Detection method for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
A technology of mycobacterium tuberculosis and mycobacteria, applied in the field of biomedical testing, can solve the problems of price restrictions, wide use, no simultaneous differential detection of MTB and NTM infection, low sensitivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] [Example 1] This example includes a kit for differentiating Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection from non-tuberculous mycobacteria
[0022] Please refer to figure 1 , the kit includes detection wells, control wells and parallel control wells, wherein the detection reagents are set as:
[0023] Test 1: MTB-specific E6+E7+C14 mixed polypeptide
[0024] Detection 2: Mycobacterium-specific mixed polypeptides;
[0025] Control 1: positive control: PMA+Inomycin);
[0026] Control 2: Negative control: no peptide;
[0027] T1 and T2 are the T-SPOT.TB detection of the parallel control, respectively.
[0028] The detection steps are as follows:
[0029] 1 Isolation of mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from tuberculosis patients Ficoll lymphocyte separation medium was used to separate PBMCs, and PBMCs were resuspended in R10 culture medium (10% calf serum in RPMI1640 culture medium) for later use.
[0030] 2ELISPOT analysis Select a 96-well plate with PVDF membrane as the reaction p...
Embodiment 2
[0035] [Example 2] Test result
[0036] A small number of pulmonary tuberculosis patients (273 cases in total, including 92 cases with strain identification results and 85 cases with only sputum smear positive, totaling 187 cases of bacterium-positive patients, and 86 cases of bacterium-negative patients with negative sputum smear and sputum culture) in the laboratory The results of blood tests are shown in Table 1 and Table 2.
[0037] Table 1 Peripheral blood ELISPOT detection results of 85 cases of MTB and 7 cases of NTM positive tuberculosis
[0038]
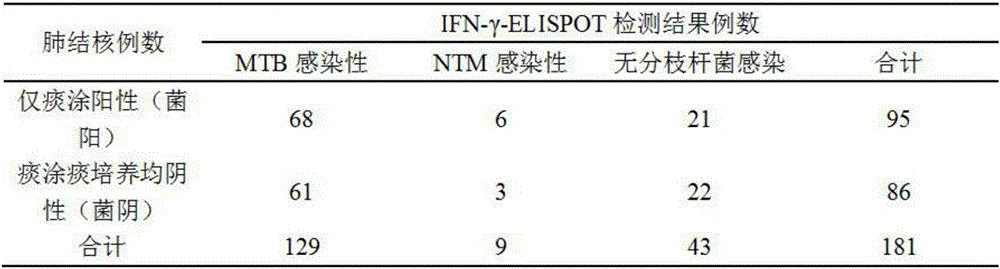
[0039] Table 2 Peripheral blood ELISPOT detection results of 95 cases of smear-positive (bacteria-positive) pulmonary tuberculosis and 86 cases of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis
[0040]
[0041]The above results suggest that there is a certain proportion of NTM infection caused by both bacteria-positive and bacteria-negative pulmonary tuberculosis. Therefore, whether it is tuberculosis (bacterium-positive and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com