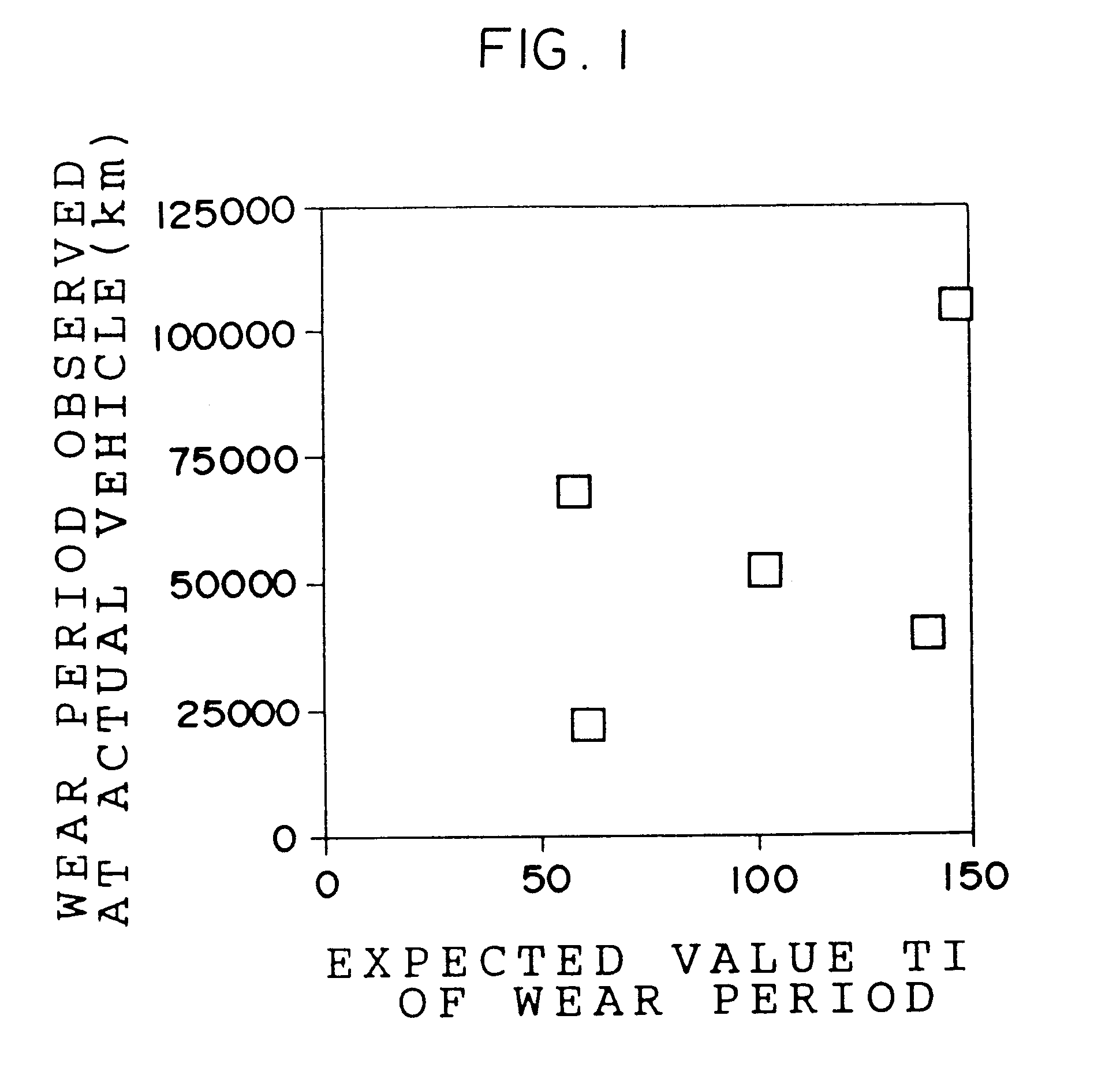Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
126 results about "Frictional energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Work, Energy and Friction. Frictional resistance between two objects which are at rest with respect to one another is called static friction, but if they have relative motion it is called kinetic friction.
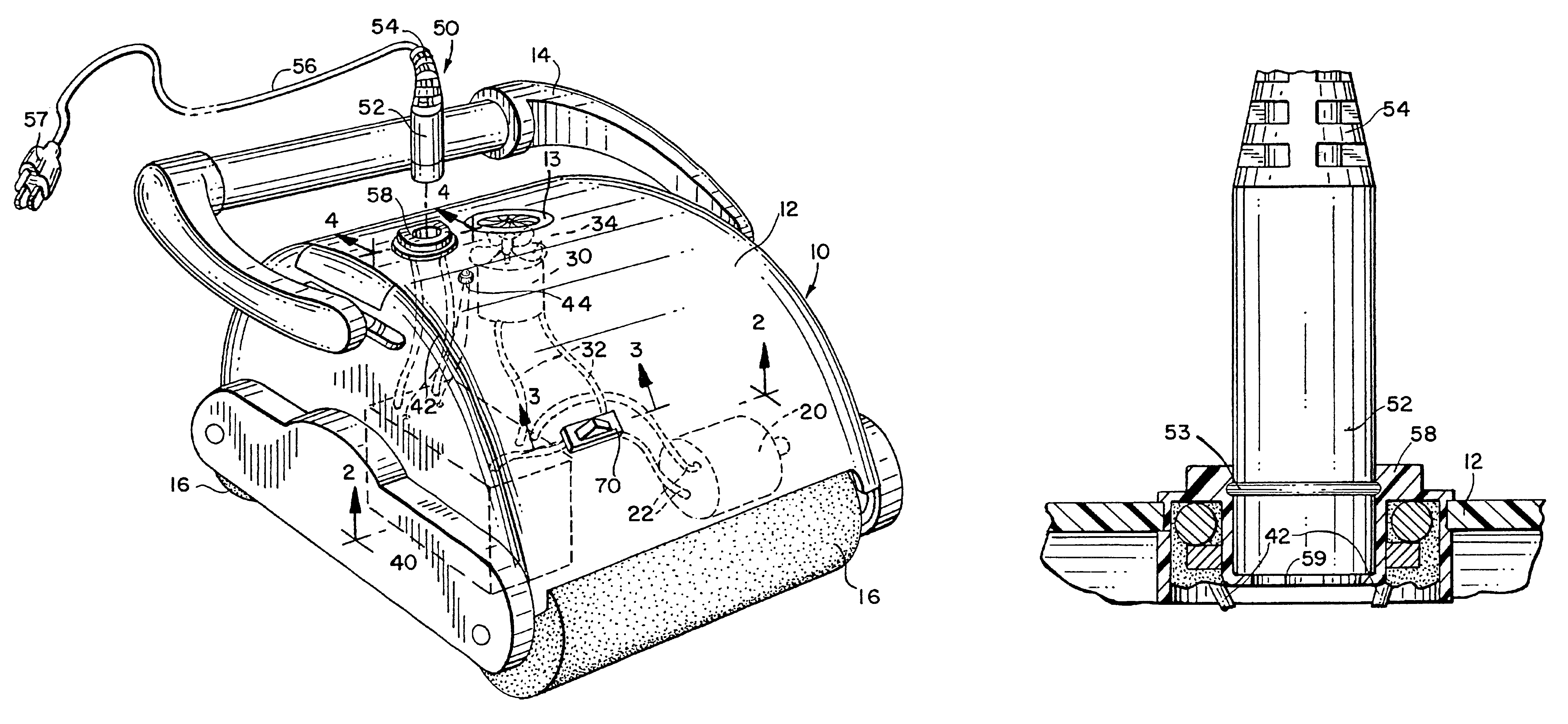
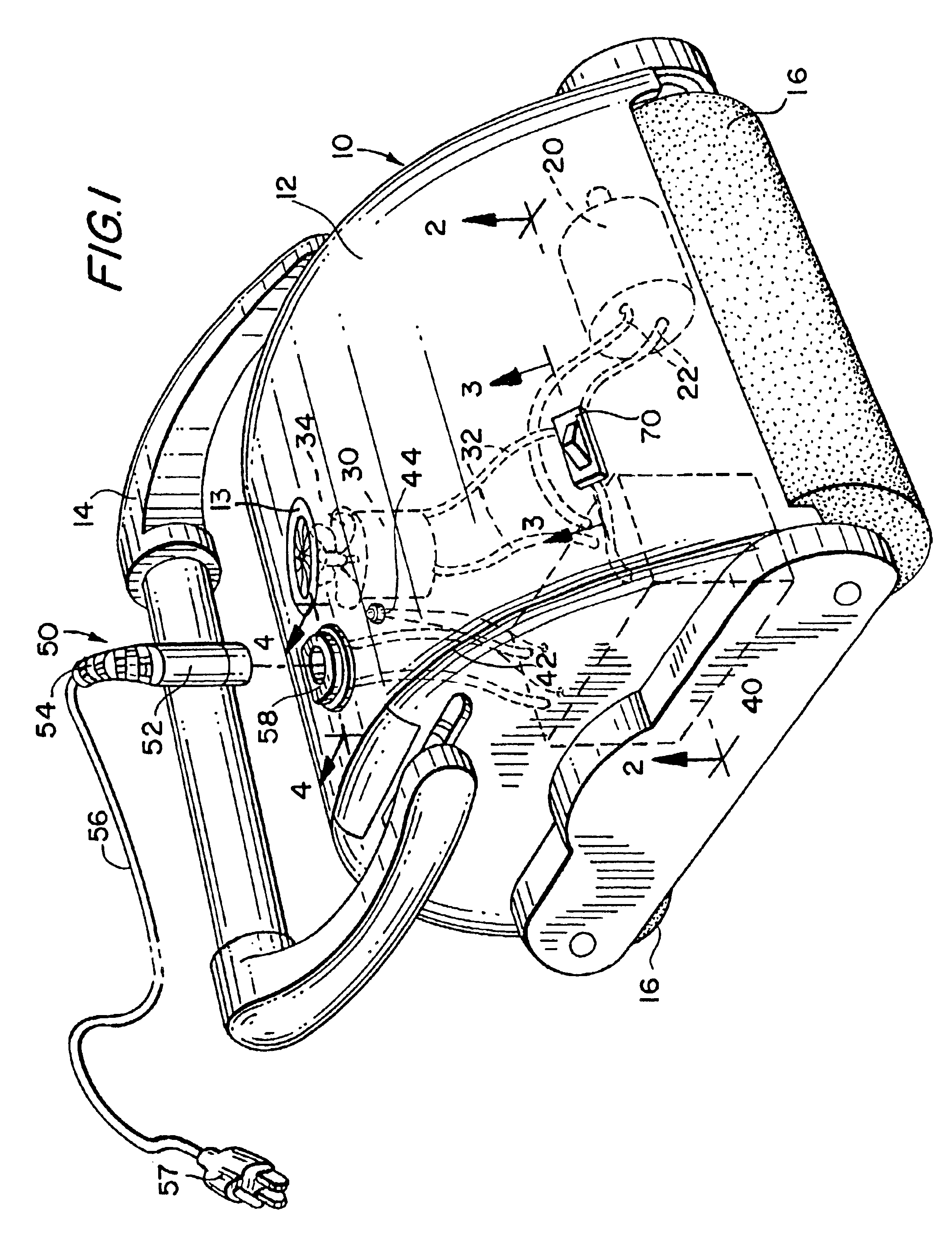
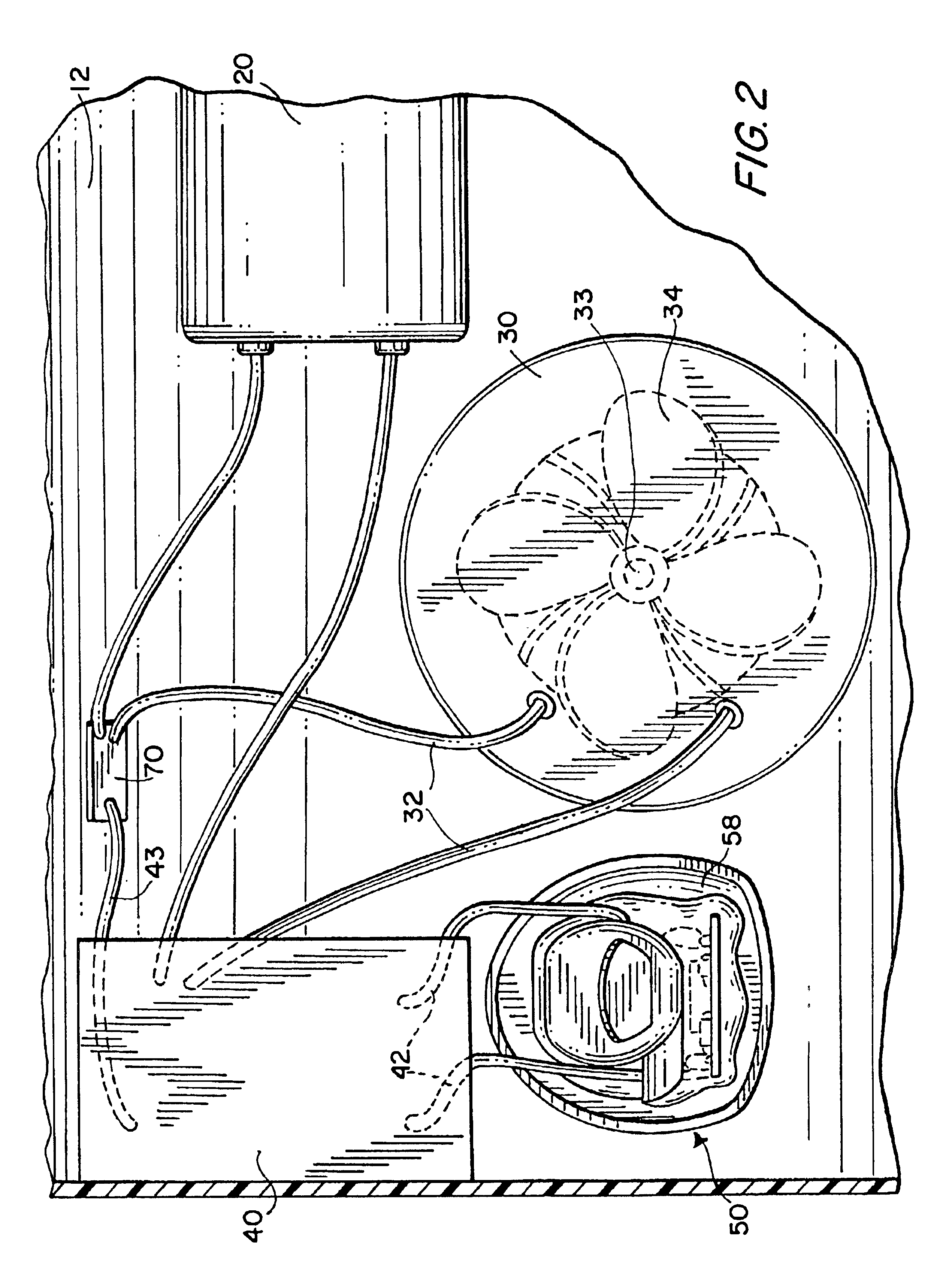
Submersible pool cleaner with integral rechargeable battery
InactiveUS6842931B2Power is requiredReduce frictionGymnasiumConnectionsMotor driveElectrical battery
A submersible robotic pool cleaner is provided with an integral sealed rechargeable battery and an inductive charging assembly, a first portion of which is mounted in the pool cleaner housing and during the charging, receives a second separate portion that is connected by a cable to a conventional power source. The pump motor drive shaft is treated with a specialized anti-friction lubricant composition to minimize frictional energy losses where the shaft contacts the seal(s) and any shaft bearing(s), to maximize efficiency and minimize the power consumption of the pump motor assembly and permit the pool cleaner to completely traverse the surfaces to be cleaned within the fully-charged power capacity of the battery.
