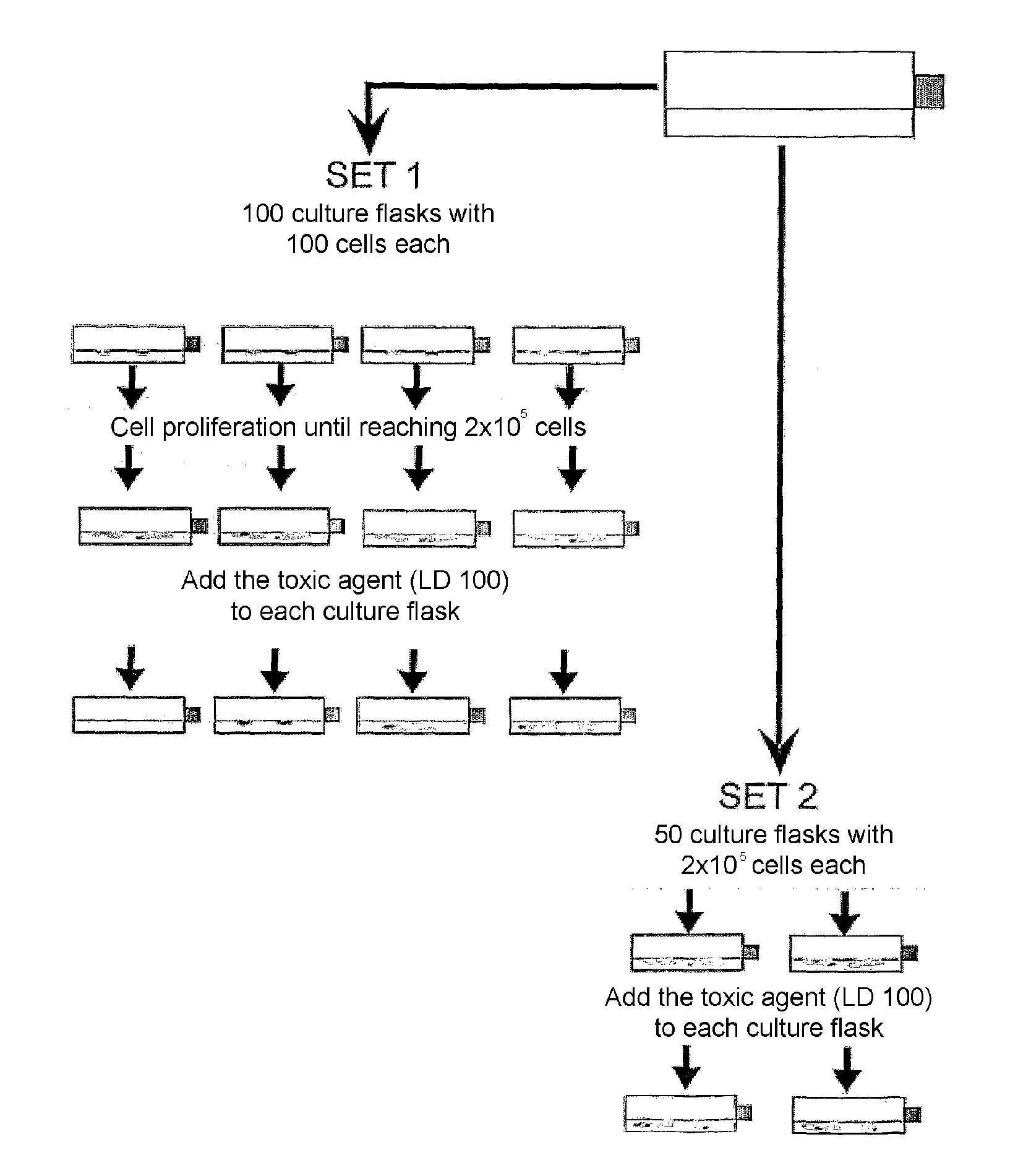
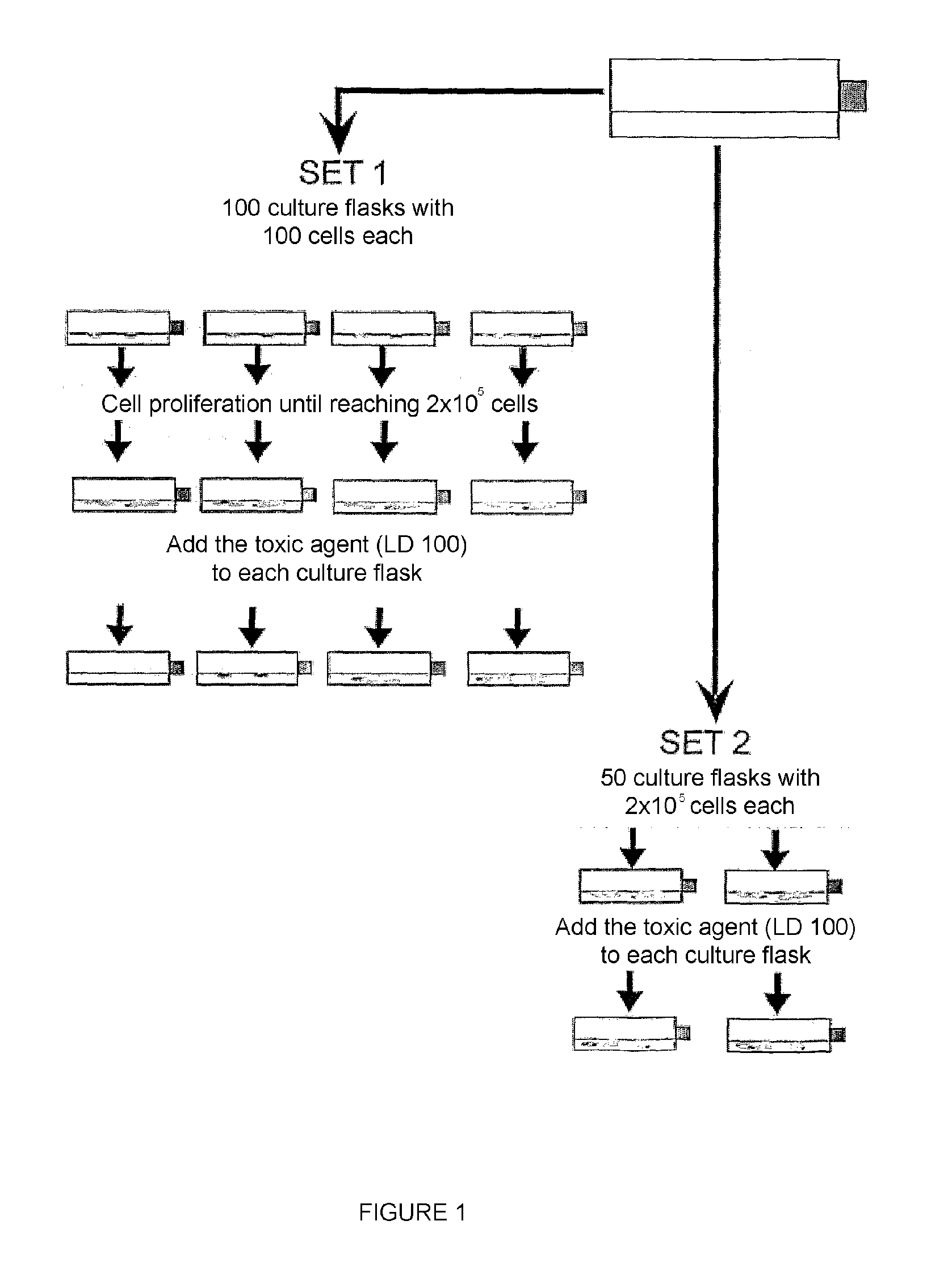
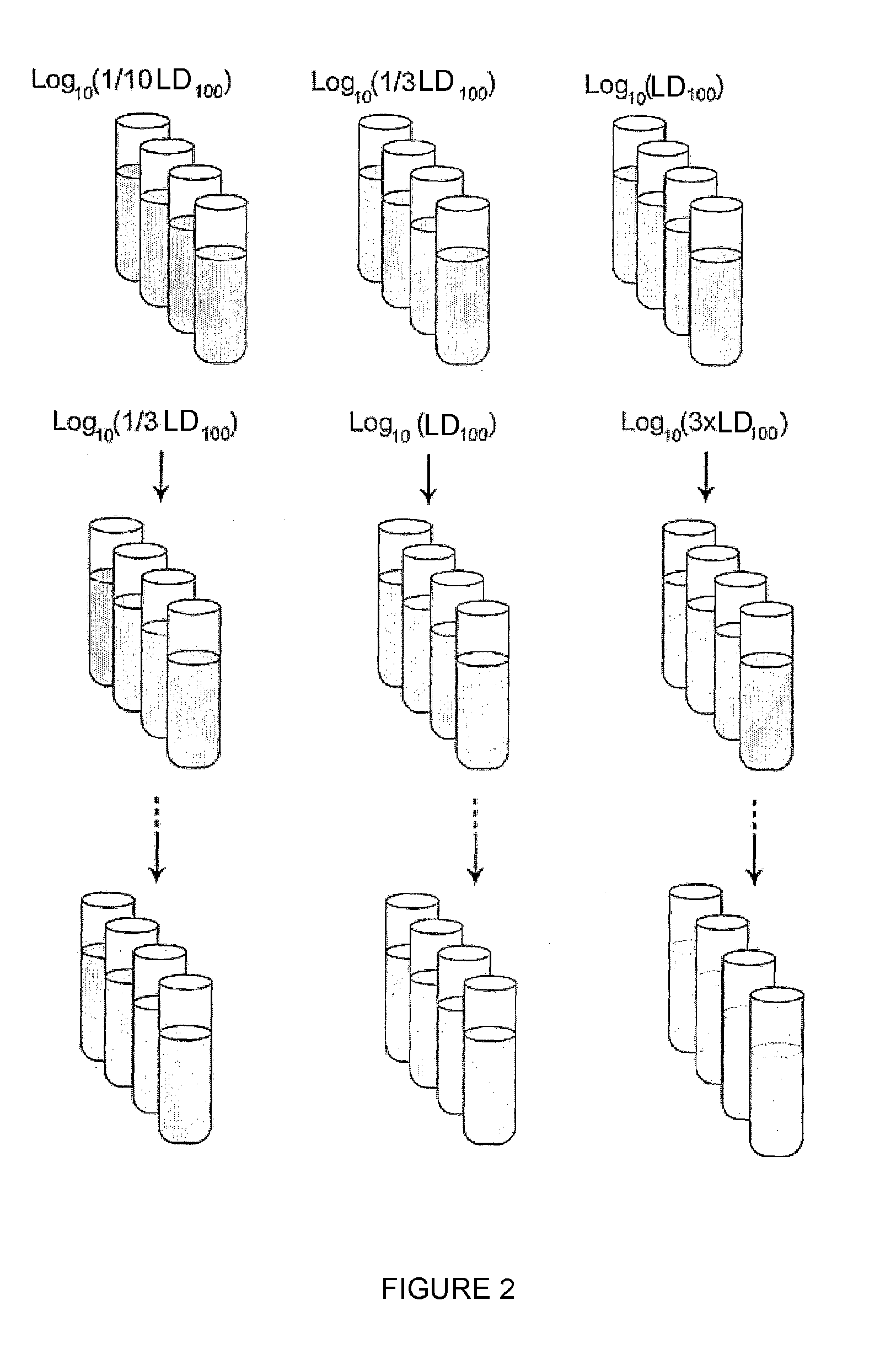
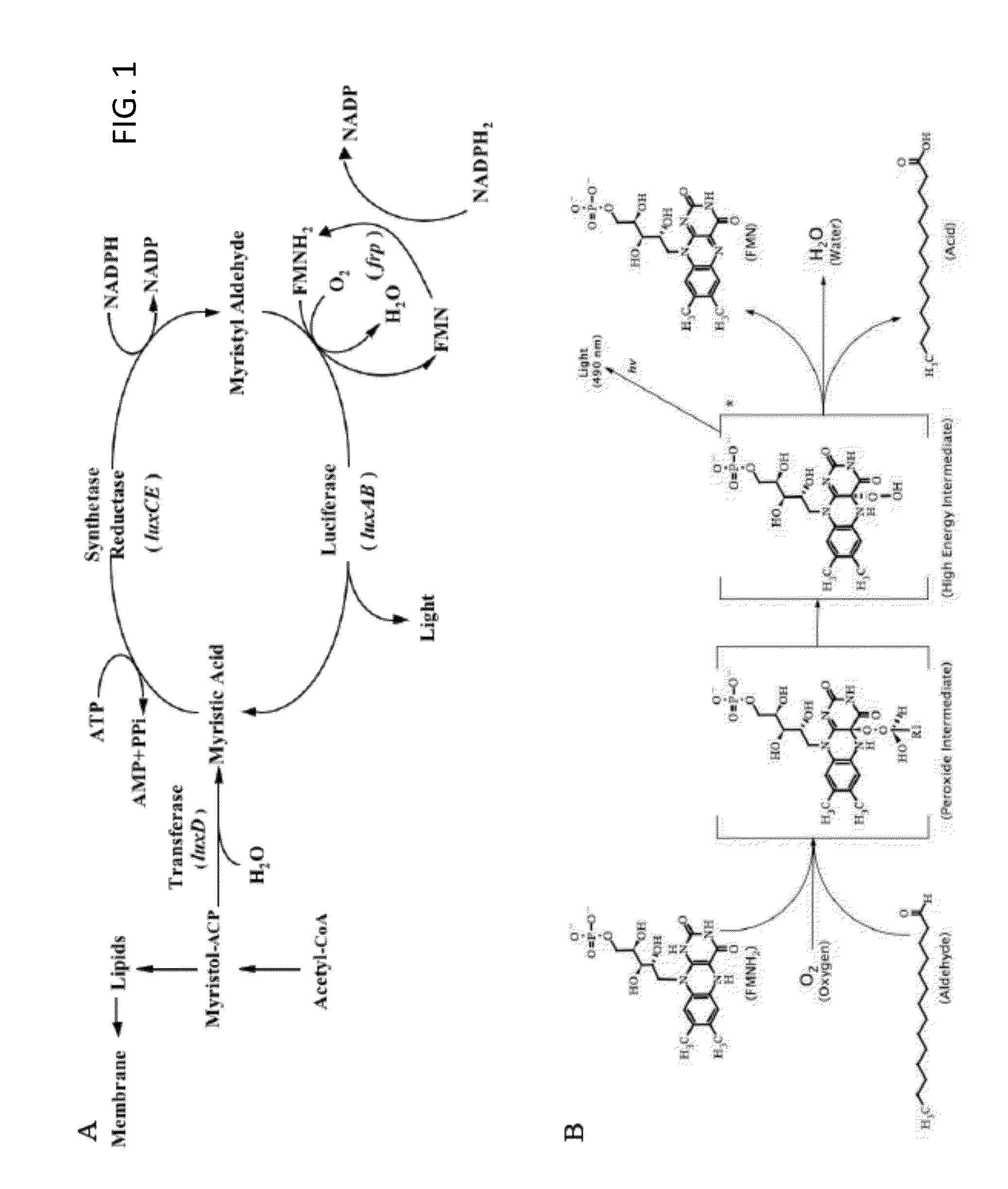
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35results about "Pollution detectors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
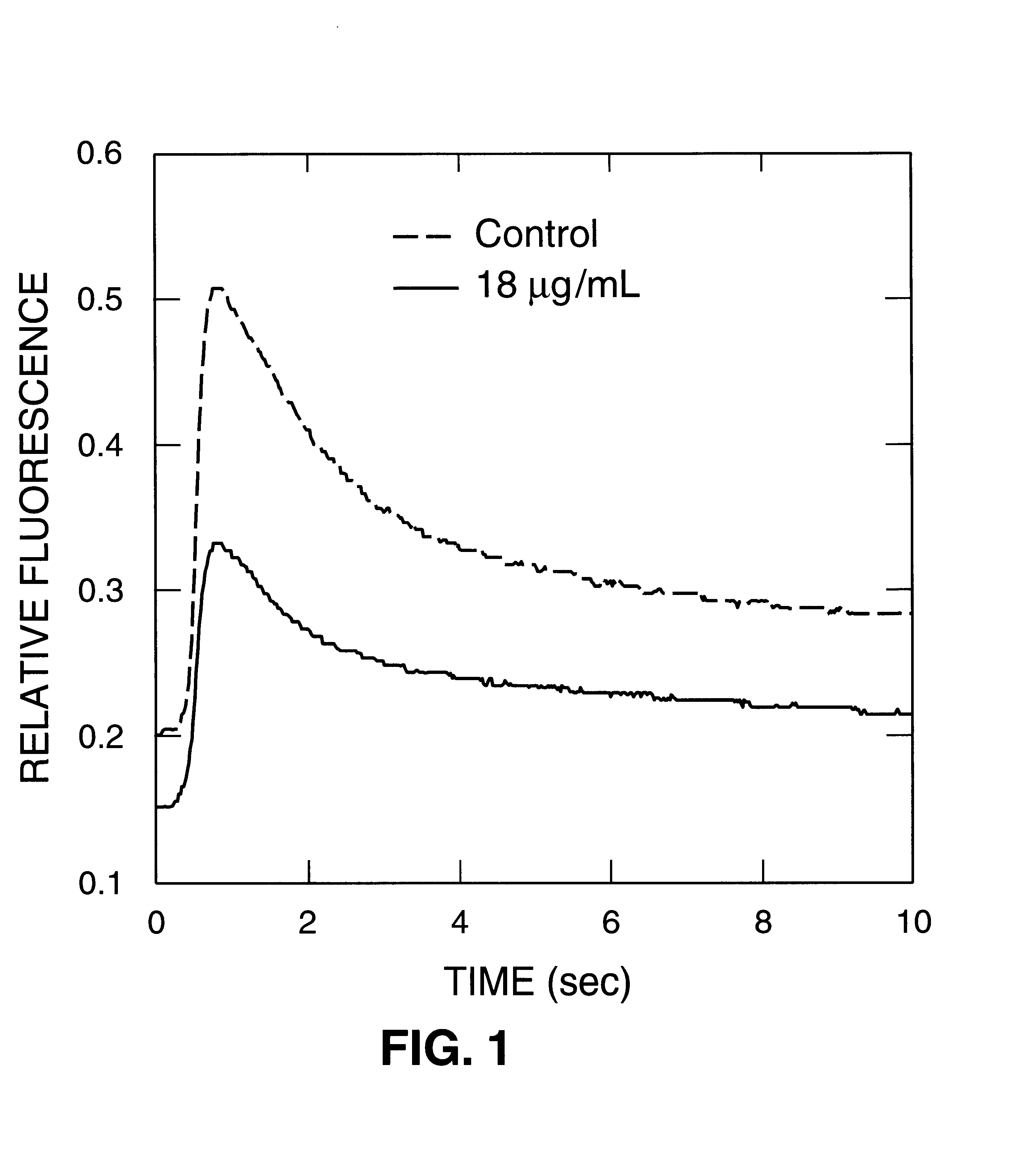
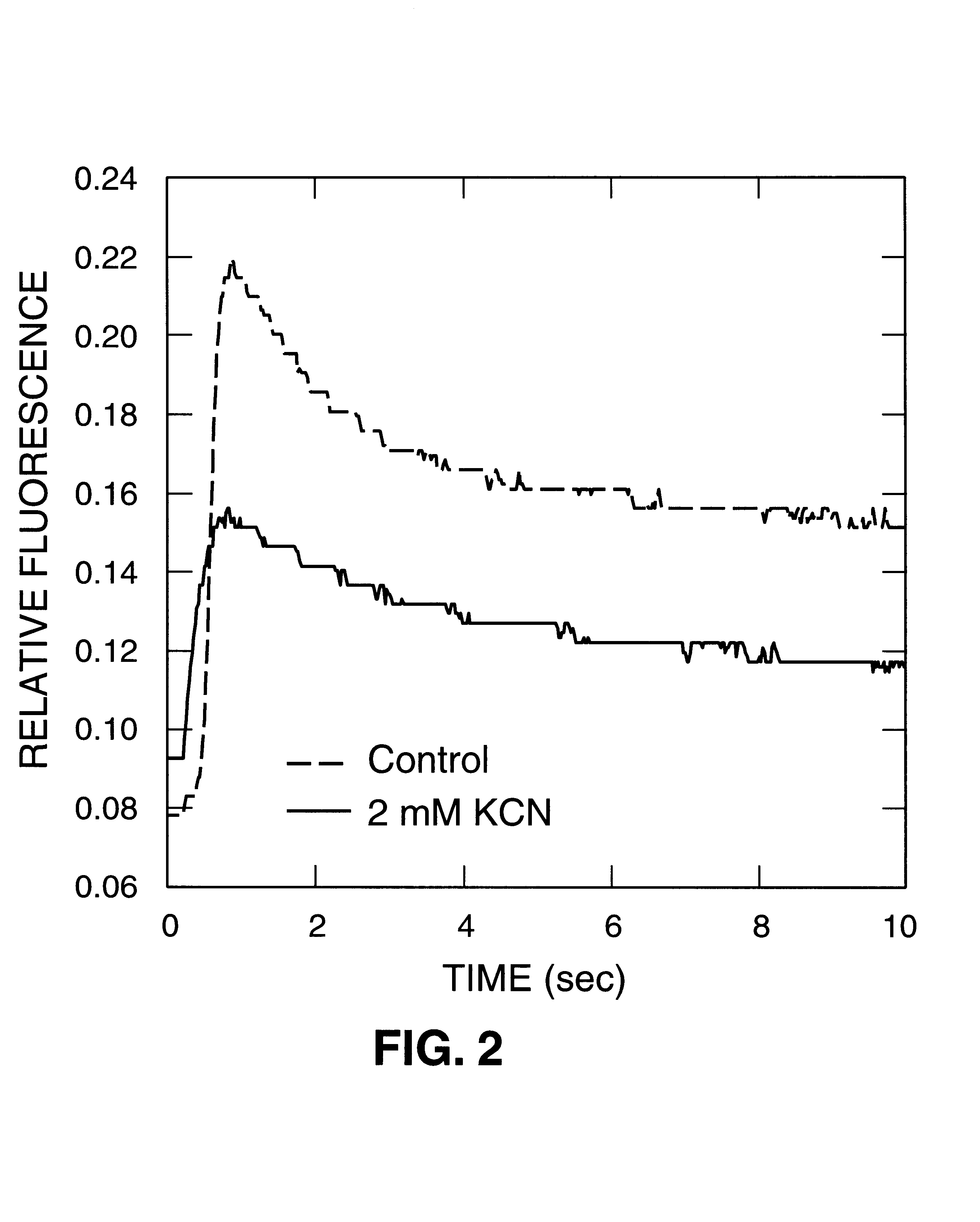
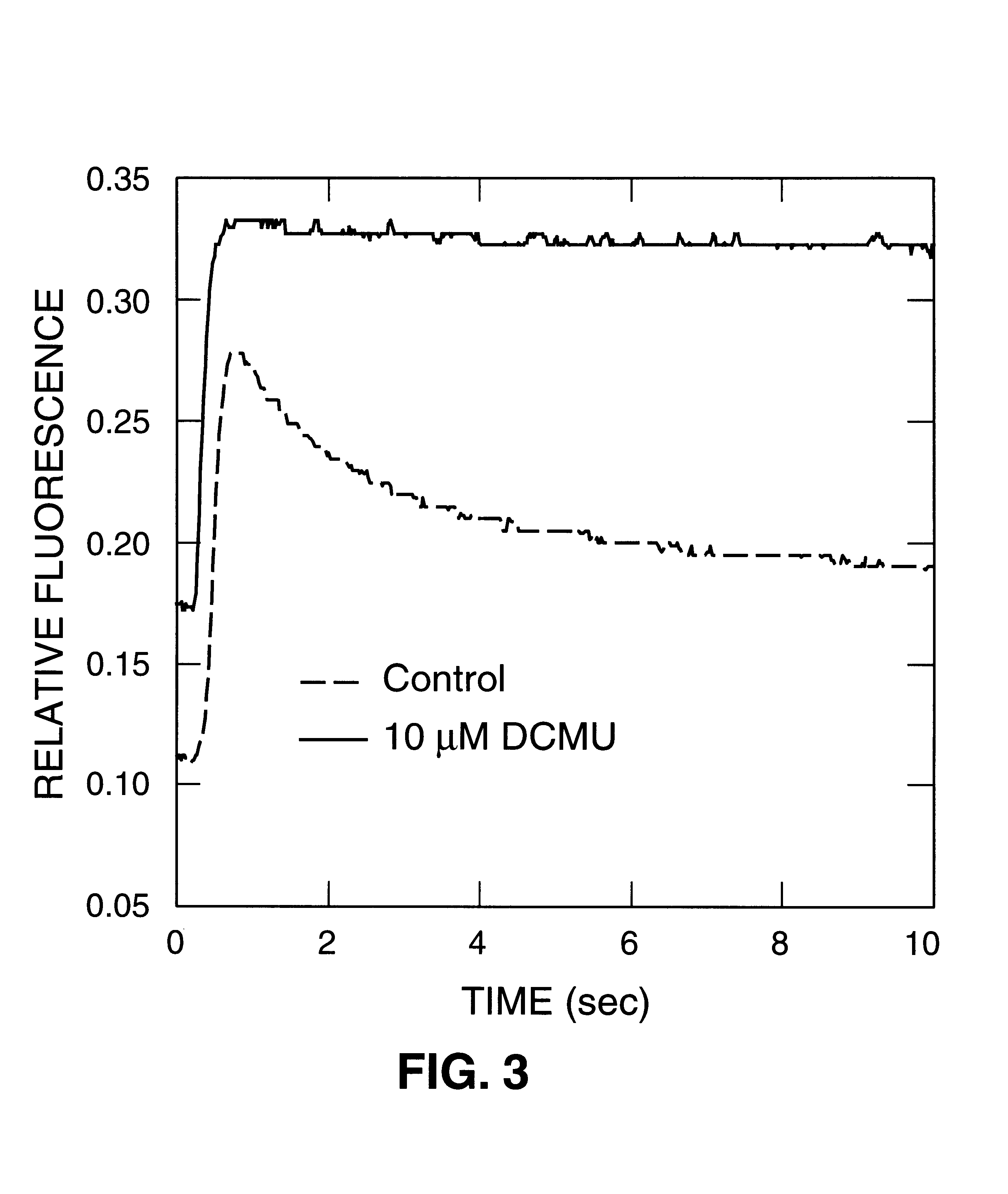
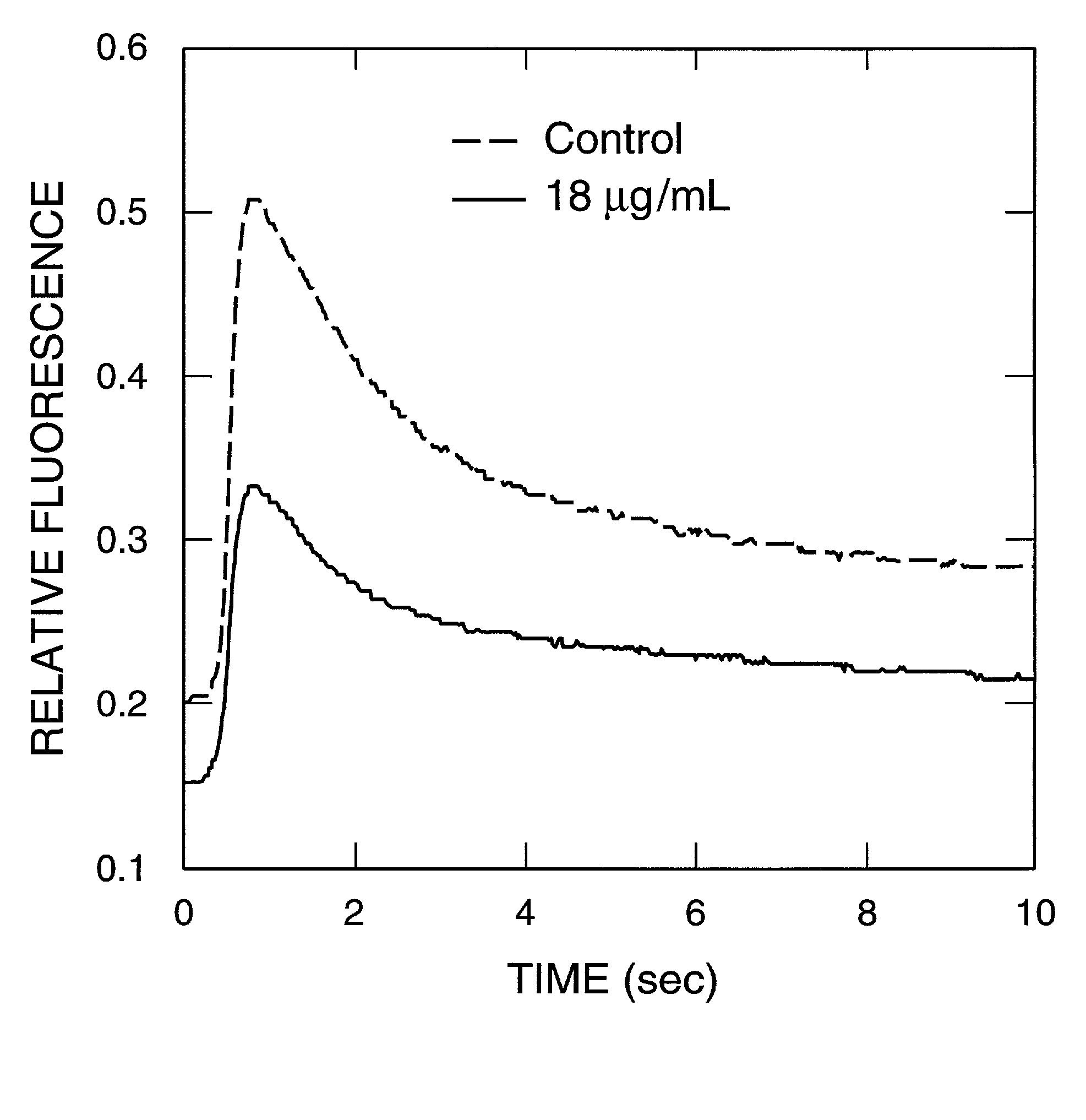
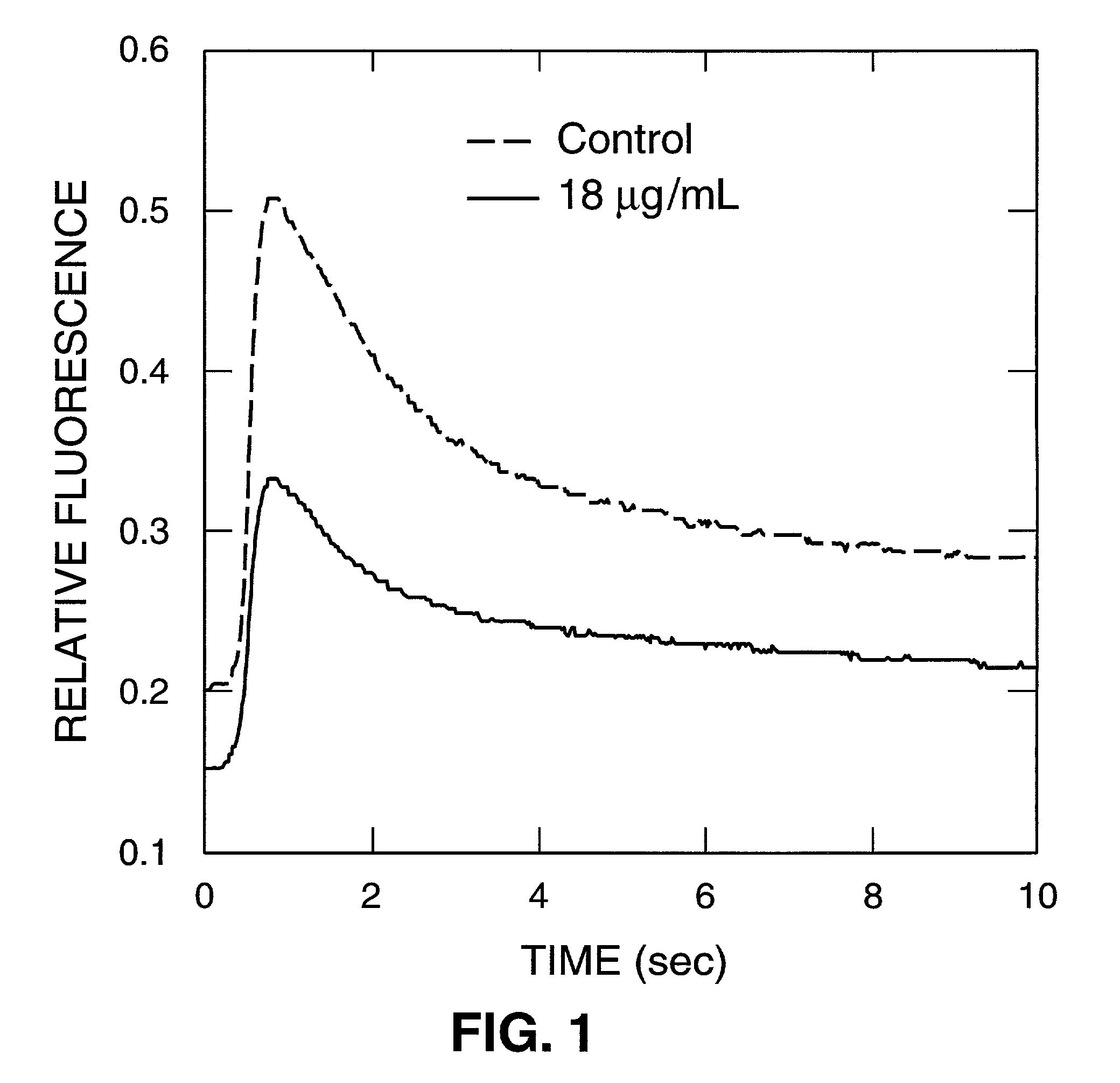
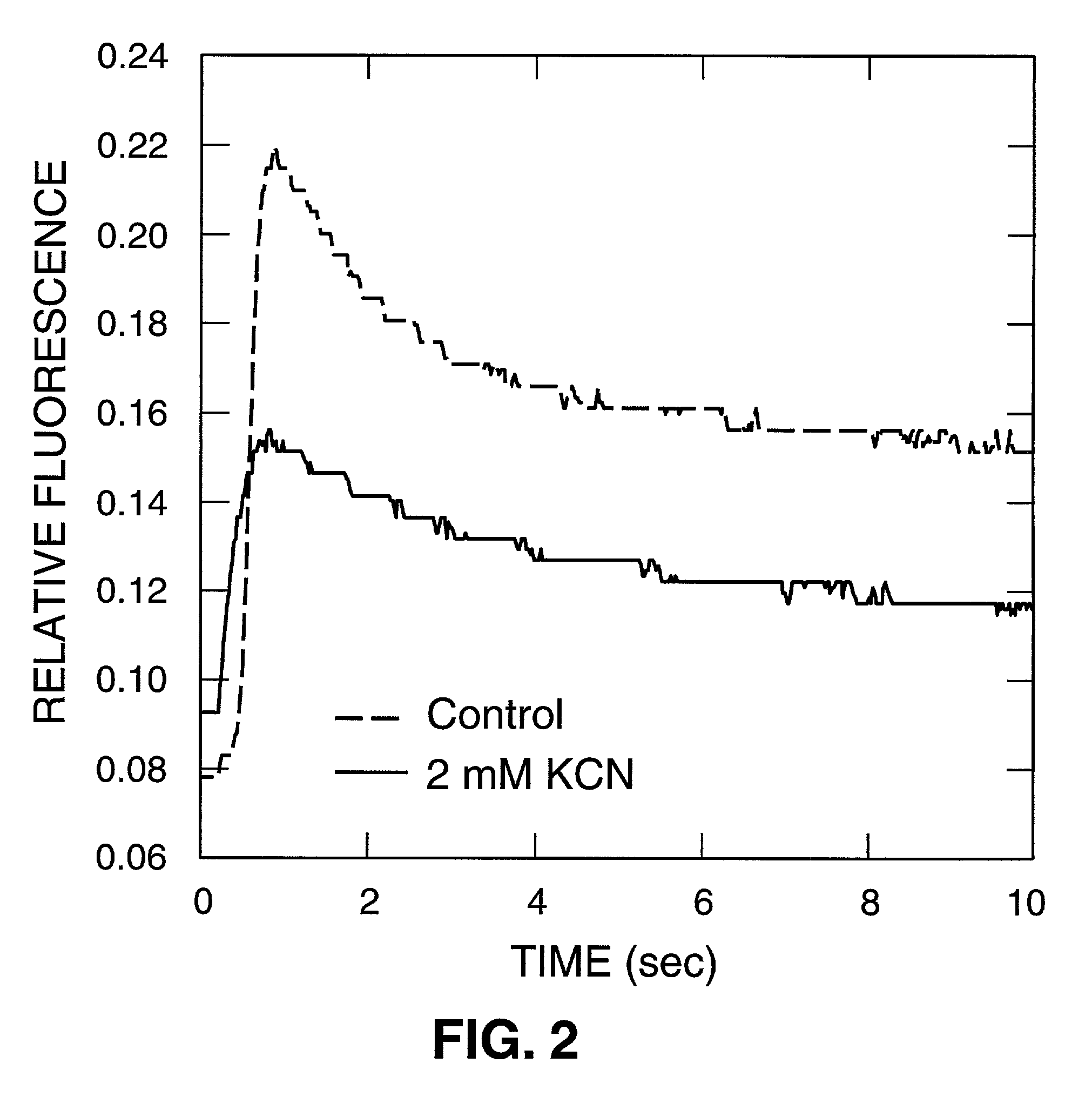
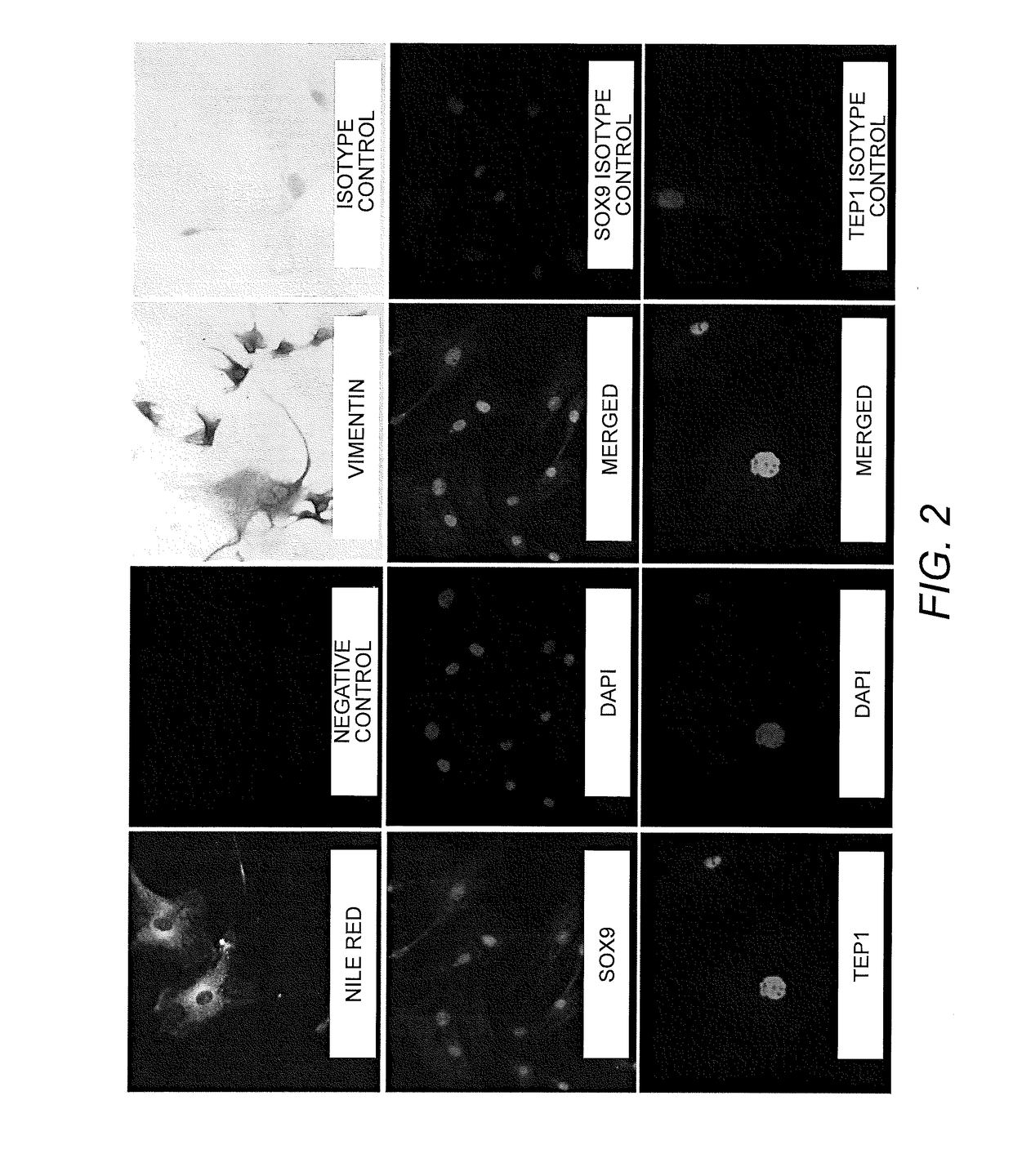
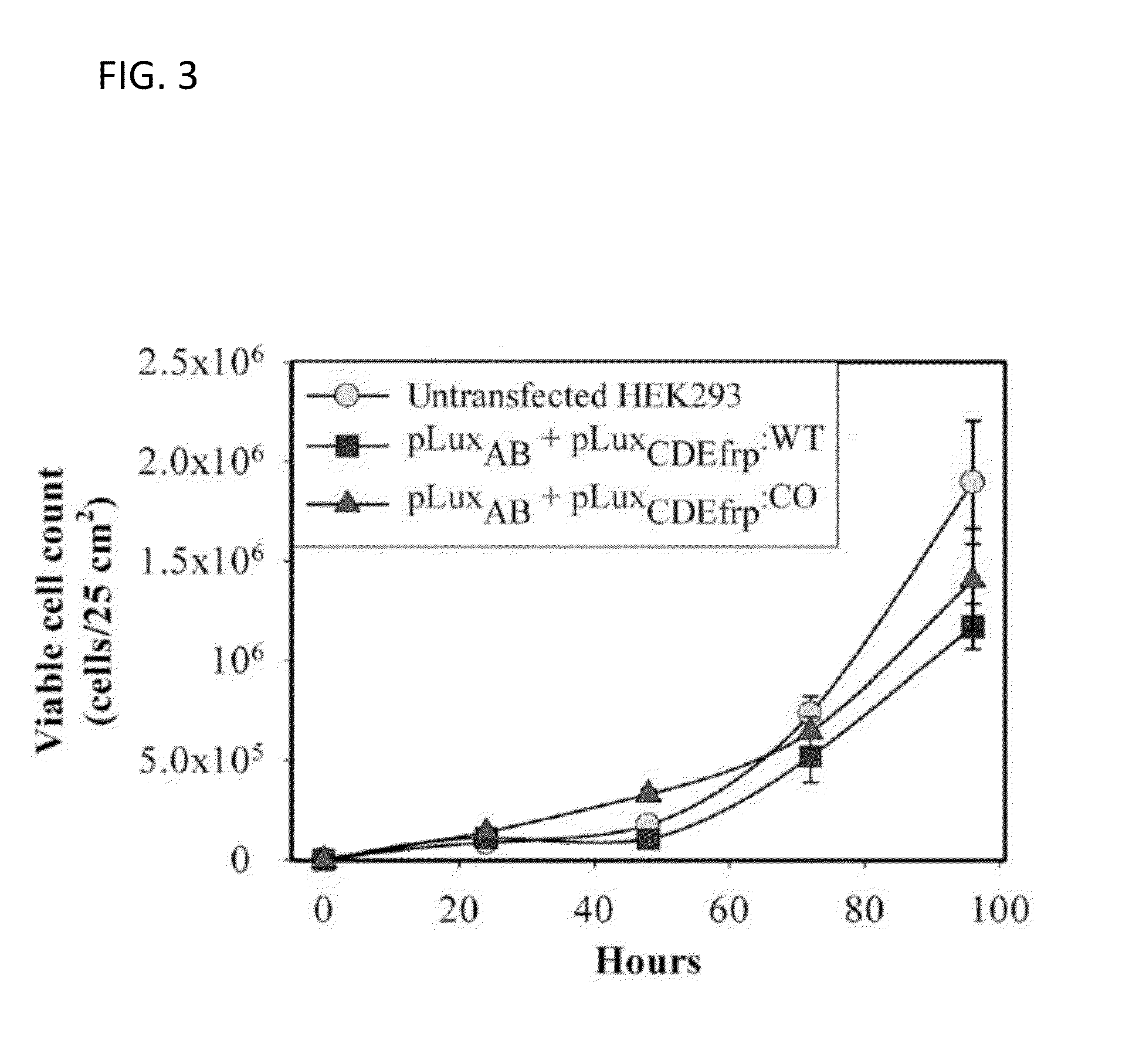
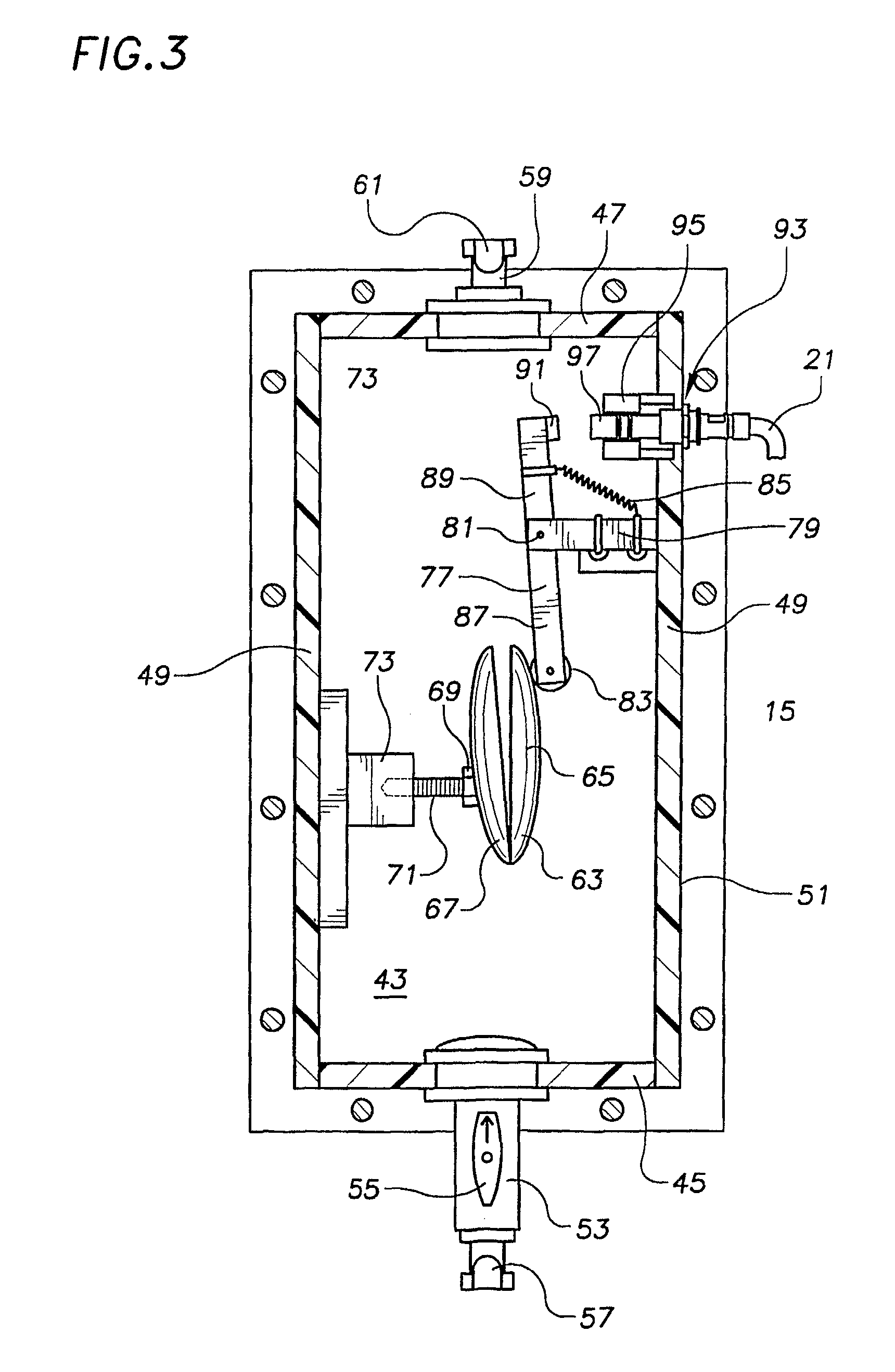
Tissue-based water quality biosensors for detecting chemical warfare agents
InactiveUS6569384B2Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementWater qualityPhotosynthetic organism
A water quality sensor for detecting the presence of at least one chemical or biological warfare agent includes: a cell; apparatus for introducing water into the cell and discharging water from the cell adapted for analyzing photosynthetic activity of naturally occurring, free-living, indigenous photosynthetic organisms in water; a fluorometer for measuring photosynthetic activity of naturally occurring, free-living, indigenous photosynthetic organisms drawn into the cell; and an electronics package that analyzes raw data from the fluorometer and emits a signal indicating the presence of at least one chemical or biological warfare agent in the water.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Plant biosensor systems
InactiveUS20050114923A1Rapid and cost-effective and accurate detectionImprove approachPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementCost effectivenessHigh spatial resolution
The invention provides a system for monitoring the bioavailability and / or toxicity of contaminants in the environment. The system includes plant biosensors that indicate the presence of contaminants, such as, for example, volatile organics or heavy metals, using an in situ monitoring approach. The plant biosensors are