Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Spatiotemporal encoding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for spatial and spectral selectivity in magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS20160139222A1Provide spaceIncrease inhomogeneityMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientResonance
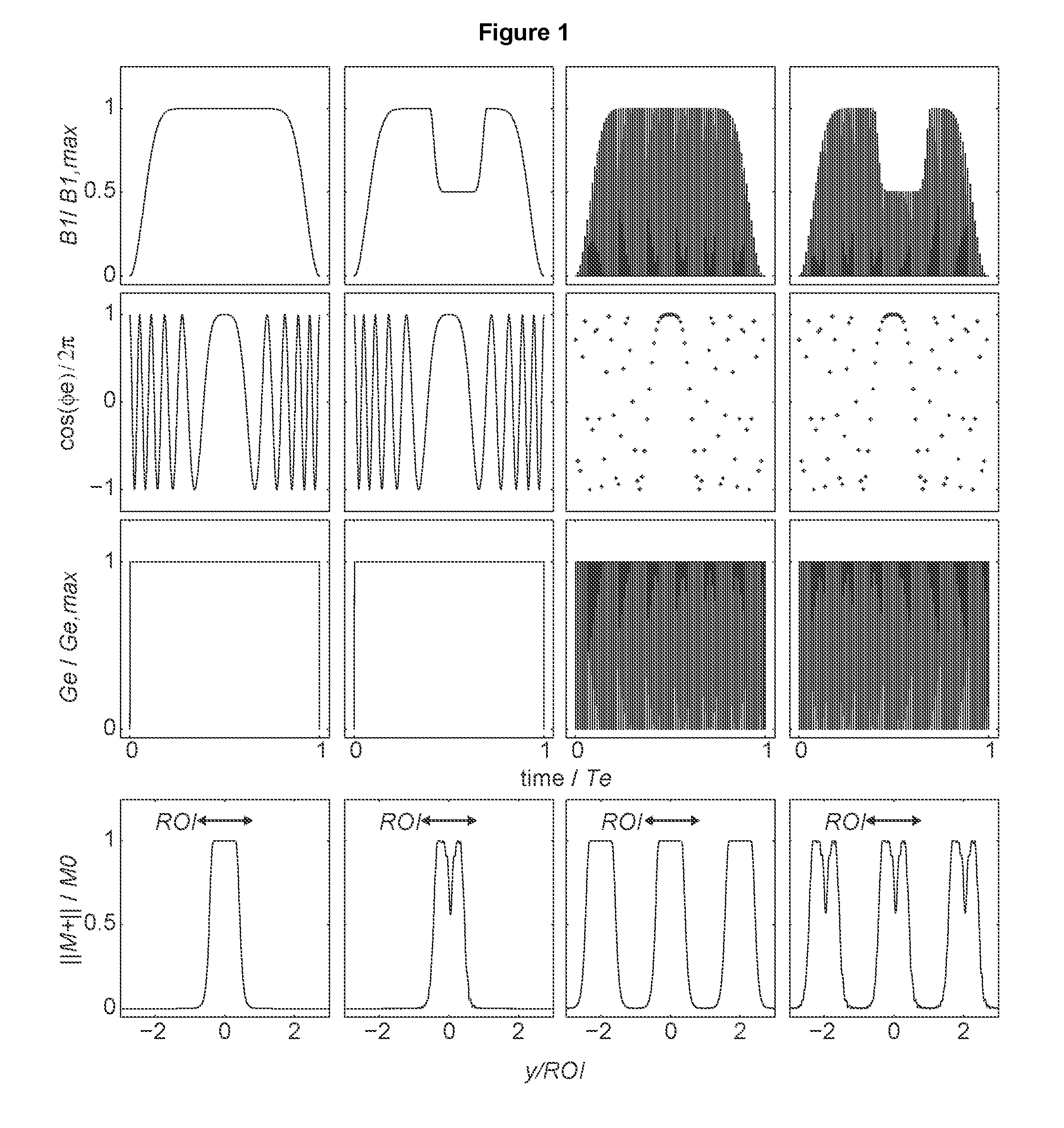
The present invention provides magnetic resonance multidimensional selectivity based on spatiotemporal encoding (SPEN). In particular, multidimensional selectivity is achieved by the concurrent application of frequency-swept irradiation and magnetic field gradients for the sequential manipulation of spins in space in one dimension or more. Simultaneous spatial and spectral selectivity is disclosed.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
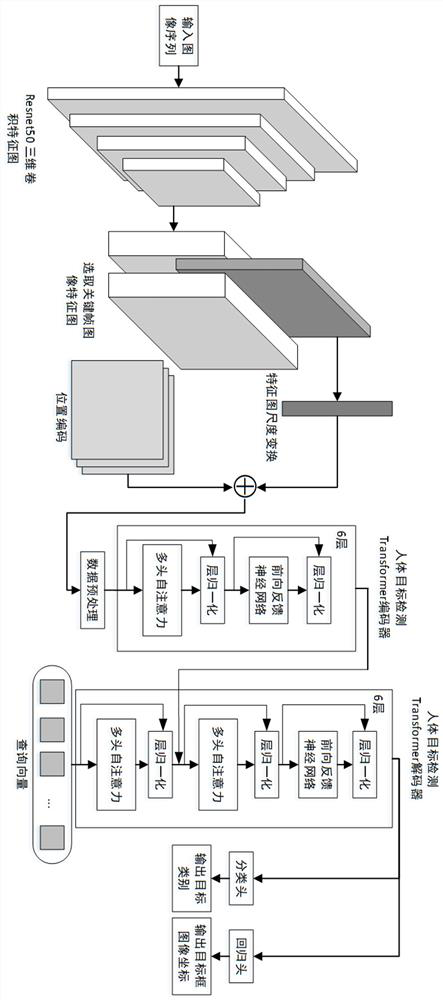
Video group behavior recognition method based on cascade Transformer
ActiveCN113673489AReduce complexityRobustCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setRadiology
The invention relates to the field of computer vision and deep learning, in particular to a video group behavior recognition method based on cascade Transformer, which comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring and generating a video data set, extracting three-dimensional spatial-temporal features from the video data set through a three-dimensional backbone network, and selecting a key frame image spatial feature map; preprocessing the key frame image spatial feature map, sending the preprocessed key frame image spatial feature map into a human body target detection Transformer, and outputting a human body target box in the key frame image; then, mapping a sub-feature map corresponding to the screened human body target box on the key frame image feature map, calculating query / key / value in combination with a key frame image surrounding frame feature map, inputting the query / key / value into a group behavior recognition Transfomer, and outputting a group level spatial-temporal coding feature map; and finally, classifying group behaviors through a multi-layer perceptron. The method has the effect of effectively improving the group behavior recognition accuracy.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Small-view-field magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-sweep super-speed orthogonal space-time coding
ActiveCN103809140AImprove spatial resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpatial encodingField of view
The invention discloses a small-view-field magnetic resonance imaging method based on single-sweep super-speed orthogonal space-time coding. The method comprises the following steps of: enabling protons in a space to automatically rotate in an excitation phase by virtue of the organic combination of an orthogonally-distributed space coding gradient and a linear frequency sweep pulse to acquire a secondary phase related to a space position, thus carrying out two-dimensional space-time coding on the automatic rotation of the protons in an imaging plane; for the automatic rotation of the protons in an orthogonal space-time coding space, only the automatic rotation of the protons with static phase distribution can be detected during a decoding sampling period, and according to the characteristic of orthogonal space-time coding, decoding sampling can be carried out on a plurality of randomly-distributed areas in the space by designing a decoding sampling gradient, thus acquiring the magnetic resonance data of a plurality of areas of interest finally. High-resolution reconstruction is sequentially carried out on acquired magnetic resonance data of the plurality of areas, and then the high-resolution small-view-field magnetic resonance images of the plurality of areas can be obtained finally.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
