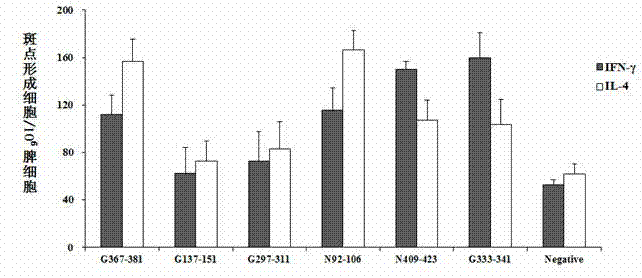
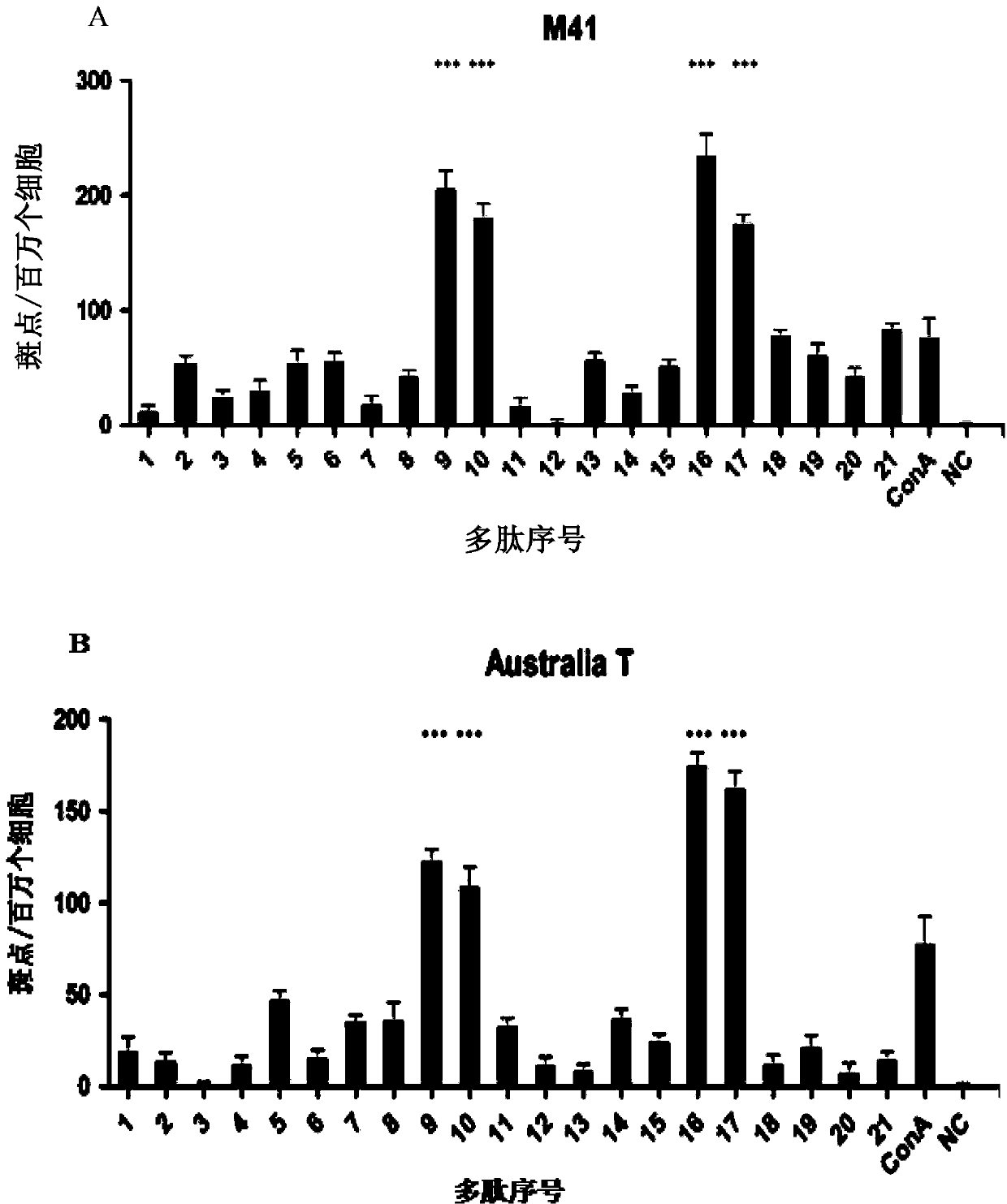
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52 results about "ELISPOT" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
ELISpot tuberculosis infection diagnostic reagent kit and its application
InactiveCN101221173AIncrease costHigh testing costPreparing sample for investigationT lymphocyteCell stimulant
The invention relates to an ELISpot tuberculosis infection diagnostic kit and the application, which adopts the genetic engineering technology to obtain a CFP10-ESAT6 fusion protein antigen from a mycobacterium tuberculosis by cloning, expression and purification, a tuberculosis specific cell stimulator is used for stimulating the peripheral blood T lymphocyte cell of the detected person to secrete a specific IFN-Gamma, then the invention is detected by ELISpot, and the whole process needs to take two days. The usage of the invention can be used for detecting whether the detected person is infected by mycobacterium tuberculosis by using the naked eye or instrument to determine the result according to the number of the generated purple blue spots, so as to assist the diagnosis of tuberculosis and differential diagnosis.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第二附属医院
Kits for Auxiliary Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
InactiveCN102297968AIncreased sensitivityReduce positive rateImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDepsipeptidesAIDS diagnosisIfn gamma
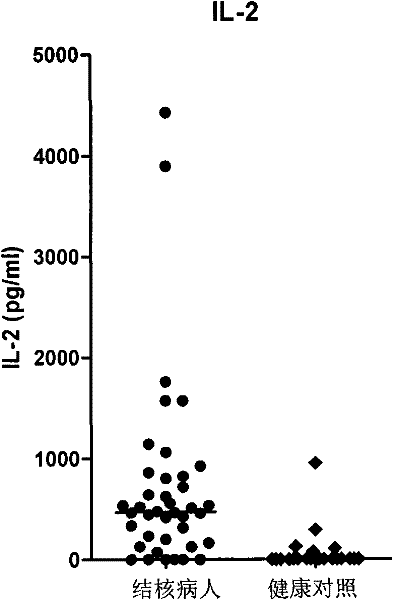
The invention discloses a kit for assisted diagnosis of tuberculosis, which comprises a specific antibody composition, wherein the specific antibody composition comprises the following five antibodies: (1) IFN-gamma antibody, (2) TNF-alpha antibody, (3) IL-2 antibody, (4) MIG antibody and (5) IP-10 antibody. The kit disclosed by the invention can distinguish a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected person from a BCG vaccinee. Compared with the ELISPOT tuberculosis diagnosis method, the tuberculosis diagnosis kit based on multi-molecular marker detection has obviously enhanced sensitivity to active tuberculosis (from 72% to 89%), and the positive rate for normal healthy persons is obviously reduced (from 27% to 16%).
