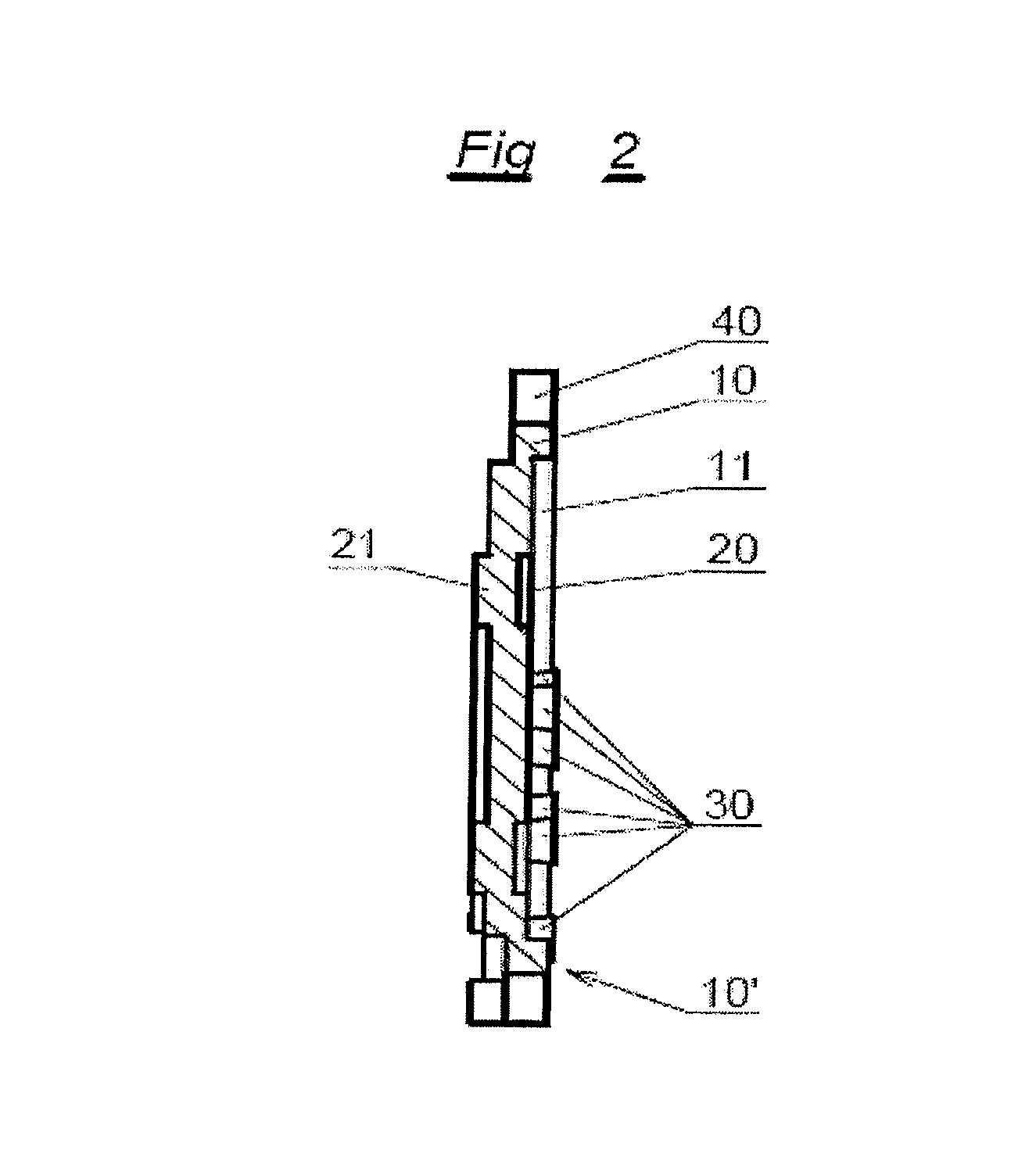
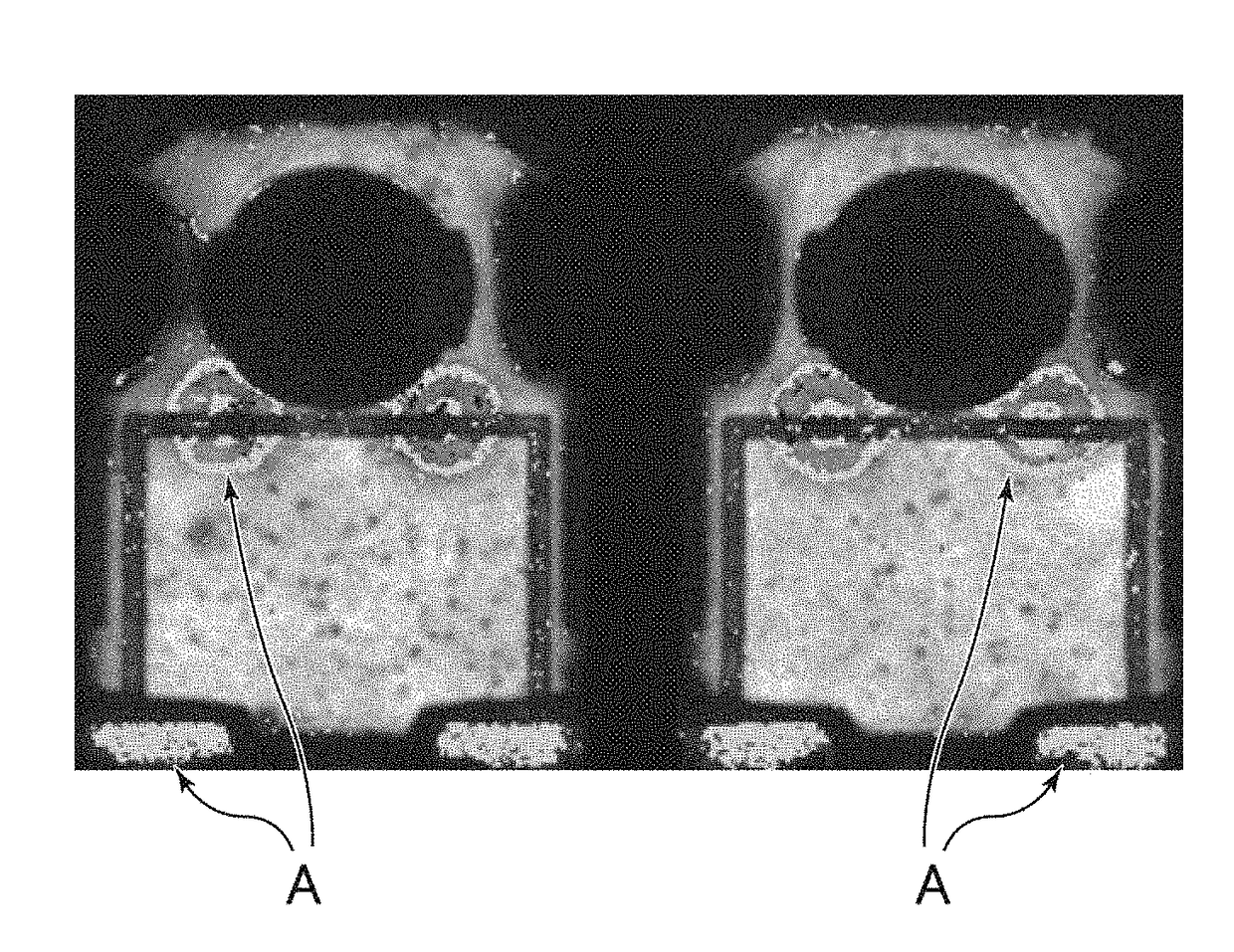
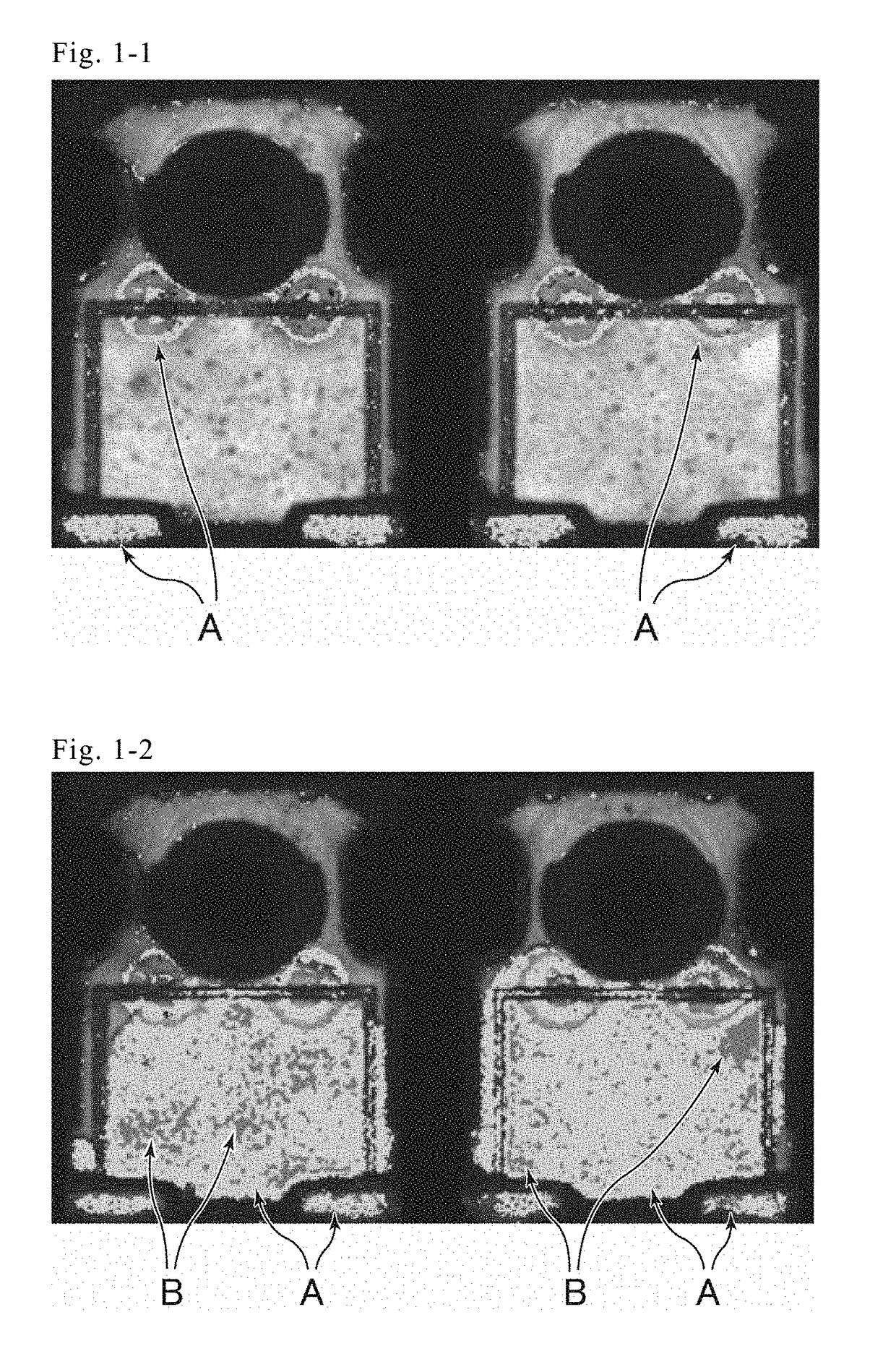
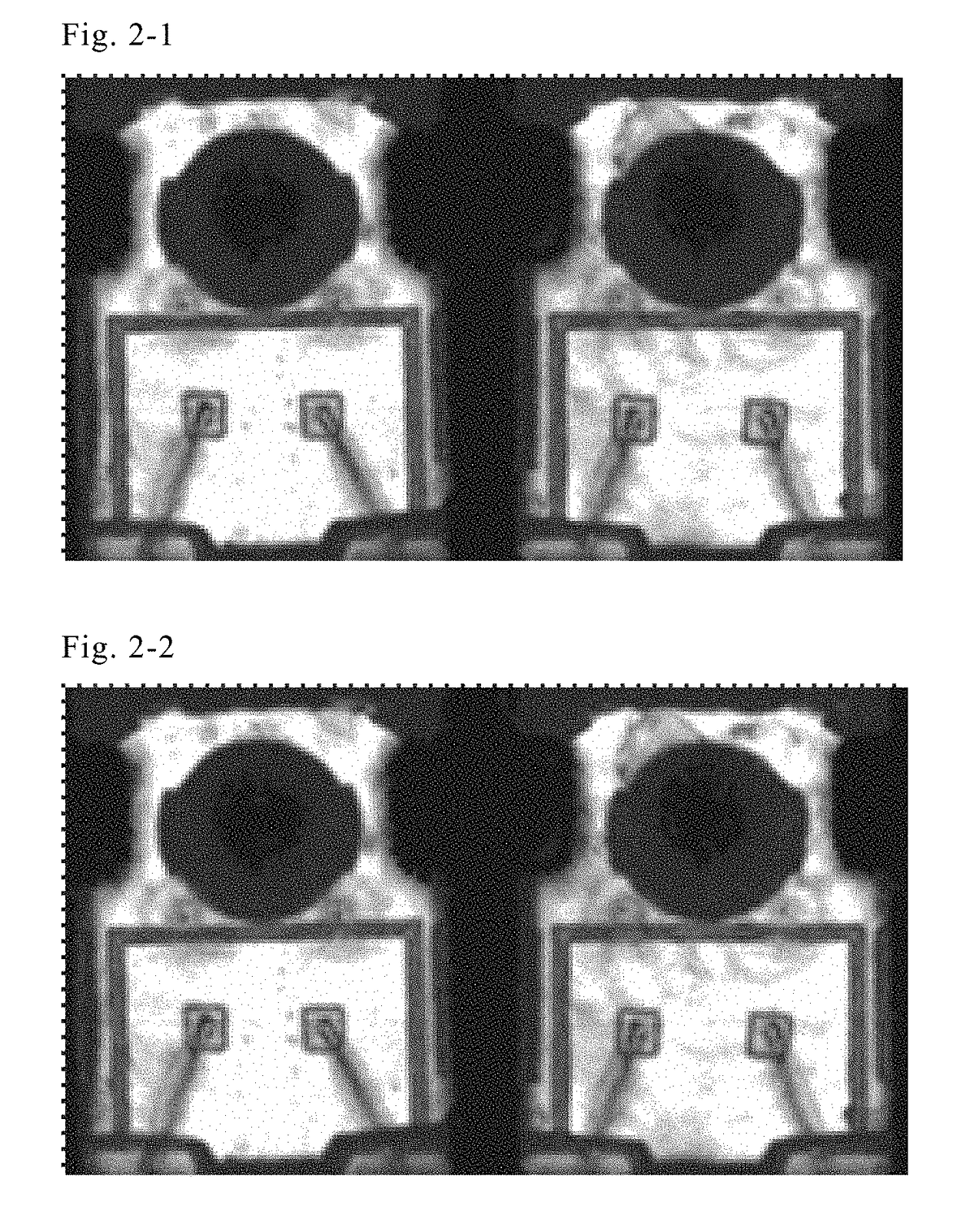
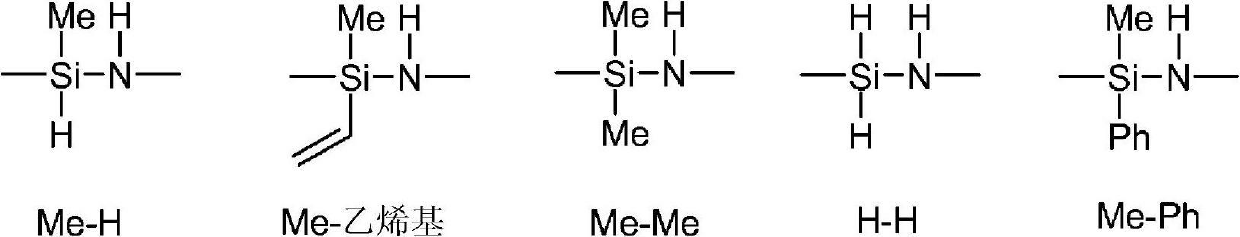Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79results about How to "Reduce crack formation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Highly-dispersed carbon nanotube-reinforced cement-based materials
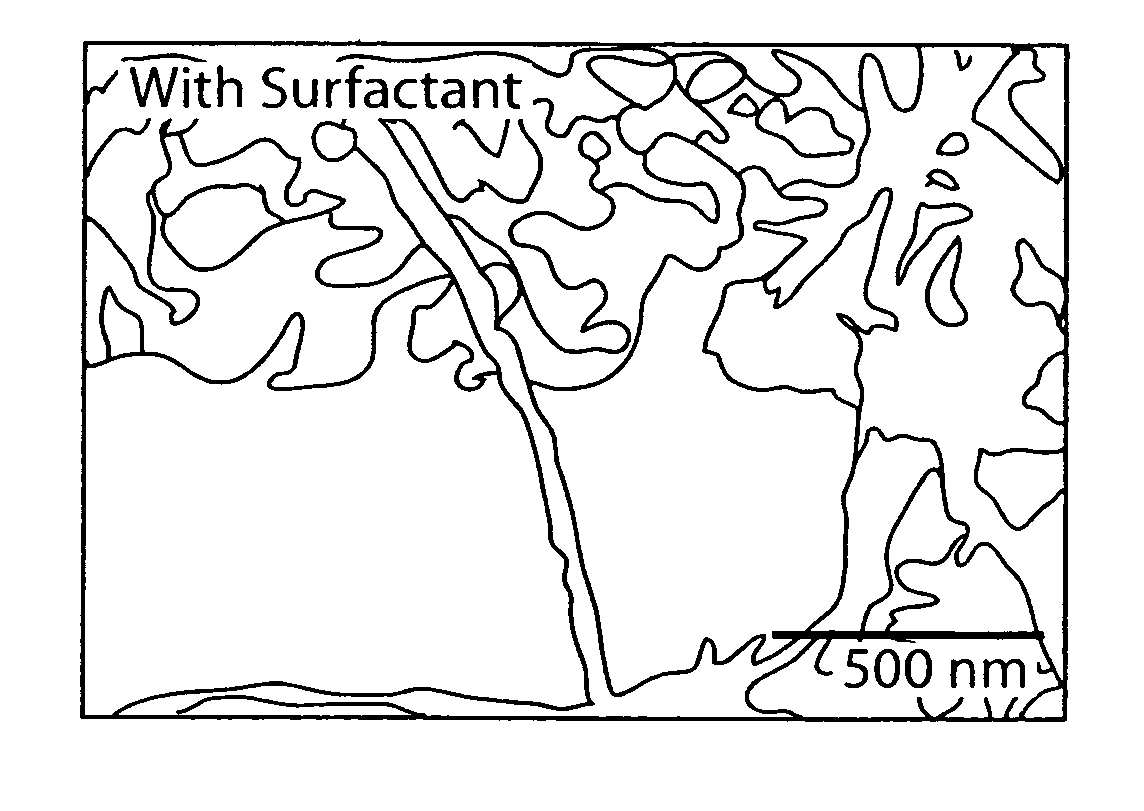
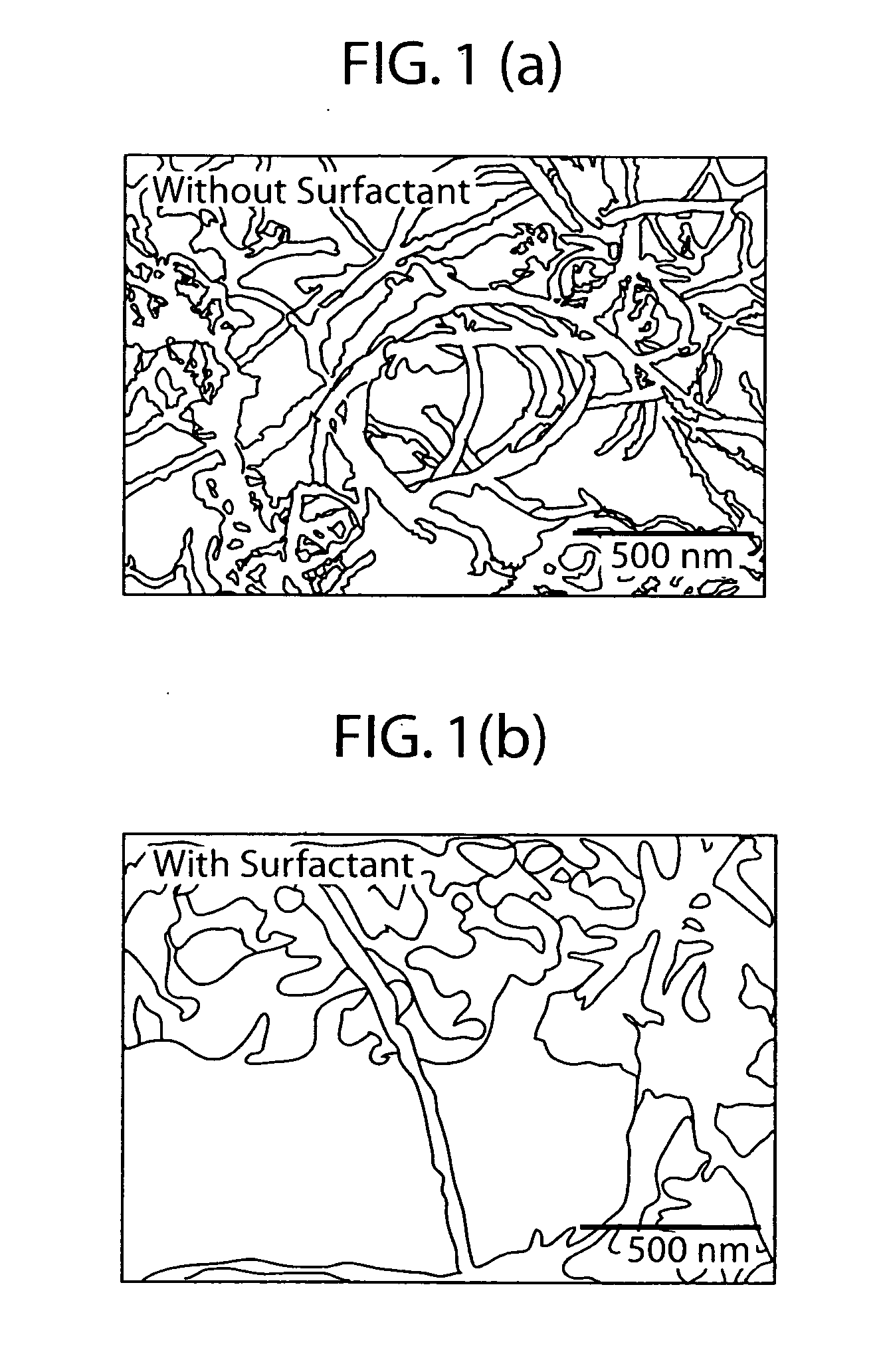
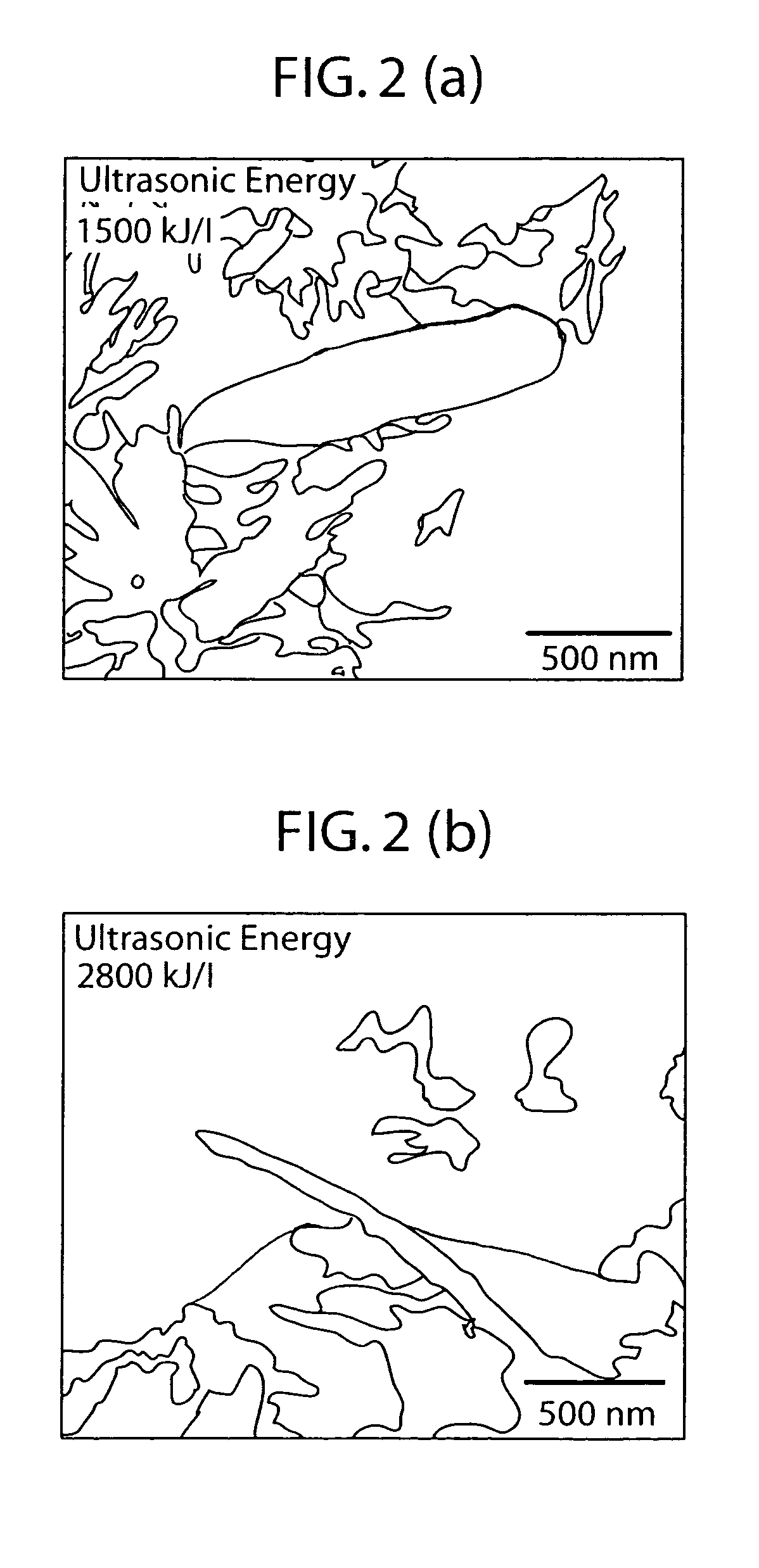
A composite cement material is prepared from cement material and carbon nanotubes, wherein the carbon nanotubes are present from about 0.02 wt % to about 0.10 wt % based on weight of cement material. The process for preparing such cement compositions includes sonicating a mixture of a surfactant, water, and carbon nanotubes; and blending the dispersion and the cement material to form a cementitious paste. The process may also include curing the cementitious paste. The composite cement materials are useful in a variety of cement applications where a reduction in nanoscale flaws and fractures is desired.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Gradient wear-resistant coating and method for preparing same
ActiveCN105543839AImprove wear resistanceHigh temperature resistantSuperimposed coating processWear resistantUltrasonic oscillation
Provided are a gradient wear-resistant coating and a method for preparing the same. Co50+0.15% CeO2 powder, Co50+0.25% CeO2+6% Ni / Wc powder and Co50+0.4% CeO2+12% Ni / WC powder are used for preparing the gradient wear-resistant coating with the structure of a bottom layer, a transition layer and a wear-resistant layer on the surface of a workpiece in a coaxial powder supply manner and a laser cladding manner, and the wear resisting performance of the work surface of a part is improved. An ultrasonic vibration device and a contour tracing electromagnetic induction heating device are adopted in the cladding process. Ultrasonic oscillation of a certain degree is applied to the area close to a cladded area of the workpiece, the grain size of a cladding layer can be remarkably refined, residual stress can be remarkably eliminated, and therefore generated cracks are reduced, and a cladding layer structure with good performance is obtained. The contour tracing electromagnetic induction heating device can be utilized for effectively reducing thermal stress brought by the temperature gradient of the cladding layer and relieving the cracking tendency. According to the technological parameters of the ultrasonic vibration device, the work frequency ranges from 10 kHz to 20 kHz, the maximum output power is 1,000 W, and the pneumatic pressure ranges from 0.3 MPa to 0.6 MPa. According to the technological parameters of the contour tracing electromagnetic induction heating device, the voltage is 380 V, the frequency is 60 Hz, and the heating temperature ranges from 150 DEG C to 1,000 DEG C.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
