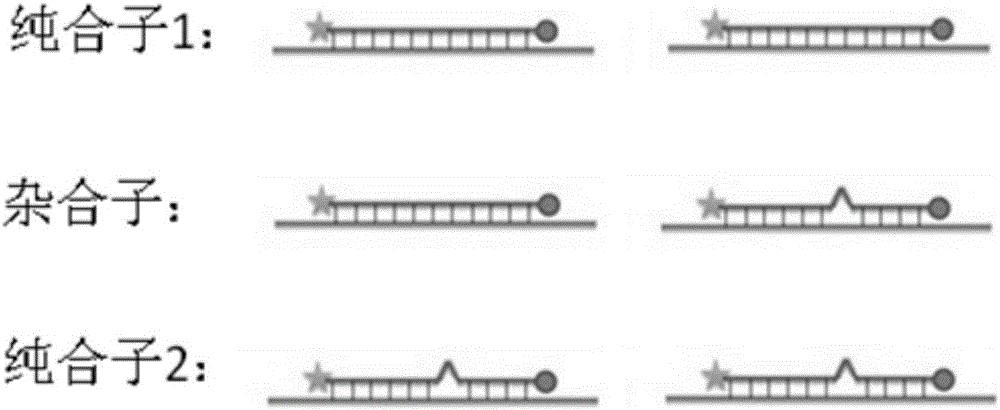
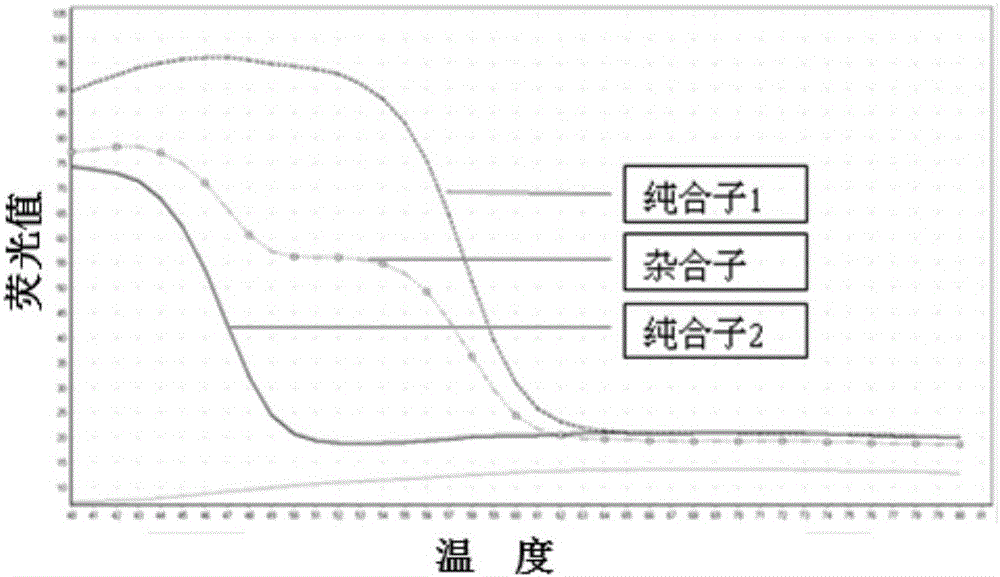
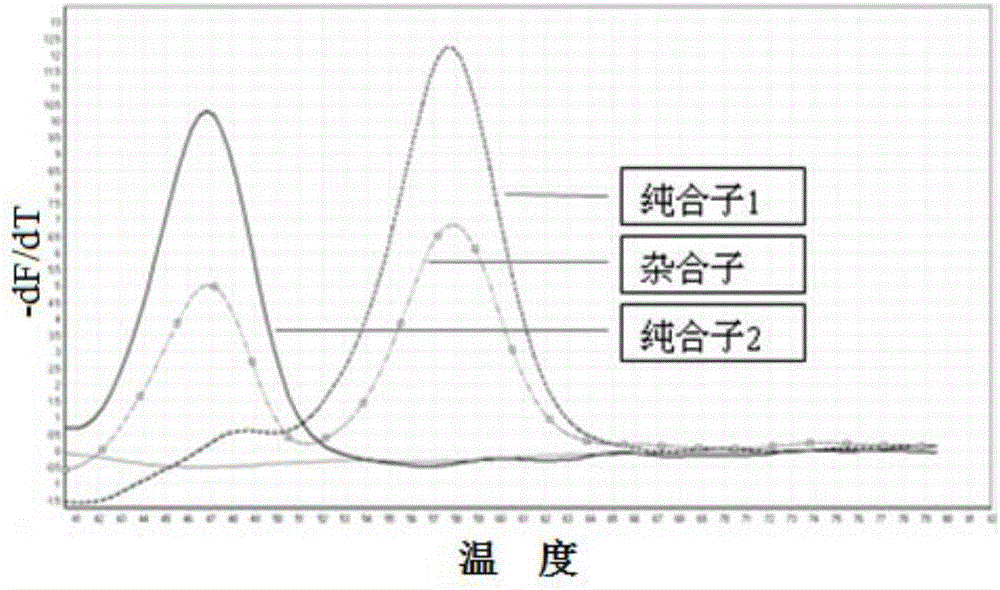
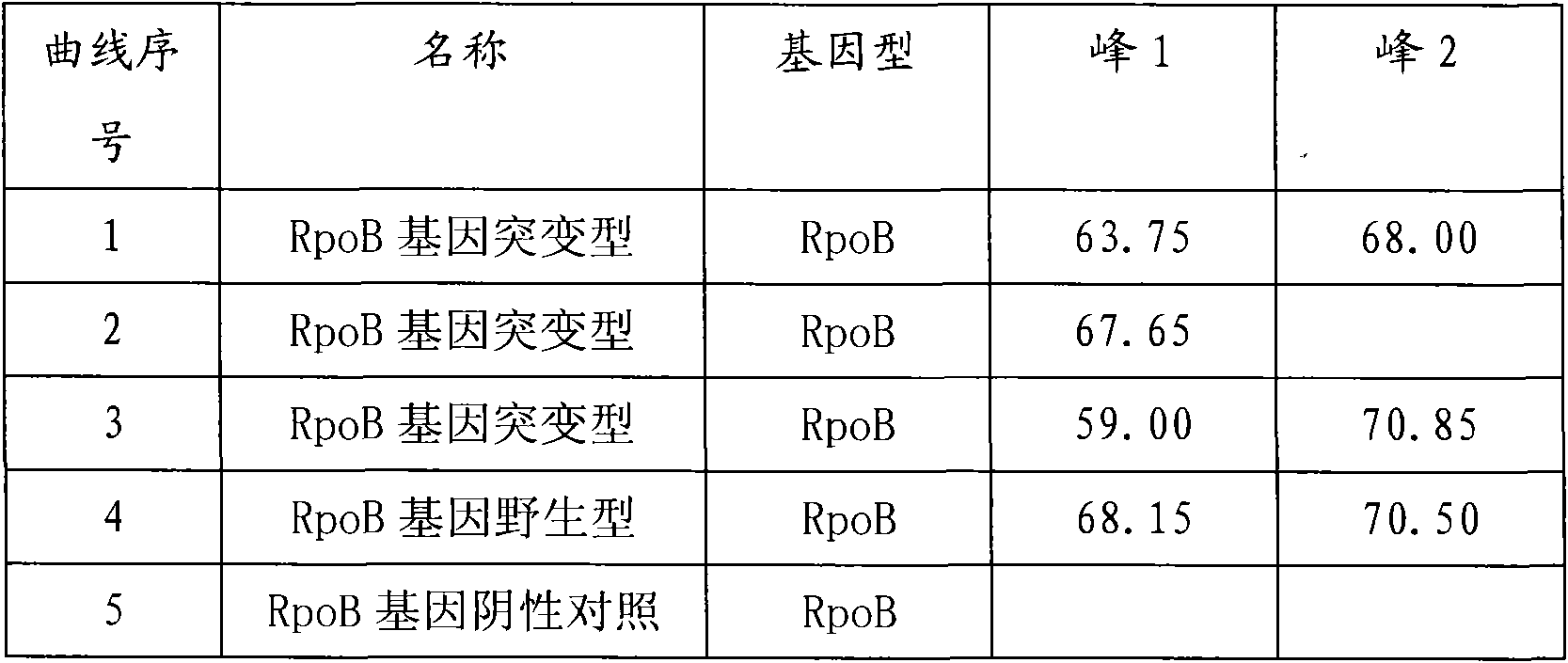
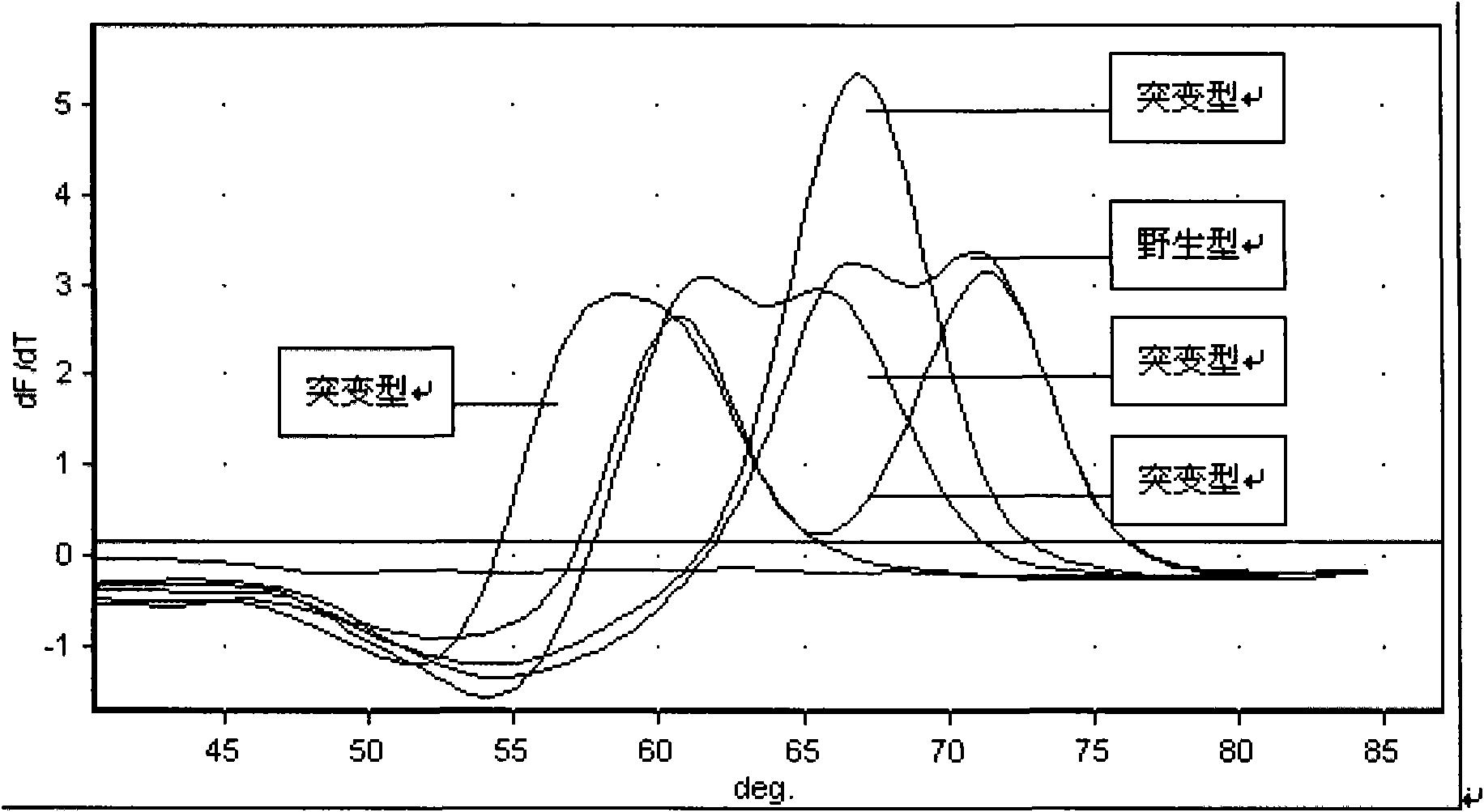
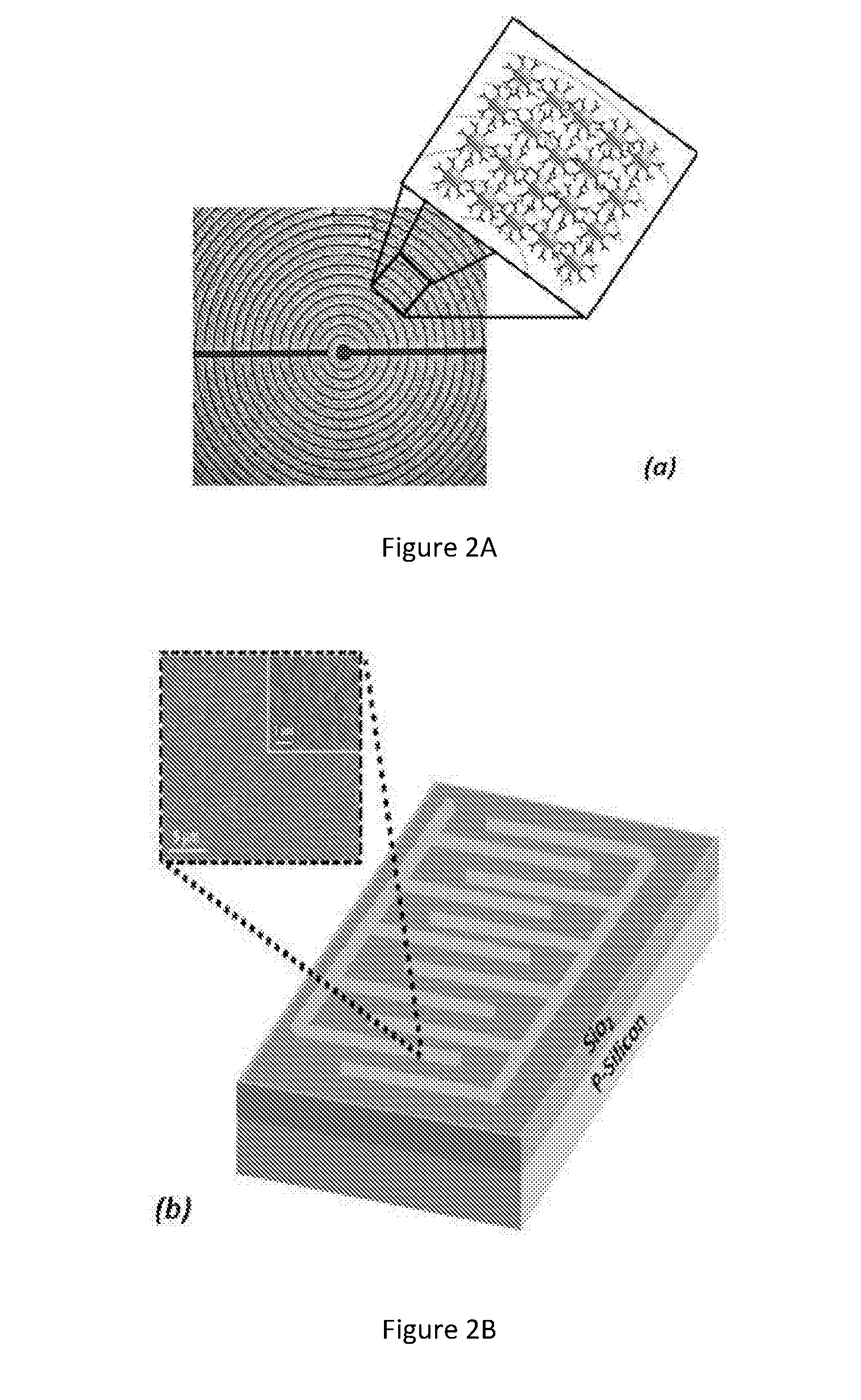
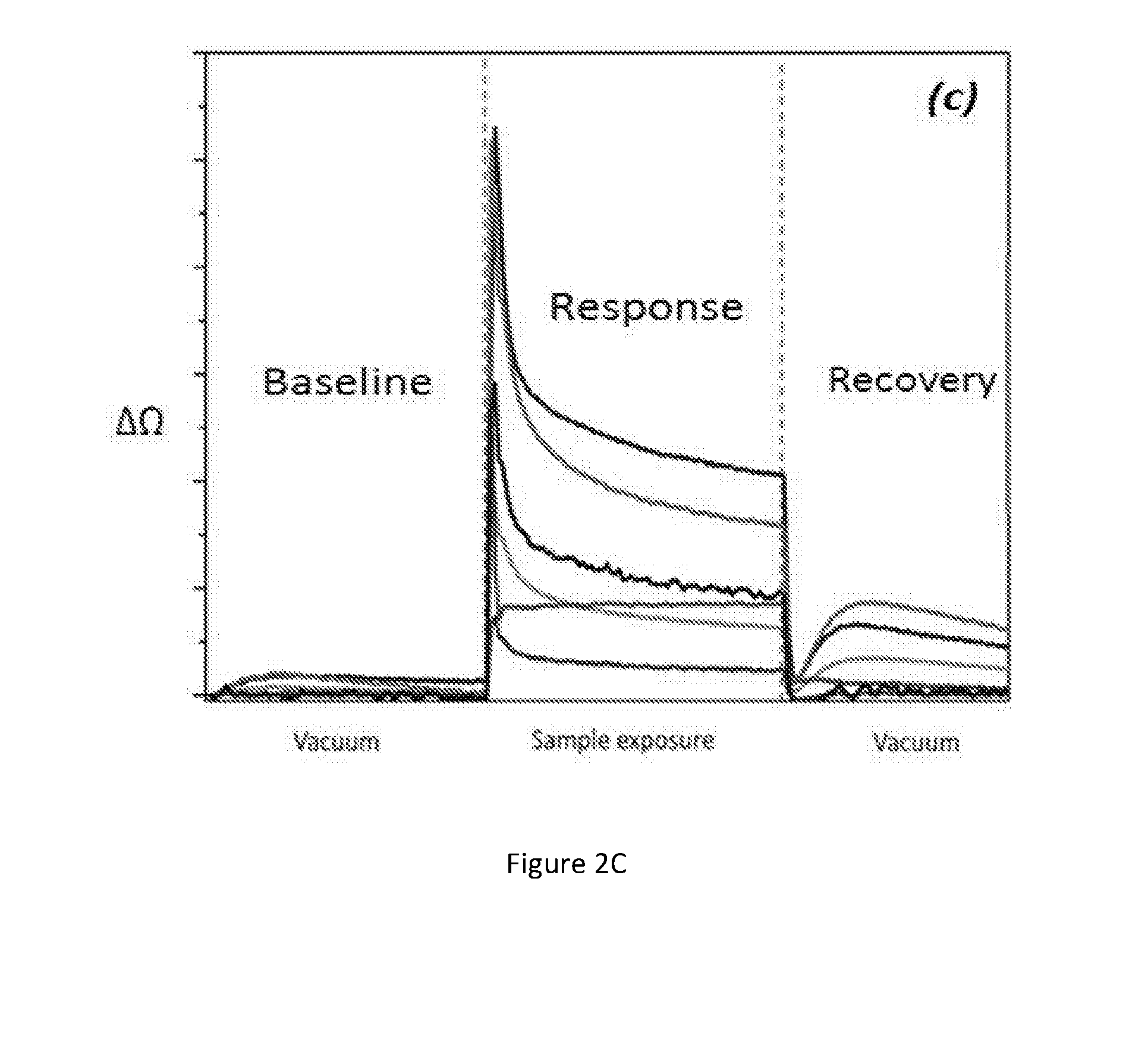
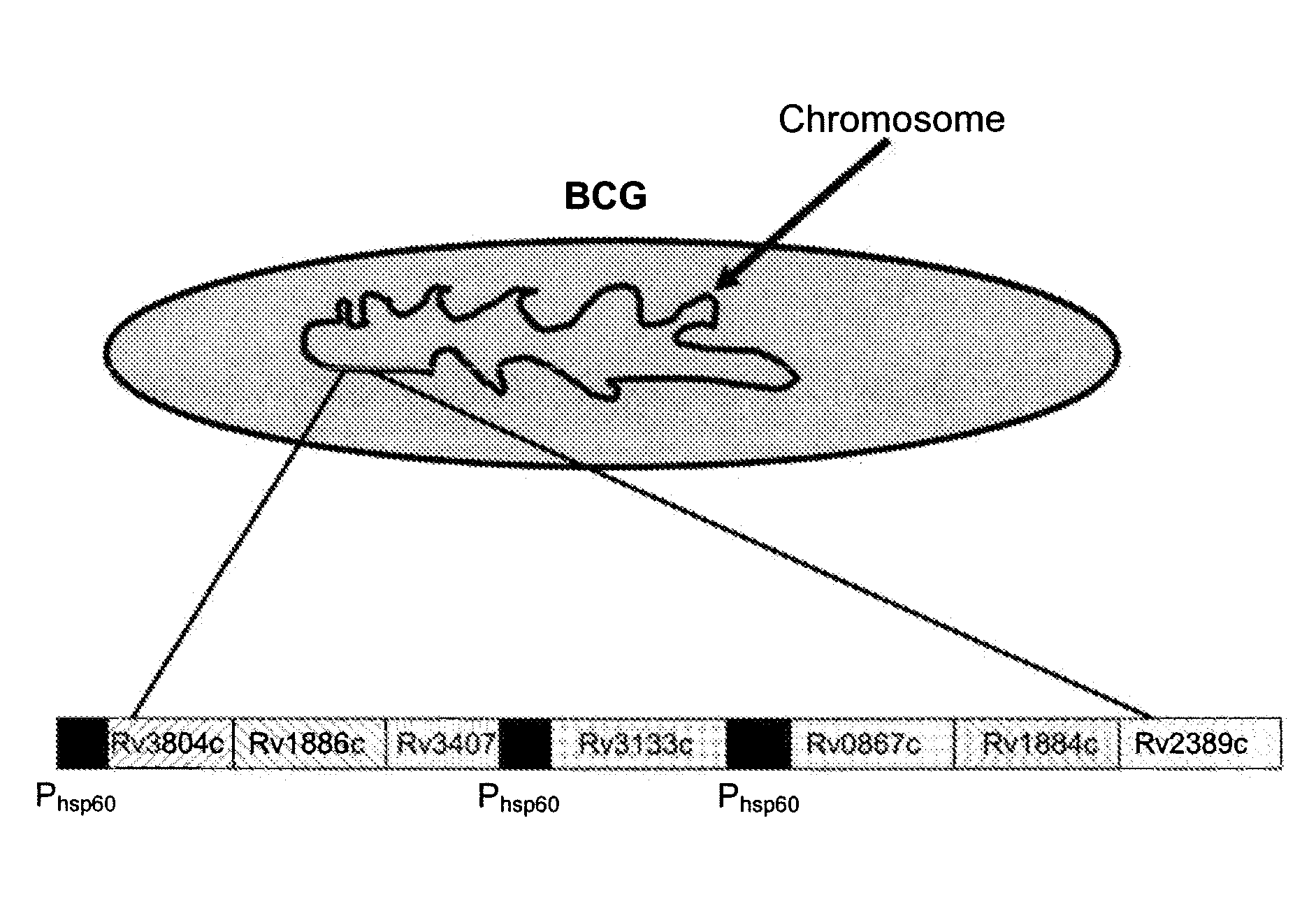
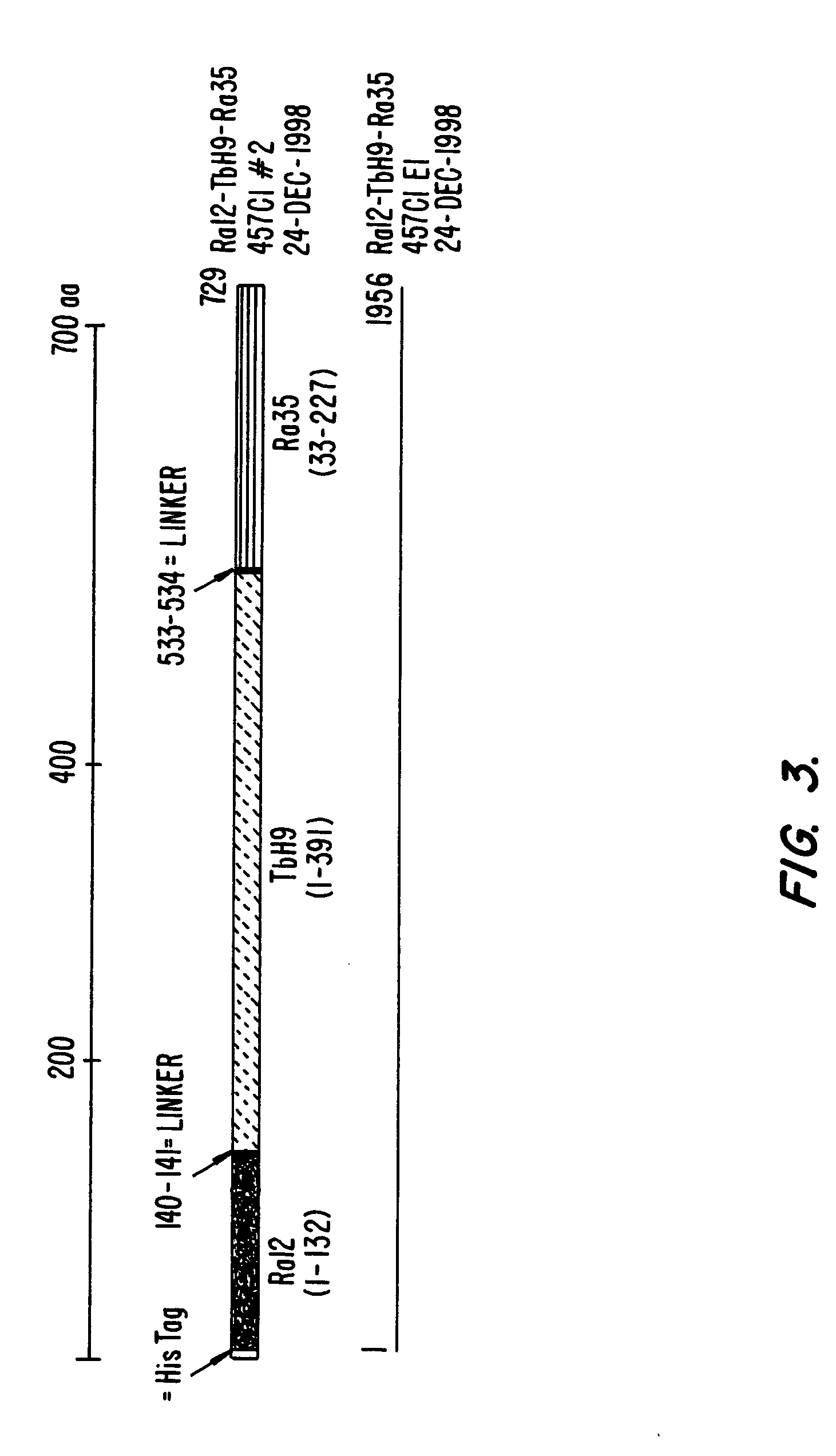
