Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Escherichia coli detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
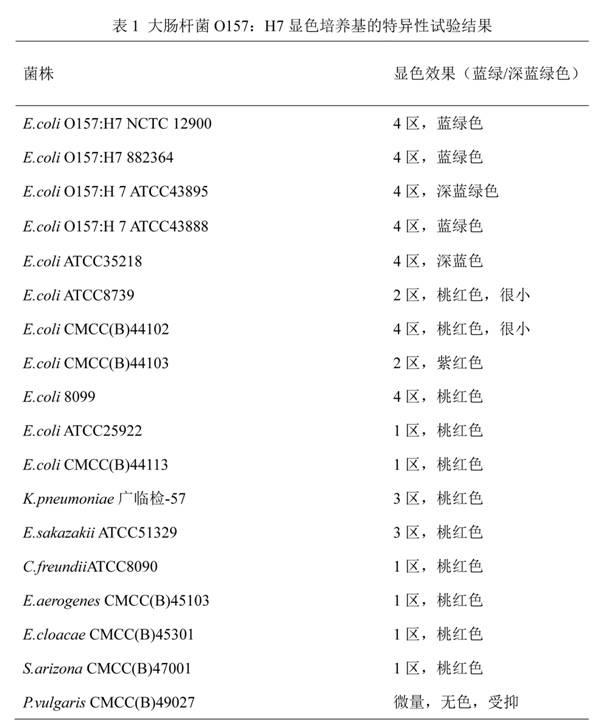
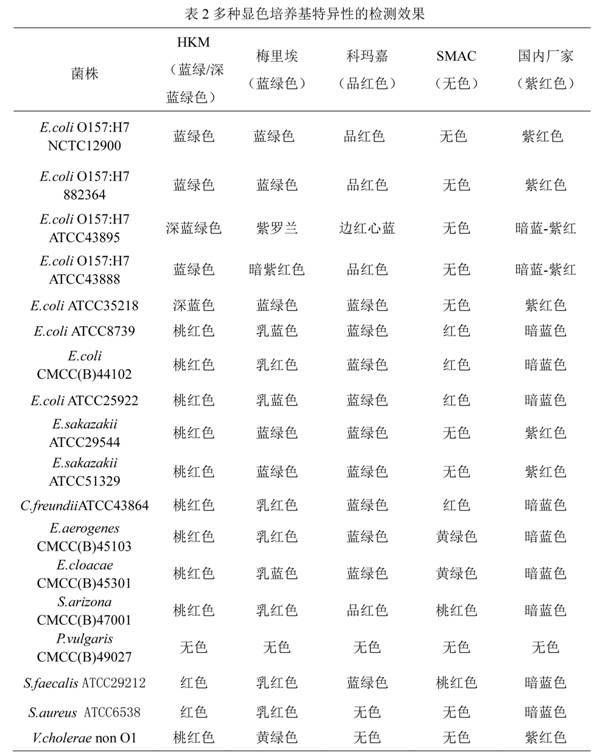
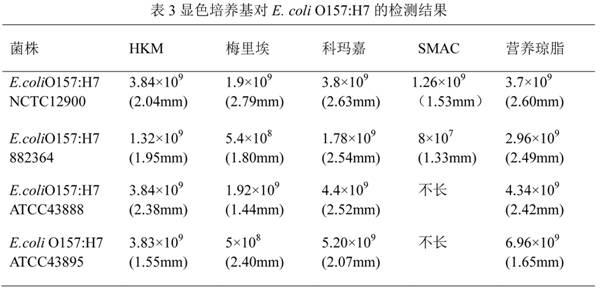
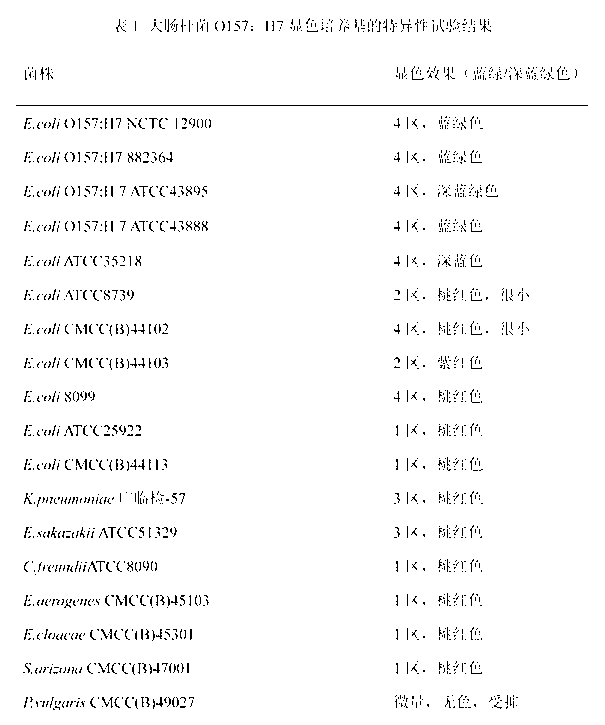
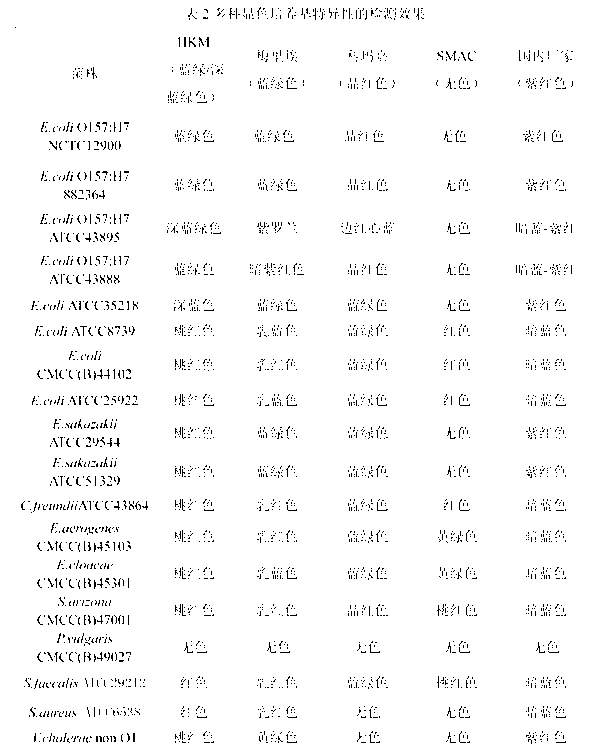
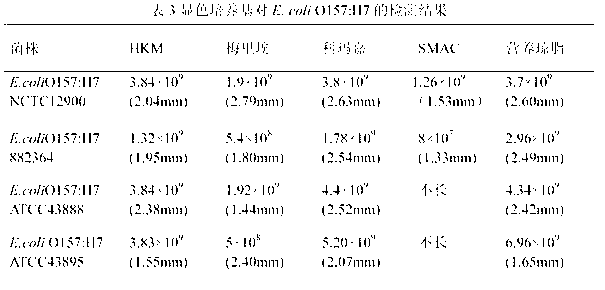
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN102424832AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
CPA primer, kit and detection method for escherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN109652574AReduce false positive resultsGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
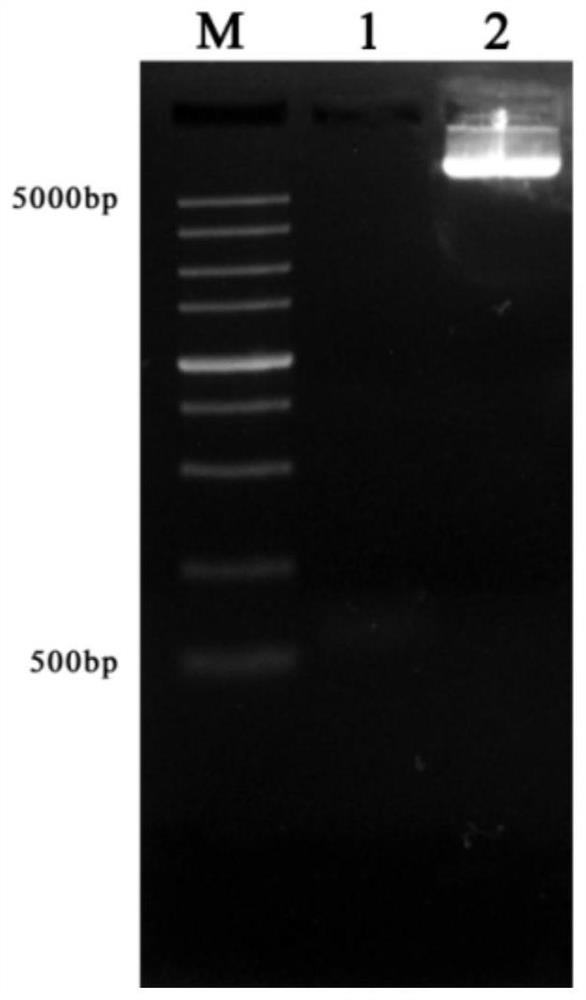
The invention discloses a CPA primer, kit and detection method for escherichia coli O157:H7. The CPA primer designed for a target rfbE comprises stripping primers 4s and 5a, a crossing amplification primer 2a1s and specific primers 2a and 3a; the nucleotide sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO.1-NO.5 respectively. A crossing priming amplification reaction detection and identification system designed for specific target sequences rfbE and stx1 of E.coli O157:H7 overcomes the defects of long required cycle, low sensitivity, high cost and difficult field application of methods in the prior art. By selecting a conserved region of the specific sequences rfbE and stx1 of a target strain, a pair of stripping primers, the crossing primer and the specific primers are designed to construct the crossing priming amplification reaction system, and a detection result is obtained within about 60 minutes to shorten the traditional cycle for detecting escherichia coli.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Online analyzer of Escherichia coli
InactiveCN102175661ARealize automatic samplingRealize automatic measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceElectricityDisplay device
The invention relates to bacterium detecting equipment and particularly discloses an online analyzer of Escherichia coli, and the online analyzer comprises a constant temperature box and a sampling pump, wherein a temperature sensor, a heating device, an analyzer mainboard, a culture dish and a fluorescence spectrophotometer are arranged in the constant temperature box; a display is arranged outside the constant temperature box; the analyzer mainboard is electrically connected with the temperature sensor, the heating device, the fluorescence spectrophotometer and the display; and the outlet of the sampling pump is in pipe joint with the culture dish, and the inlet of the sampling pump is connected with an external sample pipe. The online analyzer disclosed by the invention can be used for realizing the automation and integration of the functions such as the sampling, culturing, analyzing, displaying and the like of the Escherichia coli detection, has the advantages of high detection sensitivity, high detection speed, low cost, no secondary pollution, small maintenance amount and low operation cost and can be used for realizing the automatic online analysis and monitoring of the Escherichia coli.
