Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
116 results about "Biomass yield" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
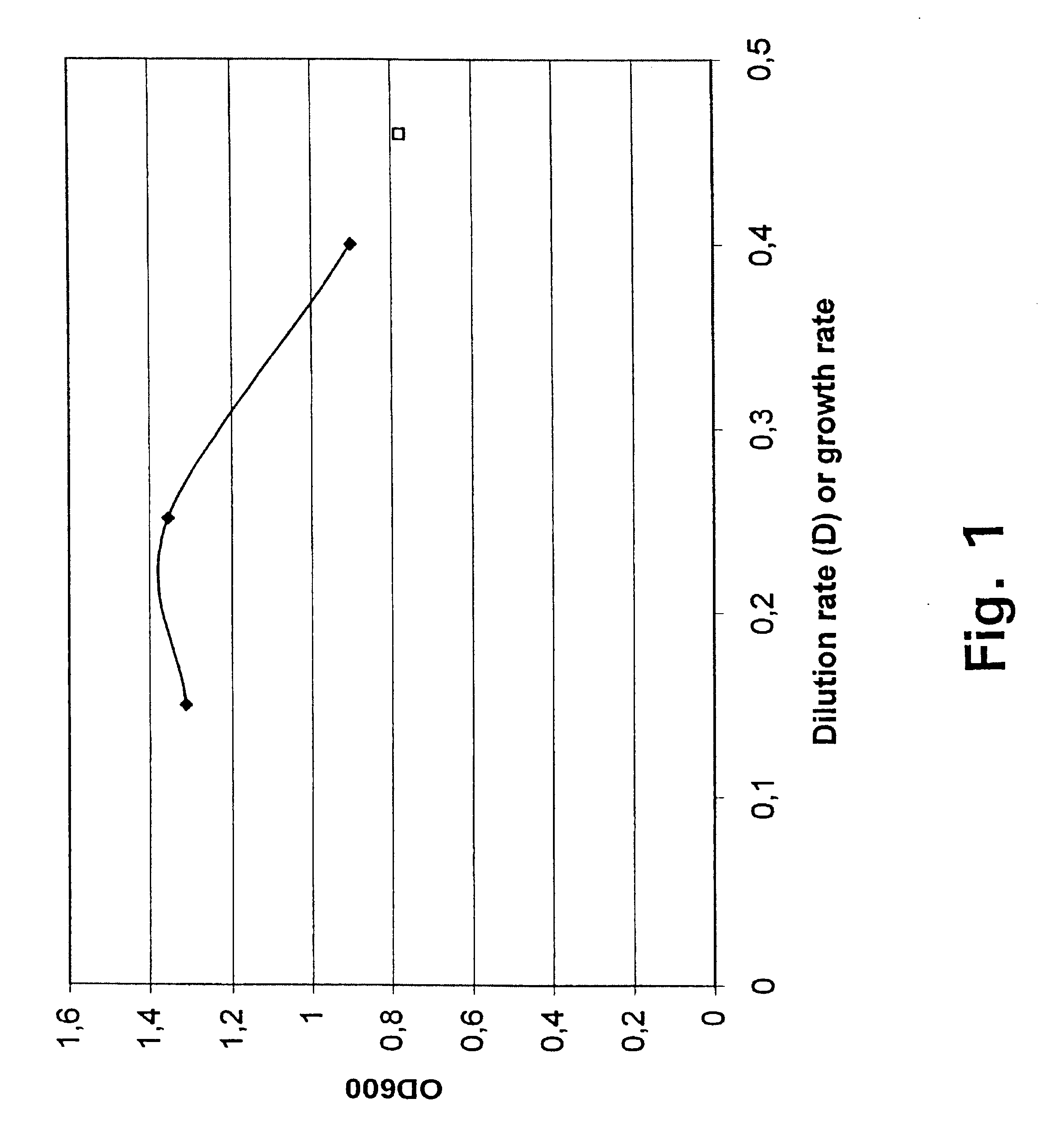
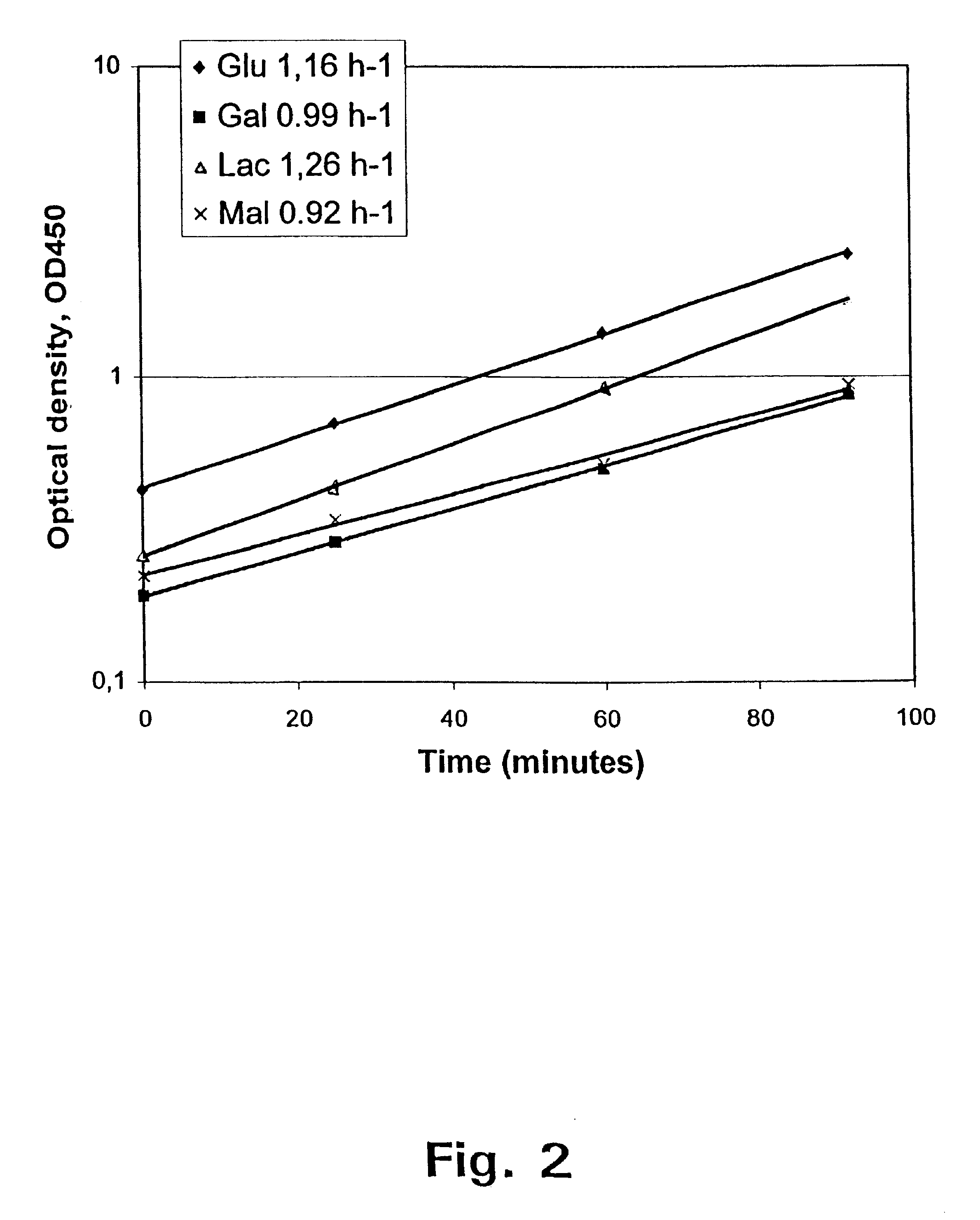
Biomass Yield (Y) The ratio of the amount of biomass produced to the amount of substrate consumed (g biomass/g substrate) is defined as the biomass yield, and typically is defined relative to the electron donor used.
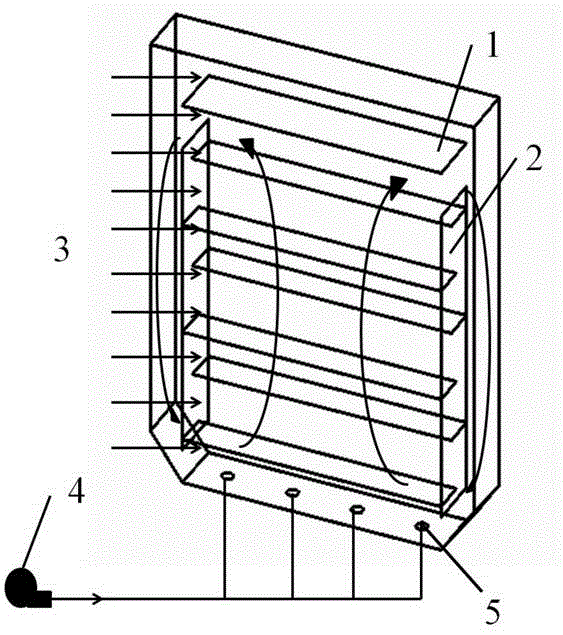
Half-dry solid state cultivation method used for industrial production of microalgae
ActiveCN102373156ADecreased mobilityThe growth state is easy to controlImmobilised enzymesUnicellular algaeSecondary metabolitePhotobioreactor
The invention provides a half-dry solid-state cultural method for industrial production of microalgae. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, inoculating microalgae cells on a solid material and allowing cell colony to maintain moist by supplementing liquid; then, adding inorganic carbon sources into the cell colony under the condition of illumination; finally, regulating and controlling and metabolism of microalgae cells by controlling parameters of components in wetting liquid, illumination intensity, the concentration of the carbon source and the like so as to realize accumulation of microalgae biomass and / or secondary metabolites. According to the invention, the practice of using considerable water as a supporting medium in the conventional liquid immersion culture method is abandoned, and the volume and weight of a culture system are reduced, thereby thoroughly solving the problem that a microalgae photobioreactor is difficult to become large-sized and has a low space utilization rate due to limit of material strength and reducing cost for equipment and operation; microalgae has high efficiency in utilizing nutrients, luminous energy and carbon sources and is fast in inducing secondary metabolites, thereby substantially improving output of biomass and secondary metabolites per unit land occupation area.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
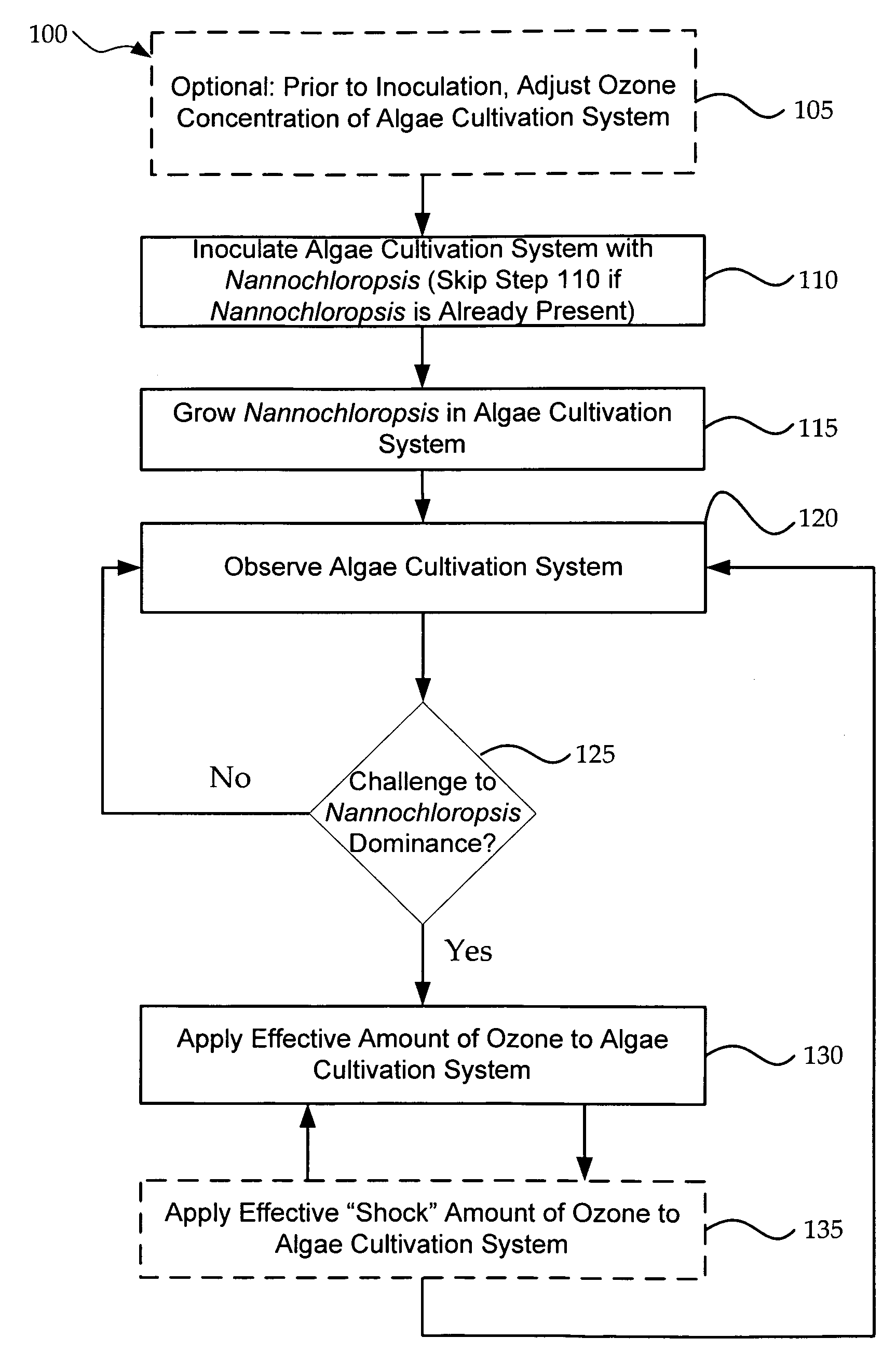
Systems and methods for maintaining the dominance and increasing the biomass production of nannochloropsis in an algae cultivation system
InactiveUS20100196995A1Increased biomass productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStream flowNannochloropsis