Owner:ZODIAC POOL SYST LLC
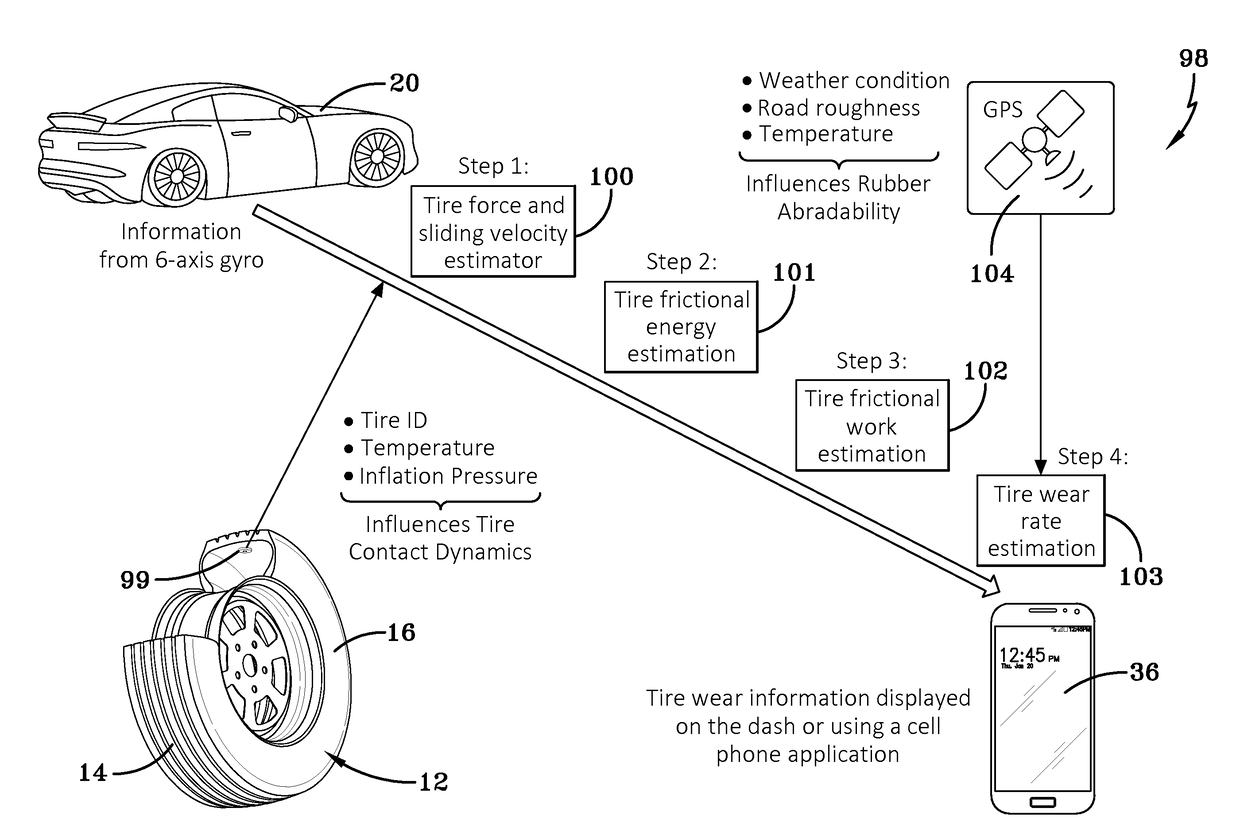
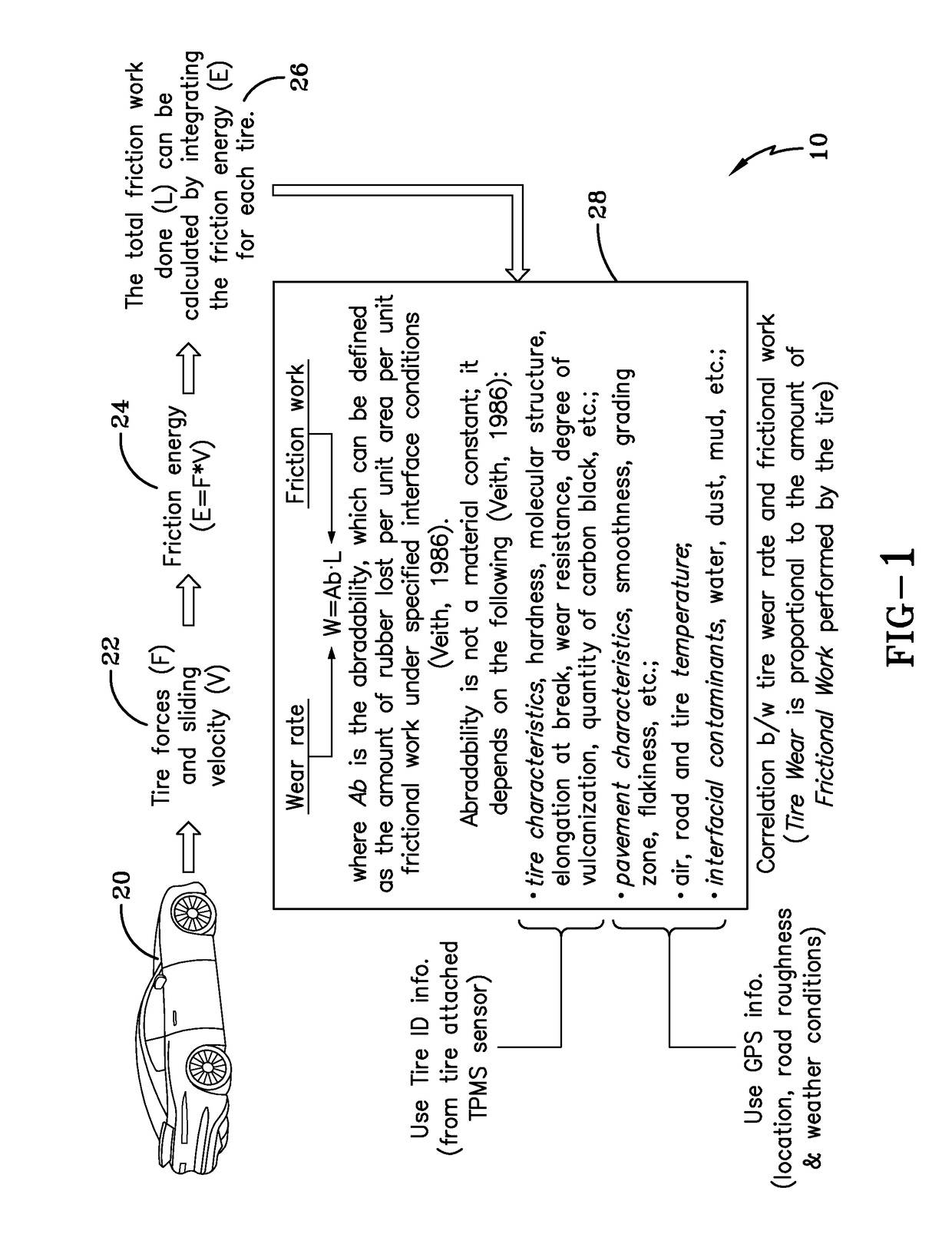
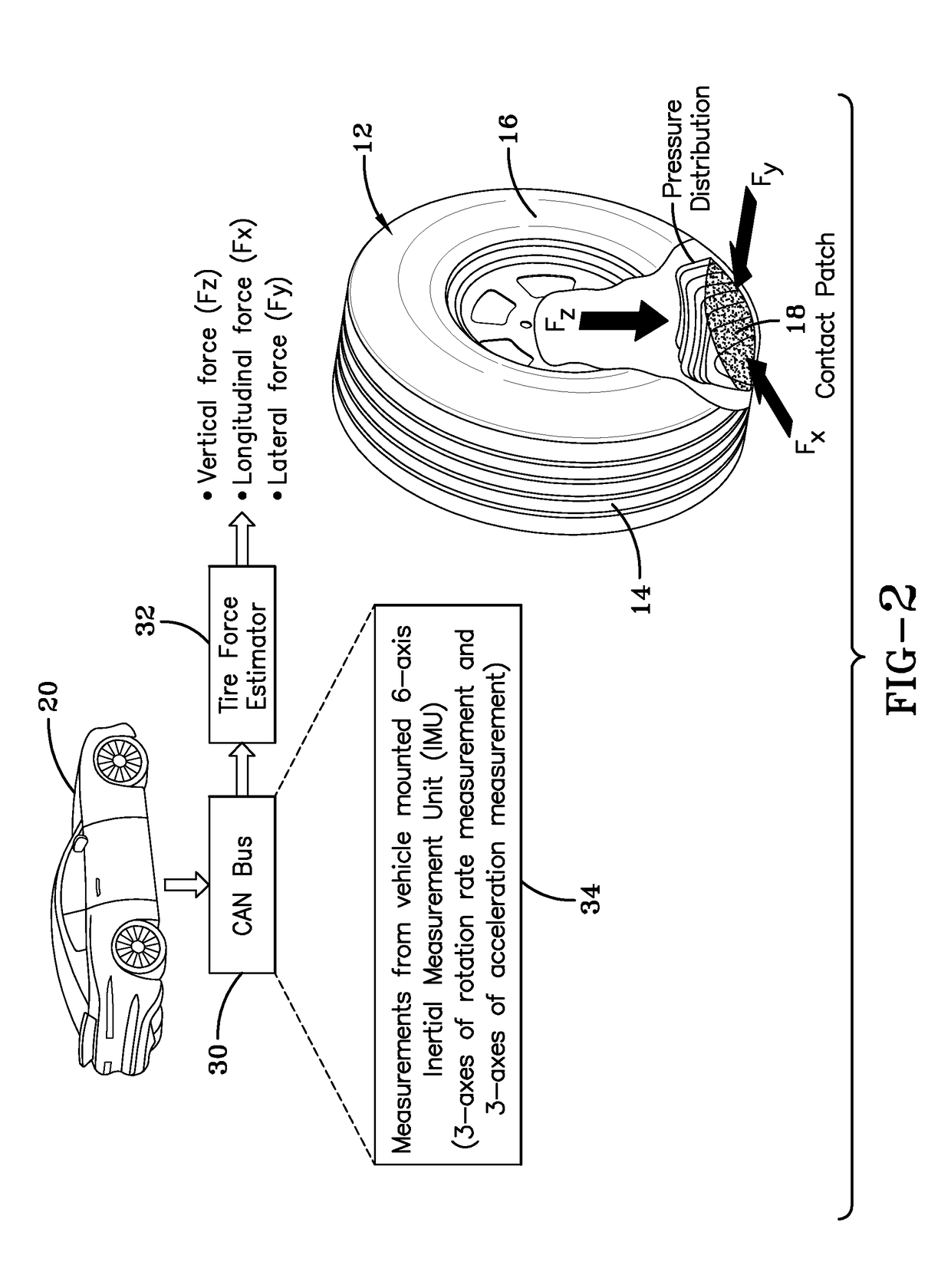
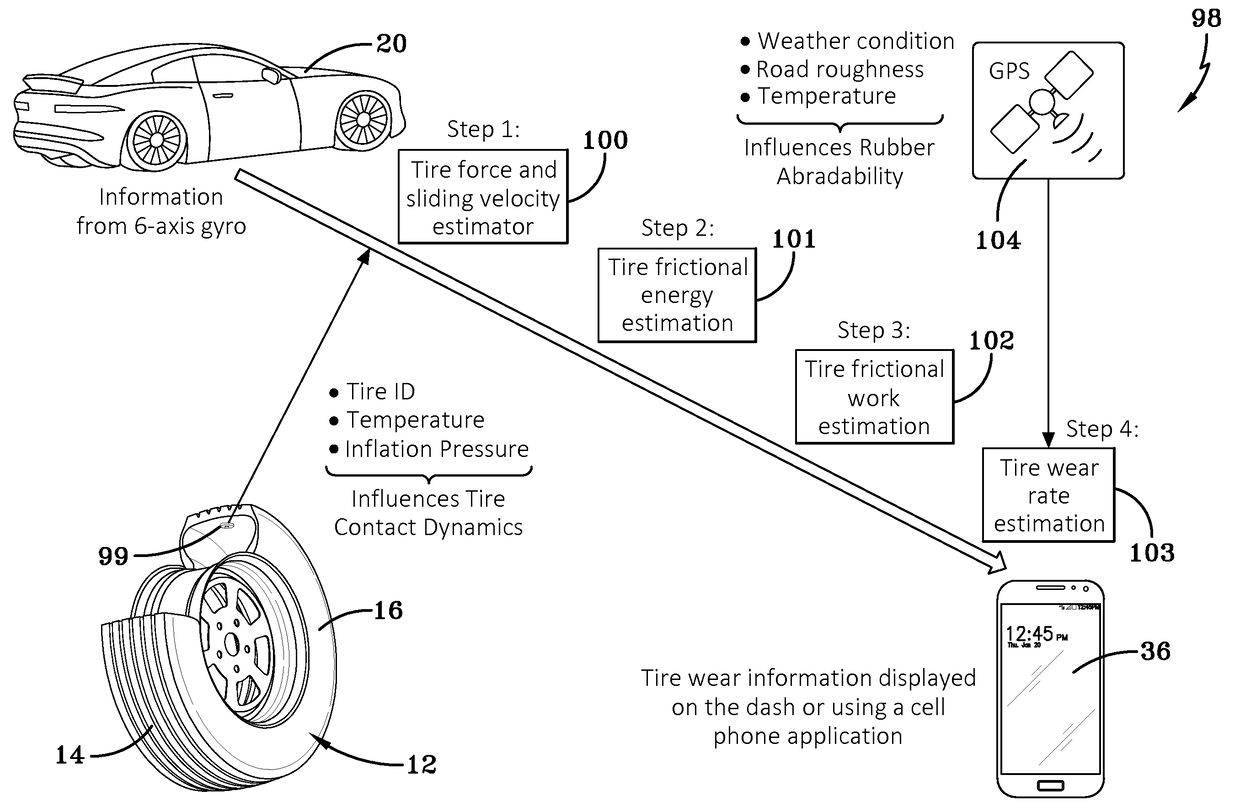
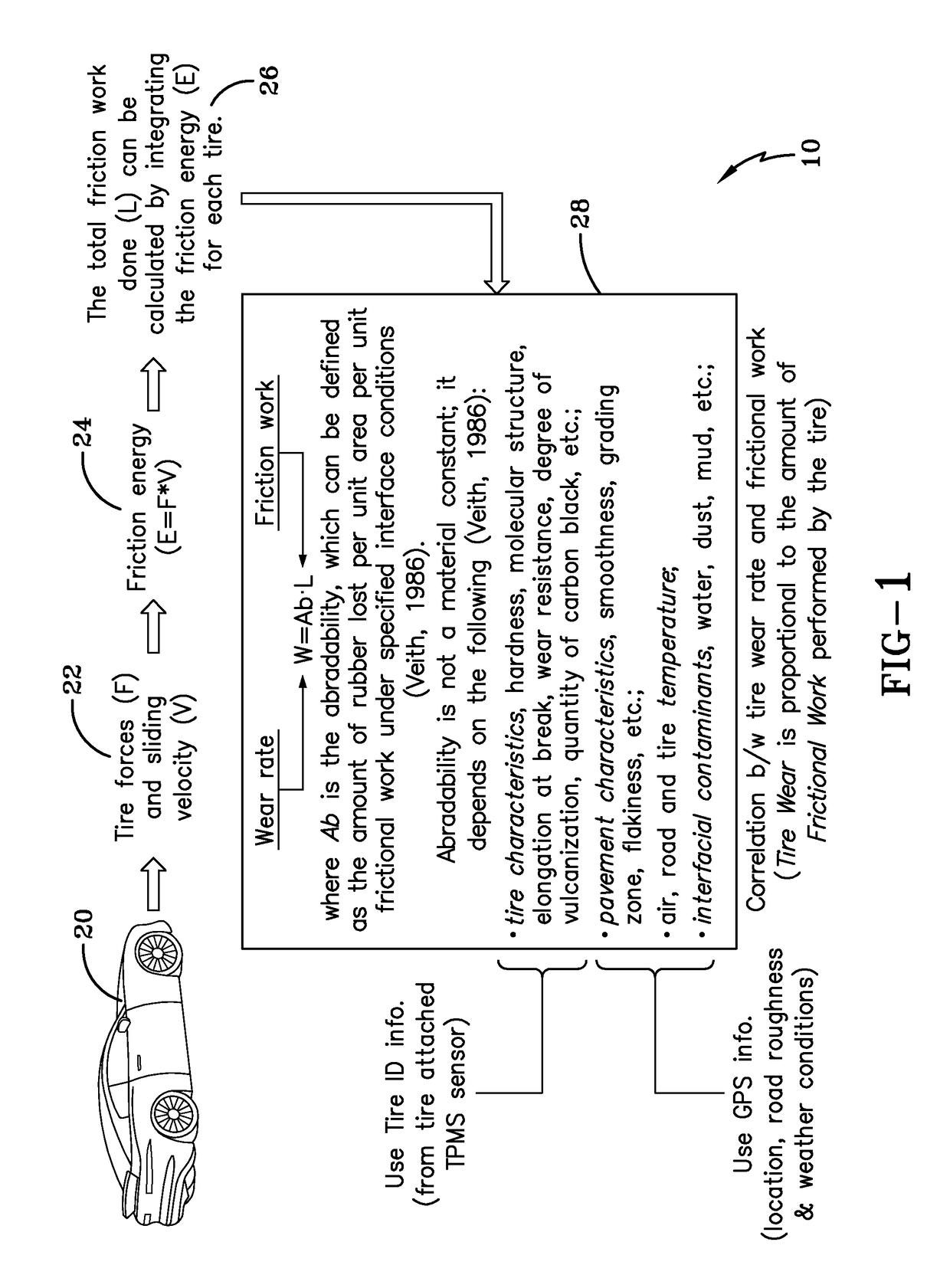
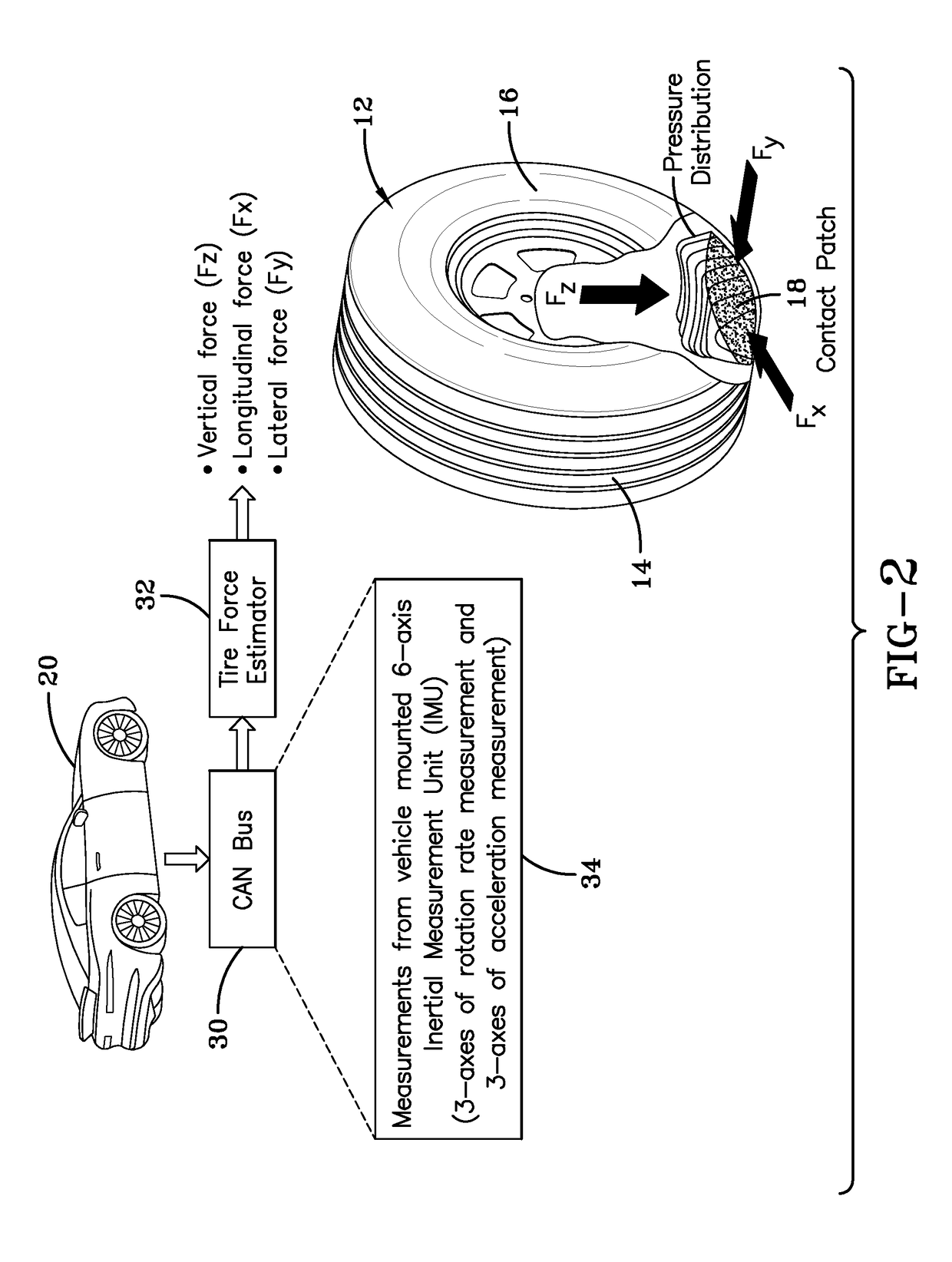
Indirect tire wear state prediction system and method
ActiveUS20170113494A1Great tractionError minimizationSatellite radio beaconingTyre measurementsState predictionPrediction system
A tire wear state estimation system estimates forces and sliding velocity generated in a tire contact patch, determines frictional energy from the tire force and sliding velocity, and generates an estimate of tire wear state based upon the frictional work done by the tire. A tire wear estimate, pursuant to the system and methodology, is made by determining the amount of frictional work performed by the tire through the integrated use of tire-mounted, GPS sourced, and vehicle-mounted sensor information.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Method of improving the overall operating efficiency of an electric motor-powered assembly
InactiveUS7143502B2Reduce frictionReduced Power RequirementsShrinkage connectionsManufacturing stator/rotor bodiesMotor driveElectrical battery
A submersible robotic pool cleaner is provided with an integral sealed rechargeable battery and an inductive charging assembly, a first portion of which is mounted in the pool cleaner housing and during the charging, receives a second separate portion that is connected by a cable to a conventional power source. The pump motor drive shaft is treated with a specialized anti-friction lubricant composition to minimize frictional energy losses where the shaft contacts the seal(s) and any shaft bearing(s), to maximize efficiency and minimize the power consumption of the pump motor assembly and permit the pool cleaner to completely traverse the surfaces to be cleaned within the fully-charged power capacity of the battery.