genetically engineered to exhibit a change in color phenotype under the control of promoter elements that are selectively responsive to the presence of a particular contaminant. The plant biosensing system provides a cost-effective approach to monitoring large and remote territories with high-spatial resolution. The transgenic plants can also be placed at strategic locations, before, during and after remedial activities at a site.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Tissue-based water quality biosensors for detecting chemical warfare agents
InactiveUS20020102629A1Decrease in photosynthetic capabilityReduce fluorescencePollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementWater qualityPhotosynthetic organism
A method of testing water to detect the presence of at least one chemical or biological warfare agent includes the steps of: a. exposing water to a measuring means for measuring photosynthetic activity of free-living indigenous photosynthetic organisms; b. measuring photosynthetic activity of indigenous photosynthetic organisms occurring naturally in the water to detect the presence of at least one chemical or biological warfare agent in the water.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
In vivo high throughput toxicology screening method
InactiveUS6855504B2Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A high throughput toxicology screening method is provided. In the subject method, at least 10 different compound compositions are tested simultaneously. Each compound composition is tested by contacting it with a plurality, e.g. from about 10 to 1000, of non-mammalian multi-cellular organisms and determining the effect of the compound composition on the organisms. The multi-cellular organisms employed in the subject methods are small, have differentiated tissues and organs and have a rapid generation time. The subject high throughput screening methods find use in a variety of applications, and are particularly suited for use in the toxicology screening of libraries of compounds, such as libraries of combinatorially produced compounds.