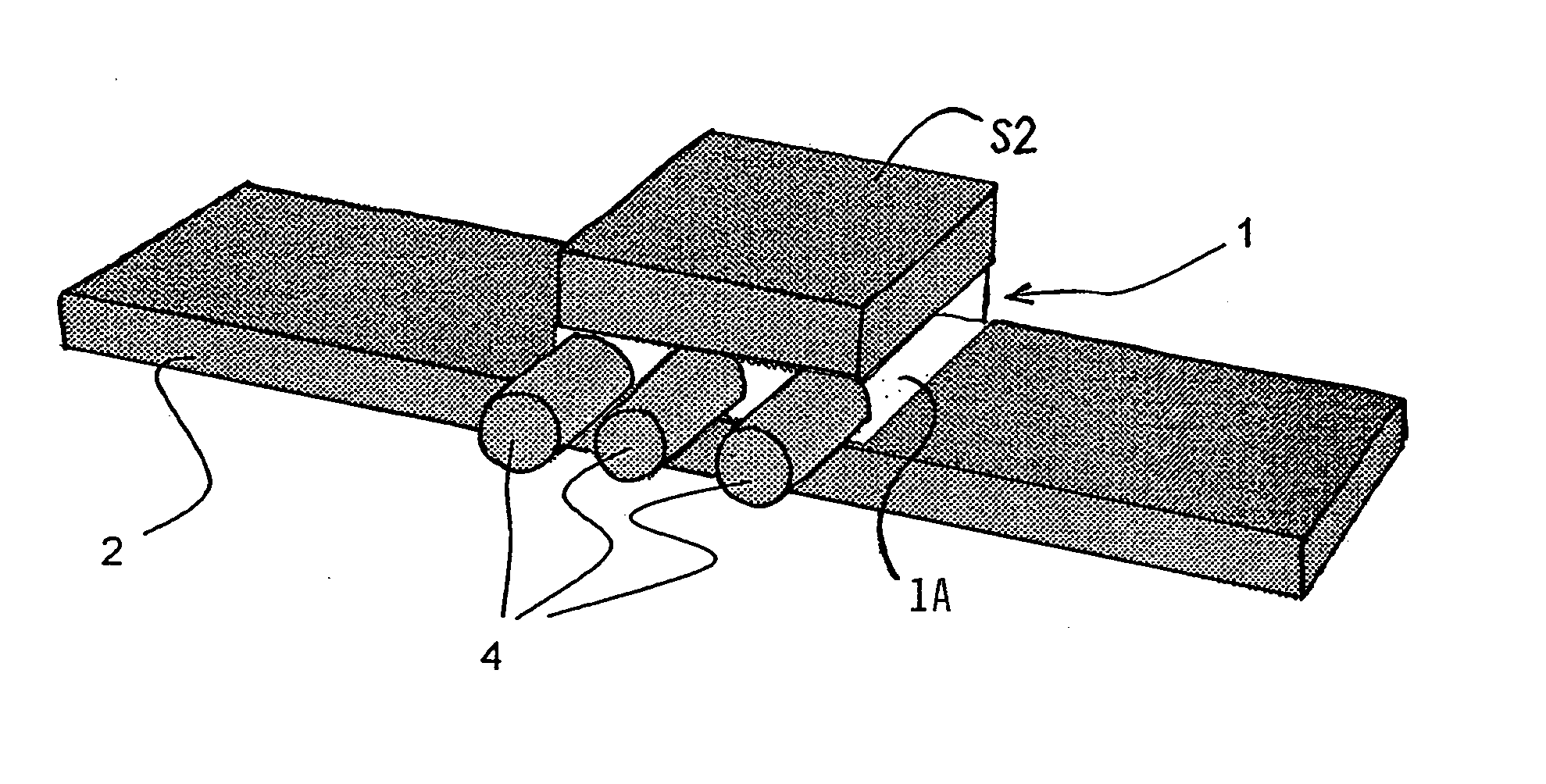
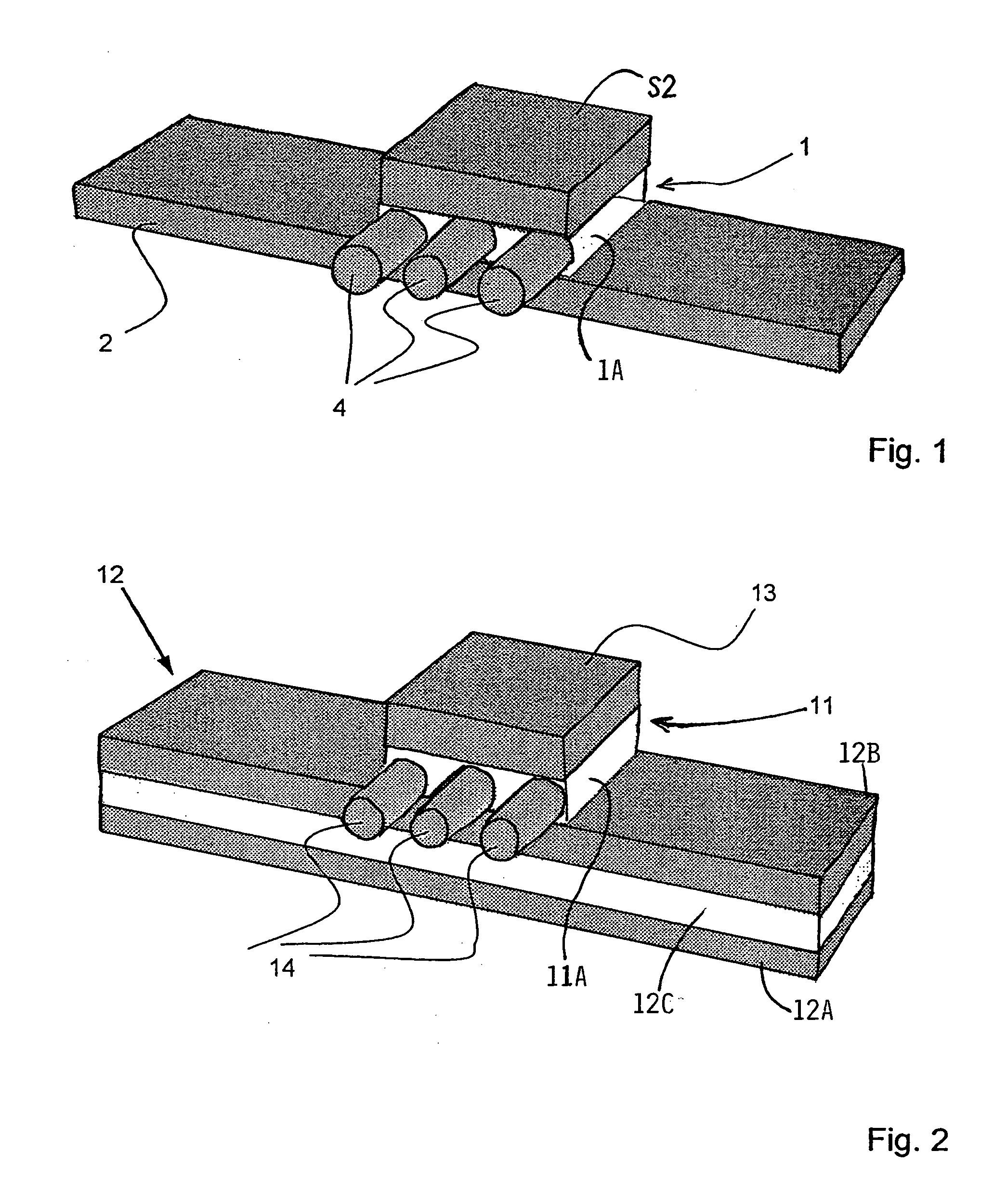
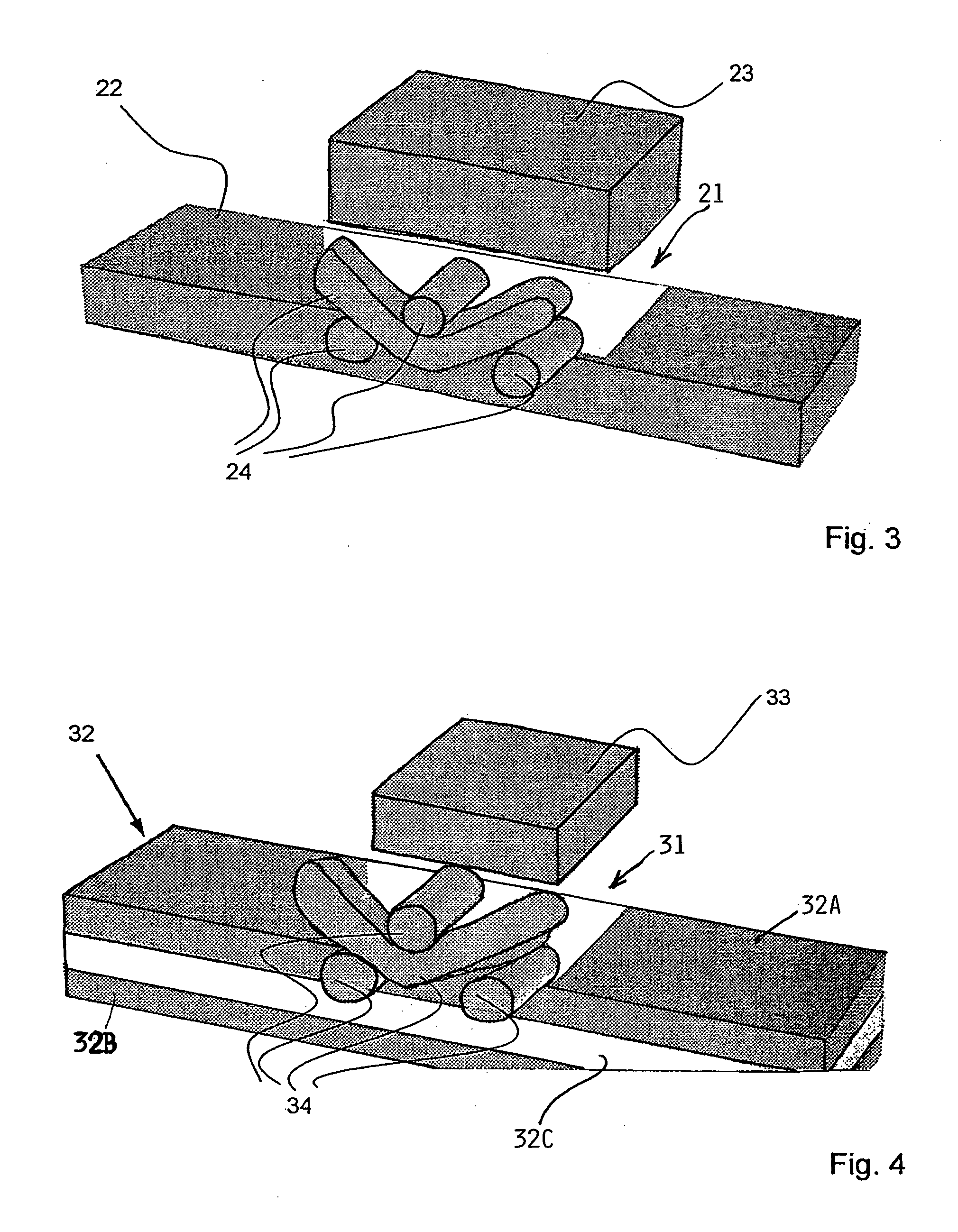
Connection between two components made of reinforced plastic and method for the production thereof
Owner:AUDI AG +1
Direct transfer of multiple graphene layers onto multiple target substrates
InactiveUS20170338312A1IncreaseIncreases production outputSolid-state devicesLaminationCvd grapheneMultiple target
Disclosed is a method of making a conductive material or active material that includes graphene or other 2-D materials. The method includes obtaining a layered stack. The layered stack including one or more conductive materials or 2-D materials separated by a metal layer, and one or more substrate materials. The stack can be subjected to a metal removal process to obtain two conductive or active materials. A first conductive or active material can include a first substrate layer attached to the first active layer. The second conductive or active material can include a second substrate layer attached to the second active layer. The first and second active layers can be conductive graphene layers.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for preparing WC hard alloy wear resistance area on petroleum drill rod surface
ActiveCN102453901AExtended service lifeImprove toughnessMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusHigh power lasersAlloy coating
The invention relates to a method for preparing a WC hard alloy wear resistance area on a petroleum drill rod surface. The method is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out a pretreatment for the petroleum drill rod surface; (2) selecting alloy powder and adjusting an automatic powder feeding device; (3) cladding a bottoming alloy coating by a high power laser; (4) cladding spherical WC and Ni-Cr-B-Si mixed alloy powder by the high-power laser; (5) carrying out defectoscopy inspection after cladding. According to the present invention, the gradient coating method is adopted to prepare the WC hard alloy wear resistance area on the petroleum drill rod surface, the nickel-base alloy powder is adopted as the bottoming layer, the high wear resistance WC hard alloy powder is adopted as the working layer, such that the good binding strength of the working layer and the substrate is ensured in the case of meeting of the working layer characteristics, and the cracks can be prevented from expanding to the substrate during the using process, wherein the nickel-base alloy powder has good toughness and high strength, and has good metallurgy compatibility with the substrate.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
Method for preparing a building material
A method of preparing a building material is provided. An aggregate material, water, a hydraulic binder material, and one or more hydraulic activators are mixed. The hydraulic binder material comprises slag material. The mixture is allowed to harden. A building material is also provided. The building material includes a slag material, and one or more hydraulic activators.