Owner:UNIVERSTAR SCI & TECH SHENZHEN
Method for detecting escherichia coli O157 based on nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology
InactiveCN107338291AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleic acid detection
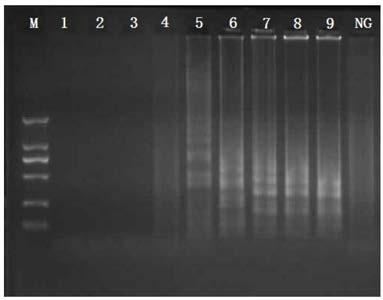
The invention relates to a method for detecting escherichia coli O157 based on a nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology. According to a virulence gene rfb E of escherichia coli O157, loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers (SEQ ID NO:1-4) are designed, and through the combination with a nano-enzyme nucleic acid test strip, the escherichia coli O157 detection method based on an LAMP nano-enzyme sensor is established. The method for detecting escherichia coli O157 based on the nucleic acid chromatography biosensing technology can be successfully used for distinguishing live bacterial cells from dead bacterial cells, and the lower limit of detection on escherichia coli O157 can reach 10 CFU / mL.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Detection method of toxicity of nanomaterials
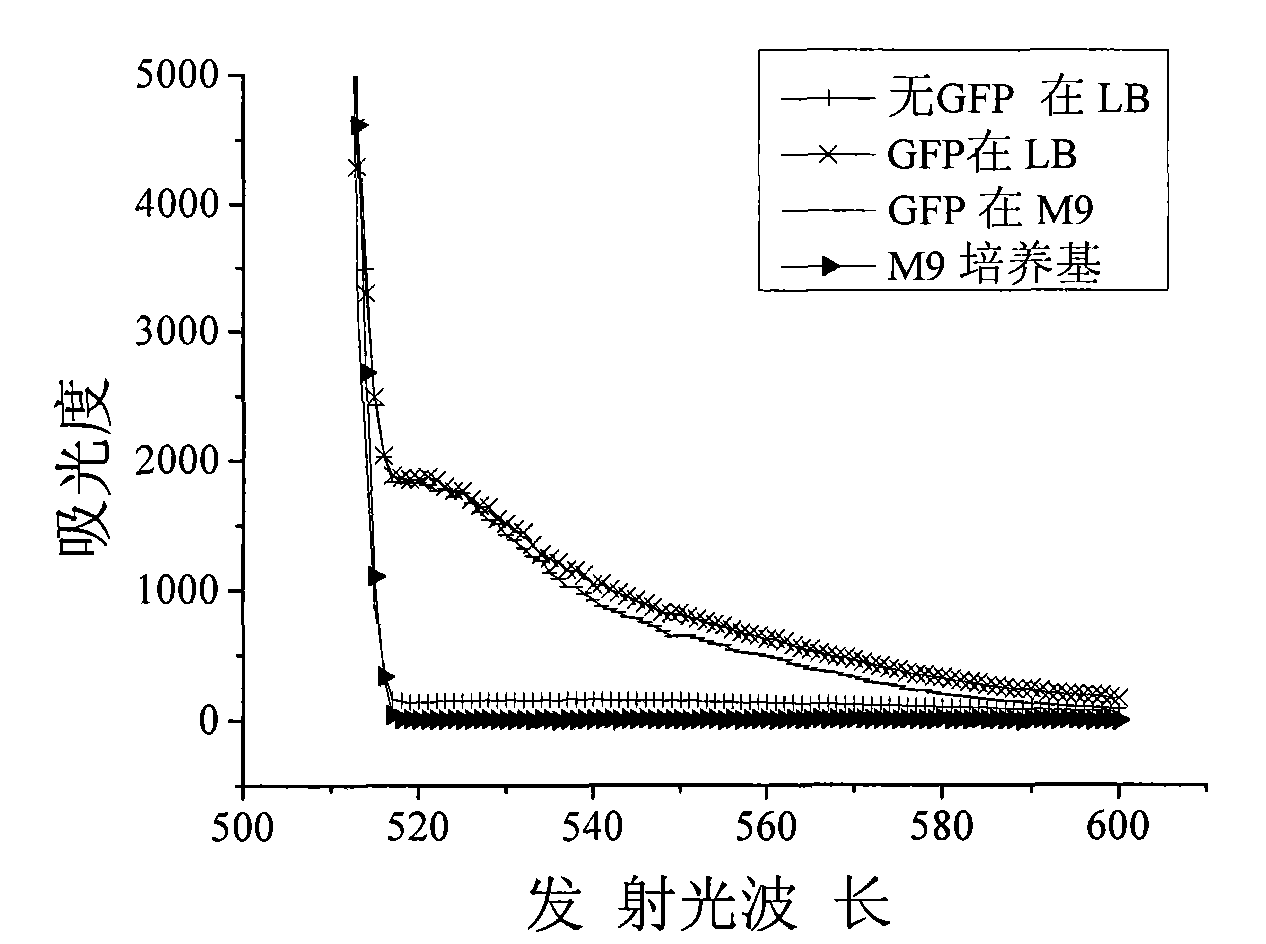
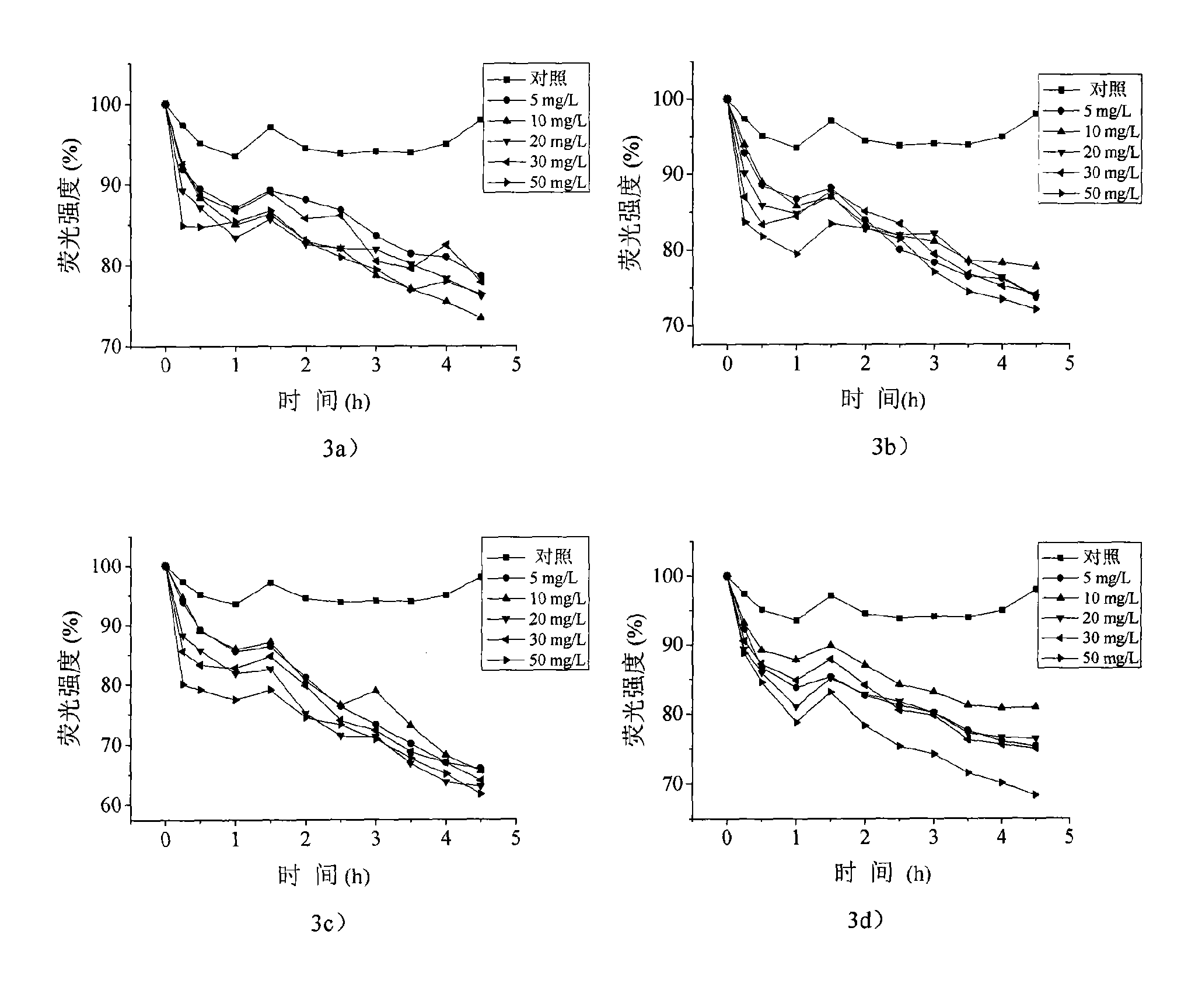
InactiveCN101671718AEfficient detectionStable detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNatural organic matterGreen fluorescent protein
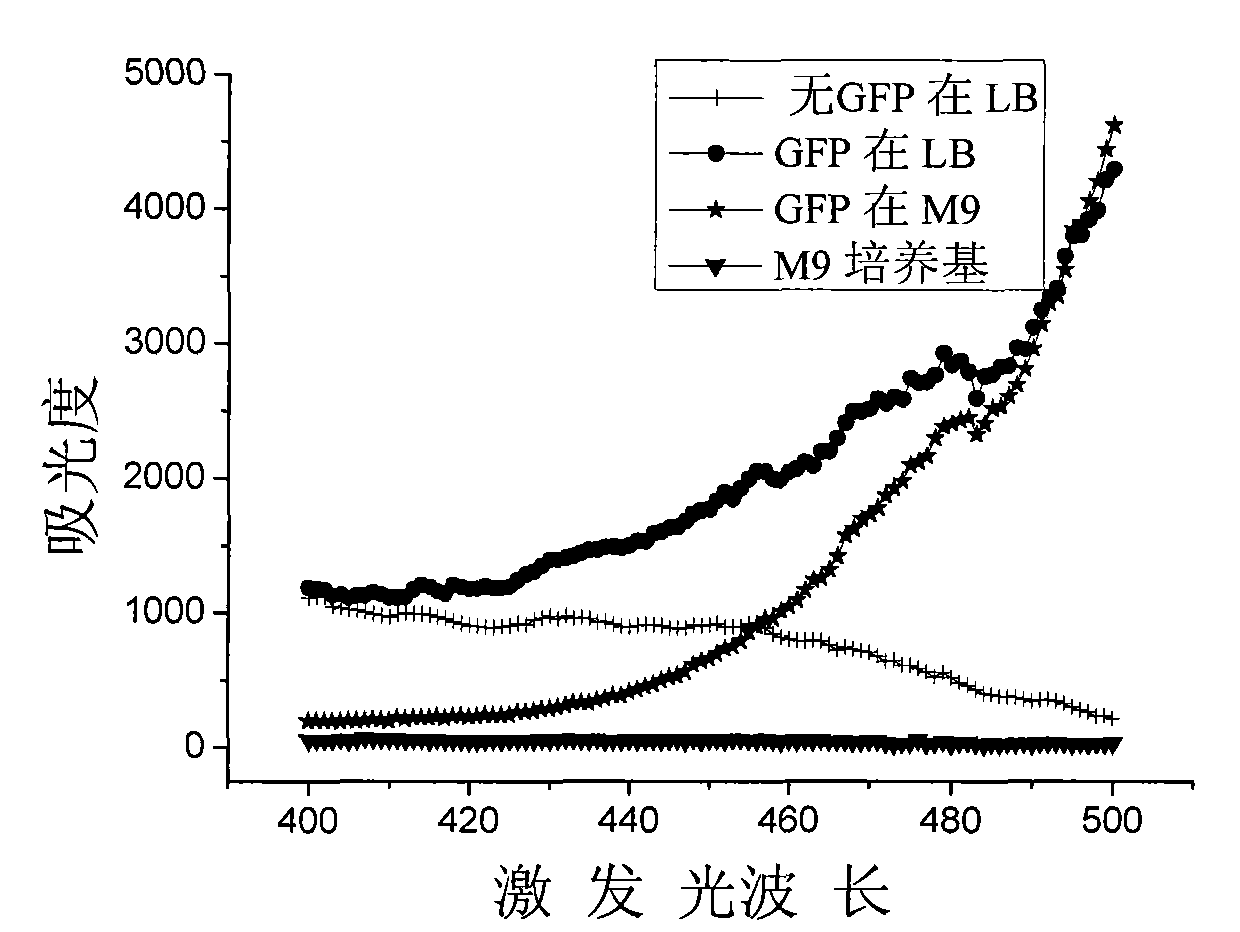
The invention relates to a detection method belonging to the technical field of environmental detection, in particular to a method for detecting toxicity of nanomaterials in the environment by adopting Escherichia coli containing green florescent protein plasmids. The method overcomes the interference of a few natural organic matters existing in the environment with the detection of toxicity of the nanomaterials so that the detection of toxicity of the nanomaterials is more convenient and accurate. The specific method selects the Escherichia coli transforming the green florescent protein plasmids as the bacterium for detection and comprises the following steps: 1. using an M9 culture medium to prepare bacterial suspension of the Escherichia coli containing the green florescent protein plasmids; 2. using ultrasonic dispersing nanomaterials to prepare suspension of nano particulate matters; and 3. culturing the nano particulate matters and the bacterial suspension of the Escherichia coliat 37 DEG C, using an enzyme-labeling instrument to detect the change of the florescence intensity of the nano particulate matters in certain period and judging the toxicity of the nano particulate matters to the Escherichia coli according to the difference of the change of the florescence intensity. The invention provides the efficient and stable detection method of toxicity of the nanomaterialsand the method is not likely to be interfered by other factors and is simple and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Coliform detection process and kit for use therein
InactiveUS20110269179A1Improve sampling efficiencyClogging problemPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementLarge intestineCulture mediums
A process comprises (a) providing (1) at least one sample suspected of comprising at least one coliform strain, (2) at least one culture device comprising at least one culture medium that is hydrated or hydratable, and (3) at least one particulate concentration agent that is substantially optically transparent when in contact with the culture medium in the culture device when the culture medium is hydrated; (b) placing the particulate concentration agent in contact with the sample such that at least a portion of the coliform strain is bound to the particulate concentration agent to form coliform-bound particulate concentration agent; (c) placing the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium; (d) incubating the culture device comprising the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium, the culture medium being hydrated; and (e) optically detecting the presence of the coliform strain without separating the coliform strain from the particulate concentration agent.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Gold nanorod biotic compound and preparation method and applications thereof
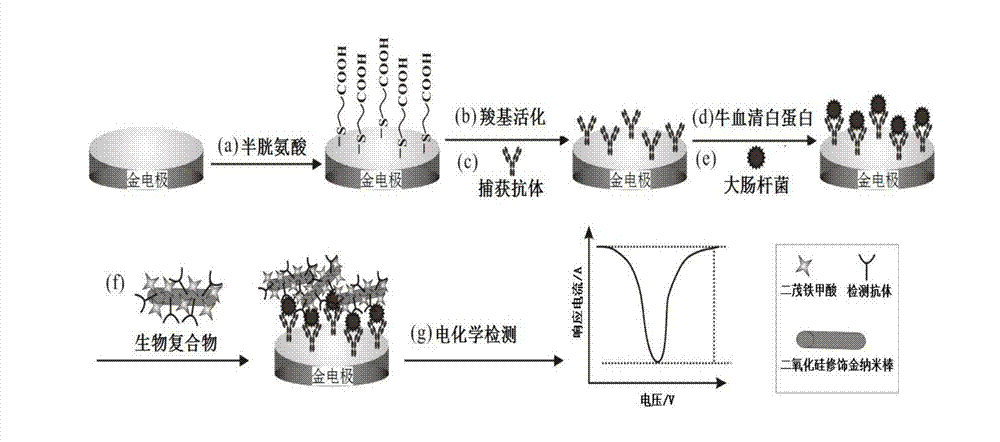
InactiveCN104493160AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial electrochemical variablesGold nanorodFerrocenecarboxylic acid
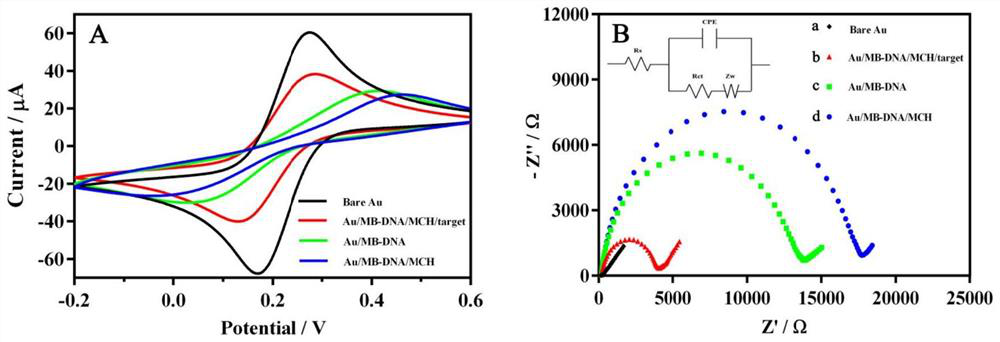
