Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
67 results about "Mycobacterium sp" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
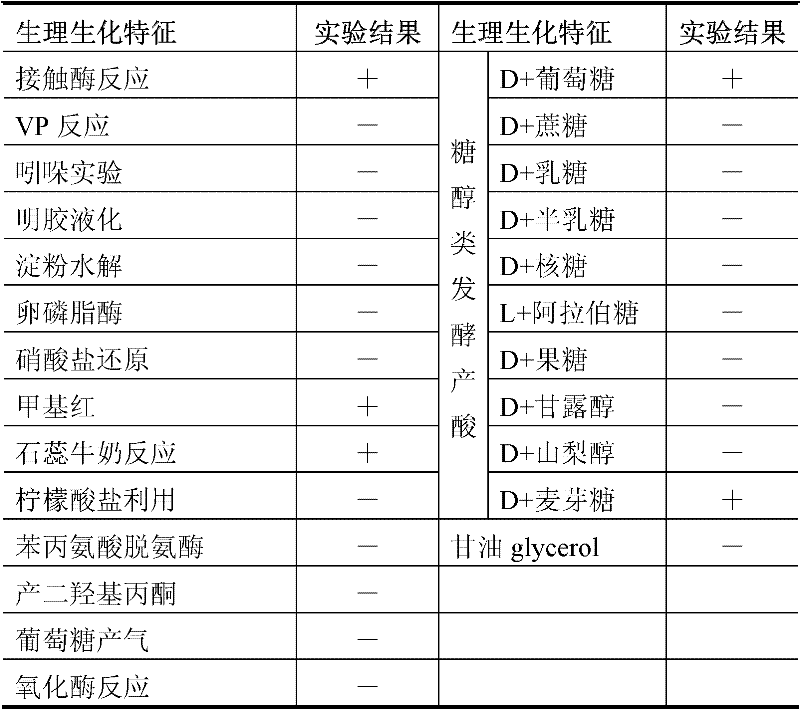
Mycobacterium sp. Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. The genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and leprosy (Mycobacterium leprae).
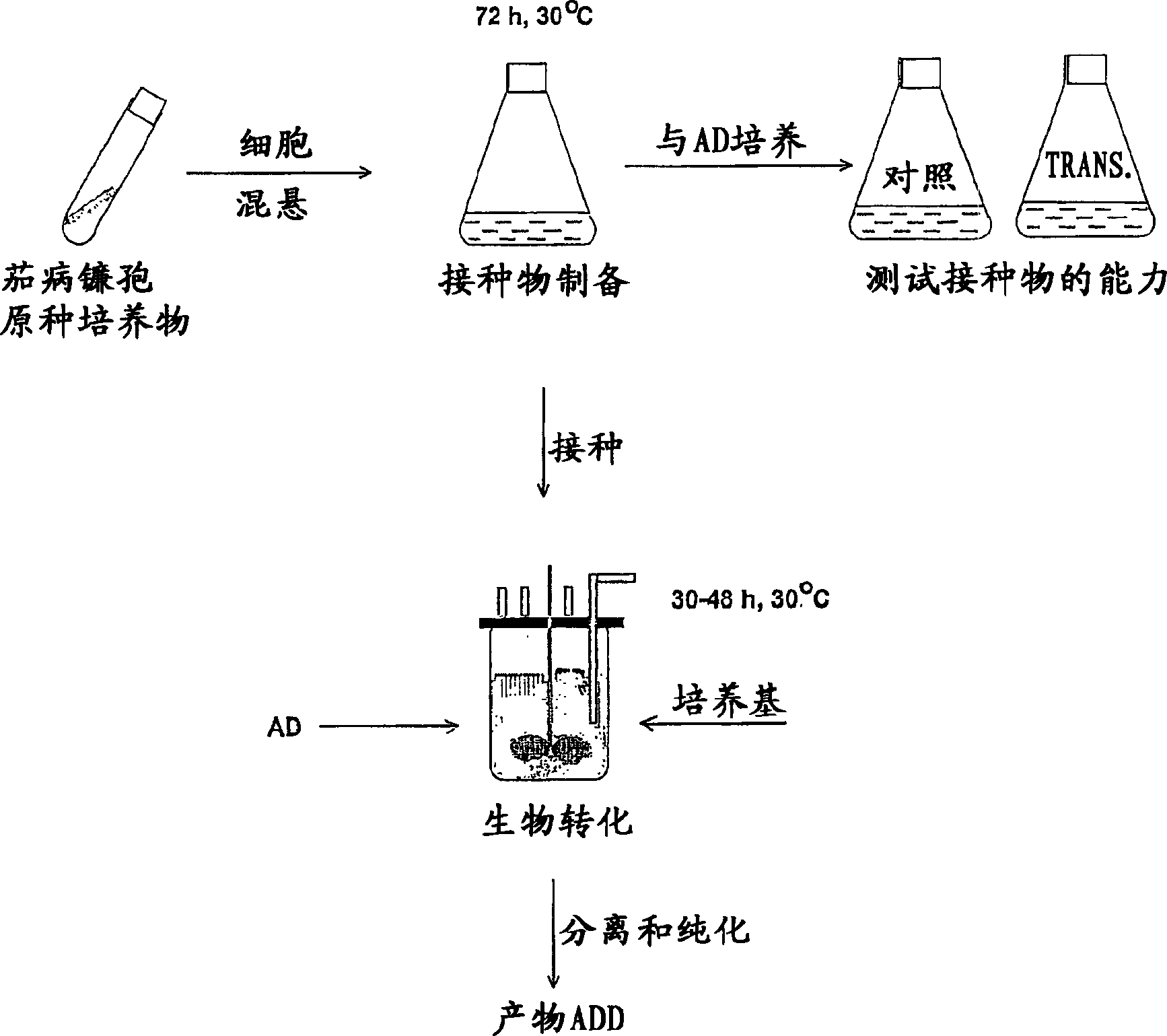
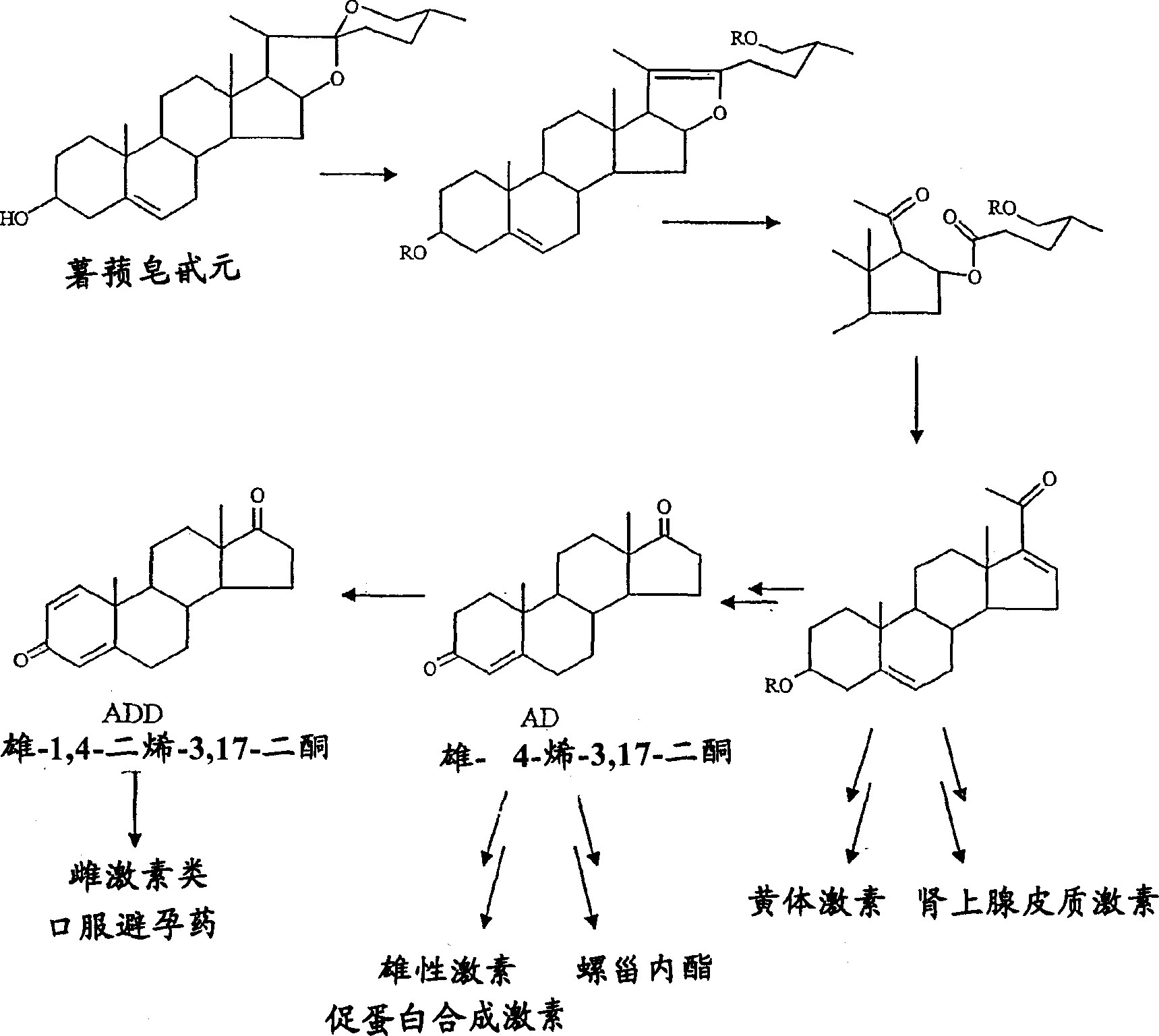
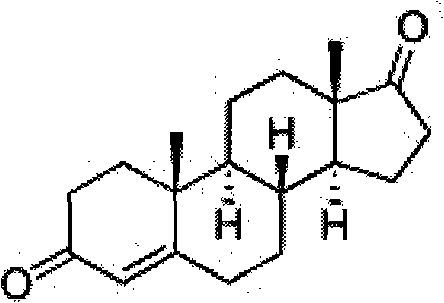
Process for fermentation of phytosterols to androstadienedione
A process of fermenting a phytosterol composition to produce androstenedione (androst-4-ene-3,17-dione) and subsequently androstadienedione (and rosta-1,4-diene,3,17-dione) comprises propagating a microbial culture of the genus Mycobacterium in a first nutrient medium, placing the microbial culture and the phytosterol composition in a bioreactor for a sufficient time to transform the composition substantially to androstenedione (the "AD solution"), propagating a fungal culture of the genus Fusarium in a second nutrient medium, and then injecting one or more of 1) Fusarium sp, or 2) the fungal culture medium into the bioreactor for a sufficient time to transform the AD solution to androstadienedione.
Owner:NV ORGANON
Mycobacterium 16F for efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and benzene organic matters and application thereof
ActiveCN102899271AEfficient degradationDegradation safetyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementKanamycinM-Xylene
The invention provides a strain of Mycobacterium sp.16F for efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and benzene organic matters, which has a preservation number of CGMCC No.6367. The mycobacterium 16F can efficiently, safely and rapidly degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and benzene organic matters, can grow and degrade by using fluorene, naphthalene, anthracene, acenaphthene, phenanthrene, pyrene and benzopyrene as the sole carbon source and energy in aerobic condition, and can utilize benzene, m-xylene, toluene, salicylic acid, catechol and other multiple aromatic organic matters. The mycobacterium 16F is sensitive to streptomycin, rifampin, tetracycline, kanamycins and other antibiotics, has good degradation effects to mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aging soils and monocyclic benzene organic matters in water bodies, can be used for restoring and purifying the water-soil environment combinedly polluted by aromatic hydrocarbon organic matters, is important for promoting sustainable development, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST OF LIGHT IND
Mixed inoculant for degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants
InactiveCN102776135AStrong growthImprove reproductive abilityBacteriaWater contaminantsOchrobactrum sp.Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
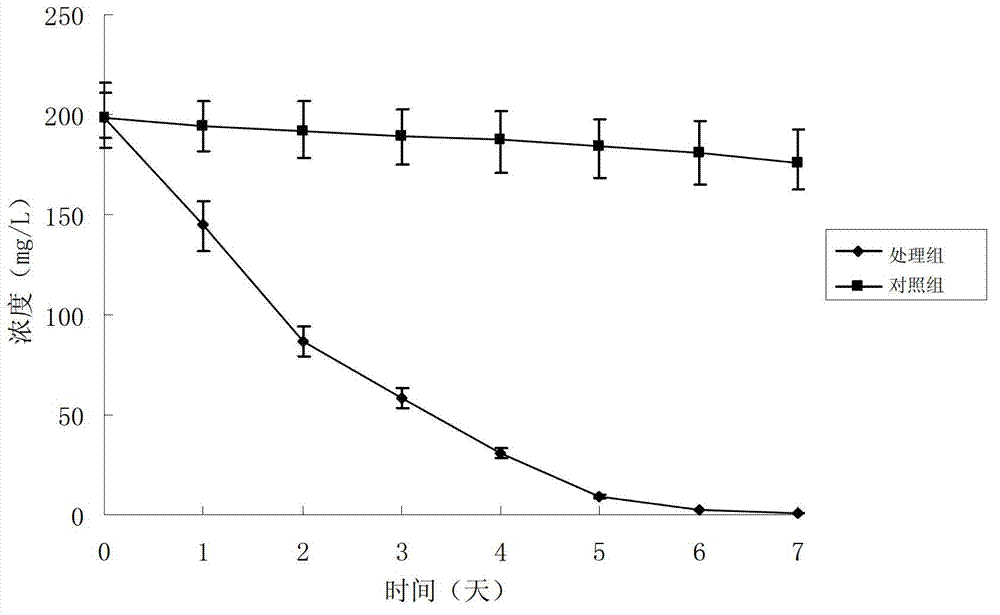
The invention relates to a rehabilitation technology of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants (PAHs), particularly discloses a mixed inoculant for degrading PAHs. The mixed inoculant comprises indigenous mixed bacteria, wherein the indigenous mixed bacteria comprise Pseudomonas sp. B08, Pseudomonas sp. BM, Bacillus sp. BYB, Bacillus sp. B07, Ochrobactrum sp. ZHL4, Gordonia sp. BGDS and Mycobacterium sp. BFZG. The mixed inoculant disclosed herein can be added according to an inoculation quantity of 5-10%, and when the initial concentration of PAHs is 180.67mgL<-1>, the total degradation rate of PAHs after being processed for 9 days can reach 91.21%.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicine
The invention discloses application of a Harmine derivative to preparation of antibacterial medicines. The bacteria is selected from Acinetobacter, Bacillus, Campylobacter, Chlamydia, Chlamydia trachomatis, Clostridium, Citrobacter, Escherichia, enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli, enteric bacteria, Enterococcus, Francisella, Haemophilus, helicobacter, Klebsiella Bacillus, Lester monocytogenes, Moraxella, Mycobacterium, Neisseria, proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, shewanella oneidensis, Shigella, Stenotrophomonas, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus and Yersinia.
