Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37results about How to "Moderate quality" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
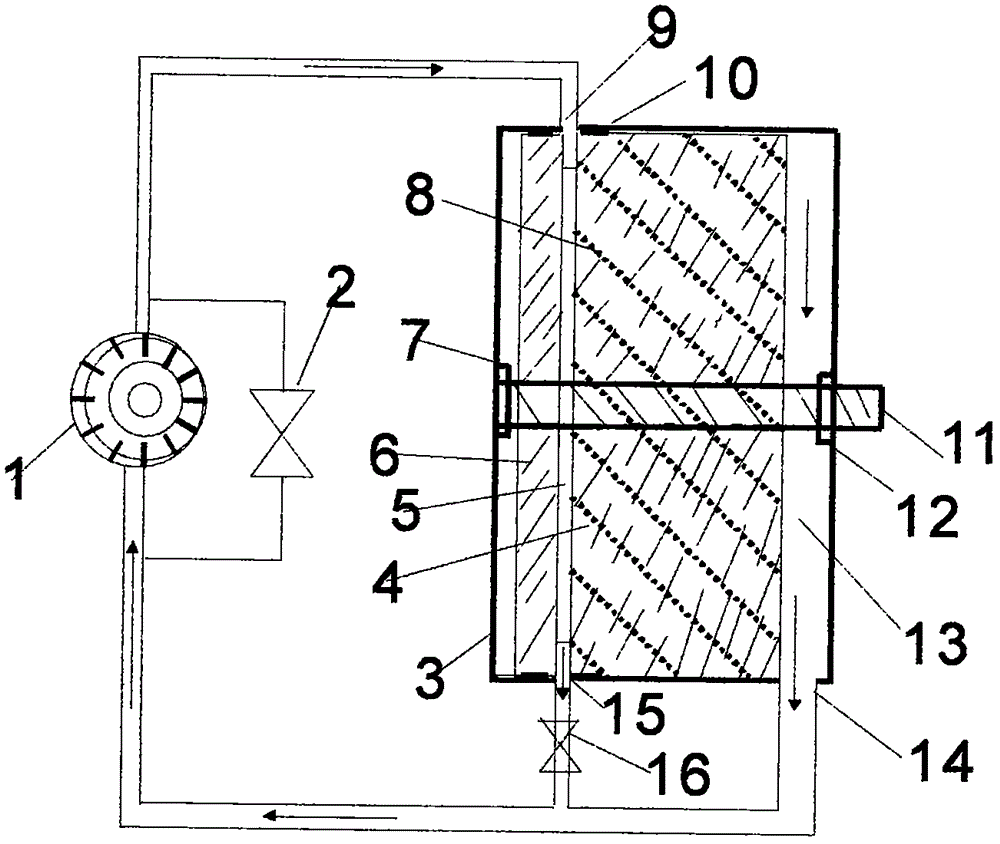
High-entropy alloy powder used on surface of riding wheel of rotary cement kiln, preparation method thereof and coating preparation method
ActiveCN106191621AHigh hardnessImprove wear resistanceMolten spray coatingChemical compositionHigh entropy alloys
The invention discloses high-entropy alloy powder used on the surface of a riding wheel of a rotary cement kiln, a preparation method thereof and a coating preparation method. The alloy powder comprises, by weight, 18%-20% of Fe, 17%-19% of Al, 17%-19% of Cr, 19%-20% of Mn, 19%-21% of Ni, 2.8%-4% of W, 0.6%-0.8% of B and 1.0%-2% of C. The alloy powder is prepared through a medium-frequency induction melting atomization one-step method. The high-entropy alloy powder and the preparation method thereof have the characteristics that pollution is small, environmental protection is realized, the steps are simple and energy consumption is low. A coating obtained through the hypersonic flame spraying process is suitable for the surface of the riding wheel of the rotary cement kiln. Bonding strength of the coating and a base body is high, the heat effect on the base body is small, tissue is good, and abrasion resistance of the riding wheel is improved after repair.
Owner:ANHUI RUITAI NEW MATERIALS TECH +1
Video transmission system, video transmission device, video reception device, and video transmission method
InactiveCN1736107AModerate qualityPulse modulation television signal transmissionCode conversionTelecommunicationsVideo transmission
There are provided a video transmission system, a video transmission device, a video reception device, and a video transmission method in which each terminal can receive video of quality appropriate for the terminal when video is received simultaneously by a plurality of terminals having different characteristics. In the system, a transmission terminal (100) performs channel division of hierarchically encoded data according to its quality and band in a channel division section (106), adds to the data, the priority calculated in a priority calculation section (112) by using terminal information, and transmits the data from a video transmission section (108) via a separate channel. Moreover, a group list calculation section (114) calculates a group list in which channels are grouped according to the quality and transmits it from a group list transmission section (116). On the other hand, a reception terminal (150) decides the reception channel in a reception channel decision section (158) by using the priority quality and the group list which have been input and receives the video in a video reception section (160).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Uniform cold conduction cooling garment
InactiveCN106263128ASolve the problem of local overcoolingAvoid local overcoolingGarment special featuresHeat-exchange elementsWorking environmentConduction cooling
The invention discloses a uniform cold conduction cooling garment, which belongs to a cooling garment and aims at solving the problem of too cold local part of the existing cooling garment. The cooling garment comprises a garment body (1) and a phase change material (2) arranged in the garment body (1), and also comprises a heat conduction film (3), wherein the heat conduction film (3) is arranged in a way of being tightly attached to the phase change material (2). The cold quantity generated by the phase change material can be uniformly guided to the human body; the too cold local part is avoided; the phase change material and the fan are combined; the body surface temperature of a user is effectively reduced, so that the user feels cool and comfortable; the work environment of operators is improved; in the use process, the wind quantity of the fan can be regulated, so that the body surface temperature can be regulated; therefore the temperature controllability is realized; the mass is proper; comfort and safety are realized; the operation range of the user is not limited; portability is realized; the moving is convenient; the endurance time is long; through the addition of materials with good heat conduction coefficient and perforation on an encapsulation belt, the heat radiation of the phase change material is enhanced; the acting time is prolonged.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Far-infrared carbon fiber composite heating film
The invention relates to a far-infrared carbon fiber composite heating film, which comprises an upper base layer, a lower base layer, a carbon fiber composite heating layer, an upper insulated flame-retardant and heat-resistant waterproof layer and a lower insulated flame-retardant and heat-resistant waterproof layer, wherein the carbon fiber composite heating layer is located between the upper base layer and the lower base layer; and the upper insulated flame-retardant and heat-resistant waterproof layer and the lower insulated flame-retardant and heat-resistant waterproof layer coat the outer sides of the upper base layer and the lower base layer, wherein the far-infrared carbon fiber composite heating film is preferably carbon fiber cloth or carbon fiber composite paper. The far-infrared carbon fiber composite heating film is simple in structure, has good flexibility and can be freely cut and folded; the flexibility is not affected in a low-temperature condition; the load resistance deviation does not exceed 8% after a single side is folded for 1,000 times at a speed of 30times / min; the security and the stability are significantly improved; the service life is long; and furthermore, the far-infrared carbon fiber composite heating film has high external insulativity, high-temperature resistance, open fire resistance and waterproofness, the internal conductivity and the heating property are good and the security is high.