Owner:程小星 +3
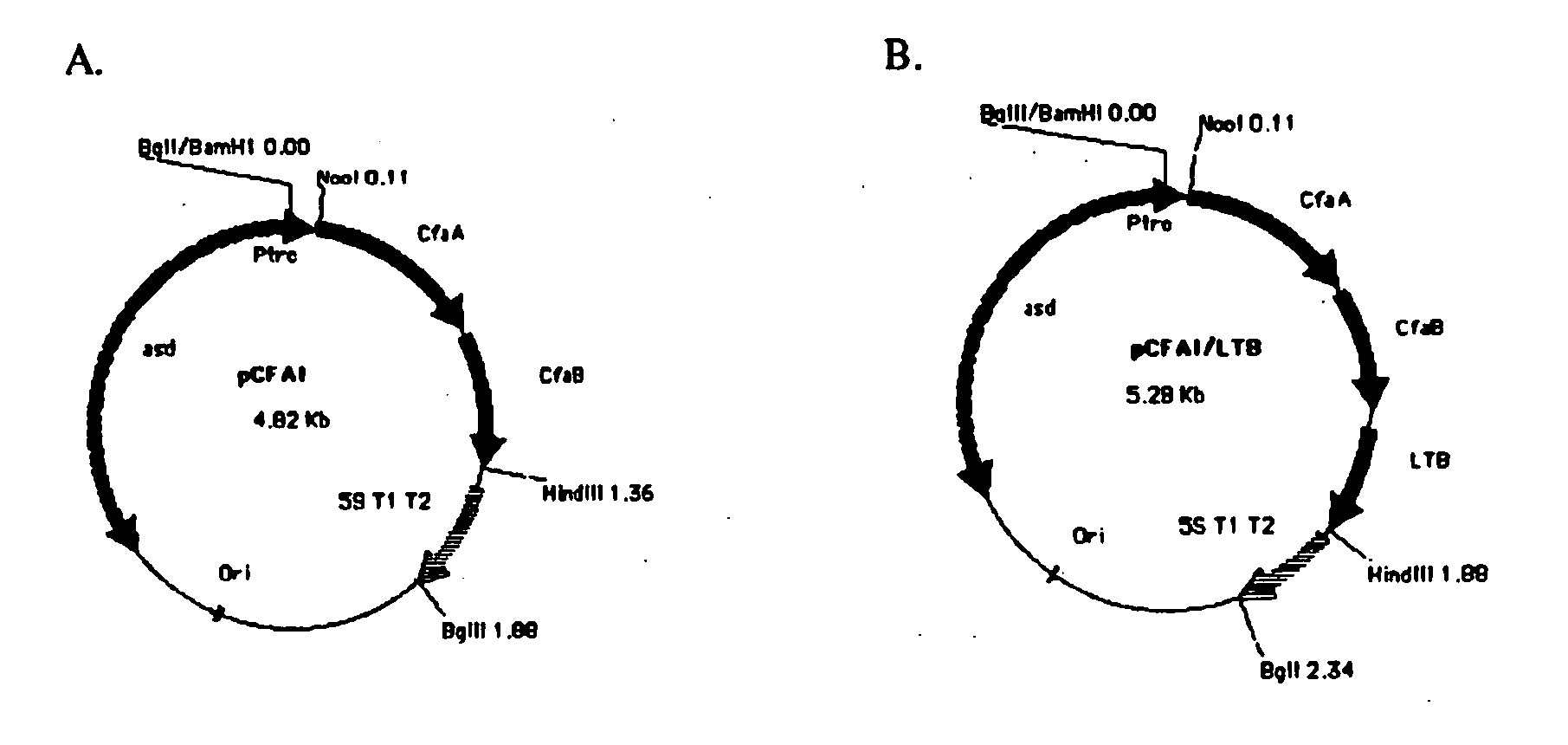
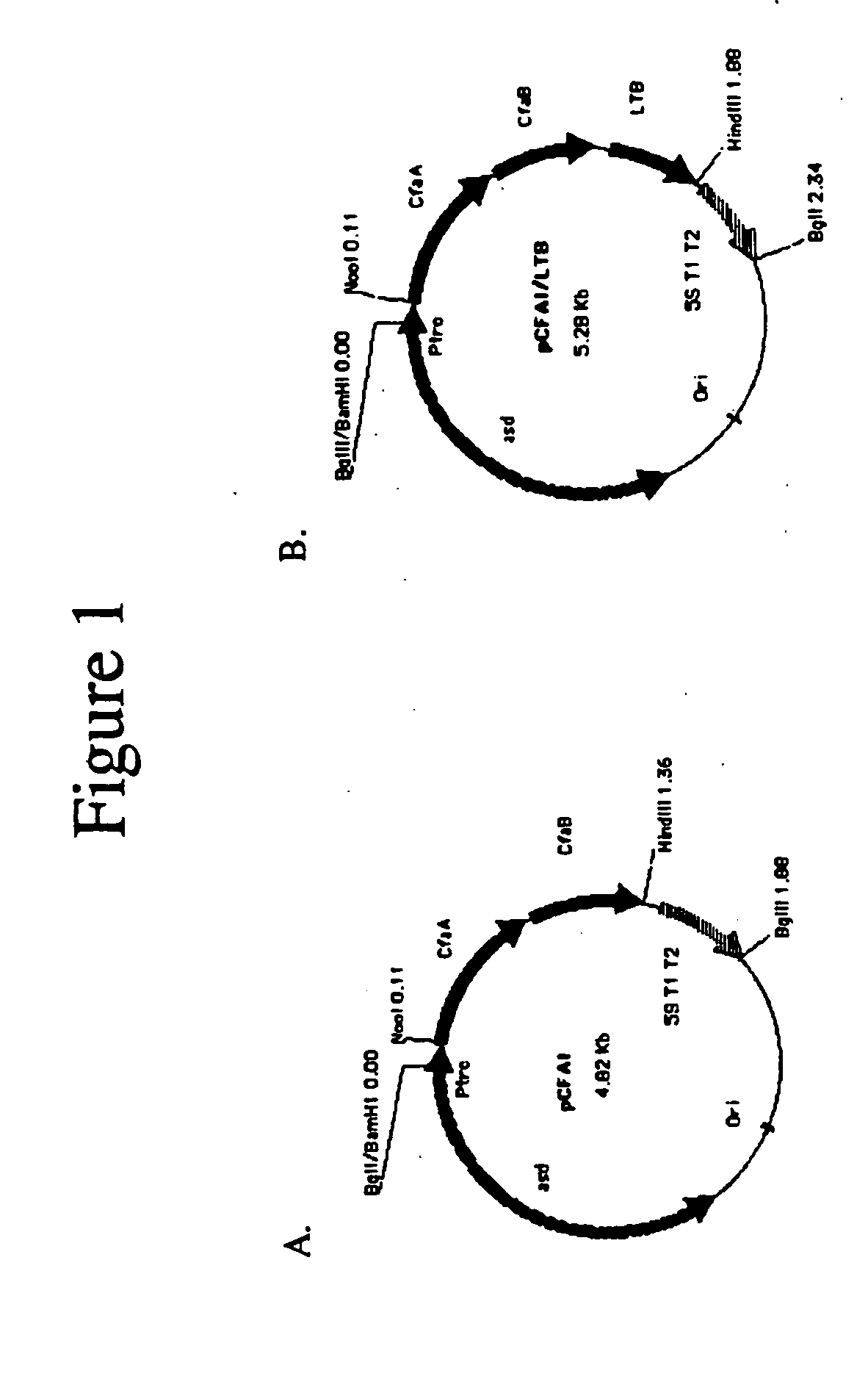
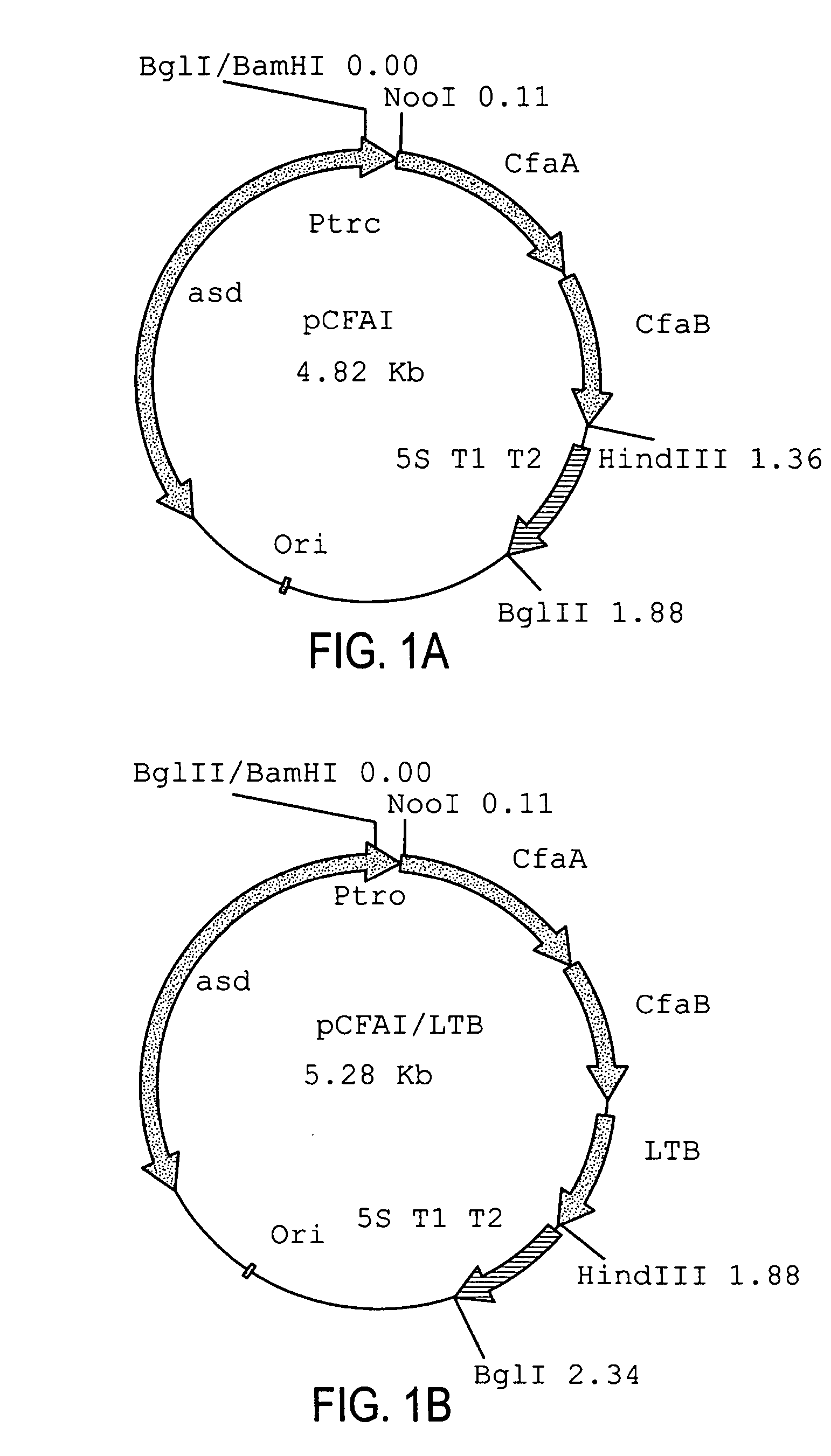
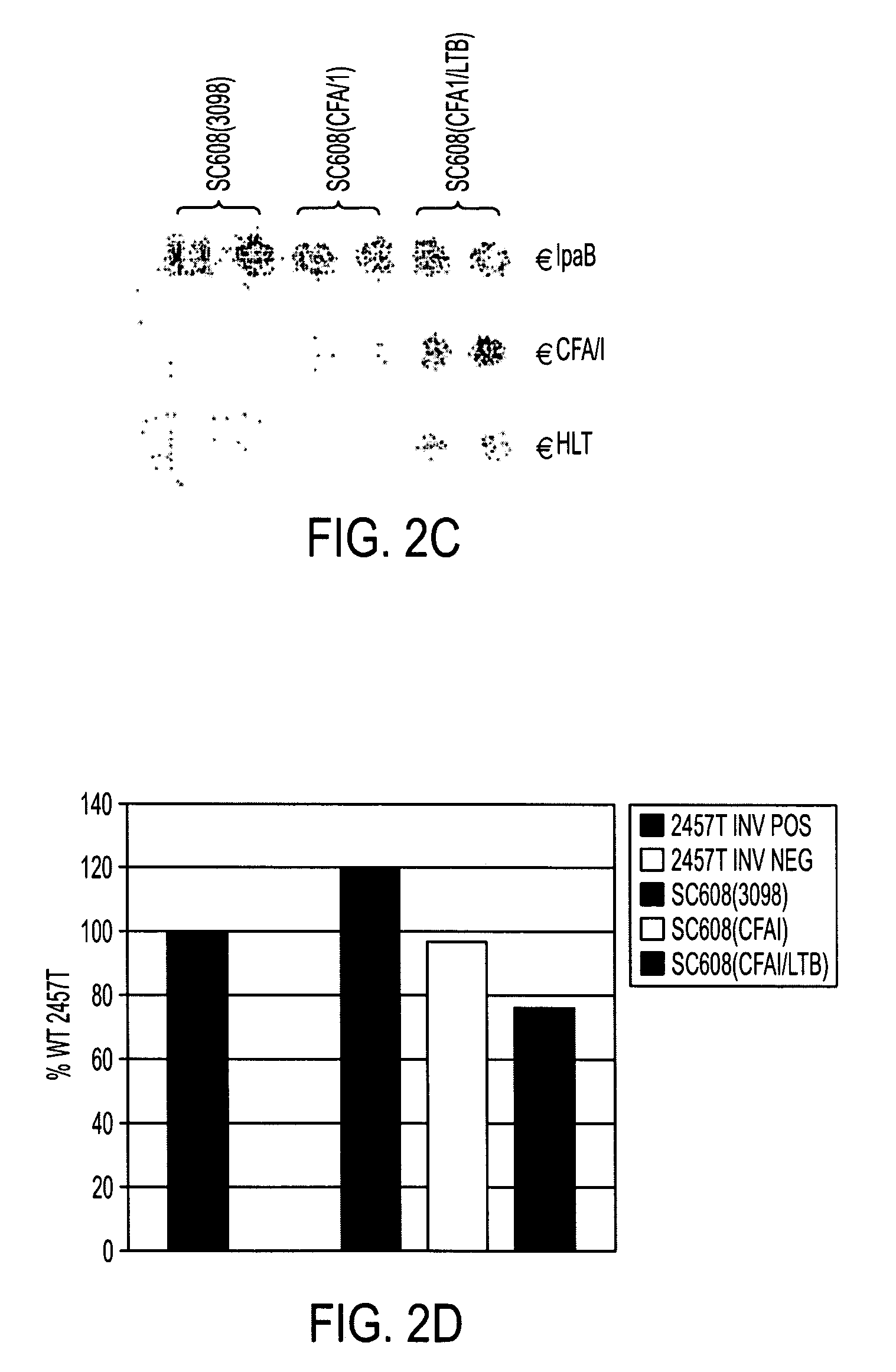
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (cfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E.coli
ActiveUS20070237791A1Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
With the goal of creating a combination vaccine against Shigella and other diarrheal pathogens we have constructed a prototype vaccine strain of Shigella flexneri 2a (SC608) that can serve as a vector for the expression and delivery of heterologous antigens to the mucosal immune system. SC608 is an asd derivative of SC602, a well-characterized vaccine strain, which has recently undergone several phase 1 and 2 trials for safety and immunogenicity. Using non-antibiotic asd-based plasmids, we have created novel constructs for the expression of antigens from enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC), including CFA / I (CfaB and CfaE) and the B-subunit from heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) in Shigella vaccine strain SC608. Heterologous protein expression levels and cellular localization are critical to immune recognition and have been verified by immunoblot analysis. Following intranasal immunization (SC608(CFAI) and SC608(CFAI / LTB) of guinea pigs, serum IgG and IgA immune responses to both the Shigella LPS and ETEC antigens can be detected by ELISA. In addition, ELISPOT analysis for ASCs from cervical lymph nodes and spleen showed similar responses. All vaccine strains conferred high levels of protection against challenge with