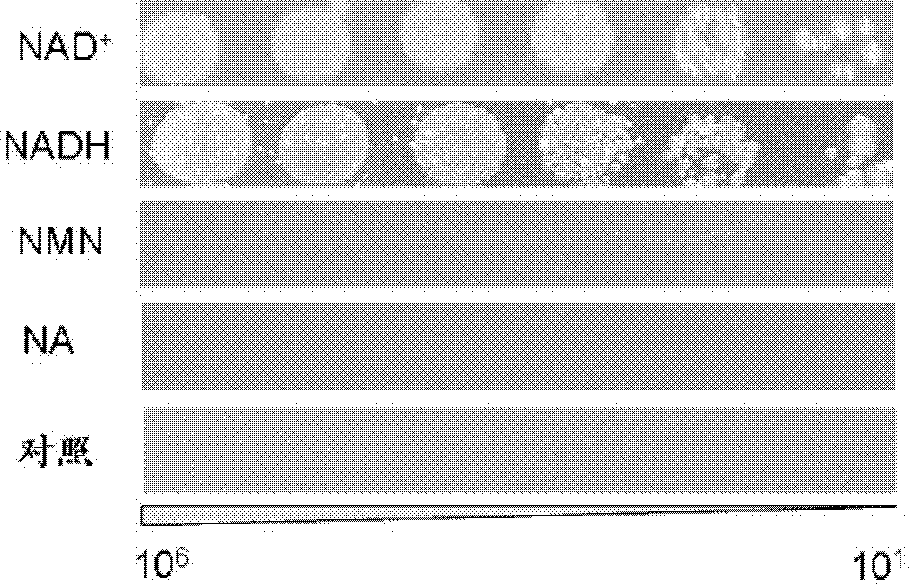
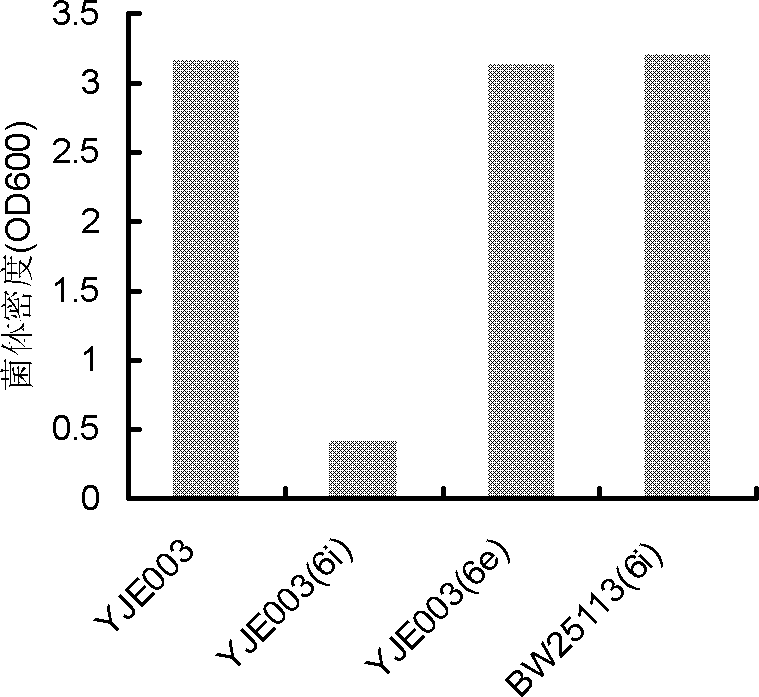
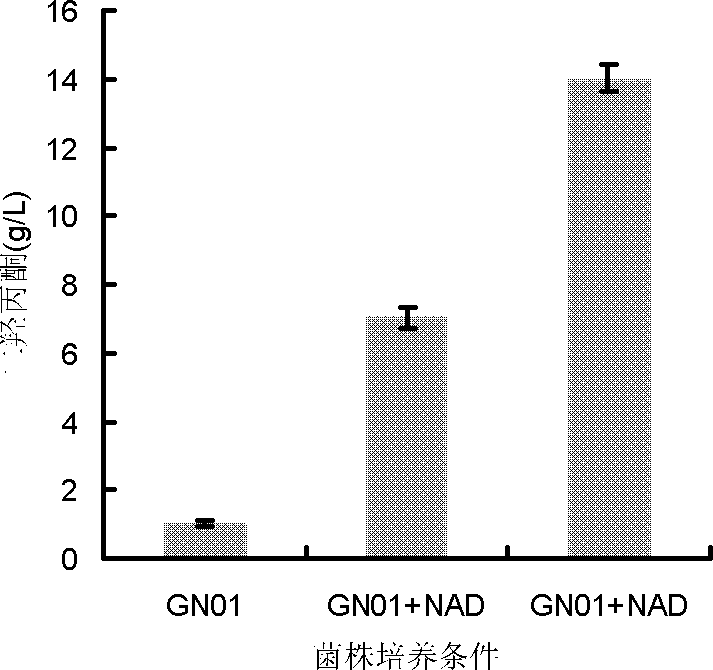
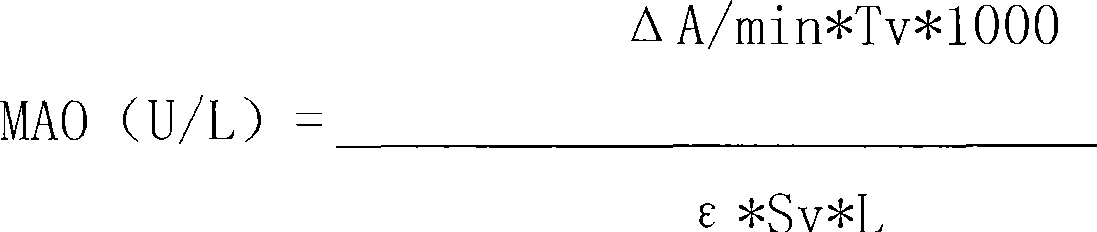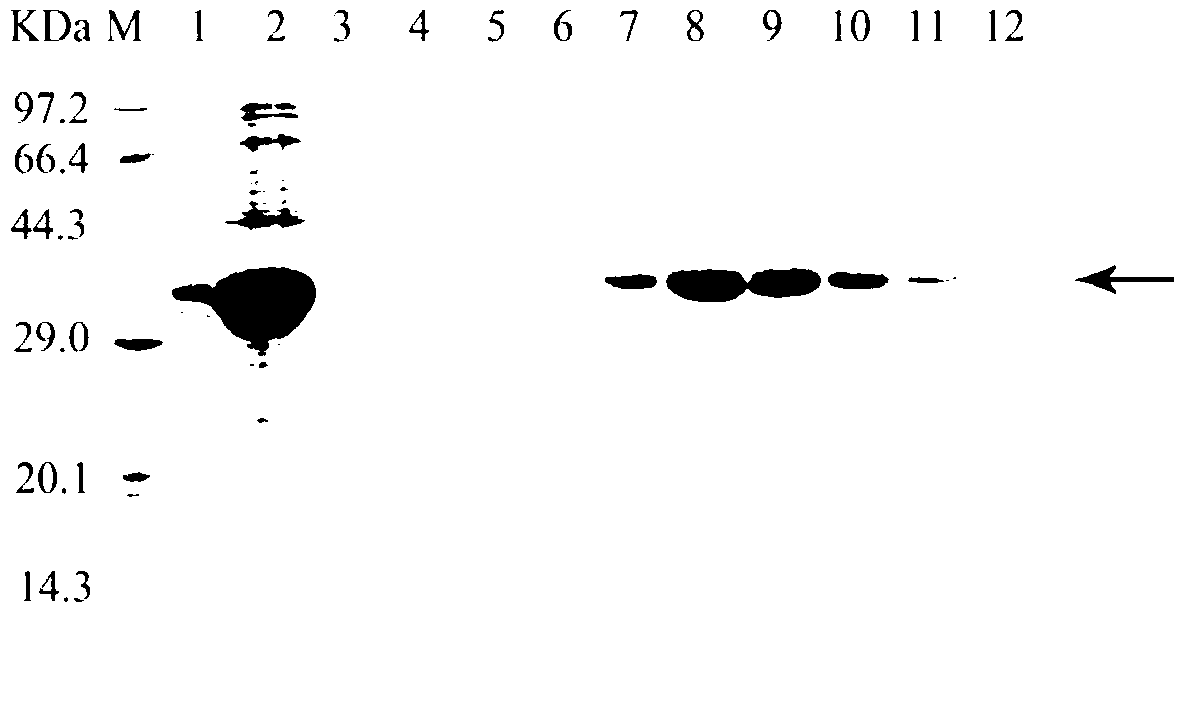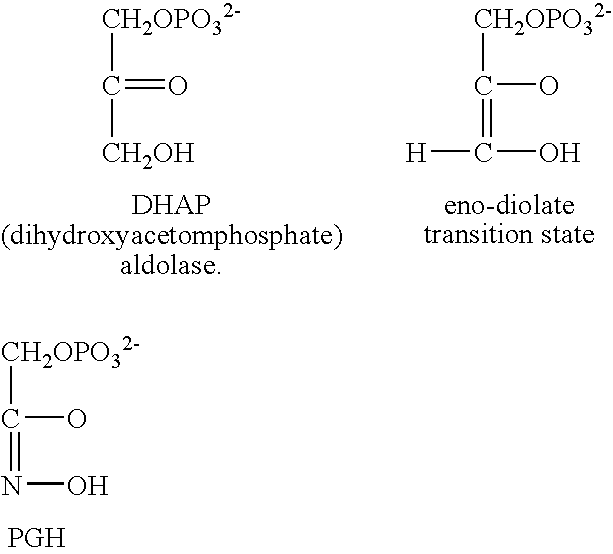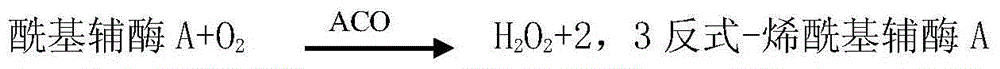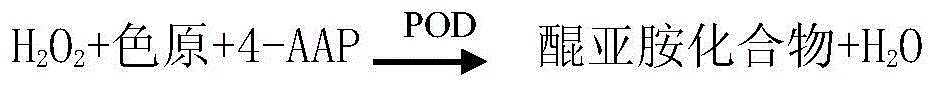Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
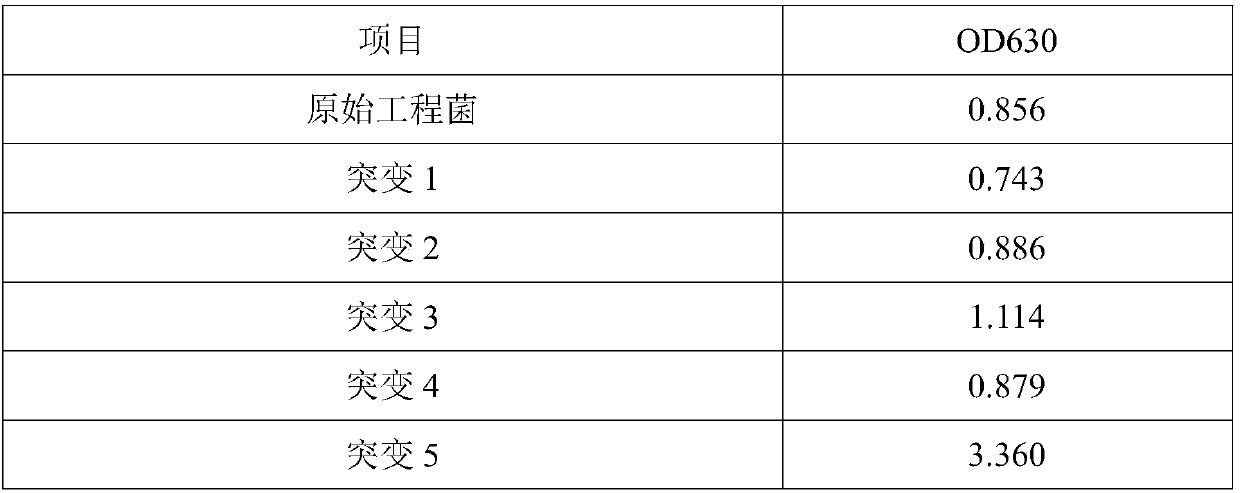
40 results about "Decoyinine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
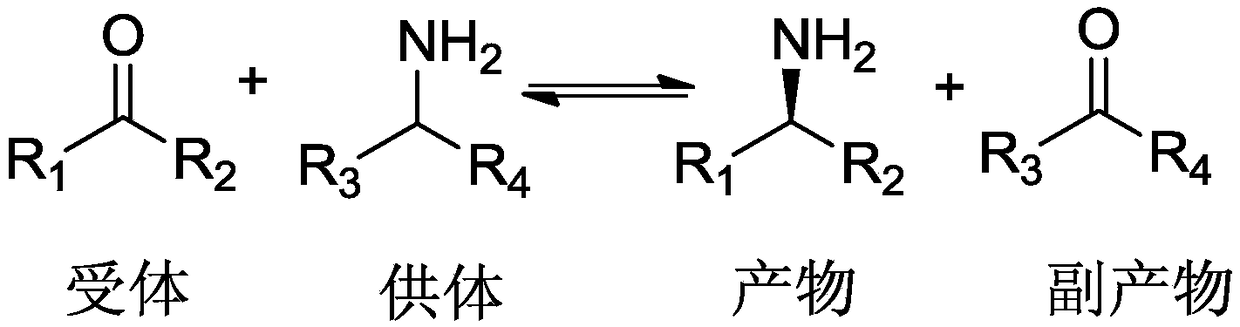
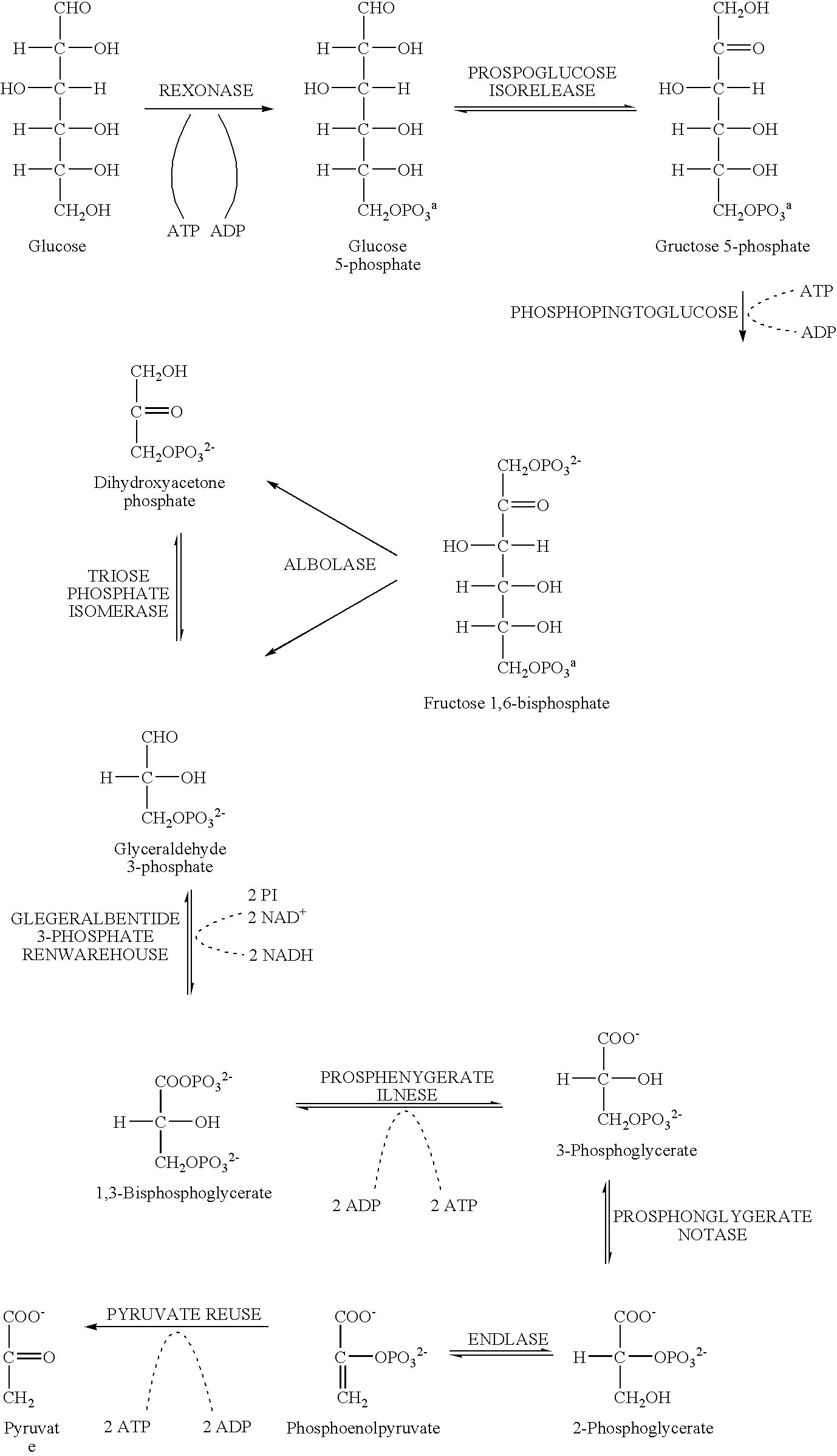
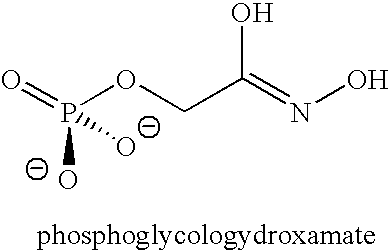
Decoyinine is used to study the inhibition of cell wall synthesis, to inhibit RNA synthesis, to lower intracellular GTP levels in Streptococcus mutans, and to initiate sporulation in Bacillus. Biochem/physiol Actions Decoyinine is a Xanthosine monophosphate (XMP) aminase inhibitor and GMP synthetase inhibitor. Other Notes
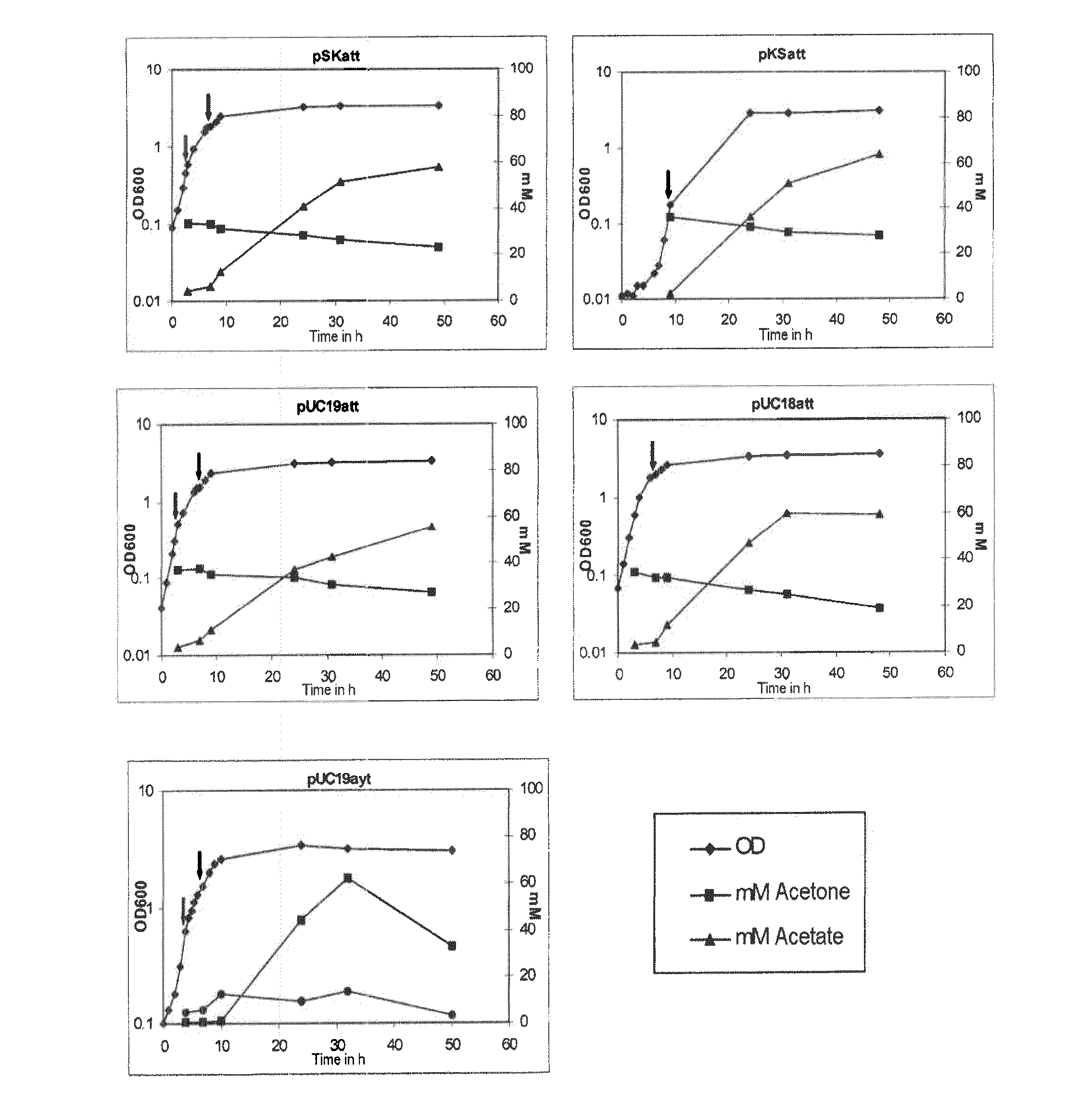
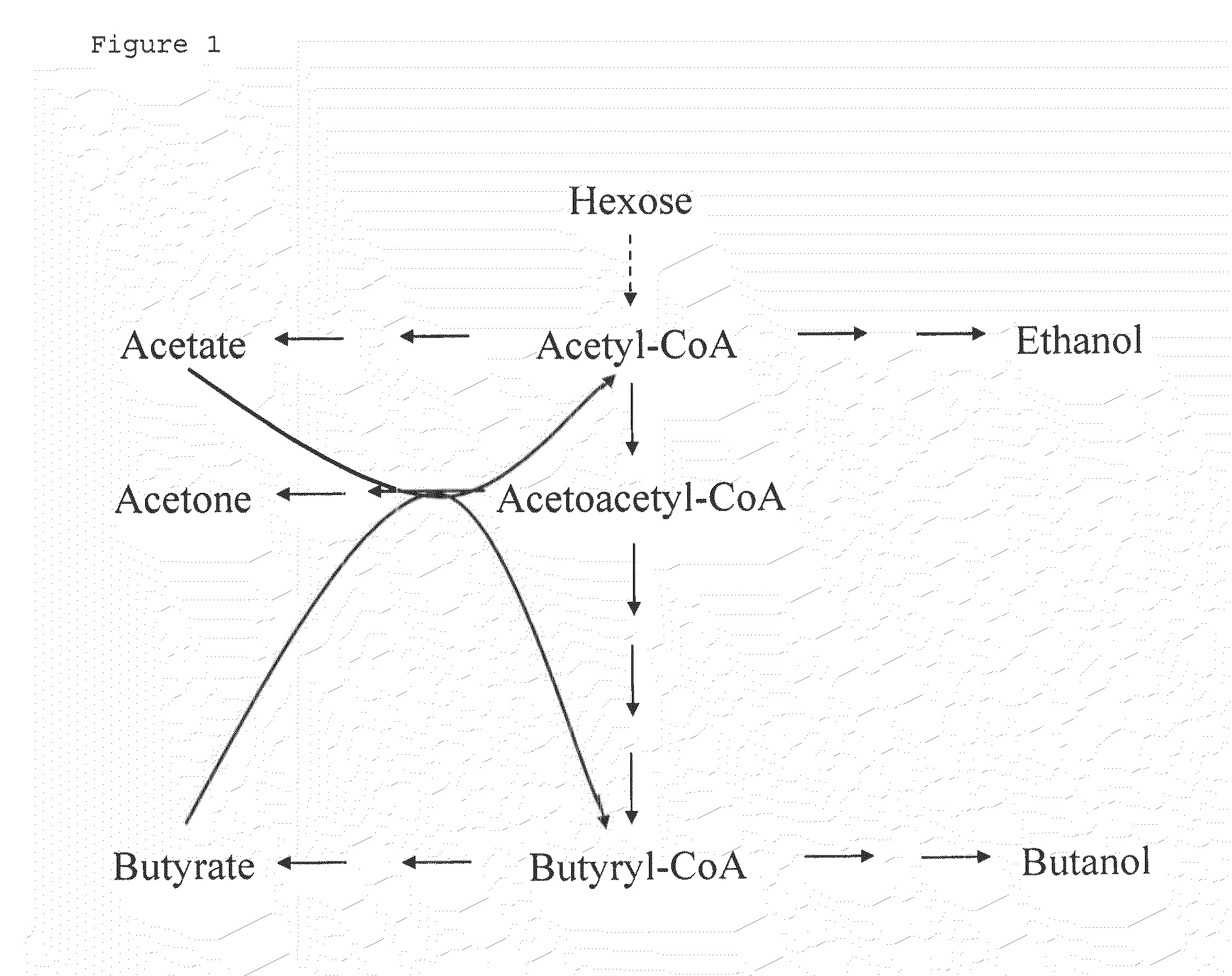
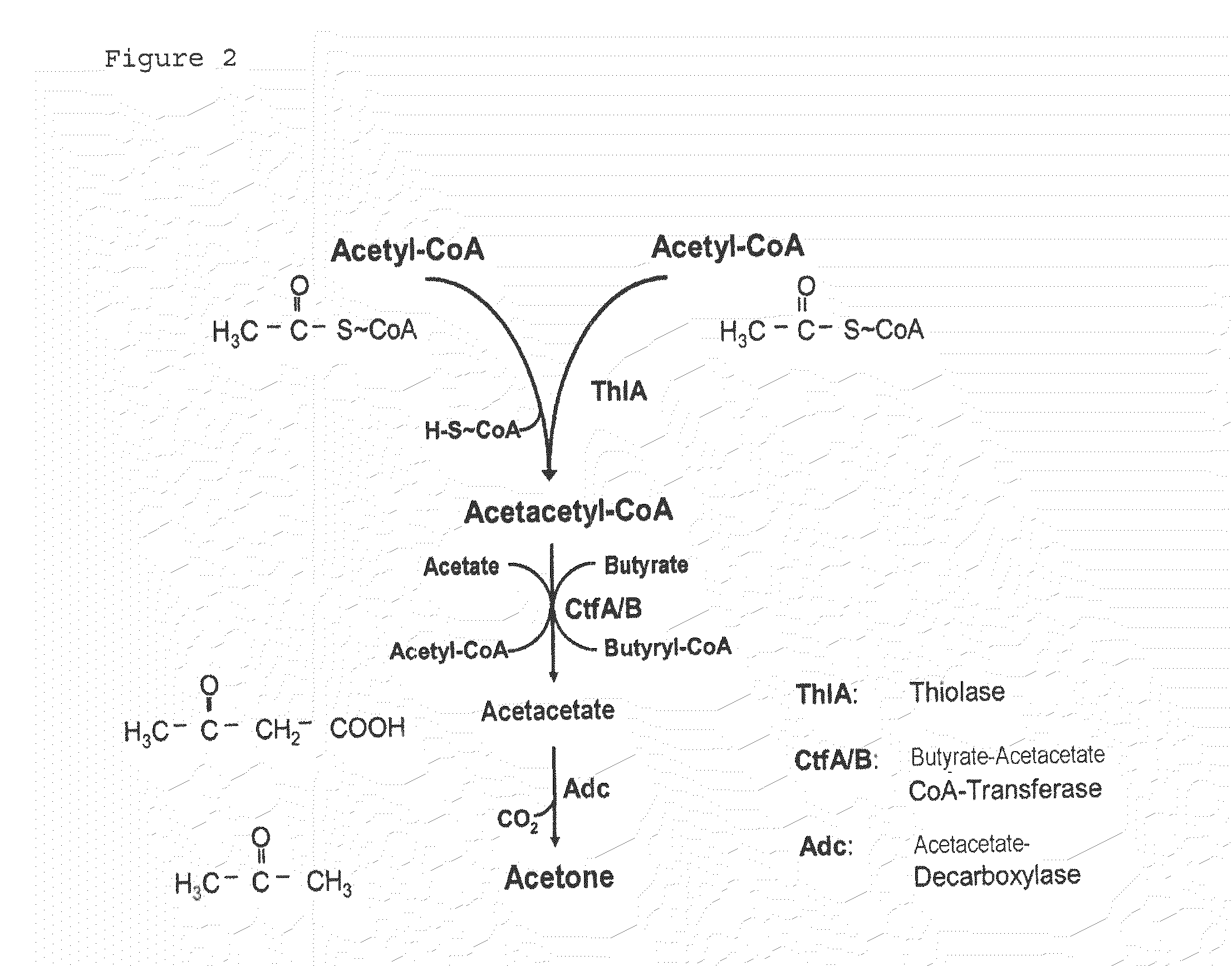
Fermentative production of acetone from renewable resources by means of novel metabolic pathway
ActiveUS20100261237A1YieldHigh yieldSugar derivativesHydrolasesAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesAcyl-CoA synthetase
The invention describes a process for preparing acetone starting from acetyl-coenzyme A comprising process steps A. enzymatic conversion of acetyl-CoA into acetoacetyl-CoA B. enzymatic conversion of acetoacetyl-CoA into acetoacetate and CoA and C. decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone and CO2, which is characterized in that the coenzyme A is not transferred in process step B to an acceptor molecule. In addition, process step B is surprisingly catalysed by enzymes of the classes of acyl-CoA thioesterase, acyl-CoA synthetase or acyl-CoA thiokinase.A completely novel metabolic pathway is concerned, because the enzymatic hydrolysis of acetoacetyl-CoA without simultaneous transfer of CoA to a receptor molecule has never previously been described for any microbial enzyme.