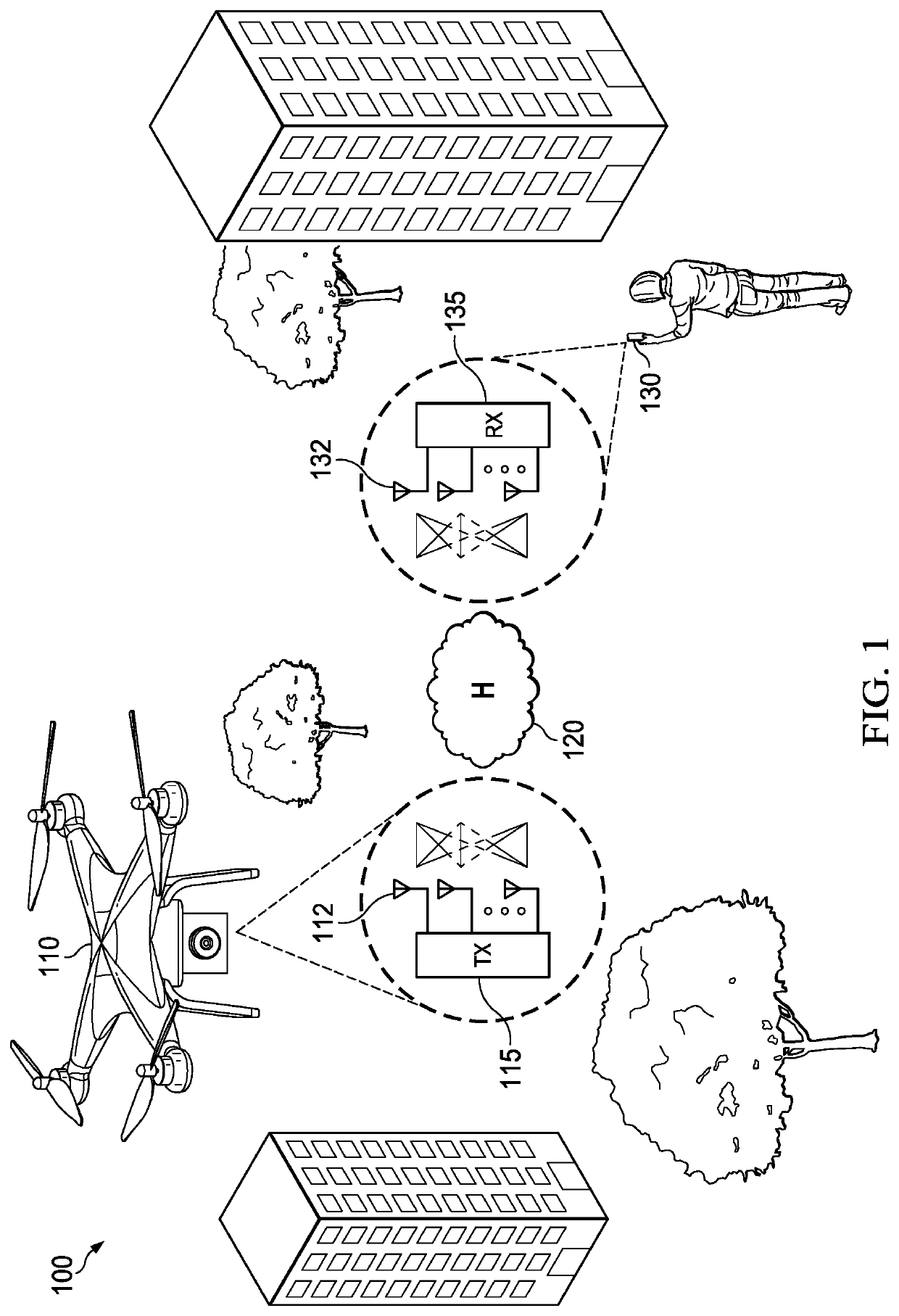
Multi-Input Multi-Output System For Enhancing Transmission Performance
InactiveUS20080240276A1Improve performanceError rateSpatial transmit diversitySecret communicationMulti inputTransmitter
The present invention relates to a multi-input multi-output (MIMO) system for enhancing transmission performance. The MIMO system uses space-time encoding and transmit antenna selection methods, and includes a transmitter (100) and a receiver (200). The transmitter (100) includes N transmit antennas (130-1, 130-4) that are more than M tansrni antennas (130-1, 130-3) used for transmitting a signal to space channel, selects the M transmit antennas (130-1, 130-3) among the N transmit antennas (130-3 130-4), and transmits symbol by space-time encoding the symbol. The receiver (200) includes M receive antenna (120-1, 210-2) for receiving a signal from the space channel, detects an information symbol by using the signal received through the receive antenna (210-1, 210-2), generates transmit antenna selection information for selecting M transmit antennas (130-1, 130-3) among transmit antennas (i30-1, . . . 7130-4) with reference to a channel estimate, and returns the information to the transmitter.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Video question answering method based on object-oriented double-flow attention network
PendingCN114428866ASolve the problem of lack of dynamic information analysisImprove exploration abilityMetadata multimedia retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionSemantic alignmentData set
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Broadband zero cross polarization space-time coding digital metasurface unit and control method
ActiveCN110911845AExtended current pathIncreased Oblique Incidence PerformanceAntennasIsolatorSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a broadband zero cross polarization space-time coding digital metasurface unit and a control method. A radiator is used. The edge of the radiator is provided with a plurality of micro-tuning sheets and a micro-tuning hole in the center. The radiator is connected with the radio frequency switch. The two states of turning off and turning on the radio frequency switch are respectively corresponding to a turning-off mode and a turning-on mode. By optimizing the sizes of the micro-tuning holes and the micro-tuning pieces, the electric field distribution of the turn-off modeand the electric field distribution of the turn-on mode are kept consistent near the target frequency as much as possible, so that the stable phase difference between the two modes is obtained, and the space-time coding digital metasurface unit can work in the regulation and control of the broadband one-bit 180-degree reflection phase. Besides, through reasonable design of the AC-DC isolator, loading of the bias circuit hardly changes the original phase difference of the unit, unit loss is avoided, and unnecessary cross polarization caused by damage to the symmetry of the unit is avoided. According to the invention, 180-degree phase shift is realized within the frequency band of 7.71-9.48 GHz.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Video prediction method based on space-time propagation level codec
ActiveCN113422952AEffective feature representationAccurate prior knowledgeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrame sequenceAlgorithm
