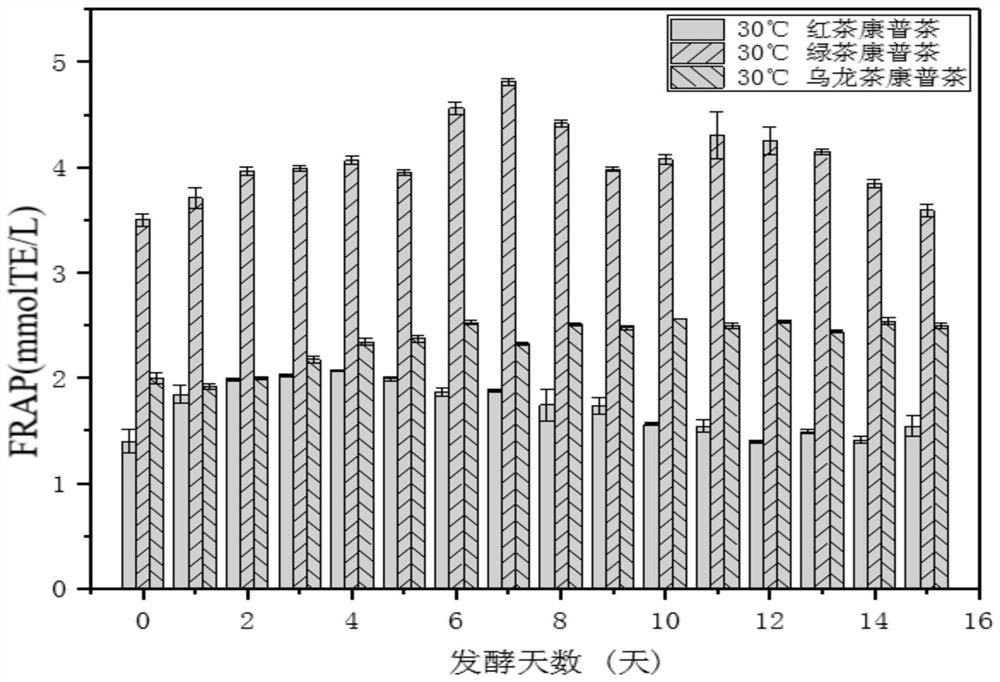
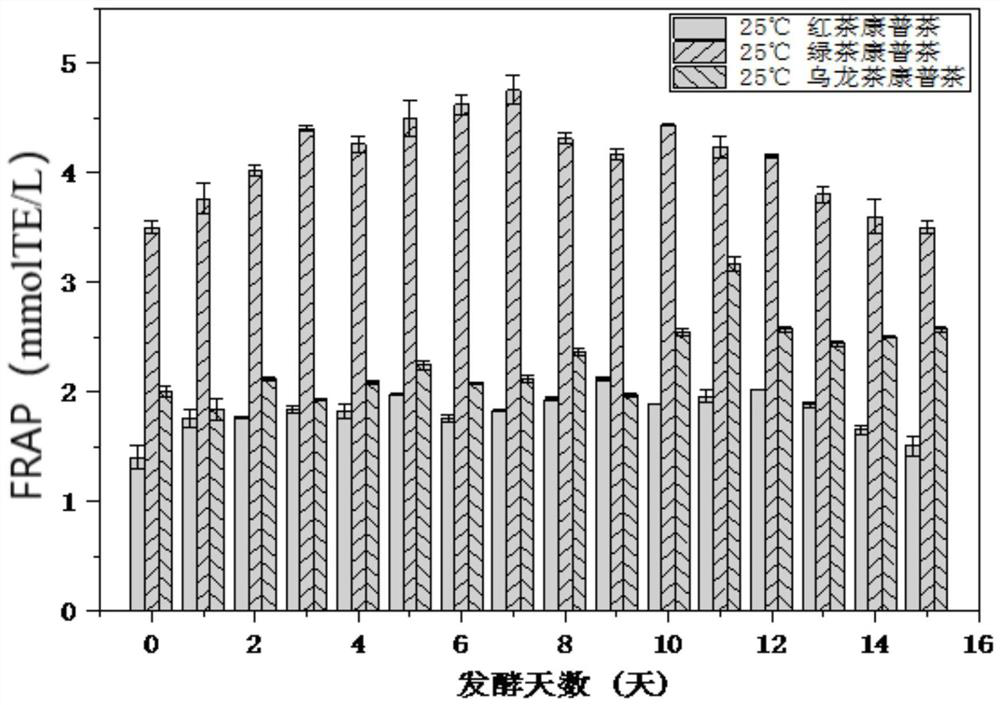
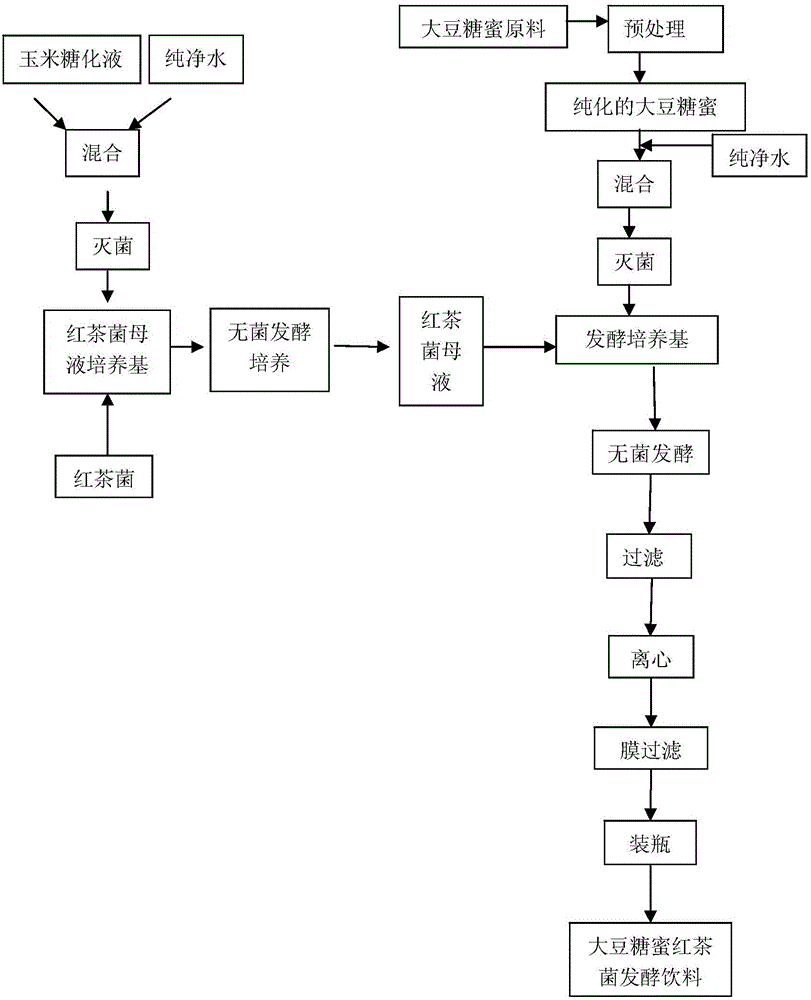
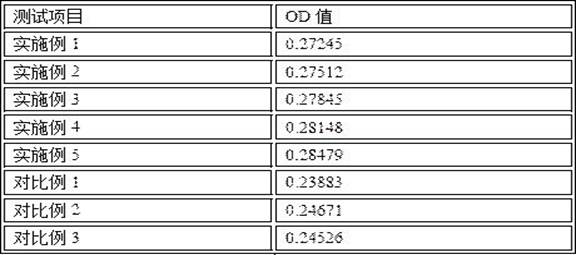
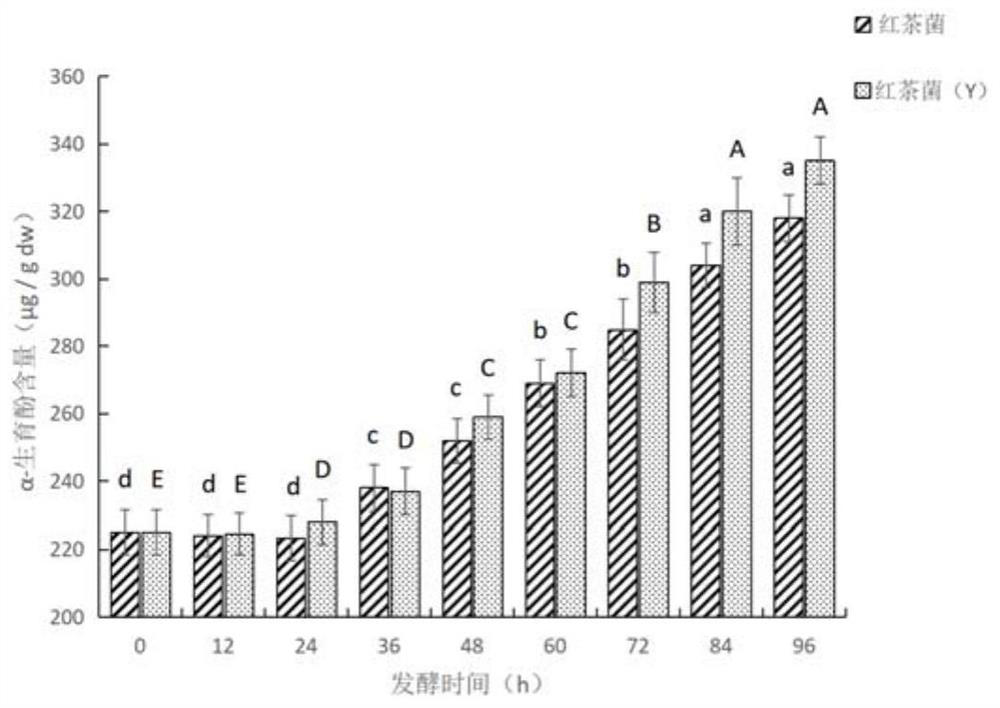
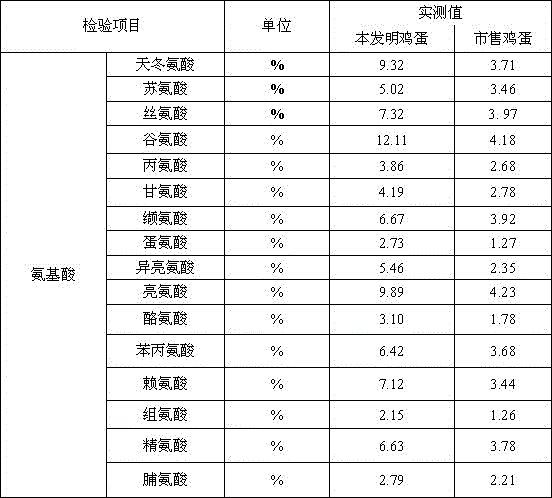
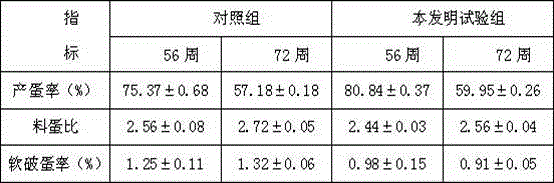
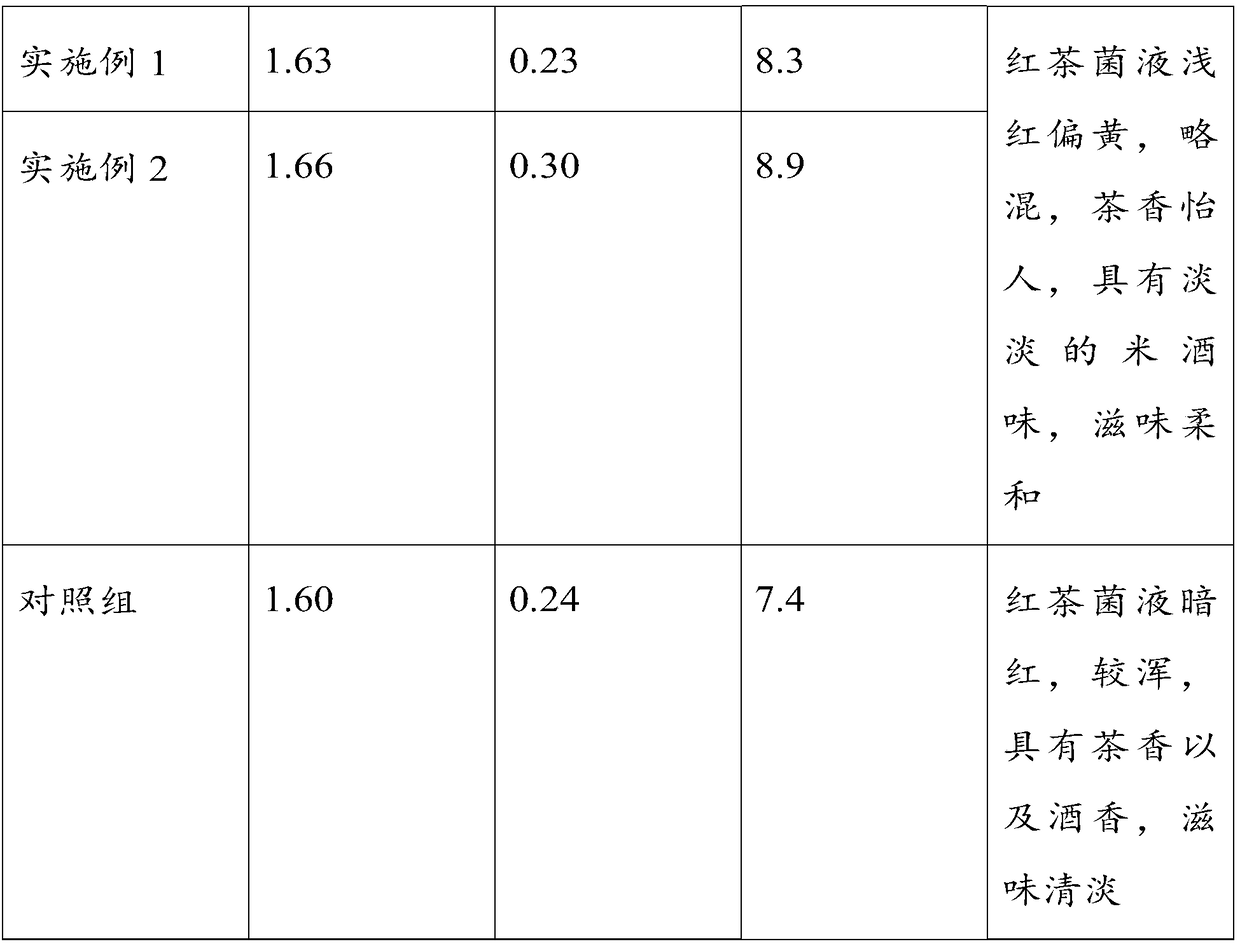
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "Kombucha Tea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A beverage made by FERMENTATION of black tea and/or green tea.
Blueberry kombucha beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103211253AImprove stabilityExtended shelf lifeFood preparationBiotechnologySodium bicarbonate
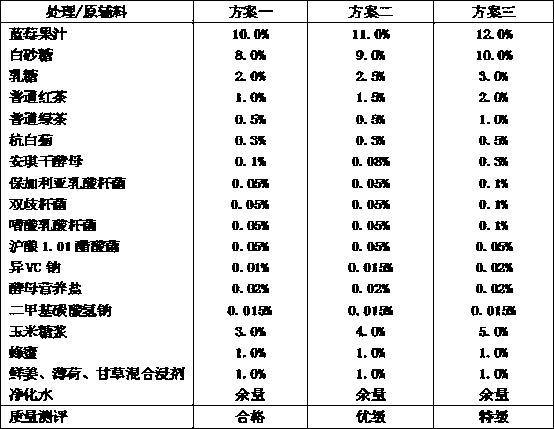
The invention discloses a blueberry kombucha beverage and a preparation method thereof. Raw materials and auxiliary materials comprise: blueberry fruit juice, white sugar, lactose, common black tea, Chrysanthemum morifolium, corn syrup, honey, mixed infusion of fresh ginger, mint and licorice, purified water, angel dried yeast, lactobacillus bulgaricus, bifidobacteria, lactobacillus acidophilus, Shanghai wine 1.01 acetobacter rancens, sodium erythorbate, yeast nutrient salt and dimethyl sodium bicarbonate. The raw materials and auxiliary materials need pretreatment steps of fermenting for 3-4t with a sandwich fermentation cylinder, shearing 5-10min with a high speed shearing machine, and then fermenting for 3-4t. A quantitative fermentation technology is used, and clarifying filtration and aseptic filtration are co-used, to raise biological stability of products. By regulation, product efficacies are strengthened, and goods performances are raised. Low temperature degasification and aseptic cold-filling are preformed, to guarantee product characteristics and quality.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG JINDI WINE IND
Black tea fungus fermented tea beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a black tea fungus fermented tea beverage and a preparation method thereof. The black tea fungus fermented tea beverage comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight of 6%-15% of tea leaves, 0.01%-0.1% of black tea fungus, 10%-15% of a sweetening agent, 2%-5% of condiments, 0.5%-2.5% of auxiliary ingredients, and the balance being water, wherein the black tea fungus is a composition of lactic acid bacteria, acetic acid bacteria and yeast of which the mass ratio of the lactic acid bacteria, the acetic acid bacteria and the yeast being (1-10) to (0-3) to (0-2); and the auxiliary ingredients are one or a composition of several kinds of peppermint candy, orange peels, momordica grosvenori and roselle pollen. According to the black tea fungus fermented tea beverage disclosed by the invention, after being fermented by black tea fungus, tea leaves generate a large quantity of active ingredients including tea polyphenols, caffeine, glucuronic acid and the like and other materials having peculiar flavor; the nutrition is rich, and the aroma of tea and the fermented aroma are integrated; through addition of the condiments and the auxiliary ingredients,the flavor and the mouth feel of the product are further improved; and the flavor and the nutrition of the fermented tea beverage are balanced, and a new way is provided for the development of the tea beverage.