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1069 results about "Tuberculoma" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
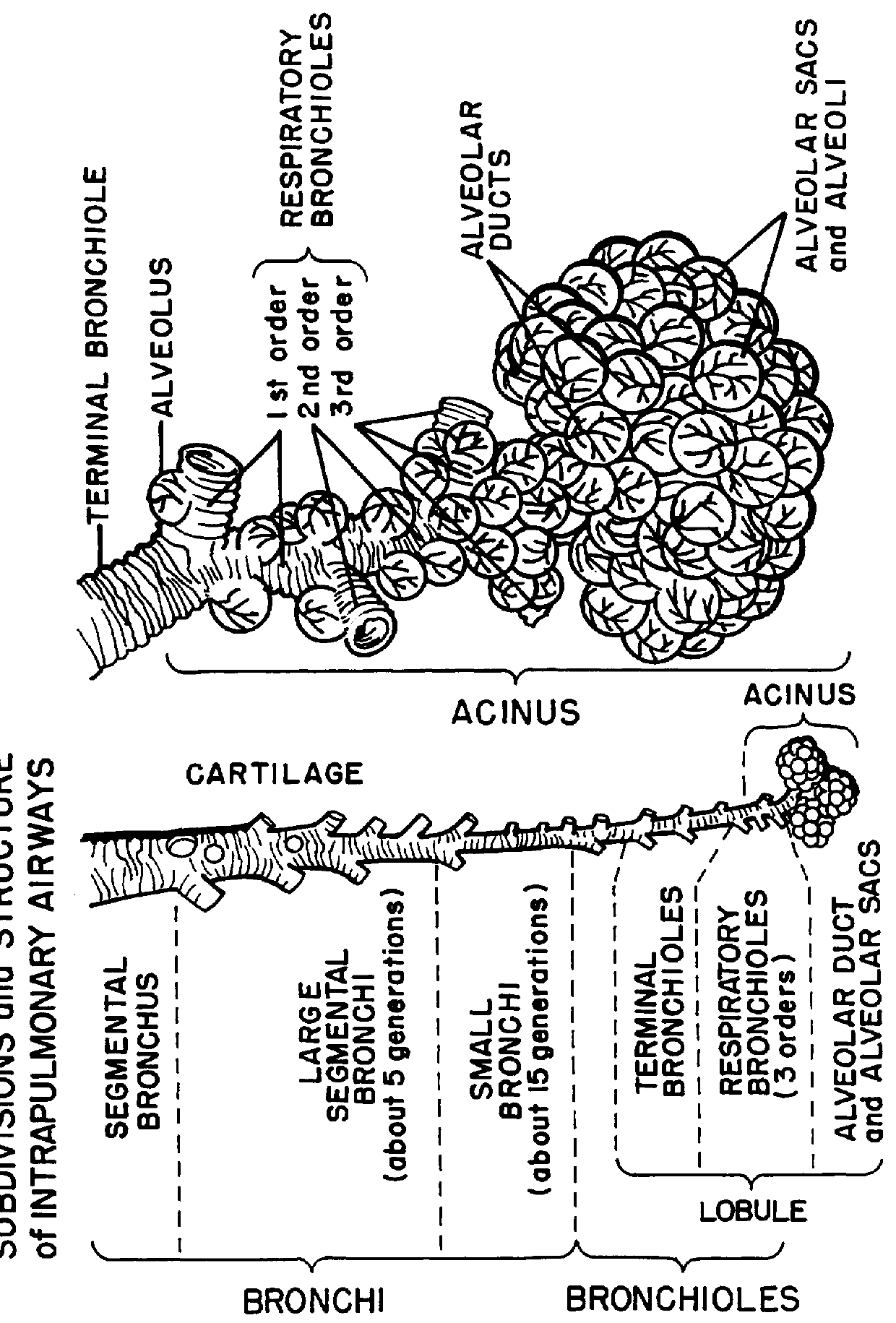
A tuberculoma is a clinical manifestation of tuberculosis which conglomerates tubercles into a firm lump, and so can mimic cancer tumors of many types in medical imaging studies. Since these are evolutions of primary complex, the tuberculomas may contain within caseum or calcifications.