Owner:OPTOS OPTIMALE OSZILLATIONSTECHN
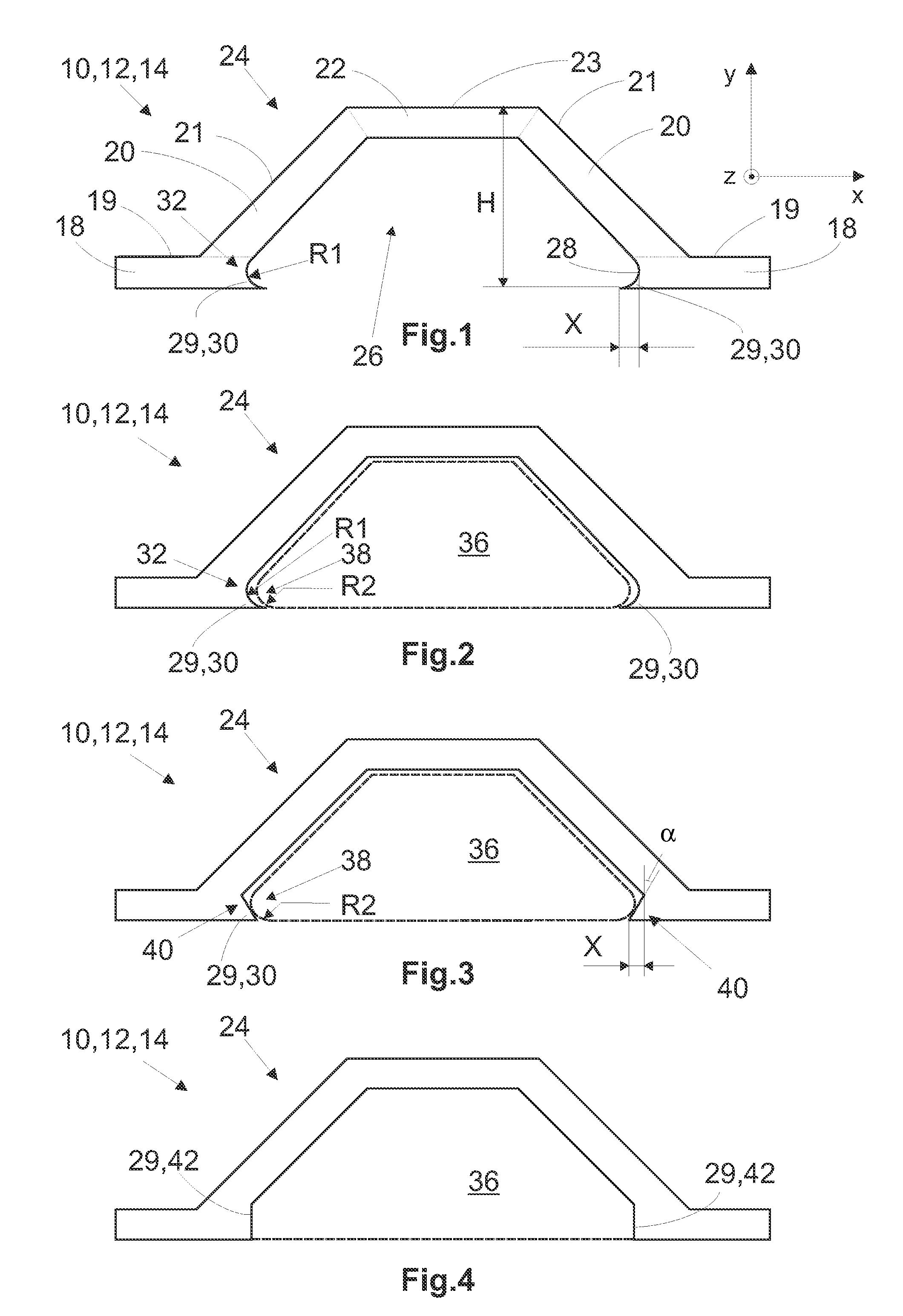
Clip Integration of Pressure Tube Mold Cores into Hardened Omega-Stringers for the Production of Stiffened Fiber Composite Skin Shells, in particular for Aeronautics and Astronautics
ActiveUS20100007056A1Simple componentsReducing and simplifying process stepNon-magnetic metal hullsEfficient propulsion technologiesComposite skinFibrous composites
The invention concerns a device for stiffening a flat component, a process for the production of a flat component, in particular a fiber composite component, and a fiber composite component. The device has a portion for producing a space for receiving a mold core for the transmission of a pressure for pressing the flat component and the device. It is characterised by means for positively lockingly and / or frictionally lockingly positioning the mold core in the space of the device. The process according to the invention includes the following steps: introducing the mold core into the portion of the device, positively lockingly and / or frictionally lockingly positioning the mold core in the portion of the device by means of the means, applying the device including the mold core to the non-hardened material layer or layers, pressing the material layers, and hardening the material layer or layers and joining the device to the material layer or layers.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
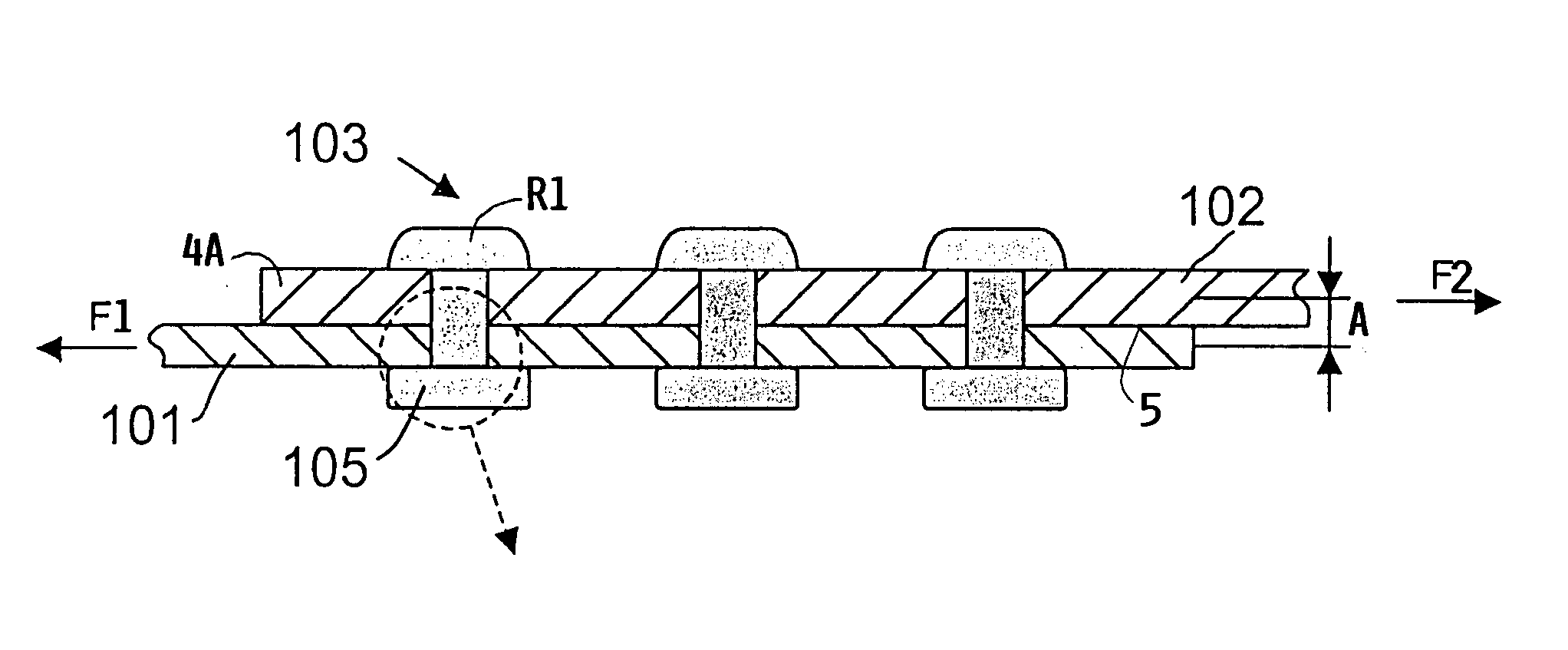
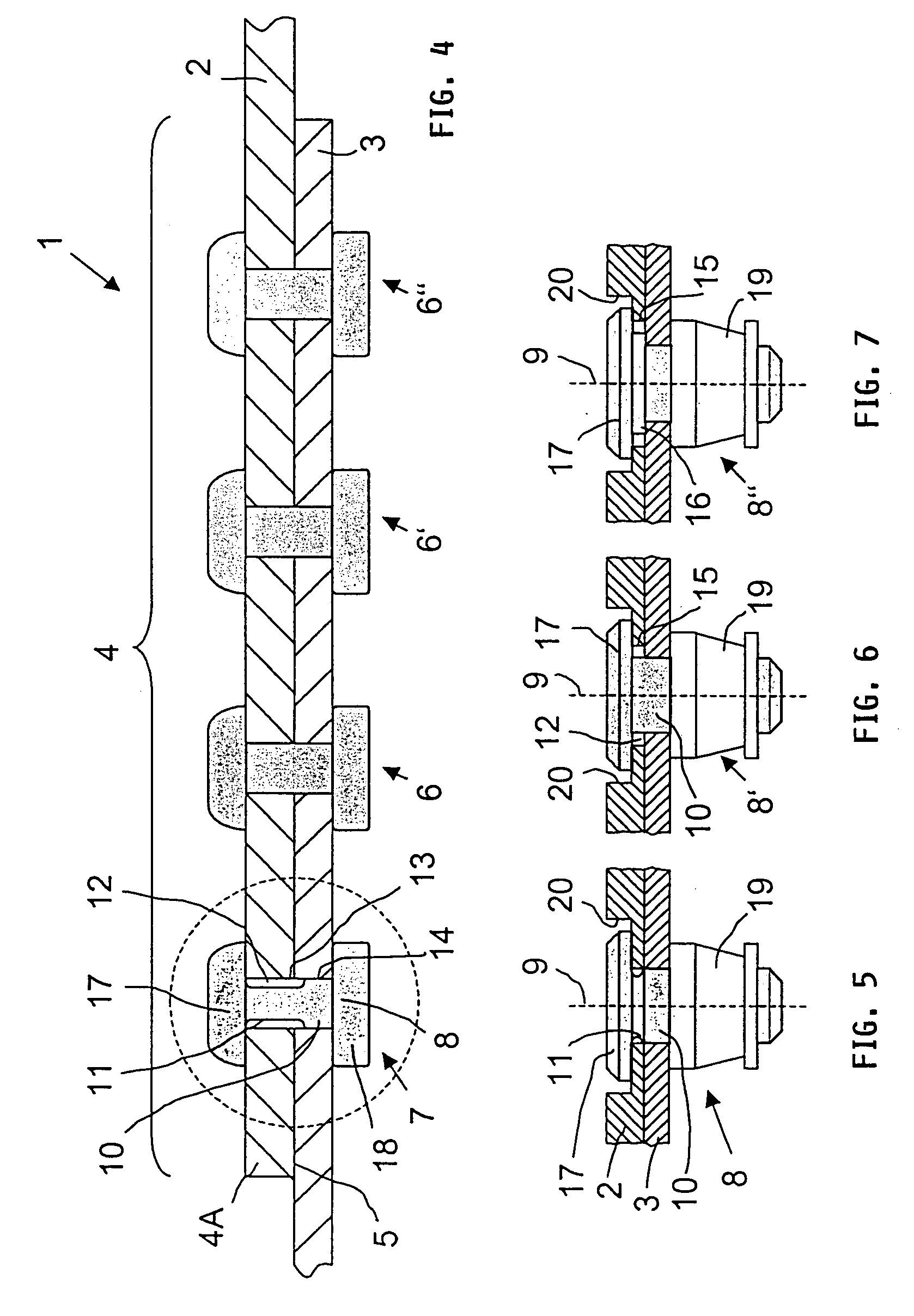
Splicing for interconnected thin-walled metal structures
InactiveUS20040052581A1Improve fatigue strengthComponent with highFuselage framesFuselage bulkheadsMetalRivet
A rivet splice that holds an upper and a lower sheet metal end portion together includes at least one row (6) of rivets that is subject to dynamic loads and a further row (7) of rivets that holds the sheet metal end portions together so that a limited sliding motion between the sheet metal end portions is possible. The further row (7) of rivets is positioned between an end edge (4A) of an upper sheet metal end portion and the at least one row (6) of rivets. The limited sliding motion provides a load relief of the at least one row of rivets thereby reducing the starting of cracks at the walls of the rivet holes and impeding the spreading of cracks.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for preparing WC (Wolfram Carbide) cemented carbide wearing layer on surface of petroleum drilling tool stabilizer through laser cladding
InactiveCN103484852AUniform coatingExcellent wear resistance and corrosion resistanceMetallic material coating processesCemented carbideAutomatic control
The invention discloses a method for preparing a WC (Wolfram Carbide) cemented carbide wearing layer on a surface of a petroleum drilling tool stabilizer through laser cladding. A tough bottoming transition layer which is in good metallurgical bonding with a matrix is formed on the surface of a shell in a fusion covering manner through rapid laser scanning by using a high-power laser, and mixture alloy powder of spherical WC and Ni-Cr-B-Si, which is wearing-resisting and excellent in corrosion resistance, is prepared on the surface of the bottoming alloy through laser cladding. The power, position, shape and the like of a laser beam of the method can be accurately controlled, selective area or even micro-area fusion covering is easy to realize, the dilution rate of coating components is low, the coating thickness can be accurately controlled, non-contact type treatment is adopted, and automatic control is easy to realize in the whole process; in addition, a laser cladding process is non-pollution on the environment, free of radiation and low in noise, has the characteristics that the productivity is high, the energy consumption is low, the cladding layer machining margin is small, the finished product rate is high, the comprehensive cost is low, and the like, and can be widely applied.
