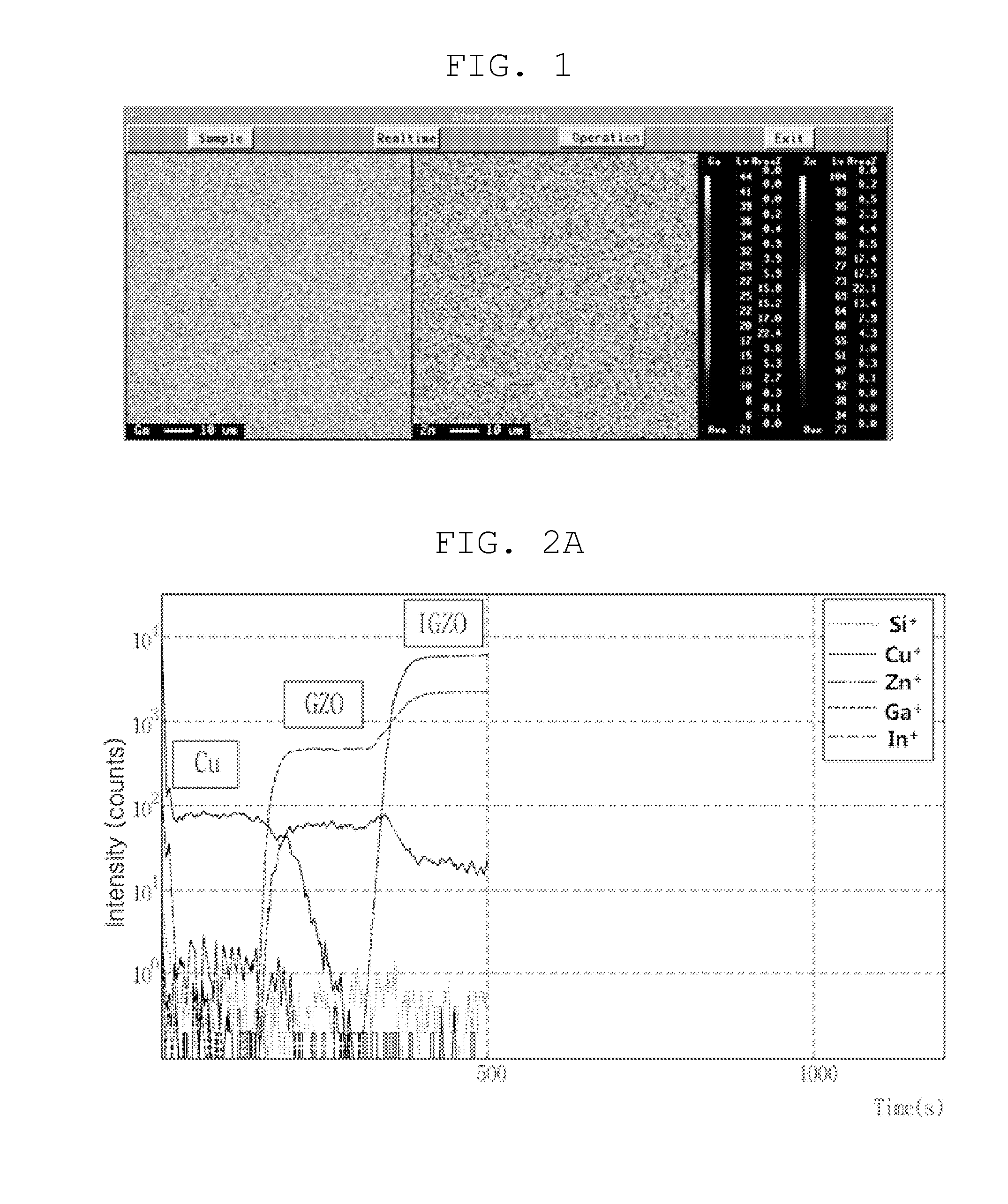
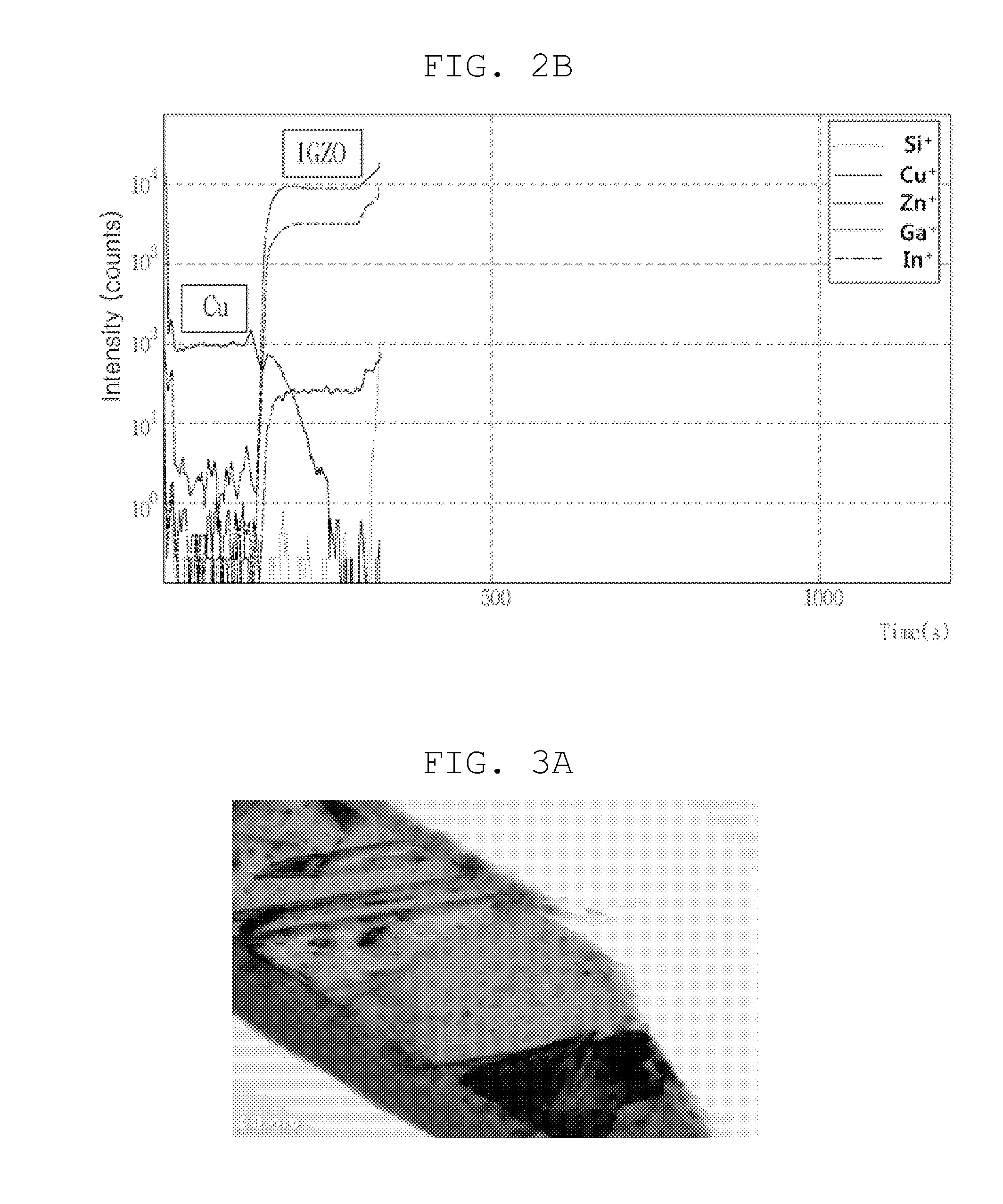
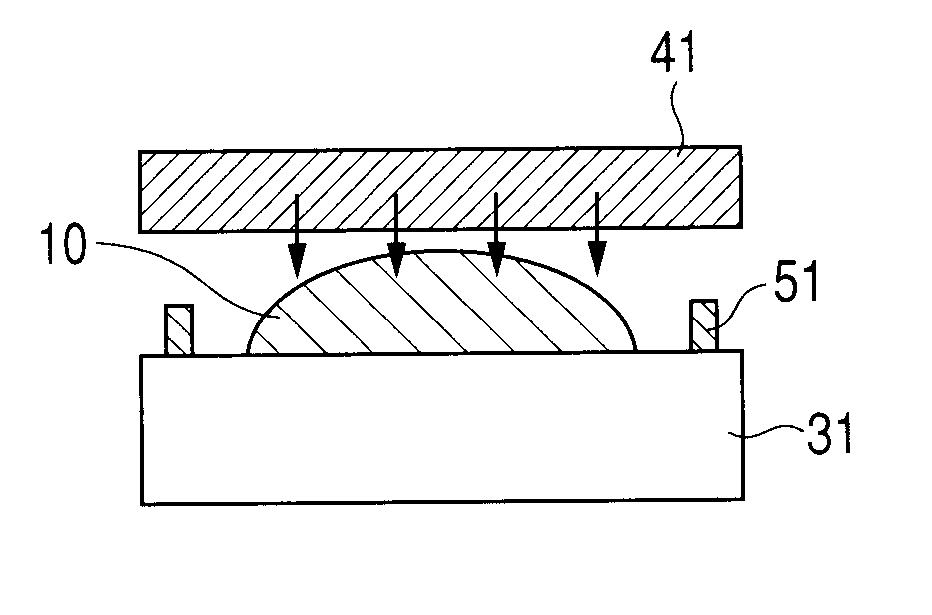
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
52results about How to "High transmittance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exposure method and apparatus
InactiveUS20050151942A1High transmittanceHigh light transmittanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusParallel platePlane parallel
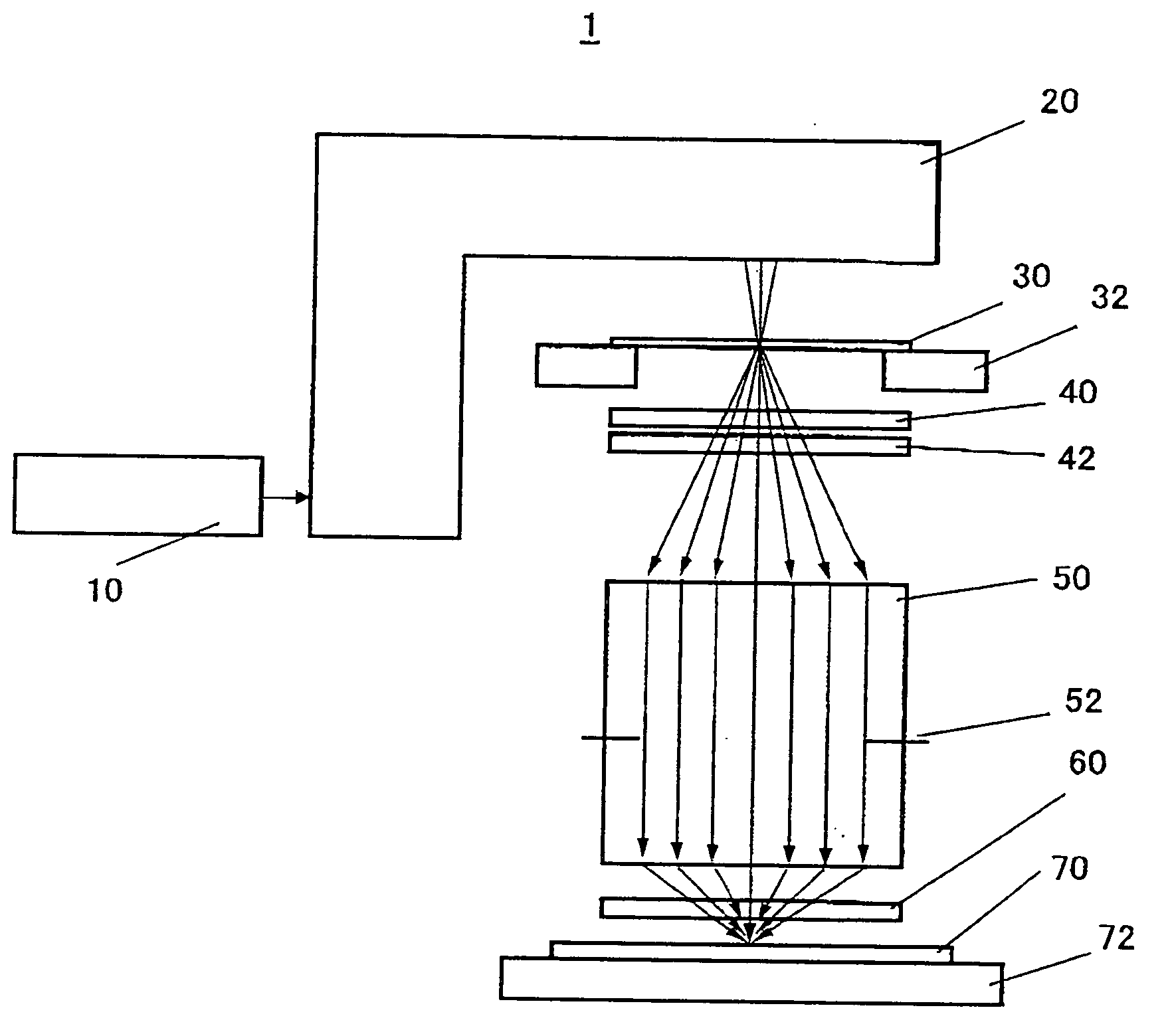
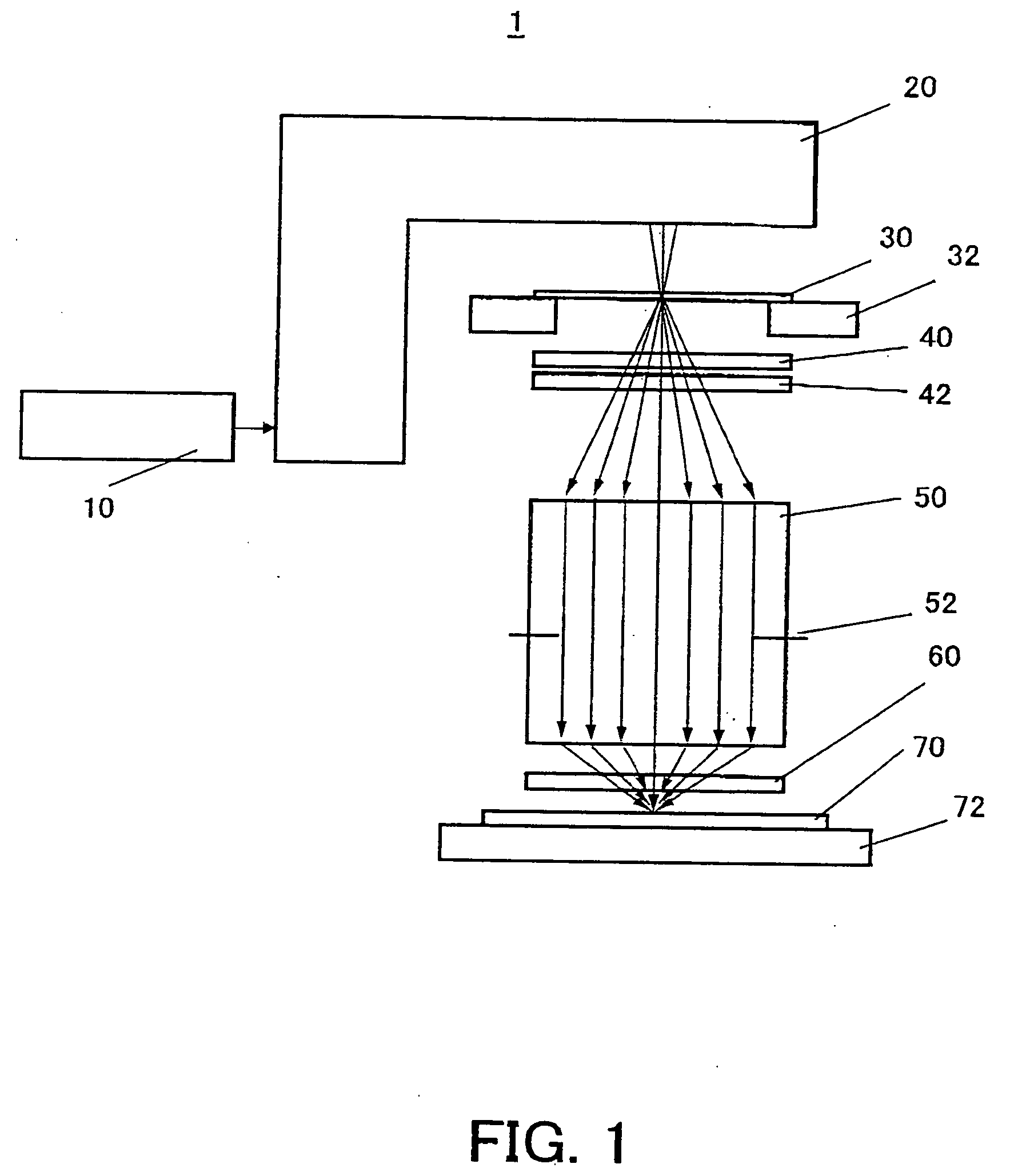
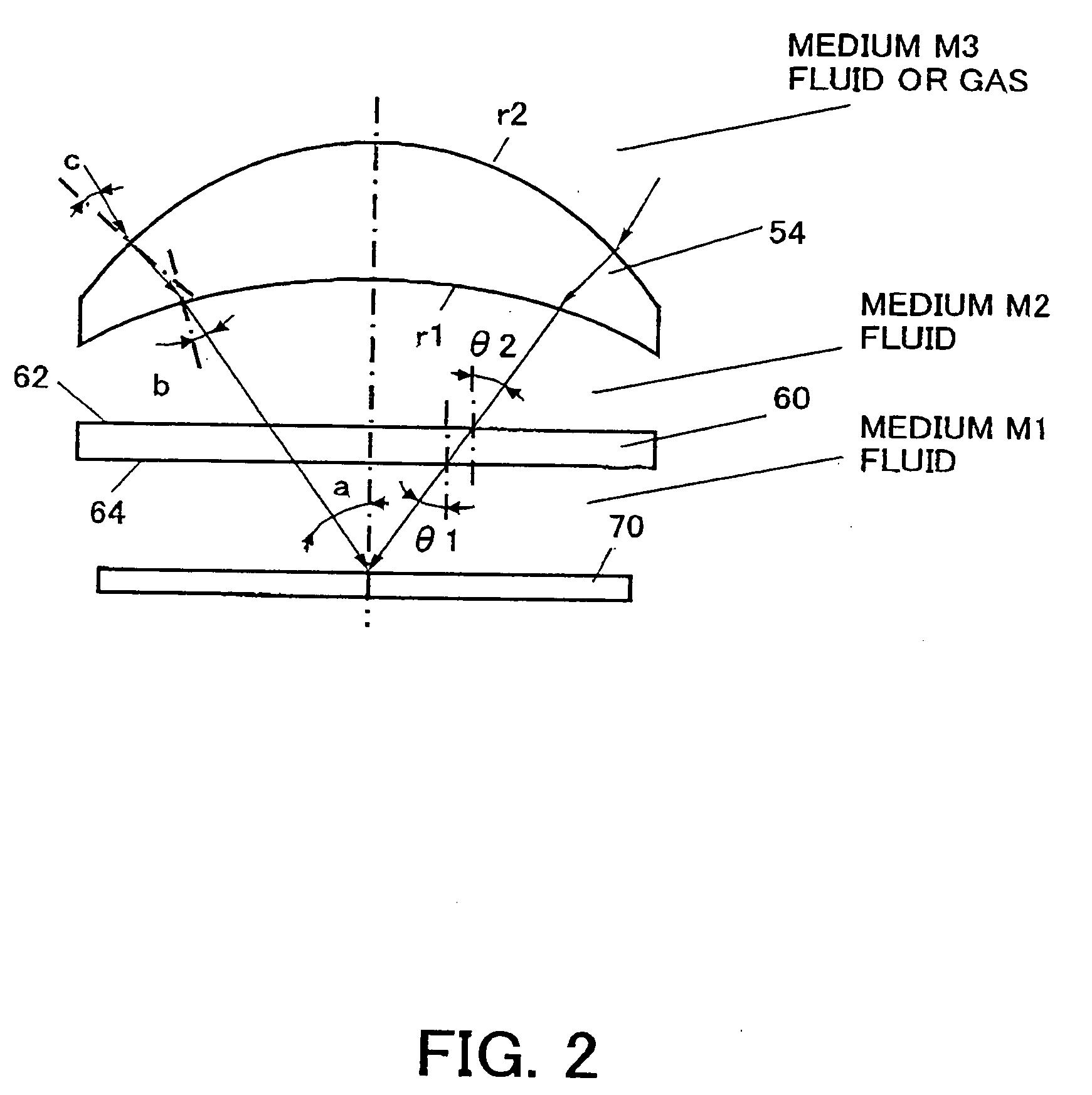
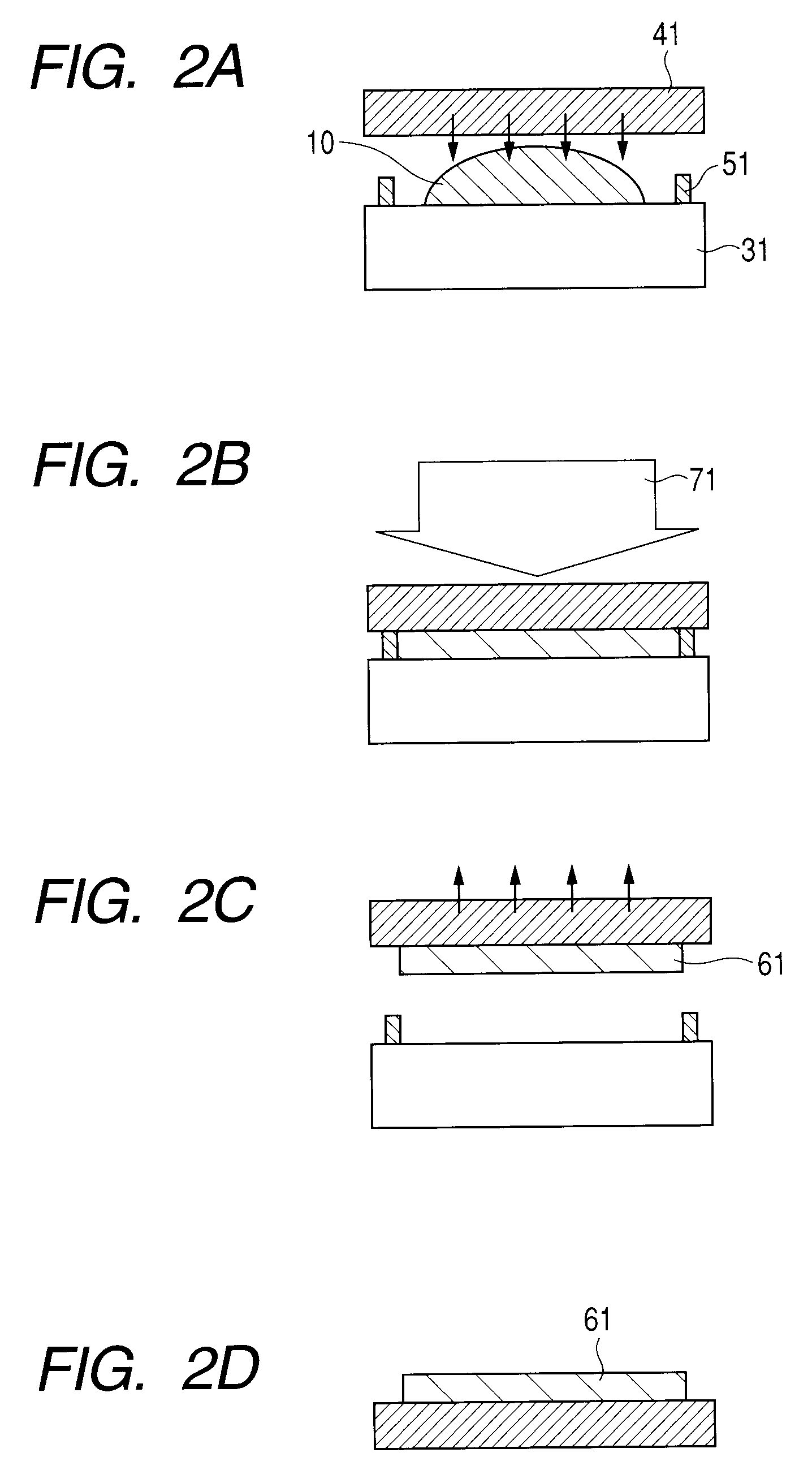
An exposure apparatus includes a projection optical system for projecting a pattern on a mask onto an object to be exposed, a final surface of the projection optical system and a surface of the object being immersed in a fluid, and a plane-parallel plate arranged between the projection optical system and the object, wherein the plane-parallel plate includes a first surface and a second surface that serves as a back surface of the first surface and opposes to the object, both the first and second surfaces being immersed in the fluid.
Owner:CANON KK
Optical information recording medium
ActiveUS7057252B2Favorable jitter valueHigh transmittanceSingle unit pavingsRecord information storageRefractive indexLaser beams
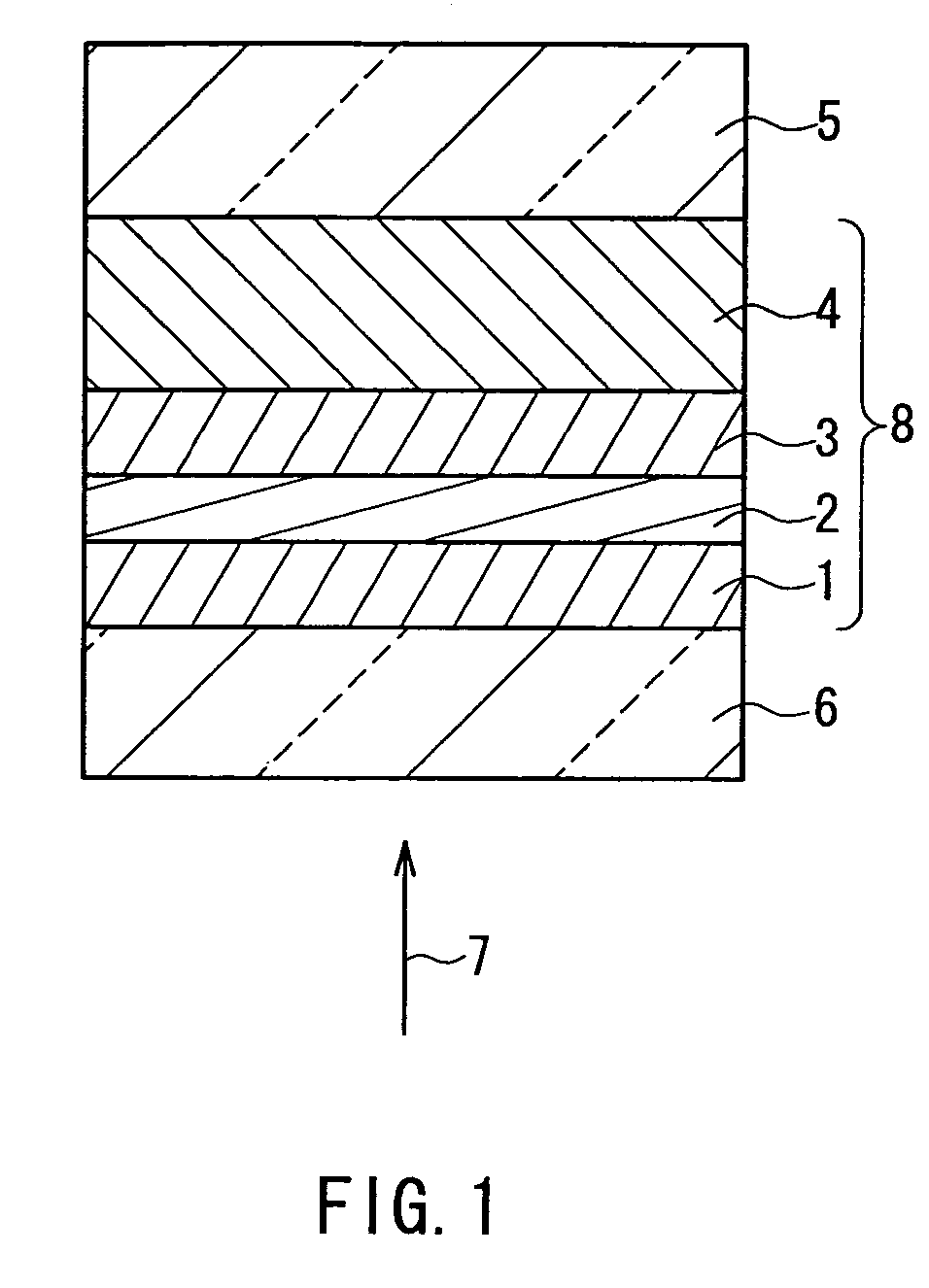
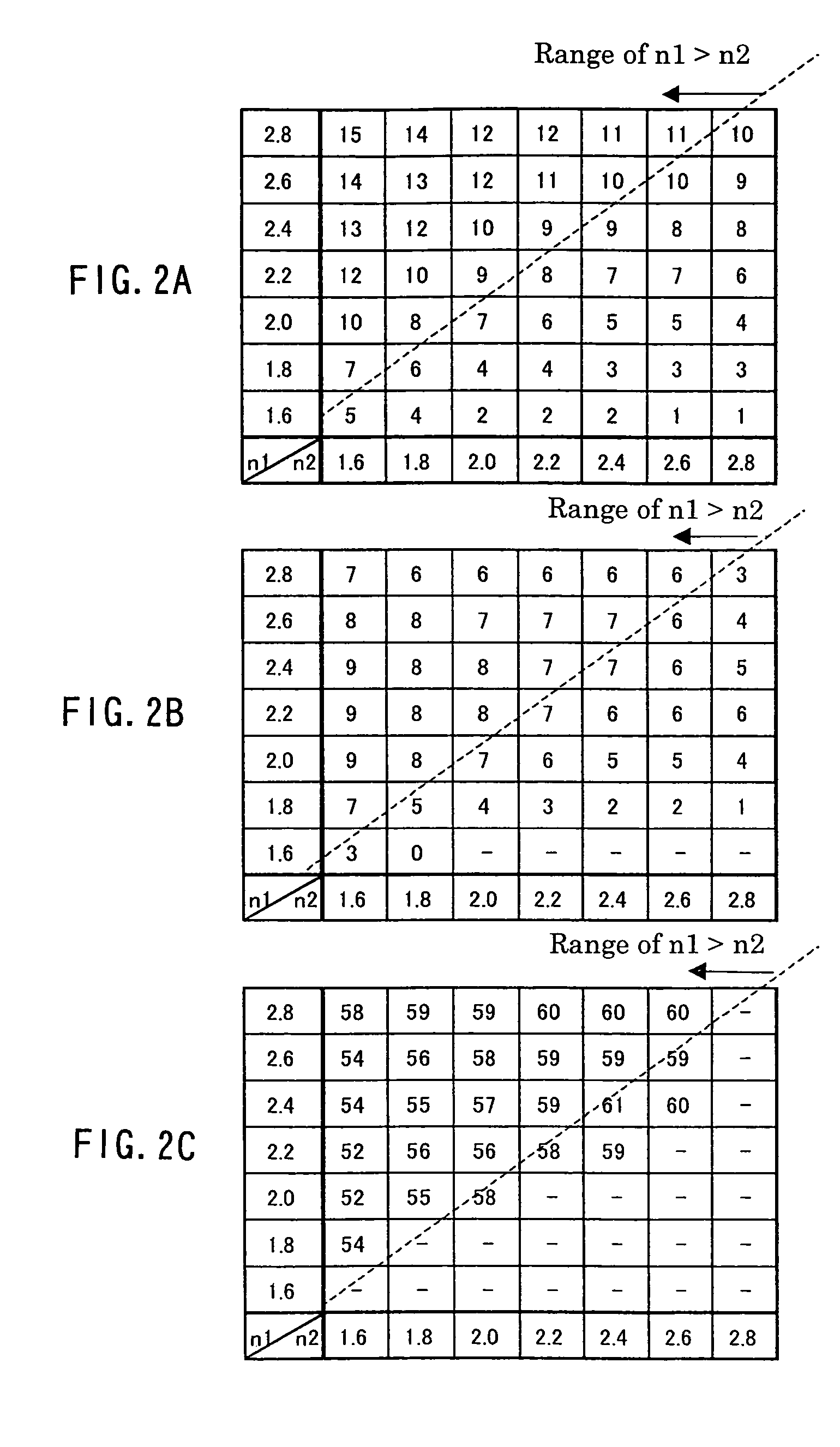
The optical information recording medium of the present invention includes an information layer provided on a substrate. The information layer includes: a recording layer with respect to which information can be recorded and reproduced through irradiation with a laser beam having a predetermined wavelength; a first protective layer that is located, with respect to the recording layer, on the side to which the laser beam is incident; and a second protective layer that is located, with respect to the recording layer, on the opposite side to the side to which the laser beam is incident. The refractive index n1 of the first protective layer and the refractive index n2 of the second protective layer at the predetermined wavelength of the laser beam that is used for recording and reproduction satisfy a relationship of n2<n1.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Transparent conductive film for flat panel displays
ActiveUS20040086717A1High transmittanceLow electric resistanceSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingTransmittanceIndium
Transparent conductive films for flat panel displays and methods for producing them are disclosed. In general, a method according to the present invention comprises: (1) providing a flexible plastic substrate; (2) depositing a multi-layered conductive metallic film on the flexible plastic substrate by a thin-film deposition technique to form a composite film, the multi-layered conductive metallic film comprising two layers of an alloy selected from the group consisting of indium cerium oxide (InCeO) and indium tin oxide (ITO) surrounding a layer of an alloy of silver, palladium, and copper (Ag / Pd / Cu); and (3) collecting the composite film in continuous rolls. Typically, the thin-film deposition technique is DC magnetron sputtering. Another aspect of the invention is a composite film produced by a method according to the present invention. Still another aspect of the