Owner:XINJIANG HUASHIDAN PHARMA RES
Biochar-based immobilized microbial agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109628353APromote degradationReduce lossesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobial agent
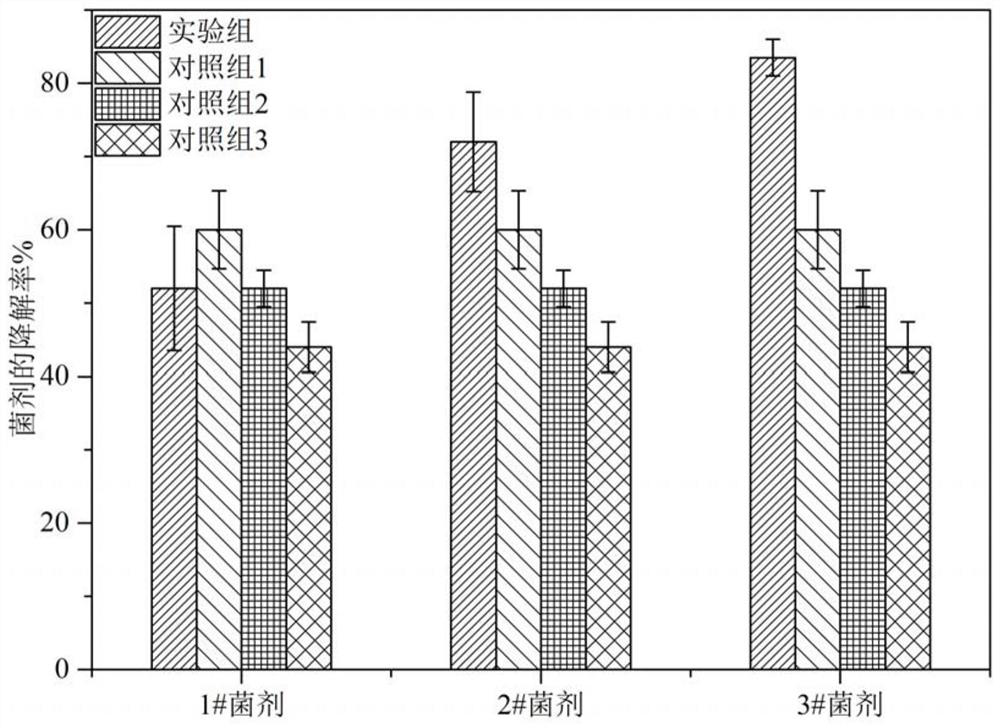
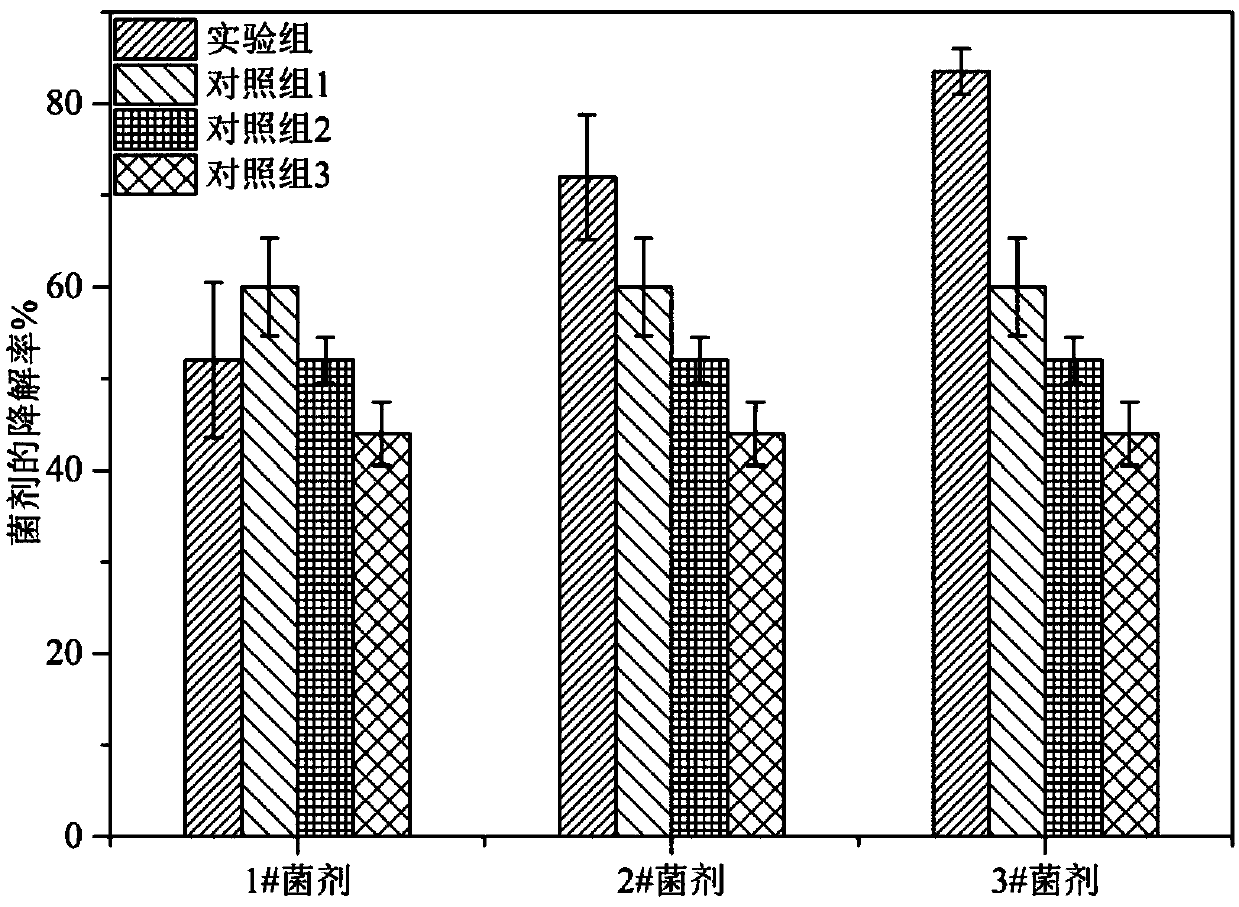
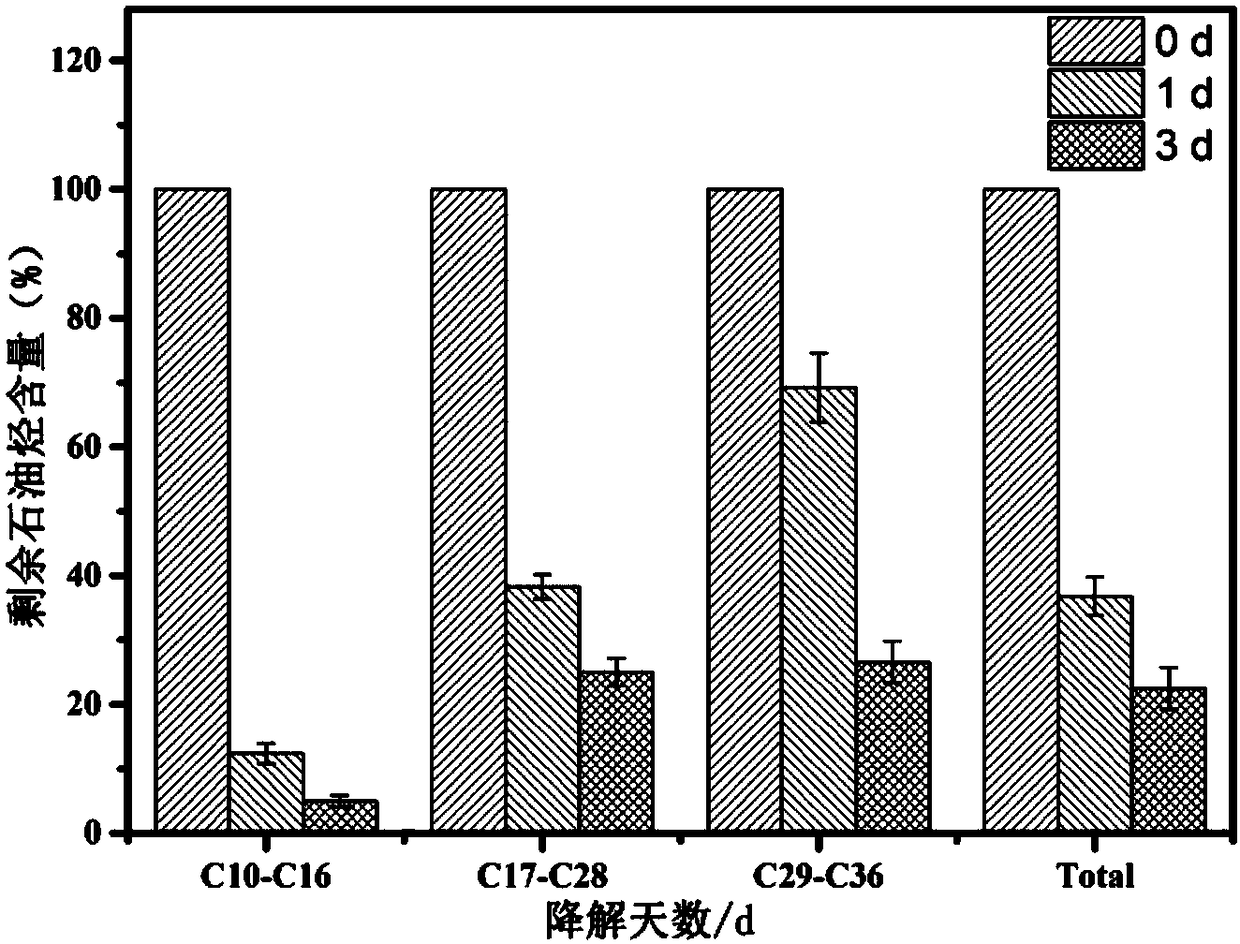
The invention relates to a biochar-based immobilized microbial agent, a preparation method and application thereof. The biochar-based immobilized microbial agent includes a biochar-based material, a bacterial body adsorbed on the biochar-based materialand a nutrient, the bacterial bodyis mycobacterium sp. CSC-6, and is deposited at the China Center for Type Culture Collection on 2017 November 27,and a deposit number isCCTCC No. M 2017726. The biochar-based immobilized microbial agent is used for degrading a petroleum. Compared with the prior art, the microbial agent prepared by a method of immobilizing an adsorbent andthe nutrient has a higher degradation ability to petroleum hydrocarbons, a degradation rate canreach 83.5%after degradingsewage containing 1.0 wt% of the petroleum for 7 days, the agent has large increase compared with the degradation rate of 52.0% of simple bacteria, and the biochar-based immobilized microbial agentis more conducive to the preservation of active bacteria.
Owner:YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
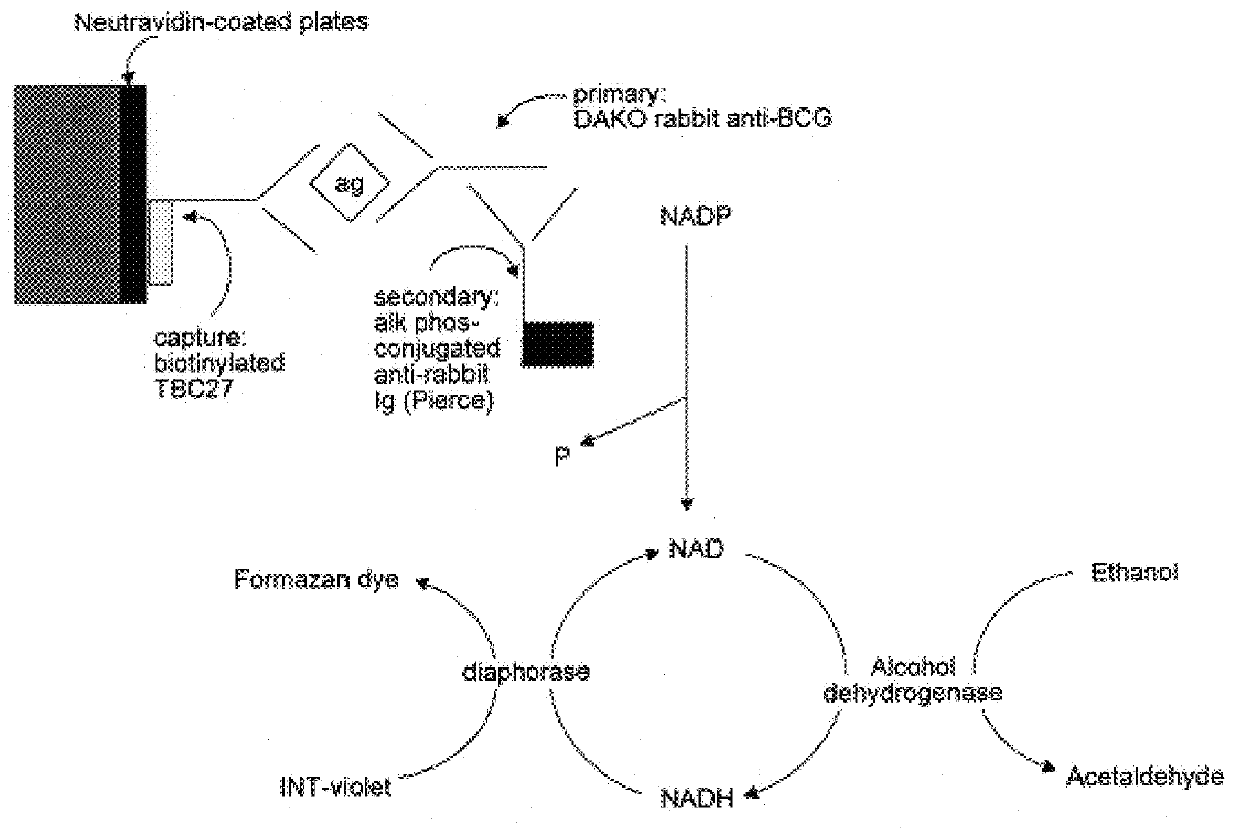
Detection of mycobacteria
InactiveUS6383763B1Rapid assessmentLess sensitiveAntibody ingredientsBiological testingMicrobiologyGenus
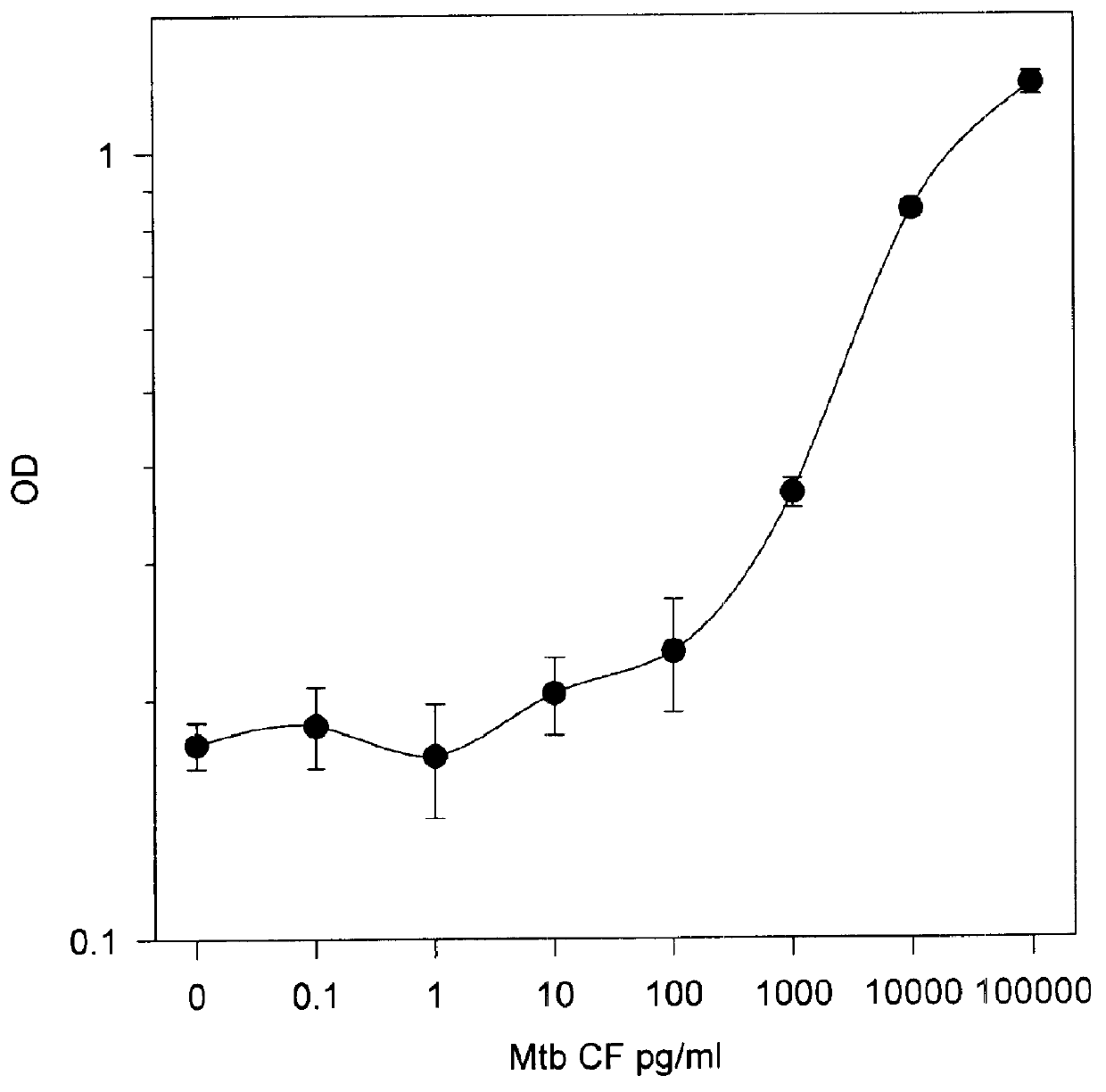
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for the detection of infection and disease due to members of the genus Mycobacterium. In particular, the present invention is well-suited to the detection and identification of patients with disease or infection due to M. tuberculosis or MAC.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Petroleum degrading bacterium, obtaining method and application thereof in crude oil degradation
ActiveCN108300674AImprove degradation efficiencyFast degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention relates to a petroleum degrading bacterium and an application thereof in crude oil degradation. The petroleum degrading bacterium is named as Mycobacterium sp.CSC-6, and is a Gram-negative bacterium. The bacterial strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) in Nov. 27th, 2017. The preservation number is CCTCC No. M2017726. The bacterial strain is in a rodshape, has a light yellow color, and is opaque. After 48 hour culture, the diameter of the bacterial colony is 9.0-11.0 mm. The log-in number of the 16Sr DNA of the bacterial strain in GeneBank is MG490974.1. Compared with the prior art, the provided bacterial strain has high degradation efficiency, can well degrade short chain hydrocarbons, middle chain hydrocarbons, and long chain hydrocarbons,and is capable of completely degrading middle chain hydrocarbons and long chain hydrocarbons in crude oil, and at the same time, the degradation speed is quick.