The invention discloses a video prediction method based on a space-time propagation level codec. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, sampling a given original video to obtain a frame sequence, and inputting the frame sequence into a low-layer visual memory coder to obtain low-layer visual coding features and low-layer memory state features; then, extracting space-time coding features from low-layer visual coding representation through a space-time propagation module, and extracting high-layer semantic features through a high-layer semantic coder; and carrying out information fusion on the obtained low-layer visual coding features, low-layer memory state features and high-layer semantic coding features through a hierarchical feature decoder, and outputting a predicted video frame. According to the method, the low-level visual memory features and the high-level semantic features can be fused, the low-level visual information is propagated in the time sequence direction through the space-time propagation module, the problem of video frame blurring can be solved to a certain extent by utilizing the priori knowledge of the first frame of the video, and the definition and visual quality of the predicted video frame are improved as a whole.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Cross-term spatiotemporal encoding for magnetic resonance imaging
A method for MRI imaging of a subject includes spatially encoding spins in a slice of the subject in orthogonal first and second directions. The encoding includes applying a chirped radiofrequency (RF) pulse concurrently with application of a magnetic field gradient pulse along the first direction. After applying of the RF pulse, a second chirped RF pulse is applied concurrently with application of a second magnetic field gradient pulse, with polarity opposite that of the first gradient pulse. An encoding magnetic field gradient, constant from applying the first RF pulse until the end of applying the second RF pulse, is concurrently applied along the second direction. Following the encoding, a spin signal is measured concurrently with application of a constant readout magnetic field gradient.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
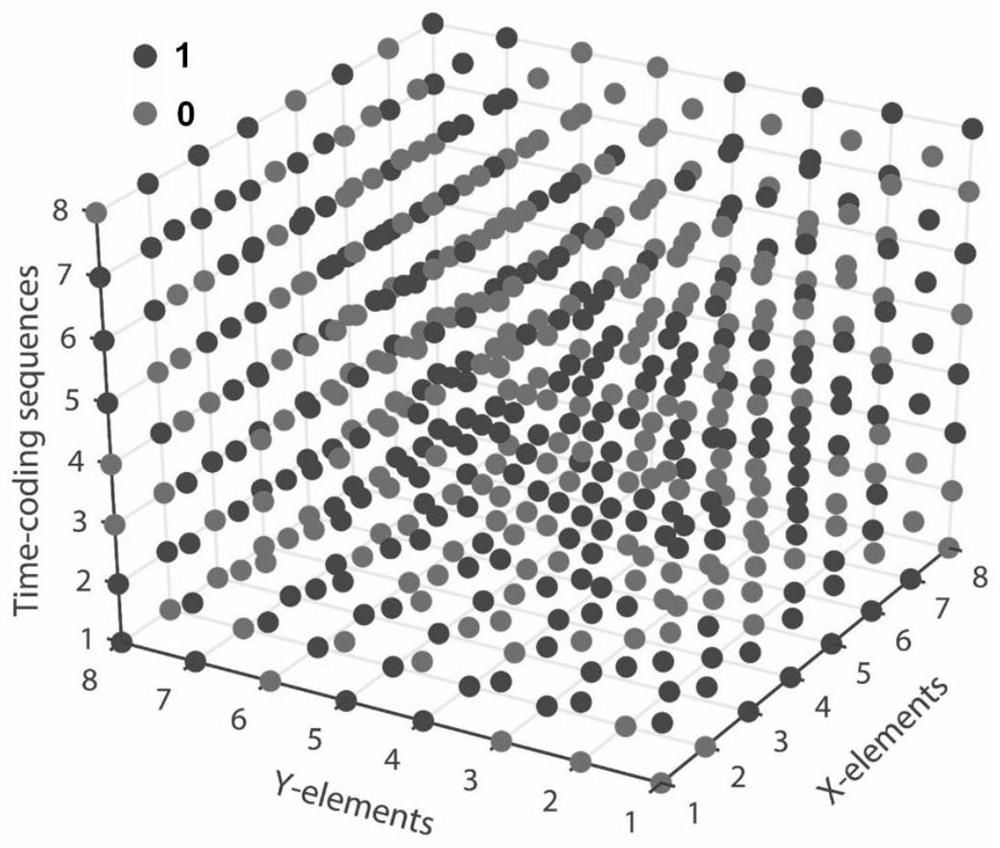
Basic unit, metasurface and arrival angle estimation method based on information metasurface
The invention relates to a basic unit. A unit structure is characterized in that the basic units are periodically arranged to form an information metasurface, a switching diode in each basic unit can be controlled by an external circuit, and then different electromagnetic responses are presented; the electromagnetic response states of the basic units can be arranged and distributed in a spatial dimension according to a spatial coding sequence, and further can be periodically circulated in a time dimension according to a time coding sequence; by designing a corresponding space-time coding matrix, the information metasurface can simultaneously regulate and control electromagnetic waves in a space domain and a frequency domain; and through carrying out signal analysis on the regulated electromagnetic waves, an arrival angle of the incident electromagnetic waves can be estimated, an arrival angle estimation and electromagnetic regulation integrated method based on the information metasurface is formed, and an incident angle of the electromagnetic waves irradiating the information metasurface can be independently regulated while the incident angle is quickly estimated in real time.
