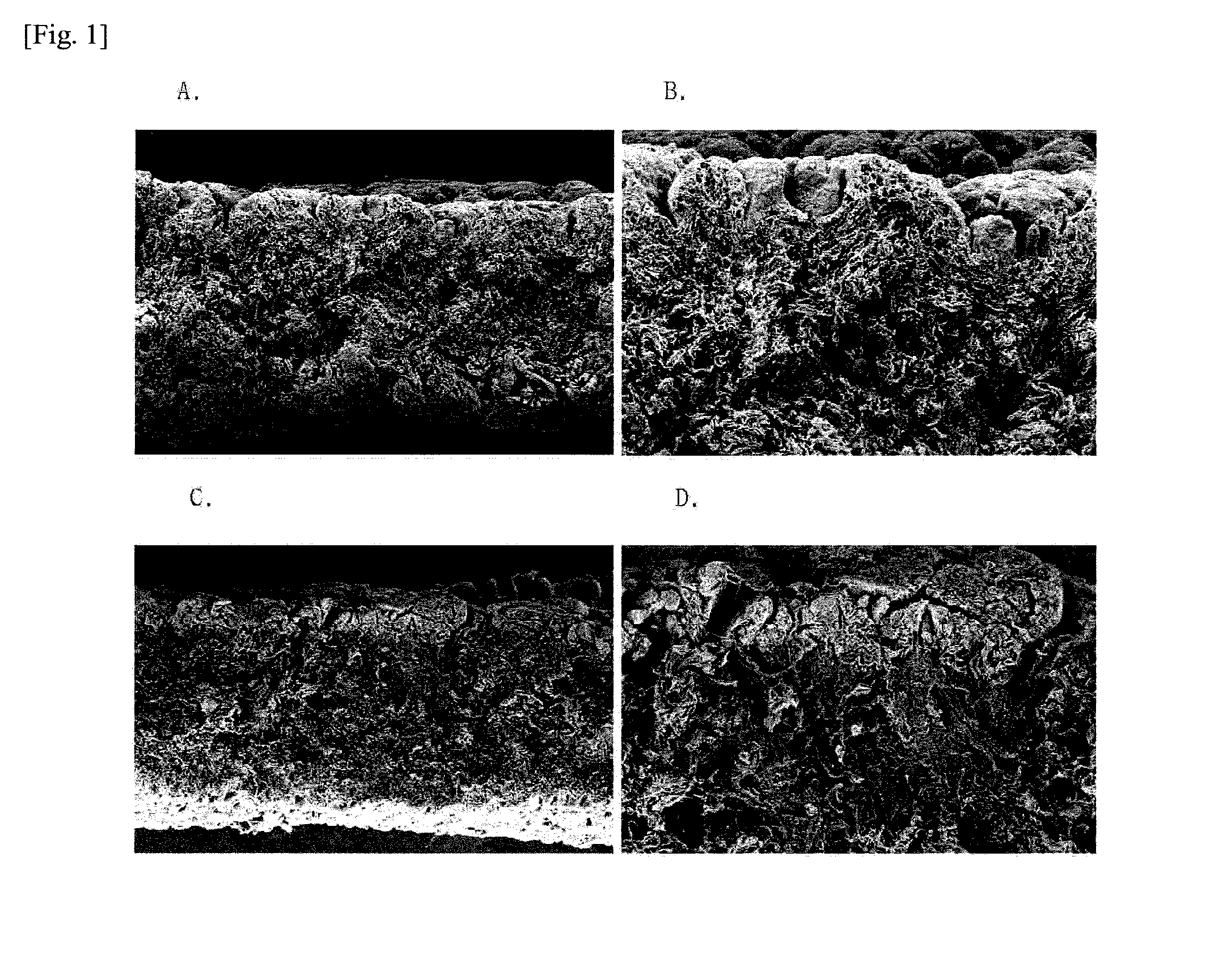
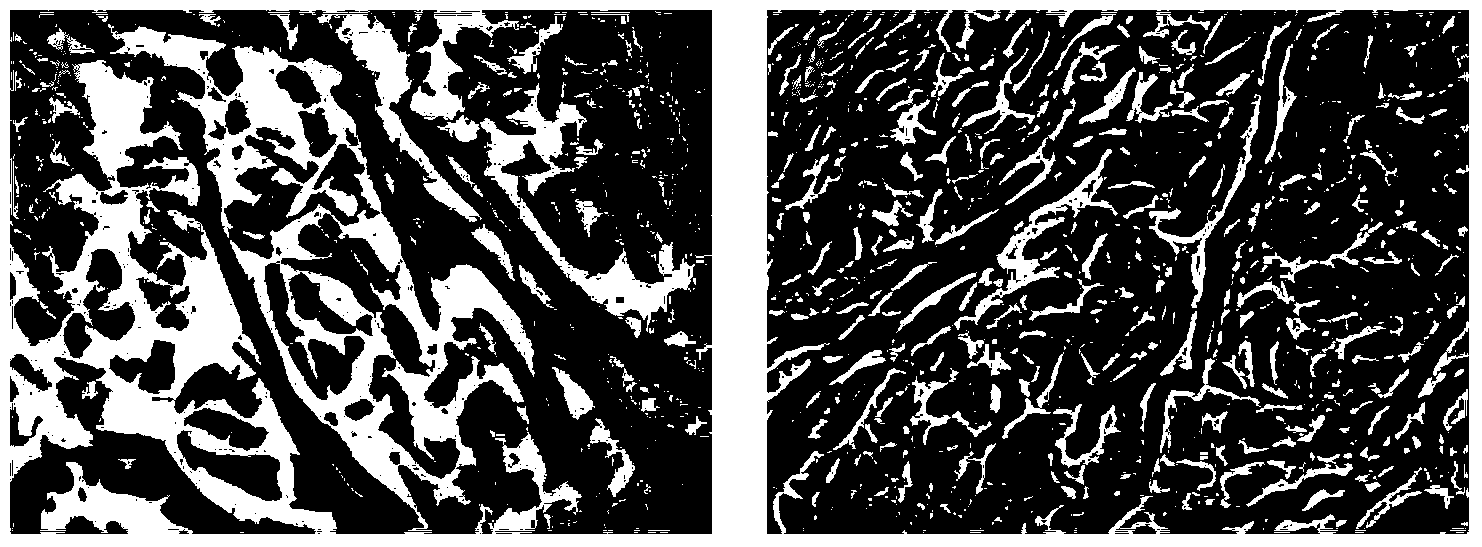
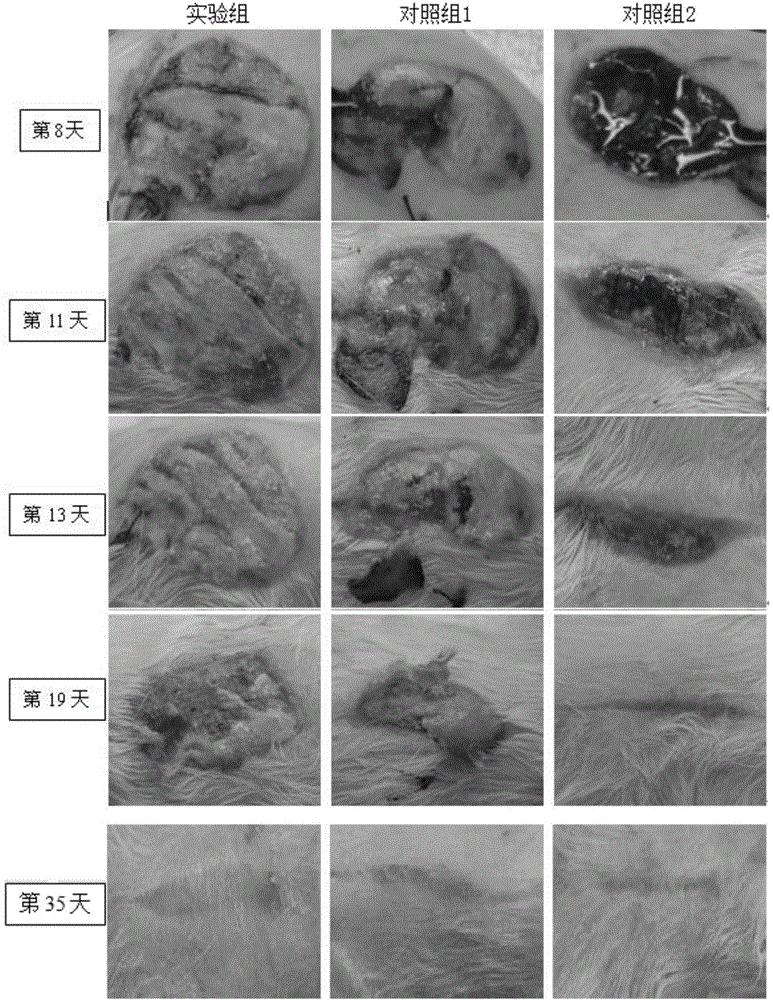
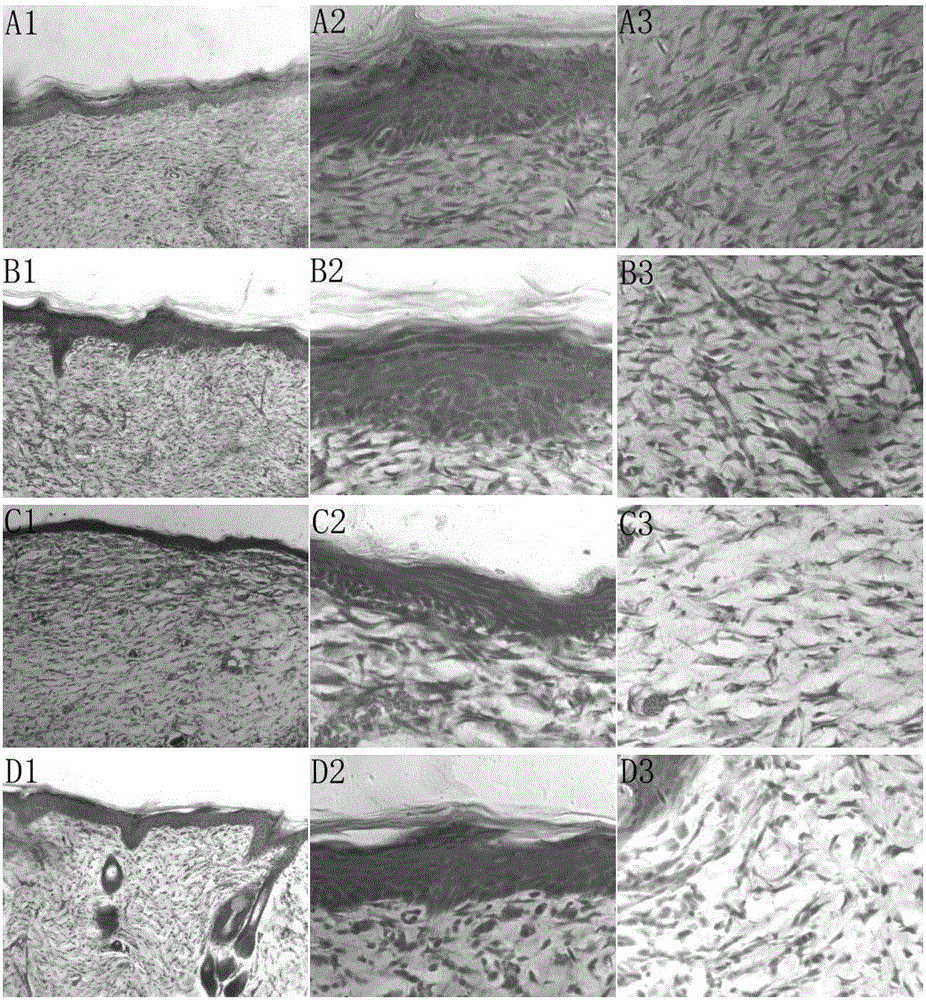
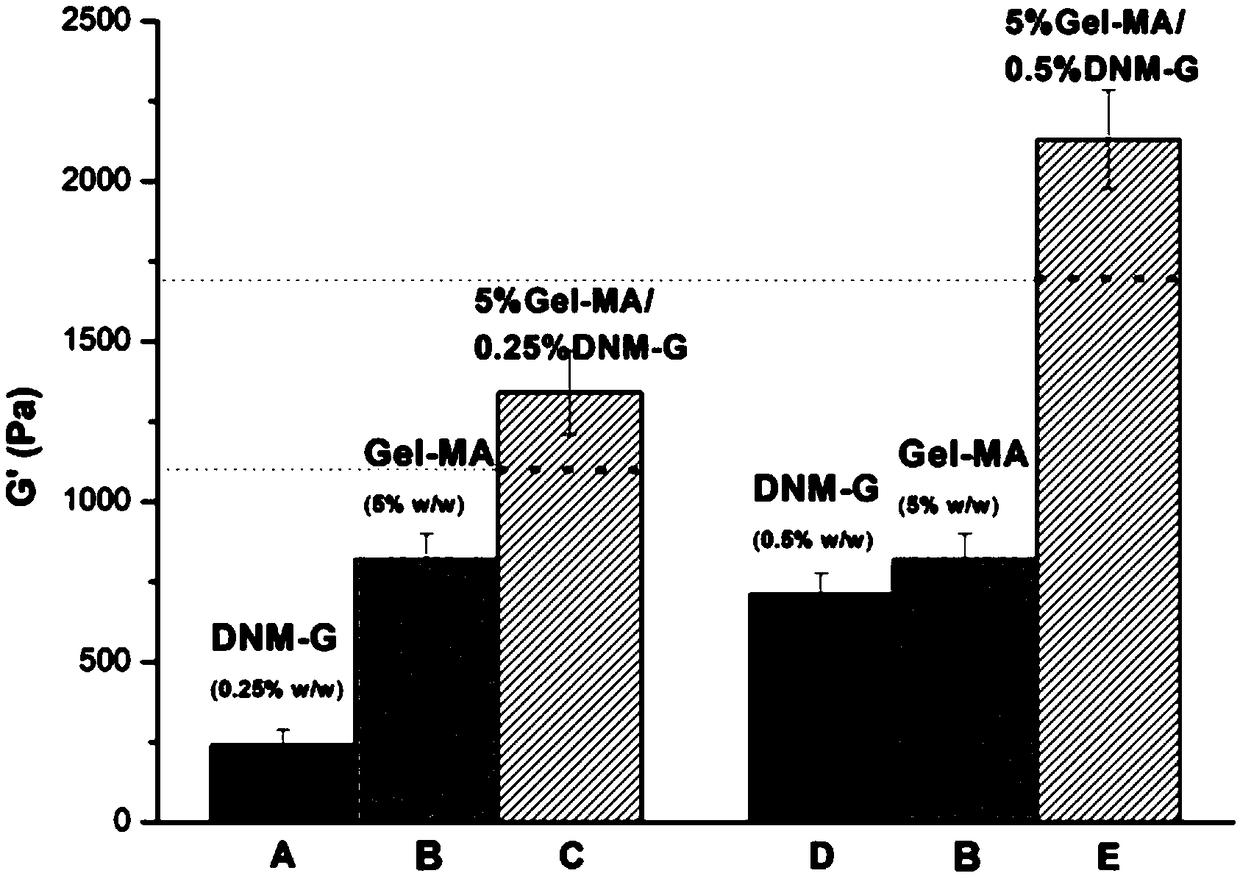
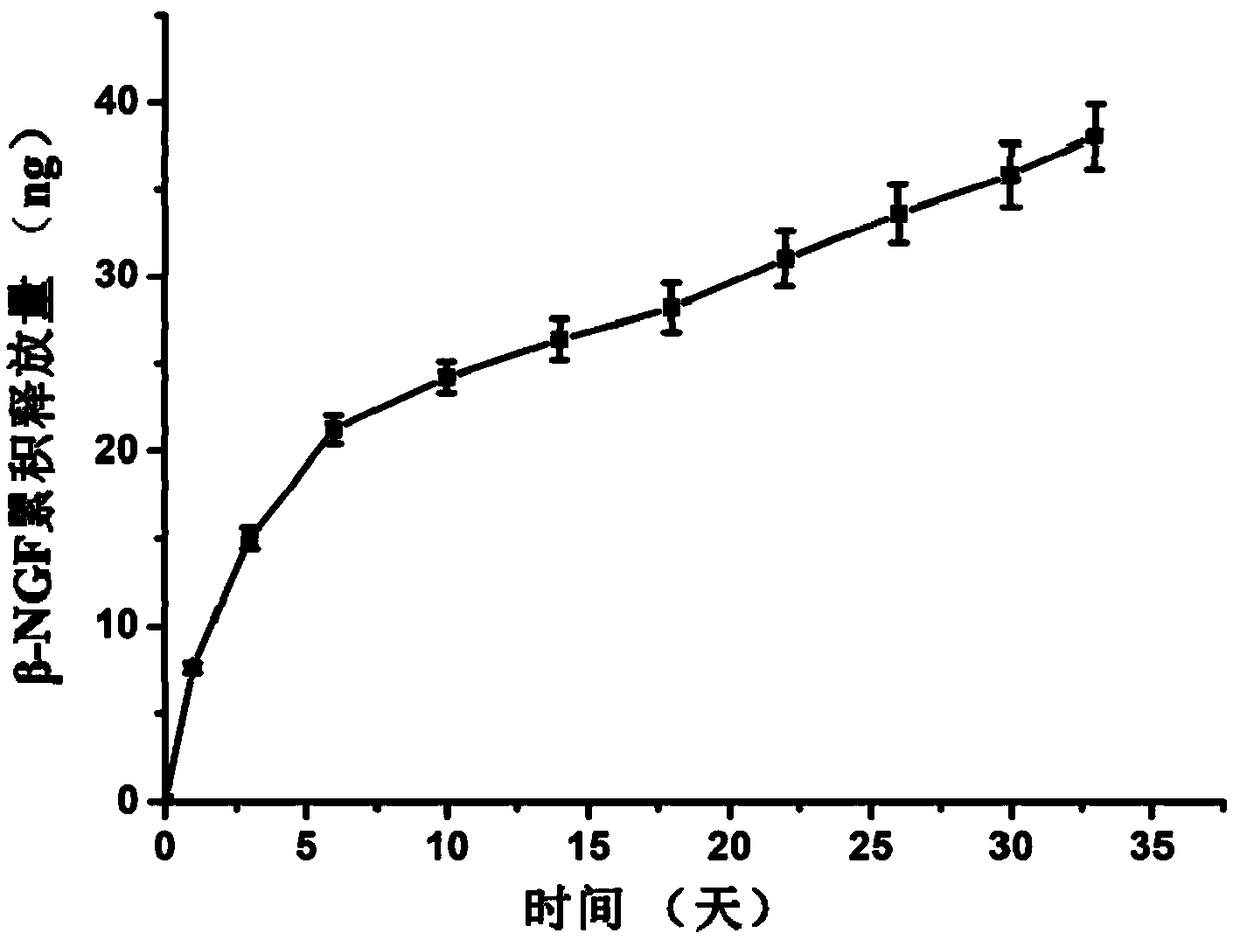
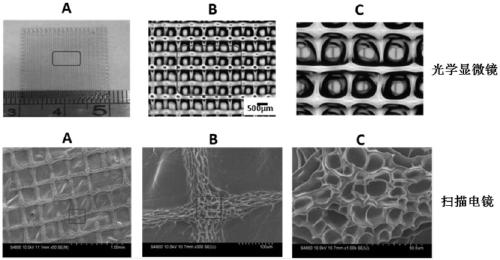
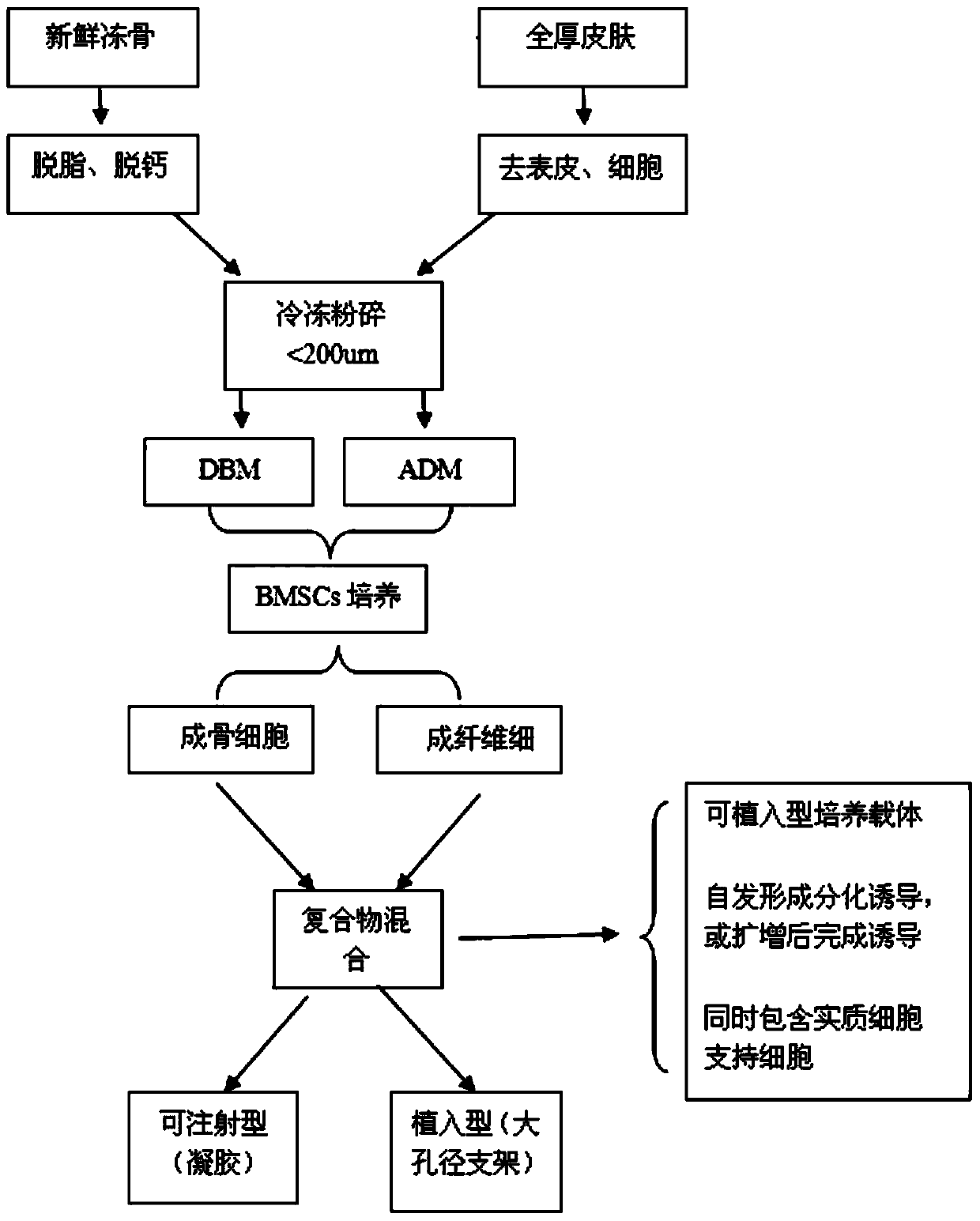
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
138 results about "Acellular Dermis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
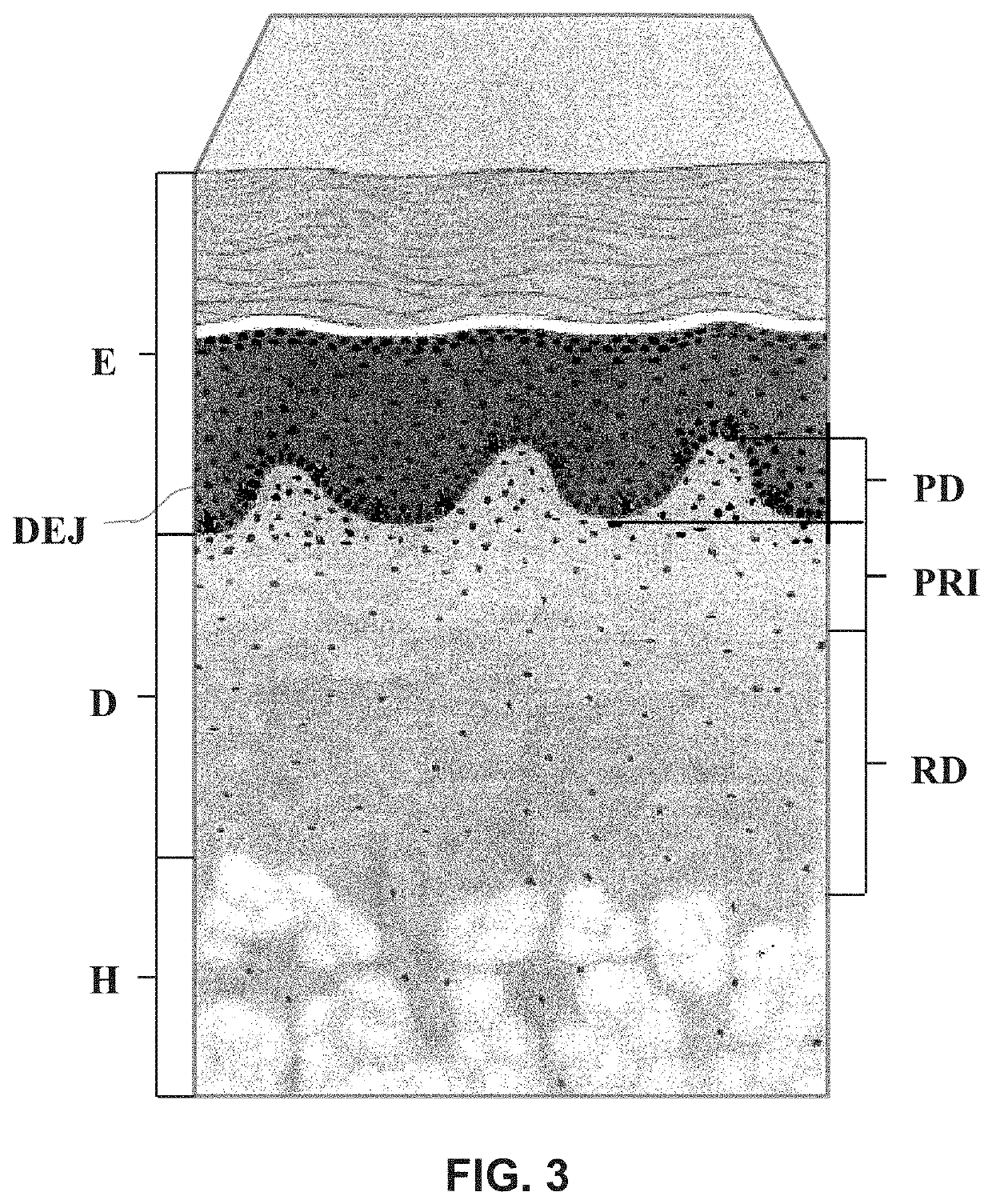
Remaining tissue from normal DERMIS tissue after the cells are removed.
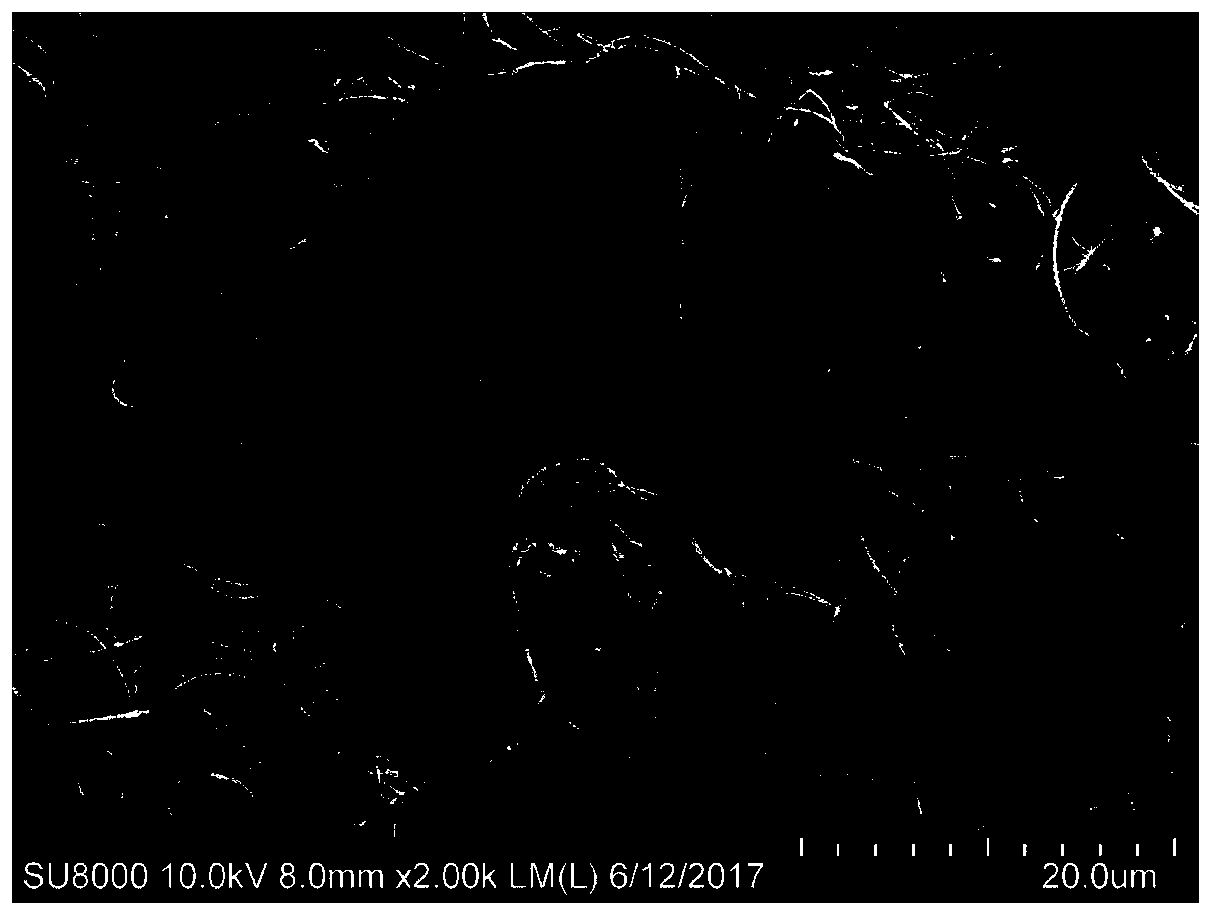
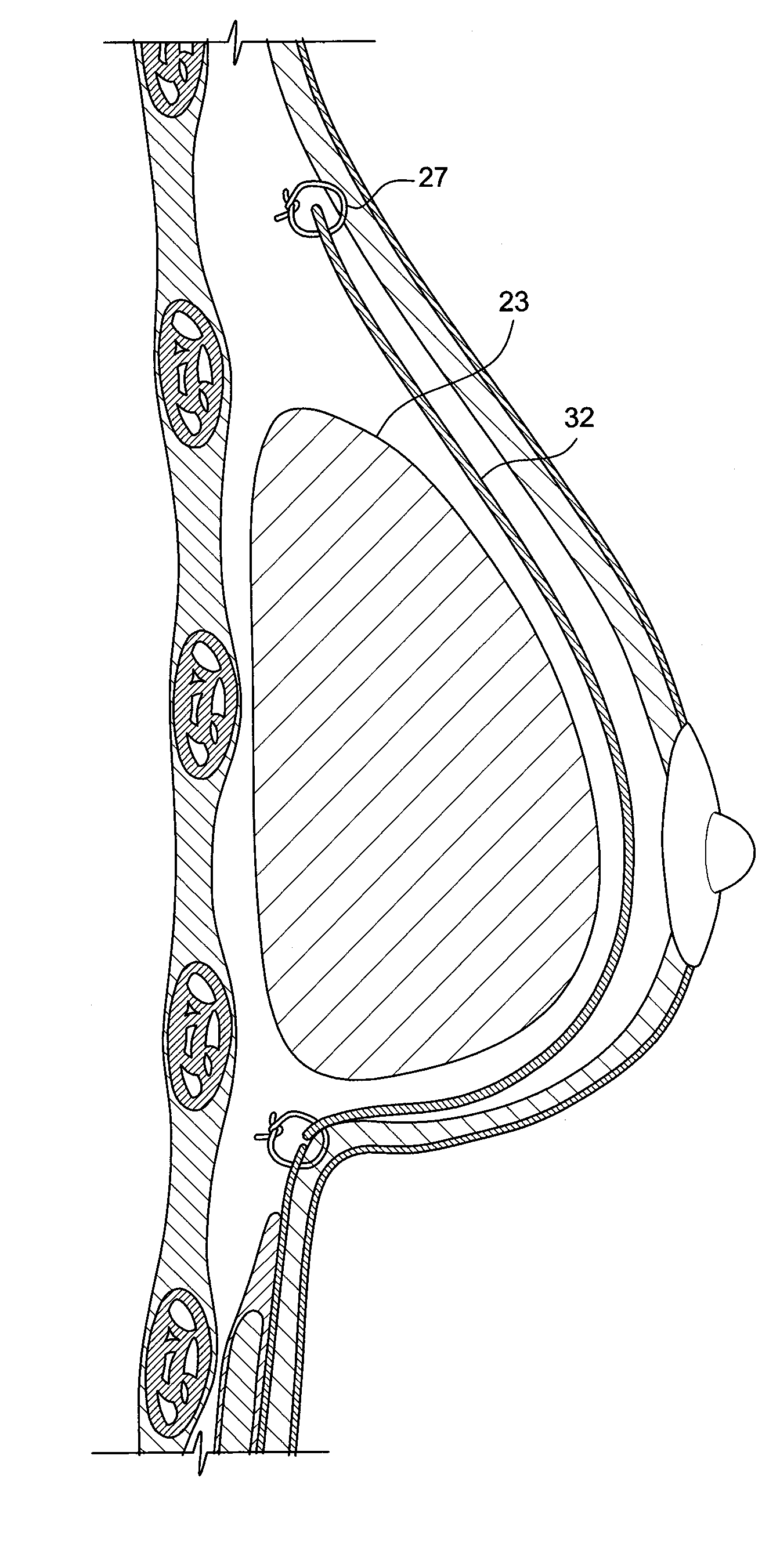