Owner:YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Method for simultaneously removing USEPA PAHs in plant bodies by utilizing compound PAHs degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107306532AEfficient removalEfficient degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAcenaphthyleneFluoranthene
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously removing USEPA PAHs in plant bodies by utilizing compound PAHs degrading bacteria. Multiple functional bacteria are prepared into a microbial compound functional fungicide, a plant absorption promoter, cytokinin 6-BA or KT, auxin 2,4-D and cysteine are added to prepare a degradation agent, then the degradation agent is inoculated in the plant bodies, and the PAHs content in the plant body is reduced; the compound fungicide is prepared from 8 PAHs degrading bacteria different in degradation spectrum, wherein the degrading bacteria are Sphingobiumsp sp. RS1 and RS2, mycobacterium sp. Pyr9, 033, Diaphorobacter sp. Phe15 and Massilia sp. Pn2, Paenibacillus sp. Phe3, Pseudomonas sp. Ph6 respectively. The acenaphthylene, acenaphthene, fluorene, phenanthrene, anthracene, fluoranthene, pyrene, benzo[a] anthracene, benzo[b]fluoranthene, benzo[k]fluoranthene, benzo[a]pyrene, dibenzo[a,h] anthracene, benzo[ghi]indene and [1,2,3-cd] pyrene in each plant body in a contaminated area can be effectively removed and degraded, the removal rate of PAHs is high, and the method has the advantages of high efficiency, environmental protection and easy operation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Double liquid phase fermentation method for degrading plant sterol and preparing androstenedione
InactiveCN103255191AImprove solubilityIncrease the amount of feedMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlant sterolEcological environment
The invention provides a method for preparing androstenedione using a double liquid phase fermentation system by fermenting Mycobacterium sp.DE6823, and aseptic distilled water is selected as a fermentation medium water phase, and rice oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil and peanut oil can be selected as an oil phase, after fermentation conversion, a solution containing androstenedione is obtained, and after condensation, decolouring, filtering, condensation, recrystallization and vacuum drying and other operations, and androstenedione whose purity is above 99% is obtained. Different oil phases can be selected, and the conversion rate of the plant sterol is in the range of 59%-85%. The invention solves the problems that the raw materials of the present androstenedione production technology in our country are limited by season and region, thereby effectively reducing destroy to ecological environment; the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, small environmental pollution, high conversion rate, low production cost, etc., and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:北京明新高科技发展有限公司
Tuberculosis vaccine
Owner:UNIV DE ZARAGOZA
Bacterium capable of degrading herbicide acetochlor and application thereof
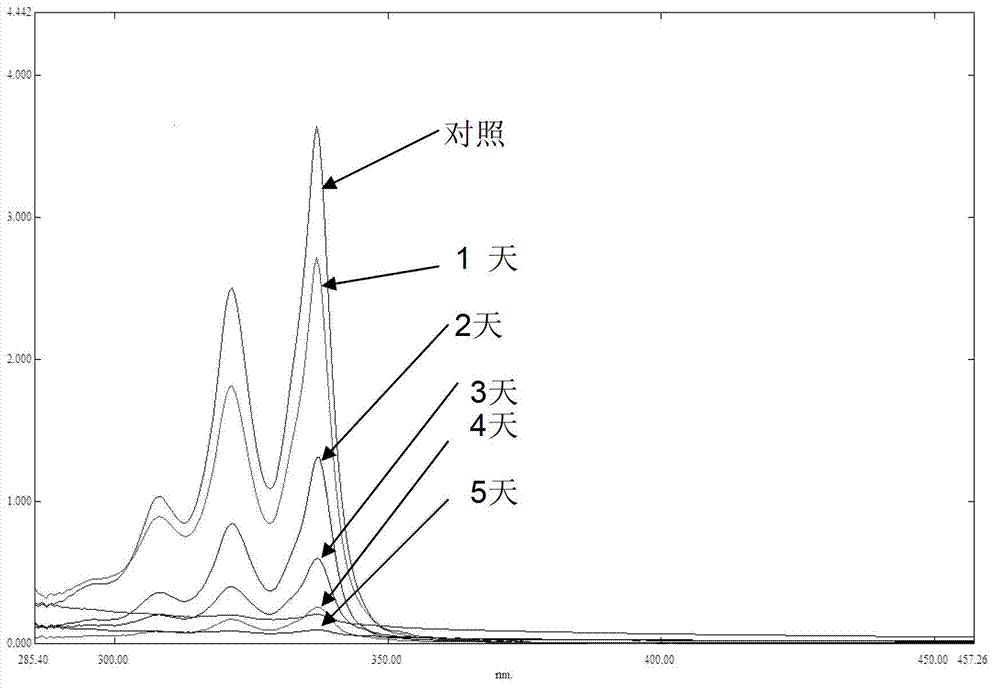
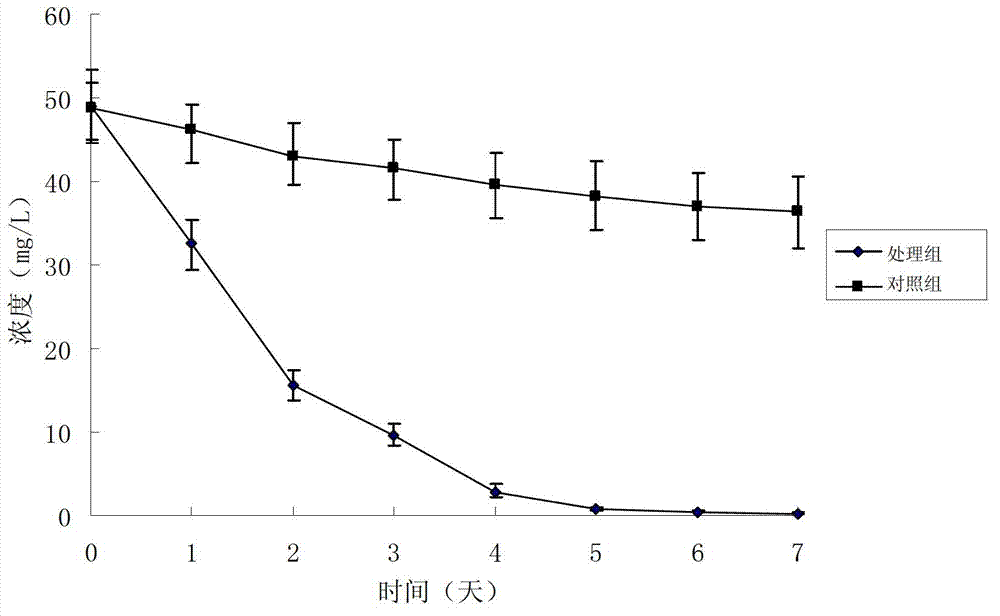
The invention discloses a bacterium capable of degrading herbicide acetochlor and an application of the bacterium. The bacterium is mycobacterium sp. YCA11 and the preservation number of the bacterium is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No. 7771. The mycobacterium sp. YCA11 with the preservation of CGMCC No.7771, disclosed by the invention, has the advantage that the degradation rate of the bacterium to 45mg / L acetochlor is up to 51.86% in 7 days in an inorganic salt culture medium, which indicates that the bacterium is capable of efficiently degrading the acetochlor and has a broad application prospect in the remediation of soil polluted by the acetochlor.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
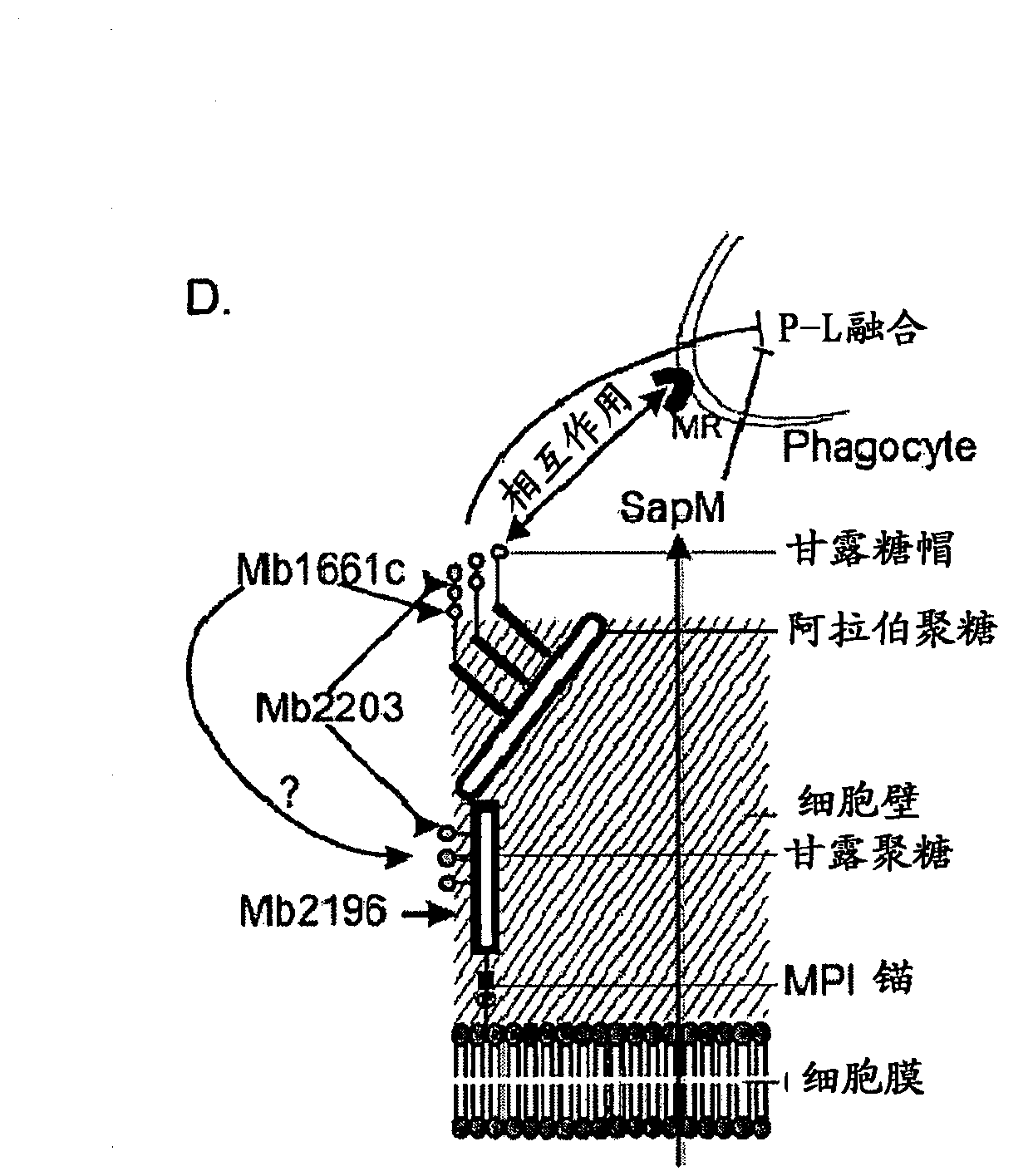
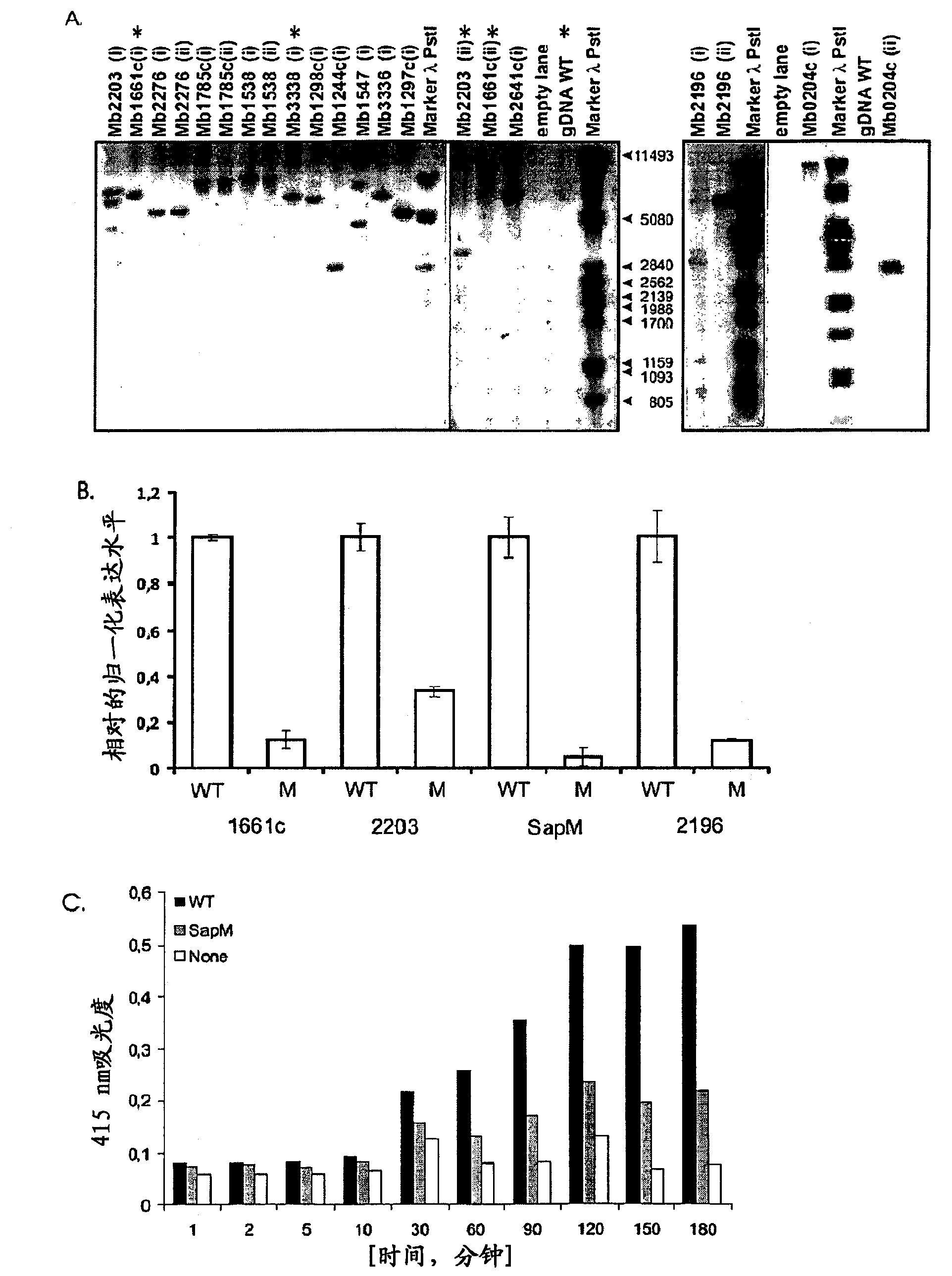
Mycobacterium mutants for vaccines with improved protective efficacy
Tuberculosis (TB) is a major health problem and currently, the only licensed TB vaccine is Mycobacterium bovis Bacille Calmette-Guerin (M. bovis BCG). In the present invention, mutation of mycobacterial components reportedly involved in phagosome maturation inhibition was evaluated for vaccine purposes, as such mutations should result in better vaccine antigen processing and presentation. Thus, BCG mutants in genes coding for ManLAM capping a-1,2-mannosyltransferases and the PI3P phosphatase SapM were evaluated as TB vaccines in a stringent mouse model. Vaccination with both ManLAM capping mutants and the SapM mutant resulted in significantly longer survival as compared to non-vaccinated mice, whereas vaccination with the parental BCG did not. Moreover, mice vaccinated with the SapM mutant survived significantly longer than mice vaccinated with the parental BCG.; The mutant BCG strains showed unaltered phagocytosis, replication, lysosome colocalization and oxidant activity in macrophages and similarly induced autophagy in the latter. Additionally, replication and granuloma formation in mice was unaffected, indicating BCG-equivalent safety of these vaccines.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +2
PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers and method for identifying mycobacterium bovis
InactiveCN102409102ASimple and precise identificationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesNucleotide
The invention provides five pairs of primers and an identification method for PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction) identification of mycobacterium bovis. The five pairs of primers respectively amplify aiming at a 16SrRNA conserved region of mycobacterium bacteria, a mycobacterium tuberculosis complex(MTBC)Rv0577 gene, Rv1970 of a mycobacterium tuberculosis RD7 region, a mycobacterium bovis pncA gene and an RD1 region gene to generate specific amplified fragments, and the nucleotide sequences of the specific amplified fragments are as shown in SEQ ID No.1-5. According to the identification method provided by the invention, the total DNA of a sample is taken as a template, PCR amplification is respectively performed by the five pairs of primers, and the result is judged according to the size of an amplified band. The primers provided by the invention can specifically identify mycobacteria, MTBC, mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium bovis and mycobacterium bovis BCG(Bacillus Calmette-Guerin), and the detection method has good sensitivity and simplicity of method and operation, and can realize quick large-flux detection of mycobacterium bovis.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Double liquid phase fermentation method for preparing androstenedione by degrading plant sterol and
InactiveCN103627769AImprove solubilityIncrease the amount of feedMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlant sterolEcological environment
The invention provides a method for preparing androstenedione using a double liquid phase fermentation system by fermenting mycobacterium sp.DE6823, and aseptic distilled water is selected as a fermentation medium water phase, and rice oil, sunflower oil, soybean oil and peanut oil can be selected as an oil phase, after fermentation conversion, a solution containing androstenedione is obtained by employing a membrane separating method, and after condensation, decolouring, filtering, condensation, recrystallization and vacuum drying and other operations, androstenedione with purity of 99% or more is obtained. Different oil phases can be selected, and the conversion rate of the plant sterol is in the range of 59%-85%. The invention solves the problems that the raw materials of the present androstenedione production technology in our country are limited by season and region, thereby effectively reducing destroy to ecological environment; and the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, small environmental pollution, high conversion rate, low production cost, etc., and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:北京明新高科技发展有限公司
Strain capable of efficiently converting phytosterol and application thereof
InactiveCN106282077AIncrease the amount of feedImprove conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismDiketone
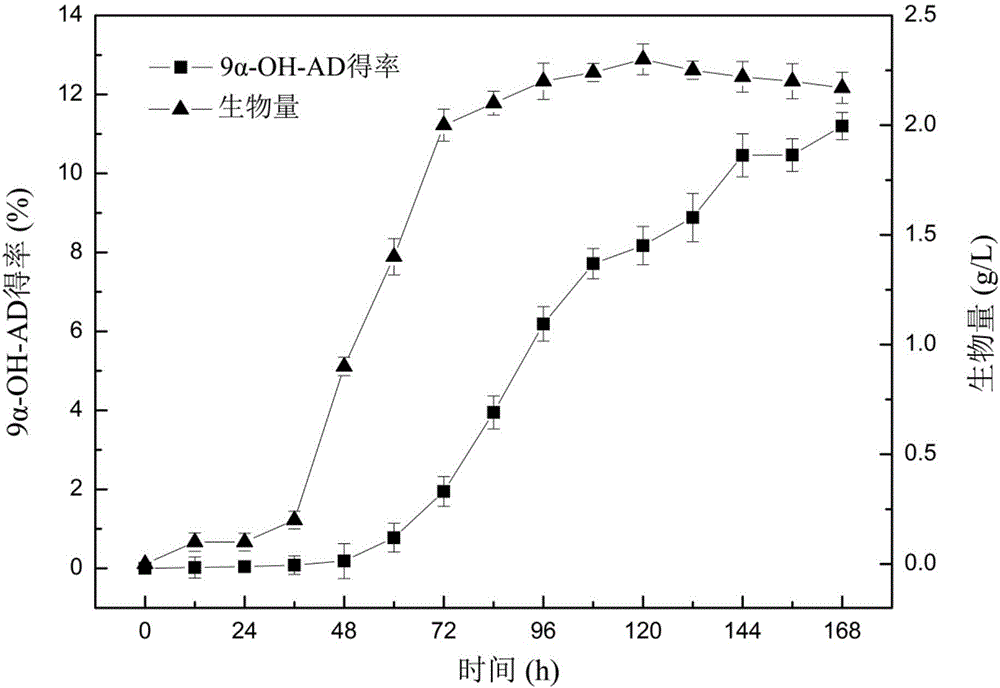
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to mycobacterium sp. LY-1 capable of efficiently converting phytosterol and application thereof. The strain is preserved in the common microorganism center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13031. The mycobacterium sp. LY-1 is capable of converting phytosterol into 9 alpha-hydroxy androstane-4-alkenyl-3,17-diketone, and the product yield is 33% under the condition that the substrate feed amount is 15 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
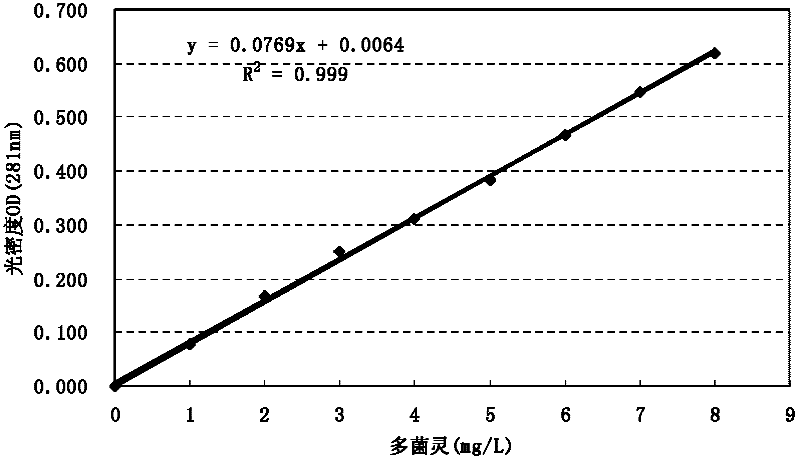
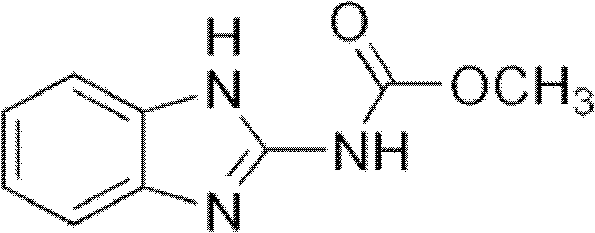
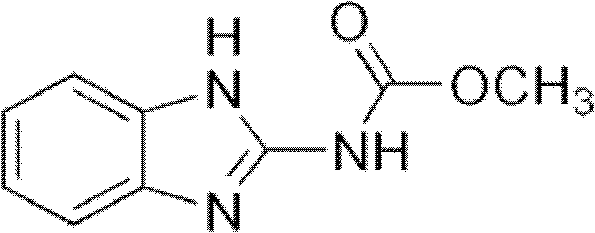
A bacterium for efficiently degrading organic pollutant carbendazim and its application
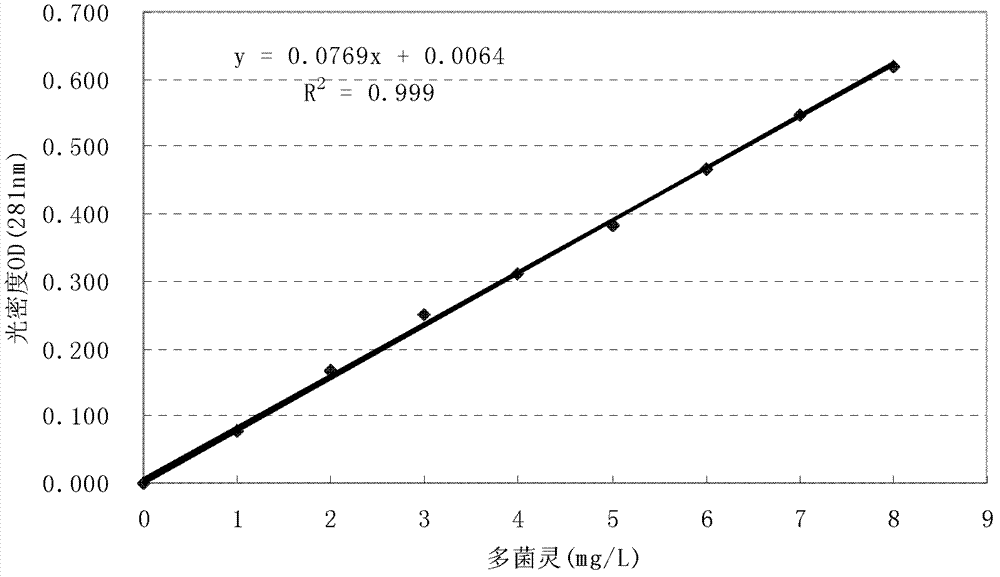
The invention discloses high-efficiency organic pollutant carbendazim degrading bacteria and use thereof. The organic pollutant carbendazim degrading bacteria are (mycobacterium sp.)DJL22, and were collection in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the collection number of organic pollutant carbendazim degrading bacteria is CGMCC No.5041. When the (mycobacterium sp.)DJL22 CGMCC No.5041 is cultured in inorganic salt culture medium for 5 days, the rate of degradation of carbendazim at a concentration of 100mg / L reaches 84.79 percent; and when the (mycobacterium sp.)DJL22CGMCC No.5041 is cultured in inorganic salt culture medium for 15 days, the rate of degradation of carbendazim at a concentration of 600mg / L reaches 62.77 percent. Therefore, the stain can efficiently degrade carbendazim and has a bright application prospect in repairing soil polluted by carbendazim.