Owner:武汉团结点金激光科技有限公司
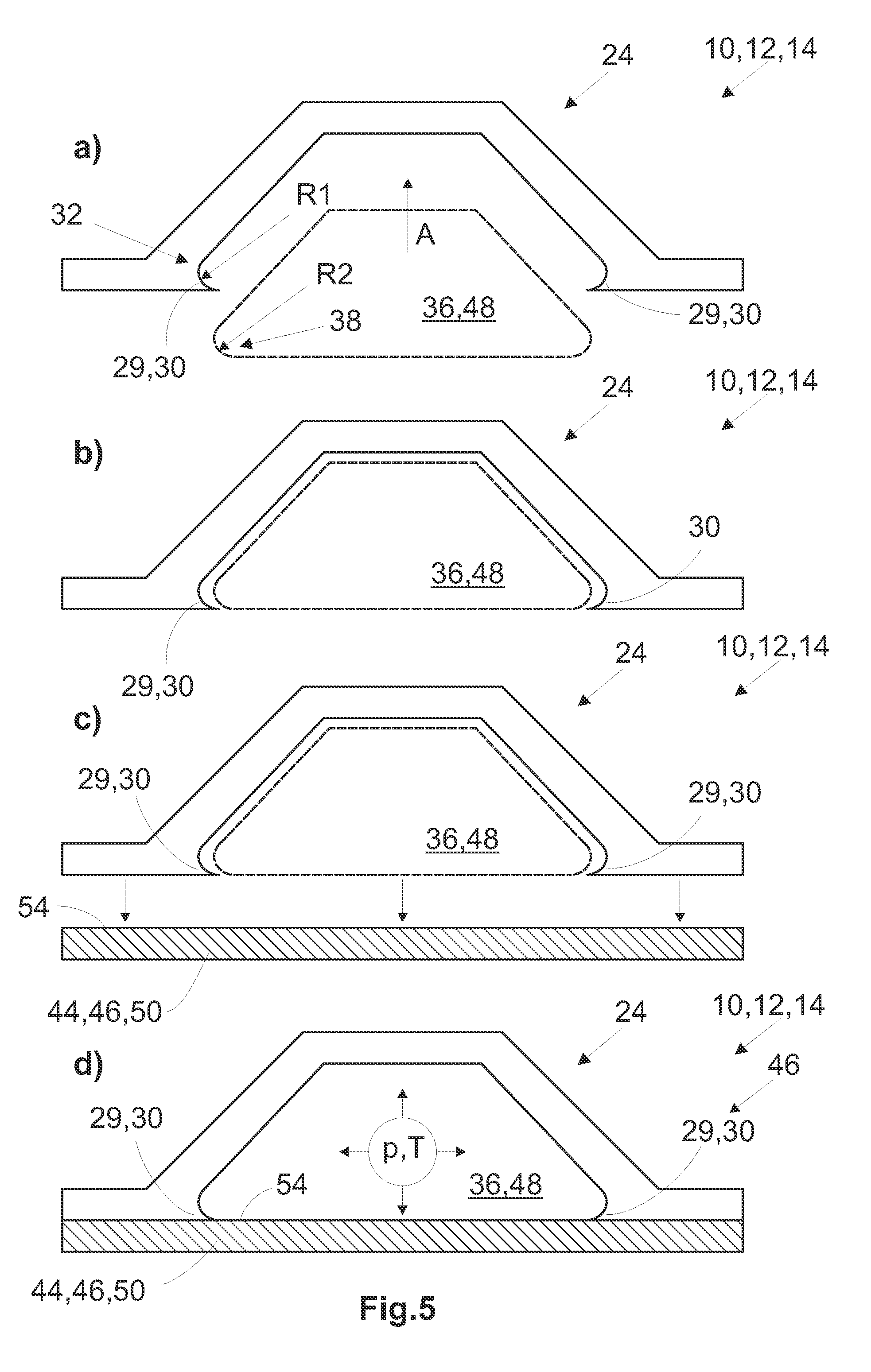
Lightweight structure especially for an aircraft and method for making such a structure
ActiveUS20050112347A1Decrease their propagationExtended service lifeNon-woven fabricsThin material handlingEngineeringParallel fiber
An additional fiber reinforced layer reduces crack propagation in a lightweight structure of an outer skin adhesively bonded to a reinforcing frame. For this purpose the additional fiber reinforced layer is interposed between the outer skin and the frame and adhesively bonded to the outer skin and to the frame. The additional layer has reinforcing fibers extending in parallel to each other or the reinforcing fibers are woven into a fabric embedded in a synthetic adhesive bonding material. The embedding of the parallel fibers or of the fiber fabric in the bonding material is performed either prior to the bonding or during the bonding of the additional layer to the outer skin and to the reinforcing frame.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for preventing crack formation and for slowing down the advancement of a crack in metal aircraft structures by means of laser shock rays
ActiveUS20110290770A1Reduce crack formationDelay progressAircraft maintainanceLaser beam welding apparatusShock waveCrazing
The present invention provides a method for preventing the forming of cracks and slowing the crack propagation in metallic airplane structural parts by laser shock peening with the following steps: Providing an airplane structural part having a crack; irradiating a first surface area of the airplane structural part close to the crack with a first pulsed laser beam having a first wavelength and a first pulsation frequency, wherein energy of the first laser beam is absorbed by the airplane structural part and a shock wave runs through the airplane structural part, which creates compressive prestressings in the airplane structural part.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
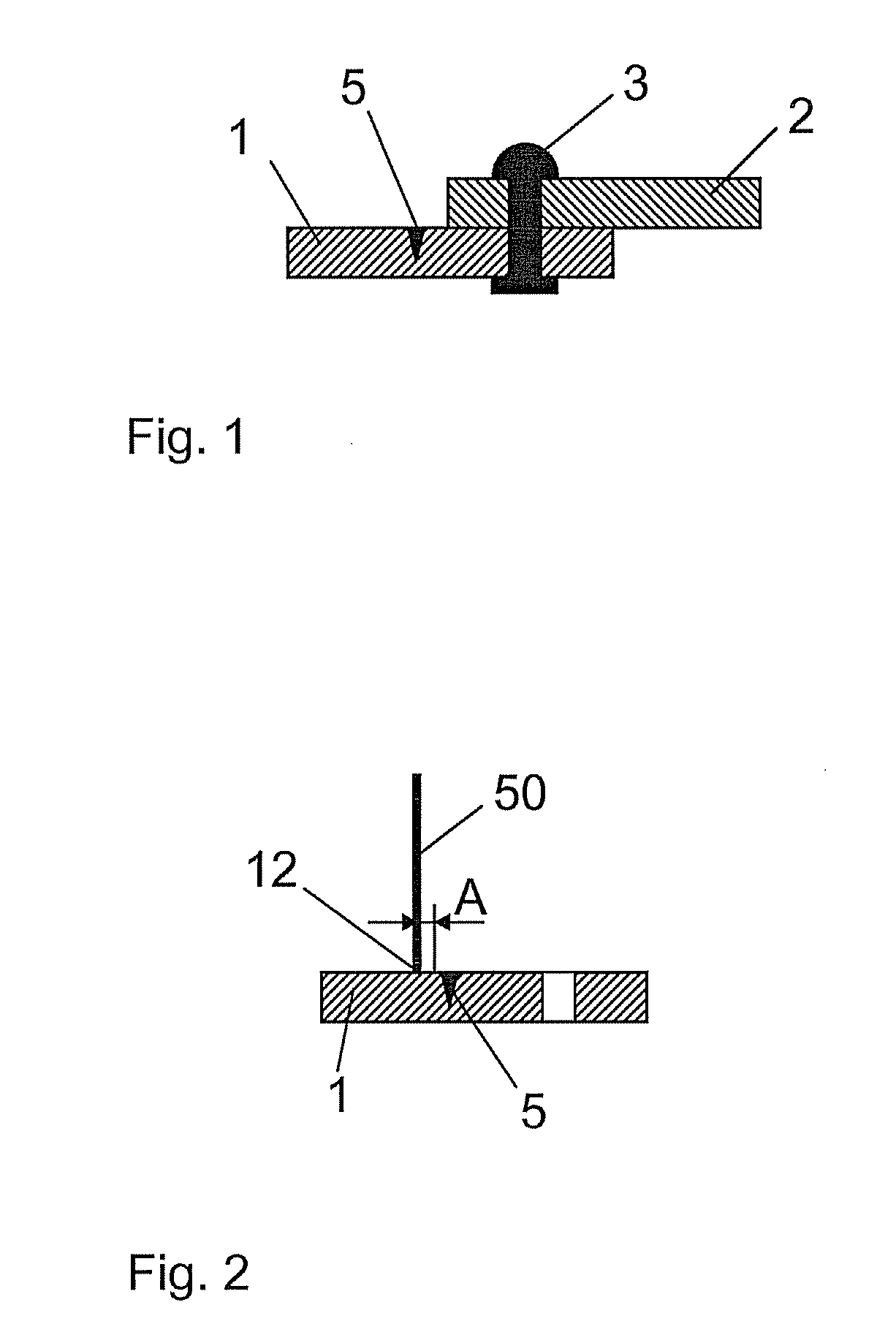
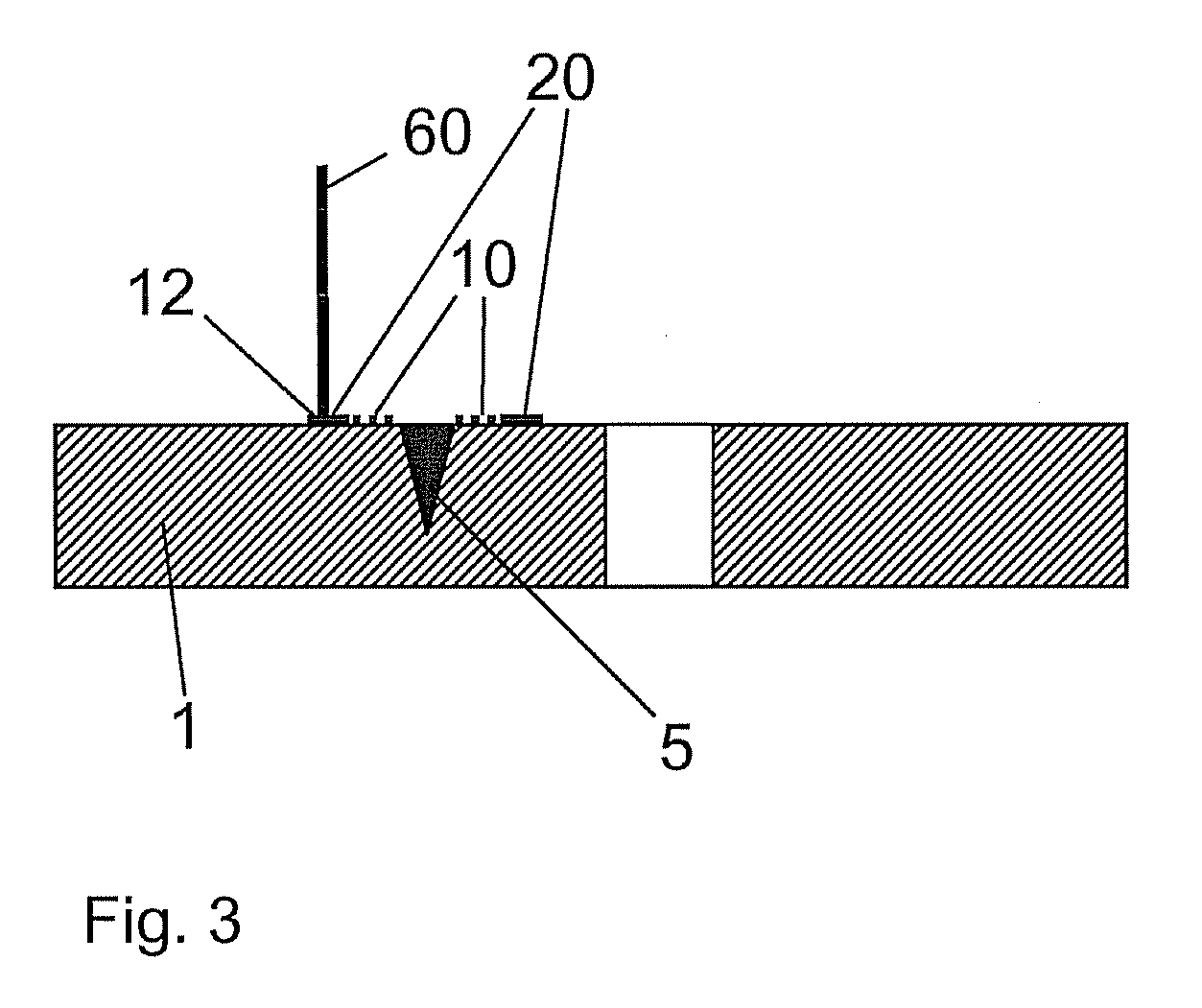
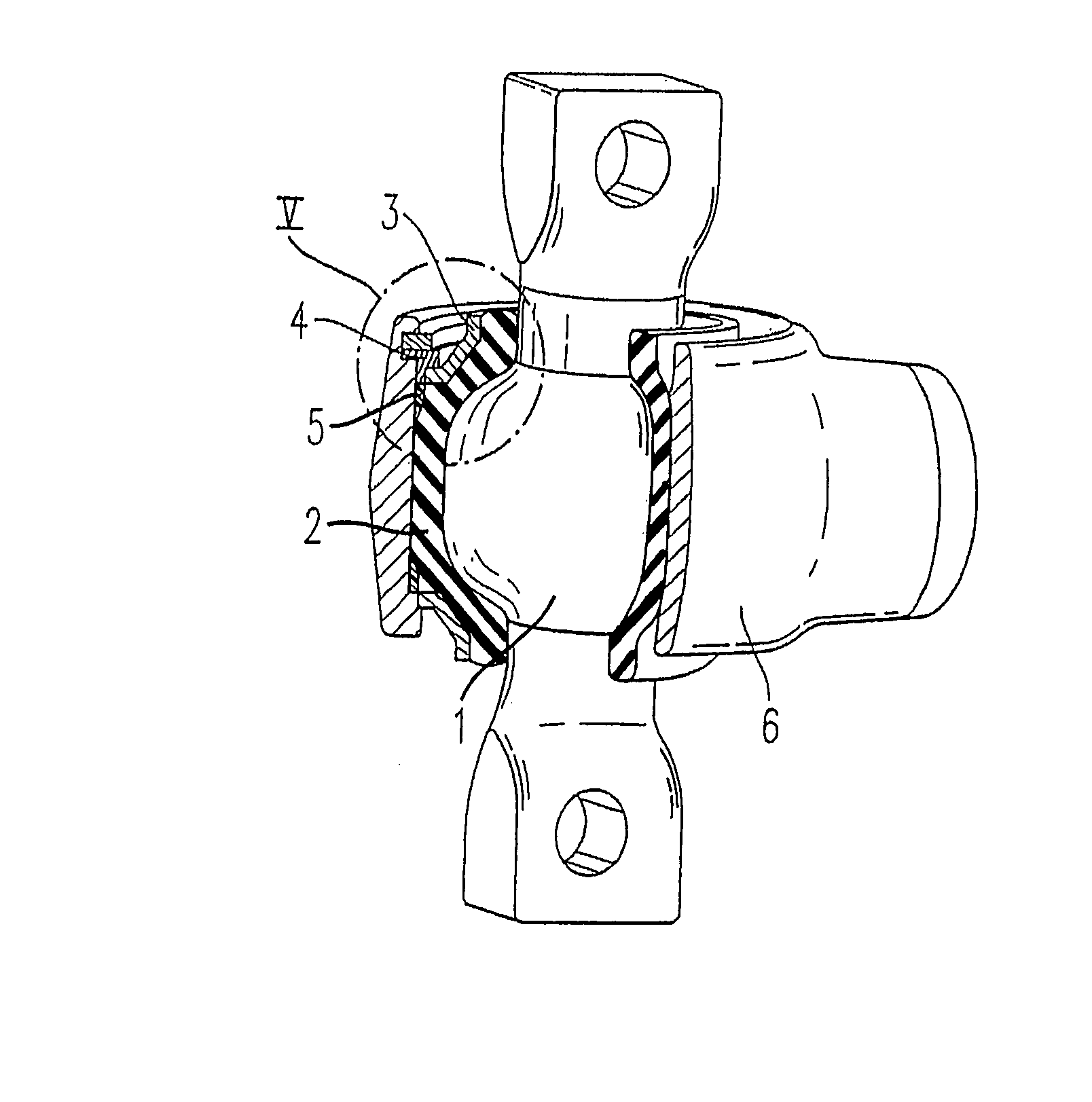
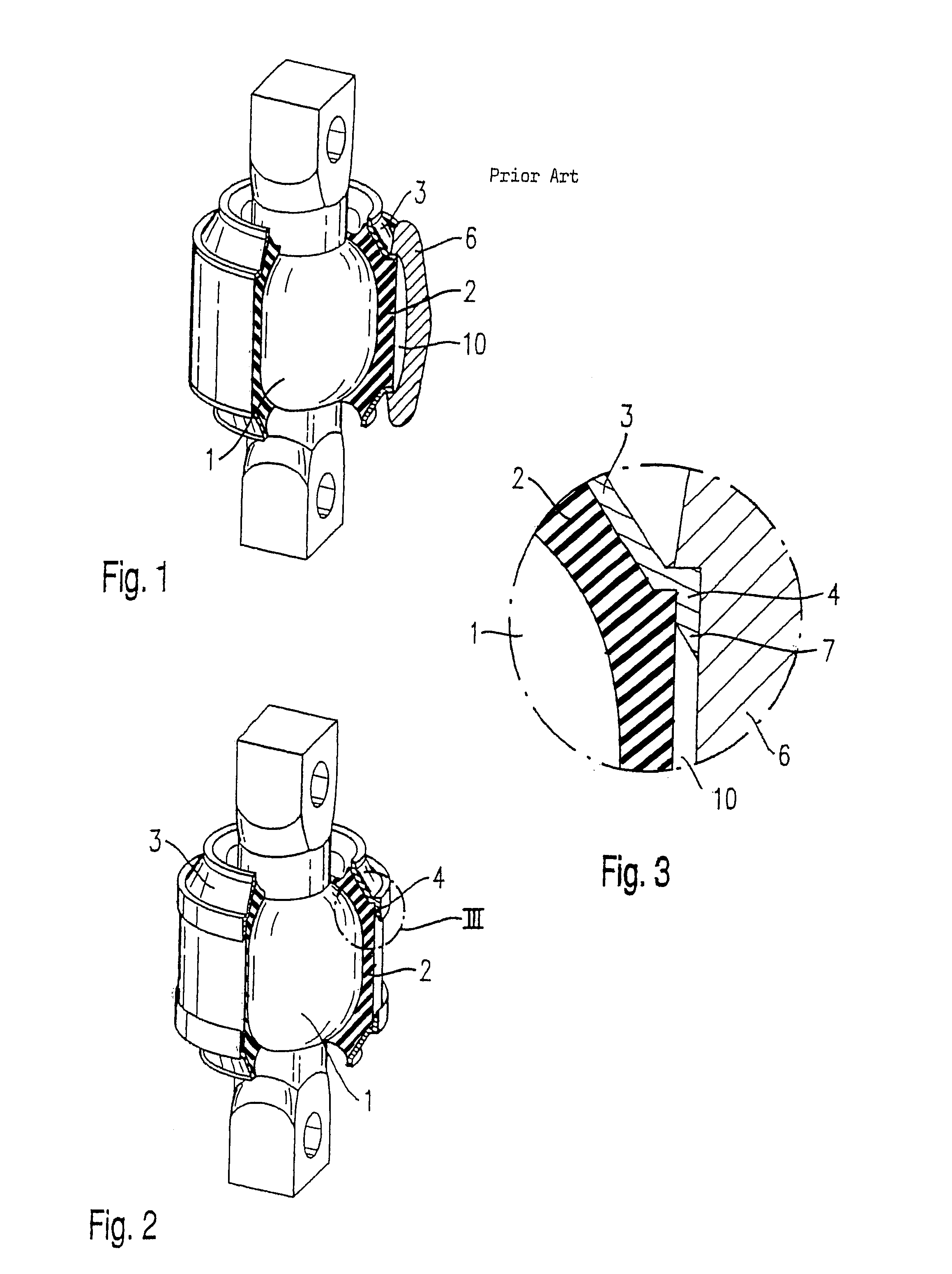
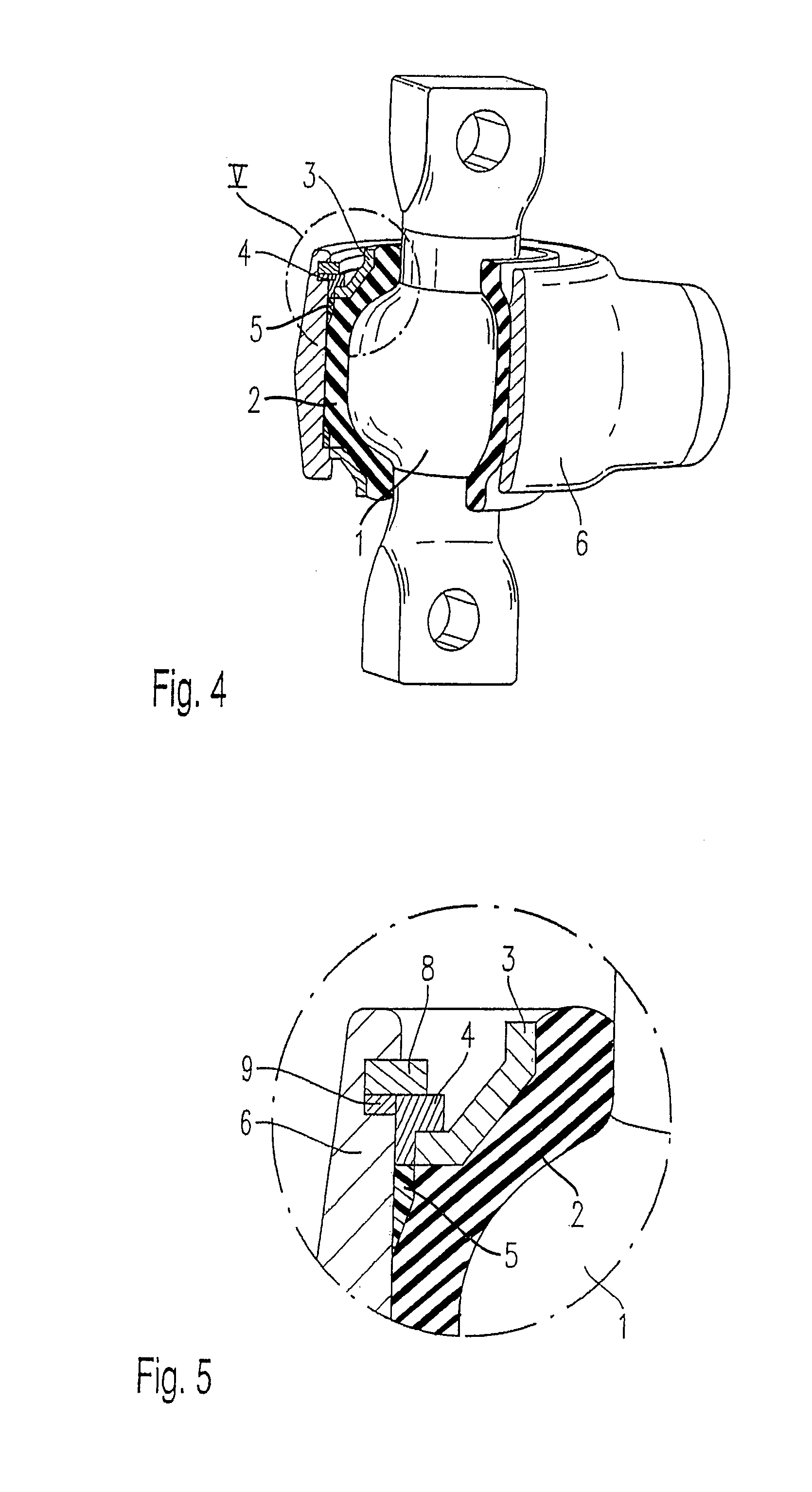
Elastomer joint
ActiveUS7306393B2Decrease in torsional rigidityEasy to useDrill bitsSprings/dampers functional characteristicsElastomerEngineering
An elastomer joint, in particular for chassis parts of motor vehicles, comprising a housing (6), an elastomer body (2) arranged in the housing (6), and a joint body (1) that is arranged in the elastomer body (2), is characterized in that the housing (6) has a cylindrical inner wall, and a spacer (4) is provided that is arranged at an axial end of the elastomer body (2) between the latter and the inner wall.