The invention discloses a gold nanorod biotic compound and a preparation method and applications thereof and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical analysis. A gold nanorod modified by silicon dioxide (AuNRs@SiO2) is used as a carrier and combined with a detection antibody (dAb) and ferrocenecarboxylic acid (Fc) to prepare dAb-AuNR-Fc which is used for amplifying escherichia coli in an electrochemical immunoassay dairy product. A 'sandwich' immunoassay model is established on basis of specificity interaction between the escherichia coli and escherichia coli antibody, and Fc combined with an electrode surface is measured by a differential pulse voltammetry to obtain a current signal. According to the gold nanorod biotic compound and the preparation method and the applications thereof, the electrochemical immunoassay method based on dAb-AuNR-Fc biotic compound is used for escherichia coli detection, the detection sensitivity, the specificity and the accuracy are high, and a novel method is provided for analysis and research of the escherichia coli in the dairy product.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for detecting the presence or absence of pathogenic Staphylococci in a test sample, including test mixture with micro particles
InactiveUS8546103B2Favorable source of coagulase substrateImprove performance consistencyMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiFirst generation
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Diarrheogenic escherichia coli detection kit and detection and typing method thereof
ActiveCN103215358AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroorganismPolymerase L
Owner:SHENZHEN CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
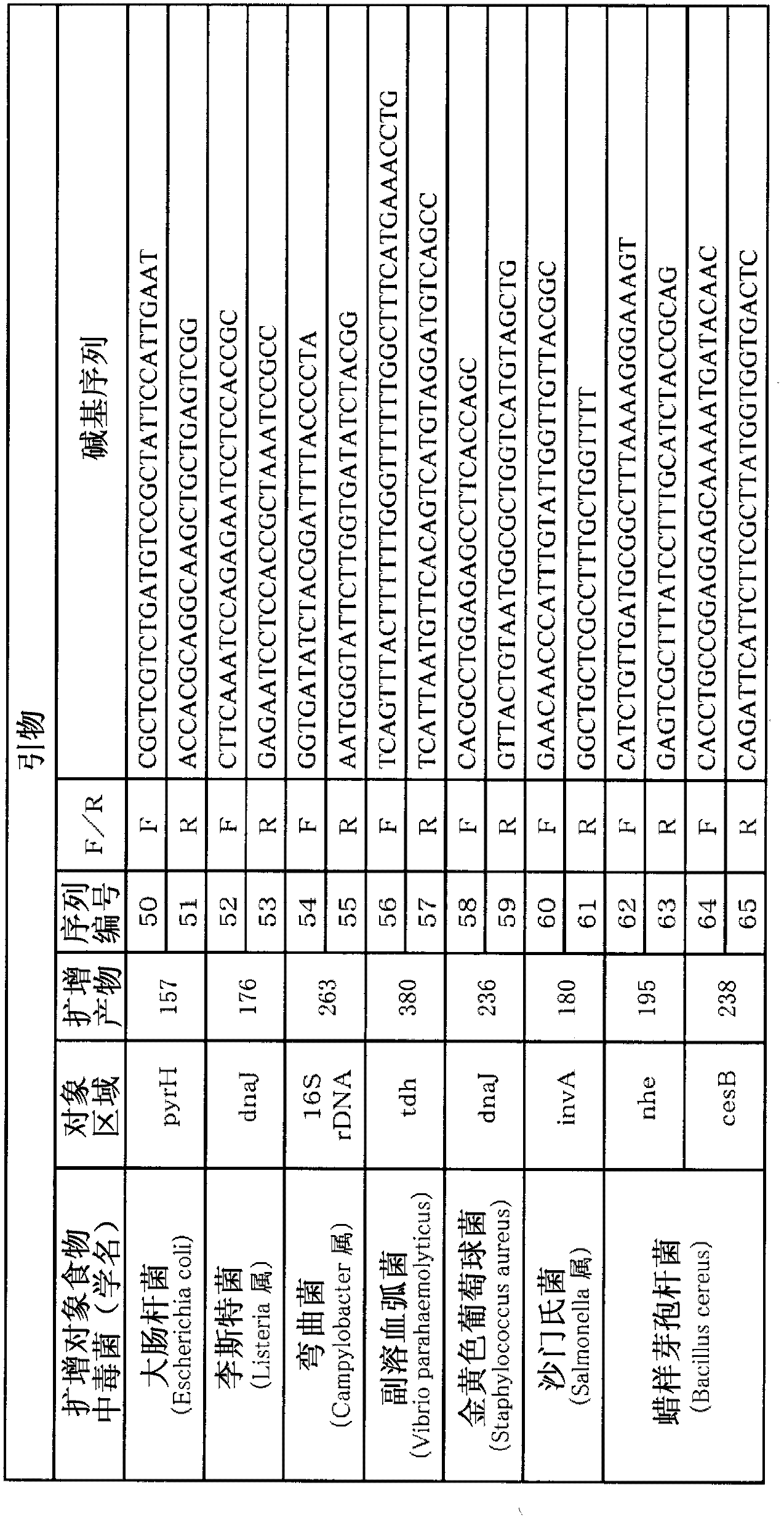
Food-poisoning bacteria detection carrier, and method for detecting food-poisoning bacteria
InactiveCN102844447ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStaphylococcus cohniiFood poisoning
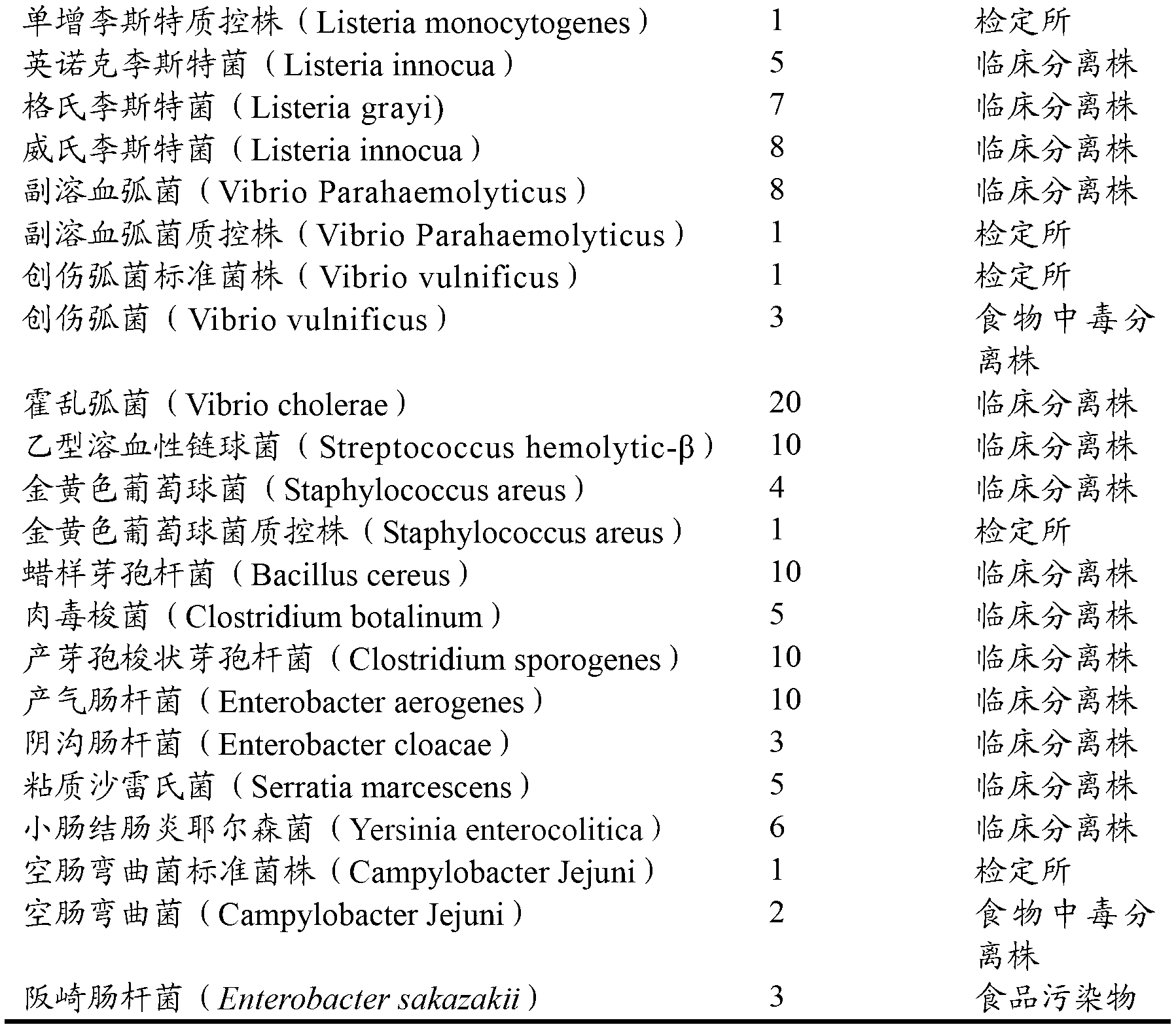
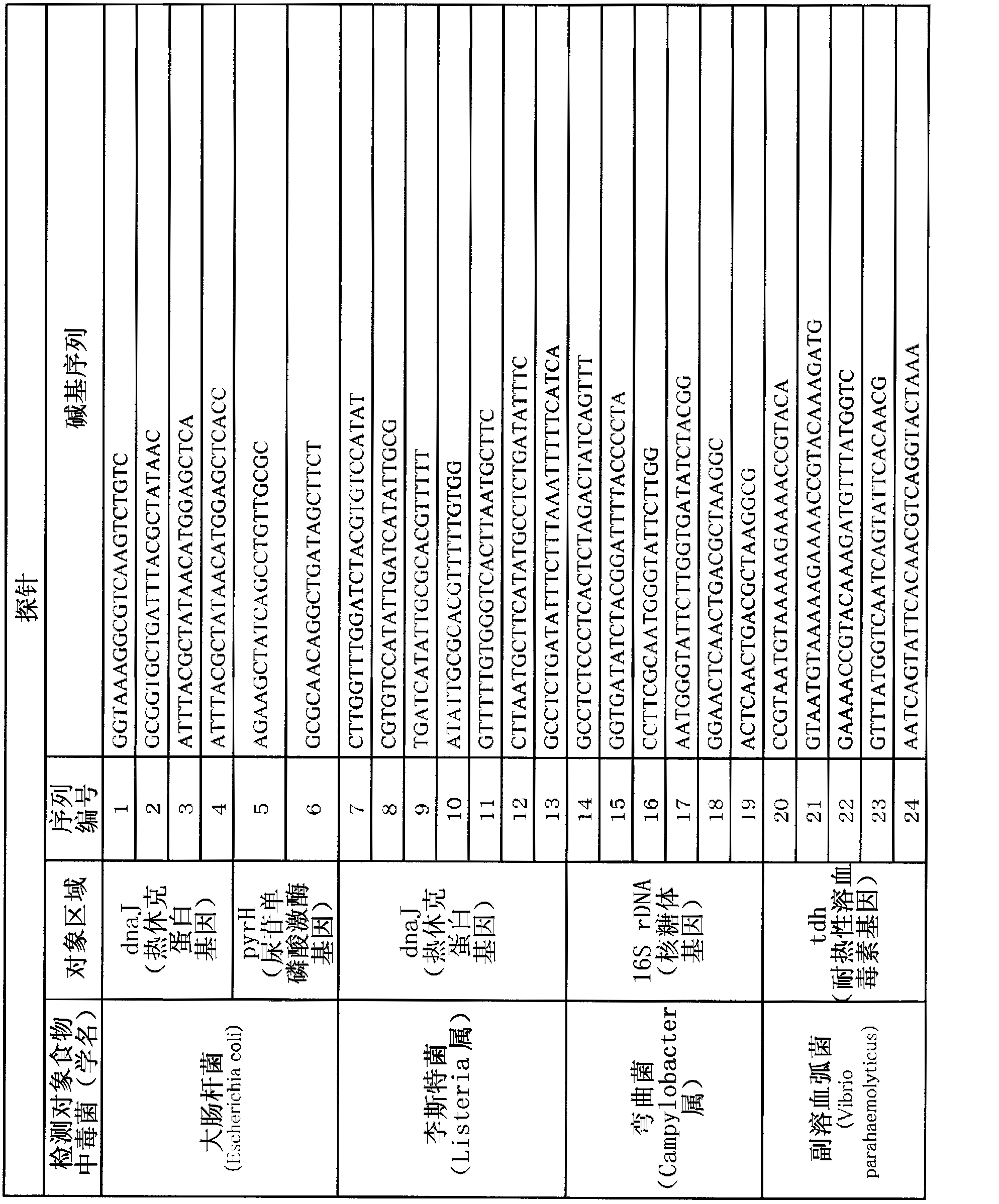
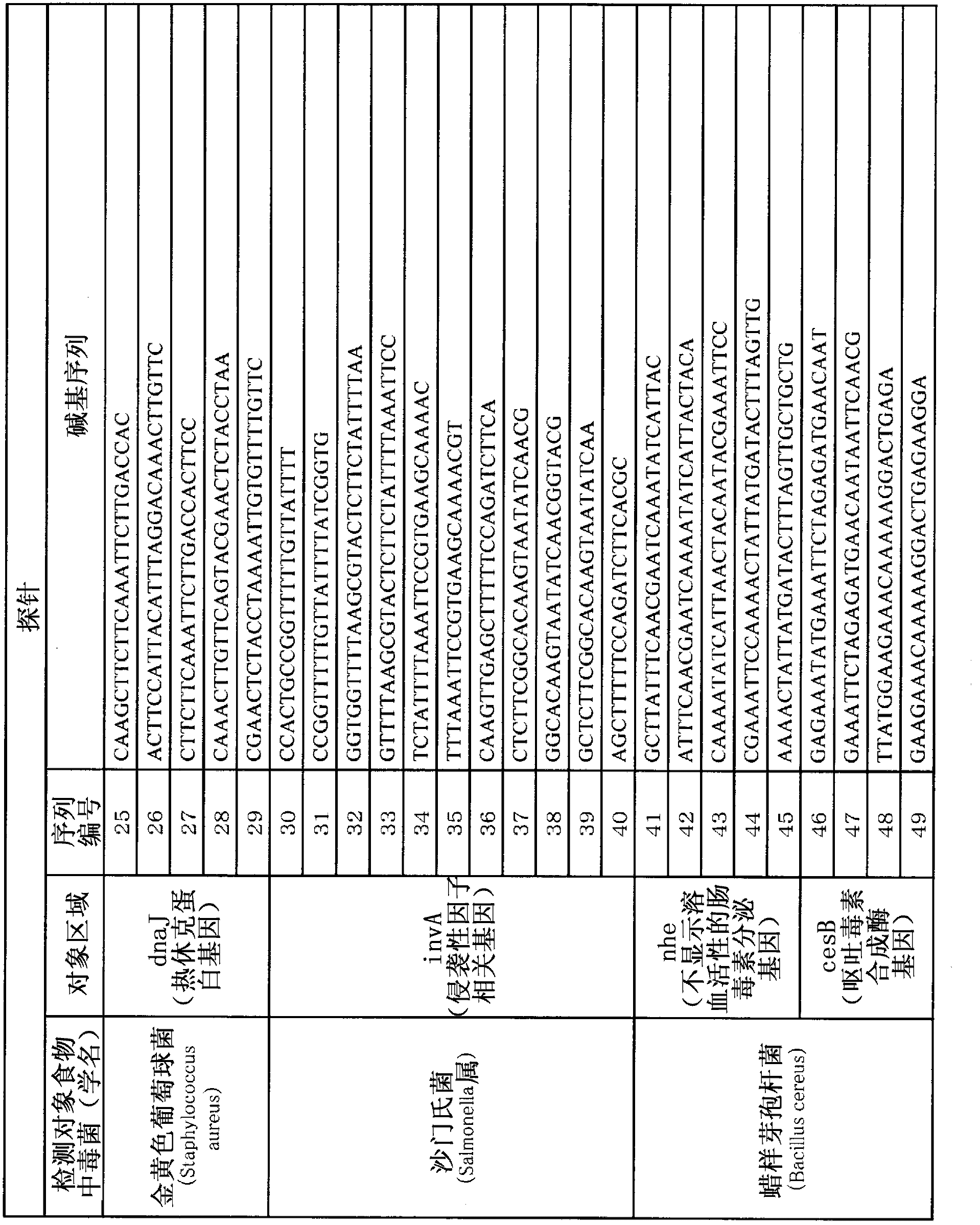
The disclosed method simultaneously and specifically detects at least two types of food-poisoning bacteria from among Escherichia coli, Listeria, Campylobacter, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, and Bacillus cereus. The food-poisoning bacteria detection carrier immobilizes one or at least two probes selected from each of at least two groups from among: an E. coli-detecting first probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 1-6 and probes (hereinafter written as "and the like") that are complementary thereto; a Listeria-detecting second probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 7-13, and the like; a Campylobacter-detecting third probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 14-19, and the like; a Vibrio parahaemolyticus-detecting fourth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 20-24, and the like; a Staphylococcus aureus-detecting fifth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 25-29, and the like; a Salmonella-detecting sixth probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 30-40, and the like; and a Bacillus cereus-detecting seventh probe group comprising the probes of sequence numbers 41-49.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN KAISHA LTD +1
Escherichia coli detection kit and use method thereof
ActiveCN101942508AHigh yieldHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLoop-mediated isothermal amplificationEscherichia coli detection
The invention provides an escherichia coli detection kit which comprises two pairs of primers designed by using fliC genes of the escherichia coli as target genes on the basis of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) technology: inner primers FIP / BIP and outer primers F3 / B3. The escherichia coli detection kit has the advantages of more comprehensive detection effect and low omission ratio.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUAFENG BIOTECH
Coli group and colibacillus testing medium
InactiveCN103725746ALow costGood for popular useMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMonopotassium phosphateMethylumbelliferone
The invention discloses a coli group and colibacillus testing medium which is prepared by dissolving 20 grams of peptone, 5 grams of lactose, 2 grams of bile salt, 1.5 grams of monopotassium phosphate, 4 grams of monopotassium phosphate, 5 grams of sodium chloride, 0.1 gram of 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indole galactoside, 0.1gram of 4- methylumbelliferone glucuronide, 1 gram of aspartic acid, 0.5 gram of casamino acid, 1 gram of yeast extracts and 20 grams of agar in 1000ml of deionized water, and the coli group and colibacillus testing medium is not only used as a plate medium, can also be used as an analoids form, and is low in cost and convenient to popularize and use.