Owner:石家庄邦迪高分子材料有限公司
Embossing device with a deflection compensated roller
InactiveCN101103204AModerate qualityReduced tendency to spread sidewaysMechanical working/deformationShaft and bearingsSurface layerMechanical engineering
A diffractive microstructure is produced on the surface layer (40) of a substrate (30) using an embossing device (1000) according to the invention. The embossing device (1000) comprises an embossing roll (10) and a backing roll (20) for exerting an embossing pressure on the surface layer (40) of the substrate (30). The embossing pressure and / or variations in temperature cause deflection of the embossing roll (10). In order to compensate the deflection, the embossing device (1000) comprises means for setting the embossing pressure (p3) exerted by the central area (CR) of the embossing roll (10) on the surface layer (40) of the substrate (30) to be at least equal to or higher than the embossing pressure (p1, p2) exerted by the end areas (ER1, ER2) of the embossing roll (10) on the surface layer (40) of the substrate (30). In a preferred embodiment the shell (21) of the backing roll (20) is supported on the central zone (CR) of the shaft (22) of the backing roll such that the ends of the shell (22) can move in relation to the shaft (22) of the backing roll. Thus, when the side of the shell (11) of the embossing roll on the substrate (30) side is bent due to the embossing pressure and becomes concave, the side of the backing roll on the substrate side becomes convex in a corresponding manner. Thus, the pressure in the central area (CR) becomes equal to or higher than in the end areas (ER1, ER2).
Owner:AVANTONE OY
Method for measuring activity concentration of kalium-subtracted total beta radionuclides in seawater
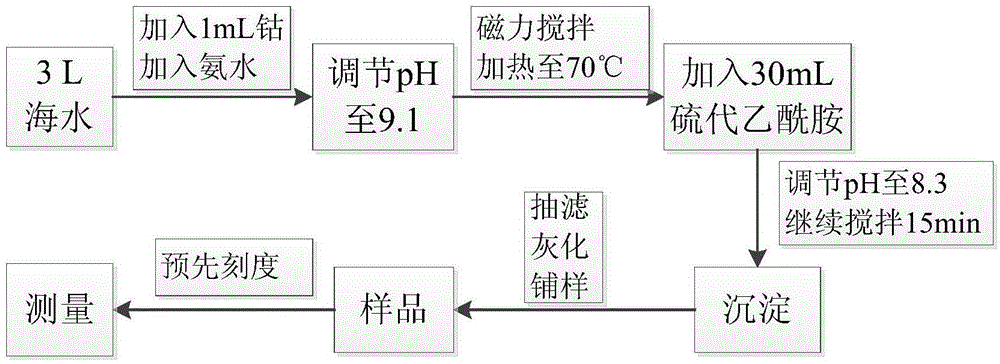
ActiveCN104898151AHigh enrichment rateUniform precipitationRadiation intensity measurementSeawaterNuclear facilities
The invention relates to a method for measuring the activity concentration of kalium-subtracted total beta radionuclides in seawater, and the method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (a) adding a cobalt carrier into used seawater, forming cobalt ion solution, adjusting the pH value of the cobalt ion solution to be greater than seven, and then adding thioacetamide into the solution to form cobalt sulfide sediments through reaction; (b) extracting and putting the cobalt sulfide sediments under the temperature from 600 DEG C to 800 DEG C for ashing; (c) adding porphyrized ashing products to a measuring disc, adding an ethyl alcohol sample, and putting the mixture on a flow-gas type proportional counter for measurement and calculation. The method achieves the measurement of beta radionuclides with the enrichment ratio being greater than 95% which is discharged into the seawater in an operation process of nuclear facilities, such as 58Co, 60Co, 59Fe, 65Zn, 110mAg and so on, thereby guaranteeing that the sediments prepared through the method are more uniform and moderate in weight. The detection lower limit is 3mBq / L, so the method is suitable for the monitoring of the activity concentration of kalium-subtracted total beta radionuclides in seawater, and is also suitable for heavy-salt water similar to a seawater sample, and heavy-salt water which contains radionuclides and is obtained through processing.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +3
Process for the production of aluminum hydroxide
ActiveUS7959895B2Improve throughputImprove wettabilityAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium hydroxideSlurry
Owner:MARTINSWERK
Hydraulic driver and vehicle thereof
ActiveCN106678089ASimple structureModerate qualityFluid couplingsAccumulator installationsEconomic benefitsOil distribution
The invention discloses a hydraulic driver with a vehicle clutch function and three vehicles thereof. An output end of an oil pump is connected with input end joint oil of an annular oil distribution cavity of a screw pipe rotor driven machine by an oil pipe; one way of an input end of the oil pump is connected with output end joint oil of the annular oil distribution cavity of the screw pipe rotor driven machine by an oil pipe with a valve, and the other way of oil pipe is connected with joint oil of a discharge cavity; when the valve is closed, a prime mover drives the oil pump; when working medium oil circularly flows, hydraulic force is generated in the annular oil distribution cavity of the driven machine to enable the working medium oil to respectively flow into a discharge cavity for circulation from each screw pipe; the hydraulic force is respectively acted on the inner walls of the rotor screw pipes to generate peripheral rotating force so as to drive the screw pipe rotor driven machine to output power; when the valve is opened, the working medium oil is circulated in a short-circuit manner by the valve to enable the screw pipe rotor driven machine to stop outputting the power; and when the valve is closed again, the screw pipe rotor driven machine immediately recovers the power outputting. The hydraulic driver serves as a clutch for large and small vehicles, and is high in fuel economic benefit and low in labor intensity of drivers.
Owner:肇庆高新区伙伴汽车技术有限公司
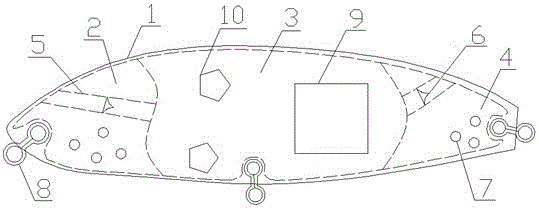
Novel bionic lure
InactiveCN105123638AImprove impact resistanceExtended service lifeBaitChemical compositionPlastic materials
The invention discloses a novel bionic lure. The novel bionic lure comprises a fish-shaped shell made of a plastic material, wherein a head part, a belly part and a tail part of the fish-shaped shell are respectively provided with a splayed ring for connection, the interior of the fish-shaped shell is divided into three cavities, namely, a fish head cavity, a fish body cavity and a fish tail cavity, the fish head cavity and the fish tail cavity are internally provided with a water flow pipeline which is collectively connected with the fish body cavity, the water flow pipelines are respectively provided with a one-way water flow valve in the fish head cavity and the fish tail cavity, the fish body cavity of the fish-shaped shell is provided with a closable clamshell, and the surface of the fish-shaped shell is coated with a layer of silver powder. The novel bionic lure is long in service life, simple in structure, moderate in quality, capable of collectively improving the induction effect by adopting physical conditions such as sound, light and shape and chemical components released by liquid lure, wide in application range, high in pertinence and good in fishing effect.
