Mycobacterium 16F for efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and benzene organic matters and application thereof
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and mycobacteria technology, applied in the fields of environmental biology and microbiology, can solve problems such as being difficult to work, and achieve broad application prospects and the effect of promoting sustainable development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1 Isolation and purification of Mycobacterium sp. 16F capable of degrading multiple polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and monocyclic benzene series organics
[0027] Specific steps are as follows:
[0028] (1) Collect heavily polluted soil samples from the Beijing Coking Plant, pass them through an 8-mesh sieve, and immediately store them in a 4°C refrigerator for later use.
[0029] (2) Add 200 μL of acetone mixed solution with a concentration of 50 g / L pyrene to an open glass bottle with a volume of 500 mL, and place it in a clean bench for 4 hours to remove the acetone, or leave the glass bottle open for 24 hours to air dry naturally.
[0030] (3) Add 200-300mL basal salt medium to the open glass bottle in step (2), stir for 30min at a speed of 120r / min, then add 50g of soil in step (1); Stir at 25-30°C in a shaker with a rotation speed of 120r / min for 14 days for enrichment and acclimatization, then shake evenly and transfer 10ml of the enrichment solution i...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Degradation experiment of embodiment 2 mycobacterium 16F
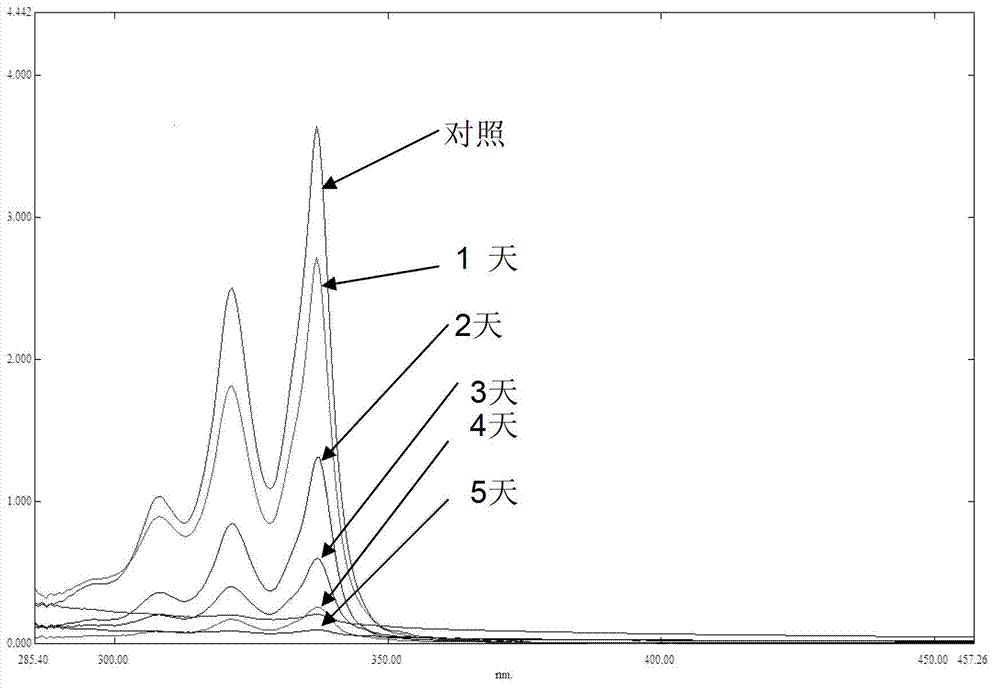
[0039] (1) Add 50g / L pyrene in acetone solution into the sterilized Erlenmeyer flask, completely volatilize the acetone solution in the ultra-clean workbench, then add inorganic salt liquid medium, so that the final concentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons is 100mg / L , insert 1% volume content of Mycobacterium sp.16F bacterial suspension, the control is the blank control without inoculation, 30 ℃, 150rpm dark shaker culture, respectively in 1 day, 2 days, 3 days, 4 days and After 5 days, it was detected by a UV spectrophotometer and a gas phase-mass spectrometer, and the UV scanning diagram is shown in figure 1 , strain 16F can degrade 75% of pyrene with an initial concentration of 100mg / L within 48 hours, and can degrade more than 92% within 5 days.