wild-type S. flexneri 2a using the Sereny test. Furthermore, serum from guinea pigs immunized with SC608 expressing CfaB and LTB contained antibodies capable of neutralizing the cytological affects of heat-labile toxin (HLT) on Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells. These initial experiments demonstrate the validity of a multivalent invasive Shigella strain that can serve as a vector for the delivery of pathogen-derived antigens.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Tuberculosis medicament resistance related tuberculosis-resisting cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope peptide derived from refflux protein and application thereof
The invention discloses a tuberculosis medicament resistance related tuberculosis-resisting cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitope peptide derived from refflux protein, namely, nonapeptide. The amino acid sequence of the nonapeptide is as follows: P5: YLGGTTGPV, or P6: YIVGFCLLV, or P7: TLTWLFAFV, or P8: GLVAGLSAV, or P9: ALGMLIAGL, or P10: MLIAGLPCL, or P11: LLCAIFAEV, or P12: RLWPTVGCL. Accordingto the invention, the HLA-A*0201 restrictive CTL epitope of a tuberculosis medicament resistance related protein antigen is predicted and analyzed by applying SYFPEITHI, BIMAS and NetCTL1.2 databasesand using an immunoinformatics mean according to a primary structure of the antigen so that the epitope peptide is obtained by virtue of selection, and the identified nonapeptide is not reported in documents. The epitope peptide is identified through an in-vitro enzyme linked immunospot (ELISPOT) experiment; and according to the result, a theoretical basis is provided for developing tuberculosis vaccine based on the medicament resistance related protein antigen and more information is provided for designing a tuberculosis polyepitope peptide vaccine based on mixed T cell epitope.