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Modulation of low carbon dioxide inducible proteins (LCI) for increased biomass production and photosynthesis
InactiveUS20130007916A1Increased biomass productionPromote photosynthesisUnicellular algaeClimate change adaptationPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
The invention provides the disclosure of a novel plant / algae / cyanobacteria photosynthesis, biomass production, and productivity pathway involving low carbon dioxide inducible (LCI) proteins. According to the invention, the activity of one or more LCI proteins may be modulated to increase the same under conditions where such proteins are typically repressed. According to the invention, modulation of LCI protein activity was able to increase biomass production by as much as 80% under elevated CO2 conditions. The invention includes methods, and genetically modified plants / algae / cyanobacteria, cells, plant parts and tissues.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Freshwater chlorella and application thereof in fixation of CO2 and production of microalgae oil
InactiveCN103215190AGreat application potentialPromote growthUnicellular algaeBiofuelsBiodieselDry weight
The invention provides freshwater chlorella sorokiniana XJ02 and application thereof in fixation of CO2 and production of microalgae oil. The preservation number of the chlorella is CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO: M2013104. The chlorella disclosed by the invention can be used for fixing 0.03-20% of CO2 at high efficiency, the CO2 fixation efficiency of chlorella is 130-343mg / L / d, the biomass (dry weight) concentration of the chlorella is 720-2250mg / L, the oil content of chlorella is 29.2-41%, the oil fatty acid of the chlorella is mainly composed of C16 and C18 short-chain fatty acids, and the chlorella is suitable for production of biodiesel. Compared with the reported microalgae, the chlorella has higher CO2 fixation efficiency and biomass yield; and the chlorella can be used for obtaining the microalgae oil at high yield by selecting an appropriate culture condition, thus the production cost of the microalgae oil can be greatly reduced. An excellent production algae is provided for high-efficient fixation of CO2 in the environment and preparation of biodiesel by the microalgae oil.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method of improving biomass yield of lactic acid bacterial cultures