Owner:NEW HOPE DAIRY HLDG
Kiwi fruit fermented beverage and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a kiwi fruit fermented beverage and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of agricultural product processing. Kiwi fruit pulp and tea fungus mother liquor are fermented at 0-30 DEG C for four times within 1-6 months, in the fermentation process, sugar and sterilization water are supplemented, and fermentation liquor, sweetening agent and water are blended into beverage. According to the method, malformed fruits, fruitlet, postmaturity fruit, kiwi fruit which are peeled difficultly, peel and seeds are fully utilized, so that the purpose of making the most of the kiwi fruit is achieved. The fermented liquid can be used for blending various fruit juice so as to prepare nutritive and delicious drinks with multiple probiotics, and also can be used for cooperated fermentation of kiwi fruit pulp and other pulp.
Owner:陈庆云
Aquilaria sinensis tea fungus health care drink
The invention belongs to the field of health care drink and specifically relates to an aquilaria sinensis tea fungus health care drink. The aquilaria sinensis tree originates in Dongguan. The aquilaria sinensis tea fungus health care drink is made by mixing the dried leaves of the aquilaria sinensis tree with water for boiling and extraction and adding sugar and black tea fungus culture mother liquor for fermentation for 5-7 days at the constant temperature of 30 DEG C. The drink contains rich tea polyphenol; however, the content of caffeine is only equal to 11.9% of that of the black tea fungus drink with the same concentration; and the aquilaria sinensis tea fungus health care drink is sour and sweet and fresh in taste, and unique in flavor, and has the functions of resisting oxidization and regulating the intestinal flora and the effects of eliminating dampness with aromatics and harmonizing stomach.
Owner:南通市星期七旅游开发有限公司
Black tea fungus beverage as well as preparation technology and application thereof
ActiveCN102805170AEasy to operateOperational Safety and HygieneTea extractionFood preparationBiotechnologyIntestinal tract diseases
The invention belongs to the technical field of the food beverage, which particular relates to a black tea fungus beverage as well as a preparation technology and application thereof. The tea fungus beverage consists of the following raw materials in parts by weight: 1000 parts of water, 100-300 parts of black tea fungus bacteria liquid, 1-10 parts of red date, 1-5 parts of longan, 1-5 parts of hawthorn, 0-5 parts of dried lichee, 2-10 parts of black tea, 0-5 parts of sea-buckthorn and 50-200 parts of sweetening agent. The black tea fungus beverage has the health-care functions such as appetizing, invigorating stomach, aiding digestion and increasing appetite, has a good promoting function on intestinal tract diseases, has the advantages of varied tastes and abundant nutrition ingredients, is suitable for both young and old and can be directly drunk by people. According to the preparation technology of the product, the black tea fungus bacteria liquid is used for preparing, and various raw materials are mixed and heated after being pre-processed and are sterilized and disinfected after being filled. The preparation technology is simple to operate, is safe and clean to operate, andis suitable for industrial production, and the production cost is lowered. The product has the functions of eliminating fat, resisting oxidation, enhancing resistance, maintaining beauty and keep young and the like.
Owner:东莞市健美滋饮料食品有限公司
Tea fungus synthesized bacterial cellulose pressure sore dressing as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103418018ALow environmental requirementsHigh biosecurityAbsorbent padsFermentationKombucha TeaMicrobiology
The invention discloses a tea fungus synthesized bacterial cellulose pressure sore dressing as well as a preparation method and the application thereof. The tea fungus synthesized bacterial cellulose pressure sore dressing is a tea fungus synthesized bacterial cellulose membrane, and the cellulose component is mainly formed by secretion and synthesis of tea fungus strains in the fermentation culturing process in a sugar tea culture medium containing carboxymethyl chitosan; the water absorption rate of the dressing is 89-94.3%, the porosity is 85-91.2%, and the water vapor transmission rate is between 1,383.5 g.m<-2>.d<-1> and 1,486.5 g.m<-2>.d<-1>. According to the invention, since the nano bacterial cellulose pressure sore dressing is prepared with a sugar tea fermentation method by adopting the tea fungus, the method for synthesis of bacterial cellulose has the advantages of low cost, low environment requirement for synthesis sites and simple technical requirements; the nano bacterial cellulose material has favorable biosecurity and histocompatibility, which cannot cause stimulation and sensitization to a wound surface, and is conducive to the promotion of wound healing.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological additive for prevention and treatment of subclinical mastitis of cows
InactiveCN104095149AIncrease milk productionGood treatment effectAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyKombucha Tea
Disclosed is a preparation method of a traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological additive for prevention and treatment of subclinical mastitis of cows. The preparation method comprises performing superfine grinding on eucommia ulmoides leaves, ginkgo leaves, purple perilla, Chinese pulsatilla roots, coneflowers, humulus scandens, shrimp shells, milkvetch roots and licorice roots; adding water and boiling through the high heat; performing soft file insulation; performing cooling and filtration; collecting filtrate; adding white sugar and boiling; cooling down to the room temperature and performing lactobacillus, tea fungi and yeast inoculation to obtain the micro-ecological additive through fermentation; enabling the cows to drink the obtained micro-ecological additive in proportion. According to the traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological additive, the functions of heat clearing and detoxification, sterilization and anti-inflammation, lactation promotion and the like are achieved, Chinese herbal medicine active materials, active small peptides, lactic acid and probiotics are rich, the amino acid is rich and balanced, the traditional antibiotic treatment method is replaced, and the harm of antibiotics to the health of the cows and antibiotic residues in the milk are reduced. According to the preparation method of the traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological additive for the prevention and treatment of the subclinical mastitis of the cows, the use is simple and convenient, drug residues are not produced, any toxic and side effect is not produced, the viable bacteria content is high, the preparation method is suitable for industrialized production, and the market prospects are good.