[0040] Bacterial suspension preparation method: Pick a single colony of the strain Mycobacterium sp.16F and inoculate it in a Erlenmeyer flask filled wi...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 Mycobacterium 16F Degradation Substrate Experiment
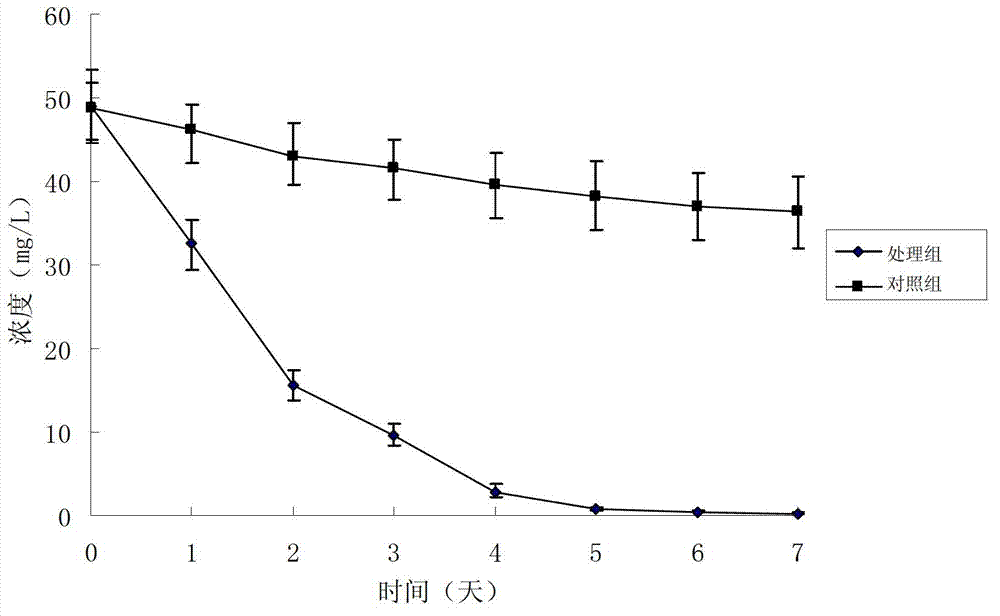
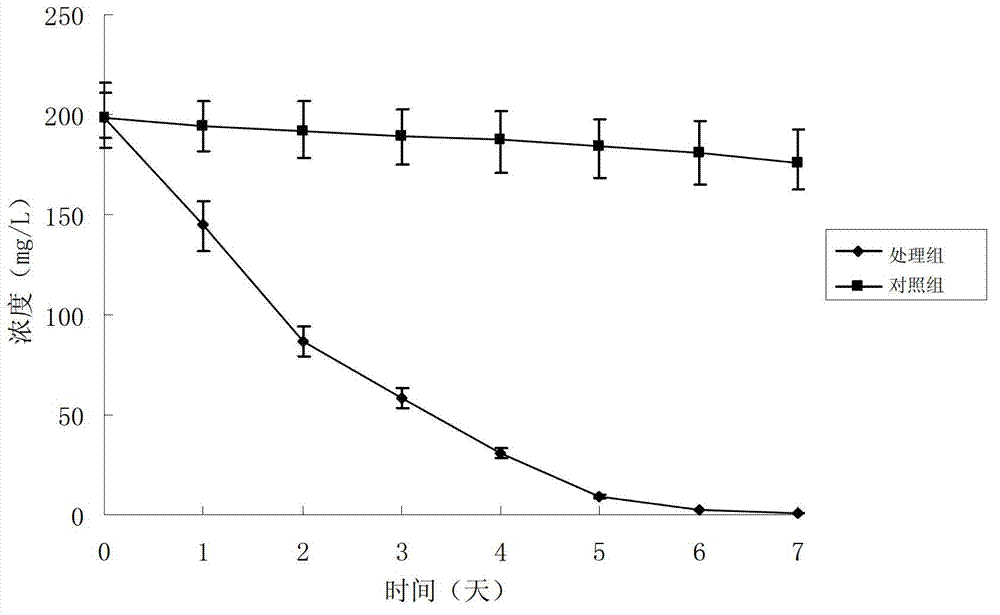
[0047] Inoculate Mycobacterium sp.16F into basal salt medium with different concentrations (50-500mg / L, see Table 1) of salicylic acid, catechol, phenol, benzene, xylene, toluene and other substrates. Substrate blank control (substrate only but no bacteria) was cultured at 150r / min and shaken at 30°C in the dark for 2 days, 4 days and 6 days to measure the biomass and detect the degradation of the substrate. The growth and degradation of Mycobacterium sp.16F are shown in Table 1. The results show that Mycobacterium sp.16F can use a certain concentration of the experimental substrate for growth, reproduction and degradation. Among them, after 4 days of cultivation, it was observed that it was initially solid or oily in the culture. Benzene, xylene, and toluene in the solution disappeared, and all of them were 100% degraded by GC-MS detection. For the tolerance of high-concentration substrates, benzene>toluene...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com