Method and a tobramycin aerosol formulation for treatment prevention and containment of tuberculosis
A method for treatment, prevention and containment of acute and chronic tuberculosis using a preservative-free concentrated tobramycin aerosol formulation delivering tobramycin to the lung endobronchial space including alveoli in an aerosol having mass medium average diameter predominantly between 1 to 5 mu . The method comprises administration of tobramycin in concentration one to ten thousand times higher than the minimal inhibitory concentration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. A method for containment of and decreasing infectivity periods of tuberculosis patients to shorter periods of time.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
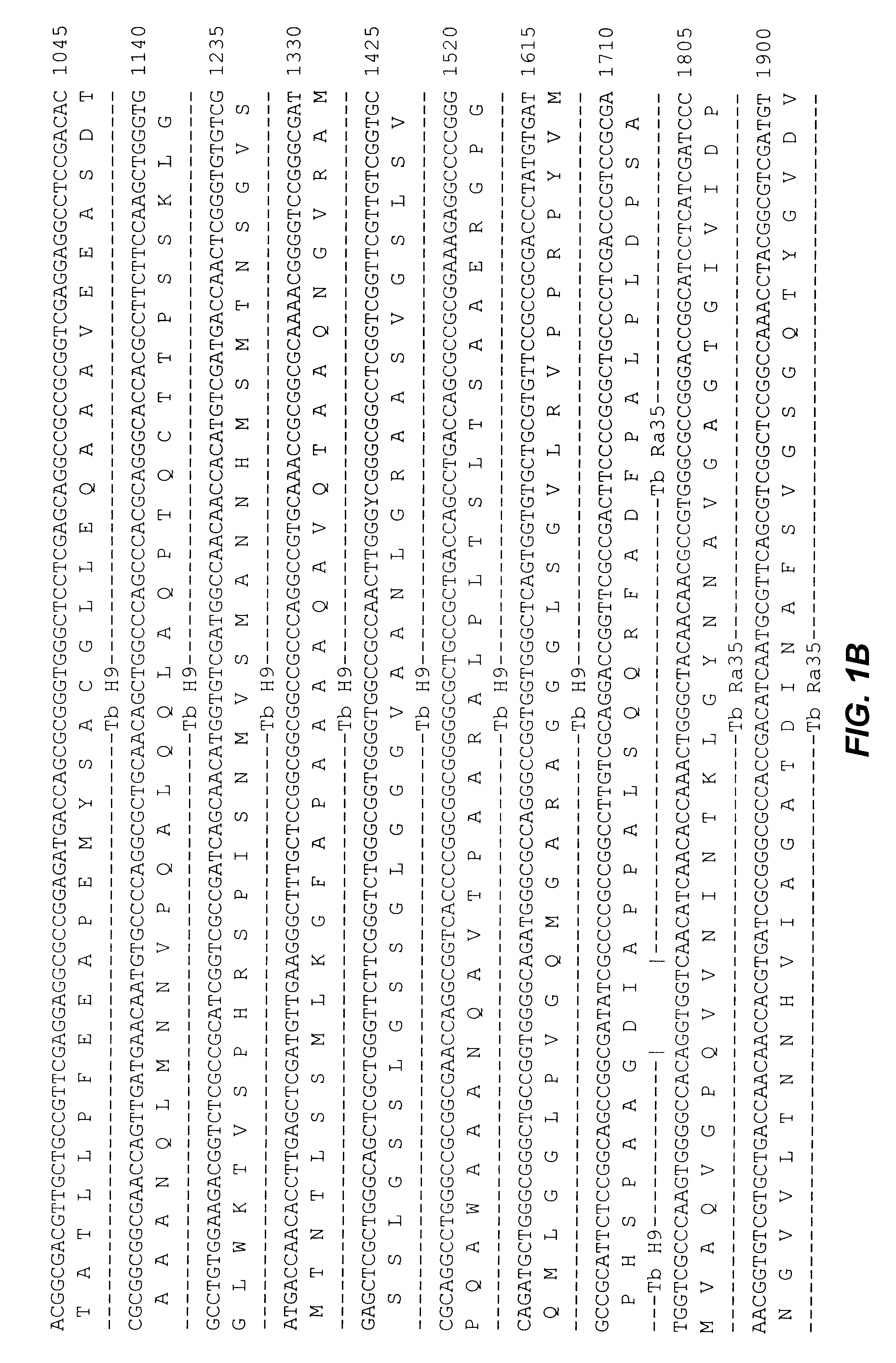
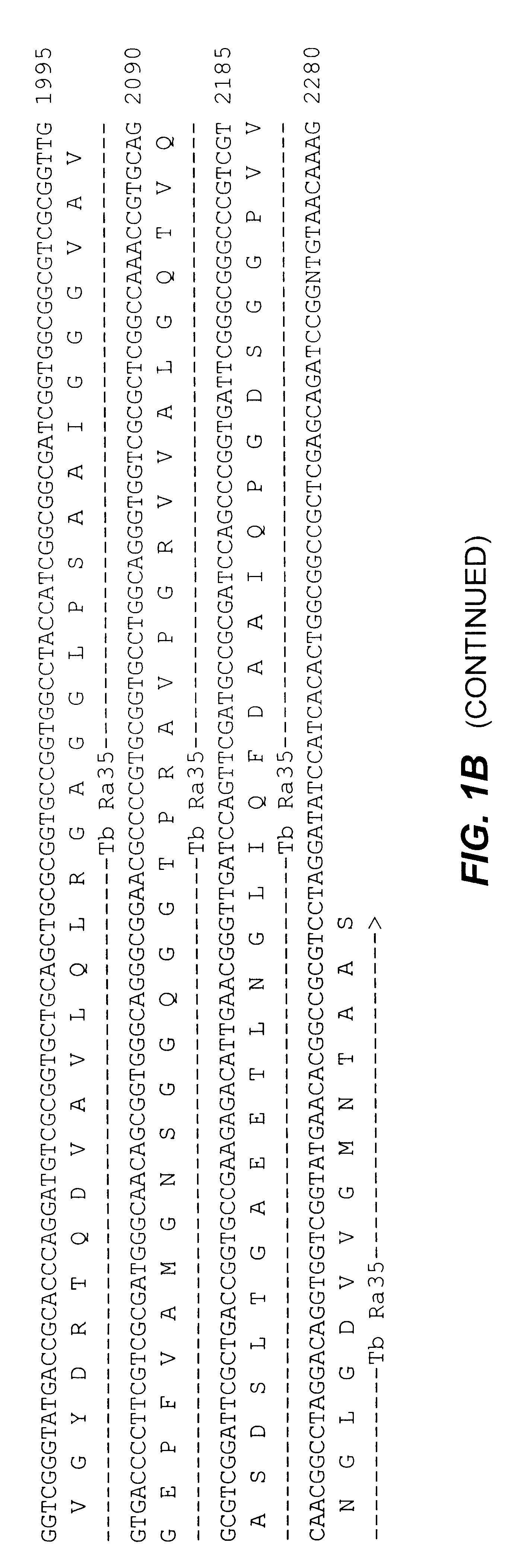
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens and their uses
InactiveUS6544522B1Improving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenMycobacterial antigen
The present invention relates to fusion proteins of Mycobacterium tuberclosis antigens. In particular, it relates to two fusion proteins, each of which contains three individual M. tuberculosis antigens, and a fusion protein of two M. tuberculosis antigens, their coding sequences, and methods for their use in the treatment and prevention of tuberculosis.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
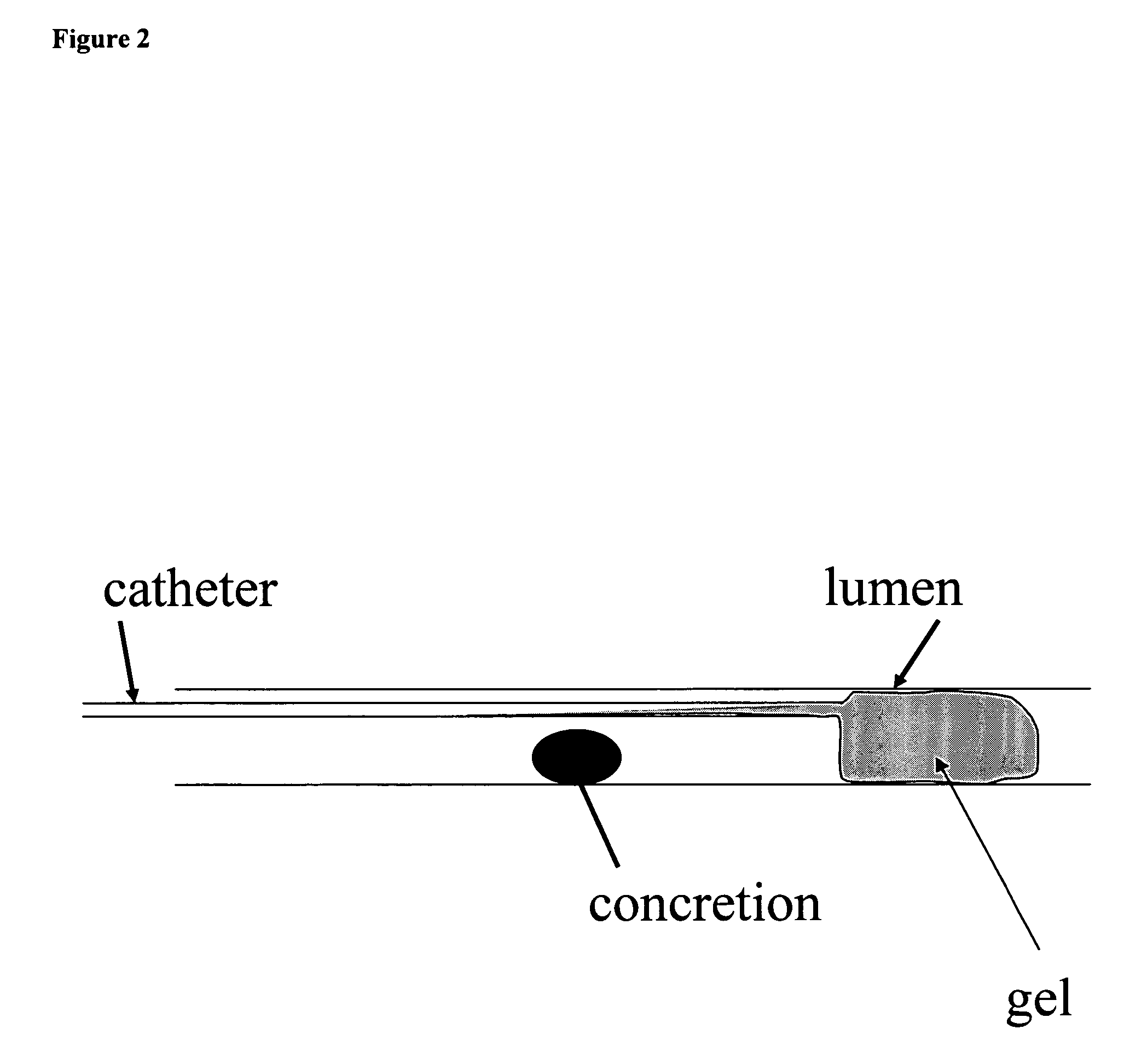
Confinement of kidney-stone fragments during lithotripsy
InactiveUS20050143678A1Surgical drugsChiropractic devicesIntracorporeal lithotripsyThermosensitive polymer
The present invention improves significantly the success rate of lithotripsy and reduces the risk of tissue damage, by injecting temporary plugs in front and behind a concretion (for extracorporeal lithotripsy) or behind a concretion (for intracorporeal lithotripsy). One aspect of the present invention relates to injecting an inverse thermosensitive polymer solution into a lumen, thereby preventing the migration of a concretion, or its fragments, upon extracorporeal or intracorporeal lithotripsy.