Owner:TOSK INC
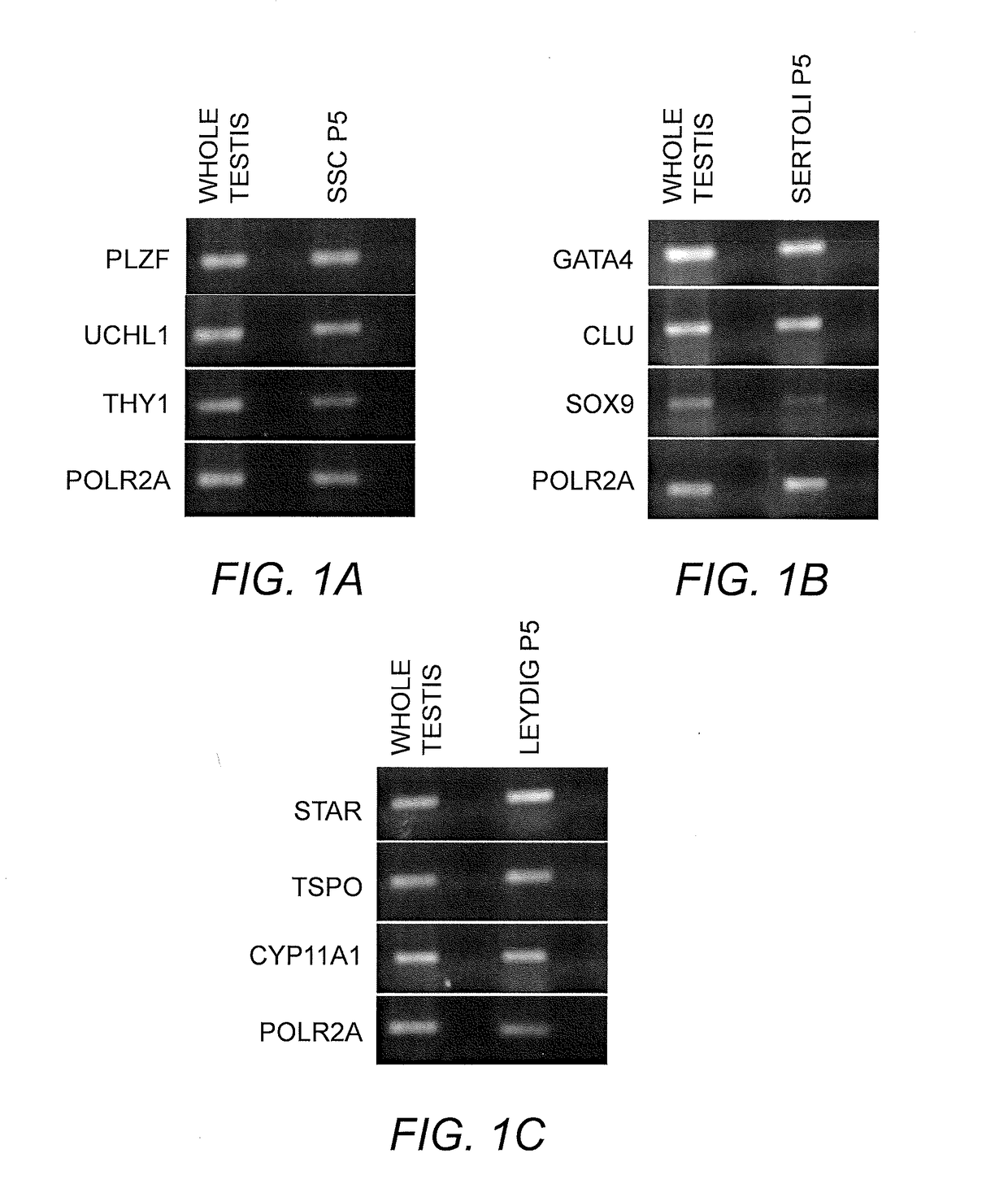
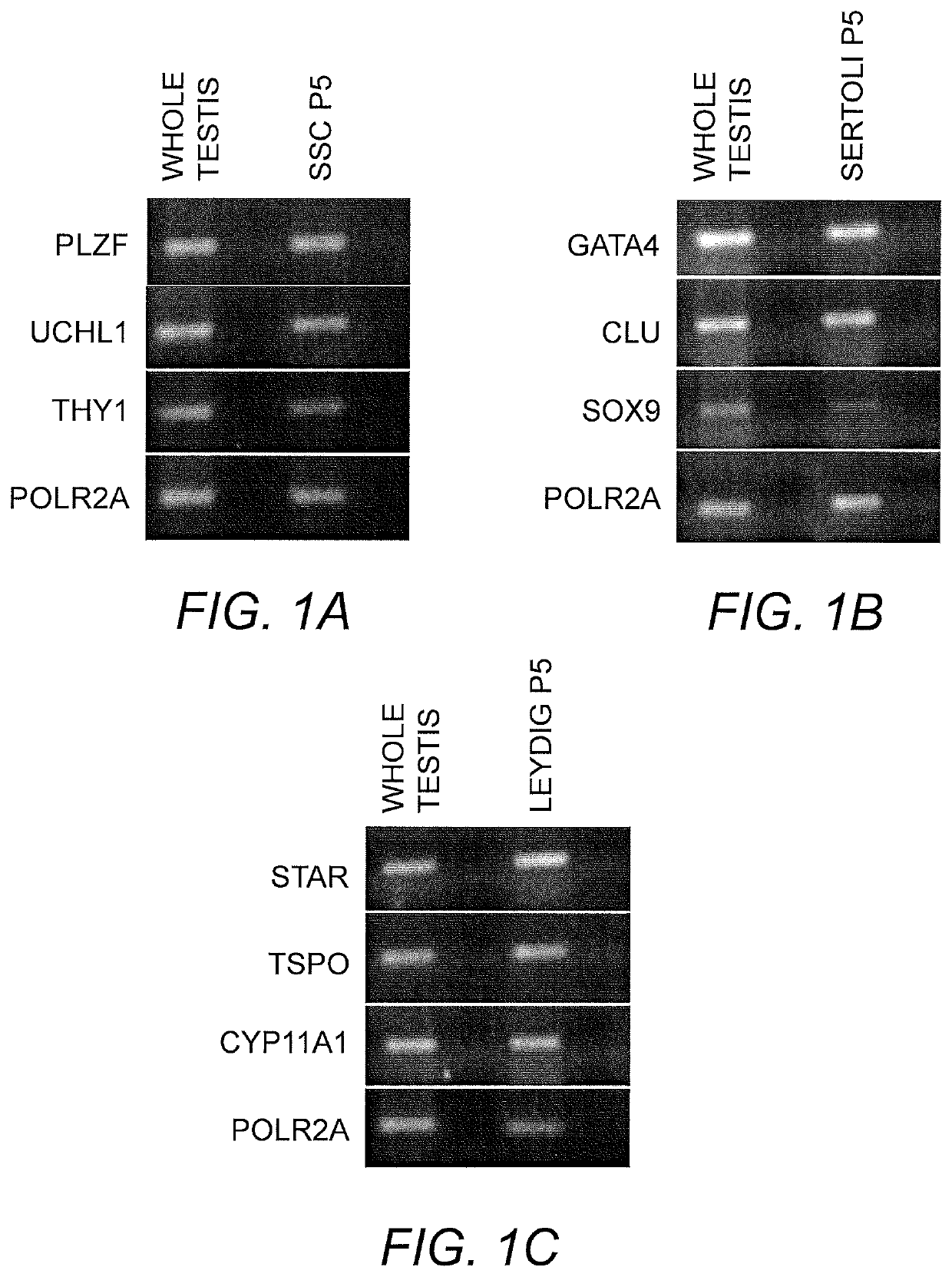
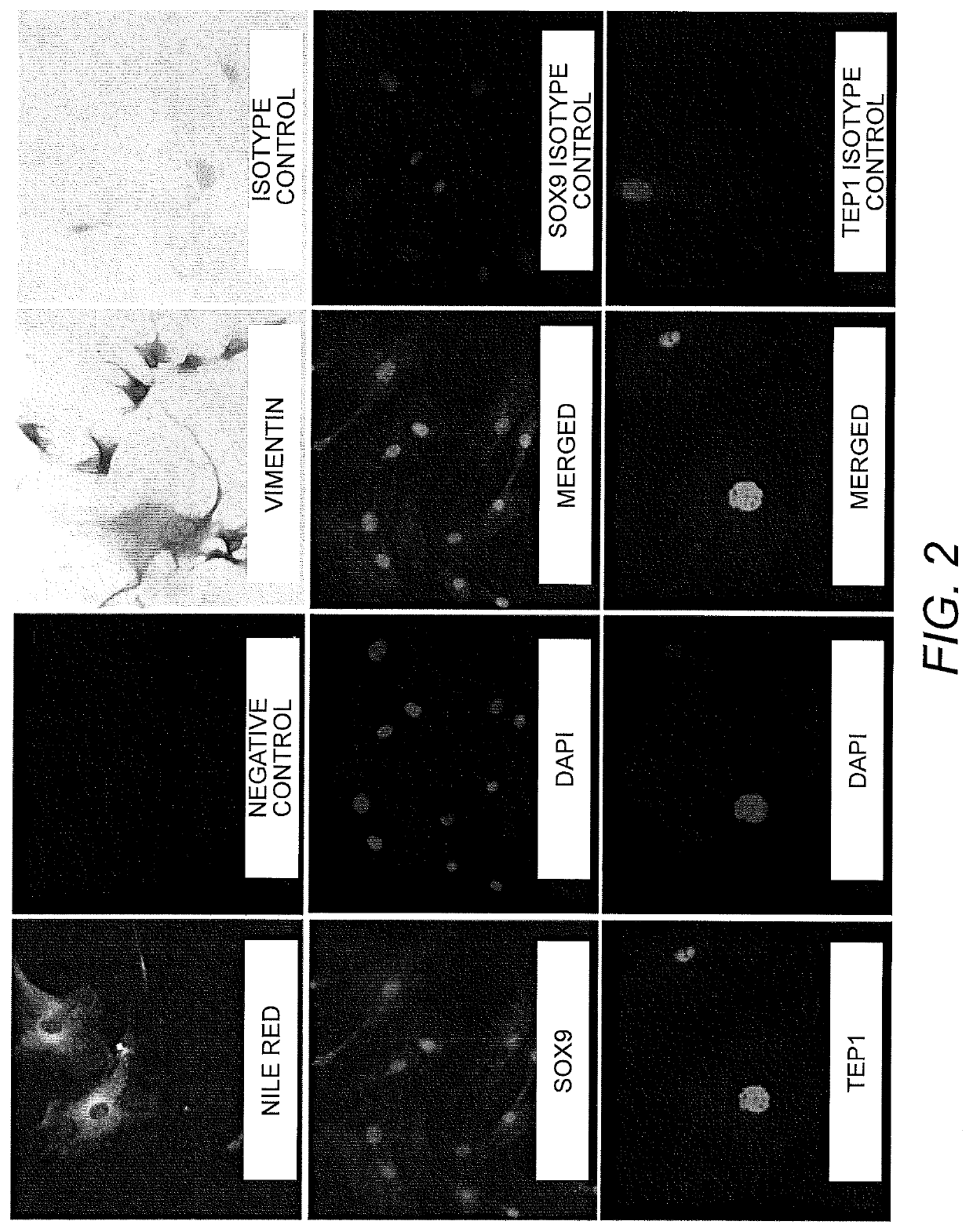
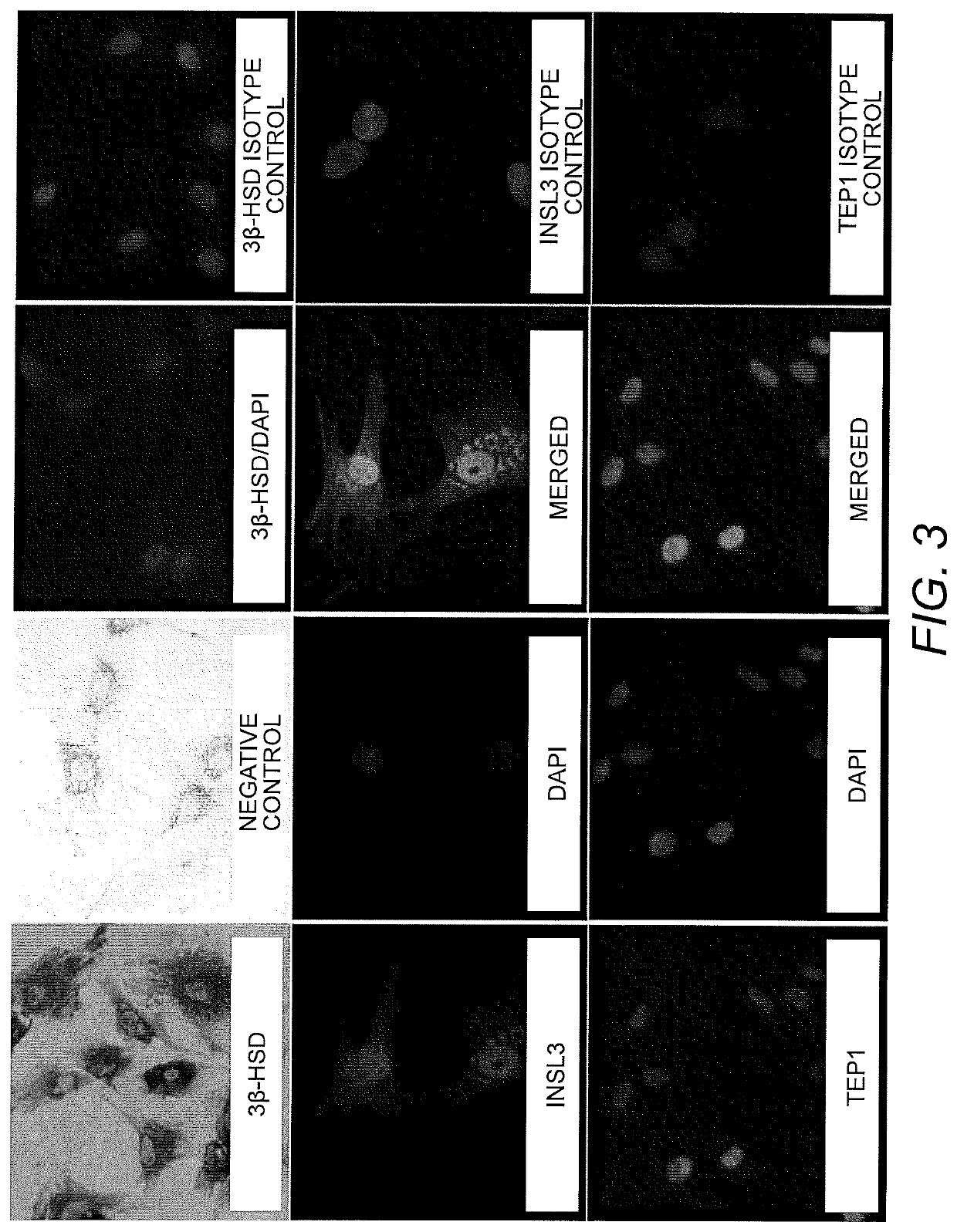
Method of producing in vitro testicular constructs and uses thereof
A cell composition composed of spermatogonial stem cells, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and optionally peritubular cells, is provided, as is a culture composition, artificial testicular construct, hydrogel composition, and device containing the same. A method for using the device as a physiologically relevant in vitro model of human testicular function to screen compounds for pharmacological or toxicological activity is also provided.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
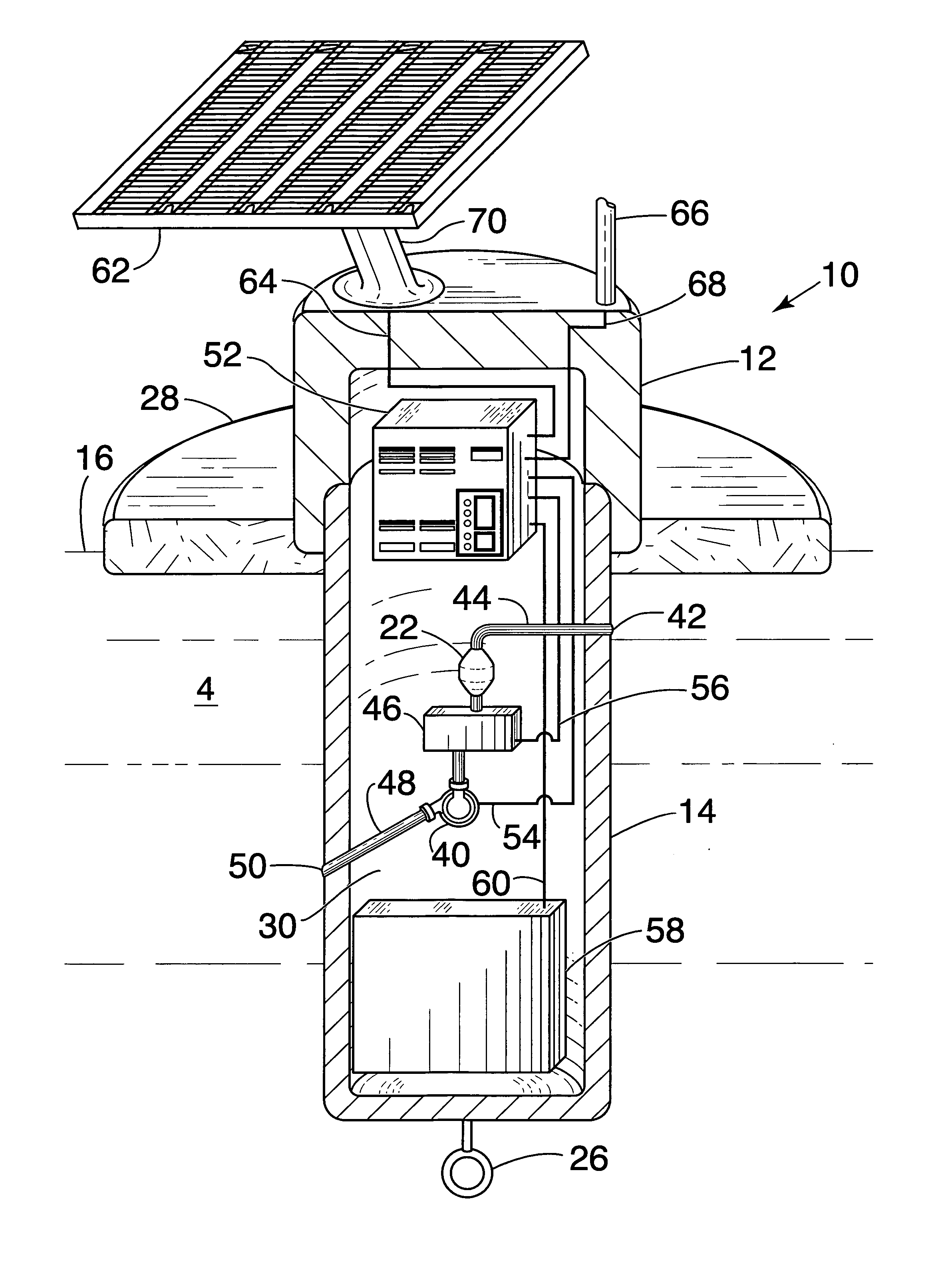
Enhanced monitor system for water protection
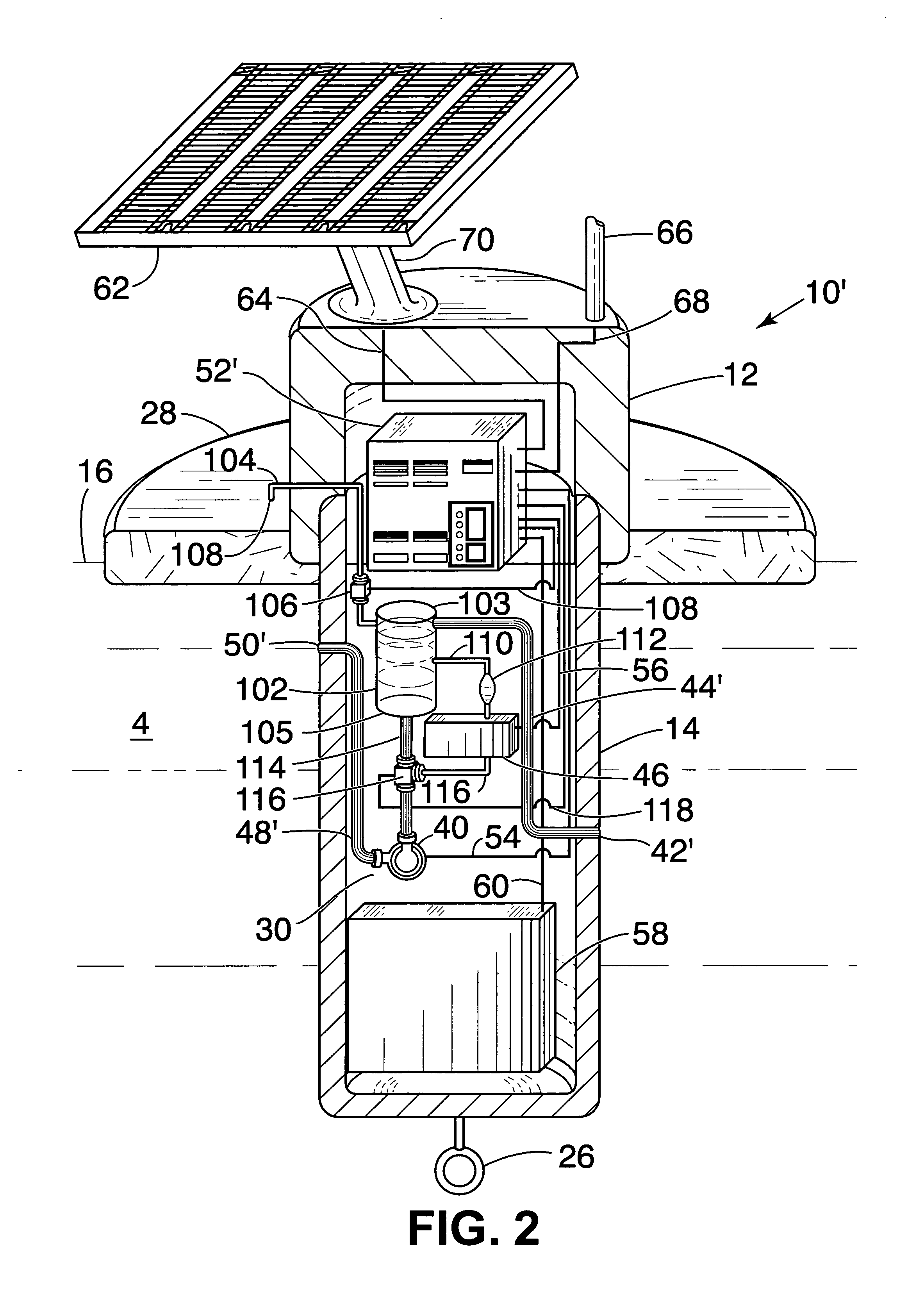
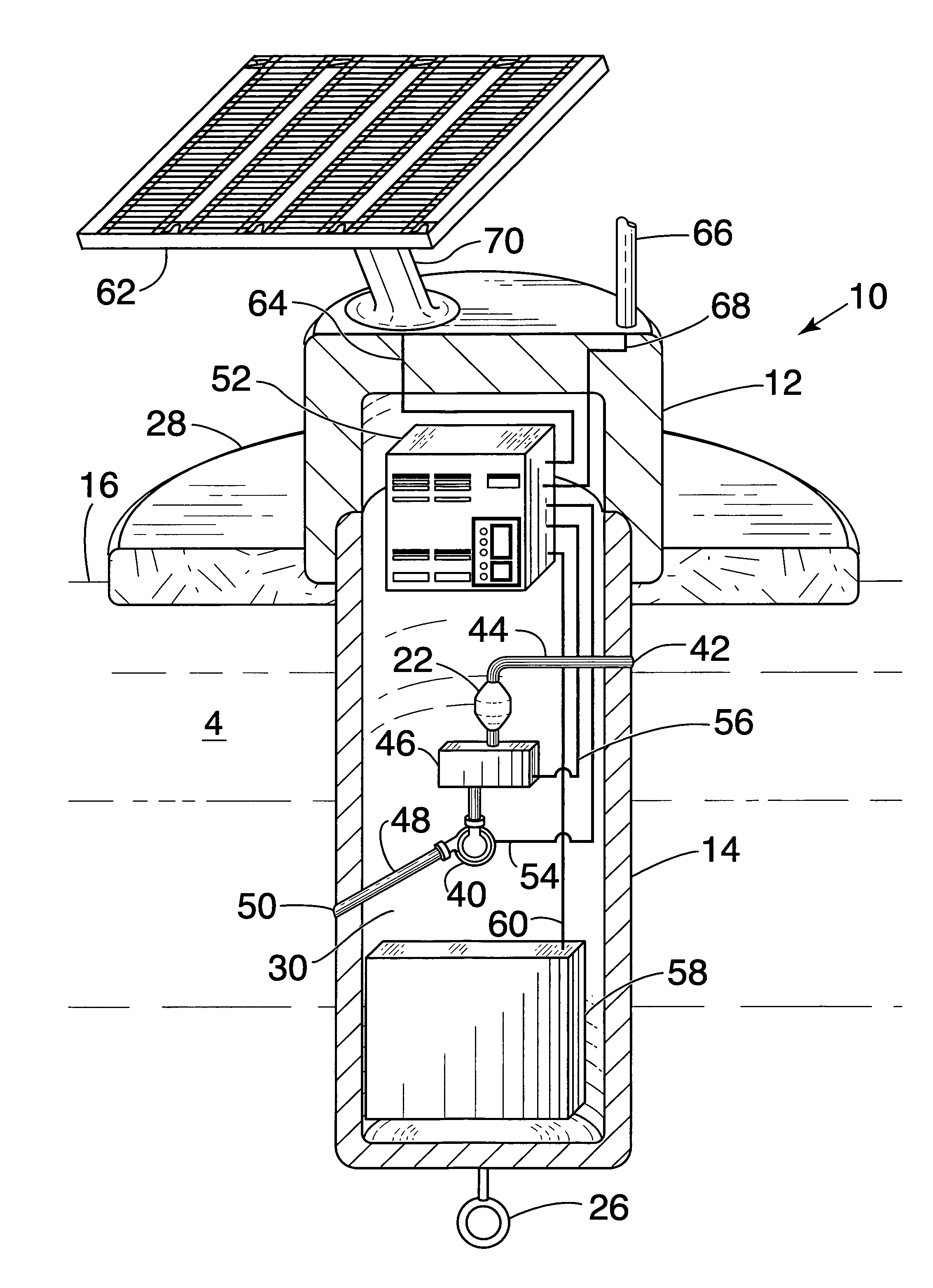
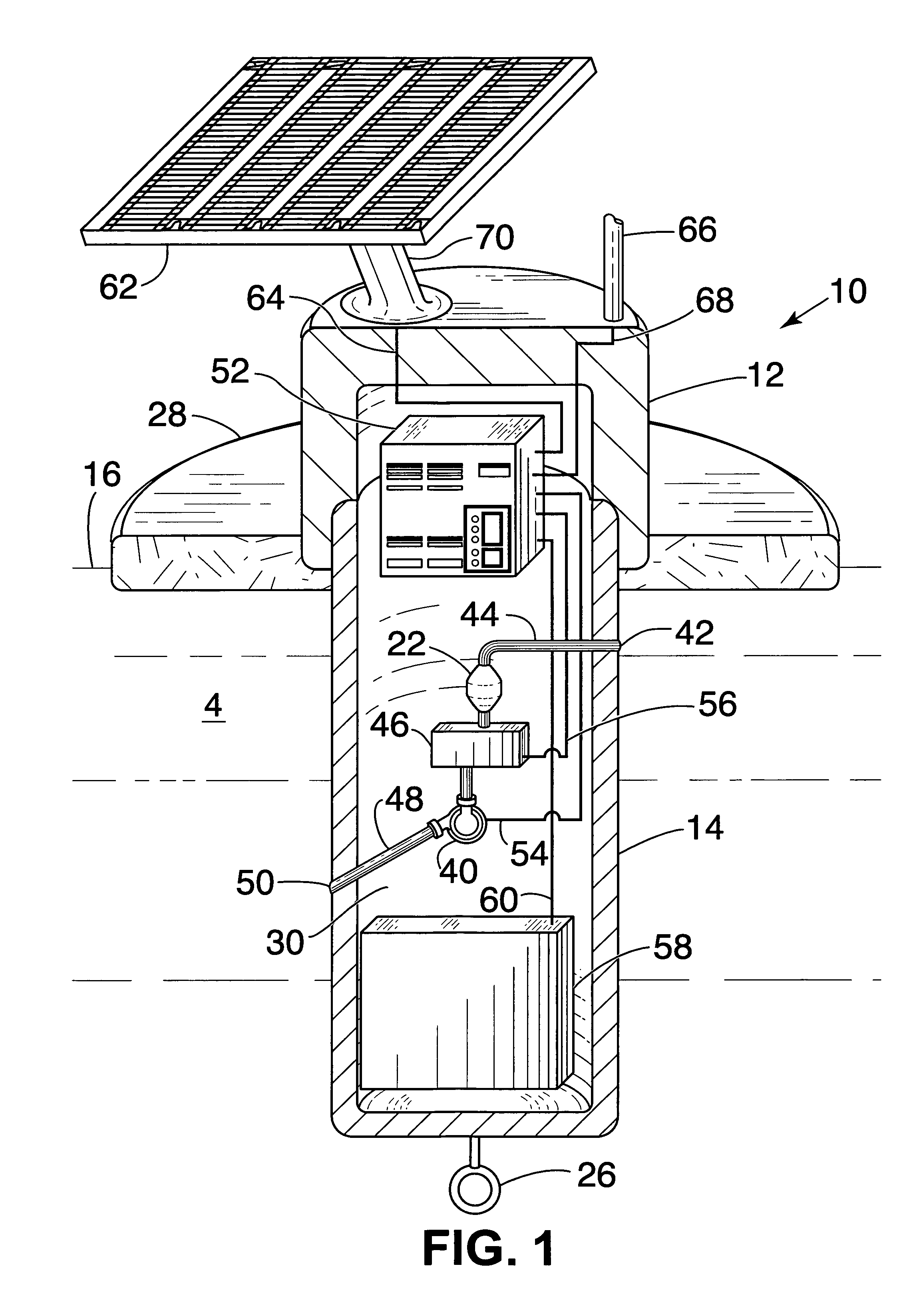
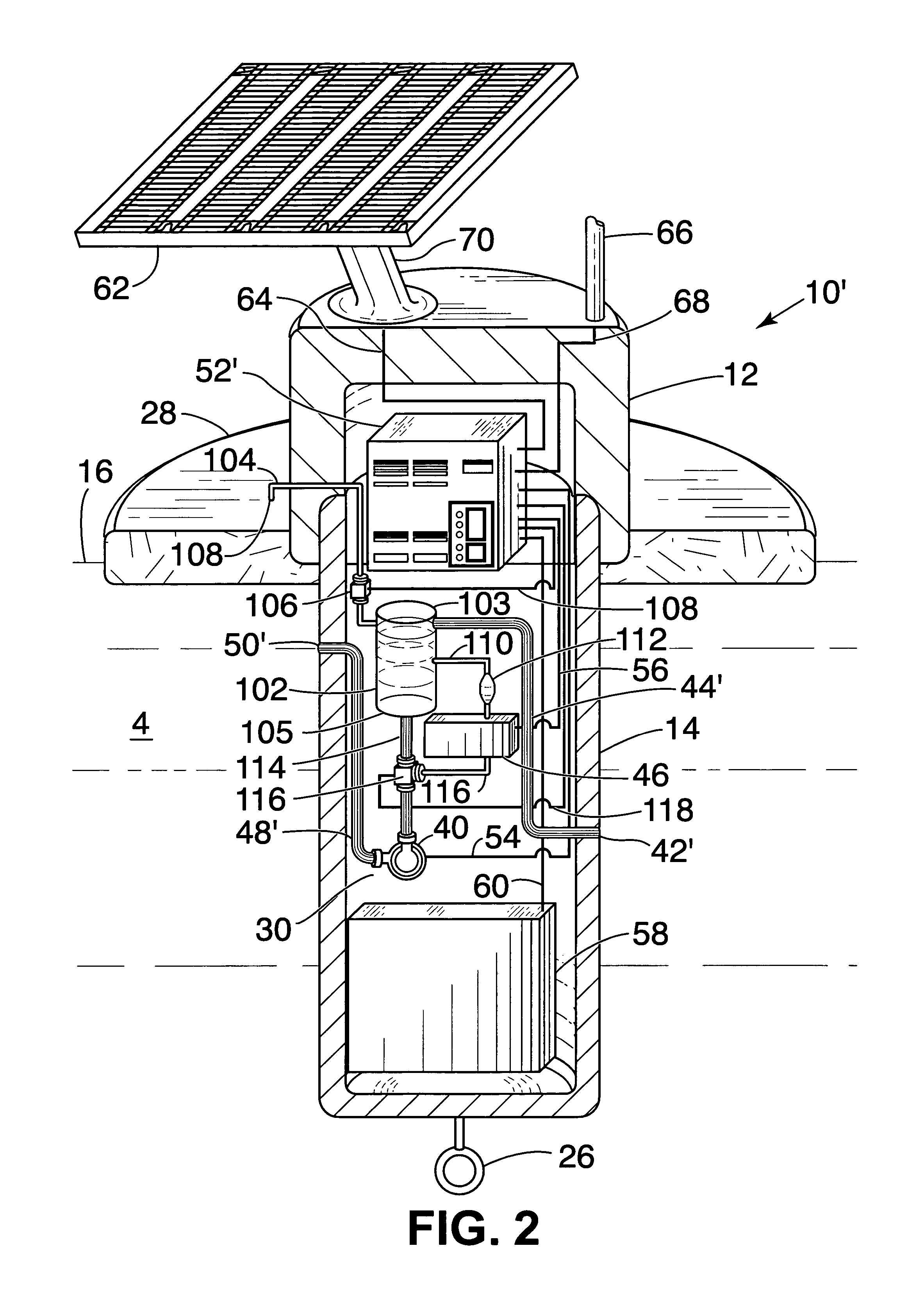
InactiveUS20050084419A1Prevent freezingAvoid overall overheatingAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPollution detectorsElectronicsWater sample
An automatic, self-contained device for detecting toxic agents in a water supply includes an analyzer for detecting at least one toxic agent in a water sample, introducing means for introducing a water sample into the analyzer and discharging the water sample from the analyzer, holding means for holding a water sample for a pre-selected period of time before the water sample is introduced into the analyzer, and an electronics package that analyzes raw data from the analyzer and emits a signal indicating the presence of at least one toxic agent in the water sample.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
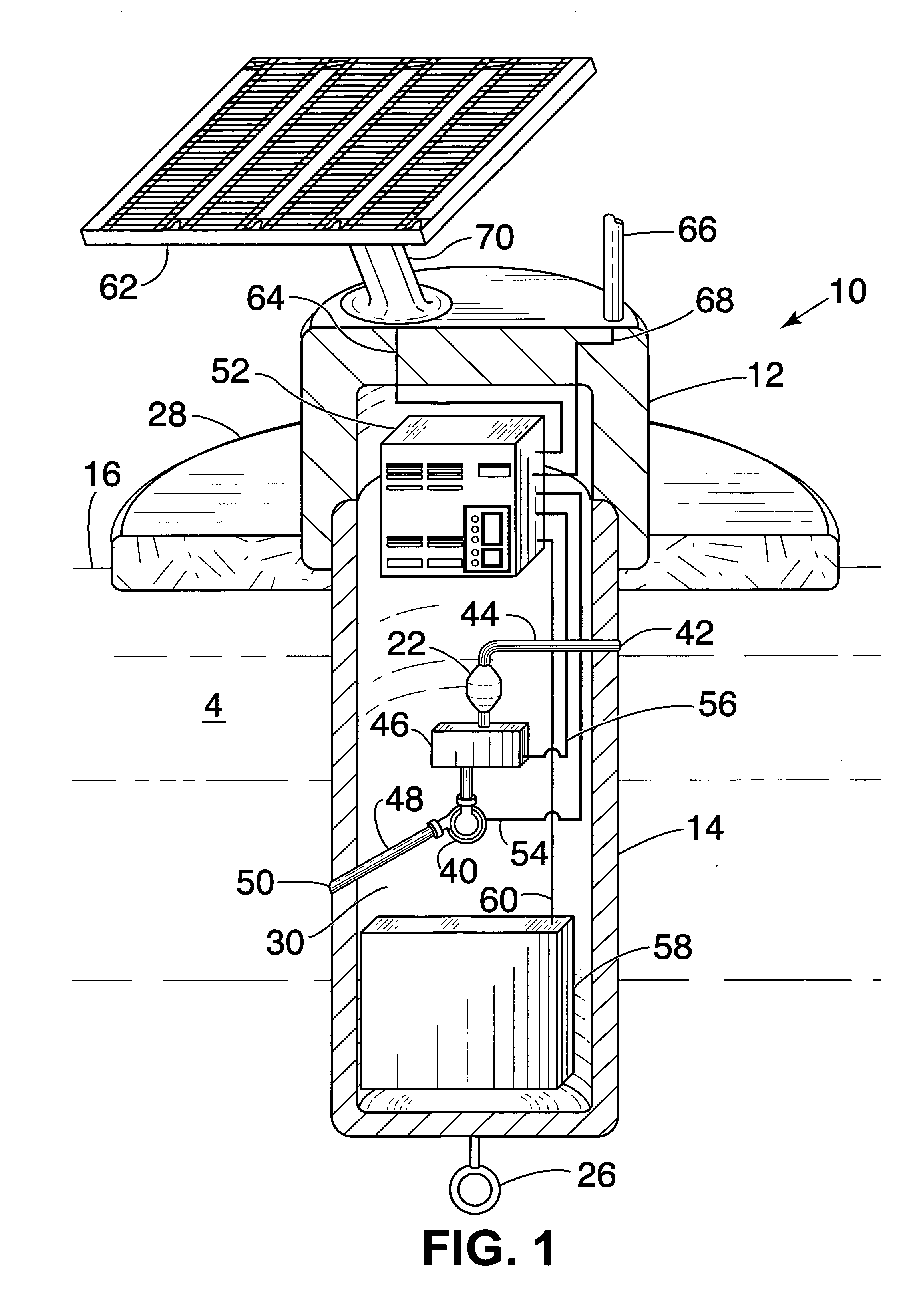
Enhanced monitor system for water protection
InactiveUS7591979B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsPollution detectorsAmount of substanceElectronics
