Genetic recombinant engineering bacterium and application thereof in catalytic synthesis of D-pantolactone
A technology of gene recombination and engineering bacteria, which is applied in the field of biocatalysis research, can solve the problems of scarcity, low catalytic efficiency of recombinant cells, and low expression level, and achieve the effects of high catalytic activity, promotion of upgrading, and good catalytic stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
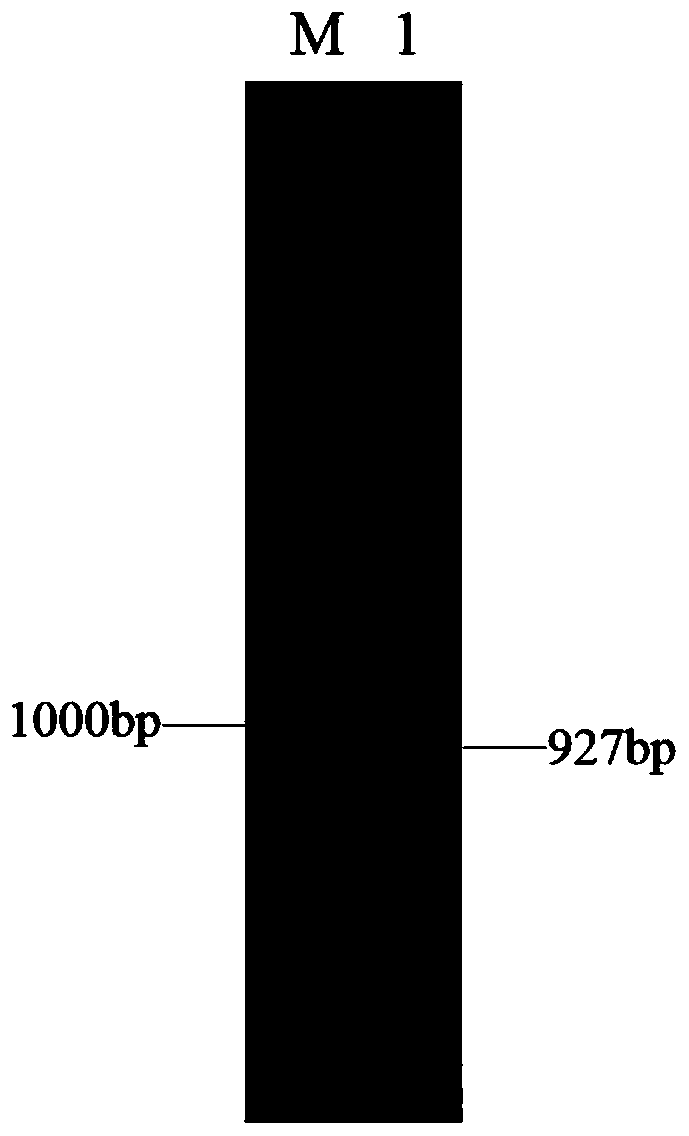
[0042] Example 1 Construction of recombinant expression plasmid pACYC-CPR-GDH
[0043] The GDH gene of glucose dehydrogenase from Bacillus subtilis 168 was cloned with primers F_GDH / R_GDH. The nucleotide sequences of primers F_GDH and R_GDH are respectively:
[0044] 5'-GGAATTCCATATGTACCCGGACCTGAAAGG-3';
[0045] 5'-CCGCTCGAGTTAACCACGACCAGCCTGGA-3'.
[0046] The GDH gene was double-digested with Nde I and Xho I, and the gene fragment after digestion was recovered; at the same time, the expression plasmid pACYCDuet-1 was double-digested with Nde I and XhoI, and the plasmid fragment after digestion was recovered. T4 ligase was used for ligation, and the ligated product was transformed into the cloning host E.coli DH5α. Screen with chloramphenicol-resistant LB solid plates to select positive transformants, and the sequence results show that the recombinant plasmid after the gene sequence is correct is the recombinant expression plasmid pACYC-GDH, which is stored at -20°C for f...