Owner:安徽欧思润新材料科技有限公司
Method for increasing Puan mountain Miao black-bone chicken laying rate
ActiveCN106172195AModerate qualityModerate, good egg qualityAnimal husbandrySexual maturityAnimal science
The invention discloses a method for increasing the Puan mountain Miao black-bone chicken laying rate. The method comprises the step that locally-proliferated black-bone hens and cocks in the Puan county of the Guizhou province and locally-naturalized Loman laying hens in the Puan county are subjected to hybridization on the basis of the combination of two-way cross, backcross, crossing fixation, local hybridization and artificial insemination methods by adopting the principle of animal genetics, good mountain Miao black-bone chicken are obtained, the phenomena that anciently-proliferated mountain Miao black-bone chicken in the Puan county of the Guizhou province are late in sexual maturity, high in broodiness and low in egg laying rate are effectively solved, the laying rate of Puan mountain Miao black-bone chicken can be greatly increased, and meanwhile the advantages that the Puan mountain Miao black-bone chicken are resistant to crude feed, strong in adaptability and disease resistance, delicious in taste, rich in fragrance, compact and tender in meat quality and the like are ensured.
Owner:GUIZHOU PROVINCE PUAN COUNTY VIENTIANE ECOLOGICALAGRI DEV CO LTD
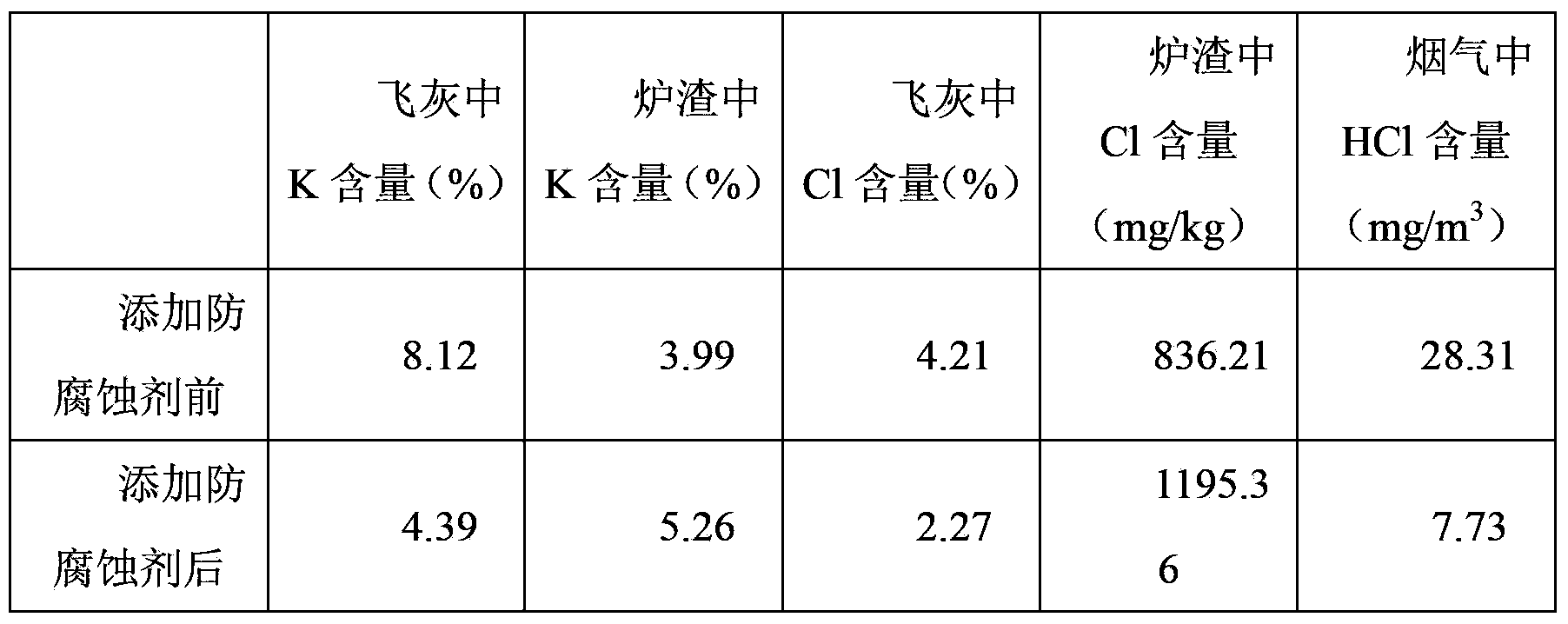
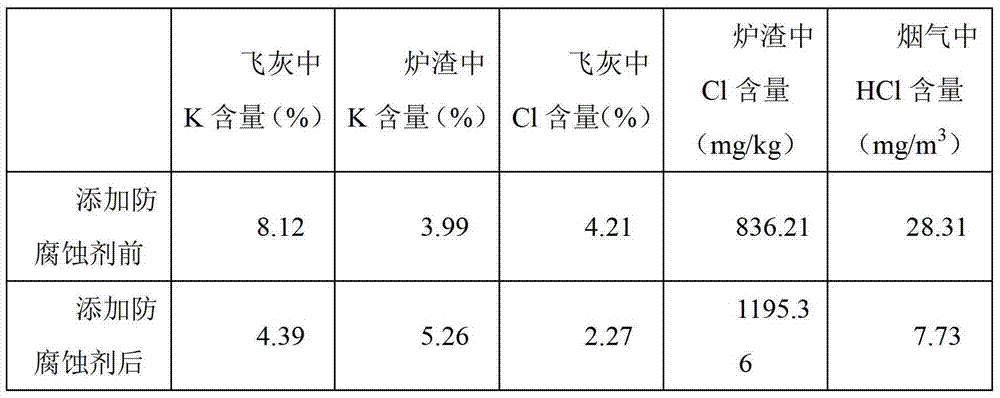
Biomass boiler anticorrosive agent, and preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a biomass boiler anticorrosive agent, and preparation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biomass combustion or boiler heating surface corrosion. The anticorrosive agent is composed of the following components in percentage by mass: 30-60% of coal ash, 10-30% of Al2(SO4)3, 20-50% of kaolin and 10-20% of CaSO4. The anticorrosive agent is granules with coarse threads on the external surface, the granular mass is 0.5-3g and is moderate, and thus, anticorrosive agent can not be blown away from the hearth by flue gas, so that the soot formation risk and soot blowing cost of the boiler heating surface can not be increased; the invention has the characteristics of stable structure, high mechanical strength, large specific area and the like; the thread appearance can increase the reaction area of the anticorrosive agent with the base metal compound and chloride, and can fix K, Na and other alkali metals and Cl into the furnace slag, thereby reducing the alkali metal corrosion and chlorine corrosion of the heating surface.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Gas-phase catalyst for regenerating diesel through catalytic cracking of waste oil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102600890AGood choiceGood activity and stabilityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a gas-phase catalyst for regenerating diesel through catalytic cracking of waste oil and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst comprises the following components by weight percent: 10-50% of Y-type molecular sieve, 0-20% of high-silicon ZSM-5 molecular sieve, 10-40% of activated aluminum oxide, 30-70% of supporter and 10-20% of adhesive. The gas-phase catalyst has the characteristics of moderate activity, high selectivity, good stability, strong metal pollution resistant capability and long service life, can be regenerated and meets the requirement of the diesel through catalytic cracking of waste oil.