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
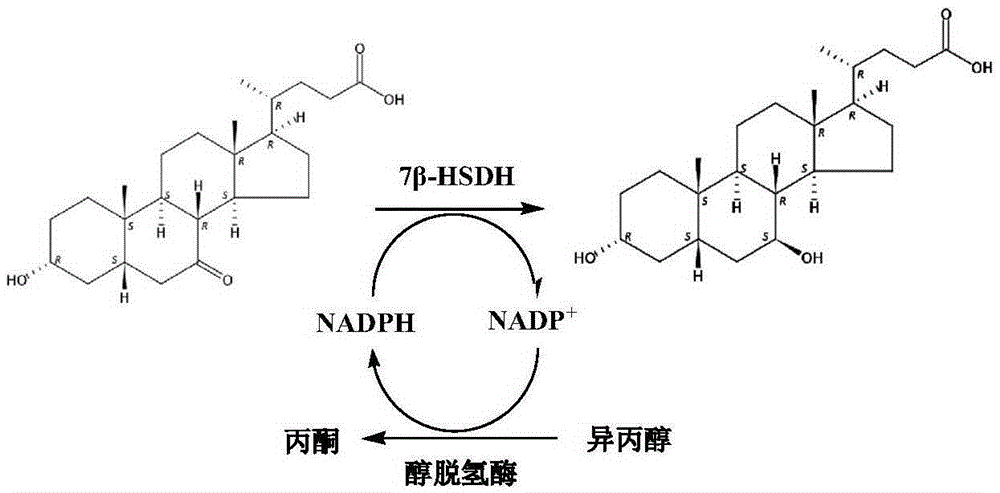
Mutant of 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, application of mutant and synthesis method
ActiveCN105274070ASuitable for industrial productionEasy to controlOxidoreductasesFermentationChemical synthesisCholic acid
The invention provides a mutant of 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, application of the mutant and a synthesis method. The mutant of the 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase is characterized in that amino acid sequences of the mutant are Seq ID NO:4, and coded nucleotide sequences are Seq ID NO:3; or amino acid sequences of the mutant are Seq ID NO:6, and coded nucleotide sequences are Seq ID NO:5. The mutant, the application and the synthesis method have the advantages that cholic acid compounds, particularly ursodeoxycholic acid, can be catalytically synthesized by the efficient 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase, mutant enzymes of the 7 beta-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase and coenzyme regeneration systems, accordingly, the substrate concentration can reach 100 g / L, the conversion rate is 99.2-99.5%, and the weight yield can reach 94-96%; and the enzymes can be inexpensively and easily obtained by the aid of a fermentation process, accordingly, the production cost and the product quality are superior to the production cost and the product quality of chemical synthesis methods, and the mutant and the synthesis method are applicable to industrial production.