An automatic, self-contained device for detecting toxic agents in a water supply includes an analyzer for detecting at least one toxic agent in a water sample, introducing means for introducing a water sample into the analyzer and discharging the water sample from the analyzer, holding means for holding a water sample for a pre-selected period of time before the water sample is introduced into the analyzer, and an electronics package that analyzes raw data from the analyzer and emits a signal indicating the presence of at least one toxic agent in the water sample.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Transgenic animals for monitoring water quality
InactiveUS20060143718A1Reduce cost per sampleIncreases time required data acquisitionPollution detectorsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuciferase GeneWater quality
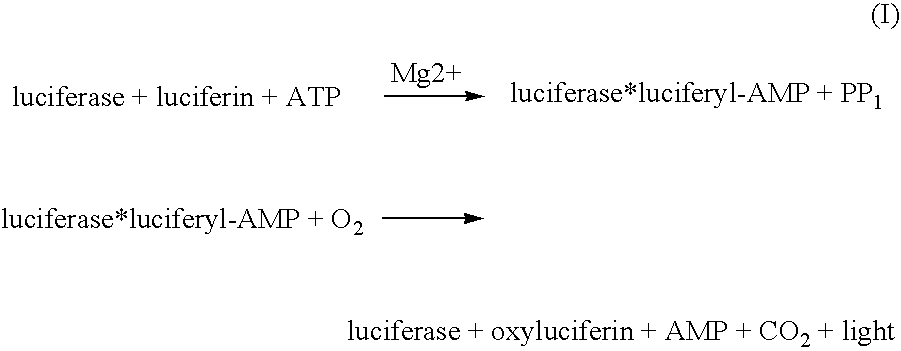
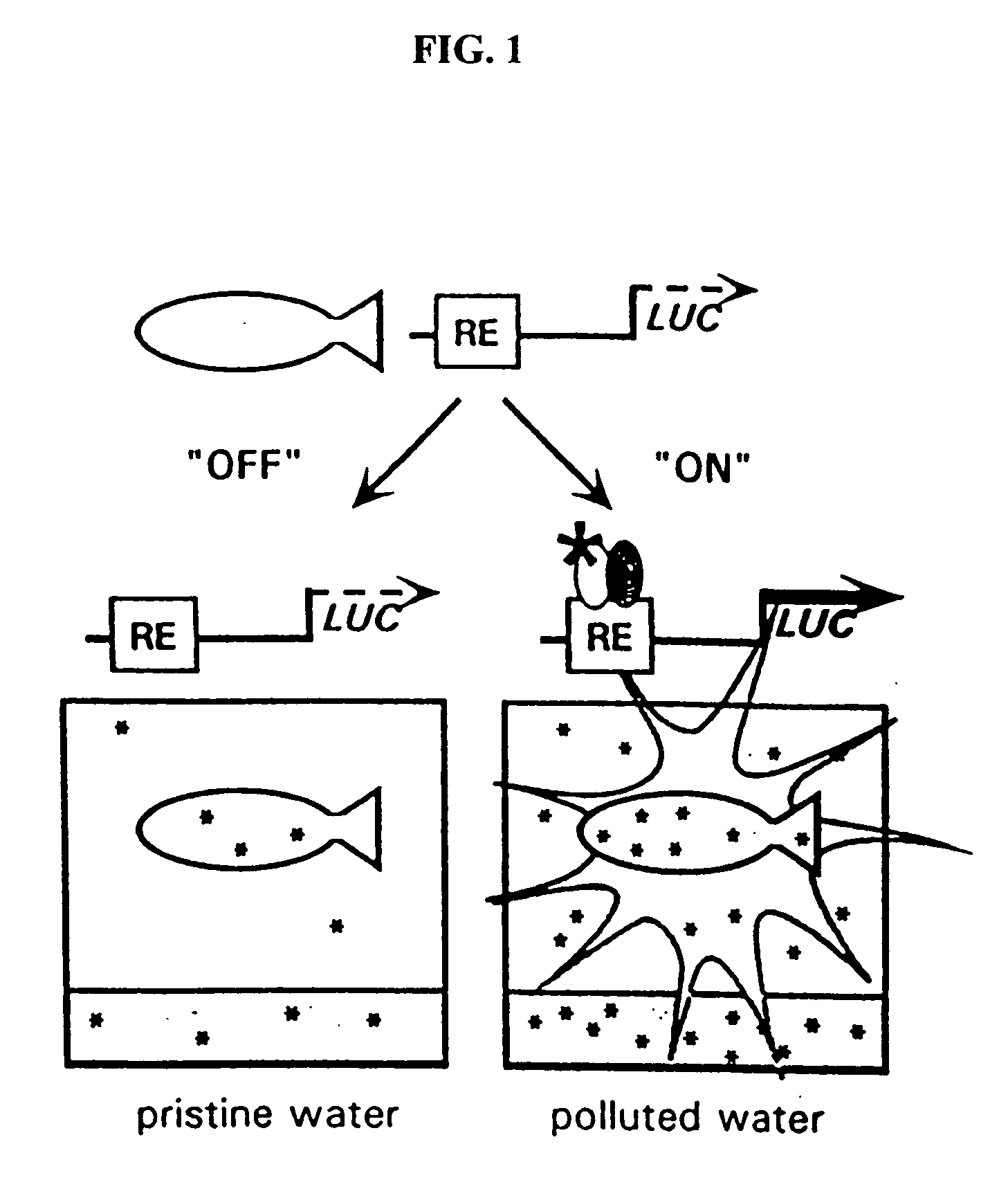
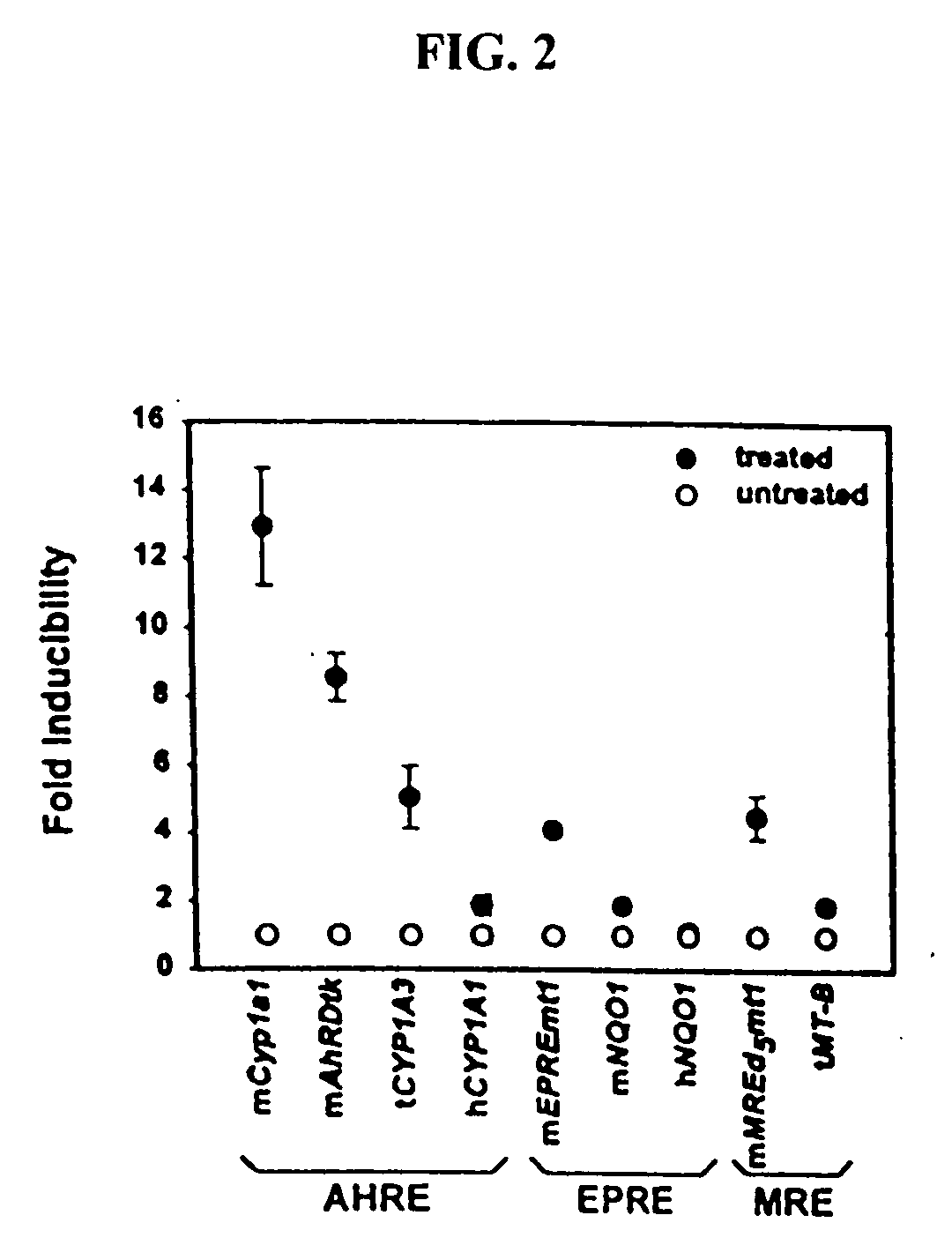
The present invention provides methods and systems that uses transgenic zebrafish with an easily assessable reporter gene under the control of pollutant-inducible DNA response elements. Transgenic zebrafish, carrying pollution-inducible response elements, are placed in the water to be tested, and the contaminants become bioconcentrated (generally 1,000- to 40,000-fold, relative to the water) in the tissues of the fish thereby activating specific response elements, which up-regulate the LUC reporter gene. Fish are then removed from the test water and placed immediately in a luminometer cuvette and incubated with luciferin. Luciferin is rapidly taken up into the tissues of the fish, oxidized by luciferase, and light is produced. The luminescence is proportional to the environmental concentration of the pollutant (to which the fish had been exposed), which drives the expression of the LUC gene by means of the various DNA motifs. The luminescence is quantitated in the luminometer. In each response element-containing construct, a specific class of polluting chemicals, allowing for differential identification of pollutants in a complex mixture activates the expression of the LUC gene. This assay does not require killing the fish and allows for repeated analysis of the same site with the same fish. The sensitivity of the system can be manipulated by varying the sequence of the response element.
Owner:NEBERT DANIEL
Cell-based biosensor for harmful airborne agents
InactiveUS7195899B1Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementAir atmosphereAir liquid interface
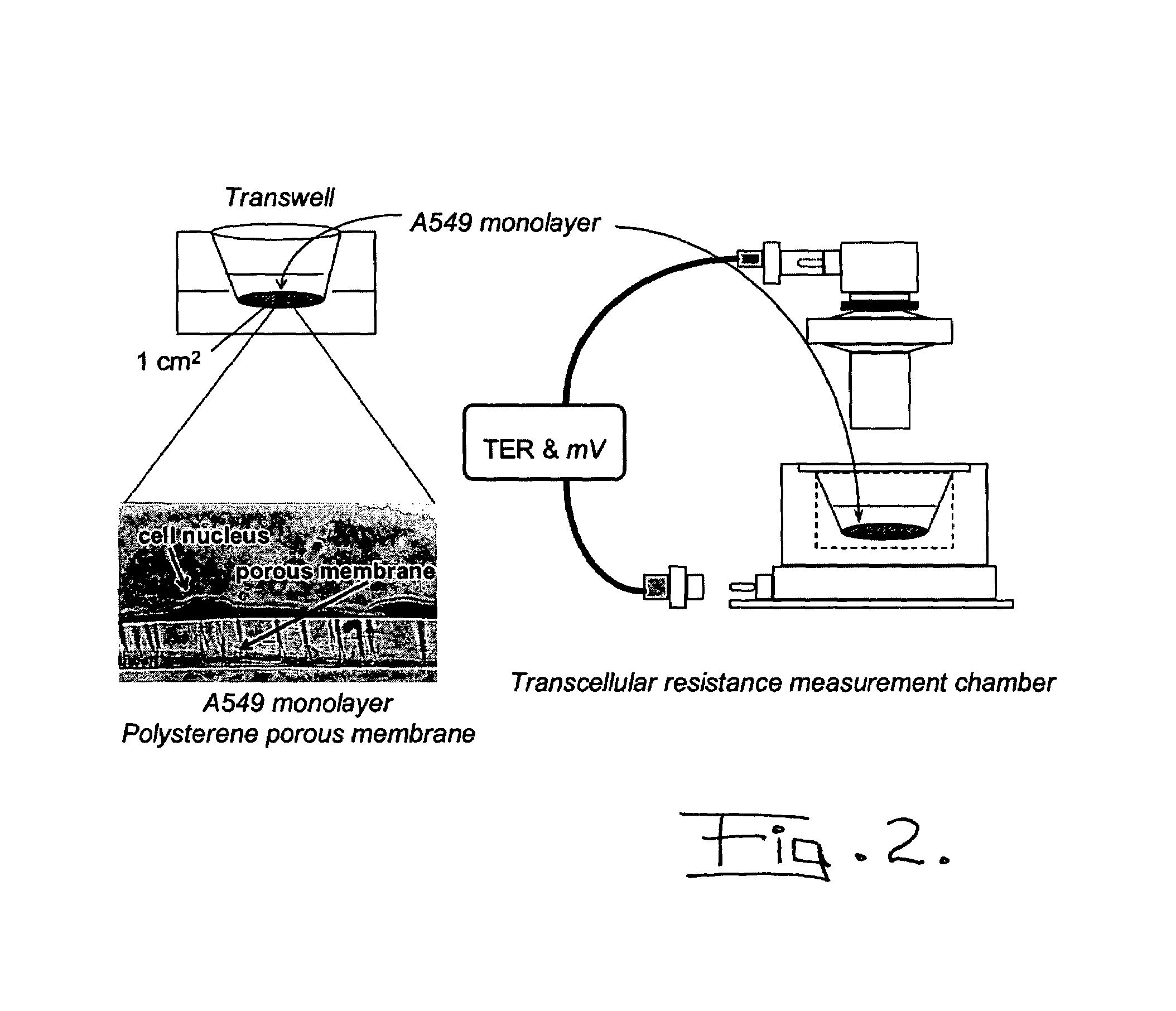
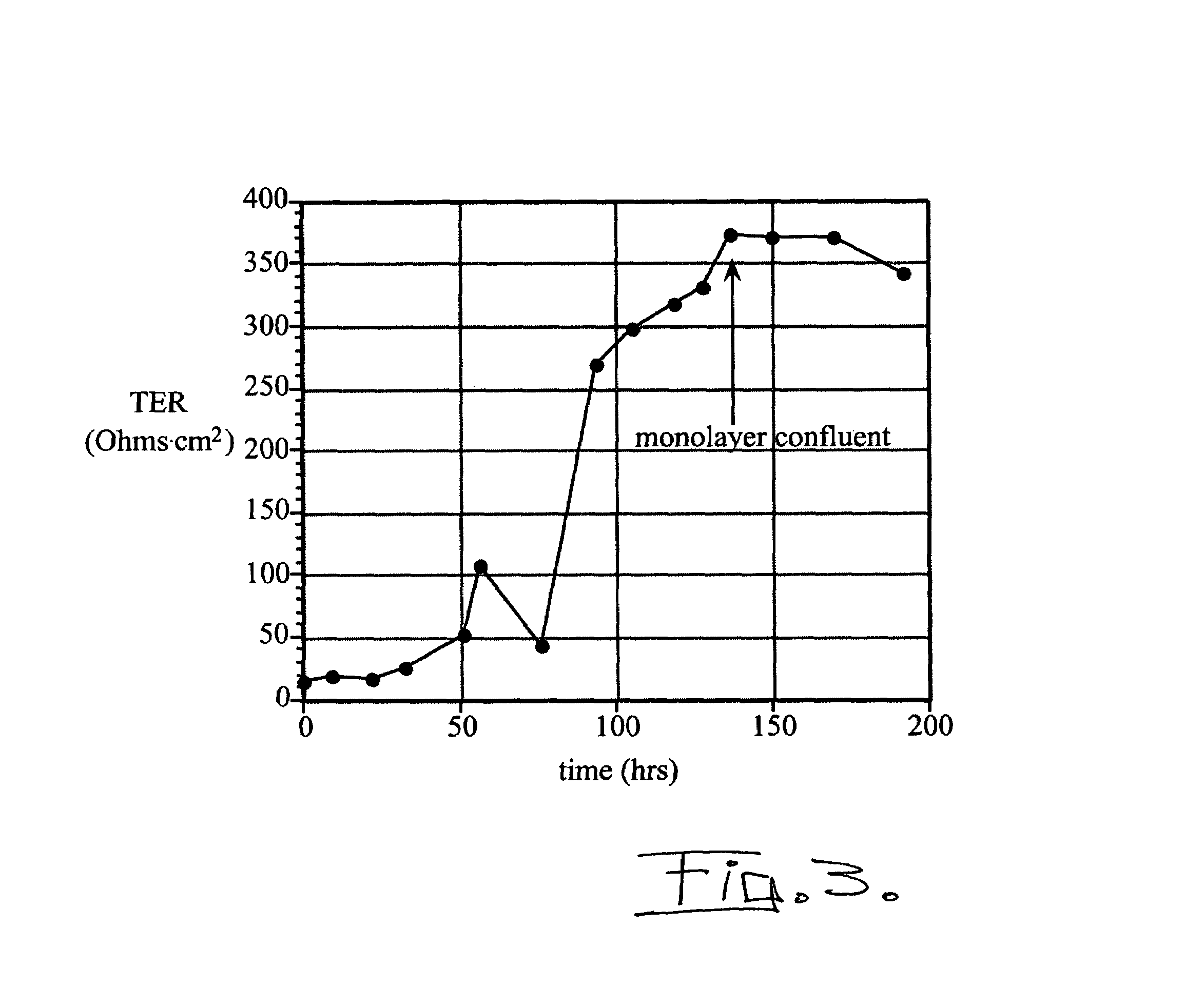