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Novel assay for detecting immune responses involving antigen specific cytokine and/or antigen specific cytokine secreting T-cells
InactiveUS20030143641A1Less laborAddressing slow performanceBiological material analysisBiological testingGamma interferonBiological activation
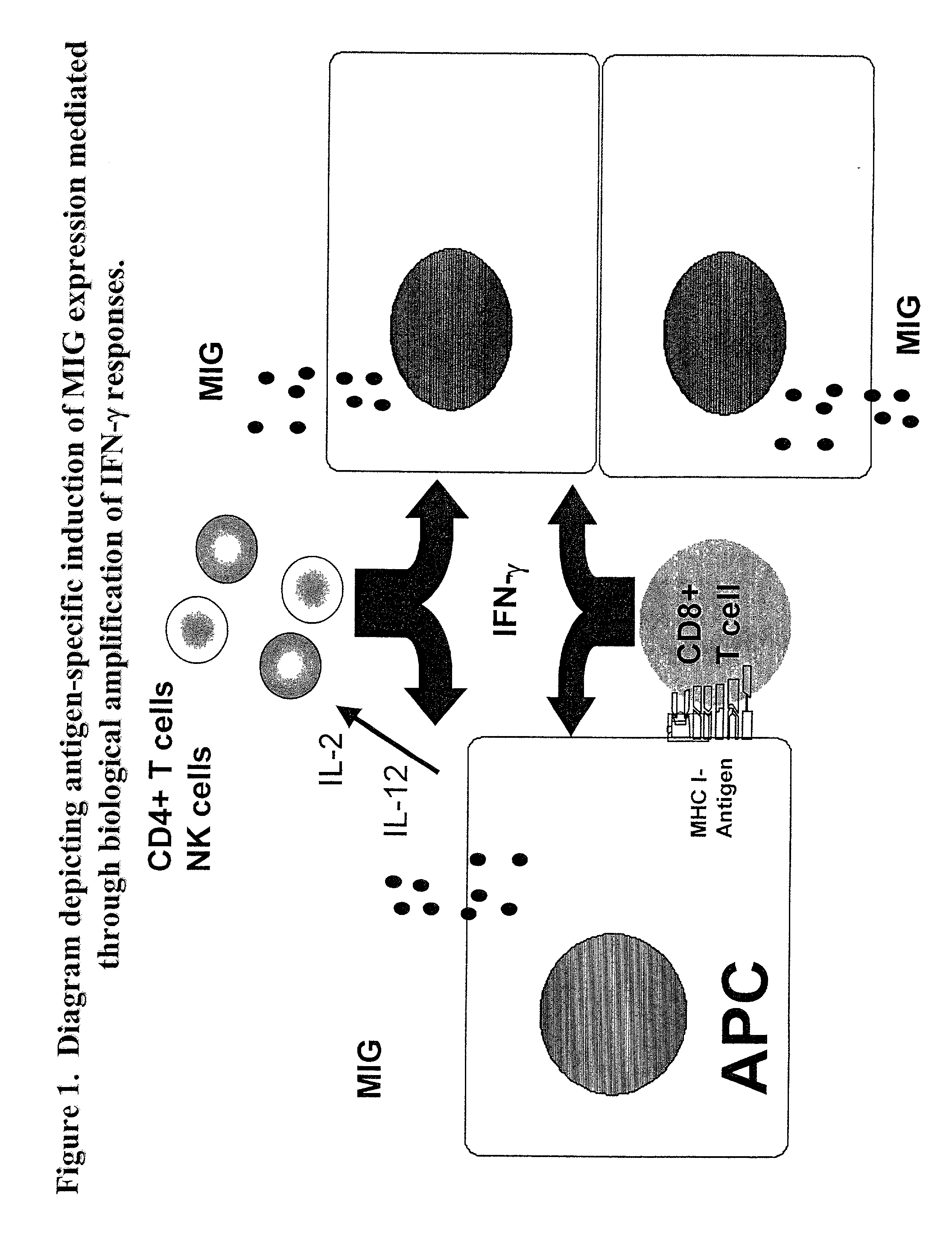
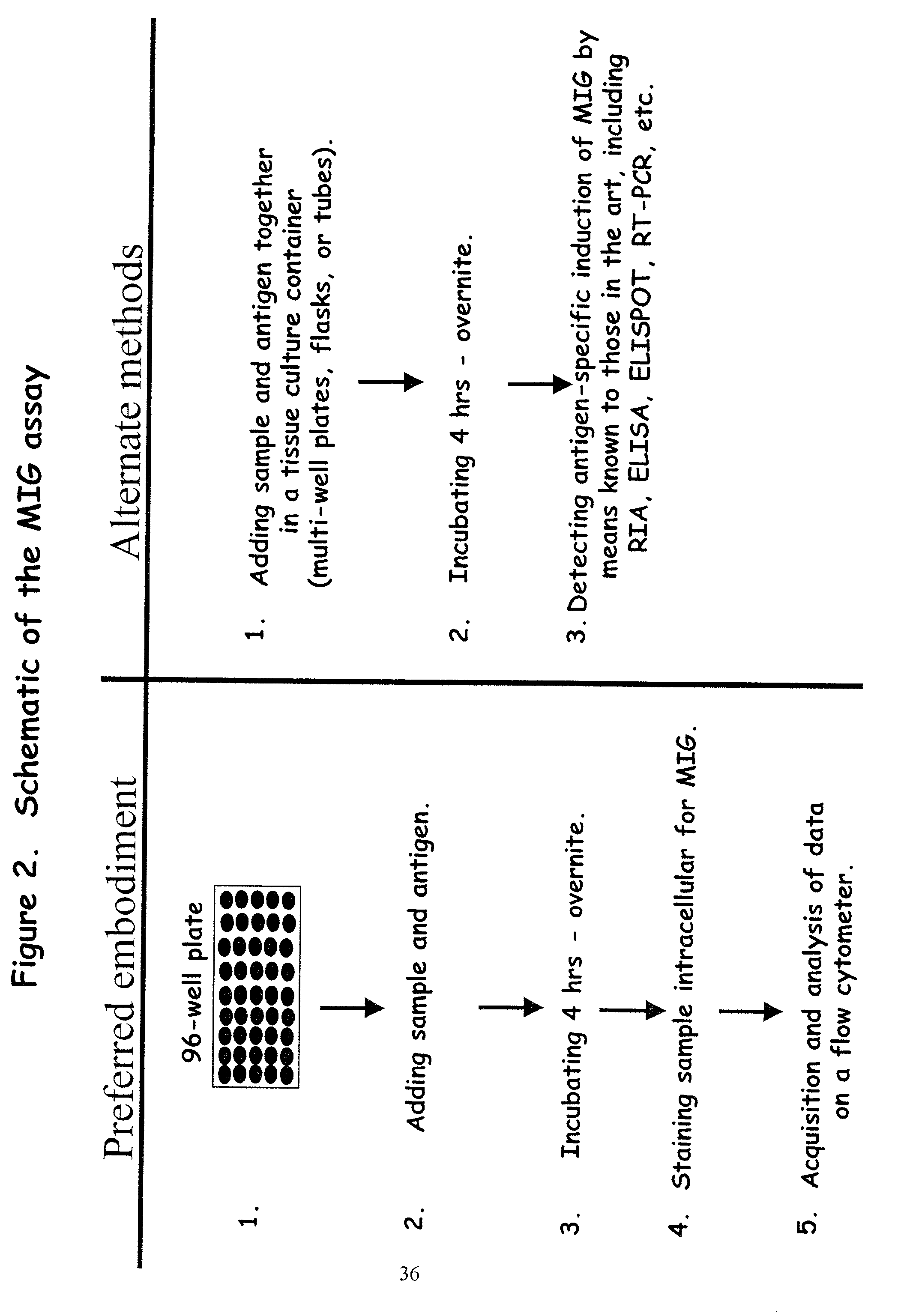
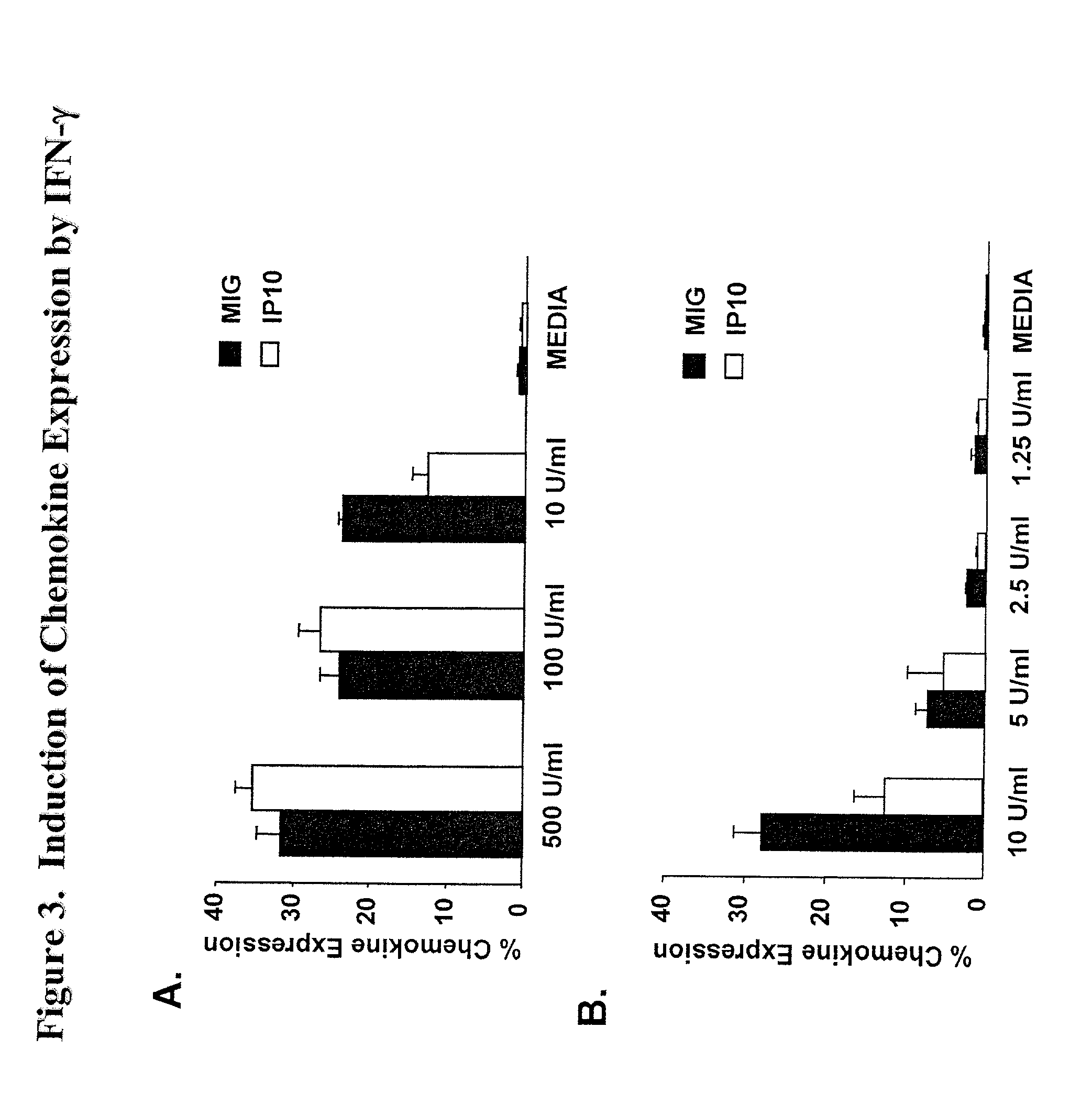
Here, we describe a sensitive and specific assay and kit for the detection of chemokines having activity that is upregulated by Th-1 cytokines (such IFN-gamma) and chemokines that upregulate the activity of Th-1 cytokines (such as IFN-gamma). In a typical embodiment, detection of the chemokine monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG) provides a measure of the biological effect of IFN-gamma rather than direct quantitation of IFN-gamma or IFN-gamma secreting cells per se. Upregulation of MIG expression was observed following in vitro activation of PBMC with defined CD8+ T cell epitopes derived from influenza virus, CMV, or EBV, and in all cases this was antigen-specific, genetically restricted and dependent on both CD8+ T cells and IFN-gamma. Responses as assessed by the MIG assay paralleled those detected by conventional IFN-gamma ELISPOT, but the magnitude of response and sensitivity of the MIG assay were superior. Our data validate this novel method for the detection of high as well as low levels of antigen-specific and genetically restricted IFN-gamma activity or MIG.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