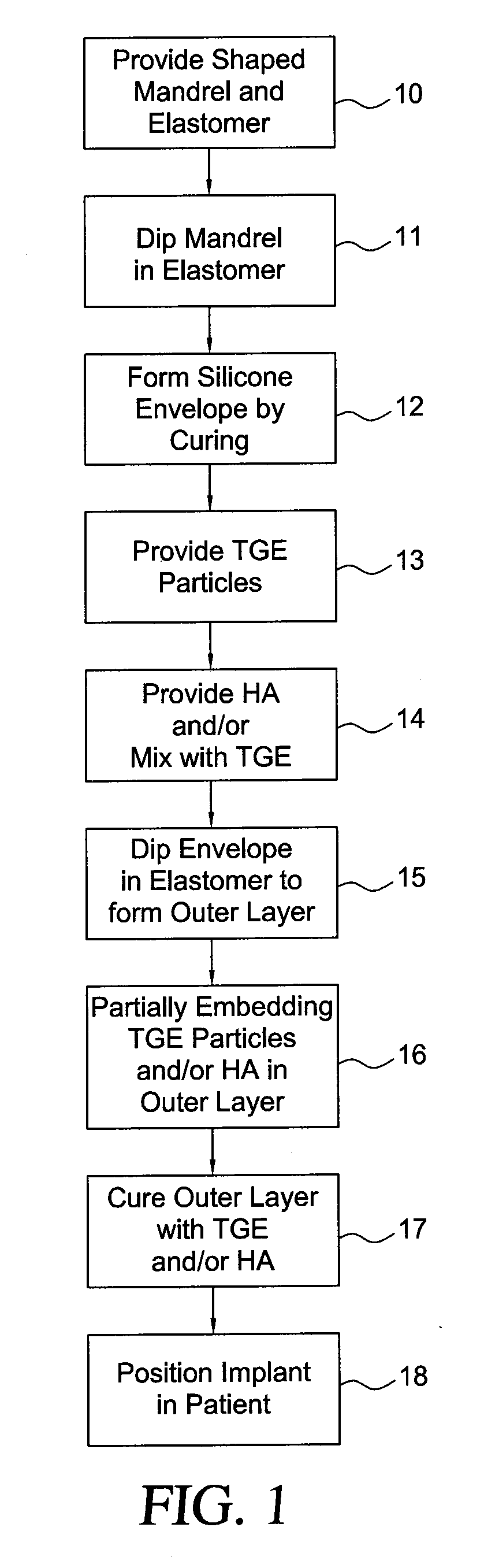
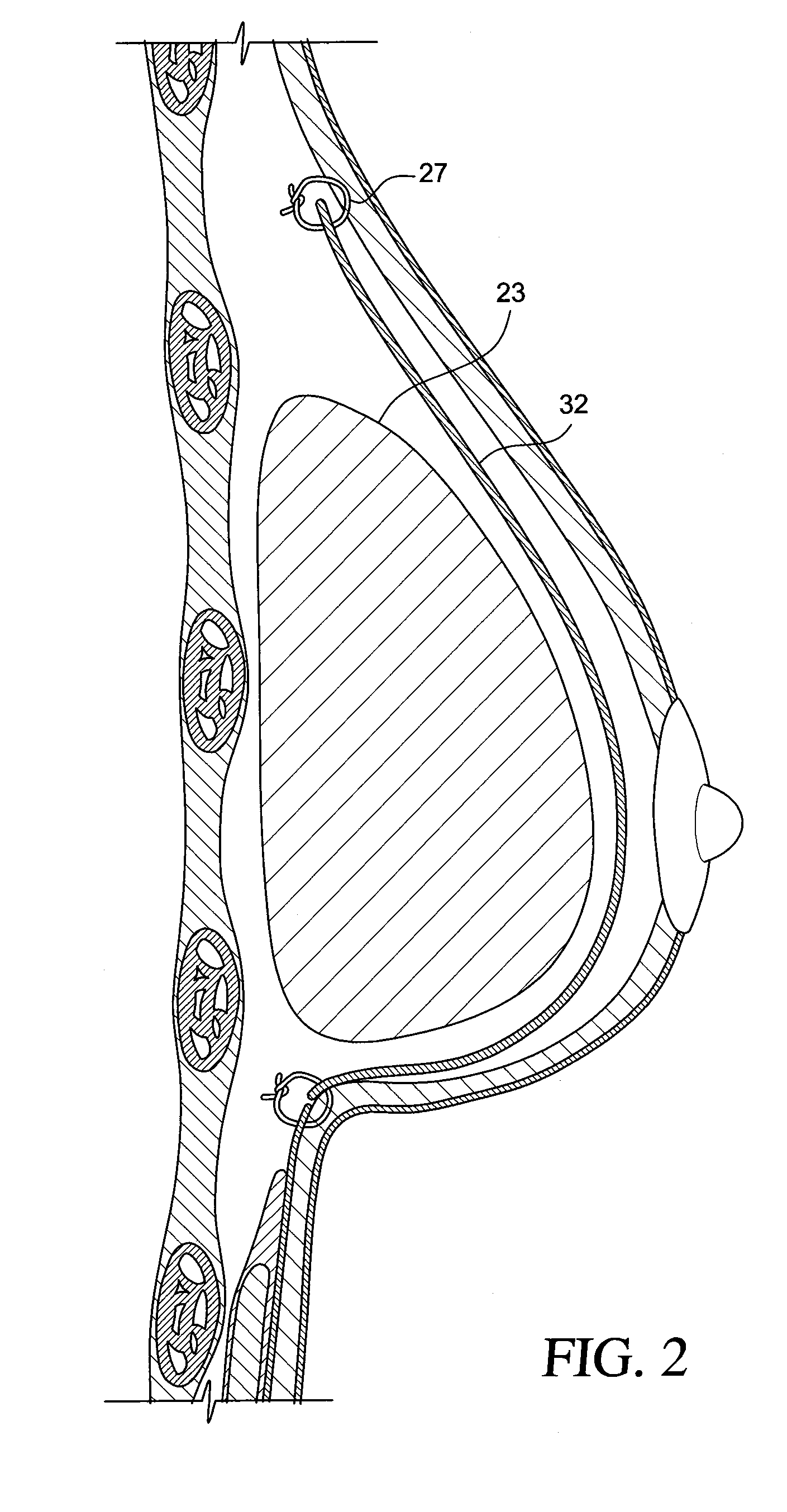
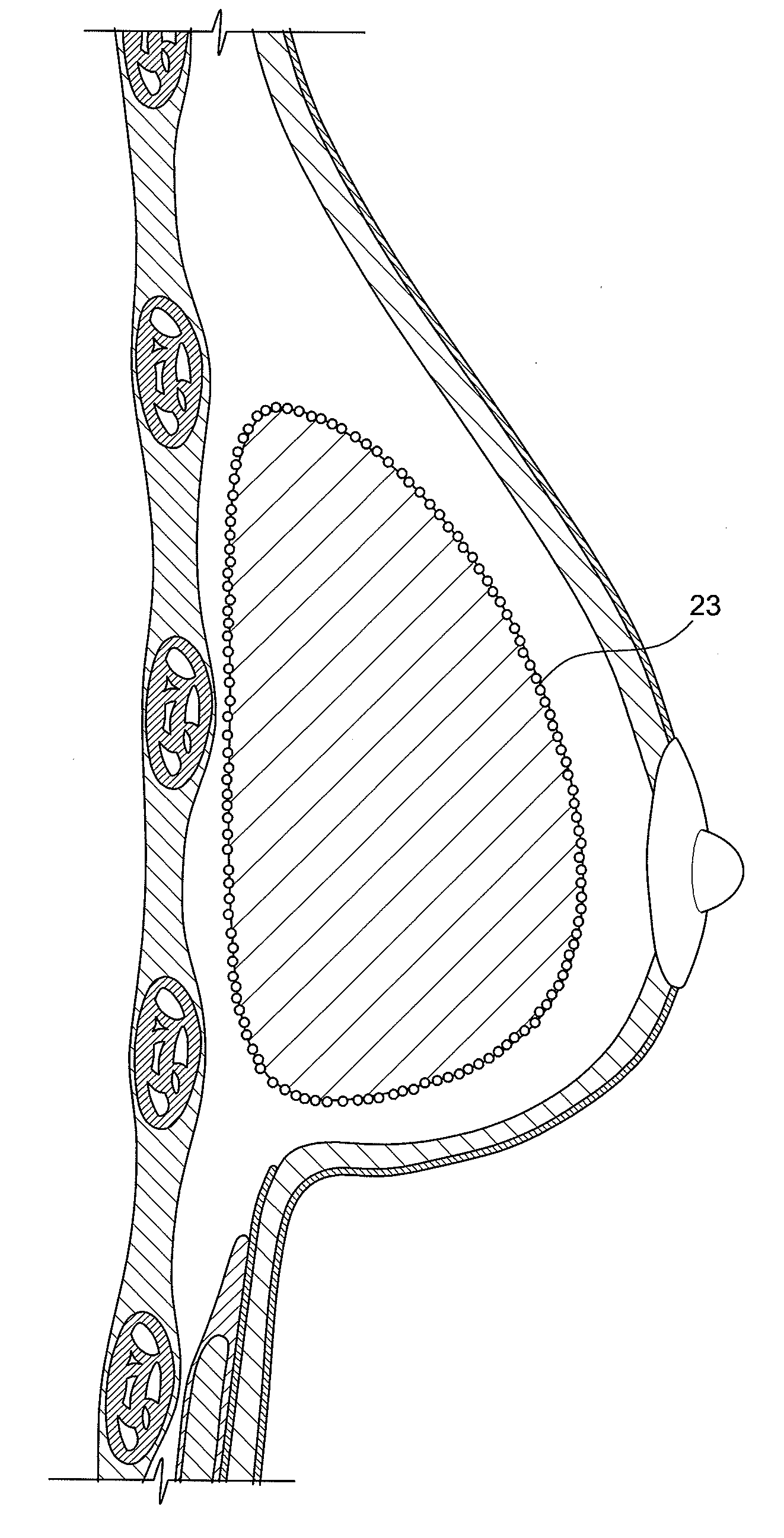
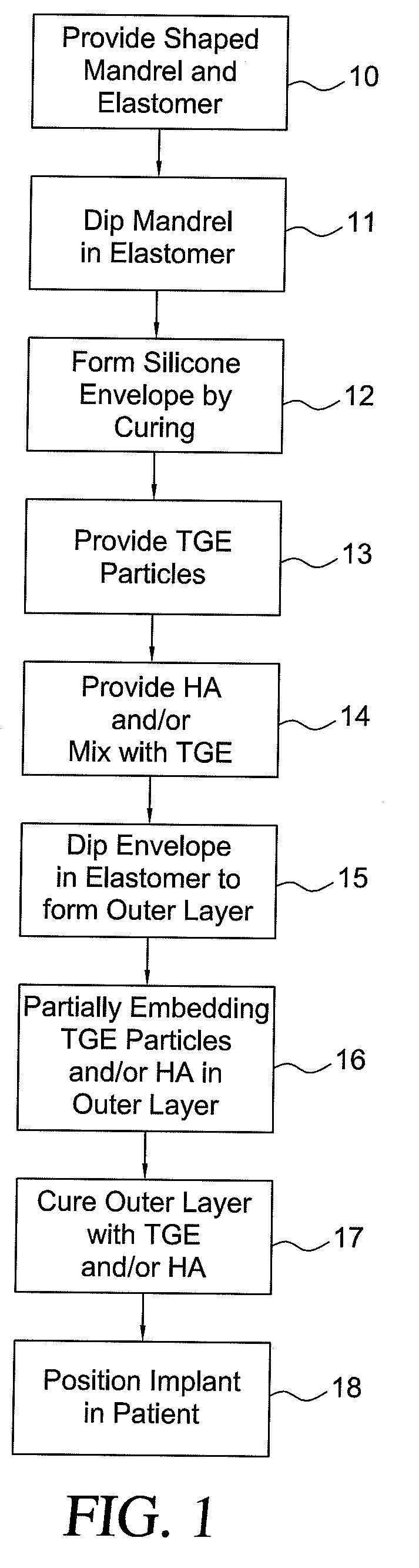
Method for texturing the surface of a synthetic implant
InactiveUS20090198333A1Increase heightReducing capsular contractionMammary implantsDiagnosticsBreast implantAcellular Dermis
A method for texturing the surface of a breast implant includes the step of partially impregnating a silicone outer surface of the implant with particles of a biologically active material such as acellular dermis of human or animal origin impregnated with hyaluronic acid. The biologically active material promotes tissue ingrowth into a plurality of cavities filled with a biologically active material.
Owner:BECKER HILTON
Method for texturing the surface of a synthetic implant
InactiveUS20090198332A1Increase heightReducing capsular contractionMammary implantsCoatingsBreast implantAcellular Dermis
A method for texturing the surface of a breast implant includes the step of partially impregnating a silicone outer surface of the implant with particles of a biologically active material such as acellular dermis of human or animal origin impregnated with hyaluronic acid. The biologically active material promotes tissue ingrowth into a plurality of cavities filled with a biologically active material.