Owner:苏州天绿生物制药有限公司
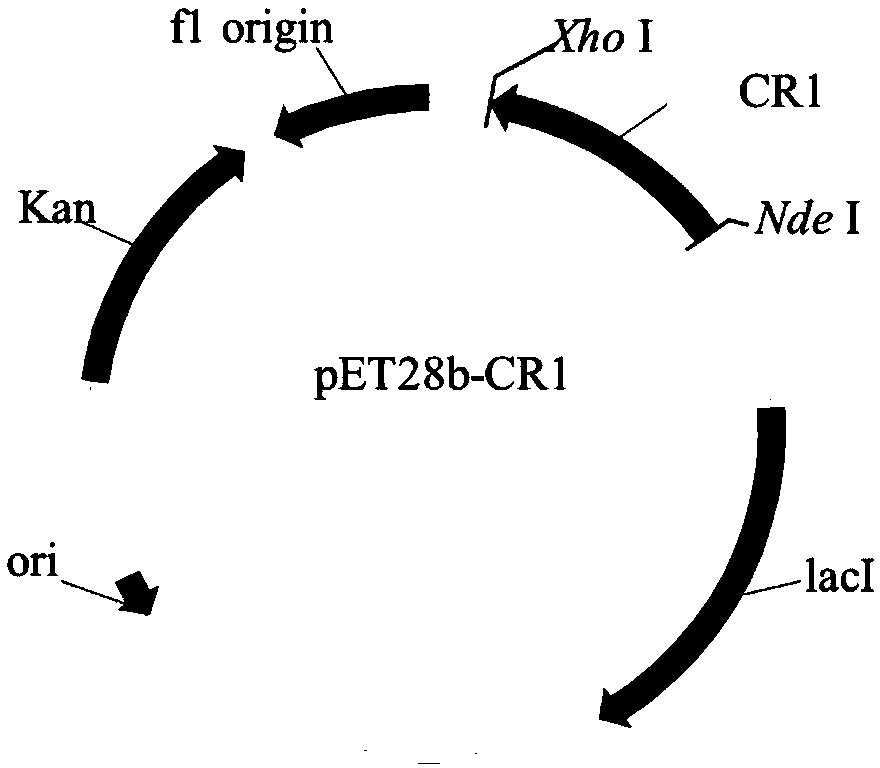
Carbonyl reductase genetically-engineered bacteria immobilized cells and application thereof
ActiveCN107653238AEmission reductionExcellent space-time yieldMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliOrganic solvent
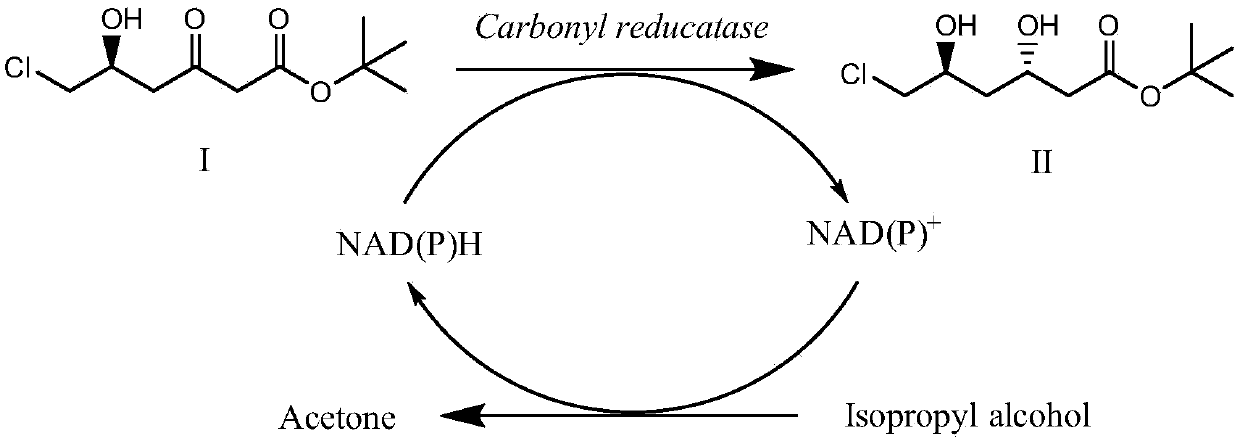
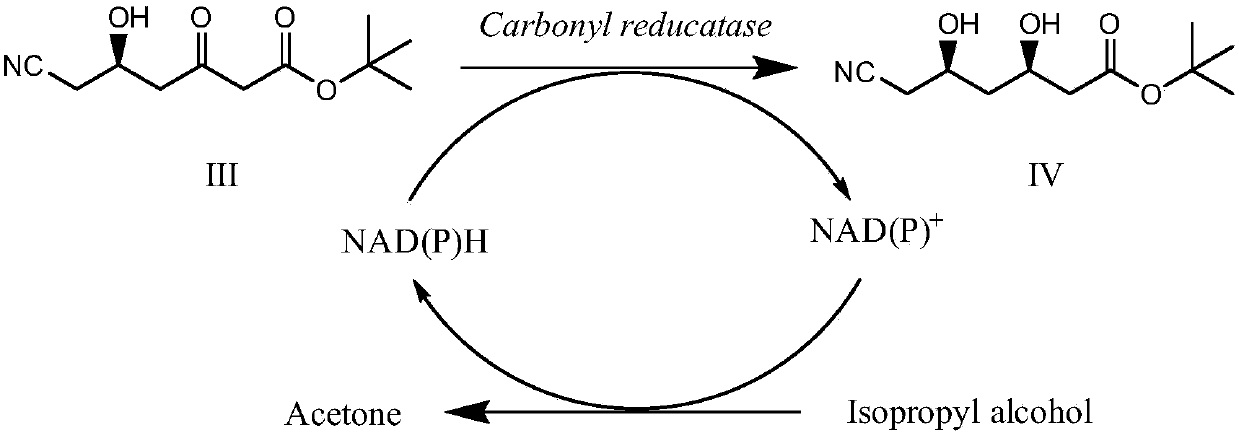
The invention provides a method of using immobilized Escherichia coli engineered bacterial cells to catalytically synthesize statin drug chiral intermediates, tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate and (3R,5R)-tert-butyl-6-cyano-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate. The method comprises: culturing carbonyl reductase-containing Escherichia coli engineered bacteria, preparing immobilized cells, and synthesizing the novel drug chiral intermediates, tert-butyl (3R,5S)-6-chloro-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate and (3R,5R)-tert-butyl-6-cyano-3,5-dihydroxyhexanoate by catalysis of the immobilized cells. The immobilized biological Escherichia coli engineered bacterial cells are used in the method as the catalyst, the stability is good, the service life is long, tolerance to organic solvents is good, the catalyst is reusable, adding expensive external coenzymes is not required, the catalyst is capable of catalyzing the synthesis of statin drug intermediates in an organic phase reaction system, the productsare high in yield and purity, the production cost can be greatly reduced, the process steps can be simplified, emission of three wastes is reduced, and the method is very worthy of application in theindustrial production of statin drug chiral intermediates.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Threonine aldolase, coding gene thereof, and application of threonine aldolase to biosynthesis of L-threo-DOPS
The invention relates to threonine aldolase, a coding gene thereof, and an application of the threonine aldolase to biosynthesis of L-threo-DOPS, and belongs to the field of a biological technology. The threonine aldolase is protein as shown in SEQID NO.1, or protein having the same functions, obtained through replacing and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues to an amino acidsequence as shown in SEQID NO.1. The threonine aldolase can use benzaldehyde with replaced 3- / 4- hydroxyl as a substrate, 5-pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme and glycine as an assistance substrate. Under the appropriate condition and in an appropriate medium, an enzyme catalysis reaction is performed, and biosynthesis is performed to obtain the L-threo-DOPS (L-threo-DOPS). The non-antipode selectivity of the method can achieve 30%. The threonine aldolase having high selectivity has important significance for biocatalysis of the L-threo-DOPS.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
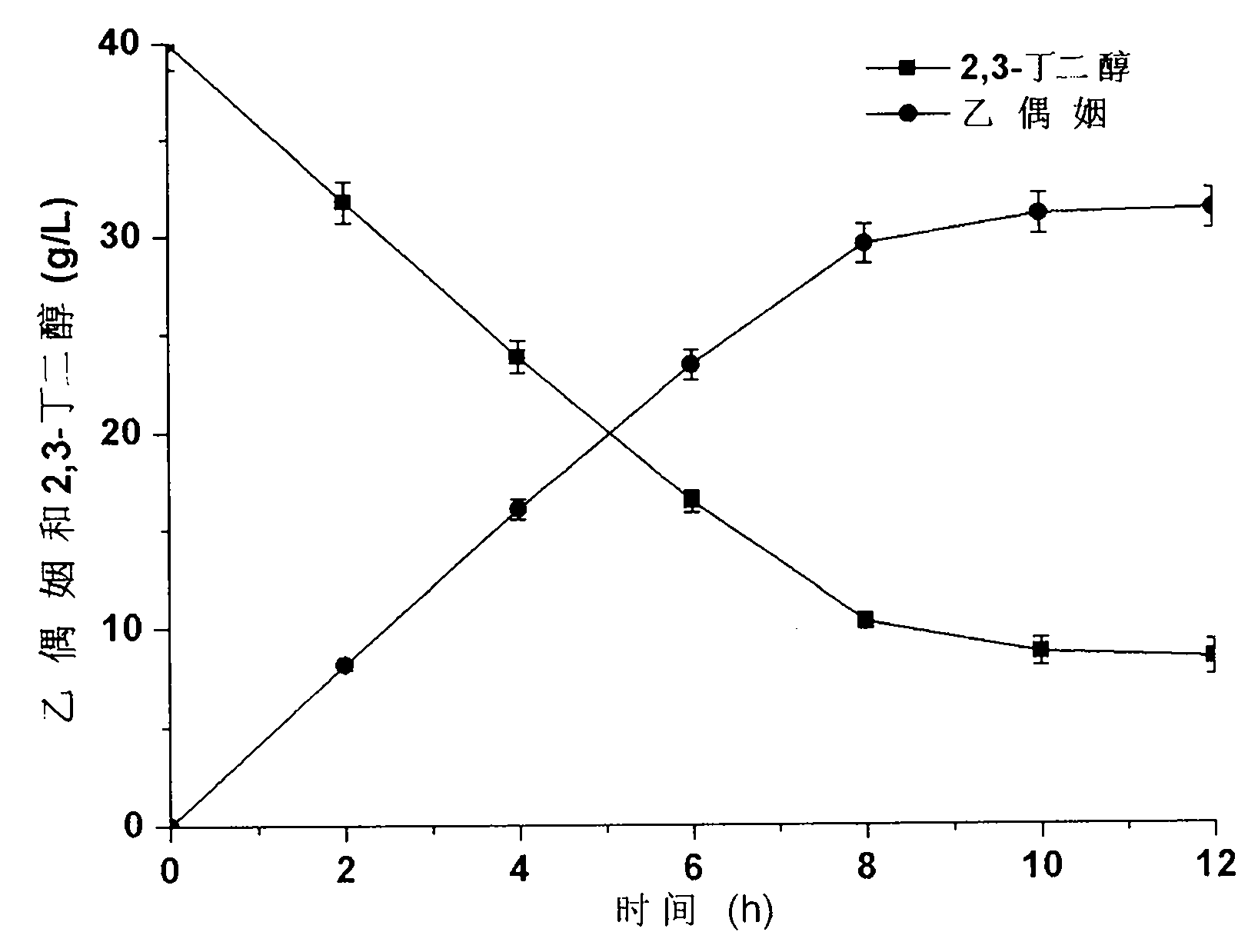
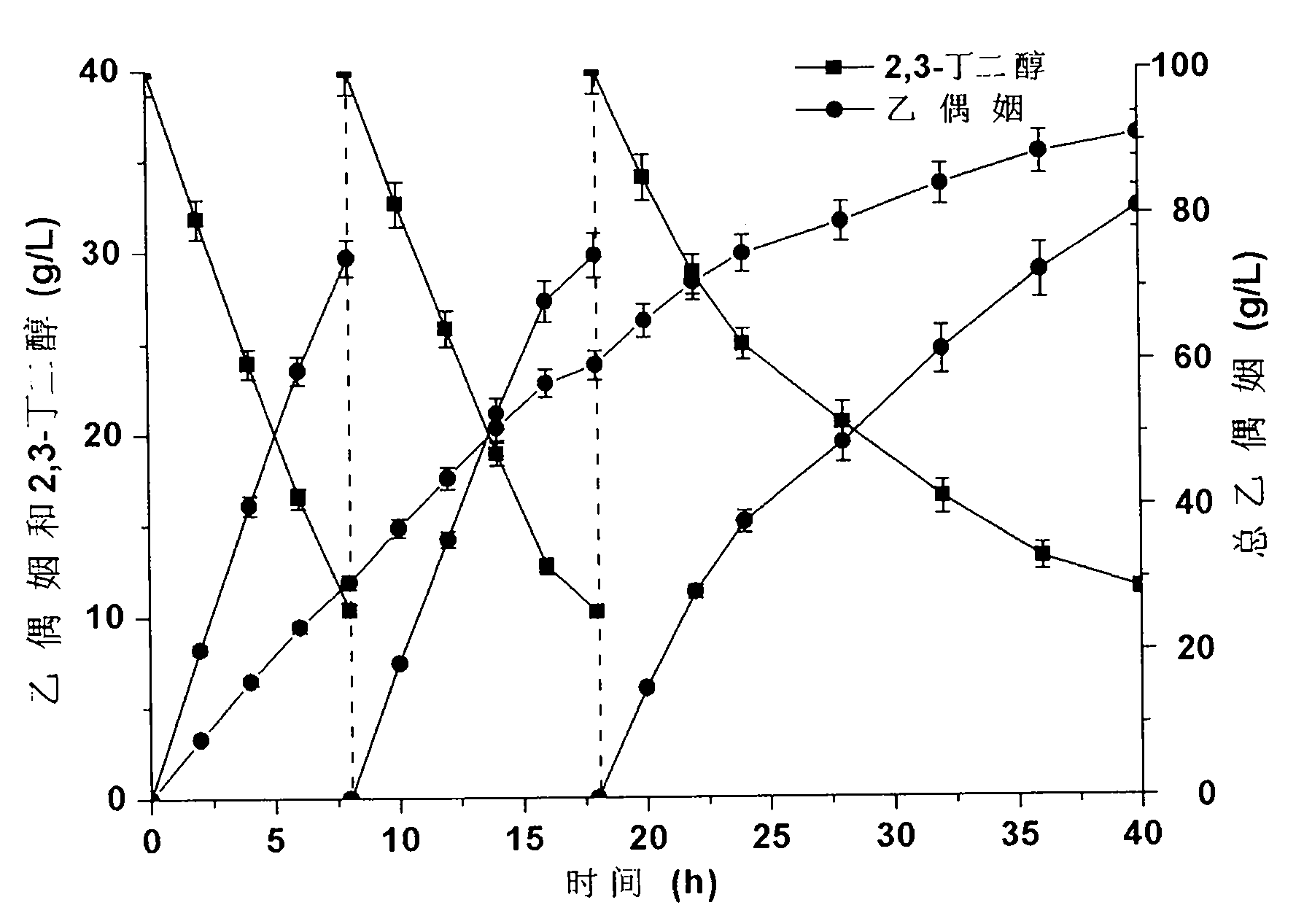
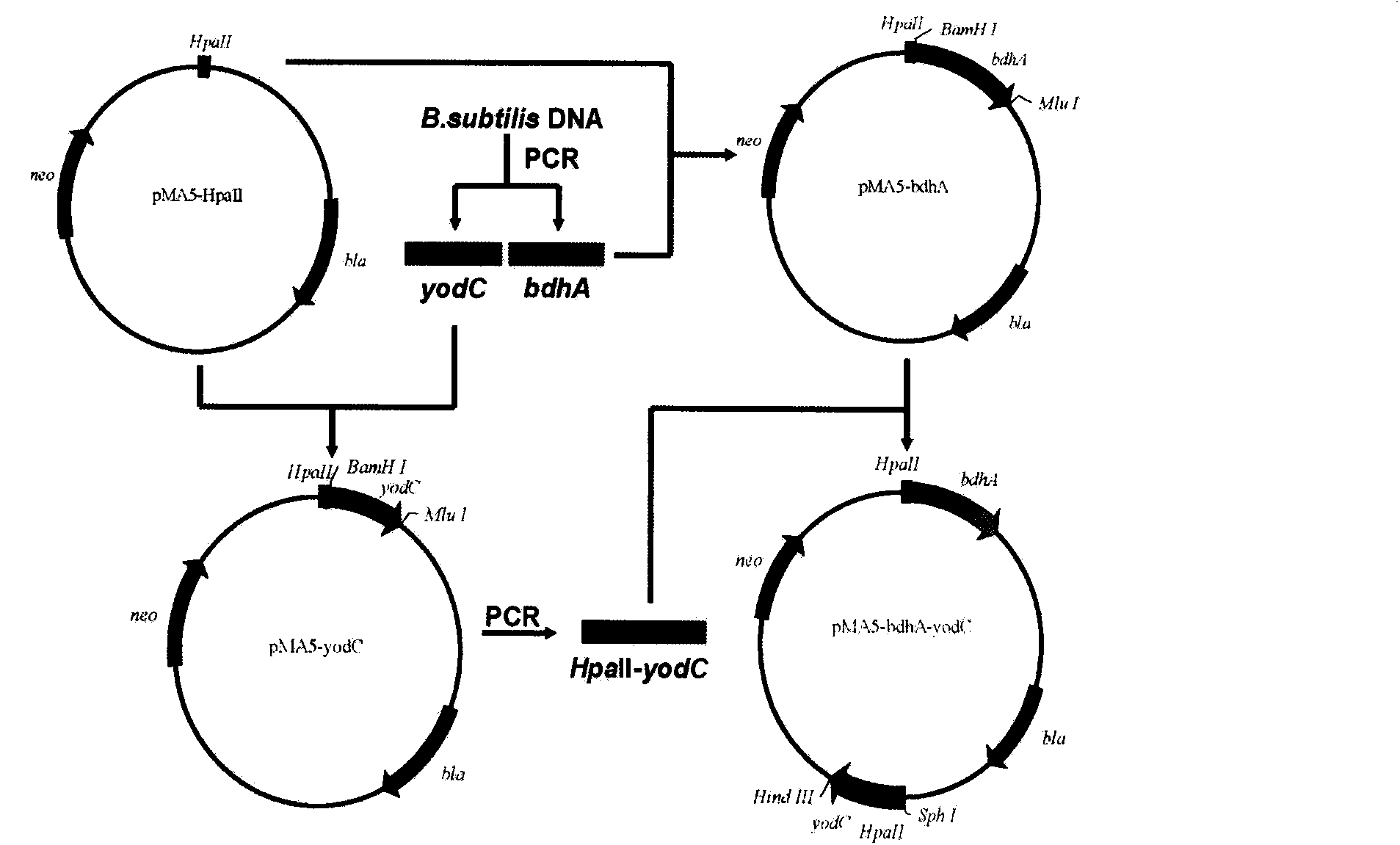
Method for producing acetoin by efficient bioconversion of 2,3-butanediol by using Bacillus subtilis nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)<+> regeneration system
InactiveCN104017764AEasy to separateLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWild typeButanediol
The invention discloses a method for producing acetoin by efficient bioconversion of 2,3-butanediol by using a Bacillus subtilis nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD)<+> regeneration system, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Acetoin reductase and educed form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide (NADH) oxidase in a high-yield acetoin strain B.subtilis JNA with independent intellectual property rights, which are autonomously screened from a laboratory are cloned by the method disclosed by the invention, and excessive coexpression of the acetoin reductase and NADH oxidase in B.subtilis JNA is carried out, so that the production of acetoin by effective conversion of the 2,3-butanediol in the wild-type high-yield acetoin bacillus subtilis by virtue of the NAD<+> regeneration system is realized for the first time at home and abroad. The enzyme activity determination and intracellular coenzyme level research on the built gene engineering strain prove that the 2,3-butanediol can be lastingly and effectively converted by B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-bdhA-yodC to produce the acetoin. 