Owner:孙建光
Nucleic acid amplification and detection of Mycobacterium species
Oligonucleotides used to prime in vitro nucleic acid amplification of 16S rRNA sequences or DNA encoding 16S rRNA sequences for many species within the genus Mycobacterium are disclosed. Kits including such oligonucleotides are disclosed. Methods of detecting Mycobacterium species using the oligonucleotides in in vitro nucleic acid amplification are disclosed.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC +1
Process for the production of piperidine derivatives with microorganisms
InactiveUS20050038254A1Significant strain improvementSignificant processingFungiOrganic chemistryRhodotorulaRhizopus
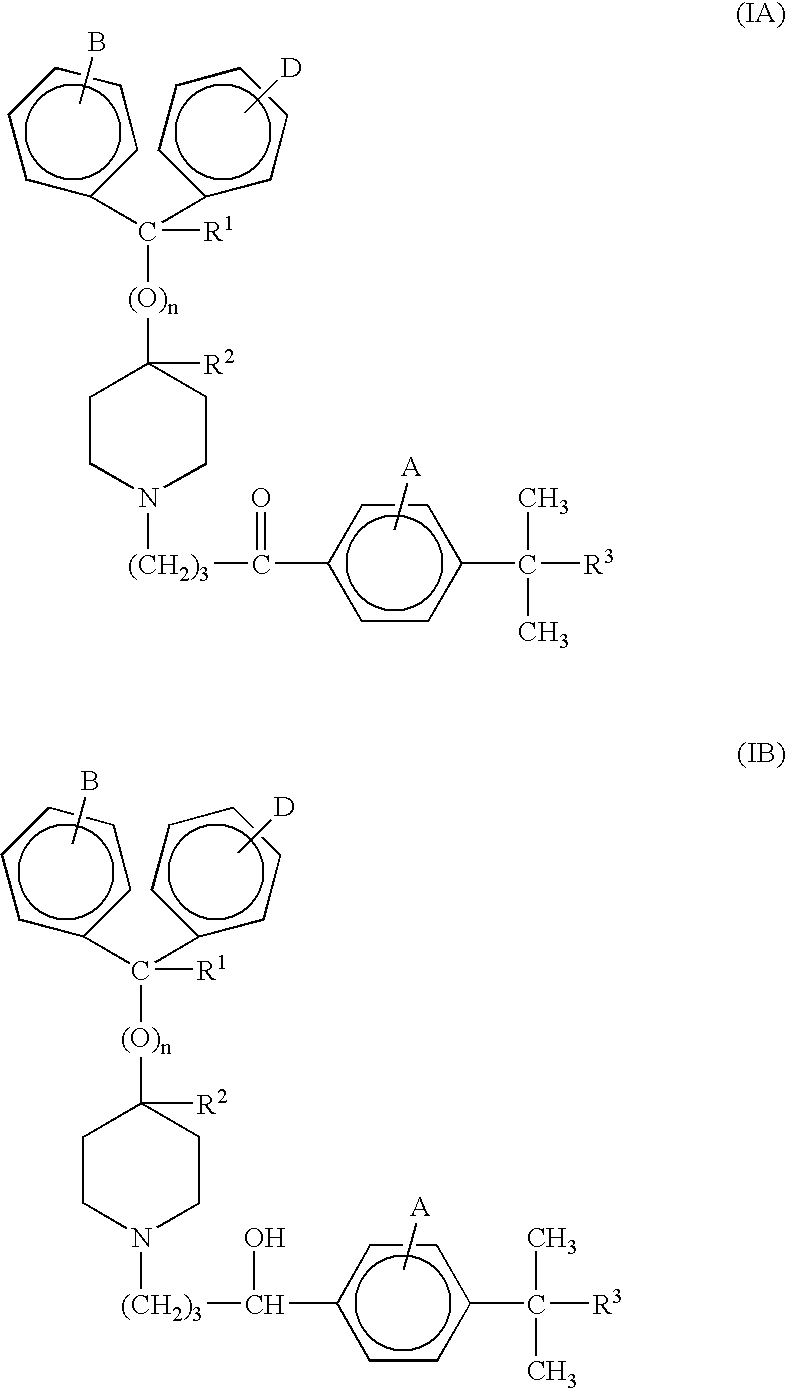
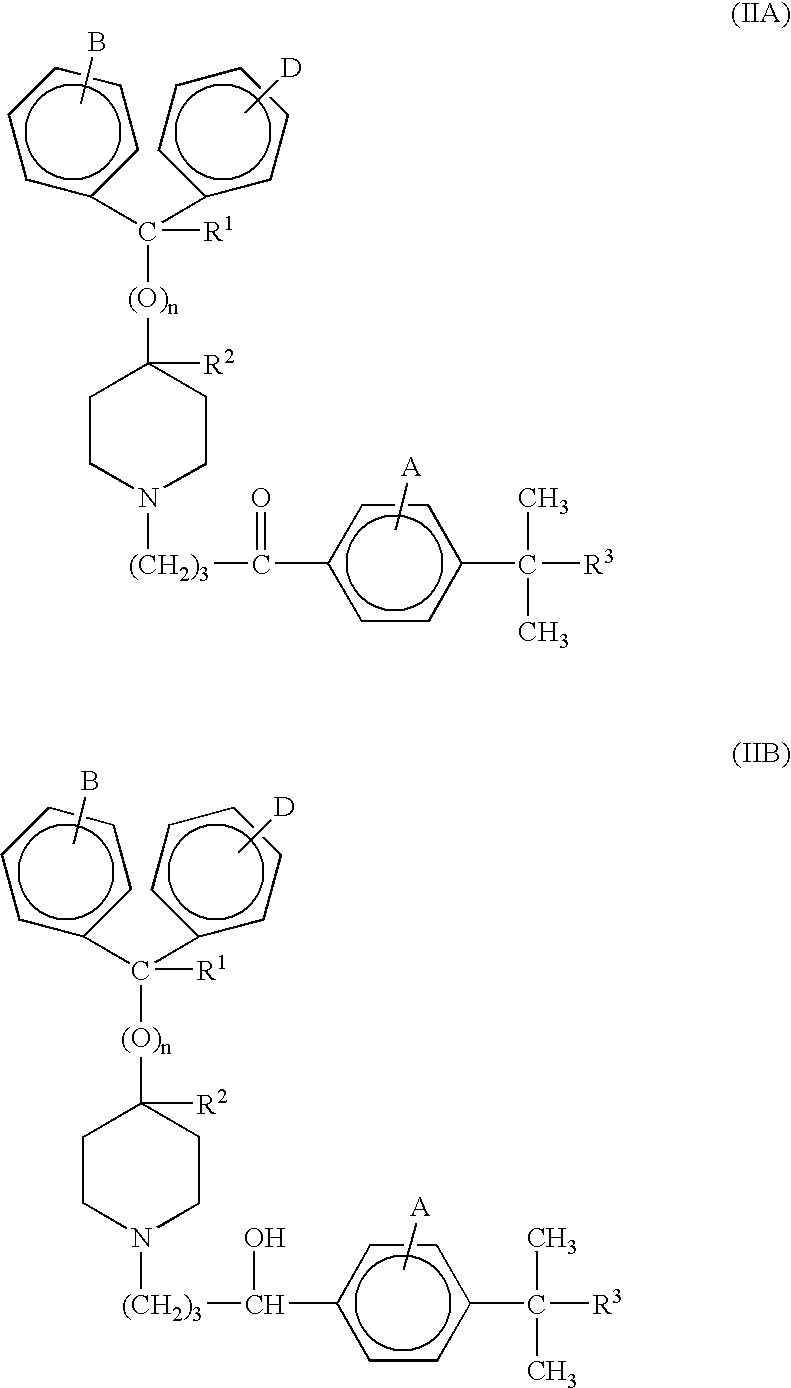
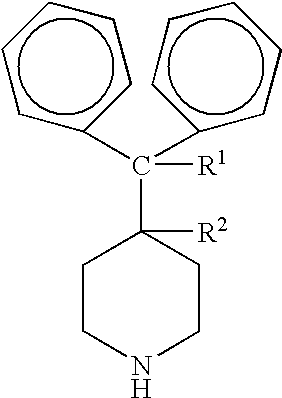
The present invention relates to the production of a product compound having a structure according to Formulae IA and / or IB: wherein n is 0 or 1; R1 is hydrogen or hydroxy; R2 is hydrogen; or, when n is 0, R1 and R2 taken together form a second bond between the carbon atoms bearing R1 and R2, provided that when n is 1, R1 and R2 are each hydrogen; R3 is —COOH or —COOR4; R4 is an alkyl or aryl moiety; A, B, and D are the substituents of their rings, each of which may be different or the same, and are selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogens, alkyl, hydroxy, and alkoxy. This process involves incubating a starting compound having a structure according to Formulae IIA and / or IIB: wherein R3 is —CH3 and R1, R2, A, B, and D are defined above. in the presence of a microorganism under conditions effective to produce the product compound. The microorganism can be from the genus Streptomyces, Stemphylium, Gliocladium, Bacillus, Botrytis, Cyathus, Rhizopus, Pycniodosphora, Pseudomonas, Helicostylum, Aspergillus, Mucor, Gelasinospora, Rhodotorula, Candida, Mycobacterium, or Penicillium. Alternatively, the microorganism can be Cunninghamella bainieri.
Owner:ALBANY MOLECULAR RESEARCH INC
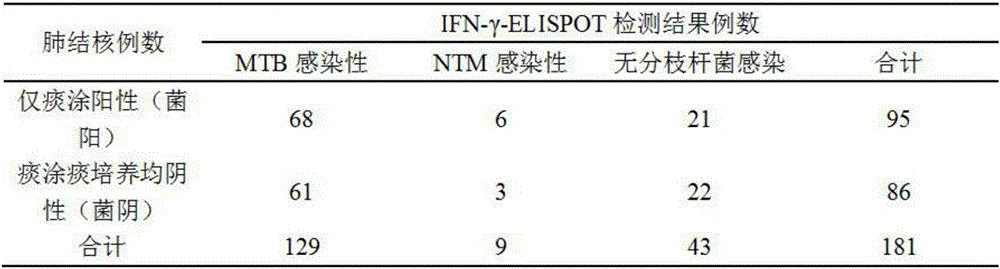
Detection method for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infections
The invention discloses a detection method for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis and non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. The detection method comprises the following steps: respectively contacting the specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis and the specific antigen of mycobacterium with a to-be-detected in-vitro T cell, and detecting a cell factor released by the T cell; comparing the detection results of the specific antigen of mycobacterium tuberculosis and the specific antigen of mycobacterium; judging that the to-be-detected in-vitro T cell is suffered from mycobacterium tuberculosis infection or non-mycobacterium tuberculosis infection according to a comparison result. According to the detection method provided by the invention, the specific antigen of mycobacterium and the ELISPOT detection method for detecting the specificity of MTB can be combined and utilized to simultaneously identify MTB and NTM infections. The detection method provided by the invention has important guidance significance on clinical diagnosis and drug usage of a doctor.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RHFAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for detecting bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) and kit for the same
InactiveUS20060211014A1Rapidly and conveniently detectingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAcid-fastMicrobiology
An object of the present invention is to provide an oligonucleotide for rapidly and conveniently detecting bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) or for identifying the bacterial species thereof, and a method and kit for detecting bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) using such oligonucleotid. The present invention provides a method for identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which comprises performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction using a primer for nucleic acid amplification that comprises a nucleotide sequence corresponding to a variable region in a 16S rRNA gene sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and has at least 3 continuous nucleotides contained in the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 at the 3′ end.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Mycobacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a mycobacterium and application thereof. The mycobacterium is classified and named as mycobacterium JYC-07, and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on June9th, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO : M 2017325. The strain Mycobacterium sp.JYC capable of converting canrenone into 9alpha-hydroxycarvenone by microorganisms is obtained by screeningand separating from a natural environment, the strain Mycobacterium sp.JYC-07 capable of producing 3-sterone-9alpha hydroxylase at high yield is further obtained through genetic engineering, the strain can efficiently convert canrenone into 9alpha-hydroxycarvenone, the conversion rate is over 90 percent, and the strain has very important significance for expanding the application of steroid raw material drug canrenone and good industrial prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU JIAERKE PHARMA GRP CORP