A method of monitoring an air atmosphere for a harmful biological or chemical agent includes providing a plurality of mammalian respiratory airway epithelial cells borne on a porous support; contacting the porous support with a cell nutrient medium and with air by positioning said porous support at an air-liquid interface between the cell nutrient liquid and the air; sampling the air atmosphere to thereby create an air flow over the air-liquid interface so that the respiratory epithelial cells borne on the porous silicone support are contacted by the sampled air; and monitoring the respiratory epithelial cells for at least one physiological parameter indicating the cells have been exposed to the harmful agent.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Sesnsor for detecting a toxic or hazardous gas mixture and operating method
InactiveUS20090029403A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyProduct gas
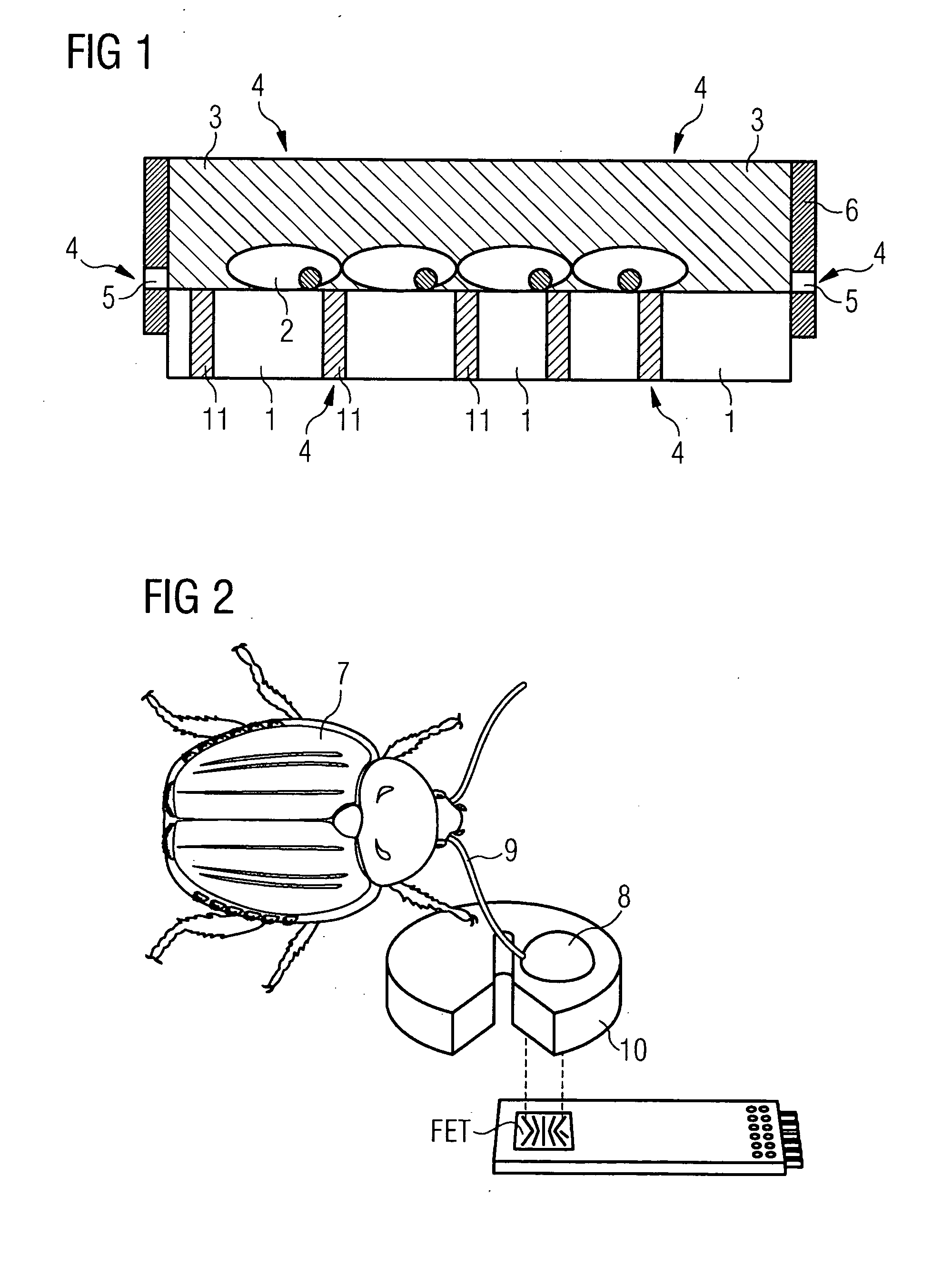
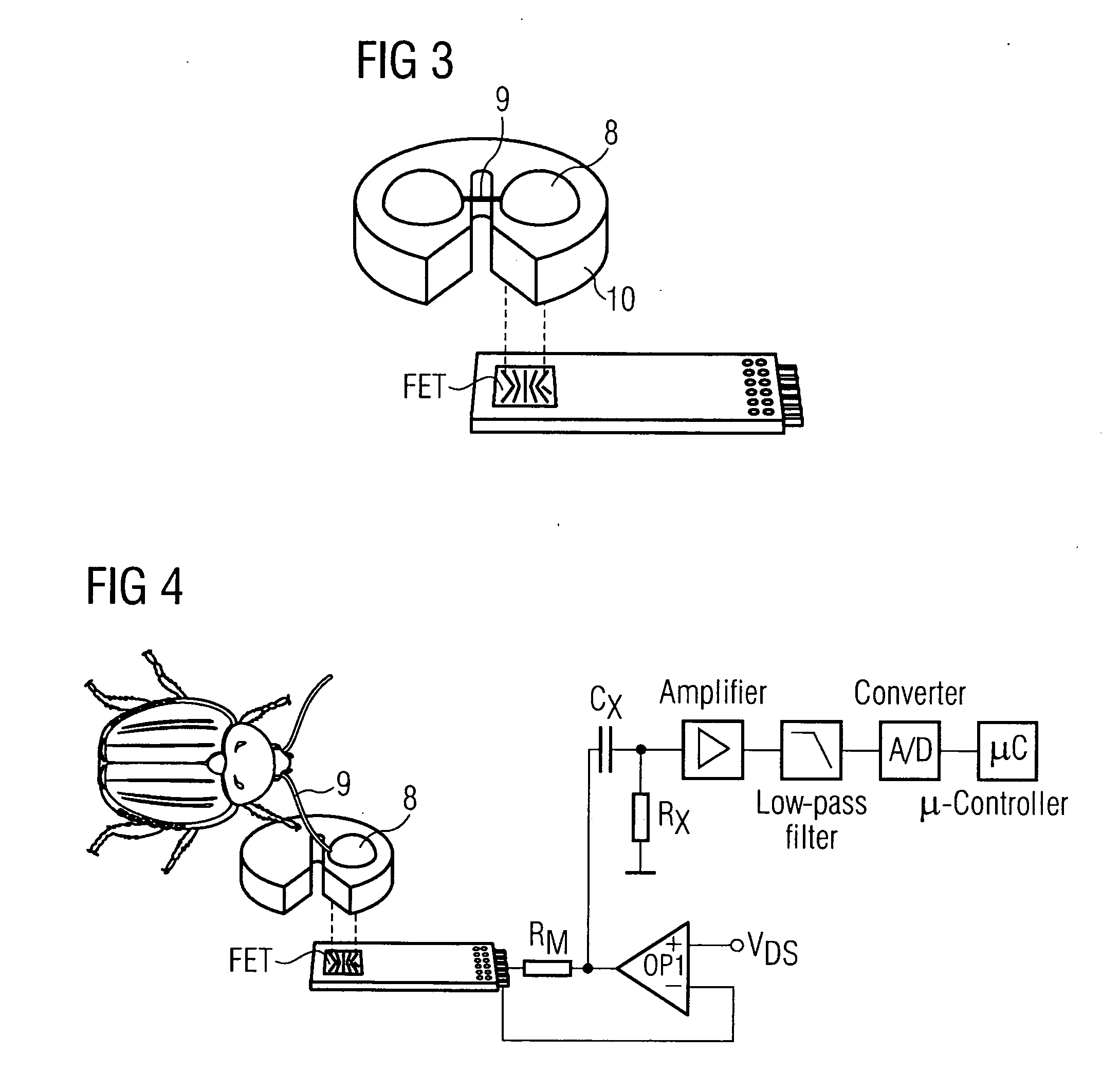
A sensor for detecting a gas mixture which substantially comprises air and contains one or a plurality of gases that exhibit a disadvantageous effect on living organisms, comprising: a sensor chip composed of silicon for reading out at least one signal which is generated at a sensitive substance given the presence of one or a plurality of target gases in the measurement gas, a sensitive substance applied on the sensor chip, comprising living cells, which respond to target gas, a signal processing unit for evaluating the signals of the Si chip.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
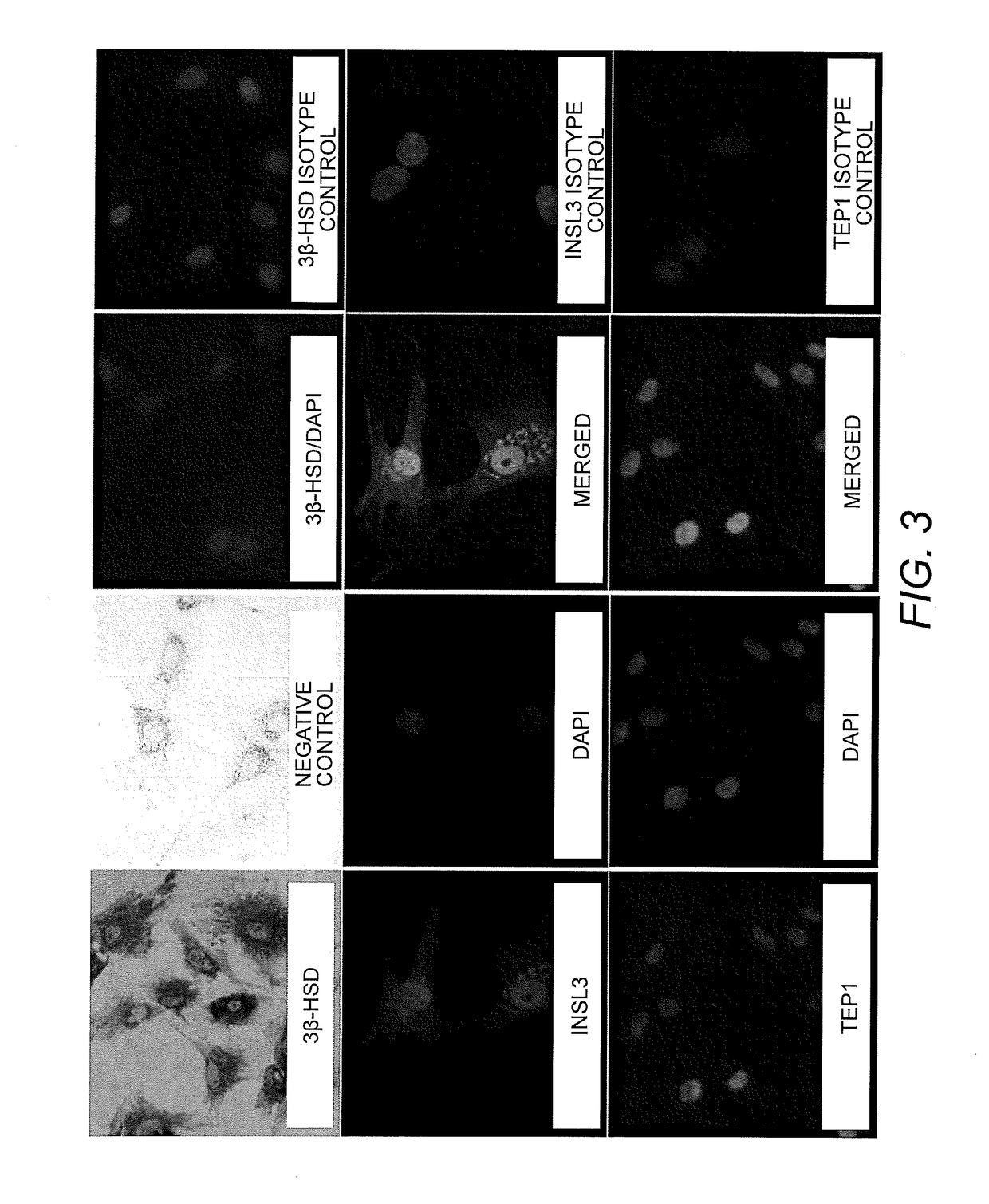
Biosensors based on microalgae for the detection of environmental pollutants
InactiveUS20100248286A1Increase concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTrue positive rateToxic material
The present invention provides biosensors based on microalgae for the determination of the presence of toxic compounds in a sample, characterized by the high sensitivity and specificity thereof with respect to the target toxic substance. The biosensors are based on the measurement of the photosynthetic activity of algae by means of monitoring the molecular oxygen production by the microalgae by using a luminescent compound the emission of which depends on the amount of oxygen in the medium.