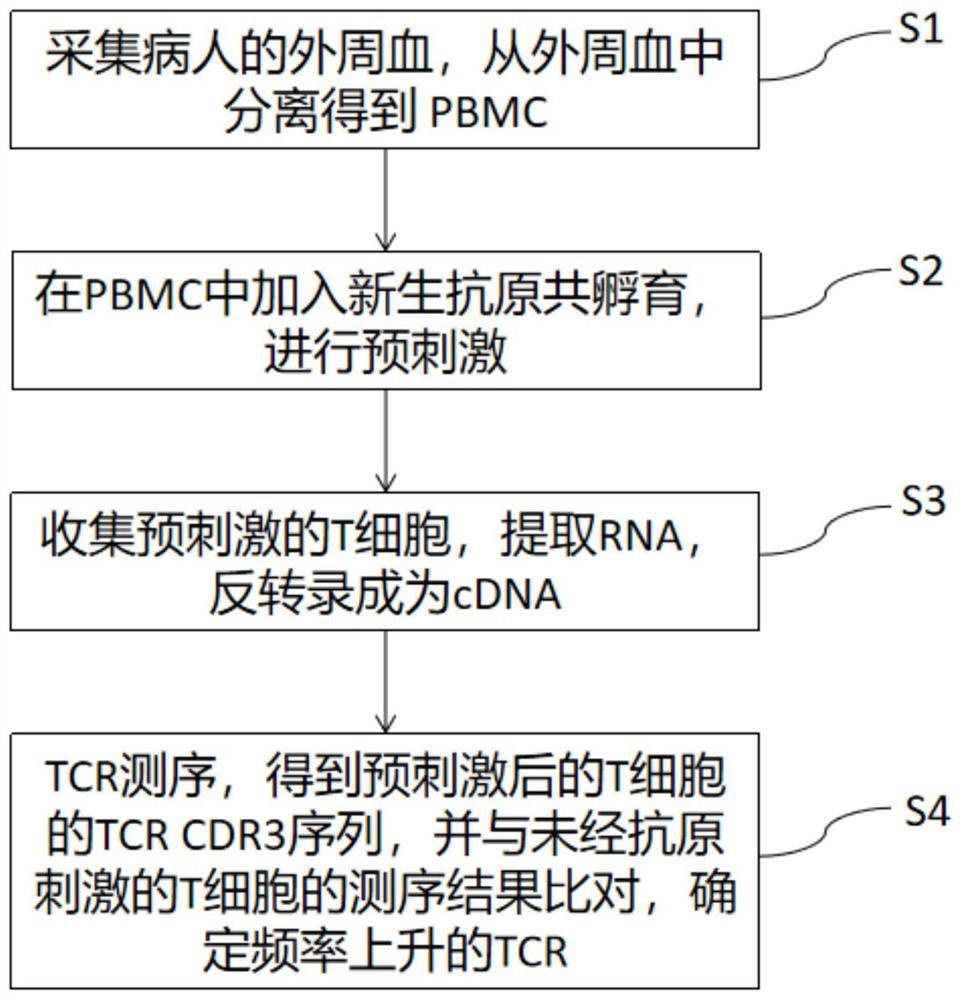
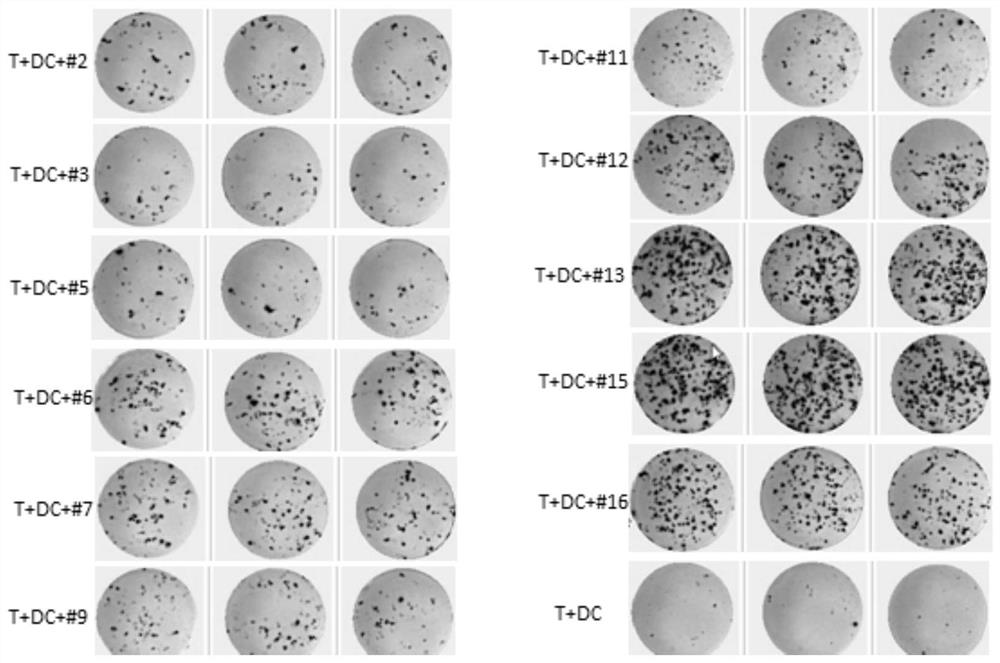
Method for simultaneously detecting neoantigen immunogenicity and neoantigen specificity TCR (T cell receptor)
PendingCN111909992AImprove efficiencyWide applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPeripheral blood mononuclear cellAntigen stimulation
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting neoantigen immunogenicity and a neoantigen specificity TCR (T cell receptor). A neoantigen polypeptide is added to peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to obtain antigen-stimulated cells, and compared with a traditional method, the method has the advantages that the time required for obtaining antigen-specific cells is shortened,the whole process of verifying the neoantigen immunogenicity and obtaining a TCR CDR3 sequence only needs 13 days, and compared with the 40-day treatment process of the traditional method, the methodsaves the time cost greatly. Compared with a traditional MHC-peptide tetramer technology, the method is low in cost, a special tetramer needs to be prepared for one antigen polypeptide in the MHC-peptide tetramer technology, the cost of the sequencing method is remarkably reduced, and compared with a traditional ELISPOT method with the test flux only reaching 10 pieces per batch, the sequencing method is not limited in test flux, higher in efficiency, high in test result accuracy and wide in applicability.