InactiveUS6610530B2Increased biomass productionReduce contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeQuinoneMitochondrial electron transport
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
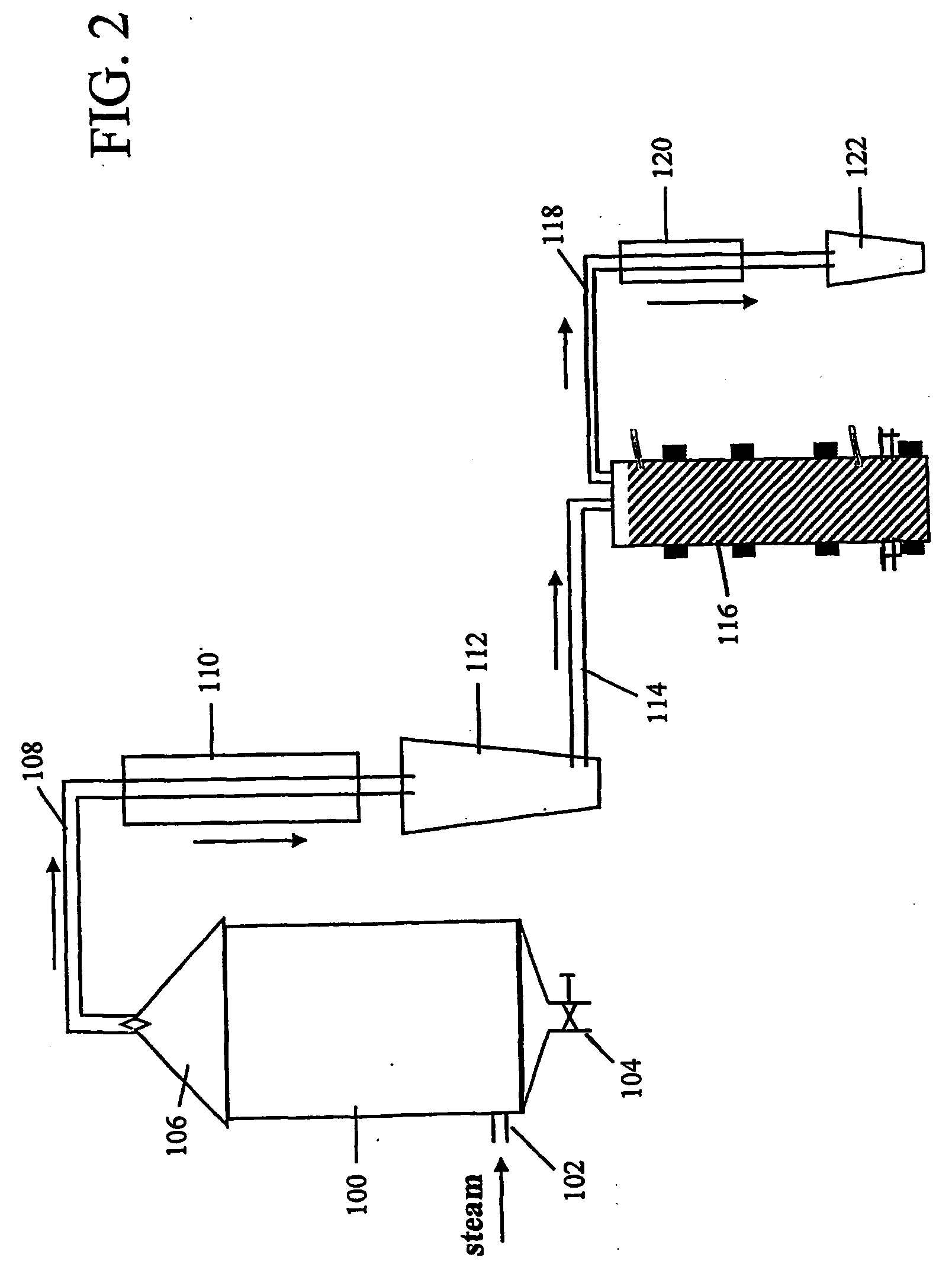
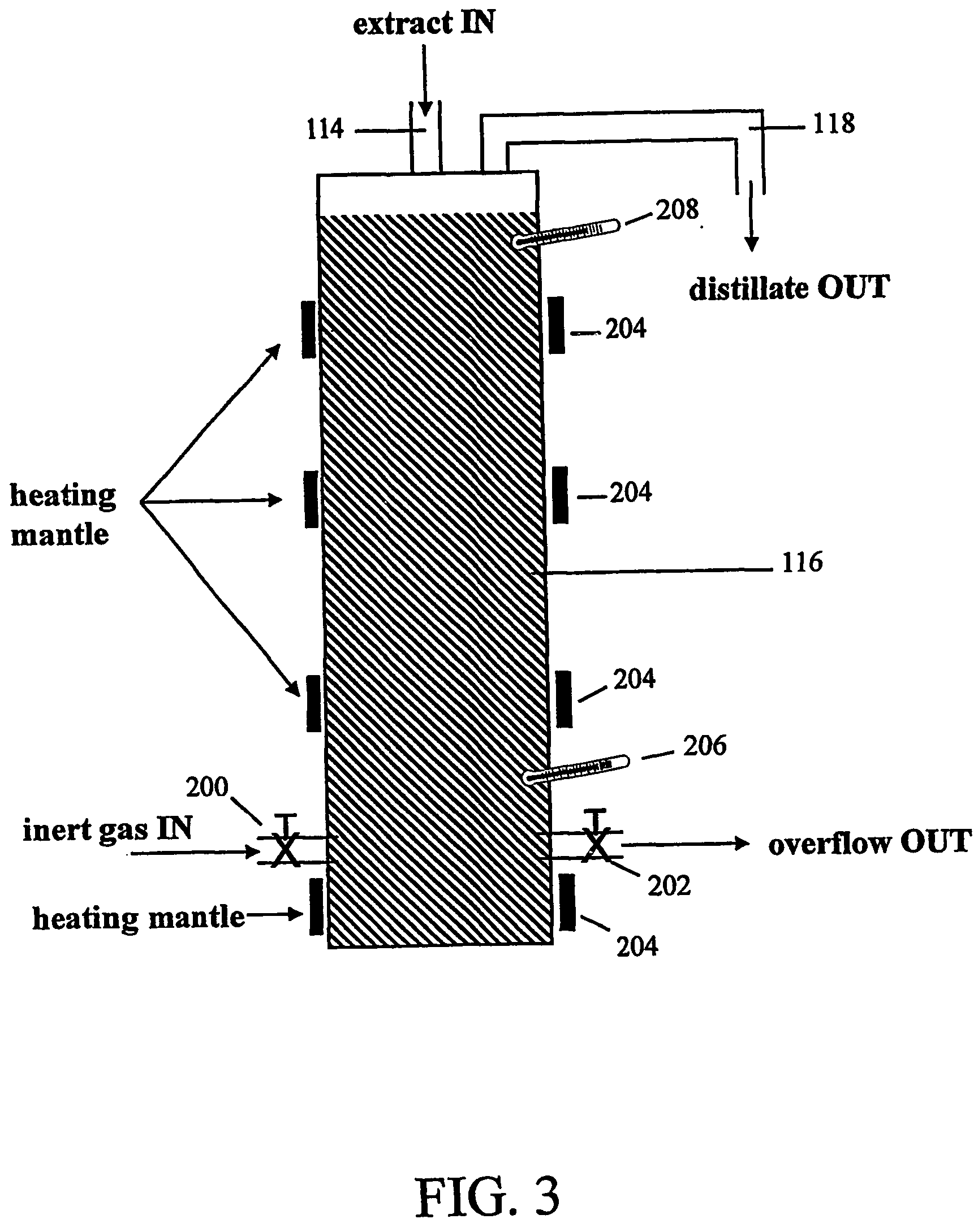
Bio-reactor for enhancing the biomass yield of plant organs
InactiveUS20020076815A1Yield maximizationEffective capacityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImpellerSupport matrix
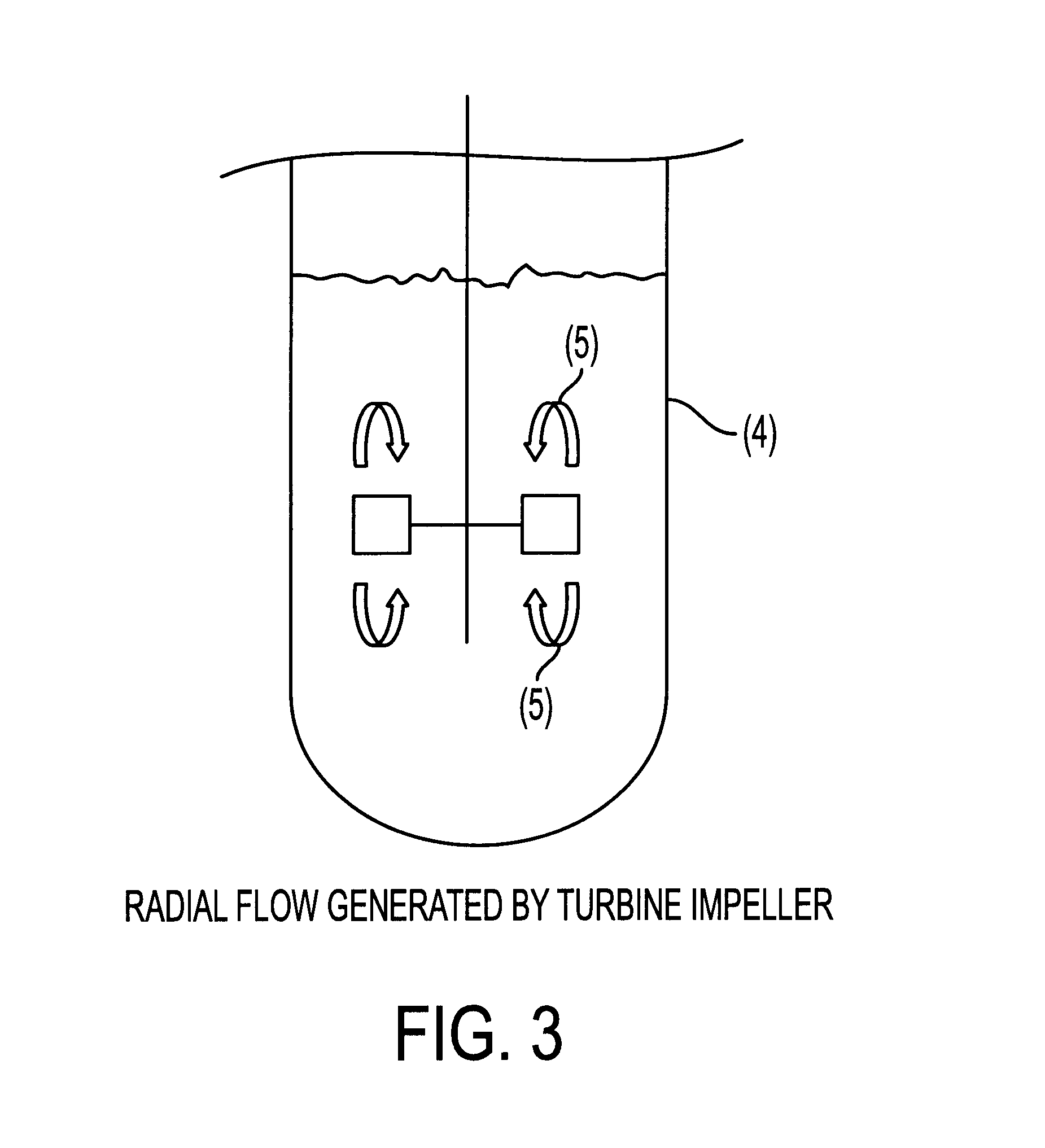
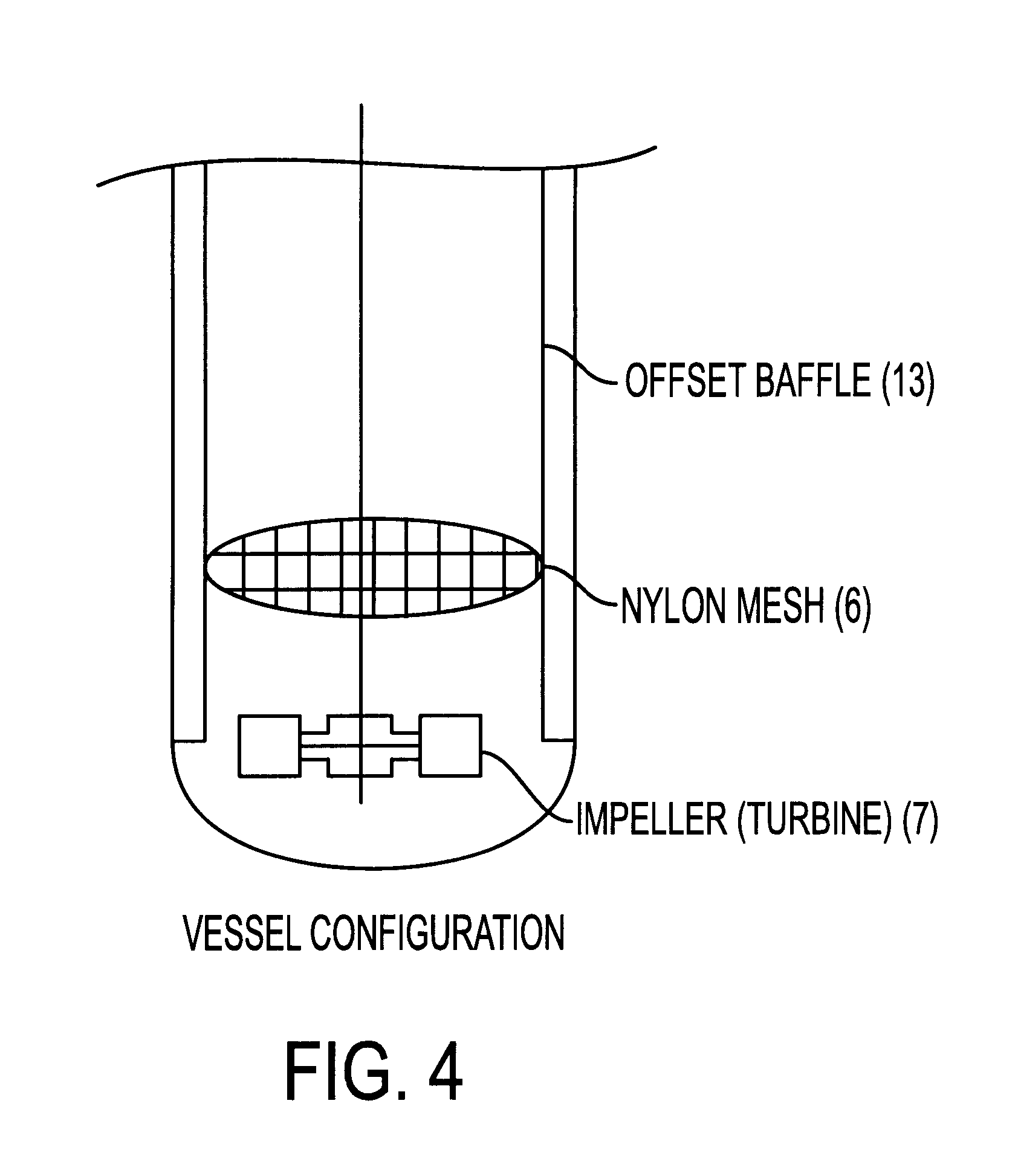
A bio-reactor for enhancing the biomass yield using a closed sterile vessel having a medium, said reactor comprising a central shaft, a support matrix oriented horizontally and dividing the vessel into an upper and a lower chamber, a means for stirring selected from turbine-2,4,6-impeller; marine blade impeller; helical blade impeller; mounted onto the central shaft and located at a predetermined distance from the support matrix so as to generate both radially and axially directed volumetric flow of the media; and at least two semi-circular sparges located both in the upper and lower compartments of the vessel at a predetermined distance from the support matrix.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
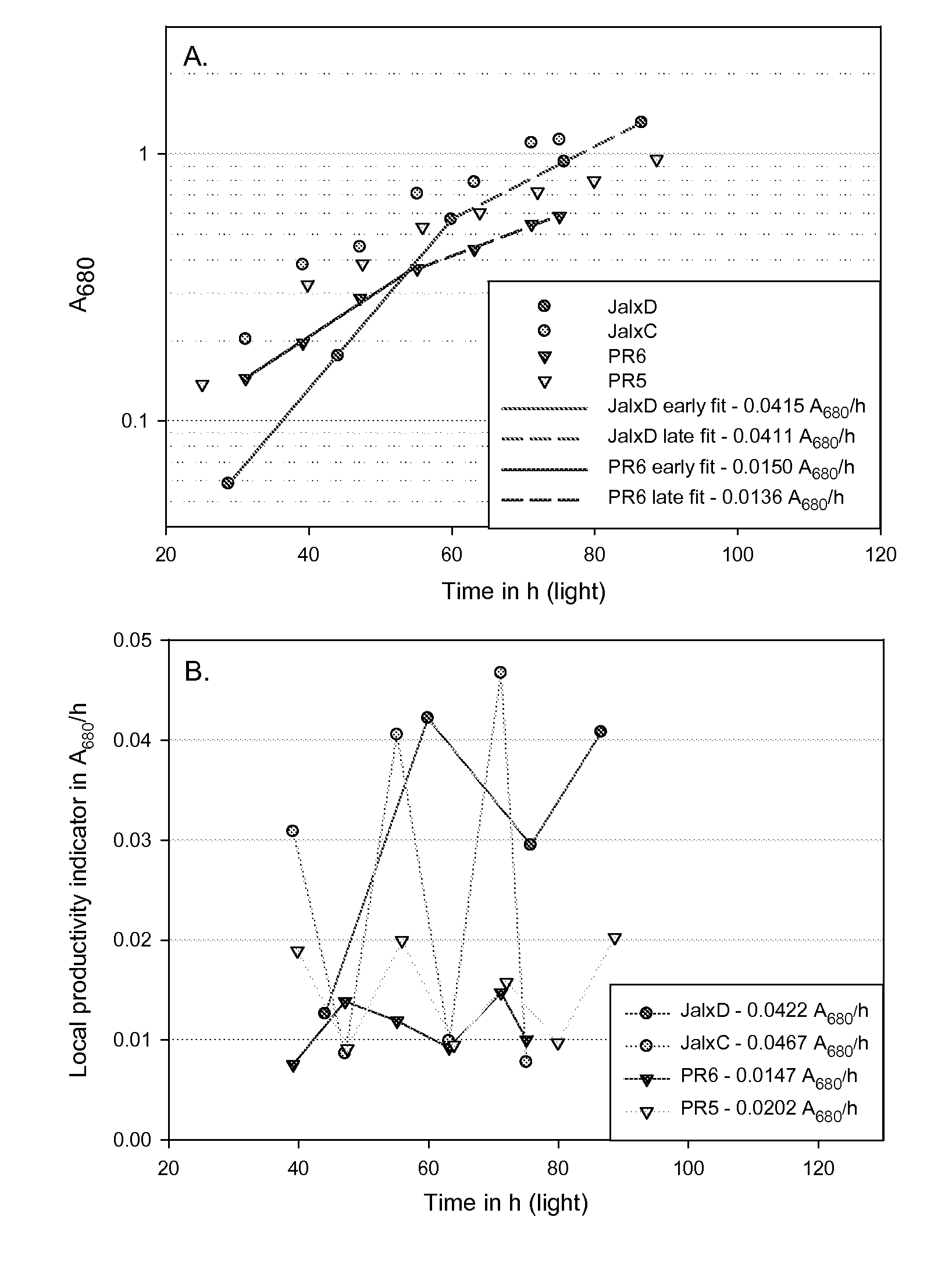
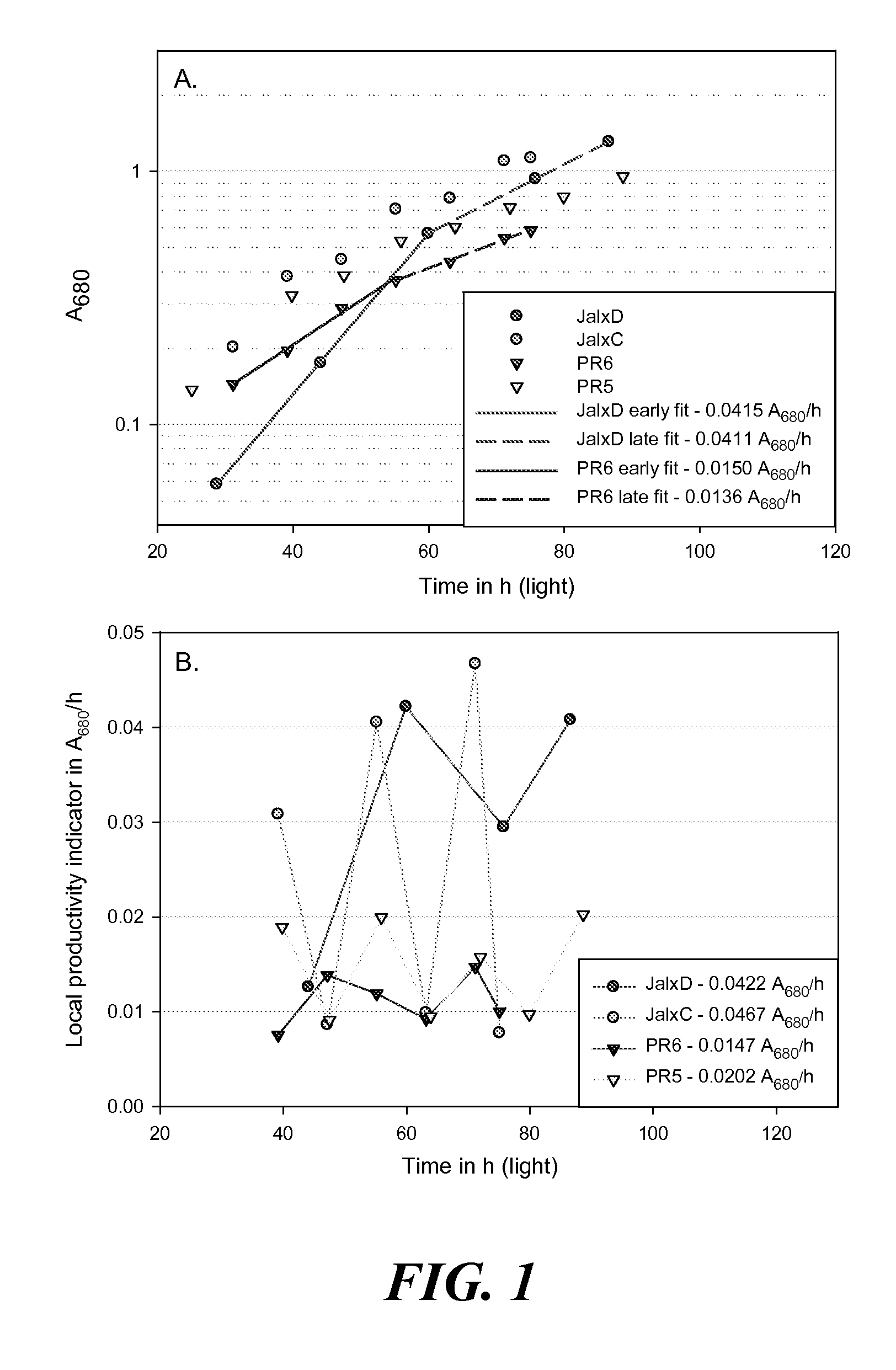
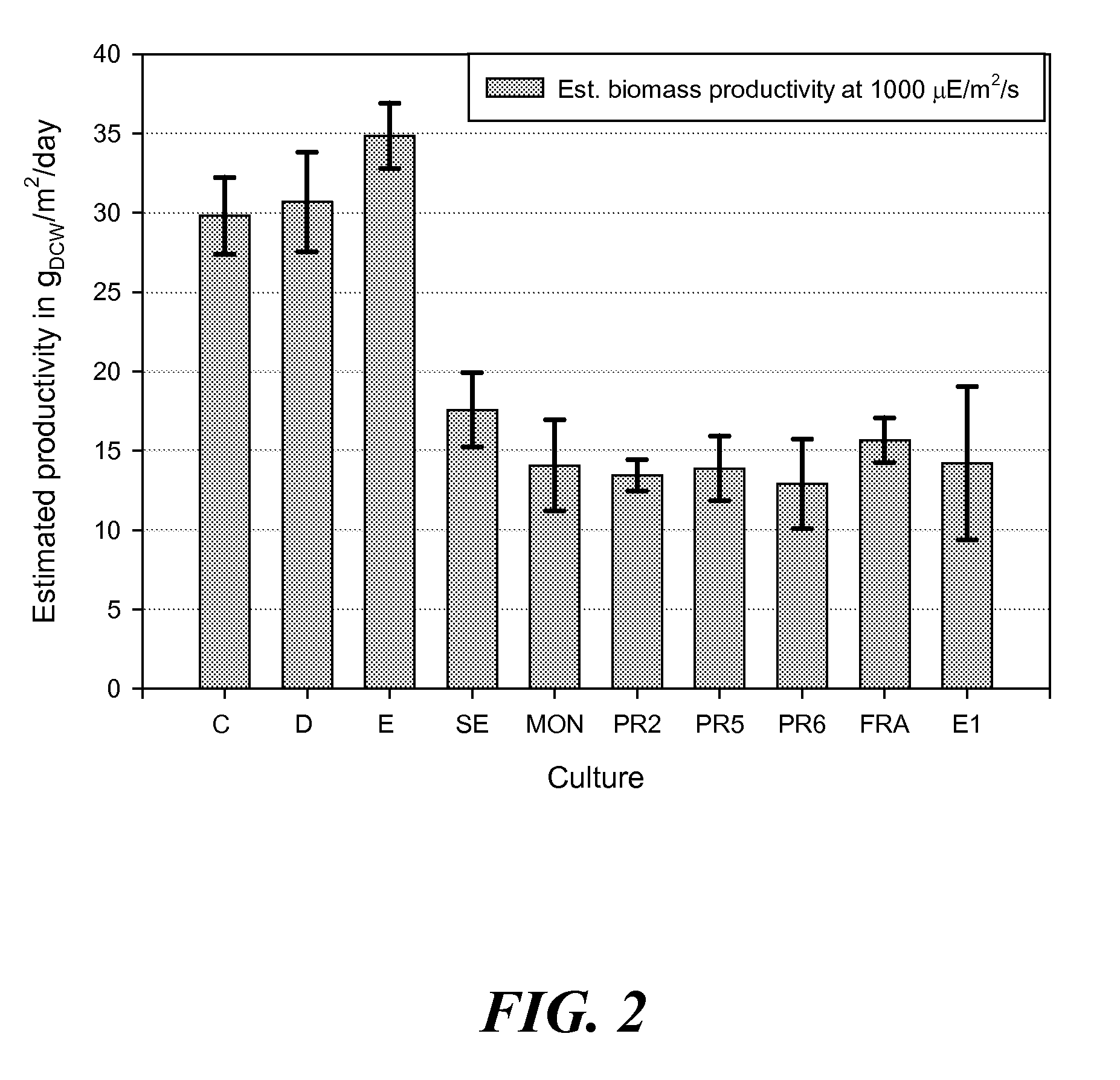
Methods for estimating intrinsic autotrophic biomass yield and productivity in unicellular photosynthetic algae
InactiveUS20100107487A1Algae productsComputation using non-denominational number representationProduction rateGram
A robust methodology is described herein for determining the algae biomass photoautotrophic yield (in gram of biomass synthesized per μmole of absorbed photons), which is useful for reliable biomass productivity estimates for selecting, comparing, and optimizing algae cultures for large-scale production. Another method is provided herein to increase dissolved inorganic carbon concentration and alleviate limitations common in aerated small-scale batches. This carbonate addition method allows for a more accurate determination of the algae culture photoautotrophic yield under small-scale experimental conditions. Also provided herein is a method for estimating a light spectrum-dependent scatter-corrected algae-specific absorption cross section, which permits the use of Beer's law to estimate the fraction of photons absorbed by a given algae culture. Determination of the algae photoautotrophic yield and absorption cross section enable a full photobioreactor parameterization and the resulting capacity to achieve highly controlled nutrients-supply conditions.