Owner:叶涌钢
Method for preparing bacterial cellulose from tofu yellow seriflux
InactiveCN108315382AReduce pollutionIncrease business incomeMicroorganism based processesFermentationBacterial celluloseAcetic acid bacteria
The invention discloses a method for preparing bacterial cellulose from tofu yellow seriflux. The method comprises the steps: collecting yellow seriflux generated in a tofu producing process, adding sugar, sterilizing and accessing acetic acid bacteria or acetic acid bacteria, saccharomycetes and lactic acid bacteria mixed bacteria or kombucha seed solution or mycoderm capable of generating bacterial cellulose to ferment to obtain bacterial cellulose. According to the method disclosed by the invention, waste-yellow seriflux generated in tofu production is fully utilized as a raw material to produce the bacterial cellulose; not only is waste turned into wealth, but also enterprise profit is improved; furthermore, the bacterial cellulose has the advantages of high yield, strong elasticity and water retention, simple technology, low equipment requirement, favorability for large-scale popularization and wide market prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
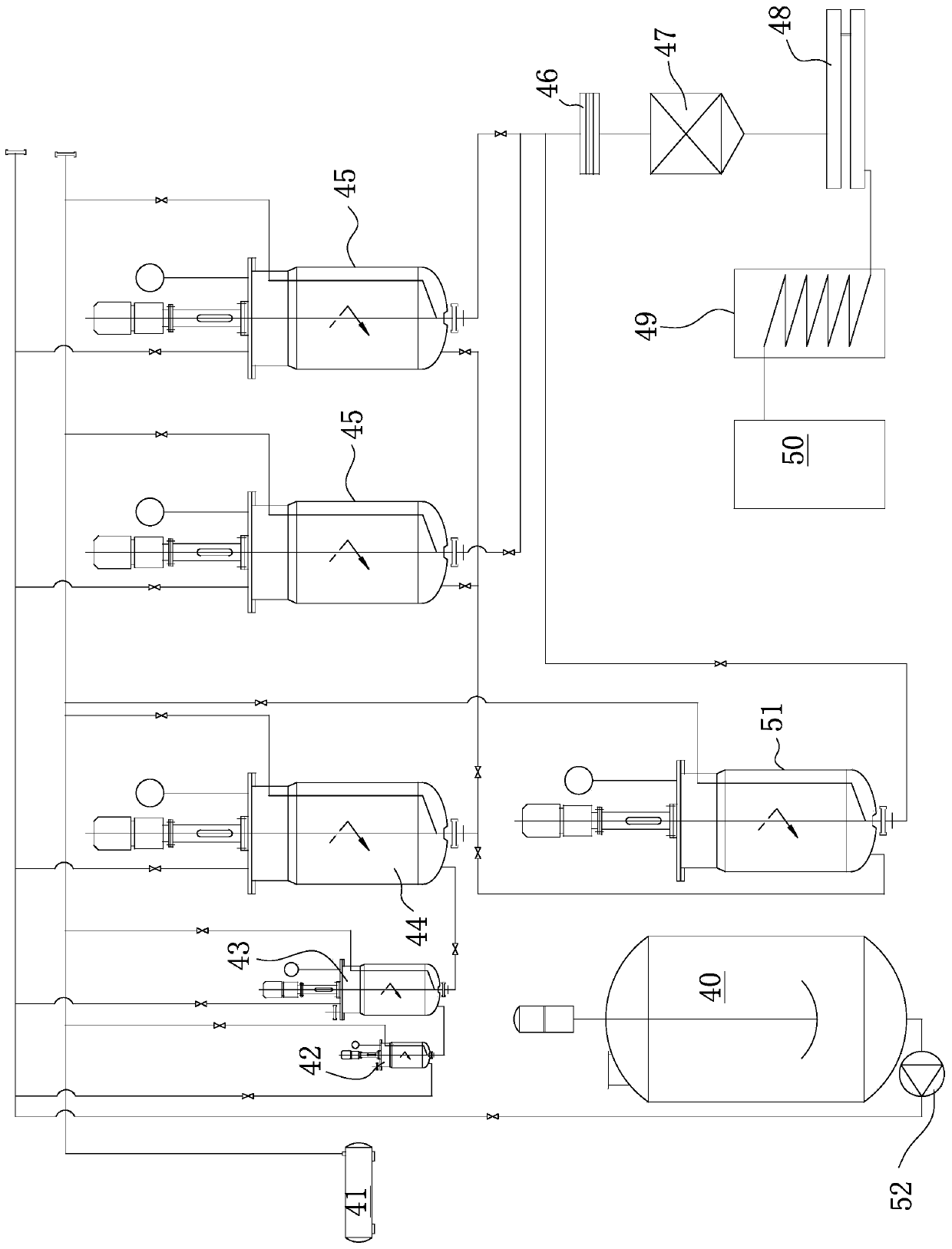
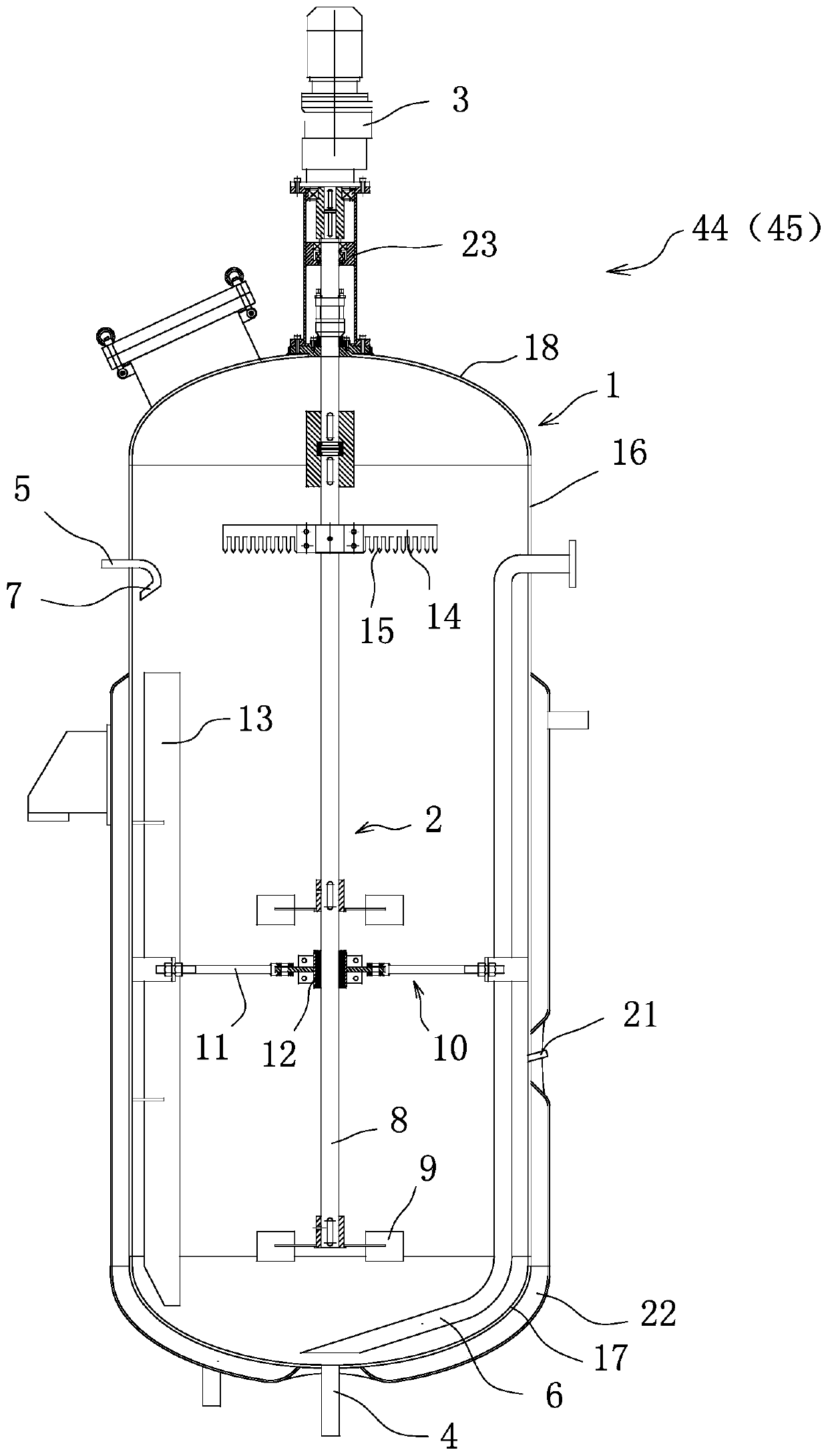
Semi-continuous black-tea fungus fermentation broth preparation method and apparatus
PendingCN110892928APrevents the phenomenon of bacterial cellulose film formationReduce generationPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologyContinuous fermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of food, and discloses a semi-continuous black-tea fungus fermentation broth preparation method and apparatus. The preparation method comprises a culture liquid preparation step, an expanding culture step, and a fermentation tank fermentation step, and further comprises a semi-continuous fermentation step, wherein the semi-continuous fermentation step is that a part of a black-tea fungus fermentation raw liquid after the fermentation tank fermentation step is discharged from the fermentation tank, and is subjected to subsequent inactivation, filtration, concentration and filling steps, and a sterilized sugar tea soup is supplemented into the tank after a part of the black-tea fungus fermentation raw liquid is discharged from the original fermentation tank, so that the remaining black-tea fungus fermentation raw liquid in the original fermentation tank is used as a seed liquid to perform continue fermentation. The method utilizes a stepwise amplification dynamic fermentation mode, and the disadvantages of long process time and relatively large flavor difference between batches of static fermentation of black-tea fungus are avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MINGHUANG NATURAL PRODS DEV
Kombucha beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a kombucha beverage and a preparation method thereof. Kombucha beverages of different taste are prepared through the steps of mixing black tea with sugar and water in proportion, performing boiling over, performing cooling to appropriate temperature, performing inoculating with kombucha mother liquid in a proportion, and performing constant-temperature aerobic fermentation for a certain time so as to obtain a kombucha stock solution; and according to different flavor and nutrient requirements, adding corresponding vegetables (purple sweet potato juice), fruits ( ginsengfruit juice), nuts (walnut pulp and macadimia nut pulp), and edible mushrooms (tremella aurantialba thick soup ). Through a multistage membrane filtration preparation method, the fermentation processof the kombucha is ended, the fermentation terminal point is rigidly controlled, and the storage period is prolonged. Original efficacy components of the kombucha can be maintained, and the pure flavor and stable quality of the kombucha can also be guaranteed; and besides, features of corresponding fruits, nuts and the like are added, and massive agriculture products are added, so that the kombucha beverage provides a technical support for processing of massive agriculture products.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing fruit vinegar from waste residues of column chromatography in momordica glycoside production
The invention provides a method for preparing fruit vinegar from waste residues of column chromatography in momordica glycoside production and belongs to the technical field of fruit vinegar preparation. The method comprises the steps as follows: (1) white sugar, tea leaves and water are boiled together, natural cooling is performed, kombucha strain mother liquor and pellicle are added, sealing is performed with gauze, standing is performed, and a white pellicle is produced on the surface layer for later use; (2) glycoside-free momordica grosvenori juice is prepared by concentrating residues of column chromatography; (3) the concentrated juice is diluted with clear water; (4) the diluted juice is inoculated with the kombucha; (5) the inoculated diluted juice solution is placed in a shaking table for fermentation, and the sugar degree and pH are adjusted; (6) gauze covering is performed, filtration is performed after open fermentation, and the required fruit vinegar is obtained. With the adoption of the method, the problem of comprehensive utilization of waste residues of column chromatography in momordica glycoside production is solved, the economic benefit of an enterprise is increased, a new technology is added to the momordica grosvenori fermentation industry, the kind of kombucha fermented drinks is also enriched, and a novel healthcare drink which is healthy and beneficial to people is brought to people.