Owner:深圳裕泰抗原科技有限公司
CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus type O and screening method of CTL epitope peptide
ActiveCN103864905AImprove bindingConvenient researchSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesCtl epitopeDisease
The invention discloses a CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide of a foot-and-mouth disease virus type O as well as a screening method and application of the CTL epitope peptide. The CTL epitope peptide is composed of nine amino acid residues, and the amino acid sequence of the CTL epitope peptide is as follows: Ala-Thr-Arg-Val-Thr-Glu-Leu-Leu-Tyr. The epitope peptide has relatively strong combining capacity with SLA (Swineleukocyteantigen)-I proteins from various strains of swine and can induce cytotoxic immune response so as to be suitable for preparing vaccines for preventing and controlling foot-and-mouth disease viruses of various strains of swine and wide in application range. According to the invention, a CTL simulated epitope peptide of a foot-and-mouth disease virus is combined with a single-chain molecule of SLA-I of six strains of constructed swine in vitro, thus a polypeptide which can be combined with a complex can be screened through mass spectrum measurement; in addition, a simulated epitope peptide which can be induced to generate the immune response capacity of T cells is determined through ELISPOT (Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay) detection. The invention provides a method for screening and authenticating the CTL epitope of the foot-and-mouth disease virus in a large scale, and lays the foundation for researching and preparing a multi-epitope vaccine of a foot-and-mouth disease.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein antigen epitope polypeptides, and screening and identification method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to screening and identification of antigen epitope polypeptides. The invention discloses screening, identification and application of a series of rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein antigen epitope polypeptides. The rabies virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein are predicted by biological information means to obtain the candidate epitope polypeptides; and a lymphopoiesis experiment, ELISPOT experiment and a stream-type cell method are utilized to carry out in-vitro experimental verification on the subsequent epitope polypeptides to obtain the four rabies virus protein antigen epitope polypeptides. The invention is characterized in that the antigen epitope polypeptides respectively comprise a Th epitope and a CTL epitope, can stimulate the lymphopoiesis of the vaccine-immunized mouse in vitro and induce the cells to secrete related cell factors, and have the functions of killing virus-infected cells and stimulating the generation of the antibody. The invention can be used for developing rabies virus epitope vaccines and detecting the vaccine effect, and has important value for developing and producing immunologic function detection kits for rabies virus vaccines.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
CD8+T cell epitope polypeptide of S1 protein of chicken IBV (Infectious Bronchitis Virus) S1 protein
ActiveCN103387604AGood immune protectionAvoid immunosuppressionAntiviralsPeptidesADAMTS ProteinsProtein engineering
The invention provides universal CD8+T cell epitope polypeptide of a chicken IBV (Infectious Bronchitis Virus) S1 protein, and belongs to the field of gene and protein engineering. The epitope polypeptides are prepared by the following steps: screening 21 epitope polypeptides in accordance with binding motif sequences in amino acid sequences of the S1 genes of the IBV virus according to the binding motif sequences of haplotype chicken major histocompatibility complex (MHC) I-type molecules; then, taking lymphocytes of three constructed SPF (Specific Pathogen Free) chicken immunized by DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) recombinant plasmids of the S1 genes containing different subtype IBVs, determining the capacity of the 21 polypeptides which induce chicken splenic lymphocytes to secrete interferon-gamma by using an ELIspot (Enzyme-Linked Immunospot Assay) method, and finally, screening to obtain four universal functional T cell epitope polypeptides of IBV, wherein the sequences are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-4. The four epitope polypeptides provided by the invention are combined in use to prepare a universal vaccine for IBV. The invention further provides a method for screening the epitope of the functional T cell of the S1 protein of the IBV.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
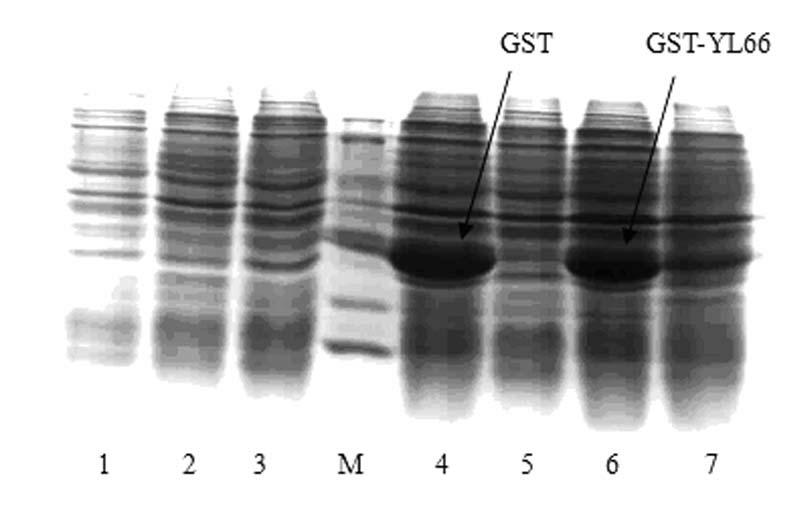
Multi-epitope vaccine YL66 and application of preparing vaccine for treating tumour
InactiveCN102657854ALearn about immune effectsGenetic material ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenIn vivo
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6 recombinant dipolymer, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101805397AIncreased antigen specificityIncreased sensitivityMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesSerodiagnosesSkin test
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering and diagnostic medicine, in particular to a mycobacterium tuberculosis ESAT-6 recombinant dipolymer, a preparation method thereof, an antigenicity analysis and an application thereof in the serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. The invention uses the DNA of a chimeric gene nucleic acid vaccine HG856A plasmid containing 2 * esat-6 copies as the template, obtains 2 * esat-6 gene segments by PCR amplification, and clones, expresses and purifies an ESAT-6 recombinant dipolymer protein in E.coli. The protein is connected with the two ESAT-6 monomers through amino acid Tyr and Val which are coded by the AccI restriction enzyme cutting site, i.e. GTC TAC, carries six* His tags at the N end, and can be purified by nickel-chelate affinity chromatography. Experiments confirm that the purified recombinant dipolymer has favorable reactogenicity and antigenic specificity. The recombinant dipolymer can be used as an antigen for the early diagnosis of the tuberculosis, including the serodiagnosis of ELISA, ELISPOT or the like, or can be used as an antigen for a skin test.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
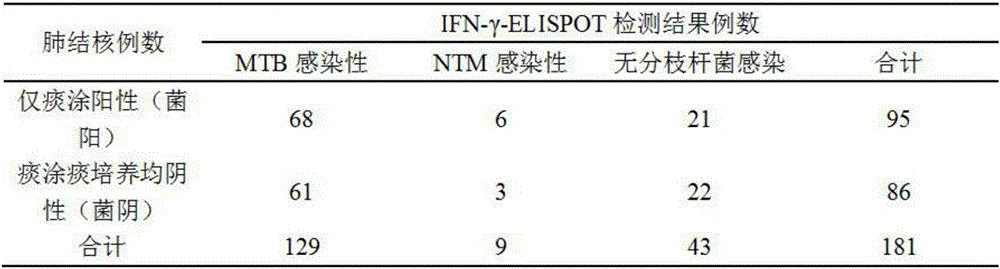
Detection method for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
The invention discloses a detection method for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. The detection method comprises the following steps: respectively contacting the specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis and the specific antigen of mycobacterium with a to-be-detected in-vitro T cell, and detecting a cell factor released by the T cell; comparing the detection results of the specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis and the specific antigen of mycobacterium; judging that the to-be-detected in-vitro T cell is suffered from mycobacterium tuberculosis infection or non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infection according to a comparison result. According to the detection method provided by the invention, the specific antigen of mycobacterium and the ELISPOT detection method for detecting the specificity of MTB can be combined and utilized to simultaneously identify MTB and NTM infections. The detection method provided by the invention has important guidance significance on clinical diagnosis and drug usage of a doctor.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RHFAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Construction of live attenuated Shigella vaccine strains that express CFA/I antigens (CfaB and CfaE) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic E. coli
ActiveUS7759106B2Reduce intrusionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaHeterologousMucosal Immune Responses
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Method for preparing tetramer from O type foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide
ActiveCN105884870ASignificant CTL functionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBiotin-streptavidin complexInclusion bodies
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a method for preparing tetramer from O type foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide. Aiming at designed foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide, two methods of ELISPOT and tetramer construction are adopted for screening and identifying the foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide, a Hebao pig SLA-2 heavy chain tetramer is constructed, expression is carried out on a prokaryotic expression system pET-21a(+) / BL21, and an inclusion body is extracted; in the foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide, polypeptide causing a specific CTL reaction is screened out through an ELISPOT method, then the polypeptide, the SLA-2 heavy chain, and existing light chains beta 2m are subjected to renaturation, biotinylation and FITC label streptavidin reactions to generate the SLA-2-BSP / peptide tetramer, and then the function of the tetramer is detected through flow cytometry. Through an ELISPOT method, a specificity polypeptide epitope of O type foot and mouth disease viruses VP1 is obtained through identification, the peptide tetramer is successfully constructed, a pig tetramer technology platform is preliminarily built, and a foundation is laid for study of pig specificity CTL immune responses and T epitope screening.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Detecting latent tuberculosis infections