Owner:GENZYME CORP +1
Compositions and methods for detecting, identifying and quantitating mycobacterial-specific nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110281754A1Inherent limitationAuxiliary diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyTuberculosis mycobacterium
Disclosed are compositions and methods for isolating, detecting, amplifying, and quantitating Mycobacterium-specific nucleic acids in a sample. Also disclosed are compositions and diagnostic kits comprising Mycobacterium IS6110-specific oligonucleotide amplification primers and labeled oligonucleotide detection probes that specifically bind to the amplification products obtained therefrom. Also disclosed are compositions and methods for the isolation and characterization of nucleic acids that are specific to one or more tubercular pathogens, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in particular, from a wide variety of samples including those of biological, environmental, clinical and / or veterinary origin.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS6991797B2High expressionEnhance immune responseBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention is based on the identification and characterization of a number of novel M. tuberculosis derived proteins and protein fragments. The invention is directed to the polypeptides and immunologically active fragments thereof, the genes encoding them, immunological compositions such as vaccines and skin test reagents containing the polypeptides.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
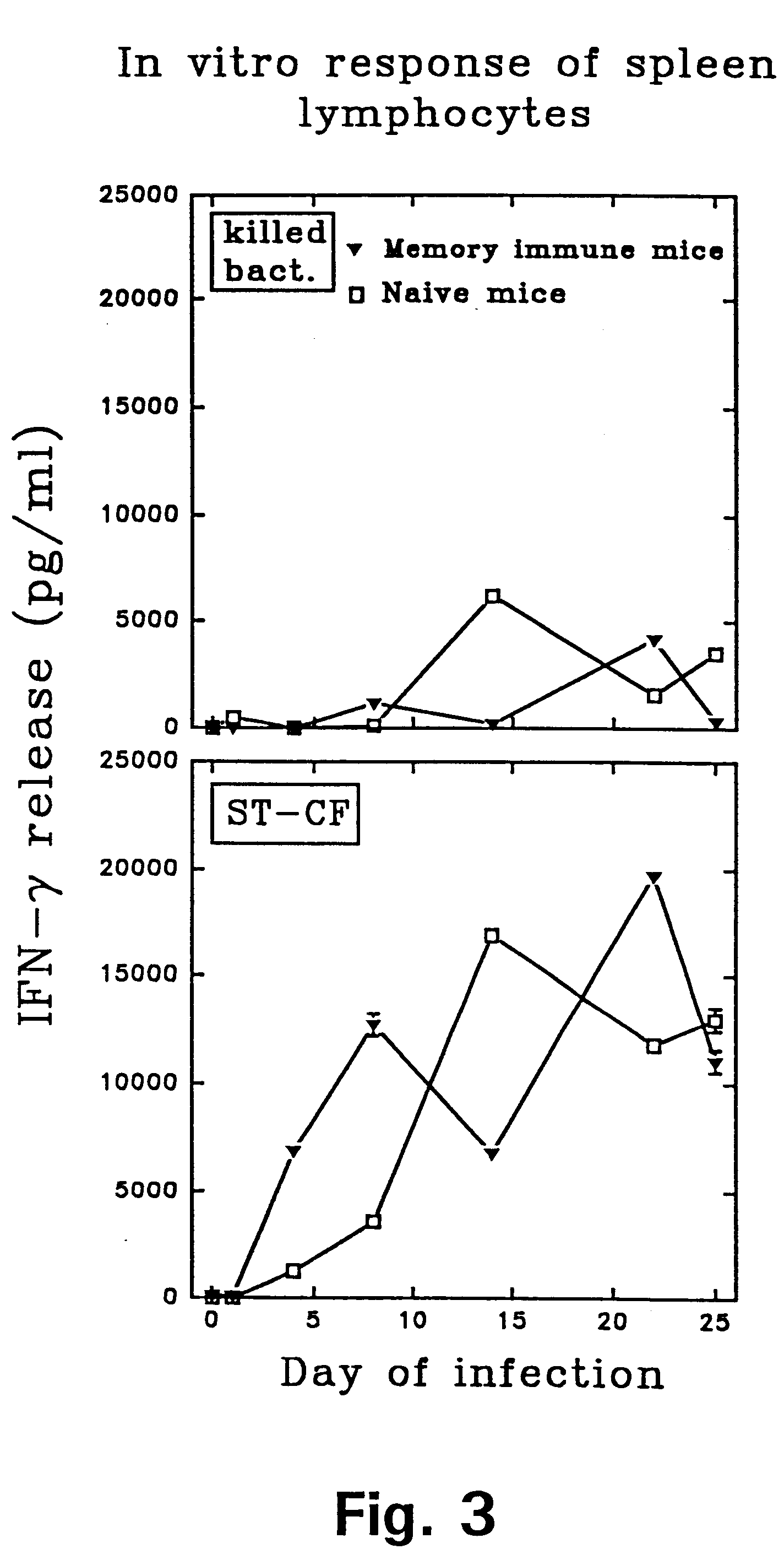
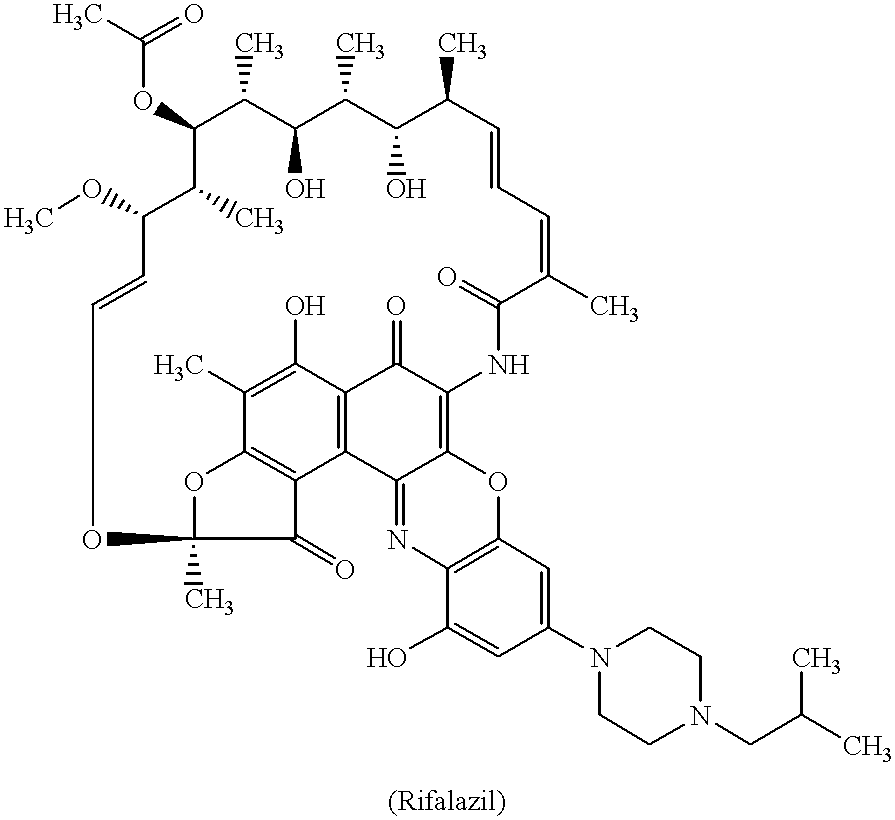
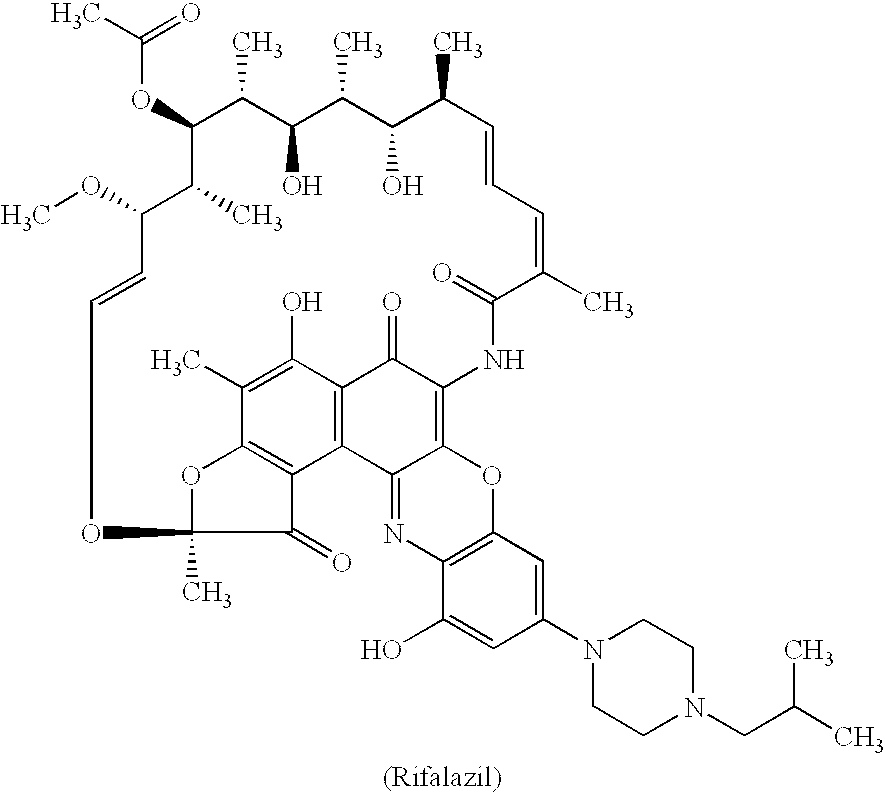
Method for treatment of bacterial infections with once or twice-weekly administered rifalazil
A method for treatment of bacterial infections with rifalazil administered once-weekly or twice-weekly. A method for treatment of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex, infections caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae and infections caused by Helicobacter pylori by administering to a patient suffering from the bacterial infection 1-100 mg of rifalazil once or twice a week. In this dose regimen, the treatment is fast, efficacious and eliminates undesirable secondary symptoms observed with daily doses of 1-50 mg of rifalazil.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
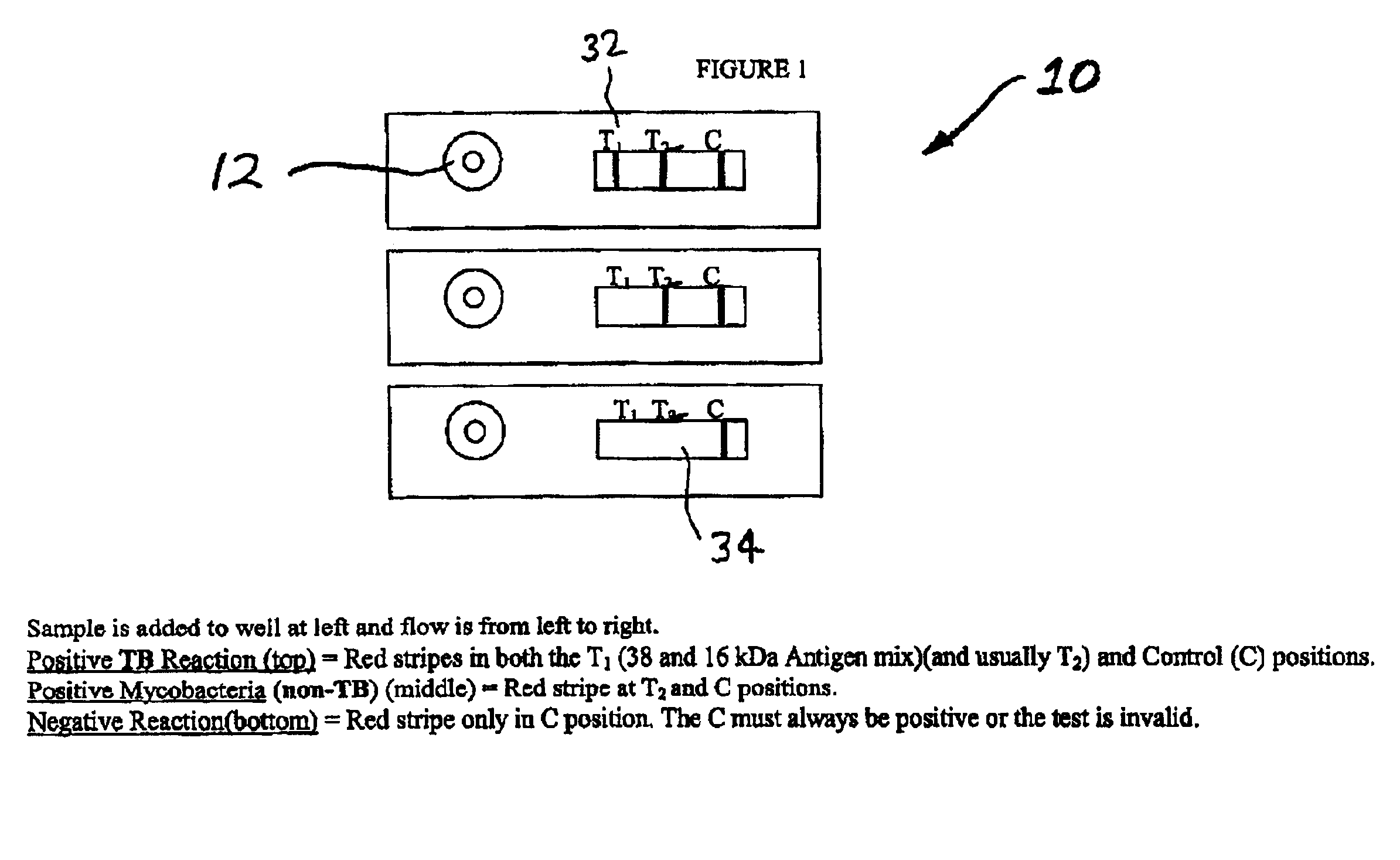
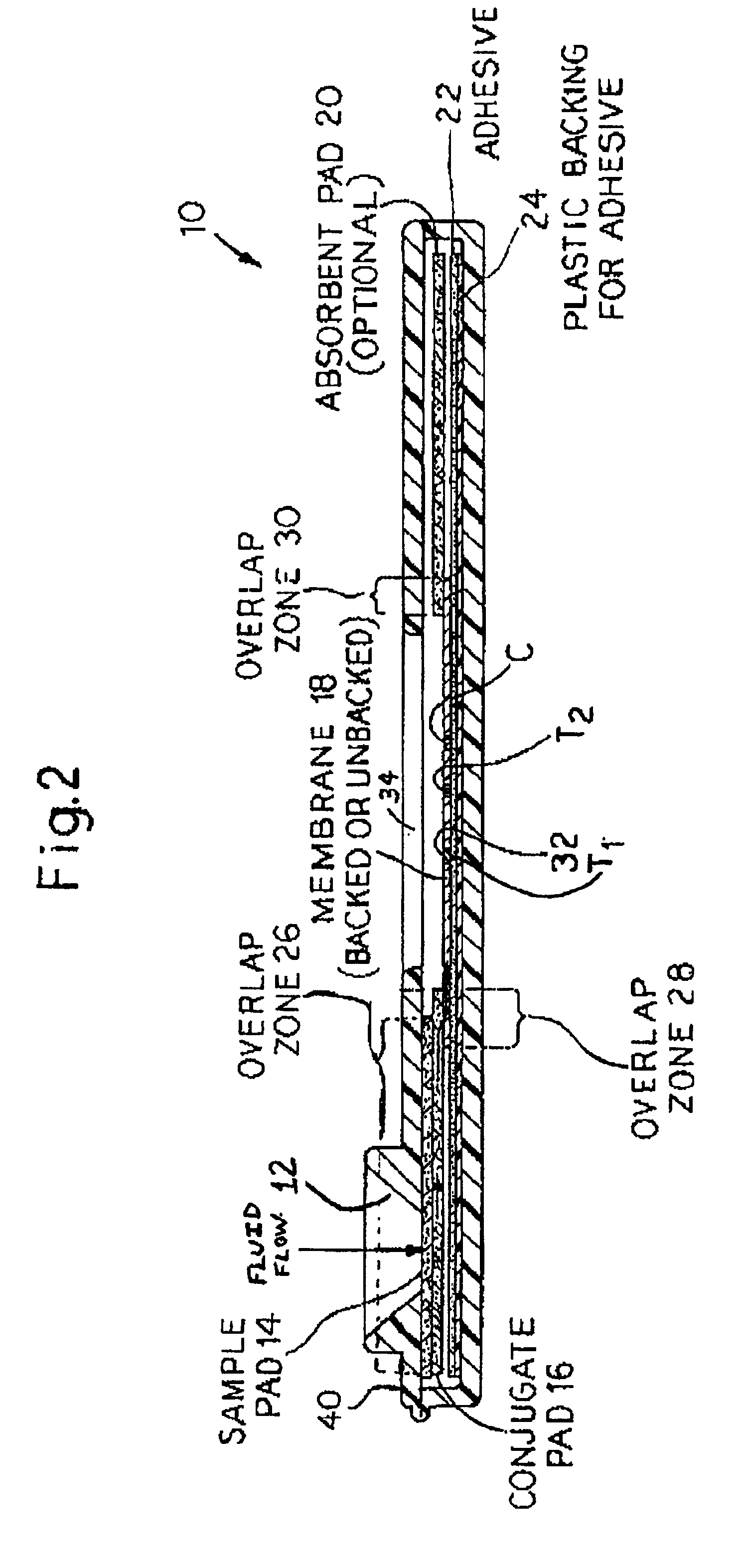
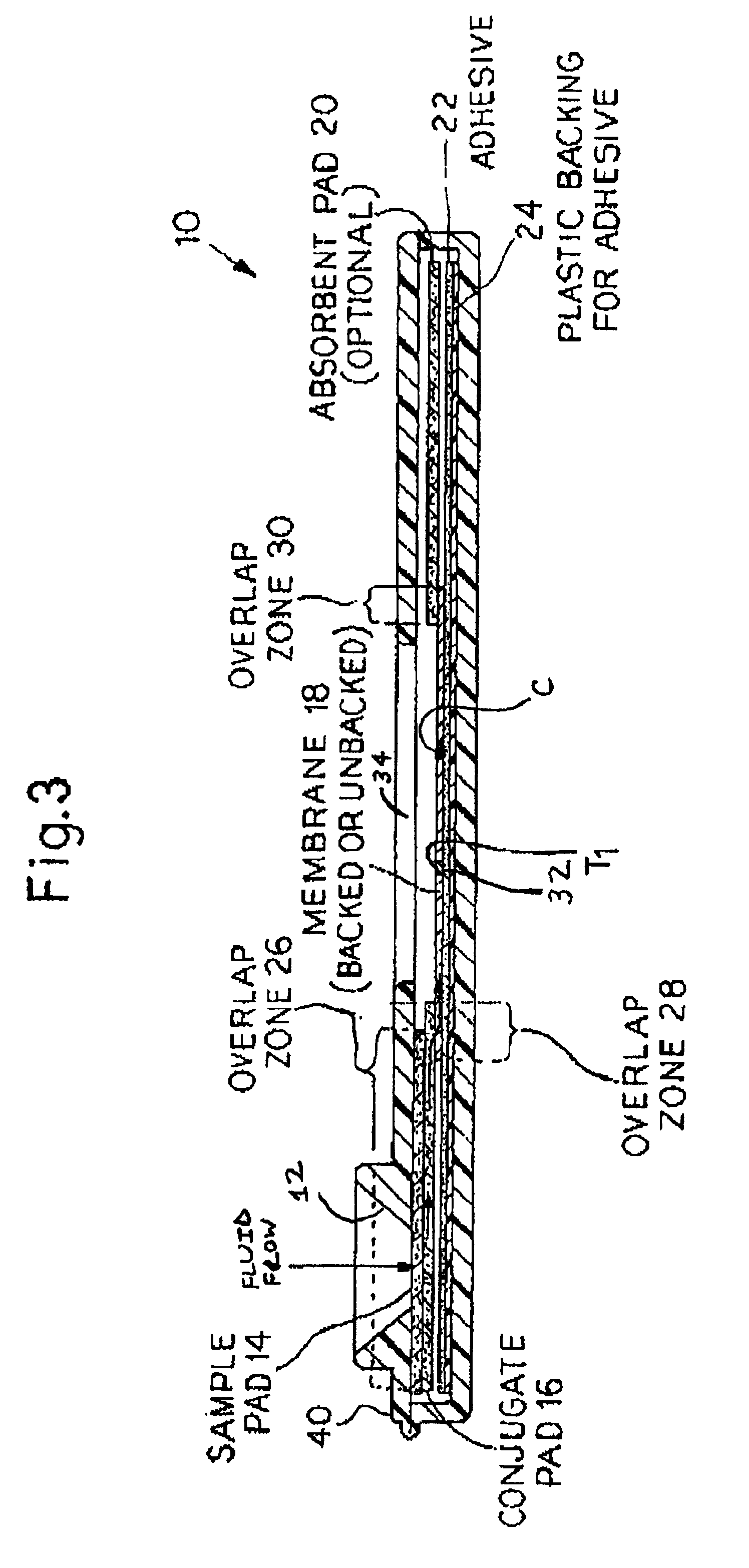
Rapid lateral flow assay for determining exposure to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other mycobacteria
InactiveUS6841159B2Auxiliary diagnosisAuxiliary judgmentBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMycobacterial antigenImmunization status
An assay method and kit is disclosed for detecting the presence of at least one predesignated, target antibody to a mycobacterium in a sample selected from one or more patient bodily fluids. The method comprises the following steps: (a) contacting the sample of one or more patient bodily fluids with at least one mycobacterium antigen on a lateral-flow assay membrane to bind to the target antibody in the sample; (b) previously, simultaneously or subsequently to step (a), binding the at least one mycobacterium antigen with a conjugated label producing a detectable signal; and (c) detecting the signal whereby the presence of the target antibody is determined in the sample by the intensity or presence of the signal. The method can further comprise the step of evaluating immunization status of the patient from whom the sample came by comparing the signal or lack thereof with immunizations previously received by the patient and in comparison to a known standard control. In a preferred embodiment, the mycobacterium antigen specifically binds to Mycobacterium tuberculosis specific antibodies. Preferably, the immunoassay of the present invention comprises a lateral-flow assay comprising a membrane, a conjugated label pad, and at least one mycobacterium antigen bound to the membrane. In a preferred embodiment, the at least one mycobacterium antigen is selected from the group consisting of 38 kDa and 16 kDa antigens.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
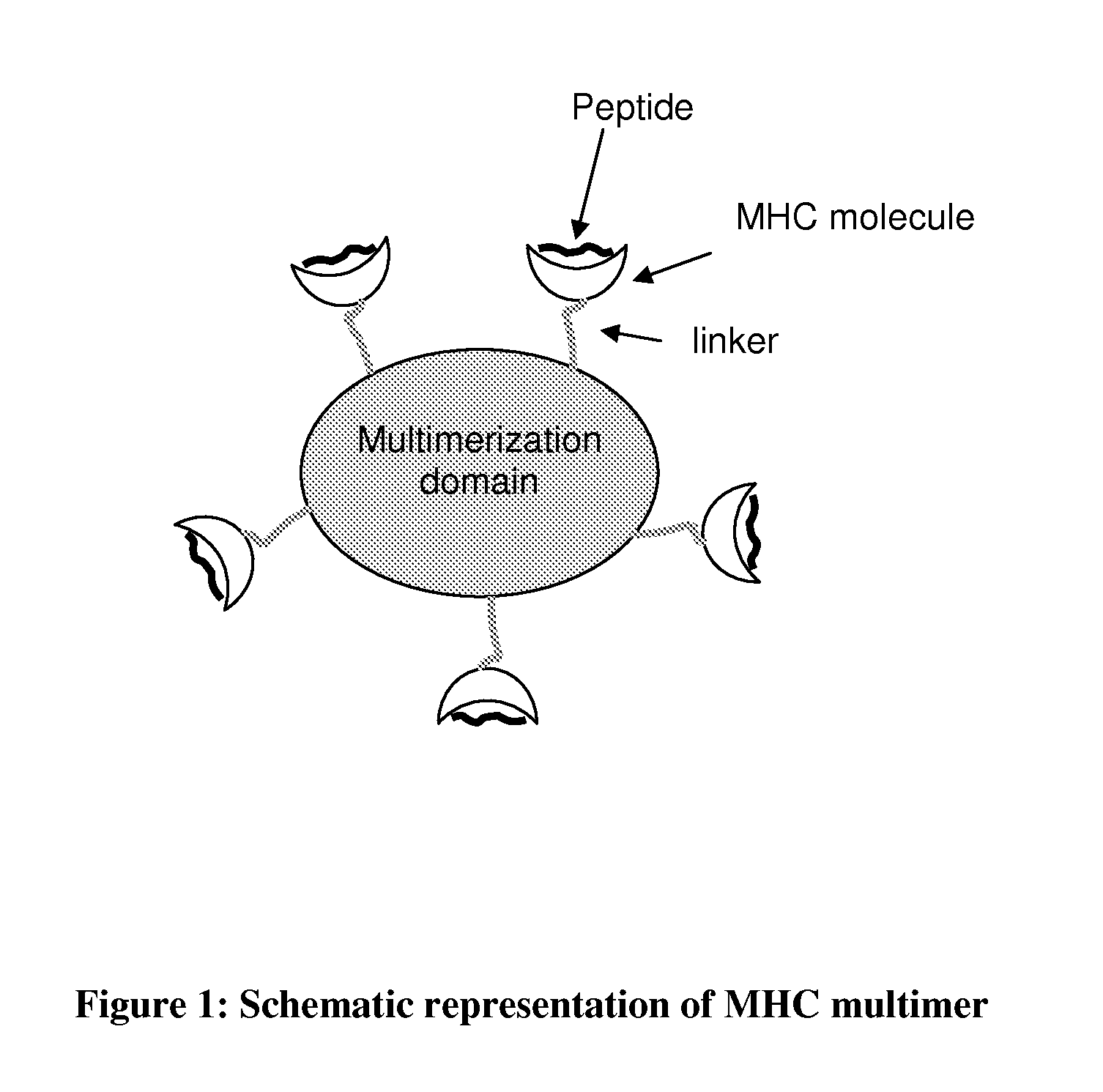
MHC Multimers in Tuberculosis Diagnostics, Vaccine and Therapeutics
The present invention relates to MHC-peptide complexes and uses thereof in the diagnosis of, treatment of or vaccination against a disease in an individual. More specifically the invention discloses MHC complexes comprising Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigenic peptides and uses there of.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Fusion proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