Embodiment 2
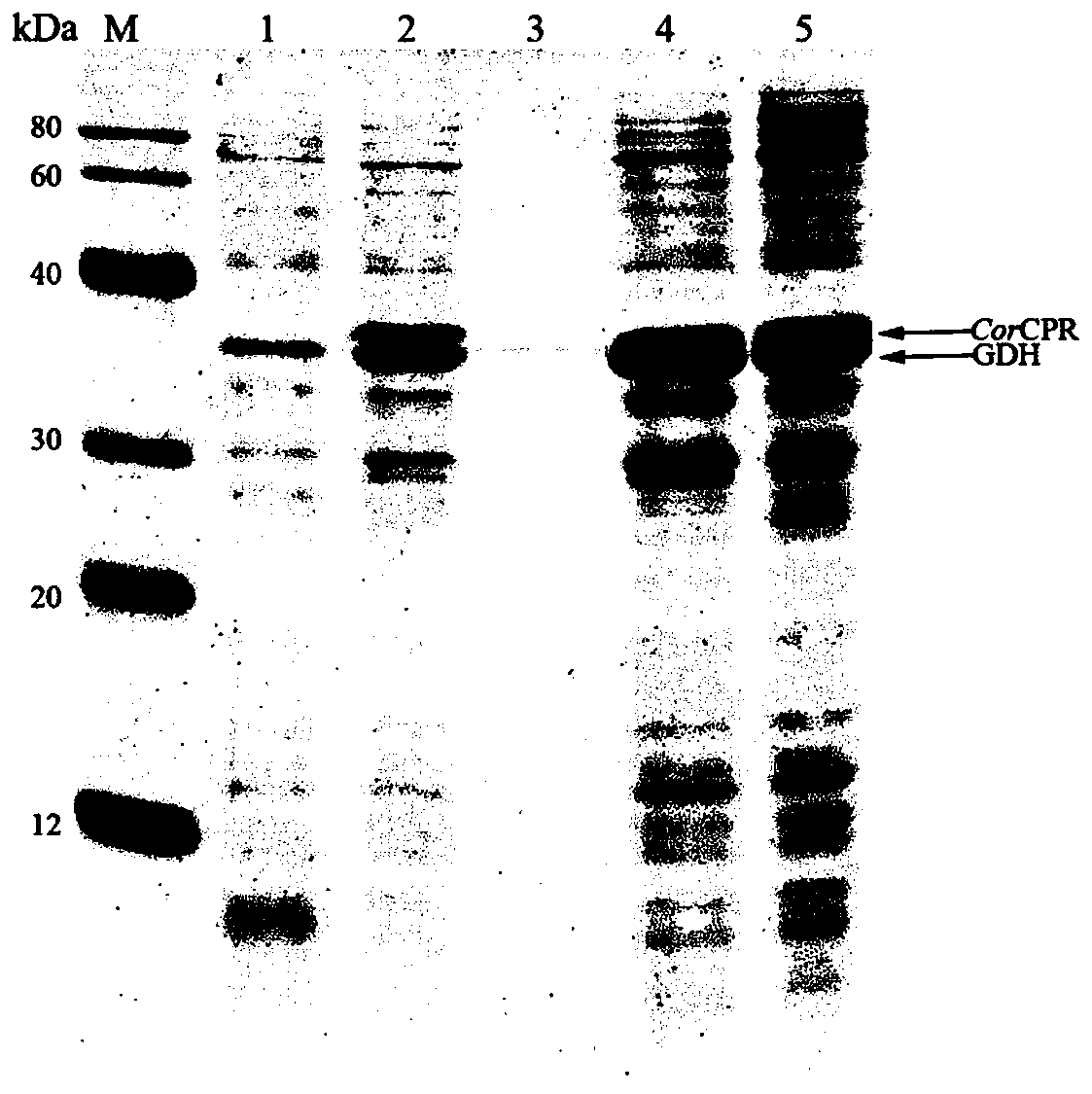
[0051] Construction and catalyst preparation of embodiment 2 genetically engineered bacteria E.coli PL01
[0052] The recombinant expression plasmid pACYC-CPR-GDH constructed in Example 1 was transformed into the expression host E.coli BL21(DE3) to obtain the genetically engineered strain E.coli PL01. Inoculate E.coli PL01 in liquid LB medium (38 μg / mL chloramphenicol) in a 10 mL test tube, and shake and culture at 37° C. and 200 rpm for 12 to 16 hours. The culture solution was inoculated into 50 mL liquid LB medium (38 μg / mL chloramphenicol) in a 250 mL triangular conical flask according to the inoculum amount of 1-5%, and cultured with shaking at 37°C and 200 rpm for 2-3 hours. species density OD 600 When the value reaches 0.6-0.8, add 0.1-0.5 mM isopropylthiogalactopyranoside (IPTG), and continue culturing for 12 hours at 18° C. and 200 rpm.