Owner:STONE LAKE PHARMA TECH
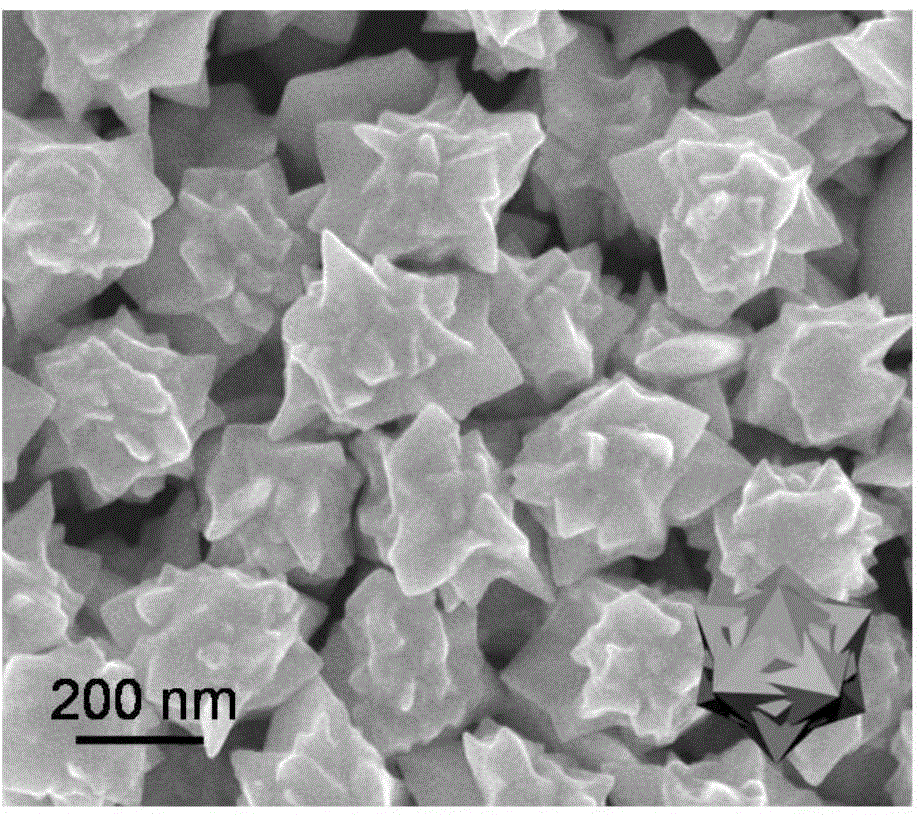
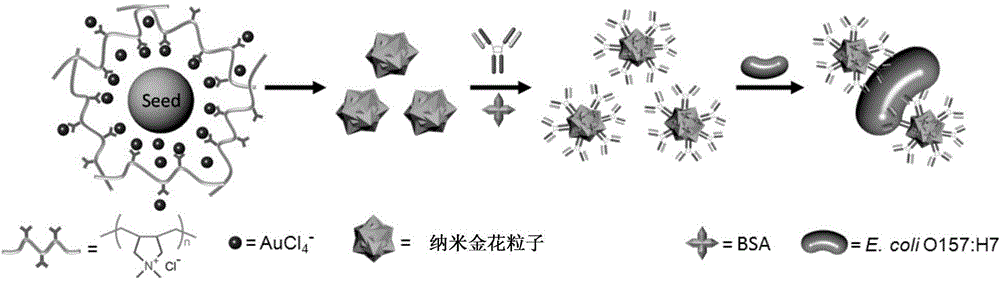
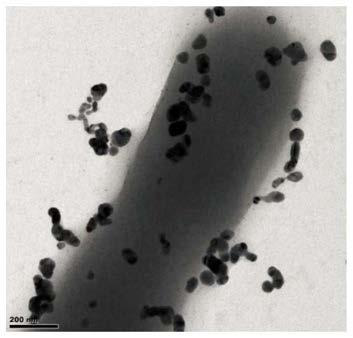
Multistage nano golden flower, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106141199AHas a nanoscale rough surfaceLarge specific surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial analysisPoly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)Medical diagnosis
The invention discloses a multistage nano golden flower, a preparation method and an application thereof. According to one embodiment, the preparation method comprises the steps of fully mixing chloroauric acid and poly diallyldimethylammonium chloride in an aqueous system, continuously stirring at room temperature until a prepared mixed solution is yellow, then adding ascorbic acid to the obtained yellow mixed solution, violently stirring, then adding a nano golden ball, quickly stirring, and then standing at room temperature. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in operation, good controllability and high productivity, a nano tip bulge is formed on the surface of the obtained multistage nano golden flower, and the multistage nano golden flower has a large specific surface area. The nano golden flower can be used as a gold-labelled antibody of an immunochromatographic strip, so as to be applied to the field of food safety, environment, medical diagnosis and the like, simple and high-sensitive analysis and detection can be performed on target objects, for example, high-sensitive detection of colibacillus can be performed, and the lower limit of the detection concentration reaches 103 CFU / mL.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Coliform detection process and kit for use therein
InactiveUS8741595B2Low costSimple and efficient and cost-effectivePhysical/chemical process catalystsPollution detectorsCulture mediumsEscherichia coli detection
A process comprises (a) providing (1) at least one sample suspected of comprising at least one coliform strain, (2) at least one culture device comprising at least one culture medium that is hydrated or hydratable, and (3) at least one particulate concentration agent that is substantially optically transparent when in contact with the culture medium in the culture device when the culture medium is hydrated; (b) placing the particulate concentration agent in contact with the sample such that at least a portion of the coliform strain is bound to the particulate concentration agent to form coliform-bound particulate concentration agent; (c) placing the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium; (d) incubating the culture device comprising the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium, the culture medium being hydrated; and (e) optically detecting the presence of the coliform strain without separating the coliform strain from the particulate concentration agent.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Primer for quickly determining enterotoxigenic eschericha coli in feed sample and application for primer
ActiveCN102559892AImprove detection efficiencyHigh detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAgricultural scienceFeed additive
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed science and detection of feed additives, and particularly relates to a primer for quickly determining enterotoxigenic eschericha coli K88 in a feed sample and application for the primer. A pair of primers is designed aiming at the pilus specific gene of the enterotoxigenic eschericha coli K88, the gradient dilution of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is used as an external standard substance; and an SYBRGreen I real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method for the enterotoxigenic eschericha coli K88 is established; by the method, the enterotoxigenic eschericha coli K88 in the feed sample can be quantified quickly and specifically; more than or equal to 2*10<2> CFU / g of enterotoxigenic eschericha coli K88 can be detected in the feed sample, and only 5 hours is required by the whole operation process; and compared with the conventional detection method, the method has the advantages of simple detection process, high detection efficiency and accuracy, short detection period and the like, and lays the foundation for development of a kit for quickly and accurately detecting the enterotoxigenic eschericha coli.