Owner:杭州绿洲能源科技有限公司
Aluminum hydroxide particles produced from an organic acid containing aluminum hydroxide slurry
InactiveUS20100152354A1Improve throughputImprove wettabilityPigmenting treatmentGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsOrganic acidAluminium hydroxide
The present invention relates to a process for producing aluminum hydroxide flame retardants from an organic acid containing aluminum hydroxide slurry.
Owner:MARTINSWERK
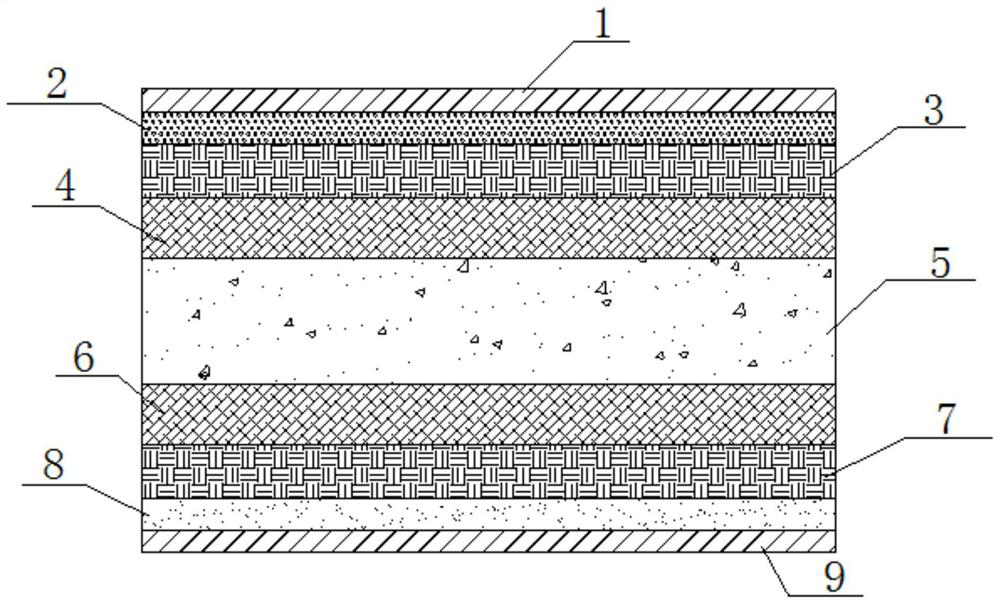
Magnesium oxide composite floor and manufacturing process thereof
InactiveCN112576003AHigh hardnessImprove fire performanceCeramic shaping apparatusFlooring insulationsGlass fiberFiber
The invention discloses a magnesium oxide composite floor and a manufacturing process thereof. The floor sequentially comprises a surface wear-resistant layer, a surface slurry layer, an upper glass fiber gridding cloth layer, an upper glass fiber short fiber felt layer, a main body material layer, a lower glass fiber short fiber felt layer, a lower glass fiber gridding cloth layer, a bottom slurry layer and a bottom wear-resistant layer from top to bottom, wherein the main body material layer contains magnesium oxide, a magnesium chloride solution, heavy calcium powder, powder and a modifier;the surface slurry layer contains magnesium oxide, a magnesium chloride solution, fossil powder, powder and a modifier; and the bottom slurry layer contains magnesium oxide, a magnesium chloride solution, fossil powder, powder and a modifier. The floor is simple in structure, the manufacturing process is simple and feasible, and the manufactured floor is good in fireproof, moisture-proof and water-resistant properties, high in strength and not easy to deform.
Owner:江苏佳运晟汇新材料有限公司
Cold-proof and icing-resistant cable
InactiveCN107400372AImprove hydrophobicityAvoid icingPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsClimate change adaptationGlass fiberCarbon fibers
The invention discloses a cold-proof and icing-resistant cable. The cable comprises a core, a shielding layer and an icing-resistant layer which are sequentially arranged from inside out, and the icing-resistant layer is produced from, by weight, 55 parts of fluorosilicon resin, 12 parts of wollastonite nano-powder, 8 parts of polyurethane, 8 parts of SiO2-glass fiber gel, 6 parts of basalt fibers, 5 parts of glass fibers, 5 parts of carbon fibers and 4 parts of polytetrafluoroethylene. The cold-proof and icing-resistant cable has the advantages of long service life and good tensile strength.
Owner:杭州千岛湖永通电缆有限公司
Method for constructing sargassum artificial algal field through inlay method
InactiveCN106171935AImprove survival rateNot easy to depositClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsBrickSargassum
The invention relates to a method for constructing a sargassum artificial algal field through an inlay method. The method comprises the following steps that S1, an artificial algal reef is constructed, and the top end face of the artificial algal reef is provided with grooves matched with bricks in shape; S2, by the adoption of an artificial seedling breeding mode, the bricks are adopted as substrata, seedlings are attached to the bricks in an artificial room for semi-flowing water cultivation, and then flowing water is adopted for cultivating fry; S3, a low-tide zone just breaking the surface of water when a spring tide ebbs is selected to serve as a restoration zone, and the artificial algal reef constructed in S1 is put in sea water in a to-be-restored area to be soaked for two weeks or more; S4, the brick substrata obtained in S2 are vertically inlaid in the artificial algal reef treated in S3 in the long-axis direction, the sides with the seedlings are outward, and accelerated cement is poured in gaps. According to the method for constructing the algal field, the seedling substrata and the artificial algal reef are operated separately, and the survival rate of sargassum is raised beneficially; moreover, the artificially cultivated seedlings are adopted as a seedling source for restoration of the algal field, and accordingly original natural algal resources cannot be damaged.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
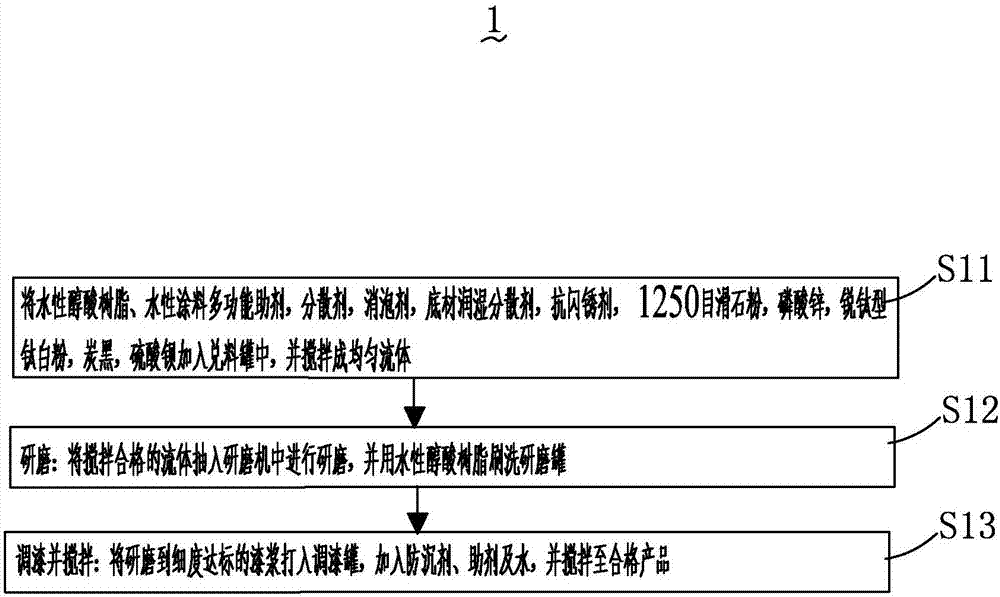
Water-based anti-rust paint and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106957592AAccelerated corrosionGood weather resistanceAnti-corrosive paintsPolyester coatingsWater basedTalc
The invention provides a water-based anti-rust paint and a preparation method thereof. The water-based anti-rust paint contains the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-60 parts of water-based alkyd resin, 0.1-0.5 part of water-based coating multifunctional auxiliaries, 0.3-0.8 part of dispersant, 0.1-0.3 part of defoaming agent, 0.1-1 part of substrate wetting dispersant, 0.1-1 part of flash rust-proofing agent, 3-10 parts of 1250-mesh talc powder, 5-15 parts of zinc phosphate, 5-15 parts of anatase titanium dioxide, 0.1-1 part of carbon black, 10-30 parts of barium sulfate, 0.1-1 part of anti-settling agent, 1-10 parts of rheological aids, 0.1-1 part of thickener, 1-10 parts of auxiliaries, and 2-25 parts of water. The water-based anti-rust paint achieves the national requirement on environment-friendly paint, is proper in price and high in quality, has excellent corrosion resistance and weather resistance, and is stable in chemical properties and thermal storage performance.