Owner:JIANGSU EMETASPACE TECH CO LTD
Space-time coding/decoding method for pulse type multi-antenna communication system
InactiveCN101394258ARadio transmissionError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDecoding methodsCommunications system
The present invention relates to a space-time coding method for a UWB pulse type transmission / reception system. The space-time code, given for P=2, 4 or 8 transmission antennas, makes it possible to code 2-PPM information symbols and to modulate the position of UWB pulse signals using coded symbols, without requiring extension of the modulation alphabet. The space-time code is real with maximum diversity, and is full speed. The space-time decoding method is capable of estimating the information symbols thus transmitted.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Efficient global space-time coding read-write system and read-write method
ActiveCN111241858ASolve the uniquenessFix security issuesCo-operative working arrangementsSatellite radio beaconingRadio frequencyTime data
The invention discloses an efficient global space-time coding read-write system. The system comprises a PC terminal, the global spatio-temporal coding read-write system further comprises a spatio-temporal coder, a radio frequency identification reader-writer, a global spatio-temporal coding server and a cloud server which are in communication connection with the PC terminal. The space-time encoderis used for acquiring space-time data; the global spatio-temporal coding server is used for encrypting the spatio-temporal data; the radio frequency identification reader-writer is further in communication connection with a radio frequency identification tag, the radio frequency identification reader-writer is used for writing information into the radio frequency identification tag or reading theinformation out of the radio frequency identification tag, and the cloud server is used for storing the information in the radio frequency identification tag. According to the efficient global space-time code read-write system and read-write method, global space-time codes and radio frequency identification read-write technologies are combined, and the problems of uniqueness, safety and high efficiency of information such as commodities can be effectively solved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BEIHANG UNIV
Video prediction method based on time sequence correction convolution
ActiveCN114758282AReduce computational overheadImprove capture abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionFrame sequence
The invention discloses a video prediction method based on time sequence correction convolution. The method comprises the following steps: sampling and preprocessing a given original video to obtain a video frame sequence, inputting the sequence into a time sequence context fusion module to obtain a fused appearance feature map and a fused space-time coding feature map, and inputting the sequence into a time sequence convolution correction module to obtain a convolution correction tensor; then, generating a prediction space-time coding feature map from the obtained fusion appearance feature map, the fusion space-time coding feature map and the convolution correction tensor through an adaptive convolution space-time encoder; and finally, decoding the predicted space-time coding feature map through a space-time memory decoder, and outputting a predicted video frame sequence. The method not only can correct the convolution kernel parameters according to the video frames at different moments, but also can model the internal relation of the space-time coding characteristics of the current video frame and the historical frame through the time sequence context fusion strategy, thereby generating a predicted video frame sequence with higher visual quality.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
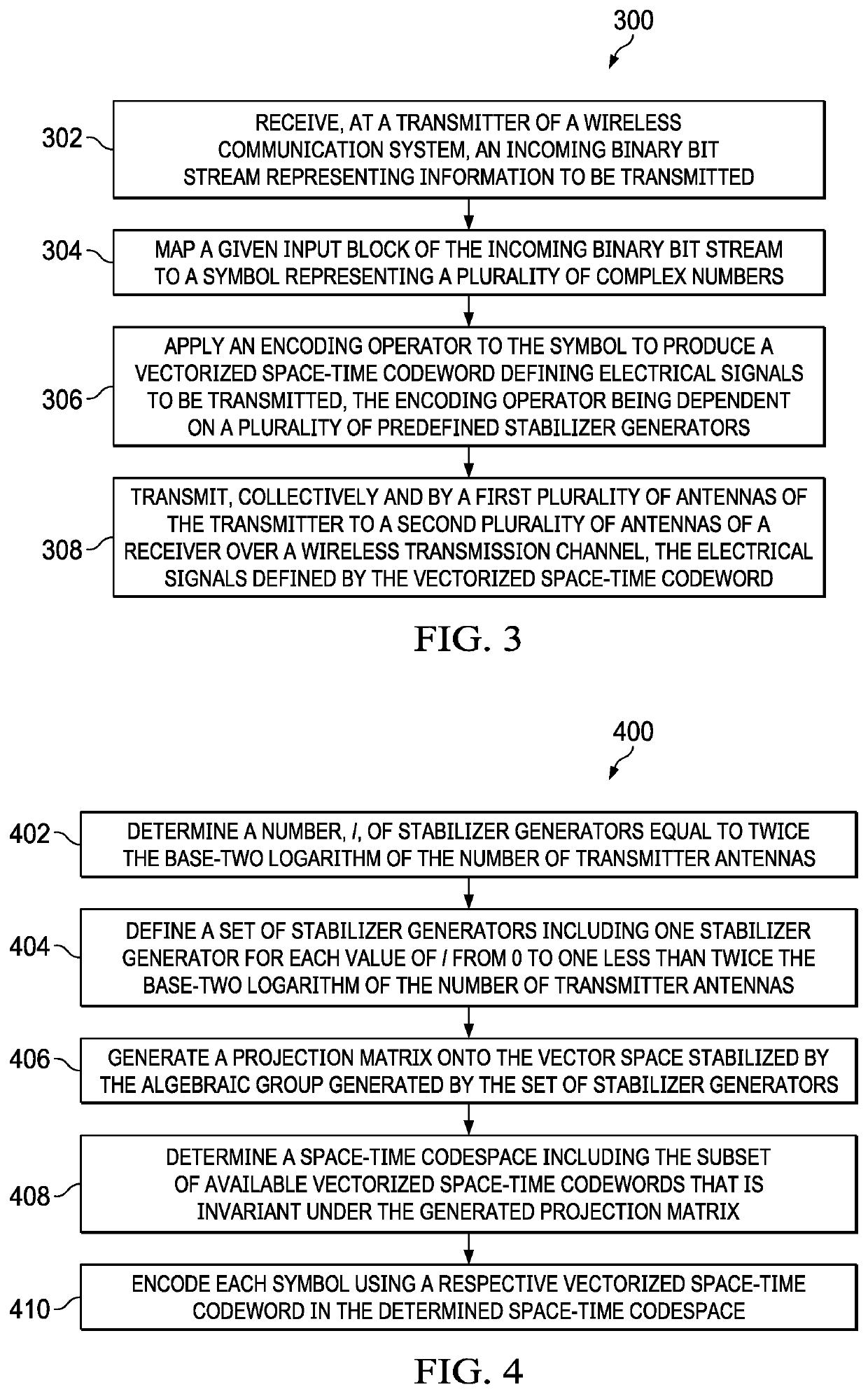
Space-time encoding in wireless communication systems
A disclosed transmitter for wireless communication includes multiple transmitting antennas, a symbol mapper for mapping an input block including multiple binary bits and representing information to be transmitted to a symbol representing an ordered plurality of complex numbers, a space-time encoder for applying an encoding operator to the symbol to produce a vectorized space-time codeword defining electrical signals to be transmitted by the transmitter, the encoding operator being dependent on a set of predefined stabilizer generators, and circuitry to collectively transmit, by the antennas to multiple receiving antennas of a receiver over a wireless transmission channel, the electrical signals defined by the vectorized space-time codeword. The receiver includes a space-time decoder for recovering the symbol from the electrical signals transmitted by the transmitter using a decoding operation that is based on maximum likelihood inference, and a symbol de-mapper for recovering the input block from the symbol.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