Owner:BECKER HILTON
Acellular dermal matrix and method of use thereof for grafting
InactiveUS8067149B2Reduce harmSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsMedicineAcellular Dermis
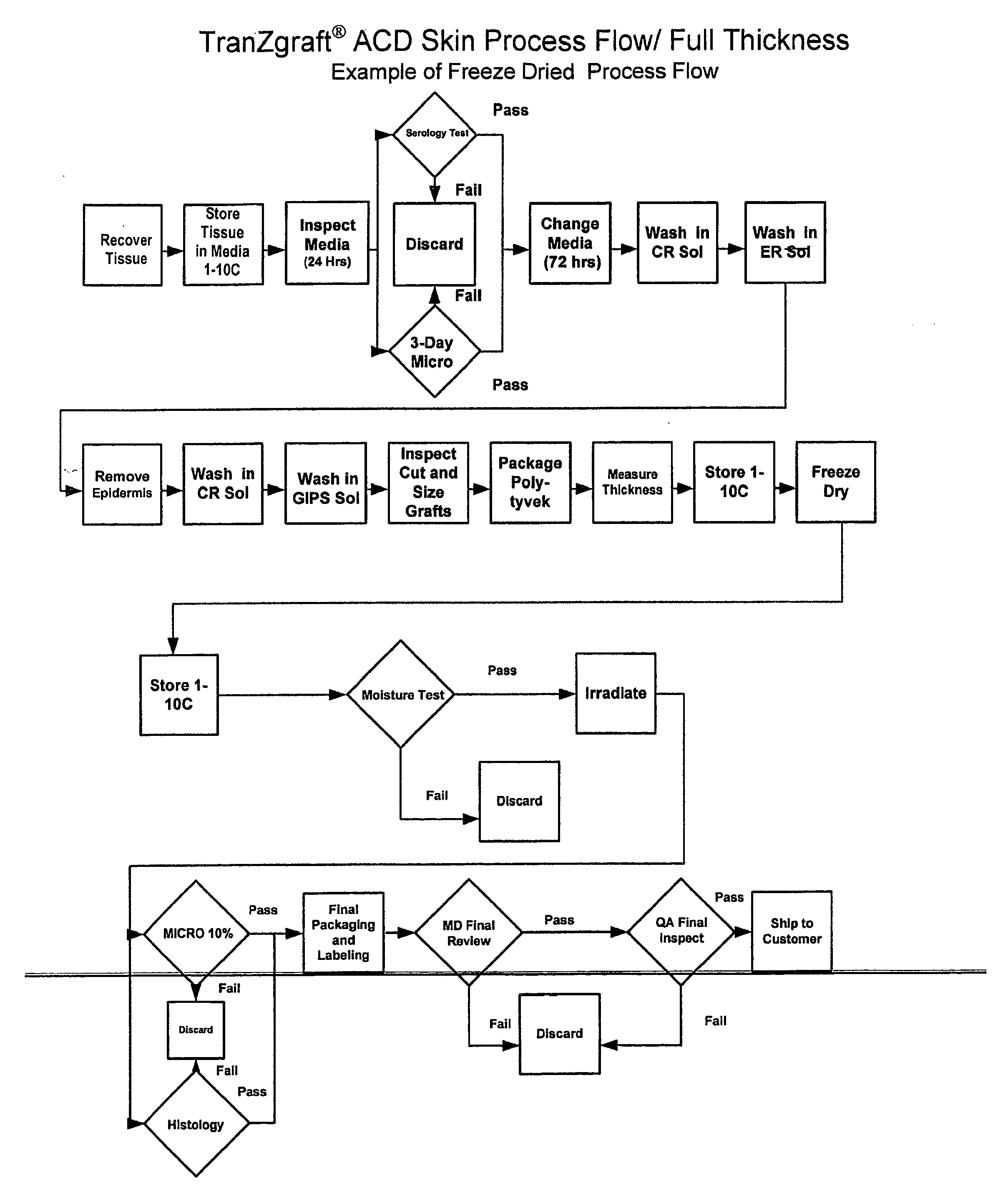
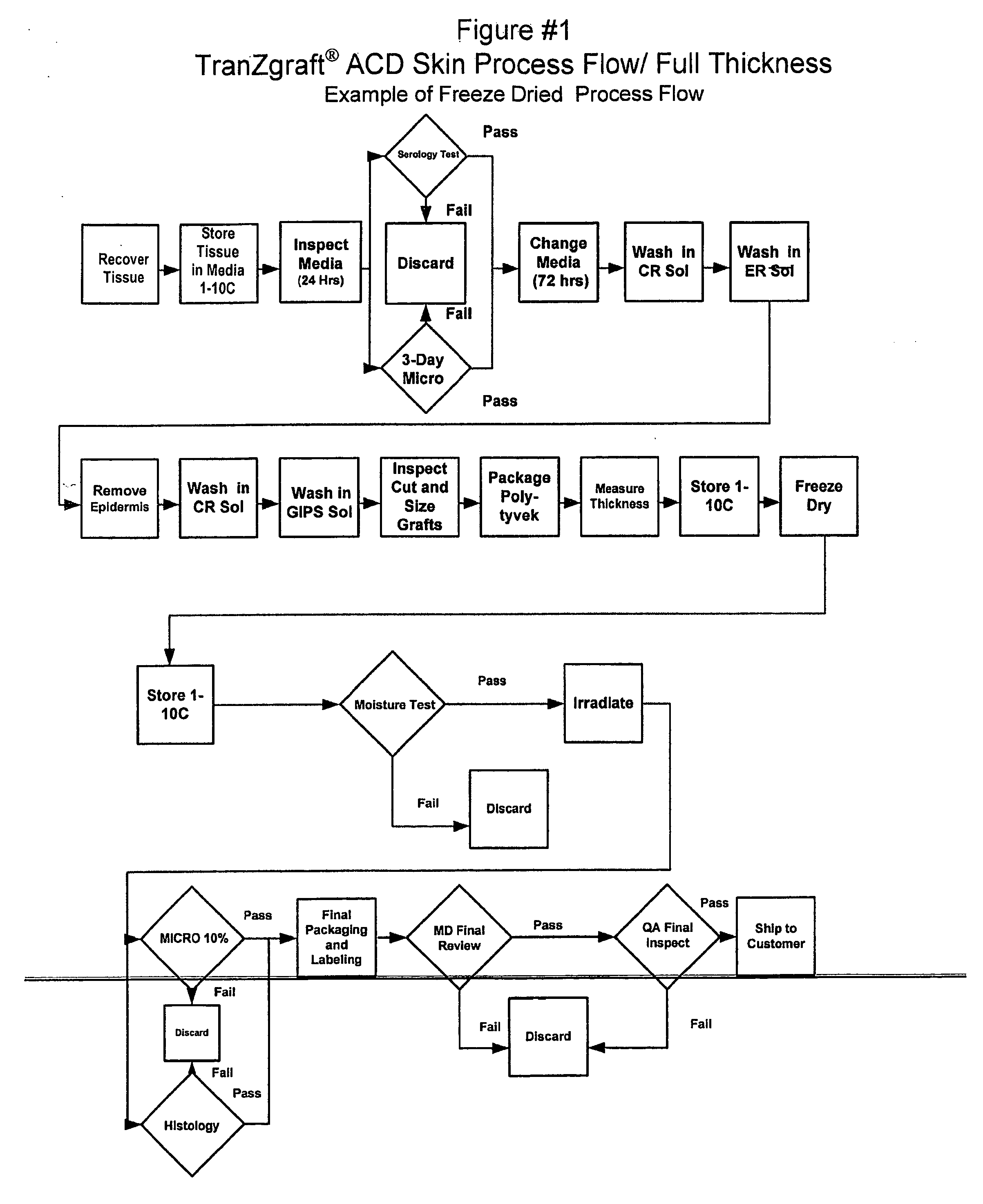
A method for processing and preserving an acellular collagen-based tissue matrix for transplantation is disclosed. The method includes the steps of processing biological tissues with a stabilizing solution to reduce procurement damage, treatment with a processing solution to remove cells, treatment with a cryoprotectant solution followed by freezing, drying, storage and rehydration under conditions that preclude functionally significant damage and reconstitution with viable cells.
Owner:LIFECELL
Acellular Dermal Allografts And Method Of Preparation
ActiveUS20130013068A1Reduce contentReduce bioburdenSkin implantsDead animal preservationProduction lineAcellular Dermis
A method for preparing a sterilized human acellular dermal allograft where the dermal allograft is sterilized by irradiation and has a greatly reduced bio-burden and enzymatic and antigenic activity. This product line of allografts can be easily used by surgeons in soft tissue replacement or repair and has an extended shelf life, of up to at least about three years.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST AS AGENT
Preparation method of acellular dermal matrix dressing
ActiveCN102580141AAchieve the inactivation effectInhibit swellingAbsorbent padsBandagesCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
The invention discloses a preparation method of an acellular dermal matrix dressing. The acellular dermal matrix is prepared from animal skin by segmented graft preparing, viruses inactivating, degreasing, decellularizing, iodizing, lyophilizing, packaging and radiation disinfecting. The method has the advantages of short degreasing time, high efficiency, complete decellurarization, light damage to natural structure of extracellular matrix of hypodermal cell, and antibacterial function.
Owner:江苏优创生物医学科技有限公司
Method For Producing An Acellular Dermal Matrix, And Acellular Dermal Matrix Produced By Same
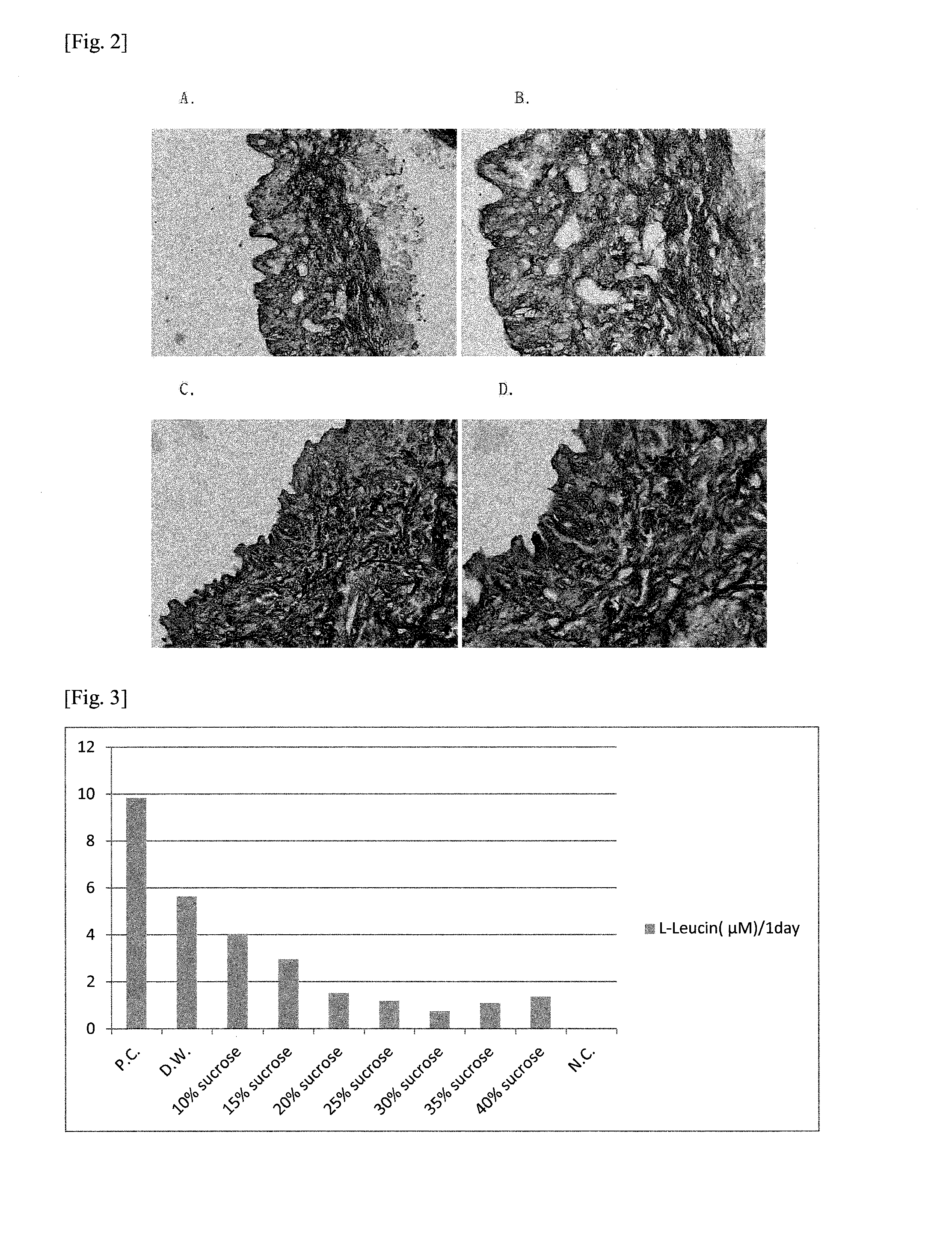
ActiveUS20120329034A1Improve stabilityMinimize changesVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsSucroseCuticle
The present invention relates to a method for producing an acellular dermal matrix, and to an acellular dermal matrix produced by same, and more particularly, to a method for producing an acellular dermal matrix, in which sucrose is added to base ingredients consisting of glycerol, propylene glycol, and a base solvent or solution so as to produce a cryoprotectant, the solution is injected into the skin below the epidermis and dermis from which cells have been removed, and freeze-drying is then performed.
Owner:CG BIO CO LTD
Compound tissue engineering scaffold containing PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) strengthening net, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a scaffold material for tissue engineering construction and a preparation method thereof, and particularly relates to a compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) strengthening net, and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA strengthening net comprises a porous scaffold having good biocompatibility and a PLGA strengthening net, wherein the PLGA strengthening net is formed by weaving PLGA fibers, and the PLGA strengthening net is tightly combined with the porous scaffold. The compound tissue engineering scaffold containing a PLGA strengthening net has mechanical property similar to that of the acellular dermal matrix, and is more beneficial to the maintenance of three-dimensional porous structures of the scaffold, thereby being more beneficial to the ingrowth of cells, blood vessels and tissues; and because of the good biocompatibility of collagen, chitosan and other naturally-derived macromolecules, the biological performance of the compound scaffold is maintained, thereby being beneficial to the adhesion, propagation and secretion of cells. Thus, the compound tissue engineering scaffold is a good renewable material applicable to the construction of tissues and organs of tissue engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Acellular dermal matrix and preparing method of acellular dermal matrix
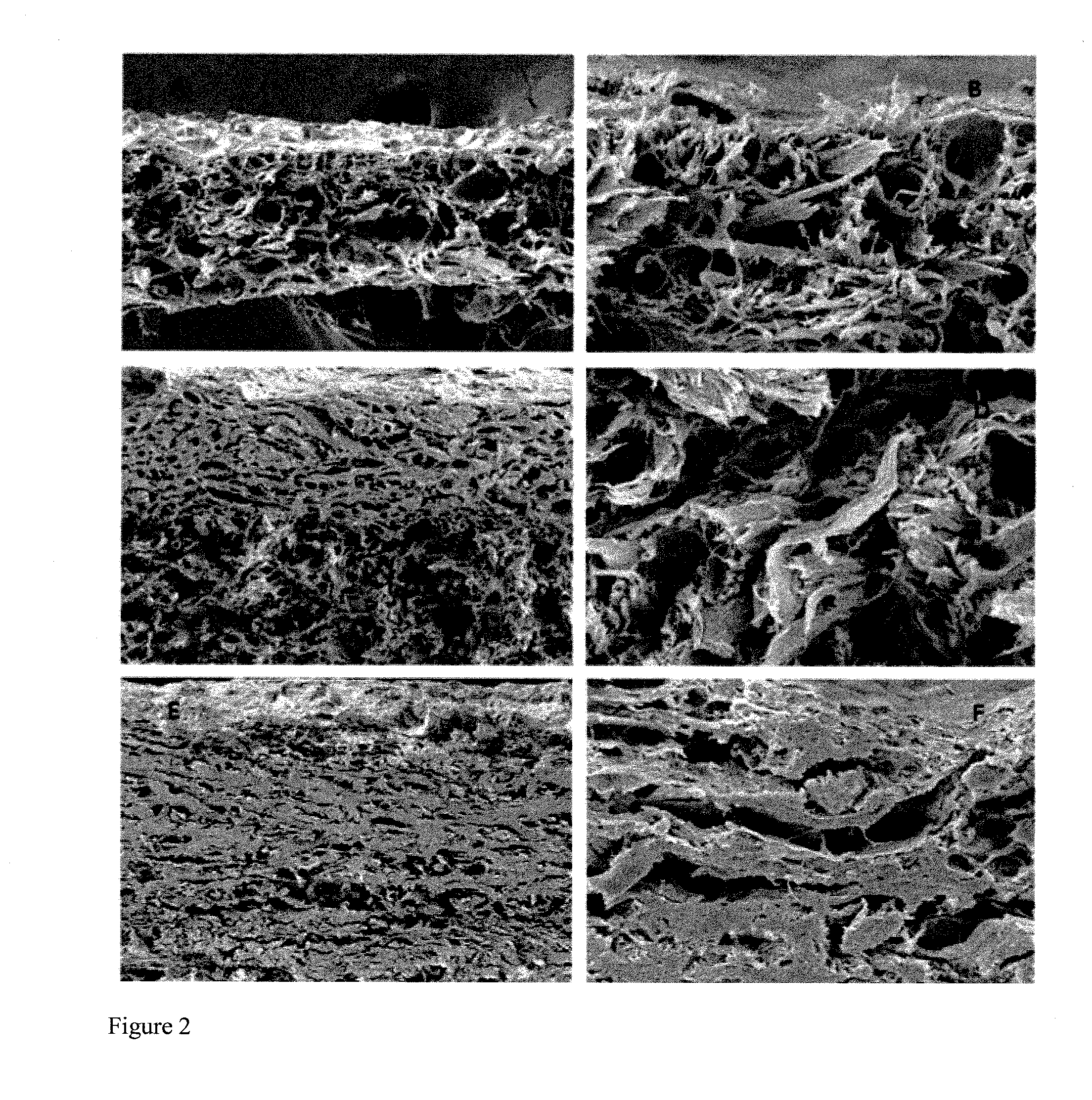
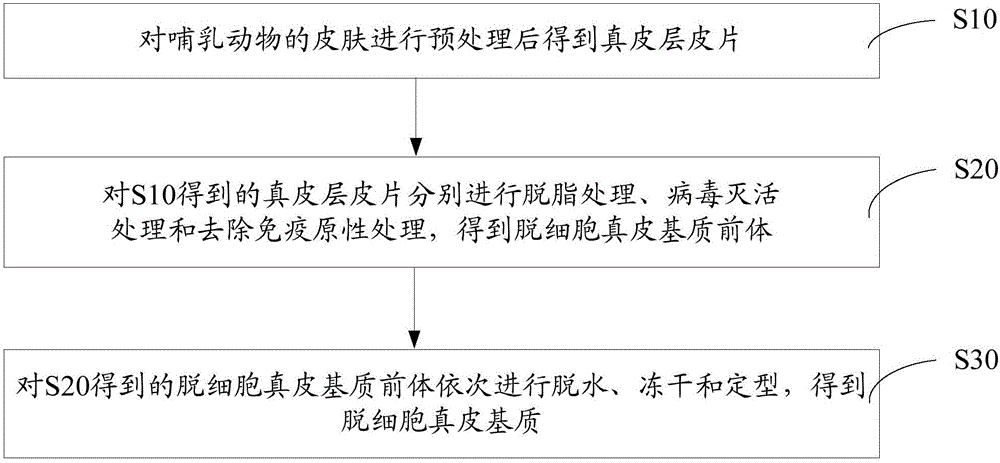
The invention discloses an acellular dermal matrix and a preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix. The preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix comprises the following steps of: performing pre-processing on the skin of a mammal to obtain a skin corium flap; respectively performing degreasing processing, virus inactivation processing and immunogenicity removal processing on the skin corium flap to obtain an acellular dermal matrix precursor (the immunogenicity removal processing operation comprises the step of alternately soaking the skin corium flap into a prolease solution and a surfactant solution); and sequentially performing dewatering, freeze-drying and shaping on the acellular dermal matrix precursor to obtain the acellular dermal matrix. The preparing method of the acellular dermal matrix has the advantages that the skin corium flap is alternately soaked in the prolease solution and the surfactant solution, so that the immunogenicity of the acellular dermal matrix can be reduced to the maximum degree; the normal collagen structure of the acellular dermal matrix is also remained; the prepared acellular dermal matrix has the proper degradation speed, good biocompatibility and good bone induction capability.