Owner:HOLLAND ALEXANDRA D
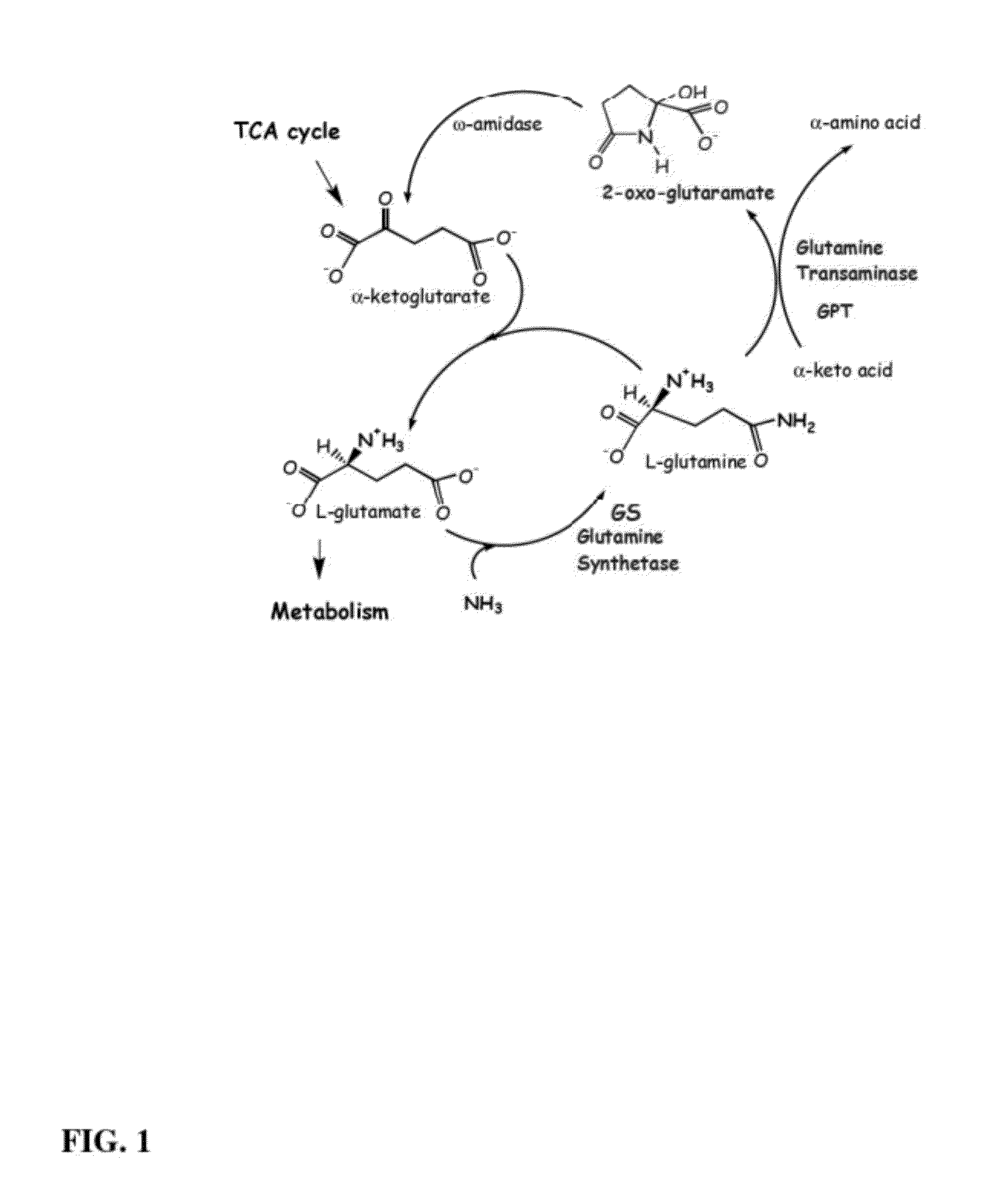
Increasing plant growth by modulating omega-amidase expression in plants
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods for increasing the leaf-to-root ratio of the signal metabolite 2-oxoglutaramate and related proline molecules in plants by modulating levels of ω-amidase to increase nitrogen use efficiency, resulting in enhanced growth, faster growth rates, greater seed and fruit / pod yields, earlier and more productive flowering, increased tolerance to high salt conditions, and increased biomass yields.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Systems and methods for maintaining the dominance and increasing the biomass production of nannochloropsis in an algae cultivation system
InactiveUS8143051B2Increased biomass productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStream flowNannochloropsis
Systems and methods for maintaining the dominance and increasing the biomass production of Nannochloropsis in an algae cultivation system are provided. Exemplary methods include applying an effective amount of ozone to Nannochloropsis growing in an algae cultivation system. A further method may include applying a shock amount of ozone above 10 milligrams / liter or higher in the inlet stream flowing into the algae cultivation system. Various exemplary embodiments may include a system for maintaining dominance and increasing the biomass production of Nannochloropsis in an algae cultivation system. The system may comprise a processor, and a computer readable storage medium having instructions for execution by the processor. The instructions for execution by the processor cause the processor to maintain dominance and increase biomass production of the Nannochloropsis in the algae cultivation system.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
Method of culturing akkermansia
A method for cost-effectively and efficiently culturing Akkermansia muciniphilais is disclosed. High biomass yields can be obtained on chemically defined media. This allows for large scale production of A. muciniphila suitable for use in humans, such as for pharmaceutical or food applications. The A. muciniphila can be produced free of animal-derived products, thereby allowing a broad-range of applications.