ActiveUS20150010927A1Accurate distinctionAccurate and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAssayLatent tuberculosis
This document provides methods and materials related to identifying mammals having a LTBI. For example, methods and materials for using ELISpot assays to identify mammals (e.g., humans) having a LTBI are provided.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Polypeptide for specificity detection of tubercle bacillus infection contamination, method and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101367867AReduce false positive rateNo change in false positive ratePeptidesMaterial analysisOrganismVaccine Immunogenicity
The present invention discloses a polypeptide with tubercle bacillus immunogenicity, which contains a sequence shown by Seq ID No.2 in the sequence table. The present invention also discloses an ELISPOT method, which utilizes the polypeptide to detect if a biological sample is infected with tubercle bacillus, and an agent box containing the polypeptide. When the polypeptide, the method and the agent box are adopted to detect the infectivity of tubercle bacillus, the false positive rate is greatly decreased, while the true positive rate can be kept unchanged.
Owner:SHENZHEN DAKEWE BIOENG
Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent infection related proteins, preparation and applications thereof
InactiveCN104805063AAuxiliary diagnosisAuxiliary differential diagnosisTransferasesDepsipeptidesNucleotideT lymphocyte
The present invention relates to Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent infection related proteins, preparation and applications thereof, wherein the three Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent infection related proteins are LTBIPr1, LTBIPr2 and LTBIPr3, and the nucleotide sequences of the protein epitope are represented by the sequences 1-3 in the sequence table. According to the present invention, the genetic engineering technology is adopted to clone, express and purify Mycobacterium tuberculosis to obtain the three protein antigens related with Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent infection; the protein antigen is adopted as the tuberculosis specific cell stimulating agent to stimulate the peripheral blood mononuclear T-lymphocyte of a subject so as to make the T-lymphocyte secrete specific IFN-gamma, and then the spot number of the T-lymphocyte secreting the IFN-gamma is detected through the ELISpot technology, wherein the whole process takes two days; and according to the generated blue-purple spot number, the result is read with the naked eye or instrument, such that the Mycobacterium tuberculosis latent infection related proteins can be used for detection of whether a subject is infected with tubercle bacillus, and active tuberculosis assisted diagnosis and differential diagnosis.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Precise localization method for analysis of Elispot by using image identification
InactiveCN102693541ASolve the exact cropping problemManufacturing precision requirements are lowImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImaging analysis
The invention discloses a precise localization method for analysis of Elispot by using image identification. The method mainly comprises the steps of transforming grey level value of an original micro-well plate single-pore coloured image; detecting the flange of the grey level image; searching for pore bottom circle of the flange detection image; carrying out pore bottom trimming for an original whole origin image. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the image characteristic of an Elispot analysis instrument is combined, the pore bottom circumference searching is conducted based on the micro-well plate based on flange detected image, the problem on precise trimming of the micro-well plate pore bottom image is solved, and the demands on positioning of a motor and manufacture precision of the micro-well plates are lowered. The method of the invention can be used for image analysis of an Elispot reader and also for similar target area positioning based on the micro-well plate image analysis.
Owner:上海铭源数康生物芯片有限公司 +1
Assay for detecting immune responses involving antigen specific cytokine and/or antigen specific cytokine secreting T-cells
Here, we describe a sensitive and specific assay and kit for the detection of chemokines having activity that is upregulated by Th-1 cytokines (such IFN-γ) and chemokines that upregulate the activity of Th-1 cytokines (such as IFN-γ). In a typical embodiment, detection of the chemokine monokine induced by gamma interferon (MIG) provides a measure of the biological effect of IFN-γ rather than direct quantitation of IFN-γ or IFN-γ secreting cells per se. Upregulation of MIG expression was observed following in vitro activation of PBMC with defined CD8+ T cell epitopes derived from influenza virus, CMV, or EBV, and in all cases this was antigen-specific, genetically restricted and dependent on both CD8+ T cells and IFN-γ. Responses as assessed by the MIG assay paralleled those detected by conventional IFN-γ ELISPOT, but the magnitude of response and sensitivity of the MIG assay were superior. Our data validate this novel method for the detection of high as well as low levels of antigen-specific and genetically restricted IFN-γ activity or MIG.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE NAVY NAVAL RES LAB WASHINGTON
Method for preparing tetramer from Asia I foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide
ActiveCN105884869ASignificant CTL functionSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesInclusion bodiesCompanion animal
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for preparing tetramer from Asia I foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide. According to the designed foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide, the foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide is screened and identified by the ELISPOT method and the tetramer construction method, pouch pig SLA-2 heavy-chain tetramer is constructed and expressed in a prokaryotic expression system pET-21a(+) / BL21, and an inclusion body is extracted. Polypeptide capable of causing specificity CTL reaction is screened from the foot and mouth disease virus polypeptide through the ELISPOT method, the polypeptide and SLA-2 heavy-chain and known light-chain beta2m are subjected to renaturation and biotinylation, the polypeptide and FITC labeled-streptavidin react to generate SLA-2-BSP / tetramer, and then the function of tetramer is detected through flow cytometry. A specificity peptide epitope of a pig Asia I foot and mouth disease virus VP1 is obtained through identification through the ELISPOT method, the tetramer is successfully constructed, the specificity CTL of the tetramer is detected, a pig tetramer technical platform is primarily built, and a foundation is laid for researching pig specificity CTL immune response and T epitope screening.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for diagnosing and treating autoimmune diseases
Disclosed are compositions and methods for detecting, isolating, and / or characterizing a T cell or autoantibody associated with type I diabetes. The composition and methods comprise the use of a hybrid insulin peptide having an N-terminal amino acid sequence taken from the human insulin peptide and a C-terminal amino acid sequence taken from a secretory granule protein that are joined through a peptide bond to form an autoimmune antigen. The detecting, isolating and characterization step further includes performing an immunoassay and / or T cell proliferation assay with the disclosed hybrid insulin peptides, where preferably, the immunoassay is an ELISPOT assay.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide and application thereof
The invention discloses a tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide which is a nonapeptide, wherein the amino acid sequence of the nonapeptide is P10: MLIAGLPCL. According to the tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL epitope peptide, immunological informatics means are adopted according to a primary structure of an antigen, an HLA-A*0201-restrictive CTL epitope of a tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related protein antigen is subjected to predictive analysis by using databases, namely SYFPEITHI, BIMAS and NetCTL1.2, the epitope peptide is obtained through screening, and assayed nonapeptides are not reported in documents. The epitope peptide is assayed through in-vitro ELISPOT experiments, and the results provide a theoretical basis for the development of tuberculosis vaccines based on resisting-drug-associated protein antigens and provide more information for designing tuberculosis multi-epitope peptide vaccines based on mixed T cell epitopes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide and application thereof