Owner:SHENZHEN LANDO BIOMATERIALS
Vascularized human skin equivalent
InactiveUS20070207125A1Accelerated rate of vascularizationImprove clinical utilityBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsSkin equivalentIn vivo
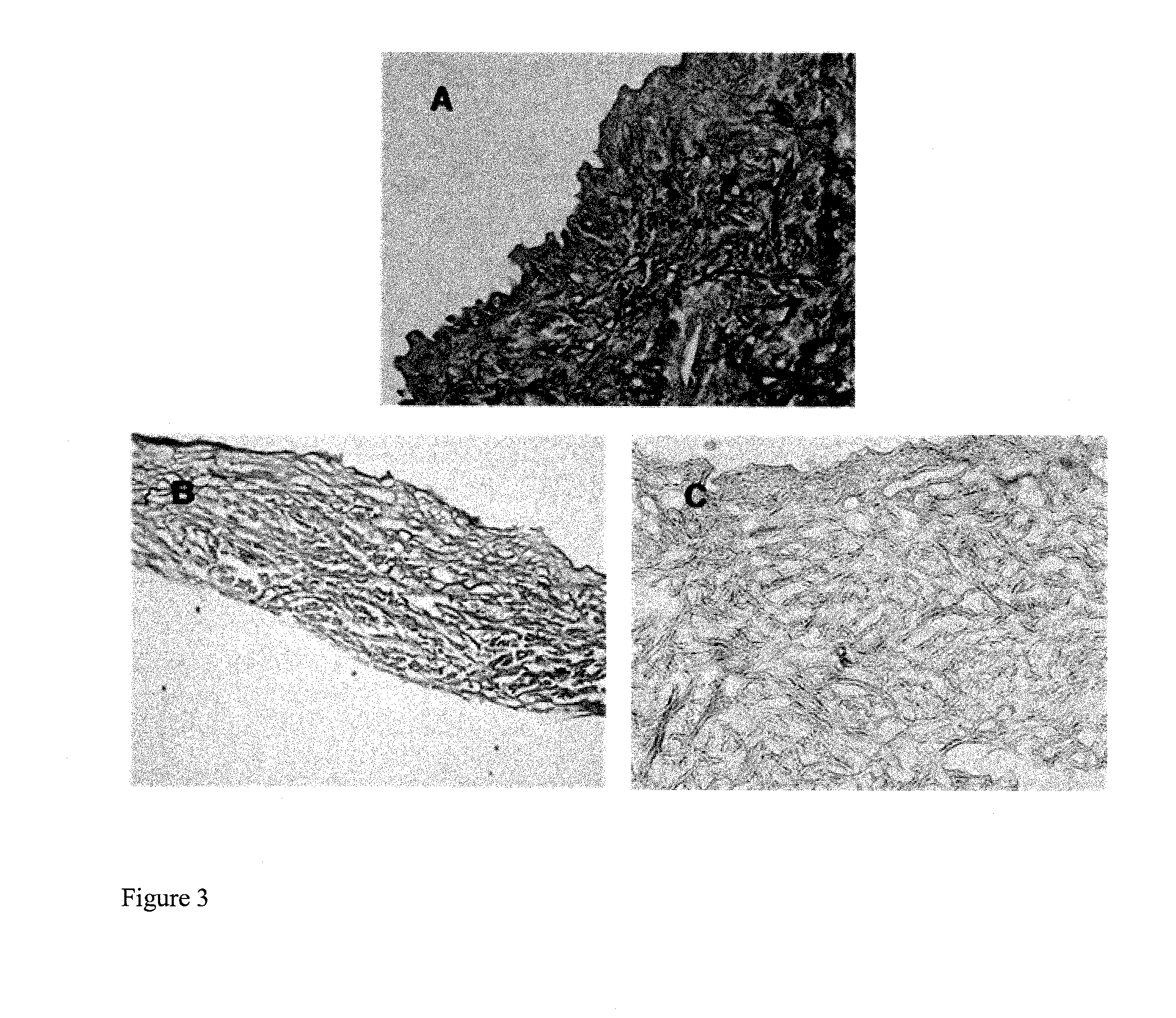
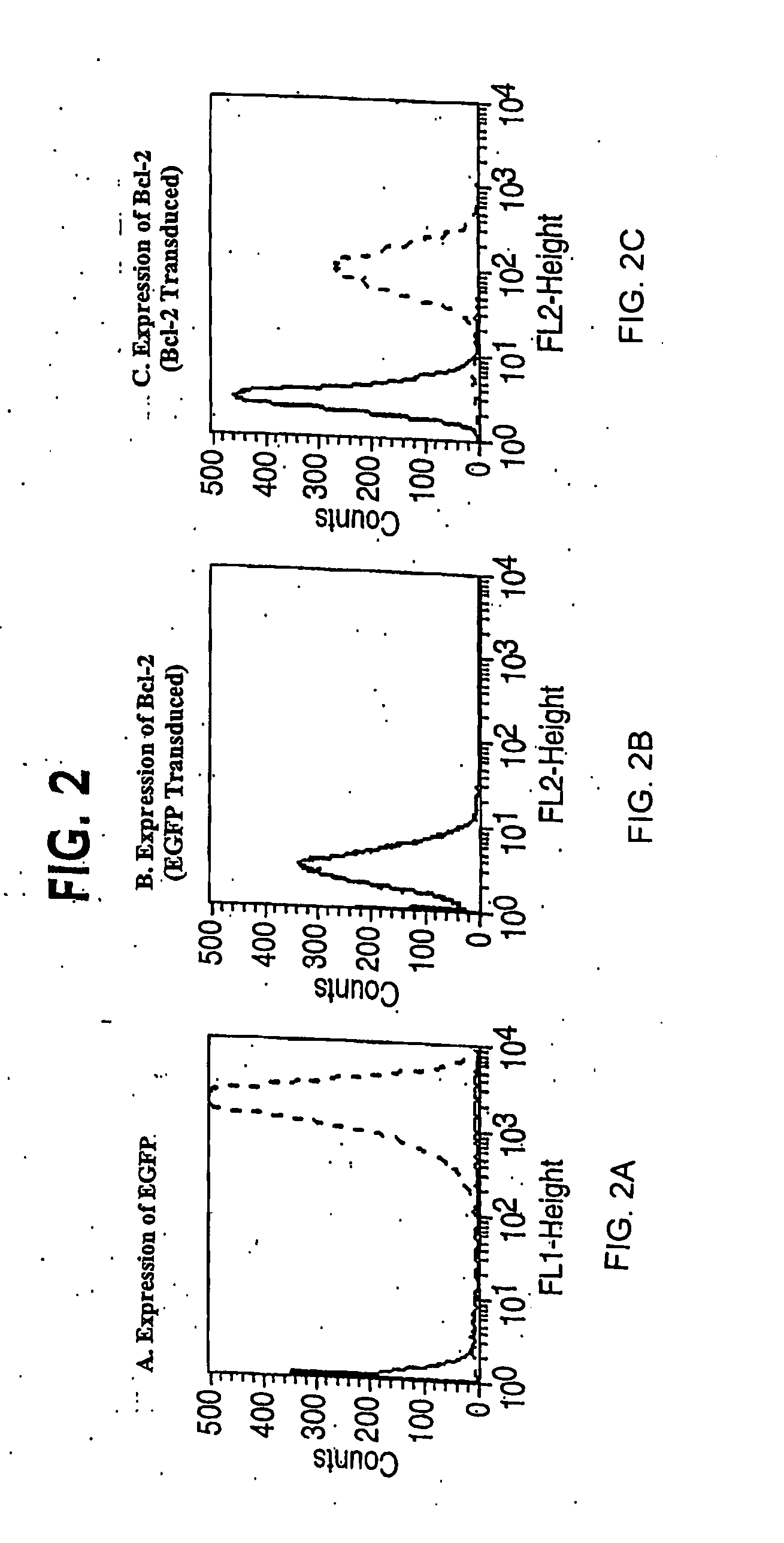
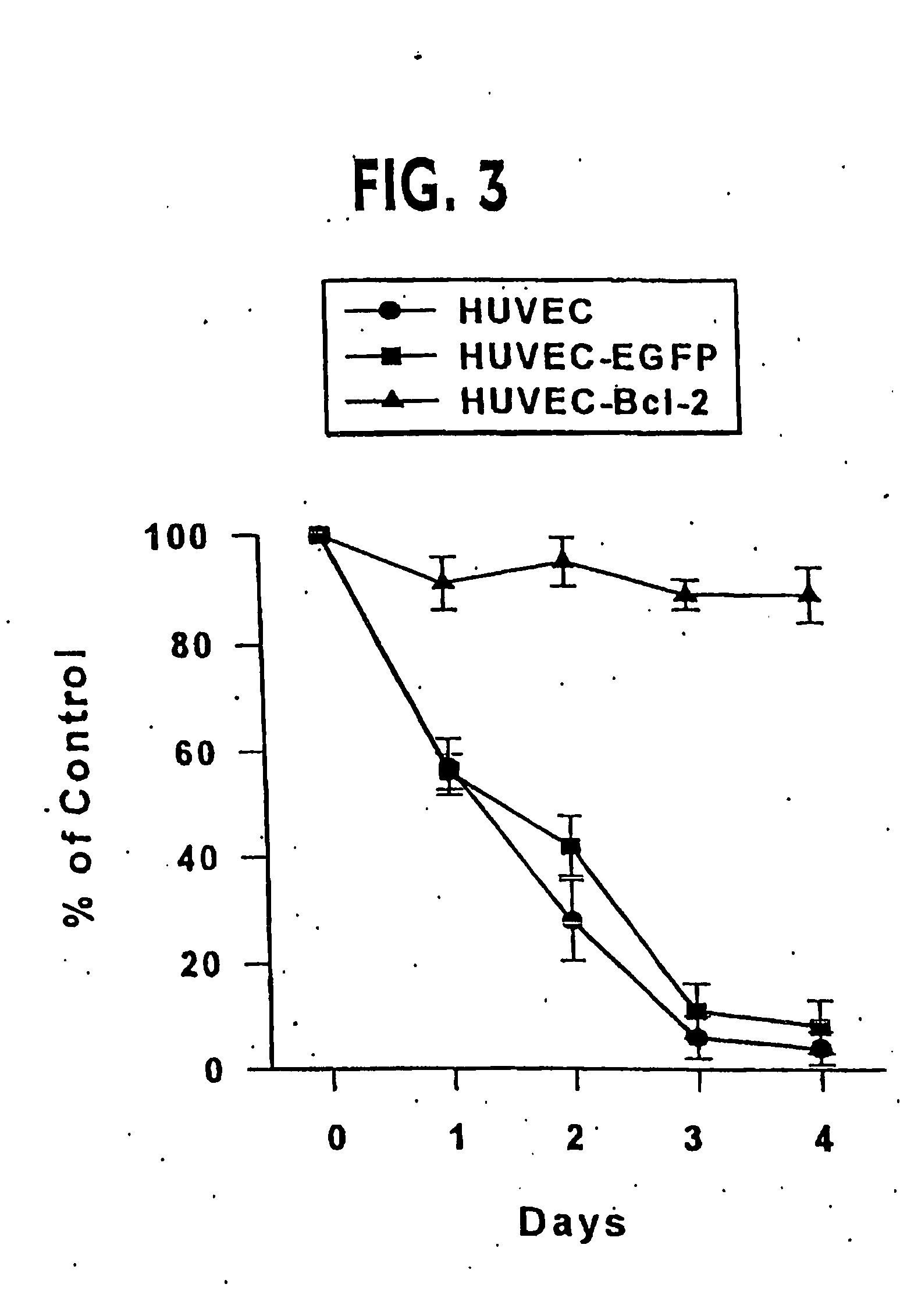
Clinical performance of currently available human skin equivalents is limited by failure to develop perfusion. To address this problem we have developed a method of endothelial cell transplantation that promotes vascularization of human skin equivalents in vivo. Living skin equivalents were constructed by sequentially seeding the apical and basal surfaces of acellular dermis with cultured human keratinocytes and Bcl-2 transduced HUVEC or umbilical cord cells sequentially. After orthotopic implantation of grafts comprising cultured human keratinocytes and Bcl-2 transduced HUVEC cells onto mice, the grafts displayed both a differentiated human epidermis and perfusion through the HUVEC-lined microvessels. These vessels, which showed evidence of progressive maturation, accelerated the rate of graft vascularization. Successful transplantation of such vascularized human skin equivalents should enhance clinical utility, especially in recipients with impaired angiogenesis.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Tissue engineered skin with basilar membrane and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101954124ASimple methodEasy to get materialsArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsEpidermis structureManufacturing technology
The invention relates to the technical fields of tissue engineering and medical wound repair. At present, a living skin substitute constructed by using the materials of polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid, collagen, hyaluronic acid, and the like as a dermic bracket has the defects that on one hand, host materials are difficult to extract, the living skin substitute has complicated manufacturing technology and is expensive in cost and difficult to widely popularize and apply clinically; and on the other hand, the living skin substitute does not have a skin basilar membrane structure so that healed skin does not resist pressure and wear, and the living skin has unfirm adhesion to the epidermis and is easy to shed and break or form water blisters so that the structural and morphological development of the normal epidermis is influenced; and allogeneic acellular dermis is taken from cadaver skin and is limited in sources and expensive in cost, and thus clinical application is limited. The invention aims at providing a skin substitute which uses surface-finished and modified amnion as the basilar membrane and blood plasma as stroma, which has the advantages of wide material sources, low cost and simple preparation method. An animal experiment proves that the complete basilar membrane and hemidesmosomes can be retained in in-vivo transplantation, and the formation of an epidermal structural form is accelerated and promoted.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Method for preparing acellular dermal matrix by utilizing ultrasonic wave
The invention discloses a method for preparing an acellular dermal matrix by utilizing ultrasonic wave. The method comprises the following steps of: removing hair from peeled mammal skin; disinfecting the skin with disinfectant, and preparing reticular-layer derma by adopting a mechanical method under the sterile condition; oscillating the derma in hyposmotic solution for 0.5-12 hours, and then oscillating the derma in hyperosmotic solution for 0.5-12 hours; repeating the steps 1-6 times; placing the derma into washing agent and processing with an ultrasonic cleaner for 12-48 hours; and washing with sterile phosphate buffer solution 1-6 times, and disinfecting with ethylene oxide to obtain the acellular dermal matrix. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the preparation process is simple and practical, cells can be thoroughly removed, and the production period is short; and the method is environmentally-friendly, has low cost and is applicable to large-scale operation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108525021ASimple structureIncrease elasticityAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationMicrosphereVascular endothelium
The invention relates to tissue-engineered skin containing blood vessels and hair follicle structures based on 3D printing and a preparation method thereof. The tissue-engineered skin is composed of an epidermal layer, an acellular dermal scaffold and a dermis layer, wherein in the epidermal layer, epidermal stem cells are used seed cells, the seed cells are printed on the upper surface of the acellular dermal scaffold through a 3D printer after being compounded with a hydrogel carrier to differentiate and form a normal epidermal structure, in the dermis layer, mesenchymal stem cells, vascularendothelial cells, dermal papilla cells and adipose-derived stem cells are used as seed cells, the seed cells and a hydrogel carrier are compounded, through the 3D printer, gelatin slow-release micropheres compounded with cytokines are printed on the lower surface of the acellular dermal scaffold, and meanwhile, the hydrogel compound of the seed cells is printed in the gelatin slow-release micropheres to form a dermis structure with a three-dimensional spatial structure.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of antibacterial acellular dermal matrix dressing material
InactiveCN106310352ALow antigenicityGood for decellularizationAbsorbent padsBandagesDermisAcellular Dermis
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological materials of tissue engineering, and particularly relates to a preparation method of an antibacterial acellular dermal matrix dressing material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting a healthy mammal, stripping the skin of the mammal, removing hair, preparing split-thickness skin, performing laser drilling, performing low temperature freeze thawing, performing ultrasonic oscillation, performing degreasing treatment, performing acellular treatment, soaking water-soluble chitosan, performing freeze drying, packaging and performing irradiation sterilization, thus obtaining the antibacterial acellular dermal matrix dressing material. The antibacterial acellular dermal matrix dressing material disclosed by the invention has a collagen three-dimensional entire structure, is thorough in decellularization and short in manufacture cycle, and has the characteristic of antibacterial function.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
Production Method For Cryopreserved Acellular Dermal Matrix, And Cryopreserved Acellular Dermal Matrix Produced Thereby
InactiveUS20120189707A1Improve stabilityEasy maintenanceDead animal preservationUnknown materialsSucroseMedicine
The present invention relates to a production method for cryopreserved acellular dermal matrix and to cryopreserved acellular dermal matrix produced thereby, and more specifically it relates to a method in which a cryopreservation agent is made by adding sucrose to basic components consisting of glycerol and a basic solution and in which the resulting solution is used in the cryopreservation of skin tissue from which the cells in the epidermis and dermis have been removed, and relates to cryopreserved acellular dermal matrix produced thereby.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND HALLYM UNIV
Acellular dermal matrix guided tissue regeneration membrane material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108355171AAvoid carryingAvoid risk of transmissionTissue regenerationProsthesisFiberTissue repair
The invention provides an acellular dermal matrix guided tissue regeneration membrane material as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of medical biological materials. The preparation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: pretreating, removing an epidermal layer, preparing a loose surface, stabilizing, performing the accellular treatment, washing, and sterilizing. A membrane material prepared by the method provided by the invention adopts fish skin as a raw material and has a three-dimensional space framework structure, and comprises a compact surface formed by a biological substrate membrane and a collagen loose surface formed by a dermal scaffold. By adopting the membrane material provided by the invention, therisk of the existing tissue restoration material in carrying and propagating the human-animal viruses can be avoided, the cell components can be completely removed, the immunogenicity is low, the clearance of the collagen fibers is increased, a corium layer structure is reserved, the tissue compatibility is good, the mechanical shielding effect is good, and the generation of new bones can be facilitated; and when used for restoring and treating the bone deficiency of an oral implantation operation, the material is digestible, and the second operation and the injury of the membrane material topatients can be effectively avoided.