Owner:HEZHOU UNIV
Traditional Chinese herbal medicine microecological preparation capable of killing and inhibiting foot and mouth disease virus in vitro and in vivo
InactiveCN103655684ALong-term preventionAvoid infectionBacteria material medical ingredientsAntiviralsYeastMicroorganism
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese herbal medicine microecological preparation capable of killing and inhibiting foot and mouth disease viruses in vitro and in vivo. The preparation is prepared from traditional Chinese herbal medicine extract fermented by black tea fungus or composite microorganisms of acetic bacteria, acetobacter xylinum, yeast and the like. According to the technical scheme, the preparation is prepared by firstly, preparing bacterium powder or a bacterium liquid of black tea fungus or composite microorganisms of acetic bacteria, acetobacter xylinum, yeast and the like, preparing the traditional Chinese herbal medicine extract, and subsequently preparing the traditional Chinese herbal medicine microecological preparation for inhibiting and killing foot and mouth disease viruses. The traditional Chinese herbal medicine microecological preparation discloses by the invention is capable of not only effectively inhibiting and killing foot and mouth disease viruses in vitro and in vivo, but also effectively inhibiting and killing foot and mouth disease viruses from intestinal tracts and respiratory tracts through mouth injection and nose injection through the breeding function of the composite acid-forming bacteria such as acetic bacteria, so that the preparation can be applied to rapid prevention in foot-and-mouth disease areas.
Owner:蒋盛军
Grape Kangpu tea as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN112674187AImprove antioxidant capacityShort fermentation timeTea extractionBiotechnologyAntioxidant capacity
The invention discloses grape Kangpu tea and a preparation method and application thereof. The grape Kangpu tea is prepared through the steps that sugar tea water serves as fermentation base liquid, the Kangpu tea is formed through fermentation of black tea fungus liquid, grapes are added for secondary fermentation, the grape Kangpu tea is obtained, and the antioxidant effect of the Kangpu tea is effectively improved. The grape Kangpu tea beverage provided by the invention is simple in preparation process, rich in nutrition, good in flavor and strong in oxidation resistance, and can be industrially produced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106173721AIncrease added valueReduce pollutionFood ingredient functionsEcological healthKombucha
The invention provides a biological beverage prepared from soybean molasses as a main raw material and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of beverages. The preparation method utilizes a corn saccharification liquid as a kombucha culture mother liquor, soybean molasses as a medium and kombucha as a fungus source to prepare the novel special soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage. Through the preparation method, the purified soybean molasses, corn saccharification liquid and kombucha are combined and produce synergism so that the tea beverage has obvious health care effects and comprehensive effects far higher than those of a food prepared only from soybeans and corn and the traditional kombucha beverage. The prepared soybean molasses-based kombucha-fermented beverage has short fermentation time and an ideal form, well retains original nutrition and function components of soybeans and corn, can be easily digested and absorbed, has a sour-sweet taste and good palatability, has a wide application range and is an ecological health beverage with beverage and medicine effects.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Serum-free culture medium for in-vitro culture and amplification of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
PendingCN112662624ANo pollution in the processSimple processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsKombucha TeaPancreatic hormone
The serum-free culture medium is characterized in that the serum-free culture medium is an aqueous solution and comprises the following components: 20-40g / L of a basal culture medium, 5-15ng / mL of a growth factor, 8-22mg / mL of kombucha fermentation liquor, 3-20mg / mL of serum protein, 1-10ng / mL of selenomethionine, 0.1-0.4 mg / mL of sodium ferulate, 3-8ng / mL of metformin, 5-12 ng / mL of 3'-deoxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, 150 mg / L-550 mg / L of Lglutamine, 30-110 [mu] M of composite vitamin and 12 mU / L-24 mU / L of insulin. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the serum-free culture medium for in-vitro culture and amplification of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The serum-free culture medium for in-vitro culture and amplification of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells disclosed by the invention is good in biological safety, can effectively improve the amplification efficiency of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, and maintains the biological effect and the multidirectional differentiation potential at the same time; the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with related requirements can be timely and accurately provided for medical scientific research teaching and clinical application.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHIA TECH CO LTD
Fungus tea jujube haw jelly and production method thereof
The invention discloses fungus tea jujube haw jelly and a production method thereof. The fungus tea jujube haw jelly is prepared from jujubes, haw, sugar and tea fungus liquid. The quality ratio of the jujubes to the haw to water to the sugar is (4-8): (3-7): (1-3): (2-8), and the addition volume of the tea fungus liquid is 8 to 12 percent. The fungus tea jujube haw jelly with a healthcare function is unique in taste and flavor, integrates the advantages of tea fungus, jujubes and haw and has functions of lowering the blood pressure, reducing the blood fat, tonifying the spleen, nourishing the stomach, supplementing the blood, promoting the circulation of qi, promoting the metabolism, improving the immunity of a human body and the like.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Stomach invigorating and spleen benefiting black tea fungus haw jelly as well as preparation method thereof
The invention discloses stomach invigorating and spleen benefiting black tea fungus haw jelly. The stomach invigorating and spleen benefiting black tea fungus haw jelly is prepared from hawthorns, water, sugar and a black tea fungus liquid, wherein the mass ratio of hawthorns to water to sugar is (8-12): (1-3): (4-10), and the amount of the added black tea fungus liquid is 5%-15% of the total mass of the haw jelly. The black tea fungus haw jelly with the health care function, which is provided by the invention, is unique in mouthfeel and flavor, integrates advantages of black tea fungus and hawthorns, and has the healthcare medicinal efficacies of appetizing, tonifying the spleen and the like.
Owner:LIAOCHENG UNIV
Collagen peptide lubricating fluid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107789611AGood biocompatibilityNo drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAdemetionineFermentation
The invention relates to collagen peptide lubricating fluid and a preparation method thereof. The collagen peptide lubricating fluid is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 5-20 parts of tea fungus fermentation liquor, 0.5-1.2 parts of hyaluronic acid, 1-2 parts of tea fungus fermentation membrane modifiers, 8-12 parts of collagen peptides, 0.3-0.5 part of cananga odorataessential oil, 3-5 parts of water soluble camellia oleosa seed oil, 0.5-1 part of hydroxyethyl urea, 0.5-1 part of hexanediol and 60-80 parts of deionized water. The collagen peptide lubricating fluidis prepared from natural plants, is carried and used conveniently and has the effects of effectively cleaning and improving sexual excitation, and therefore, the collagen peptide lubricating fluid isa lubricating product which can be used for a long time.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for reducing residues of organophosphorus pesticides in Chinese wolfberry fruits with kombucha
The invention discloses a method for reducing residues of organophosphorus pesticides in Chinese wolfberry fruits with kombucha. The method comprises the following steps of making CICC 33068 into a CICC 33068 fungus suspension, CICC 20441 into a CICC 20441 fungus suspension and CICC 23165 into a fungus suspension; mixing the CICC 33068 fungus suspension with the Acetobacter sp CICC 20441 fungus suspension and the Lactobacillus plantarum CICC 23165 fungus suspension to obtain a mixed fungus suspension, adding the mixed fungus suspension into tea liquor containing cane sugar, performing standing culture to obtain a velum namely kombucha, and completely fermenting the kombucha so as to obtain kombucha fermentation liquor; and after applying organophosphorus pesticides namely chlorpyrifos, sprinkling the kombucha fermentation liquor onto Chinese wolfberry fruit plants at a fruiting period and soil, so that the residues of the organophosphorus pesticides namely the chlorpyrifos in the Chinese wolfberry fruits are reduced. The kombucha can produce esterase which is harmless to human bodies but has the effect of degrading the organophosphorus pesticides namely the chlorpyrifos, so that the residues of the chlorpyrifos can be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
New preparation method and application of kombucha protein
PendingCN111733104AIncrease contentHigh extraction rateAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiotechnologyInorganic salts
The present invention discloses a new preparation method and an application of kombucha protein, and belongs to the technical field of kombucha protein. The method comprises the following steps: adding black tea leaves after water boiling out, conducting decocting for 5 min-1 h under a boiling-out condition, filtering tea leaf residues, adding sucrose and inorganic salt to tea liquid for stirringand complete dissolving, then cooling the tea liquid, adding kombucha in the cooled tea liquid, conducting irradiation under weak ultraviolet lights after uniform stirring, then conducting constant-temperature fermentation in an electric thermostat to obtain kombucha fermentation liquid; and filtering and centrifuging the kombucha fermentation liquid, collecting supernatant, also adding two-aqueous-phase liquid formed by organic reagent-salt, conducting uniform stirring, conducting centrifugation after putting still and sedimentation, collecting supernatant, repeating for multiple times, concentrating the supernatant under reduced pressure to obtain a concentrated solution, and drying the concentrated solution to obtain the kombucha protein. The new preparation method can significantly increase output content of the kombucha protein extracted from the kombucha fermentation liquid.