Owner:THK RHYTHM AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
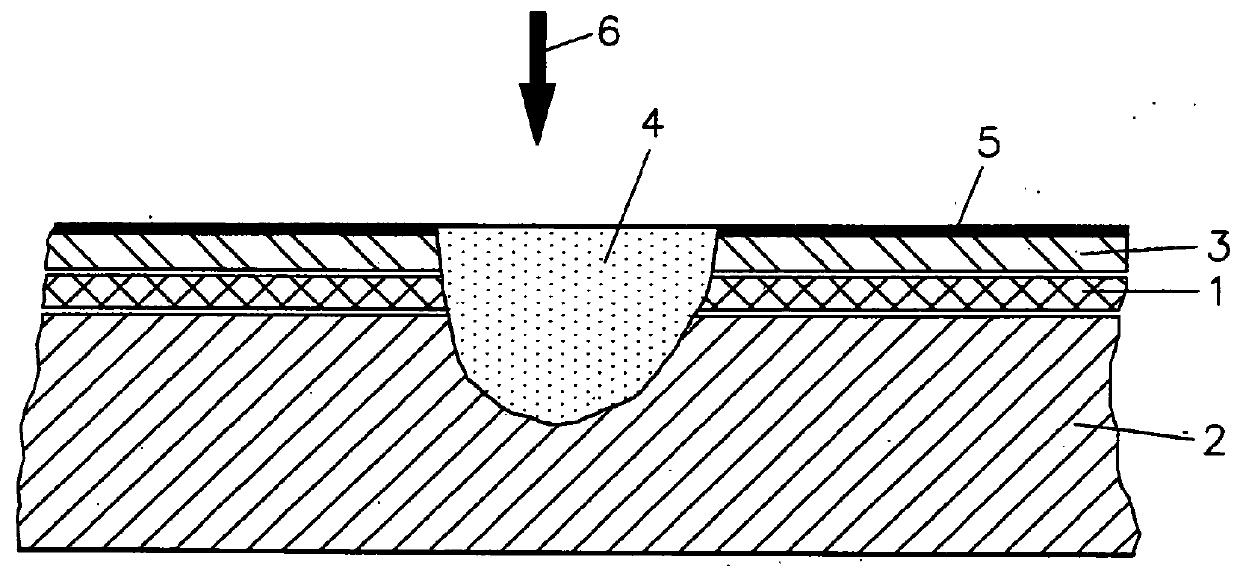
Aluminum and copper material interconnection and method of producing such an interconnection
InactiveUS20160031042A1Reduce decreaseReduce reflectionCooking-vessel materialsWelding/cutting media/materialsInterconnectionWeld seam
In a material-interlocking connection between aluminum and copper in a layer assembly comprising an aluminum layer disposed on a copper element and a copper layer disposed on the aluminum layer, a weld seam is formed on the top copper layer so as to form a weld which extends through to top copper layer and the aluminum layer into the copper element so as to form in the weld seam an alloy of copper and aluminum.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
Method for preparing a building material
A method of preparing a building material is provided. An aggregate material, water, a hydraulic binder material, and one or more hydraulic activators are mixed. The hydraulic binder material comprises slag material. The mixture is allowed to harden. A building material is also provided. The building material includes a slag material, and one or more hydraulic activators.
Owner:OPTOS OPTIMALE OSZILLATIONSTECHN
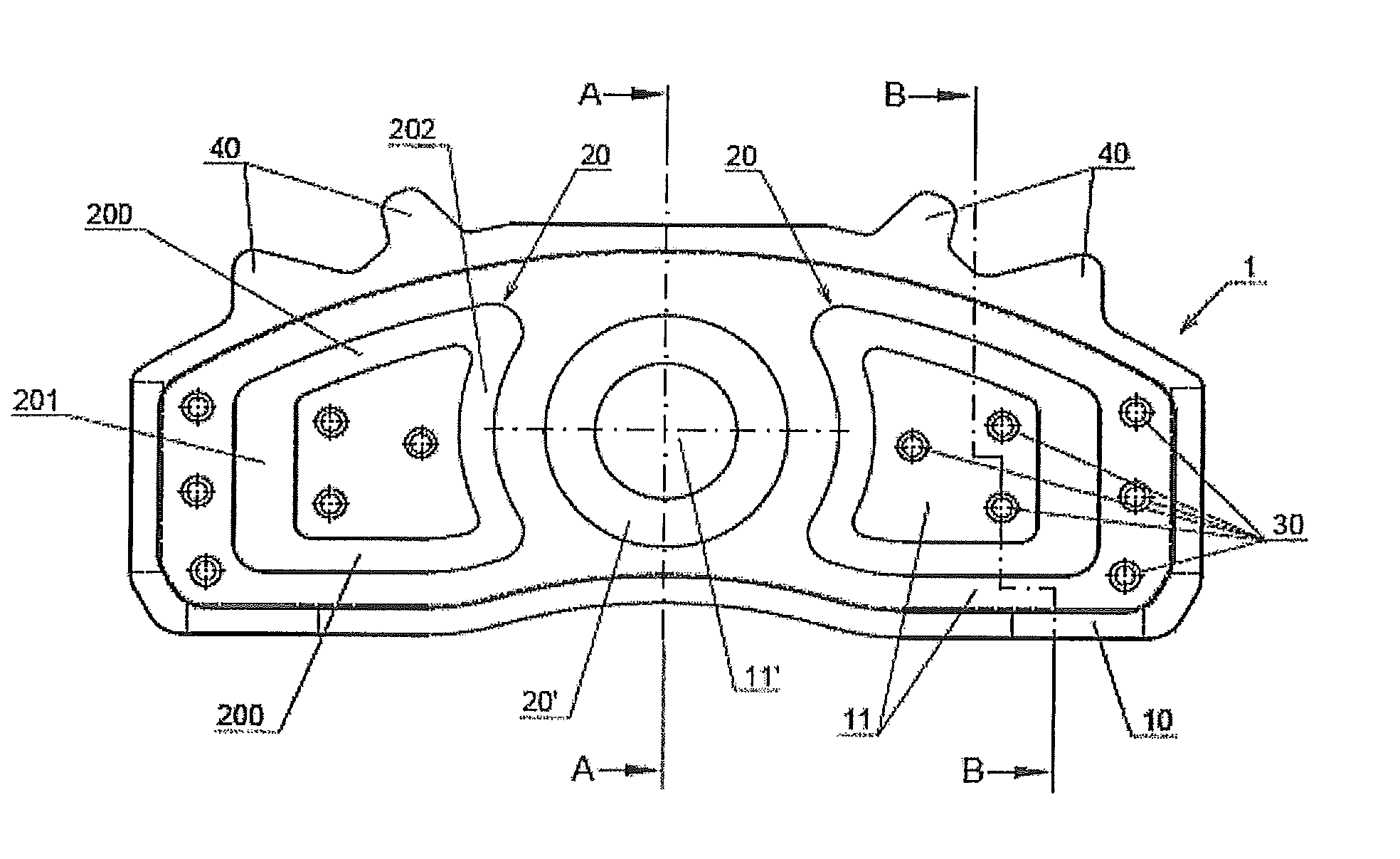
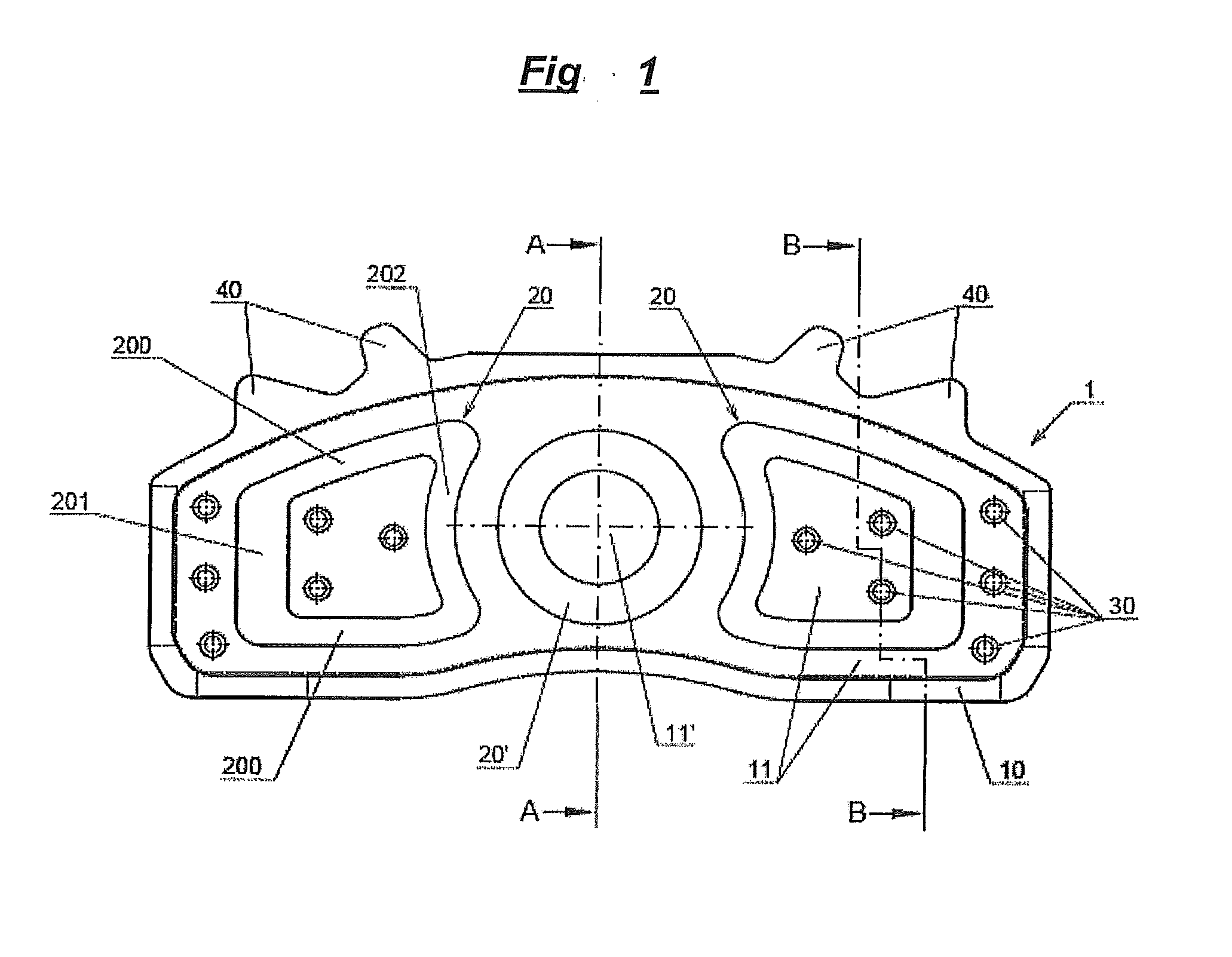
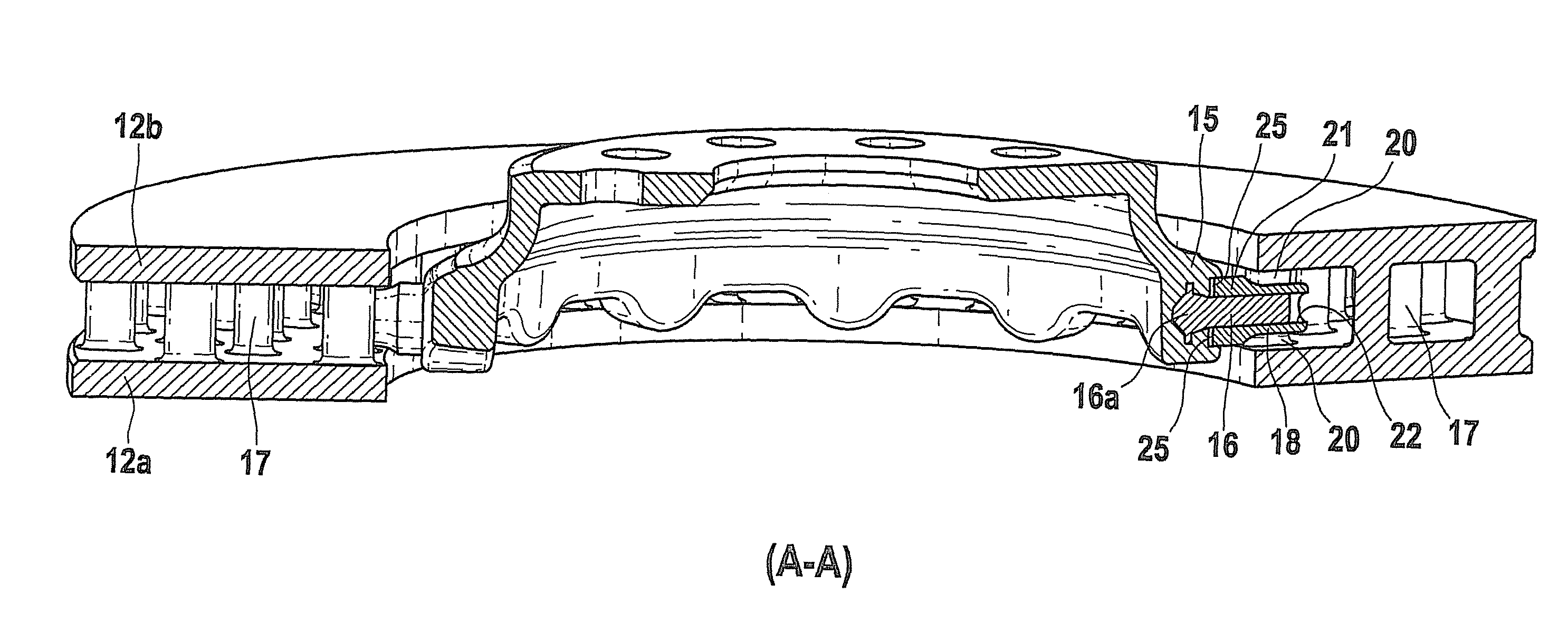
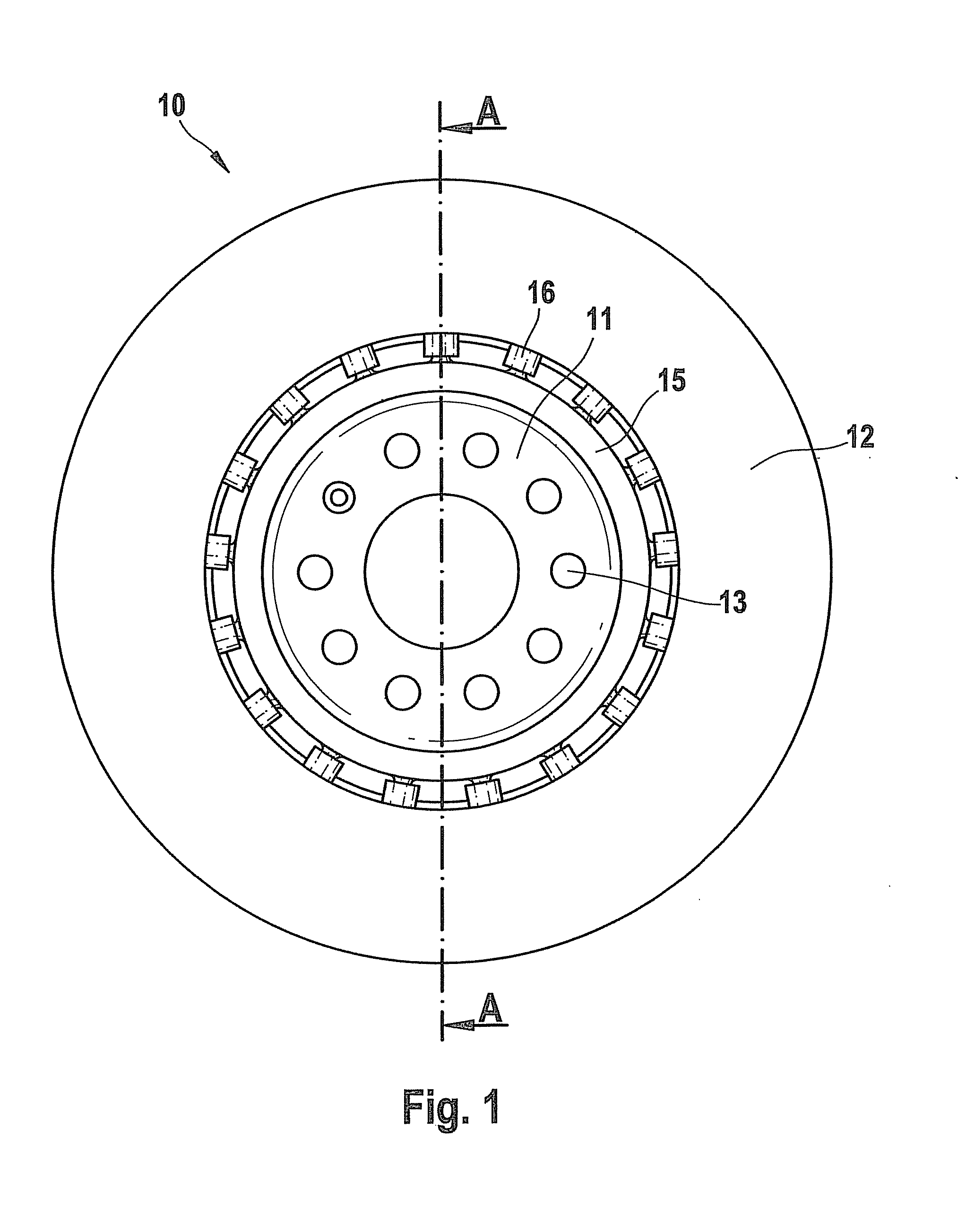
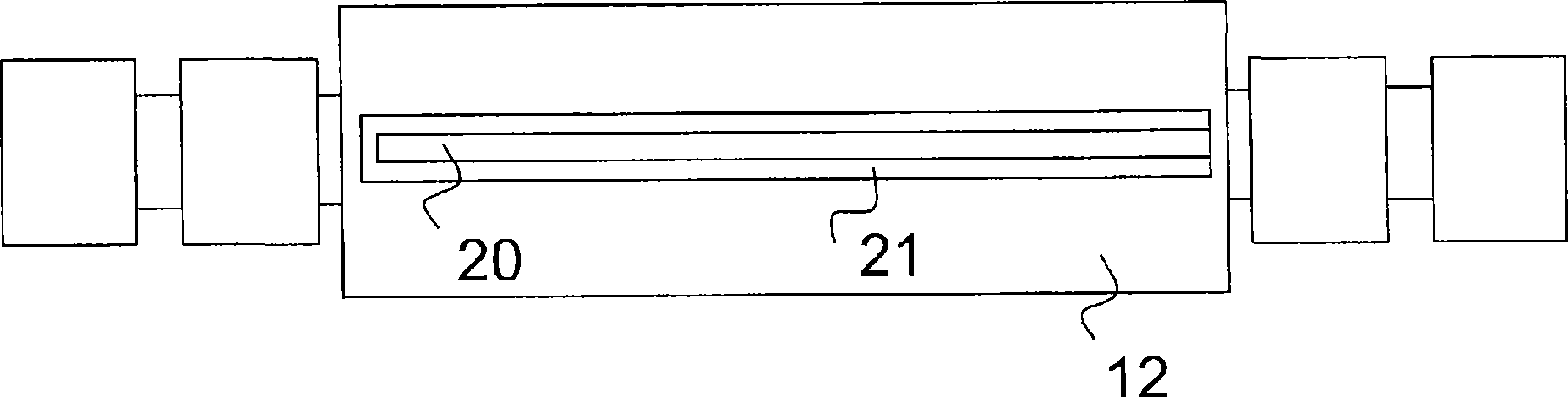
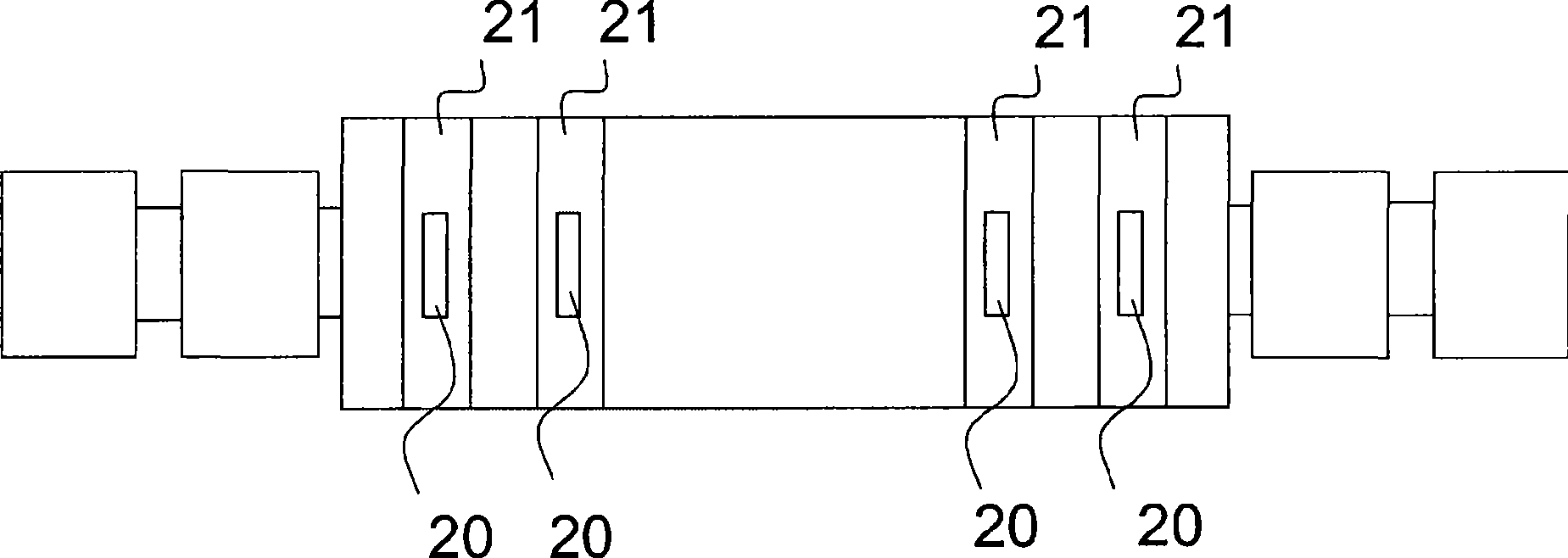
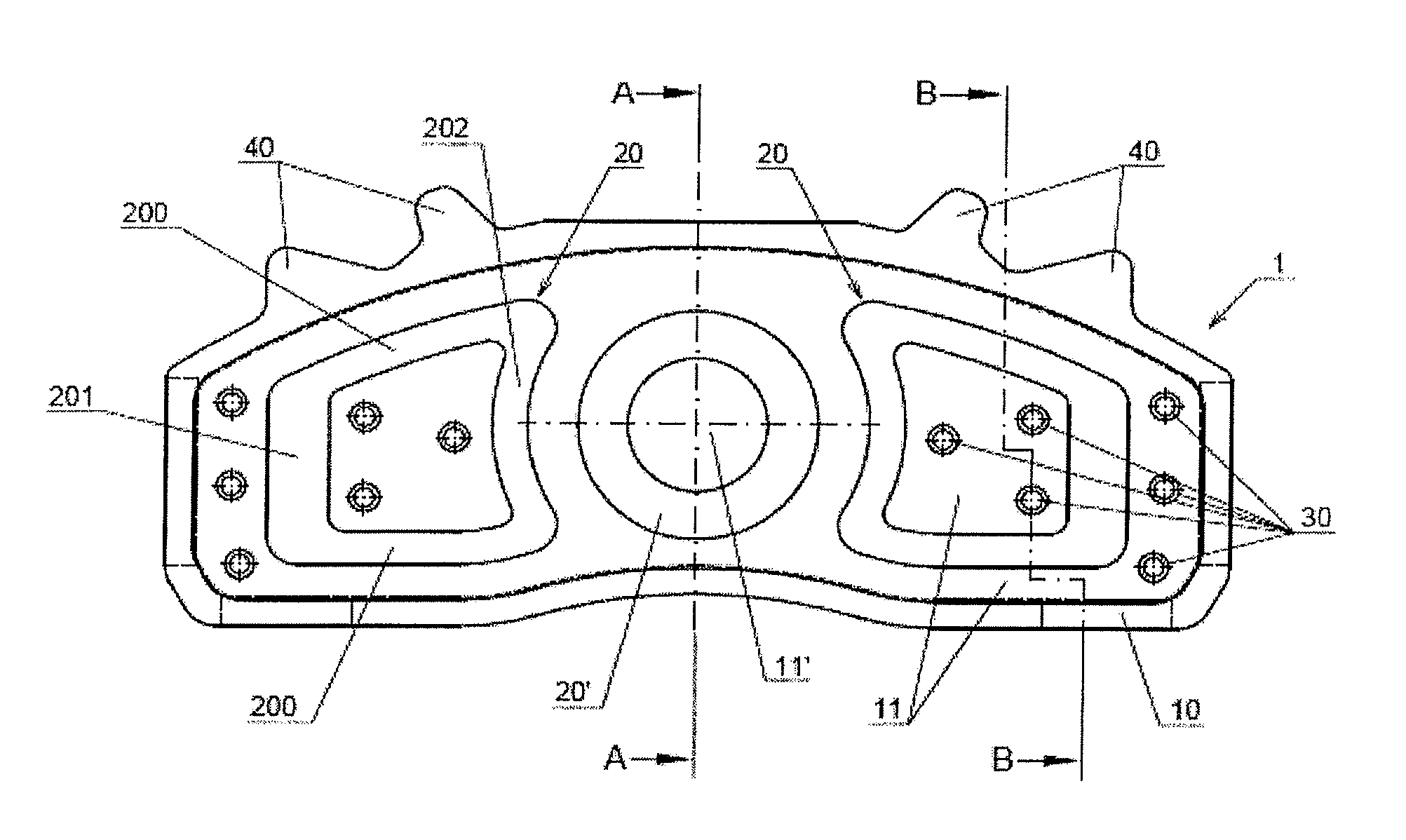
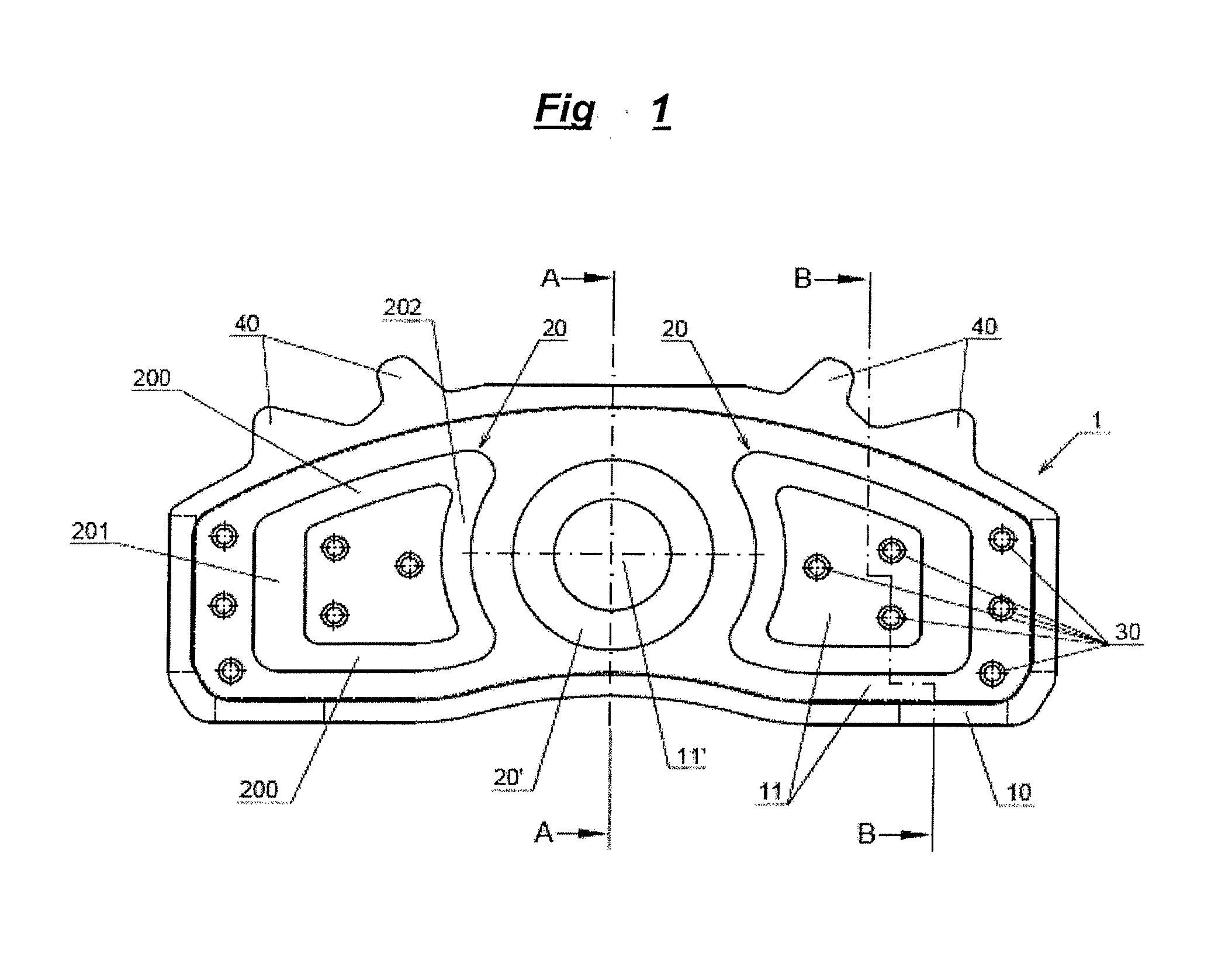
Friction lining carrier plate
InactiveUS20130277159A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease stiffnessBraking membersFriction liningMetal sheet
The invention relates to a friction lining carrier plate (1), which has a metal sheet, to a friction lining, to a friction lining receptacle and to a brake. The metal sheet is formed in such a manner that it has a first and second recess (11, 20) on the friction lining side, wherein the metal sheet has at least a second recess (20) on the friction lining side, wherein the first and second recesses (11, 20) have a differing depth. The first and second recesses on the friction lining side are each formed as an elevation on the side of the actuation means.
Owner:TMD FRICTION SERVICES +1
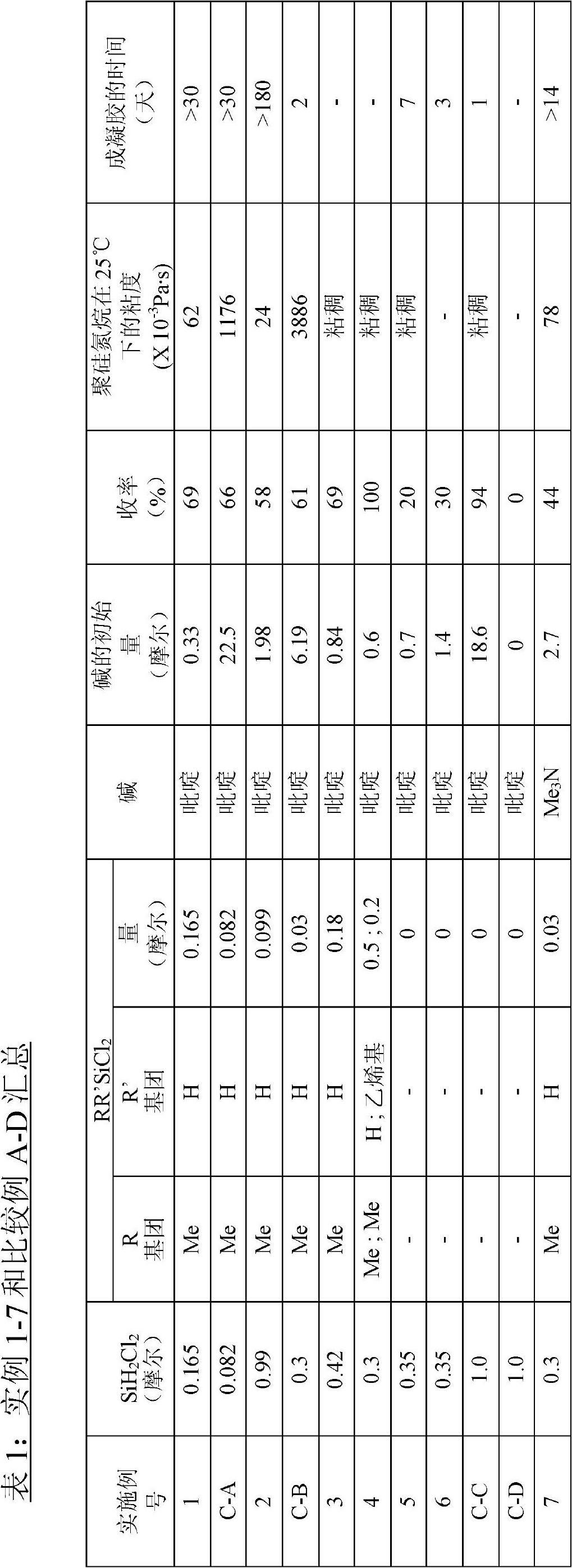
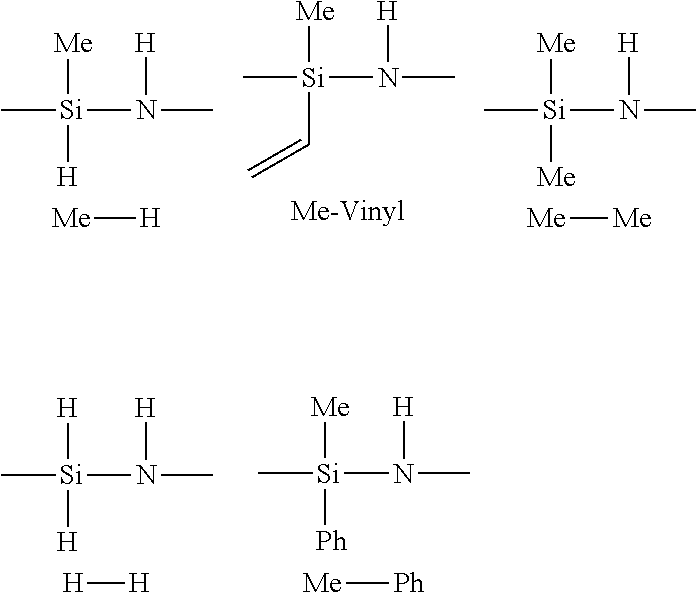
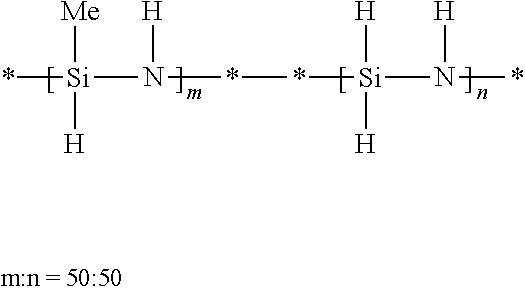
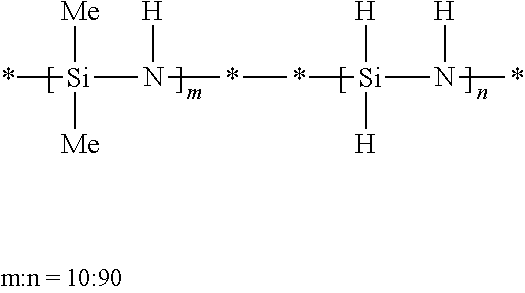
Process for preparing shelf-stable curable polysilazanes, and polysilazanes prepared thereby
A process for preparing curable oligomeric and / or polymeric polysilazanes comprises (a) forming at least one dihalosilane-base adduct by reacting at least one dihalosilane with at least one base; (b) optionally, combining at least one dihalosilane-base adduct and at least one organodihalosilane; and (c) carrying out ammonolysis of at least one dihalosilane-base adduct or of the resulting combination of at least one dihalosilane-base adduct and at least one organodihalosilane; with the proviso that the base (1) is used for the dihalosilane-base adduct formation in a limited amount that is less than or equal to twice the stoichiometric amount of silicon-halogen bonds in the dihalosilane or (2) is used for the dihalosilane-base adduct formation in excess of this limited amount and, prior to the ammonolysis, the total amount of the resulting reacted and unreacted base is reduced to no more than this limited amount.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Joined bodies, luminous containers and assemblies for high pressure discharge lamps
InactiveUS7187128B2Improve joint strengthAvoid crackingSolid cathode detailsTube/lamp vessels closingEngineeringHigh pressure