invention is a composite film comprising a multilayered film as described above formed on a flexible plastic substrate, wherein the composite film has a combination of properties including: transmittance of at least 80% throughout the visible region; an electrical resistance of no greater than about 10 Omega / square; a root-mean-square roughness of no greater than about 2.5 nm; and an interlayer adhesion between the multi-layered metallic film and the remainder of the composite film that is sufficiently great to survive a 180° peel adhesion test.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Wire grid type polarization element, manufacturing method thereof, liquid crystal device, and projection type display apparatus
InactiveUS20090027773A1High transmittanceHigh qualityOptical articlesPolarising elementsEngineeringLiquid crystal devices
There is provided a wire grid type polarization element equipped with a plurality of lines of metal grid on a translucent substrate. A plurality of lines of groove like concave portions are formed on the substrate, and the metal grid is embedded in the plurality of lines of groove like concave portions.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Transparent composite panel
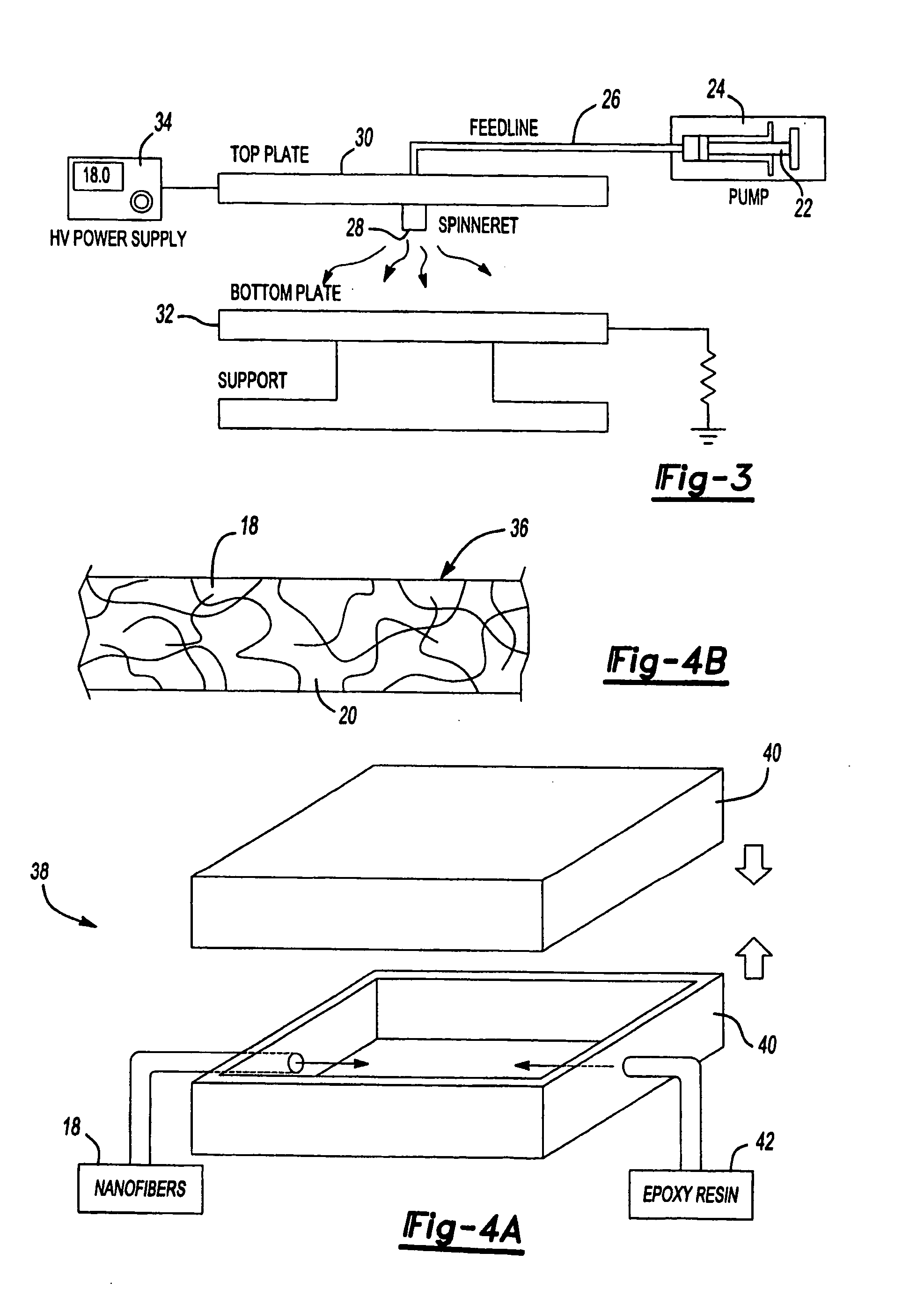
InactiveUS20060024483A1High transmittanceHigh light transmittanceMaterial nanotechnologyEfficient propulsion technologiesFiberNanofiber composites
A transparent nanofiber composite panel that includes a plurality of transparent nanofibers integrated in random orientations within a transparent matrix is provided. The transparent nanofibers have a diameter that is less than the wavelength of visible light. The extremely small diameter of the transparent nanofibers allows the transparent panel to be substantially insensitive to an RI ‘mismatch’ between the transparent nanofibers and the transparent matrix. Additionally, due to random orientation of the transparent nanofibers within the transparent matrix the transparent nanofiber composite panel possesses substantially isotropic material properties such that the transparent nanofiber composite panel can be incorporated as a structural, load bearing, component of a larger structure.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Transparent electrode for display device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20100032186A1Low contact resistanceHigh transmittanceNon-insulated conductorsSolid-state devicesElectrically conductiveNitrogen
The present invention relates to a transparent electrode for a display device which includes a first transparent conductive film containing nitrogen, and a second transparent conductive film not containing nitrogen, wherein the first transparent conductive film is in contact with an aluminum alloy film. In accordance with the present invention, there is obtained a transparent electrode for a display device which is capable of, even when a barrier metal layer to be generally provided between an aluminum alloy film and the transparent electrode is omitted, controlling the variance small while keeping the low contact resistance, and further which is also excellent in light transmission characteristics.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Conductive oxide film, display device, and method for forming conductive oxide film