Owner:WAGENINGEN UNIV
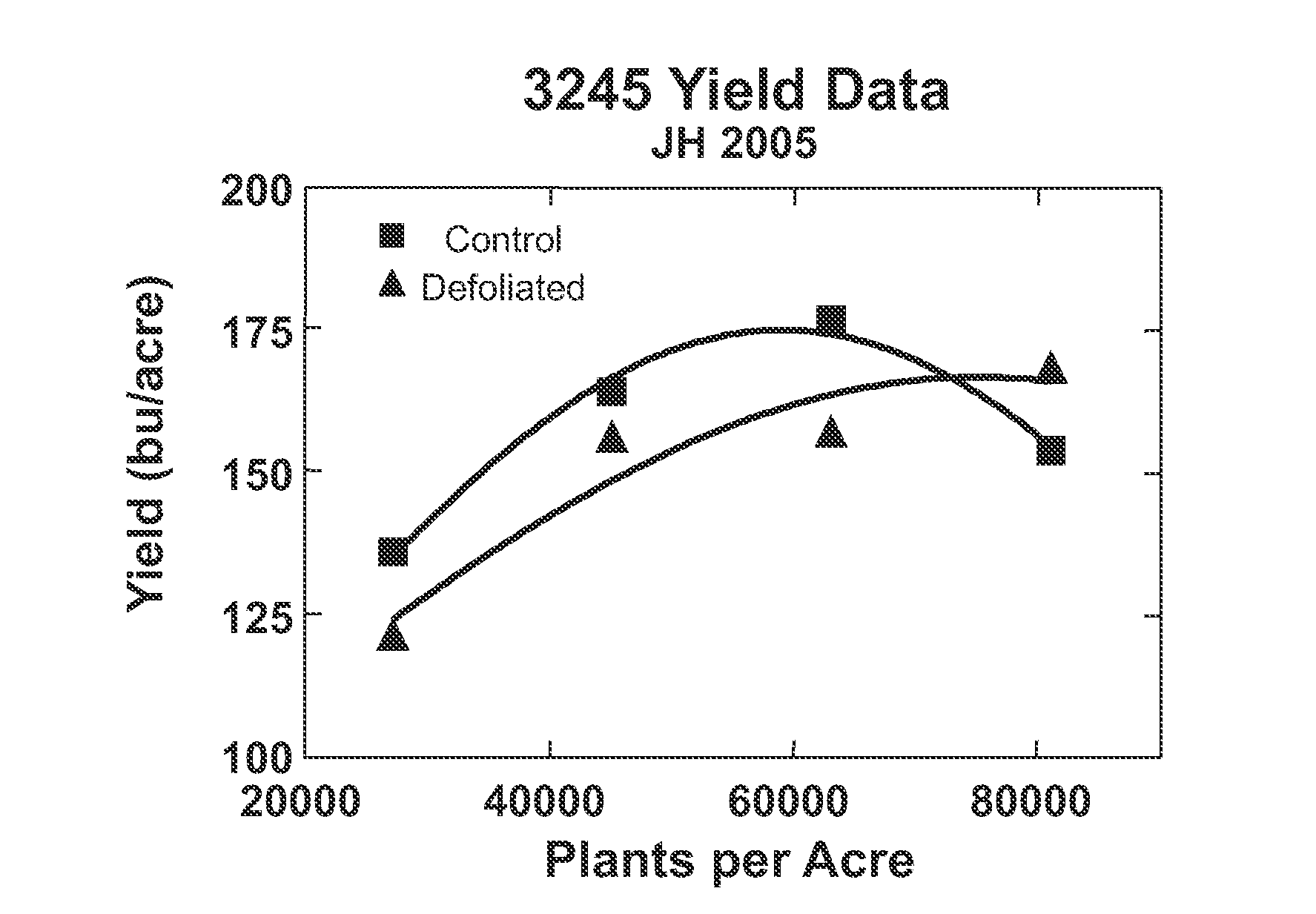
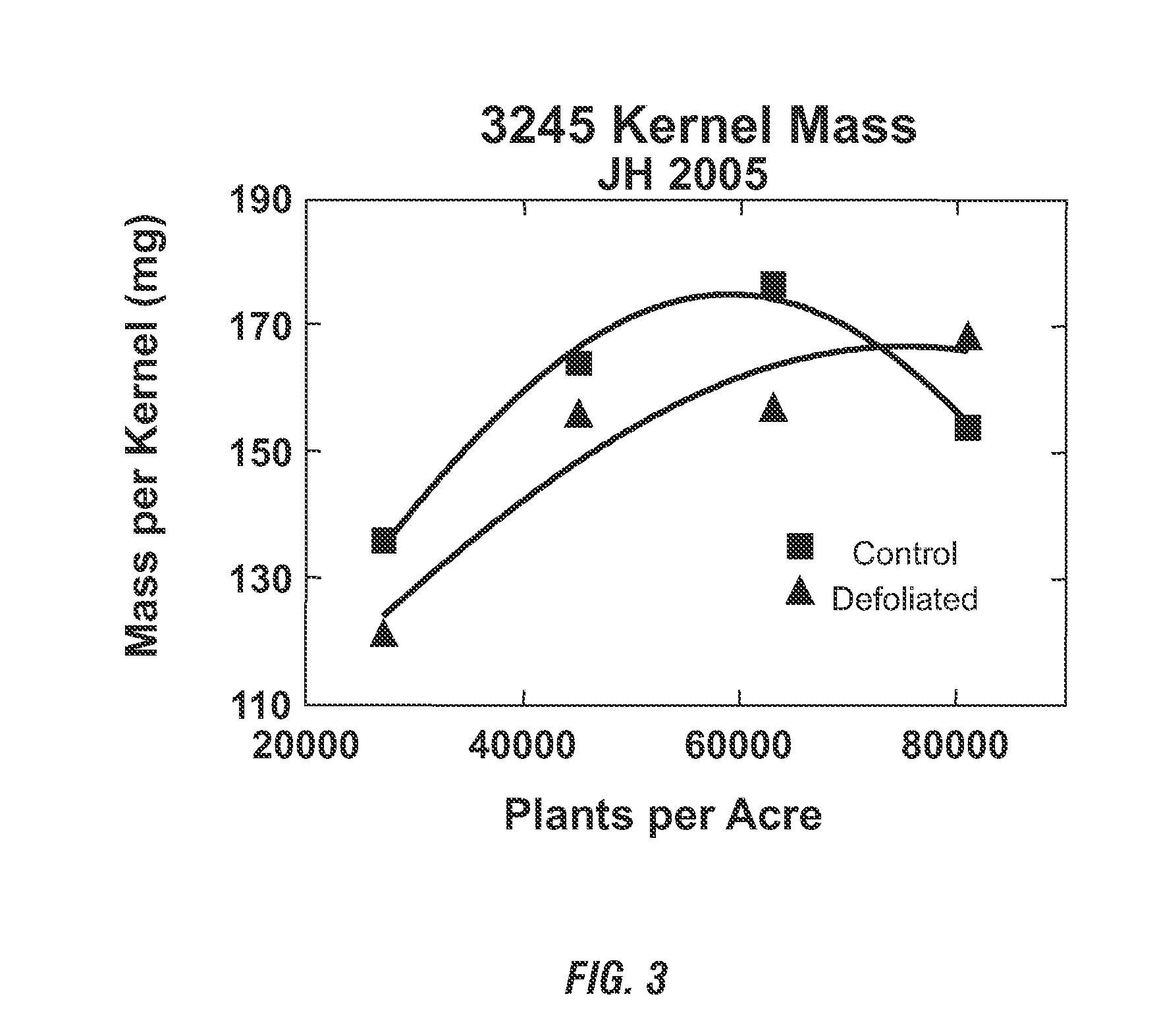
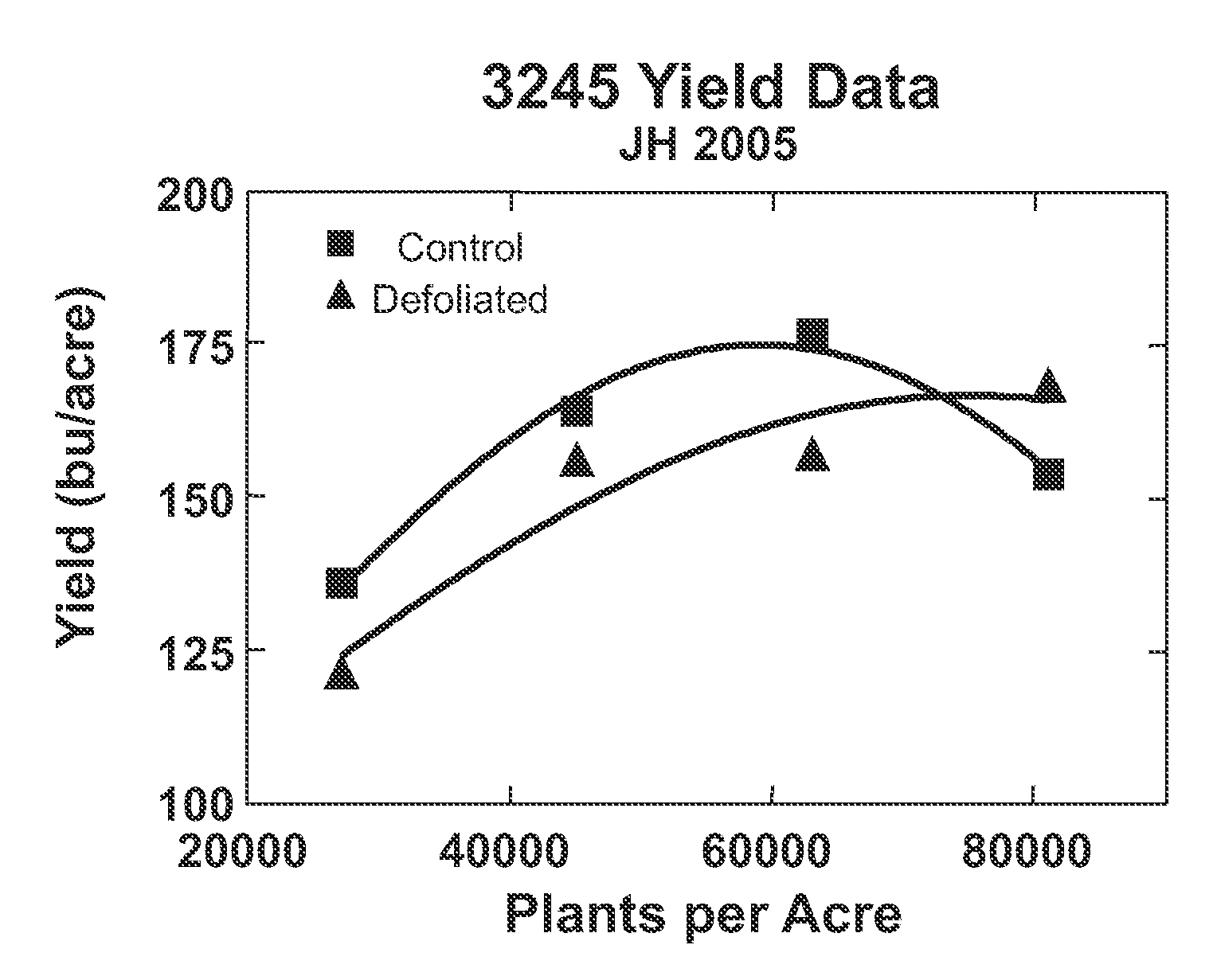
Methods to increase yield of plants grown at high populations
ActiveUS20110036002A1Increase food productionMass and weight is increasedSeed and root treatmentCrop conditionersHigh densityHigh population
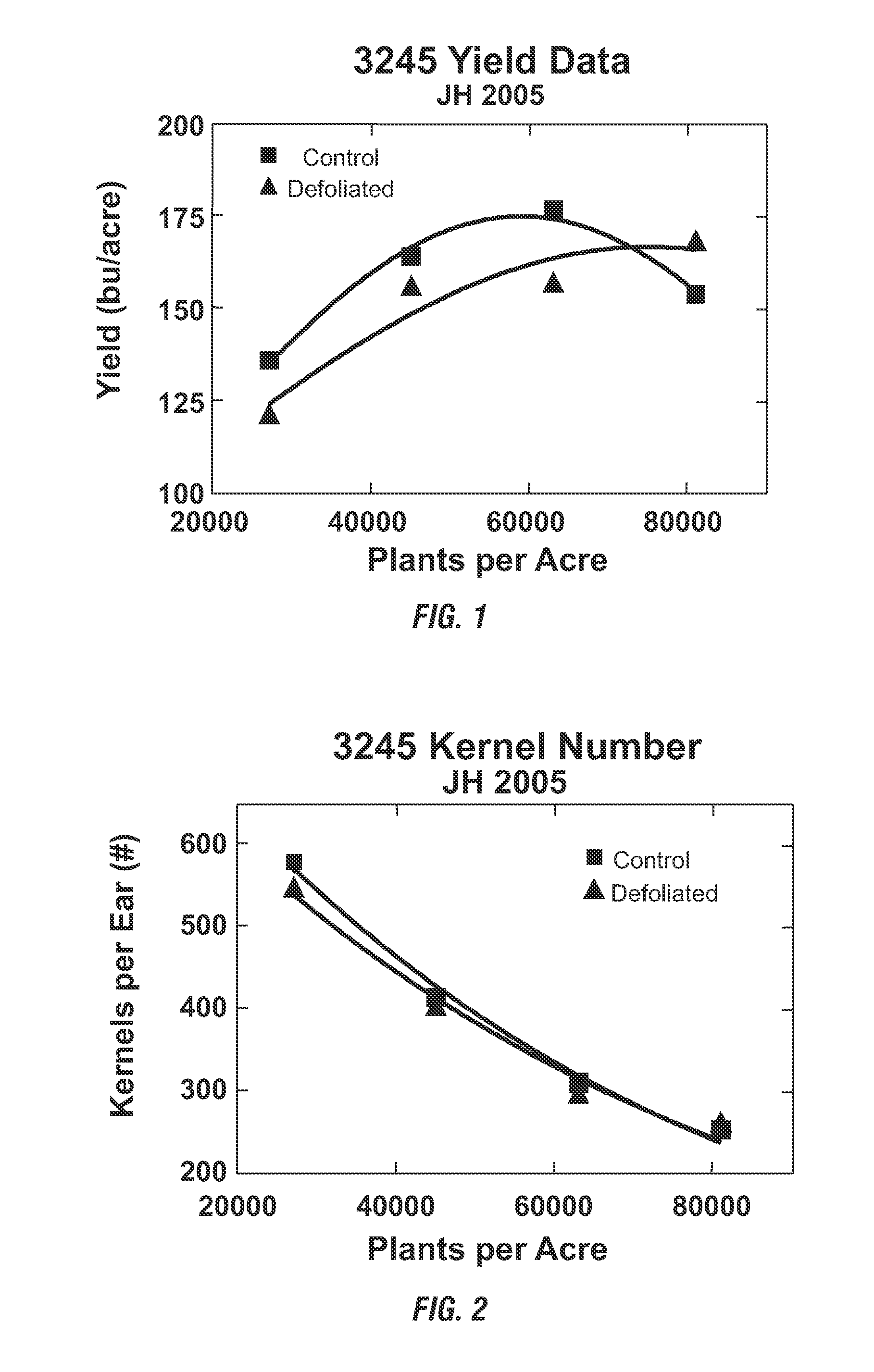
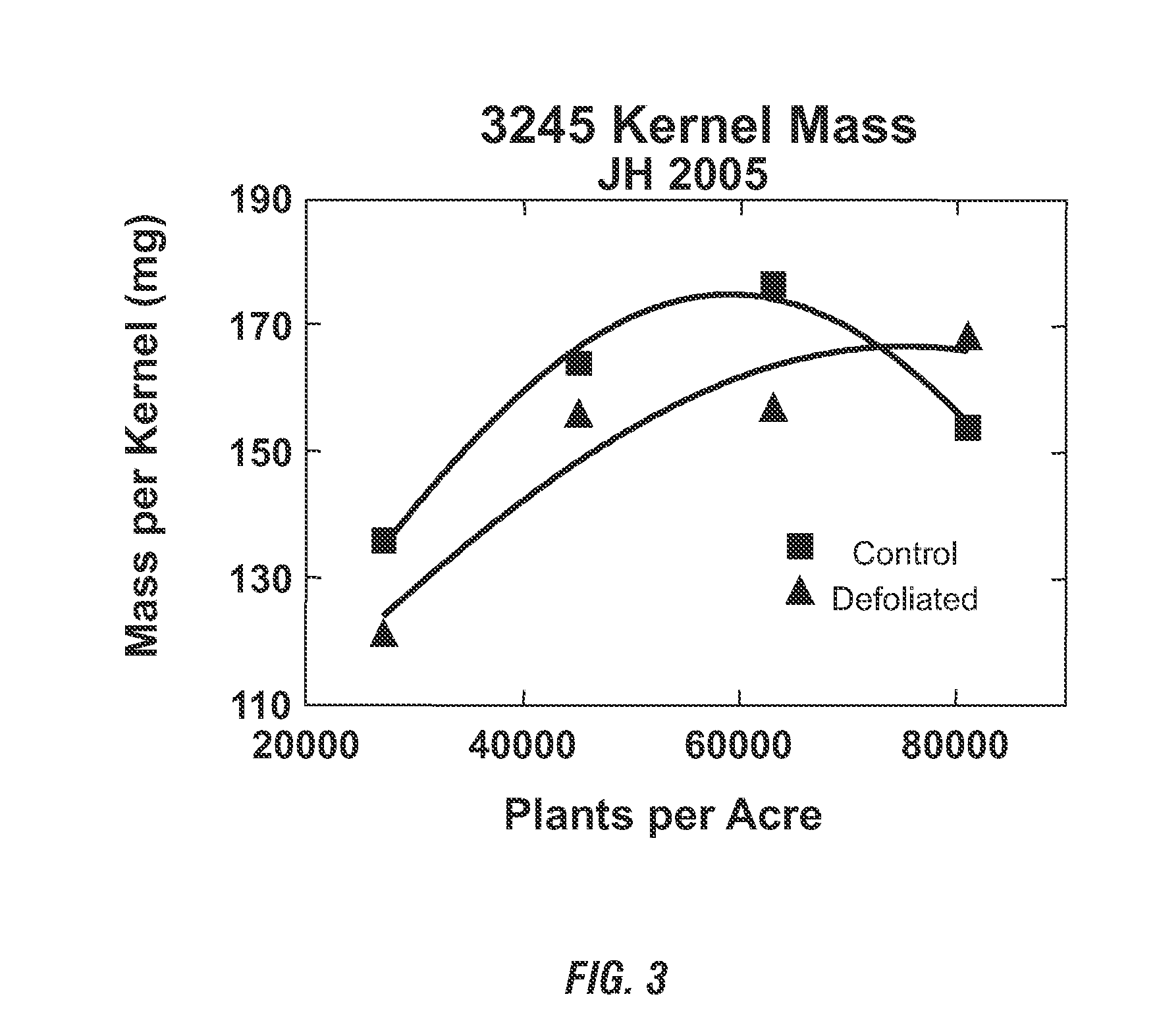
An increase in the total grain and biomass yields and photosynthetic rates of plants grown at high densities is achieved by novel methods of defoliating the primary-source leaf of a majority of such plants. In particular the methods provide for increased grain and biomass yields, including for example, increased average kernel mass for maize plants, and photosynthetic rates through the timely removal of the primary-source leaf of a majority of the plants grown at high densities. This invention also relates to seeds obtained by using the disclosed methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for producing building materials and wood substitutes from fast-growing carbon sink grass
InactiveCN107032668AFast consumptionSave clean developmentReed/straw treatmentPulping with inorganic basesBiosphereFiber
The invention discloses a method for producing building materials and wood substitutes from fast-growing carbon sink grass. The fast-growing carbon sink grass is planted on barren hills and slopes, in marginal land and in polluted land required to be remedied, and biomass yield increase with leaps and bounds is realized through mowing; dynamic CO2 gas in the atmosphere is transferred to the biosphere, a static solid organic carbon compound is formed, excessive CO2 remaining in the atmosphere is allocated to the industry chain including production and storage of products with plants as a raw material, the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is adjusted, and global climate warming is inhibited. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) the planted fast-growing carbon sink grass is harvested at proper time; (2) the fast-growing carbon sink grass is pretreated according to the technical requirements of processing of foaming fiber boards, combined walls, lightweight brick tiles, flame-retardant thermal insulation boards, the wood substitutes and paper substitutes; (3) the foaming fiber boards, the combined walls, the lightweight brick tiles, the flame-retardant thermal insulation boards, the wood substitutes and the paper substitutes are produced. With grass to replace wood, deforestation is reduced, and the ecological environment is protected.