120g / L of 2,3-butanediol can be finally converted into about 92.5g / L of acetoin by the B.subtilis JNA / pMA5-bdhA-yodC when the temperature is 40 DEG C and the pH is 8.0 under the optimal whole-cell conversion condition of adding 5mM of MnC12, the acetoin yield can be up to 2.31g / (L.h), and is the highest lever for producing the acetoin from the bacillus subtilis in the current report, and a foundation is provided for industrial production of the acetoin from microorganisms.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
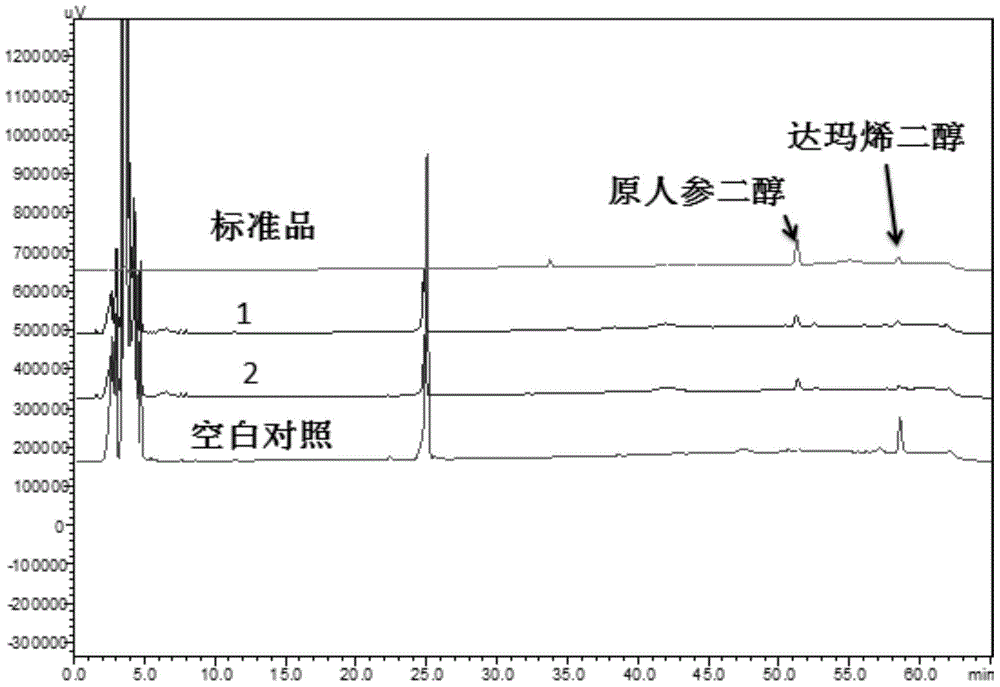
NADPH-cytochrome P450 reducing ferment and application thereof
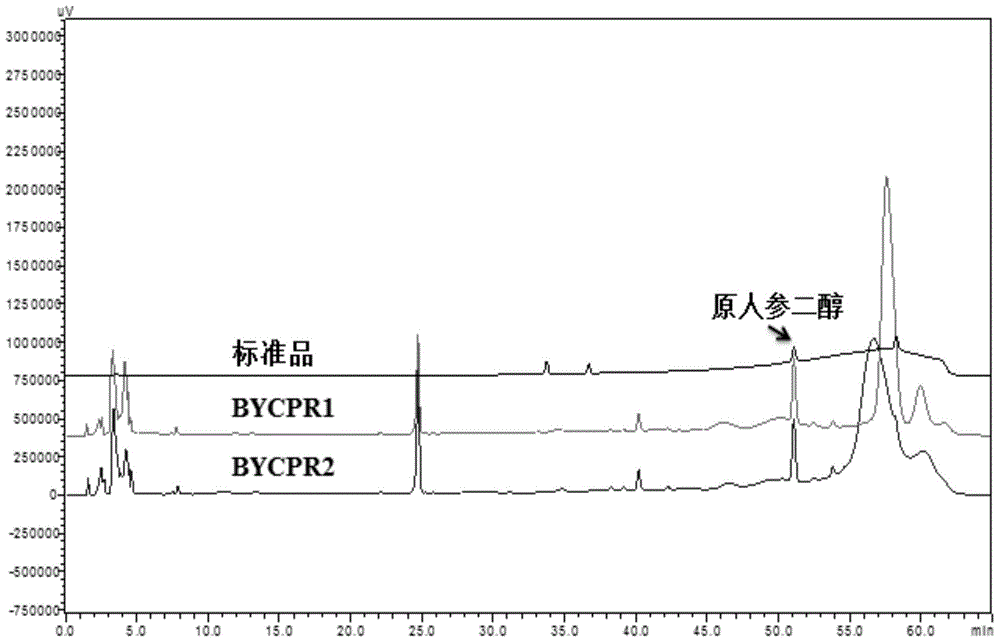
Provided is a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADPH)-cytochrome P450 reductase and a use thereof. Also provided is a polynucleotide encoding the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, an expression vector and a host cell which express the NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase, and a method for producing the protopanoxadiol.
Owner:SYNBIOTECH (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Construction method and application of metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing hydracrylic acid from acetic acid
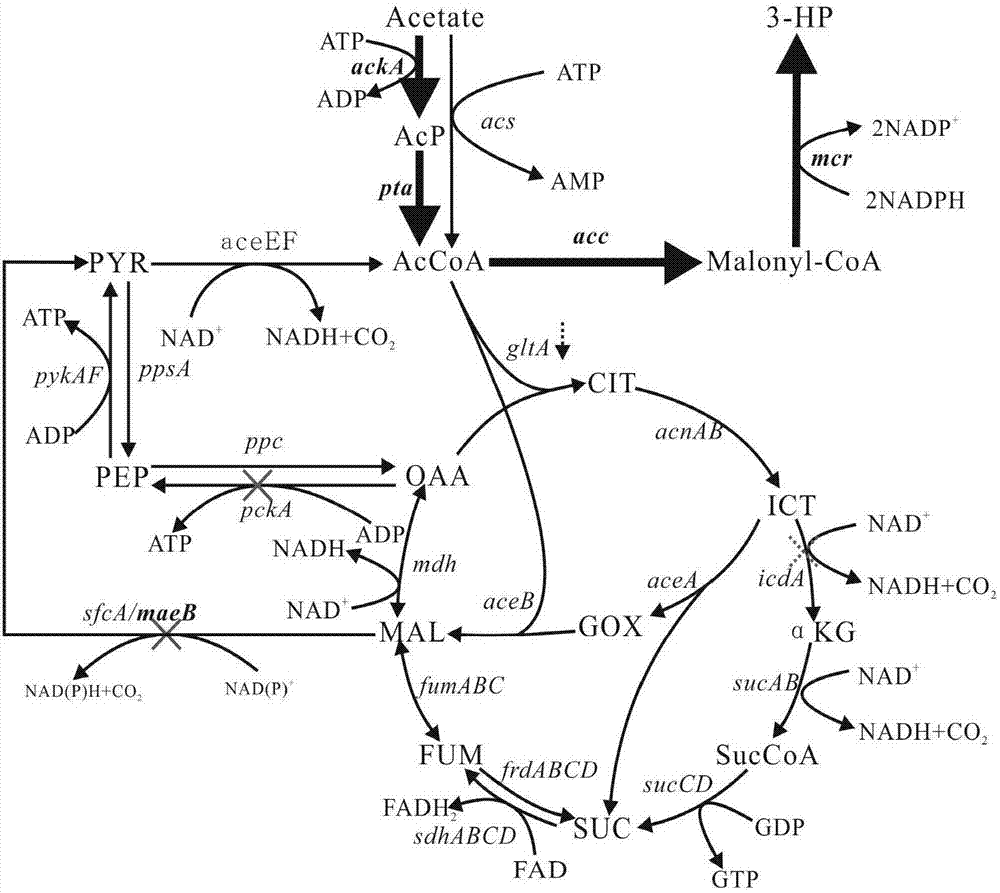
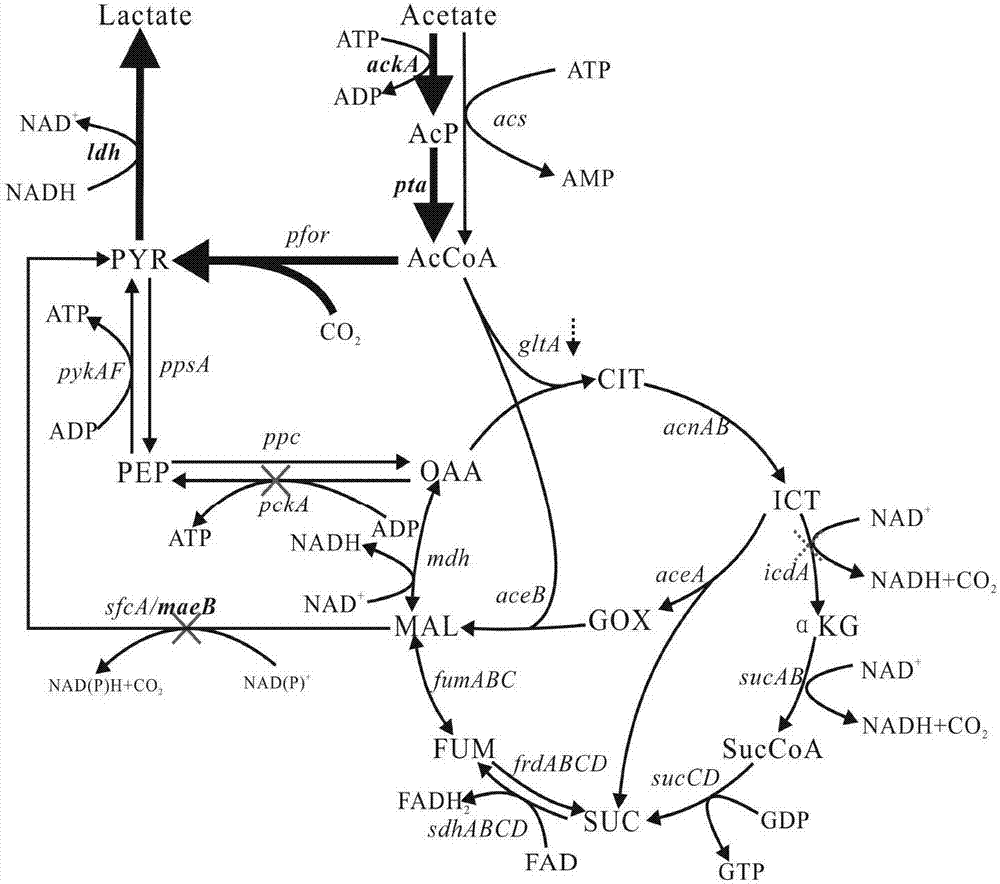
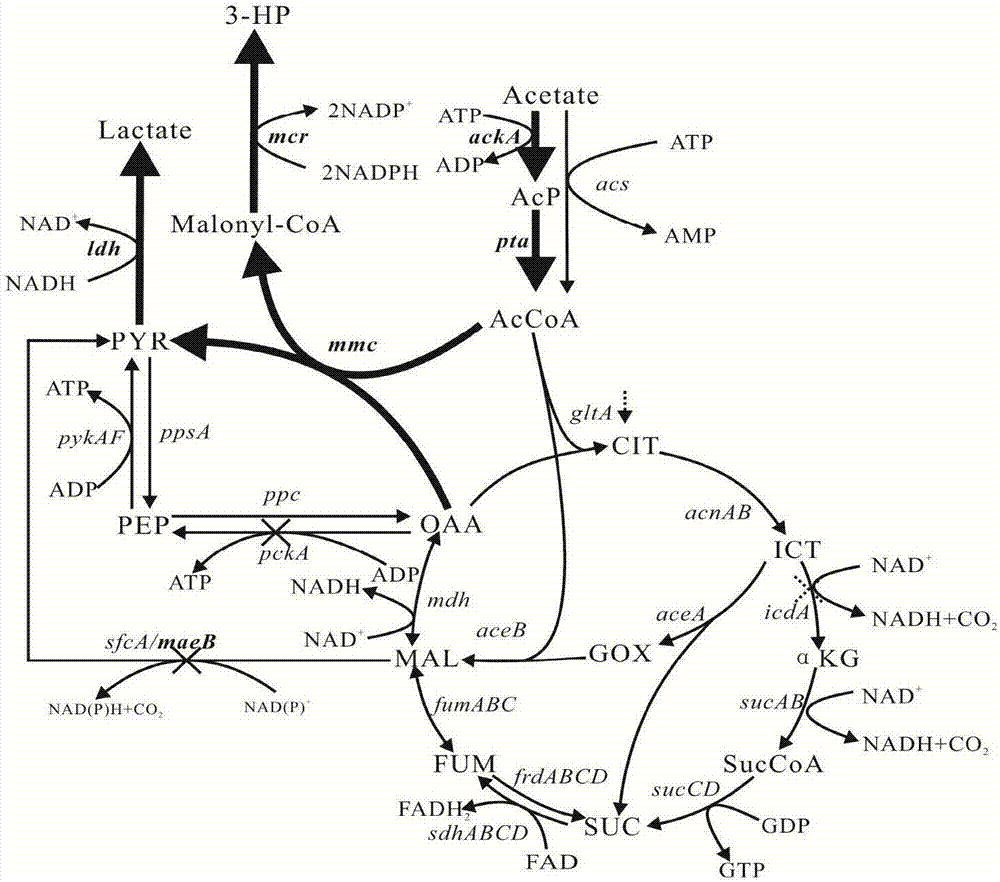
The invention discloses a construction method of a metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing hydracrylic acid from acetic acid. Escherichia coli reformed by metabolic engineering isutilized for producing hydracrylic acid by fermenting acetic acid; and construction ways are as follows: constructing a metabolic way for producing hydracrylic acid from acetyl CoA, and / or over-expressing relevant genes of an acetic acid intake way so as to increase the transmission rate of acetic acid, and / or blocking or decreasing TCA circle so as to increase metabolic flow of acetyl CoA flowingtowards a target metabolite, and / or reducing decarboxylic reaction between malic acid or oxaloacetic acid so as to delete a byproduct generation way, and / or deleting key genes in an alcohol production way so as to regulate metabolic flow of an acetyl CoA node and / or regulating intracellular oxidation reduction balance through coenzyme engineering. According to the construction method, a production way for exogenously expressing hydracrylic acid is constructed, the metabolic ways, the adjustment and control are analyzed, and escherichia coli is reformed by virtue of a metabolic engineering measure, so that the prepared strain can be utilized for producing hydracrylic acid in a culture medium taking acetic acid as a carbon source.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Lysine decarboxylase strain and application thereof in production of pentamethylenediamine
InactiveCN109652356AIncrease productivityBacteriaMutant preparationEscherichia coliLysine decarboxylase activity
The invention discloses a lysine decarboxylase strain and an application method thereof in the production of pentamethylenediamine. The lysine decarboxylase strain adopts recombinant bioengineering bacteria obtained by introducing a lysine decarboxylase gene into escherichia coli by a genetic engineering method as a starting strain, a high enzyme activity lysine decarboxylase strain is obtained bymutagenesis screening, the preservation number is CGMCC No. 16762, and compared with original engineering bacteria, the lysine decarboxylase activity is increased by 3.93 times. The invention furtherdiscloses the application of the lysine decarboxylase strain in the production of the pentamethylenediamine, the lysine decarboxylase strain is subjected to fermentation culture to obtain a fermentation broth containing the lysine decarboxylase, the fermentation broth is added in an amount of 5% in the lysine hydrochloride and a coenzyme solution, the conversion is carried out for 3 h at 40 DEG C, the highest content of the pentanediamine is 326.3 g / L, and the molar conversion of the lysine hydrochloride reaches 99.98%.