ActiveUS20140063368A1High conductivityHigh transmittanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsZinc oxides/hydroxidesHigh transmittanceOptoelectronics
One embodiment of the present invention provides a conductive oxide film having high conductivity and high transmittance of visible light. The conductive oxide film having high conductivity and high transmittance of visible light can be obtained by forming a conductive oxide film at a high substrate temperature in the film formation and subjecting the conductive oxide film to nitrogen annealing treatment. The conductive oxide film has a crystal structure in which c-axes are aligned in a direction perpendicular to a surface of the film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Reflection -type photointerrupter
ActiveUS20100109021A1High transmittanceSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhysicsOpto electronic
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Liquid-Crystal Display Device
ActiveUS20090033848A1High transmittanceMinimized in color shiftingNon-linear opticsSecondary layerLiquid-crystal display
To provide a highly efficient liquid-crystal display device wide in viewing angle and minimized in color shifting.This invention includes a first substrate, a second substrate, a liquid-crystal layer sandwiched between the first substrate and the second substrate, and a plurality of pixels each surrounded by scan lines and signal lines arranged in a matrix format on the second substrate; with a first pixel electrode, a second pixel electrode, a first common electrode, and a second common electrode being arranged in the pixel region of the second substrate above which the liquid-crystal layer is disposed, the first pixel electrode and the first common electrode being arranged on a first layer, the second pixel electrode and the second common electrode being arranged on a second layer, the first pixel electrode and the second common electrode being overlapped upon each other in the pixel region, and the second pixel electrode and the first common electrode being overlapped upon each other in the pixel region.
Owner:PANASONIC LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Light uniformization structure and light emitting module
ActiveUS20110134648A1High transmittanceImprove luminous efficiencyPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceMicrostructureRefractive index
A light uniformization structure and light emitting module is related to a light uniformization structure including a first material layer having a plurality of microstructures in a surface thereof, a second material layer having a plurality of microstructures in a surface thereof, and a spacer layer. The spacer layer is located between the first material layer and the second material layer, and a refractive index of the spacer layer is smaller than a refractive index of the first material layer and a refractive index of the second material layer.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Zinc oxide-based sputtering target, method of manufacturing the same, and thin-film transistor having barrier layer deposited using the same
InactiveUS20130341181A1Improve contact characteristicHigh transmittanceCellsVacuum evaporation coatingZincOxide