Owner:UNIV COMPLUTENSE DE MADRID
Coliform detection process and kit for use therein
InactiveUS20110269179A1Improve sampling efficiencyClogging problemPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementLarge intestineCulture mediums
A process comprises (a) providing (1) at least one sample suspected of comprising at least one coliform strain, (2) at least one culture device comprising at least one culture medium that is hydrated or hydratable, and (3) at least one particulate concentration agent that is substantially optically transparent when in contact with the culture medium in the culture device when the culture medium is hydrated; (b) placing the particulate concentration agent in contact with the sample such that at least a portion of the coliform strain is bound to the particulate concentration agent to form coliform-bound particulate concentration agent; (c) placing the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium; (d) incubating the culture device comprising the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium, the culture medium being hydrated; and (e) optically detecting the presence of the coliform strain without separating the coliform strain from the particulate concentration agent.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Autonomous lux reporter system and methods of use
InactiveUS20130031644A1High expressionPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementResponse elementFishery
Disclosed are systems for expression of an autonomous lux reporter system in a vertebrate cell, such as mammalian or fish cell. In some examples the lux reporter system is operably connected to a pollutant-inducible DNA response element. Also disclosed are transgenic zebrafish, carrying pollution-inducible response elements, and methods of using such zebrafish to monitor pollutants.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
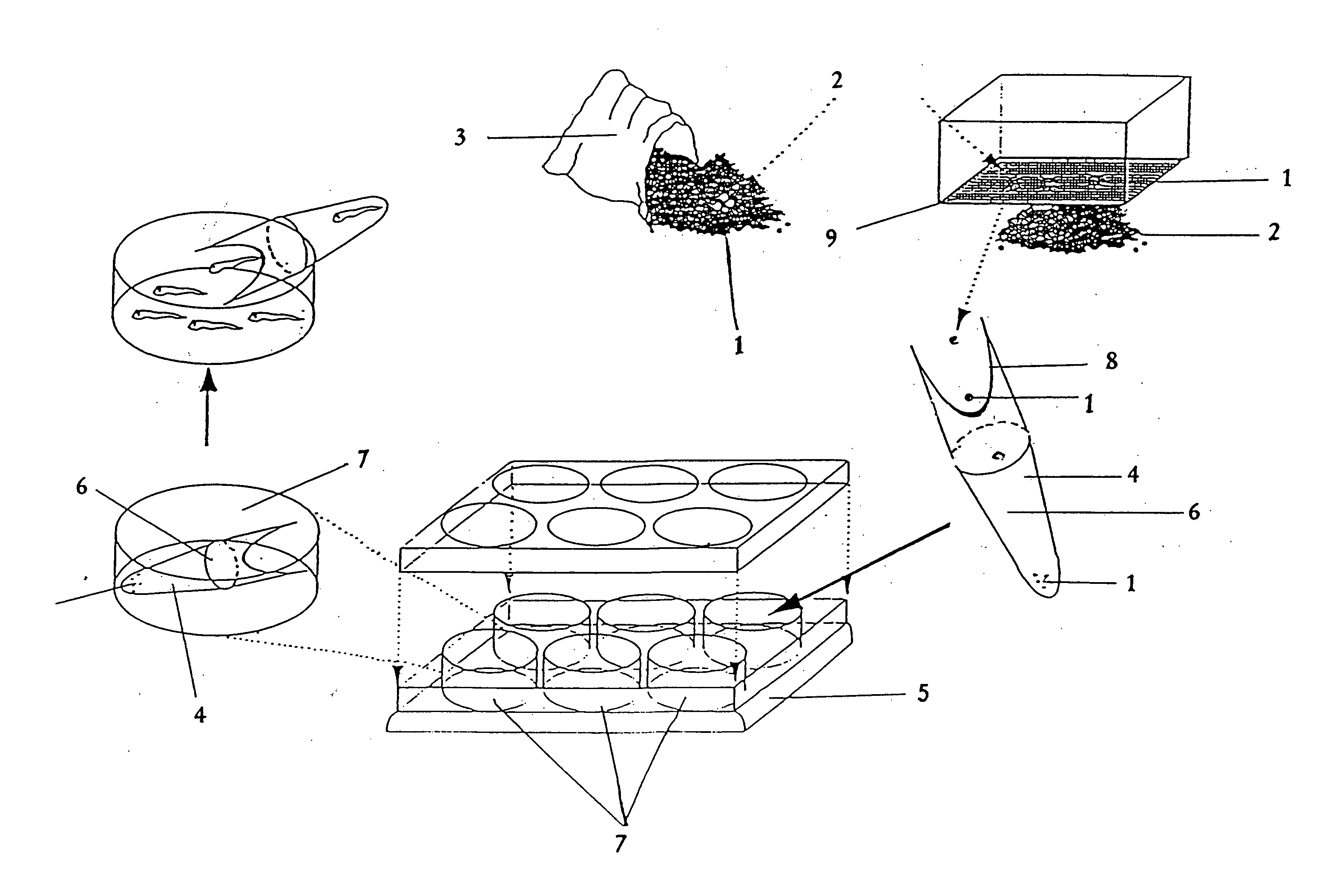
Immobilized microbial system as well as preparation method thereof and water toxicity detection method
ActiveCN106047849AHigh activityEasy to preparePollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementCross-linkMicroorganism
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fish hatching method and apparatus
InactiveUS20060140862A1Cost-effective useShort durationBiocidePollution detectorsDiapausePlant species
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Coliform detection process and kit for use therein
InactiveUS8741595B2Low costSimple and efficient and cost-effectivePhysical/chemical process catalystsPollution detectorsCulture mediumsEscherichia coli detection
A process comprises (a) providing (1) at least one sample suspected of comprising at least one coliform strain, (2) at least one culture device comprising at least one culture medium that is hydrated or hydratable, and (3) at least one particulate concentration agent that is substantially optically transparent when in contact with the culture medium in the culture device when the culture medium is hydrated; (b) placing the particulate concentration agent in contact with the sample such that at least a portion of the coliform strain is bound to the particulate concentration agent to form coliform-bound particulate concentration agent; (c) placing the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium; (d) incubating the culture device comprising the coliform-bound particulate concentration agent in contact with the culture medium, the culture medium being hydrated; and (e) optically detecting the presence of the coliform strain without separating the coliform strain from the particulate concentration agent.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
In vivo high thoroughput toxicololgy screening method
InactiveUS20020176821A1Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A high throughput toxicology screening method is provided. In the subject method, at least 10 different compound compositions are tested simultaneously. Each compound composition is tested by contacting it with a plurality, e.g. from about 10 to 1000, of non-mammalian multi-cellular organisms and determining the effect of the compound composition on the organisms. The multi-cellular organisms employed in the subject methods are small, have differentiated tissues and organs and have a rapid generation time. The subject high throughput screening methods find use in a variety of applications, and are particularly suited for use in the toxicology screening of libraries of compounds, such as libraries of combinatorially produced compounds.
Owner:TOSK INC
Method for testing toxicity of high algae-laden aquatic organisms
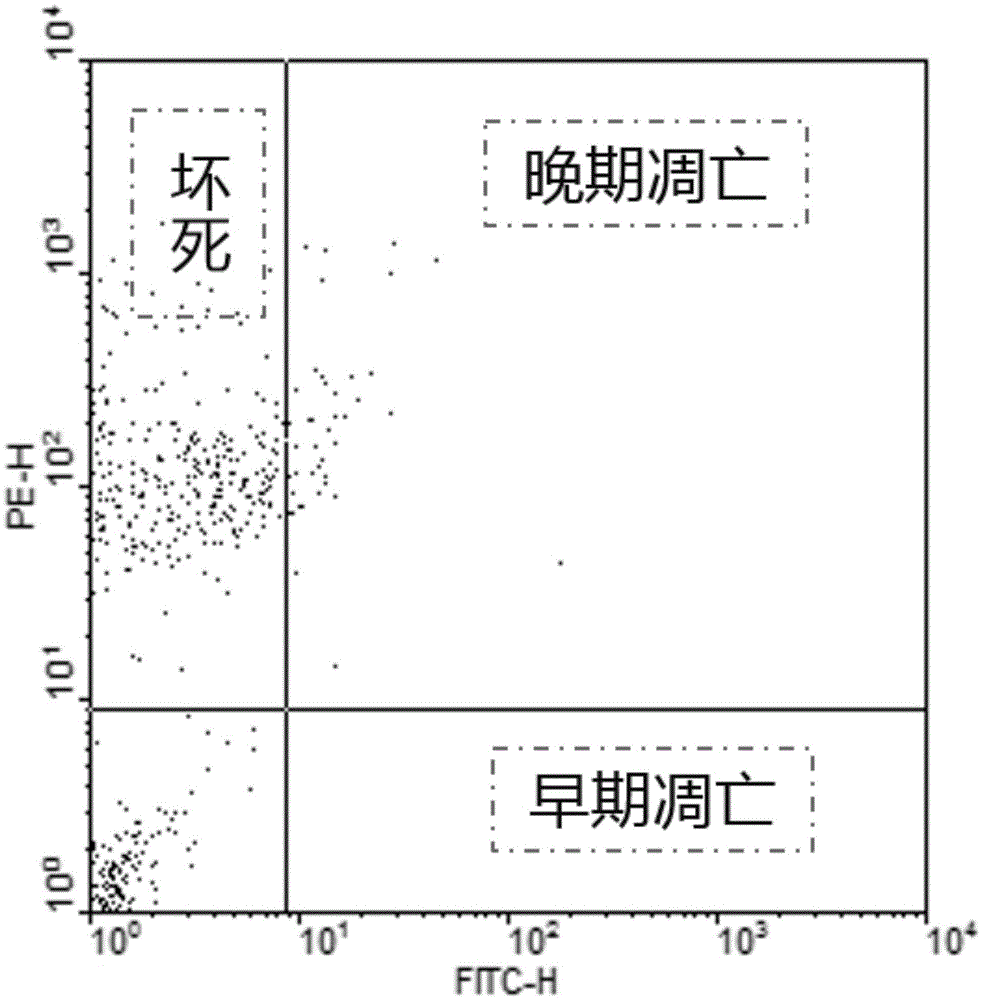
InactiveCN105483202AFacile apoptosis rateSimple death ratePollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting toxicityPhosphate
The invention discloses a method for testing the toxicity of high algae-laden aquatic organisms. The method comprises the steps that saccharomyces cerevisiae is cultured in a solid medium containing 5% of YPD and 1.5% of agar firstly, after clone is grown out, a YPD fluid medium of 5% is inoculated with monoclone, and overnight shake cultivation is conducted based on 180-250 rpm and 25-58 DEG C; phosphate buffer is added to a culture solution with the OD value of 1.5-1.8 to obtain a blank sample A, a high algae-laden water sample is added to the culture solution with the OD value of 1.5-1.8 to obtain a detection sample B, and the two samples are placed on a mixer for oscillation lasting 2 h; cell washing is conducted on the sample A and the sample B twice by means of PBS, and cell suspension with the concentration of 1*105-1*106 cel ls / mL is prepared; the sample A and the sample B are both added to Annexin V-FITC of 5 mug / mL to be evenly mixed, and then propidium iodide of 5 mug / mL is added to be evenly mixed; reaction is conducted at the room temperature away from light for 5-15 min; flow cytometry detection is conducted within 1 h; the proportion of dead cells, the proportion of living cells and the proportion of apoptotic cells are detected by means of flow cytometry; the apoptosis rate and the death rate of the sample B are compared with those of the blank sample A, so that water toxicity is judged. Early warning technical support is provided for high algae-laden water pollution, so that high water supply quality is guaranteed.
Owner:上海艾耐基科技股份有限公司 +1
Apparatus for detecting toxicity in water using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria
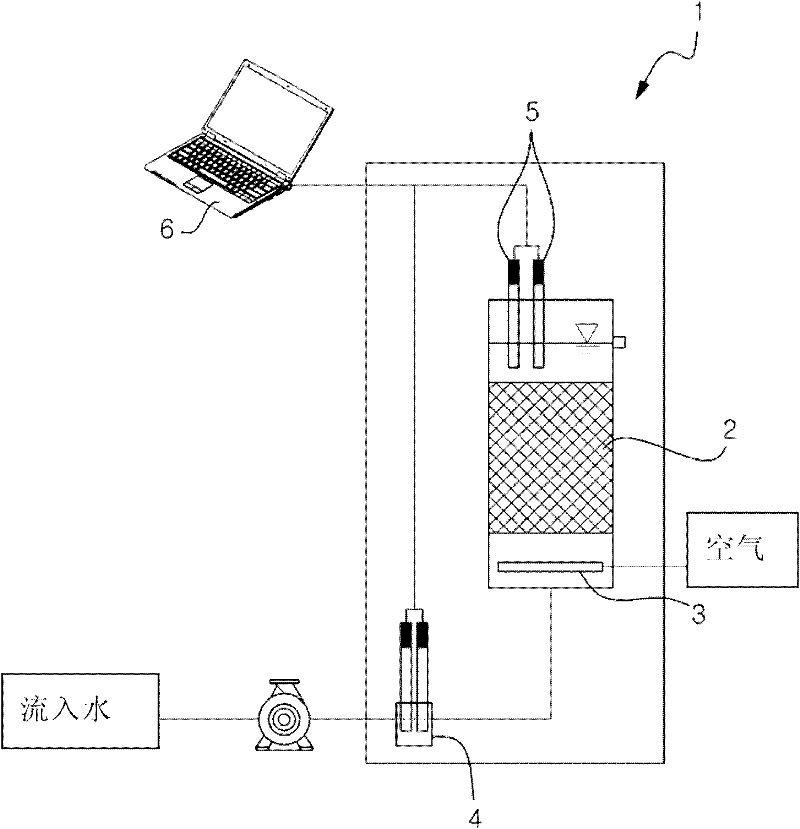
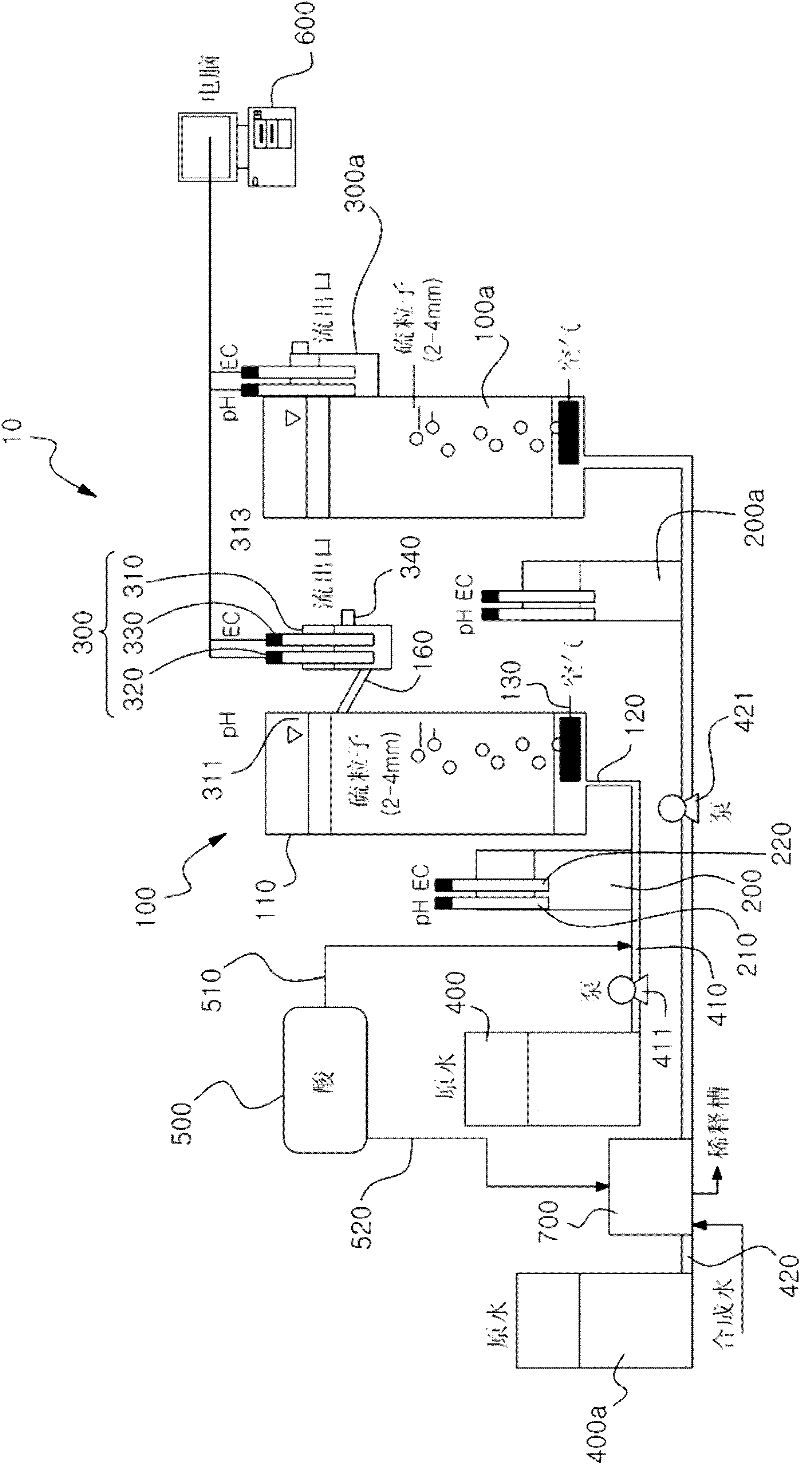
InactiveCN102243204AStable and reliable experimental resultsReduce activity barrierPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementWater useSulfur
The present invention relates to an apparatus for detecting toxicity in water using sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, in which air and a water sample are introduced into a reactor containing sulfur-oxidizing bacteria and sulfur particles, and then the amount of sulfuric acid resulted from oxidation of the sulfur particles by the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria is analyzed based on the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of the water sample, thereby detecting toxicity in the water sample. In the apparatus, the measured values of pH and electrical conductivity (EC) are not affected by air bubbles generated when the air and the water sample are introduced into the reactor, and the activity of the sulfur-oxidizing bacteria is not adversely affected by the pH of the water sample, so that accurate measurement results can be obtained. In addition, the apparatus comprises a plurality of reactors, and thus can continuously perform the detection of toxicity.