Owner:雷学军
Method for concurrently improving spirulina biomass and polysaccharide yield
InactiveCN105647825AHigh polysaccharide yieldPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDownstream processingDry weight
The present invention relates to biomass and polysaccharide accumulation through spirulina culture, specifically to spirulina culture using the control of the addition of a nutritional salt so as to concurrently accumulate biomass and polysaccharides. According to the present invention, spirulina cells cultured to achieve a exponential growth phase are transferred into a nutrition limiting culture medium, natural illumination or artificial illumination is performed, culture is performed to achieve a stable phase, and the spirulina cells are harvested, wherein the biomass yield is 1-4 times the biomass yield of the culture under the rich nutrition condition, the polysaccharides yield is increased by 0.8-20 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition, and the polysaccharide content achieves 45-80% of the spirulina dry weight, and is increased by 2-6 times compared to the culture under the rich nutrition condition; and the contradiction that the spirulina biomass and the polysaccharide cannot be concurrently accumulated is solved, the rapid and efficient spirulina polysaccharide production is achieved, the advantages of low nutrition salt consumption, low production cost, high polysaccharide content and the like are provided, the downstream processing operations are easily simplified, and the industrial production of the spirulina polysaccharide can be promoted.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Culture method for increasing biomass and grease yield of microalgae
ActiveCN103484372AIncreased biomass productionIncrease productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesNannochloropsis salinaNitrogen
The invention discloses a culture method for increasing the biomass and grease yield of microalgae in the technical field of algal biological culture. The culture method comprises the following steps: culturing the microalgae in a nutrition-rich culture medium until a logarithmic phase with a nutrition-rich and nutrition-poor two-stage culture method for Nannochloropsis salina at first, then concentrating and collecting the microalgae, and inoculating the microalgae to a phosphorus-free or microelement-free nutrition-poor medium with the microalgae for continuous culture. According to the method, additional nutrition does not need to be added, so that the cost is reduced, the biomass yield, the cell grease content and the final grease yield of the microalgae are greatly increased, and the shortcoming that only the cell grease content is increased but the final grease yield is still very low in a traditional nitrogen-free culture process is overcome; in the absence of phosphorus, the grease content of the microalgae reaches 46% and the biomass and grease yields are increased by 30% and 117% respectively; and in the absence of microelements, the grease content of the microalgae reaches 40% and the biomass and grease yields are increased by 65% and 133% respectively.
Owner:博露(厦门)生物股份有限公司
Pesticidal compositions from prunus
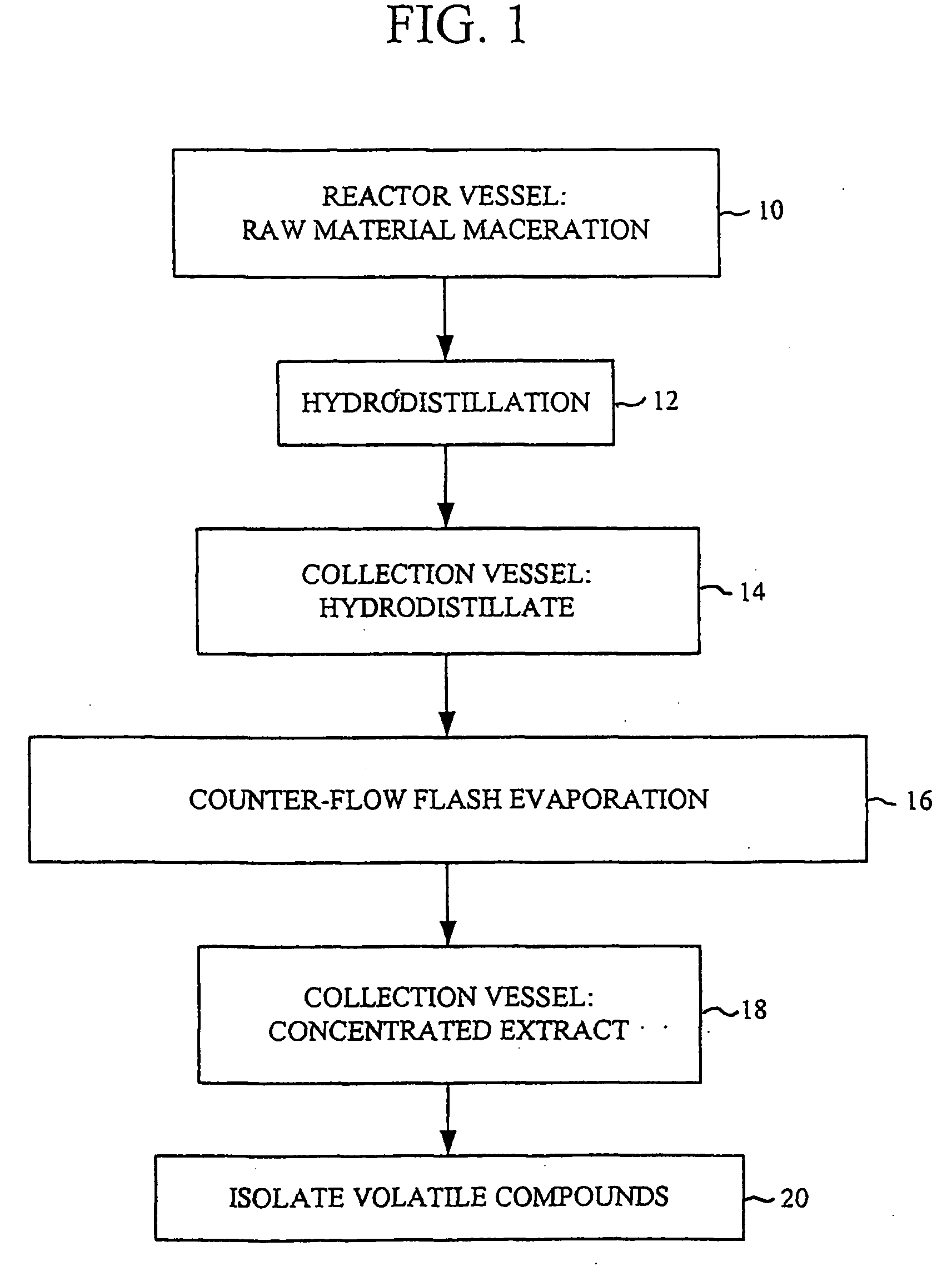
InactiveUS20040105901A1Reduce the valueReduce plant survivalCompound screeningBiocideBenzoic acidSoil treatment
The foliage and stems of plant species from the family Rosaceae, genus Prunus, yield natural pesticides when macerated. Hydrodistillation of macerated plant biomass yields a concentrated solution of organic volatile compounds that act synergistically as a natural pesticide. Volatile compounds liberated from Prunus biomass include 2-propanol, hexanal, trans-2-hexenal, 1-hexanol, cis-3-hexenol, mandelonitrile, benzoic acid, benzaldehyde, benzyl alcohol, hydrocyanic acid and others. These compounds may be removed from the distillate and reformulated to form a standard concentrated solution, with benzaldehyde, mandelonitrile and hydrogen cyanide being the major components. The extracts may be used as a soil treatment or soil fumigant for soil-borne pests. They also may be formulated for application as solutions with or without a surfactant or formulated as powders for foliar treatment. In a particular application, such extracts may be applied to postharvest commodities such as fruits, vegetables, roots, grains and nuts to protect against certain fungi and insects.
Owner:BRANCH RES LLC
Method for extracting polysaccharide from chlorella
The invention discloses a method for extracting polysaccharide from chlorella. The method comprises the following steps: performing multi-stage culture on chlorella, and extracting the cultured chlorella by using an inorganic alkali solution, wherein a culture medium without glucose is adopted in one-stage culture of chlorella. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the biomass yield of chlorella is high, and the main component, namely, polysaccharide, of chlorella can be easily, rapidly and conveniently obtained. Compared with a conventional method, the method is feasible, convenient to operate, safe and reliable, simple in equipment, low in cost and applicable to industrial on-scale production.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Method for culturing marine oil-producing microalgae
InactiveCN102191179APromote accumulationProtect environmentUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationLight exposure
The invention discloses a method for culturing marine oil-producing microalgae, which is characterized in that: the marine microalgae are culture by using daily sewage to supply nutritional salts and using high-concentration carbon dioxide to provide a carbon source, so the biomass yield of the marine microalgae is improved; and the microalgae are subjected to direct high-light exposure so as to improve the oil and fat yield of the marine microalgae. In the invention, the culture cost of the oil-enriched marine microalgae is lowered, the process of inducing the oil and fat accumulation in microalgae is simplified, and the industrialization of the large-scale culture of oil-enriched marine microalgae is promoted.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Bio-reactor for enhancing the biomass yield of plant organs
InactiveUS6589780B2Yield maximizationIncreased biomass productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImpellerSupport matrix
A bio-reactor for enhancing the biomass yield using a closed sterile vessel having a medium, said reactor comprising a central shaft, a support matrix oriented horizontally and dividing the vessel into an upper and a lower chamber, a means for stirring selected from turbine-2,4,6-impeller; marine blade impeller; helical blade impeller; mounted onto the central shaft and located at a predetermined distance from the support matrix so as to generate both radially and axially directed volumetric flow of the media; and at least two semi-circular spargers located both in the upper and lower compartments of the vessel at a predetermined distance from the support matrix.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method of improving biomass yield of lactic acid bacterial cultures
InactiveUS20020034815A1Increased biomass productionReduce contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiotechnologyQuinone
A method of enhancing biomass yield of a lactic acid bacterial species cell culture, comprising cultivating the cells in a process comprising the steps of providing conditions that results in a reduced glycolytic flux and providing conditions that enable the cells to have, under aerobic conditions, a respiratory metabolism. The increased yield of biomass may be the result of an increased yield of ATP which can be obtained by activating the native ATP synthase activity of the H+-ATPase complex by lowering the ATP / ADP ratio, e.g. by carbon source limitation, and / or by increasing the proton gradient (membrane potential) of the cells, e.g. by enhancing or establishing an electron transport chain which can be achieved by enhancing expression of dehydrogenases or electron transport chain components, by adding to the medium a quinone or porphyrin compound or by enhancing the expression of the H+-ATPase activity.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Transgenic plants with increased seed yield, biomass and harvest index
The present invention provides methods for producing seeds and plants with increased biomass production. More specifically, the present invention provides methods for producing plants having increased yield for a number of plant traits, including seed number, seed weight, number of seed heads, flag leaf weight, and total plant weight. The present invention also provides methods for improving the harvest index of a plant. In a preferred embodiment, the method of the present invention comprises introducing into a plant a nucleic acid selected from the group consisting of a nucleic acid comprising SEQ ID NO: 3, which hybridizes to SEQ ID NO: 3 under high stringency conditions and encodes and retains SH2 - Nucleic acid of a polypeptide with biological activity of REV6-HS, fragment of SEQ ID NO: 3 encoding a peptide retaining biological activity of SH2-REV6-HS, encoding a polypeptide comprising SEQ ID NO: 4 or its SH2-REV6-SH organism Nucleic acids of fragments of biological activity, and nucleic acids encoding SH2HS or SH2RTS polypeptides. The present invention also relates to plants obtained by the methods provided herein.
Owner:RES & DEV INST
Method for improving biomass yield
InactiveUS20120054917A1Increased biomass productionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyHaplotype
A method for predicting harvestable biomass yield in a crop comprising: genotyping a sample obtained from a crop plant for one or more markers genetically linked to a polynucleotide sequence having at least 50, 55, 60, 65, 70, 75, 80, 85, 90, 95, 97, 98, 99 or 100% identity to SEQ BD NO 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 or 25, whereby the markers individually or collectively identify a haplotype associated with yield in a plurality of crop plants and correlating the haplotype with the harvested biomass yield.