Owner:AQUATRON
Indirect tire wear state prediction system and method
ActiveUS9873293B2Error minimizationSatellite radio beaconingTyre measurementsState predictionFrictional energy
A tire wear state estimation system estimates forces and sliding velocity generated in a tire contact patch, determines frictional energy from the tire force and sliding velocity, and generates an estimate of tire wear state based upon the frictional work done by the tire. A tire wear estimate, pursuant to the system and methodology, is made by determining the amount of frictional work performed by the tire through the integrated use of tire-mounted, GPS sourced, and vehicle-mounted sensor information.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
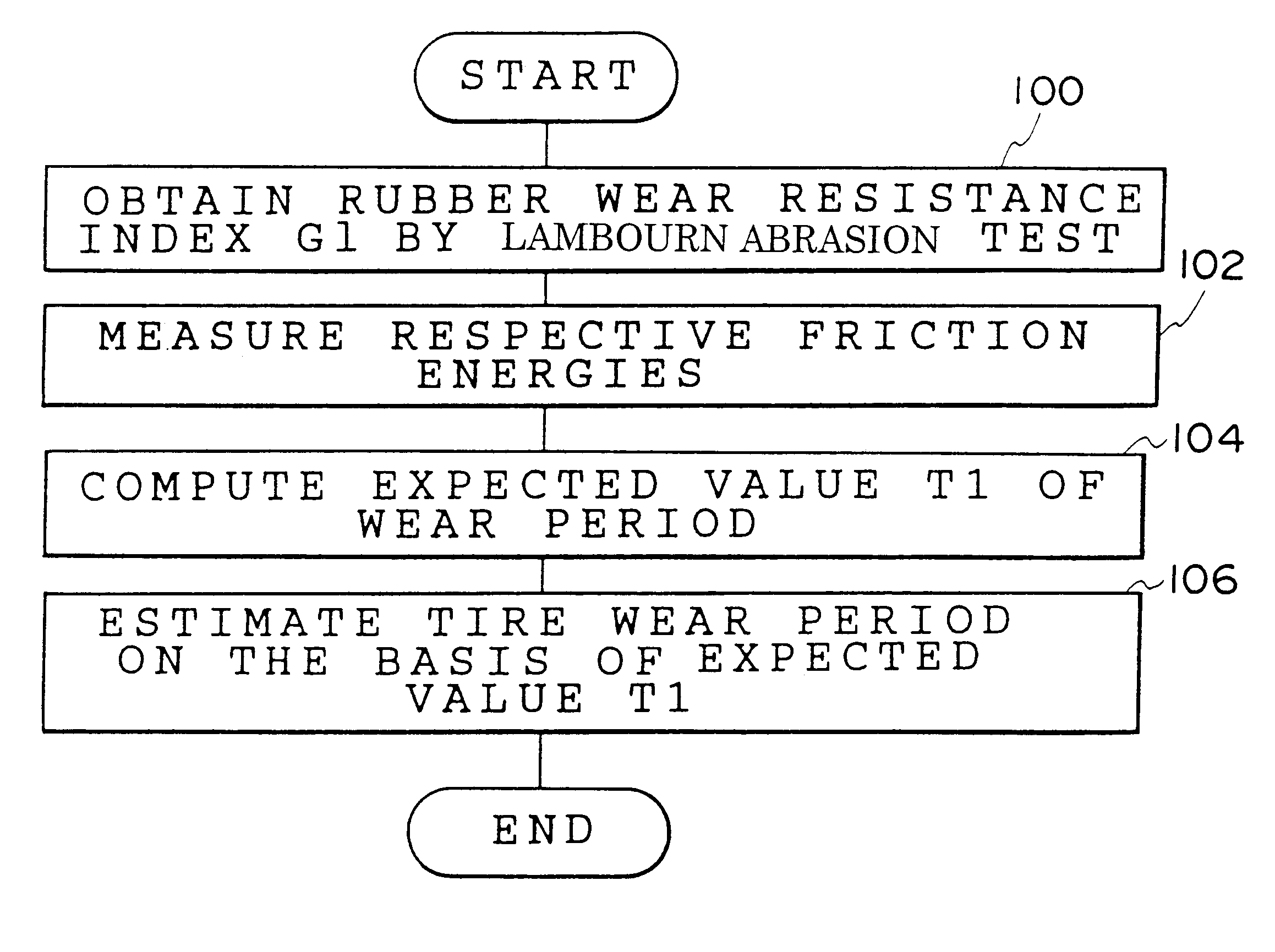
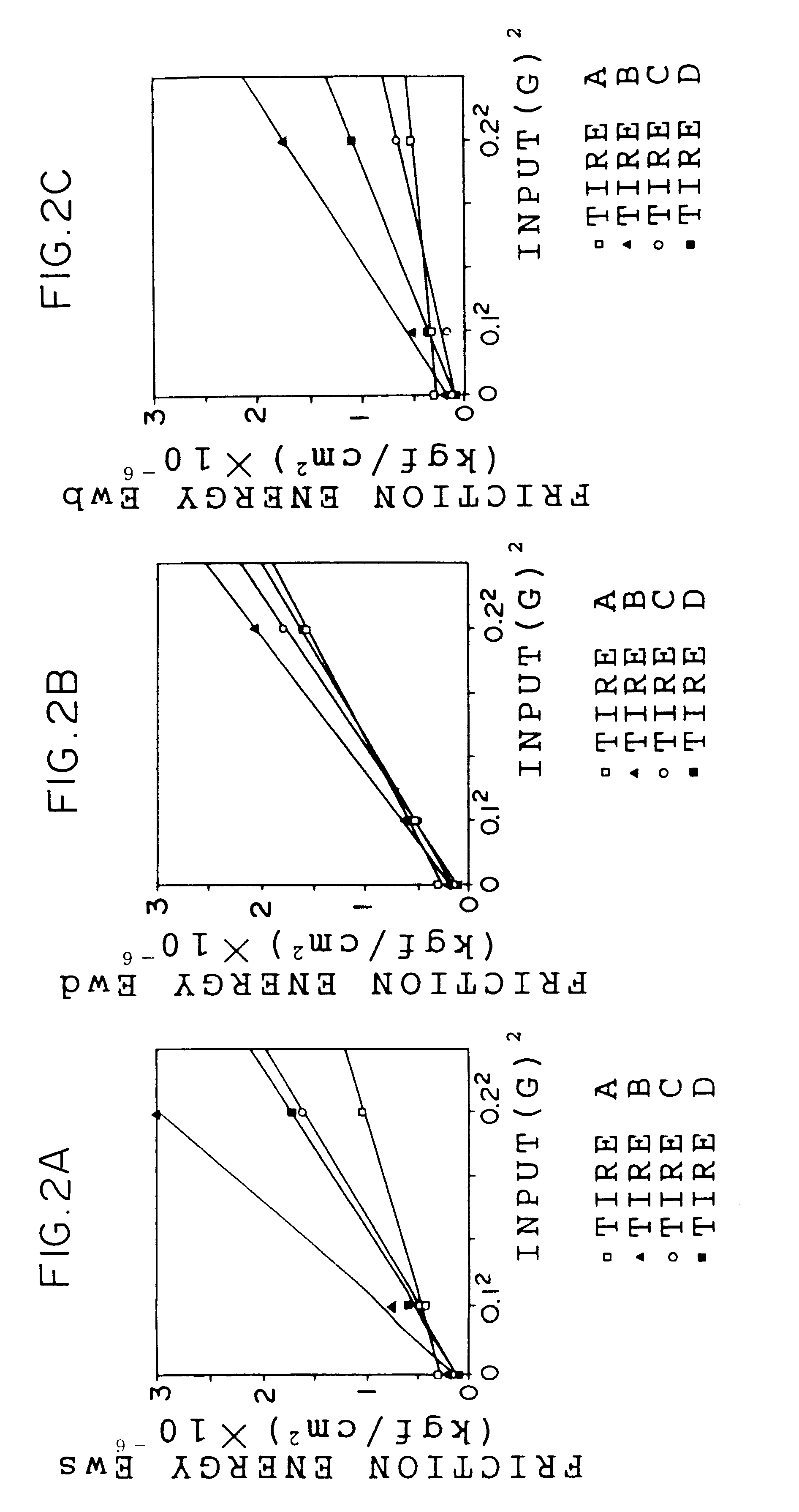
Method for estimating a tire wear life
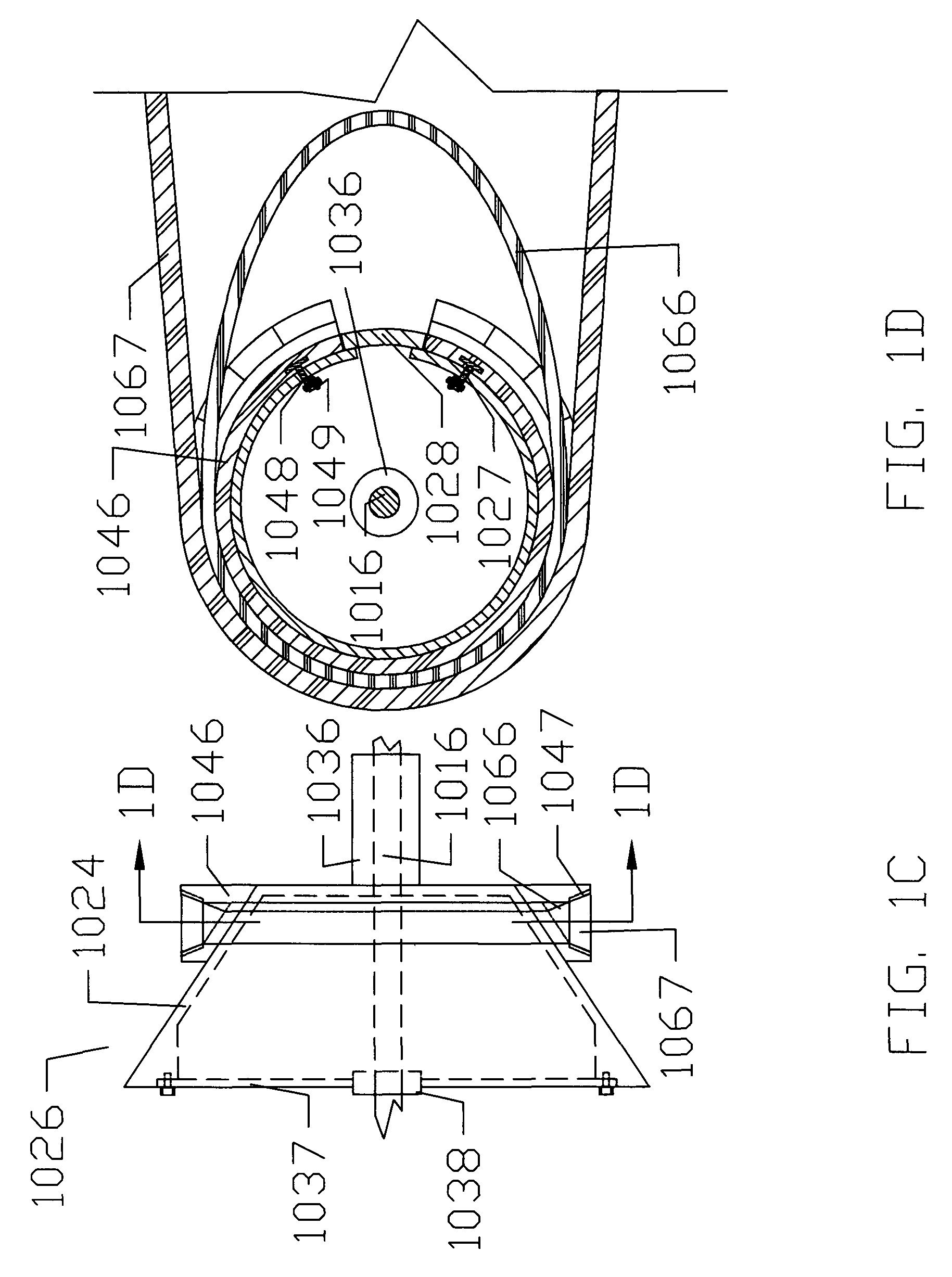
A wear resistance index G1 of a tire whose wear life is to be estimated is measured by the Lambourn abrasion tester. Then, friction energies in free rolling, when the tire is fitted with a toe angle, under application of a side force, under application of a braking force and under application of a driving force of the tire are measured. An expected value of the wear life T1 is calculated using the wear resistance index G1 and the friction energies thus obtained and the wear life of the tire is estimated on the basis of the expected value of the wear life T1. The wear life of a tire can be estimated accurately in a short time in accordance with the method for estimating a tire wear life of the present invention.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
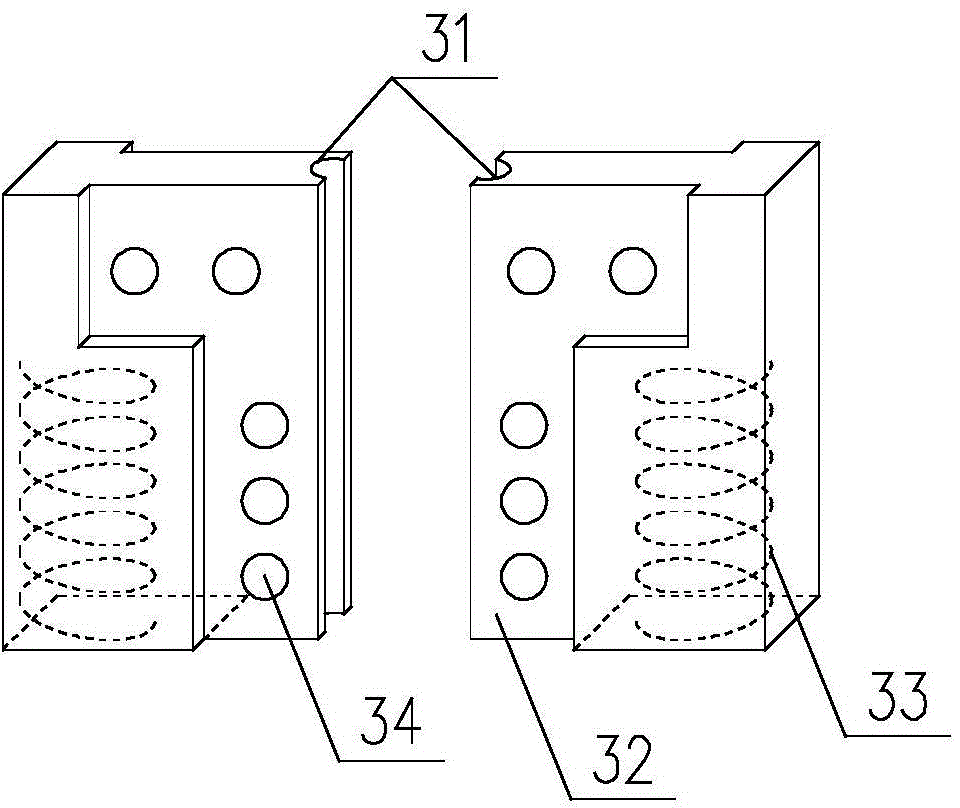
Frictional energy dissipation self-centering shear wall structure with easily restored bottom
ActiveCN104878852AImprove repair efficiencyReduce residual deformationWallsShock proofingPre stressPre stressing
The invention discloses a frictional energy dissipation self-centering shear wall structure with an easily restored bottom. The frictional energy dissipation self-centering shear wall structure with the easily restored bottom comprises at least one structure unit, and the structure unit comprises an ordinary prefabricated wall section, a spiral stirrup reinforcement prefabricated wall section, an easily restored wall section located at the lower side of the spiral stirrup reinforcement prefabricated wall section, friction dampers located at two sides of the easily restored wall section, and an un-bonded pre-stressed tendon located in the wall body; the spiral stirrup reinforcement prefabricated wall section comprises an inside spiral stirrup, a pre-embedded plate inserted in the spiral stirrup, and T-shaped connecting plates connected with the easily restored wall section and further connected with slotted spiral stirrup reinforcement wall blocks of the easily restored wall section; the easily restored wall section comprises two slotted spiral stirrup reinforcement wall blocks; each friction damper comprises an upper support and a lower support. The frictional energy dissipation self-centering shear wall structure with the easily restored bottom is capable of effectively eliminating the plastic deformation of the concrete shear wall and simplifying the self-centering shear wall restoring method, and the engineering structure restoring cost and difficulty are greatly lowered after an earthquake.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Cone with torque transmitting members for continuous variable transmissions
A cone to which one or several torque transmitting member(s) are attached as to form at least one torque transmitting arc on the surface of the cone. The torque transmitting member(s) will be used for torque transmission between at least one rotational energy conveying device and the cone. The torque transmitting member(s) are attached in a manner such that significant circumferential sliding that occurs between the torque transmitting surface(s) of the torque transmitting member(s) and the torque transmitting surface(s) of the rotational energy conveying device(s) when the pitch diameter of the torque transmitting member(s) is changed can be eliminated, such that wear and frictional energy losses are significantly reduced, and positive engagement devices, such as teeth, can be used for torque transmission between the torque transmitting member(s) and the rotational energy conveying device(s). The cone with torque transmitting member(s) can be used to construct various Continuous Variable Transmissions that have a long life, low frictional energy losses, and can be made non-friction dependent.
Owner:TAY ARMIN SEBASTIAN
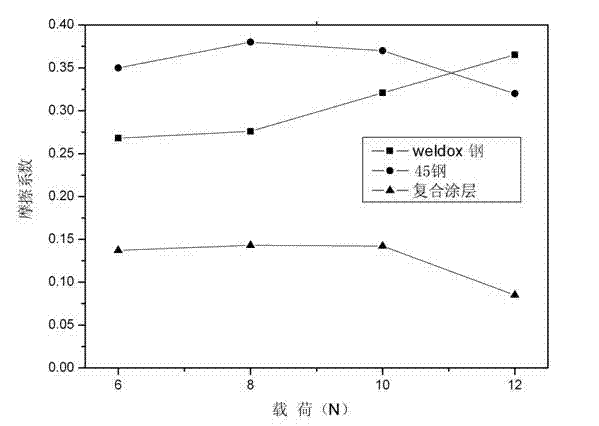
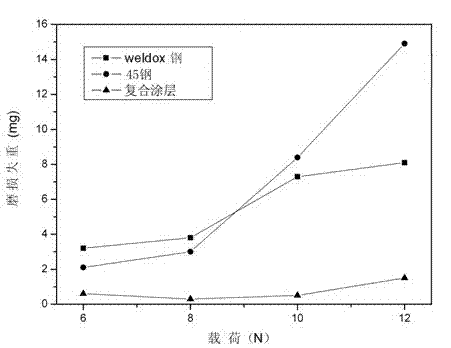
Wear-resistant and antifriction composite coating for aluminum alloy component surfaces and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105624670AImprove microstructureReduce coefficient of frictionMetallic material coating processesAdhesiveWear resistance
The invention relates to a wear-resistant and antifriction composite coating for aluminum alloy component surfaces. The coating is composed of, by weight, 13-15% of tungsten carbide powder, 18-20% of titanium diboride powder, 2.0-4.0% of cerium oxide powder, 3.0-5.0% of nickel-coated molybdenum disulfide powder and the balance nickel-base alloy powder, wherein the components are blended through adhesives and then are arranged on the aluminum alloy component surfaces in a laser cladding mode for forming the coating; in the nickel-coated molybdenum disulfide powder, the coating ratio of nickel is 71-73%; nickel-base alloy is composed of, by weight, 0.75-0.85% of C, 15-16% of Cr, 3.5-4.5% of Si, 3.0-4.0% of B, 14.5-15.5% of Fe and the balance Ni. The coating is high in wear resistance and low in friction coefficient and solves the friction and wear problems of aluminum alloy used for friction members of mechanical equipment at high loads or impact loads, the service life is prolonged, and the friction energy consumption is lowered.