A zinc oxide (ZnO)-based sputtering target, a method of manufacturing the same, and a thin-film transistor (TFT) having a barrier layer deposited using the same. The zinc oxide-based sputtering target includes a sinter containing zinc oxide doped with gallium oxide, the content of the gallium oxide ranging, by weight, from 10 to 50 percent of the sinter, and a backing plate bonded to the rear surface of the sinter to support the sinter. The zinc oxide-based sputtering target can be subjected to direct current (DC) sputtering, and improve the contact and etching characteristics of a barrier layer that is deposited using the same.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +2
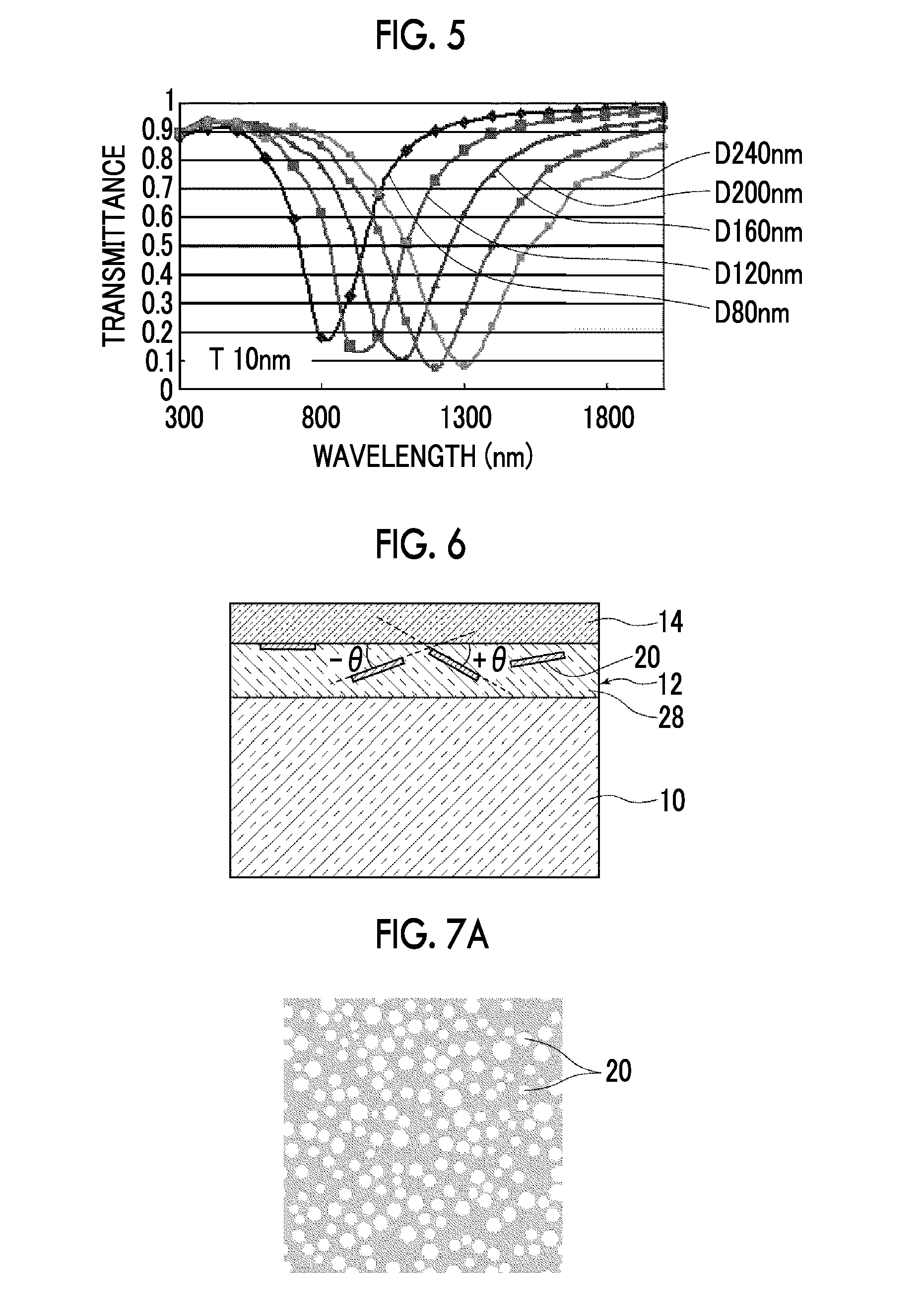
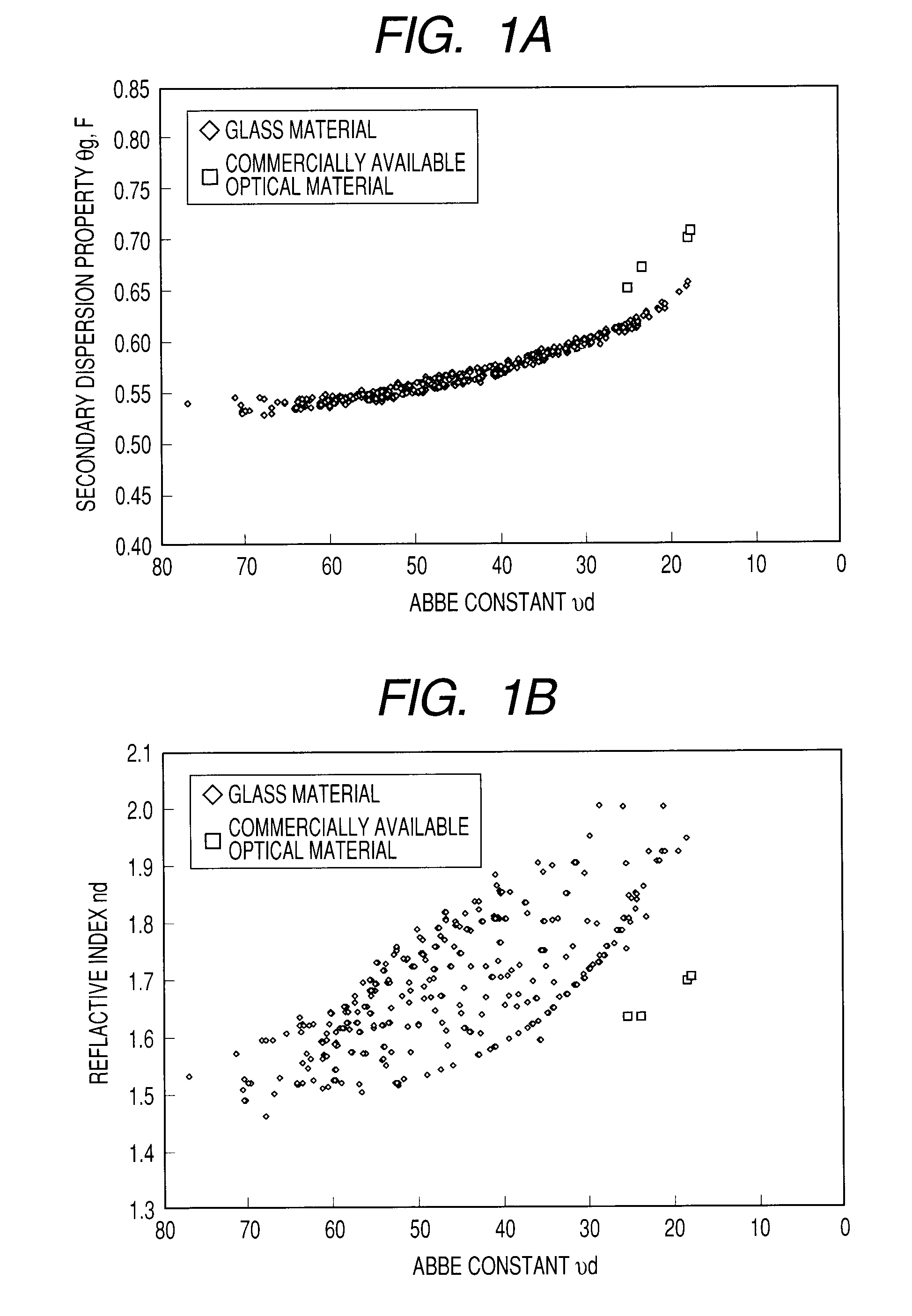
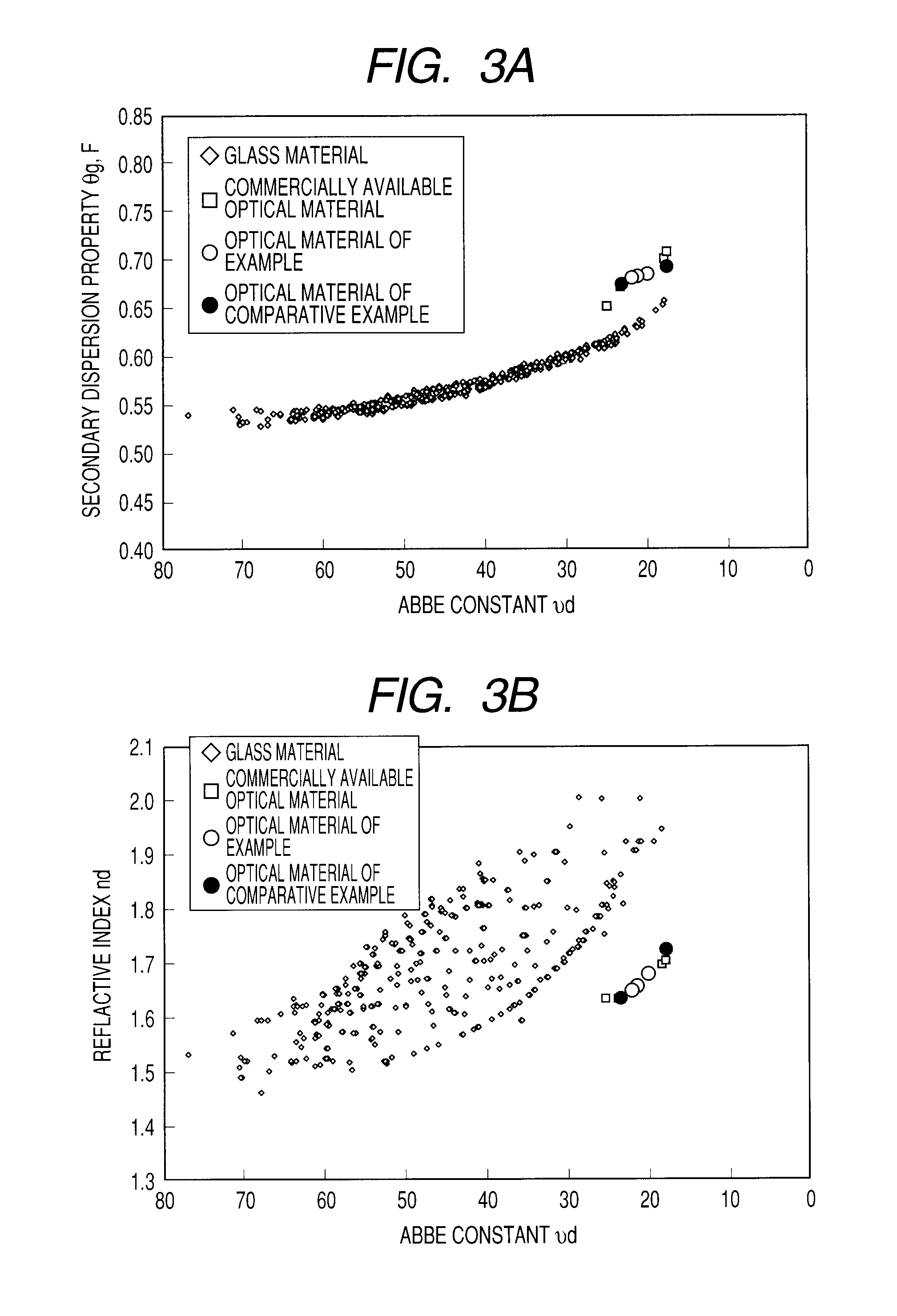
Optical material and optical element
InactiveUS20100076138A1High transmittanceLow optical scattering propertyAnti-corrosive paintsOptical elementsThiol groupSulfur containing
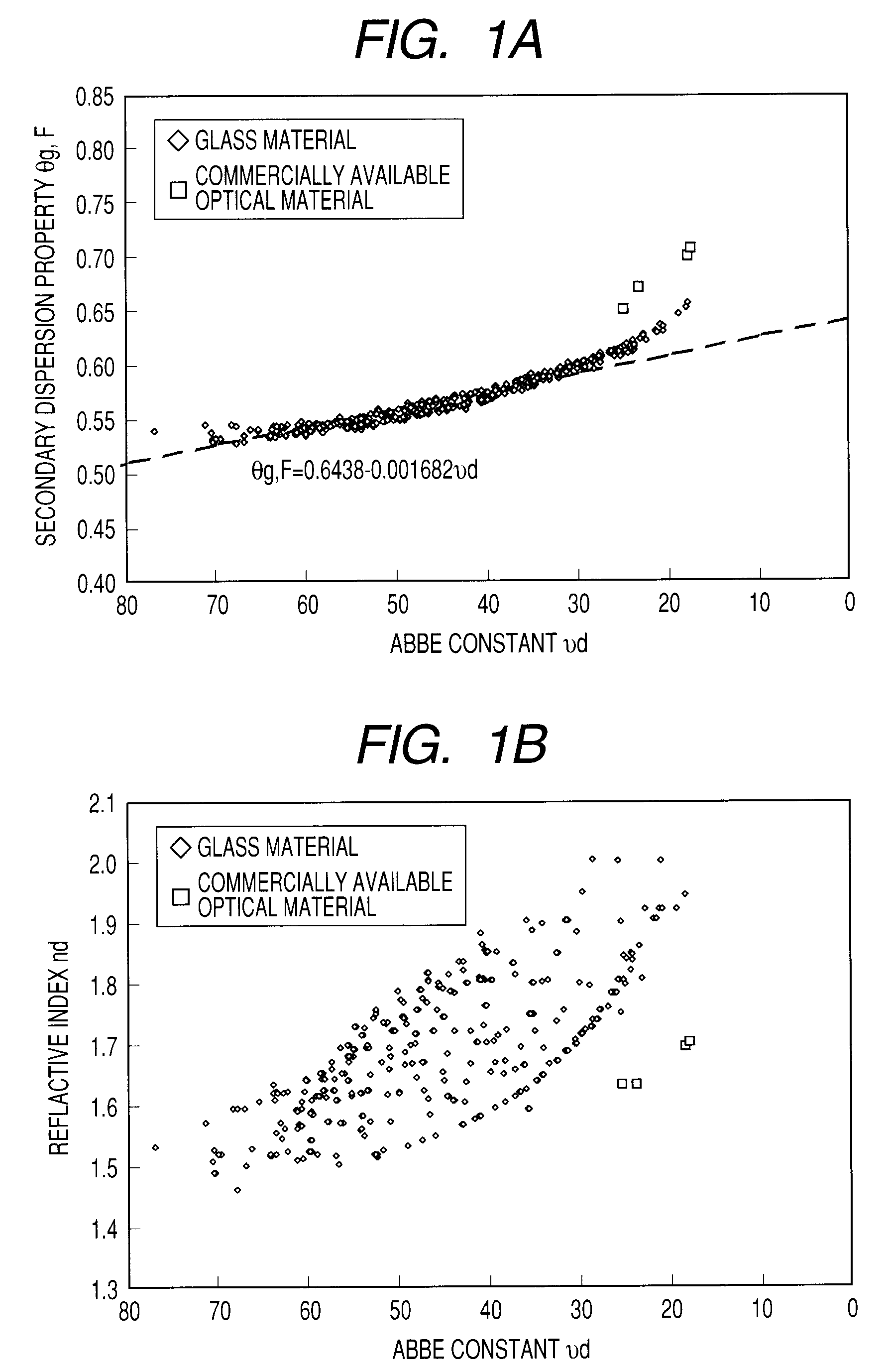
Provided is an optical material including a polymer of a mixture which contains a sulfur-containing compound, a fluorene compound with a fluorene skeleton, and an energy polymerization initiator. The sulfur-containing compound contains, in a molecule, at least one kind of group selected from the group consisting of a sulfide group, a sulphone group, a sulfoxide group, a thiol group, and a thioester group. A refractive index of the polymer of the mixture is 1.65 or more to less than 1.92, an Abbe constant thereof is 15 or more to less than 22, and a difference Δθg,F between a secondary dispersion property θg,F thereof and a secondary dispersion property θg,F of a normal optical material which is expressed by θg,F=0.6438−0.001682νd is 0.05 or more to less than 0.13.
Owner:CANON KK
Flip-chip type semiconductor luminescent device structure and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN102683531AReduce absorptionAchieve optimal processingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsActive layer
The invention discloses a flip-chip type semiconductor luminescent device structure and a manufacture method thereof. The flip-chip type semiconductor luminescent device structure comprises a supporting base plate, a luminous epitaxial layer and a light-transmitting growth substrate, wherein the luminous epitaxial layer is located on the supporting base plate and is sequentially formed by a p-shaped semiconductor layer, a luminous active layer, an n-shaped semiconductor layer and a buffering layer, and the light-transmitting growth substrate is located on the luminous epitaxial layer. The flip-chip type semiconductor luminescent device structure is characterized in that a regular graphical air interlayer is located between the light-transmitting growth substrate and the luminous epitaxial layer and has optical matching thickness. By means of the graphical air interlayer located between the light-transmitting growth substrate and the luminous epitaxial layer and having the optical matching thickness, the effects of light transmitting and radiation can be achieved.
Owner:XIAMEN SANAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Transparent conductive film and production method therefor
ActiveUS20150357077A1High transmittanceHigh reliabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingConductive coatingElectrically conductive
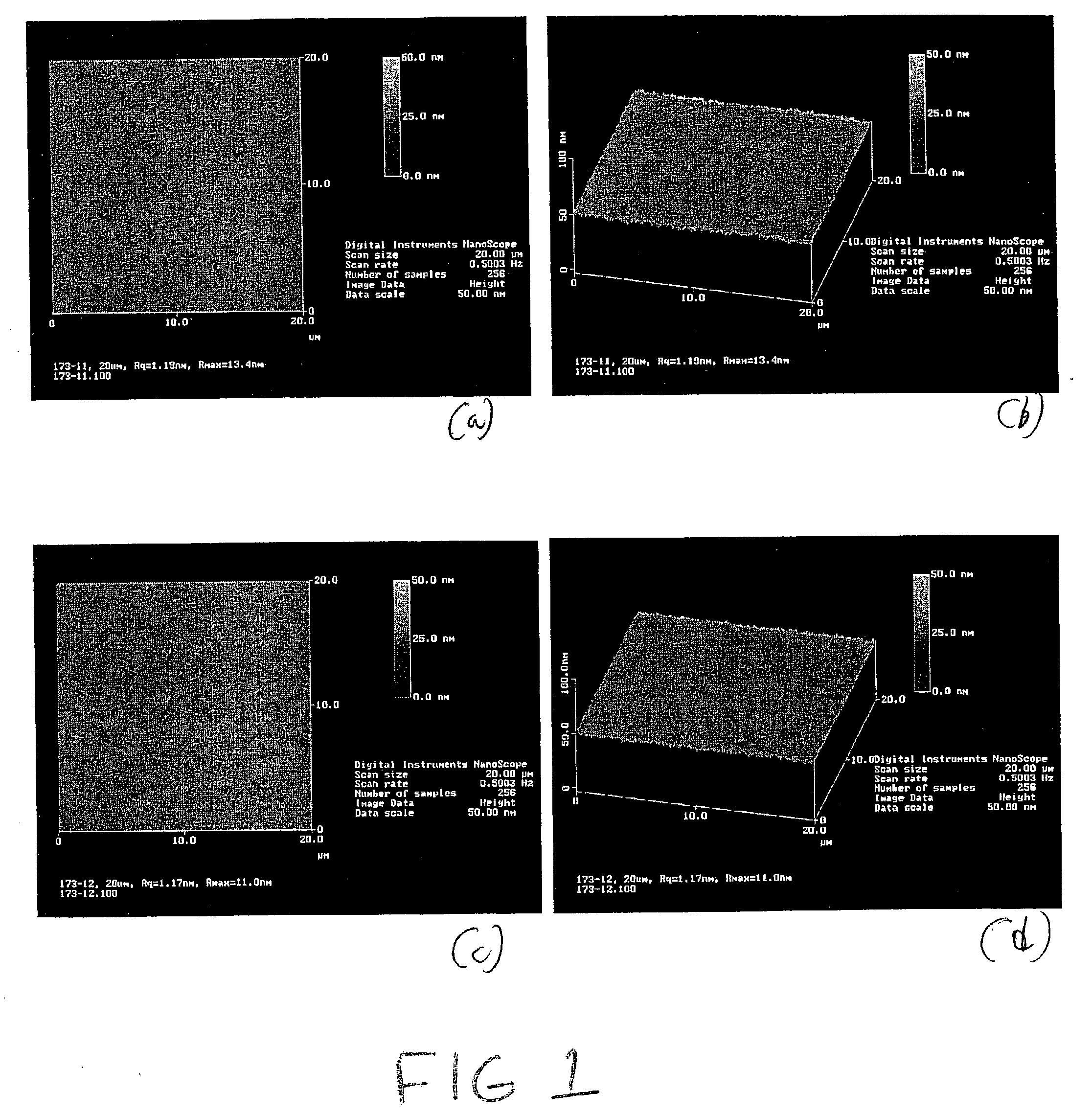