Owner:SHANDONG SHOUGUANG JUNENG GOLDEN CORN CO LTD +3
Genetically engineered bacterium, and applications thereof in preparation of L-phosphinothricin
ActiveCN108795835AIncrease enzyme activityImprove stabilityBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium, and applications thereof in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The genetically engineered bacterium comprises Escherichia coli and recombinant plasmids transferred into Escherichia coli; the recombinant plasmids contain transaminase gene and pyridoxal phosphate synthetic route enzyme gene; the nucleotide sequence of the transaminase geneis represented by SEQ ID NO.1; the nucleotide sequence of the pyridoxal phosphate synthetic route enzyme gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.2-5. According to the applications, genetic engineering technology is adopted to express ribose-5-phosphate pathway synthesis key gene PdxST in Escherichia coli, or enhance Escherichia coli self PLP synthesis pathway key gene epd, pdxJ, and dxs expression; preparation of the coenzyme reinforced transaminase genetically engineered bacterium through construction is capable of increasing intracellular coenzyme PLP content obviously, avoiding adding of externally-sourced PLP in production of L-phosphinothricin using the genetically engineered bacterium, increasing transaminase enzyme activity and stability obviously, prolonging transaminase half life, reducing production cost, and increasing L-phosphinothricin production efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombinant escherichia coli immobilized cell and application to production of xylitol from xylose mother liquor
ActiveCN108977432ASimple production methodIncreased space-time yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli immobilized cell and application to production of xylitol from xylose mother liquor. The immobilized cell is prepared by the steps: jointly guiding xylose reductase gene and glucose dehydrogenase gene into host escherichia coli to obtain recombinant escherichia coli containing bi-enzyme gene, then fermenting and culturing the recombinant escherichia coli and taking wet somatic cell to be immobilized to obtain the recombinant escherichia coli immobilized cell. According to the recombinant genetically-engineered bacterium E.coli BL21(DE3) / pCDFDuet-1-XR-GDH disclosed by the invention, bi-enzyme coexpression of xylose reductase and glucose dehydrogenase is achieved, no extra coenzyme is added into a bi-enzyme coupling system, a productionmethod is simple and efficient, the space time yield is far higher than a fermentation method, the xylose conversion rate in the xylose mother liquor can reach 99% or above, and glucose is utilized asan auxiliary substrate; after 200g / L xylose is catalyzed by the recombinant cell and reacts for 30 h, the xylitol yield is 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10
The present invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10. The genetically engineered bacteria comprises coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria and desired genes transferred into the coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria, and the desired genes are a demethylnaphthoquinone methyltransferase gene, a 2-octo isoprene-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-hydroquinone hydroxylase gene and a 3-demethyl ubiquinone-93-methyl transferase gene. Rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF in a coenzyme Q10 synthetic route are transferred into rhodobacter sphaeroides, and by in-series over-expression of the three rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF, coenzyme Q10 synthesizing capability of the rate-limiting enzyme genes can be strengthened; and compared with the rhodobacter sphaeroides with no desired gene being transformed, by use of the genetically engineered bacteria for coenzyme Q10 producing, the yield of the coenzyme Q10 is increased by more than 20%.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
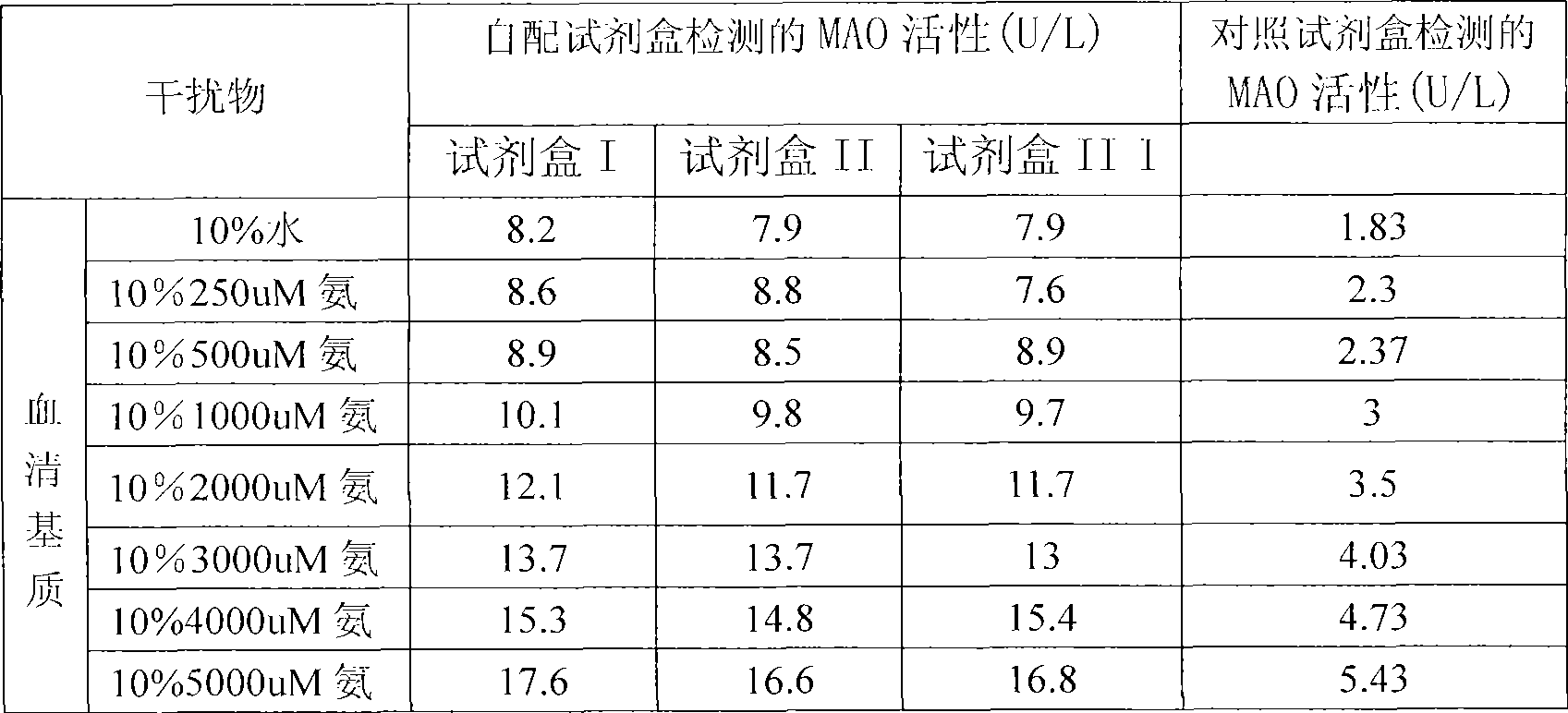
Reagent kit for monoamine oxidase MAO single-reagent measurement
InactiveCN101498662AEasy to operateEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSemi automaticOxygen
The invention discloses a kit of single reagent used for diagnosing monoamine oxidase (MAO) in serum. MAO hydrolyzed benzylamine, butyl amine, amyl amine, Beta-phenylethyl amine and other amine compounds are utilized to produce oxygen; the oxygen reacts with glutamate dehydrogenase in a coupling way; oxidized coenzyme is formed by the reaction of reduced coenzyme; and the activity of sample MAO formed by quantitative reaction is calculated through measuring the descending speed of the absorbance of light with a wavelength of 340 nm; in addition, enzyme and substrate enzyme which can slowly generate reduced nicotinoyl coenzyme are added in the reaction process, so that an enzyme-substrate enzyme-nicotinoyl coenzyme slow reaction system is formed in single reagent and the nicotinoyl coenzyme can be compensated slowly and circularly and further the single reagent can be stabilized when the concentration of the single reagent achieves a certain balance. The kit is convenient for use and simple is structure, can be used on a common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or a semi-automatic / full-automatic biochemical analyzer for rapid measurement without using a special or additional apparatus and has low cost.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
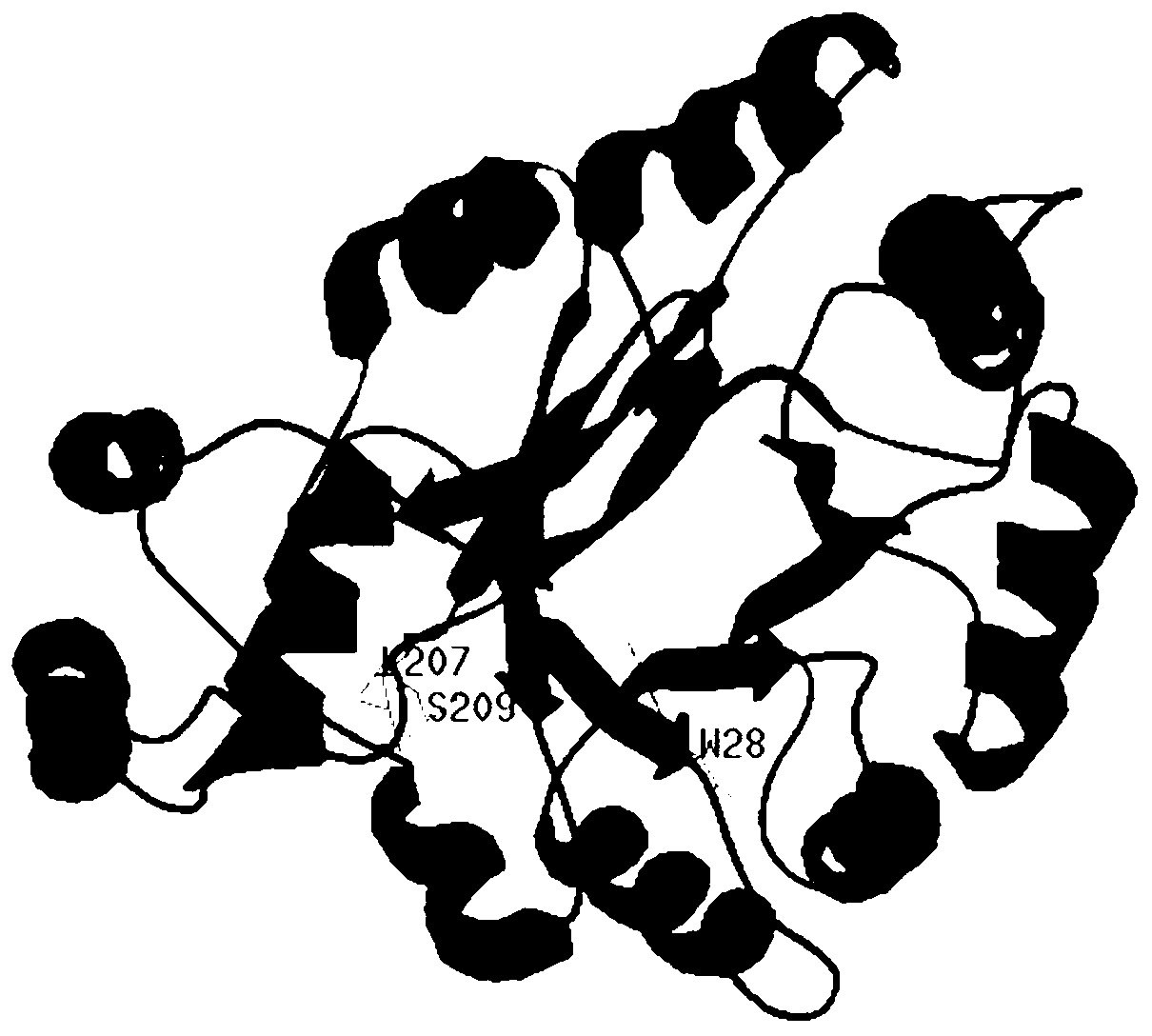
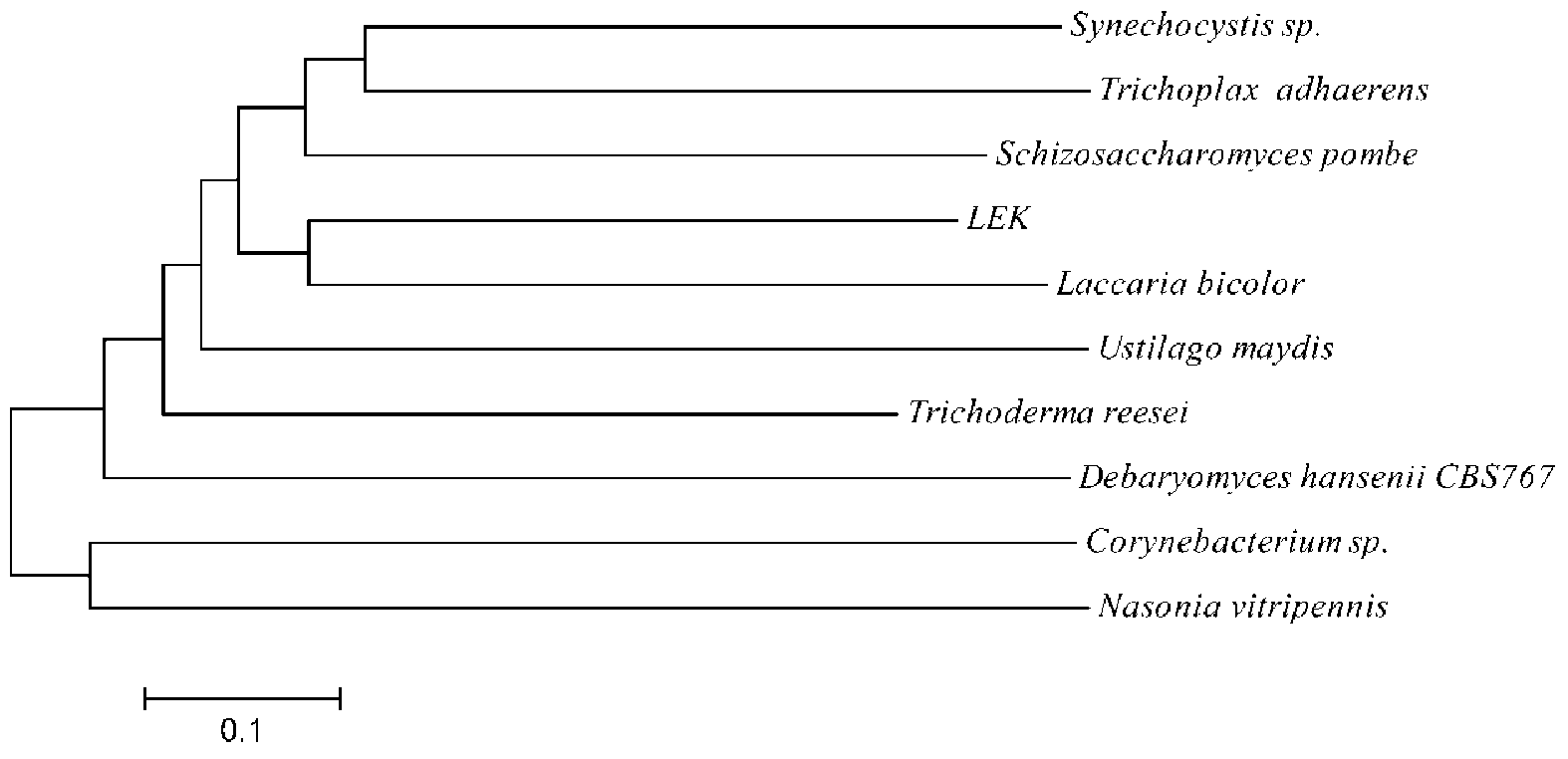
Ketone reductase LEK, encoding gene, mutant and application of mutant
ActiveCN103289970AHigh optical purityReduce manufacturing costOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringSite-directed mutagenesisMutant
The invention discloses a ketone reductase LEK, an encoding gene, a mutant and an application of the mutant in a preparation of ethyl (R)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate (CHBE) by biological catalysis. The ketone reductase LEK has 95% or more homology with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ. ID.NO. 2. The mutant of the ketone reductase LEK is a mutant W28A obtained by mutating W at position 28 in the amino acid sequence of the ketone reductase LEK into A. The R-type ketone reductase, i.e., the ketone reductase LEK, is developed, then site-directed mutagenesis and transformation of the reductase are carried out, and a coenzyme regeneration cycle reaction system is established. The conversion rate of the preparation of (R)-CHBE by catalysis reaches 100% and the e.e. value is more than 99%, and simultaneously the Km value of the reductase is relatively low and is 14.08 mM. The catalytic reaction system has no need of adding an expensive coenzyme NADPH, and thereby reducing the production cost; and at high substrate concentrations, the catalytic reaction system can be used for large-scale preparation of products with high optical purity, has relatively high production efficiency, and is in favor of industrialization production.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Construction and applications of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide auxotroph escherichia coli