The present invention relates to compositions and fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium sp. antigens, and nucleic acids encoding such compositions and fusion proteins. The compositions of the invention increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Hybrids of M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS7037510B2Improving immunogenicityImprove propertiesBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological memoryImmunodominant Antigens
The present invention discloses fusion proteins of the immunodominant antigens ESAT-6 and Ag85B from Mycobacterium tuberculosis or homologues thereof, and a tuberculosis vaccine based on the fusion proteins, which vaccine induces efficient immunological memory.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS7311922B1Good antigenicityHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenSerum ige
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
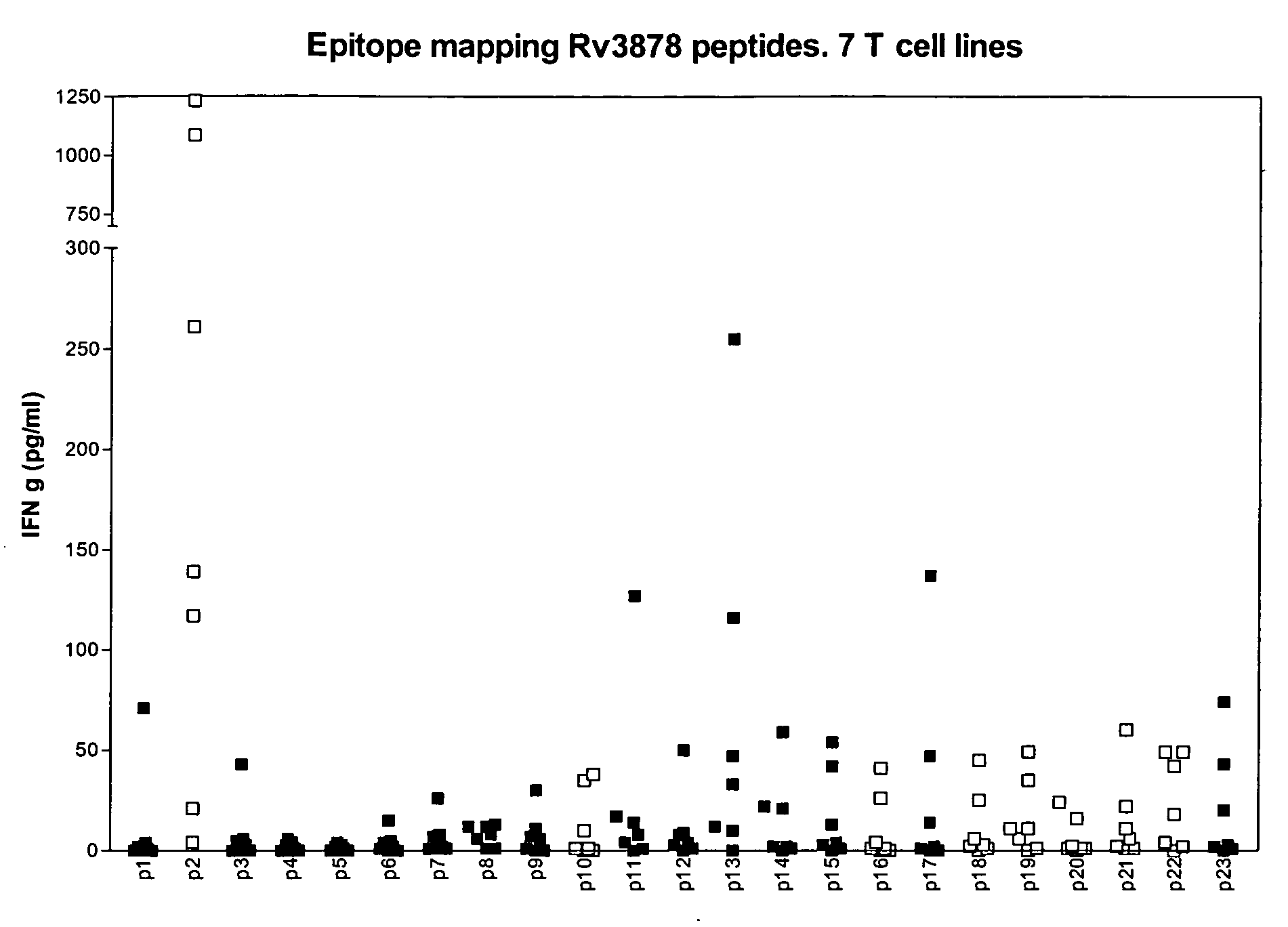
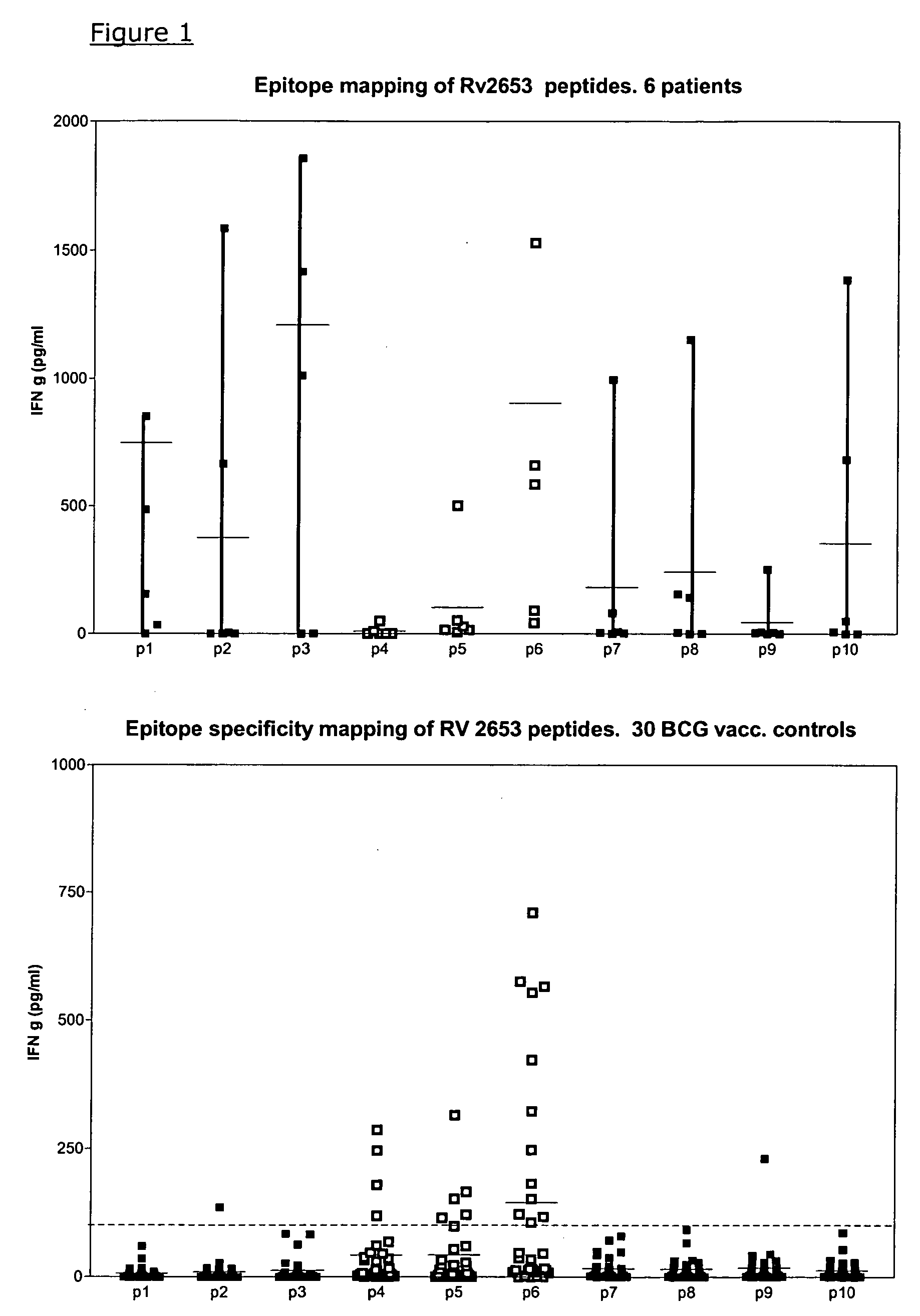
Specific epitope based immunological diagnosis of tuberculosis
ActiveUS20060115847A1Easy to identifyTesting is superfluousBacterial antigen ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSkin allergy testPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The currently used method for immunological diagnosis of tuberculosis infection, the tuberculin skin test, is problematic for a number of reasons; it has low specificity in BCG vaccinated individuals, a high interobserver variance and requires skill to be read and interpreted. Furthermore it requires an extra visit to the clinic to have the test read. Both people vaccinated with BCG and those exposed to non-tuberculosis mycobacteria give a positive skin test result similar to that seen in a TB infected individual. This also applies for purified protein derivative (PPD) when used in a blood cell based test. The present invention discloses the development of an immunological TB diagnostic tool based on a combination of epitopes from proteins encoded by regions of the M. Tuberculosis (M. tub.) genome, that are not present in the BCG vaccine strain or in the most common non-tuberculosis mycobacteria. Four recently characterized proteins with this diagnostic potential were selected. Peptides from these proteins were tested one by one with peripheral blood mononuclear cells from microscopy or culture confirmed TB patients as well as from healthy BCG vaccinated controls. Some combinations of peptides showed a sensitivity level comparable to the level seen with the two wellknown M. tuberculosisspecific proteins ESAT 6 and CFP 10. An epitope combination with these peptides combined with ESAT 6 and CFP 10 gave a sensitivity of 93%, representing a raise in sensitivity of about 26-33% compared to using ESAT6 or CFP 10 alone. The results from a panel of TB patients, using a collection of the new specific epitopes clearly demonstrates, that addition of other specific epitopes to the already known specific antigens, increases the sensitivity of a diagnostic assay based on cell mediated immune response.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Concretion mycobacterium nucleic acid screening method based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique
InactiveCN101157954ASimple methodSensitive and specificMicrobiological testing/measurementMycobacteriumScreening method
The invention pertains to the clinical medicine field, disclosing a Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA screening method which is based on a Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. A nucleic acid detecting method which is based on Loop-mediated isothermal amplification technical principle, detects the Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum. By adopting specific primers, and utilizing LAMP technology platform to amplify the specific area of target gene, the Mycobacterium tuberculosis in sputum is screened and detected in molecular level with the auxiliary of a series of quality control and internal control detecting system. The invention is characterized by simpleness and convenience, economy, quick speed, sensitivity and specific performance, and has wide application prospect.
Owner:中华人民共和国徐州出入境检验检疫局
Method for treatment of bacterial infections with once or twice-weekly administered rifalazil