Nucleic acid amplification and detection of Mycobacterium species
Oligonucleotides used to prime in vitro nucleic acid amplification of 16S rRNA sequences or DNA encoding 16S rRNA sequences for many species within the genus Mycobacterium are disclosed. Kits including such oligonucleotides are disclosed. Methods of detecting Mycobacterium species using the oligonucleotides in in vitro nucleic acid amplification are disclosed.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC +1
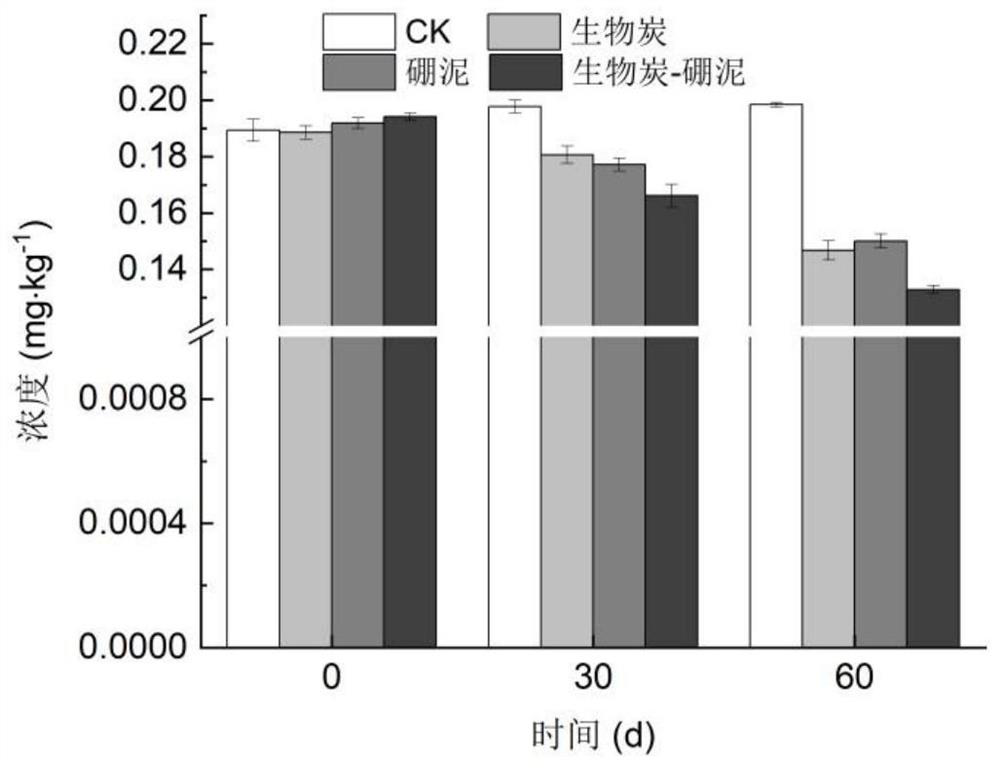
Composite immobilized microbial agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN114807111AImprove degradation ratePromote degradationFungiBacteriaPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicroorganism
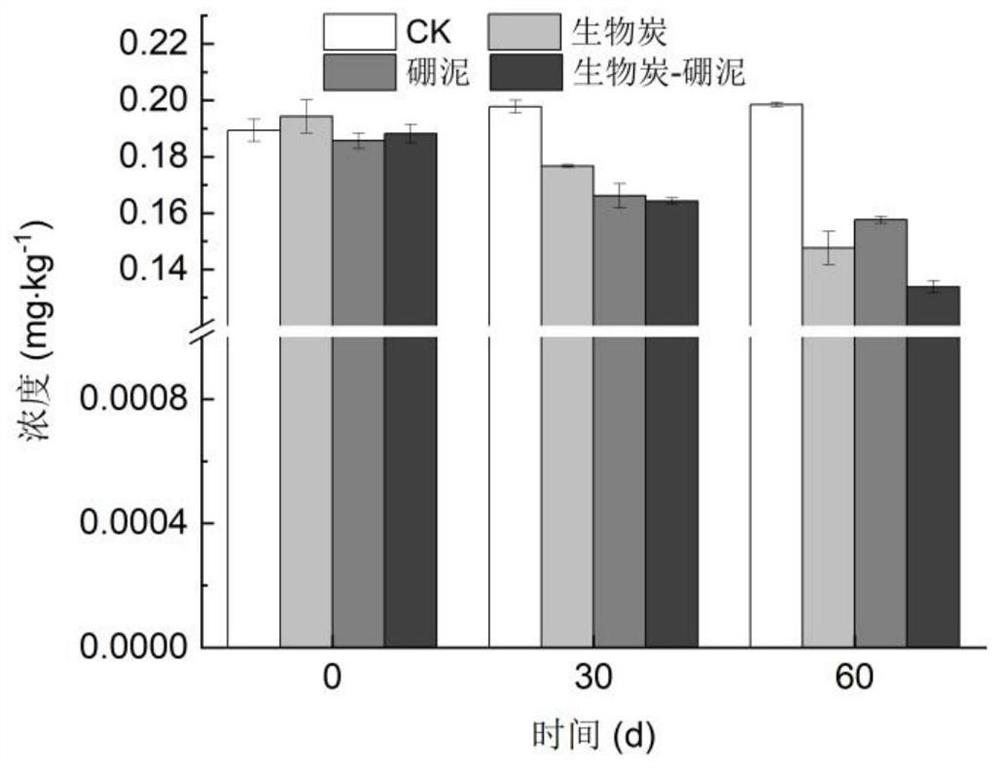
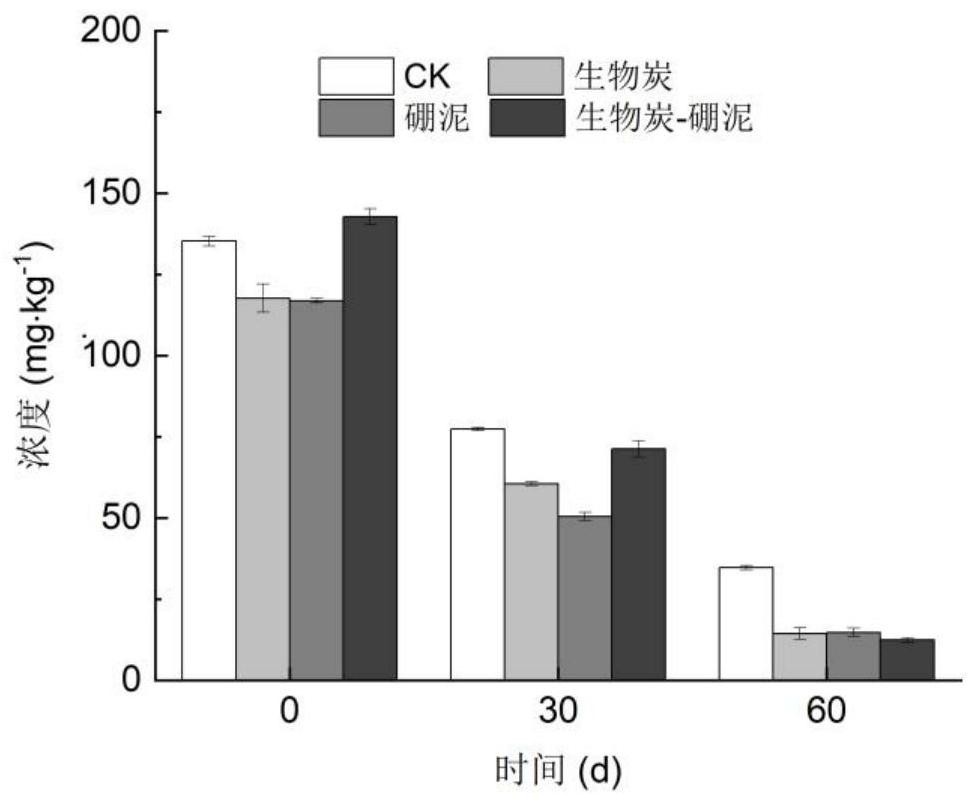
The invention relates to a composite immobilized microbial agent which comprises a composite microbial agent and a composite immobilized carrier, the composite microbial agent comprises a Mucor sp.FMM microbial agent, an Aspergillus niger SF05 microbial agent and a Mycobacterium sp.BFZG microbial agent, and the composite immobilized carrier comprises a composite immobilized carrier and a composite immobilized carrier. The composite immobilized carrier comprises biochar and boric sludge. The composite immobilized microbial agent can be used for promoting remediation of cadmium-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composite contaminated soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
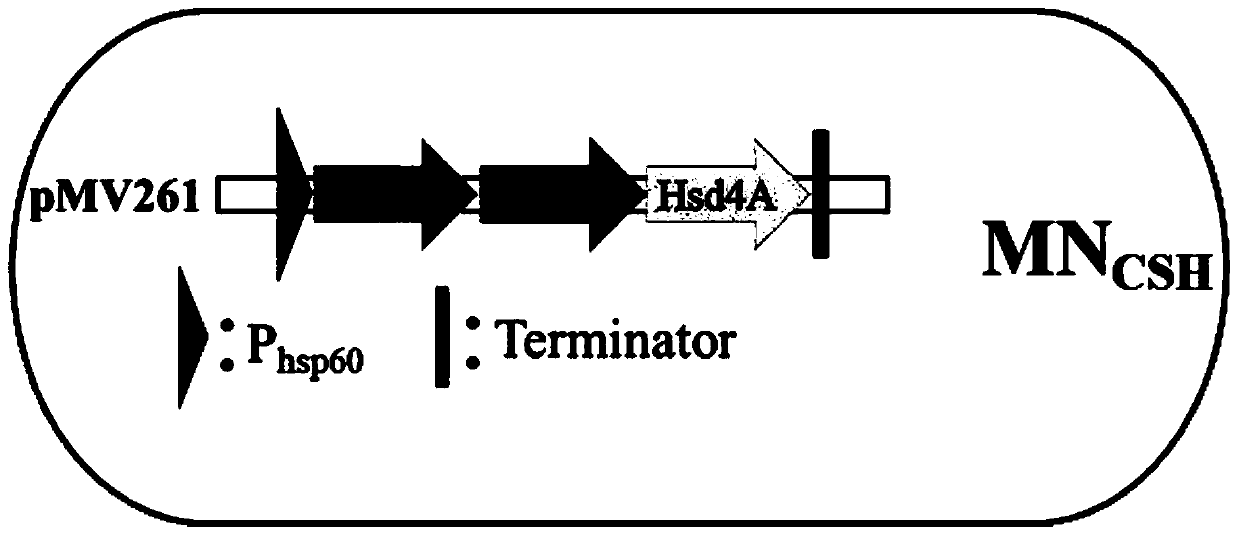
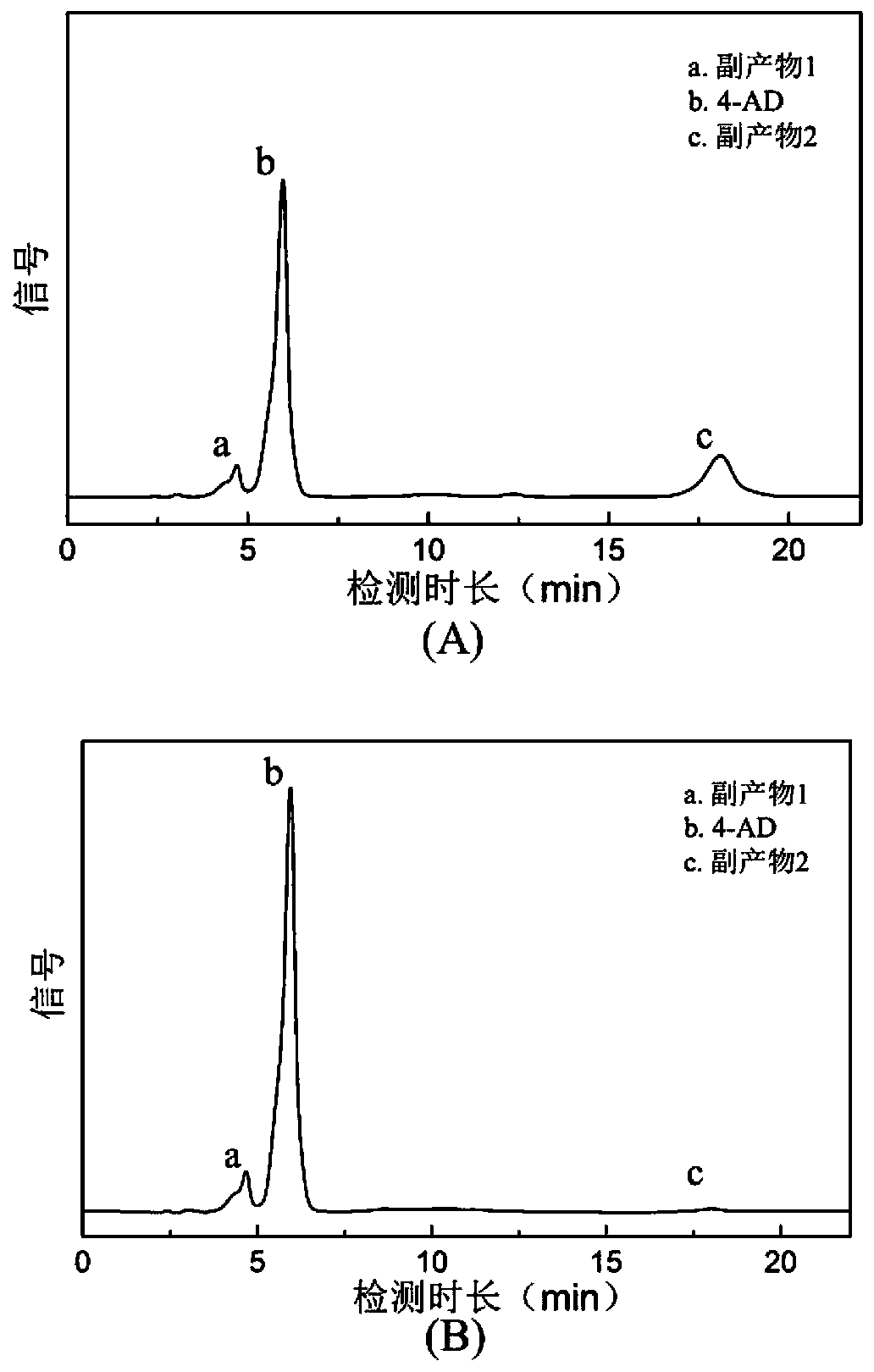
High-androstenedione-producing recombinant mycobacterium and construction method and application of high-androstenedione-producing recombinant mycobacterium
ActiveCN111454871AIncrease productionIncrease metabolic fluxBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCatalytic transformationSterol
The present invention discloses a high-androstenedione-producing recombinant mycobacterium and a construction method and an application of the high-androstenedione-producing recombinant mycobacterium.The construction method is as follows: cholesterol oxidase gene ChoM2, sterone C27 monooxygenase gene Smo2 carrying an RBS fragment and 17[beta]-hydroxysterol dehydrogenase gene Hsd4A carrying an RBSfragment are introduced into mycobacterium sp. CICC 21097 to obtain the high-androstenedione-producing recombinant mycobacterium MNCSH. A fermentation main product of the recombinant strain obtainedby the method is 4-androstenedione, the yield is 90% or more, the selectivity is 90% or more, formation of by-products is reduced and the yield of the androstenedione is increased. Compared with an original strain, the recombinant strain has better catalytic conversion performance and can improve production efficiency, and the processing method is simple and efficient.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
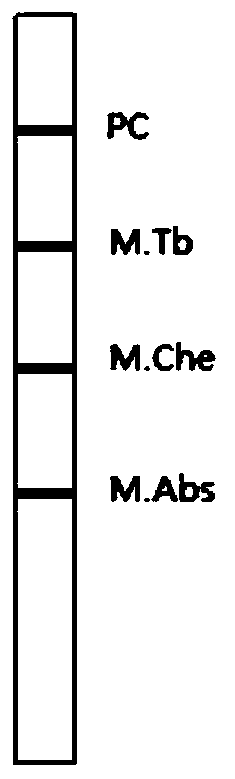
Film strip for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium chelonae, mycobacterium abscessus, and preparation and use methods of film strip
The present invention belongs to the field of microbial gene detection and particularly relates to a film strip for identifying mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium chelonae, mycobacterium abscessus, and preparation and use methods of the film strip. Specific probes comprise base sequences for detecting the mycobacterium tuberculosis in SEQ ID NO.1-2; base sequences for detecting the mycobacterium chelonae in SEQ ID NO.3-4; base sequences for detecting the mycobacterium abscessus in SEQ ID NO.5-6 and mycobacterium quality control probes SEQ ID NO.7-8; and corresponding primer pairs are SEQ ID NO.9-10. The established detection method can rapidly and accurately distinguish the mycobacterium tuberculosis, mycobacterium chelonae and mycobacterium abscessus, can be used as a useful supplementary identification method for a commercialized mycobacterium strain identification kit, and has good clinical application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN HAIHE HOSPITAL
Primer composition for detecting mycobacterium sp. and the detection method
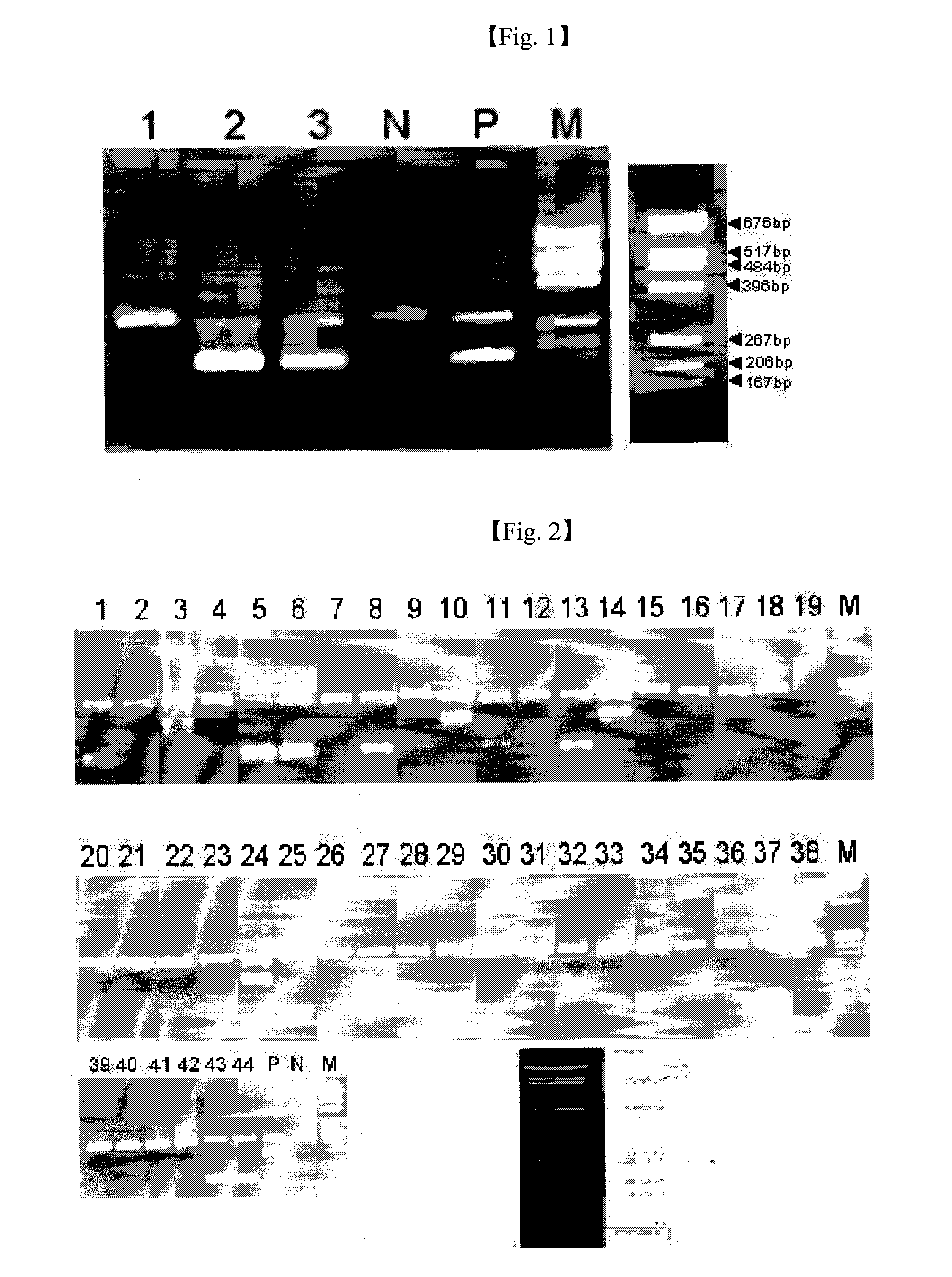
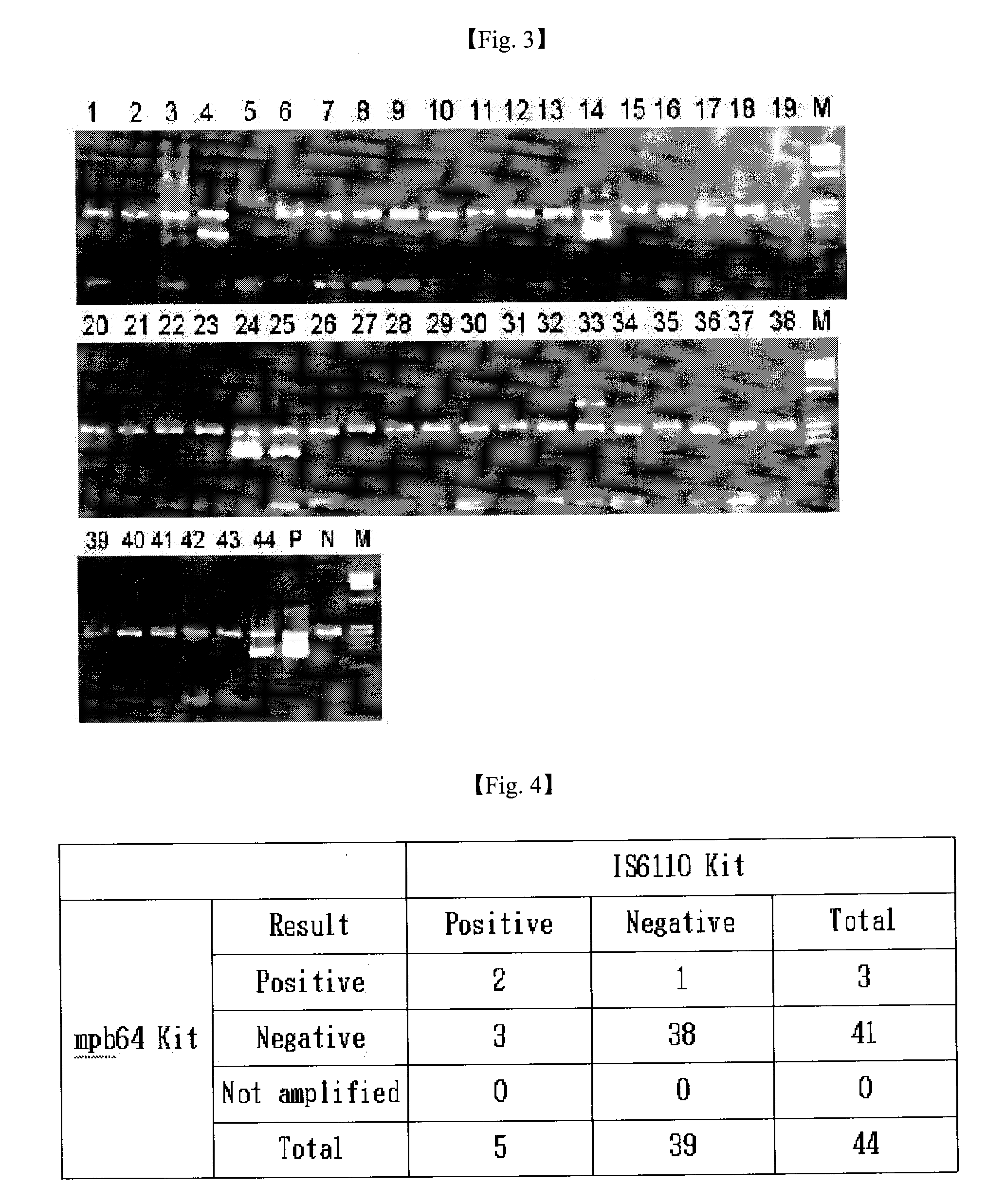
InactiveUS20090136923A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMycobacterium spPcr method
Disclosed are a primer composition including two pairs of primers targeting one gene (mpb64) concerning Mycobacterium sp., and a pair of primers targeting a human-derived gene (HLA-DR); and a method for detecting Mycobacterium sp. using a multiplex one-tube nested PCR method in which their primers are used to amplify two genes in one tube at the same time. The method of the present invention may provide a useful guide post capable of clinically diagnosing Mycobacterium sp. in a specimen in a more specific, rapid and convenient manner.
