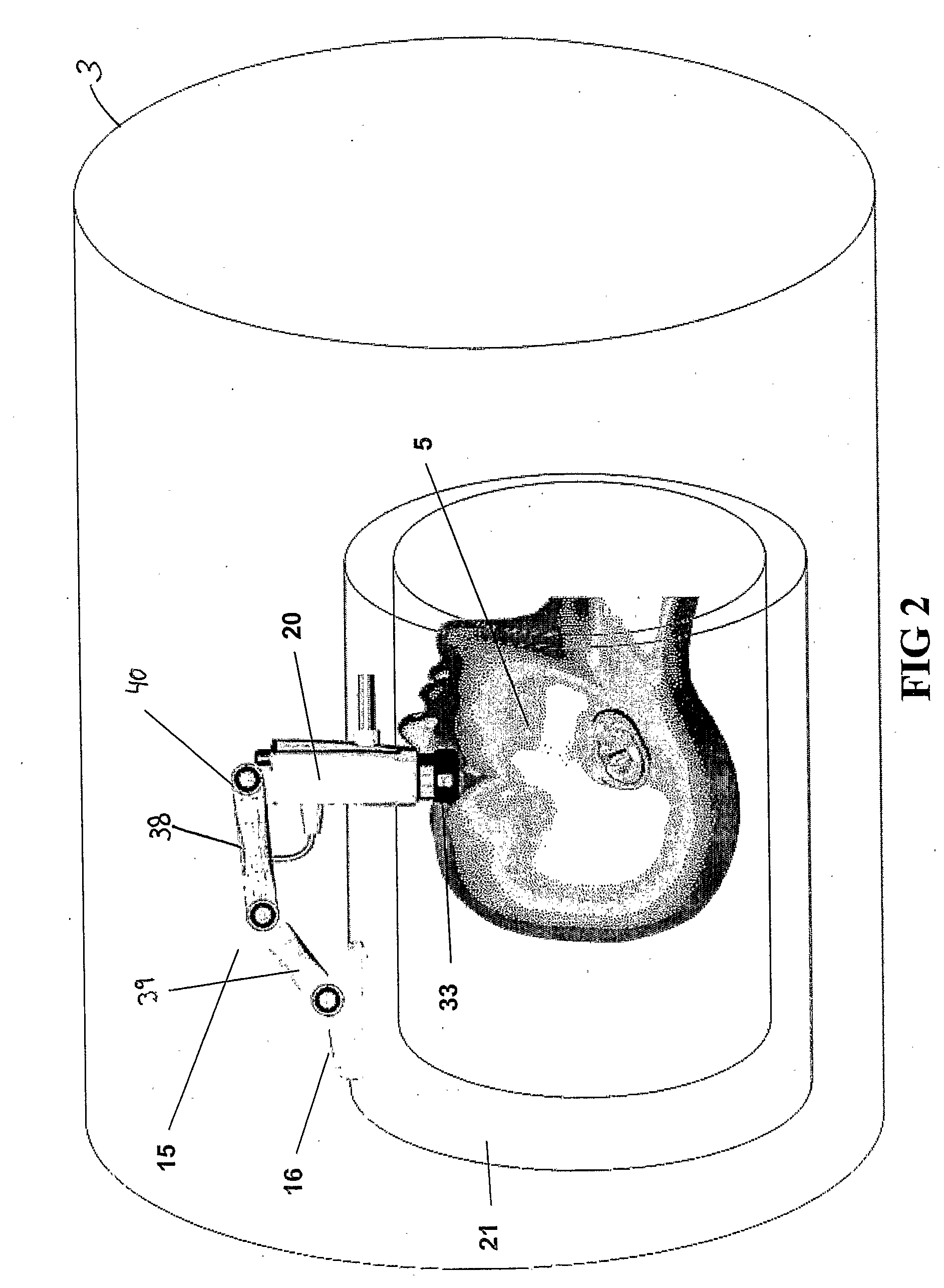
The present invention relates to an apparatus for providing high resolution images to patients positioned in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device (3), the MRI device (3) comprising a head coil (21), the head coil arranged to surround a patient's (5) head and to provide MRI images thereof, the apparatus comprising means (12, 13, 14) for receiving video or picture image signals from an external source. According to the present invention, the apparatus further comprises means (14, 28, 34, 29) for displaying a video or picture image, said display means being arranged in a housing (20), said housing (20) being suspended in an arm comprising at least two successive members (38, 39), wherein a joint (40) between the housing (20) and the adjacent member (38), a joint or joints (41) between the successive members (38, 39), and a joint (42) between an attachment element (16) for attaching the apparatus to the head coil (21), or other part of the MRI device (3), and the member (39) adjacent to the coil attachment element (16), each is hinged to allow rotation of the joints (40, 41, 42).
Owner:NORDICNEUROLAB
Integrated microchip incorporating atomic magnetometer and microfluidic channel for nmr and MRI
ActiveUS20090256561A1Low costHigh sensitivityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMicrofluidic channelMR - Magnetic resonance
An integral microfluidic device includes an alkali vapor cell and microfluidic channel, which can be used to detect magnetism for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Small magnetic fields in the vicinity of the vapor cell can be measured by optically polarizing and probing the spin precession in the small magnetic field. This can then be used to detect the magnetic field of in encoded analyte in the adjacent microfluidic channel. The magnetism in the microfluidic channel can be modulated by applying an appropriate series of radio or audio frequency pulses upstream from the microfluidic chip (the remote detection modality) to yield a sensitive means of detecting NMR and MRI.
Owner:GOVERNMNET OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF COMMERCE THE NAT INST OF STANDARDS & TECH +1
Data detection device for use in combination with an MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20150002150A1Easily and efficiently detectedRequired additionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysicsTimestamp
The invention relates to a data detection device for use in combination with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus. A magnetic field detection unit (34) serves to detect a temporally varying magnetic field generated by the MRI apparatus, and a timestamping unit (35) generates magnetic field detection timestamps in dependence of the detected temporally varying magnetic field. This allows determining a temporal relation to acquired MRI data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com