Owner:ROTHAMSTED RES LTD
Freshwater Chlorella sorokiniana GS30 and application thereof
InactiveCN103952312AEfficient emission reductionEffectively fixedUnicellular algaeBiofuelsBiodieselEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of biomass energy, and in particular to a freshwater chlorella strain (i) Chlorella sorokiniana ( / i) GS03 and application thereof to industrial flue gas CO2 fixation and production of microalgae biodiesel. The chlorella strain (i) C.sorokiniana ( / i) GS03 provided by the invention has a preservation number of CCTCC M2013607, and higher CO2 tolerance, higher fixation efficiency of high-concentration carbon dioxide and higher biomass yield and oil yield compared with the reported microalgae strains. Therefore, the invention can greatly reduce microalgal oil production cost, and provides a good production strain for algae for efficient fixation of CO2 in typical industrial flue gas environment and biodiesel production from microalgae oil, and shows great application prospect in the field of biomass energy.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for comprehensive utilization of energy grass in fields of feeds, biogas and paper pulp
InactiveCN104605153ATake advantage ofNot dischargedFood processingAnimal feeding stuffResource utilizationPulp and paper industry
The invention discloses a method for the comprehensive utilization of energy grass in the fields of feeds, biogas and paper pulp, and belongs to the field of biomass resource utilization. For obtaining the highest biomass yield per unit land area, and fully utilizing the energy grass (an economic crop with a huge application potential), according to the method, the applications of the energy grass in the three fields of the feeds, the biogas and the paper pulp are organically combined, and through creative tests and full actual application effect contrasts, a set of effective comprehensive utilization method of the energy grass is developed.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Device and method for cultivating diatom
ActiveCN105838585AReduce energy consumptionHigh energy consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh densityHigh energy
The invention discloses a device and a method for cultivating diatom. The device for cultivating the diatom comprises a cultivation container, a diatom attaching plate and inflation pipes. The cultivation container is used for accommodating cultivation media, the diatom attaching plate is arranged inside the cultivation container, and the inflation pipes are arranged inside the cultivation container and are used for blowing air to the diatom attaching plate. The method for cultivating the diatom includes a diatom seed cultivation step, a mass cultivation step, a harvesting step and a low-temperature stimulation step. According to the technical scheme, the device and the method have the advantages that problems of strict conditions, high energy consumption, vulnerability to pollution and low cell density of existing micro-diatom liquid cultivation can be solved by the aid of the device and the method; the device is simple in structure, the diatom biomass yield can be effectively increased by the device and the method, micro-diatom can be cultivated without strict conditions, the device and the method are low in energy consumption, pollution can be prevented, and high-density diatom cells can be generated.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Down-regulation of a homeodomain-leucine zipper i-class homeobox gene for improved plant performance
Methods for modulating plants using optimized ZmME293 down-regulation constructs are disclosed. Also disclosed are nucleotide sequences, constructs, vectors, and modified plant cells, as well as transgenic plants displaying increased seed and / or biomass yield, improved tolerance to abiotic stress such as drought or high plant density, improved nitrogen utilization efficiency, increased ear number and / or reduction in time to scenescence.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor and microalgae culture method using flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor
ActiveCN103952286AIncrease biomassEnhance stirringBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFlue gasAlgae
The invention relates to biomass energy utilization technologies, and aims to provide a flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor and a microalgae culture method using the flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor. The flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor is in a box type structure, the top of the box type structure is provided with an opening with a diameter of 3cm, the box type structure is internally divided into three regions by partitions, the three regions are respectively a center flow rising region and two side flow descending regions; the microalgae culture method includes the following steps: inoculating a microalgae liquid to the flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor, setting a light source at one side of the flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor, and using a gas pump to send air or industrial flue gas into the flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor. The flat-plate gas-lift circulation type algae culture photosynthetic reactor can form a rotating alternate large eddy flow, strengthens the gas-liquid mixing and mass transfer, can significantly improve the algae fluid flow field and promote the flash effect, and is beneficial to enhancing the photosynthesis and biomass yield of microalgae.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
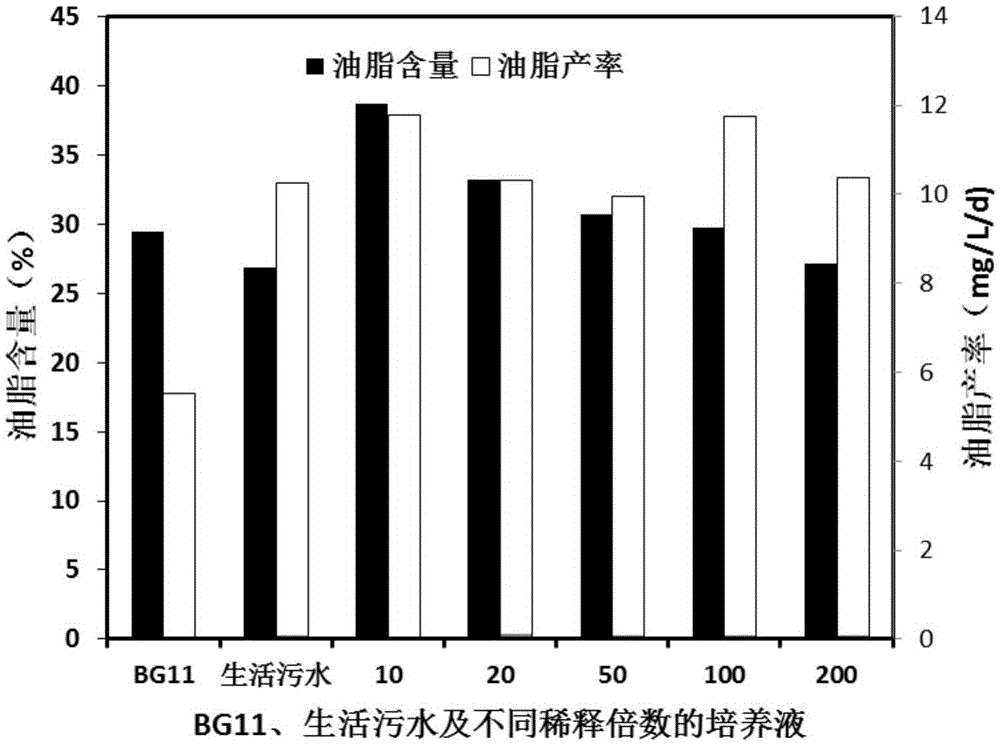
Method for cultivating chroococcus by domestic-wastewater-diluted kitchen waste anaerobic digestion solution
InactiveCN105483015AIncrease growth rateHigh yieldUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesMixed cultureCulture fluid
The invention discloses a method for cultivating chroococcus by a domestic-wastewater-diluted kitchen waste anaerobic digestion solution and belongs to the technical field of microalgae biology. The method is characterized in that BG11, domestic wastewater, a digestive fluid and culture solutions diluted by different times are utilized for constant-temperature light culture of chroococcus SDEC-6 and chroococcus SDEC-6 is harvested in the last growth stage. Results show that the biomass, the growth rate, the lipid content and the like of chroococcus SDEC-6 in domestic wastewater and at different dilution times are higher than those of BG11, the biomass and the lipid content, obtained by diluting a culture medium by 100 times, are higher than those of domestic wastewater. In conclusion, a mixed culture solution obtained by the domestic-wastewater-diluted kitchen waste anaerobic digestion solution can serve as a high-quality substitutive medium, promote biomass yield and lower the culture cost and is worthy of popularization.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
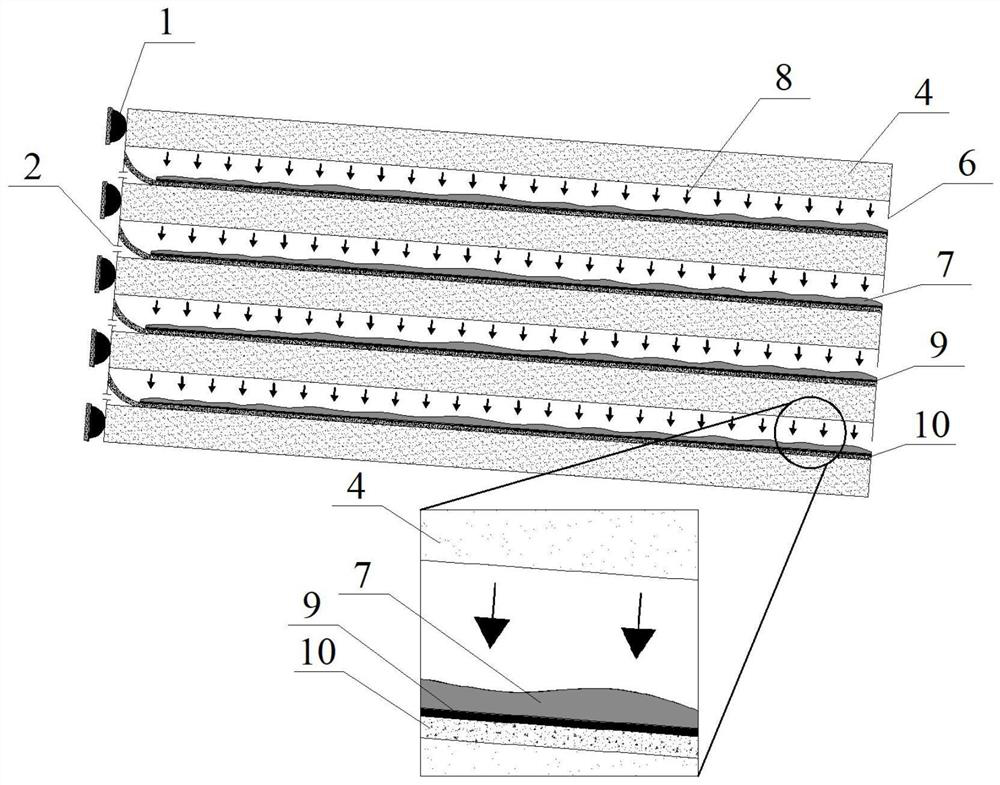
Multilayer stacked adsorption type microalgae biological membrane photobioreactor based on light guide carrier
PendingCN111647501AGood light transmission performanceHigh light conversion efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLight-emitting diodeCulture mediums
The invention provides a multilayer stacked adsorption type microalgae biological membrane photobioreactor based on a light guide carrier. The multilayer stacked adsorption type microalgae biologicalmembrane photobioreactor is mainly composed of a plurality of layers of stacked solid light guide plates, wherein an LED (light emitting diode) lamp strip is mounted at the left side of each layer ofthe solid light guide plate; light reflection membranes with high light reflectivity are stuck on the other surfaces except the left side end face and the lower surface; and a liquid culture medium source layer, a micro-pore filtering membrane and a microalgae biological membrane, which are made of a porous material, are flatly paved on the upper surface of each solid light guide plate in sequencefrom bottom to top. The plurality of layers of the stacked solid light guide plates are arranged on a reactor bracket; the adjacent light guide plates are separated by the bracket; and a liquid culture medium inlet is formed in the left side of the bracket and a liquid culture medium outlet is formed in the right side of the bracket. According to the multilayer stacked adsorption type microalgaebiological membrane photobioreactor, the light guide plates are used as light source transmission and conversion media and adsorption type microalgae biological membrane carriers, and microalgae cellsare cultured in a multilayer stacking manner, so that the microalgae biomass yield of a unit occupied area is improved.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods to increase yield of plants grown at high populations
ActiveUS8250807B2Increase food productionMass and weight is increasedSeed and root treatmentCrop conditionersHigh densityHigh population
An increase in the total grain and biomass yields and photosynthetic rates of plants grown at high densities achieved by novel methods of defoliating the primary-source leaf of a majority of such plants. In particular the methods provide for increased grain and biomass yields, including for example, increased average kernel mass for maize plants, and photosynthetic rates through the timely removal of the primary-source leaf of a majority of the plants grown at high densities. This invention also relates to seeds obtained by using the disclosed methods.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Low-phosphor culture medium for chlorella heterotrophy culture
InactiveCN101173215AReduce phosphorus and nitrogen contentReduce investmentUnicellular algaePhosphorD-Glucose
The invention relates to a low phosphorous culture medium for heterotrophic nutrition culturing chlorella, belonging to technical field of biology. The invention adopts the components and the concentration content of the components (mg / l) as following: Glucose x H2O is 5000 to 50000; KH2PO4 is 10 to 1000; KNO3 is 300 to 7500; MgSO4 x 7H2O is 1000 to 1250; EDTA is 500 to 625; H3BO3 is 114.2 to 142.75; CaCl2 x 2H2O is 111 to 138.75; FeSO4 x 7H2O is 49.8 to 62.25; ZnSO4 x 7H2O is 88.2 to 110.25; MnCl2 x 4H2O is 14.2 to 17.75; MoO3 is 7.1 to 8.875; CuSO4 x 5H2O is 15.7 to 19.625, and Co(NO3)2 x 6H2O is 4.9 to 6.125. The invention can be used in culturing chlorella and the dosage of KH2PO4 is only 1.6% to 16% to the former Basal prescription, but the inoculum concentration, the specific growth rate, the yield of the biomass, the percent conversion of biomass to glucose, the growing trend and the culturing time are all equal to the former Basal cultivation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com