The transparent conductive film of the invention includes a transparent conductive coating provided on at least one surface of an organic polymer film substrate, wherein the transparent conductive coating is a crystalline coating of an indium-based complex oxide having a tetravalent metal oxide content of 7 to 15% by weight as calculated by the formula {(the amount of the tetravalent metal element oxide) / (the amount of the tetravalent metal element oxide+the amount of indium oxide)}×100 (%), has a thickness of 10 to 40 nm and a specific resistance of 1.3×10−4 to 2.8×10−4 Ω·cm, has main X-ray diffraction peaks corresponding to (222) and (440) planes, and has a ratio (I440 / I222) of (440) peak intensity to (222) peak intensity of less than 0.2. The transparent conductive film of the invention has a crystalline thin coating with a low level of specific resistance and surface resistance.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Polymers, resist compositions and patterning process
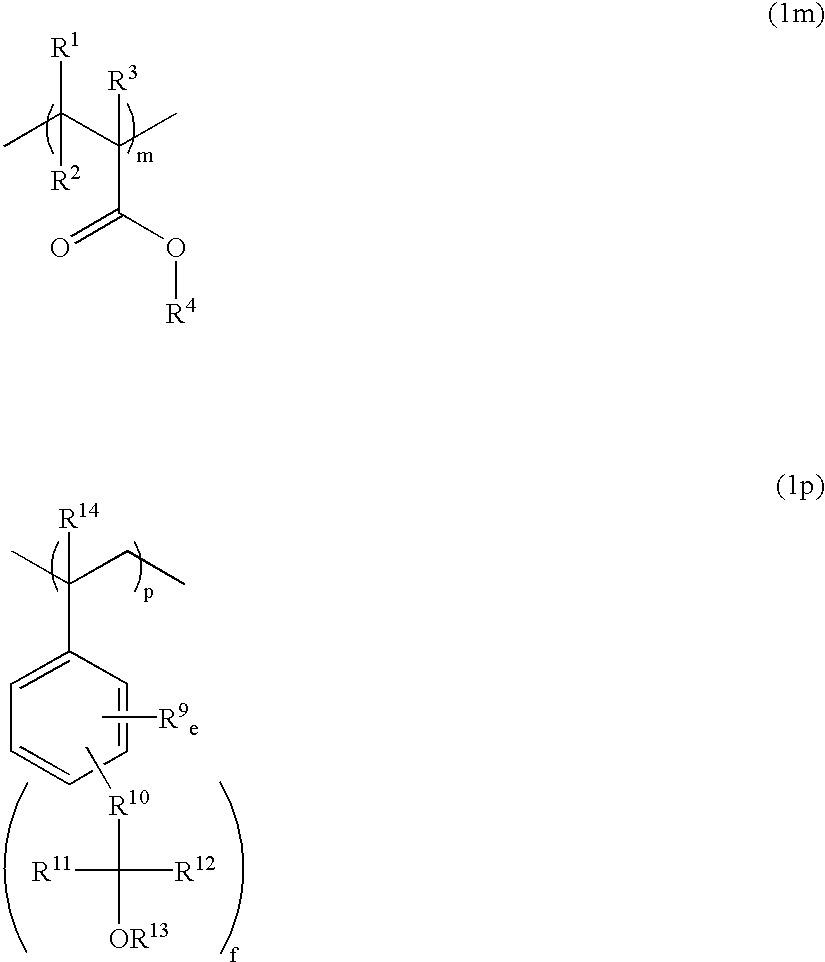
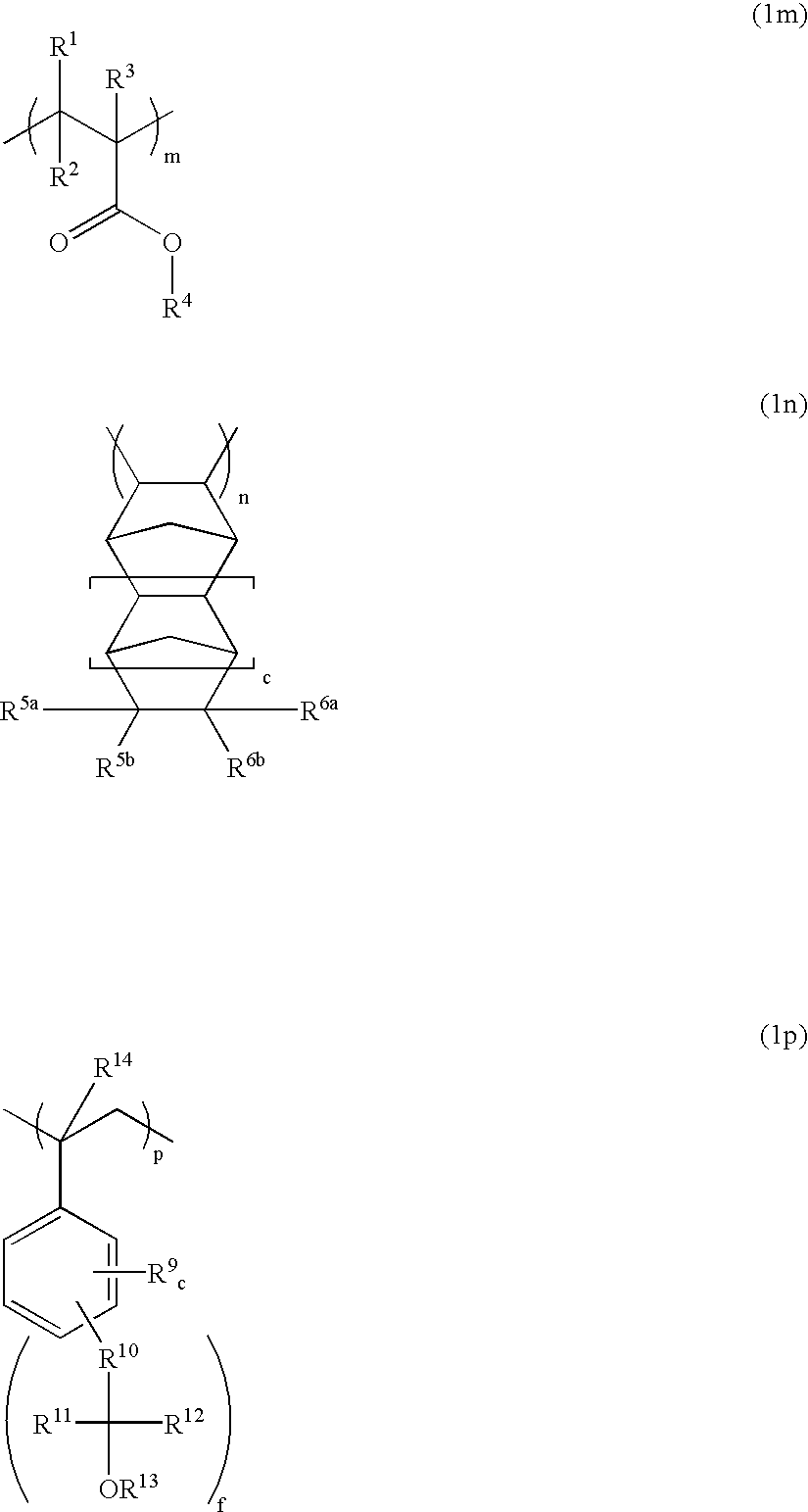
InactiveUS6864037B2High transmittanceImprove etch resistanceRadiation applicationsPhotosensitive material processingNorborneneResist
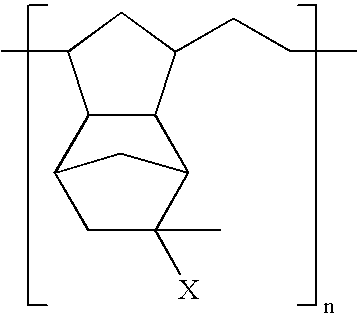
A copolymer of an acrylic monomer having at least one C6-20 alicyclic structure with a norbornene derivative or styrene monomer having a hexafluoroalcohol pendant is highly transparent to VUV radiation and resistant to plasma etching. A resist composition using the polymer as a base resin is sensitive to high-energy radiation below 200 nm, has excellent sensitivity, transparency and dry etching resistance, and is suited for lithographic microprocessing.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD +2
Anti-reflection optical member
ActiveUS20160291207A1Low reflectanceHigh transmittanceLayered productsOptical articlesPrincipal planeRefractive index
An anti-reflection optical member has a laminated structure including: a transparent substrate having a first refractive index greater than that of a predetermined medium; a metal-microparticle-containing layer containing metal microparticles; and a dielectric layer having a second refractive index greater than that of the predetermined medium, in this order. At least 60% of the metal microparticles are flat particles with a diameter-to-thickness ratio of 3 or more. Principal planes of the flat metal particles are surface-oriented in the range from 0° to 30° relative to the surface of the metal-microparticle-containing layer. In the metal-microparticle-containing layer, the metal microparticles are disposed without forming a conductive path. The dielectric layer has such a thickness that light reflected at the surface of the dielectric layer of incident light entering the laminated structure from the surface is interfered and canceled by light reflected at the interface between the dielectric layer and the metal-microparticle-containing layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical material and optical element
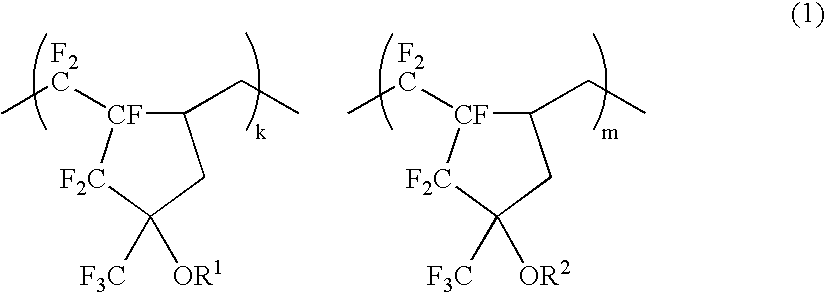
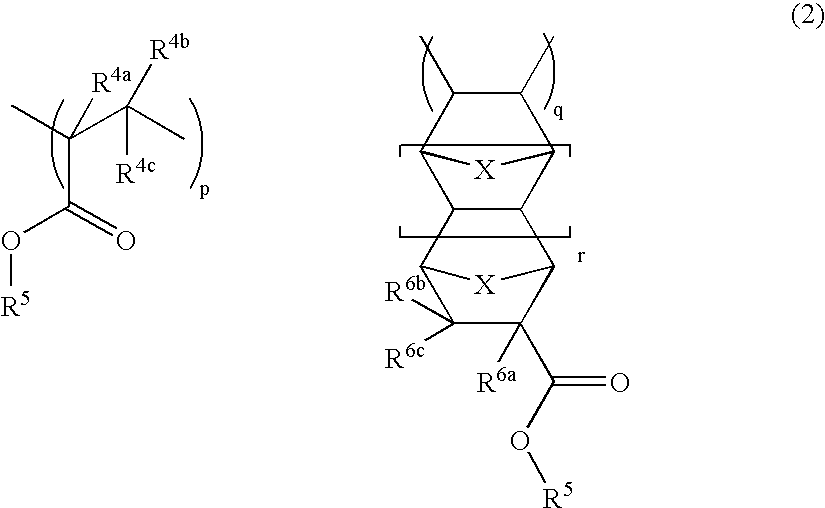
ActiveUS20100076106A1High transmittanceHigh refractive indexOrganic chemistryOptical elementsAbsorption rateHigh transmittance