A joined body is provided, including a first member having a first joining face and sapphire exposed at the first joining face and a second member having a second joining face and sapphire or polycrystalline alumina exposed at the second joining face. The first member and second member are joined by providing a raw material for the joining material between the first and second members and heat treating the raw material at a temperature of 1730° C. or lower.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Cellulose ether composition for the extrusion of mineral shaped bodies and also a process for the extrusion of mineral shaped bodies using this cellulose ether composition
A description is given of a cellulose ether composition as additive for the extrusion of mineral masses which comprises 70 to 99.9% by weight of cellulose ether and 0.1 to 30% by weight of superabsorbent polymer, as well as a process for the extrusion of mineral masses using these compositions as additive.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method for preparing WC hard alloy wear resistance area on petroleum drill rod surface
ActiveCN102453901BExcellent wear resistance and corrosion resistanceImprove surface wear resistanceMetallic material coating processesHigh power lasersAlloy
The invention relates to a method for preparing a WC hard alloy wear resistance area on a petroleum drill rod surface. The method is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out a pretreatment for the petroleum drill rod surface; (2) selecting alloy powder and adjusting an automatic powder feeding device; (3) cladding a bottoming alloy coating by a high power laser; (4) cladding spherical WC and Ni-Cr-B-Si mixed alloy powder by the high-power laser; (5) carrying out defectoscopy inspection after cladding. According to the present invention, the gradient coating method is adopted to prepare the WC hard alloy wear resistance area on the petroleum drill rod surface, the nickel-base alloy powder is adopted as the bottoming layer, the high wear resistance WC hard alloy powder is adopted as the working layer, such that the good binding strength of the working layer and the substrate is ensured in the case of meeting of the working layer characteristics, and the cracks can be prevented from expanding to the substrate during the using process, wherein the nickel-base alloy powder has good toughness and high strength, and has good metallurgy compatibility with the substrate.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
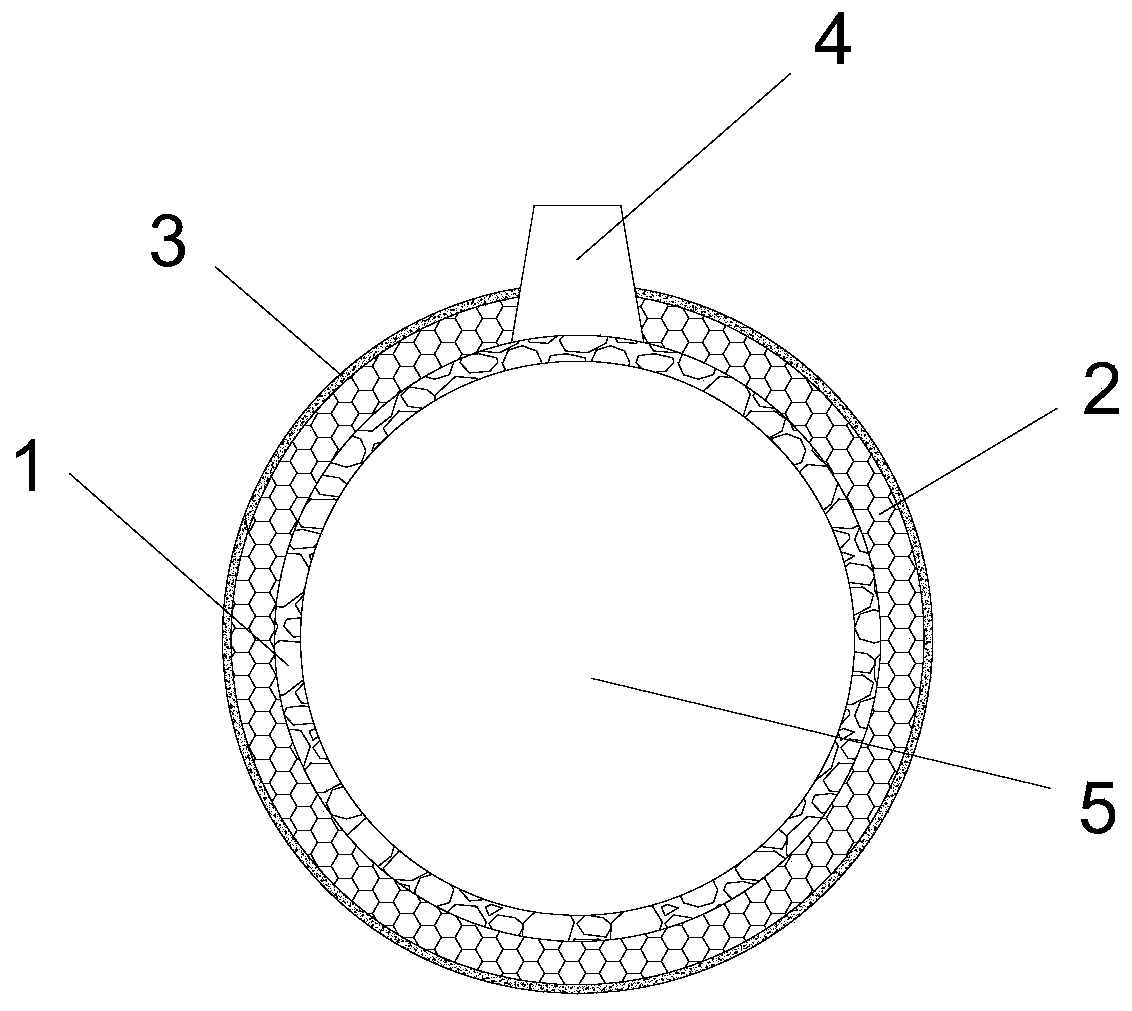
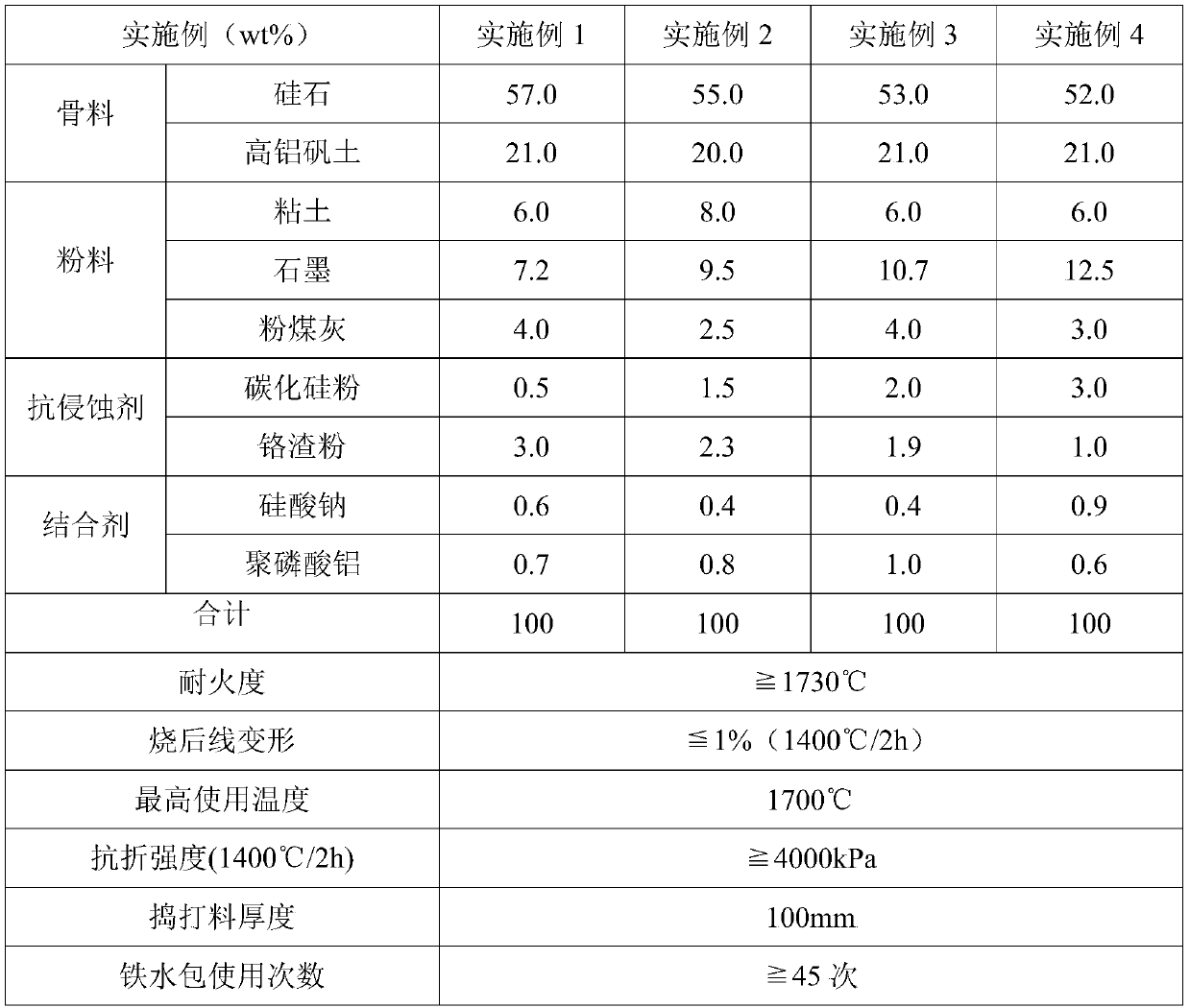
Ramming material for ladle lining and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a ramming material for a ladle lining and a preparation method thereof. The ramming material comprises the following raw materials: 52 to 57 percent of silica, 20 to 23 percent of high-alumina bauxite, 5 to 10 percent of clay, 5 to 15 percent of graphite, 0.1 to 5 percent of fly ash, 0.2 to 5 percent of silicon carbide power, 0.1 to 3 percent of chromium slag powder, 0.1 to 1 percent of sodium silicate and 0.1 to 1 percent of aluminum polyphosphate. Advantages of the invention are as follow: as that structure strength is high in the use process, it will not cause ladleleakage accidents due to loosening, peeling and other damages in the use process, thus ensuring the safety of people and equipment around the ladle during lifting and transporting, preventing molteniron from sticking to the ladle, preventing wrapping of molten iron in slag, improving the recovery rate of molten iron, and greatly improving the safety and economy.
Owner:鄂尔多斯市瀚博科技有限公司
Brake disk
A brake disk is described that has a friction ring and a disk pot that is connected to the friction ring via connecting elements. On the webs of the friction ring, bearer webs are fashioned into which the connecting elements extend. In addition, the bearer webs are fashioned in such a way that cooling air can flow around them.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
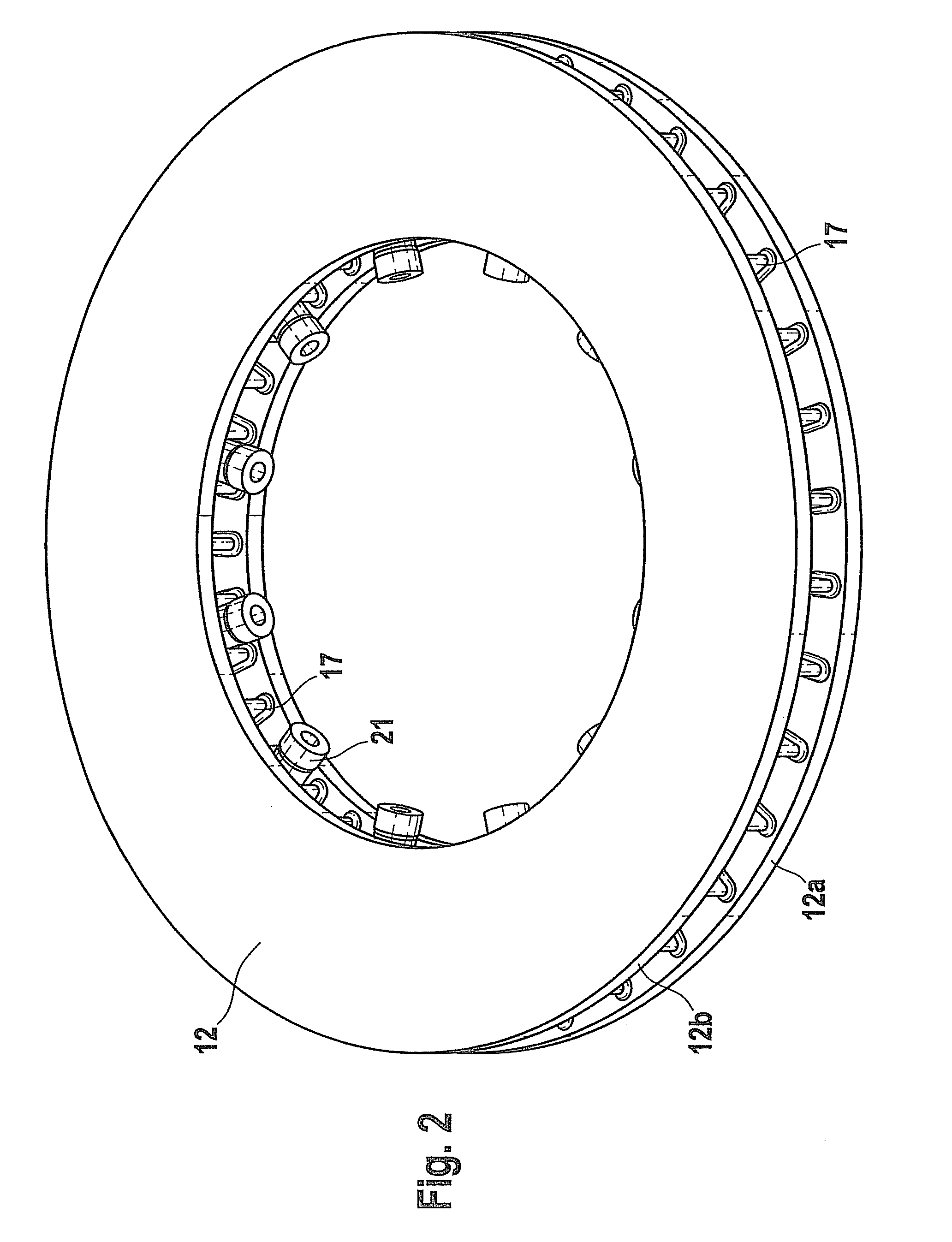
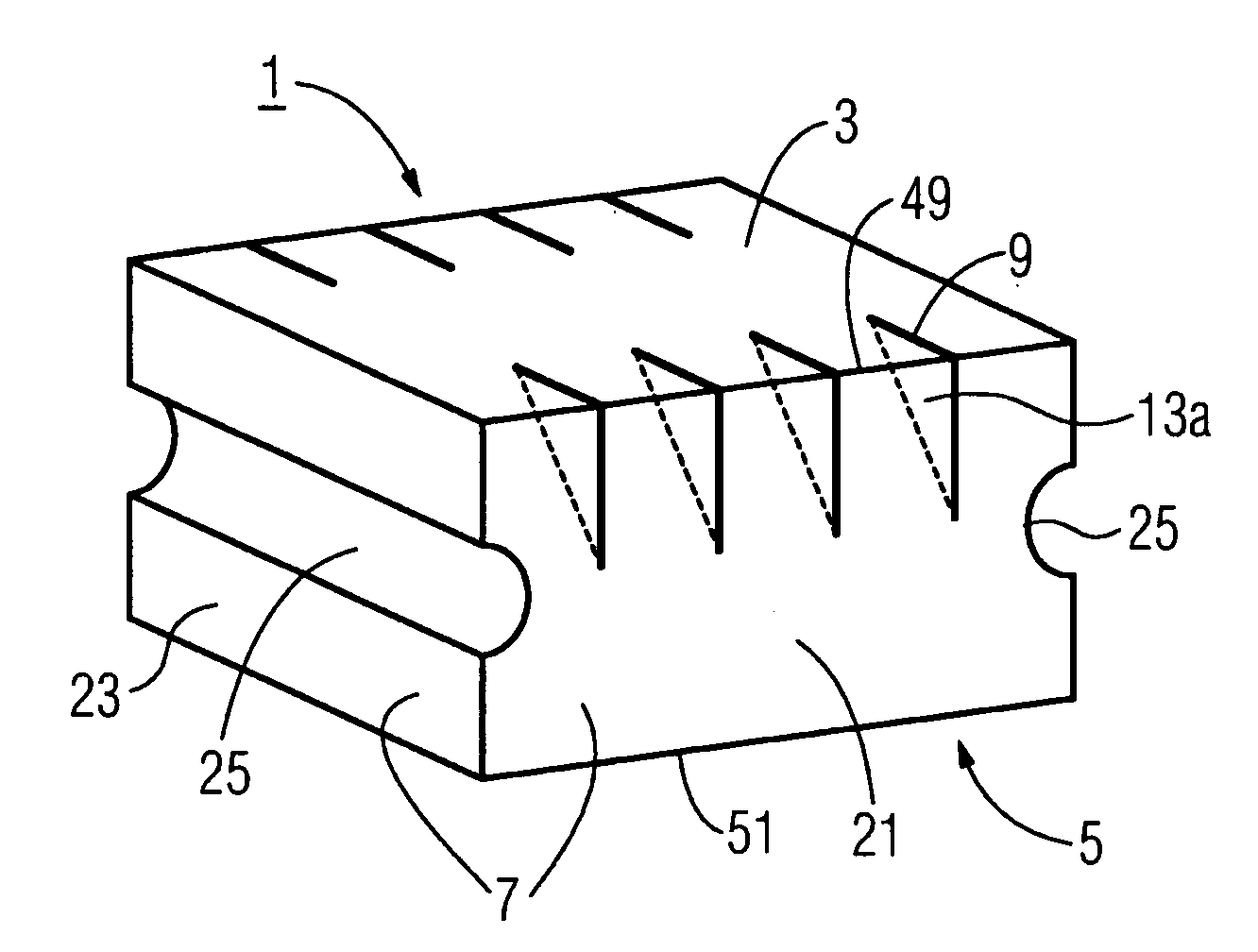
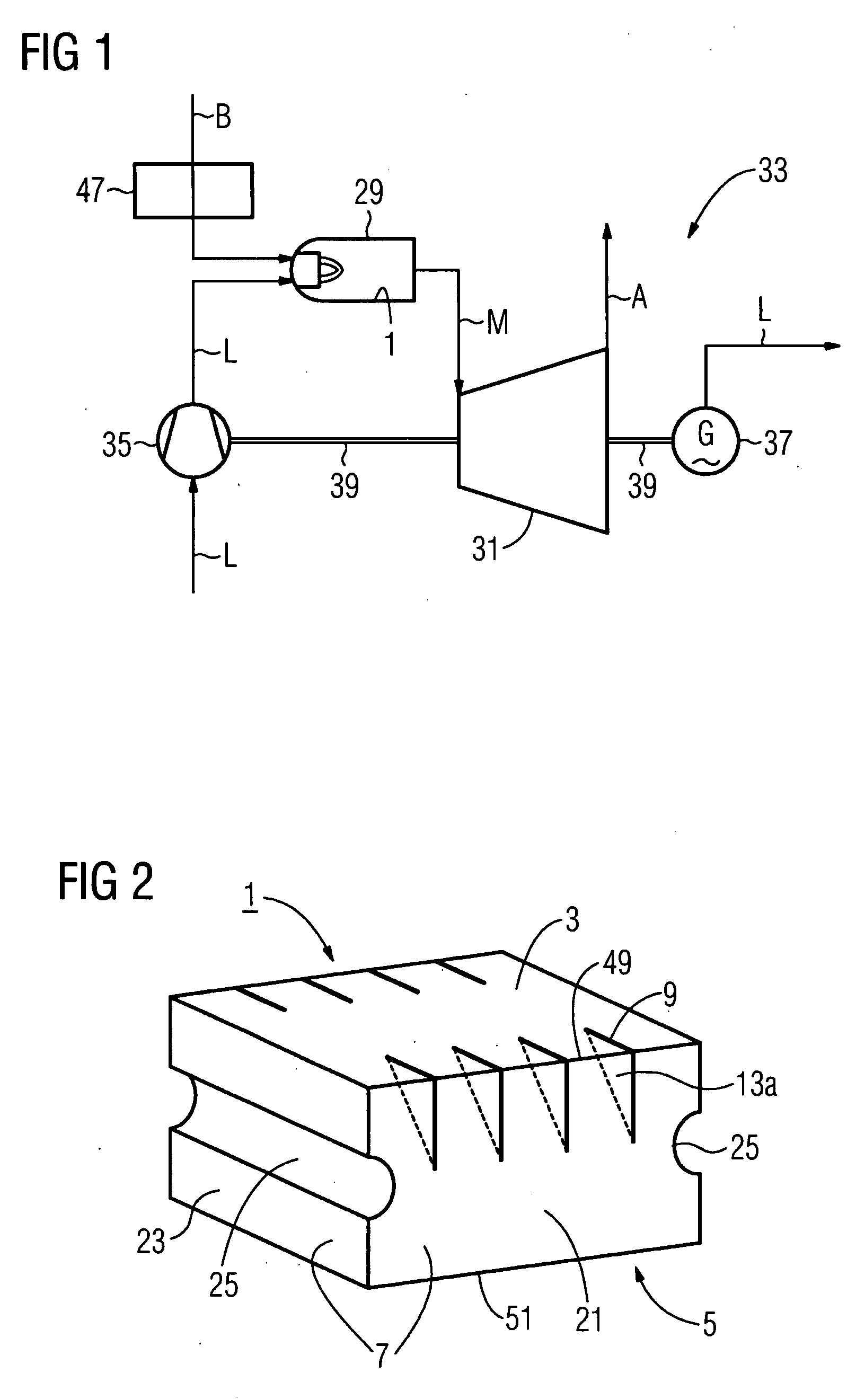
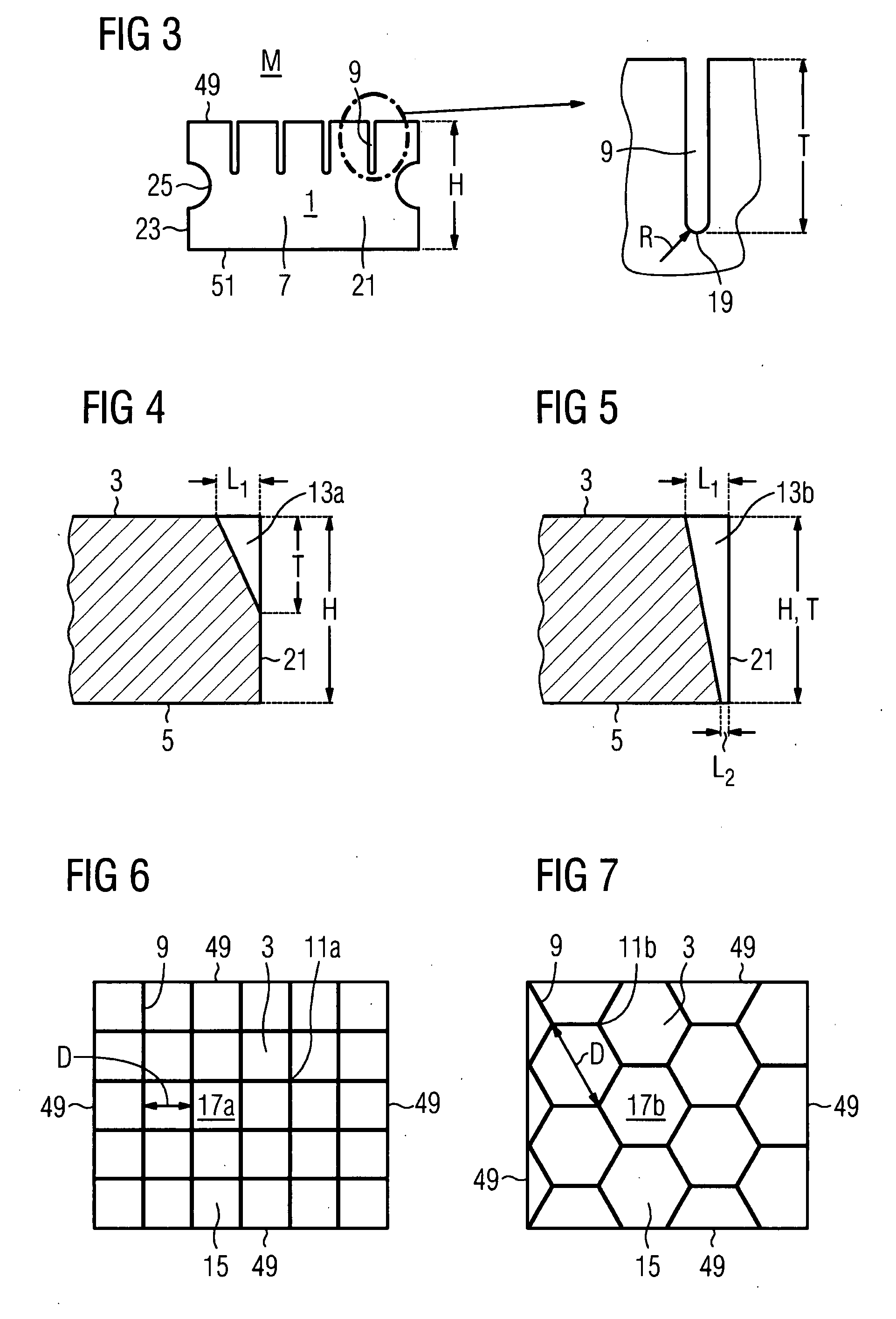
