Construction method and application of metabolic engineering escherichia coli strain for producing hydracrylic acid from acetic acid
A technology of hydroxypropionic acid and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of slow growth, low production, and rapid inactivation of Klebsiella
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1. Construction of 3-hydroxypropionic acid, lactic acid and simultaneous production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid and lactic acid metabolic pathway
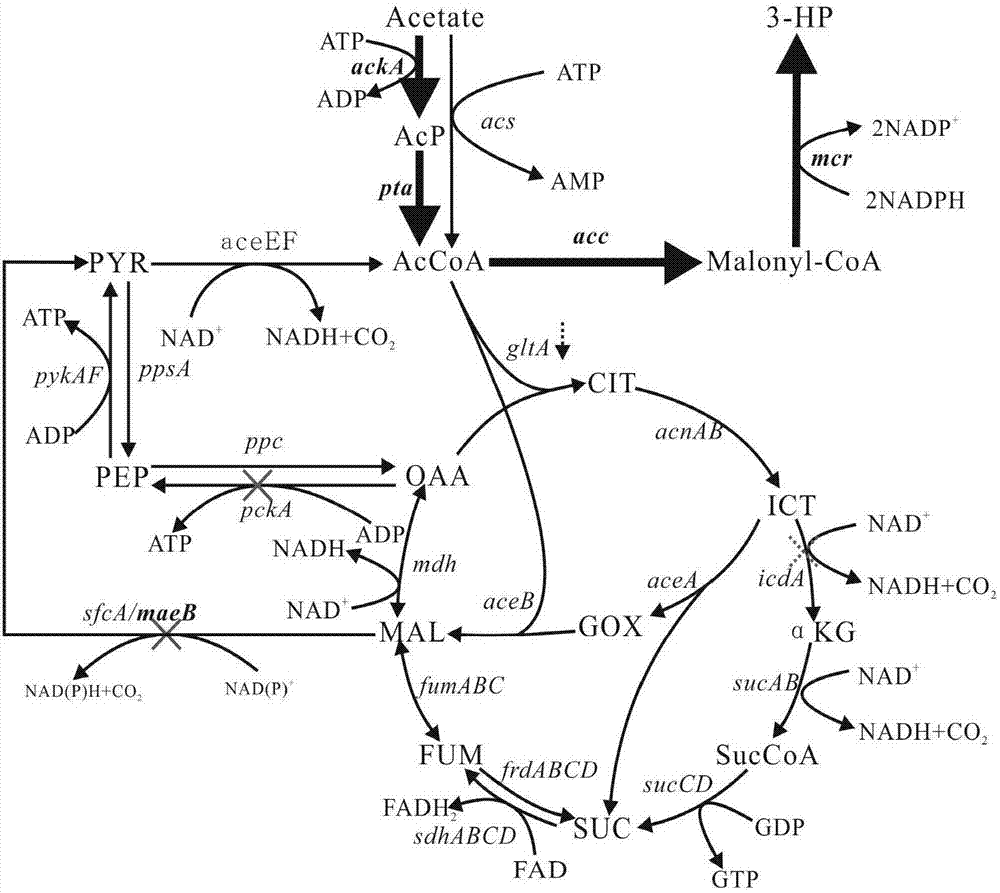
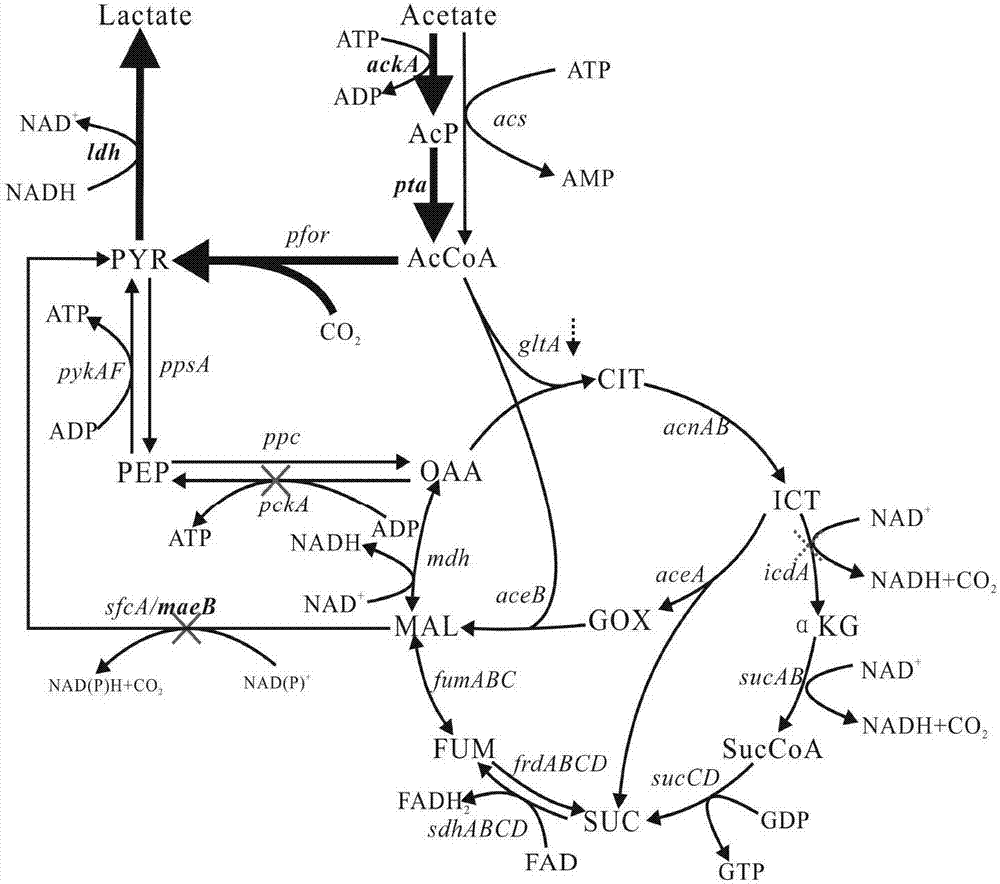
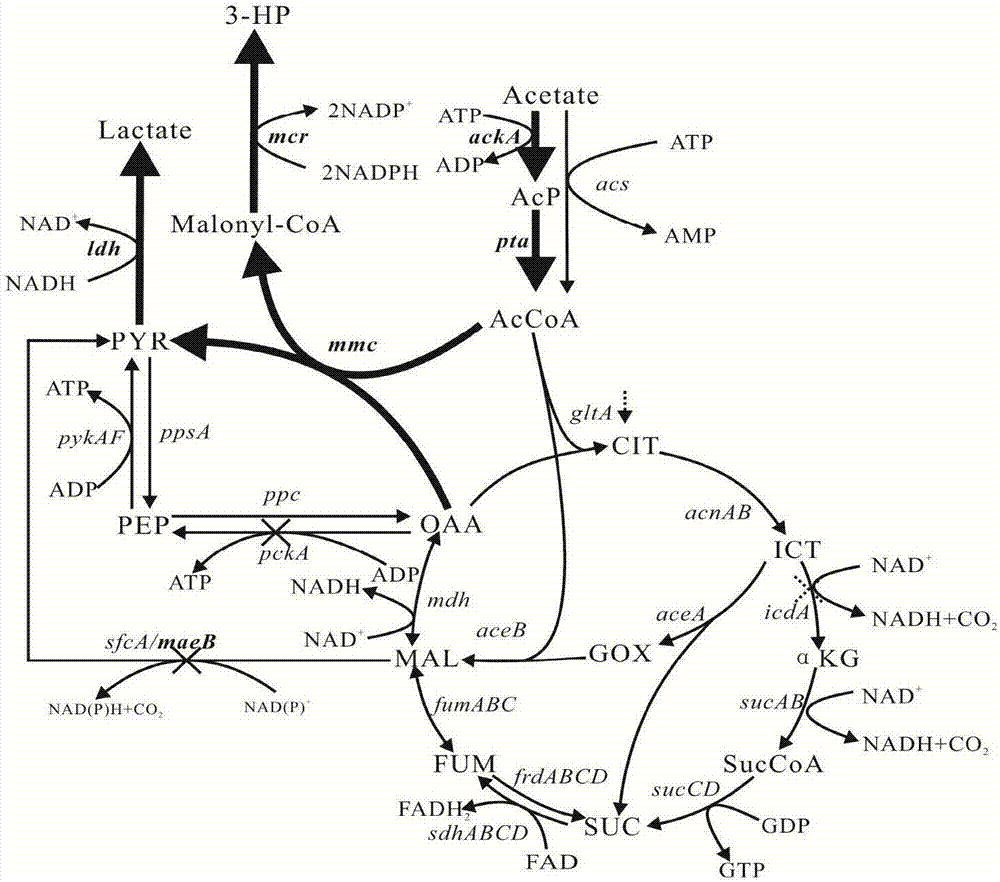
[0044] Using acetic acid as a carbon source to produce 3-hydroxypropionic acid, lactic acid, and 3-hydroxypropionic acid and lactic acid at the same time, acetic acid is first converted into acetyl-CoA, part of acetyl-CoA is converted into target metabolites, and part of acetyl-CoA enters the central metabolism way. To convert acetyl-CoA to different metabolites of interest, different plasmids were constructed. The specific operation is as follows:
[0045] Construction of 3-hydroxypropionic acid production pathway: Acetyl-CoA first generates malonyl-CoA under the action of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and then generates 3-HP under the action of malonyl-CoA reductase. Therefore, genes encoding acetyl-CoA carboxylase and malonyl-CoA reductase from different sources can be selected for overexpression. This patent selects ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2. to host bacterium related gene (ack, pta, ldh) promoter replacement