Owner:QINGDAO MARINE BIOPHARMACEUTICAL RES INST
Soft tissue repair grafts and processes for preparing and using same
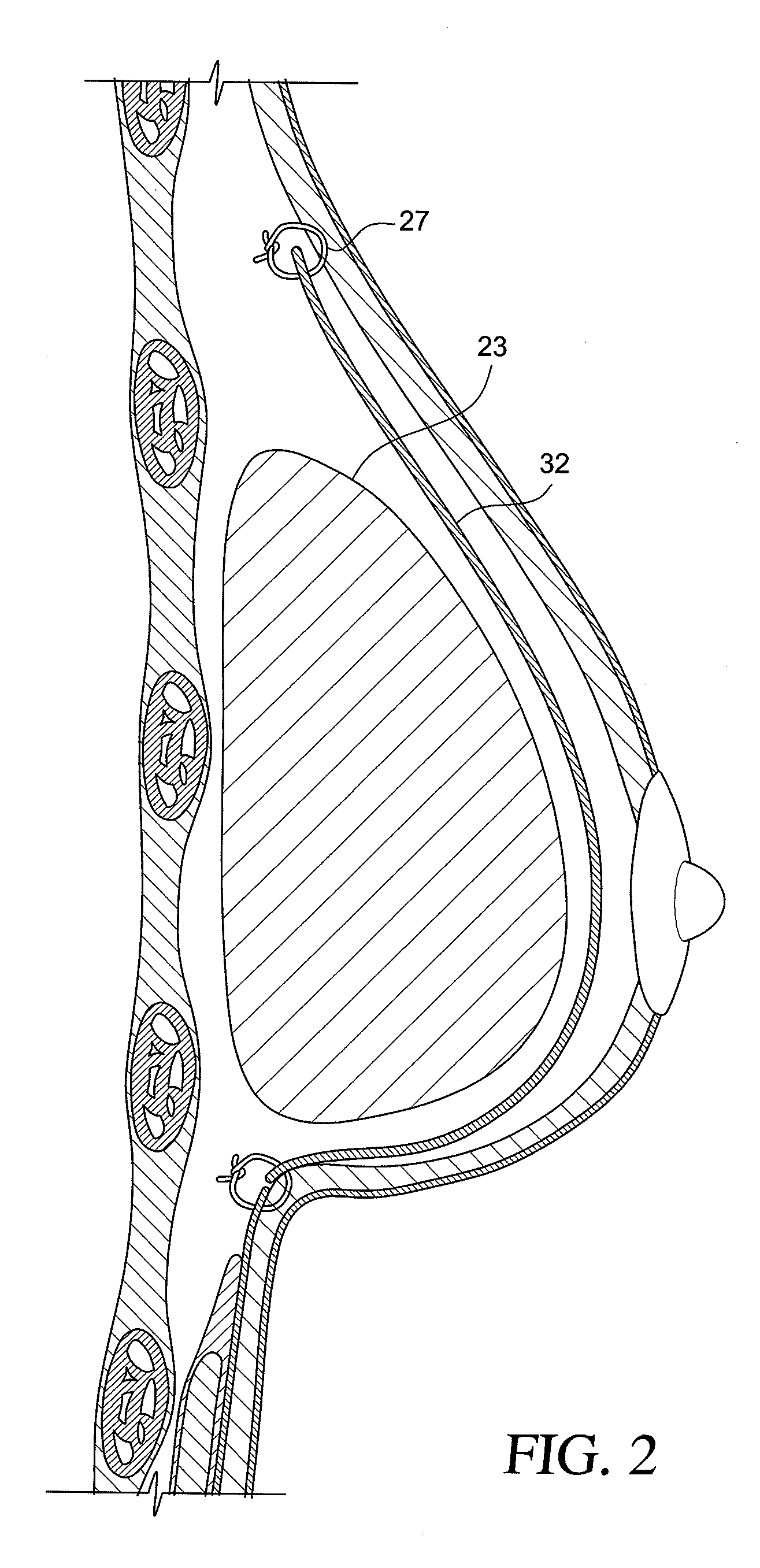
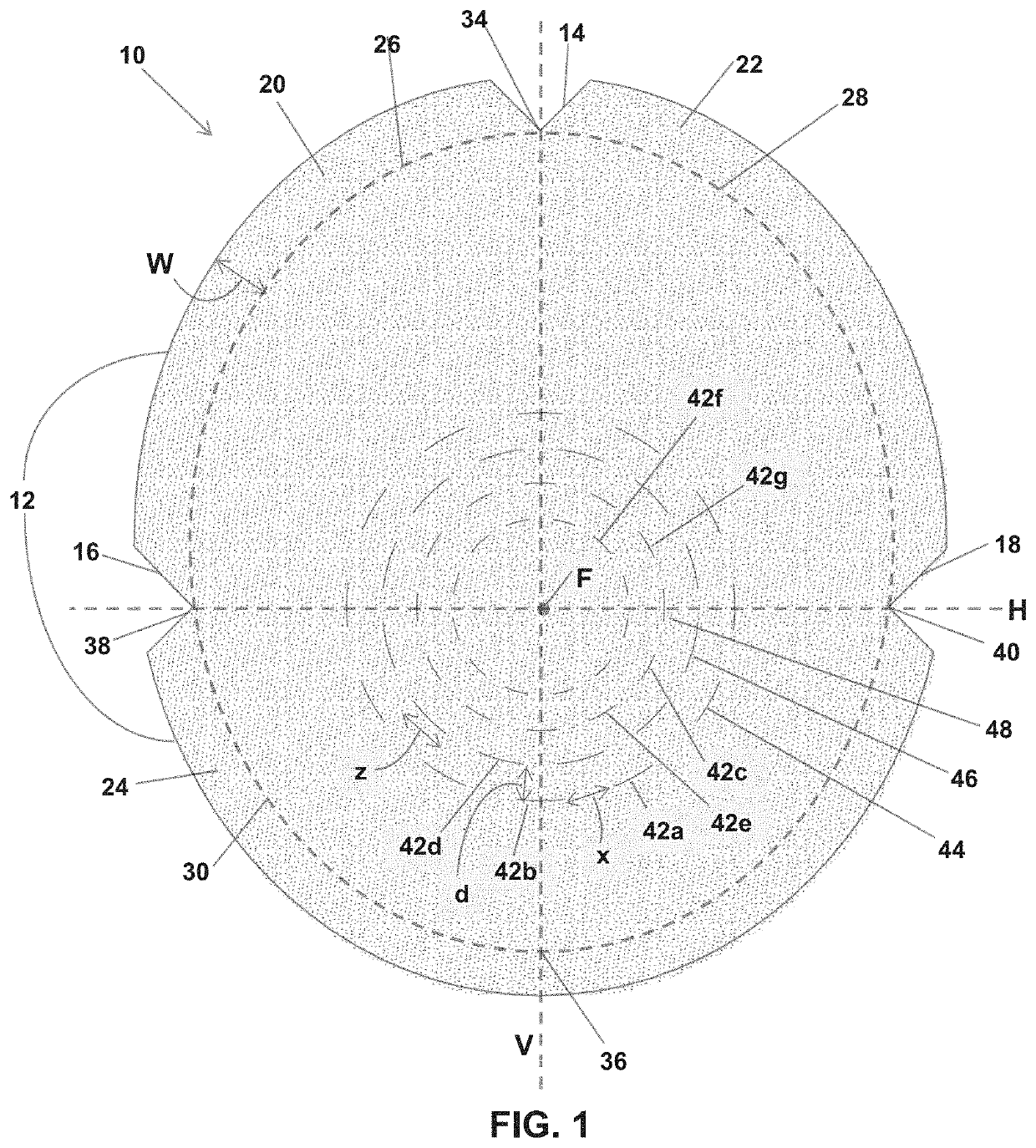
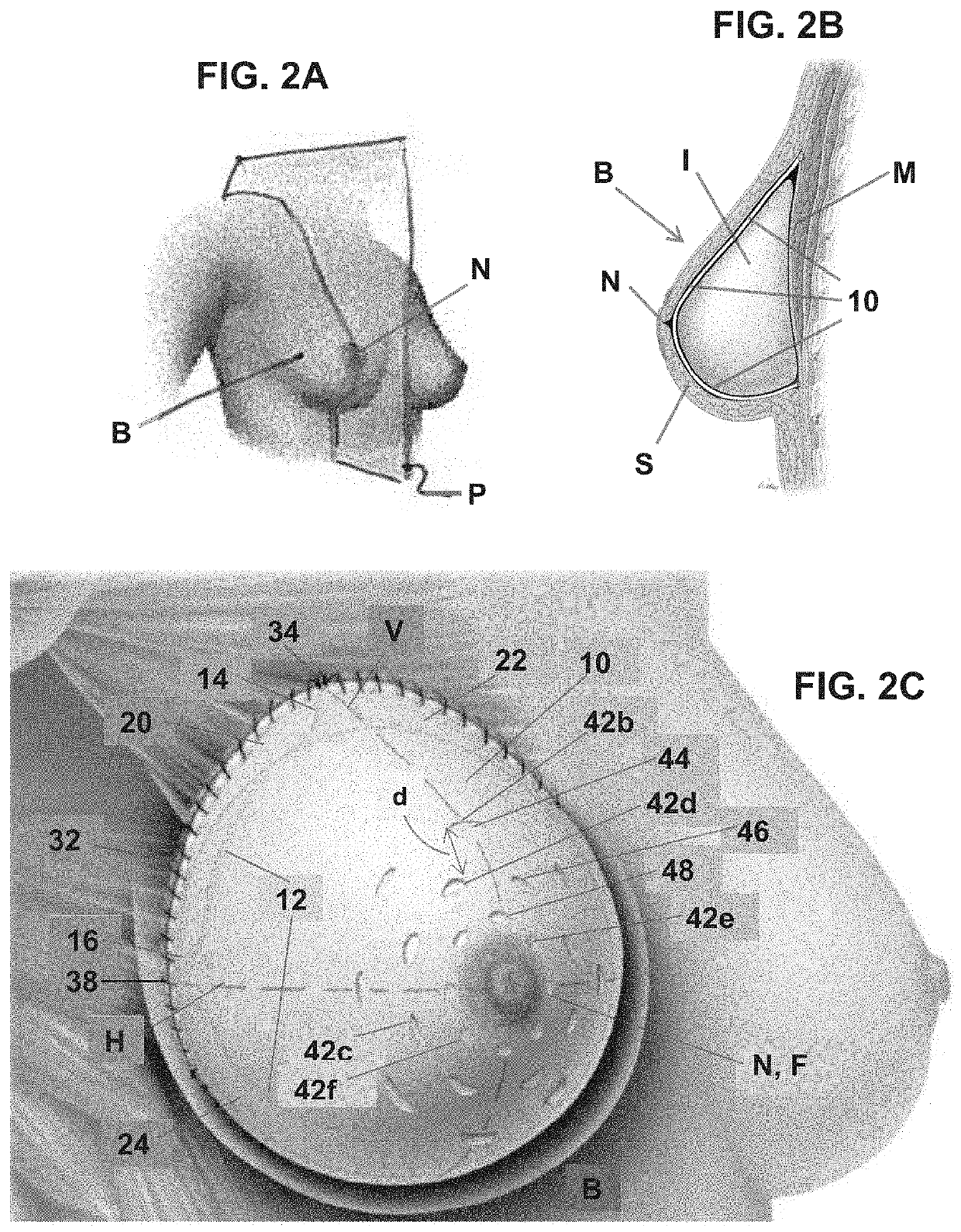
Soft tissue repair grafts are provided for supporting, covering, and / or retaining an implant positioned in the body of a subject. The grafts are particularly suitable for use for pre-pectoral breast reconstruction with a breast implant or tissue expander. The grafts include positional notches for more accurate positioning in a subject. The grafts also include at least one cuff element which is folded to form a reinforced folded edge for suturing the graft more securely to adjacent tissues than previously known grafts. The grafts also include a plurality of arcuate slots which form a plurality of circular patterns arranged concentrically about a focal point, thereby enabling the grafts to expand without tearing and to conform more closely to the implant and / or adjacent body tissues such as the breast pocket, than previously known grafts. Acellular dermal matrices are particularly suitable for making the soft tissue repair grafts.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC +1
Preparation method of composite soft-tissue patch
ActiveCN101773687APromote ingrowthPromote proliferationProsthesisMicrosphereBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite soft-tissue patch. Sustained-release microspheres containing human cell culture secretion are mixed with gel solution, then the mixture is compounded with an acellular dermal matrix under vacuum, and after drying and sterilization, the composite soft-tissue patch is obtained. The prepared composite patch can improve the biocompatibility and the bioactivity of the dermal matrix effectively. The experiment shows that compared with the single acellular dermal matrix, the patch can promote cell proliferation and collagen formation effectively and has better biocompatibility and better tissue remolding. The patch can be widely applied to closure of various wound surfaces, repair of various soft-tissue defects and reinforcement of weakplaces and can be prepared into micro particles to be used for filling various fine and weak or dented places by injection, thus having wider application prospect in clinic.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Chitosan quaternary ammonium salt porcine acellular dermal matrix dressing material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106421868ALow antigenicityReduce releasePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAbsorbent padsFiberAcellular Dermis
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical engineering, and particularly relates to a chitosan quaternary ammonium salt porcine acellular dermal matrix dressing material and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the chitosan quaternary ammonium salt porcine acellular dermal matrix dressing material specifically comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a chitosan quaternary ammonium salt; S2, processing a porcine acellular dermal matrix; and S3, preparing the chitosan quaternary ammonium salt porcine acellular dermal matrix dressing material. The chitosan quaternary ammonium salt porcine acellular dermal matrix dressing material disclosed by the invention completely reserves morphological structures and components of cells, has the characteristic of low antigenicity, and meanwhile can induce fiber-forming cells and vascular endothelial cells with regeneration capacity to grow therein.
Owner:GUANGDONG TAIBAO MEDICAL SCI TECH
Compound biological ink and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109054496AGood 3D printable propertiesProtectiveAdditive manufacturing apparatusInksIonic strengthHydrogen
The invention discloses compound biological ink. Preparation raw materials of the compound biological ink comprise acellular dermis matrix hydrogel, a crosslinking curing agent and a bioactive molecule; the invention further discloses a preparation method of the compound biological ink; the preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the acellular dermis matrix hydrogel: afterremoving target tissues or fat tissues and connective tissues of organs, repeatedly treating with a 1 to 5 percent trion x-100 water solution and a 1.5 to 7 percent sodium deoxycholate water solutionfor a plurality of times in sequence, so as to obtain acellular tissues; freezing and drying the acellular tissues; then crushing and treating through pepsin to obtain a sticky gel solution; then regulating the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) and ion strength at 2 to 8 DEG C; raising the temperature to 33 to 39 DEG C to obtain the acellular dermis matrix hydrogel; (2) adding the crosslinking curing agent, an active factor and a short peptide, and compounding at 1 to 8 DEG C to obtain the compound biological ink. The compound biological ink prepared by the method disclosed by the invention has goodbioactivity and a 3D (Three Dimensional) printable property.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Acellular dermal matrix compound film material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101314055AImprove performanceImprove mechanical propertiesProsthesisAcetic acidFreeze-drying
The invention discloses an acellular dermal matrix complex film material and a preparation method thereof. The method is characterized in that: 18 to 28 weight portions of collagen is dissolved into a solution by an acetic acid aqueous solution with a concentration between 0.2 and 0.5mmol / L; 10 to 24 weight portions of polyvinyl alcohol and 10 to 40 weight portions of chitosan are respectively dissolved into solutions with different concentrations by distilled water at a temperature of between 85 and 95 DEG C and at a temperature of between 40 and 60 DEG C, and the collagen solution and the polyvinyl alcohol solution and / or the chitosan solution are mixed according to the proportion and then are evenly stirred to prepare a mixed liquid; the mixed liquid is evenly coated on the surface of an acellular dermal matrix material to ensure that the thickness of a film reaches between 0.5 and 2.5cm and the film is quickly frozen, and then the acellular dermal matrix complex film material is produced through freeze drying; and finally carbodiimide is adopted to modify so as to prepare an acellular dermal matrix composite collagen-polyvinyl alcohol and / or chitosan film material.