Owner:中国人民解放军理工大学野战工程学院
Method and apparatus for monitoring thermal load of vehicle clutch
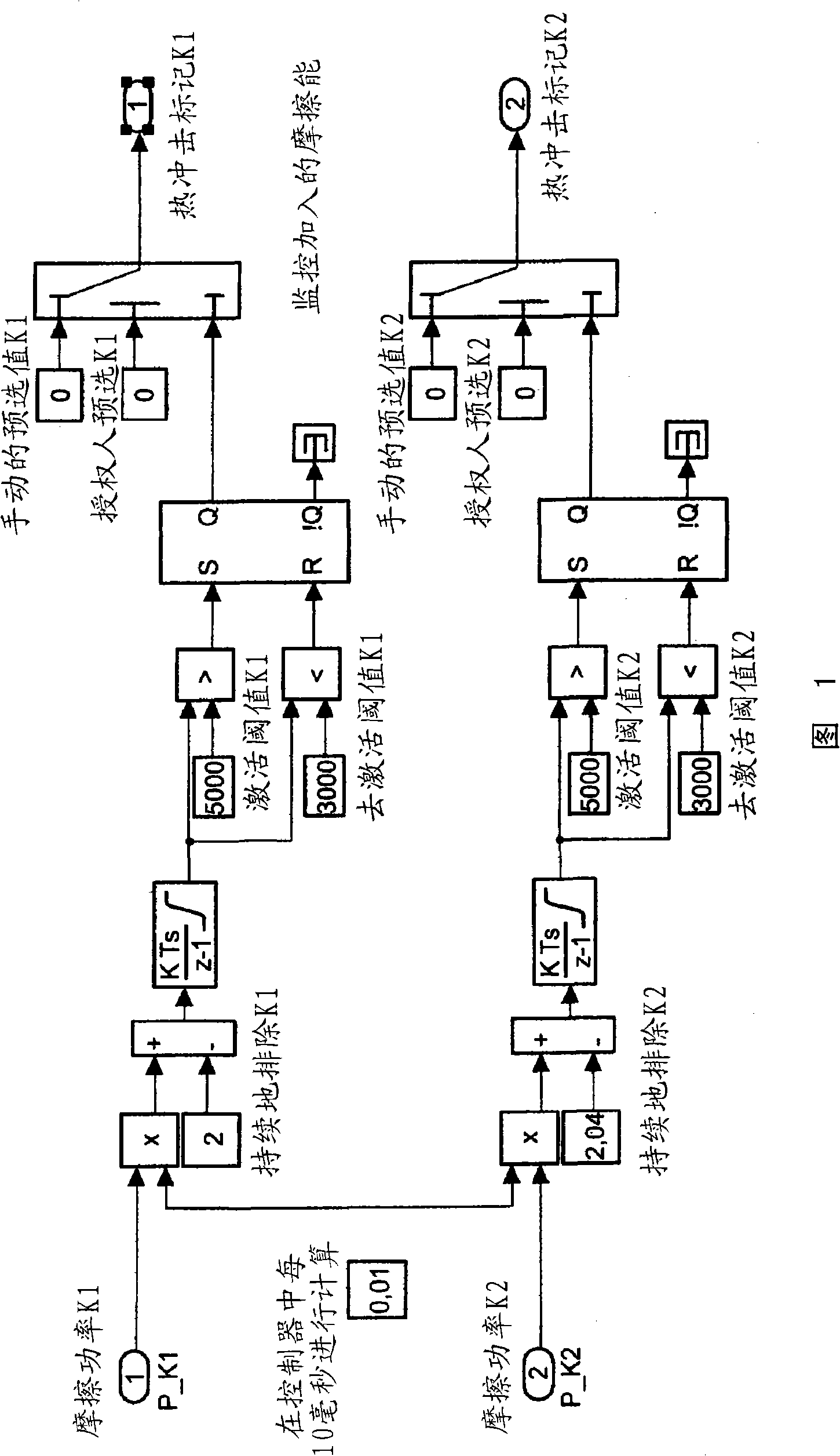
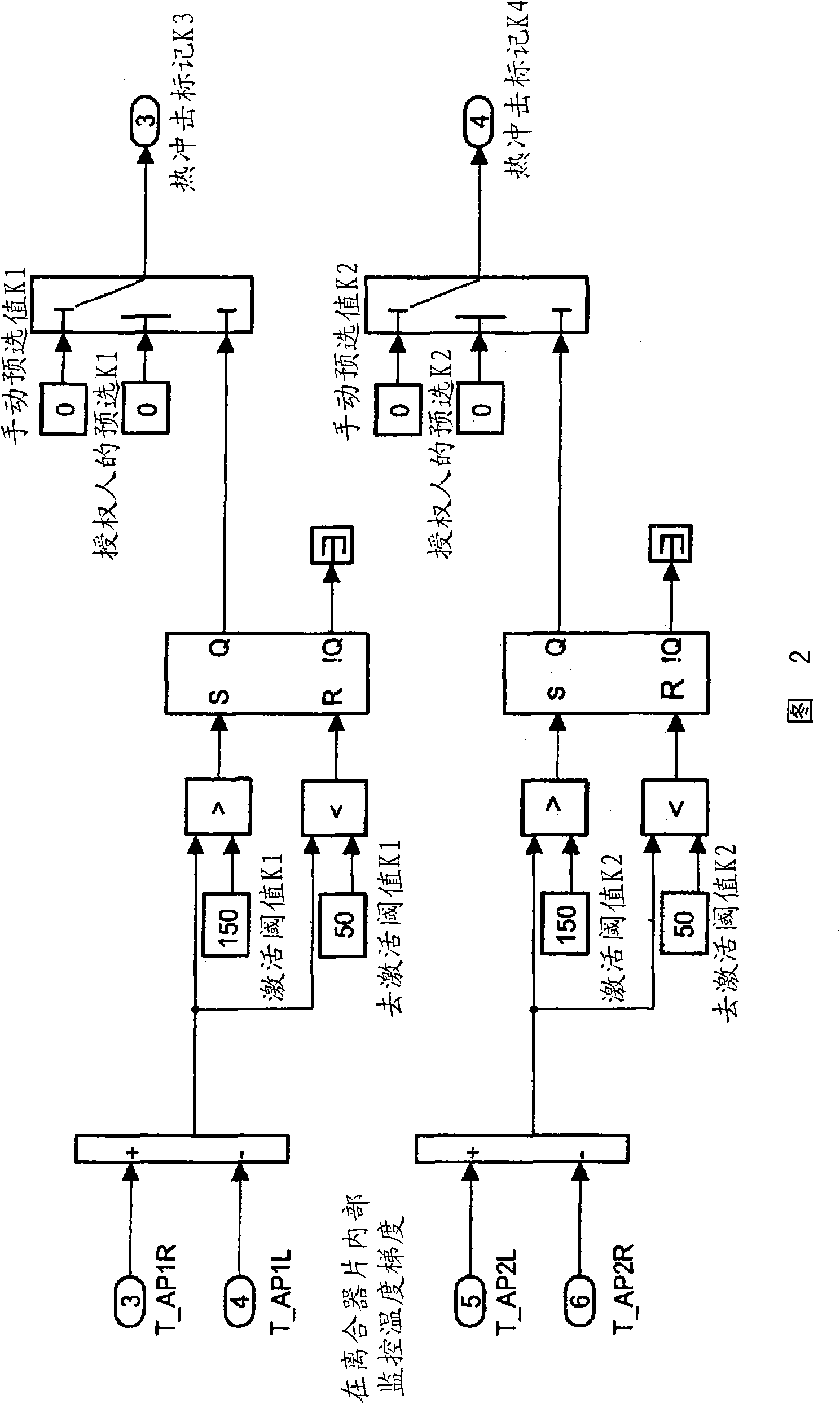
The invention discloses a method for monitoring a thermal load of a clutch a car, specifically for avoiding a thermal shock of the clutch, preferably a double clutch of double clutch transmission, wherein comprising calculating and / or determining a thermal load of the clutch. A controller is provided for controlling the clutch. Therefore, the shortage is overcame to confirm and / or calculate the speed and / or the torque of an engine and / or the rotation speed of a transmission input shaft, and thereby determining the friction power of the clutch; the friction power is integrated over a certain time interval. When the integrated friction power is currently matched and reaches the determined frictional energy threshold value, that is, during danger of a thermal overloading of the clutch, the clutch is at least partially disconnected.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Load size measuring apparatus and method
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
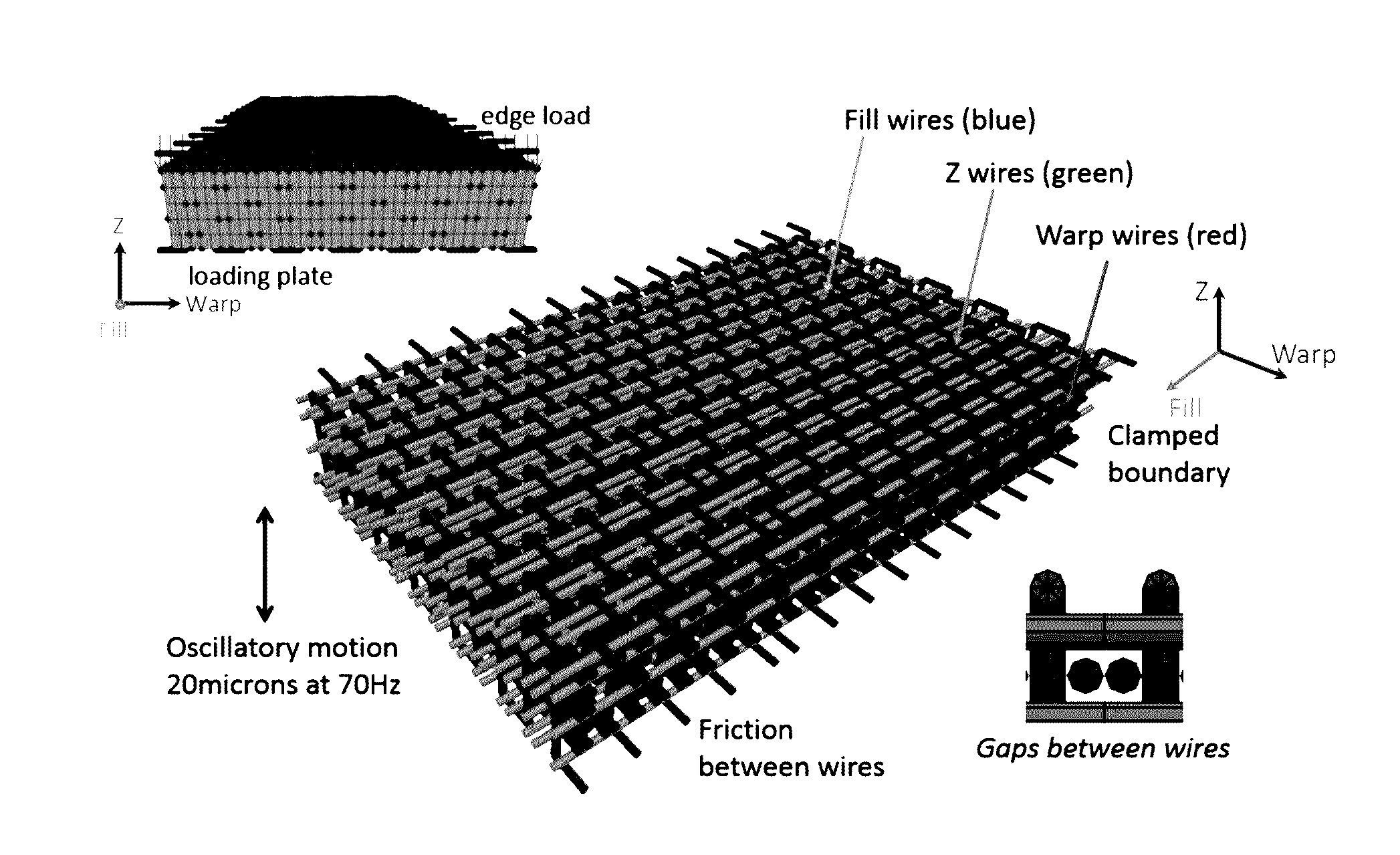
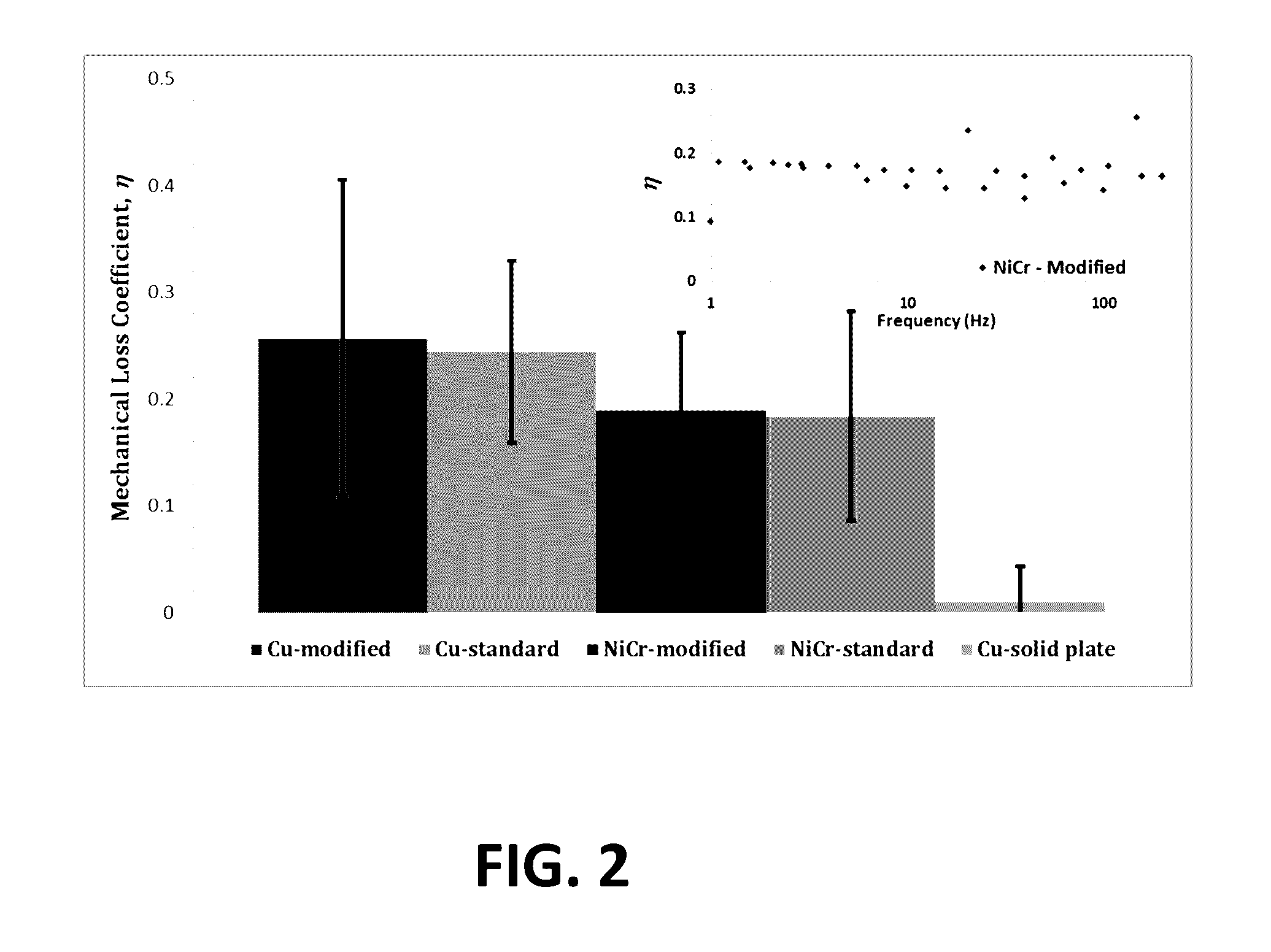
Three dimensional lattice weaves with tailored damping properties
The present invention is directed to three dimensional weaves composed of wires or yarns that offer the potential for damping not achievable with solid materials, including high temperature damping. Three damping mechanisms have been identified: (1) Internal material damping, (2) Frictional energy dissipation (Coulomb damping), and (3) inertial damping (tuned mass damping). These three damping mechanisms can be optimized by modifying the wire material chemistries (metals, ceramics, polymers, etc.), wire sizes, wire shapes, wire coatings, wire bonding, and wire architecture (by removing certain wires). These have the effect of modifying the lattice and wire stiffnesses, masses, coefficients of friction, and internal material damping. Different materials can be used at different locations in the woven lattice. These design variables can also be modified to tailor mechanical stiffness and strength of the lattice, in addition to damping.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Coating composition with functions of friction resistance and wear resistance
The invention relates to a coating composition with functions of friction resistance and wear resistance, which is a powdered mixture composed of titanium carbide powder, nickel-coated calcium fluoride powder, nickel-coated graphite powder, yttrium oxide powder and nickel-based alloy powder, the weight ratio of each component is that: 23-25, 13-15, 8-10, 1, 50-55, wherein the mass part of each element in the nickel-based alloy are: 0.8% of C, 15.5 of Cr, 4% of Si, 3.5% of B, 15% of Fe and 61.2% of Ni. The coating composition with functions of friction resistance and wear resistance can be deposited on a frictional pair surface of a member through a plasma spraying mode to form a self lubricating coating, and is capable of greatly reducing the frictional coefficient, raising the wear resistance performance of the frictional pair of the member, solving the problems of friction resistance and wear resistance of a stress mechanical device with dry friction and high contact which is exposed in the adverse environment, and reducing the frictional energy consumption of the machinery.
