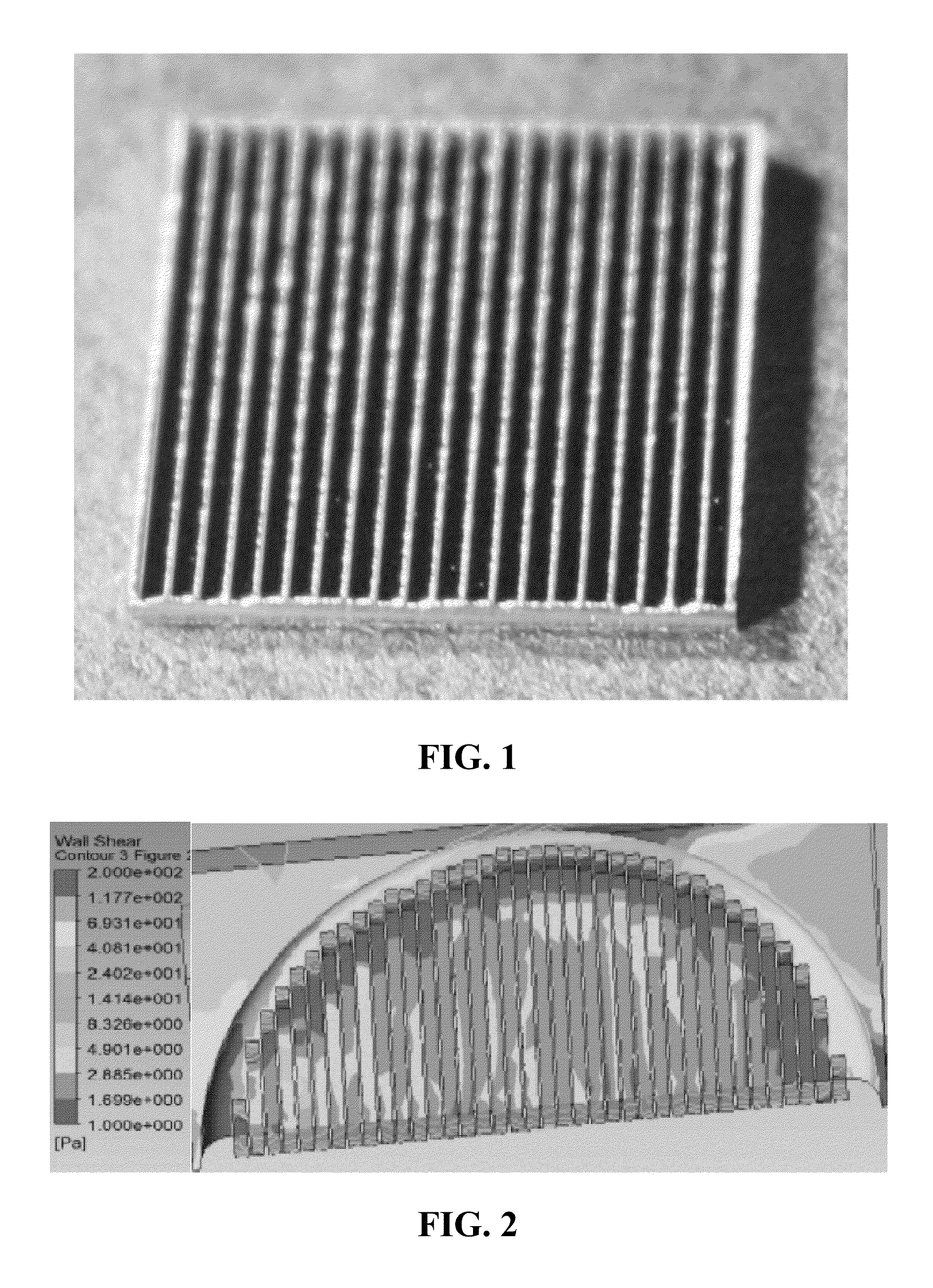
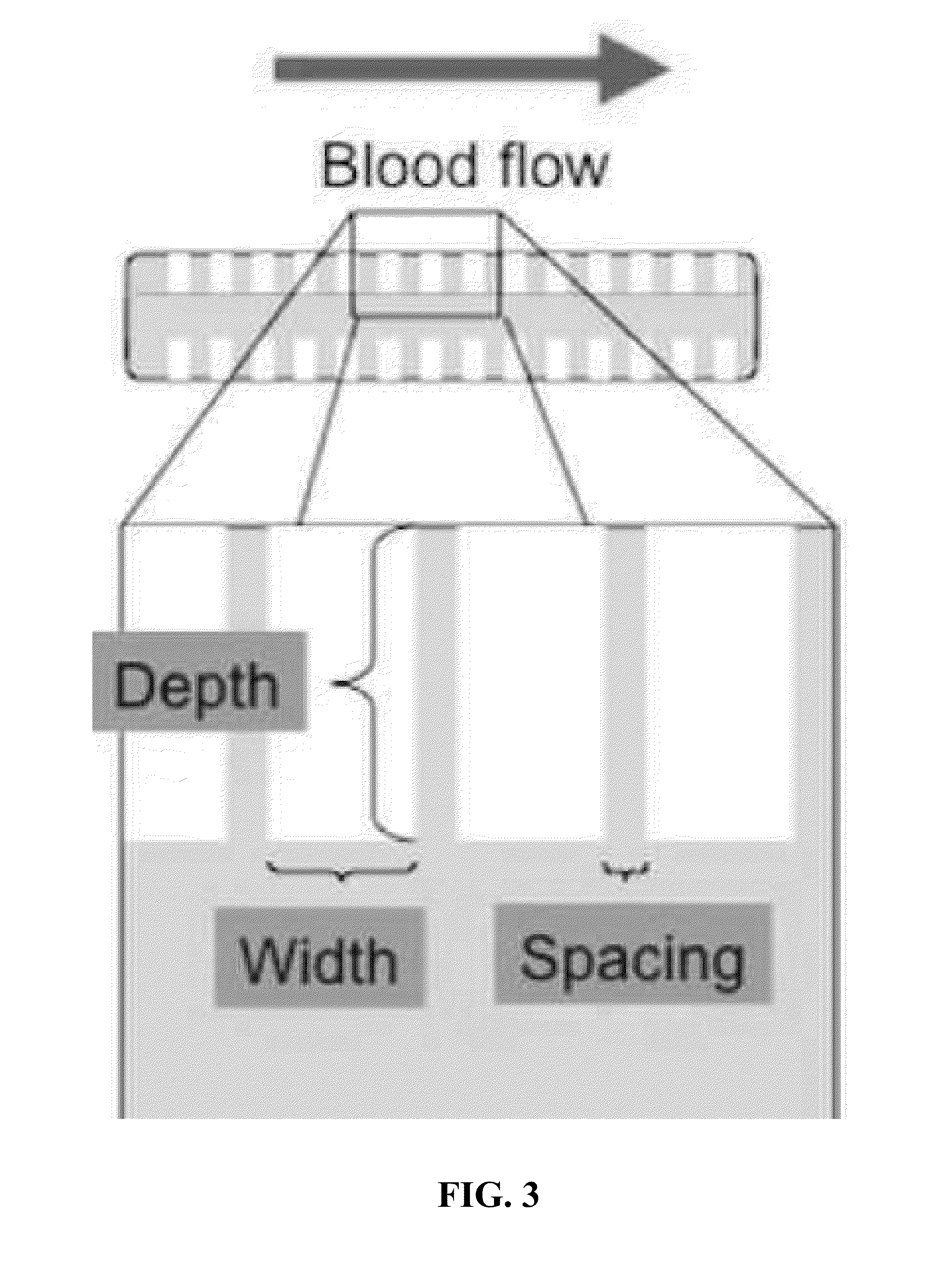
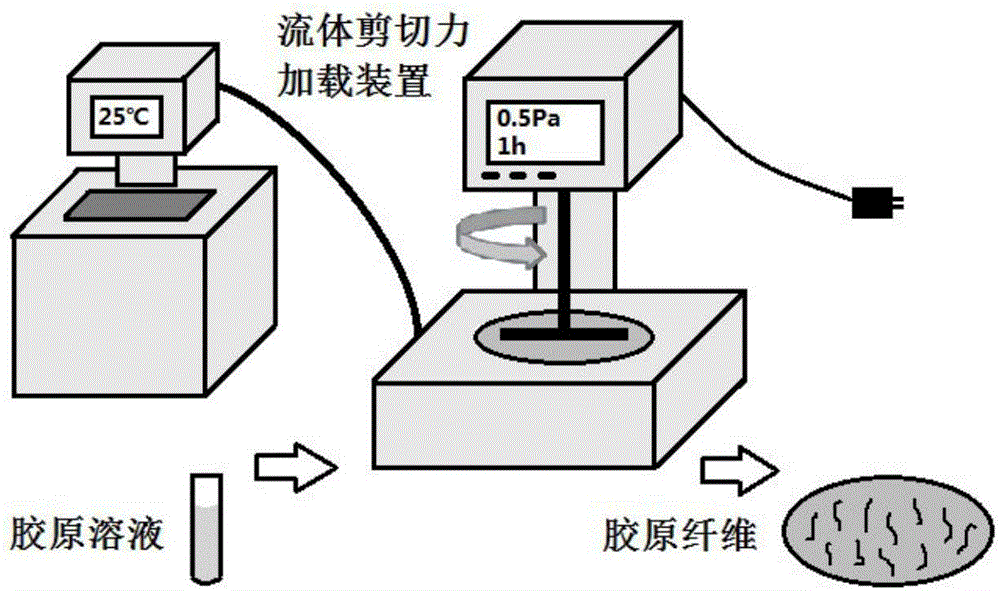
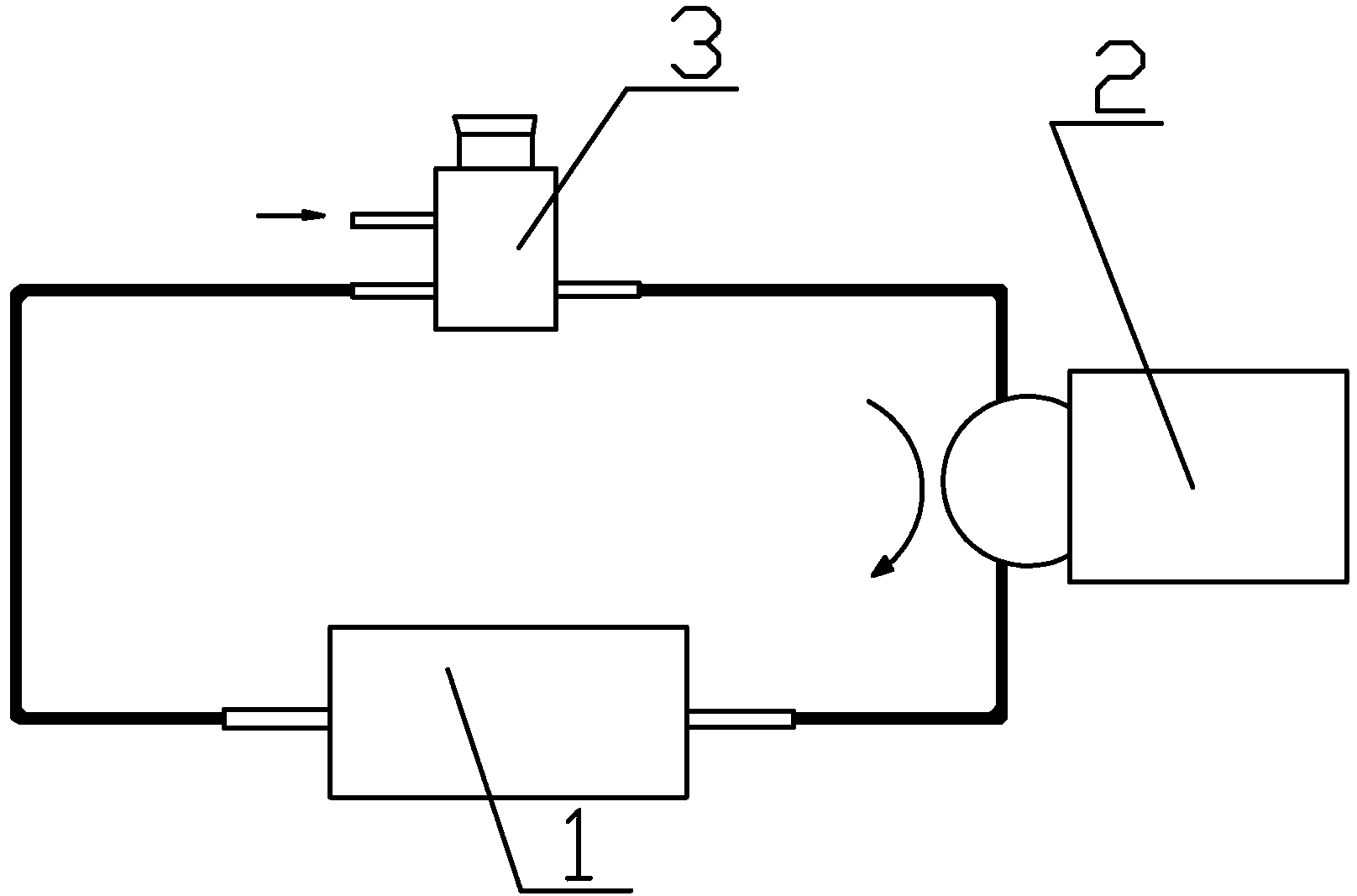
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Fluid shear stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
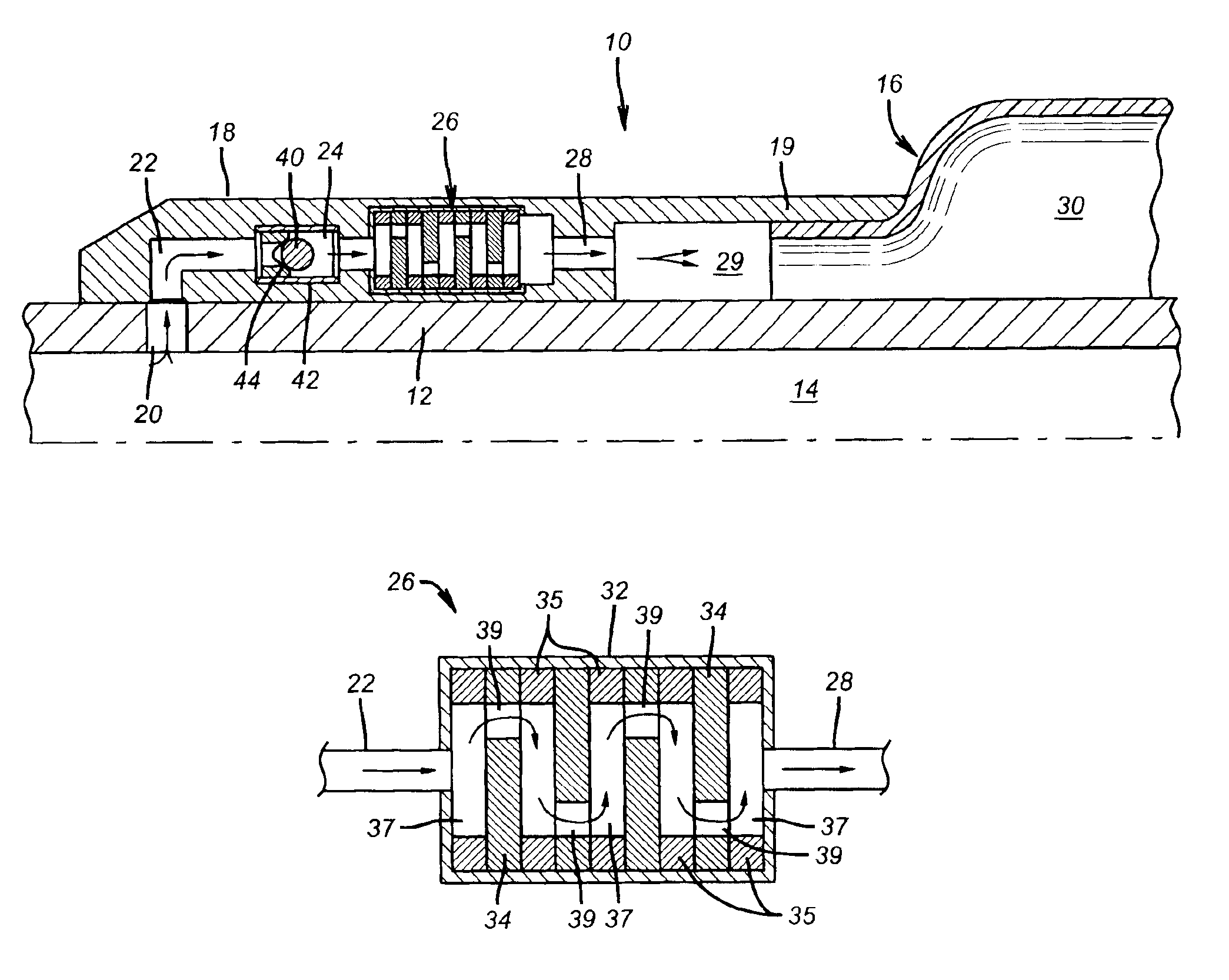
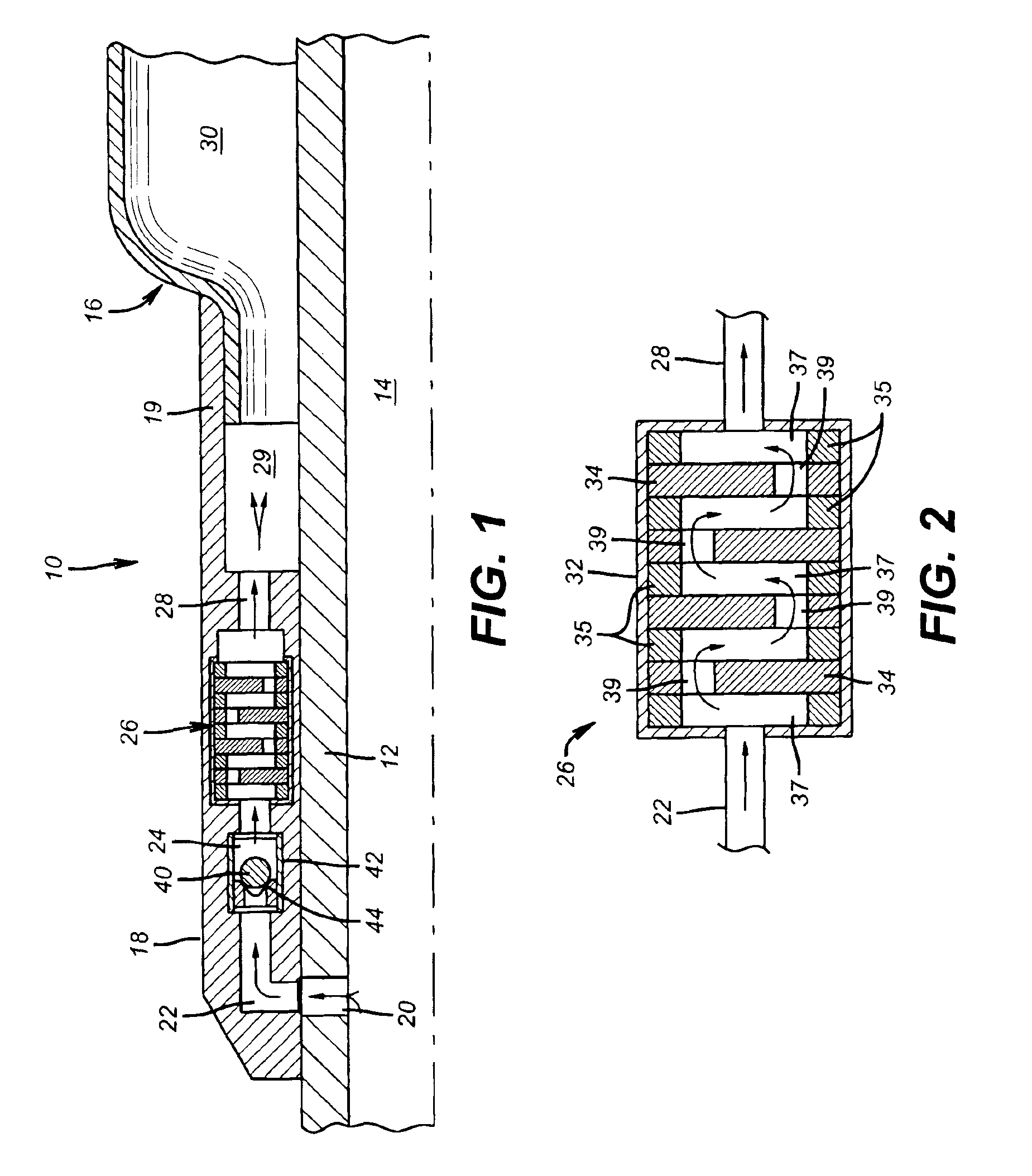
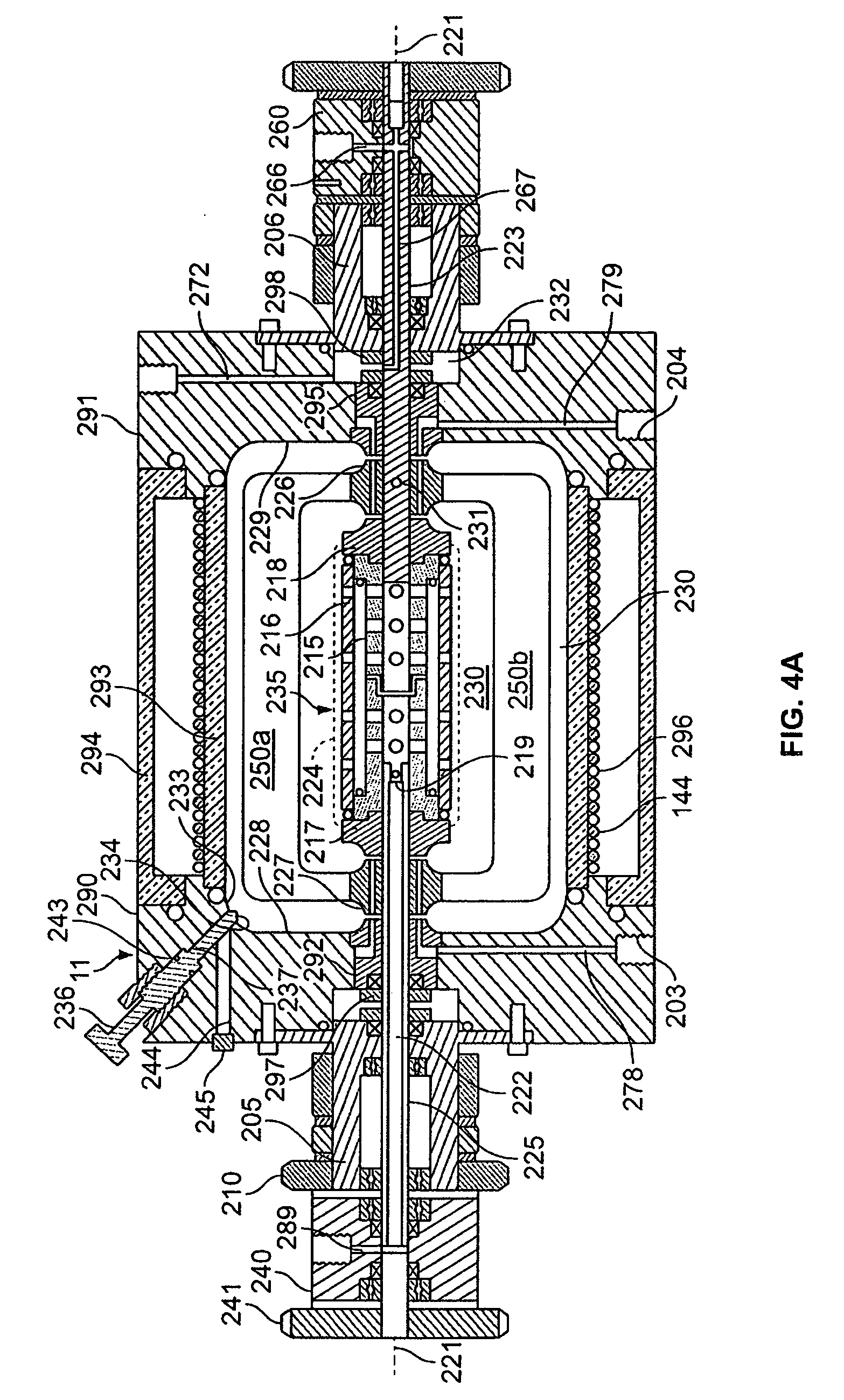
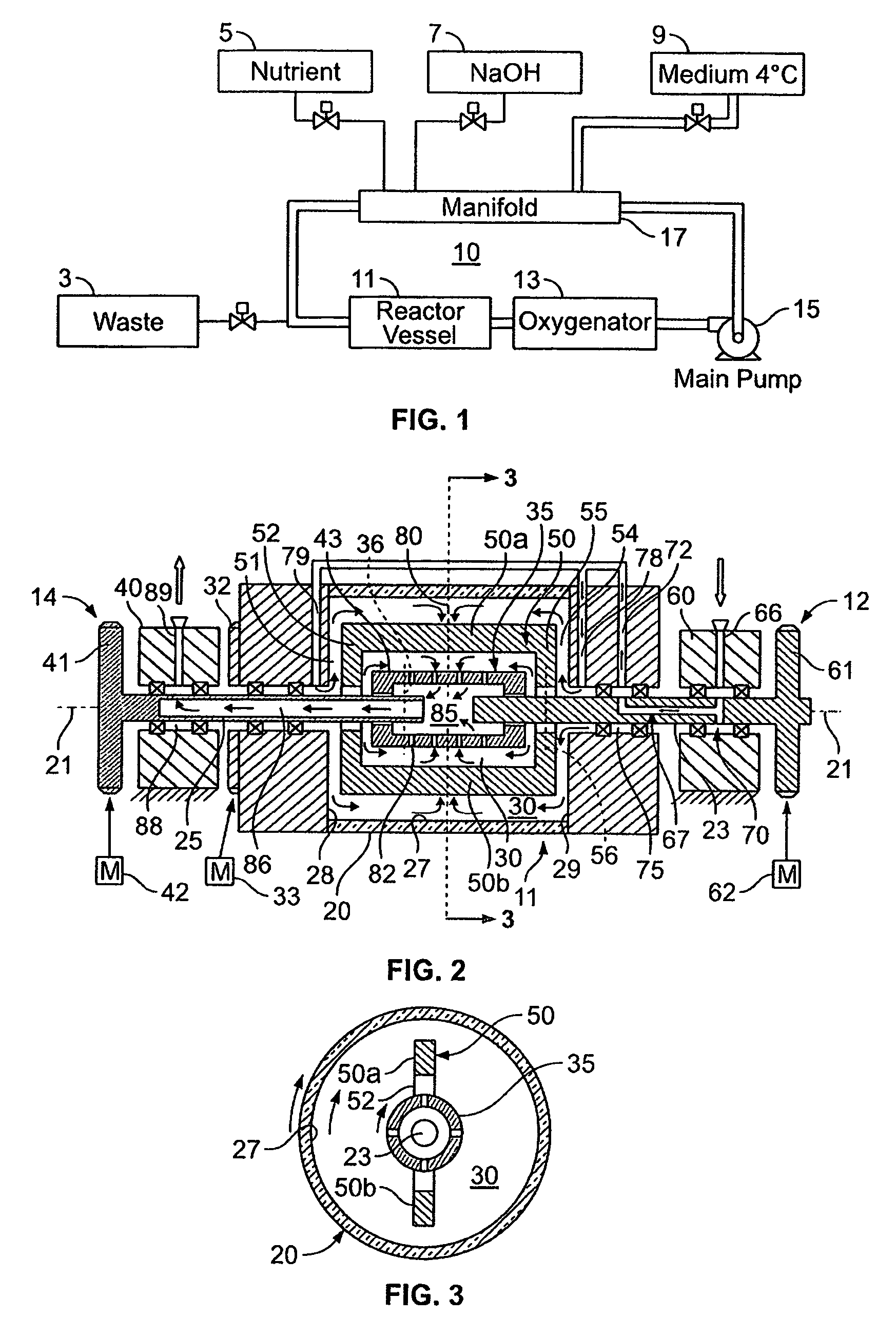
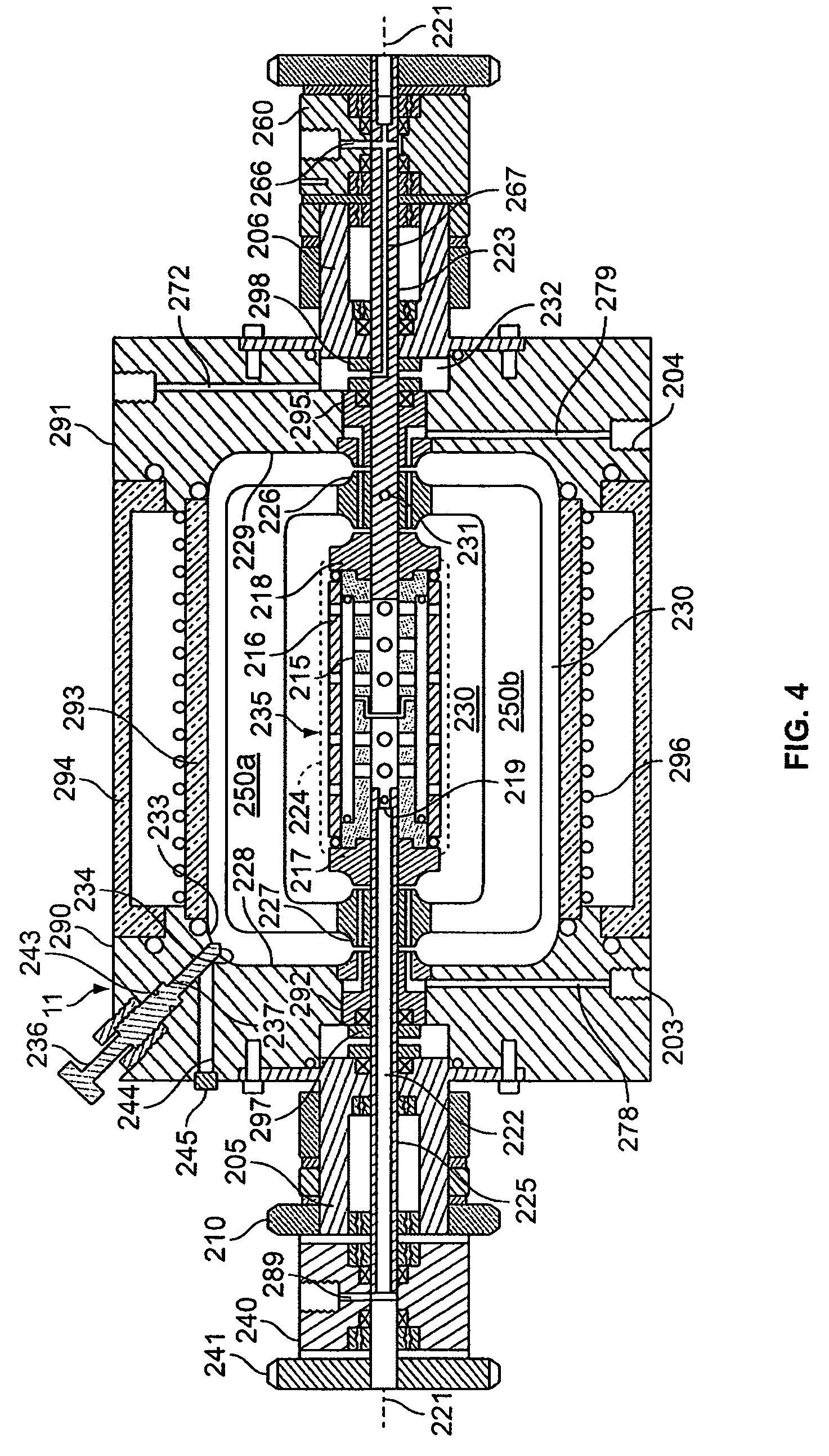
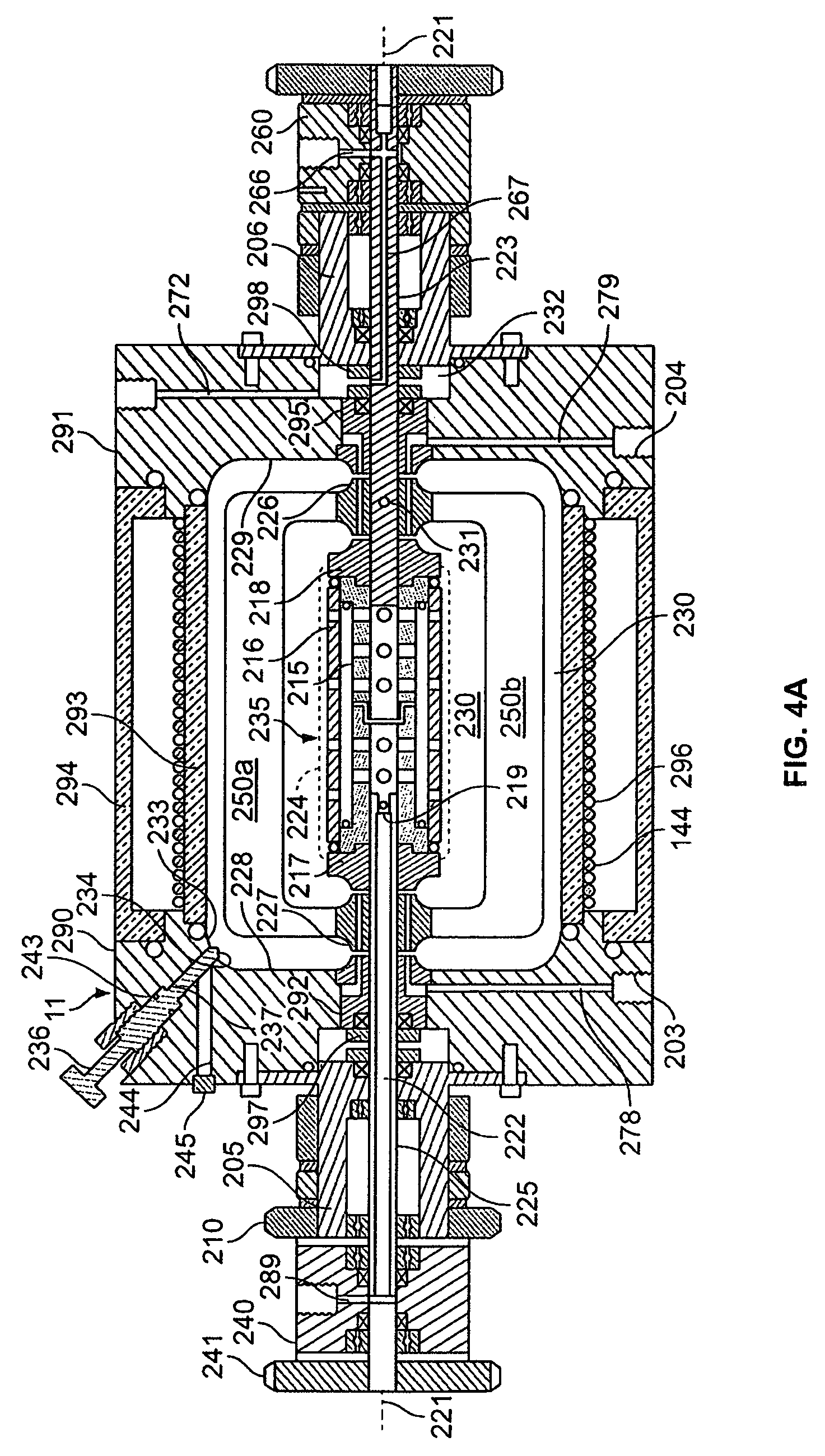
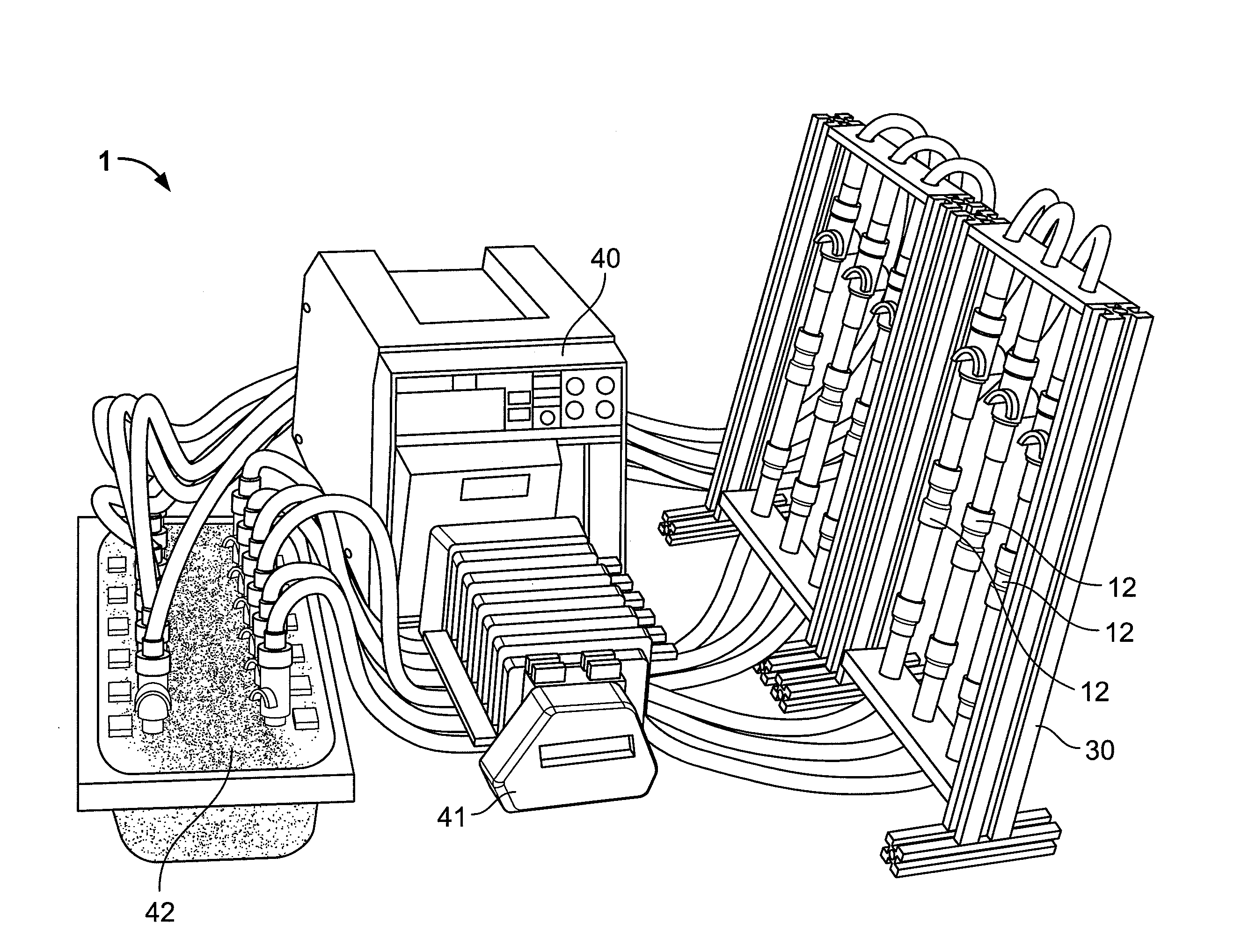
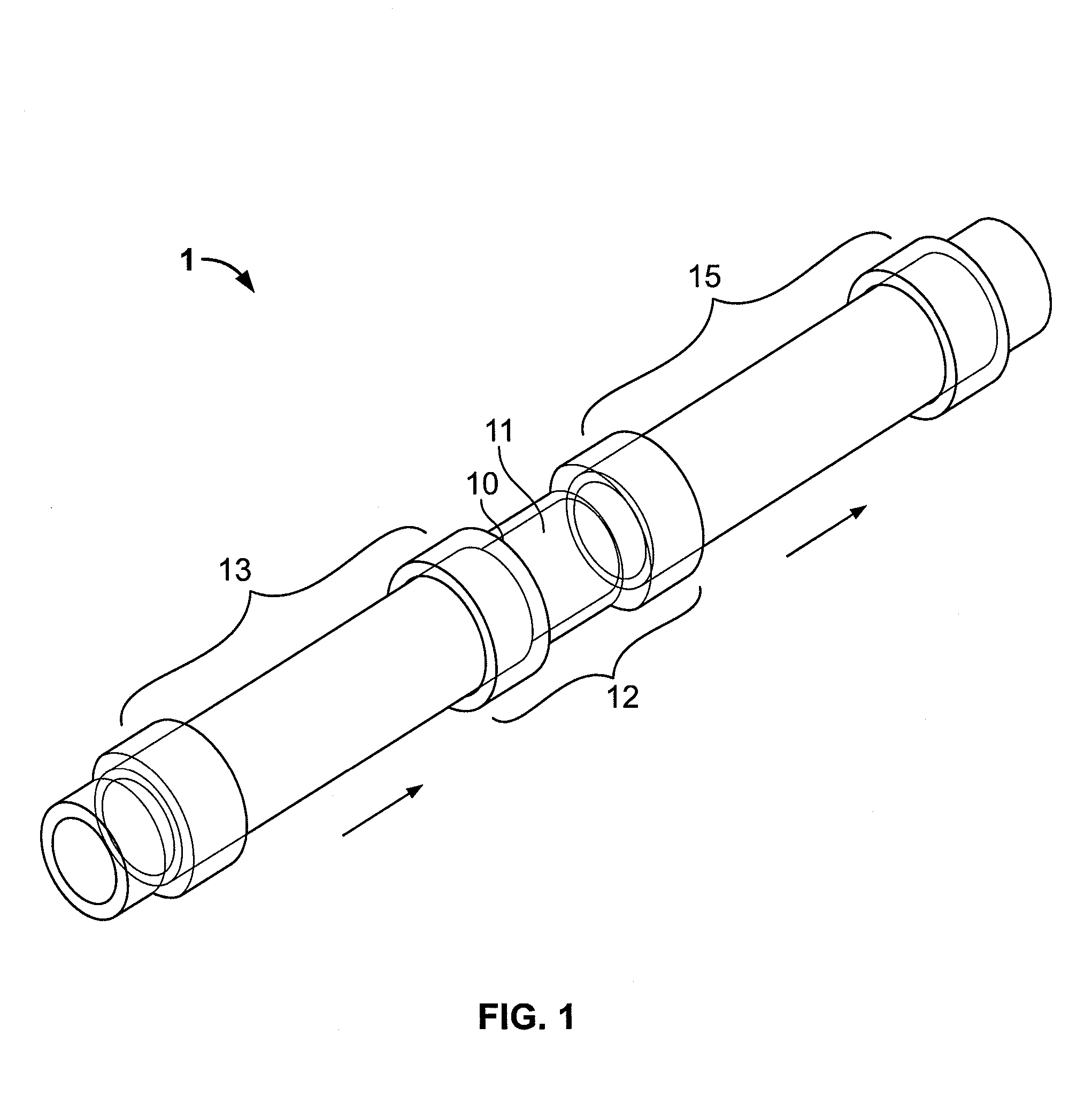
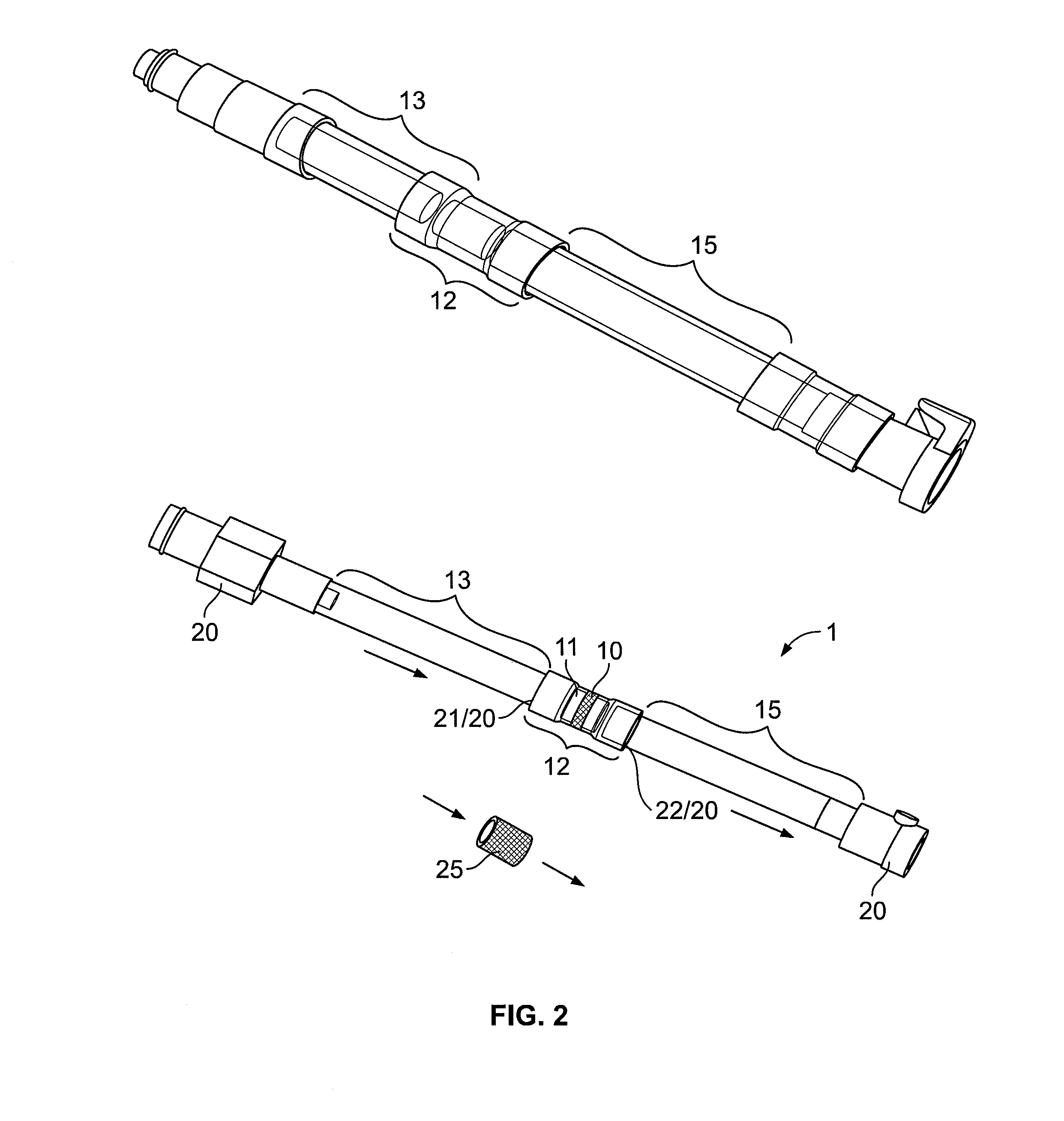
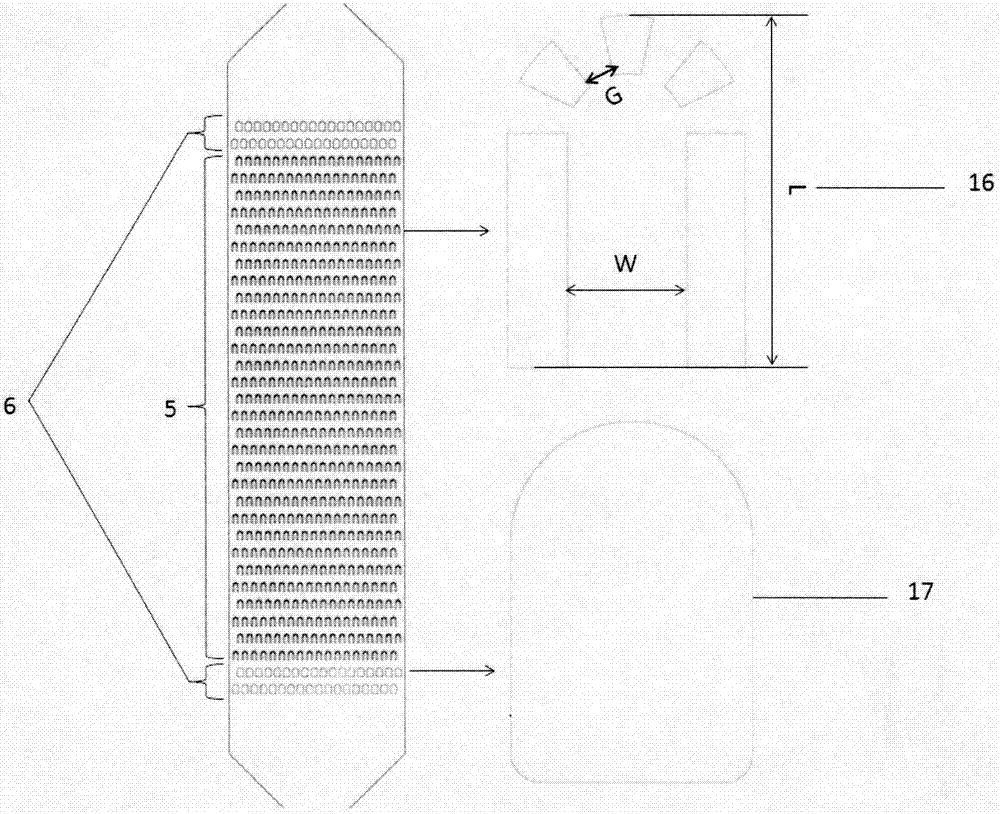
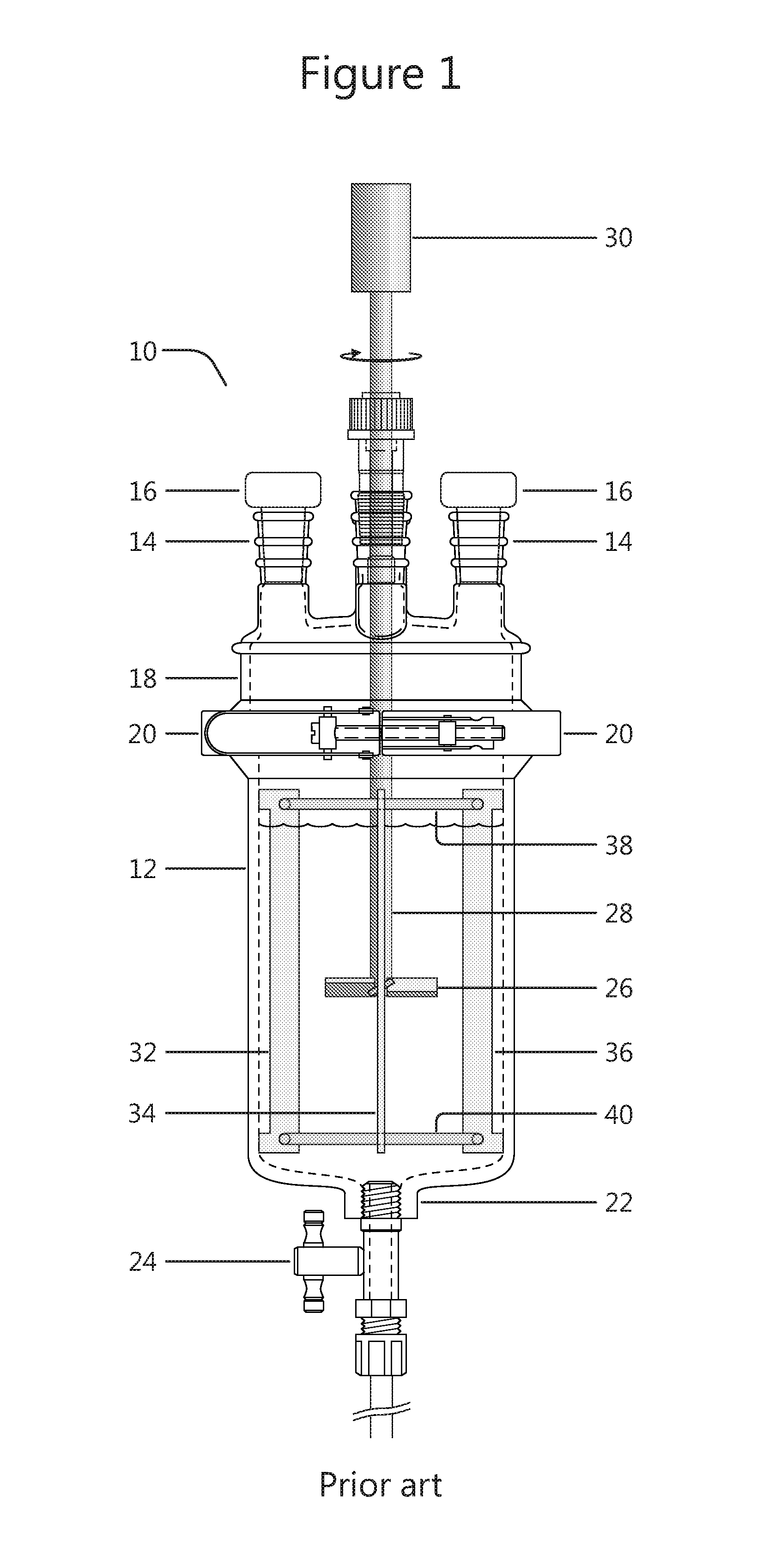
Shear activated inflation fluid system for inflatable packers
A subterranean well packer is inflated by a pumped transfer of rheotropic fluid through a tortuous flow channel into a packer sealing element expansion chamber. The tortuous flow channel and fluid delivery pressure are coordinated with the fluid properties to impose sufficient fluid shear stress for inducement of a substantial phase change in said rheotropic fluid after entry into expansion chamber.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Three-dimensional cell to tissue development process
InactiveUS20060240550A1Improve productivitySpeed up the processVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsSuspended particlesSpatial Orientations
The present invention relates to an improved three-dimensional cell to tissue development process using a specific time varying electromagnetic force, pulsed, square wave, with minimum fluid shear stress, freedom for 3-dimensional spatial orientation of the suspended particles and localization of particles with differing or similar sedimentation properties in a similar spatial region.