Owner:河北晨虹油漆有限公司
Process for the production of aluminum hydroxide
ActiveUS20100061924A1Improve wettabilityImprove throughputAluminium hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium hydroxideSpray dried
Owner:MARTINSWERK
A method for determining the activity concentration of potassium-removed total beta radionuclides in seawater
ActiveCN104898151BHigh enrichment rateUniform precipitationRadiation intensity measurementPotassiumSeawater
The present invention relates to a method for determining the activity concentration of potassium-removed total beta radionuclides in seawater, which is characterized in that it comprises the following steps: (a) adding a cobalt element carrier to the taken seawater to form a cobalt ion solution, and then adjusting When the pH value reaches alkaline, add thioacetamide to form a cobalt sulfide precipitate; (b) take the cobalt sulfide precipitate and place it at 600~800°C for ashing; (c) add the finely ground ashing powder to the measuring pan For the product, add ethanol to spread the sample, place it in a flow-type proportional counter for measurement and then calculate it. The enrichment rate of 58Co, 60Co, 59Fe, 65Zn, 110mAg and other beta radionuclides discharged into seawater during the operation of nuclear facilities by this method is higher than 95%, thus ensuring that the final precipitate obtained by this analysis method is relatively uniform and of high quality. Moderate; its detection limit level is 3mBq / L, which is suitable for monitoring the activity concentration of potassium-removed total beta radionuclides in seawater, and is also suitable for high brine similar to seawater samples and high brine containing radionuclides after treatment etc. monitoring.
Owner:SUZHOU NUCLEAR POWER RES INST +3
Combined beam for shock-proof safety bin and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN111379459AModerate qualityModerate hardnessProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingShock avoidanceEngineering
The invention discloses a combined beam for a shock-proof safety bin. The combined beam comprises combined beam bodies, beam combining mechanisms, beam columns, bearing columns, short slot holes and long slot holes. The combined beam has the beneficial effects that through holes with diameters of 12 cm are drilled out in positions, at common height, of steel raw materials with diameters of 60 cm and height of 20 cm as long slot holes, and through holes with length of 22 cm and diameters of 12 cm are separately drilled in positions, which are mutually perpendicular to the long slot holes, in the sides of the steel raw materials as short slot holes; the steel raw materials are used as the beam combining mechanisms, wooden cylinders with proper length and diameters of 12 cm are selected as the beam columns; the beam combining mechanisms are arranged in the form of an equilateral rectangle; and the beam columns are inserted for connecting the short slot holes to the long slot holes as thecombined beam. The combined beam is moderate in mass and hardness, and is more stable in framework structure while conveniently mounted.
Owner:张峻华
A kind of anticorrosion packing box and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109928026BImprove anti-corrosion performanceFully combinedAnti-corrosive paintsLinings/internal coatingsLacquerEngineering
The invention discloses an anticorrosion packaging box. The packaging box comprises a box body and a top cover; the outer wall and the inner wall of the box body and the outer wall and the inner wallof the top cover are provided with anticorrosion layers; and the outer wall of the anticorrosion layer located on the outer side of the packaging box is provided with glazed zapon lacquer. After a series of operations of preparing materials, mixing oil, adding grease, adding powder, adding anticorrosion oxides, adding a binder, conducting defoaming and cooling, cleaning the packaging box, sprayinganticorrosion liquid and spraying the glazed zapon lacquer, the anticorrosion packaging box with good quality can be obtained, the prepared anticorrosion liquid is moderate in viscosity, not liable to be layered, easy to spray andfree of bubble, various components are fully combined, and the combination property are good, so that the anticorrosion liquid can form a good coating film after spraying, is not liable to crack, good in film forming effect and adhesion and not liable to fall off, and the anticorrosion performance of the packaging box is greatly improved.
Owner:深圳市新鸿兴包装有限公司
Colored pencil lead with high flexural strength and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a colored pencil lead with high flexural strength and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of pencil lead manufacturing. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving and stirring 25-30 parts by mass of cellulose nitrate in a reaction kettle by using a solvent, adding 25-30 parts by mass of whiskers, 15-20 parts by mass of a lubricant, 5-10 parts by mass of wax and 13-17 parts by mass of toner, uniformly stirring, immediately adding 1-3 parts by mass of a dispersant, stirring for a period of time, adding 1-3 parts by mass of a plasticizer, continuously stirring, removing most of the solvent, and carrying out roller milling, rod beating, core extrusion, straightening, drying and end cutting to obtain a finished product. And the colored pencil lead with excellent performance is obtained. The colored pencil lead prepared by the method has the characteristics of high flexural strength, good coloring degree, high writing lubricity and the like, and multi-specification large-scale production can be realized without purchasing new equipment in the preparation process.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