Owner:BIOCORE
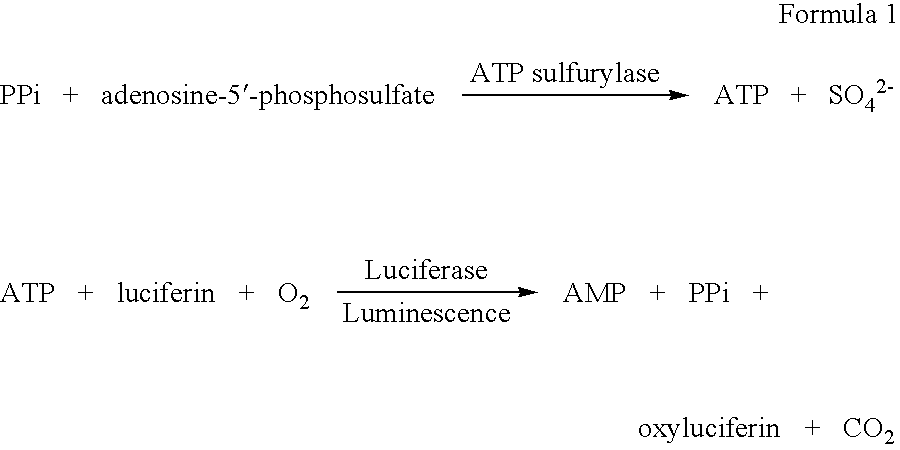
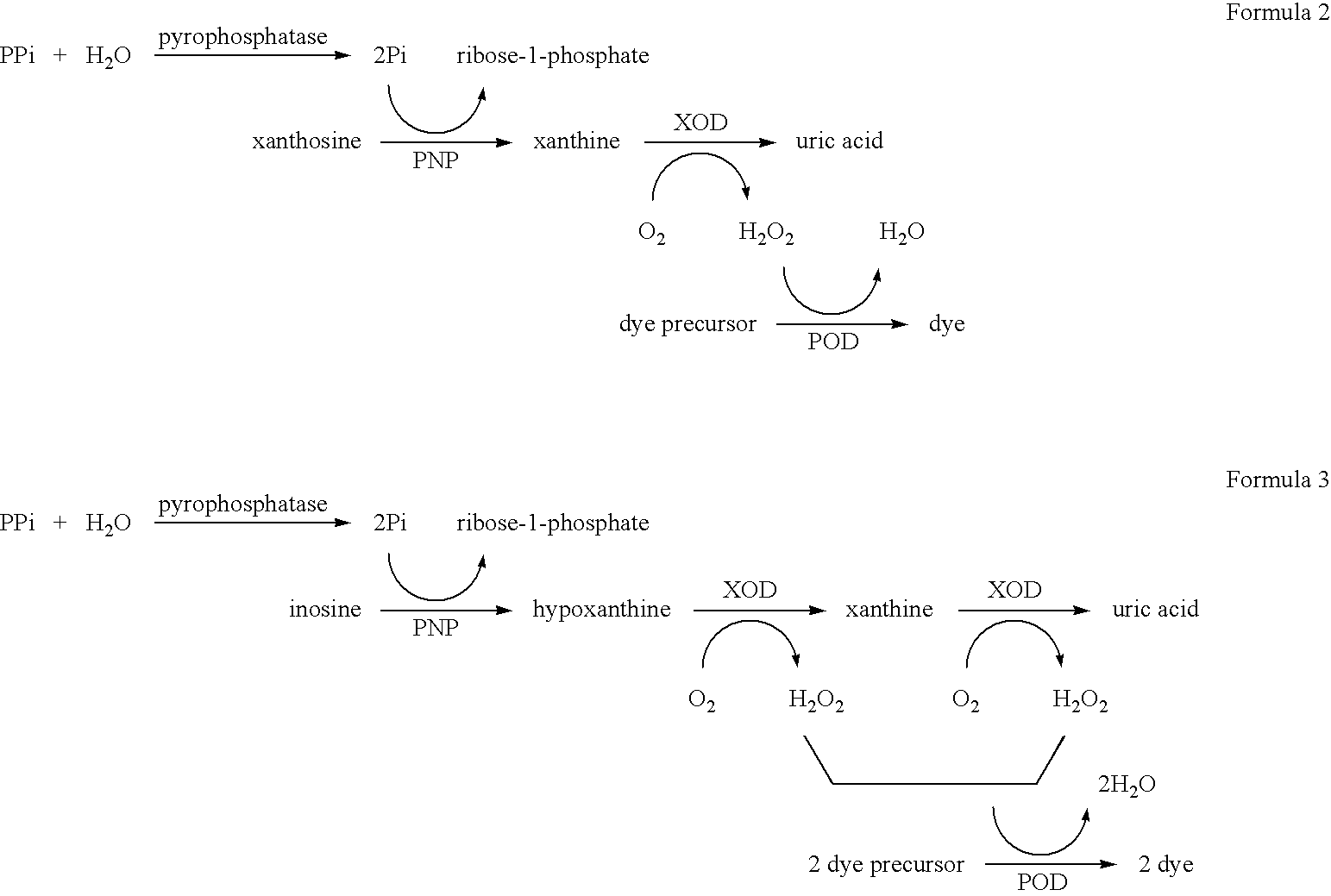
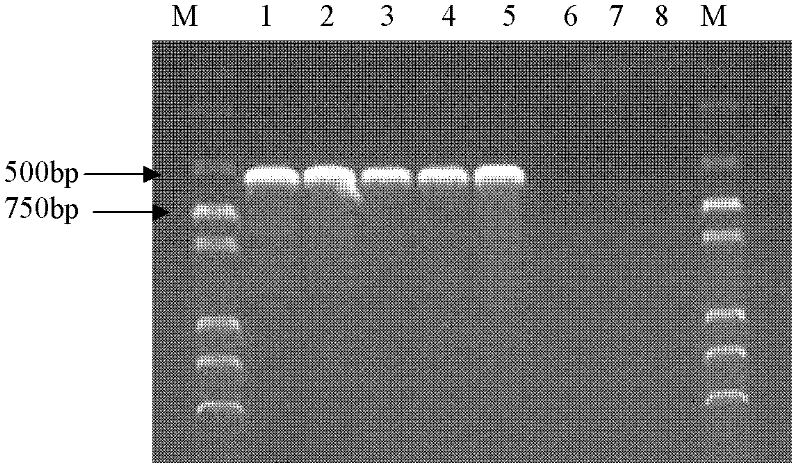
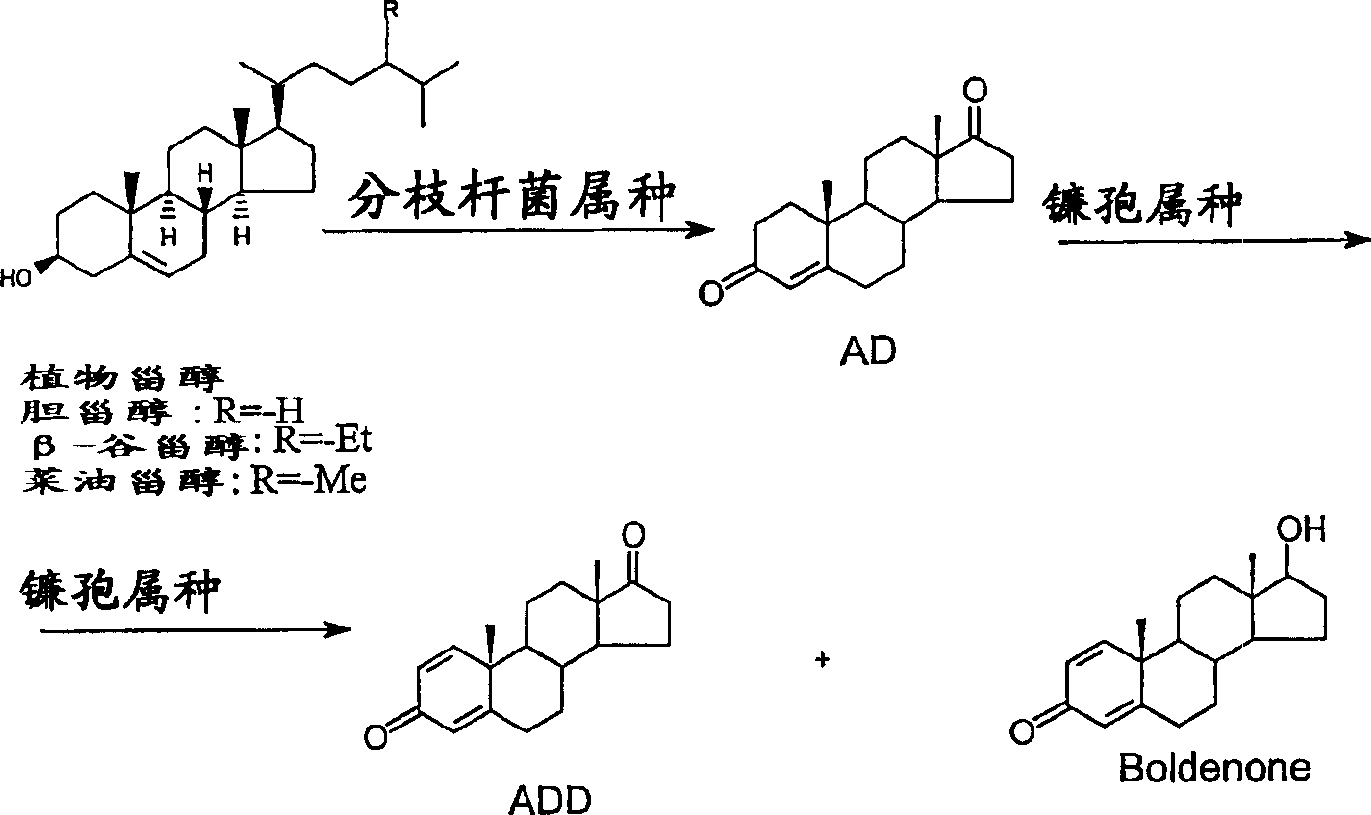
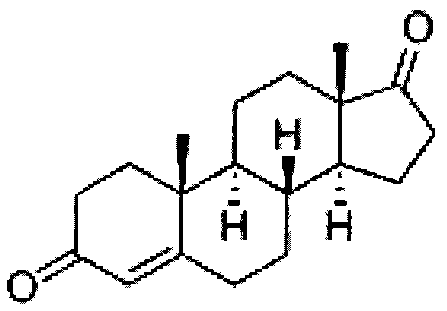
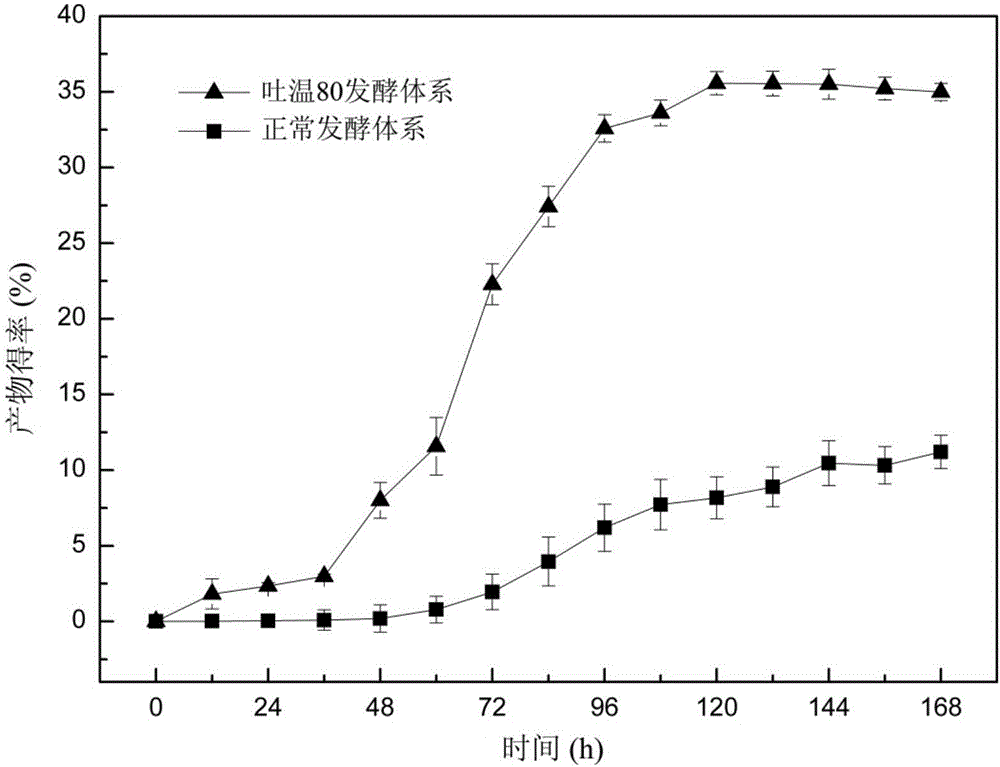
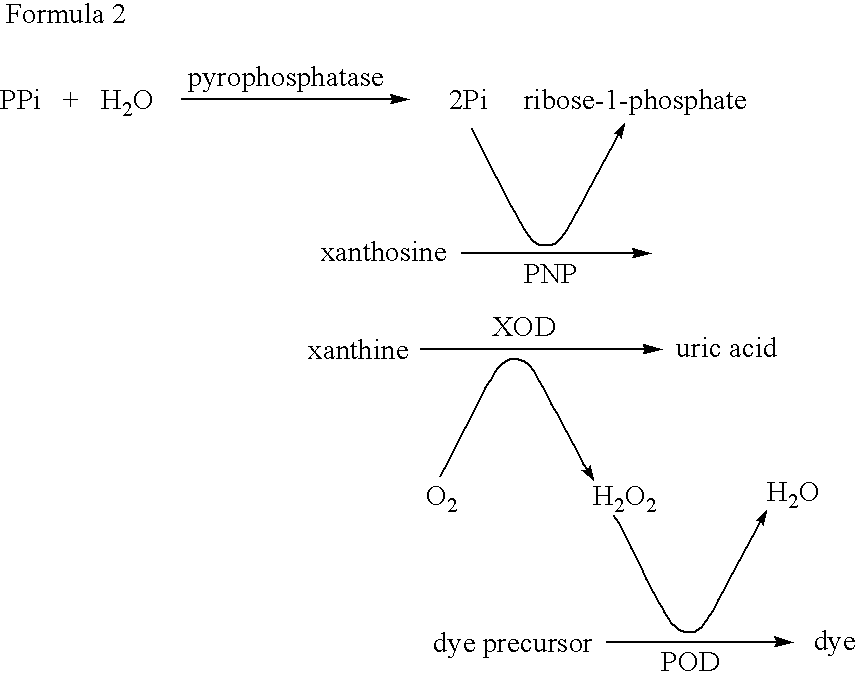
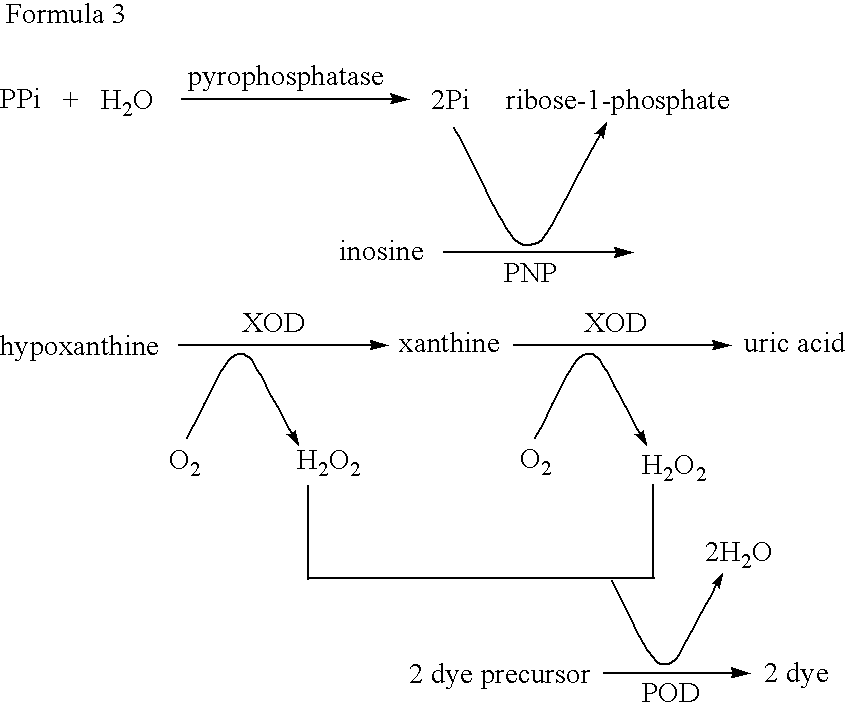
17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant
ActiveCN112592904AIncrease enzyme activityAchieve conversionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousEnzyme Gene
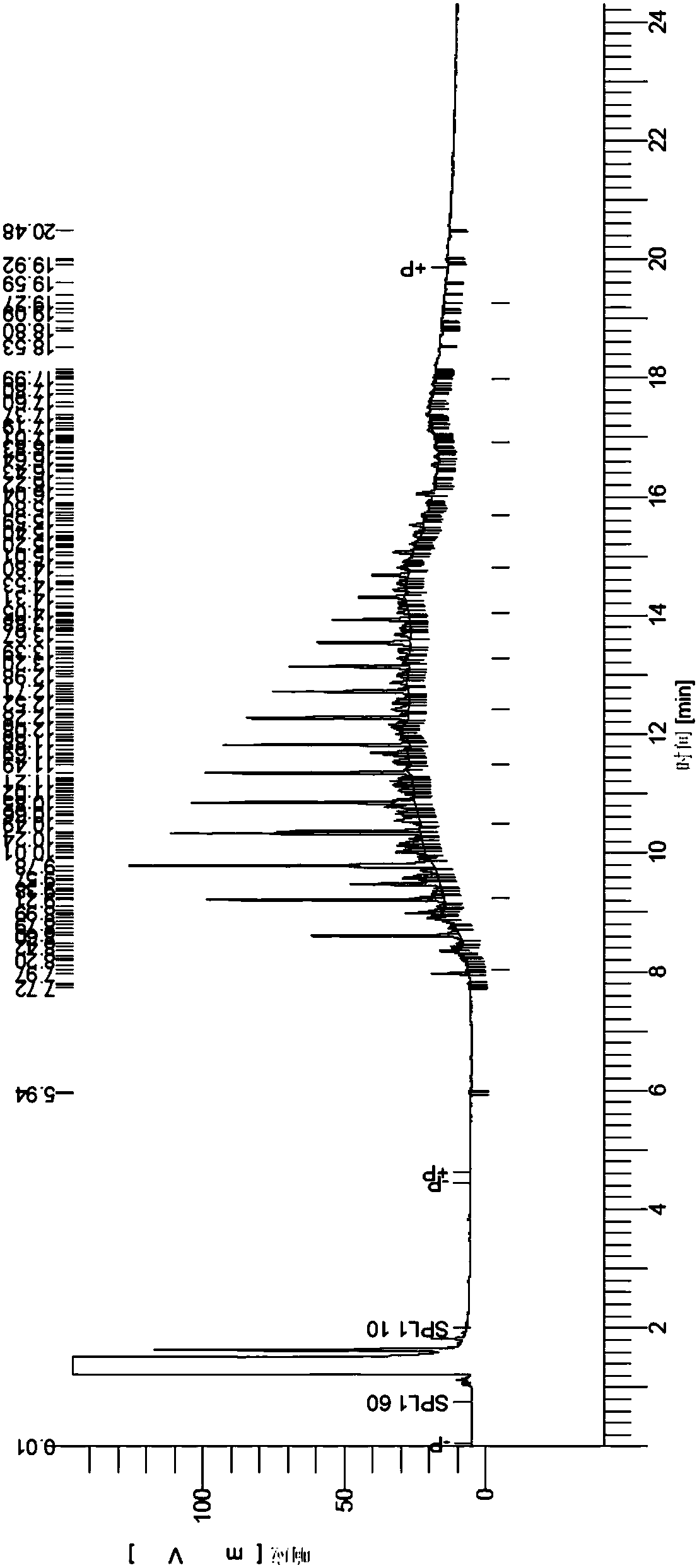
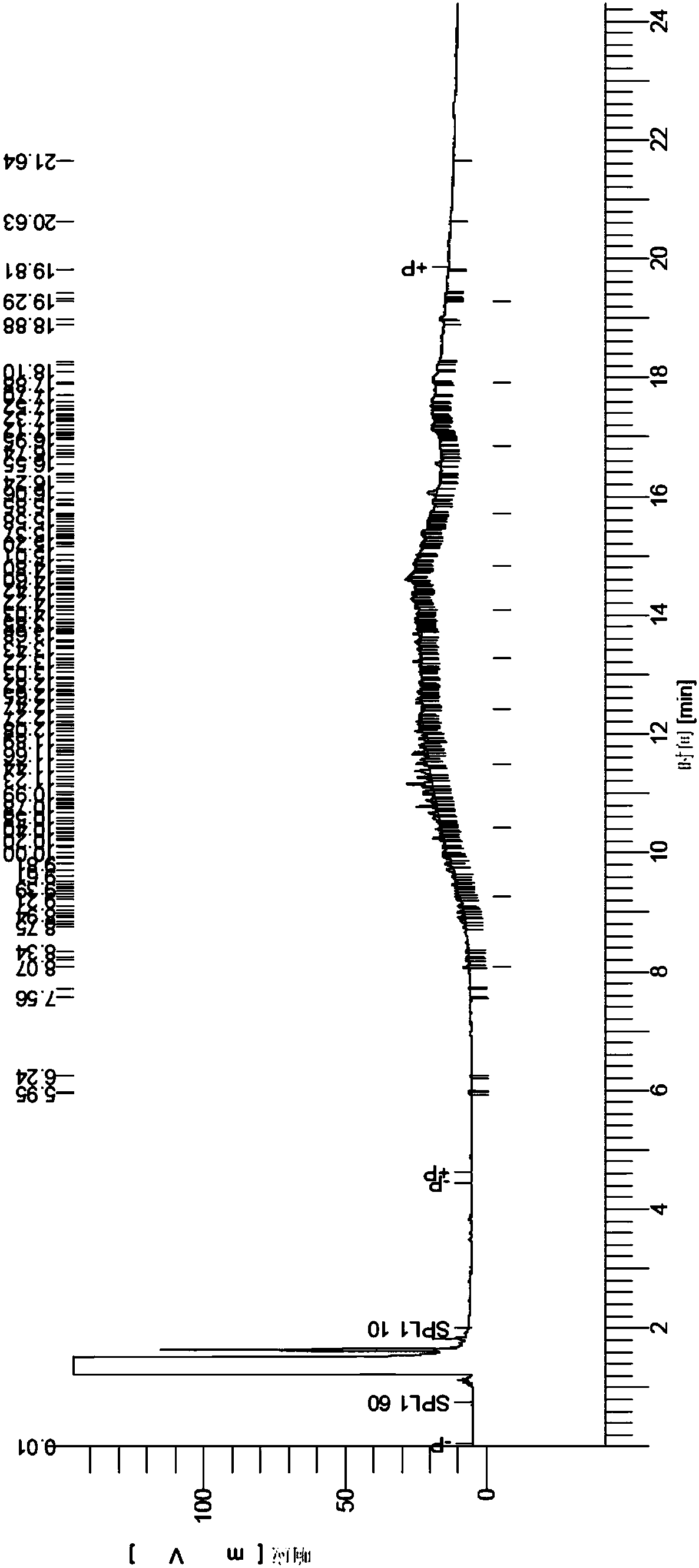
The invention discloses a 17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of the mutant, and belongs to the field of enzyme gene engineering and enzyme engineering. The invention provides actinomycete 17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 17[beta]-HSDy1 from mycobacterium sp. LY-1 and a gene sequence of the 17[beta]-HSDy1. By taking pMA5 as an expression plasmid and bacillus subtilis WB600 as an expression host, heterogenous expression of the 17[beta]-HSDy1 of the mycobacterium sp. LY-1 is realized. A key T239 site of the dehydrogenase obtained throughsoftware simulation is mutated into tyrosine, and the enzyme activity is improved by 19.2% and reaches 9571.77 U.mg<1>. An enzyme activity-growth curve of recombinant bacillus subtilis WB600-pMA5-17[beta]HSDy1-T239Y obtained by mutation is measured, and the specific enzyme activity of the recombinant bacillus subtilis WB600-pMA5-17[beta]HSDy1-T239Y reaches the maximum after fermentation is performed for 28 hours. The heterologously expressed strain can be used for production of androstane-1,4-ene-3,17-dione converted boldenone, and has potential industrial application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting bacteria of the genus mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) and kit for the same
InactiveUS20090023141A1Rapidly and conveniently detectingMicrobiological testing/measurementAcid-fastMicrobiology
An object of the present invention is to provide an oligonucleotide for rapidly and conveniently detecting bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) or for identifying the bacterial species thereof, and a method and kit for detecting bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium (acid-fast bacteria) using such oligonucleotid. The present invention provides a method for identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which