Heat shield element for lining a combustion chamber wall, combustion chamber and gas turbine
InactiveUS20090077975A1Short section lengthRisk of crack is greatContinuous combustion chamberLining supportsCombustion chamberMaterial Crack
The invention relates to a heat shield element for lining a combustion chamber wall, to a combustion chamber and to a gas turbine. The heat shield element comprises a hot side that can be exposed to a hot medium, a wall side opposite said hot side, and a peripheral side adjoining the hot side and the wall side and having a peripheral side surface. Relief slots are introduced into the material in an area of the heat shield element that is susceptible to material cracks induced by thermal stress, thereby limiting crack propagation.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Process for preparing shelf-stable curable polysilazanes, and polysilazanes prepared thereby
A process for preparing curable oligomeric and / or polymeric polysilazanes comprises (a) forming at least one dihalosilane-base adduct by reacting at least one dihalosilane with at least one base; (b) optionally, combining at least one dihalosilane-base adduct and at least one organodihalosilane; and (c) carrying out ammonolysis of at least one dihalosilane-base adduct or of the resulting combination of at least one dihalosilane-base adduct and at least one organodihalosilane; with the proviso that the base (1) is used for the dihalosilane-base adduct formation in a limited amount that is less than or equal to twice the stoichiometric amount of silicon-halogen bonds in the dihalosilane or (2) is used for the dihalosilane-base adduct formation in excess of this limited amount and, prior to the ammonolysis, the total amount of the resulting reacted and unreacted base is reduced to no more than this limited amount.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Zirconium based alloy and component in a nuclear energy plant
InactiveUS7292671B1Optimize with respectImprove corrosion propertyOptical rangefindersFuel elementsNuclear power plantRadiation
Owner:WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC SWEDEN
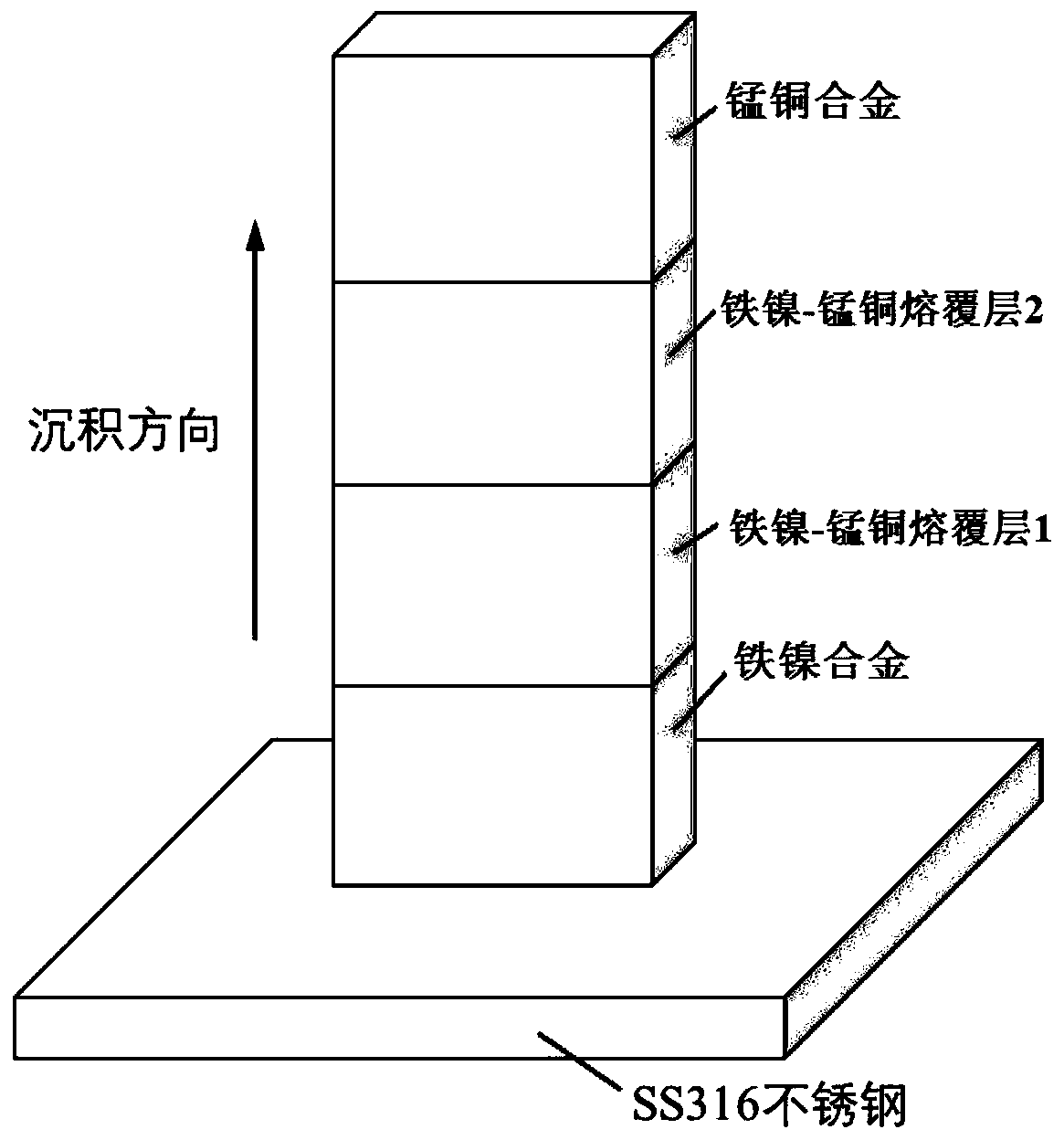
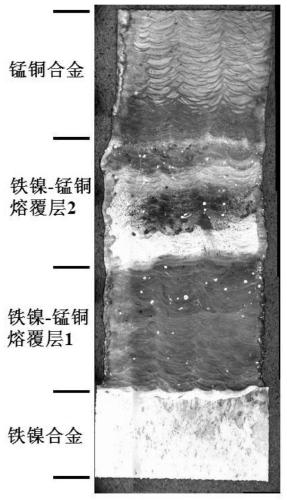
Laser additive manufacturing method for iron nickel-manganese copper dissimilar material metal part
ActiveCN111408720AAvoid crackingAvoid defects such as undissolved particlesAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyFernicoManganese
The invention discloses a laser additive manufacturing method of an iron nickel-manganese copper dissimilar material metal part. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, an iron-nickel alloy is deposited on a substrate by adopting a laser additive manufacturing method; secondly, mixed powder composed of iron-nickel alloy powder with the iron-nickel alloy powder mass content larger than 70% or smaller than 50% and manganese-copper alloy powder serves as a raw material, and an iron nickel-manganese copper transition area is formed through deposition with the laser additive manufacturing method; and thirdly, manganese-copper alloy is deposited on the iron nickel-manganese copper transition area through the laser additive manufacturing method, the substrate is removed, and the iron nickel-manganese copper dissimilar material metal part is obtained. According to the method, by adjusting the deposition direction and controlling the transition path of the mixed powder, the defects of cracking, undissolved particles and the like of the iron nickel-manganese copper gradient material are overcome, and the obtained iron nickel-manganese copper dissimilar material metal part is compact in structure and small in transition area size, has the damping performance and low expansion performance and is wide in application range.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Episubstrates for Selective Area Growth of Group III-V Material and a Method for Fabricating a Group III-V Material on a Silicon Substrate