Owner:ENG COLLEGE OF ENG CORPS PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cones, configurations, and adjusters for friction and non-friction dependent continuous variable transmissions
Owner:TAY ARMIN SEBASTIAN
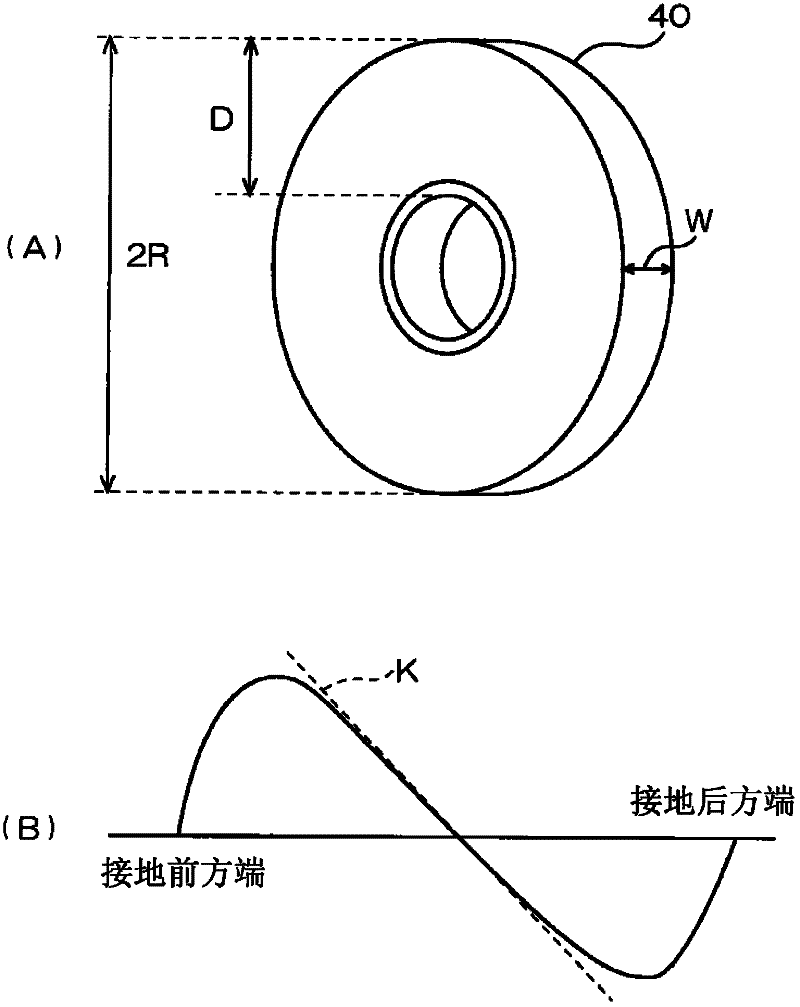
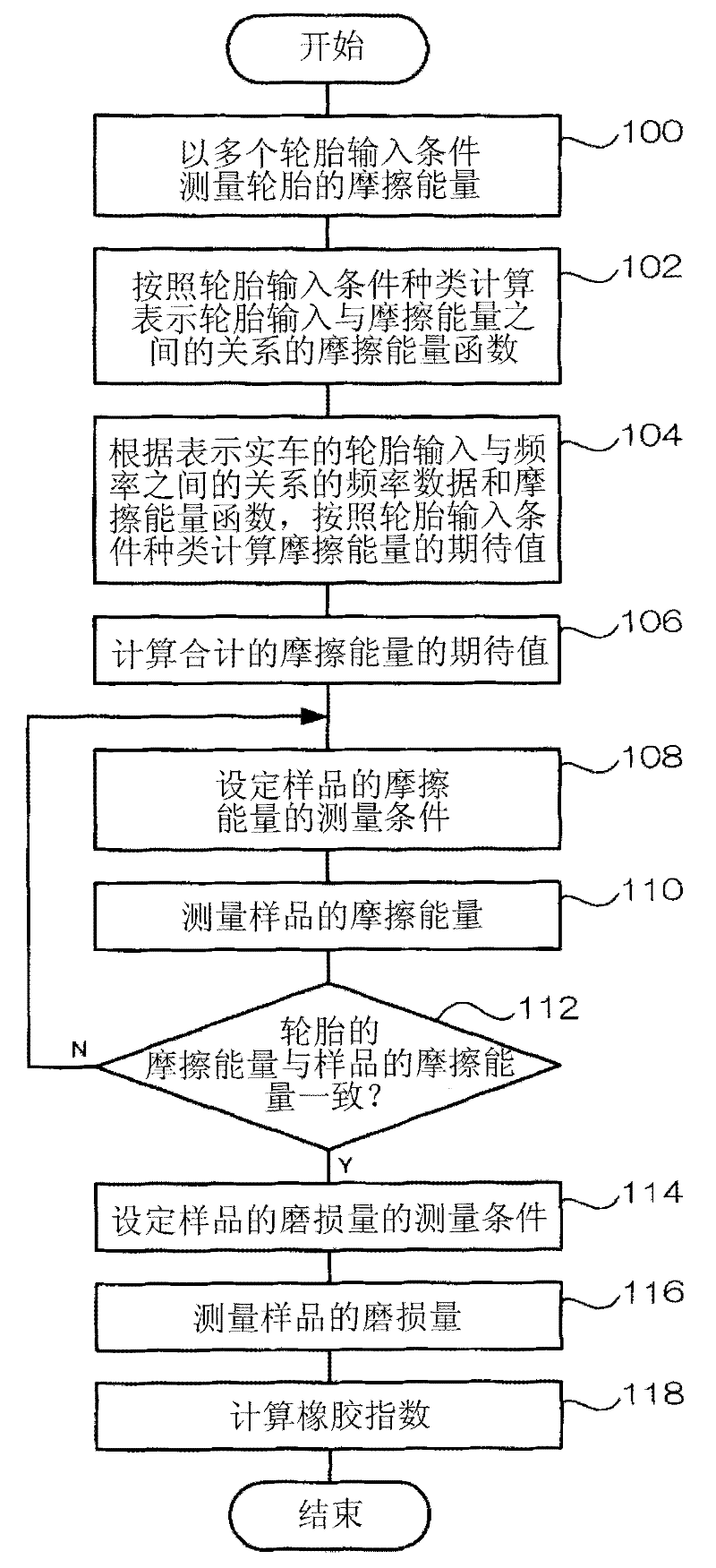
Tire rubber index calculating method, device, and program
ActiveCN102483372AHigh precision measurementHigh precision computingUsing mechanical meansTyre measurementsProcess engineeringFrictional energy
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Damping mechanism
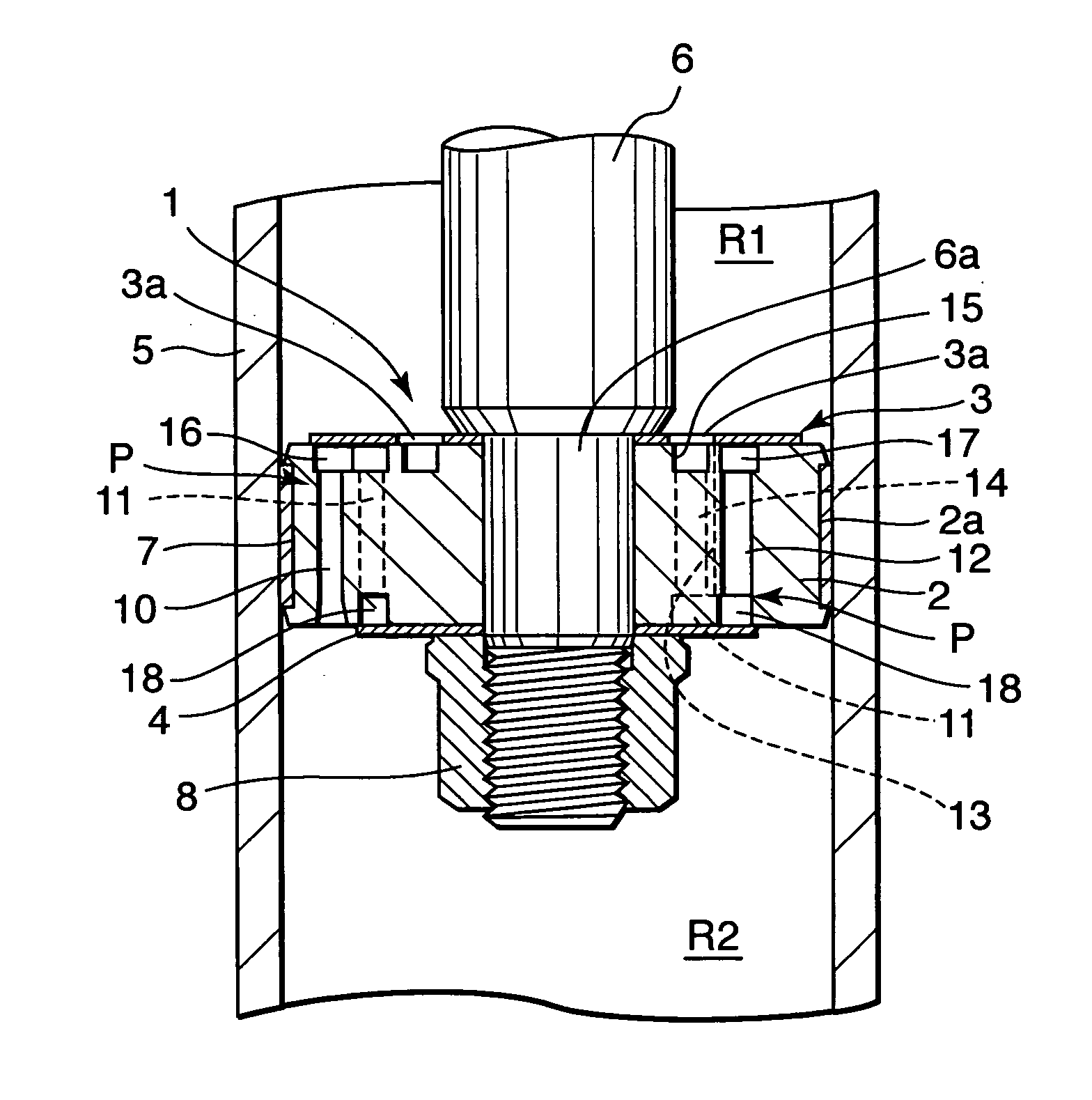
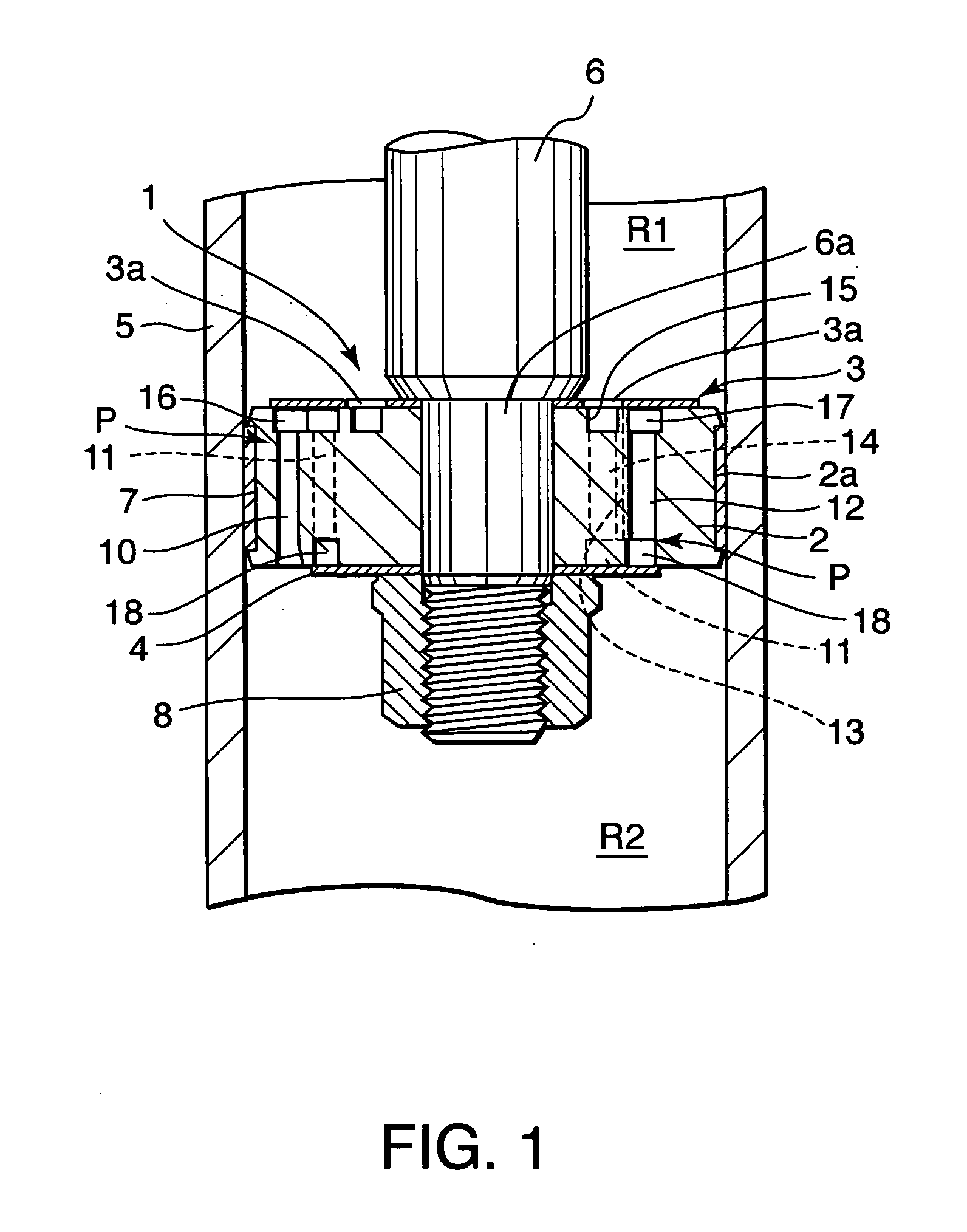
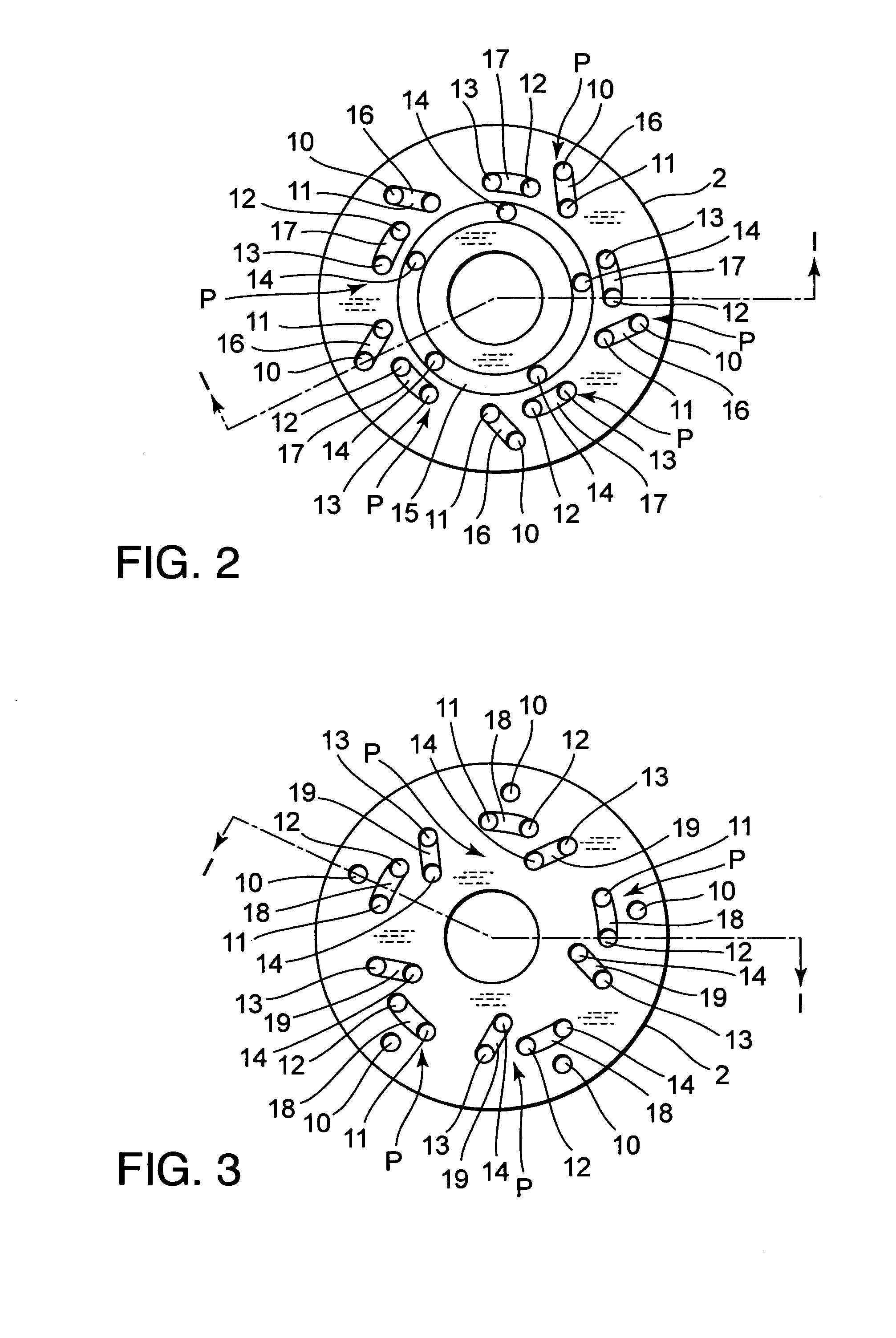
ActiveUS20100294604A1Preferable characteristicEasy constructionSpringsLiquid based dampersPath lengthEngineering
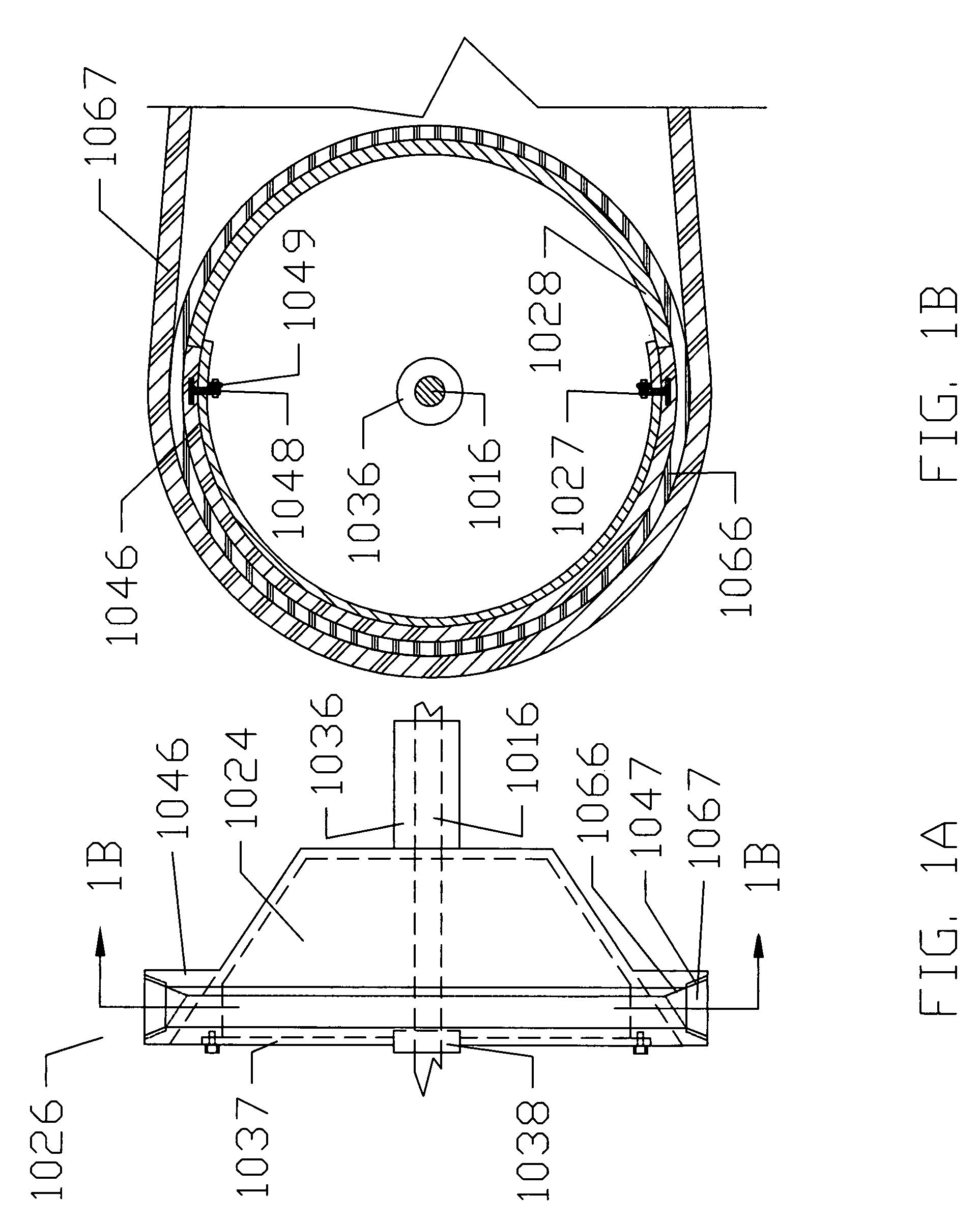
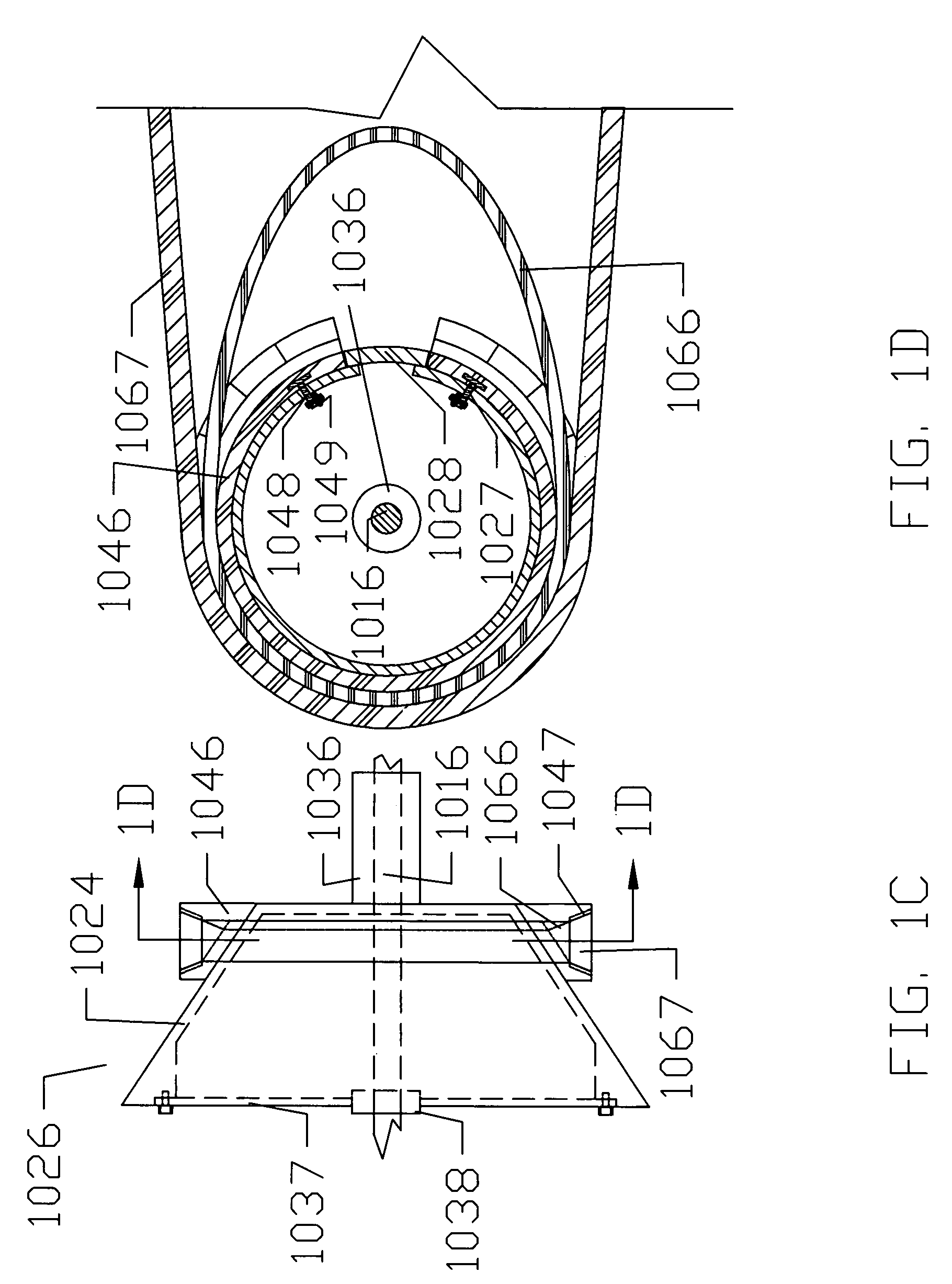
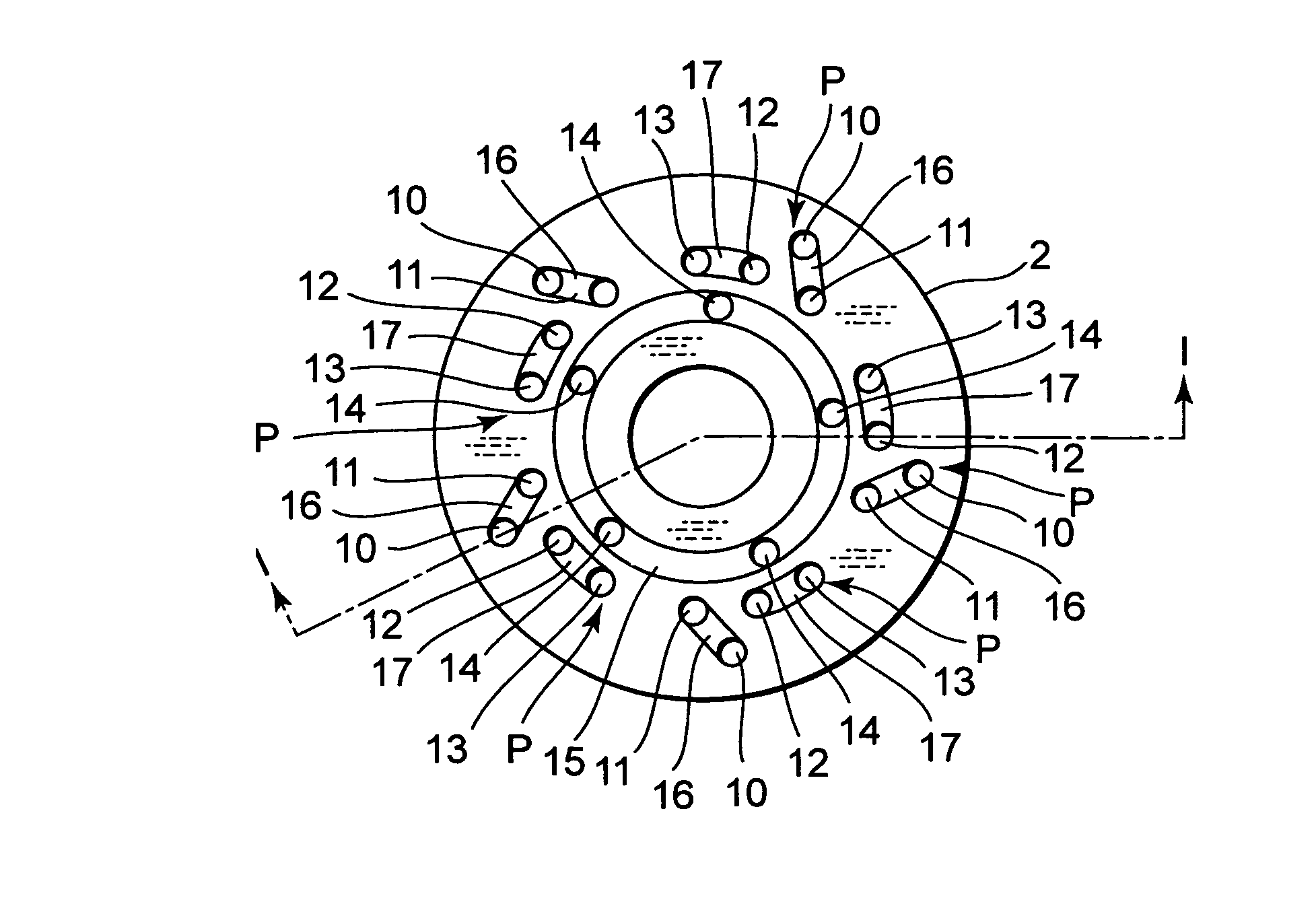
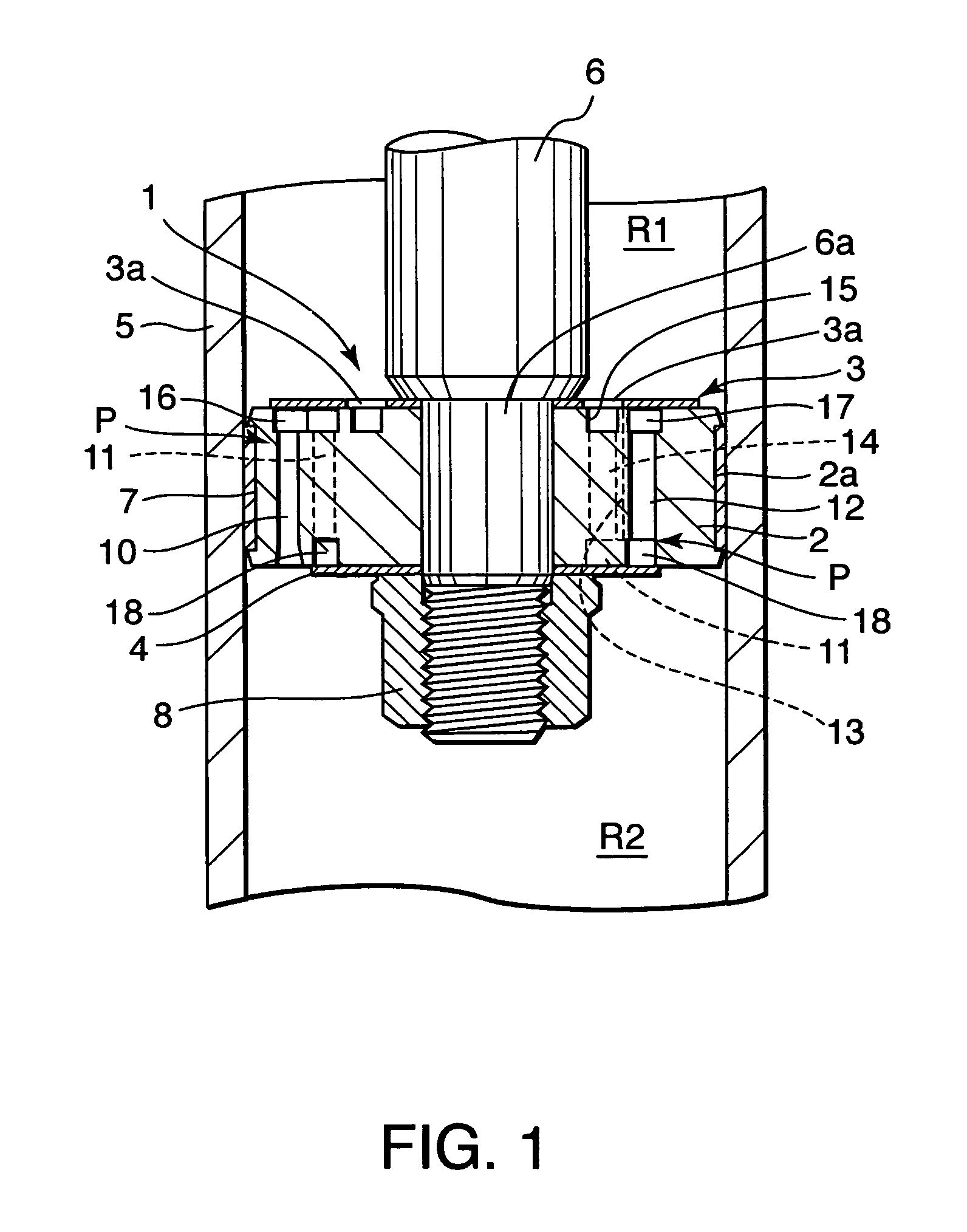
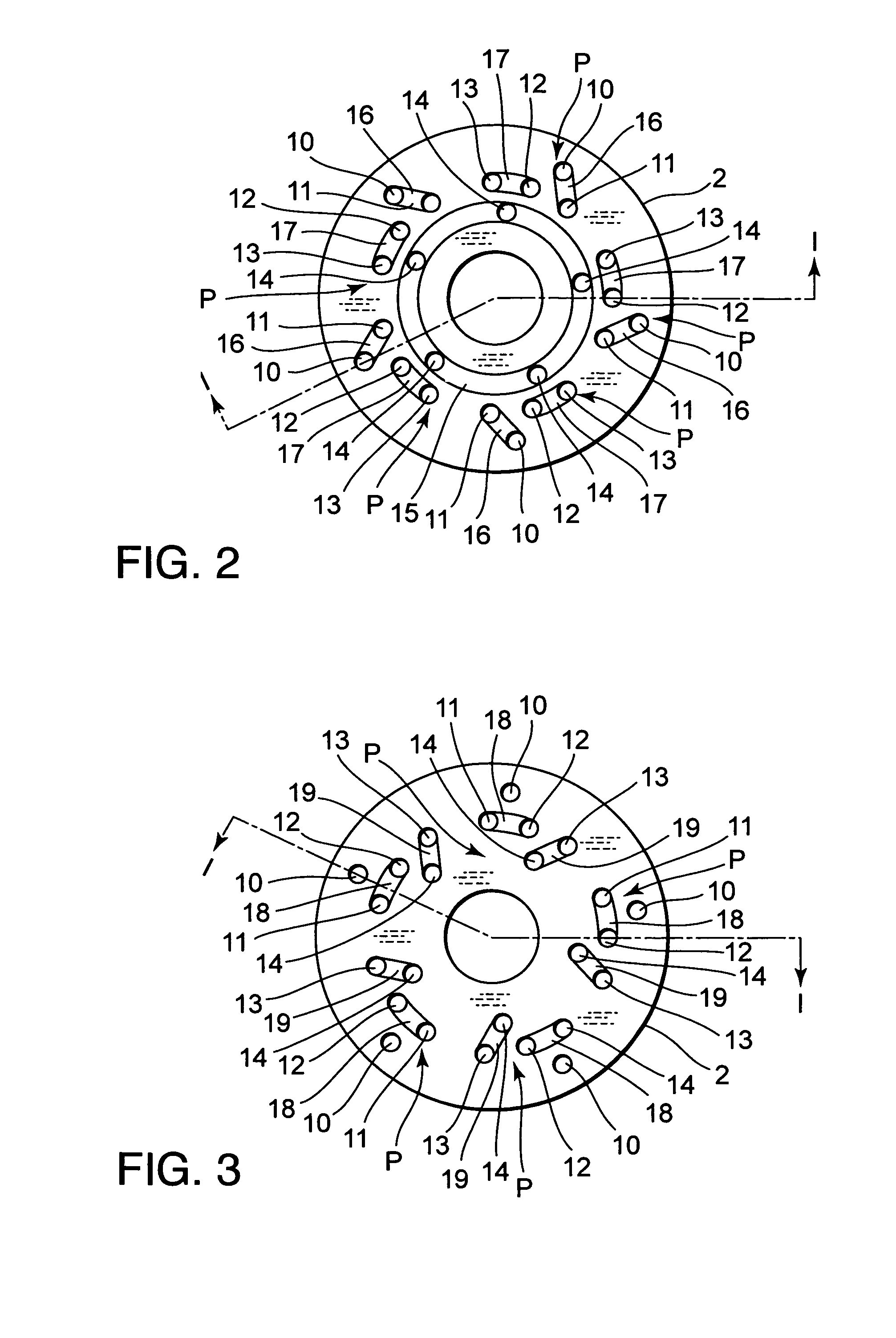
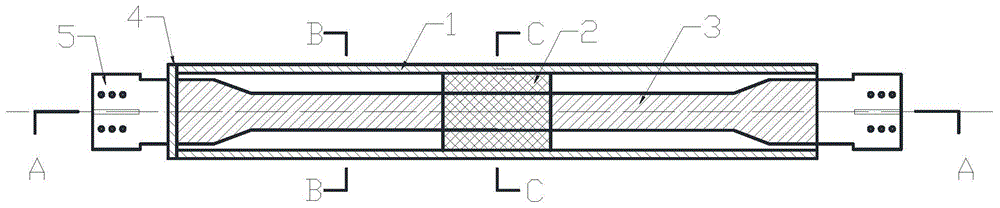
A damping mechanism (1) that generates a damping force in response to a liquid flow between a first liquid chamber (R1) and a second liquid chamber (R2) comprises a partitioning member (2) separating the first liquid chamber (R1) and the second liquid chamber (R2) and a flow passage (P) formed in the partitioning member (2) to connect the first liquid chamber (R1) and the second liquid chamber (R2). The flow passage (P) comprises an odd number of through-holes (10-14) greater than three which penetrate the partitioning member (2) and are connected in series. A large amount of frictional energy loss due to a long path length occurs in the flow passage (P) and causes the damping mechanism (1) to generate a sufficient damping force.
Owner:KYB CORP
Cones, configurations, and adjusters for friction and non-friction dependent continuous variable transmissions
Owner:TAY ARMIN SEBASTIAN
Damping mechanism
InactiveUS8016088B2Preferable characteristicEasy constructionSpringsShock absorbersPath lengthEngineering
Owner:KYB CORP
Anti-biofouling friction power generation coating material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111040495AGood triboelectric performanceEfficient collectionAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesBiofoulingElectric current flow