A method for treatment of bacterial infections with rifalazil administered once-weekly or twice-weekly. A method for treatment of tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, infections caused by Mycobacterium avium complex, infections caused by Chlamydia pneumoniae and infections caused by Helicobacter pylori by administering to a patient suffering from the bacterial infection 1-100 mg of rifalazil once or twice a week. In this dose regimen, the treatment is fast, efficacious and eliminates undesirable secondary symptoms observed with daily doses of 1-50 mg of rifalazil.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS7083796B2Good antigenicityHigh sensitivityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsSerum igeBiology
The present invention relates to compositions and fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium sp. antigens, and nucleic acids encoding such compositions and fusion proteins. The compositions of the invention increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Polypeptide vaccine and vaccination strategy against mycobacterium
A vaccine is provided wherein a polypeptide or combination of peptides from M. tuberculosis is administered to a subject to elicit an immune response. The polypeptide vaccine is administered as part of a prime-boost strategy with BCG vaccine to increase the immunoprotection in a subject such that prevention or elimination of disease is achieved. Finally, a pharmaceutical package is provided that encompasses a polypeptide vaccine for M. tuberculosis that when administered to a subject elicits immunoprotection.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY +1
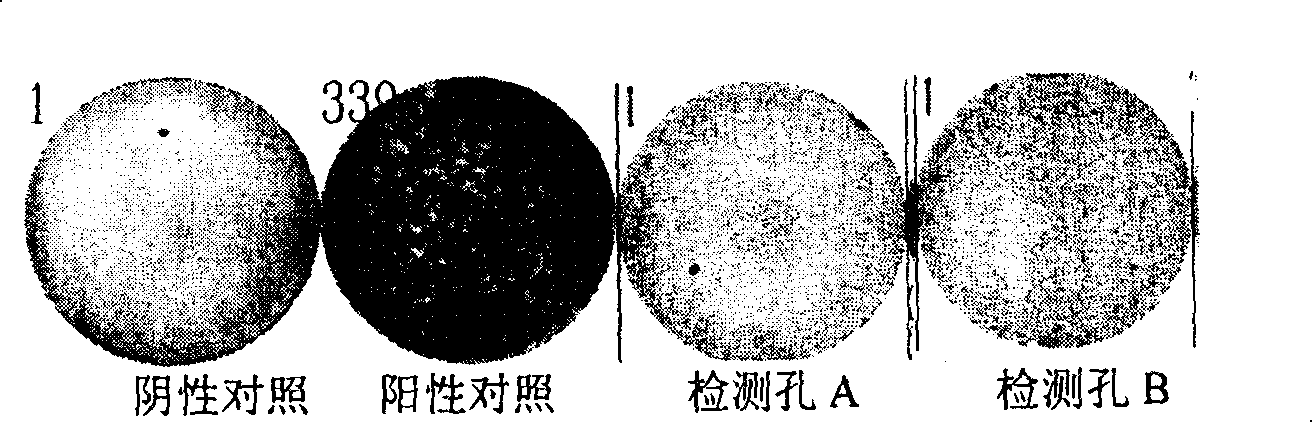
ELISpot tuberculosis infection diagnostic reagent kit and its application
InactiveCN101221173AIncrease costHigh testing costPreparing sample for investigationT lymphocyteCell stimulant
The invention relates to an ELISpot tuberculosis infection diagnostic kit and the application, which adopts the genetic engineering technology to obtain a CFP10-ESAT6 fusion protein antigen from a mycobacterium tuberculosis by cloning, expression and purification, a tuberculosis specific cell stimulator is used for stimulating the peripheral blood T lymphocyte cell of the detected person to secrete a specific IFN-Gamma, then the invention is detected by ELISpot, and the whole process needs to take two days. The usage of the invention can be used for detecting whether the detected person is infected by mycobacterium tuberculosis by using the naked eye or instrument to determine the result according to the number of the generated purple blue spots, so as to assist the diagnosis of tuberculosis and differential diagnosis.
Owner:中国人民解放军总医院第二附属医院
Fusion proteins of mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS20080269151A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAntigenTuberculosis mycobacterium
The present invention relates to fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium species antigens. In particular, it relates to nucleic acids encoding fusion proteins that include two or more individual M. tuberculosis antigens, which increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
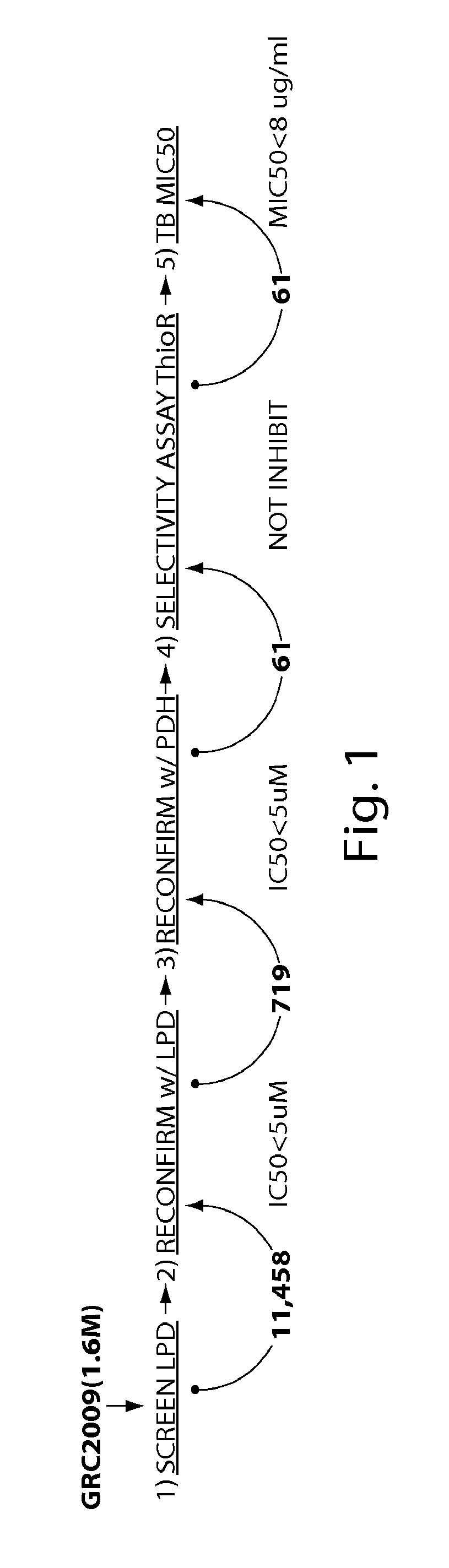
Compounds and methods for treating tuberculosis infection
The present invention provides compounds which are potent inhibitors against Lpd activity, PDH activity, and / or the growth of tubercle bacillus, and thus are useful in the treatment of tuberculosis infection and associated conditions. The present invention is further directed to in vitro- and in vzivo-based methods of inhibiting Lpd and / or PDH activity. In certain embodiments, these methods are useful in inhibiting Lpd and / or PDH activity key to a pathogen's survival.
Owner:ACAD SINICA
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) combination, detection method and kit for detecting liver damage susceptible genotype of antitubercular drug
ActiveCN106119363AReduce drug riskImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsAntituberculous drugs
The present invention relates to an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) combination, detection method and kit for detecting liver damage susceptible genotype of an antitubercular drug and belongs to the technical field of medical molecular biological diagnosis; the SNP combination includes 7 SNP sites, and nucleotide sequences of the 7 SNP sites are shown sequentially as in SEQ ID NO. 1-7; the present invention also relates to an SNP detection method, comprising PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification and double-labeled probe melting curve analytical reaction, and primer pairs and double-labeled probe sequences for detection of the 7 SNP sites are shown as in SEQ ID NO. 8-20. The SNP site combination, detection method and kit provided herein enables quick, accurate, simple and high-throughput detection for a patient's genotype and prediction for the liver damage risk due to the patient using the antitubercular drug.