InactiveCN102925398ACapable of transmembrane transportIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousEscherichia coli
The present invention discloses construction and applications of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) auxotrophic Escherichia microbe, wherein NAD transporter protein is introduced to the Escherichia microbe, an intracellular NAD biosynthesis pathway is blocked, and the Escherichia engineered bacteria growing dependent on exogenous pyridine nucleotide coenzyme is constructed. The NAD auxotrophic Escherichia can be used in the field of bio-technology, and can be provided for screening inhibition drugs for pyridine nucleotide coenzyme metabolism, improving oxidation reduction biotransformation efficiency, and establishing non-antibiotic screening platforms for gene cloning and protein heterogenesis expression.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Glucose dehydrogenase mutant with improved specific enzyme activity of catalytic xylose
ActiveCN106754776ASolve problems that cannot be effectively usedReduce manufacturing costBacteriaOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringCompanion animal
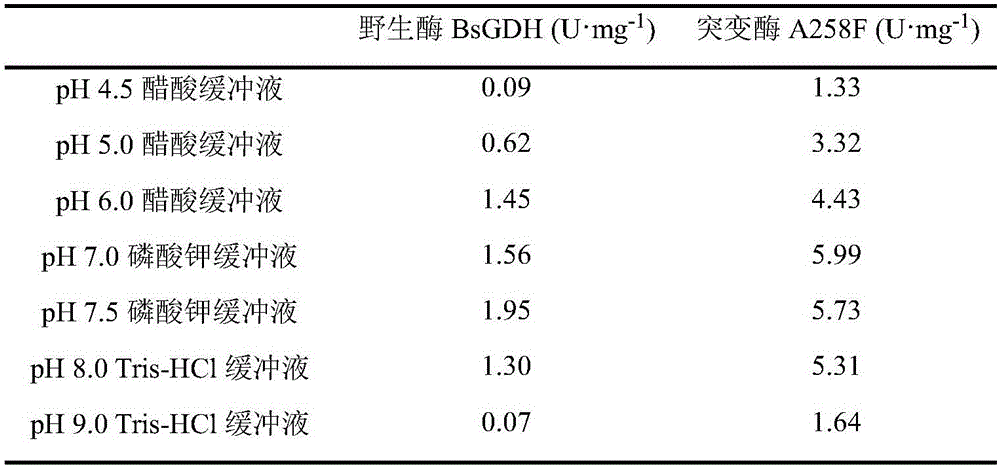
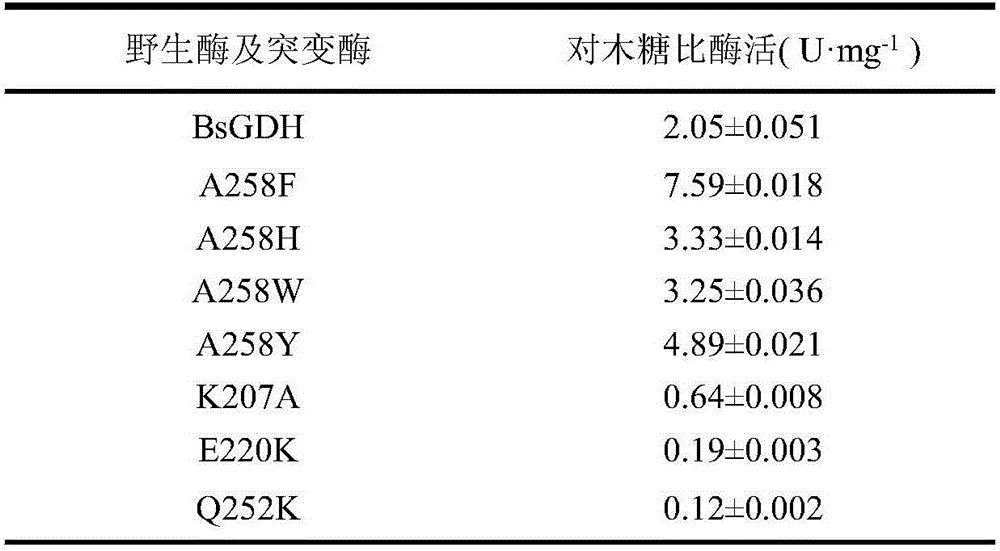
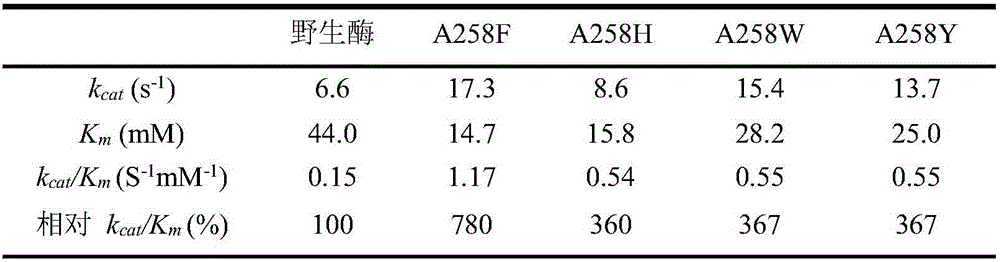
The invention discloses a glucose dehydrogenase mutant with improved specific enzyme activity of catalytic xylose and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. A recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-GDH (A258F) containing a target gene is successfully built. A mutate enzyme A258F is subjected to induced expression through the recombinant strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET-GDH (A258F); and a crude enzyme fluid is purified through His-Trap affinity chromatography to obtain a pure enzyme A258F. Through optimizing an enzyme activity determination condition, the specific enzyme activity of the A258F in a potassium phosphate buffer solution of pH 7.0 at 55 DEG C reaches 7.59U.mg<-1>. A novel substrate is provided for a coenzyme cycle of glucose dehydrogenase for asymmetric transformation reaction by the work; the problem that a xylose resource cannot be effectively utilized is solved; reduction of the production cost is facilitated; an excellent strain is provided for xylose utilization in industry; and a foundation is laid for transformation of the substrate specificity of the enzyme through a gene engineering method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
D-lactic acid dehydrogenase of Sporolactobacillus inulinus, coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a D-lactic acid dehydrogenase derived from Sporolactobacillus inulinus, a coding gene and application thereof. The D-lactate acid dehydrogenase provided by the invention is (a) or (b) as below: (a) a protein composed of an amino acid sequence shown in a sequence 1 in the sequence table; and (b) a sequence 1 derived protein, with D-lactate acid dehydrogenase activity, obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or several amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence shown as the sequence 1. The D-lactate acid dehydrogenase provided by the invention can use NADH or NADPH as a coenzyme to catalyze pyruvic acid for generation of D-lactic acid, and can also use NADH as a coenzyme to catalyze phenyl pyruvic acid for generation of D-phenyl lactic acid; and a generated product has optical purity reaching 100% (without L-product generation). Therefore, the invention has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing coenzyme Q10 by fermenting genetic recombinant bacteria
ActiveCN103820506AIncrease productionLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationCoenzyme F420Biological activation
The invention discloses a method for producing coenzyme Q10 by fermenting genetic recombinant bacteria. According to the method, an NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) kinase gene is transplanted into a strain of efficient expression reducing coenzyme Q10. The culture conditions of recombinant bacteria optimization are inclined activation, seed culture and fermental cultivation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the recombinant bacteria constructed by genetic engineering means are strong in stability; the yield of the coenzyme Q10 of the recombinant bacteria is 1.63g / L and increased by 21.6 percent compared with an original strain; the coenzyme Q10 can meet the requirement on industrial production.
Owner:HUNAN KEYUAN BIO PRODS
Transaminase-coenzyme co-immobilization engineering bacteria and application
ActiveCN110106130AEmission reductionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliSitagliptin
The invention provides a method for catalytic synthesis of a sitagliptin chiral intermediate (3R)-3-amino-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6,7,8-teralin-1,2,4-triazol[4,3-a]pyrazine-1-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluoro-phenyl)buta-1-one by means of engineering bacterium cells containing transaminase-coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate co-immobilization Escherichia coli, E.coli). The method comprises the steps of culturing engineering bacteria containing transaminase Escherichia coli, preparing co-immobilization cells, and synthesizing the immobilization cell asymmetric catalysis itagliptin chiral intermediate. The transaminase-PLP co-immobilization cells are adopted as a catalyst, the stability is good, the service life is long, the organic solvent is good in tolerance, repeated usage can be performed, no expensiveexogenous coenzyme needs to be added in the reaction process, and the production cost is greatly lowered. The method is simple in technology, low in cost and high in product yield and purity, and hasthe quite high application value in the industrial production of the sitagliptin chiral intermediate.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Methods for indentifying compounds that modulate an enzyme in the coenzyme a biosynthetic pathway in a pathogenic microoganism
InactiveUS20060094075A1Inhibitory activityGrowth inhibitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenic microorganismCoenzyme A biosynthesis
A method for the identification and treatment of pathogenic microorganism infections by inhibiting one or more enzymes in a metabolic pathway by inhibiting the conversion of substrate to produce the penultimate or ultimate product particularly by inhibiting the activity of one or more of the enzymes in the pathway, and compounds and pharmaceutical compositions for inhibiting infections of pathogenic microorganisms by inhibiting such enzymes.