Owner:河北方田农牧科技有限公司 +1
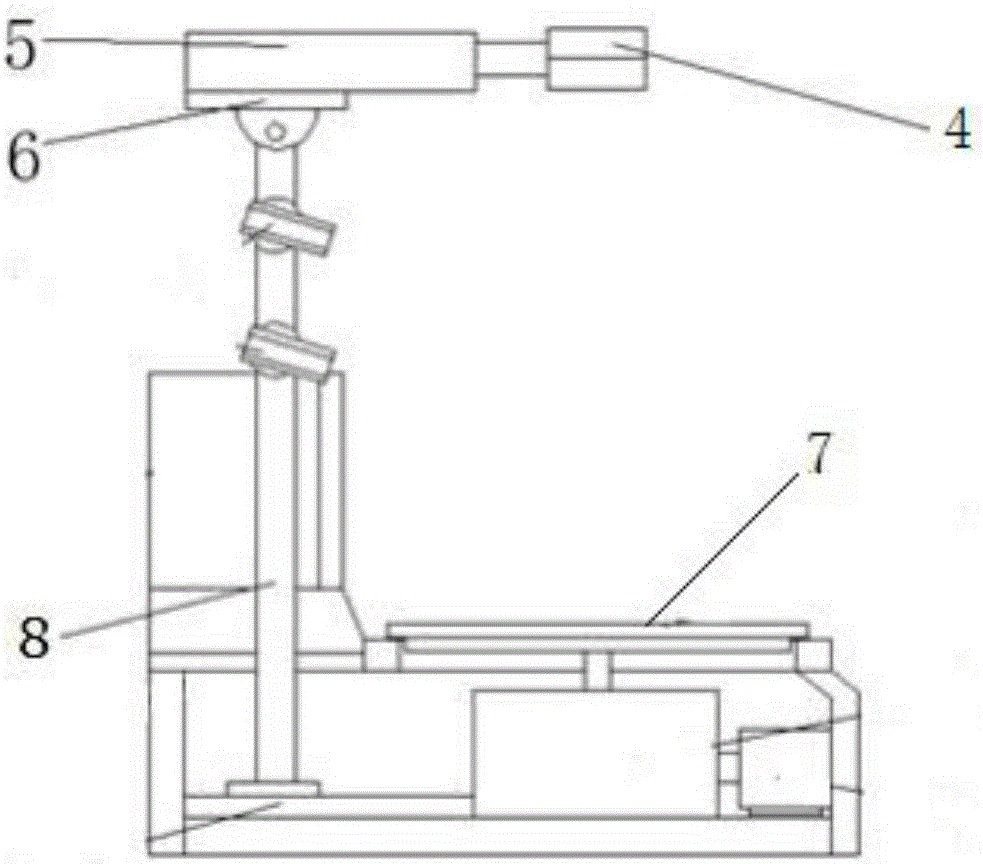
Detection device for rapidly detecting colibacillus
InactiveCN106497779ACompatible with growth temperatureRealize multi-directional shootingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAbsorption filterEngineering
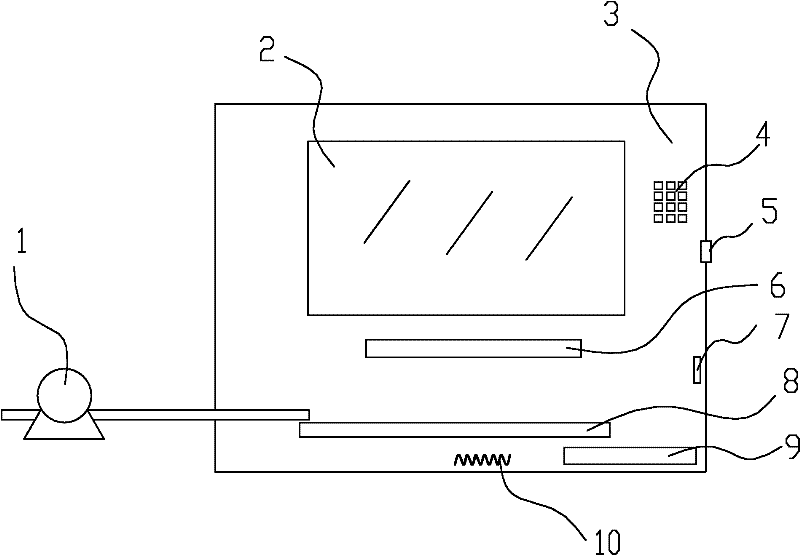
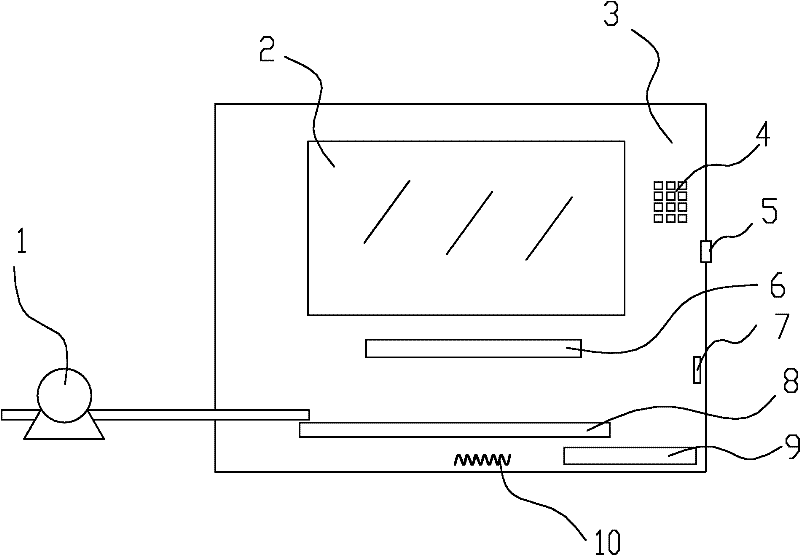
The invention provides a detection device for rapidly detecting colibacillus. The detection device comprises a detection case, a detection box is arranged at the top of the detection case, a heating box is arranged at the bottom of the detection box, an adjusting rod is arranged on one side of the detection case, a digital camera is arranged on the adjusting rod, the detection box comprises a colibacillus detection culture device, a heating device is arranged at the bottom of the detection box, the detection box comprises a box body and a pressure cover, a transparent glass plate is spread on the inner side of the bottom wall of the box body, a culture medium layer of the colibacillus is adhered on the transparent glass plate, water absorption filter paper is spread on the culture medium layer, the pressure cover is arranged on the water absorption filter paper, a lifting device is arranged on the adjusting rod, an angle adjusting table is arranged at the top of the lifting device, a telescopic rod is fixedly connected on the angle adjusting table, a camera mounting frame is connected at the output end of the telescopic rod, and the digital camera is mounted on the camera mounting frame and connected with a computer through a data line. The detection device has the advantage that working efficiency is improved.
Owner:天津伊科斯迪科技有限公司
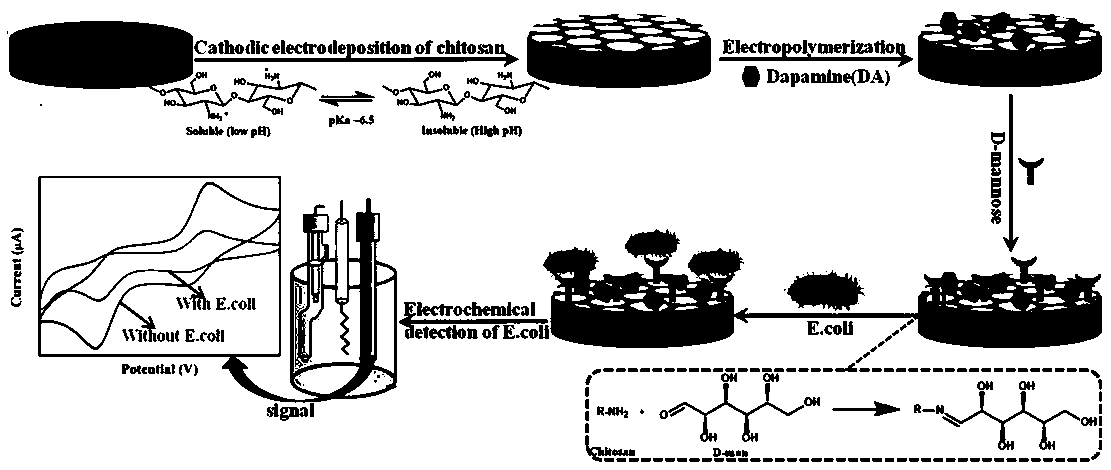
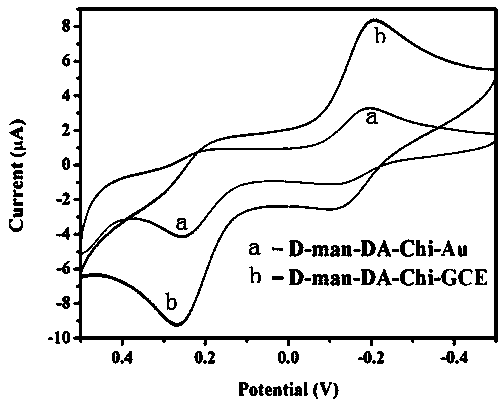
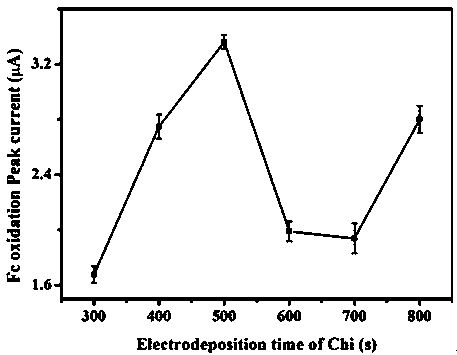
Preparation and detection method of escherichia coli electrochemical biosensor
ActiveCN110907519AImprove responsivenessHigh selectivityMaterial electrochemical variablesResponse sensitivityElectrochemical biosensor
The invention relates to a preparation and detection method of an electrochemical biosensor for escherichia coli, belonging to the field of biomedicine. The invention provides a preparation method andapplication of a D-mannose-dopamine-chitosan modified electrochemical biosensor based on Fc-Ru < 3 + > mediation of a double-electron mediator . A sensor comprises an electrode material, surface filmmodification of an electrode, an immobilized bioactive compound and the double-electron mediator, and the electrode material is glassy carbon. The electrode surface film is a dopamine and chitosan film; wherein an immobilized bioactive compound is D-mannose; and a component of the dual-electron mediator is Fc-Ru < 3 + >. The electrochemical sensor has the advantages of high response sensitivity to escherichia coli in a detection system, strong selectivity, good stability and simple preparation, and can be used for escherichia coli detection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method and reagents for detecting the presence or absence of staphylococcus aureus in a test sample
InactiveUS20110027823A1Small amountFavorable source of coagulase substrateMicrobiological testing/measurementStaphylococcus cohniiStaphylococcus pseudintermedius
A presence / absence test for Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) involves placing a first generation test sample in a solution that will clot in the presence of S. aureus. The solution contains components that will selectively grow S. aureus and also contains clotting factors that will react with S. aureus, if S. aureus is present in the sample, to clot the solution. Examples of specimen samples that can be tested include nasal swabs and lesion swabs, among others. The test can also be modified to detect the presence or absence of methicillin resistant S. Aureus (MRSA). The addition of micro particles having a size in the range of about 0.1 micron to about 1.0 mm provides localities where the bacteria agglomerate, thereby significantly decreasing the clotting time, and providing a significantly stronger clot. The micro particles can be used in other bacteria tests to accelerate the production of an end result. Such other tests can include a vancomycin-resistant enterococcus test; a Group B Streptococcus test; a test for hemolytic E. coli; and a test for Listeria monocytogenes, to name a few. These tests are all performed in a liquid broth-type reagent mixture and do not necessarily involve clotting of the broth.