[0053] The cells are collected by centrifugation for 5-10 minutes under the condition of 5000-10000×g, which is used as a catalyst...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Optimization of reaction conditions for the catalytic synthesis of D-pantolactone by genetically engineered bacteria E.coli PL01
[0055] In a 5mL 0.1M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) reaction system containing 0.5g genetically engineered bacteria E.coliPL01 resting cells, 100mM KPL, 125mM glucose was reacted at 35°C and 200rpm for 20min.
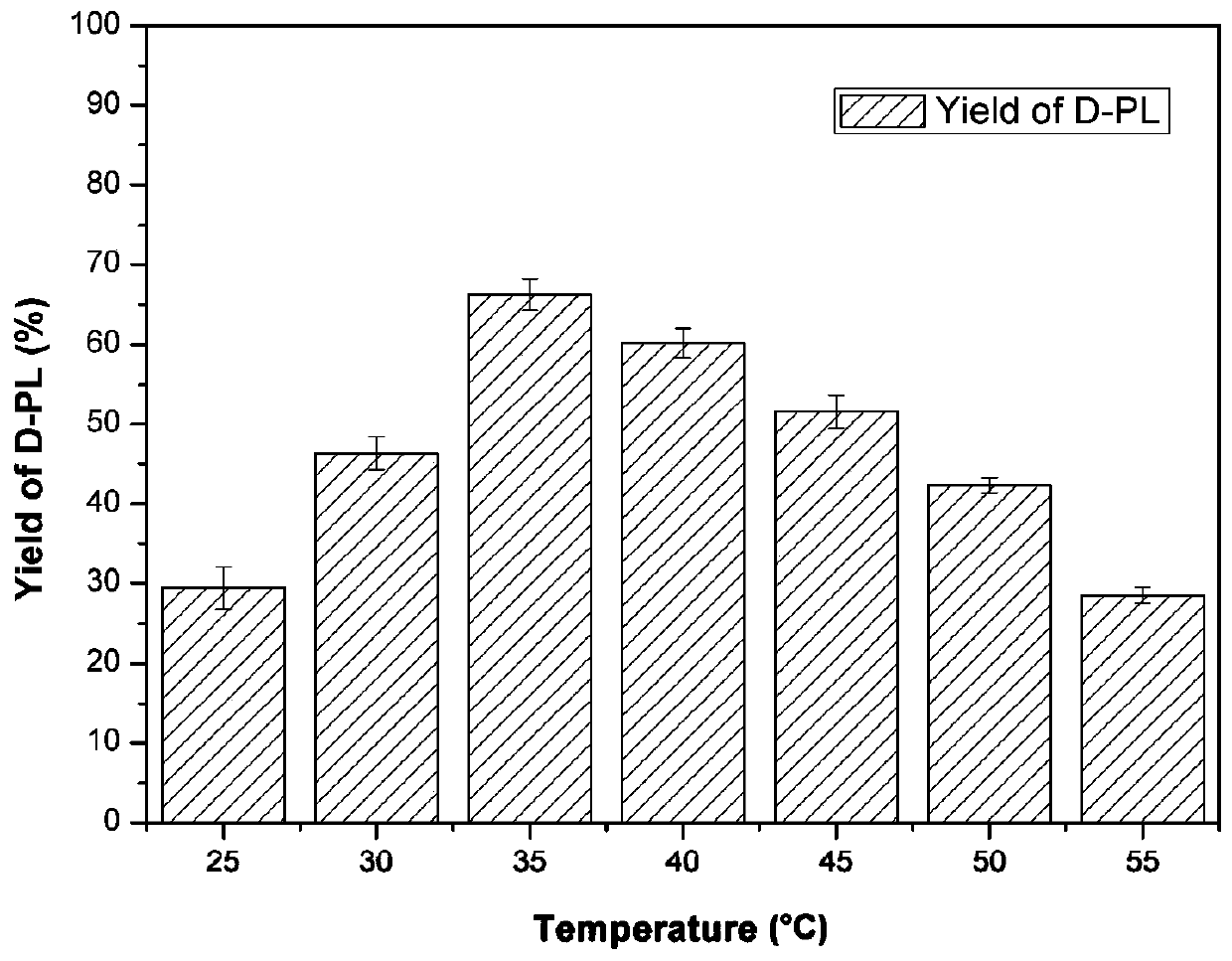
[0056] The optimum pH value for the synthesis of D-PL catalyzed by E.coli PL01 was 6.5 ( image 3 ), the optimum reaction temperature is 35°C ( Figure 4 ), the mol ratio of adding glucose and substrate KPL in the reaction solution is 1.25:1 ( Figure 5 ), the intracellular coenzymes of genetically engineered bacteria can be self-sufficient, and there is no need to add NADP to the reaction system + ( Image 6 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com