Owner:SCHECHTER ALAN M
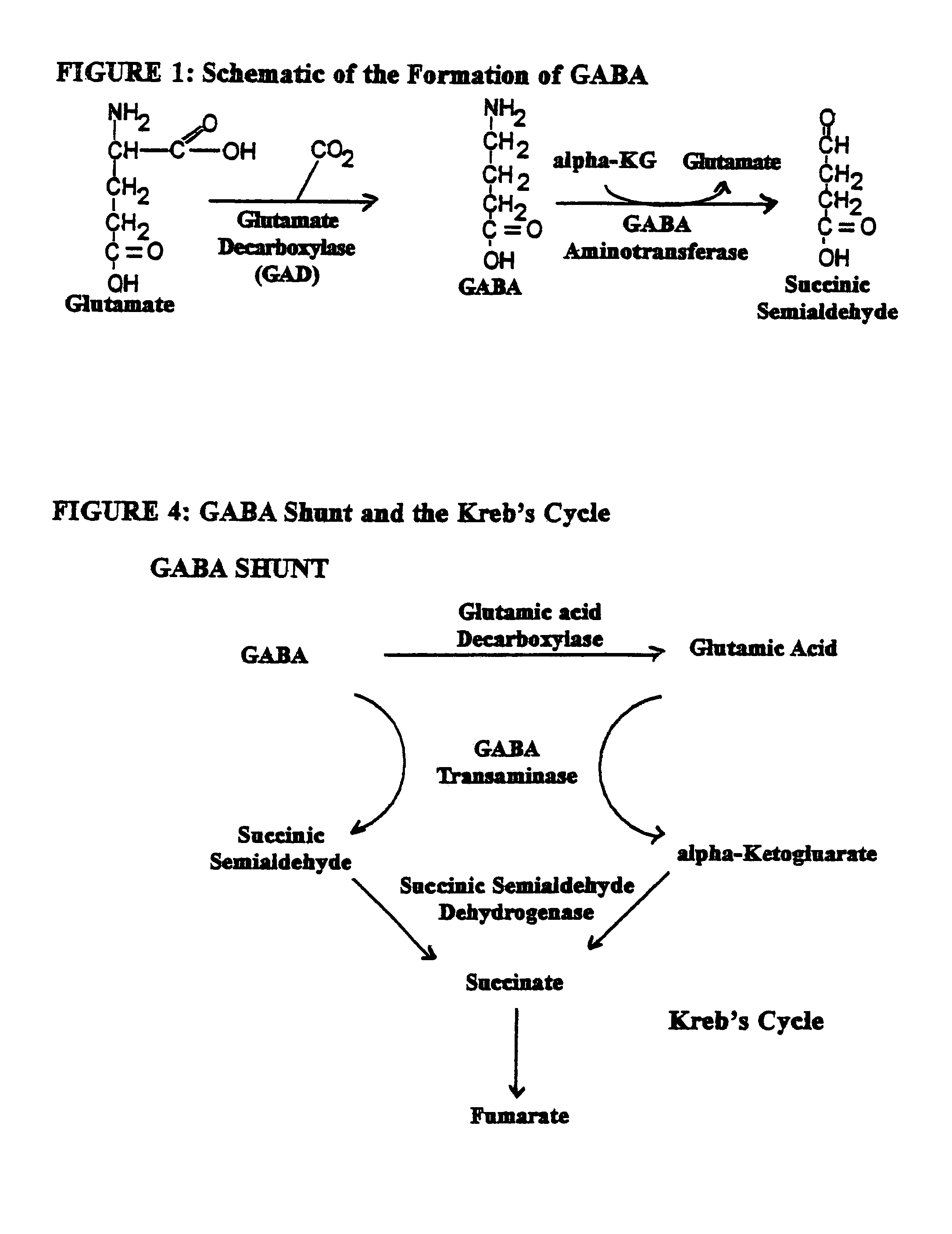
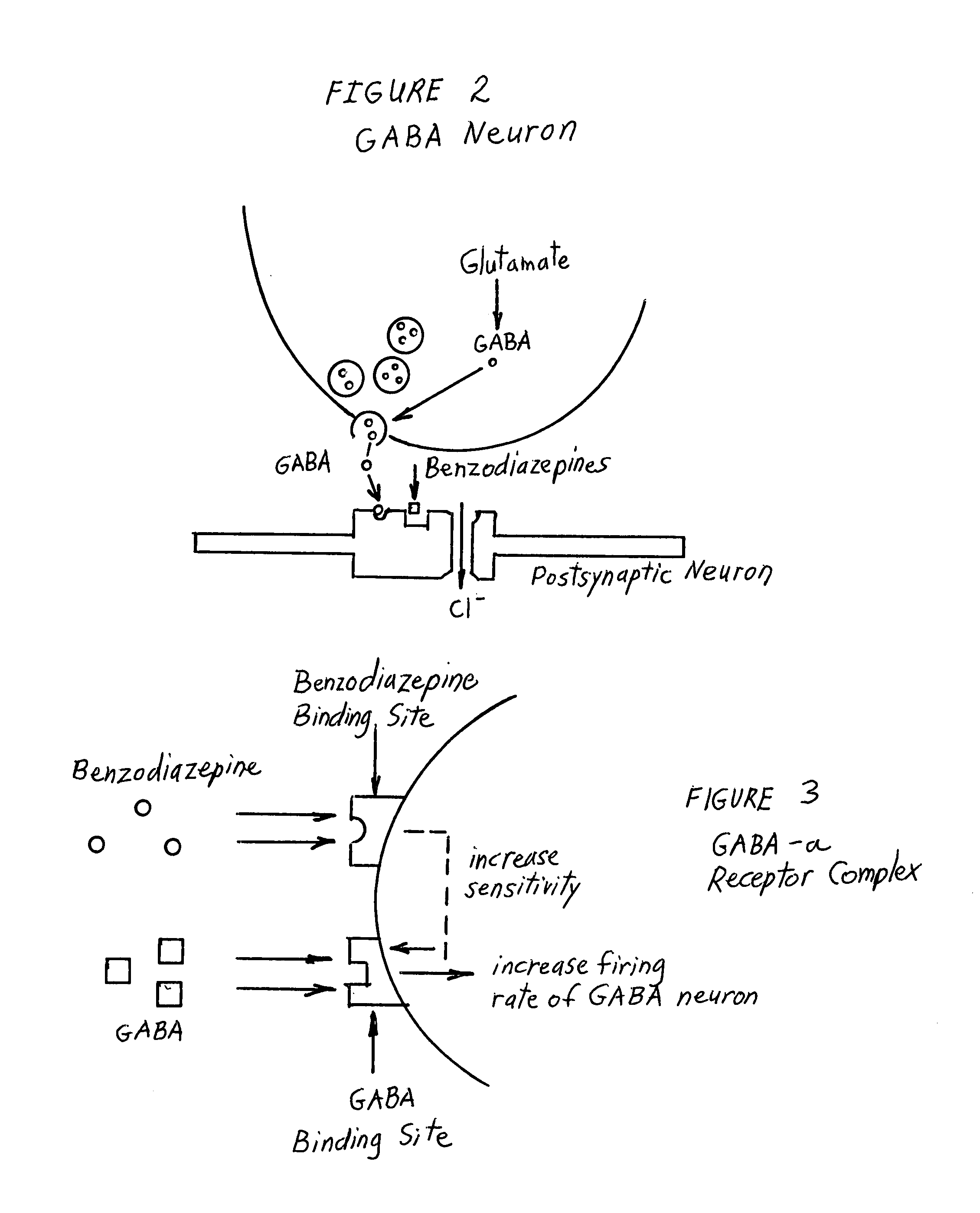
Enkephalinase inhibitor and GABA precursor loading as anti-anxiety compositions
ActiveUS7255882B2Improve the level ofPreventing significant perturbation and instabilityBiocideNervous disorderBenzodiazepinePanic
Benzodiazepine withdrawal induced anxiety is treated by administration of an enkephalinase inhibitor, and a gamma-aminobutyric acid (“GABA”) precursor, or an endorphin or enkephalin releaser. These components promote restoration of normal neurotransmitter function and are non-addictive. Use of the enkephalinase inhibitor D-phenylalanine, the GABA precursor glutamine, the serotonin precursor 5-HTP, glycine, and taurine, in combination with coenzymatic functionality of folic acid is preferred for activation of ligand-gated Cl− channel in the central nervous system. Food supplement embodiments provide the human body nutritional supplements to intake certain neurotransmitter precursor substrates, thereby enabling patients of all ages to self-regulate their ability to quell perturbations to equilibrium and simultaneously to adverse effects upon normal physiological and psychological functioning attributable to induced anxiety and panic associated with benzodiazepine withdrawal.
Owner:BIESER ALBERT HOWARD +1
Escherichia coli coenzyme metabolic-pathway transformation and biotransformation method
InactiveCN104561070AAdd lessIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCoenzyme A metabolismEscherichia coli
The invention relates to an escherichia coli coenzyme metabolic-pathway transformation and biotransformation method. According to the method, a coenzyme metabolic pathway is transformed by a homologous recombination method, a coenzyme degradation related gene yjaDyrfE in protein expression host bacterium escherichia coli JM109 (DE3) is removed and the concentration of endogenous coenzyme during reproduction of the host bacterium is increased. When a host bacterium expression enzyme system transformed by the method is used for preparing chiral molecules by biotransformation by a biological reduction method, the addition of coenzyme in a transformation system can be remarkably reduced or no coenzyme is added in the transformation system.
Owner:郁庆明
Genetic recombinant engineering bacterium and application thereof in catalytic synthesis of D-pantolactone
ActiveCN110452861AImprove catalytic stabilityAchieve in situ regenerationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses a genetic recombinant engineering bacterium and application thereof in catalytic synthesis of D-pantolactone and belongs to the field of biocatalytic research. The genetic recombinant engineering bacterium takes escherichia coli as a host bacterium, the host bacterium contains recombinant expression plasmids containing a conjugated polyketide reductase gene and a glucose dehydrogenase gene, and the nucleotide sequence of the conjugated polyketide reductase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The engineering bacterium simultaneously expresses polyketide reductase and glucose dehydrogenase through induction; the engineering bacterium is applied to the asymmetric catalytic synthesis of D-pantolactone, the in-situ regeneration of a coenzyme NADPH is realized through a synergistic effect of the two enzymes, and the purpose of efficient production from keto-pantolactone to D-pantolactone can be achieved. A method simplifies a production process, avoids addition of extra coenzymes at the same time and reduces the production cost.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Detection method of rhodobacter sphaeroides phage in coenzyme Q10 production
ActiveCN105087562AStrong specificityEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBacteroidesFluorescence
The invention relates to the field of detection of a rhodobacter sphaeroides phage, and in particular relates to a rapid detection method of a rhodobacter sphaeroides phage in coenzyme Q10 production, wherein the detection method is achieved by selecting any one pair of primers in three pairs of specific primers, and conducting fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection on a probe corresponding to each pair of primers. The detection method, which selects specific primers and probes to determine the contamination condition of the coenzyme Q10 in accordance with the status of contaminated rhodobacter sphaeroides in coenzyme Q10 fermentation production, is rapid in detection and high in sensitivity, and the detection method is achieved by directly collecting a fermentation product from fermentation production in any stage and any scale and extracting genome DNA, and conducting fluorescence quantitative PCR detection; therefore, the method is simple, and is capable of rapidly and accurately detecting the phage within about two hours in the whole detection process; in the case of phage contamination, the method can completely avoid an event of phage contamination in a later stage of expanded production by immediately stopping the expanded production of the fermentation product of the current time, so as to reduce unnecessary loss.
Owner:SHENZHOU BIOLOGY & TECH CO LTD
Genetic engineering synechocystis capable of promoting regeneration of intracellular coenzyme NADPH and application of synechocystis
InactiveCN105567621APromote regenerationImprove regeneration efficiencyBacteriaFermentationFerredoxin—NADP(+) reductaseIntracellular
The invention discloses engineering synechocystis PCC6803 capable of promoting regeneration of an intracellular coenzyme NADPH and a construction method and application of the synechocystis. Homologous recombination is performed on a gene petH of ferredoxin-NADP reductase (FNR) which can catalyze regeneration of the coenzyme NADPH to obtain recombinant plasmids pKW-omega-PpetE-petH, the recombinant plasmids are transformed into the synechocystis PCC6803, the FNR gene is integrated in chromosomal DNA of the synechocystis through homologous recombination, and high-strength expression of the FNR can be regulated and controlled according to the concentration of Cu<2+>. The engineering synechocystis constructed through the method can promote overexpression of the FNR, improve the total enzyme activity of the intracellular FNR and greatly promote the regeneration efficiency of the intracellular coenzyme NADPH. The synechocystis obtained through the method can be applied to the biological catalysis and conversion process which has the large quantity demand on the coenzyme and the biotechnology field by promoting regeneration of the intracellular coenzyme NADPH of microalgae and has the wide application prospect.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase
ActiveCN104480077AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementLigasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseNucleotide
The invention discloses recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase. The amino acid sequence of therecombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is shown in SEQ ID No.2 and the nucleotide sequence of the recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.The recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase has the characteristics of high thermal stability and high activity; the retaining rate of enzyme activity is 59.6% after the recombination acetyl coenzyme A synthetase is treated for 30 min at the temperature of 60 DEG C and is much improved compared with constitutive enzyme; an apparent Km value of a catalyzed oleic acid acetylation reaction is 1.2*10<-5>M; the thermal stability of enzyme in a kit can be improved, and temperature influences can be avoided or reduced in the transportation and utilization processes of the kit.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
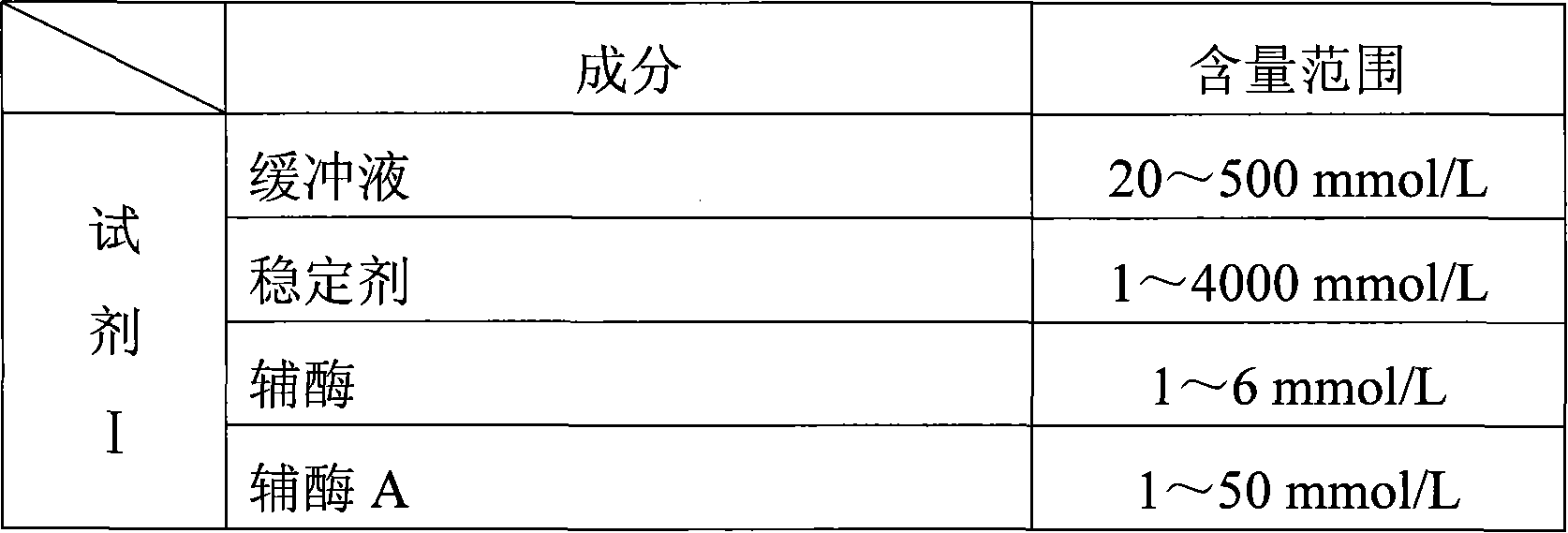
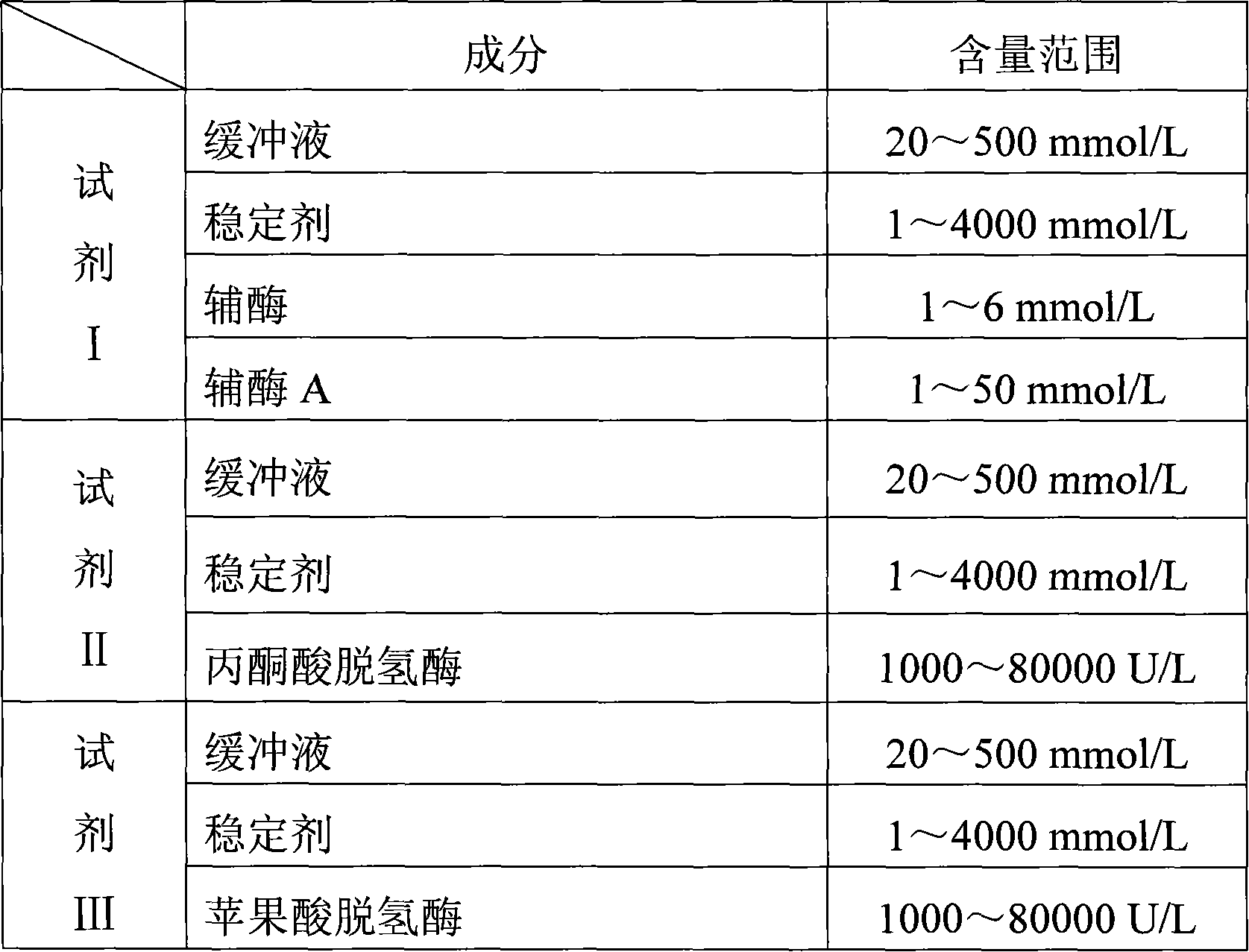
Method for measuring malic acid concentration and malic acid diagnose reagent kit
InactiveCN101082571AThe test result is accurateFree from pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbancePyruvic acid
The invention relates to a kind of double enlarge method, enzyme colorimetric method and enzyme linked method and a diagnosis reagent box applying the malic acid dehydrogenase coupling pyruvate dehydrogenase enzymatic reaction ratio colorimetric method / end-point method. The reaction of the malic acid dehydrogenase enzymolysis malic acid generates pyruvate and at the same time makes the coenzyme reducing the reduction coenzyme. The pyruvate generated by acid dehydrogenase enzymolysis malic acid makes the coenzyme reducing the reduction coenzyme again by the coupling reaction of pyruvate dehydrogenase. Because of making the coenzyme reducing the reduction coenzyme two times the reaction sensitivity is enhanced double. So we can assay the degree / speed of the ascent absorbance at the place of 340nm. It can measure and calculate the density of citric acid by measuring the degree / speed of the fall-way absorbance at the place of 340nm. The method has high specificity and it is not polluted by the endogenous and exogenous object and the test result is precise and accurate. The invention can get the array result by the ultraviolet / visible light analytic instrument so it is convenience to extend and apply.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Process for extracting bacterial cell coenzyme Q10
InactiveCN101274884BIncreasing concentration gradientDiffusion thinQuinone separation/purificationBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to a technology for extracting coenzyme Q10 in bacterial cells, which pertains to the technical field of microbiology engineering. Thalli is automatically and quantitatively put into from the dog-house of a continuous countercurrent device under the control of a weigh-instrument, a solvent is injected from a solvent inlet under the control of a flowmeter and the leaching solution and the thalli form reverse continuous countercurrent leaching process under the push of a shovel-like thruster; the concentration gradient is large, relative movement exists between the solventand the thalli and the thalli moves from the left end to the right end of an extraction container continuously under the function of the shovel-like thruster while the solvent moves from the right end to the left end of the container under the action of pressure; a diffusion boundary layer is thin and fast to be updated and the coenzyme Q10 is extracted after 2 to 10 hours of reaction of the thalli which enters from the left end of the device after the contact of the solvent and the thalli; the thalli enters a rake type dryer from the right end of an extraction device by press treatment and residual organic solvent in the thalli is treated with drying treatment in the rake type dryer; the yield of the coenzyme Q10 reaches more than 90 percent.