Owner:PILOTS POINT LLC
Multiplex PCR detection primers and multiplex PCR detection method for Escherichia coli O<157>
PendingCN108950029AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPositive control
The invention relates to multiplex PCR detection primers and a multiplex PCR detection method for Escherichia coli O<157>. The multiplex PCR detection primers comprise three pairs of primers. The three pairs of primers respectively amplify the rfbE, fliC, and stx1 genes of O<157>, and the sequences of the primers are as shown in a sequence table in the specification. The above primers are used formultiplex PCR detection of Escherichia coli O<157> DNAs; a positive control, a negative control and a blank control are set; and PCR amplification conditions comprise denaturation at 94 DEG C for 5 min, pre-denaturation at 94 DEG C for 30 s, annealing at 48-52 DEG C for 45 s, extension at 72 DEG C for 45 s, 30-35 amplification cycles, and finally, extension at 72 DEG C for 5 min. The detection primers and the detection method for the Escherichia coli O<157> in the invention have the advantages of specificity and sensitivity, and can accurately identify the Escherichia coli O<157>.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
An offshore escherichia coli detection method
InactiveCN104593476ALow costIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismEnrichment broth
An offshore escherichia coli detection method is provided. According to the method, escherichia coli in seawater is intercepted onto a filter membrane by a suction filtration system, the filter membrane is put into a culture medium and cultured and is a microfiltration membrane having a pore diameter of 0.45 [mu]m, a bile lactose enrichment broth is added into a detection solution to perform bacteria-proliferating operation for 30-48 h, and if the solution is muddy and a gas is generated, it is determined that the escherichia coli is detected. The culture medium is an eosin-methylene blue agar plate, the culture time is 10-12 d, and colony growth conditions of the escherichia coli are observed after culturing. If a typical escherichia coli colony grows and is separated from the eosin-methylene blue agar plate, it is determined that the escherichia coli are detected. Compared with traditional microbe detection methods, the method is low in cost, rapid, convenient, simple, and high in sensitivity.
Owner:大连大公检验检测有限公司
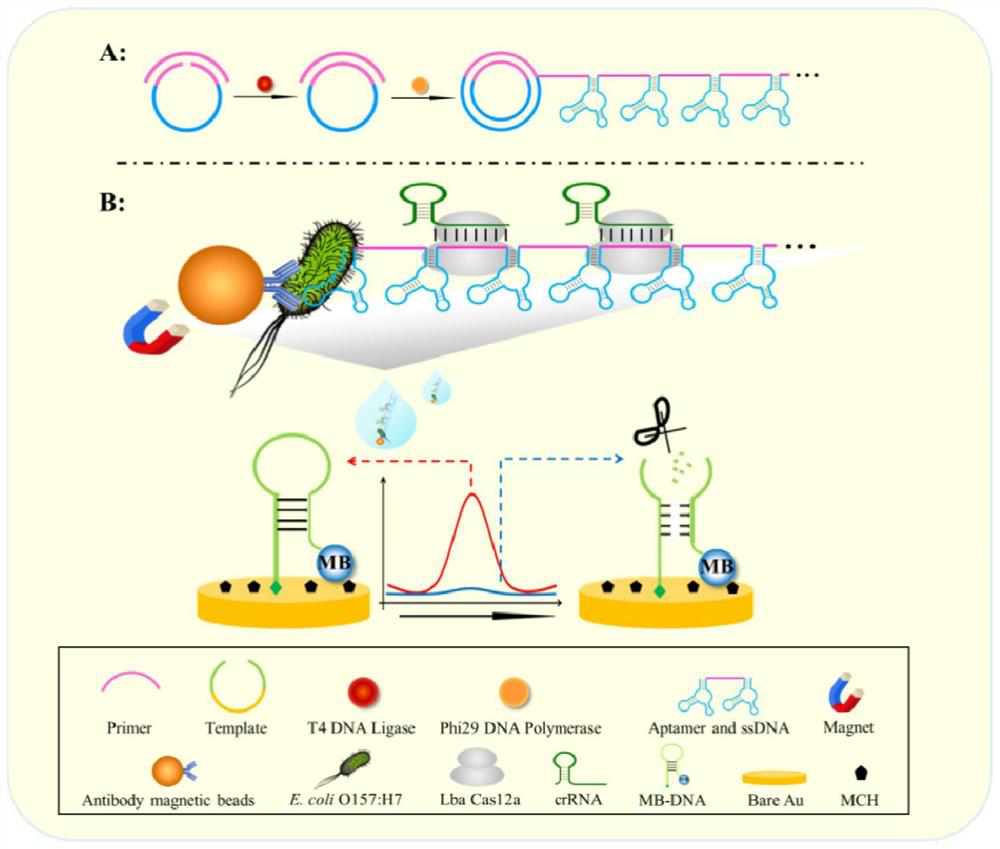
CRISPR/Cas12a-RCA electrochemical sensor detection system and application thereof
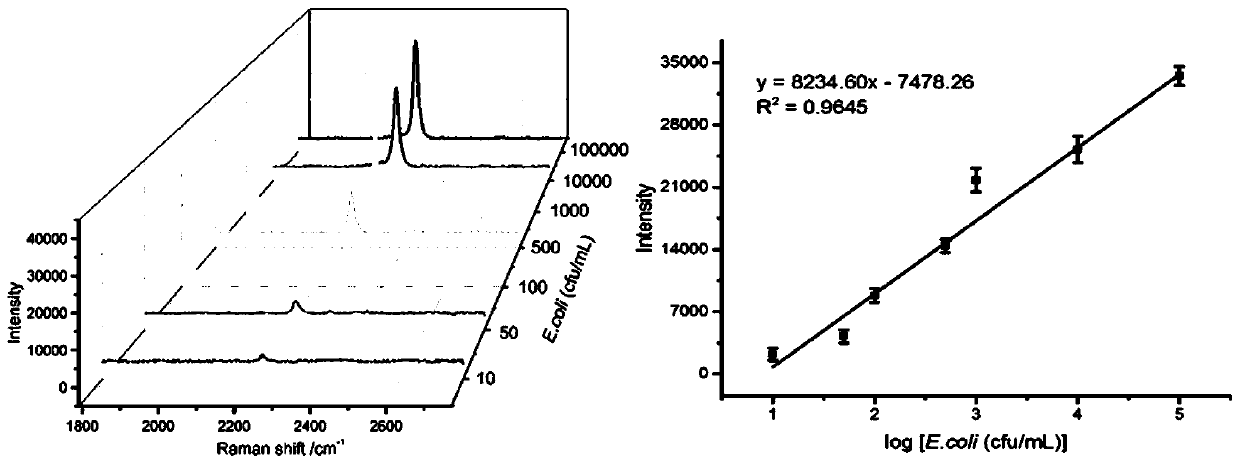
PendingCN113686934AHigh detection specificityWide detection concentration rangeMaterial electrochemical variablesPathogenic bacteriaClinical diagnosis
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas12a-RCA electrochemical sensor detection system and application thereof. According to the present invention, the CRISPR / Cas12a-RCA electrochemical sensor detection system can be used for the detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7, has characteristics of simple operation and low cost, can accurately distinguish Escherichia coli O157: H7 from different bacteria, and has strong detection specificity; the detection concentration range is also wide, a good linear relation is achieved within the range of 10-107 CFU.mL <-1 >, the detection sensitivity is high, the lowest detection limit is 10 CFU.mL <-1 >, and the detection result is accurate and reliable. The detection method is not only suitable for detecting escherichia coli O157: H7 in food, but also has huge application potential in detection of other pathogenic bacteria or clinical diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY +1
MGB probe multiple fluorescence quantitative PCR method for detecting colibacillus 0157
InactiveCN1952647AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceHigh concentrationConserved sequence
A method of testing colibacillus O157 with MGB probe multiline fluorescence gauging PCR, is disclosed, the recombinant plasmid is constructed, the synthesized primer and the Taqman-MGB probe are designed, diploid fluorescence gauges PCR, the segment of saving sequences of rfbE, vt2 of the colibacillus O157 are augmented by PCR to obtain the goal segment, the goal segment is connected with PMD 18-T Vector to obtain the recombinant plasmid, then the recombinant plasmid is converted to DH5a competence bacillus coli cell, enlarged the culture to obtain the recombinant plasmid with high concentration, then the recombinant plasmid with high concentration is diluted by 10 times ratio to be the standard sample, the standard sample and the sample to be measured are combined together to gauge the PCR by diploid fluorescence, the calibration curve is formed by the standard sample, the content of the colibacillus O157 can be calculated in the sample to be measured based on the calibration curve. The MGB probe is used in the invention that has higher sensibility and specificity, and detects the content of the colibacillus O157 in the sample quickly and precisely; two specificity virogenes of the colibacillus O157 can be detected at the same time, so it is a quick and precise method of testing colibacillus O157.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
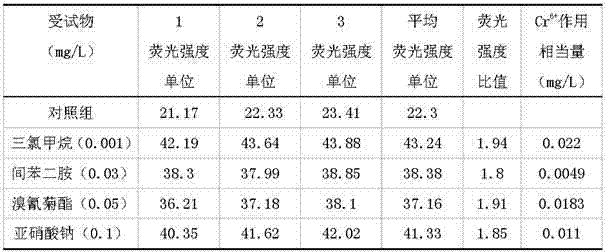
Water quality genotoxicity detection method based on semiconductor opening switch (SOS) effect of recombinant Escherichia coli
ActiveCN102175659BNo risk of diseaseEasy to trainFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotechnologyRecombinant escherichia coli
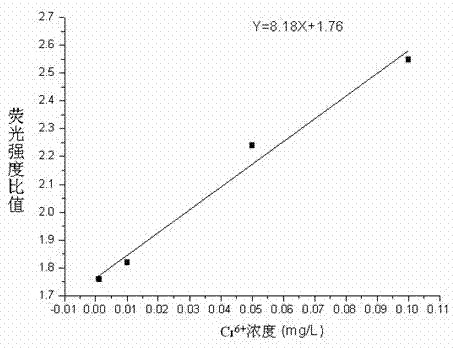
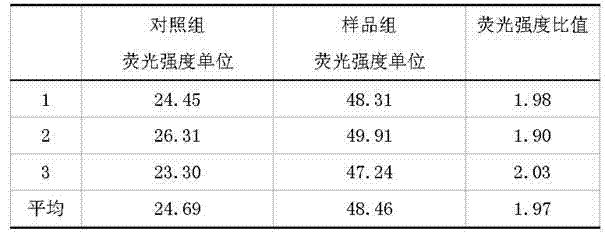
The invention discloses a water quality genotoxicity detection method based on a semiconductor opening switch (SOS) effect of recombinant Escherichia coli. The method comprises the following steps of: recovering, activating and culturing recombinant Escherichia coli storage to obtain Escherichia coli detection solution; contacting a water sample to be measured with the detection solution, and simultaneously setting a contrast; centrifuging, ultrasonically disintegrating and performing other post-treatment on the contacted detection solution, and detecting a fluorescence intensity ratio of thewater sample to be measured; measuring a fluorescence intensity ratio of the Cr6+ solution with different concentrations, which is contacted with the detection solution by using the same method; drawing a standard curve between the fluorescence intensity ratio and the Cr6+ concentration, and substituting the fluorescence intensity ratio of the water sample to represent the water quality toxicity of the water sample through the Cr6+ concentration. The method has no pathogenic risk, is easy and convenient to culture and operate, high in detection sensitivity and low in cost; the final result isrepresented by Cr6+ equivalent concentration, and can be compared with results of other biological detection methods; and the method is suitable for rapidly detecting genotoxicity of an environmentalsample.