A digitally programmable space-time encoding metamaterial
ActiveCN108511916BControl space propertiesIncrease freedomAntennasFrequency spectrumElectromagnetic response
The invention discloses a digital programmable space-time coding meta-material comprising a time varying artificial electromagnetic surface and a digital control module; the artificial electromagneticsurface is formed by periodically arranging time varying encoding units in space, wherein each unit structure is integrated with a switching diode; the digital control module provides different biasvoltages so as to present different electromagnetic responses; the basic units can be controllable in space layout, and can periodically cycle in the time dimension according to a corresponding time encoding sequence, thus forming corresponding harmonic wave energy distribution in the frequency domain, finally regulating electromagnetic waves in space domain and frequency domain. The time-space encoding matrix is designed; the space-time coding meta-material can realize many fancy functions, such as harmonic wave beam scanning and scattering energy inhibition. In addition, the time dimension of the encoding meta-material can be explored, thus accurately controlling the meta-material frequency spectrum energy, and providing very important application prospects in the wireless communicationfields.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
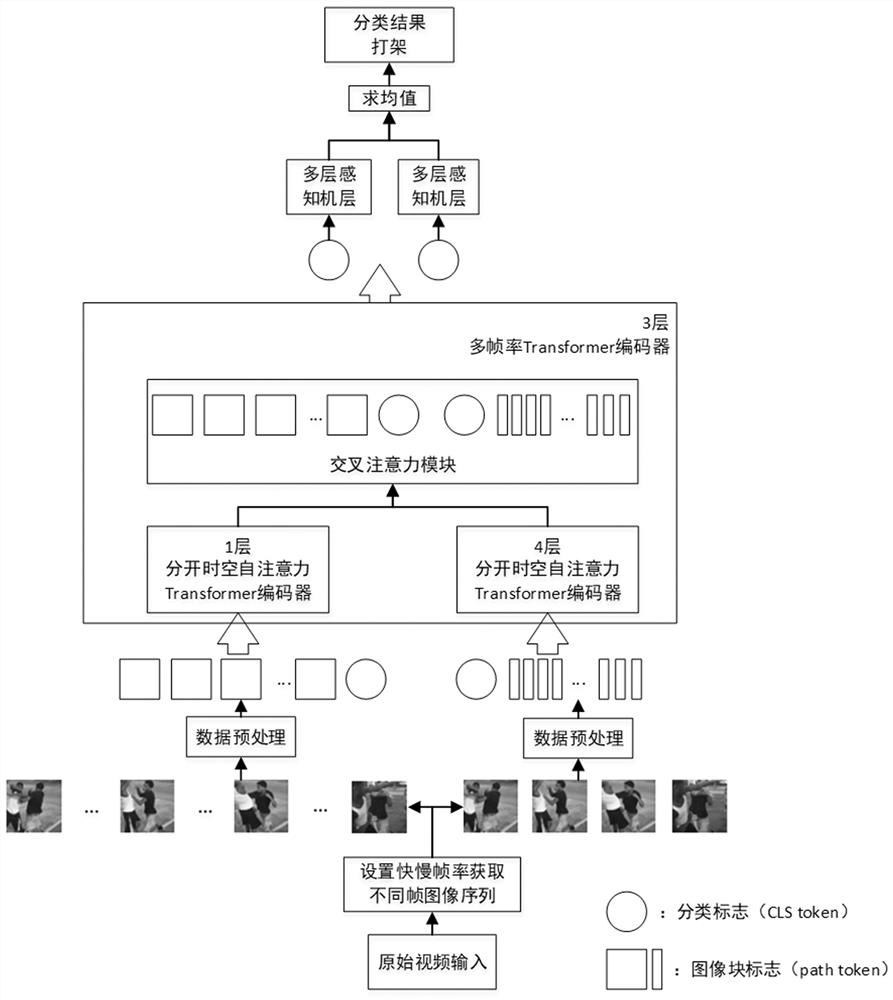
Fight recognition method and device based on dual-channel cross-attention mechanism
ActiveCN113936339BEfficient extractionImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setMonitoring system
The invention discloses a fight recognition method and device based on a dual-channel cross-attention mechanism. The method first collects and generates video data sets, sets two frame rates of fast and slow to obtain different frame image sequences, and sends them to the fast and slow channels respectively after preprocessing. The fast and slow channel adopts the Transformer encoder based on the separate spatiotemporal self-attention mechanism to extract the spatiotemporal encoding features of the image sequence; then, through the cross-attention module, the CLS token of one channel and the patch token information of the other channel are fused to realize the fusion of dual-channel spatiotemporal encoding features; finally , the fused spatio-temporal coding features are passed through the multi-layer perception machine head for fighting behavior recognition. The invention can effectively extract the spatio-temporal features of the video through the dual-channel Transformer model and the cross-attention module, improve the accuracy of fighting behavior recognition, and is suitable for indoor and outdoor monitoring systems.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
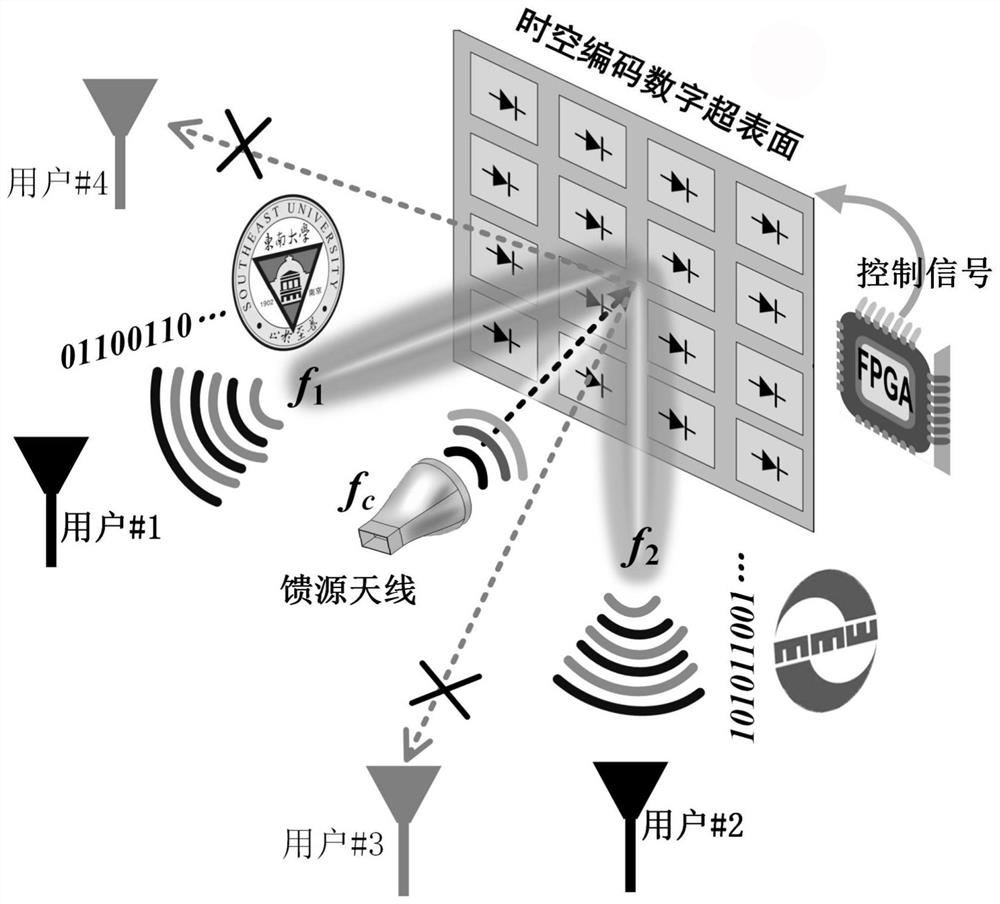
Multi-user wireless communication system and method based on space-time coding metasurface
ActiveCN110365616BSimple structureEliminate the RF moduleMultiple modulation transmitter/receiver arrangementsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsInterference (communication)RF module
The invention discloses a multi-user wireless communication system based on a time-space coded supersurface. The transmitting end mainly includes a time-space coded metasurface, a feed antenna, and a digital control module; the receiving end is a traditional demodulation device. The invention also discloses the wireless communication method of this system. The feed antenna transmits a single-tone signal to the metasurface, and uses an algorithm to optimize the space-time encoding matrix, and jointly controls the energy distribution of the reflected signal in the space domain and the frequency domain, so that different harmonics The spatial beam of the system points to users in a specific direction for direct encoding of information; through the digital control module, different space-time encoding matrices are switched in real time, and different information is transmitted to multiple designated users simultaneously and independently, while users in other directions cannot demodulate. The transmitter has the characteristics of directional modulation, which can realize confidential communication and anti-interference; it also acts as a space mixer and antenna radiation, eliminating the need for digital-to-analog conversion, mixing and amplification RF modules, simplifying the communication transmitter architecture.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A single-scan spatio-temporal coding imaging reconstruction method based on residual network
ActiveCN109597012BResistance to distortionHigh-resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMR - Magnetic resonanceSingle scan
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
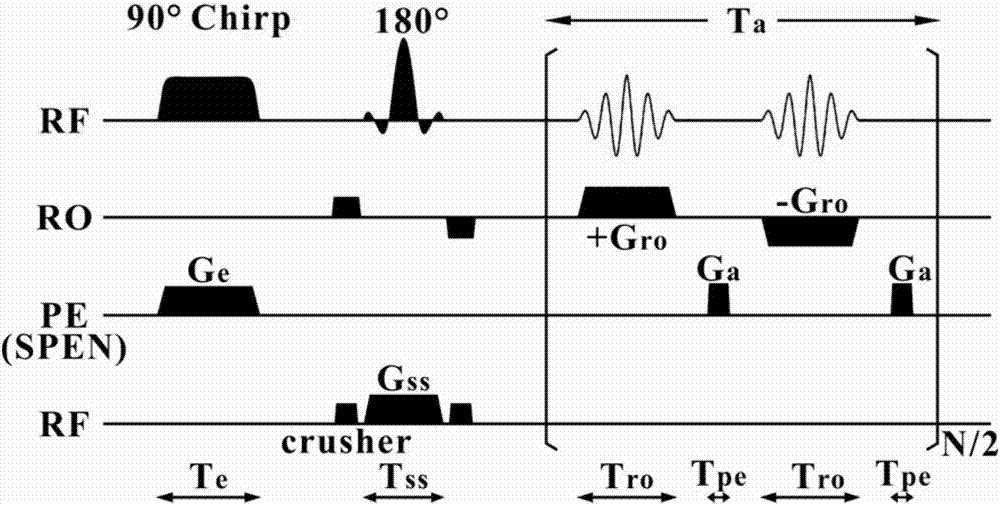
A Water-fat Separation and Reconstruction Method Based on Single-Scan Spatiotemporal Encoded Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveCN106841273BHigh resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceWater resource assessmentSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Imaging quality