Owner:SHENZHOUSPACEBIOTECHGRP +1
Process for extracting bacterial cell coenzyme Q10
InactiveCN101274884AIncreasing concentration gradientDiffusion thinQuinone separation/purificationBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention relates to a technology for extracting coenzyme Q10 in bacterial cells, which pertains to the technical field of microbiology engineering. Thalli is automatically and quantitatively put into from the dog-house of a continuous countercurrent device under the control of a weigh-instrument, a solvent is injected from a solvent inlet under the control of a flowmeter and the leaching solution and the thalli form reverse continuous countercurrent leaching process under the push of a shovel-like thruster; the concentration gradient is large, relative movement exists between the solvent and the thalli and the thalli moves from the left end to the right end of an extraction container continuously under the function of the shovel-like thruster while the solvent moves from the right end to the left end of the container under the action of pressure; a diffusion boundary layer is thin and fast to be updated and the coenzyme Q10 is extracted after 2 to 10 hours of reaction of the thalli which enters from the left end of the device after the contact of the solvent and the thalli; the thalli enters a rake type dryer from the right end of an extraction device by press treatment and residual organic solvent in the thalli is treated with drying treatment in the rake type dryer; the yield of the coenzyme Q10 reaches more than 90 percent.
Owner:SHENZHOUSPACEBIOTECHGRP +1
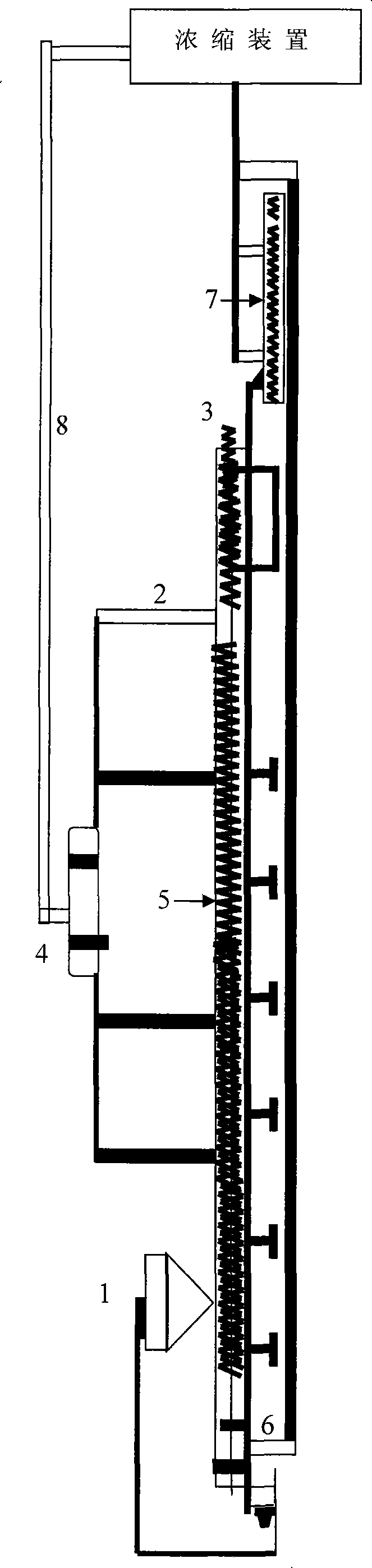
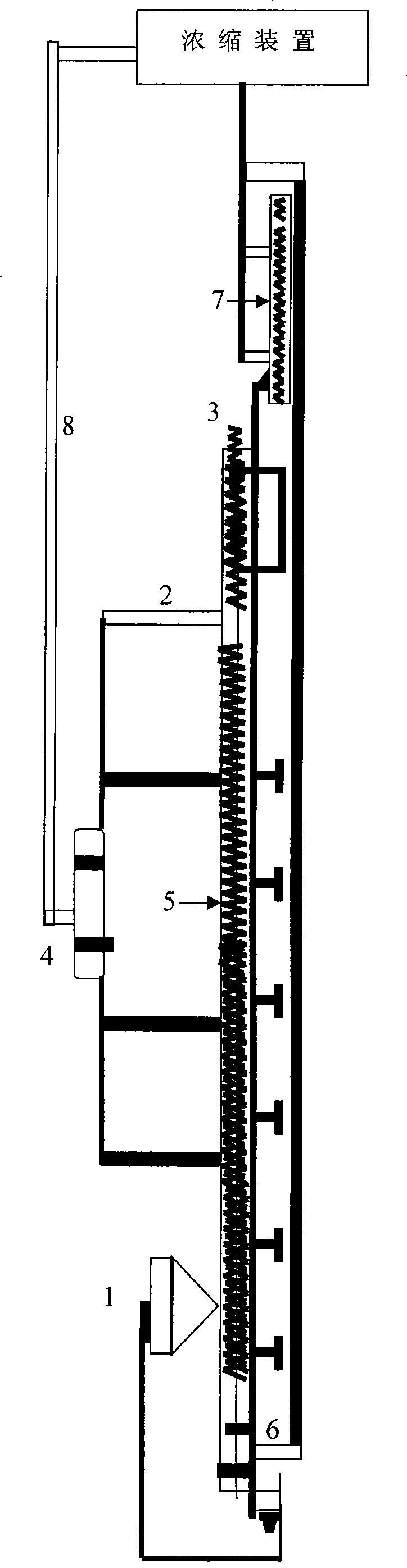
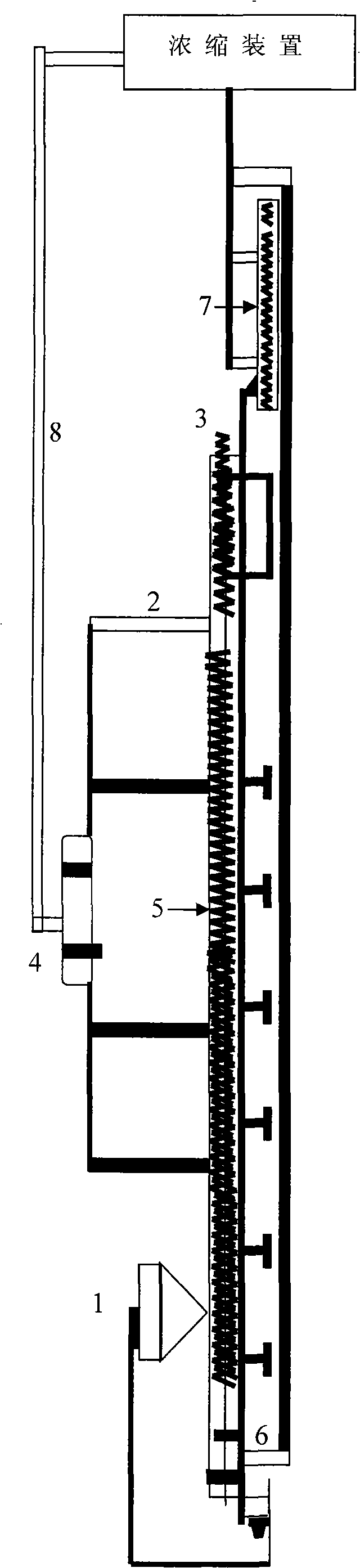
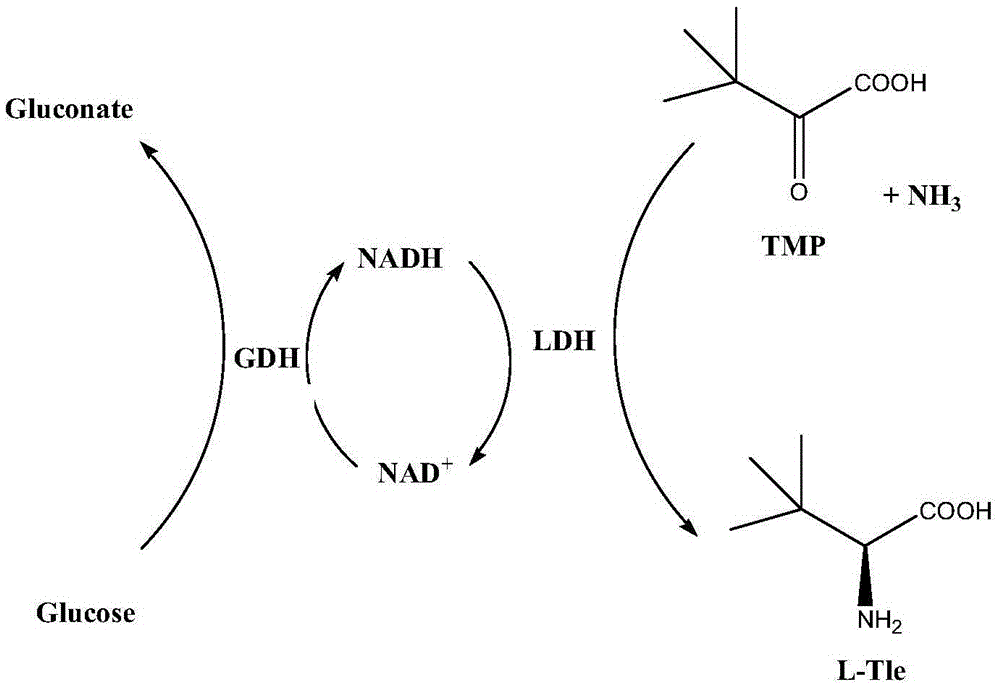
Method for preparing L-tert-leucine by coupling leucine dehydrogenase with glucose dehydrogenase
ActiveCN105603016AAchieve recyclingAchieve zero additionOrganic chemistryFermentationHigh concentrationNiacin
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-tert-leucine by coupling leucine dehydrogenase with glucose dehydrogenase, belonging to the technical field of enzyme engineering and chiral medical intermediate preparation. The method comprises the following steps: adding substrates trimethylpyruvic acid and glucose into a reaction system; adjusting the pH value of the system to 8.0-9.0; and adding a crude enzyme (containing leucine dehydrogenase, glucose dehydrogenase and coenzyme) with broken co-expressed strain and cultured by a culture medium added with substances such as niacin, and then starting reactions while controlling the temperature at 25-30 DEG C and pH value at 8.0-9.0 in the reaction process to generate L-tert-leucine. In the invention, a system in which leucine dehydrogenase is coupled with glucose dehydrogenase is adopted, and the L-tert-leucine is prepared by use of the coenzyme contained in the thalli; and the method has the characteristics of high concentration of single-batch reaction substrates, high reaction efficiency, no coenzyme addition and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Monoamine oxidase diagnosing reagent kit and method for measuring monoamine oxidase activity concentration
InactiveCN101097202AFast measurementImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDissolutionAbsorbance
The invention relates to a monoamine oxidase diagnosis reagent box of Enzymatic Recycling Method, and the invention also relates to method principle for detecting the solution of monoamine oxidase, constitute and component of reagent, which belongs to the technical field of medical checking measurements. The reagent box in the invention can be dry powder state, and used after dissolution; it also can be formulated to be liquid agent for direct usage. The component of reagent box mainly contains: buffering liquid, alpha- ketoglutaric acid, glutamate dehydrogenase EC 1.4.1.2, EC 1.4.1.3, EC 1.4.1.4, Glutamate oxidase EC 1.4.3.7, EC 1.4.3.11, reduction type coenzyme and stabilizer, and the component can be matched to form single-reagent reagent box, two-reagent reagent box, and three- reagent box; The enzymatic reaction is generated between sample and reagent by mixing sample and reagent with definite volume, then the reactants is placed under the ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect ascend degree of absorbance at main wavelength of 340nm, so concentration of monoamine oxidase can be calculated. The invention can obtain the detecting result by ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the sensibility is high, precision is well, and easy to be spread.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com