Owner:上海澜海生物科技有限公司
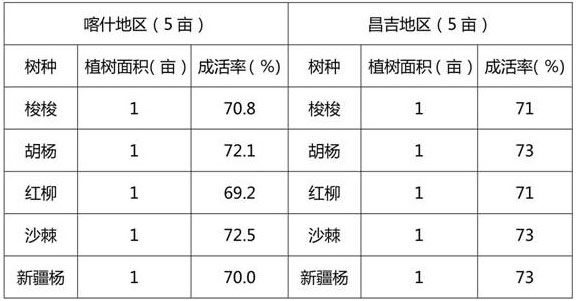
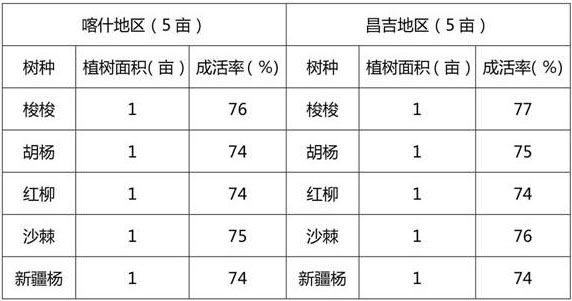
Biological bacterium solution for increasing survival rate of trees in arid and saline-alkali areas, preparation and application
The invention discloses a biological bacterium solution for increasing the survival rate of trees in arid and saline-alkali areas, preparation and application. The biological bacterium solution comprises: (a1) a base solution, which comprises well water, EM bacteria, mycorrhizal bacteria, kombucha, an element fertilizer and brown sugar in a weight ratio of 100: 0.5: 0.01: 0.1: 1: 10 in sequence; and (a2) a finished bacterium solution product, which comprises the well water, the base solution, bacillus subtilis, trichoderma harzianum, actinomycetes, mineral potassium fulvate and chelated glutamic acid in a weight ratio of 1000: 2: 0.01: 0.01: 0.01: 1: 0.5 in sequence. The biological bacterium solution provided by the invention can give full play to the interference, repairing and compounding effects of bacteria on tree cells, enlarge the absorption range of the root systems of the trees, enlarge the nutrient absorption and conveying capacity of the trees and enhance the drought resistance and saline-alkali adaptability of the tree cells, thereby improving the survival rate of the trees and achieving the effect of greatly saving water.
Owner:左政
Fermented soybean milk free of beany flavor and rich in vitamins and preparation method and application of fermented soybean milk
The invention discloses fermented soybean milk free of beany flavor and rich in vitamins and a preparation method and application of the fermented soybean milk, and belongs to the technical field of food fermentation. The preparation method of the fermented soybean milk effectively improves the vitamin content of the fermented soybean milk. The preparation method of the fermented soybean milk mainly comprises the following steps that soybeans are cleaned, peeled, de-embryonated and soaked; the soybeans are treated by a jet cavitation machine, slurry and slag separation is carried out, and flash evaporation is carried out; soybean milk and a stabilizer are taken, dissolved, blended, homogenized, sterilized and cooled; and a kombucha agent or a mixture of the kombucha agent and prebiotics is fermented. The fermented soymilk is fermented by whole plants, has no beany flavor, bitterness and unpleasant odor, tastes fine and smooth, is rich in vitamins, and has rich fermented bean flavor and tea flavor; and the product is rich in nutrition, free of animal raw materials, low in production cost and good in flavor.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological feed additive for laying hens at egg laying later stage
InactiveCN105995152ASolve the problem of instability at high temperatureReduce inflammationAnimal feeding stuffWorking-up animal fodderBiotechnologyAnimal science
The invention relates to a preparation method of a traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological feed additive for laying hens at an egg laying later stage. The preparation method comprises the following steps of taking traditional Chinese medicines including forsythia suspensa, astragalus membranaceus, radix codonopsis, Chinese angelica, radix isatidis, motherworts, purple perilla, spina date seeds, radix ophiopogonis and licorice roots, performing superfine grinding on the traditional Chinese medicines, adding an alcohol solution, performing boiling over with a strong fire, performing heat preservation with a soft fire, performing cooling, performing filtration, concentrating filtrate, adding white sugar, performing boiling over, performing cooling to normal temperature, inoculating lactobacilli, red tea funguses and bifidobacteria, performing fermentation until white fungus blocks grow, and performing low-temperature concentration on bacterial liquid; and then weighing modified starch, arabic gum, cyclodextrin and syrup, adding the weighed modified starch, the weighed arabic gum, the weighed cyclodextrin and the weighed syrup to the concentrated bacterial liquid, performing stirring during adding, after uniform mixing and stirring, performing high-pressure homogenizing, and performing spray drying so as to obtain the traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological feed additive. The traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological feed additive disclosed by the invention has the efficacies of increasing the number of beneficial bacterium groups in intestinal tracts, enhancing immune functions, strengthening stress resistance of chicken bodies, strengthening disease resistance of the chicken bodies, increasing egg production and the like. Compared with a control group, the traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecological feed additive disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the egg laying rate is increased by 4.86% and 7.27%, the feed-egg rate is reduced by 7.65% and 5.82%, and the rate of soft and broken eggs is reduced by 23.64% and 31.72%; feeds are saved, the cost is reduced, and the economic benefits are increased.
Owner:丁玉兰
Processing method of kombucha solid beverage
The invention discloses a processing method for a black tea fungus solid beverage. The processing method sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) preparing tea soup; (2) inoculating; (3) fermenting; (4) centrifuging; (5) sterilizing; (6) spraying and drying, namely adding a maltodextrin drying aid into concentrated liquid and uniformly mixing; and then drying by using a spraying dryer under the condition that an air inlet temperature is controlled at 150-180 DEG C, an air outlet temperature is controlled at 70-90 DEG C, and the water content is 5-7% after spraying and drying, thus preparing black tea fungus dried powder; and (7) blending and putting into bags, namely mixing and blending following materials into mixed powder I in percentage by weight: 1%-3% of instant black tea powder, 2%-3% of citric acid, 0.15%-0.45% of sodium citrate, 90%-96% of white granulated sugar powder; uniformly mixing the mixed powder I and the black tea fungus dried powder according to the ratio of (15%-50%) to (85%-50%) to obtain mixed powder II; and putting the powder into the bags. The sterilization treatment guarantees the stability of product properties and the product obtained by concentration and drying procedures is convenient to store and transport.
Owner:上海百山生物技术有限公司
Preparation method of digestion-promoting black tea beverage
PendingCN111109408AKeep the fragrance of glycolGreat tasteMilk preparationTea extractionBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
The present invention discloses a preparation method of a digestion-promoting black tea beverage. The method comprises the following steps of black tea stock solution preparation, kombucha black tea stock solution preparation, lactic acid bacteria stock solution preparation, mixed liquid preparation, homogenization and sterilization treatment. The preparation method of the digestion-promoting black tea beverage introduces components of kombucha and lactic acid bacteria into traditional black tea, so that the black tea beverage has functions of promoting intestinal peristalsis and helping digestion while retaining sweet and mellow fragrance, and is more in line with modern people concepts of health care.