Owner:济南市供排水监测中心
Primer for detecting Escherichia coli, and method and application of primer
InactiveCN104862394AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotide sequencingEscherichia coli detection
The invention discloses a primer for detecting Escherichia coli, and a method and an application of the primer. The nucleotide sequence of the primer is indicated in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2, an Escherichia coli detection method is established for the involved primer, and the detection method has the advantages of fine specificity, good sensitivity, rapidness and reliability in detection and simplicity in operation. A kit comprising the primer is designed, and the Escherichia coli is conveniently detected. The specific primer is designed for specific genes LafF of the Escherichia coli and can be used for rapidly, simply, conveniently and accurately detecting the Escherichia coli.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
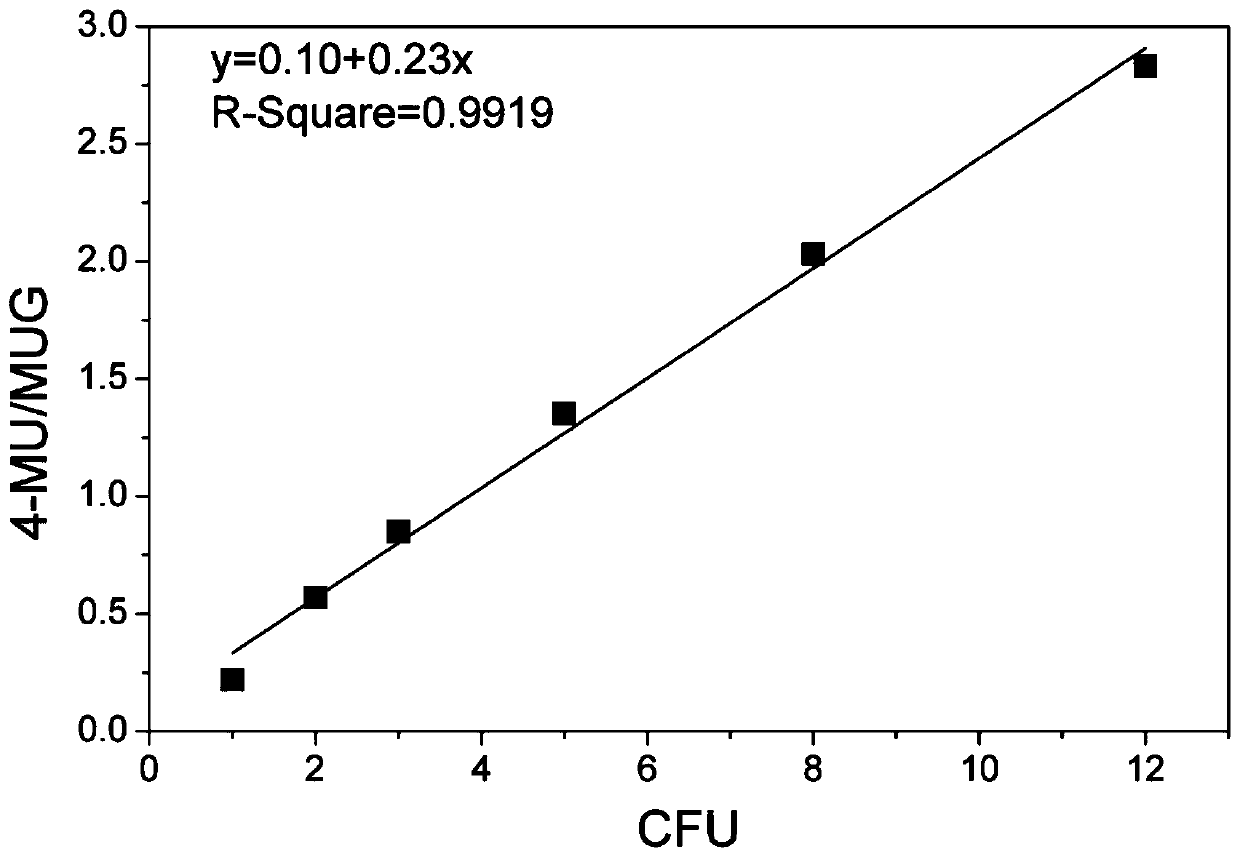
Method for rapidly detecting Escherichia coli
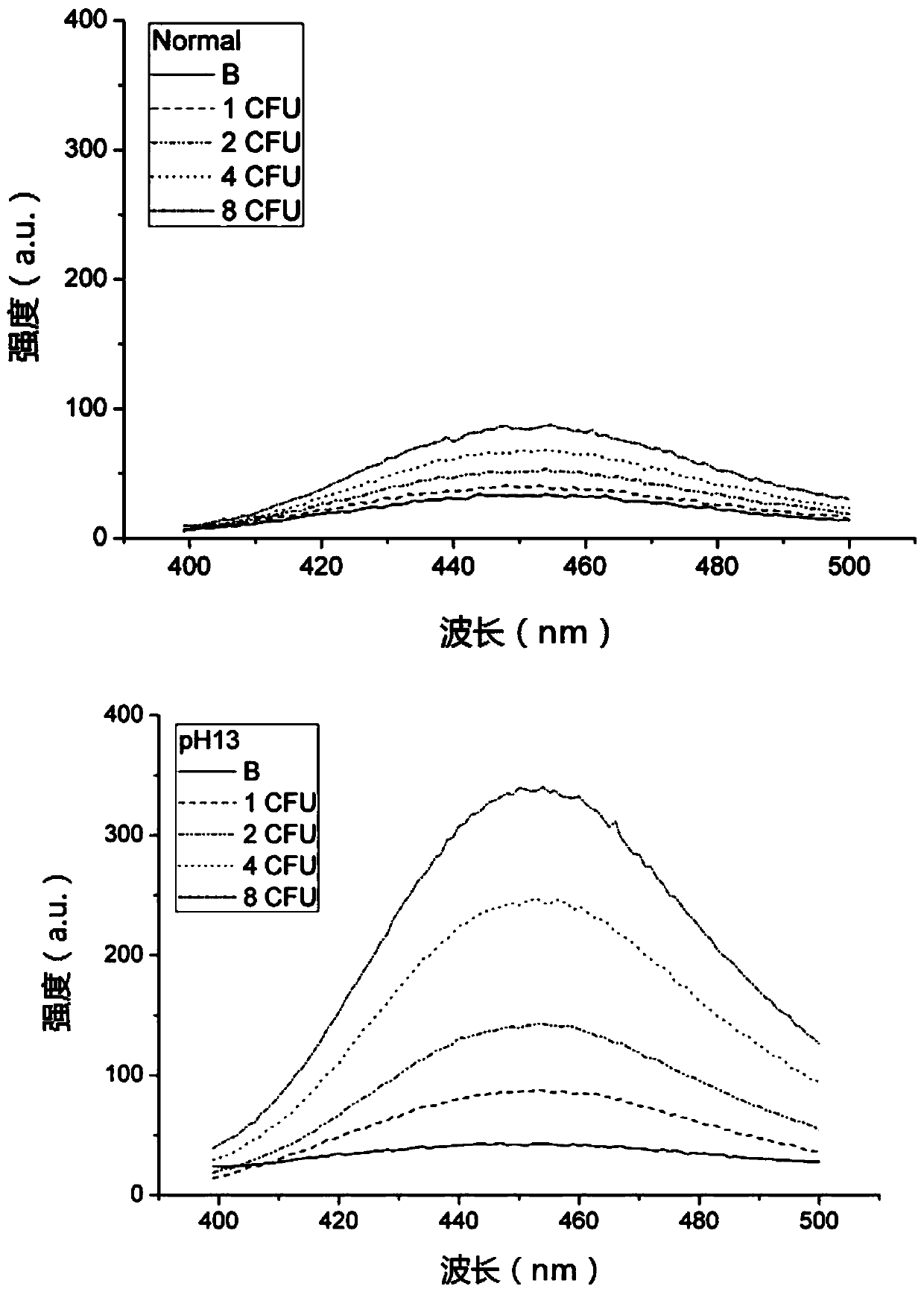
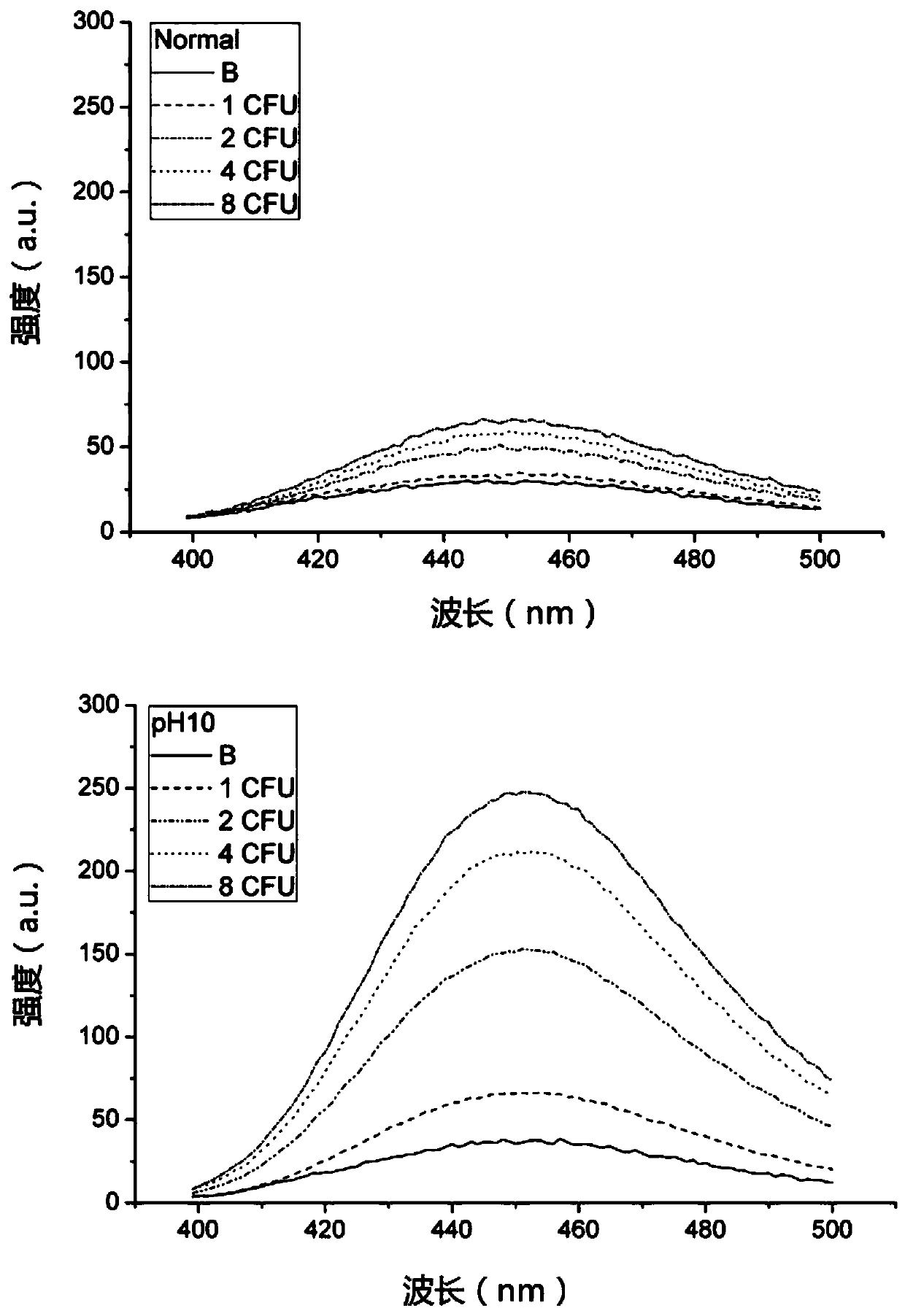
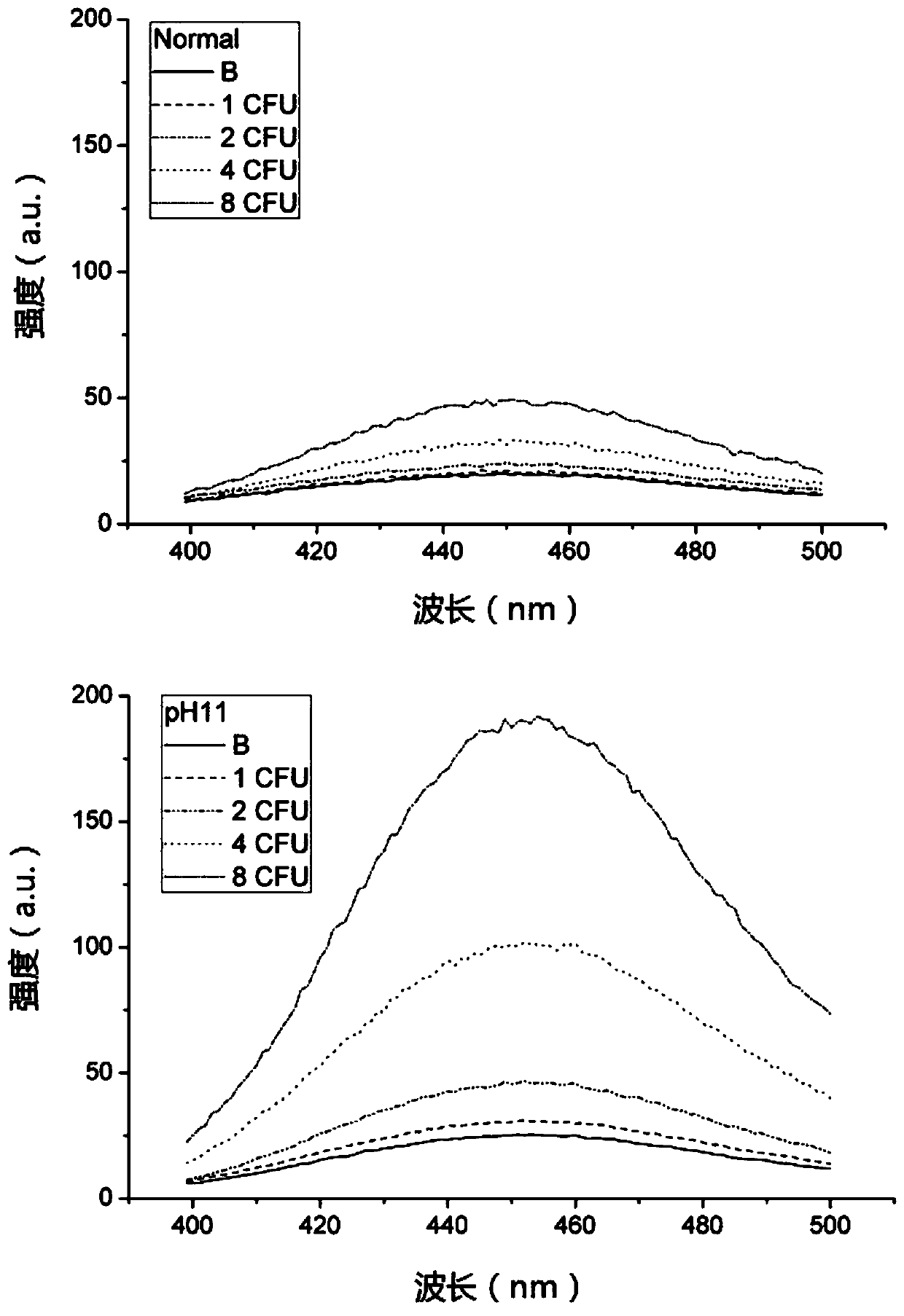
PendingCN110846376ALower absorption peakAbsorption peak increasedMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnterobacterialesBiology
The invention relates to a method for rapidly detecting Escherichia coli, belongs to the technical field of Escherichia coli detection, and solves the technical problems that 366nm excitation and 450nm emission are combined, a background MUG has a certain fluorescence intensity at 450nm after 366nm excitation, a product signal cannot be separated from a background signal when the concentration ofthe Escherichia coli is low and 4-MU yield is less, and a sample with very low concentration of the Escherichia coli in water samples cannot be detected by an existing method in the prior art. According to the method for rapidly detecting the Escherichia coli, by a ratio fluorescence method, reduction of an absorption peak of the background MUG and increase of an absorption peak of a product 4-MUcan be simultaneously utilized, and the ratio of absorption peak values of the background MUG and the product 4-MU and the concentration of the Escherichia coli are linearly fitted. Compared with a single method of 366nm excitation and 450nm emission, fitting linearity is better, detection accuracy is improved, incubation time of Escherichia coli detection can be shortened, and distinction can beachieved by the aid of ratio fluorescence when 4-MU yield cannot reach distinction degree.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for determining escherichia coli content in water
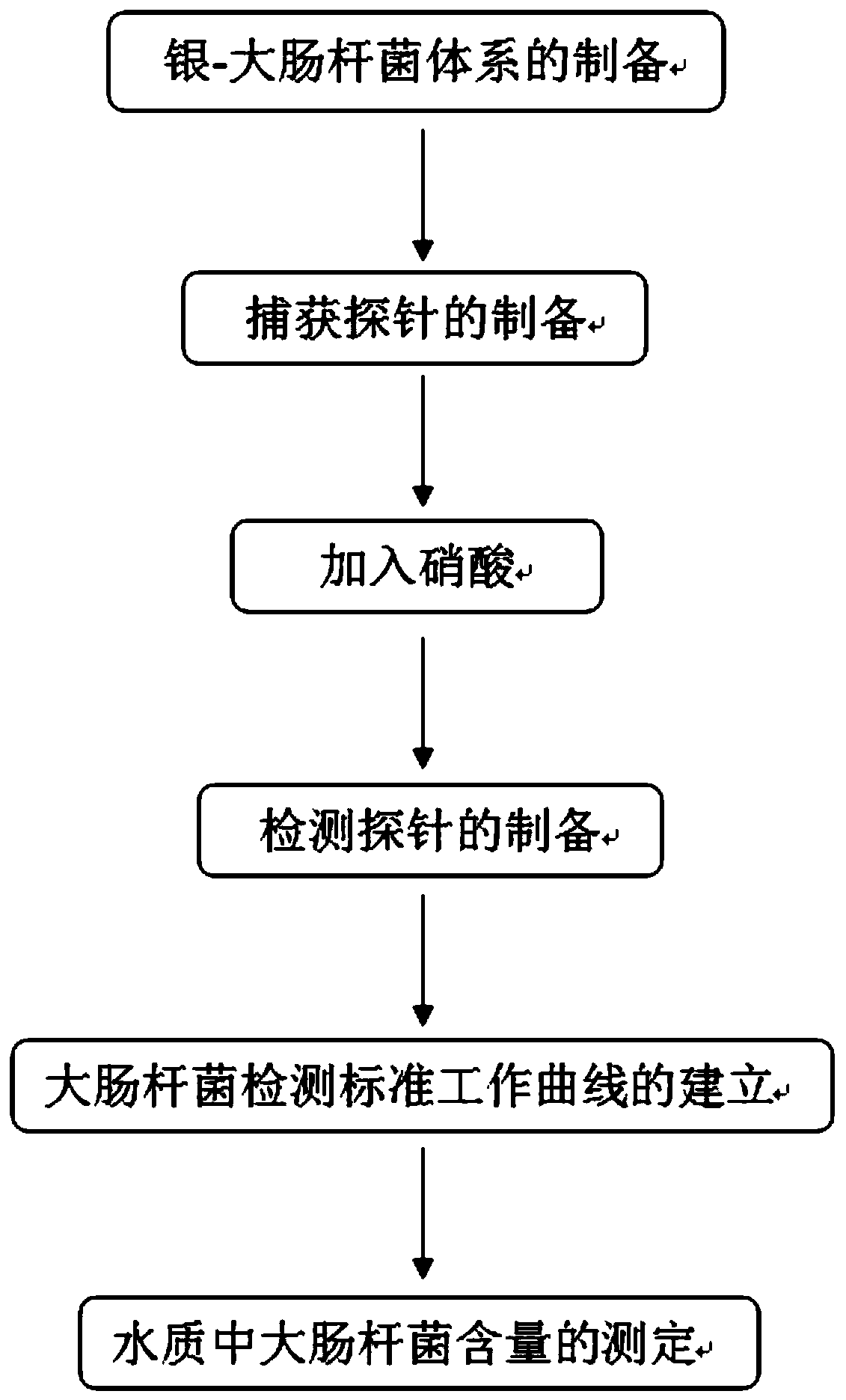
PendingCN111337470AIn situ reductive growthAvoid interferenceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEnterobacteriales
The invention relates to the technical field of microbiological detection, and provides a method for determining the content of escherichia coli in water. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of a silver-escherichia coli system, preparation of a capture probe, addition of nitric acid, preparation of a detection probe, establishment of an escherichia coli detection standard workingcurve, and determination of the content of escherichia coli in water. The invention provides an SERS detection method of escherichia coli. The SERS detection method can be used for specifically, sensitively and quickly detecting the content of escherichia coli in water.
Owner:WUHAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Fluorescent signal enhancement method for detecting escherichia coli by enzyme substrate process
InactiveCN111073950AEnhanced absorption peakEnhanced Fluorescence Intensity DifferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEnterobacterialesEnzyme
The invention relates to a fluorescent signal enhancement method for detecting escherichia coli by an enzyme substrate process, and belongs to the technical field of escherichia coli detection. An enzyme substrate targeted by the method provided by the invention is MUG, and the technical problems that a combination of 366 nm excitation and 450 nm emission is adopted in the prior art, after the MUGbackground is excited by 366 nm, the MUG background has certain fluorescence intensity at 450 nm, when the concentration of escherichia coli is very low, the yield of 4-MU is low, a product signal isinseparable from a background signal, so that water samples with an extremely low escherichia coli concentration cannot be detected by current methods are solved. The method for detecting the escherichia coli by the enzyme substrate process provided by the invention adopts the manner of adding one-step operation after the end of incubation and before fluorescence measurement; the operation is that the pH is adjusted to >=9 by using an alkaline reagent, the absorption peak of the product 4-MU can be obviously enhanced, the absorption peak of the substrate MUG changes little, so that the product signal can be separated from the background signal; and through the operation provided by the invention, the difference in fluorescence intensity between the product signal and the background signalis increased by five times, and the method is particularly suitable for detection of the escherichia coli with a very low concentration.