Owner:THE 309TH HOSPITAL OF CHINESE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY +1
Method and kit for detecting multi-drug resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis (MDR-TB)
ActiveCN101845503AAccurate Diagnostic InformationShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMulti-drug-resistant tuberculosisGenes mutation
The invention relates to a method adopting double-label probe detection and melting curve analysis for diagnosing the infection of multi-drug resistant mycobacterium tuberculosis and a kit which utilizes the method to detect multiple gene mutations related to drug resistant tuberculosis at the same time, and the invention belongs to the life science and biological technical field. The kit of the invention contains a primer designed for multiple gene mutations related to drug resistant, a double-label oligonucleotide probe capable of detecting multiple common gene mutation sites related to drug resistant tuberculosis and a DNA polymerases with heat stability and without 5' nuclease activity, and the kit can be used to detect at least 16 common gene mutation sites related to drug resistant tuberculosis under proper PCR reaction conditions. The detection method and kit of the invention can be used in the early diagnosis of multi-drug resistant tuberculosis and overcome the problems of the existing technology that the detection time is long, a great deal of manpower and large material resources are needed, the detection cost is high, etc.
Owner:无锡锐奇基因生物科技有限公司
Sensor Technology for Diagnosing Tuberculosis
ActiveUS20150301021A1Enhanced sensitivity and selectivityFast and reliable diagnosisVibration measurement in solidsImmobilised enzymesMedicineNanoparticle
A sensor technology comprising a single nano-material (gold nanoparticles and / or carbon nanotube) based sensor or a plurality of sensors in conjunction with a pattern recognition algorithm for non-invasive and accurate diagnosis of tuberculosis caused by M. tuberculosis bacteria in a subject. The sensor technology is suitable for population screening of tuberculosis, particularly in resource-poor and developing countries.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
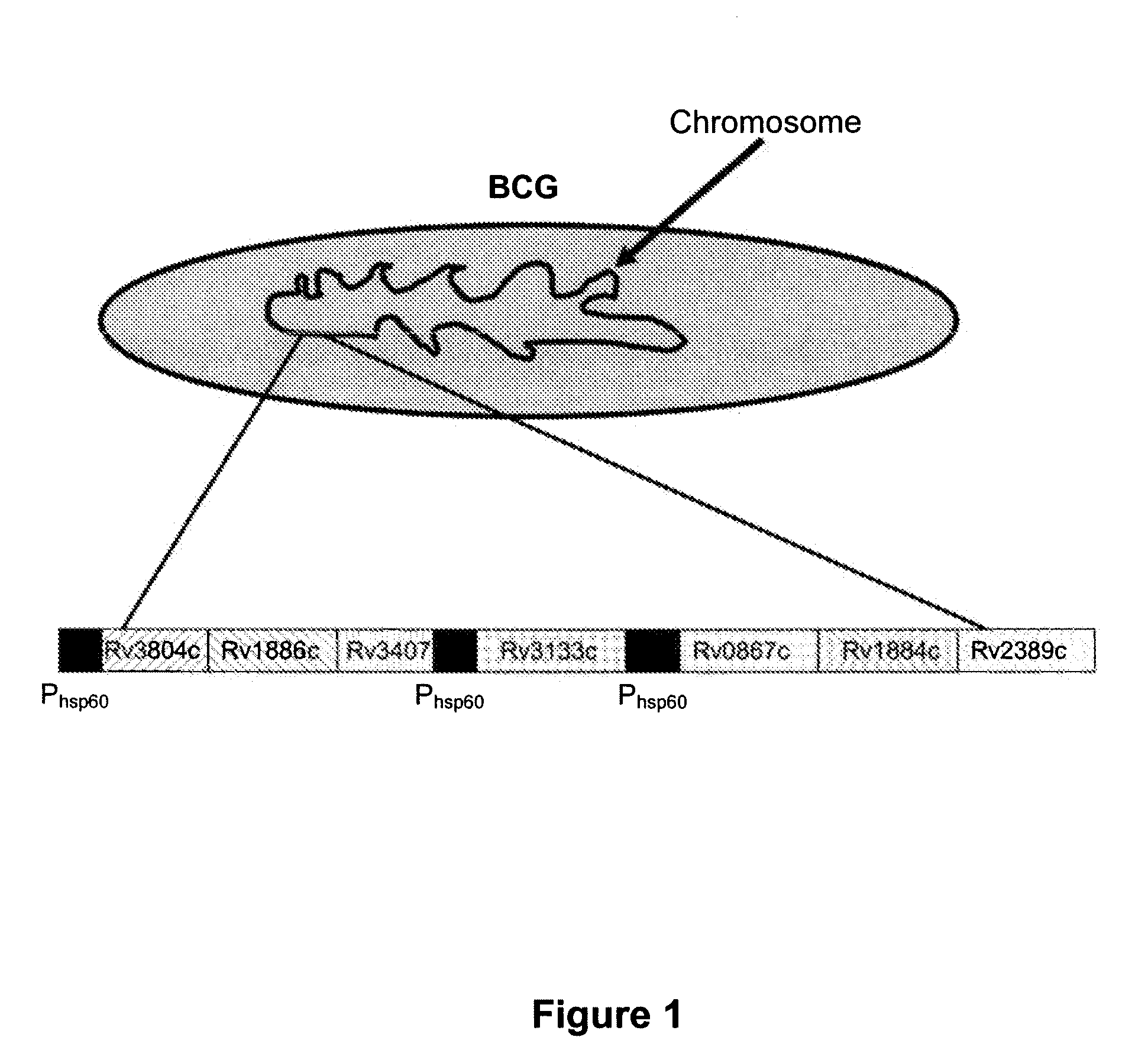
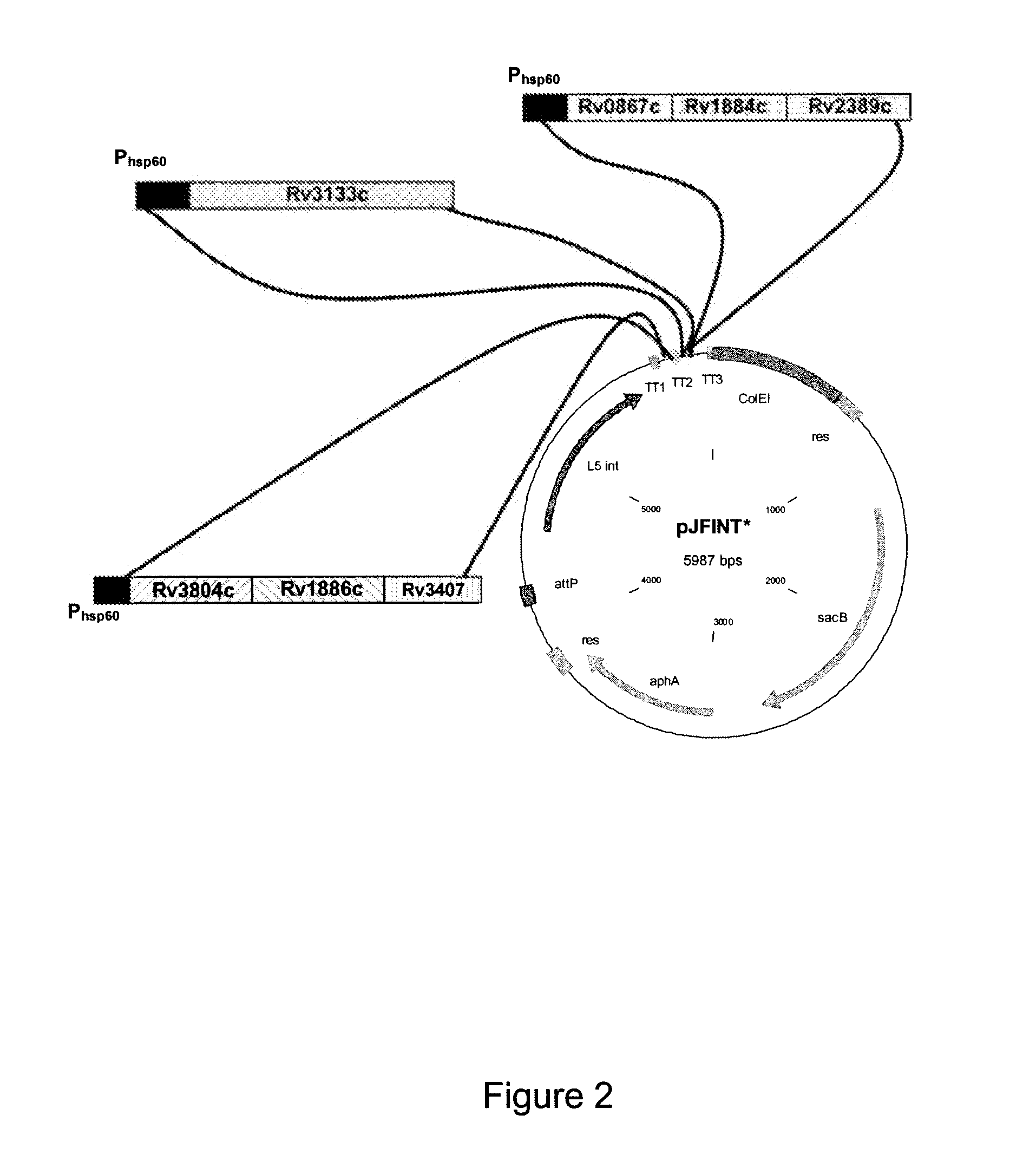
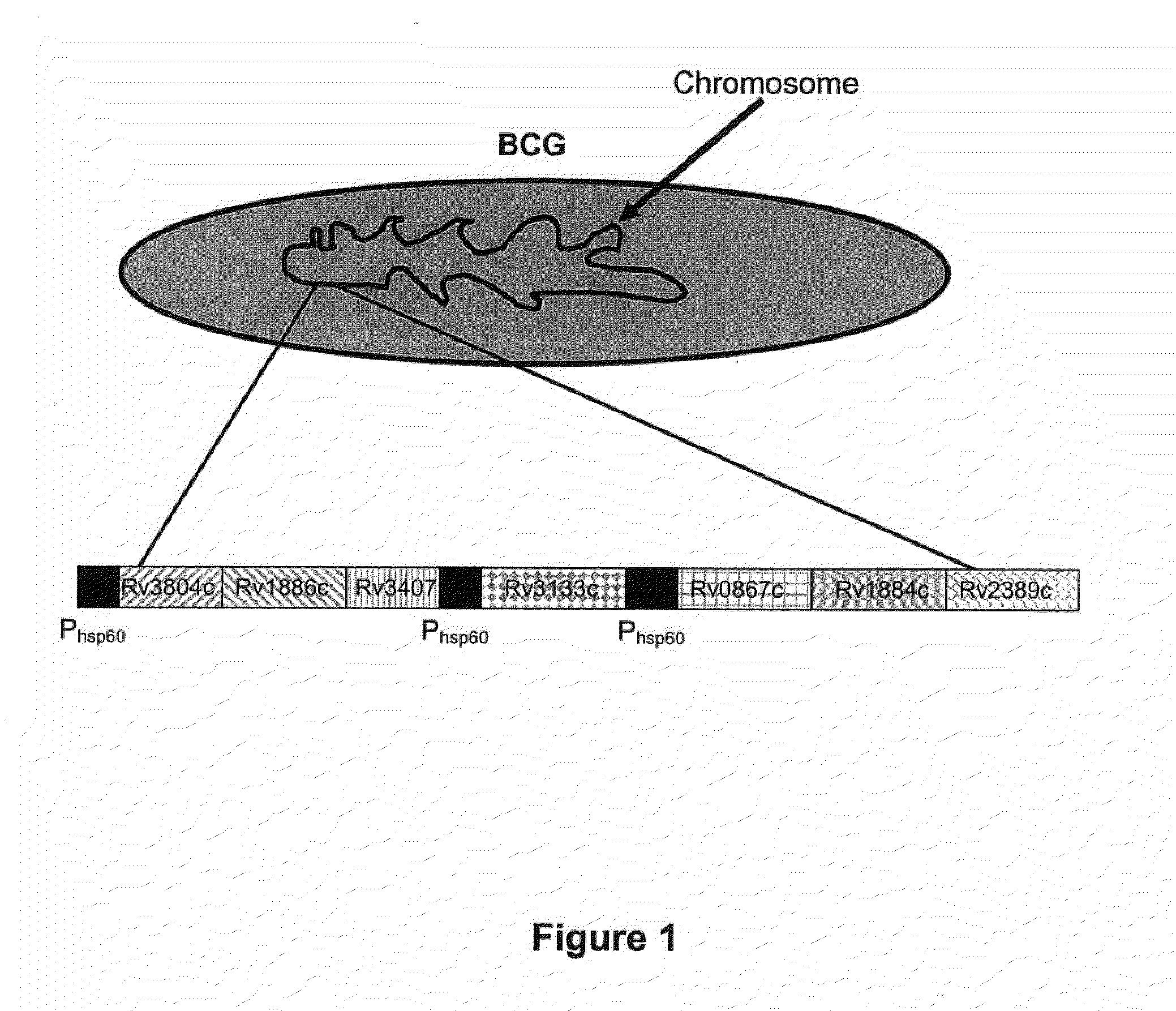
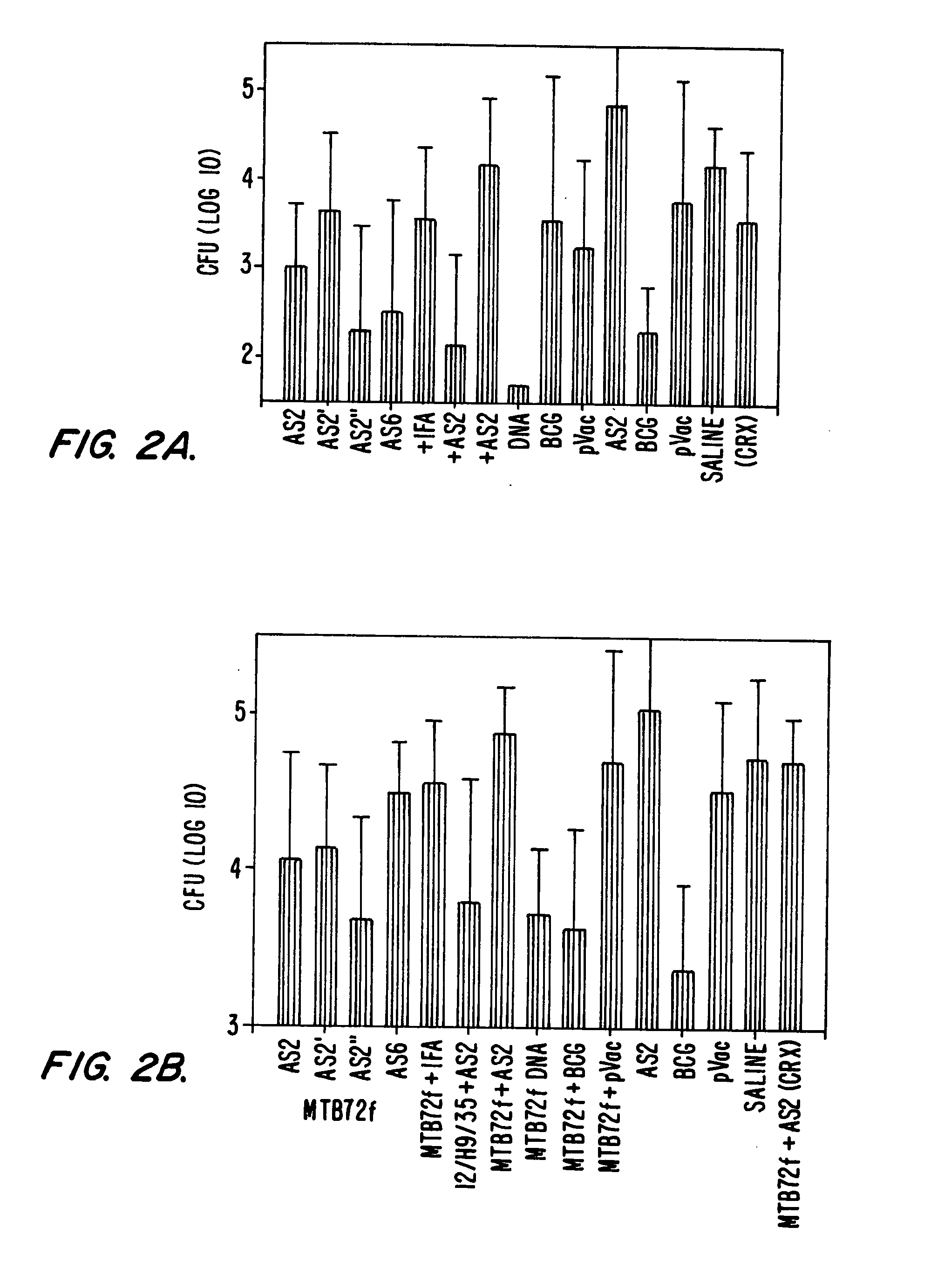
Novel recombinant bcg tuberculosis vaccine designed to elicit immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis in all physiological stages of infection and disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Method for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in biological fluids
A method for detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in biological fluids provides immunoassay methods, diagnostic kits, and an immunochromatoraphic assay device for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens in biological specimens, preferably body fluids and tissues. The preferred body fluids are blood, serum, plasma, urine, pulmonary fluid, sputum, cerebrospinal fluid, and the preferred tissue is the lung biopsy specimen. The immunoassays require two primary antibodies against RD1, RD2, or RD3 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. At least one of the primary antibodies is attached to a solid carrier. Optional, a second antibody against an animal species producing one of the primary antibodies can be added. Either the other primary antibody or the secondary antibody is labeled with a detection agent, which can be an enzymatic marker, a fluorescent or luminescent agent, a radio active label or a color particle. The biological specimens may be used directly, concentrated or diluted for the immunoassays.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Novel Recombinant BCG Tuberculosis Vaccine Designed to Elicit Immune Responses to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in all Physiological Stages of Infection and Disease
A vaccine against Mycobacteria tuberculosis (Mtb) is provided. The vaccine comprises a recombinant Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG) subunit-based vaccine in which one or more Mtb antigens and one or more Mtb resuscitation or reactivation antigens are overexpressed, and in which at least a portion of the DosR regulon is up-regulated. The vaccine is protective against active Mtb infection both pre- and post-exposure to Mtb, and thus prevents disease symptoms due to the recurrence of a latent Mtb infection.