Owner:郎溪松果生态农业有限公司
Culture method of kombucha and application thereof
InactiveCN108713758AAvoid it happening againReduce the chance of infectionFungiBacteriaBlack teaContamination rate
The invention relates to a culture method of kombucha and application thereof, and relates to the field of brewing. The culture method comprises the following steps: mixing water and the black tea, extracting, filtering, then mixing a filtrate and edible sugar, and sterilizing to obtain base liquid; placing the base liquid having the temperature of 28-33 DEG C in a sterilized open container, and then inoculating with mother kombucha, sealing the open end of the container by using gauze, leaving to stand for fermentation for 7-14 days under the conditions that the light intensity is 4000-7000lx, the humidity is 30-40% and the temperature is 28-33 DEG C to obtain red brown flocculent or lumpy kombuch floating on the surface of the base liquid, wherein the inoculation amount of the mother kombucha is 2-3% of the mass of the base liquid. By the culture method, operation is controllable and simple, large-scale production can be achieved, and the contamination rate of a cultured culture is low; meanwhile, the culture method of the kombucha can be applied to food processing, beverage processing or health-care product processing, and has wide application range.
Owner:贵州湄潭兰馨茶业有限公司
Kombucha and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112931650AStrong inhibitory activitySolve the technical problem of insufficient health care functionPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologySucrose
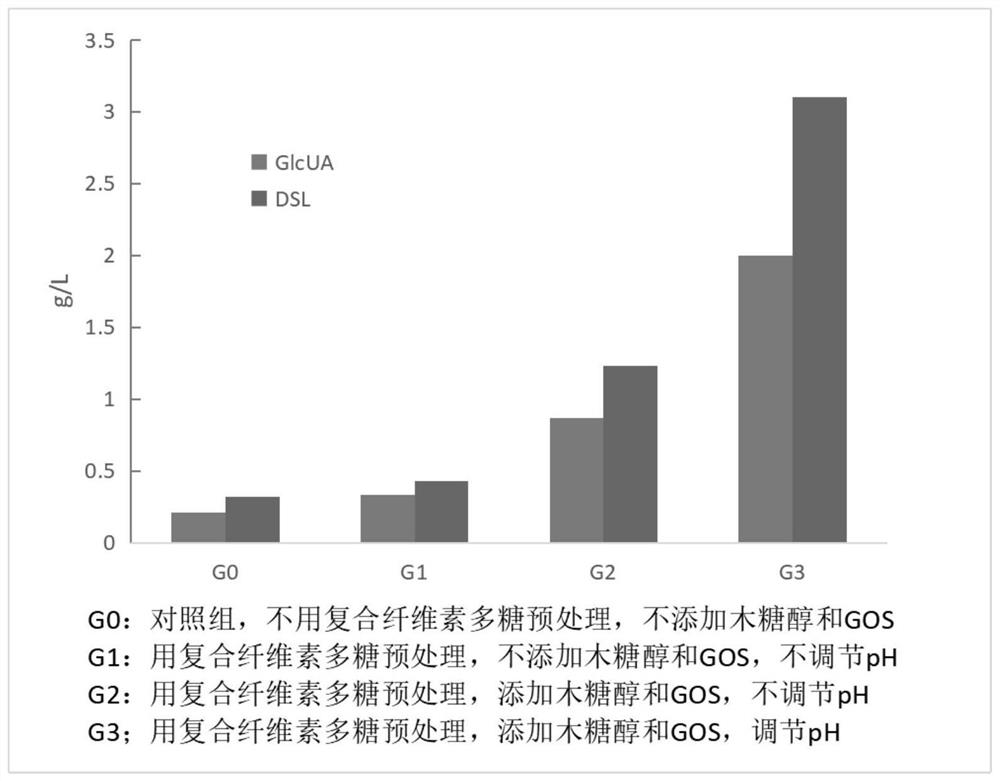
The kombucha is prepared from the following raw materials: tea, cane sugar or glucose, water, compound polysaccharide enzyme, saccharomycetes, lactic acid bacteria, xylitol, galactooligosaccharide GOS and acetic bacteria. The GlcUA content of the kombucha reaches 2.2 g / L or above, and the DSL content of the kombucha reaches 3.3 g / L or above. The preparation method of the kombucha comprises the following steps: mixing the black tea, the cane sugar or the glucose and the water according to a certain proportion, performing heat preservation extraction, adding the composite polysaccharide enzyme, and treating for about 1-3 hours; removing tea leaf residues, sterilizing filtrate, cooling to inoculation temperature, inoculating saccharomycetes and lactic acid bacteria, fermenting for about 3 days, adjusting the pH value to 5.0 or above, adding the xylitol and the galactooligosaccharide GOS, inoculating acetic bacteria, and continuously fermenting until the mixture is mature; and removing insoluble substances from the obtained mature fermentation liquor in a centrifugation or membrane filtration manner, wherein the obtained filtrate is the kombucha containing a large amount of GlcUA and DSL. According to the invention, the content of GlcUA and DSL is increased, so that the technical effect of effectively improving the health-preserving and health-care effects of the kombucha is achieved.
Owner:漯河微康生物科技有限公司
Method for preparing traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecology oral preparation for preventing ascariasis
InactiveCN104997867ATreatable damageHealing damageBacteria material medical ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsBiotechnologyPumpkin seed
A method for preparing a traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecology oral preparation for preventing ascariasis comprises the steps of preparing euphorbia helioscopia, azedarach, kaladana, kaladana, pumpkin seeds, pomegranate bark, coptis chinensis, gynostemma pentaphylla, astragalus membranaceus, codonopsis pilosula and radix glycyrrhizae; conducting superfine grinding on all the traditional Chinese medicines, adding an ethanol solution, boiling with strong fire, keeping warm with slow fire, conducting cooling and filtering, concentrating filter liquor, adding white sugar, boiling, cooling to the normal temperature, inoculating lactobacillus, tea fungus and acetobacter xylinum, and obtaining white fungus blocks after fermentation is conducted for 96-118 h; conducting dilution with the proportion of the white fungus blocks to bacterial liquid being 1 to 50-80, conducting secondary fermentation for 18-24 h, and obtaining the micro-ecology oral preparation. The traditional Chinese medicine micro-ecology oral preparation can increase the number of effective microbial communities in the intestinal tract, improve immunity and improve the disease resistance of pigs. The oral preparation has the advantages that preventing effect is good, cure rate reaches 90.0%, preparing method is simple, viable content is high, using is convenient, environment friendliness is realized, and no residue exists.