Owner:NASA +1
Three-dimensional cell to tissue development process
InactiveUS7456019B2Culture is increasedImprove abilitiesArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsSpatial OrientationsSuspended particles
An improved three-dimensional cell to tissue development process using a specific time varying electromagnetic force, pulsed, square wave, with minimum fluid shear stress, freedom for 3-dimensional spatial orientation of the suspended particles and localization of particles with differing or similar sedimentation properties in a similar spatial region.
Owner:NASA +1
Bioreactor device for exposing a cell culture to a fluid shear force imparted by a fluid flow
InactiveUS20080057571A1Easy and non-destructive removalEasy to separateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid shearEngineering
A system for exposing a cell culture to a fluid shear force imparted by a fluid flow is provided. Specifically, various embodiments of the present invention provide flow chambers defining channels for retaining a cell culture in the fluid flow wherein the flow chambers may be removably disposed within a bioreactor system such that the flow chambers may be removed and / or replaced without disturbing the cell cultures retained therein or disposed elsewhere within the bioreactor system. The flow chambers are composed of a transparent material such that a user of the system may observe the development of the cell culture retained within the chamber as the cell culture is imposed to a fluid shear stress imparted by the fluid flow.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
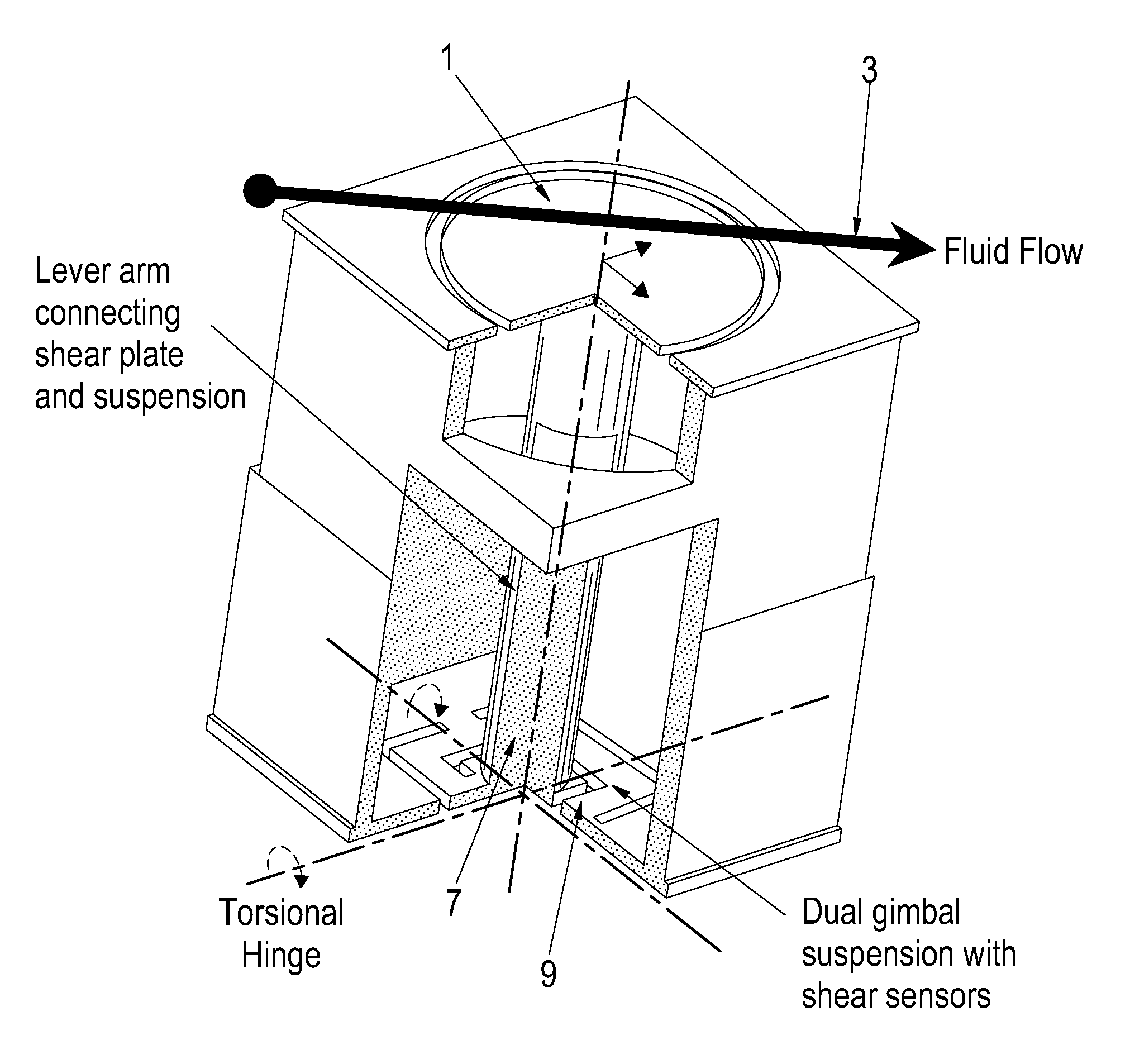
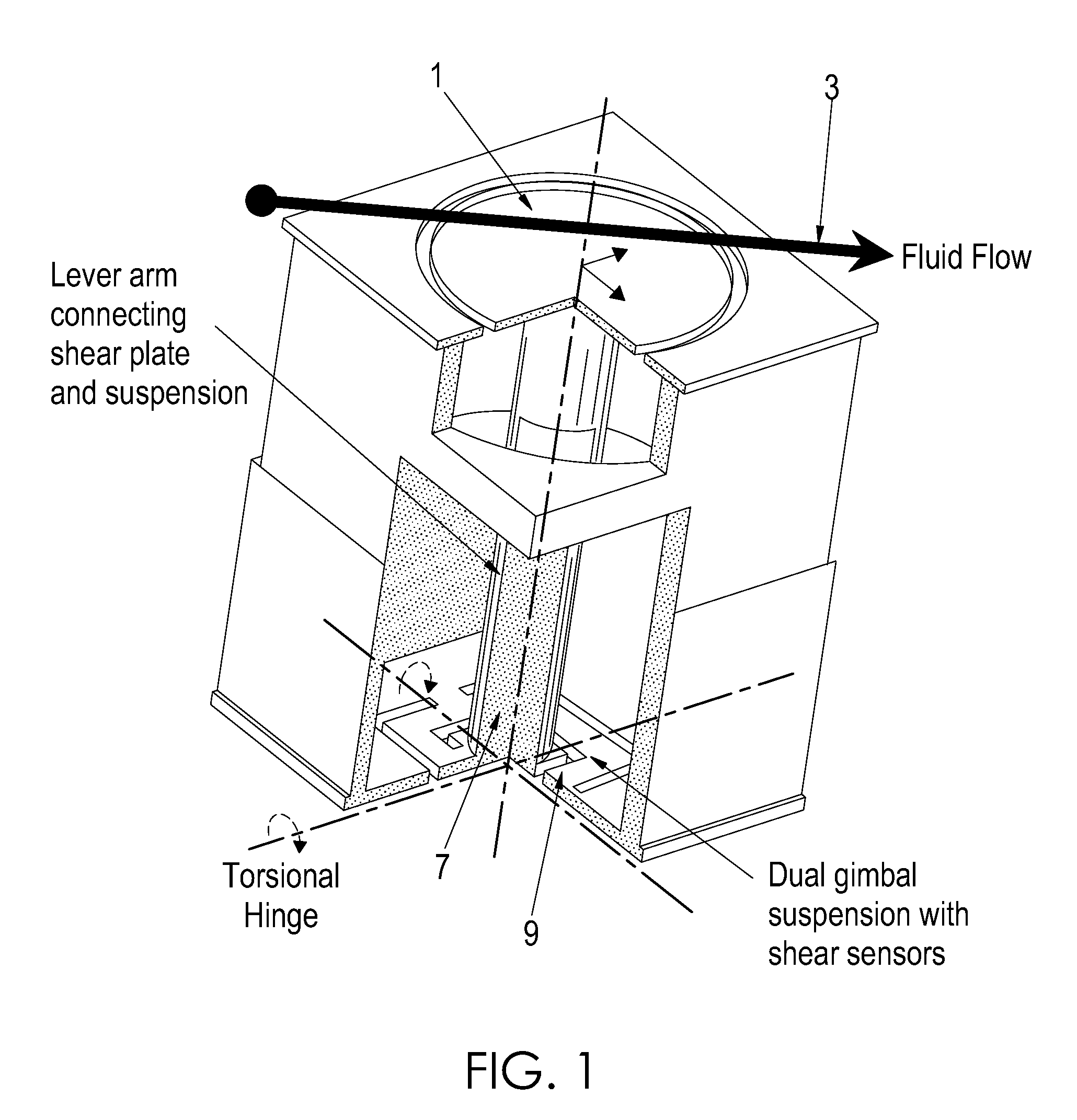
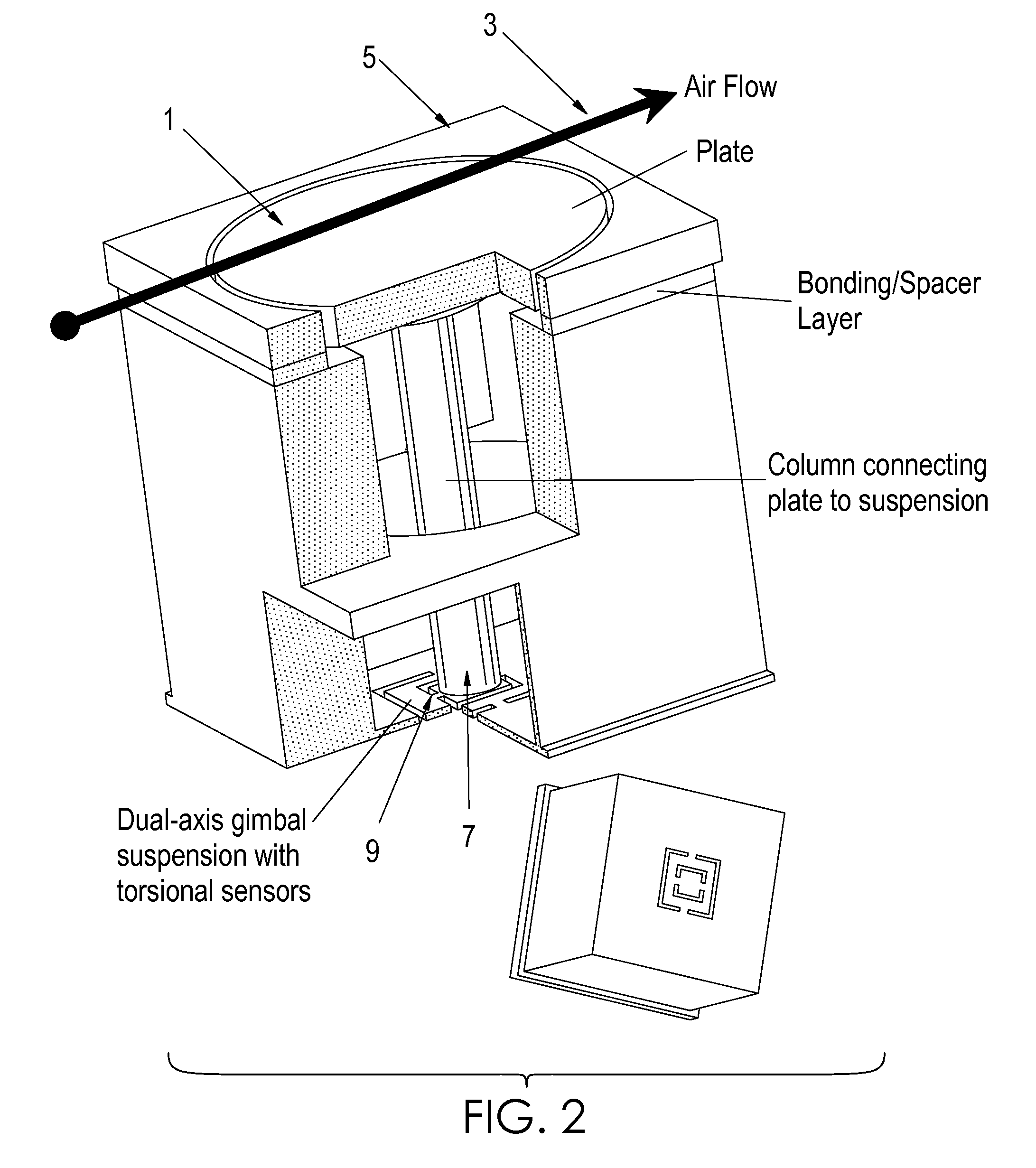
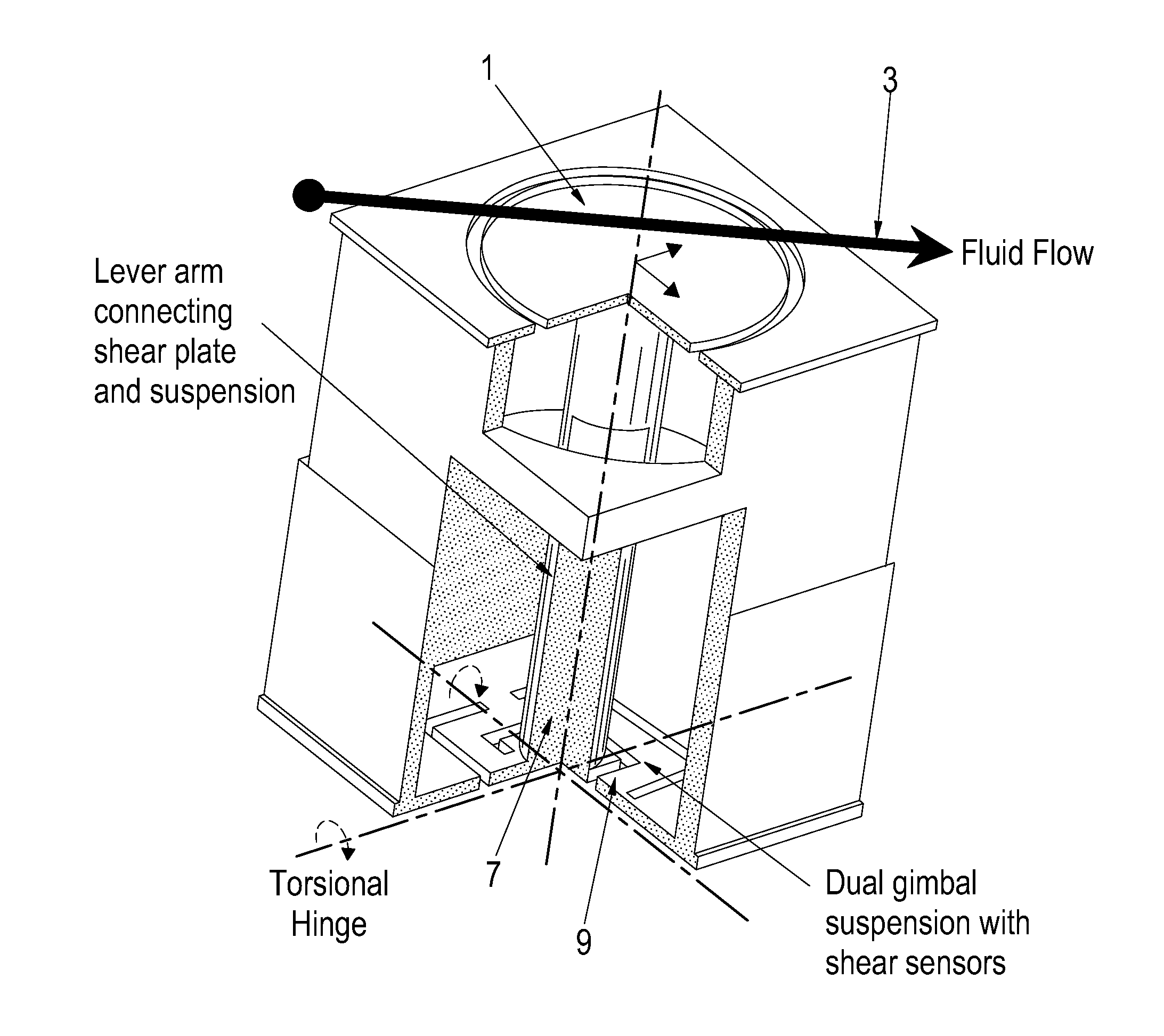
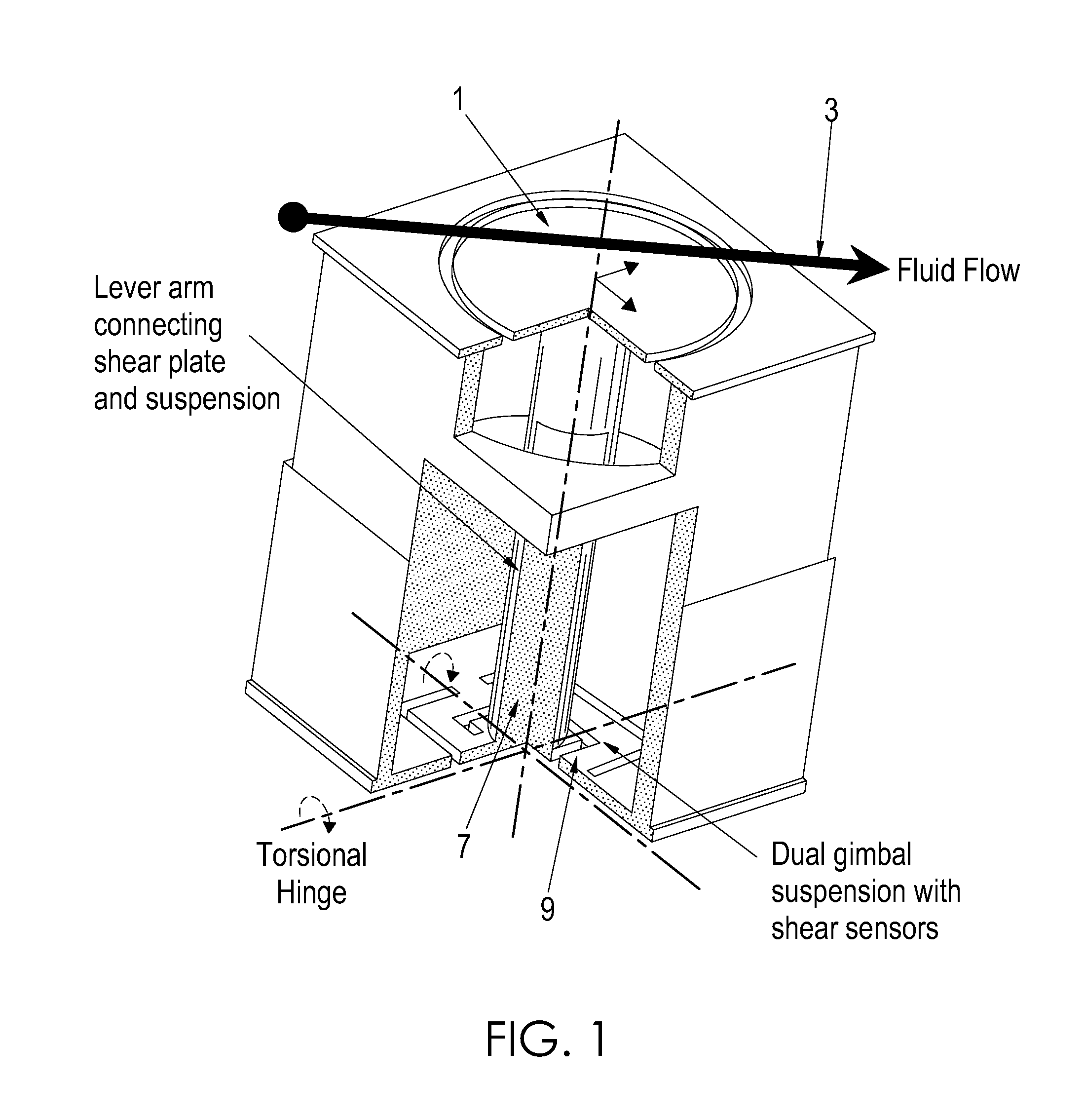
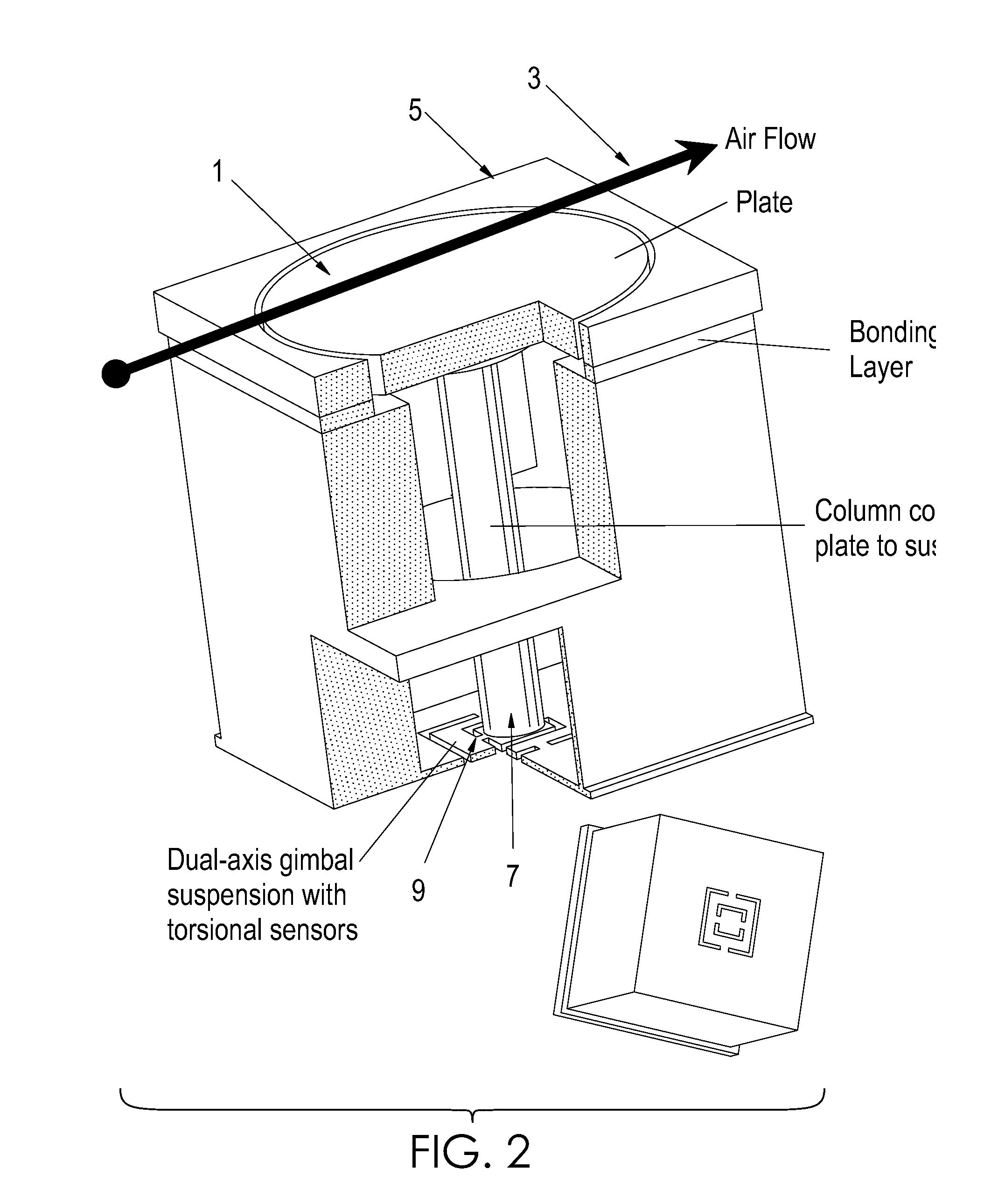
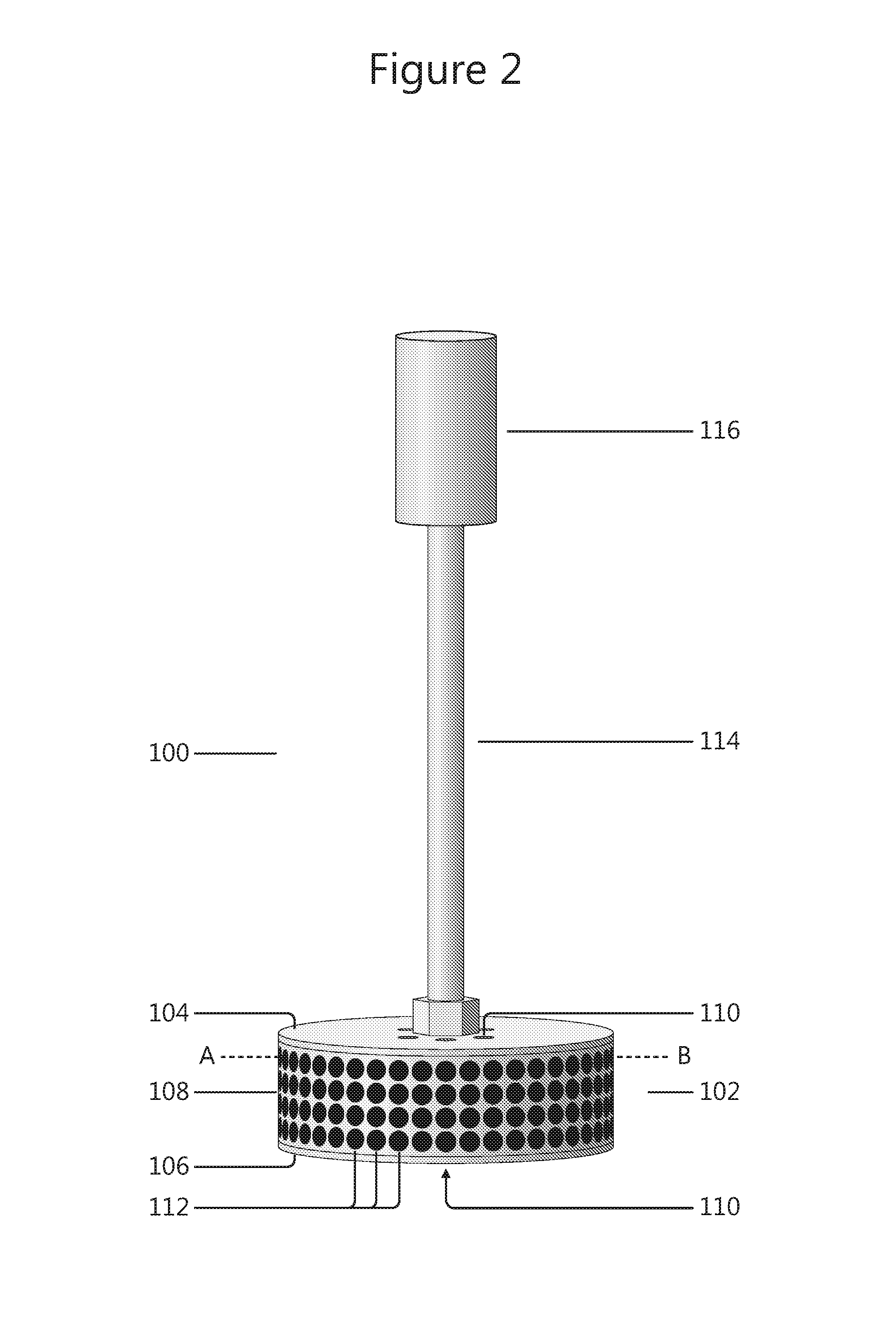
Two-axis direct fluid shear stress sensor
A micro sized multi-axis semiconductor skin friction / wall shear stress induced by fluid flow. The sensor design includes a shear / strain transduction gimble connected to a force collecting plate located at the flow boundary surface. The shear force collecting plate is interconnected by an arm to offset the tortional hinges from the fluid flow. The arm is connected to the shear force collecting plate through dual axis torsional hinges with piezoresistive torsional strain gauges. These gauges are disposed on the tortional hinges and provide a voltage output indicative of applied shear stress acting on the force collection plate proximate the flow boundary surface. Offsetting the torsional hinges creates a force concentration and resolution structure that enables the generation of a large stress on the strain gauge from small shear stress, or small displacement of the collecting plate. The design also isolates the torsional sensors from exposure to the fluid flow.
Owner:NASA
Artery blood vessel simulation microfluid control device enabling direct observation under high-power objective
ActiveCN103805511AEasy to observeReduce volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseFine structure
The invention discloses an artery blood vessel simulation microfluid control device enabling direct observation under a high-power objective. The device is provided with a transparent microfluid channel module (1), an elastic membrane (2), a negative pressure generation module (3) and a cover glass (10) sequentially from top to bottom, wherein a microfluid channel (8) is arranged at the bottom of the microfluid channel module (1) and used for enabling fluid flow; the negative pressure generation module (3) is internally provided with a negative pressure hollow groove (9) going through the top to bottom and used for generating negative pressure enabling the elastic membrane to deform; the total thickness of the elastic membrane (2) and the cover glass (10) is less than or equal to 300 microns. The microfluid control device disclosed by the invention not only can simulate the physiological and pathological conditions of the organs and tissues bearing the fluid shear stress and mechanical drawing force in vivo at the same time, but also enables direct observation under the high-power objective so as to realize real-time observation of the dynamic and static change in the fine structure and microfluid channel of a single cell; therefore, a more effective tool is provided to the related basic research and the drug screening for artery blood vessel diseases.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Mechanical loading flow chamber device for co-culturing in-vitro cells
InactiveCN101942389ATo achieve the purpose of co-cultivationReach vertical spreadBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringCultured cell
The invention provides a mechanical loading flow chamber device for co-culturing in-vitro cells. The device comprises an upper flow chamber, a lower flow chamber, a permeable film, a first perfusion system and a second perfusion system, wherein the permeable film is arranged between the upper flow chamber and the lower flow chamber and used for separating the upper and lower flow chambers and two kinds of different cells can be inoculated onto the upper surface and the lower surface of the permeable film; the first perfusion system is communicated with the upper flow chamber through a first passage way; and the second perfusion system is communicated with the lower flow chamber through a second passage way. In the invention, micropores of the permeable film allow the two kinds of co-cultured cells to be connected through synapses and keep mutually permeated perfusates in the upper and lower chambers in seepage balance so that cytokines are vertically diffused. The upper and lower chambers can apply flow shear stresses onto the cells on the two sides of the film respectively, so that the two kinds of cells can bear the shear stress while being co-cultured on line respectively. The device can culture two kinds of different cells in vitro in the same environment and can apply double shear stresses in different modes onto the two kinds of cells at the same time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