The invention provides an anti-biofouling friction power generation coating material and a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of friction power generation coatings. A coating prepared from the anti-biofouling friction power generation coating material has good triboelectrification performance, friction energy in the environment can be effectively collected, the current generated in the friction testing process is 0.1-30 microamperes, and the voltage is 1-200 V; and the coating also has good anti-biofouling performance, has a protection effect on a base material, and has a biofouling coverage area of 3-10%. The coating material disclosed by the invention has friction power generation and antifouling properties; according to the friction power generation coating, mechanical energy can be converted into electric energy, so that adhesion of organisms on the surface of the coating is inhibited, the antifouling effect can be improved, the obtainedcoating can be cured at normal temperature, has good environmental adaptability and constructability and can be applied onto the surfaces of various materials, and the application range of the friction power generation coating is greatly expanded.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
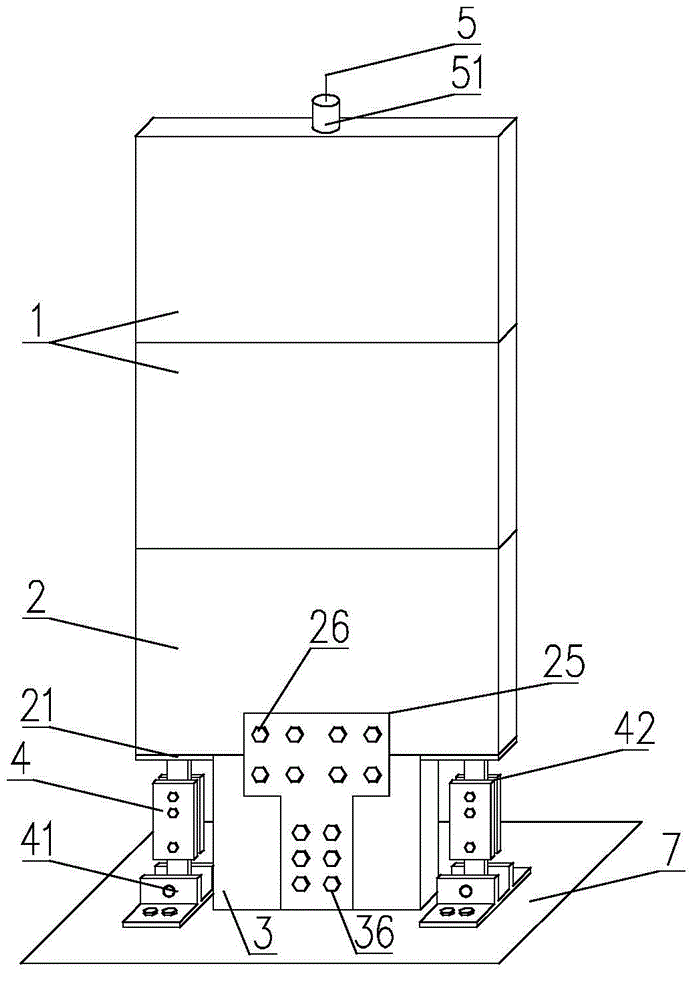
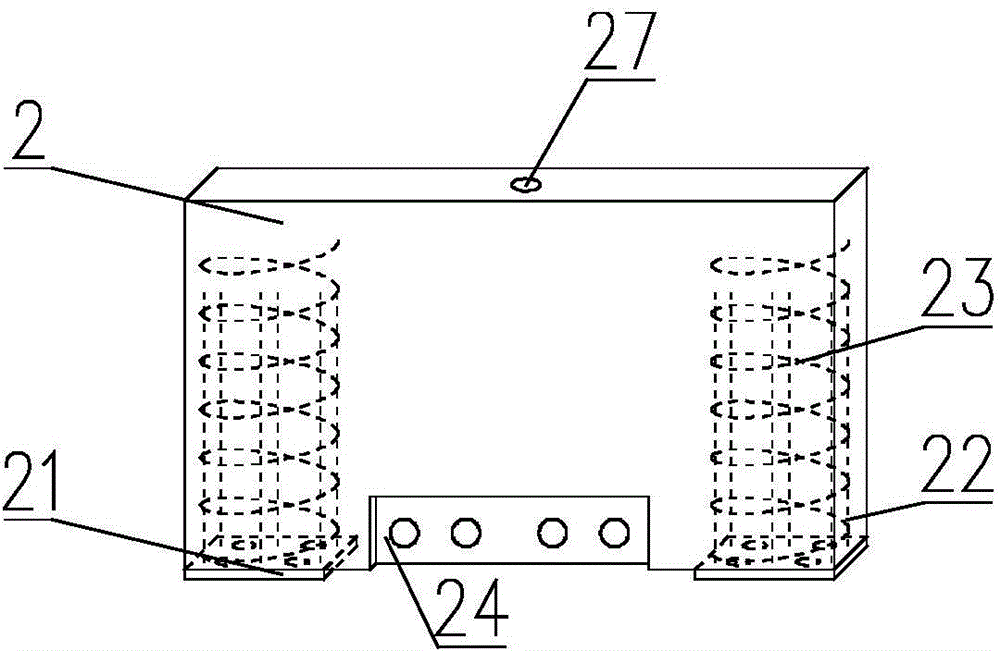
Frictional energy dissipation type buckling-restrained brace
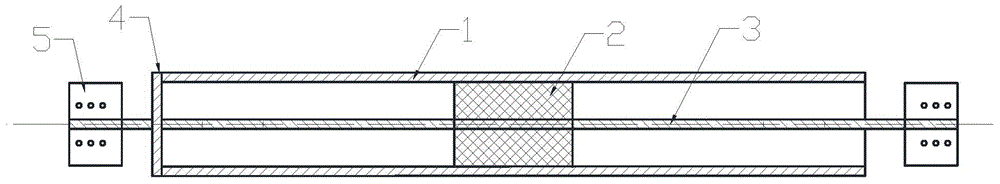
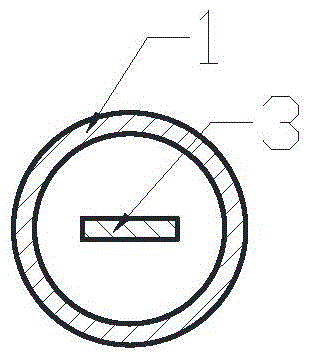
The invention relates to a frictional energy dissipation type buckling-restrained brace, which belongs to the field of seismic control of building structures. The frictional energy dissipation type buckling-restrained brace comprises a restraining member (1), a piston (2) and an energy dissipation core (3). The piston (2) is arranged at the middle of the energy dissipation core (3), the restraining member (1) sleeves the surface of the piston (2), the restraining member (1) is fixed at one end of the energy dissipation core (3) through an end plate (4), and connecting steel plates (5) are arranged at both ends of the energy dissipation core (3). Since the invention arranges the piston in the conventional buckling-restrained brace, the frictional energy dissipation mechanism is introduced. When inter-story displacement takes place in a structure, the energy dissipation core can be plastically deformed to dissipate energy, at the same time, the energy dissipation core and the restraining member shift relatively, the piston fixed on the energy dissipation core and the restraining member move relatively, energy is dissipated by the friction between the piston and the restraining member, and thereby the energy-dissipating capability of the buckling-restrained brace is effectively enhanced.