Provided is an optical material which has a high transmittance, a high refractive index, a low Abbe constant, a high secondary dispersion property, and a low water absorption rate. The optical material includes a polymer of a mixture which contains: a sulfur-containing compound represented by the following general formula (1):a sulfur-containing compound represented by the following general formula (2):and an energy polymerization initiator, in which a content of the sulfur-containing compound represented by the chemical formula-2 is 10% by weight or more to 60% by weight or less, an Abbe constant (νd) of the polymer of the mixture satisfies 18<νd<23, and a secondary dispersion property (θg,F) thereof satisfies 0.68<θg,F<0.69.
Owner:CANON KK
Early-bearing and high-yield Camellia oleifera cultivation method
ActiveCN105494002AIncrease productionHigh transmittanceCultivating equipmentsDiseaseCamellia oleifera
The invention relates to an early-bearing and high-yield Camellia oleifera cultivation method and belongs to the technical field of economic forest planting. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) establishment of forest land: selection of nursery stocks, land preparation, application of base fertilizer and planting; (2) management of a young forest: application of fertilizer, tending and weeding as well as tree shape pruning; (3) disease and pest control: disease control and pest control; (4) transplantation. With the adoption of the Camellia oleifera cultivation method, 60 kg of camellia oil is averagely produced per mu in the fifth year after planting, compared with the traditional yield of 10-15 kg of the camellia oil per mu, the yield is increased by 3-5 times, and the method is an important early high-yield and high-efficiency technology for Camellia oleifera. A Camellia oleifera high-yield forest has an area of 23 mu, 61.25 kg of the camellia oil is averagely produced per mu in 2015, and 1408.75 kg of the camellia oil is produced totally.
Owner:资源县贵盟金油茶开发有限责任公司
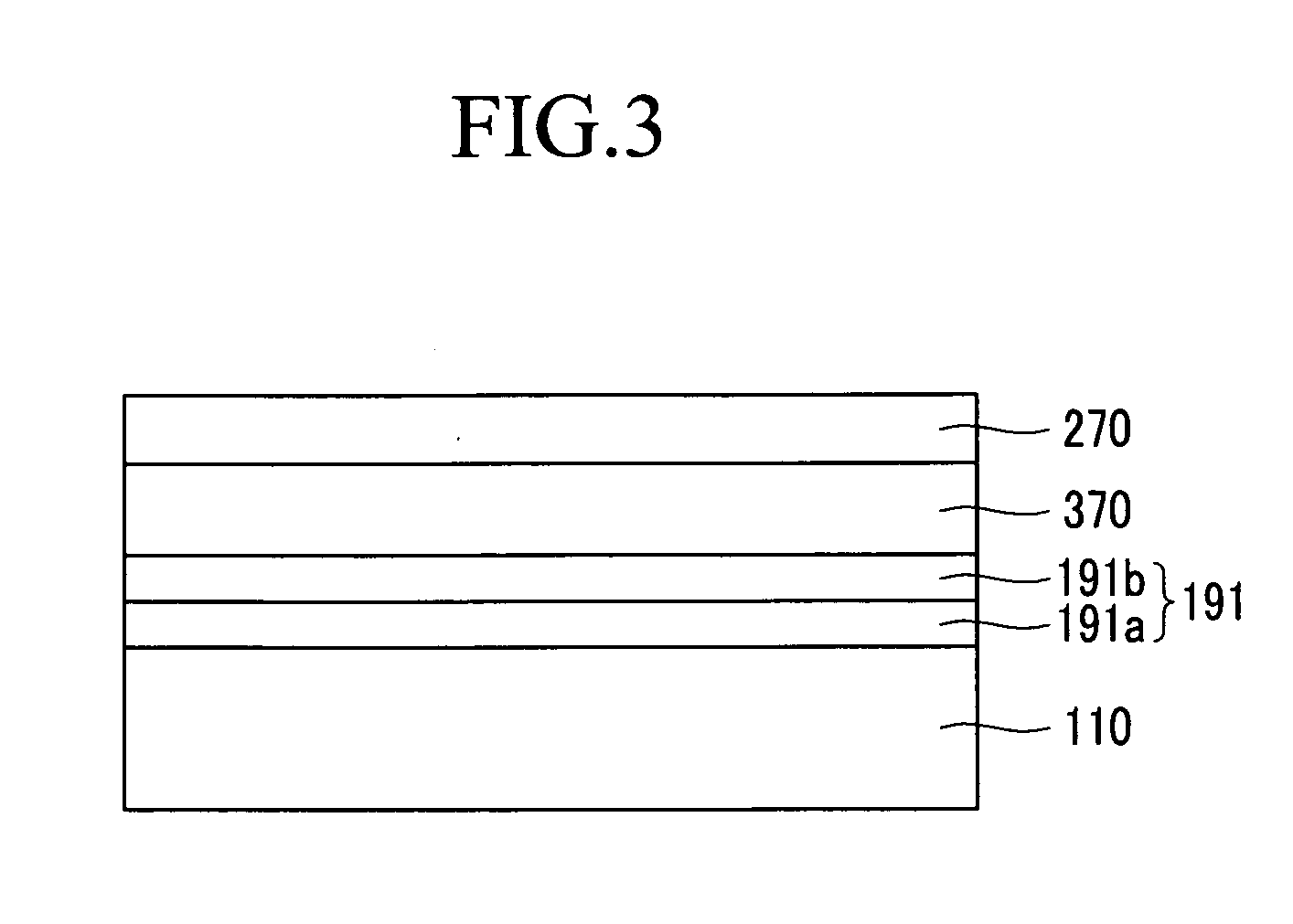
Information recording medium and method for manufacturing same
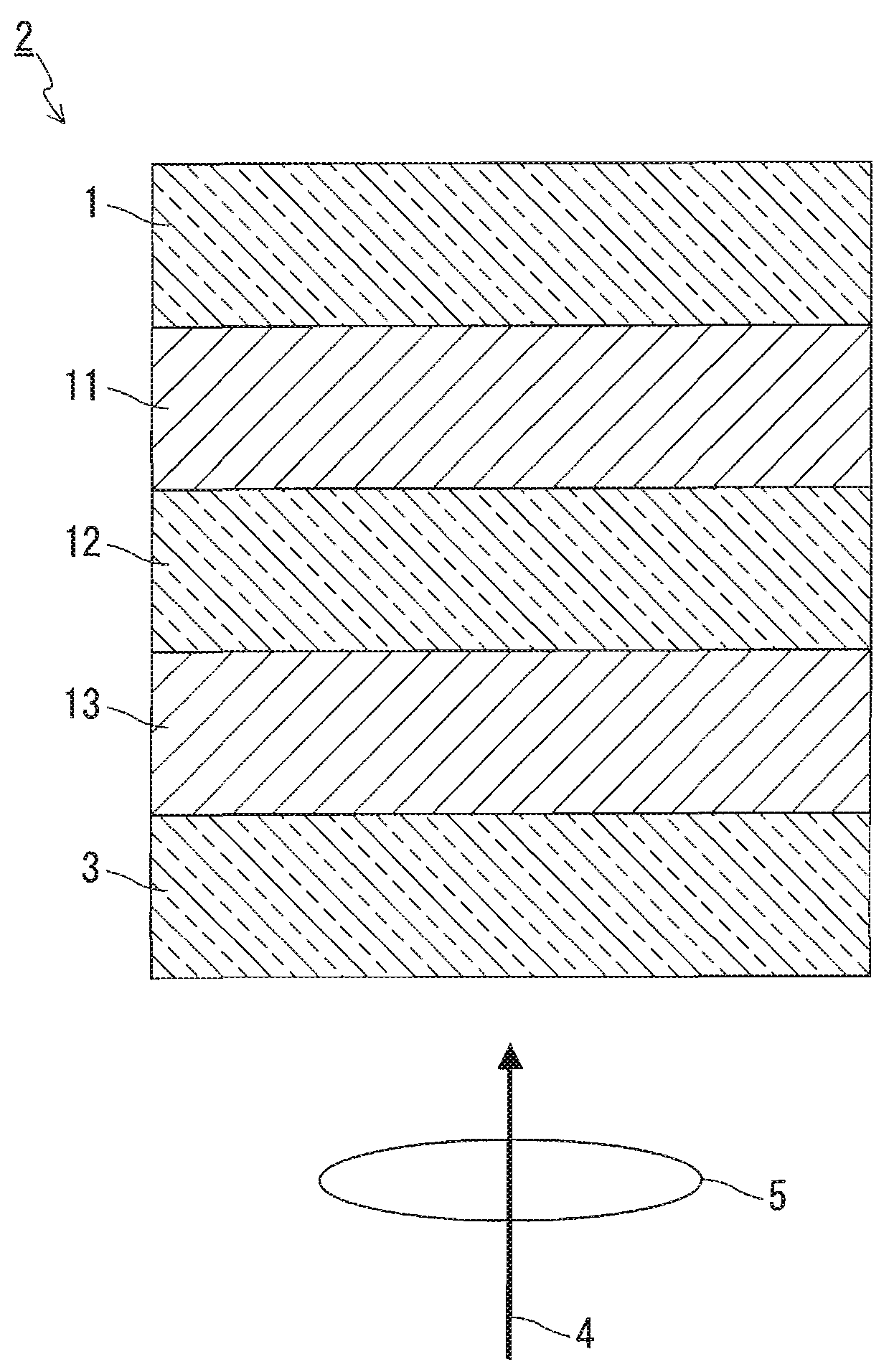
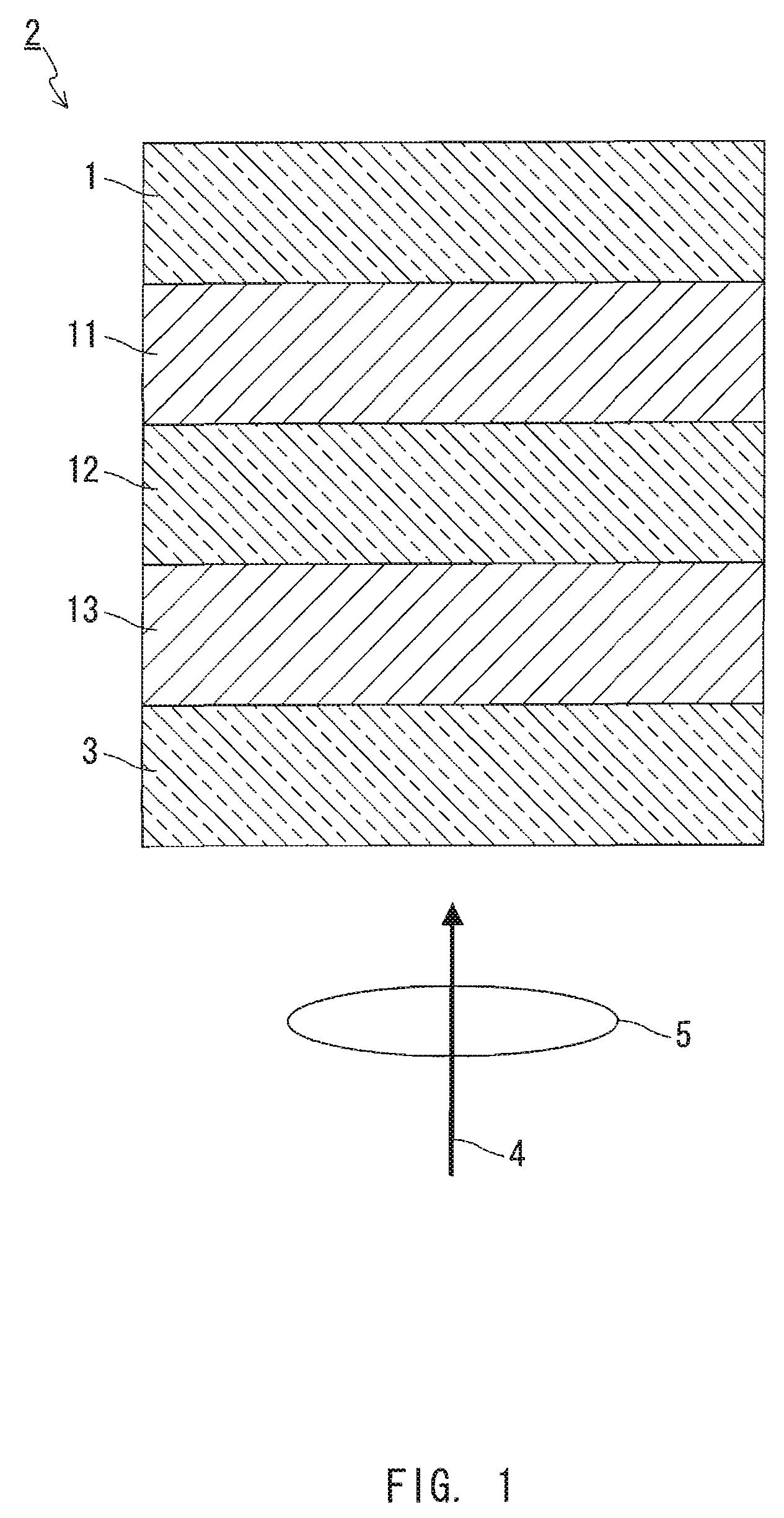
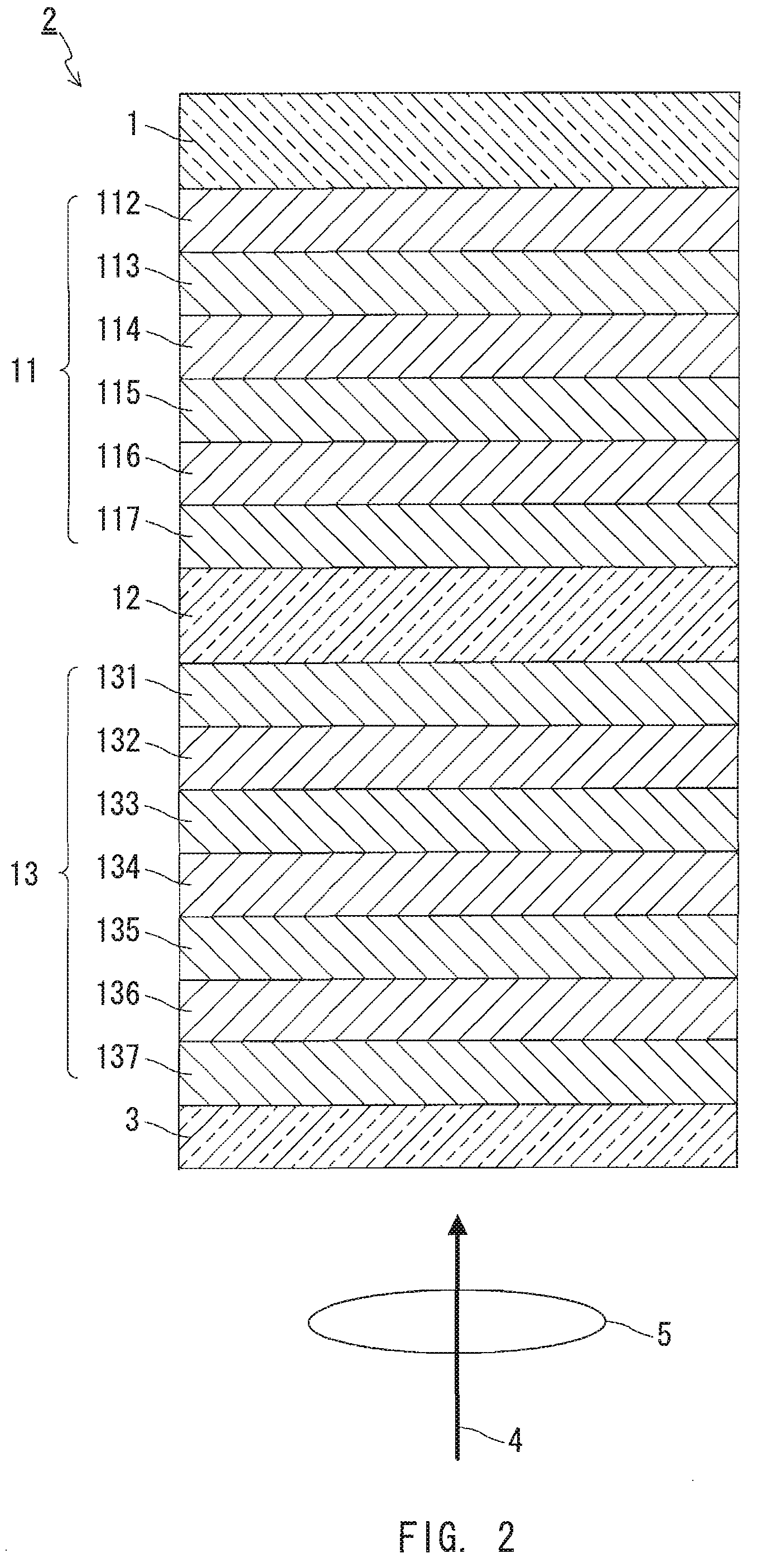
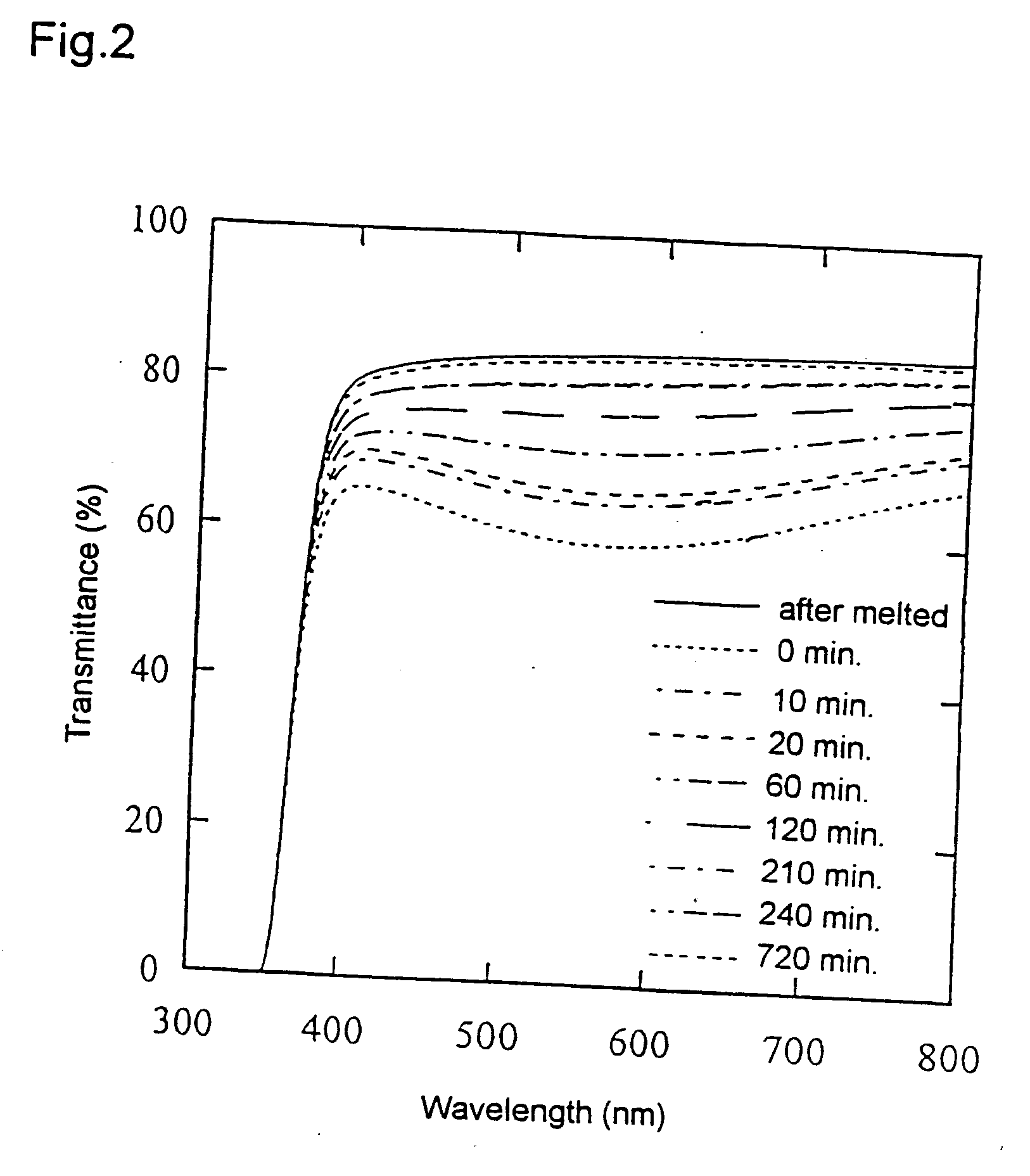
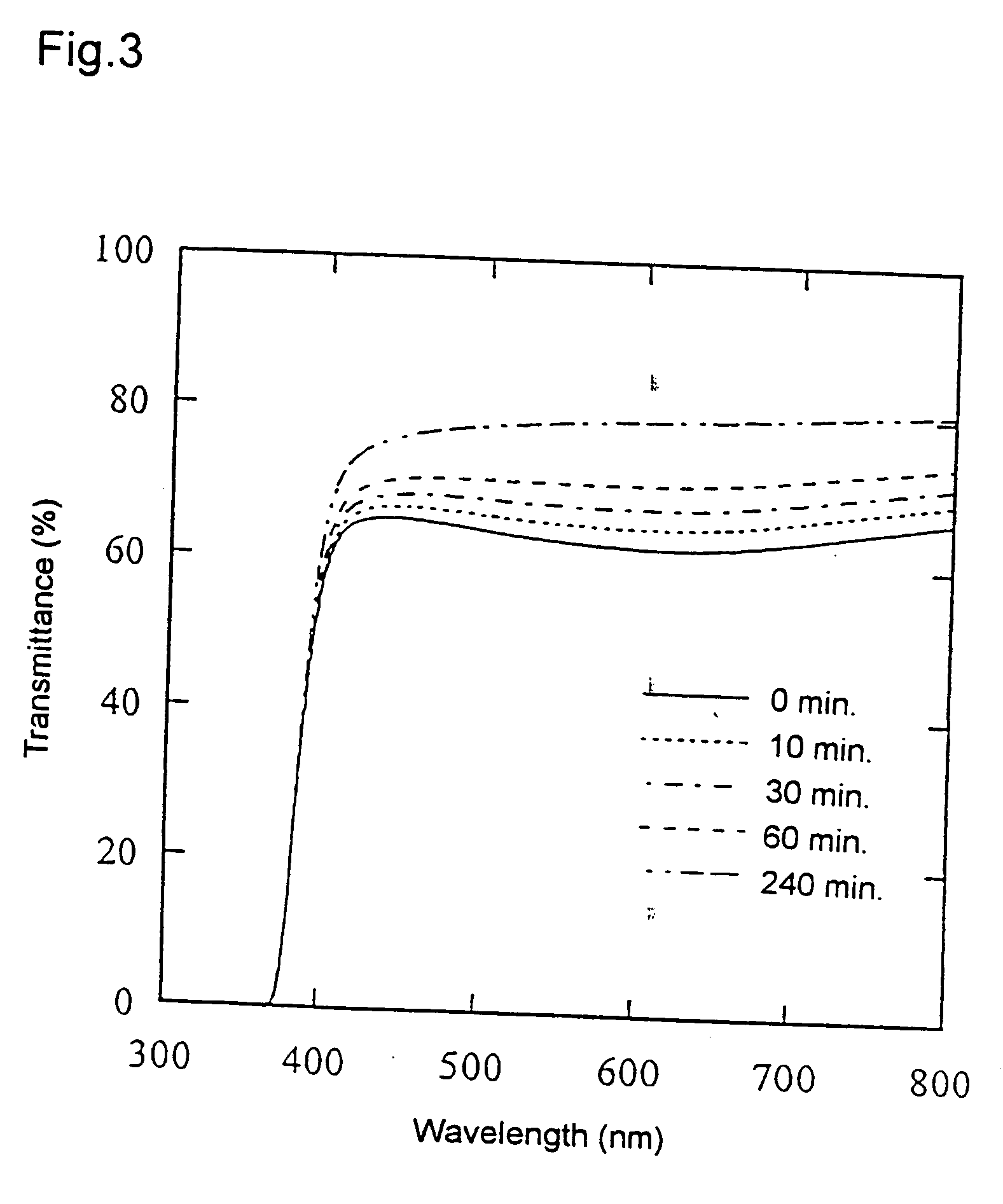
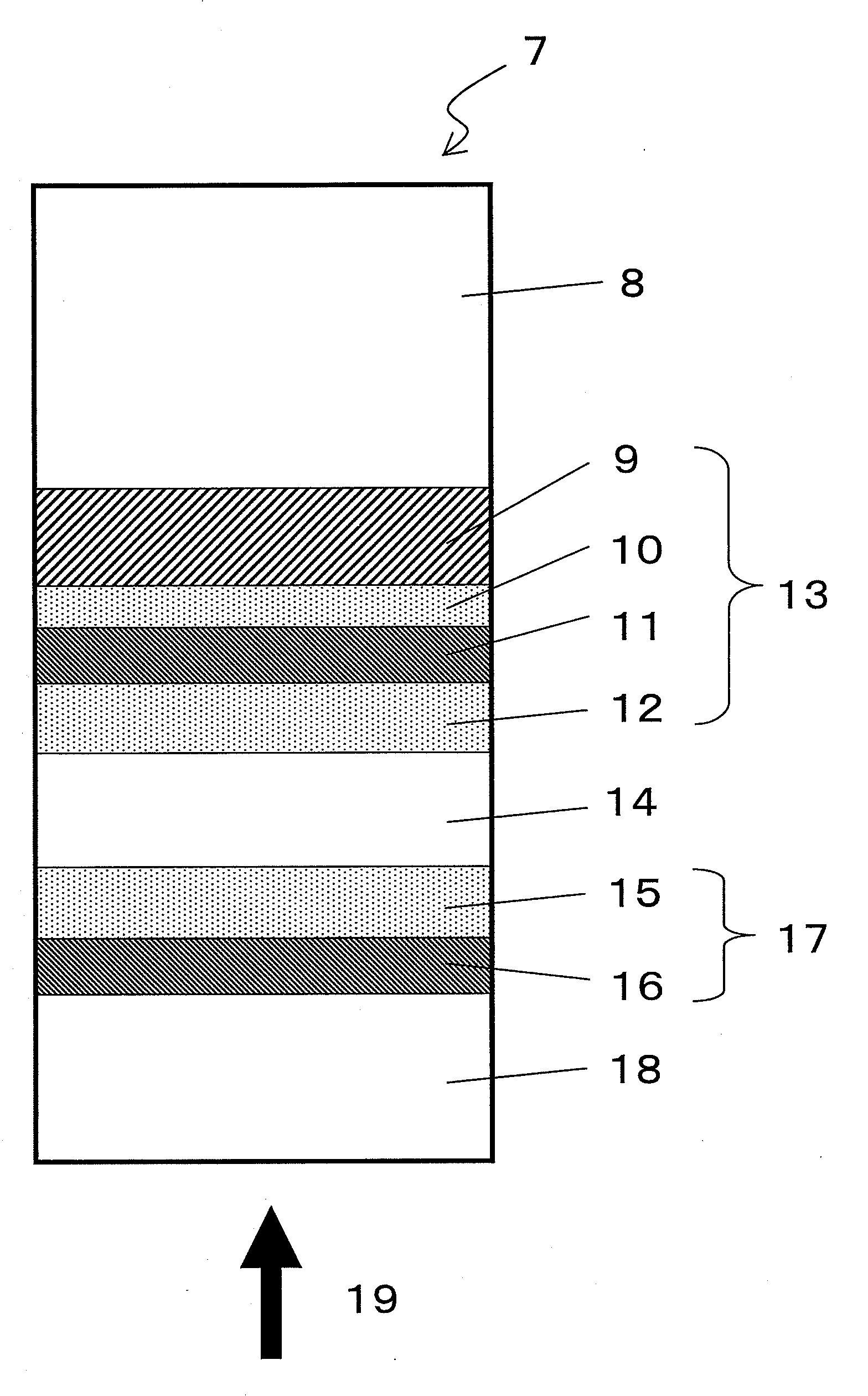
InactiveUS20090086608A1High transmittanceGood characteristicLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusPhysicsTransmittance
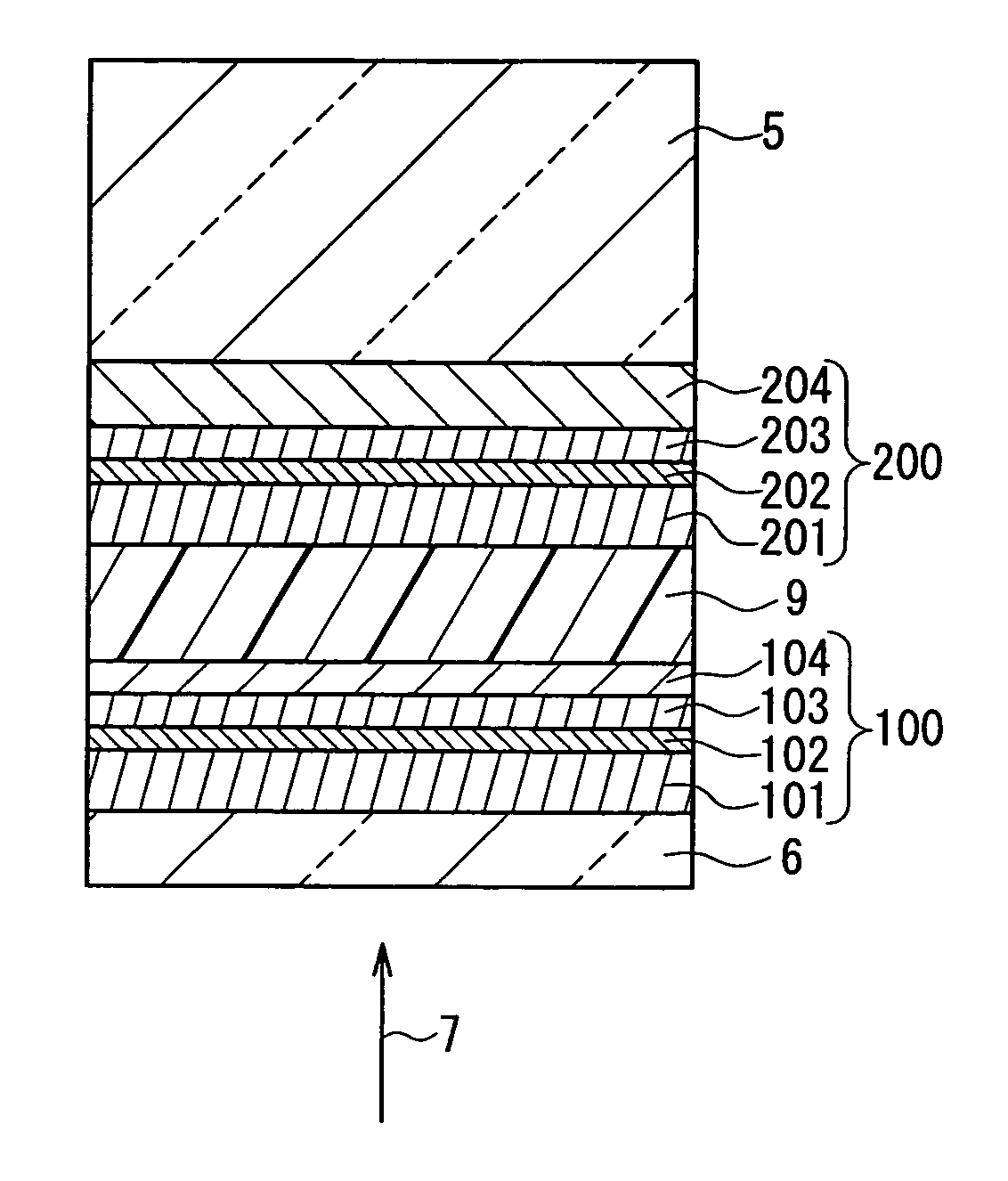
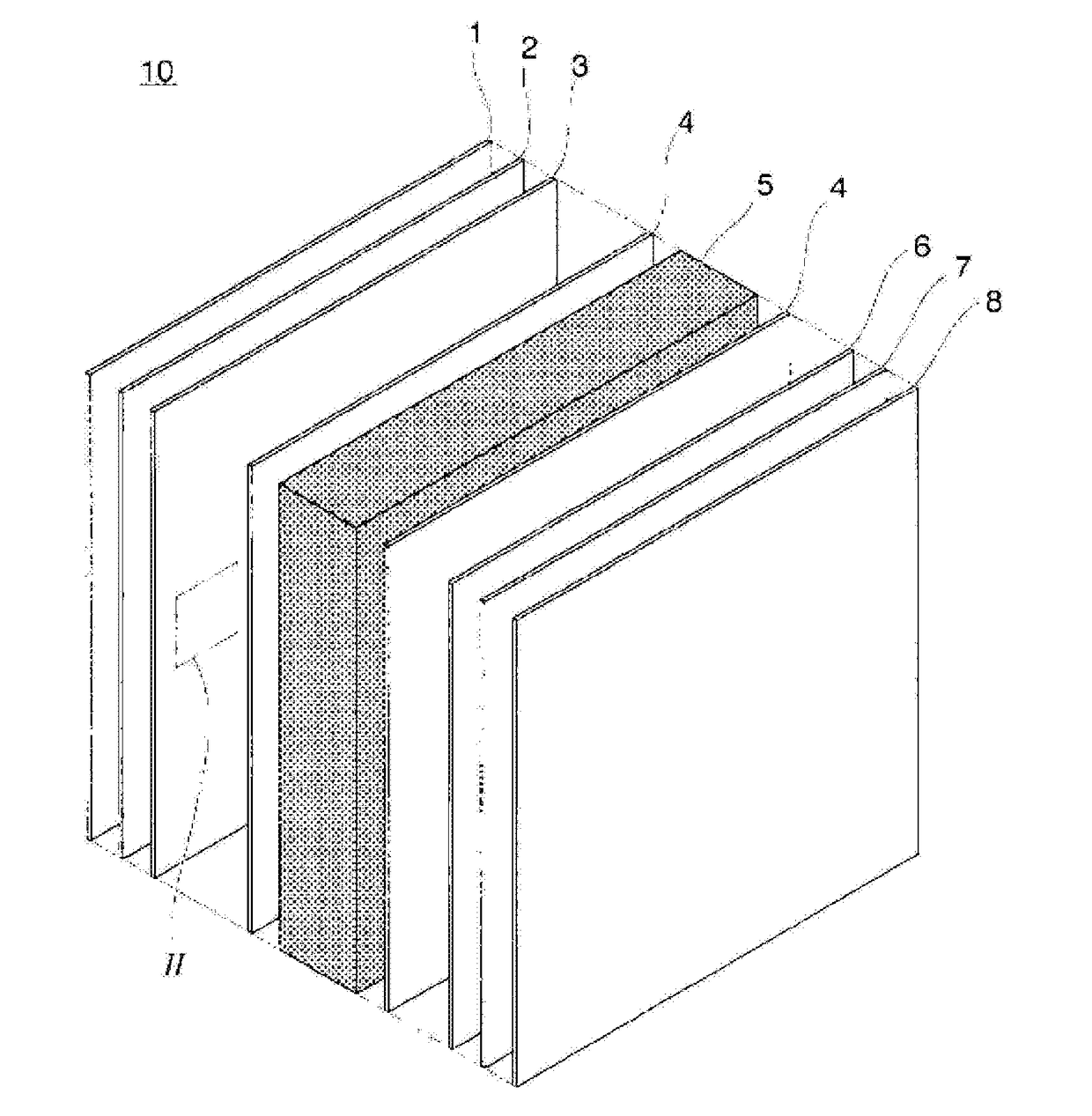
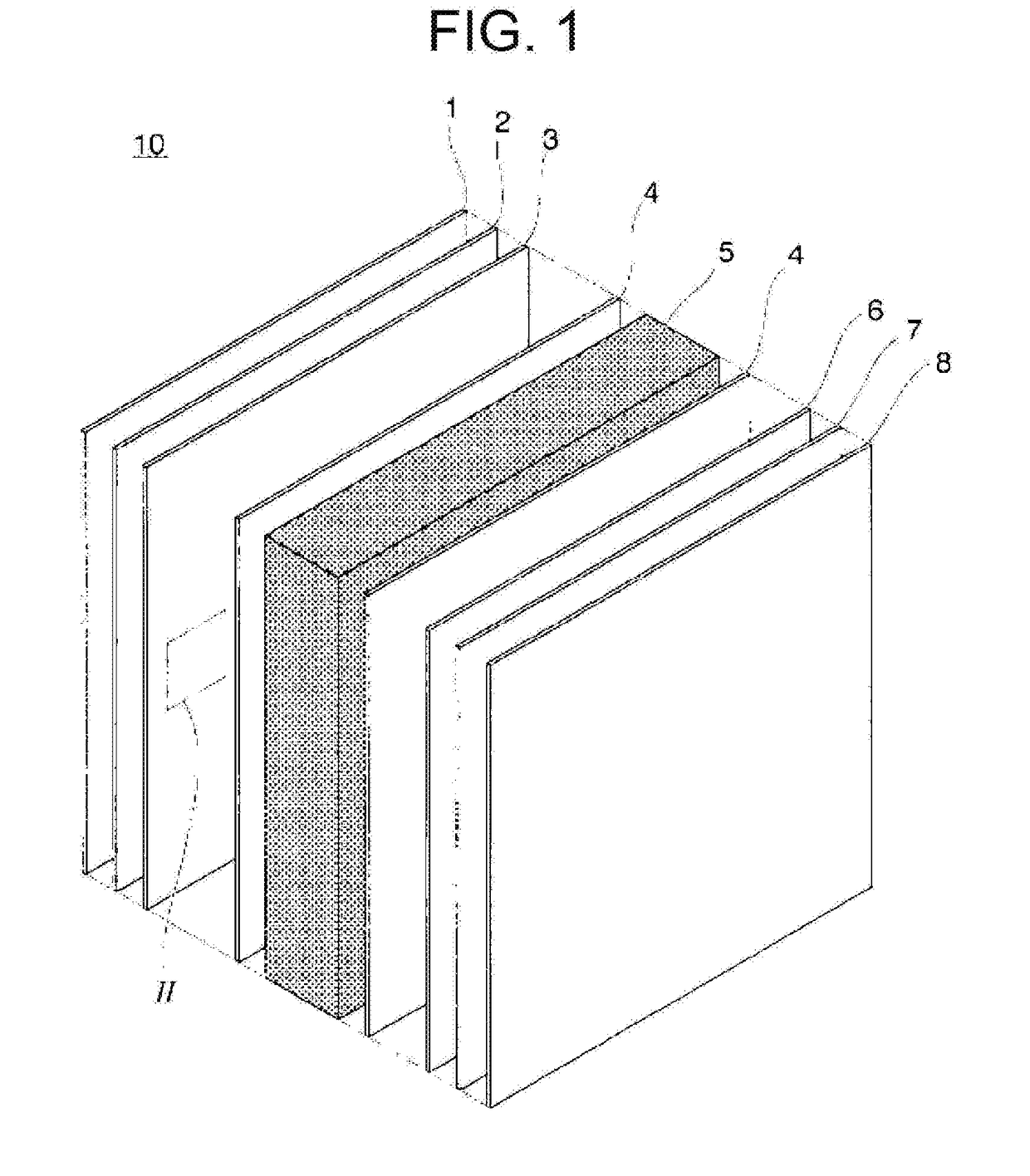
An information recording medium of the present invention includes N information layers on a substrate (1), where N is an integer of 2 or more. Information is recorded / reproduced by irradiating each of the information layers (11, 12) with a laser beam (4). When the N information layers are referred to as a first information layer to an N-th information layer sequentially from the opposite side to a laser beam incident side, the L-th information layer included in the N information layers includes at least a recording layer (135) capable of undergoing a phase change through laser beam irradiation, a reflective layer (132), and a transmittance adjusting layer (131) in this order from the laser beam incident side, where L is an integer satisfying 2≦L≦N. The transmittance adjusting layer (131) contains Nb, oxygen (O), and at least one element M selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, Y, Cr, Zn, Ga, Co, Bi, In, Ta, and Ce. In the transmittance adjusting layer (131), the content of Nb is at least 2.9 atom %.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Process for the production of glass molded article, optical element produced by the process, and method of treating glass