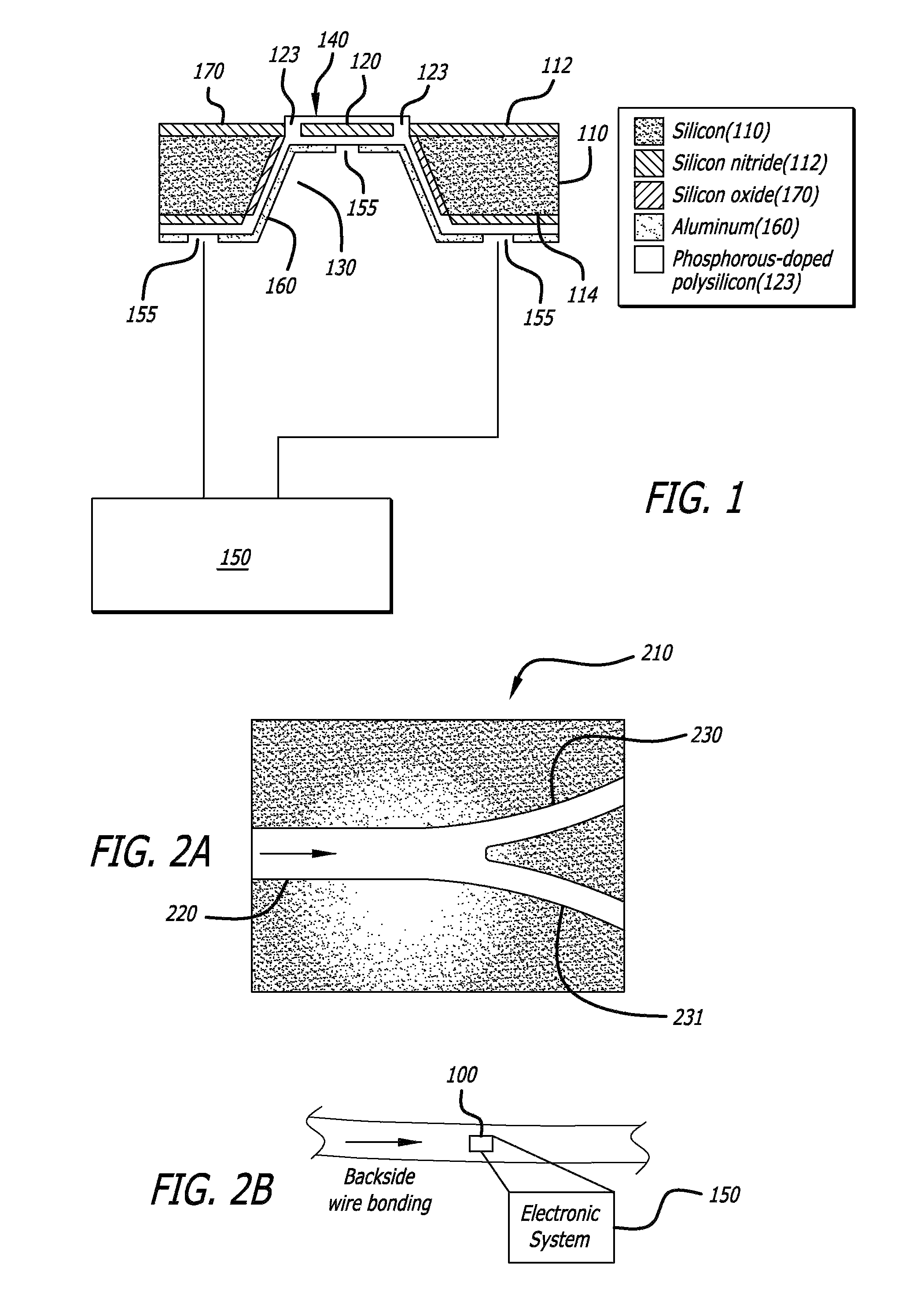
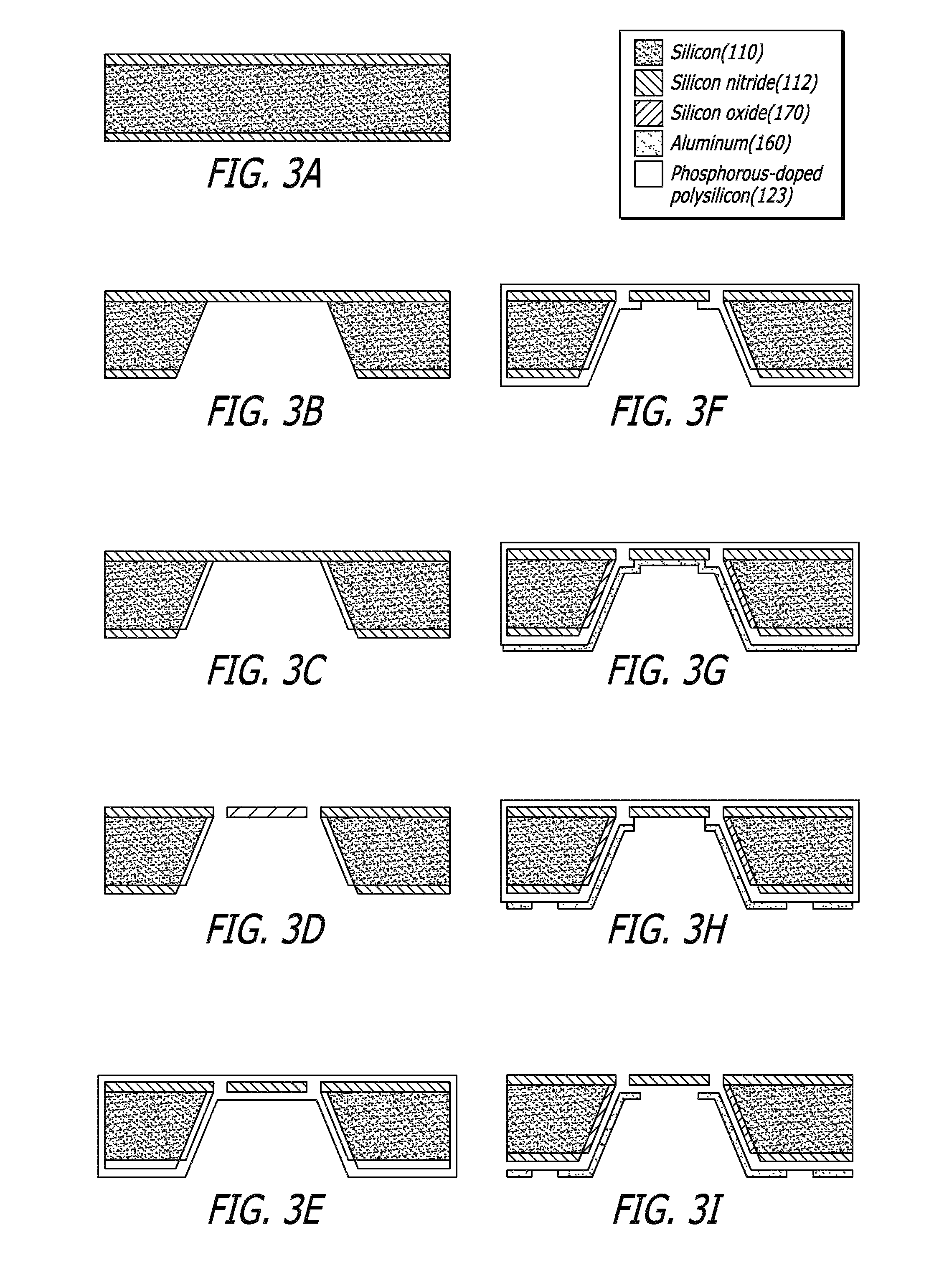
MEMS vascular sensor
A micromachined sensor for measuring vascular parameters, such as fluid shear stress, includes a substrate having a front-side surface, and a backside surface opposite the front-side surface. The sensor includes a diaphragm overlying a cavity etched within the substrate, and a heat sensing element disposed on the front-side surface of the substrate and on top of the cavity and the diaphragm. The heat sensing element is electrically couplable to electrode leads formed on the backside surface of the substrate. The sensor includes an electronic system connected to the backside surface and configured to measure a change in heat convection from the sensing element to surrounding fluid when the sensing element is heated by applying an electric current thereto, and further configured to derive from the change in heat convection vascular parameters such as the shear stress of fluid flowing past the sensing element.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Preparation method of carbon nanotube / alloy composite with directionally aligned carbon nanotubes
The invention provides a preparation method of a carbon nanotube / alloy composite with directionally aligned carbon nanotubes. The method comprises the following steps: first, evenly mixing a carbon nanotube powder and an alloy powder according to proportion, and consolidating into block blanks; then heating the block blanks to a superplastic forming temperature of the alloy material in vacuum; and finally applying external force to form a velocity gradient field in the block blanks, so that carbon nanotubes align directionally along a filament line under the effect of fluid shear stress, and cooling and solidifying to obtain the carbon nanotube / alloy composite with directionally aligned carbon nanotubes. The invention solves the problem of directional alignment of carbon nanotubes in a carbon nanotube / alloy composite, so as to give full play to the performance of carbon nanotubes.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Process for coculturing cord blood hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells in dynamic suspending condition
InactiveCN101285053AExert nourishmentPlay a supporting roleSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood/immune system cellsCord blood stem cellCytokine
The invention discloses a method for co-culturing cord blood stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, belonging to the biotechnology and tissue engineering technical field. The method is characterized by adding no blood serum but only cytokine and trophocyte; wrapping the trophocyte calcium alginate-chitosan gel beads; using microcarrier and rotating wall vessel to implement the co-culture of cord blood stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells; and separating and obtaining the cord blood-derived stem cells respectively. The invention has the advantages that: the microcarrier provides a surface for the cord blood mesenchymal stem cells to adhere to, so the adherent, dynamic, suspension culture of the cord blood mesenchymal stem cells can be implemented. The rotating wall vessel provides an environment for hemopoietic stem cell to suspend and growth in, and also reduces the damages caused by fluid shear stress to the hemopoietic stem cells. The throphocyte can nourish the cord blood stem cells outside the gel beads, replace partially blood serum and contribute to the separation and harvest of different cells.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
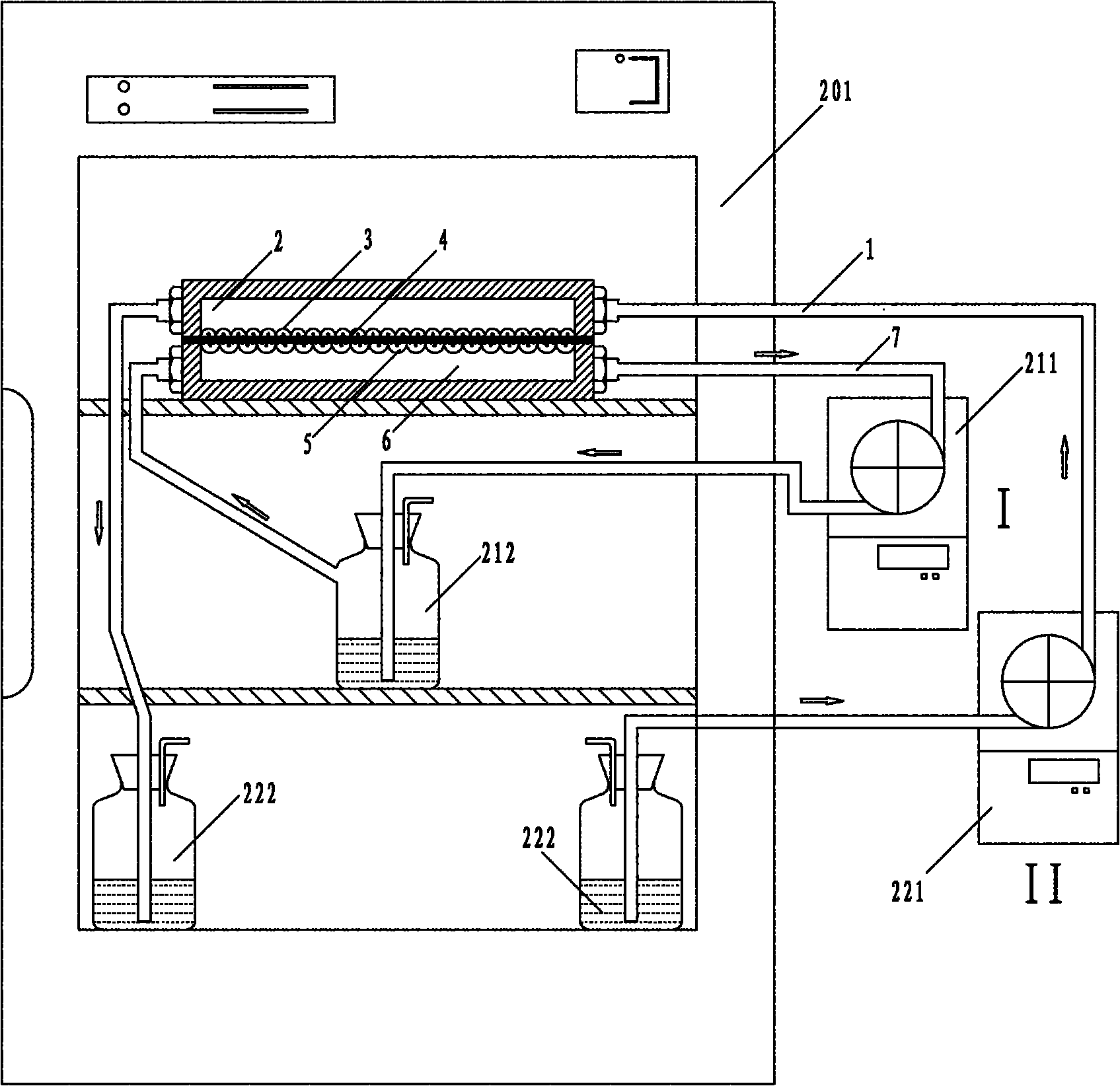
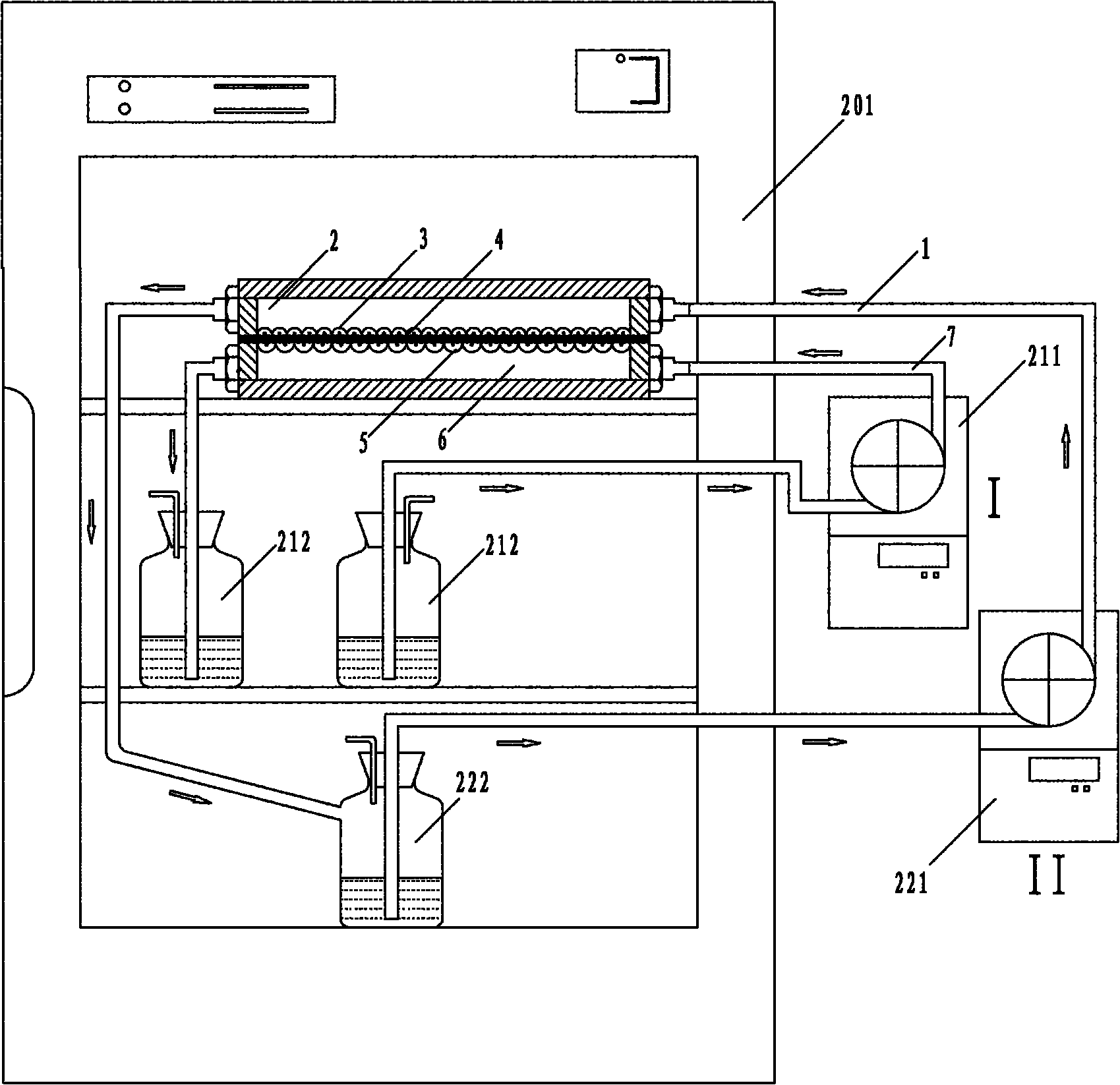
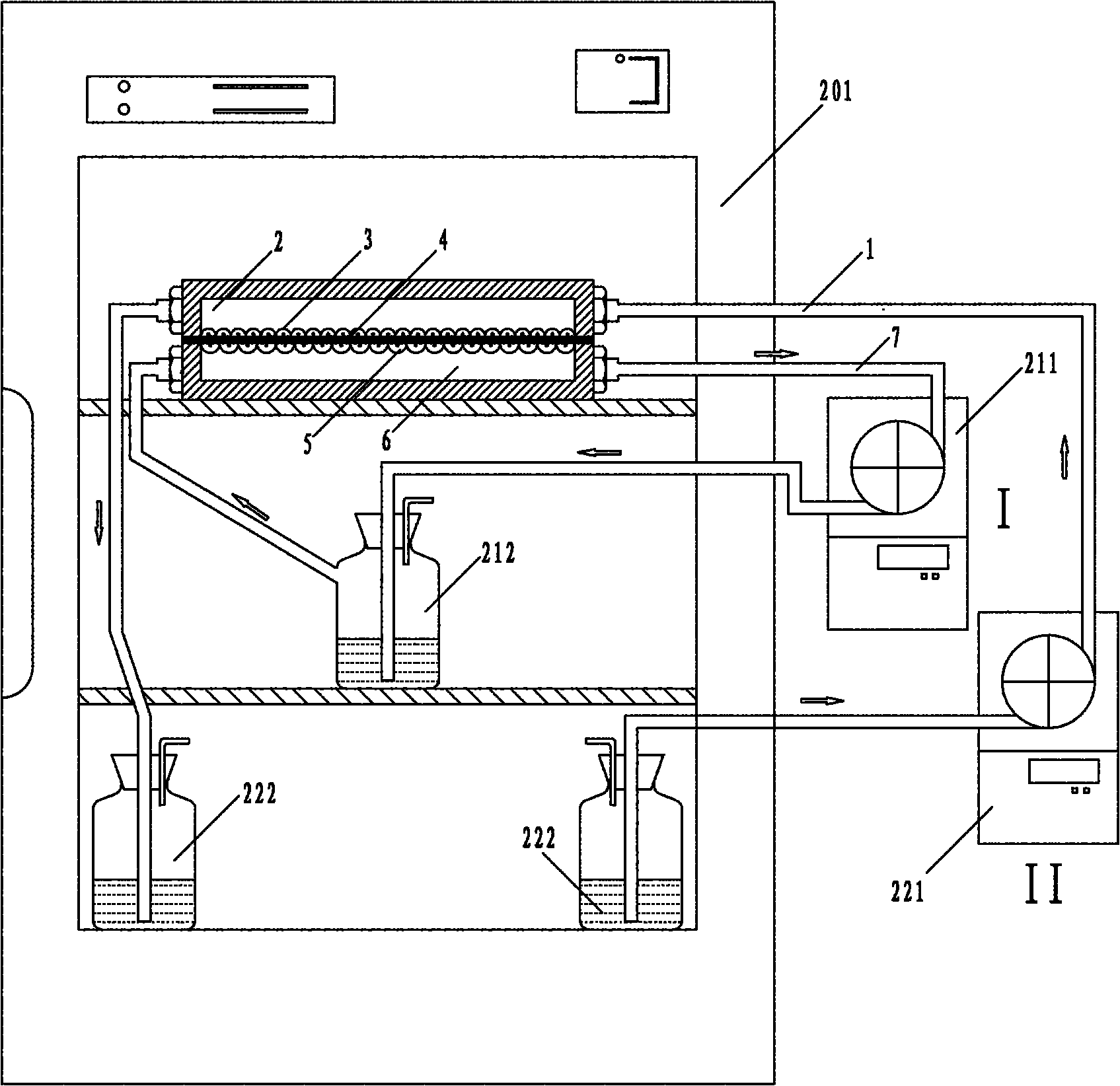
Bionic three-dimensional fluid shear stress cell culture device and shear stress loading method thereof
InactiveCN102174397AReduce restrictionsQuick assemblyTissue cultureTissue/virus culture apparatusPeristaltic pumpBionics
The invention discloses a bionic three-dimensional fluid shear stress cell culture device and a shear stress loading method thereof. The bionic three-dimensional fluid shear stress cell culture device is characterized by consisting of a peristaltic pump (1), a perfusion small chamber (2), a 1-to-8 switcher (3), an air filter membrane (4), a waste liquid bottle (5), a straight-through valve (6), aculture medium (7), a liquid storage bottle (8) and a processing silicon tube (9), wherein one end of the perfusion small chamber is connected with the peristaltic pump (1), and the other end of the perfusion small chamber is connected with the waste liquid bottle (5) through the 1-to-8 switcher (3); the waste liquid bottle is connected with the liquid storage bottle (8) through the straight-through valve (6); and the liquid storage bottle (8) is connected with the peristaltic pump (1) through the 1-to-8 switcher (3).
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
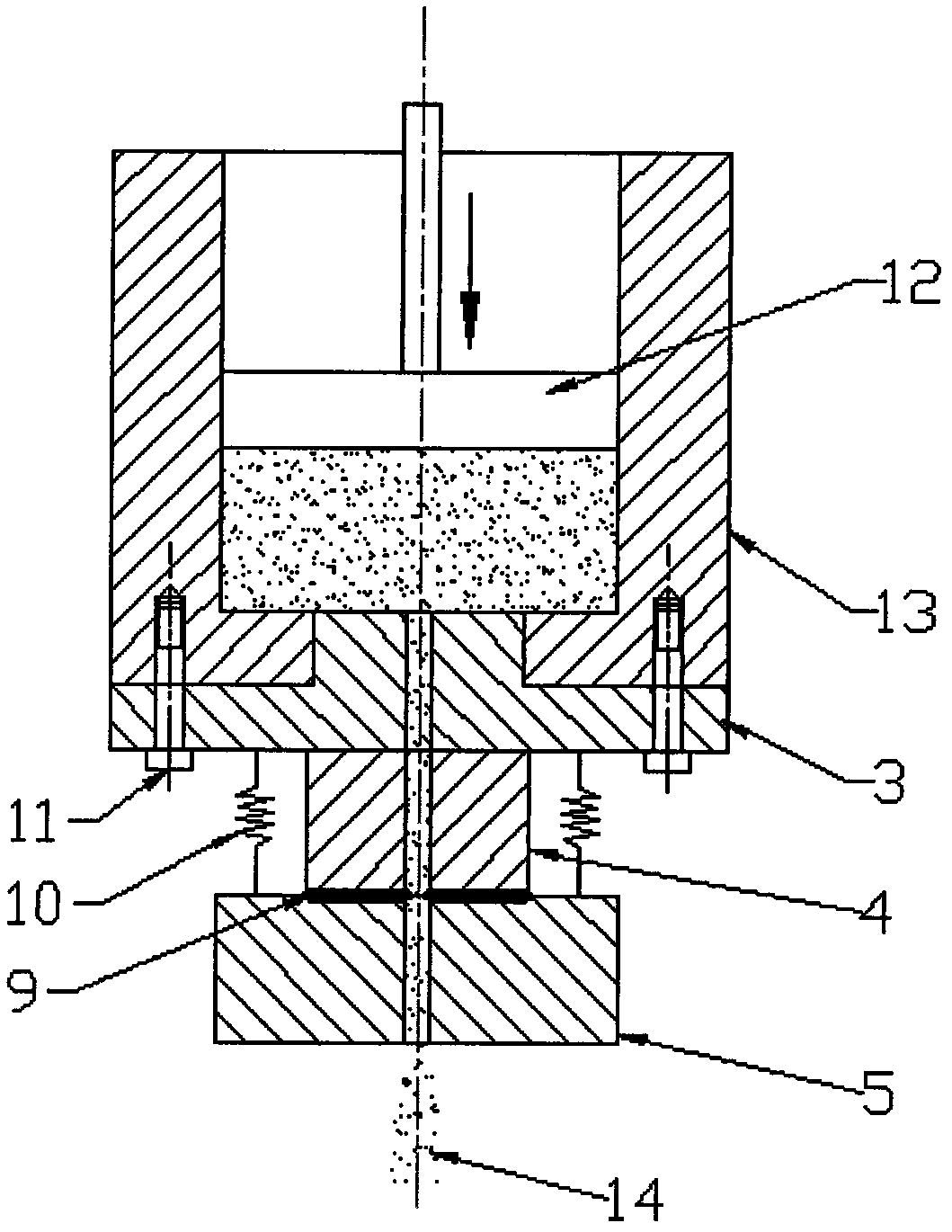
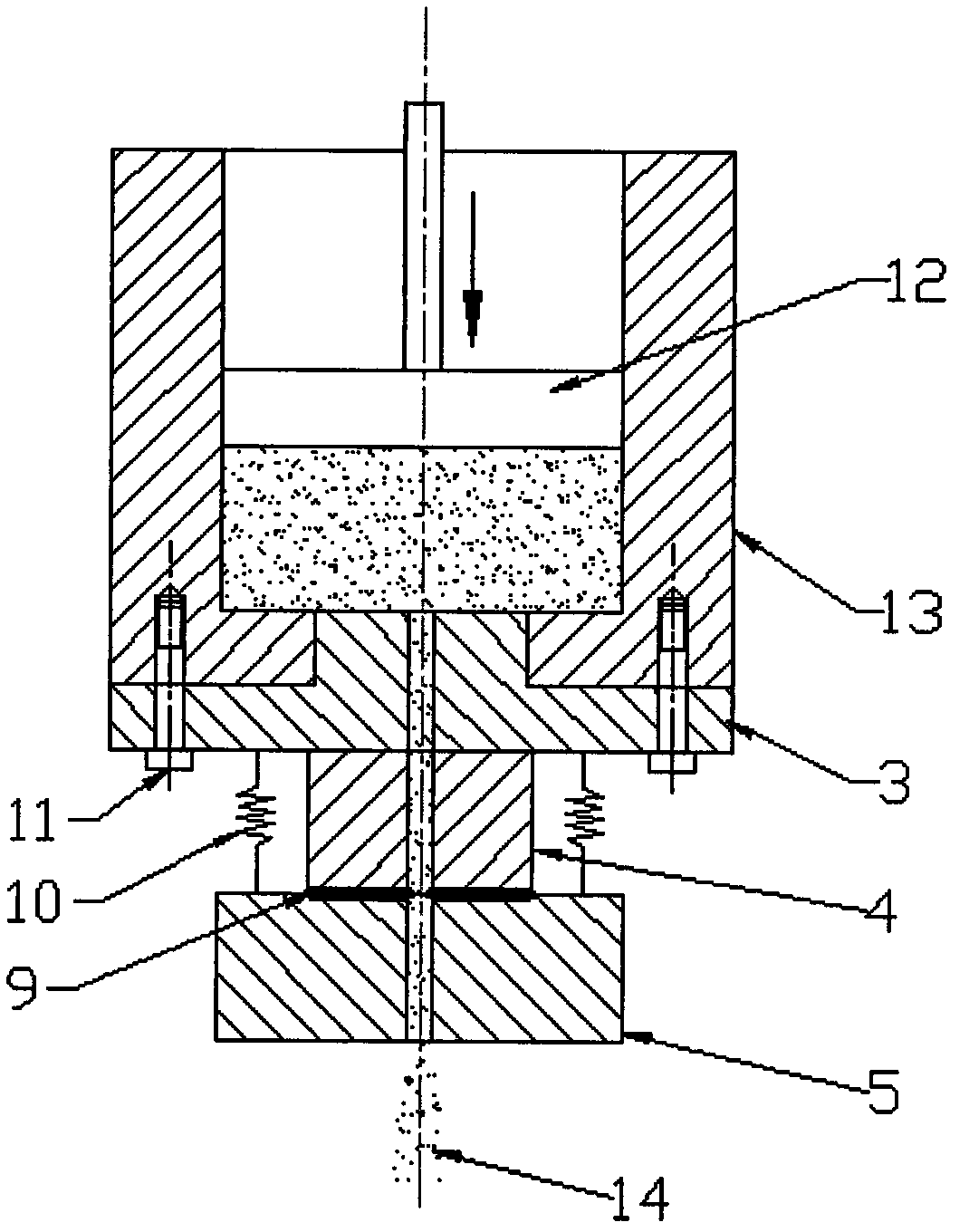
Method for measuring fluid shear stress in capillary and device
InactiveCN102323186AEliminate systematic errorsImprove test accuracyDirect flow property measurementMeasurement deviceTest sample
The invention discloses a method for measuring the fluid shear stress in a capillary and an implementing device thereof, and belongs to the field of material testing. The method comprises the following steps of: slicing a capillary die into at least three sections, i.e. an inlet section, a middle section and an outlet section, along the axial direction according to differences of test sample fluid in the capillary in the flow condition; and only measuring the stress of a test sample at the position of the middle section so as to calculate the shear stress of the test sample in the capillary. The measuring device for implementing the method comprises a charging barrel, a plunger rod, the capillary die and a force measuring element. The force measuring element is arranged in the middle section of the die and can be used for measuring an acting force between the middle section and the outlet section. In the testing process, the test sample in the charging barrel outflows through the capillary under the squeezing action of the plunger rod. The change of a force value measured in the middle section of the die corresponds to the shear force applied to the capillary wall of the middle section of the die. Due to the adoption of the method and the implementing device thereof, the influence of a pressure drop of an inlet region and an outlet region in a capillary rheometer on the measurement of the fluid shear stress in the capillary is completely eliminated, and the testing accuracy of the capillary rheometer is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH +1