Owner:路安交科(北京)监测科技有限公司
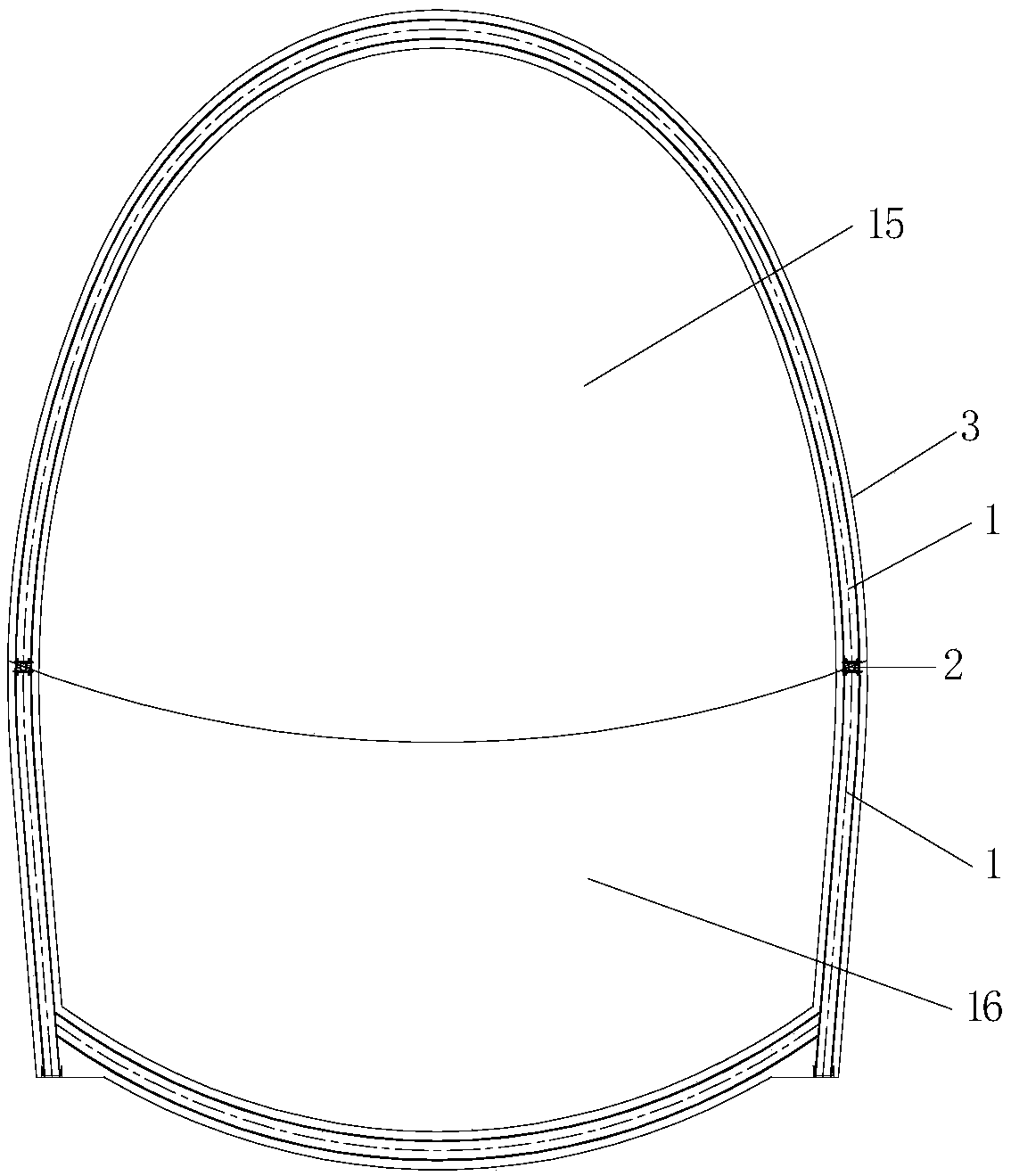
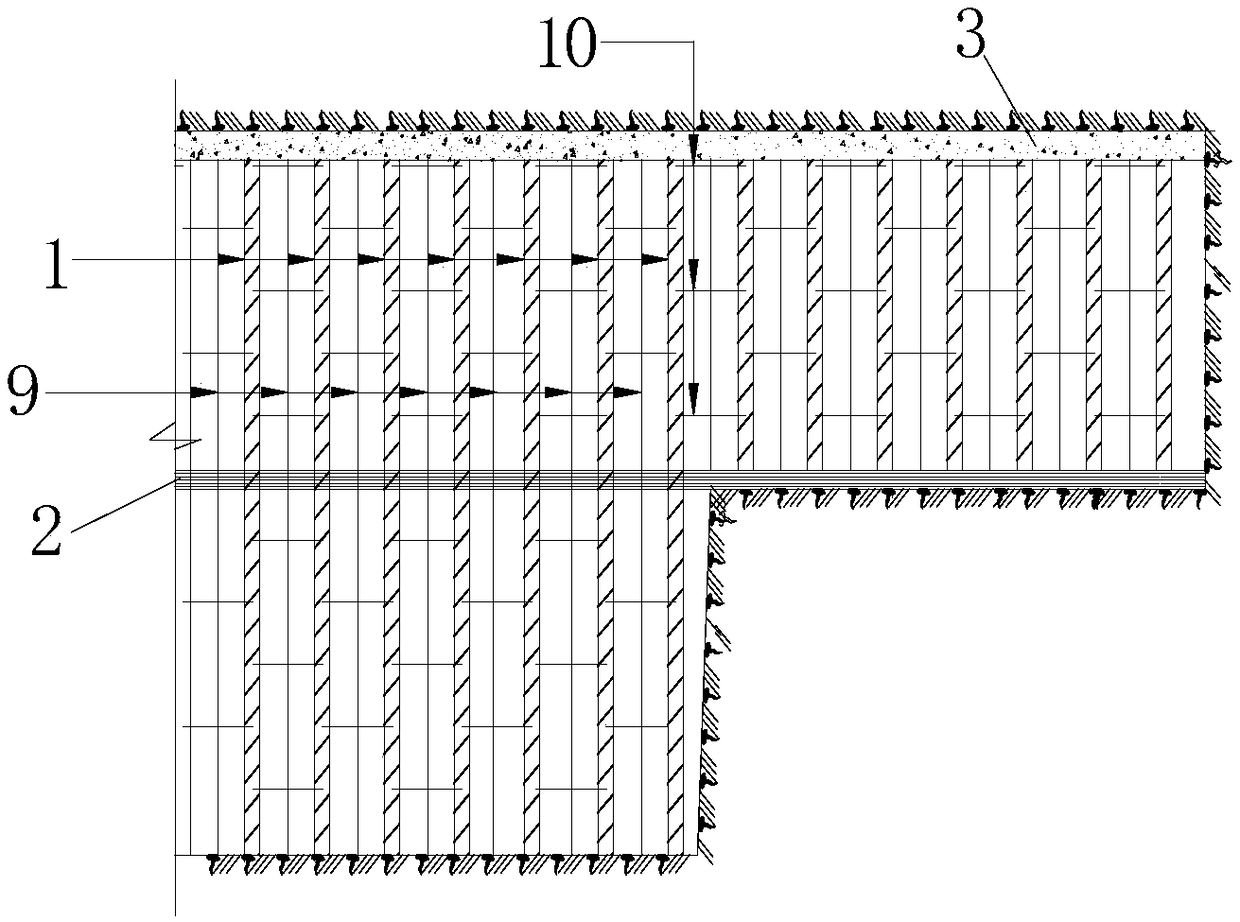
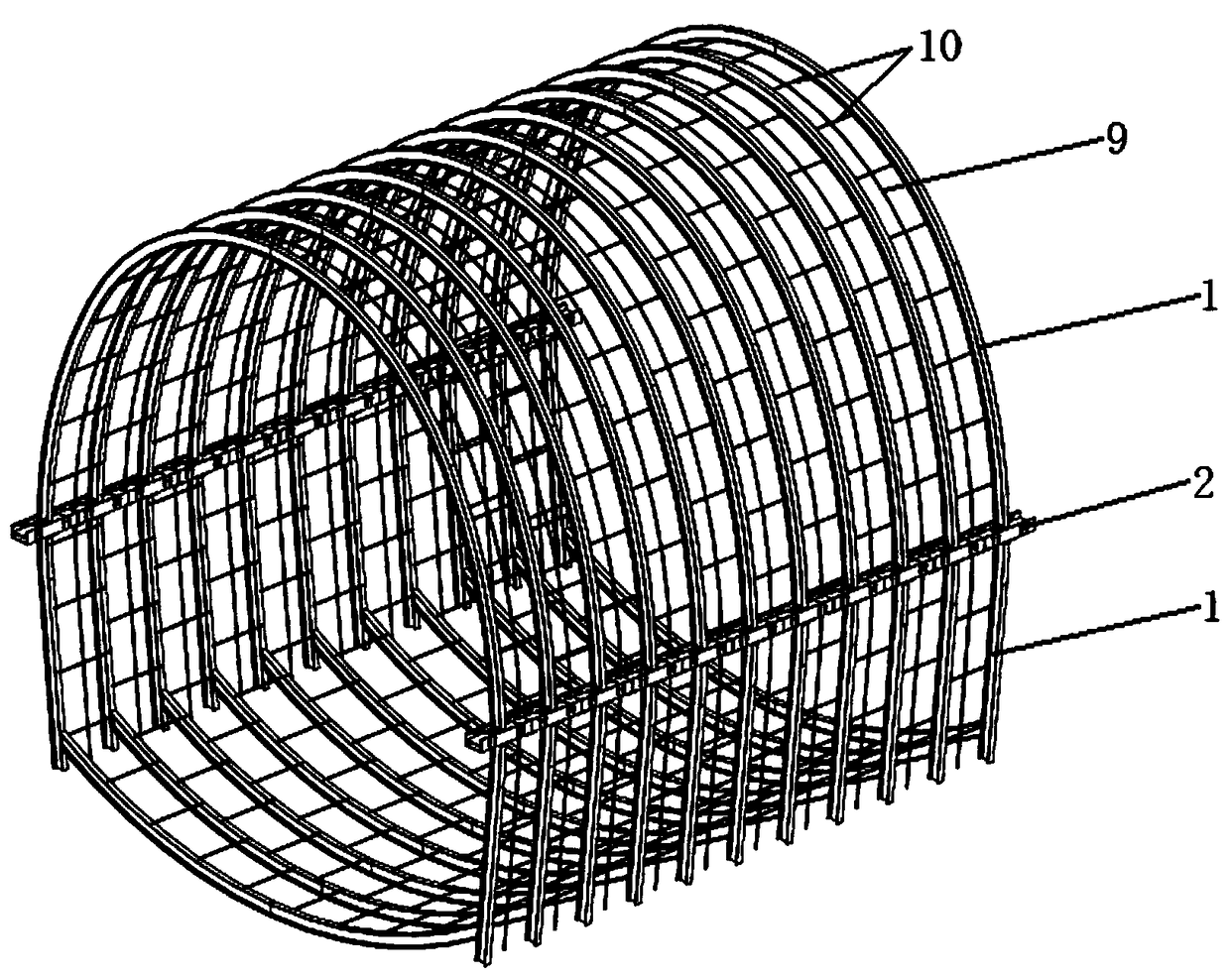
Frictional-energy-consumption-longitudinal-beam-based hybrid spraying-steel frame overall avoidance changing initial-supporting structure and construction method thereof
ActiveCN108979677AImprove coordination and deformation abilityAvoid breaking awayUnderground chambersTunnel liningShotcreteFriction effect
The invention discloses a frictional-energy-consumption-longitudinal-beam-based hybrid spraying-steel frame overall avoidance changing initial-supporting structure and a construction method thereof. The structure comprises a steel frame, a frictional energy consumption longitudinal beam, a sprayed concrete, reinforcing meshes, longitudinal threaded steel bars, and circumferential threaded steel bars. The steel frame is formed by bold bending of profile steels. The frictional energy consumption longitudinal beam mainly includes an upper support member and a lower support member that are made ofchannel steels; and energy is consumed by the friction effect between flanges of the upper support member and the lower support member. And the longitudinal threaded steel bars and the circumferential threaded steel bars are added in the sprayed concrete between two steel frame units. While coordinated deformation of the initial support of the tunnel and the surrounding rock, the frictional energy consumption longitudinal beam enables the initial support to have the certain pressing-resistant and shearing-resistant performances; with the longitudinal steel bars and circumferential steel barsand longitudinal arrangement of the frictional energy consumption longitudinal beam, the joint deformation capability of the tunnel steel frame and the initial supporting structure formed by the sprayed concrete between the steel frames is strengthened, so that the structure damage caused by deformation incompatibility of the steel frame and the sprayed concrete is avoided and thus a coupling effect of the harness with softness is realized.