Owner:KNU IND COOPERATION FOUND
Biologically based test system
The invention is concerned with a biologically based test system for the detection of inorganic and organic pollutants in water samples. In particular, the present invention is concerned with the development of a strategy for the control of background expression of biosensors in the biologically based test system. Furthermore, the present invention provides a test kit for determining concentrations of inorganic and organic pollutants in water samples, the test kits are suitable for field tests.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT FUER UMWELTFORSCHUNG GMBH UFZ
Method of producing in vitro testicular constructs and uses thereof
A cell composition composed of spermatogonial stem cells, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and optionally peritubular cells, is provided, as is a culture composition, artificial testicular construct, hydrogel composition, and device containing the same. A method for using the device as a physiologically relevant in vitro model of human testicular function to screen compounds for pharmacological or toxicological activity is also provided.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Anuran cross-species molecular sensors
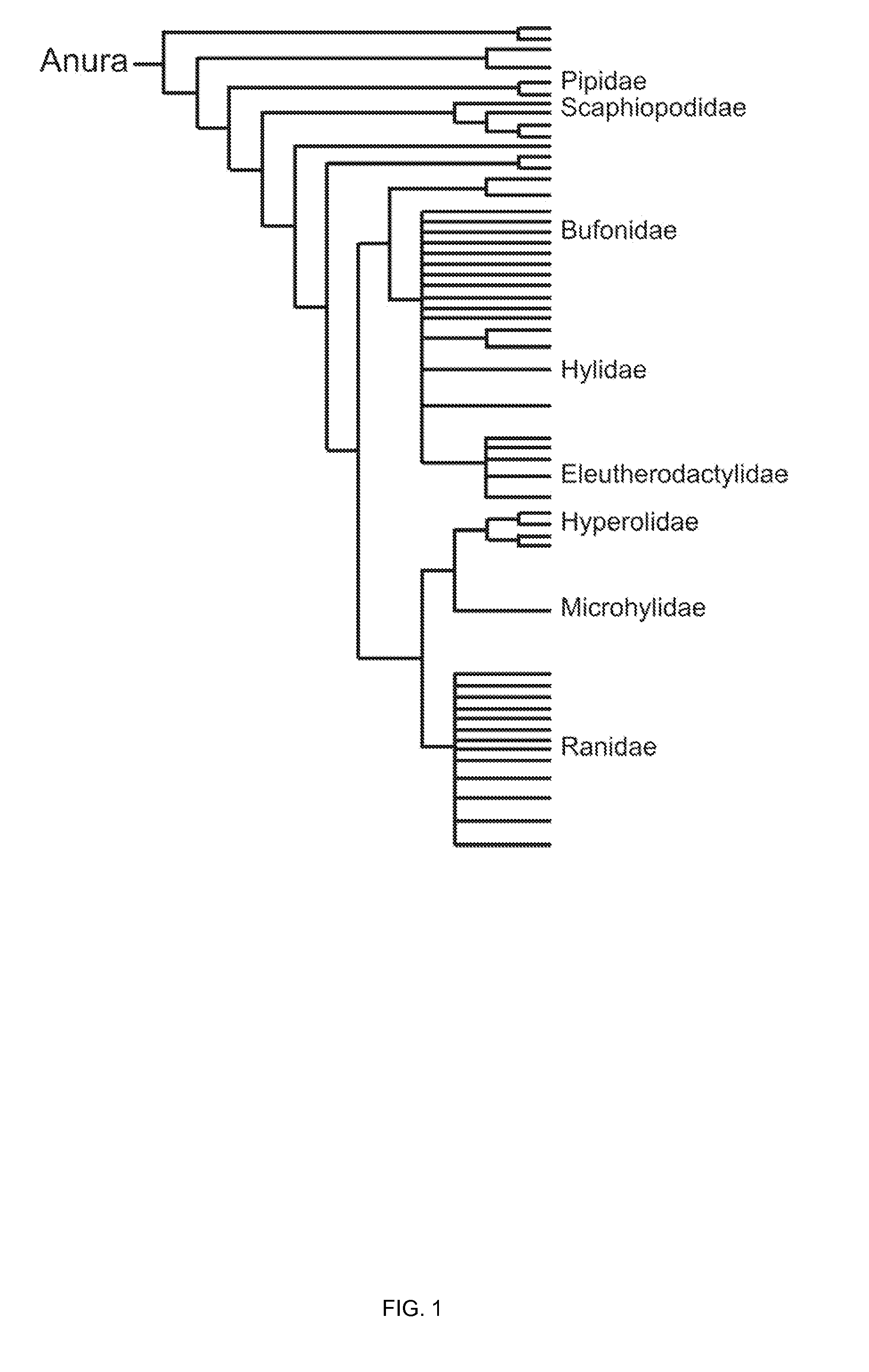
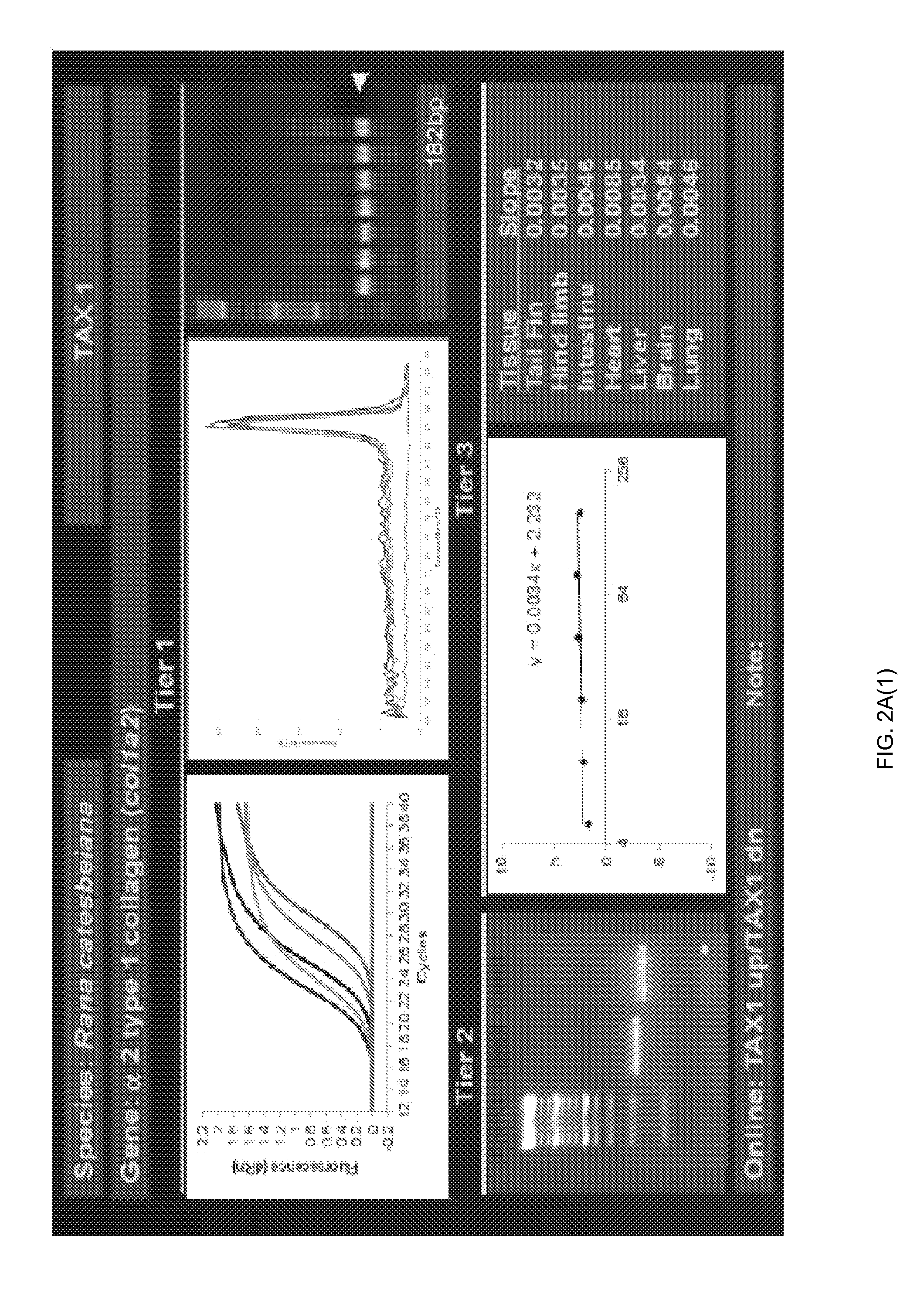
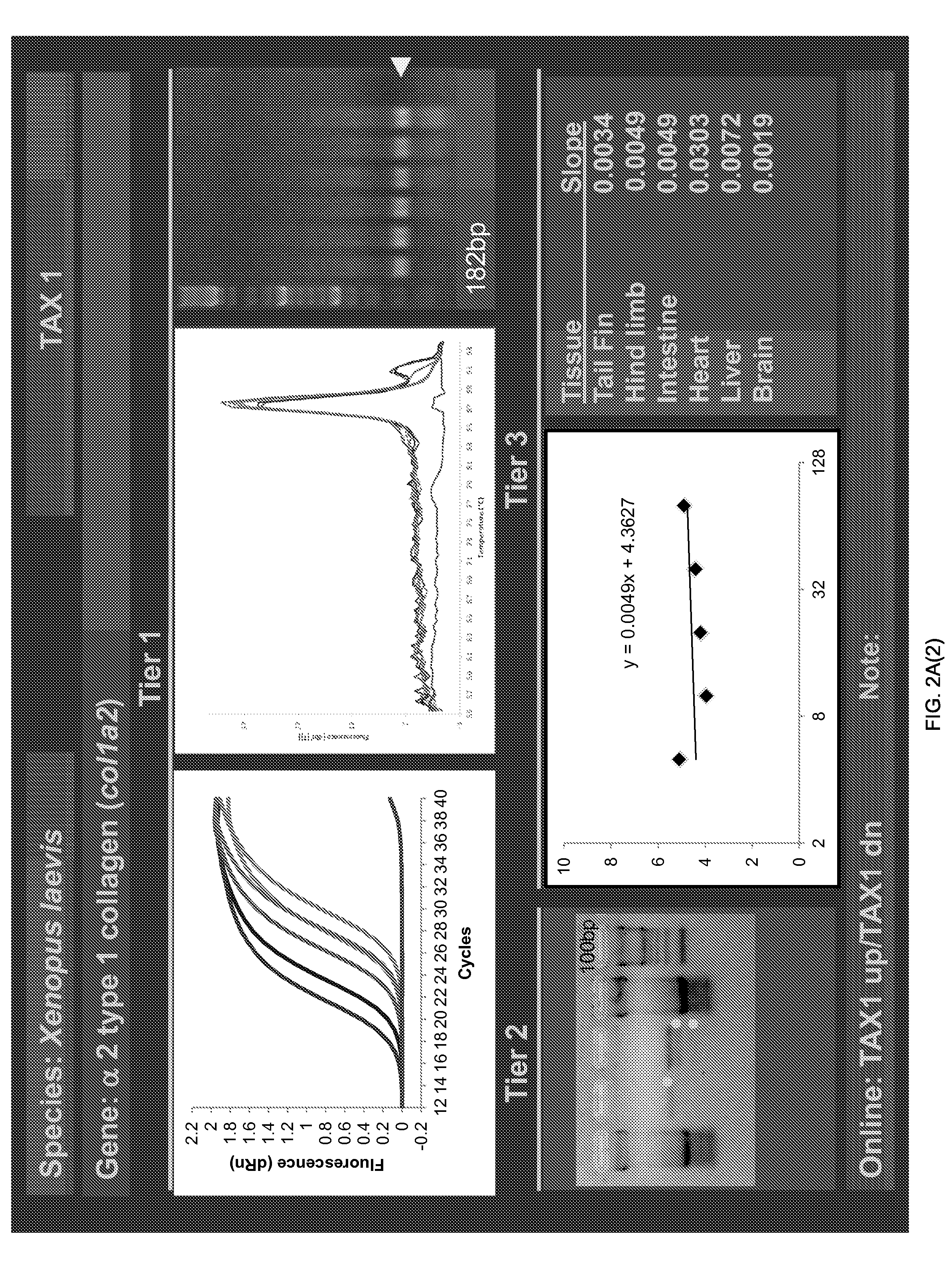
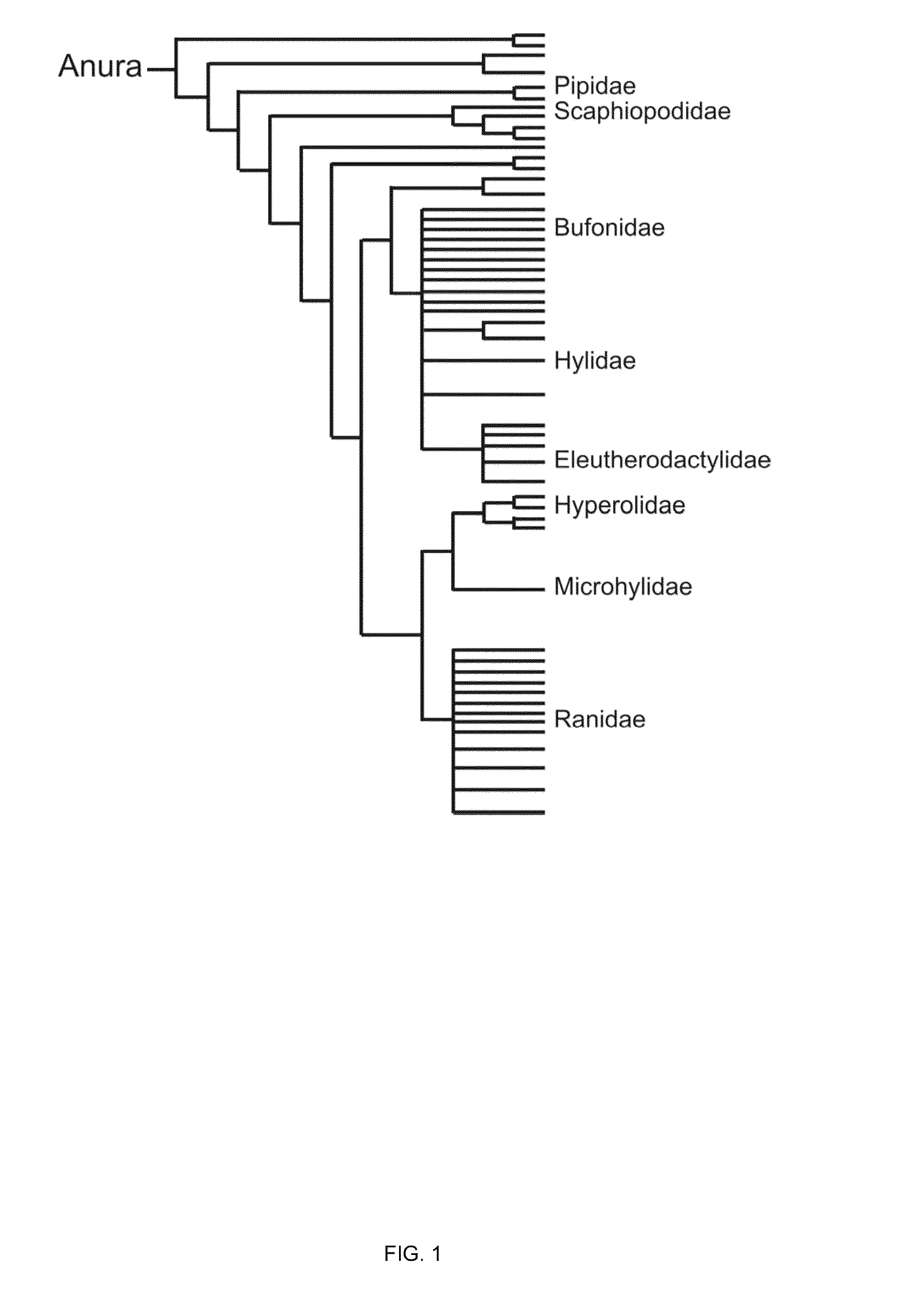
ActiveUS20150094228A1Sufficient genomic resourceExtensive resourcesNucleotide librariesPollution detectorsSequence designEnvironmental toxicology
Described herein are DNA primer sequences designed for the determination of gene or transcript information from Anuran species, and which may be used in studies for developmental and / or toxicity testing and for environmental toxicology or ecological assessment. Also described herein is a rapid, sensitive, high-throughput assay useful for supporting potential risk assessment across vertebrate clades, and that is also useful for evaluation of complex contaminant mixtures.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV
Water monitoring system using bivalve mollusks
InactiveUS7330794B2High precisionEasy to installTesting/calibration apparatusPollution detectorsToxicantMonitoring system
A toxicant detection system comprises at least one watertight chamber containing a mollusk. Water to be screened is introduced into the chamber. The mollusk is preferably supported on a mounting structure which facilitates quick mounting of the mollusk in the device, comprising a releasable element affixed to the shell of the mollusk, e.g., a bolt which is screwed into a nut affixed to the mollusk's shell. A sensing apparatus is provided which includes a movable member supported in the chamber so that it engages the shell of the mollusk, and moves when the shell opens and closes. The sensing apparatus detects the position of the mollusk shell based on the position of the movable member. The sensing apparatus preferably includes a Hall effect transducer which co-acts with a magnet carried on the movable member. The system allows for accurate readings of the small movements of the mollusk shell which aid in detecting toxicants, and also provides for installation of mollusks of varying sizes, without the need to move components of the standard configuration of the chamber. Methods and systems for detecting or identifying a toxicant in water being screened are also described.
Owner:AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
Fish hatching method and apparatus
InactiveUS20040013608A1Cost-effective useShort durationBiocidePollution detectorsDiapausePlant species
Owner:UNITED STATES ARMY U S ARMY MEDICAL RES & MATERIEL COMMAND +1
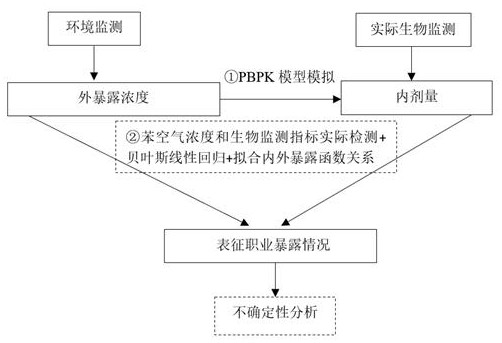
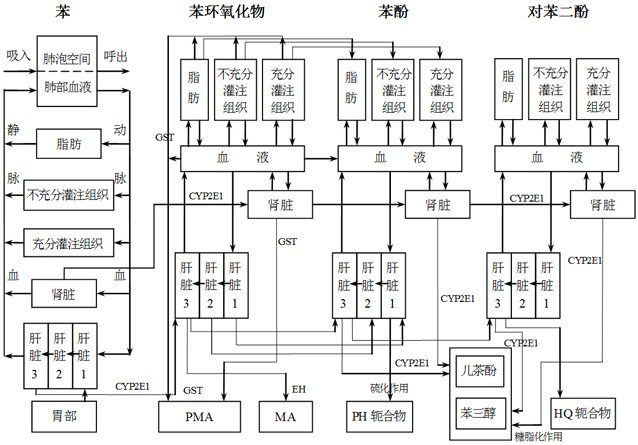
A low-dose benzene occupational exposure assessment method and system
ActiveCN114420295BScientific Hazard AnalysisSmall doseMedical data miningPollution detectorsBenzeneOccupational exposure
The invention proposes a low-dose benzene occupational exposure assessment method and system; including determining benzene content; determining benzene operations and key risk management objects; determining contact biomarkers for low-dose benzene exposure tracking; and performing exposure assessment according to scenarios. The invention solves the problem of being unable to quantitatively evaluate low-dose occupational exposure to benzene, helps scientifically analyze the degree of benzene occupational hazards, and provides a basis for clarifying key control points and key control groups of benzene occupational disease hazards.