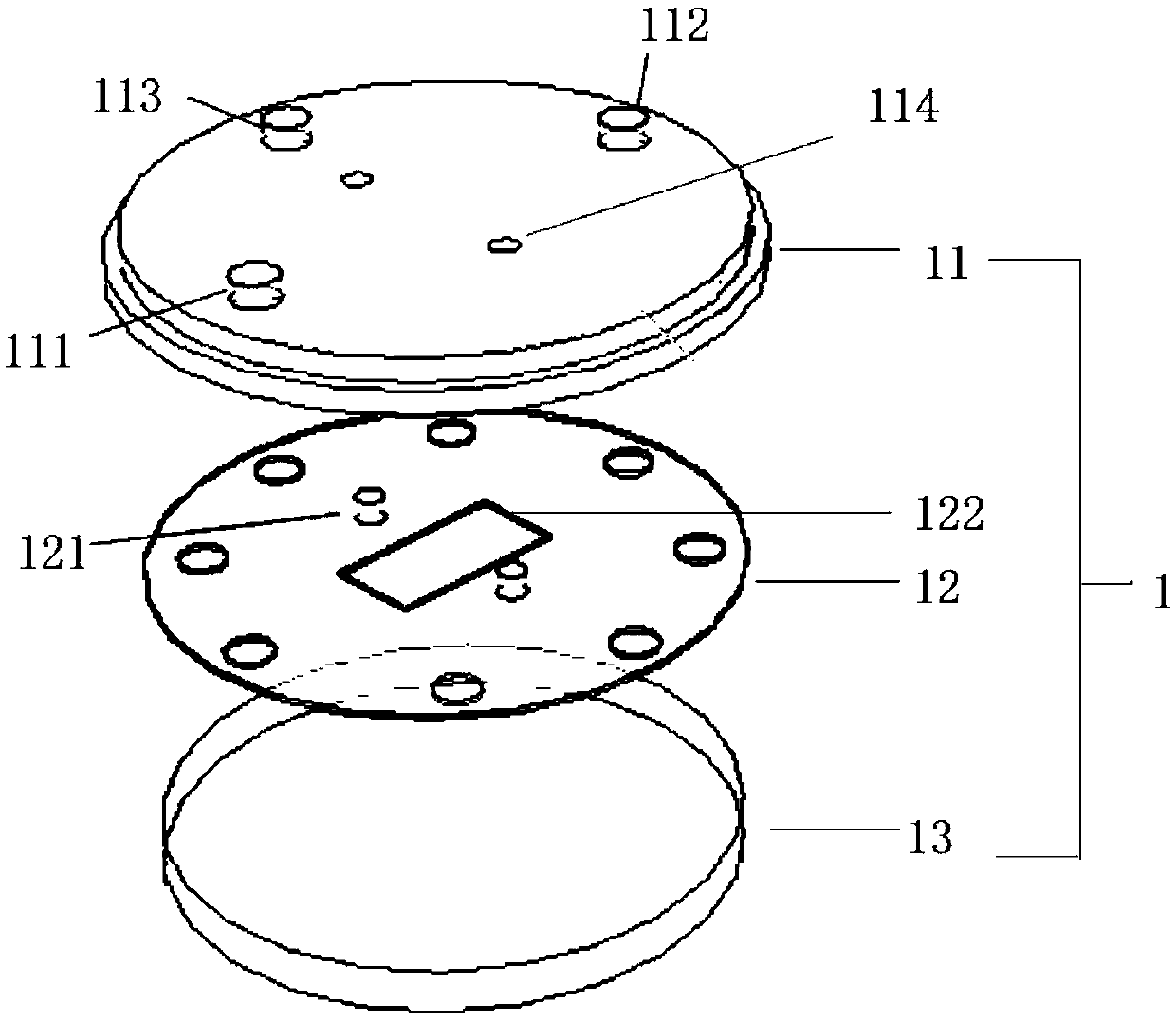
Array-type cell dynamic culturing and regionalization processing micro-fluidic chip, and preparation method and application of same
ActiveCN107881106ASuitable for long-term cultivationGood biocompatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue/virus culture apparatusControl layerMicro column
The invention discloses an array-type cell dynamic culturing and regionalization processing micro-fluidic chip which includes, in a manner of being successively encapsulated from top to bottom, a flowing layer, a control layer, a thin film layer and a glass layer. The flowing layer is composed of an array-type cell culture zone, a buffer structure zone, a cell inoculation micro-pipe, a left liquidfeeding micro-pipe, a central liquid feeding micro-pipe and a right liquid feeding micro-pipe; the array-type cell culture zone is provided with a plurality of array-type U-shaped culture grooves anda plurality of U-shaped micro-columns are disposed in the buffer structure zone; the control layer is composed of a plurality of micro-pumps in a manner that an end-sealed structure is composed of one inlet and a plurality of micro-cavities in series connection. The micro-fluidic chip is used for carrying out fluid shear stress dynamic loading and regionalization processing of more than two biochemical factors / medicines, and researching interaction between processed cells and non-processed cells. The micro-fluidic chip breaks through conventional cell culture and treatment modes, and has beneficial to simulation of a fluid micro-environment and a biochemical micro-environment in cells in tissue under different physiological or pathological conditions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Biological culture micro-fluidic chip suitable for microgravity gyroscope assembly and cell culture method thereof
ActiveCN113388517AReduce aspect ratioReduce usageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiochemistry
The invention provides a biological culture micro-fluidic chip suitable for microgravity gyroscope assembly and a cell culture method thereof. A chip soft film completely covers a culture chip body, the side face of the biological culture micro-fluidic chip is fixed through a detachable fixing device, sealing is formed between the soft film and a culture chip interface layer, and the biological culture micro-fluidic chip is fixed to a fixing position of a microgravity gyroscope. The chip greatly reduces the depth-to-width ratio of a culture chamber, reduces the use amount of a culture medium, can meet the parallel culture requirement, and meanwhile effectively reduces the damage of fluid shear stress to a culture target.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Novel bacterial biofilm culture device suitable for atomic force microscope (AFM) to perform in-situ detection
InactiveCN104928148AShorten the timeImprove high temperature resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMagnetic force microscopeBiofilm
The invention discloses a novel bacterial biofilm culture device suitable for an atomic force microscope (AFM) to perform in-situ and high-flux detection on the micro-nanostructure and biomechanical characteristics of biofilms. Biofilms have a wide application to the field of sewage treatment, and during the treatment process, the fluid shear stress has an impact on the physiological properties of bacteria, but the conventional bacterial biofilm culture device cannot meet the requirements of the AFM for real-time and in-situ detection. According to the novel bacterial biofilm culture device suitable for the atomic force microscope (AFM) to perform in-situ detection, provided by the invention, the micro-fluidic technique and the characteristic of the AFM are combined, so that the culture device, of which the culture part comprises a culture substrate, small culture rooms and a cover plate (8 small detection rooms are integrated on the same one culture substrate), is designed; the device can be embedded into an AFM detection platform to stimulate a sewage treatment system and perform in-situ detection on the micro-nanostructure and biomechanical characteristics of bacterial biofilms. The device is made of polycarbonate, can perform high temperature sterilization, and is reusable, economical and environment-friendly. A plurality of detection samples are integrated together, therefore, the detection time of the AFM is shortened, and the characteristic of high flux is achieved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Two-axis direct fluid shear stress sensor
InactiveUS20090223302A1Facilitate pivotal movementFlow propertiesSurface/boundary effectWall shearStress induced
A micro sized multi-axis semiconductor skin friction / wall shear stress induced by fluid flow. The sensor design includes a shear / strain transduction gimble connected to a force collecting plate located at the flow boundary surface. The shear force collecting plate is interconnected by an arm to offset the tortional hinges from the fluid flow. The arm is connected to the shear force collecting plate through dual axis torsional hinges with piezoresistive torsional strain gauges. These gauges are disposed on the tortional hinges and provide a voltage output indicative of applied shear stress acting on the force collection plate proximate the flow boundary surface. Offsetting the torsional hinges creates a force concentration and resolution structure that enables the generation of a large stress on the strain gauge from small shear stress, or small displacement of the collecting plate. The design also isolates the torsional sensors from exposure to the fluid flow.