Owner:KUNMING SURVEY DESIGN & RES INST OF CREEC
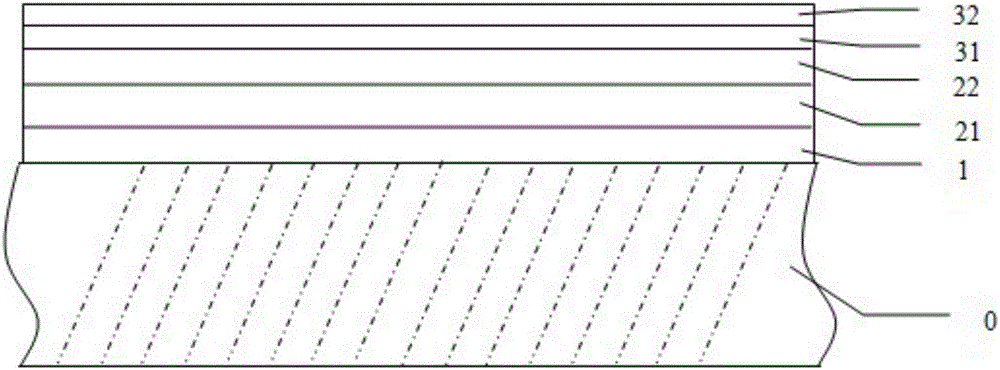
Anti-erosion and friction-resistant film for fan blades of aeto-turbofan engine and preparation method of anti-erosion and friction-resistant film
InactiveCN106321494AImprove friction resistanceImprove adhesionPump componentsEngine fuctionsHardnessEngineering
The invention discloses an anti-erosion and friction-resistant film for fan blades of an aeto-turbofan engine and a preparation method of the anti-erosion and friction-resistant film. The anti-erosion and friction-resistant film for the fan blades of the aeto-turbofan engine comprises a blade base (0), a transition layer (1), a friction-resistant film layer and an anti-erosion film layer from inside to outside sequentially, and is deposited from inside to outside by starting from the blade base sequentially. The anti-erosion and friction-resistant film has excellent anti-erosion and friction-resistant capacity and high surface hardness, and the surface hardness is higher than 3,200 HV. A chromium nitride layer located on the outermost layer has high hardness and low friction coefficient, and the anti-erosion performance of a film surface is improved; adopted nitride layers have excellent corrosion resistance, so that the service life of each fan blade of the aeto-turbofan engine is prolonged.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF AERONAUTICS
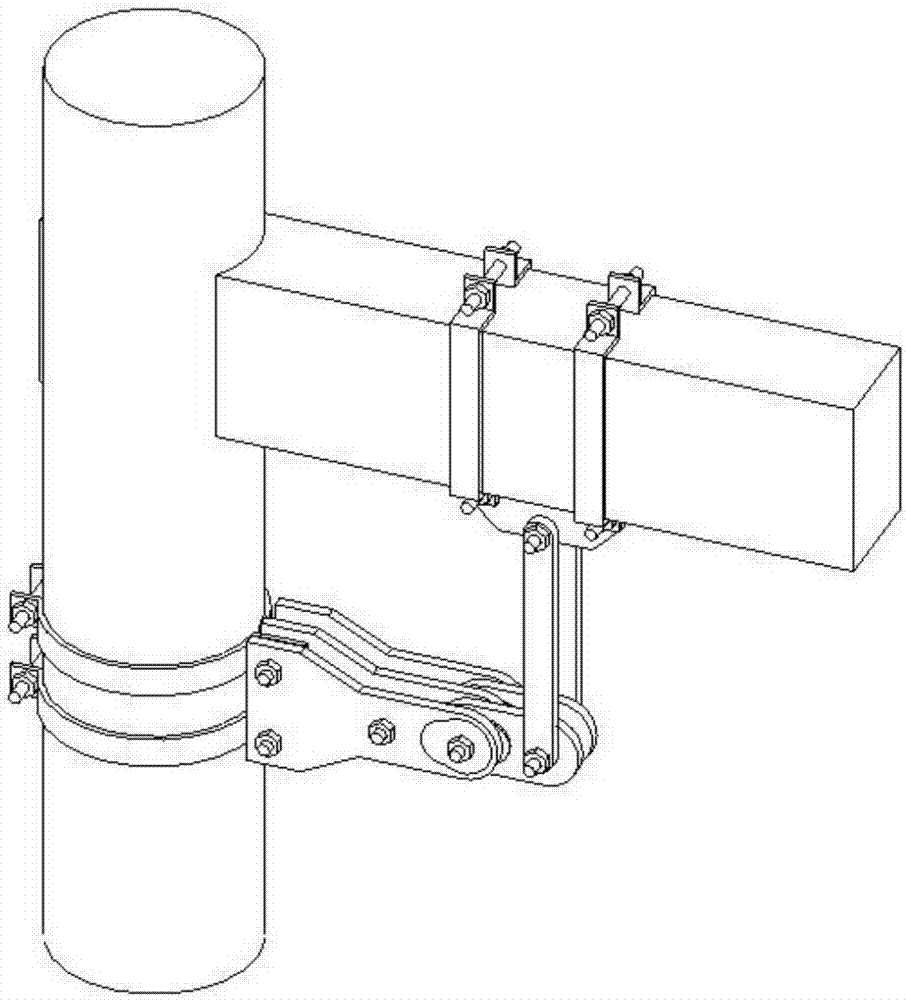
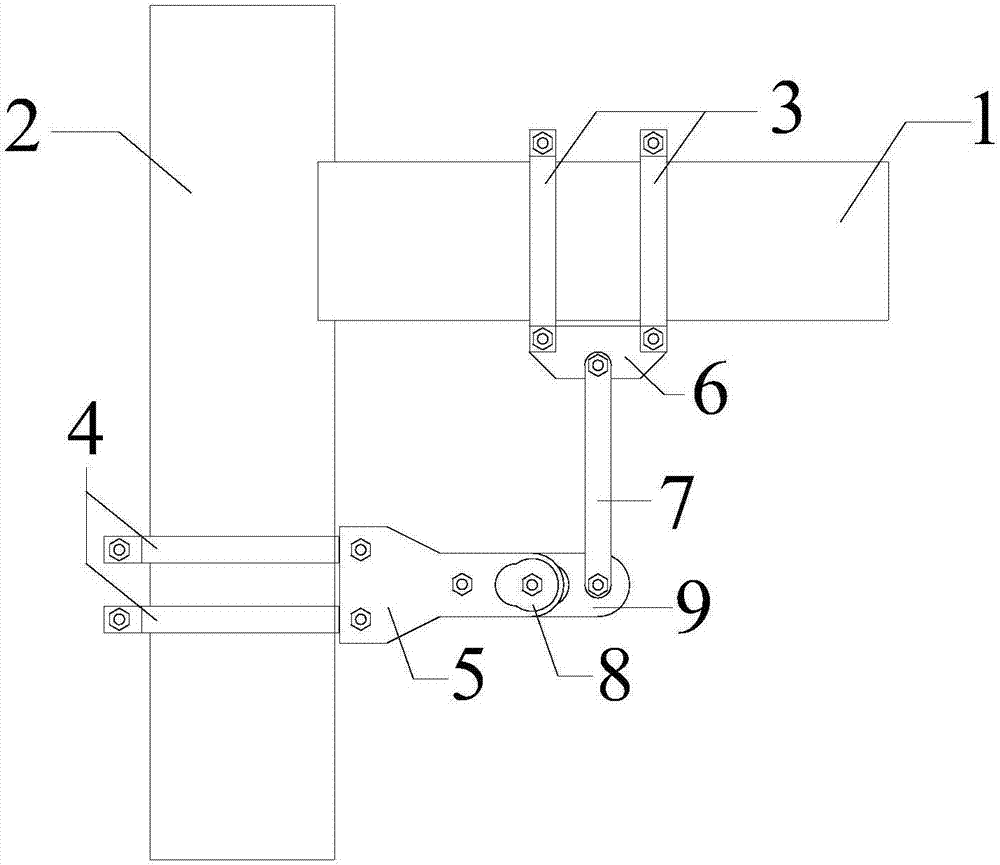
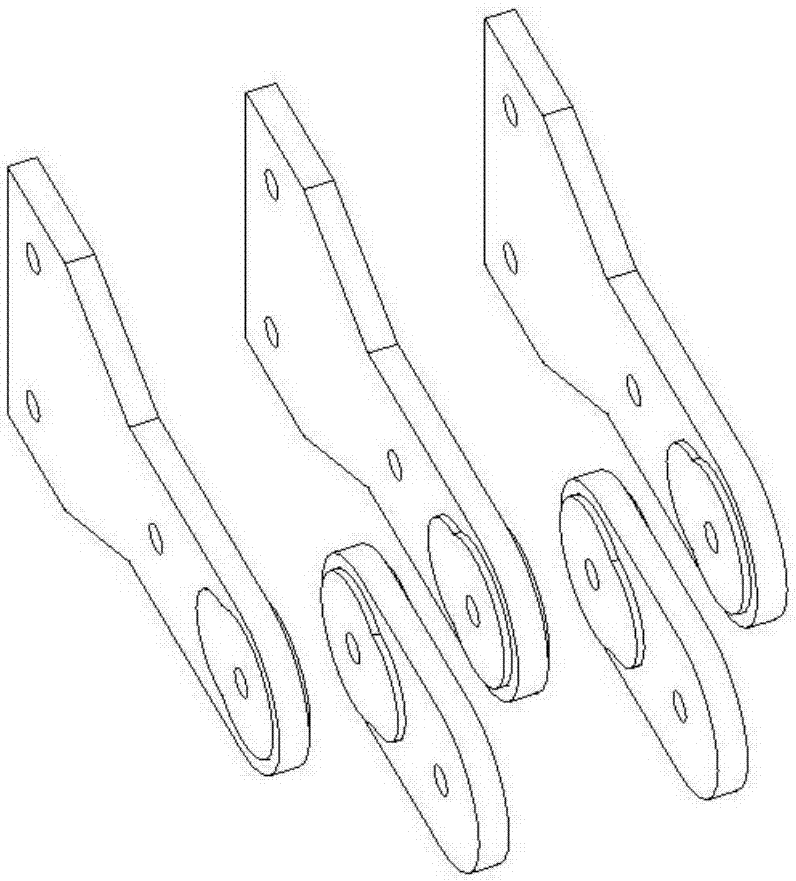
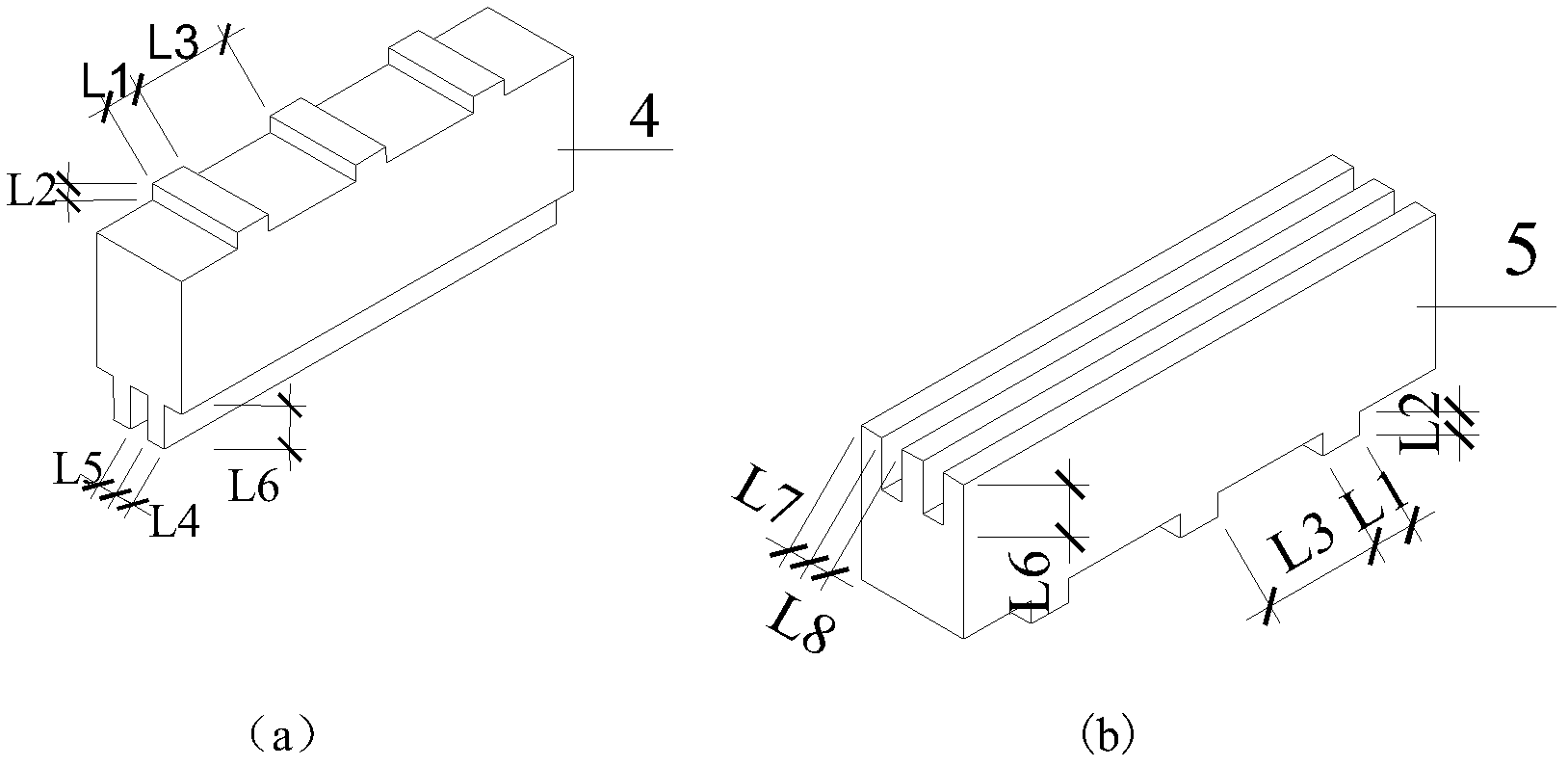
Semi-rigid node friction energy dissipation device
ActiveCN107190877AUniform and stable frictionOvercome limitationsBuilding repairsProtective buildings/sheltersMortise and tenonStructural engineering
The invention discloses a semi-rigid node friction energy dissipation device which comprises a wood column and a wood beam connected with the wood column through a mortise and tenon node. A friction energy dissipation device body is connected between the wood column and the wood beam which are at the mortise and tenon node; the friction energy dissipation device body is connected to the wood column and the wood beam through a beam-end connecting piece and a column-end connecting piece correspondingly; the friction energy dissipation device body comprises a beam-end connecting rod connected to the beam-end connecting piece and a plurality of column-end connecting rods connected to the column-end connecting piece; the multiple column-end connecting rods are connected with the beam-end connecting rod through middle connecting pieces provided with friction sheets in the middles; the friction energy dissipation device body provides stiffness before beam-column nodes conduct displacement and provides frictional energy dissipation after the beam-column nodes conduct displacement. The semi-rigid node friction energy dissipation device relieves the limitation of a friction energy dissipation device in the aspect of friction force control and has the advantages of being high in durability, flexible in use and easy to mount.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Multi-ribbed composite wallboard internally provided with special-shaped filling building blocks
InactiveCN102155060AImproved frictional energy dissipationIncrease the areaWallsShock proofingFilling materialsArchitectural engineering
The invention provides a multi-ribbed composite wallboard internally provided with special-shaped filling building blocks; the multi-ribbed composite wallboard comprises rib beams (1), rib columns (2), the special-shaped filling building blocks (3) and a flexible filling material (6), wherein the rib beams (1) and the rib columns (2) form sashes; each sash is provided with a special-shaped filling building block (3) which comprises an upper special-shaped filling building block (4) and a lower special-shaped filling building block (5); the upper special-shaped filling building block (4) and the lower special-shaped filling building block (5) are meshed at a contact surface of the upper special-shaped filling building block (4) and a lower special-shaped filling building block (5); the upper special-shaped filling building block (4) and a lower special-shaped filling building block (5) horizontally and relatively slide under the action of external force; and the flexible filling material (6) is filled in gaps among the special-shaped filling building blocks (3) and the rib columns (2). The multi-ribbed composite wallboard not only can increase the frictional energy consumption effect of multi-ribbed composite walls and reduce the seismic response of the multi-ribbed structure, but also can avoid the condition that excessive building blocks are filled in the sashes, avoid the occurrence of external plane dropping of the sashes and ensures the whole service behavior of the building blocks in the sashes.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Fighting type top
ActiveCN104841135AImprove controllabilityImprove durabilityTopsToy gearsElectric machineryControl theory
The invention discloses a fighting type top. The fighting type top is characterized by comprising a top body, a motor and rolling wheels, wherein a rotating shaft of the motor and the rolling wheels are connected through a clutch transmission set; when the motor rotates in the first direction, the rolling wheels synchronously rotate in the opposite directions, so that rotation of the fighting type top is achieved; when the motor rotates in the second direction, the rolling wheels synchronously rotate in the same direction, so that movement of the fighting type top is achieved. Movement of the electric top can be achieved through control over rotation of the motor in the first direction or the second direction, a player can autonomously select to attack or avoid the opposite side in a fighting game, the interaction between the electric top and the player is effectively improved, and the technical level of the player can also be reflected; friction between the rolling wheels and the contact surface is rolling friction, the energy consumption of friction is lower, and therefore the persistence of rotation of the top is improved; in addition, due to the contact between the two rolling wheels and the contact surface, the stability of the top can be higher, the top can be more flexible, and the top cannot easily be inclined in a collision fighting process in the fighting game, and the fighting winning percentage is increased.
Owner:ALPHA GRP CO LTD +2
Cones, configurations, and adjusters for friction and non-friction dependent continuous variable transmissions
Cones or cone assemblies with one or two oppositely positioned torque transmitting devices, such as torque transmitting arcs of constant pitch (formed by torque transmitting members) or teeth. The torque transmitting devices will be used for torque transmission between at least one means for coupling, such as transmission belt or chain, and a cone or cone assembly. The cones or cone assemblies can be used to construct CVT's for which significant circumferential sliding between the torque transmitting surfaces of the torque transmitting devices and the torque transmitting surfaces of the means for coupling engaged to them due to change in pitch diameter can be eliminated, as to reduce wear and frictional energy loses typical in similar devices of prior art and allow the usage of positive engagement devices, such as teeth, in coupling the torque transmitting devices with their means for coupling. CVT's that consist of at least one cone or one cone assembly of this invention that is coupled by a means for coupling to at least one means for conveying rotational energy, such as a pulley, a sprocket, a cone assembly of this invention, or a cone of this invention. Adjuster systems that can increase the performance of the CVT's of this invention and other CVT's that suffer from either or both transition flexing and a limited duration at which the transmission ratio can be changed, so that efficient non-friction dependent CVT's and efficient friction dependent CVT's that do not suffer from transition flexing and / or a limited duration at which the transmission ratio can be changed can be constructed.
Owner:TAY ARMIN SEBASTIAN
Seat belt arrangement
A seat-belt arrangement including an energy-absorbing force limiter. A first component, for example in the form of a retractor reel spool is movable relative to a second component, for example the frame-work of the retractor. The spool carries with it elements presenting friction faces which co-operate with further elements carried by the frame. A stack of Piezo-electric elements apply a compressional force driving together the elements having the friction faces to provide a controlled frictional energy-absorbing effect.
Owner:AUTOLIV DEV AB
Method of recognizing conveyor belt wear condition
ActiveUS10221019B2Accurate identificationHigh correlationConveyorsControl devices for conveyorsSurface roughnessProcess engineering
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Friction energy recovery vibration absorber with inner and outer double-layer vibration absorption structure
ActiveCN112065919AAvoid collisionNo secondary vibration hazardBatteries circuit arrangementsNon-rotating vibration suppressionElectrical conductorBi layer
The invention provides a friction energy recovery vibration absorber with an inner and outer double-layer vibration absorption structure. The friction energy recovery vibration absorber comprises theinner-layer vibration absorption structure, the outer-layer vibration absorption structure, an inner-layer damping adjustment and energy conversion device and an outer-layer damping adjustment and energy conversion device, wherein the inner-layer vibration absorption structure comprises a mass block (5), an inner-layer guide column (7), an inner-layer vibration absorption spring (12) and an inner-layer insulating shell (14), the inner-layer damping adjustment and energy conversion device comprises inner-layer electrode metal (4) and an inner-layer dielectric plate (6), the outer-layer vibration absorption structure comprises an outer-layer guide column (3), an outer-layer vibration absorption spring (13) and an outer-layer insulating shell (17), and the outer-layer damping adjustment and energy conversion device comprises outer layer electrode metal (1) and an outer layer dielectric plate (2). According to the friction energy recovery vibration absorber with the inner and outer double-layer vibration absorption structure, through the contact sliding type conductor-dielectric independent layer friction power generation principle, only contact and friction exist between a dielectricand a metal electrode, collision among materials is avoided, and secondary vibration damage is avoided.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
A method for study that effect of the gradient change of the rigidity of base brace on the friction force
ActiveCN109299580AEasy to operateStrong controllabilityDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsNormal loadStudy methods
The invention discloses a research method for the influence of the base support rigidity gradient change on the friction force. Comprises the following steps: step 1, establishing a molecular dynamicsmodel. The model system consists of a square graphene sheet adsorbed on the tip of a simulated atomic force microscope probe and a monolayer graphene substrate supported by a rigidity gradient. Step2, the effect of the stiffness gradient on the average friction force of graphene. As the stiffness increases, the friction energy consumption decreases. When the stiffness exceeds a certain criticalvalue, the friction force does not decrease any more. Step 3, the influence of stiffness gradient on the normal load. When the bracing stiffness is large, the normal deformation of the substrate is small, the distance between the sheet and the substrate is small, and the Van der Waals force between layers is large. Step 4, the internal mechanism of the influence of the stiffness gradient on the friction force. The friction force is caused by the potential gradient of the interface barrier and the thermal vibration of the atoms with different stiffness, and the boundary barrier caused by the asymmetric deformation of the atoms on both sides of the boundary transition zone and the sudden change of the degree of freedom constraint.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Contactor electromagnetic system
ActiveCN103646824AShort decay timeImprove buffering effectElectromagnetic relay detailsEngineeringEnergy loss
The invention provides a contactor electromagnetic system which comprises a base, a coil, a magnetic yoke, an armature and an elastic buffering piece, wherein the coil, the magnetic yoke and the armature are arranged in the base, the elastic buffering piece is disposed between the coil and the base. A mounting hole is formed on the magnetic yoke and the extending direction of the mounting hole is perpendicular to the axial direction of the coil. The elastic buffering piece is a sheet spring, the middle of the sheet spring is an arc which is inserted in the mounting hole and protrudes towards an impacted part of the base, and the arc top is deformed due to compression of the wall of the mounting hole so as to buffer vibration of the armature and the magnetic yoke when the magnetic yoke and the armature bounce in opposite directions after impacting the base. According to the invention, vibration of the armature and the magnetic yoke can be quickly attenuated and stopped due to large energy loss of the sheet spring in the compression and elastic recovery processes, energy loss generated when the armature and the magnetic yoke impact the base and frictional energy dissipation generated when the two ends of the sheet spring slide in a reciprocating mode on the base or the coil in the compression and elastic recovery processes of the sheet spring.
Owner:DELIXI ELECTRIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com