Owner:JIANGYIN BENXIANG BIOTECHOLOGY
Preparation method of microcarrier-cell compound with induction activity and application of compound
The invention discloses a preparation method of a microcarrier-cell compound with induction activity and an application of the compound. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively using decalcified bone matrix particles and acellular dermal matrix micro particles to culture bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for 7-21 days, differentiating into osteoblasts and fibroblasts to obtain an osteoblast-particle compound and a fibroblast-particle compound, and then, mixing evenly. The activity of the seed cells of the prepared product are higher, the product can be used for preparing repair material for treating lacunar bone defect and segmental bone defect, the in vivo repair effect is better, and the in vivo repair effect of tissue-engineered bone for more than two times; supporting cell components are added in the construction process of the tissue-engineered bone to promote the bone formation effect of bone parenchymal cells in bone formation in vivo, the new bone strength, the matrix component content and the calcification extent can be improved for 1.5-2 times, the utilization rate of the seed cells is obviously improved, the type of the bone repair seed cells is enriched, and the bone defect repair effect is greatly improved.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Tendon reinforcing repairing material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103480041AEasy to wrapGood biocompatibilityProsthesisCell-Extracellular MatrixBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a tendon reinforcing repairing material and a preparation method of the tendon reinforcing repairing material. The repairing material takes animal original dermis as the raw material and is prepared by steps of pretreatment, preparation of a holder layer, preparation of a mechanical reinforcing layer, and preparation of a tendon reinforcing repairing material. The tendon reinforcing material comprises the holder layer and the mechanical reinforcing layer, wherein the holder layer reserves the integrity of the structure and component of an extracellular matrix to the greatest degree, and due to the introduction of the mechanical reinforcing layer, the acellular dermal matrix has better mechanical property compared with the acellular dermal matrix prepared by the traditional technology, for the biocompatibility, mechanical strength and biological activity are improved and balanced. According to the requirements of different indications on materials, the preparation method can prepare membrane materials and curl materials in different thicknesses. The tendon reinforcing repairing material is widely applicable to repairing of acute and old tendon injury.
Owner:SHAANXI RUISHENG BIOTECH
Tissue engineering skin and application thereof
ActiveCN104667353AIncrease the number ofImprove proliferative abilityProsthesisDermisAcellular Dermis
The invention relates to the field of tissue engineering, in particular to tissue engineering skin and an application thereof. A construction method of the tissue engineering skin comprises steps as follows: umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are adopted as seed cells, an ADM (acellular dermal matrix) serves as a support, and the tissue engineering skin is constructed and obtained. The tissue engineering skin can restore skin wounds more effectively, and the construction method of the tissue engineering skin is simple and convenient and comprises few operation steps.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
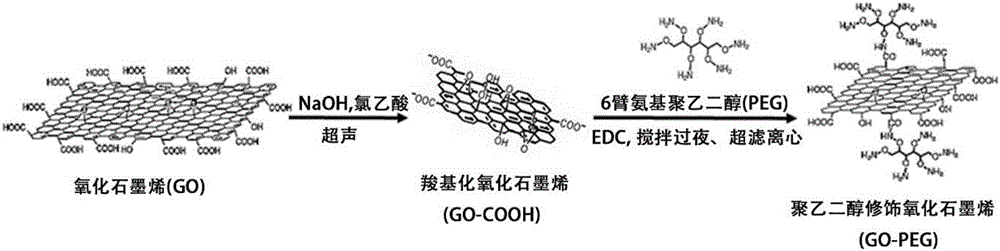
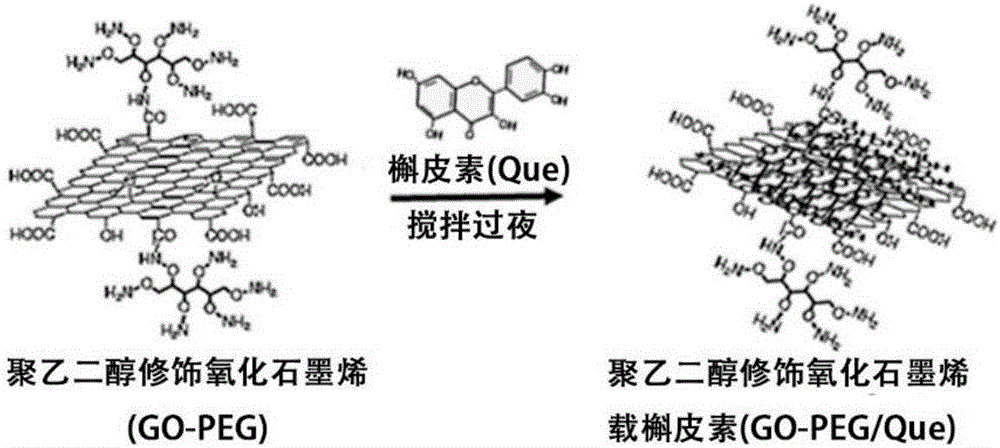
Preparation method of 3D drug composite stent for polyethylene glycol modified graphene oxide loaded quercetin cross-linked acellular dermal matrix
ActiveCN107519534AGood water solubilityHigh drug loading rateProsthesisCross-linkPolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a 3D drug composite stent for a polyethylene glycol modified graphene oxide loaded quercetin cross-linked acellular dermal matrix. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a circular acellular dermal matrix (ADM) stent from ICR rat full skin; secondly, grafting 6-arm amino polyethylene glycol (PEG) to GO to prepare polyethylene glycol modified graphene oxide (GO-PEG) under the condition that graphene oxide (GO) is catalyzed by EDC; thirdly, adsorbing quercetin (Que) to GO-PEG, and cross-linking prepared GO-PEG / Que to the surface of an ADM stent; and finally, preparing the 3D drug composite stent for the polyethylene glycol modified graphene oxide loaded quercetin cross-linked acellular dermal matrix (ADM-GO-PEG / Que). After the composite stent is transplanted to a diabetic skin wound, effects of transferring drug and healing the wound can be achieved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Laser micropore porcine acellular dermal matrix and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a laser micropore porcine acellular dermal matrix and a preparation method thereof. Pore diameters of micropores in the dermal matrix are between 0.1 and 0.2 millimeter, and space between the micropores is 1 millimeter. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: fixing a porcine acellular dermal matrix sample on a processing platform of laser processing equipment by a four-point suspension fixing method, and regulating parameters of the laser processing equipment, so that the minimum emitting energy of the laser processing equipment is 10,000 watts / millimeter square, wherein the puncture step size of lasers is 1 millimeter, and the pore diameters are between 0.1 and 0.2 millimeter; and performing puncture on the sample to obtain the micropore porcine acellular dermal matrix. By the preparation method, the efficiency of laser puncture is the highest; and in the prepared micropore porcine acellular dermal matrix, the pore diameters are between 0.1 and 0.2 millimeter, the space between the micropores is 1 millimeter, and the micropores are uniform and fine in distribution, so seepage on wound substrates can permeate through uniform meshes to better nourish skin pieces, promote revascularization, improve the survival rate of the skin pieces and reduce the formation of scars during transplantation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Acellular dermal matrix-based hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109821071AImmune immune rejection reaction is smallLow cytotoxicityProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingAcellular Dermis