Owner:NASA
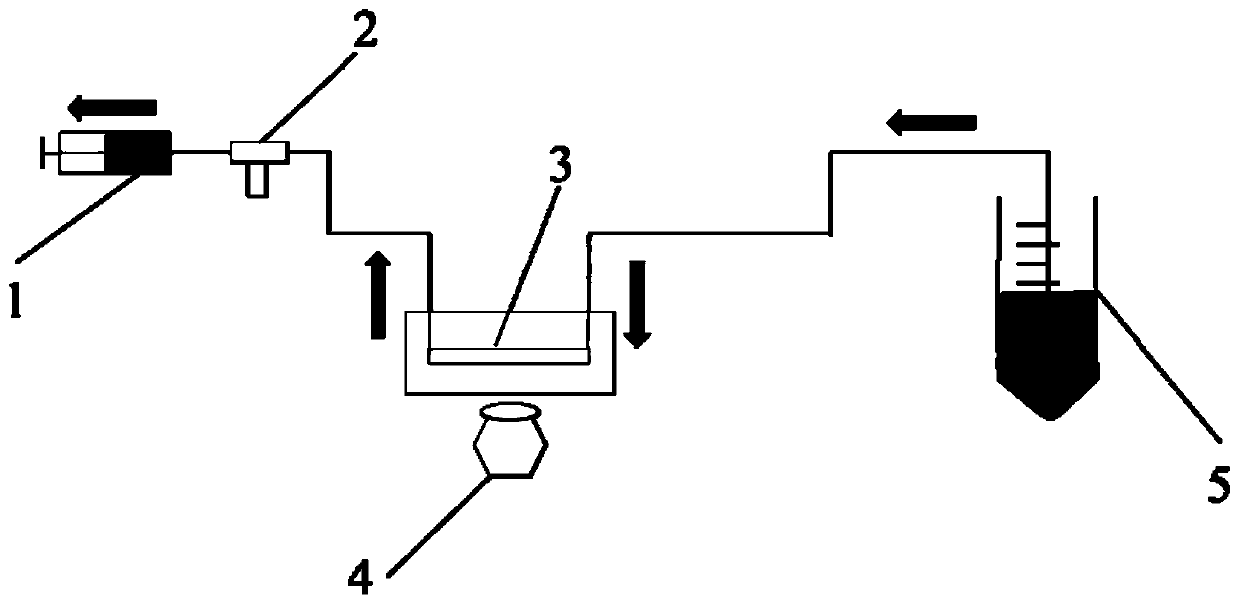
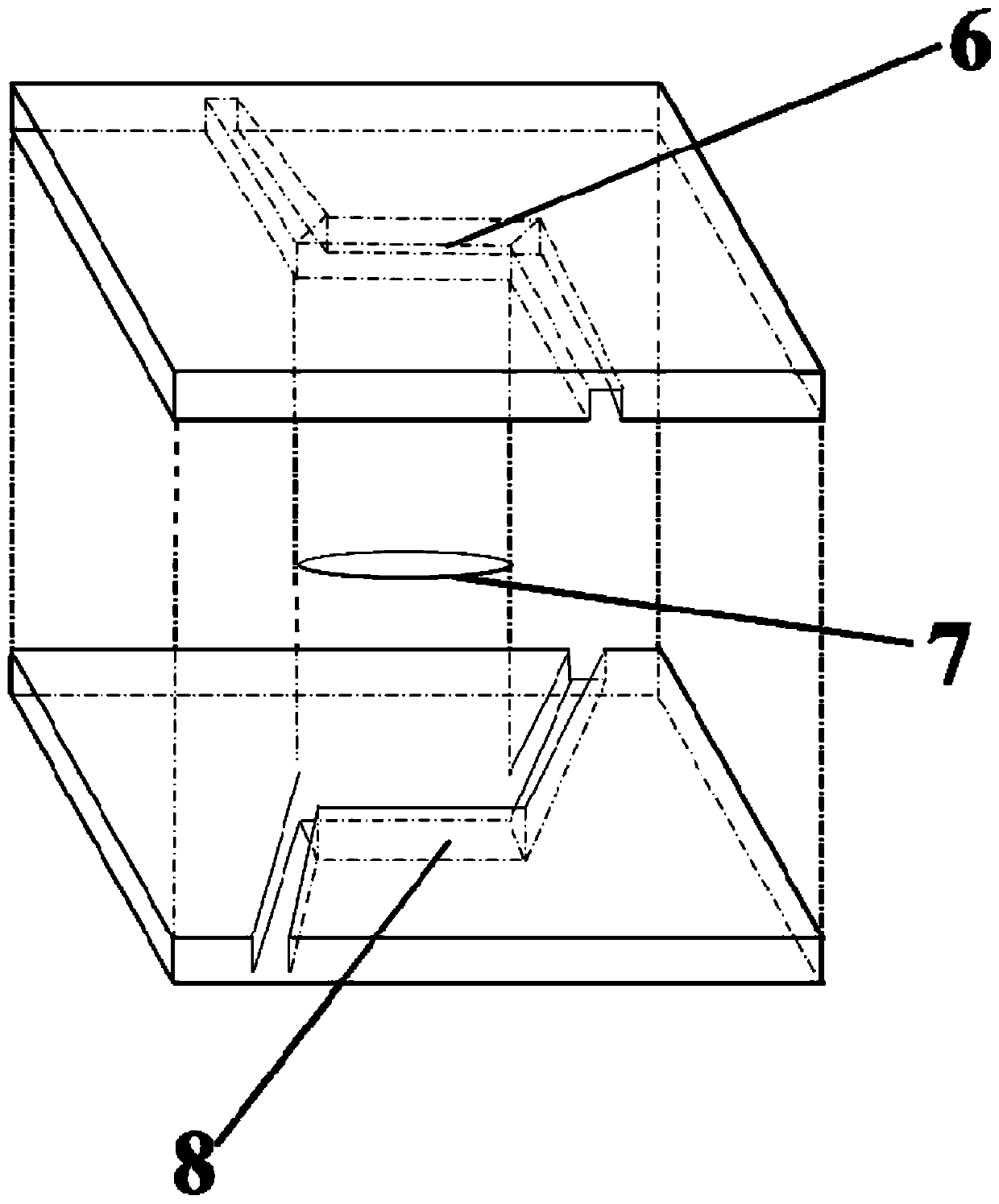
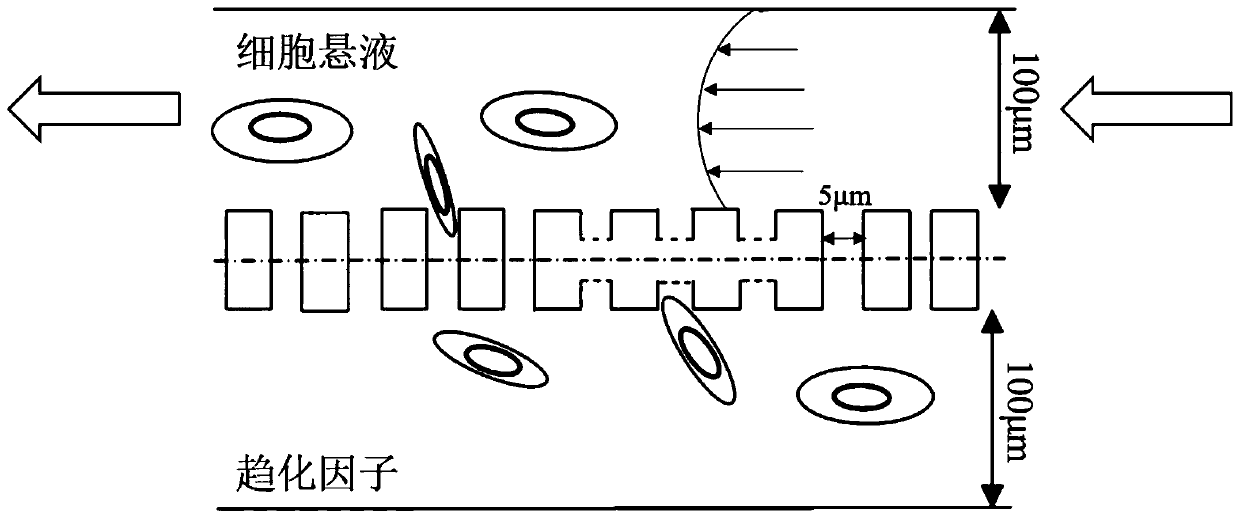
Micro-fluidic chip device for inducing transmembrane migration of cancer cells through fluid shear stress
InactiveCN110117524AMigration dynamic monitoringEasy to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbnormal tissue growthHuman body
The invention discloses a micro-fluidic chip device for inducing transmembrane migration of cancer cells through fluid shear stress. The device can simulate the true blood flow environment of the human body, and transmembrane migration behaviors of the cells under mechanical conditions are studied. The device comprises an injection pump, a three-way valve, a micro-fluidic chip, an inverted microscope, a silicone tube and a liquid storage apparatus. The injection pump is connected with the three-way valve, the three-way valve is connected with the micro-fluidic chip, the micro-fluidic chip is connected with the liquid storage apparatus, and the inverted microscope is used for observing the migration of the cells in channels of the micro-fluidic chip; the micro-fluidic chip comprises the upper and lower channels simulating the blood vessel and a thin film in the middle. The invention further provides a processing method of the micro-fluidic chip. The provided chip device has the advantages of being easy to manufacture, small in size, capable of precisely controlling the magnitude of shear stress and achieving dynamic monitoring and the like, and thus a feasible tool is provided for studying the effect of the fluid shear stress on tumor transfer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Experimental device and method for simulating in-vivo hydrodynamic environment
InactiveCN109628307AEasy maintenanceImprove adhesionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeristaltic pumpWater baths
The invention relates to an experimental device and method for simulating an in-vivo hydrodynamic environment, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The components of the device include a flat flowsmall chamber device, a timing switch, a peristaltic pump, a vacuum pump, a heating washer, a liquid storage bottle and a water bath pot. The invention provides the experimental device and method forsimulating the in-vivo hydrodynamic environment; additional carbon dioxide supply is not need to maintain the physiological pH value, and fluid shear stress stimulation is loaded to cells and other culture materials stably; the whole device does not need to be placed in an incubator for operation, on one hand, the operation difficulty is greatly reduced, on the other hand, the problem of instability of gas supply by gas cylinders is well solved, and the repeatability of the whole experiment is good.
Owner:南昌市第一医院
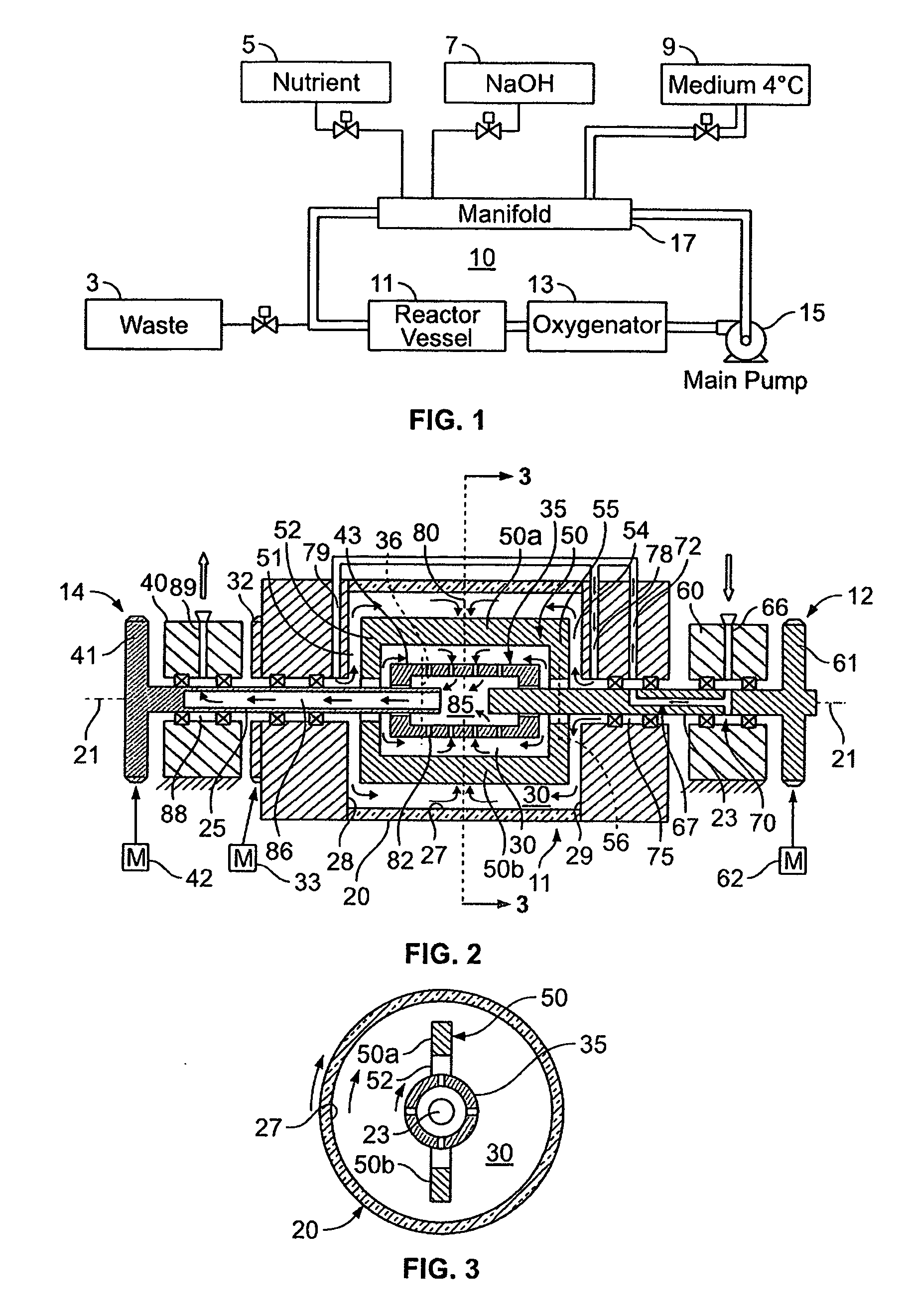
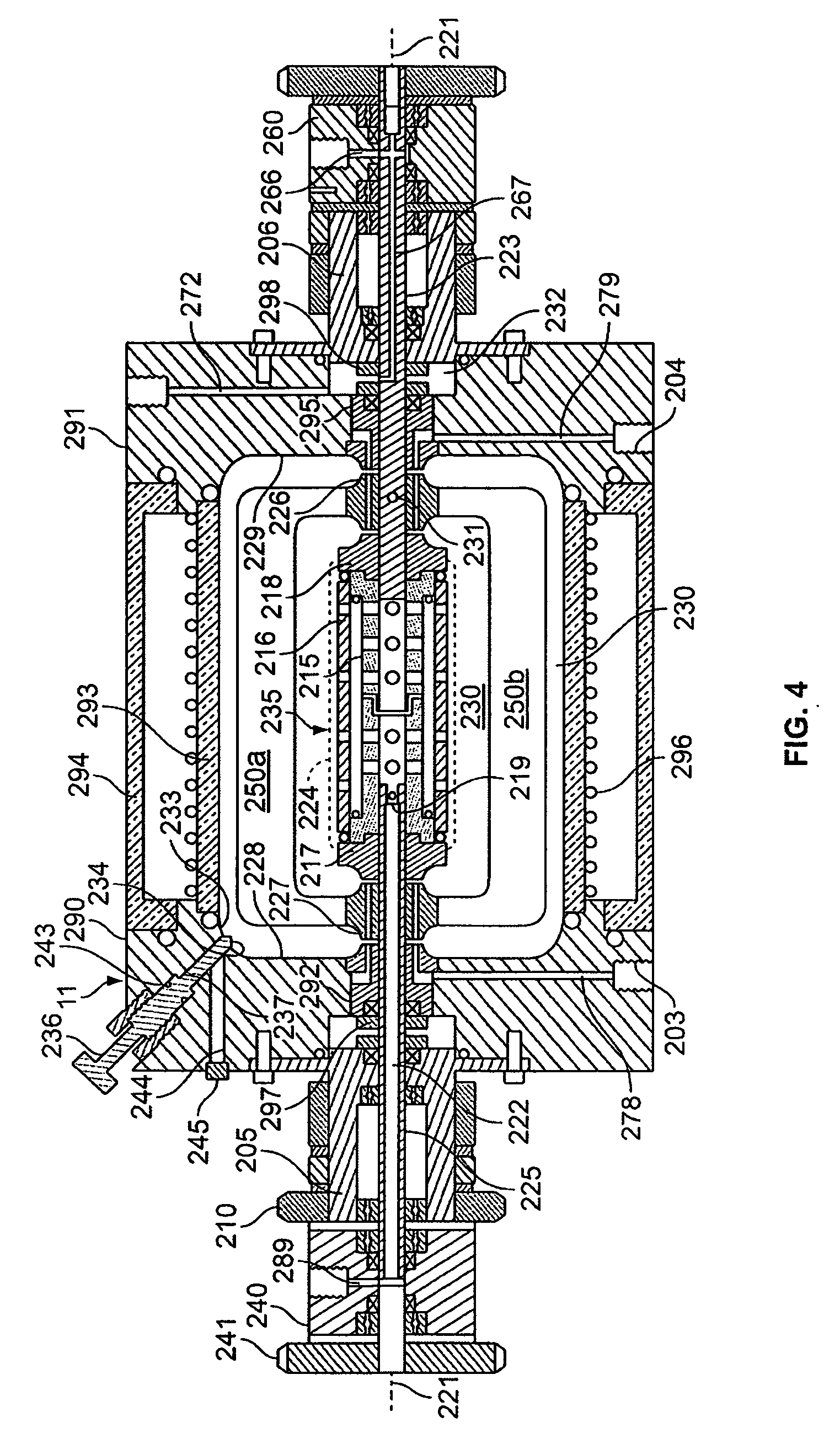
Method and device for regulating tower plate type perfusion bioreactor
ActiveCN103266182AAdjustable flow rateRegulating Fluid ShearBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPerfusion bioreactorFluid shear
The invention relates to the technical field of bioreactors in medical instruments, and in particular relates to a method and a device for regulating a tower plate type perfusion bioreactor. The method for regulating the tower plate type perfusion bioreactor comprises the following steps of: (1), regulating a regulating valve on each layer of tower plate; (2), cultivating cells under same fluid inlet structure parameters; (3), determining a tower plate layer number N with an optimum cultivation effect; (4), computing the flowing speed M of a fluid on the surface of an N-th layer of tower plate; (5), computing structure parameters A(i) of a fluid inlet between adjacent layers of tower plates; (6), regulating the regulating valve on each layer of tower plate; and (7), continuing cultivating the cells on the surface of each layer of regulated tower plate. According to the method and the device, the structure parameters of an inflow port in each layer of tower plate in the perfusion bioreactor can be regulated, so that the fluid shear stress between the adjacent layers of tower plates can be regulated according to a geometric structure, an optimization way is provided for distribution of the fluid shear stresses in each layer of tower plate, and the fluid shear stresses of all layers of tower plates can be optimized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Z-type simple parallel plate flow chamber
InactiveCN106811412AGood biocompatibilityGood solvent resistanceTissue/virus culture apparatusStress based microorganism growth stimulationBuffer tankDie swell
The invention provides a Z-shaped simple parallel plate flow chamber, which includes a bottom plate, a cover plate and a glass slide. The bottom plate is provided with a glass slide slot and an observation hole, and the cover plate is provided with an entrance and exit and an entrance and exit buffer groove. The level of the buffer platform at the entrance and exit of the slide is higher than the effective area of the slide, and the entrance and exit of the cover plate are perpendicular to the groove surface of the entrance and exit buffer tank, so that the fluid pressure will not directly act on the entrance and exit structure. The flow in the effective action area of the slide is stable, the effective action area is defined, and the effective action area ratio is improved. The fluid shear stress received by the cells in the effective action area of the slide is very uniform, which weakens the inlet and outlet effects of the parallel plate flow chamber. It can meet the needs of cell biomechanical experimental research, and by adjusting the inlet flow, the fluid shear stress can be regulated.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
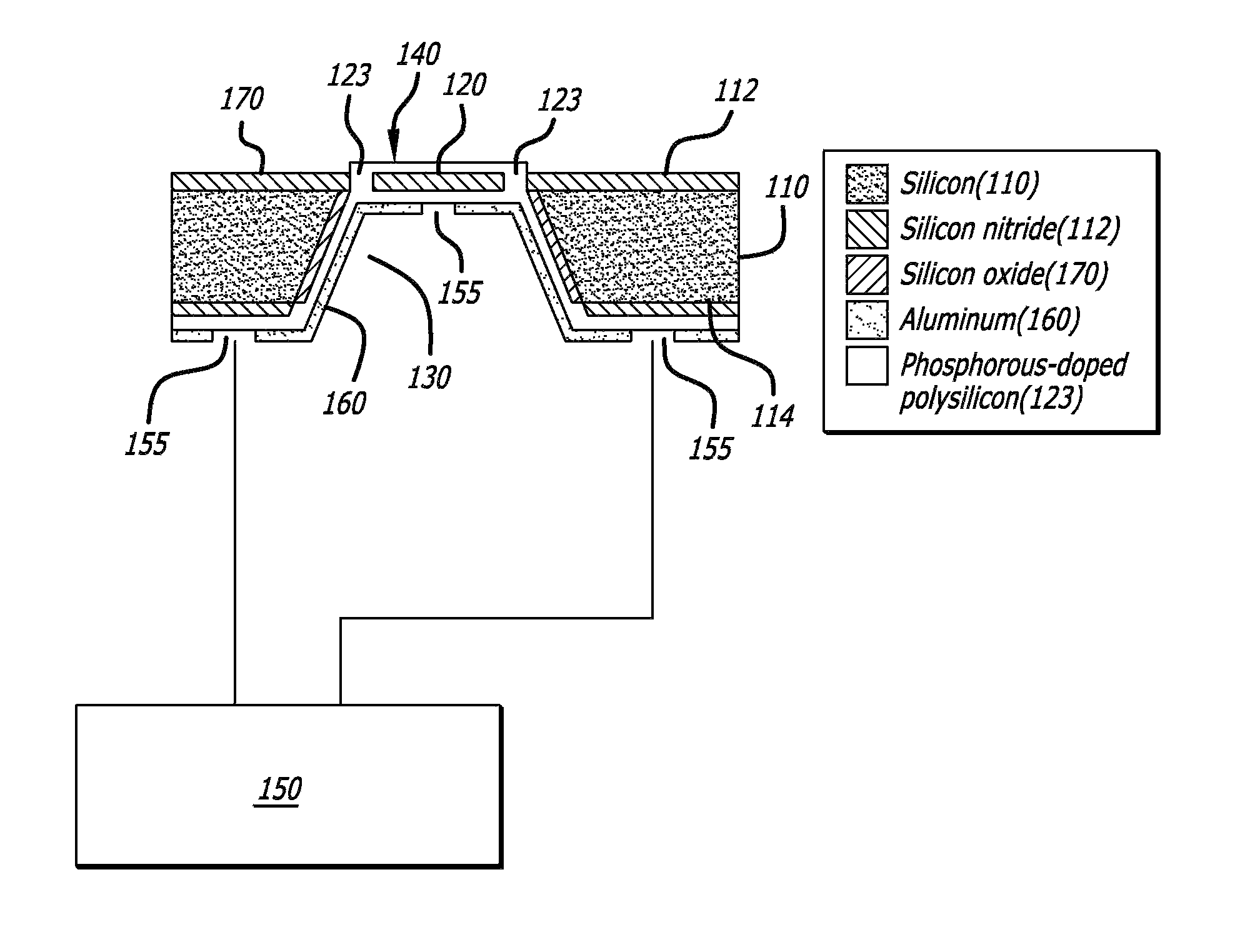
Biomedical implant for use in fluid shear stress environments
ActiveUS20140350671A1Promote cellular adhesionPromote cellular survivalStentsPaper/cardboard articlesLiving cellBiomedical engineering
The present invention relates to a biomedical implant for use in a fluid shear stress environment of a subject. The biomedical implant of the present invention includes a patterned surface having a plurality of cellular niches. The cellular niches of the patterned surface are effective to maintain at least one localized layer of living cells within the plurality of cellular niches by decreasing fluid shear stress within the cellular niches as compared to fluid shear stress measured outside of the cellular niches, with the fluid shear stress measured outside of the cellular niches having a peak fluid shear stress of at least about 50 dynes per square centimeter (dynes / cm2). The present invention also relates to methods of making and using the biomedical implant. The present invention further relates to a biomedical implant system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Flow shear stress mediated collagen self-assembly method
ActiveCN105641747AHigh simulationPromote reproductionTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberCone and plate viscometer
The invention provides a flow shear stress mediated collagen self-assembly method, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials and biomechanics. According to the method, a self-assembly mechanism of collagen is started under a neutral condition, and a flow shear action in a constant direction is applied to the collagen by utilizing a cone-and-plate viscometer and other mechanical loading devices. Compared with a traditional self-assembly method, the method has the advantages that a mechanic-chemical coupling system is constructed by taking the biomechanic microenvironment into consideration, and a real assembling process in a body is better simulated. Under mediation of a fluid shear stress, collagenous fibers are rearranged, so that subsequent deposition of hydroxyapatite can be facilitated. The novel collagenous fiber material has good biocompatability and degradability, has a mechanical characteristic matched with the collagen of human bone tissues, and has a wide application space.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Cellar mechanical simulation system for researching tumor cell epithelium-mesenchyma conversion
InactiveCN103409312ALong shear stress area lengthLarge difference in forceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEpitheliumEngineering
The invention discloses a cellar mechanical simulation system for researching tumor cell epithelium-mesenchyma conversion. The cellar mechanical simulation system for researching tumor cell epithelium-mesenchyma conversion comprises a constant flow pump, a liquid storage bottle and an in-vitro cellar mechanical stimulation device, and the constant flow pump, the liquid storage bottle and the in-vitro cellar mechanical stimulation device are connected in series through a conduit to form a closed ring. Compared with the prior art, the cellar mechanical simulation system for researching tumor cell epithelium-mesenchyma conversion allows a plurality of glass slides to be disposed, tumor cells planted on the glass slides to undergo shear stress loading, the loaded flow field to be uniform and stable and the shear stress loading having different sizes to be realized through the flow adjustment. The system can be used for observing the dynamic situation of the epithelium-mesenchyma conversion of the tumor cells planted on the glass slides after the action of the fluid shear stress and observing the local migration and adherence capability of the shear stress acted upstream cells to the downstream through the series-connected glass slides.