The invention discloses a tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL (Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte) epitope peptide which is a nonapeptide, wherein the amino acid sequence of the nonapeptide is P8: GLVAGLSAV. According to the tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related efflux-protein-sourced tuberculosis resisting CTL epitope peptide, immunological informatics means are adopted according to a primary structure of an antigen, an HLA-A*0201-restrictive CTL epitope of a tuberculosis-resisting-drug-related protein antigen is subjected to predictive analysis by using databases, namely SYFPEITHI, BIMAS and NetCTL1.2, the epitope peptide is obtained through screening, and assayed nonapeptides are not reported in documents. The epitope peptide is assayed through in-vitro ELISPOT experiments, and the results provide a theoretical basis for the development of tuberculosis vaccines based on resisting-drug-associated protein antigens and provide more information for designing tuberculosis multi-epitope peptide vaccines based on mixed T cell epitopes.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Analyte-releasing beads and use thereof in quantitative elispot or fluorispot assay
InactiveUS8569074B2Quantitative precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAnalyteDrug release
A method of quantifying analyte secreted by a cell or released from a drug delivery vehicle, typically by ELISpot or fluorispot assay is described. Quantification is possible through the use of an analyte-releasing reagent that includes a bead and the analyte releasably bound to the bead, or a container pre-spotted with analyte released from the reagent. The reagent or pre-spotted containers can be used to provide a standard curve for release of the analyte. By detecting analyte secreted by one or more cells or drug released by a drug delivery vehicle, and comparing the detected analyte to the standard curve, it is possible to quantify the amount of analyte released by the one or more cells or drug released by the drug delivery vehicle. Kits and reagents for practicing the methods of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
ELISpot diagnostic kit for neuromyelitis optica and its application
ActiveUS20150140569A1High sensitivityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisStructural analysisNeuromyelitis optica
An ELISpot diagnosis kit for NMO and its application are characterized in that, the polypeptide fragment specific to NMO effector T-cell is obtained through topological conformation analysis of aquaporin-4 (AQP-4), followed by the structural analyses of the related polypeptides after combination and rearrangement so as to screen out the brand-new polypeptide fragment suitable for NMO disease diagnosis. In the ELISpot experiment, by utilizing the obtained polypeptide fragment, stimulate the effector T-cell in the NMO disease to secrete IL-4, proving the feasibility and scientific value of that polypeptide fragment in the NMO diagnosis. This method is with strong specificity, high sensitivity and easy operations, and it can be developed into the diagnosis kit for the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of NMO in the clinical examination, laying the foundation for the early discovery and treatment of NMO.
Owner:XU JUN
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific human leukocyte antigen-A33 (HLA-A33) restrictive epitope peptides and application thereof
The invention relates to hepatitis B virus (HBV) specific human leukocyte antigen-A33 (HLA-A33) restrictive epitope peptides and application thereof. An HLA-A33 restrictive cell level epitope peptide screening platform is constructed; and 5 important HBV specific HLA-A33 restrictive epitope peptides (namely SEQ ID No: 5, 7, 9, 10 and 19) are determined by combining computer simulation analysis, detecting on the cell level epitope peptide screening platform and using three detection technologies of trimerical protein level renaturation, tetrameric patient's blood sample detection and Elispot detection. The invention also discloses the application of the screened HBV specific HLA-A33 restrictive epitope peptides in preparation of a medicament for treating hepatitis B in examinees, and specifically, the hepatitis B of the examinees is of HLA-A33 type. The invention also provides a medicament for treating the HLA-A33 hepatitis B in the examinees, and the medicament contains one or more of the 5 HBV specific HLA-A33 restrictive epitope peptides (namely SEQ ID No: 5, 7, 9, 10 and 19) and a medicinal carrier.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for screening point mutation BIRC5 antigen epitope peptide
PendingCN113611362AEasy to filterQuick filterTumor rejection antigen precursorsTumor specific antigensAntigen epitopeCtl epitope
The invention relates to a method for screening point mutation BIRC5 antigen epitope peptides, and the method comprises the following specific steps: 1), comprehensively predicting CTL epitope peptides of BIRC5 antigen 9 amino acid residues by using NetMHCpan 4.1 and SYFPEITHI on-line prediction systems, and changing the types of corresponding amino acid residues through a point mutation technology to improve the score of on-line prediction; 2) according to the amino acid sequence obtained in the step 1), artificially synthesizing a corresponding epitope peptide, co-incubating the epitope peptide and T2 cells, and detecting the actual binding capacity of the epitope peptide and HLA-A2 molecules; 3) establishing specific CTLs cloning in vitro by utilizing the mutant peptide obtained by screening in the step (2), and identifying the immunological activity of the mutant peptide induced CTLs for specifically recognizing and killing target cells by utilizing ELISPOT experiment, calcein killing and other methods. The invention lays a foundation for further preparation of tumor peptide vaccines.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Dominant epitope peptide of Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN113717257AUnderstanding ImmunobiologySimple designSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsMHC class IImmunogenicity
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial immunity, and particularly relates to dominant epitope peptide of Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The epitope peptide is composed of sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1-25. According to the dominant epitope peptide of Ebola virus envelope glycoprotein as well as the coding gene and application thereof, potential epitopes derived from EBOV GP are predicted and verified through an ELISpot test, protection properties of the potential epitopes in different isolates around the world are subjected to a variety of deep analyses, so that screened dominant isolates are verified. The binding affinity and immunogenicity of the epitopes and proper sites of respective MHC class I molecules are further predicted, which is finally helpful for understanding the immunobiology of the EBOV GP and perfecting the epitope vaccine design for virus in the future.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Antituberculous CTL epitope peptide and application thereof
The invention discloses a polypeptide. An amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown as SEQ ID No. (sequence identifier number) 1 or 2. The invention further provides a drug composition, food ora health care product containing the polypeptide and a corresponding application of the polypeptide. An epitope peptide is obtained through screening and identified by in-vitro ELISPOT (enzyme-linkedimmunospot assay), a cell killing experiment and the like; a theoretical basis is provided for subsequent development of a tuberculosis vaccine and a diagnostic agent based on a drug-resistant mutation antigen; and more options are provided for a design of a multi-epitope tuberculosis vaccine based on a mixed T cell epitope.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
A kind of O-type foot-and-mouth disease ctl epitope peptide and screening method
ActiveCN103864905BConvenient researchImprove bindingSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesCtl epitopeDisease
The invention discloses an O-type foot-and-mouth disease CTL epitope peptide, a screening method and application thereof. The CTL epitope peptide is composed of nine amino acid residues, and its amino acid sequence is: Ala-Thr-Arg-Val-Thr-Glu-? Leu-Leu-Tyr. The epitope peptide can have strong binding ability with SLA-I proteins derived from different strains of pigs and can cause cytotoxic immune response, and is suitable for the preparation of vaccines for the prevention and treatment of various strains of porcine foot-and-mouth disease viruses, and has a wide range of applications. The invention uses the constructed six-strain pig SLA-I single-chain molecule to bind the CTL mimetic epitope peptide of foot-and-mouth disease virus in vitro, mass spectrometry to screen the polypeptide that can bind to the complex, and through ELISPOT detection, it is determined that it can induce T cell immune response Capable mimotope peptides. The invention provides a method for screening and identifying a large number of CTL epitopes of foot-and-mouth disease virus in the future, and lays a foundation for developing a porcine foot-and-mouth disease multi-epitope vaccine.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com