Owner:天津渤化讯创科技有限公司 +1
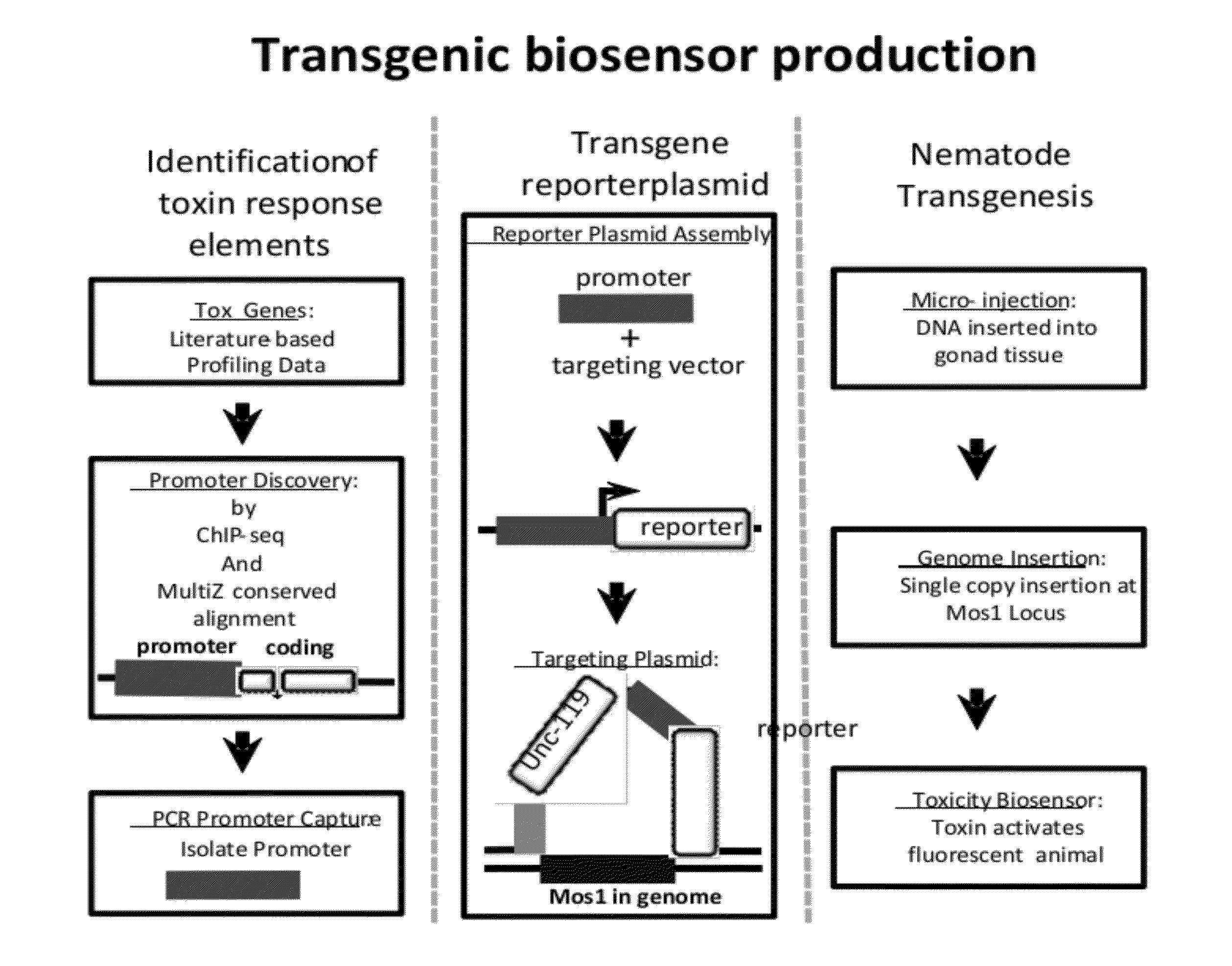
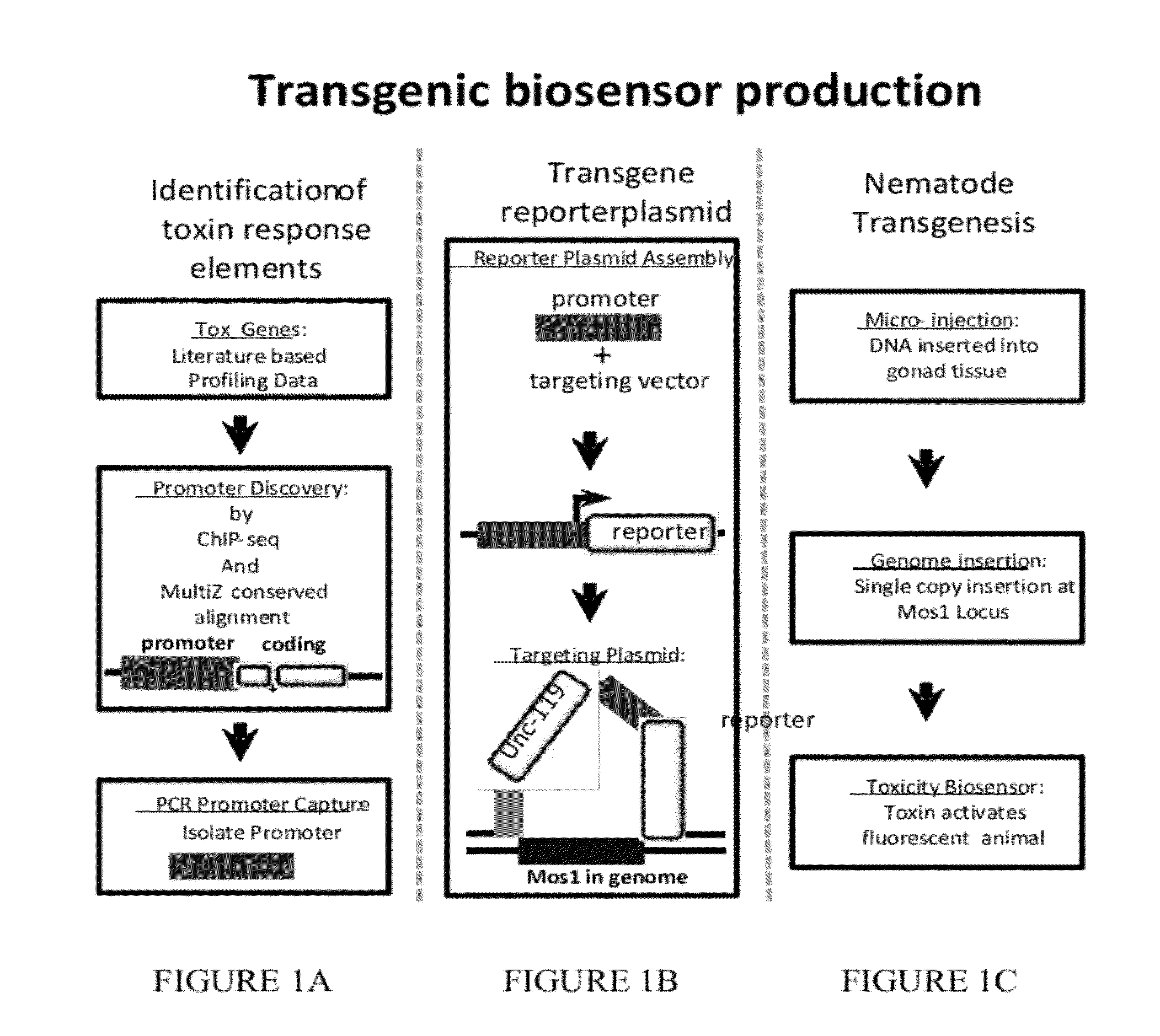
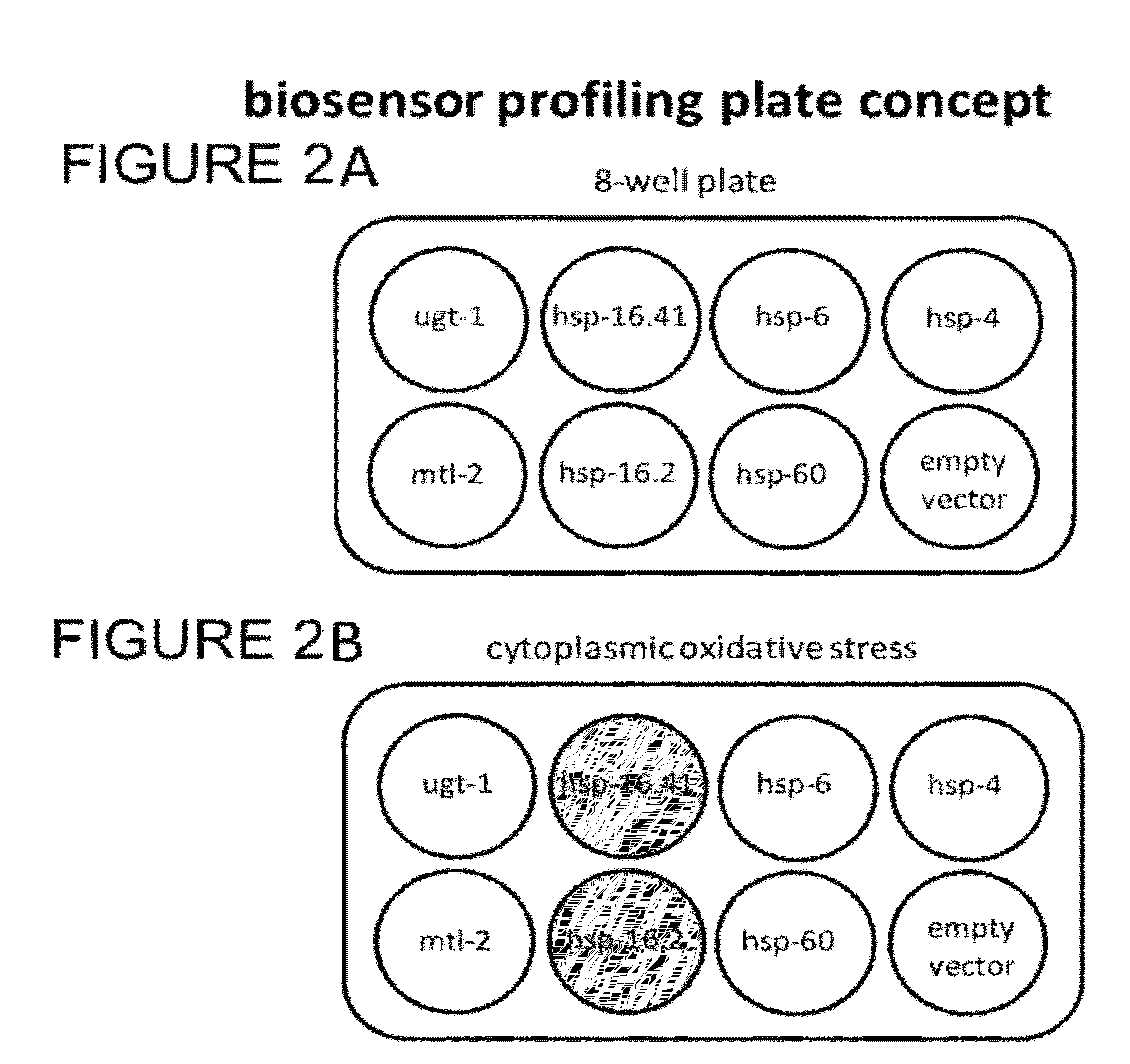
Transgenic biosensors
Systems and methods relate to transgenic organisms and their use as biosensors are described. In some embodiments, the systems and methods include a first population of transgenic organisms that includes a first constitutively expressed reporter gene, and a first transgene that includes a first inducible promoter from a response pathway gene, wherein the first inducible promoter is coupled to a first reporter gene. Other embodiments are described.
Owner:KDT INC
Polybrominated diphenyl ether sensory protein and whole-cell microbial sensor constructed by polybrominated diphenyl ether sensory protein
ActiveCN113717260AImprove monitoring sensitivityBacteriaPollution detectorsDecabromobiphenyl etherDecabromodiphenyl ether
The invention discloses a polybrominated diphenyl ether extracellular sensing protein and a whole-cell microbial sensor constructed by the polybrominated diphenyl ether extracellular sensing protein. The amino acid sequence of the polybrominated diphenyl ether extracellular sensing protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3. According to the present invention, a polybrominated diphenyl ether recognition sensing protein is cloned from Sphingobium xenophagum C1, can specifically recognize polybrominated diphenyl ether, is fused with luciferase, is transferred into the Sphingobium xenophagum C1 with high cell surface hydrophobicity, and is subjected to overexpression of the fusion protein on the bacterial cell outer membrane to prepare the hydrophobic chassis whole-cell microbial sensor, the sensor has specific response to decabromodiphenyl ether and low-brominated homologs thereof, has obvious advantages in the aspect of monitoring hydrophobic organic pollutants, can remarkably improve the monitoring sensitivity of the hydrophobic organic pollutants, and has wide application prospects in organic pollution monitoring.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
A kind of immobilized microbial system and its preparation method and detection method of water toxicity
ActiveCN106047849BHigh activityThe detection method is simplePollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementCross-linkPlant tissue
The invention provides a fixed microbial system, comprising: a microbial carrier prepared by carbonizing plant tissue; and microorganisms attached to the surface of the microbial carrier. The invention also provides a preparation method of the fixed microorganism system and a detection method of water body toxicity. The present invention adopts plant carbonization tissue one-step method to prepare the fixed microbial system, and the preparation method is simple; and the fixed microbial system provided by the present invention adopts the attachment method to fix the microorganisms, so that the microorganisms are naturally deposited on the surface of the pores of the carrier material without cross-linking solidification process; in addition, the microbial carrier used in the present invention has a three-dimensional space network structure and has better mass transfer performance. Therefore, the fixed microbial system provided by the present invention has better activity in the process of detecting water body toxicity, can be repeatedly applied to water body toxicity detection, and has better detection effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
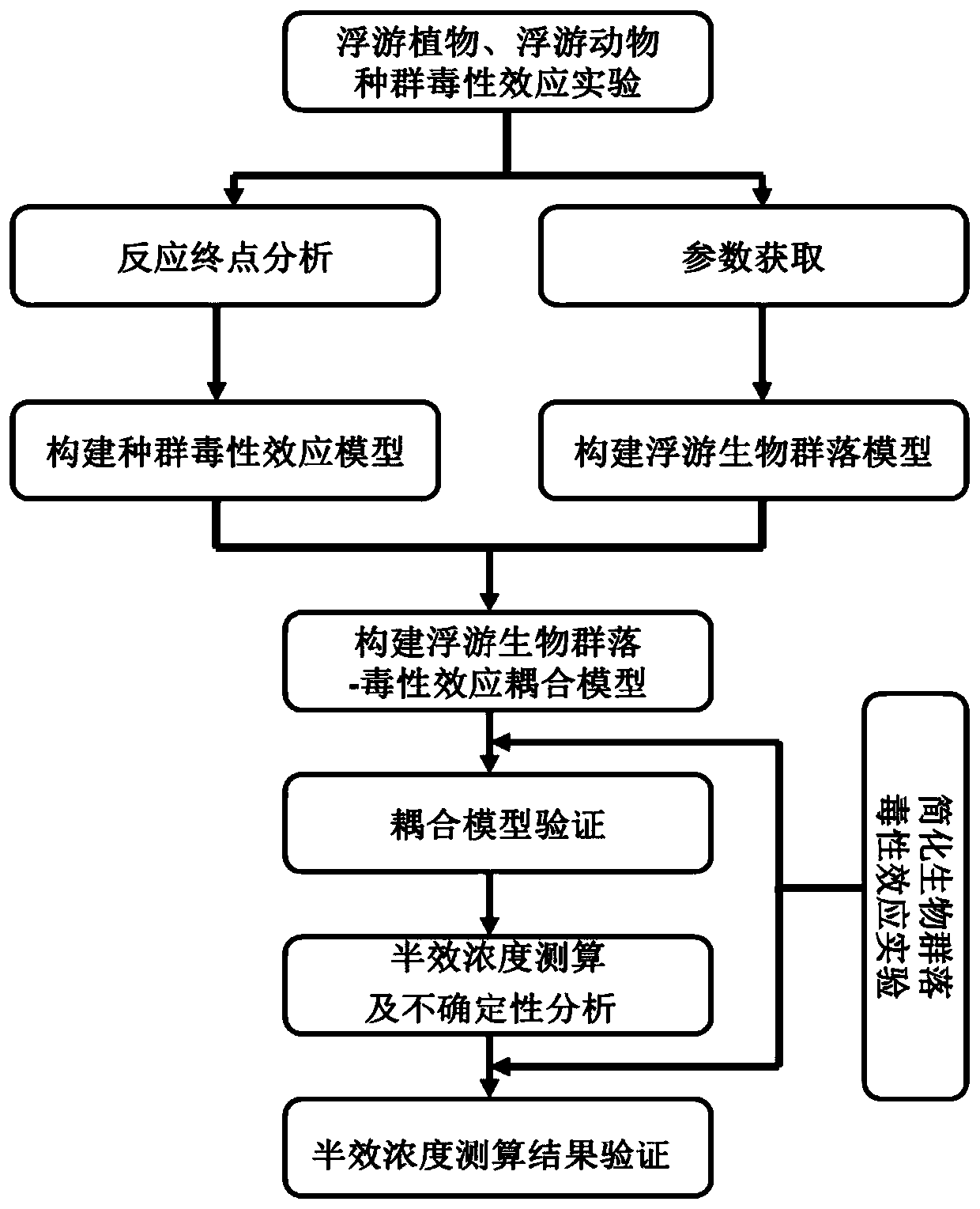
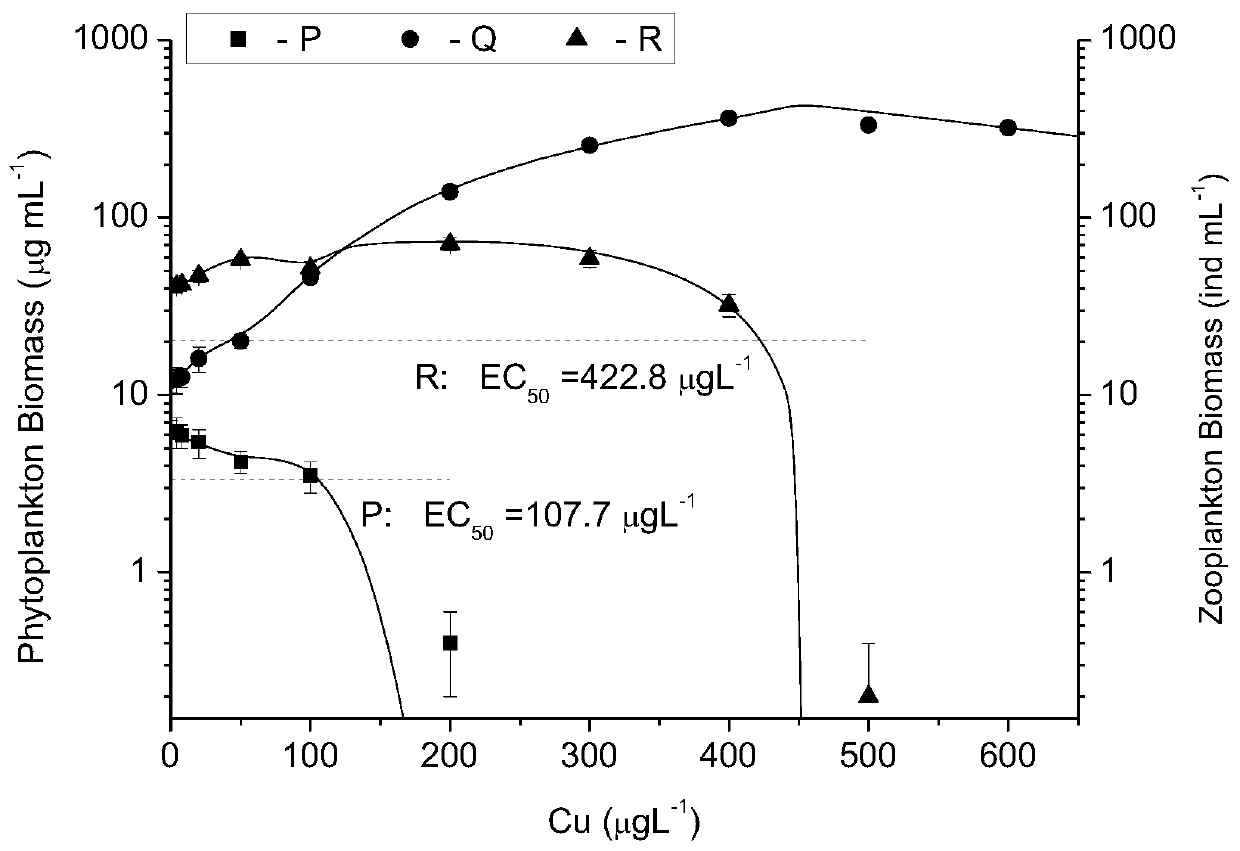
Method for measuring and calculating half-effect concentration of ecological toxicity effect of environmental pollutant
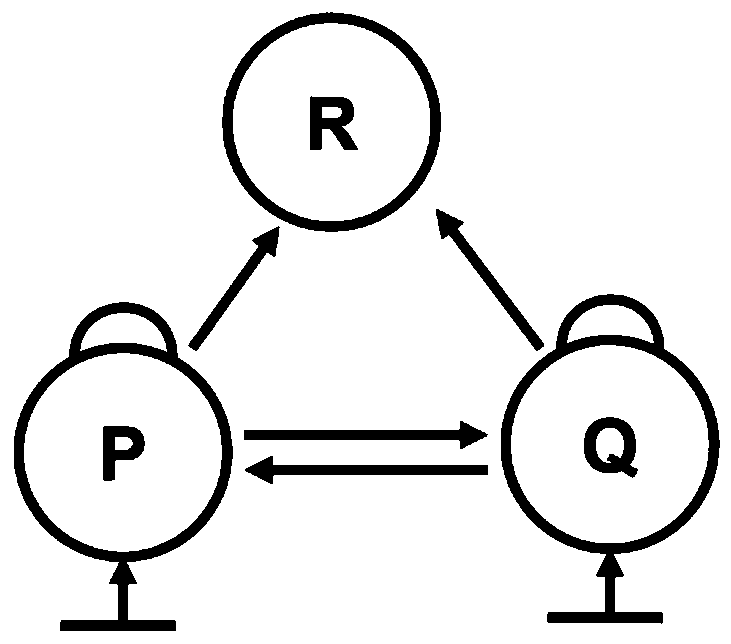
PendingCN110724724ATake advantage ofImprove accuracyPollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementEcological relationshipNutrition
The invention discloses a method for measuring and calculating half-effect concentration of an ecological toxicity effect of an environmental pollutant. The method is based on toxicity effect experiment results of single species, and comprises the following steps: constructing a community model by utilizing the ecological relationship among the populations; combining a plurality of reaction endpoints at different nutritional levels and population levels, and calculating the half-effect concentration of the ecological toxicity effect of the pollutants by taking the degree that a simplified planktonic community steady-state biomass array (P*, Q*, R*) deviates from an original steady-state biomass array (P0, Q0, R0) under a certain pollutant concentration as a criterion. According to the method. The ecological correlation of the toxic effect of the pollutants is considered, so that the accuracy and scientificity of measurement and calculation are improved; a large amount of existing single species toxicity effect experimental data can be fully utilized, and the cost is saved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Anuran cross-species molecular sensors
ActiveUS9448227B2Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designEnvironmental toxicology
Described herein are DNA primer sequences designed for the determination of gene or transcript information from Anuran species, and which may be used in studies for developmental and / or toxicity testing and for environmental toxicology or ecological assessment. Also described herein is a rapid, sensitive, high-throughput assay useful for supporting potential risk assessment across vertebrate clades, and that is also useful for evaluation of complex contaminant mixtures.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV
Popular searches
Analysis by electrical excitation Biological testing Fluorescence/phosphorescence Particle suspension analysis Other foreign material introduction processes Vector-based foreign material introduction Plant genotype modification Material analysis by optical means In-vivo testing preparations Immunoassays
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com