Owner:XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
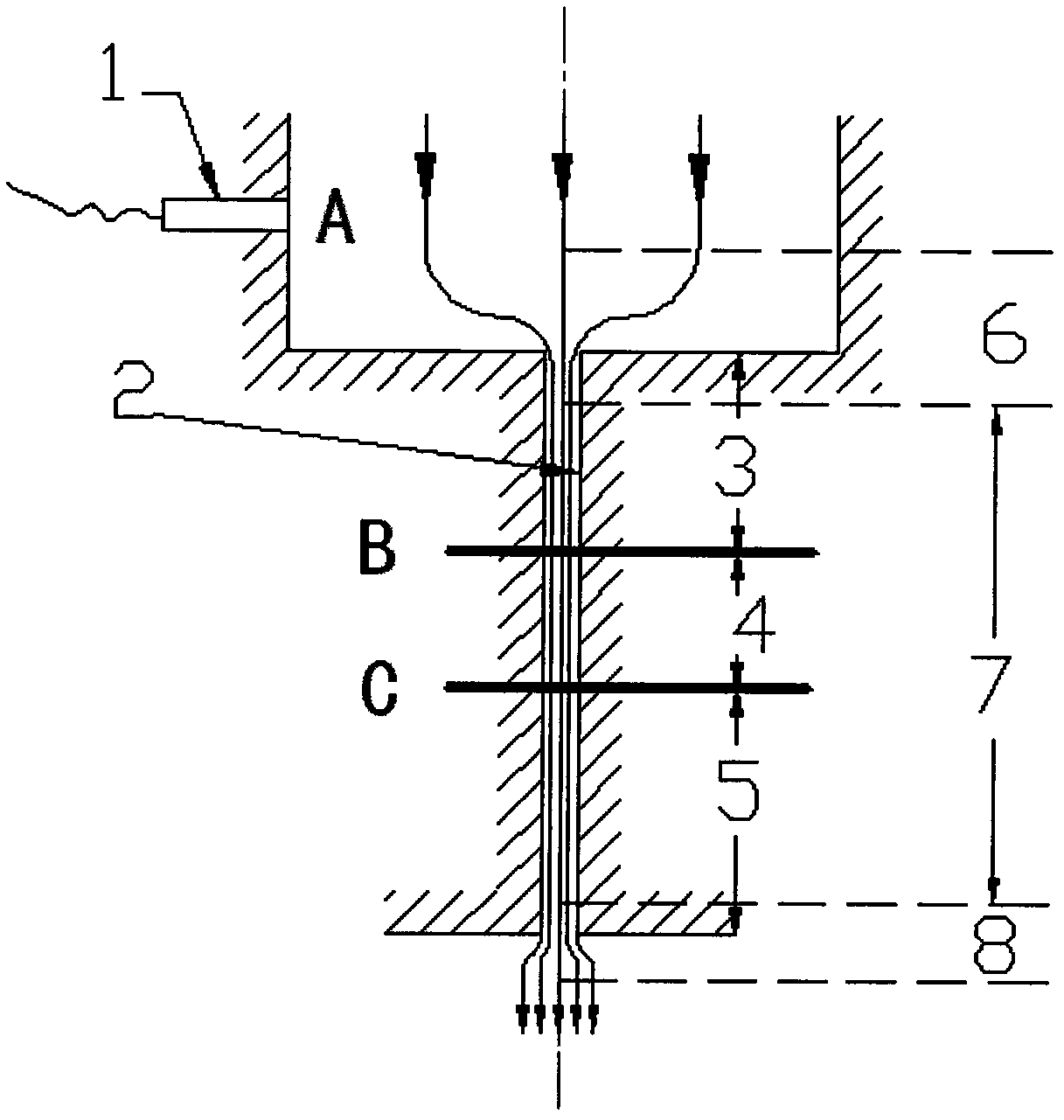
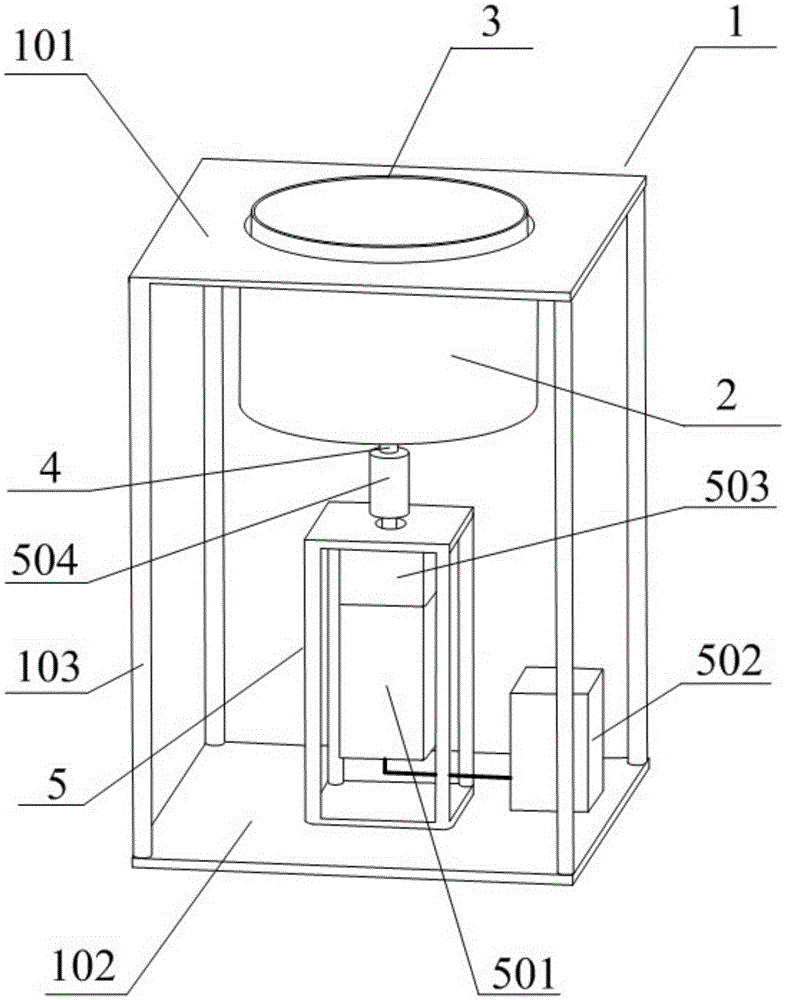
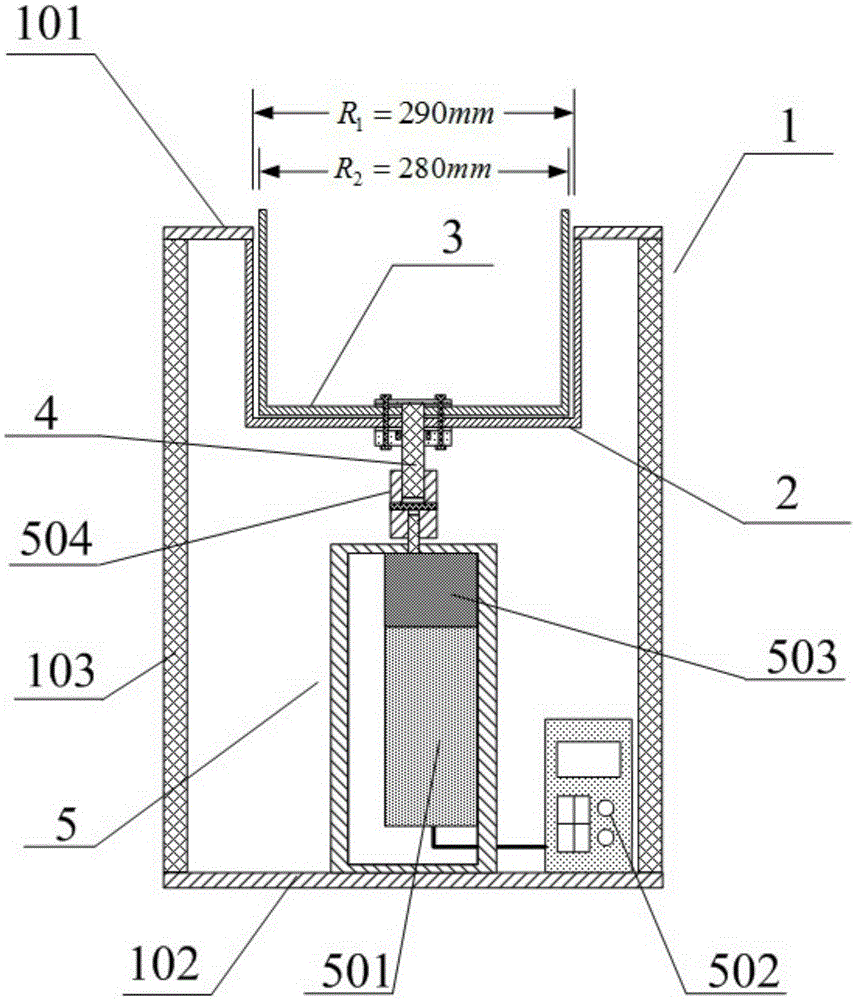
Fluid shear stress generator
The invention relates to the field of fluid experimental equipment and discloses a fluid shear stress generator. The fluid shear stress generator comprises a support frame, a fixed bucket, a rotating bucket, a revolving shaft and a vertical type rotation driving component; the fixed bucket is located on the upper portion of the support frame, the vertical type rotation driving component is located on the lower portion of the support frame, the rotating bucket is located inside the fixed bucket and is coaxial with the fixed bucket, the upper end of the revolving shaft penetrates through a round hole formed in the center of the bottom of the fixed bucket and is coaxially connected with the bottom of the rotating bucket, and the lower end of the revolving shaft is in axial connection with the vertical type rotation driving component. The fluid shear stress generator forms a coaxial cylinder type structure, fluid with the fluid shearing force in linear variation can be generated, the fluid shearing force at each position can be obtained accurately, the fluid shear stress generator further has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in cost, stable in generated fluid shearing force, large in volume and easy to adjust, and thus the fluid shear stress generator can be further widely applied to various fluid shearing force experiments.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for separating exosome from fluid shear stress perfusate
The invention discloses a method for separating exosome from fluid shear stress perfusate. A method of performing freeze-drying, redissolution and concentration on exosome in the fluid shear stress perfusate is adopted, so that the exosome in the fluid shear stress perfusate can be concentrated by about 10 times, in the concentration course, the exosome is not damaged, depletion of the exosome isnot caused, the obtained exosome is complete in structure, high in purity and low in hybridprotein pollution, the exosome in massive cell perfusate can be extracted in one time, costly equipment is not needed, used consumptive materials are low in price, and the extraction method is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Device for culturing in vitro cells through single axis rotating and online shearing
InactiveCN102181364BRealize the simulated microgravity effectFacilitate biomechanical researchTissue/virus culture apparatusStress based microorganism growth stimulationPeristaltic pumpBiomechanics
The invention discloses a device for culturing in vitro cells through single axis rotating and online shearing, belonging to the technical field of biomechanics engineering. The device mainly comprises a fixed rotating drum, flow chambers, a peristaltic pump, a liquid storage bottle, a waste liquid bottle, a motor and a base, wherein the flow chambers are fixed on the fixed rotating drum; the motor drives the fixed rotating drum to rotate at 360 degrees to ensure the sum of gravitational vector of a circle of rotation of the fixed rotating drum to be zero to simulate the microgravity effect; the rotational speed is voluntarily set along with rotation of the motor; the liquid storage bottle and the waste liquid bottle are fixed on the base; the liquid storage bottle is connected with the peristaltic pump; the peristaltic pump pumps the culture liquid to the flow chambers while the fixed rotating drum rotates to apply the fluid shear stress to the flow chambers; and the culture liquid flows back to the waste liquid bottle via the flow chambers. The device can be used for studying and exploring the biological effects of the cells after the cells are subjected to mechanical stimulation under the action of the microgravity, provides cellular and molecular mechanism basis for the astronauts to cope with the movement measures during space flight and has application prospect.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Biomedical implant for use in fluid shear stress environments
The present invention relates to a biomedical implant for use in a fluid shear stress environment of a subject. The biomedical implant of the present invention includes a patterned surface having a plurality of cellular niches. The cellular niches of the patterned surface are effective to maintain at least one localized layer of living cells within the plurality of cellular niches by decreasing fluid shear stress within the cellular niches as compared to fluid shear stress measured outside of the cellular niches, with the fluid shear stress measured outside of the cellular niches having a peak fluid shear stress of at least about 50 dynes per square centimeter (dynes / cm2). The present invention also relates to methods of making and using the biomedical implant. The present invention further relates to a biomedical implant system.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
A reactor for biological or chemical transformation
ActiveUS20160243462A1Facilitated reaction kineticsLower the volumeImmobilised enzymesShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersSolid reactionChemical transformation
The present invention relates to a new reactor for performing, by means of at least one solid reaction member, biological or chemical transformation, or physical or chemical trapping from, or release of agents to, a fluidic medium, which reactor is comprised of a reactor vessel comprising means for enhancing fluidic shear stress, and a transformation device operatively mounted in said reactor vessel. The invention also provides a kit of parts comprising a reactor vessel comprising means for enhancing fluidic shear stress and a transformation device. Finally, the invention provides a method of using said reactor and / or said kit of parts for biological or chemical transformation or physical or chemical trapping from, or release of agents to, a fluidic medium, by means of at least one solid reaction member.
Owner:SPINCHEM AB
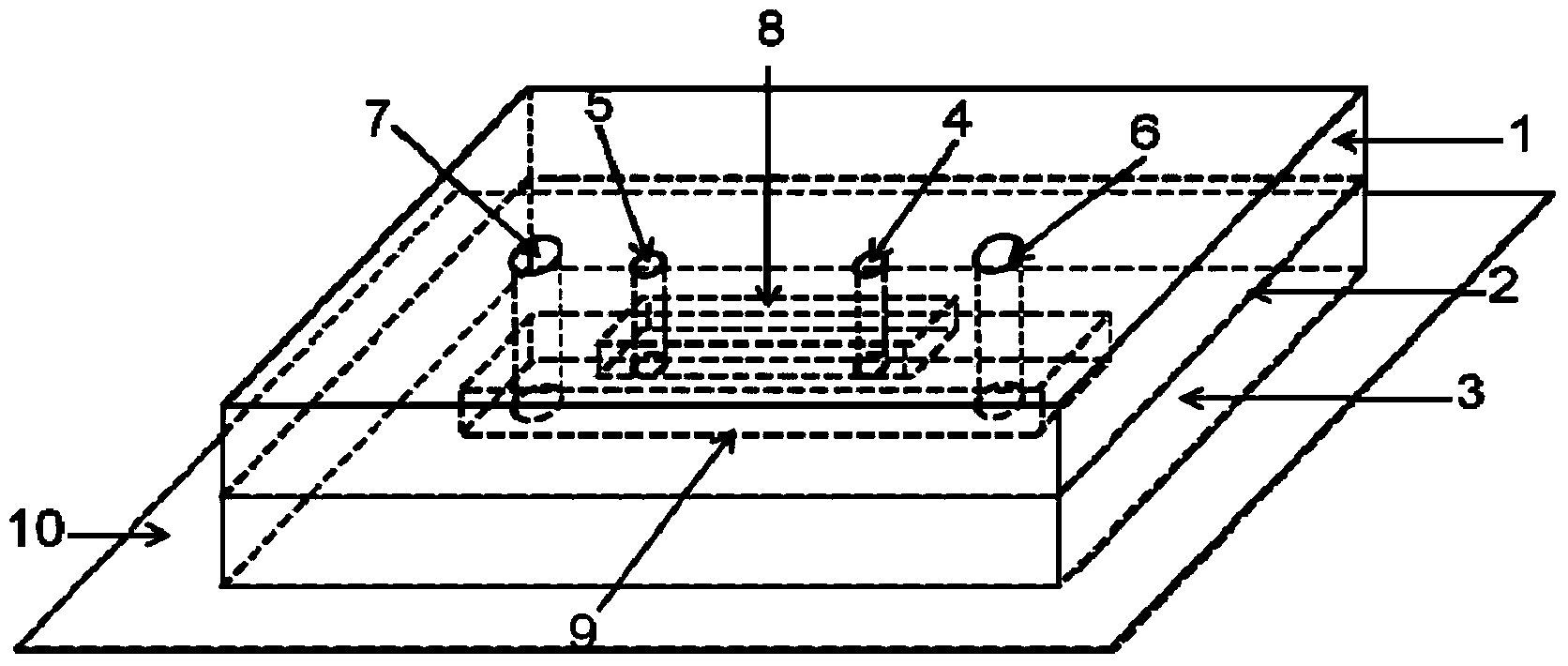
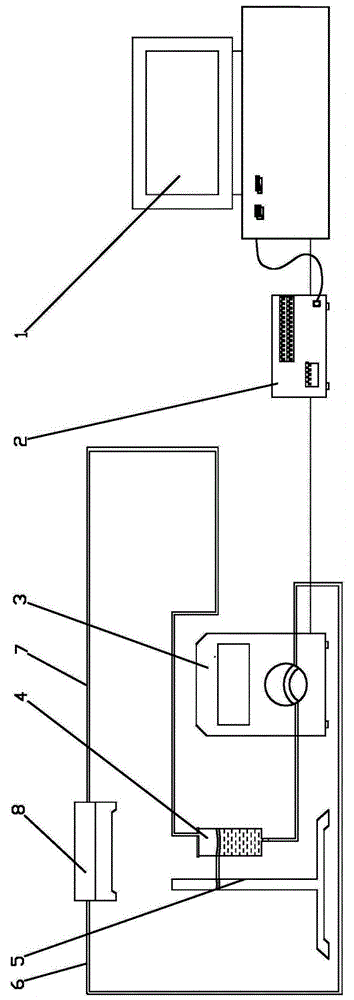
Experimental apparatus for testing shear stress of cell fluid
InactiveCN106701558ASimple structureInnovative designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPeristaltic pumpLiquid storage tank
The invention relates to an experimental apparatus for testing shear stress of cell fluid, which relates to the technical field of experimental devices for testing the shear stress of the cell fluid, and particularly relates to the experimental apparatus for testing shear stress of the cell fluid. The experimental apparatus comprises a principal computer (1), a pump controller (2), a peristaltic pump (3), a liquid storage tank (4), a support (5), a water outlet pipe (6), a water return pipe (7) and a fluid chamber (8), and is characterized in that the pump controller (2) is connected with the principal computer (1) and the peristaltic pump (3), the liquid storage tank (4) is installed on the support in a matching manner, a water returning opening is formed in the upper portion of the liquid storage tank (4), a water outlet is formed in the lower portion of the liquid storage tank (4), an inlet is formed in one end of the fluid chamber (8), an outlet is formed in the other end of the fluid cell (8), one end of the water outlet pipe (6) is connected with the water outlet of the liquid storage tank (4), and the other end is connected with the inlet of the fluid cell (8) in the matching manner by virtue of a pump head of the peristaltic pump (3).