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photoresponsive gel microspheres for dPCR-method nucleic acid detection and application of photoresponsive gel microspheres in Escherichia coli detection
PendingCN113881791AAchieve thermal cyclingSimple processMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicrosphereEnterobacter
The invention provides photoresponsive gel microspheres for dPCR-method nucleic acid detection and application of the photoresponsive gel microspheres in Escherichia coli detection. A composite nanomaterial with efficient photothermal conversion characteristics and good biocompatibility is prepared through coating each silica microsphere sequentially with an MXene layer and a silica coating; and a hydrogel mixed solution doped with the composite nanomaterial is emulsified into composite gel microspheres through a micro-fluidic chip, so that a gel-sol-controllable-conversion and temperature-control microcarrier with photoresponsiveness is obtained. The prepared composite gel microspheres can generate heat under near-infrared light to be converted into sol micro-droplets so as to ensure diffused contact of a system, a PCR temperature cycle process can be completed under programmed light stimulation, and the composite gel microspheres are solidified into spheres after reaction so as to stably store monoclonal information. The novel method does not depend on complex and expensive equipment, is wide in application range, can be used for effectively detecting the most common pathogen Escherichia coli infecting a human body, and has a huge value in multiple aspects such as public health.
Owner:WENZHOU INST UNIV OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Meat product pressing device for detecting escherichia coli by applying immunology
InactiveCN105638839ASimple structureLow costMeat processingMaterial analysisEngineeringImmunologic function
The invention discloses a meat product pressing device for detecting escherichia coli by applying immunology, comprising a pressing mechanism, a horizontal base and a pulley set, wherein the pressing mechanism comprises a box, a first pull rod and a second pull rod, the box is mounted at the middle of the horizontal base, the inner part of the box is horizontally provided with a pressing plate, the left side of the box is provided with a first support, the bottom of the first support is mounted on the horizontal base, one end of the first pull rod is hinged to the middle of the first support, the other end of the first pull rod is provided with a pulling rope, the pulling rope is connected with the pulley set, one end of the second pull rod is hinged to the middle of the upper surface of the pressing plate, and the other end of the second pull rod is hinged to the middle of the first pull rod; one corner of the pressing plate is also provided with escherichia coli test paper. The meat product pressing device has a function of detecting the escherichia coli, is used for judging whether a meat product is polluted or not, and is high in practicability and economic value.
Owner:刘剑
Chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7
ActiveCN102424832BHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyThio-
The invention discloses a chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7. The medium comprises agar, peptone, beef extract powder, sodium chloride, sorbitol, inositol, neutral red, beta-galactosidase chromogenic substrate, beta-glucuronidase chromogenic substrate, isopropyl-beta-D- thiogalactopyranoside, natrium taurocholicum, potassium tellurite and cefixime. The chromogenic medium used for detecting esherichia coli O157:H7 of the present invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good specificity, direct bacterial strain discrimination according to colony color, short detection period and strong operationality, is suitable for treating high-reflux samples, is capable of comprehensively, systematically and accurately detecting and preliminarily identifying the esherichia coli O157:H7 in food production and environment, and provides a novel approach for rapidly detecting the microbes.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com