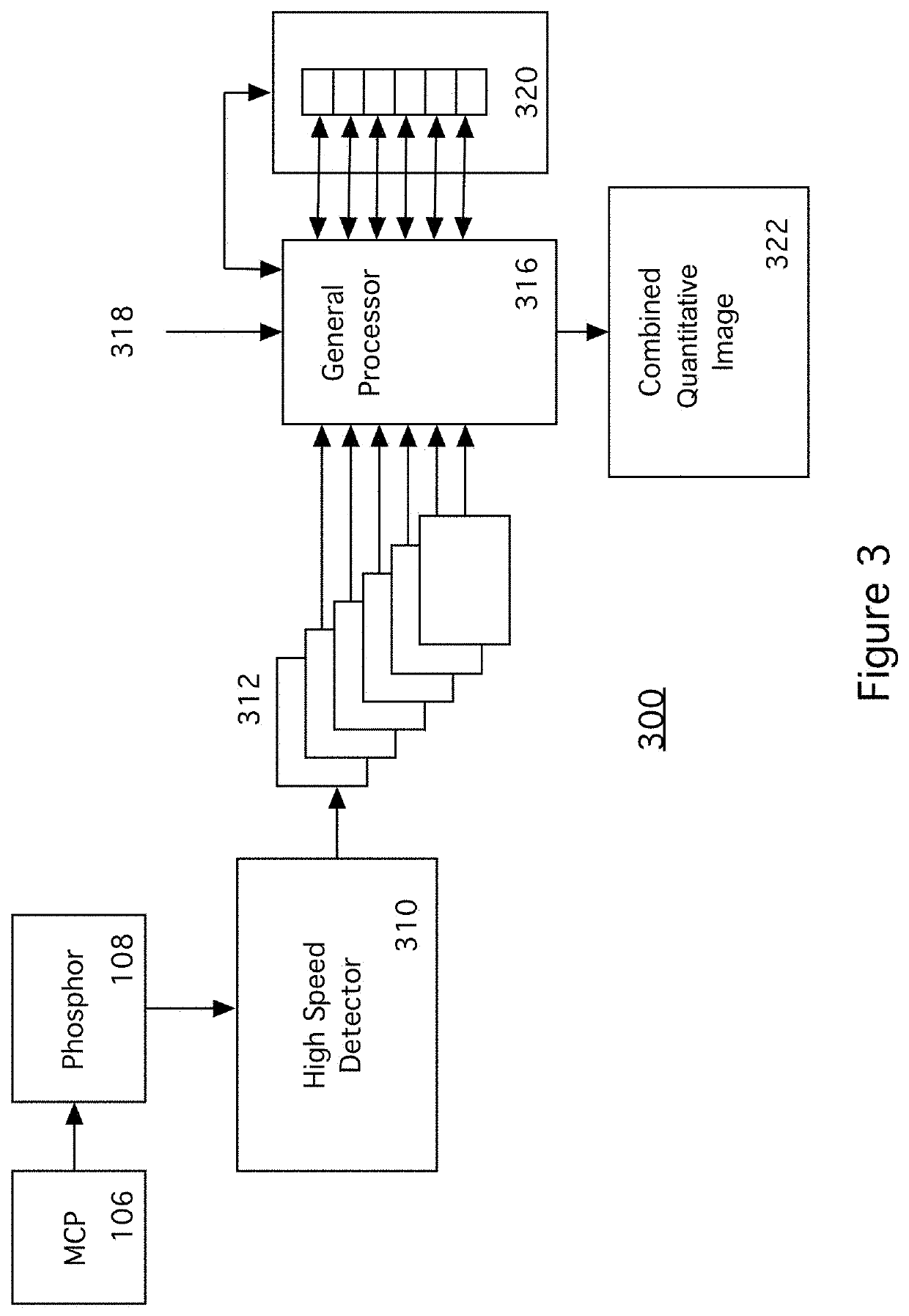
High Speed Two-Dimensional Event Detection and Imaging Using an Analog Interface and a Massively Parallel Processor
ActiveUS20210293979A1Improves processing partIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMassively parallelCounting rate
A quantitative pulse count (event detection) algorithm with linearity to high count rates is accomplished by combining a high-speed, high frame rate camera with simple logic code run on a massively parallel processor such as a GPU or a FPGA. The parallel processor elements examine frames from the camera pixel by pixel to find and tag events or count pulses. The tagged events are combined to form a combined quantitative event image.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
High-strength woven bag production device and use method thereof
ActiveCN113529187AHigh strengthModerate qualityFilament forming substance formingFilament handlingYarnHeater Rod
The invention discloses a high-strength woven bag production device and a use method thereof. The device comprises a yarn drawing machine, a yarn outlet cavity, a refrigerator, a feeding port, a heater, a yarn outlet, a winding roller, a yarn guide and a shell; the yarn outlet cavity is connected to the middle end of the yarn drawing machine; the left end of the yarn outlet cavity is connected with the yarn outlet; the winding roller and the yarn guide are arranged on the left side of the yarn drawing machine; the yarn drawing machine is provided with a thermoplastic cavity in the upper end of the yarn outlet cavity and a yarn splitting cavity in the lower end of the yarn outlet cavity; a molding pipe extending to the yarn splitting cavity from the rear portion of the left end is arranged at the middle end of the thermoplastic cavity; the right end of the molding pipe is connected with one ends of a plurality of refrigeration pipes; the other ends of the refrigeration pipes are connected with the refrigerator; one ends of a plurality of heating pipes are arranged at the left end of the molding pipe; the other ends of the heating pipes are connected with the heater; the right end of the molding pipe is connected with a plastic collecting cavity; the upper end of the plastic collecting cavity is connected with a plastic melting cavity; a heating rod is arranged at the middle end of the plastic melting cavity; and the upper end of the heating rod is fixed to the lower end of the inner wall of the shell.
Owner:山东广成塑业有限公司
Biomass boiler anticorrosive agent, and preparation and application thereof
The invention discloses a biomass boiler anticorrosive agent, and preparation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of biomass combustion or boiler heating surface corrosion. The anticorrosive agent is composed of the following components in percentage by mass: 30-60% of coal ash, 10-30% of Al2(SO4)3, 20-50% of kaolin and 10-20% of CaSO4. The anticorrosive agent is granules with coarse threads on the external surface, the granular mass is 0.5-3g and is moderate, and thus, anticorrosive agent can not be blown away from the hearth by flue gas, so that the soot formation risk and soot blowing cost of the boiler heating surface can not be increased; the invention has the characteristics of stable structure, high mechanical strength, large specific area and the like; the thread appearance can increase the reaction area of the anticorrosive agent with the base metal compound and chloride, and can fix K, Na and other alkali metals and Cl into the furnace slag, thereby reducing the alkali metal corrosion and chlorine corrosion of the heating surface.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
Anticorrosion packaging box and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109928026AImprove anti-corrosion performanceNothing producedAnti-corrosive paintsLinings/internal coatingsLacquerEngineering
The invention discloses an anticorrosion packaging box. The packaging box comprises a box body and a top cover; the outer wall and the inner wall of the box body and the outer wall and the inner wallof the top cover are provided with anticorrosion layers; and the outer wall of the anticorrosion layer located on the outer side of the packaging box is provided with glazed zapon lacquer. After a series of operations of preparing materials, mixing oil, adding grease, adding powder, adding anticorrosion oxides, adding a binder, conducting defoaming and cooling, cleaning the packaging box, sprayinganticorrosion liquid and spraying the glazed zapon lacquer, the anticorrosion packaging box with good quality can be obtained, the prepared anticorrosion liquid is moderate in viscosity, not liable to be layered, easy to spray andfree of bubble, various components are fully combined, and the combination property are good, so that the anticorrosion liquid can form a good coating film after spraying, is not liable to crack, good in film forming effect and adhesion and not liable to fall off, and the anticorrosion performance of the packaging box is greatly improved.