A water-fat separation and reconstruction method based on single-scan spatio-temporal encoding magnetic resonance imaging, involving a magnetic resonance imaging method. The method uses a single-scan spatio-temporal encoding imaging sequence to encode and collect water-fat signals, in which a 90-degree linear sweep pulse is combined The spatiotemporal encoding gradient gives the water-lipid signal a quadratic phase during the excitation phase. Based on this characteristic, by selecting appropriate filters to preprocess the collected data, the prior knowledge images of water and lipids can be obtained to guide the separation and reconstruction of water and lipids. In the water-fat separation stage, the prior knowledge image is used as the initial value and weighted information. By solving the super-resolution improvement and edge artifact removal algorithm equations in the water-fat environment, a water map with high resolution and high signal-to-noise ratio can be obtained. and fat chart. The proposed method can effectively achieve water-lipid separation in single-scan spatio-temporally encoded magnetic resonance imaging, while improving the image quality of the separated images and promoting clinical application.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Space-time encoding in wireless communication systems
ActiveUS11218195B2Spatial transmit diversityError preventionCommunications systemWireless transmission
A disclosed transmitter for wireless communication includes multiple transmitting antennas, a symbol mapper for mapping an input block including multiple binary bits and representing information to be transmitted to a symbol representing an ordered plurality of complex numbers, a space-time encoder for applying an encoding operator to the symbol to produce a vectorized space-time codeword defining electrical signals to be transmitted by the transmitter, the encoding operator being dependent on a set of predefined stabilizer generators, and circuitry to collectively transmit, by the antennas to multiple receiving antennas of a receiver over a wireless transmission channel, the electrical signals defined by the vectorized space-time codeword. The receiver includes a space-time decoder for recovering the symbol from the electrical signals transmitted by the transmitter using a decoding operation that is based on maximum likelihood inference, and a symbol de-mapper for recovering the input block from the symbol.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Asynchronous space-time coding metasurface
The invention discloses an asynchronous space-time coding metasurface. Specifically, by applying control signals with different time periods to different units on the metasurface, a dynamic space electromagnetic wave wavefront can be generated. The method has the beneficial effects that by applying control signals with different time periods to different space units, space electromagnetic waves can be effectively controlled, and a new dimension capable of controlling the electromagnetic waves is developed for the field of artificial electromagnetic metamaterials. Dynamic electromagnetic wave wavefront can be generated and effectively controlled, and therefore space automatic scanning of electromagnetic waves can be achieved. In addition, when the material is used as a radar target, the radar cross-sectional area of the material is time-varying under a static condition, which is not possessed by traditional materials. Under the irradiation of monochromatic electromagnetic waves, multiple frequencies can be generated at will. Compared with a traditional multi-frequency generation system (such as a frequency control array), the system is simple in hardware structure, and does not need related devices such as a local oscillator source.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
A device and method for authenticating blockchain data using spatio-temporal information
ActiveCN111586029BPut an end to the possibilityReliable data sourceSecuring communicationData OriginTime information
The invention discloses a device and method for authenticating block chain data using spatio-temporal information. The device includes a spatio-temporal block chain terminal, a spatio-temporal encoding module, a block chain module and a server; The data generated within a certain period of time can be uploaded to the blockchain system only if it is correct and valid; it eliminates the possibility of counterfeit terminals transmitting data to the blockchain system; The possibility of data transmission in the block chain system, so as to ensure that the source of the data transmitted to the block chain is reliable; the time of the device is guaranteed to be difficult to tamper; the smart contract of the block chain is adopted, which has the characteristics of not being tampered with, and realizes distributed Storage ensures that even if some server node data is lost or damaged, the system can still operate normally.