Owner:夏亚一
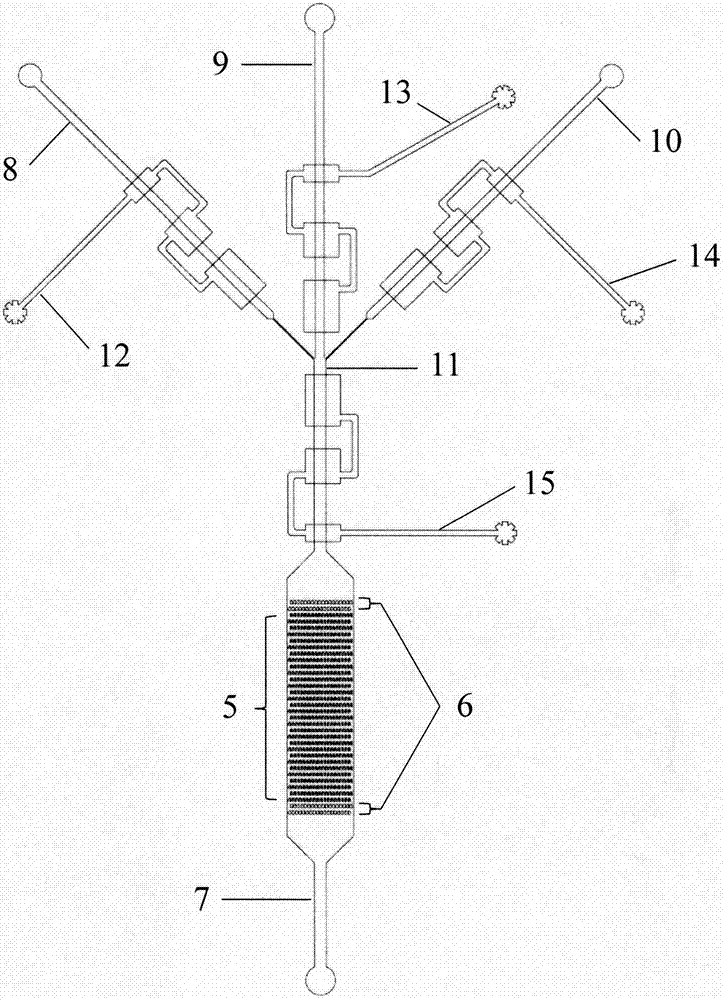
Chute plate apparatus and assay method for studying the effect of fluid shear stress on cells
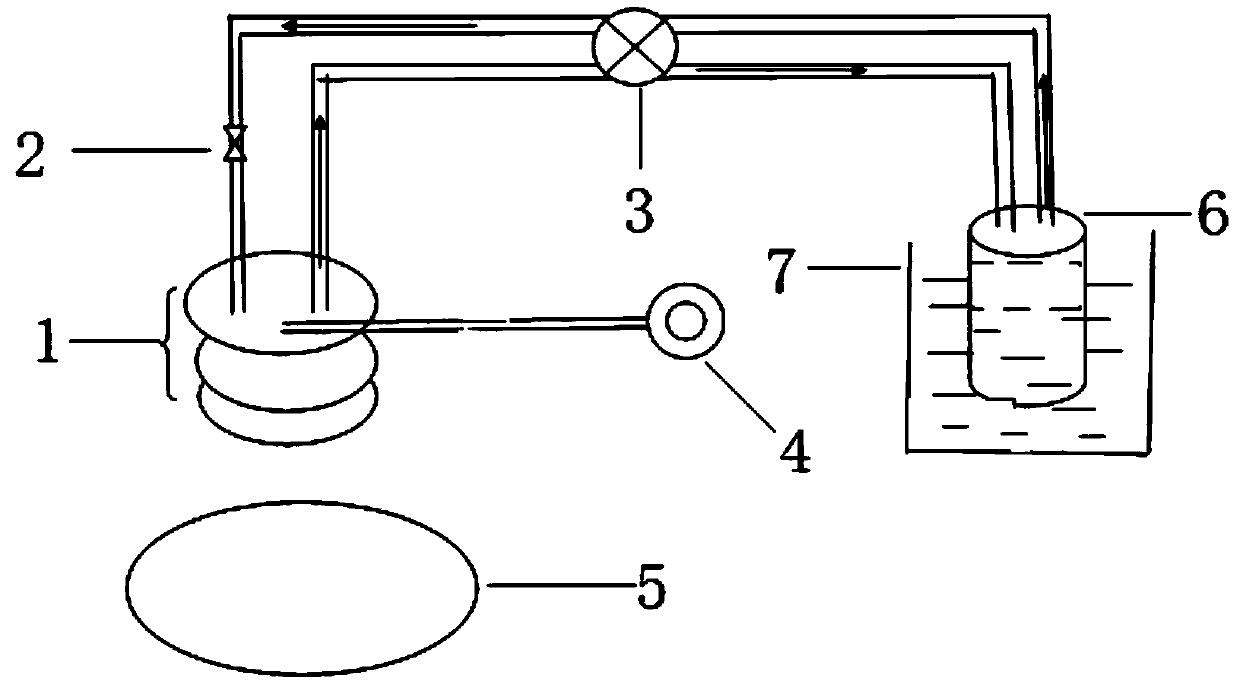
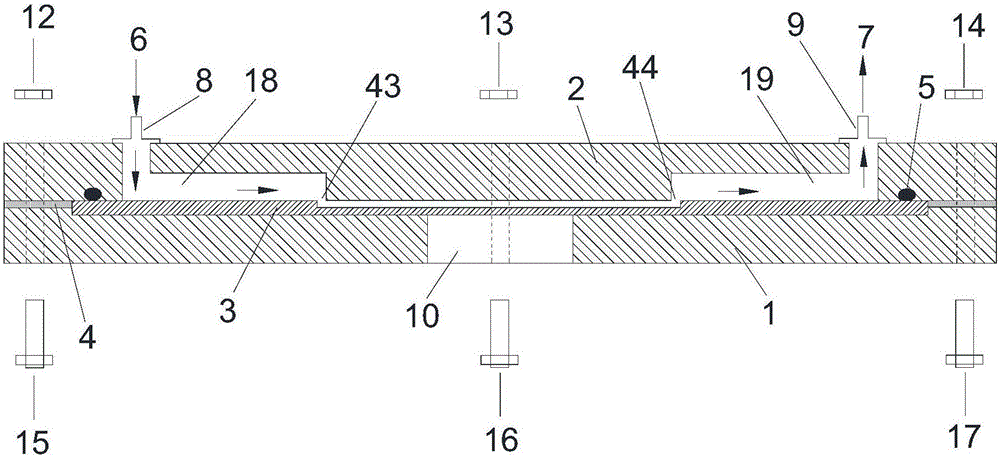
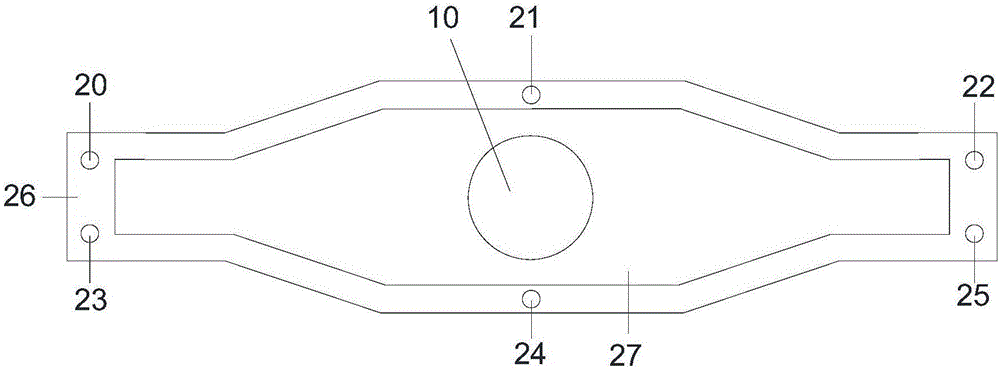
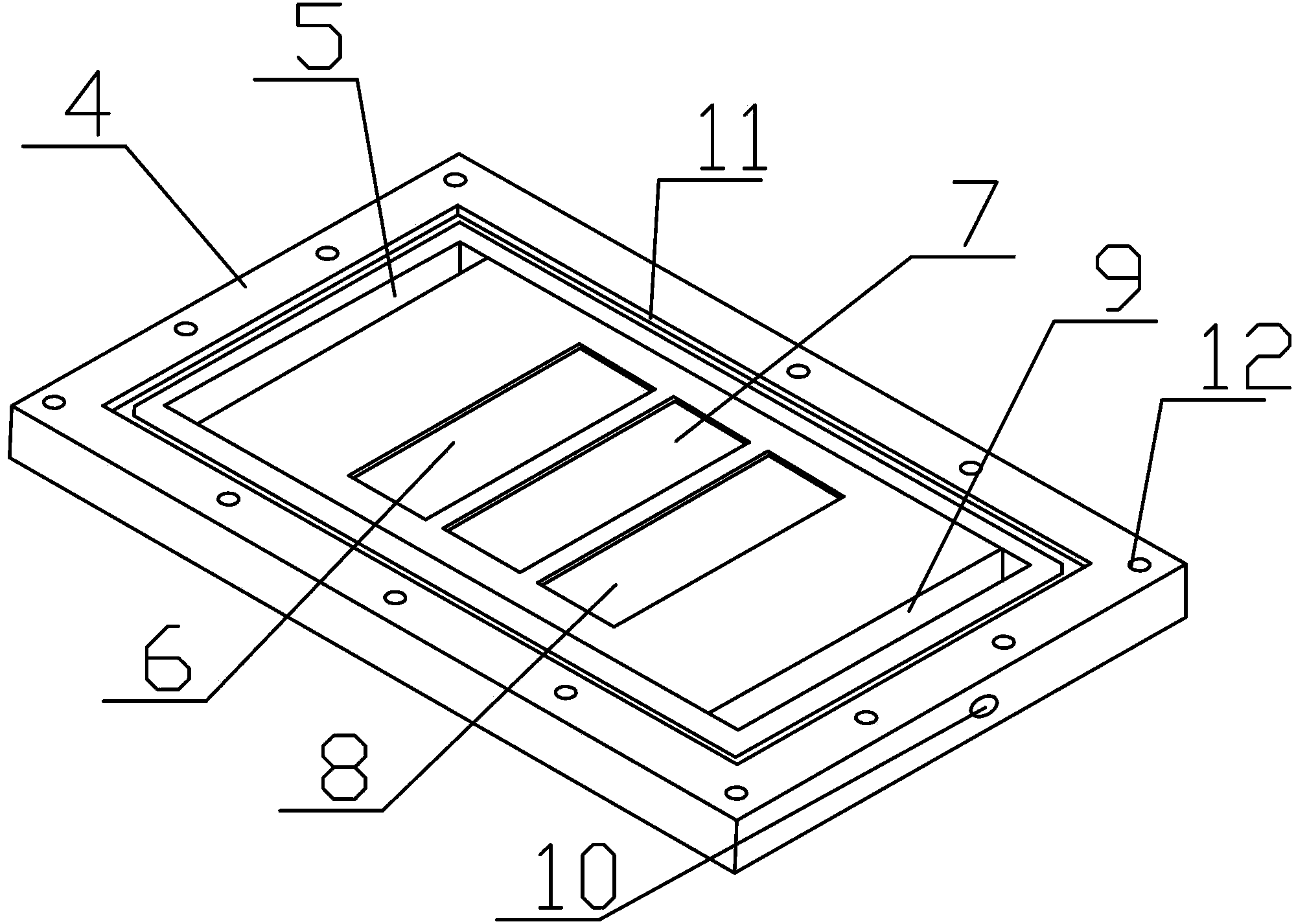
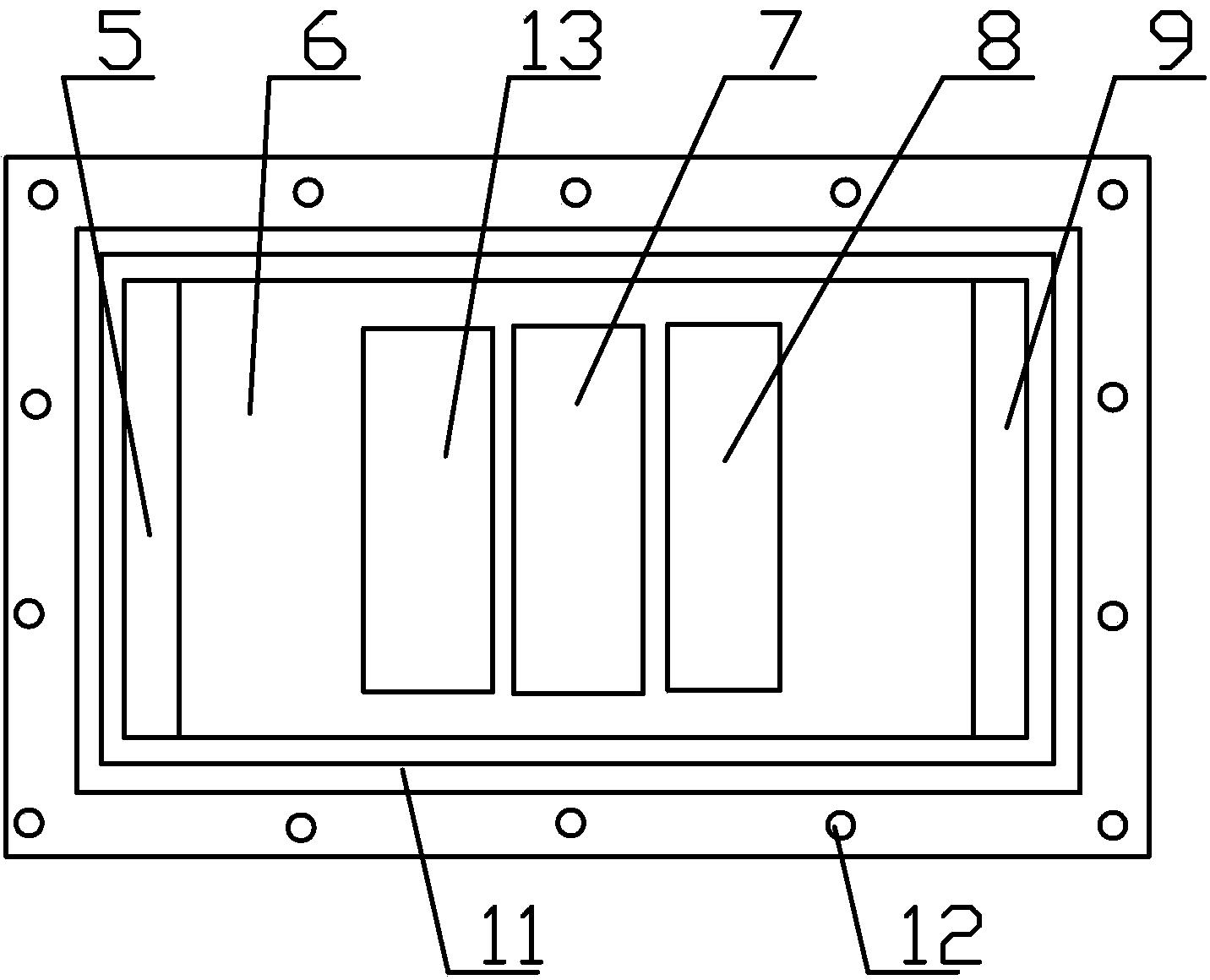
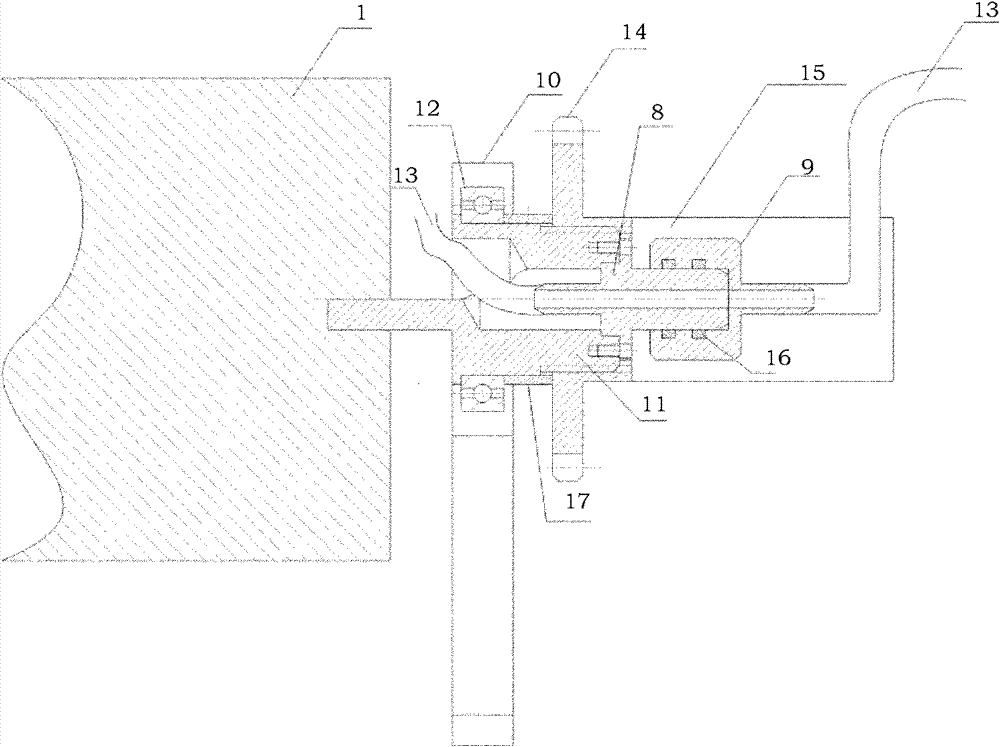
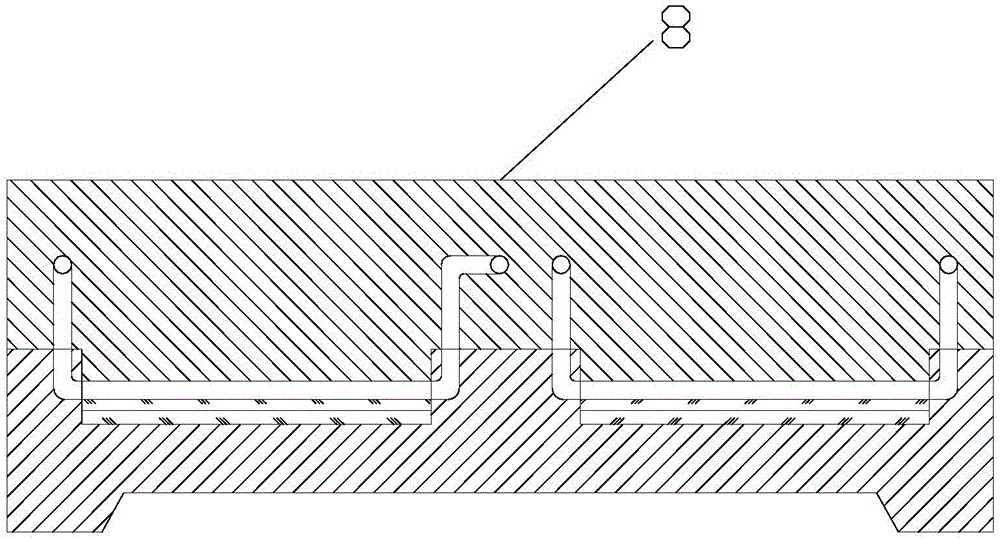
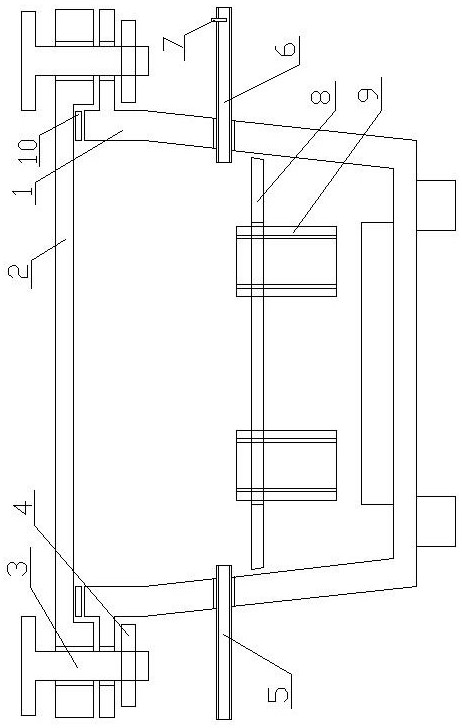
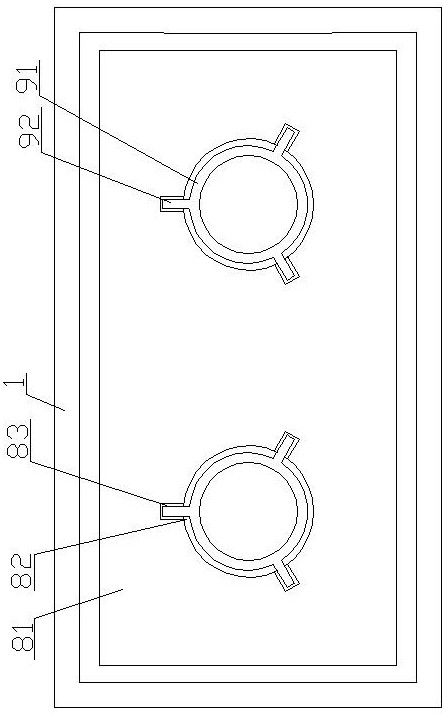
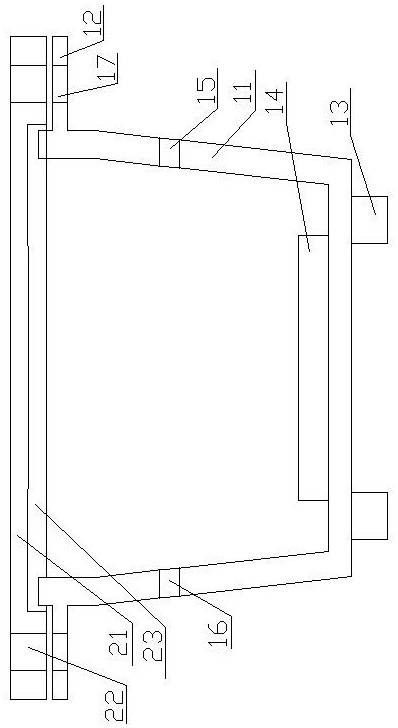
ActiveCN109655379BAchieving direct contact culturePrecise size controlDirect flow property measurementEngineeringMechanical engineering
A chute plate device and measurement method for studying the influence of fluid shear stress on cells, comprising a box shell (1) for accommodating cell carriers, arranged on the box shell (1) and used for adjusting the box shell (1) ) into the input tube (5) for injecting the flow fluid that produces shear stress on the cells, and the output tube that is arranged on the box shell (1) and is used to discharge the flow fluid that produces shear stress on the cells in the box shell (1) (6), the signal pick-up sensor (7), which is arranged in the output tube (6) and is used to pick up the signal of the shear stress acting on the cell, passes through the box shell (1) to accommodate the cell carrier, and passes through the input tube ( 5) and the output tube (6), to realize the flow fluid that produces shear stress on the cells, and the signal pickup sensor (7), to pick up the signal used to pick up the shear stress acting on the cells, no longer using a The flat plate is grooved, thus improving the precision of the effects of fluid shear stress on the cells.
Owner:WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com