Owner:深圳市新鸿兴包装有限公司
Measuring tool for insulating pull ring of thyristor converter valve assembly and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN112815809AModerate qualityEasy to operateAngles/taper measurementsControl engineeringWork time
The invention provides a measuring tool for an insulating pull ring of a thyristor converter valve assembly and a measuring method thereof, and the measuring tool comprises a pedestal which is provided with a supporting part which extends lengthwise; two measuring heads, respectively fixed at two ends of the supporting part; an arc surface being arranged on one side, far away from the supporting part, of the measuring head in the lengthwise extending direction; the arc surfaces having preset radians, and the distance between the two arc surfaces being a preset distance, so that the arc angle of the arc wall and the inner wall length of the insulating pull ring can be detected according to the preset radians and the preset distance when the insulating pull ring sleeves the arc surfaces; a measuring sliding block, arranged on the supporting part in a sliding manner; the measuring slide block can slide along the lengthwise extension direction so as to detect the straightness of the linear wall. The embodiment of the invention provides a measuring tool for an insulating pull ring of a thyristor converter valve assembly and a measuring method of the measuring tool. The measuring tool and the measuring method can improve the working efficiency, reduce the working time and are suitable for detecting the quality of a large batch of insulating pull rings.
Owner:XIDIAN POWER RECTIFIER XIAN +1
Percussive drill bit for rock drilling and method for the manufacture of such drill bit
InactiveCN101878346BImprove controllabilityInherent controllabilityDrill bitsFriction weldingControllability
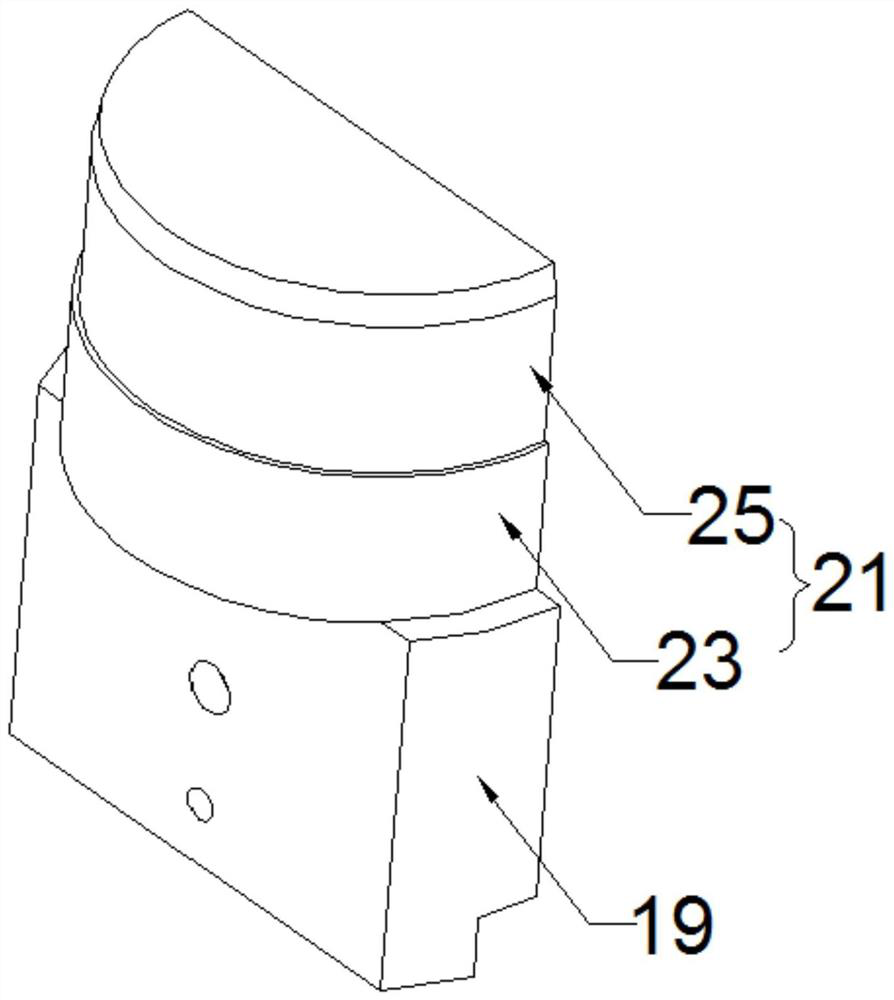
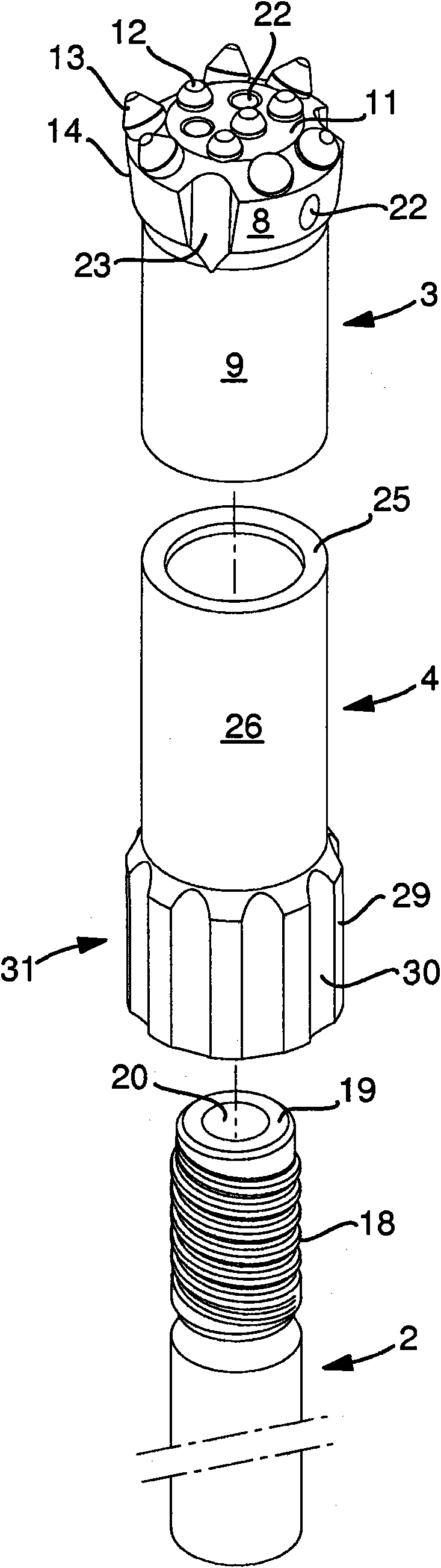
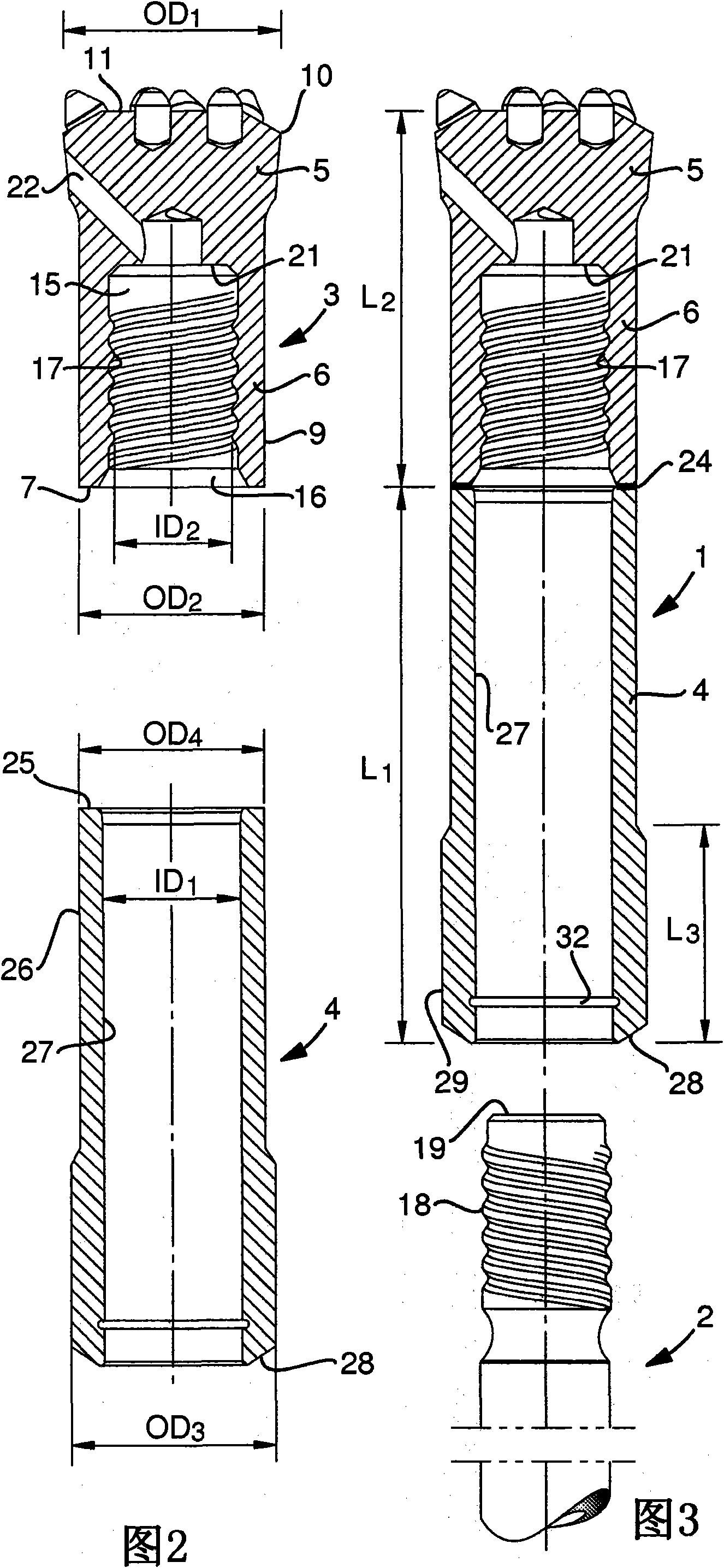
A drill bit for percussive rock drilling of the type that comprises a front head and a tubular skirt, which extends rearward from the head to a rear, ring-shaped end and includes an internal thread for the transfer of combined impact and rotary motions to the drill bit is disclosed. The rear end of the skirt is, via an unelastic joint, e.g., a friction weld, united to a front end of a sleeve having an envelope surface, from which a plurality of projections are peripherically spaced-apart from each other project, e.g., ridges, having the purpose of guiding the drill bit in the drill hole. By assembling the drill bit of two parts, the internal thread can be turned with high accuracy and smoothness, at the same time as the drill bit is given an inherent good controllability. In an additional aspect, a method for the manufacture of such a drill bit is also disclosed.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Dynamic wet type airflow adsorption device
InactiveCN109569104AImprove adsorption capacityImprove efficiencyDispersed particle filtrationTransportation and packagingProcess engineeringFilter material