comprises performing a nucleic acid amplification reaction using a primer for nucleic acid amplification that comprises a nucleotide sequence corresponding to a variable region in a 16S rRNA gene sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and has at least 3 continuous nucleotides contained in the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 at the 3′ end.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
A biochar-based immobilized microbial agent and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109628353BPromote degradationReduce lossesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a biochar-based immobilized microbial bacterial agent, a preparation method and application thereof. Biochar-based immobilized microbial bacterial agents include biochar-based materials, and bacterium and nutrients adsorbed on biochar-based materials. The bacterium is mycobacterium CSC-6 (Mycobacterium sp.CSC-6), in 2017 It was deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on November 27, and its deposit number is: CCTCC No.M 2017726. The biochar-based immobilized microbial bacterial agent is used for degrading petroleum. Compared with the prior art, the bacterial agent prepared by the method of fixing and adsorbing bacterial agent + nutrient in the present invention has a higher degradation ability to petroleum hydrocarbons, and after 7 days of degrading sewage containing 1.0wt% petroleum, the degradation rate can reach 83.5% %, compared with the degradation rate of 52.0% of the simple bacterial agent, it has a greater improvement. At the same time, the biochar-based immobilized microbial agent is more conducive to the preservation of active bacteria.
Owner:YONKER ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



















![17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant 17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ba68e28d-5840-442c-b947-7c136c5df8e8/HDA0002876088250000011.png)
![17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant 17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ba68e28d-5840-442c-b947-7c136c5df8e8/HDA0002876088250000012.png)
![17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant 17[beta]-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase mutant of mycobacteria and heterologous expression of mutant](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/ba68e28d-5840-442c-b947-7c136c5df8e8/HDA0002876088250000021.png)