Owner:INT AIDS VACCINE INITIATIVE INC
Fusion proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
InactiveUS20060193876A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsMycobacterial antigenSerology
The present invention relates to compositions and fusion proteins containing at least two Mycobacterium sp. antigens, and nucleic acids encoding such compositions and fusion proteins. The compositions of the invention increase serological sensitivity of sera from individuals infected with tuberculosis, and methods for their use in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tuberculosis infection.
Owner:CORIXA CORP
Blood transcriptional signature of mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
InactiveCN102150043AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInfected patientMycobacterium Infections
The present invention includes methods, systems and kits for distinguishing between active and latent mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a patient suspected of being infected with mycobacterium tuberculosis, and distinguishing such patients from uninfected individuals, the method including the steps of obtaining a gene expression dataset from a whole blood obtained sample from the patient and determining the differential expression of one or more transcriptional gene expression modules that distinguish between infected and non-infected patients, wherein the dataset demonstrates an aggregate change in the levels of polynucleotides in the one or more transcriptional gene expression modules as compared to matched non- infected patients, thereby distinguishing between active and latent mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.
Owner:BAYLOR RES INST +2
Kit and method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and application
ActiveCN102004155ALow costQuality assuranceBiological testingMycobacterium InfectionsLatent tuberculosis
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine examination, and particularly relates to a kit and a method for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis infection and application. The invention discloses a novel mycobacterium tuberculosis detection reagent by screening specific T cell epitope of mycobacterium tuberculosis, wherein the reagent contains polypeptide or analog thereof represented by SEQ ID No.1-10. The method detects cell factors released from T cells by using single or more SEQ ID No.1-10 polypeptides to contact the T cells of mycobacterium tuberculosis infected individuals. The method can effectively detect active tuberculosis or latent tuberculosis infection, and is free from disturbance of Bacilli Calmette Guerin (BCG) inoculation vaccines. The invention also discloses a diagnostic kit and other application based on the polypeptide and the method. Compared with the gamma interferon release experiments in the prior art, the method can obviously improve the detection rate without reducing the specificity and has high clinical application value.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
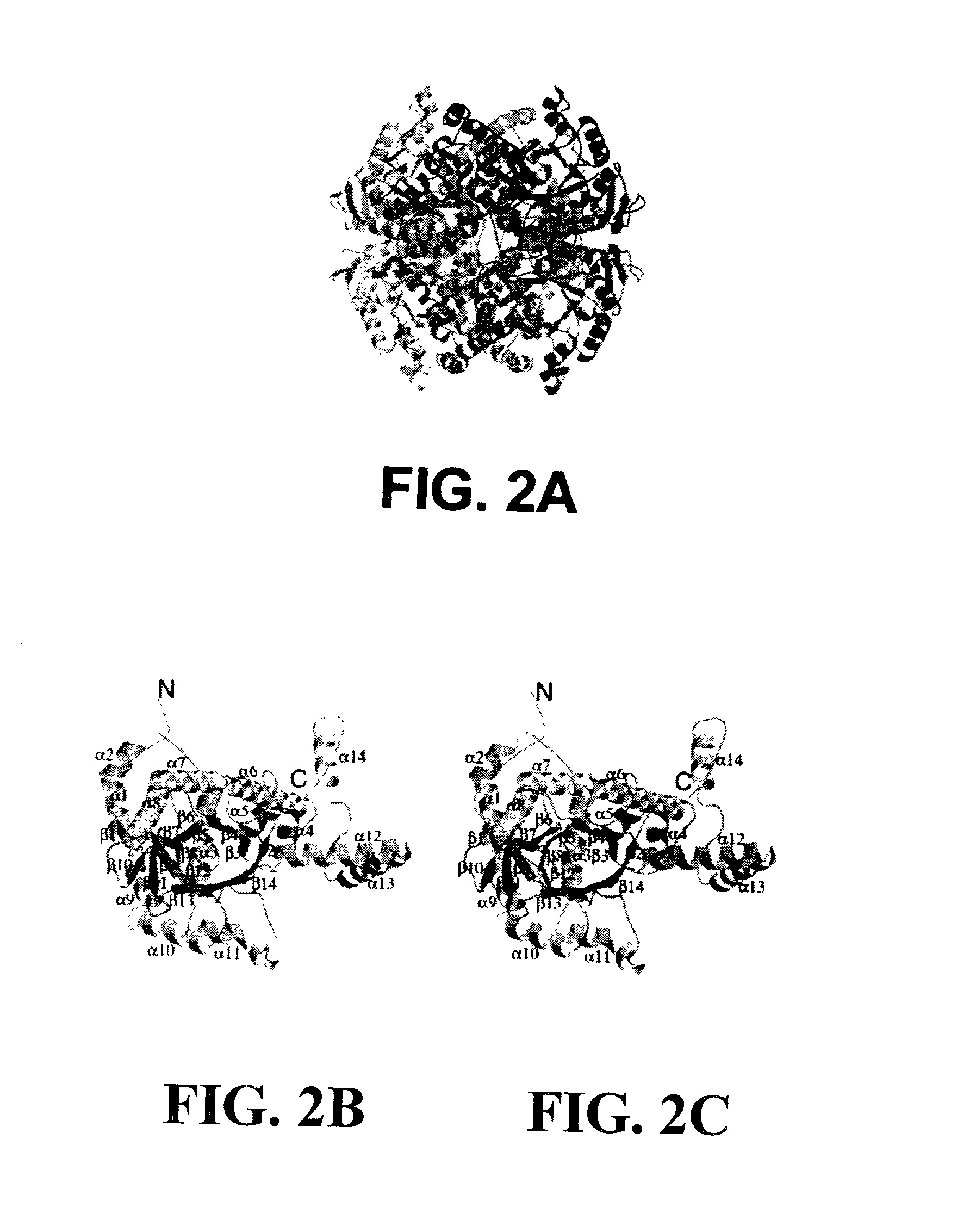
Structure of isocitrate lyase enzyme from mycobacterium tuberculosis and inhibitory agents to combat persistent infection
InactiveUS20030018166A1Reduce usagePromote recombinationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMalate synthaseMicroorganism
The invention provides methods and compositions for use in identifying inhibitors of biochemical pathways important for persistent infection, allowing the identification and / or design of improved therapeutics for treating persistent infections by pathogenic microbes. Particularly disclosed is the importance of the glyoxylate shunt to the persistent phase of various infectious agents, including Mycobacteria, such as M. tuberculosis, and the identification of preferred targets for drug development, including the enzymes isocitrate lyase (ICL) and malate synthase. Crystals and three-dimensional structures of M. tuberculosis ICL, without ligand and in complex with two inhibitors are also disclosed, for exemplary use in the design of inhibitors and therapeutic agents.
Owner:BIOCHAIN INST
Kits for Auxiliary Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
InactiveCN102297968AIncreased sensitivityReduce positive rateImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsDepsipeptidesAIDS diagnosisIfn gamma
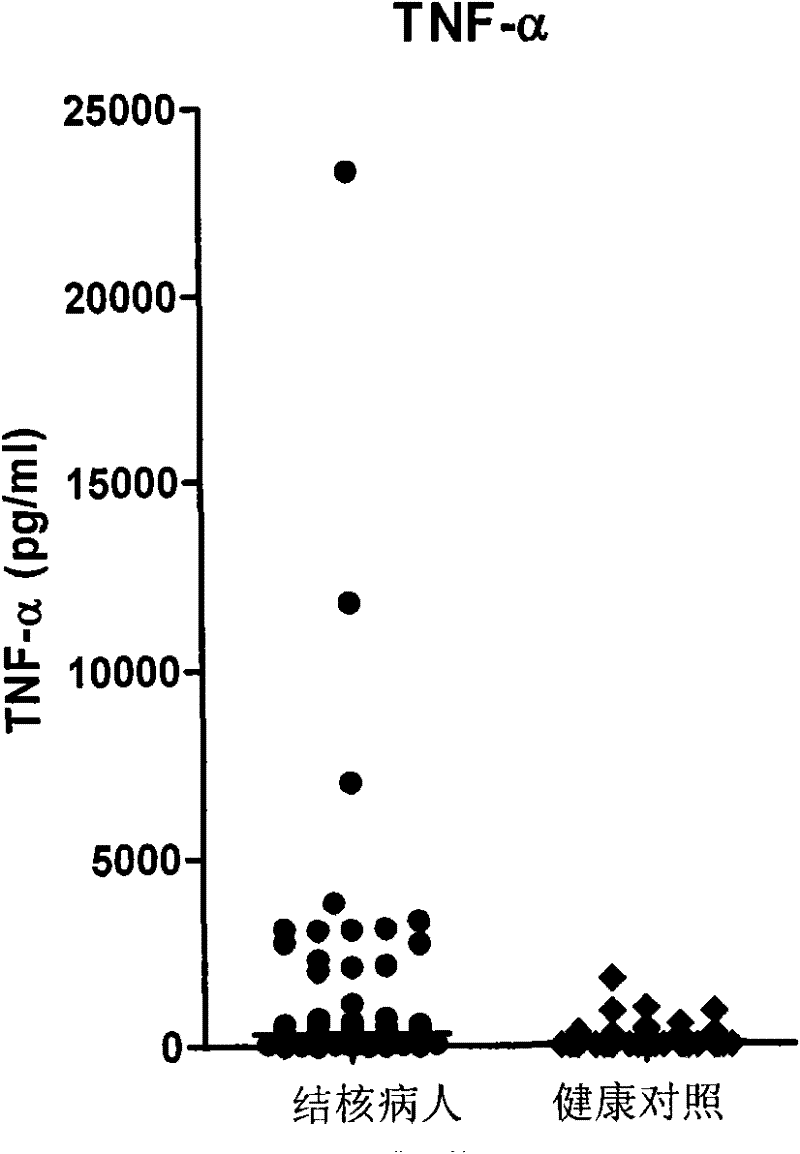
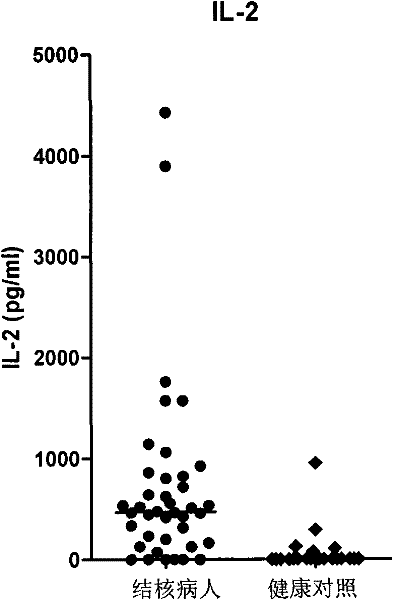
The invention discloses a kit for assisted diagnosis of tuberculosis, which comprises a specific antibody composition, wherein the specific antibody composition comprises the following five antibodies: (1) IFN-gamma antibody, (2) TNF-alpha antibody, (3) IL-2 antibody, (4) MIG antibody and (5) IP-10 antibody. The kit disclosed by the invention can distinguish a Mycobacterium tuberculosis infected person from a BCG vaccinee. Compared with the ELISPOT tuberculosis diagnosis method, the tuberculosis diagnosis kit based on multi-molecular marker detection has obviously enhanced sensitivity to active tuberculosis (from 72% to 89%), and the positive rate for normal healthy persons is obviously reduced (from 27% to 16%).
Owner:程小星 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com