[0049] For the use of MG1655 as the starting bacterium to produce 3-HP and lactic acid with acetic acid as the sole carbon source and to produce 3-HP and lactic acid simultaneously, the expression of ack and pta was enhanced by replacing the promoters of ack and pta, thereby increasing the uptake rate of acetic acid. The promoter replacement method adopts the Red recombination method, and the replaced promoter is derived from the mutation of the trc promoter and is constitutively expressed. The resulting strain was named HY01, and the strain was preserved by the laboratory.
[0050] For the production of lactic acid and simultaneous production of lactic acid and 3-hydroxypropionic acid, the promoter of the lactate dehydrogenase coding gene (ldh) was replaced by Red recombination on the basis of HY01 strain, and the strain was named HY011. The specific operation is as follows: first, the...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3. Knockout of related genes to increase the yield and yield of the target product
[0056] For the production of lactic acid, the respiratory chain strength was reduced by knocking out ubiX to accumulate lactic acid, and ubiX was knocked out in the HY011 strain to obtain the HY012 strain.
[0057] Since the gene expression of the gluconeogenesis pathway is up-regulated in the medium with acetic acid as the carbon source, excess carbon source flows to the gluconeogenesis pathway. Therefore, the red recombination method was used to knock out the genes pckA, adhE, and sfcA. The pckA knockout strains on the basis of HY 01 and HY012 were named HY 02 and HY 022, and the icdA knockout strains on the basis of HY 02 and HY 022 were named HY 03 and HY 032. For the production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid , further knocked out maeB on the basis of HY 02, and named the strain HY 031.
[0058] The specific operation of gene knockout is as follows: For the knockout of gene ub...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com