Owner:北京数码汇博科技有限公司 +1
A broadband zero-crossing polarization spatiotemporal coded digital metasurface unit and its control method
The invention discloses a broadband zero cross polarization space-time coding digital metasurface unit and a control method. A radiator is used. The edge of the radiator is provided with a plurality of micro-tuning sheets and a micro-tuning hole in the center. The radiator is connected with the radio frequency switch. The two states of turning off and turning on the radio frequency switch are respectively corresponding to a turning-off mode and a turning-on mode. By optimizing the sizes of the micro-tuning holes and the micro-tuning pieces, the electric field distribution of the turn-off modeand the electric field distribution of the turn-on mode are kept consistent near the target frequency as much as possible, so that the stable phase difference between the two modes is obtained, and the space-time coding digital metasurface unit can work in the regulation and control of the broadband one-bit 180-degree reflection phase. Besides, through reasonable design of the AC-DC isolator, loading of the bias circuit hardly changes the original phase difference of the unit, unit loss is avoided, and unnecessary cross polarization caused by damage to the symmetry of the unit is avoided. According to the invention, 180-degree phase shift is realized within the frequency band of 7.71-9.48 GHz.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Wireless sending device, wireless receiving device and data transmission method
ActiveCN104145462BReduce computationSpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsDifferential codingComputer science
The radio transmission device of the present invention is provided with: a plurality of transmission antennas; The initial symbol generating part (2), as the reference signal when differential encoding starts, generates the initial symbol; The differential encoding unit (differential encoding section 3, transmission signal power Calculation section 6, one-square-root calculation section 7), carry out differential encoding to the transmitted symbol mapped with information bit to generate the symbol after differentiation; Perform space-time encoding to generate signals transmitted from each transmitting antenna, and the differential encoding unit determines the differential encoding generated in this differential encoding process based on the power of the initial symbol or the power of the differentially differentiated symbol generated last time. The power of the following symbol.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method for magnetic resonance imaging using slice quadratic phase for spatiotemporal encoding
ActiveUS11009576B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsRadio frequencyPhase modulation
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
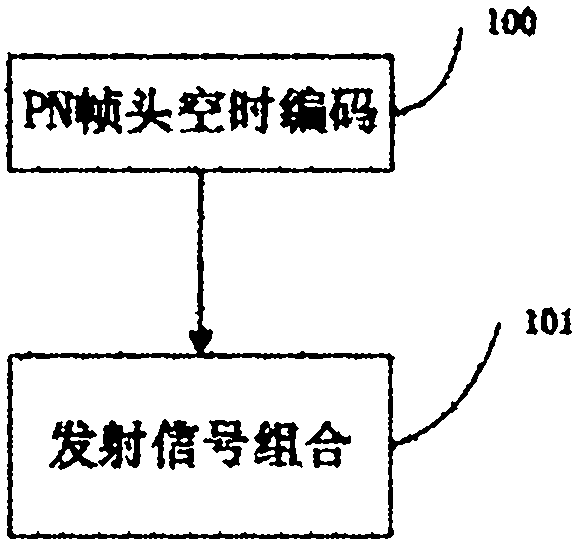
Transceiving method and realization device thereof used for single frequency network signals
InactiveCN102148667BSolving Multipath Interference ProblemsHigh gainBaseband system detailsMulti-frequency code systemsMultipath interferenceDigital television
The invention discloses a transceiving method and a realization device thereof used for single frequency network signals in the technical field of digital television networks, which comprise the steps as follows: a PN frame header after PN frame header time coding processing and transmitting signal combined processing is inserted in front of a data section at a transmitting end; moreover, relevant PN processing and channel estimation processing are implemented at a receiving end. Aiming at solving a problem that received signals can not be effectively resolved due to multipath interferences caused by the single frequency network in overlapping areas, coding processing is implemented on the PN frame header before modulation, and then data jointing and demodulating transmitting are implemented; during receiving, a transmitting signal is obtained through relevant processing and channel estimation on the received and coded PN frame header as well as known PN frame header. The invention greatly improves the signal-to-noise of the channels, and can obtain an effective signal from the interfered signals more easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Video prediction method based on spatiotemporal propagation hierarchical codec
ActiveCN113422952BEffective feature representationAccurate prior knowledgeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionFrame sequence
The invention discloses a video prediction method based on a time-space propagation hierarchical codec. The method of the present invention first samples the given original video to obtain the frame sequence and inputs it to the low-level visual memory encoder to obtain the low-level visual coding features and low-level memory state features; features, and extract high-level semantic features through a high-level semantic encoder; then fuse the obtained low-level visual coding features, low-level memory state features, and high-level semantic coding features through a hierarchical feature decoder to output predicted video frames. The method of the present invention can not only integrate the low-level visual memory features and high-level semantic features, but also make the low-level visual information spread along the time sequence direction through the spatio-temporal propagation module, and can also use the prior knowledge of the first frame of the video to solve the video frame blur problem to a certain extent, Improve overall clarity and visual quality of predicted video frames.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Programmable non-reciprocal transmission and frequency conversion system based on space-time coding metasurface
ActiveCN110444896BThe method is simple and flexibleEasy for experimental processingProgramme controlComputer controlIsolatorFrequency mixer