Owner:上海仁康科技有限公司
Acellular dermal graft
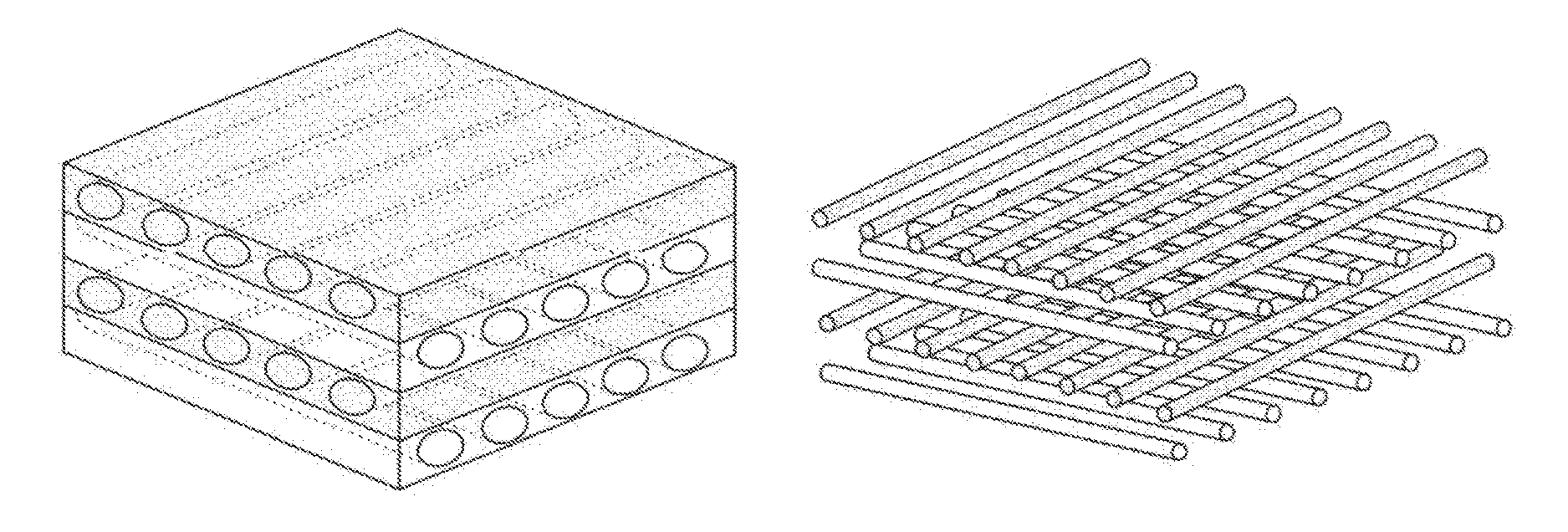
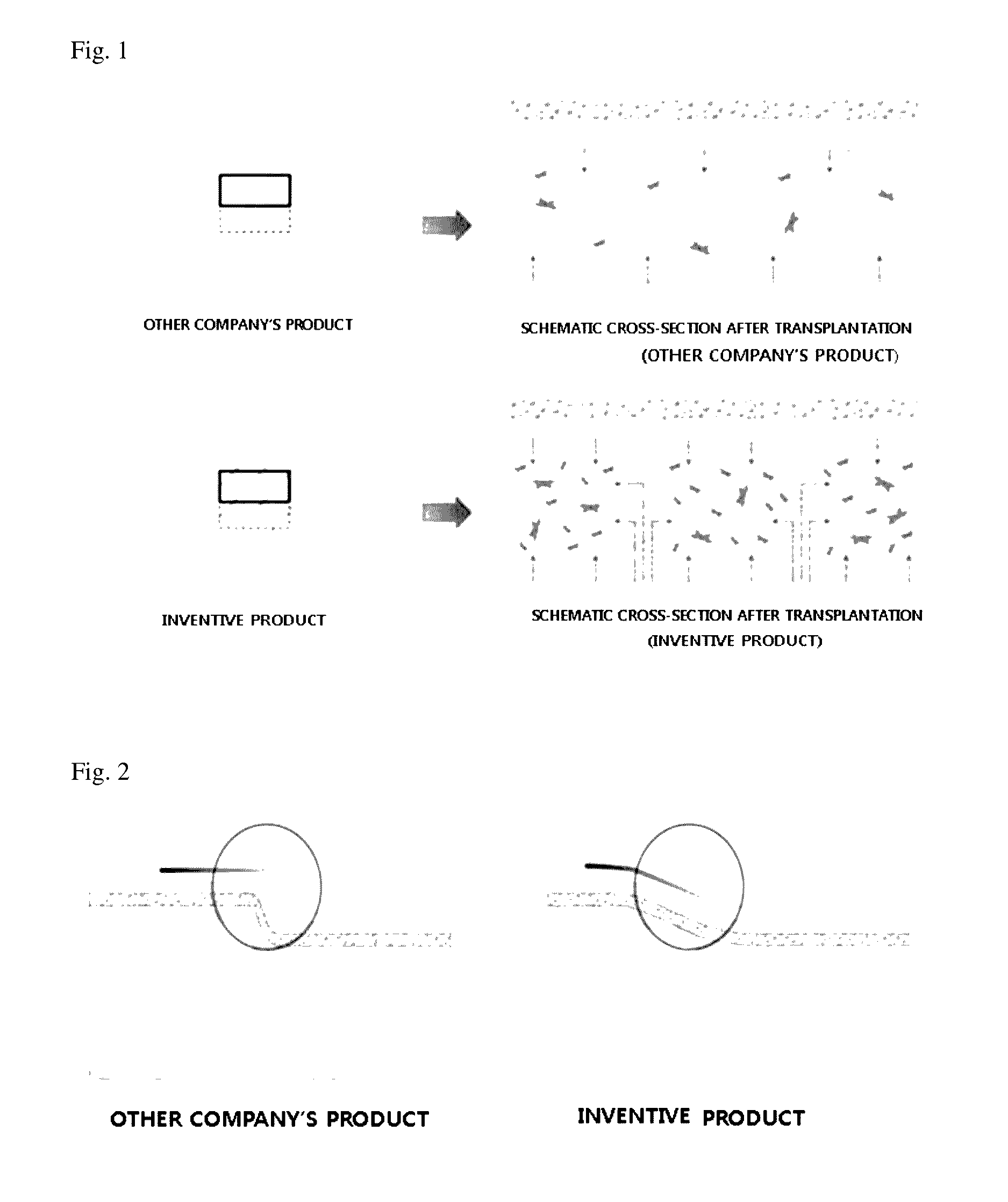
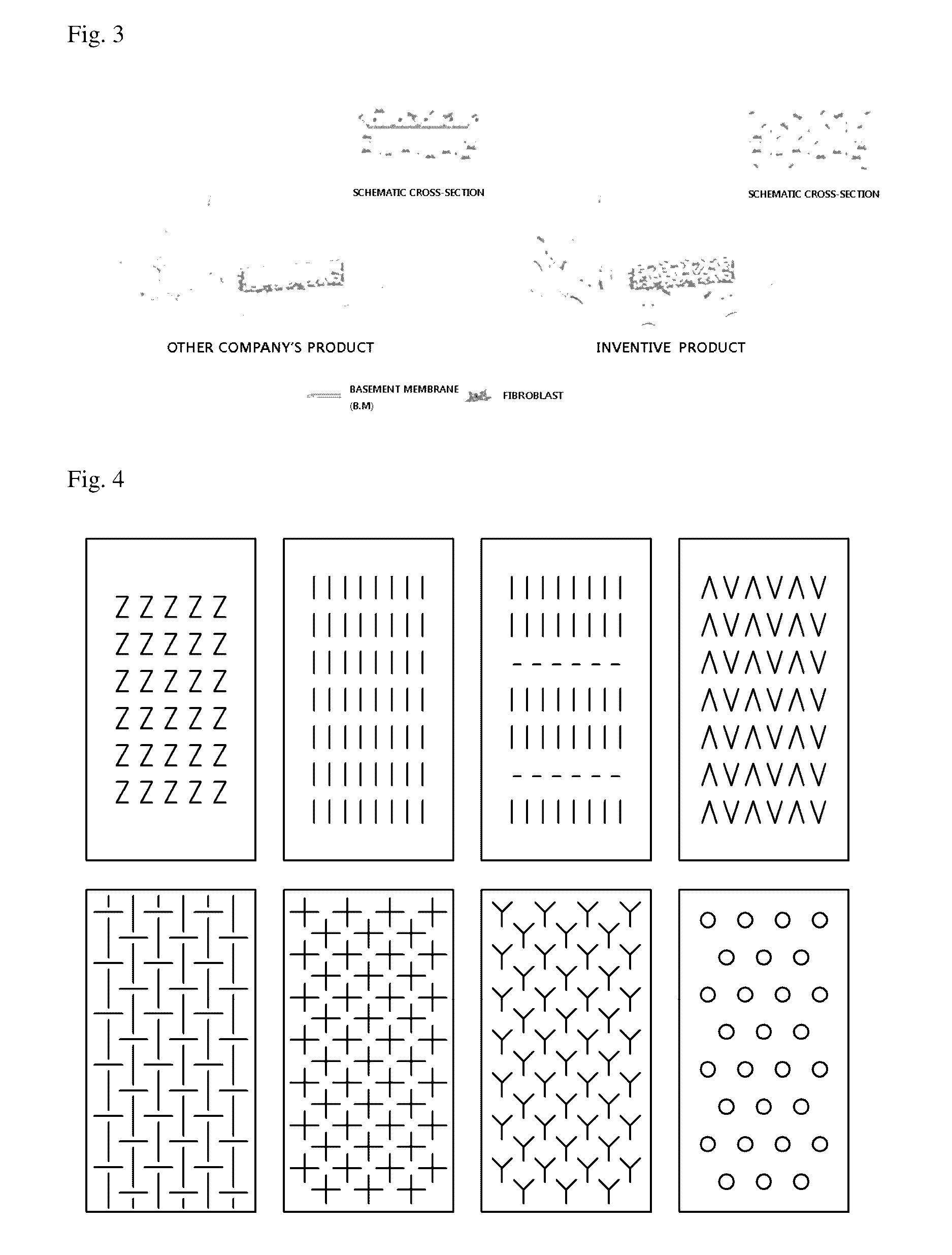
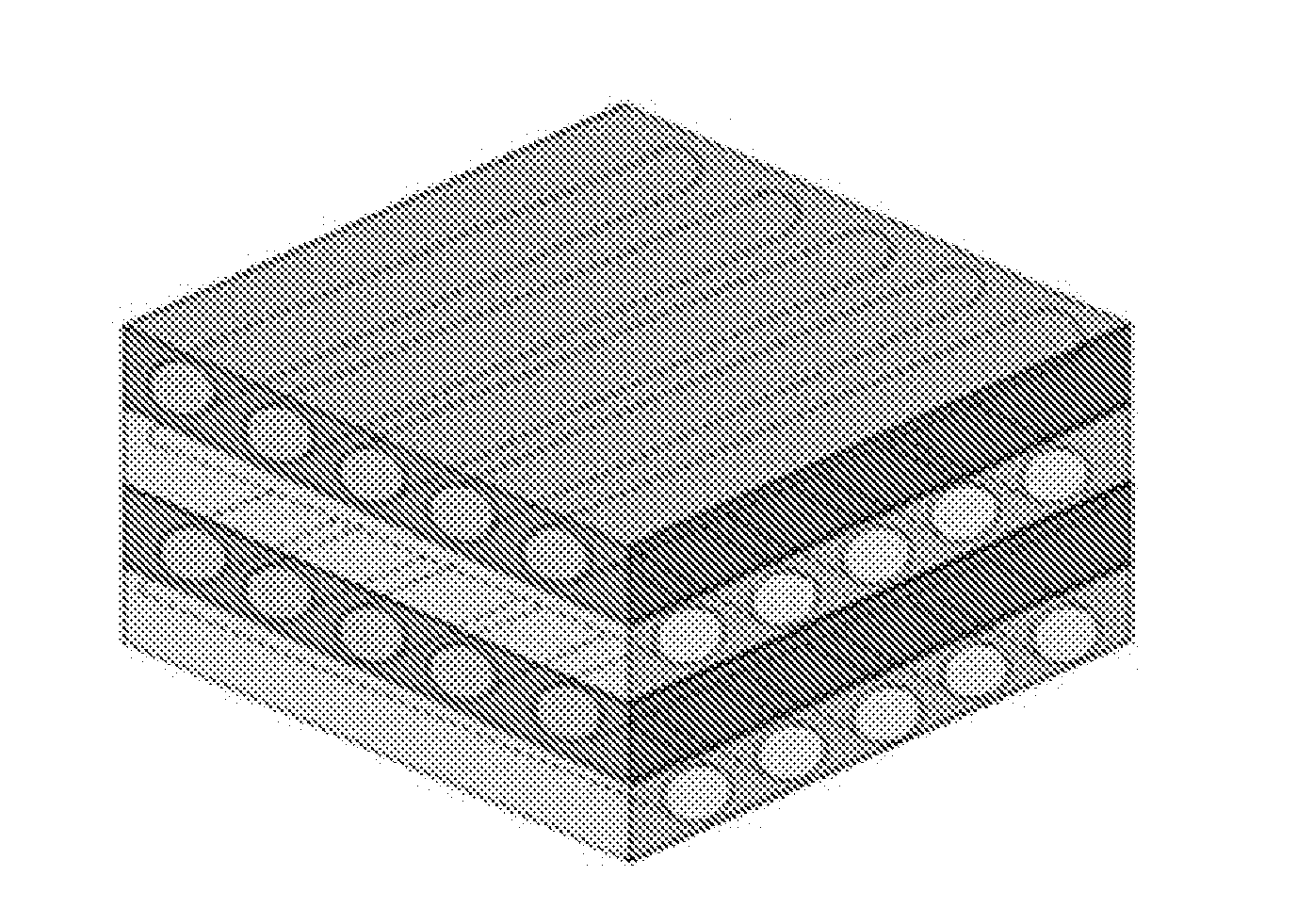
ActiveUS9532866B2Improves flexibility and extensibilityStablySkin implantsExtensibilityAutologous tissue
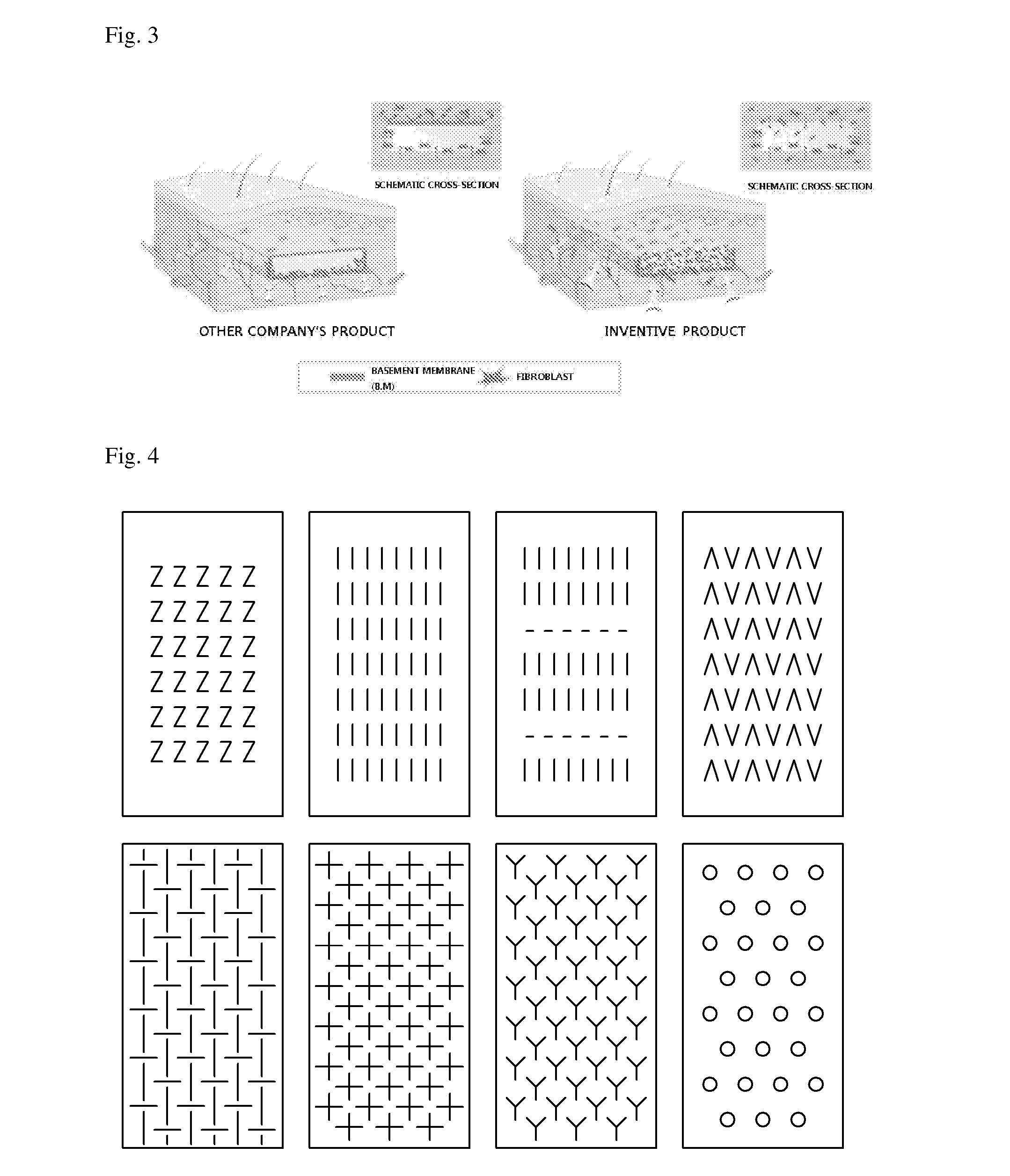
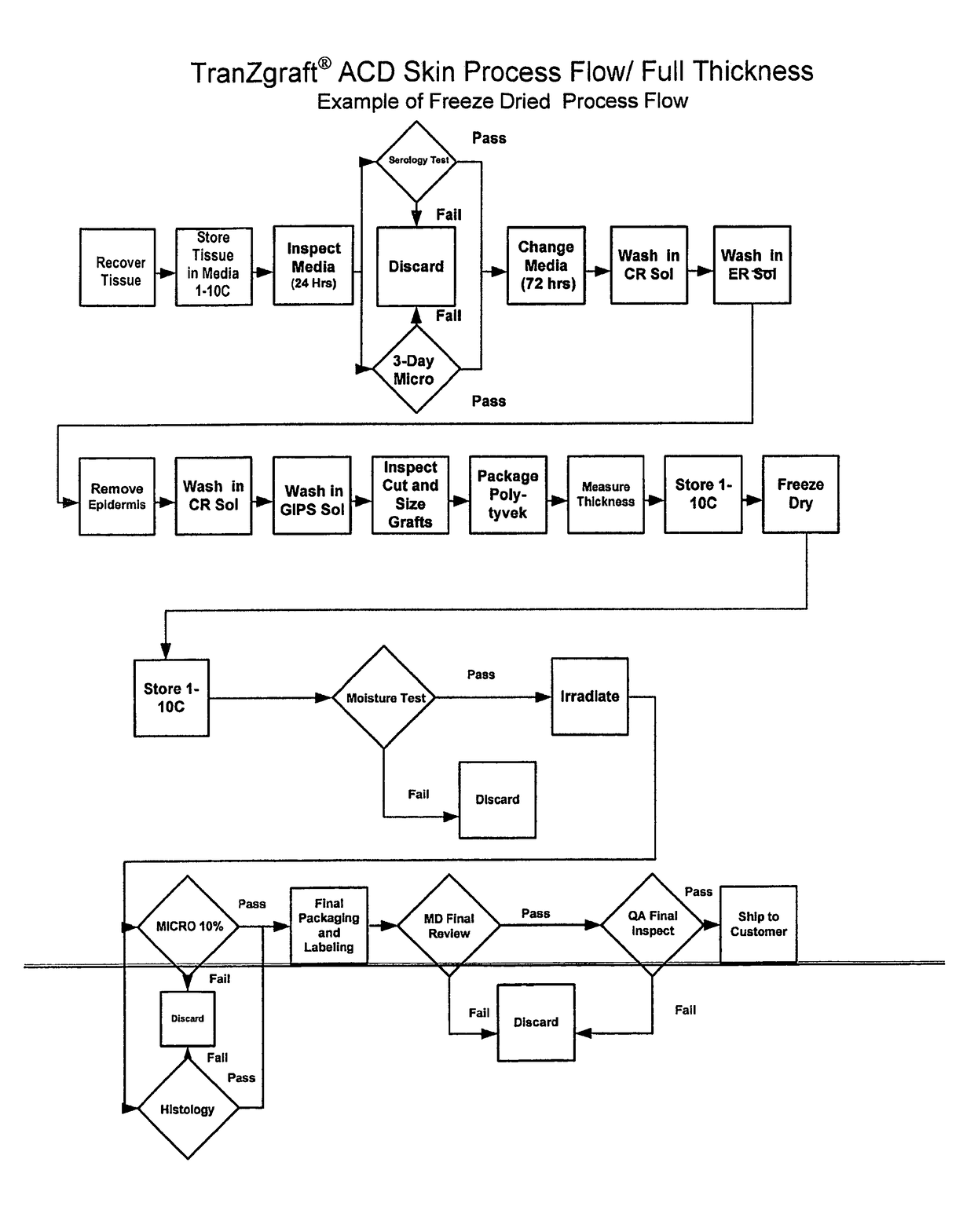
An acellular dermal graft is provided. The acellular dermal graft may be useful in minimizing side effects caused after transplantation since an environment favorable for formation of new blood vessels and proliferation of autologous tissues is provided by forming a multi-penetration structure in an acellular dermal tissue, removing a basement membrane layer and / or subjecting corners to slope cutting, and transplantation is stably performed within a short transplantation time due to improved extensibility and flexibility of tissues. The acellular dermal graft may be useful in reducing a time required to recover tissues after transplantation since the transplantation is stably performed due to improved grafting reaction with a host tissue by enhancing uptake of fibroblasts and promoting angiogenic activities. Also, the acellular dermal graft may be useful in maintaining smooth external appearance since hypodermic implantation is easily performed upon transplantation, and the skin at a graft site does not protrude after transplantation.
Owner:L&C BIO CO LTD
Acellular dermal graft
ActiveUS20150057751A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilitySkin implantsExtensibilityAutologous tissue
An acellular dermal graft is provided. The acellular dermal graft may be useful in minimizing side effects caused after transplantation since an environment favorable for formation of new blood vessels and proliferation of autologous tissues is provided by forming a multi-penetration structure in an acellular dermal tissue, removing a basement membrane layer and / or subjecting corners to slope cutting, and transplantation is stably performed within a short transplantation time due to improved extensibility and flexibility of tissues. The acellular dermal graft may be useful in reducing a time required to recover tissues after transplantation since the transplantation is stably performed due to improved grafting reaction with a host tissue by enhancing uptake of fibroblasts and promoting angiogenic activities. Also, the acellular dermal graft may be useful in maintaining smooth external appearance since hypodermic implantation is easily performed upon transplantation, and the skin at a graft site does not protrude after transplantation.
Owner:L&C BIO CO LTD
Acellular dermal allografts and method of preparation
ActiveUS9888999B2Reduce contentReduce bioburdenSkin implantsDead animal preservationProduction lineMedicine
A method for preparing a sterilized human acellular dermal allograft where the dermal allograft is sterilized by irradiation and has a greatly reduced bio-burden and enzymatic and antigenic activity. This product line of allografts can be easily used by surgeons in soft tissue replacement or repair and has an extended shelf life, of up to at least about three years.
Owner:MIDCAP FINANCIAL TRUST AS AGENT
Xenogeneic acellular dermis and preparation method thereof
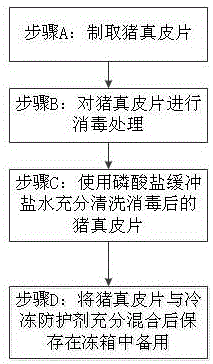
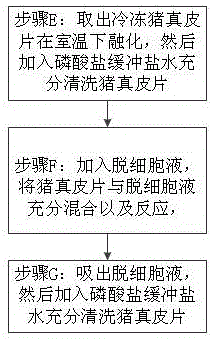
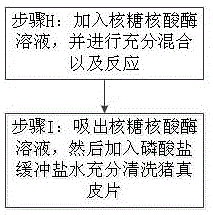
InactiveCN106310384APrevent productionAvoid damageProsthesisFreeze thawingRadiation-protective agents
The invention discloses xenogeneic acellular dermis and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises steps of acquiring and preserving a pig dermal slice and conducting acellular treatment, wherein the pig dermal slice is preserved with the addition of a cryoprotective agent, and for the acellular treatment, a mild detergent is adopted to break cells. According to the xenogeneic acellular dermis and the preparation method thereof provided by the invention, freeze-thaw cycles are avoided, and by adding the cryoprotective agent in a freezing process, damage to the bio-activity of collagen is relieved and the rapid recovery of a wound surface is promoted; residual ribonucleic acid is effectively removed by virtue of a ribonuclease solution, so that an adverse reaction caused by the residual ribonucleic acid is avoided; [alpha]-galactose is effectively removed by virtue of an [alpha]-galactosidase solution, so that an acute immune response in human body caused by the [alpha]-galactose is relieved and even avoided; by conducting electron beam end sterilization in an anti-radiation protective agent or by conducting [gamma] radiation under a dry ice condition, damage of the radiation to the pig dermal slice is reduced while conducting the sterilization; and the xenogeneic acellular dermis, which is packaged in an aluminum foil inside and outside dual-layer bag, can be conveniently opened and used by a doctor.
Owner:江西瑞诺健医学科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com