InactiveUS20150115277A1Reduce crack formationImprove crystal qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLapping machinesSilicon
The embodiments disclose a silicon substrate with a group III-V material and a method for fabricating a group III-V material on a silicon substrate. The method involves providing a silicon substrate. A first layer formed atop the silicon substrate, is subsequently patterned to expose the underlying silicon substrate. A group III-V material layer is formed over the patterned first layer and also on the exposed silicon substrate. The group III-V material layer is subjected to chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) to expose the first layer resulting in the formation of a plurality of areas suitable for growing a device layer on the silicon substrate.
Owner:INTERUNIVERSITAIR MICRO ELECTRONICS CENT (IMEC VZW)
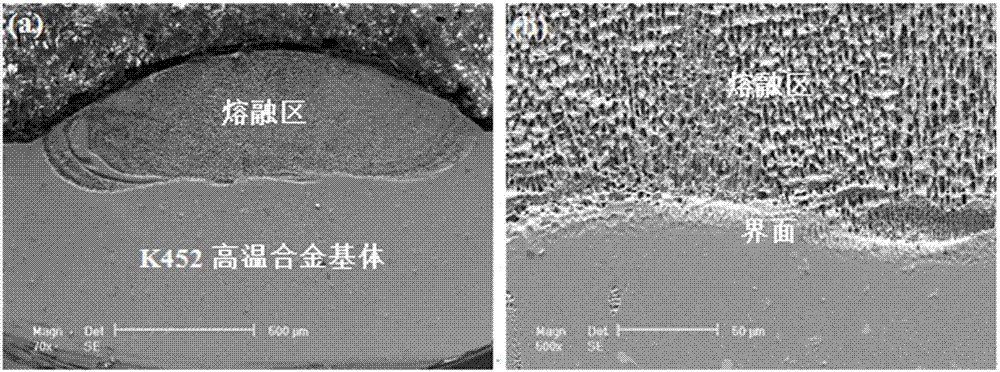
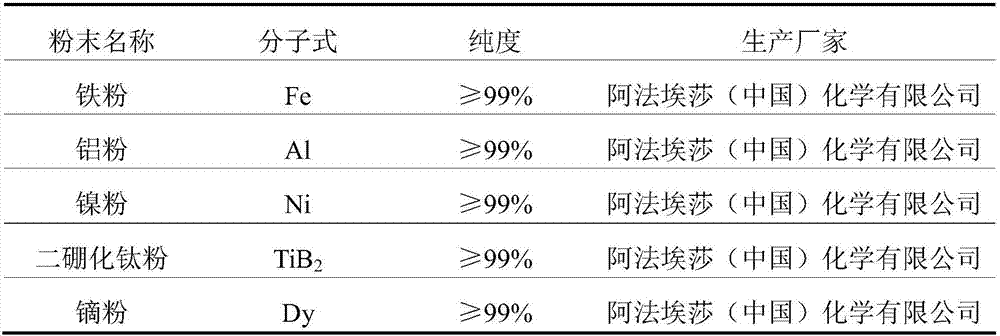
Nickel-based multi-component laser cladding powder and laser cladding method for powder
ActiveCN106884109AImprove wettabilityImprove high temperature ductilityMetallic material coating processesAlcoholCrack free
The invention relates to the field of laser cladding materials, and discloses nickel-based multi-component laser cladding powder. The powder comprises, by mass, 10-25% of Fe, 6-15% of Al, 1-5% of TiB2, 0.5-1.0% of Dy and the balance Ni. The invention further discloses a laser cladding method for the powder. The method comprises the steps that the nickel-based multi-component laser cladding powder and absolute ethyl alcohol are mixed, the surface of a cladding base material is evenly covered with the mixture, drying is carried out after roll pressing, a preformed layer is formed, and the cladding layer can be obtained through laser cladding. By means of the technology, the crack-free laser cladding layer can be obtained, the hardness is high, the cost is low, the fusion degree is improved, the strength and plasticity are ensured, and the powder is suitable for repair machining of various parts.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
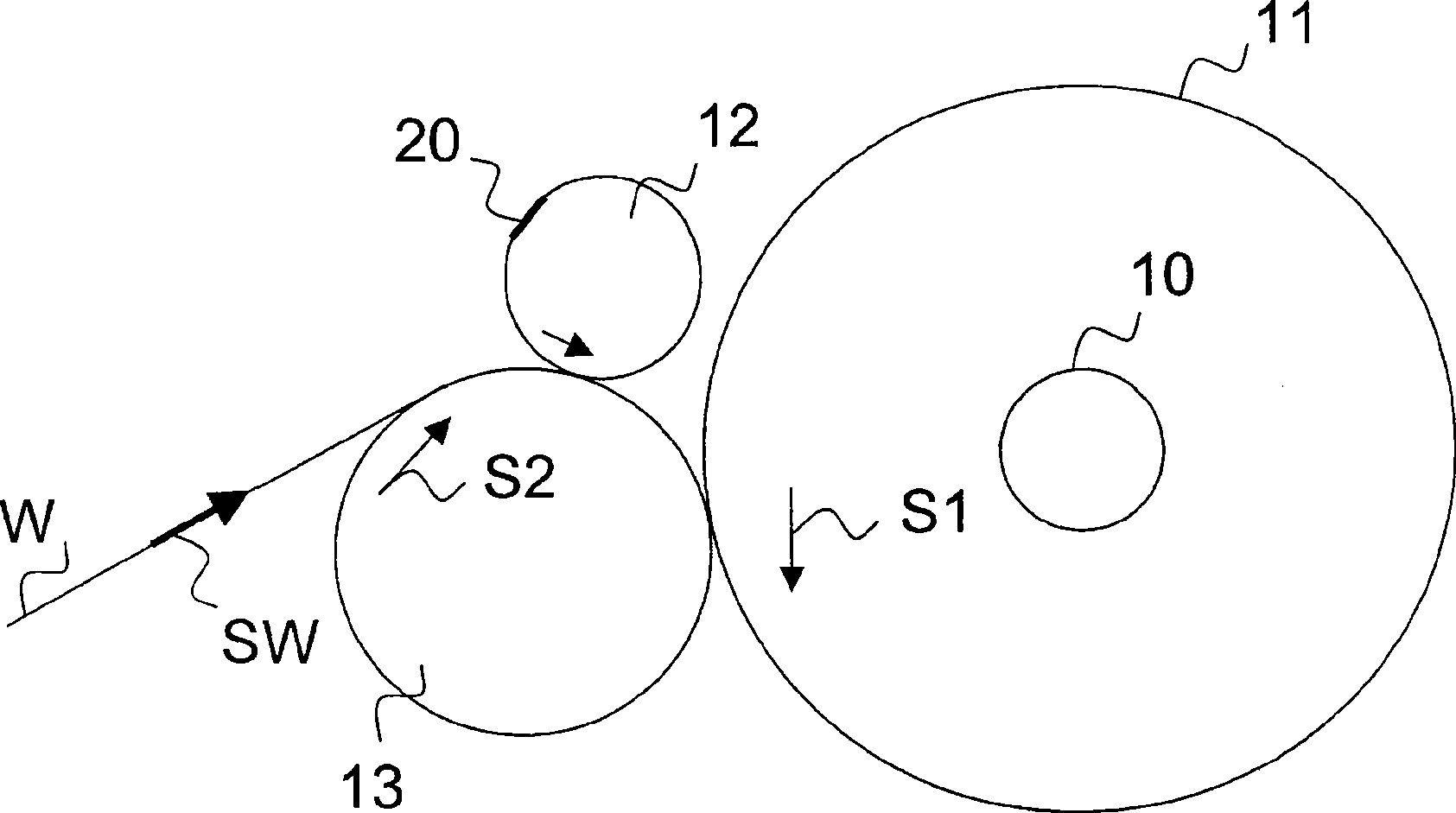
Method in connection with a reel-up of a fibre-web machine
The invention relates to a method in connection with a change process of a reel-up of a fibre-web machine, which method is applied when performing a change of reeling of a web (W) from a web roll (11) being completed to a new web roll for reeling the next roll around a reeling shaft (12). In the method, for fastening the surface layer / surface layers of the web roll (11) to the web roll (11) beingcompleted, at least one two-sided tape (20) is adhered from its one side to the web (W) being passed to the web roll (11) being completed or to the surface of the web roll (11) and said tape (20) is adhered from its other side to the surface of the web roll (11) being completed / to the surface of the web (W) being reeled onto the web roll (11) being completed due to the effect of a reeling nip between the reel drum (13) and the web roll (11) or a pressing-roll nip between the web roll (11) and a pressing roll (14) or due to the effect of the tightness (T) of the web.
Owner:METSO PAPER INC
Method for reducing the weight of a friction lining carrier plate
InactiveUS20160250676A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease stiffnessBraking elementsFriction liningEngineeringMetal sheet
Owner:TMD FRICTION SERVICES +1
Curable resin composition and sealing material using same
ActiveUS20180037720A1Reduce compoundingReduce crack formationOther chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCyanate esterPolymer chemistry
The present invention aims to provide a resin composition containing a cyanate ester compound which can reduce the formation of carbamate compounds so that the resin composition can be suitably used as an sealing material. The present invention relates to a curable resin composition containing a cyanate ester compound and a dehydrating agent.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com