The invention provides a dynamic wet type airflow adsorption device. The device includes a liquid supply device and at least one adsorption module. The liquid supply device is used for supplying a liquid. The at least one adsorption module is coupled to the liquid supply device, and each of the adsorption modules further has a porous filter material and a driving unit. The porous filter materialsabsorb the liquid, the porous filter materials are disposed on one side of an airflow channel and are in contact with airflow in the airflow channel, and the normal direction of the surface on which the porous adsorption filter materials are in contact with the airflow is orthogonal to the flow direction of the airflow. The driving units are coupled to the porous filter materials and are used fordriving the porous filter materials to perform a displacement movement. The wet type airflow adsorption device of the invention utilizes the liquid as a medium, combines porous materials as filter materials, and adsorbs a pollution source by wet porous filter materials.
Owner:SOULLEADER CO LTD
Podophyllotoxin external-use formulation prescription for treating pointed condyloma and herpes genitalis, dosage form series and preparation method
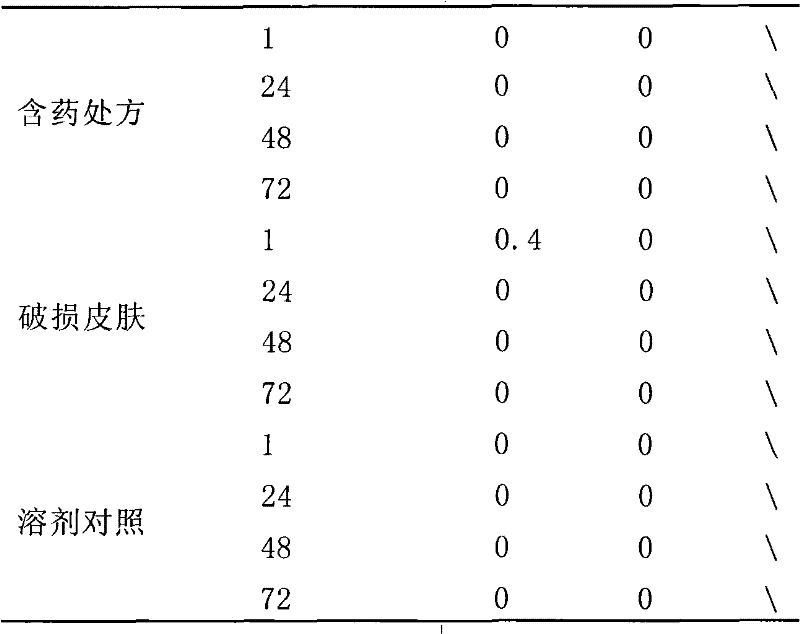
ActiveCN101375845BSolve solubilitySolve the irritatingOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryAcute toxicity testingSide effect
The invention discloses a podophyllotoxin preparation formula for external use for the treatment of condyloma acuminatum and genital herpes, a series of formulations and a preparation method, and belongs to the field of pharmacy. The weights or the volumes of all the ingredients of the formula of 100ml of the podophyllotoxin preparation for external use are as follows: 0.5g of podophyllotoxin, 20ml-80ml of main solvent, 1ml-3ml of penetration enhancer 1, 0.5g-2.5g of penetration enhancer 2, 20ml-80ml of cosolvent and 0.03-0.5g of preservative. The podophyllotoxin preparation for external use has the advantages that the types and the amount of excipients and the proportion of main drugs are reasonable, the drug administration is carried out by a liniment, a spray or other formulations which are applicable to the external use, the main drug can be rapidly absorbed by the horny layer and the epidermis, the efficacy is significant, the local toxicity or side effects are small, the skin acute toxicity is very low, and the podophyllotoxin preparation has no irritation and weak allergy and does not hinder the skin normal functions; the podophyllotoxin preparation has no systemic toxicityor side effects, thereby being safe and effective. The preparation prepared by the formula has the advantages of good appearance, moderate viscosity, easy coating, spraying drug administration, feasible process, controllable quality, simple preparation process, and suitability for industrial batch production.
Owner:BEIJING HUMANWELL JUNWEI PHARM TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com