The invention discloses a programmable non-reciprocal transmission and frequency conversion system based on a space-time coding metasurface. The programmable non-reciprocal transmission and frequencyconversion system consists of the space-time coding metasurface and a digital control circuit, wherein the metasurface is formed by periodically arranging time-varying programmable units in space; each unit integrates a plurality of adjustable devices; and multi-bit phase period modulation is presented under the driving of the digital control circuit. According to a specifically designed time andspace phase gradient, efficient frequency conversion and abnormal reflection of incident electromagnetic waves are realized, so that time reversal symmetry is broken through, and a non-reciprocal effect is realized in a space domain and a frequency domain. In addition, different space-time coding matrixes are output through the digital control circuit; the system can be switched between reciprocaland non-reciprocal transmission; a non-reciprocal reflection angle and a harmonic frequency can be adjusted in real time; the dynamic programmable system is realized; and the system has potential applications to the fields of space frequency conversion, Doppler deception, directional transmission, radio frequency stealth, secret communication, isolators, duplexers, frequency mixers and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
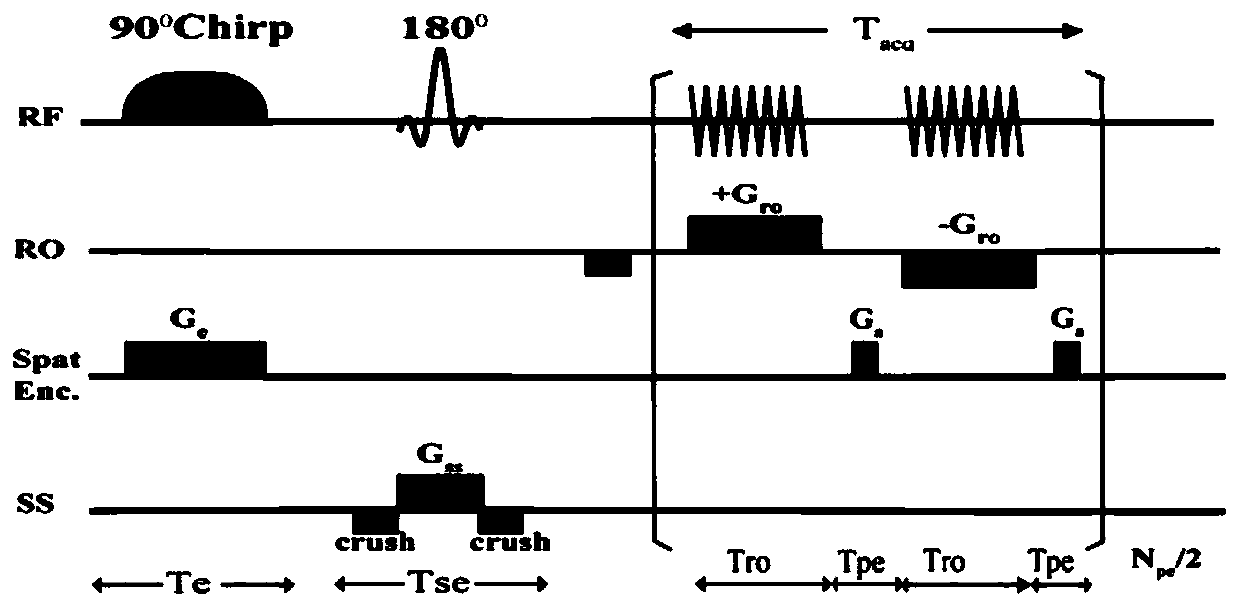
Multi-echo multi-slice spatio-temporal encoding magnetic resonance imaging method based on segmented excitation
ActiveCN108226835BAvoid image distortionReduced sampling timeMagnetic measurementsSignal onPhase gradient
The invention discloses a segmented excitation based multi-echo multi-layer space-time coding magnetic resonance imaging method, and relates to a magnetic resonance imaging method. The method comprises the following steps: dividing an imaging object into several segments; selecting an imaging segment through a 90-degree segment selection pulse; performing time-space coding of intra-segment core spinning through a 180-degree linear frequency sweep pulse; enabling the core of non-imaging segment to spin to a heat balance state by using a 180-degree hard pulse; storing the spinning information byusing the same pulse as the 90-degree segment selection pulse; sequentially exciting multiple target layers by using multiple 90-degree layer selection pulses; in combination with the specific dispersed phase gradient of frequency coding dimension, enabling the signals on different layers to form echoes at different sampling moments; changing the center frequency of the layer selection pulse andrelevant pulse gradient, to obtain magnetic resonance data on each layer in the segment; modifying the center frequency of the segment selection pulse, and selecting different imaging segments; repeating the above operations to obtain data of the whole imaging object; dividing the data of multiple echoes acquired at the same time, according to the echo number; and performing super-resolution reconstruction of the data on each layer, to obtain a multi-layer high-resolution magnetic resonance image.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
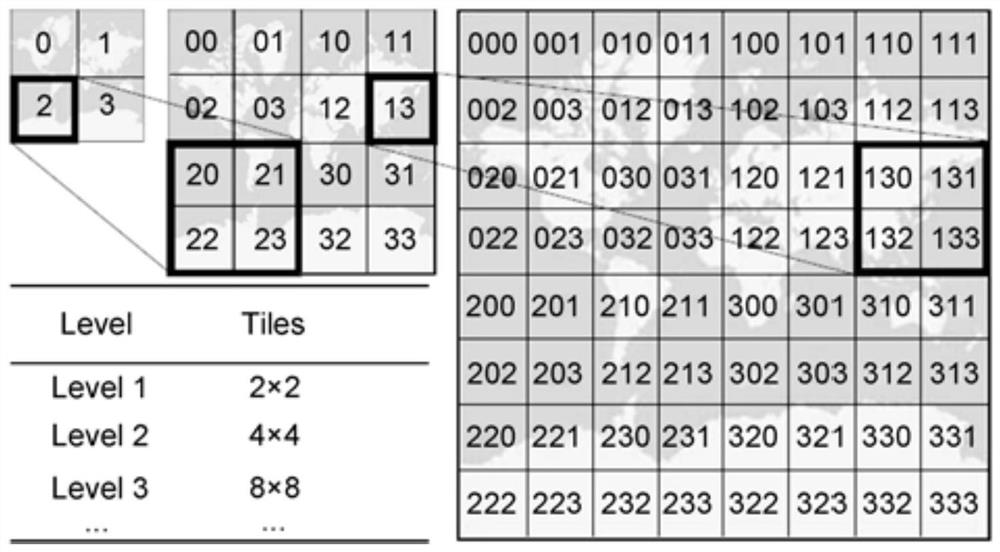
Space-time encoding method, space-time index and query method and device
ActiveCN109992636BEfficient organizationEfficient managementGeographical information databasesSensing dataComputer vision
One or more embodiments of this specification disclose a space-time coding method, a space-time index and query method and device, which are used to realize efficient organization, management and query of massive multi-source remote sensing data. The method includes: subdividing the longitude-latitude space of the earth according to a specified subdivision method to obtain multiple grids; wherein, the numbers of grids corresponding to the longitude direction and the latitude direction are the same; Hierarchical; Integer encoding is performed on the coordinate information corresponding to each of the grids to obtain first coded values corresponding to each of the grids; establishing the grids and the first encoding values corresponding to each of the grids An association relationship between the encoded value and the remote sensing image data. The technical solution can use the global multi-scale grid integer coding to realize the location association with the multi-source remote sensing data, and realize the space-time index and query of the multi-source remote sensing data.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
A video group behavior recognition method based on cascaded transformers
ActiveCN113673489BReduce complexityRobustCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesData setKey frame
The present invention relates to the field of computer vision and deep learning, and in particular to a video group behavior recognition method based on cascaded Transformers. First, a video data set is collected and generated, and the video data set is extracted through a three-dimensional backbone network to extract three-dimensional spatio-temporal features, and a key frame image space is selected. Feature map; preprocess the key frame image space feature map and send it to the human target detection Transformer to output the human target frame in the key frame image; then, map the sub The feature map is combined with the frame feature map around the key frame image to calculate the query / key / value, input the group behavior recognition Transformer, and output the group-level spatio-temporal encoding feature map; finally, the group behavior is classified by the multi-layer perceptron. The invention has the effect of effectively improving the accuracy of group behavior recognition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com