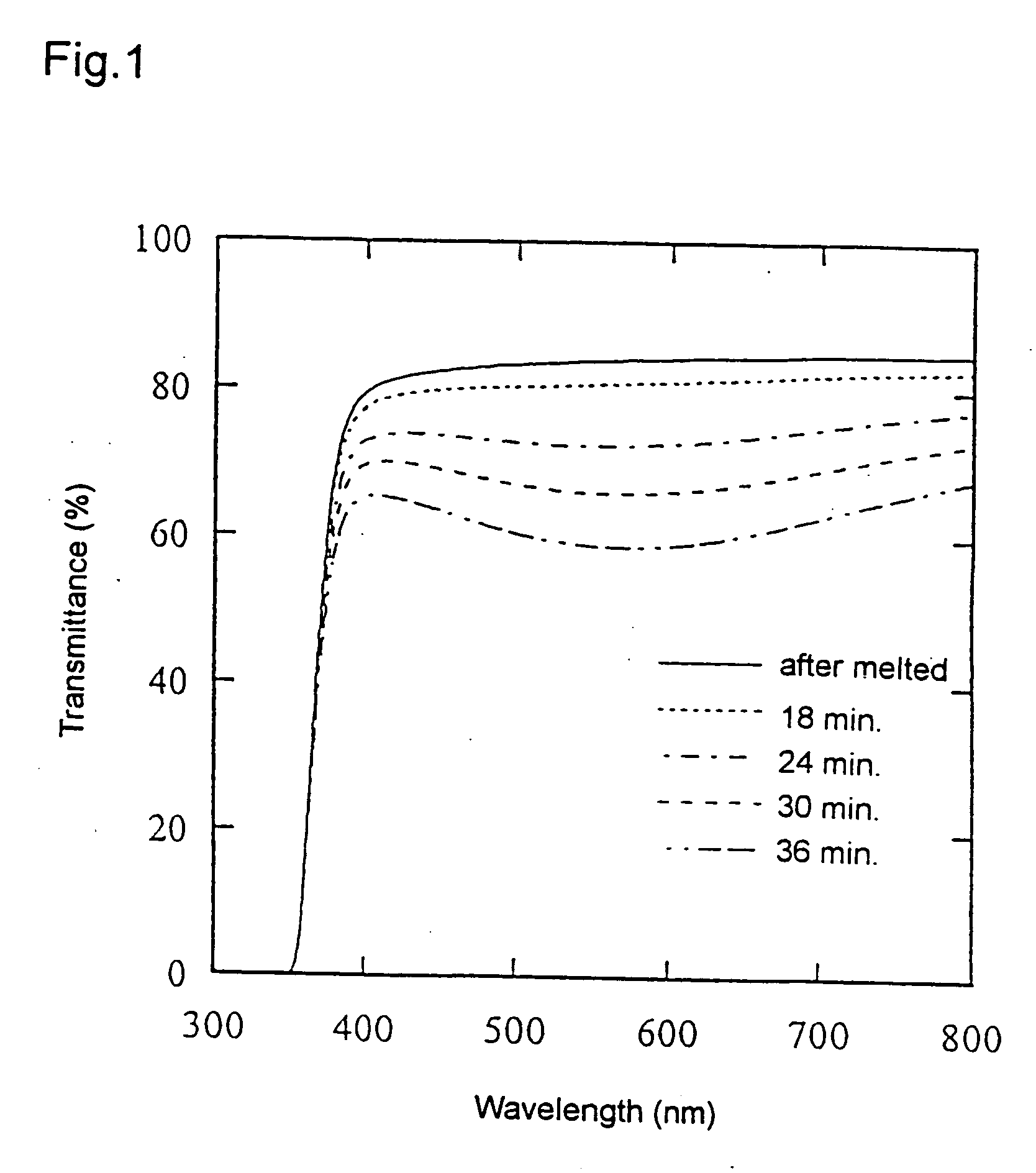
InactiveUS20050011228A1Efficiently produceHigh transmittanceGlass pressing apparatusGlass press-moulding apparatusTitanium dioxideHigh transmittance
Provided are a process for the production of a precision press-molded article having a high transmittance and a method of treating a glass to color or decolor the glass, the process comprising heat-treating a press-molded article containing at least one selected from WO3, Nb2O5 or TiO2 in an oxidizing atmosphere to produce a glass molded article, and the method comprising heat-treating a colored glass containing at least one oxide of WO3 and Nb2O5 in an oxidizing atmosphere to decolor the glass, or heat-treating a glass containing at least one oxide selected from WO3, Nb2O5 or TiO2 in a non-oxidizing atmosphere to color the glass.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Optical Information Recording Medium, Method Of Manufacturing The Same, And Sputtering Target
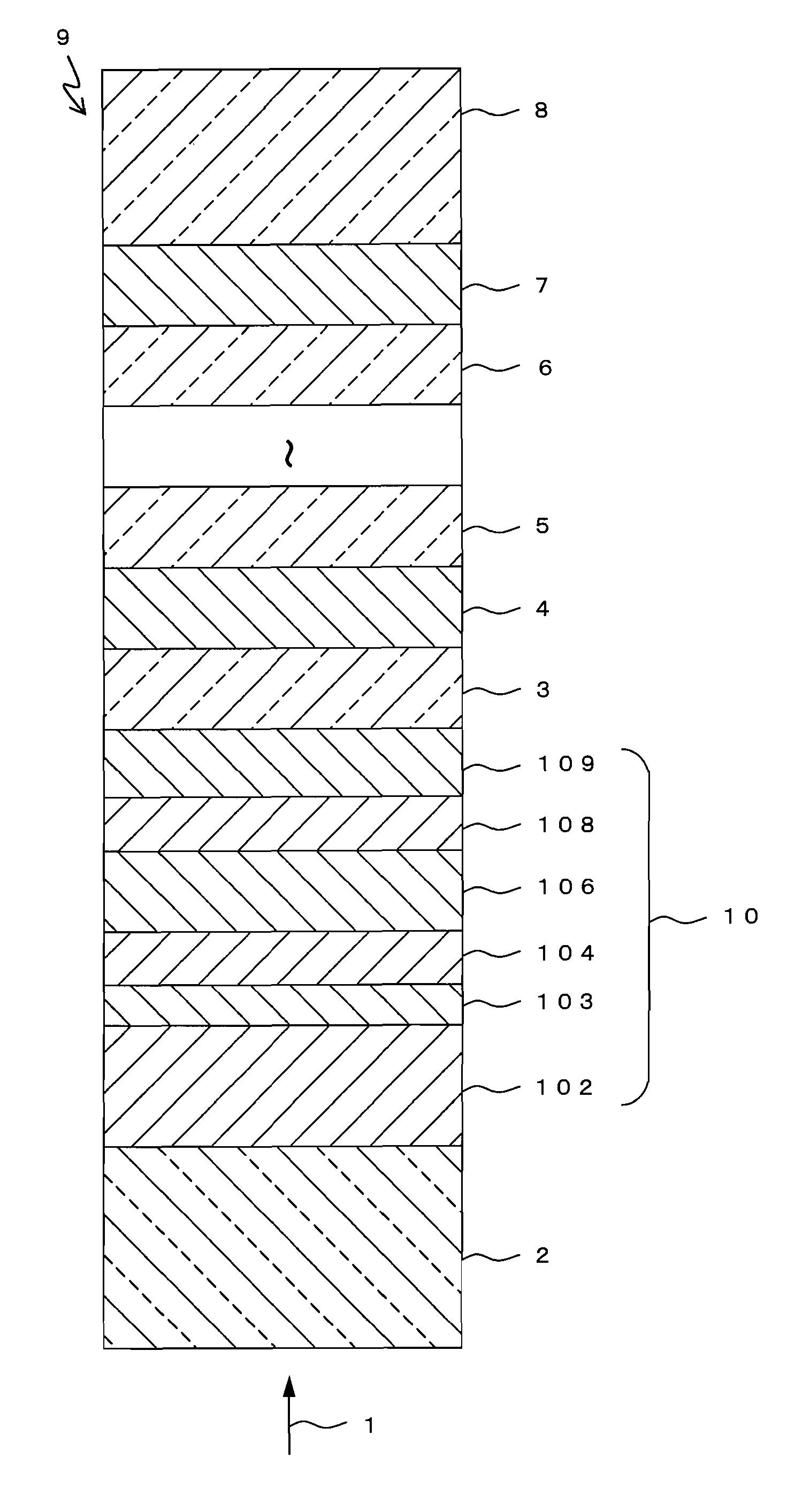
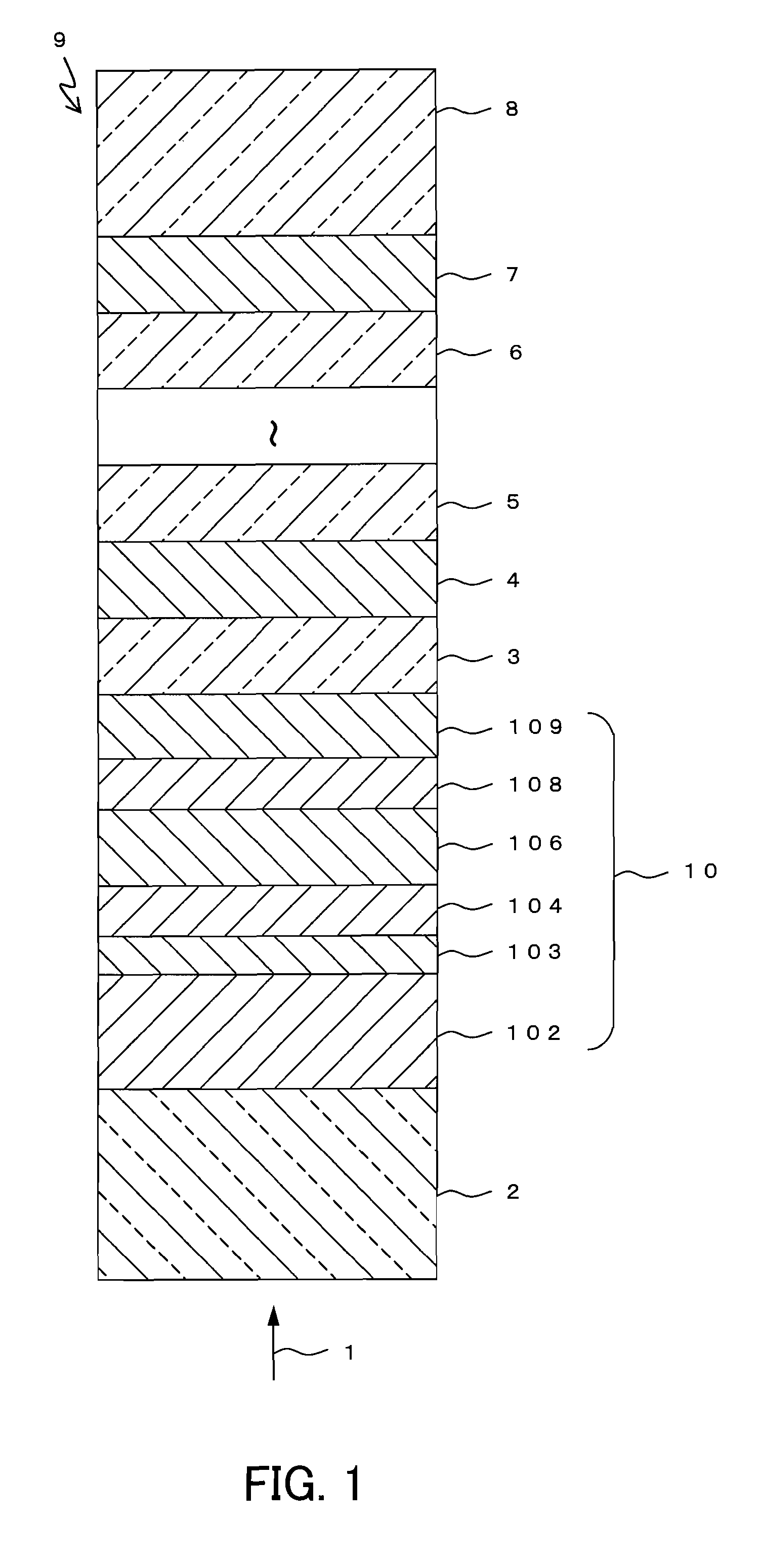
InactiveUS20100151179A1High film formation rateHigh transmittanceCellsLayered productsTransmittanceReflective layer
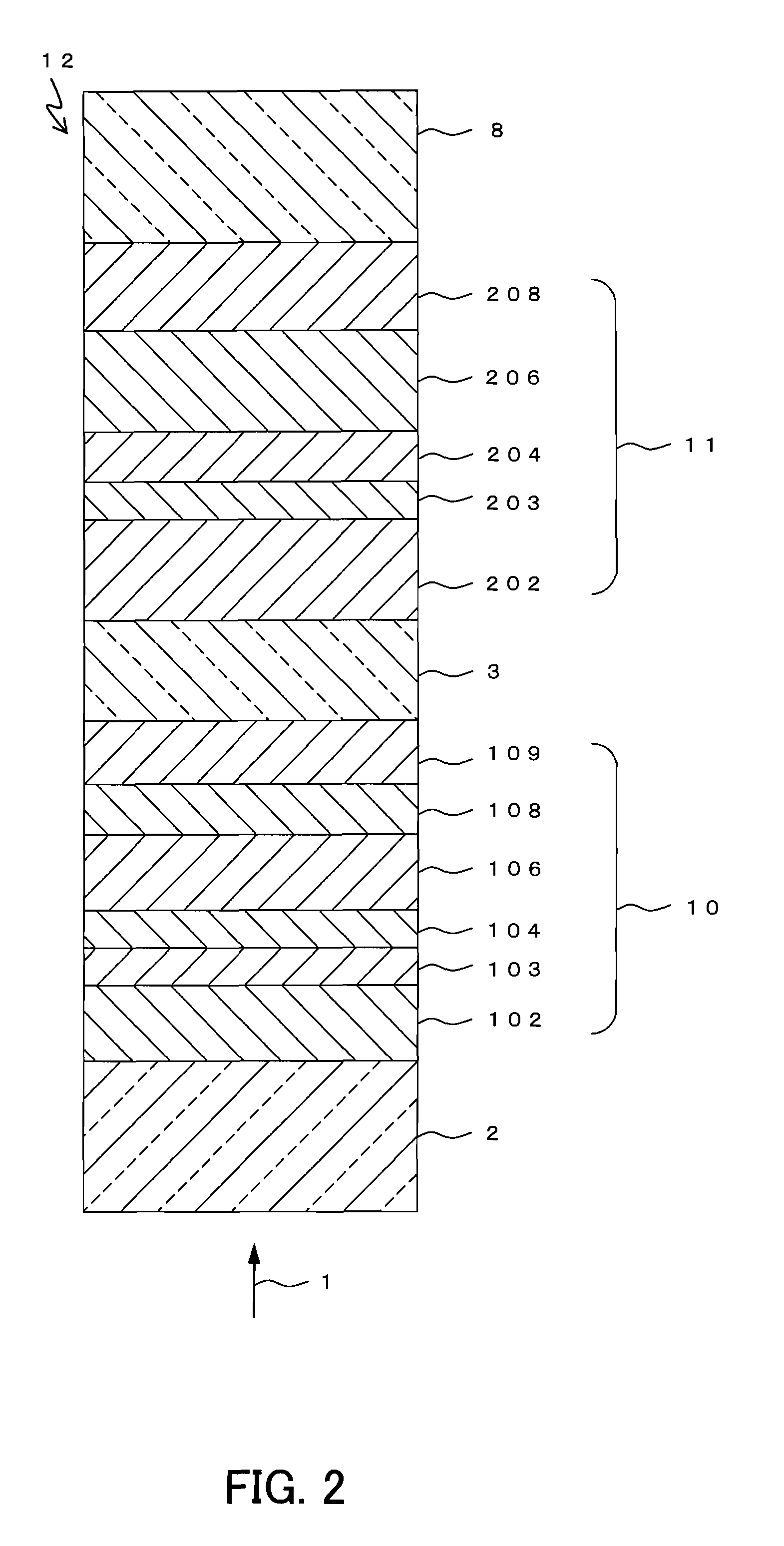
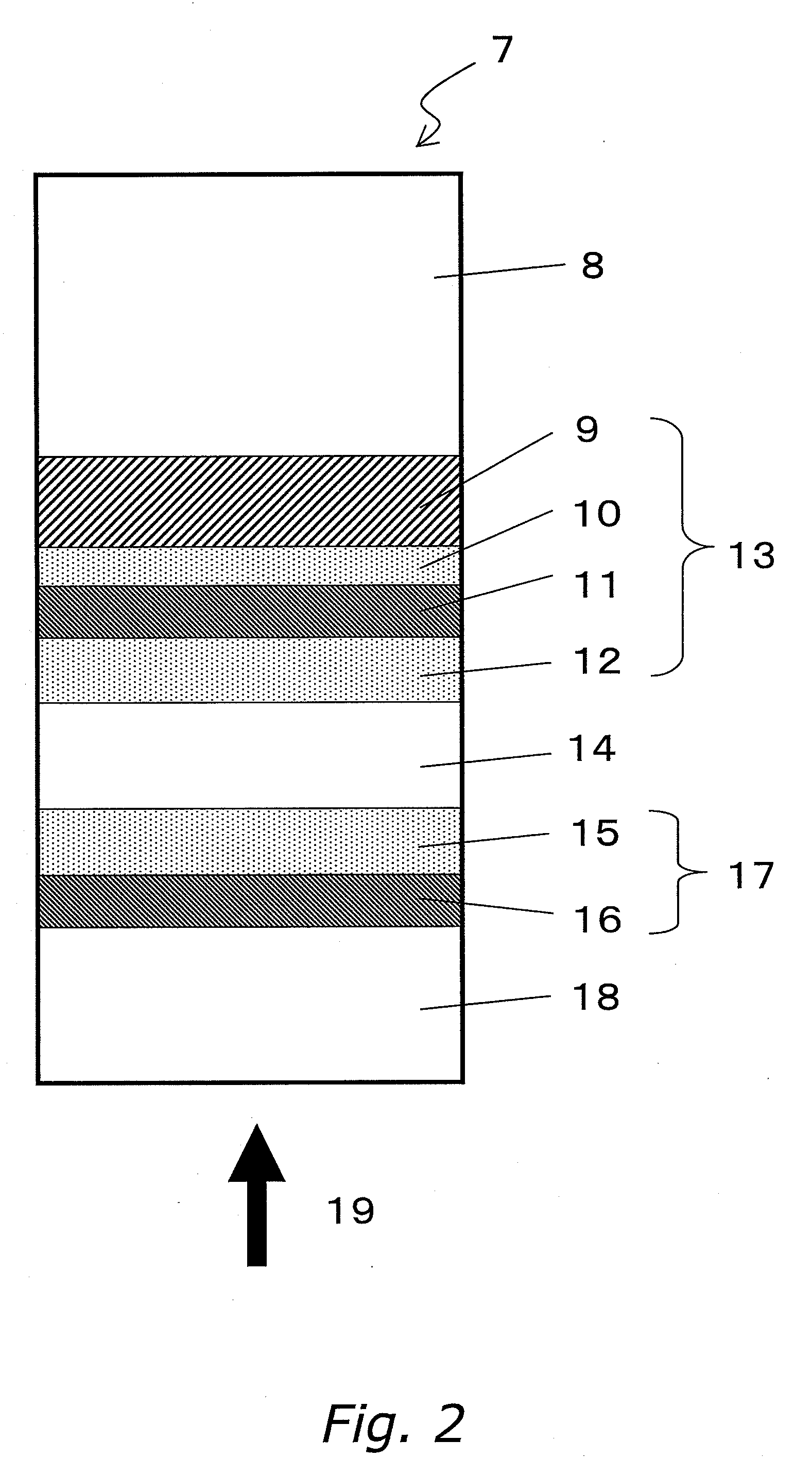
An optical information recording medium (9) of the present invention is an optical information recording medium including: N information layers, where N is a natural number of 2 or more; and an intermediate layer for separating the N information layers optically from each other. With the N information layers being referred to as a first information layer (10) to an N-th information layer (7) sequentially from an optical beam incident side, a first information layer (10) corresponding to an L-th information layer included in the N information layers includes a recording layer (104) on which information can be recorded by irradiation with an optical beam, a reflective layer (108), and a transmittance adjusting layer (109) in this order from the optical beam incident side, where L is an at least one natural number that satisfies 1≦L≦N−1. The transmittance adjusting layer (109) contains tungsten (W) and oxygen (O).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Liquid crystal display element
ActiveUS20180307070A1High transmittanceQuick responsivenessLiquid crystal compositionsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayCholesteric liquid crystal
The liquid crystal display element includes: two transparent substrates, at least one of the two transparent substrates having an electrode; a liquid crystal composition sandwiched between the two transparent substrates and containing one or two or more liquid crystal compounds; and a copolymer included in the liquid crystal composition, the copolymer being a cured product of a polymerizable composition that contains two or more polymerizable compounds. The polymerizable compounds used include one or two or more polymerizable, photo-alignable compounds (Vn), and the content of the polymerizable composition is 1% by mass or more and less than 40% by mass based on the total weight of the polymerizable composition and the liquid crystal composition. The liquid crystal display element of the present invention is applicable to various operational modes such as TN, STN, ECB, VA, VA-TN, IPS, FFS, π cell, OCB, and cholesteric liquid crystal modes.