Owner:郭庆
Preparation method and application of kombucha product
PendingCN114052105AImprove antioxidant capacityHigh in polyphenolsTea extractionBiotechnologyAntioxidant capacity
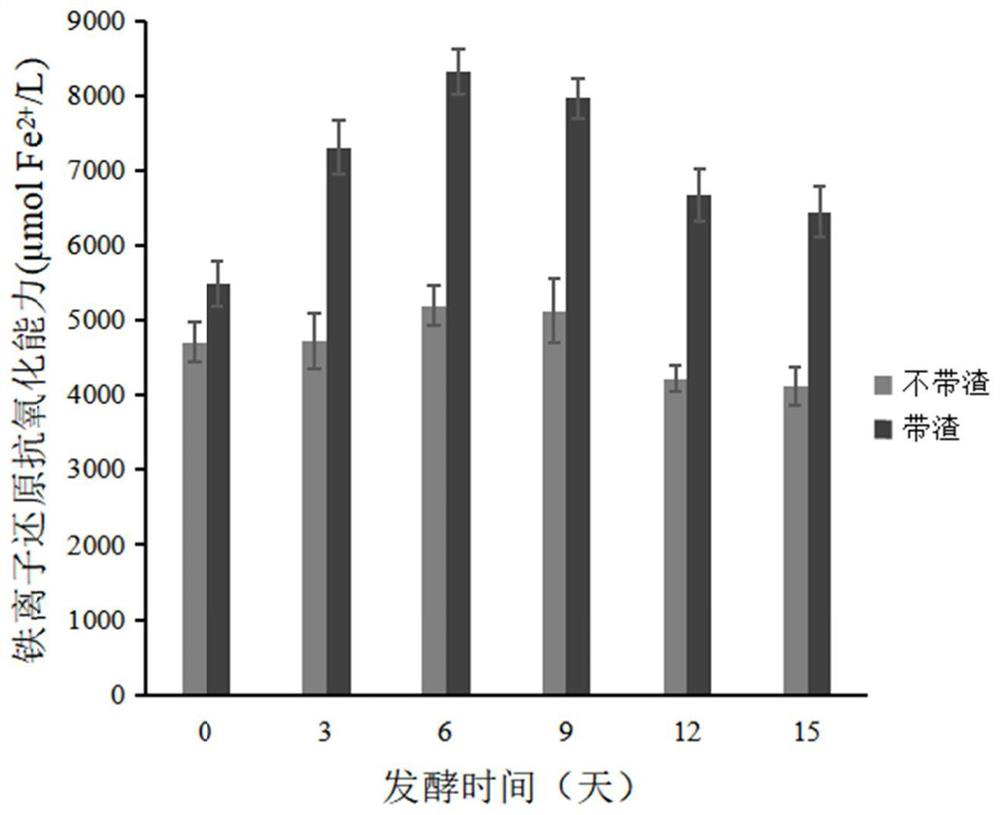
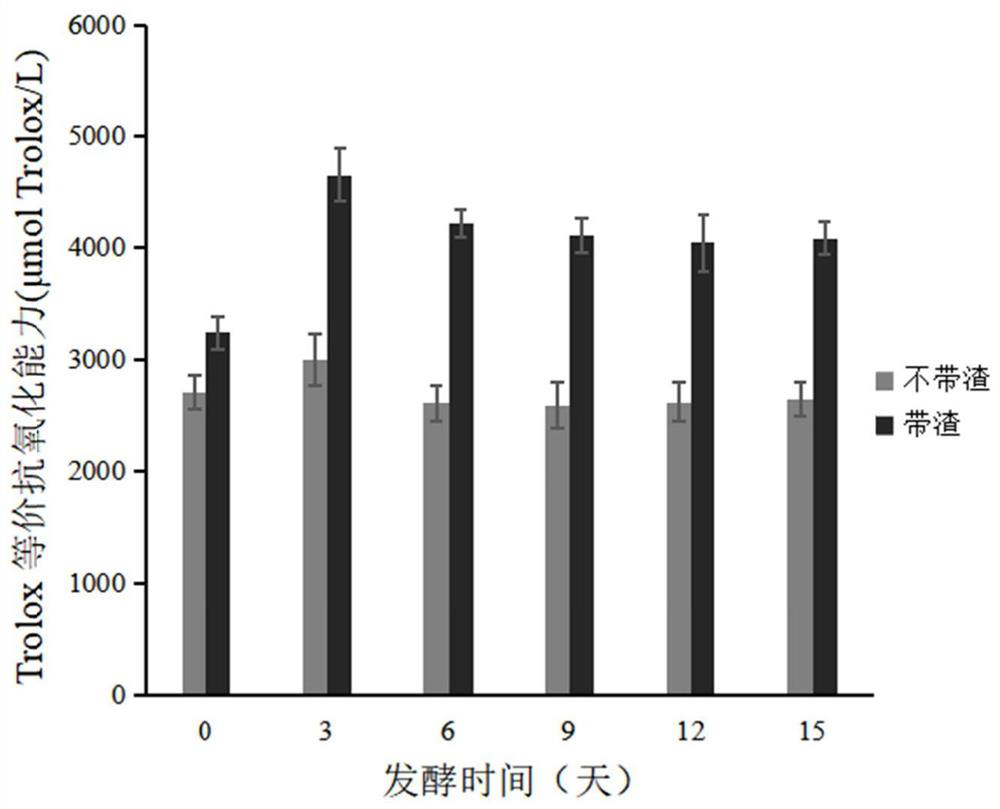
The invention relates to the technical field of food processing, in particular to a preparation method and application of a kombucha product. The kombucha product is prepared by fermenting unfiltered black tea water in the presence of kombucha mother liquor, and compared with a kombucha product prepared by fermenting filtered black tea water in the presence of kombucha mother liquor, the oxidation resistance and the polyphenol content of the prepared kombucha product are remarkably improved. In addition, the preparation method is easy to operate, high in efficiency, suitable for large-scale industrial production and good in application prospect.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Beverage prepared from grape and tea leaves, and preparation method and device thereof
InactiveCN108467809AGood effectSignificant energy savingAlcoholic beverage preparationSiphonVitis vinifera
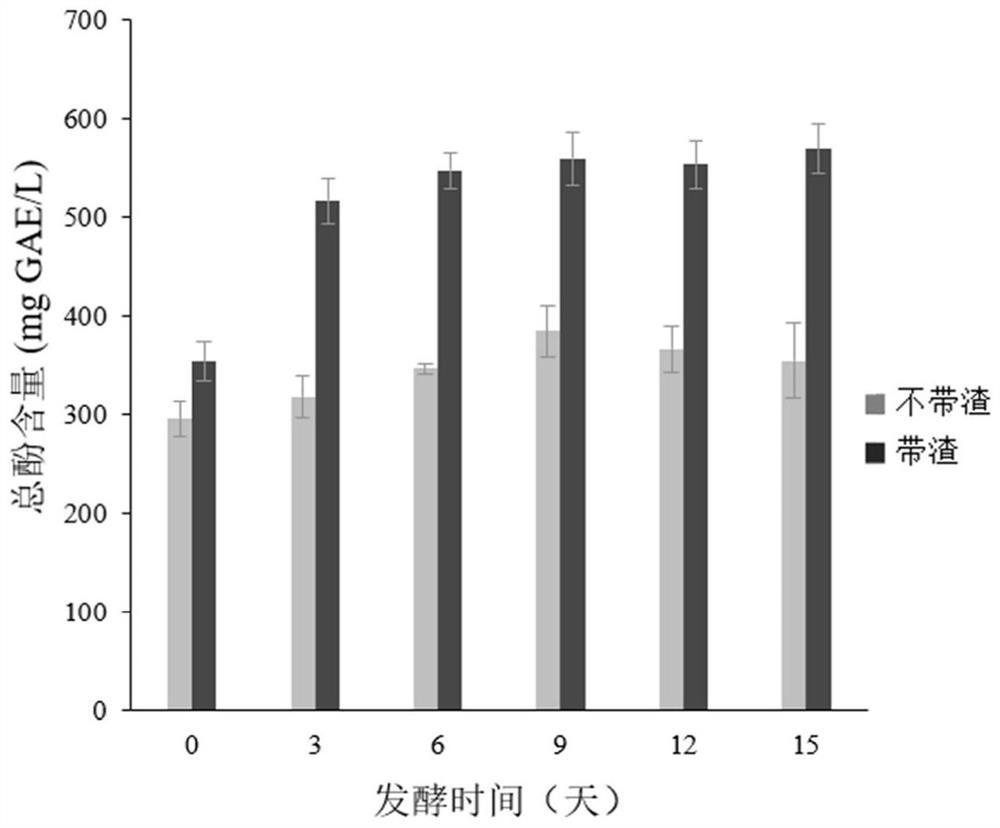
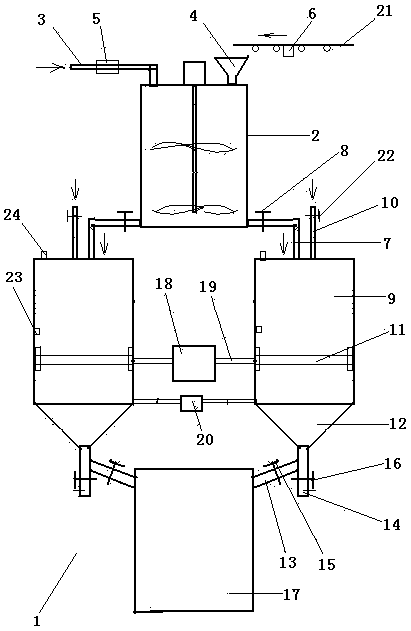
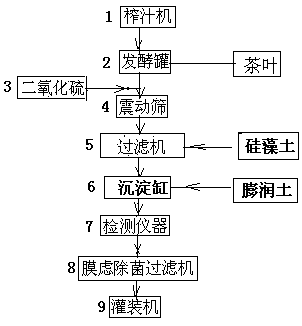
The invention provides a beverage prepared from grape and tea leaves, and a preparation method and a device thereof. According to the beverage, the tea leaves are added in a grape fermentation process, black tea fungi are produced, the sugar content in red wine is reduced, the faint scent of the tea leaves in red wine is increased, and the obtained red wine has light red color, has the alcohol content of 8%-12% vol and the sugar content of 5-10 g / L, and is rich in faint scent of the tea leaves. The preparation device comprises a juicer, a fermentation tank, a vibrating screen, a filter, a precipitation cylinder, a detection instrument, a filter membrane bacteria-removing filter and a filling machine. The beverage contains the nutrient substances of the red wine, tea leaves and black tea fungi, is beneficial to people health and rich in the faint scent of the tea leaves, and provides a new choice for consumers; the beverage is filtered by a diatomite filter, bentonite is added, the materials are stirred and are precipitated by a precipitation cylinder, and an upper clarified liquid is sucked by a siphon method; the beverage has the advantages of good effect and remarkable energy saving.
Owner:HUNAN GUDONGCHUN TEA IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com