Owner:DAINIPPON INK & CHEM INC
Optical information recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090263613A1Good reliabilityHigh transmittanceLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusThermal conductivityHigh transmittance
An optical information recording medium that can simultaneously achieve both a high transmittance and high signal quality of an information layer, improve the reliability of long-term conservation, and reduce the manufacturing cost, and a manufacturing method thereof are provided. To achieve this, according to the present invention, in an optical information recording medium comprising at least one information layer on a substrate, at least one of the information layers has a recording layer and a dielectric layer, the recording layer contains Te, O, and M (M is one or a plurality of elements selected from Au, Pd, and Pt) as major components, the dielectric layer has a thermal conductivity of 0.01 W / K·cm or more, and the dielectric layer has an extinction coefficient of 0 through 1.0 inclusive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Member for displaying projected image and projection system
ActiveUS20180074315A1Wide view angleHigh transmittanceInstrument arrangements/adaptationsProjectorsProjection systemScanning electron microscope
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Organic light emitting diode device
ActiveUS20110133633A1Low resistanceHigh transmittanceDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesYb elementIndium
An organic light emitting diode device including a first electrode; a second electrode facing the first electrode; and an emitting layer interposed between the first electrode and the second electrode, wherein the first electrode includes an ytterbium (Yb) alloy represented by the following Chemical Formula 1:Yb-M (1), andin Chemical Formula 1, M is a metal including at least one of silver (Ag), calcium (Ca), chromium (Cr), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), ruthenium (Ru), indium (In), and tungsten (W).
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Resist compositions and patterning process
ActiveUS6866983B2High transmittanceImprove etch resistancePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistCarboxylic group
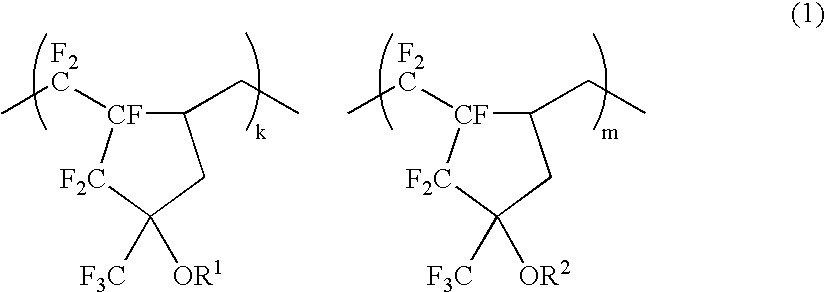
A resist composition comprising a blend of a polymer comprising recurring units k and m of formula (1) wherein R1 and R2 each are hydrogen or an acid labile group, 0<k<1, 0<m<1 and 0<k+m≦1, and another polymer comprising recurring units having carboxyl groups whose hydrogen atoms are replaced by acid labile groups as a base resin forms a resist film which is improved in transparency, alkali dissolution contrast and plasma etching resistance.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
Touch screen, method for producing touch screen, touch display device
ActiveUS20160077628A1Reduce product costHigh transmittanceLithography/patterningRadiation applicationsElectrically conductiveHigh transmittance
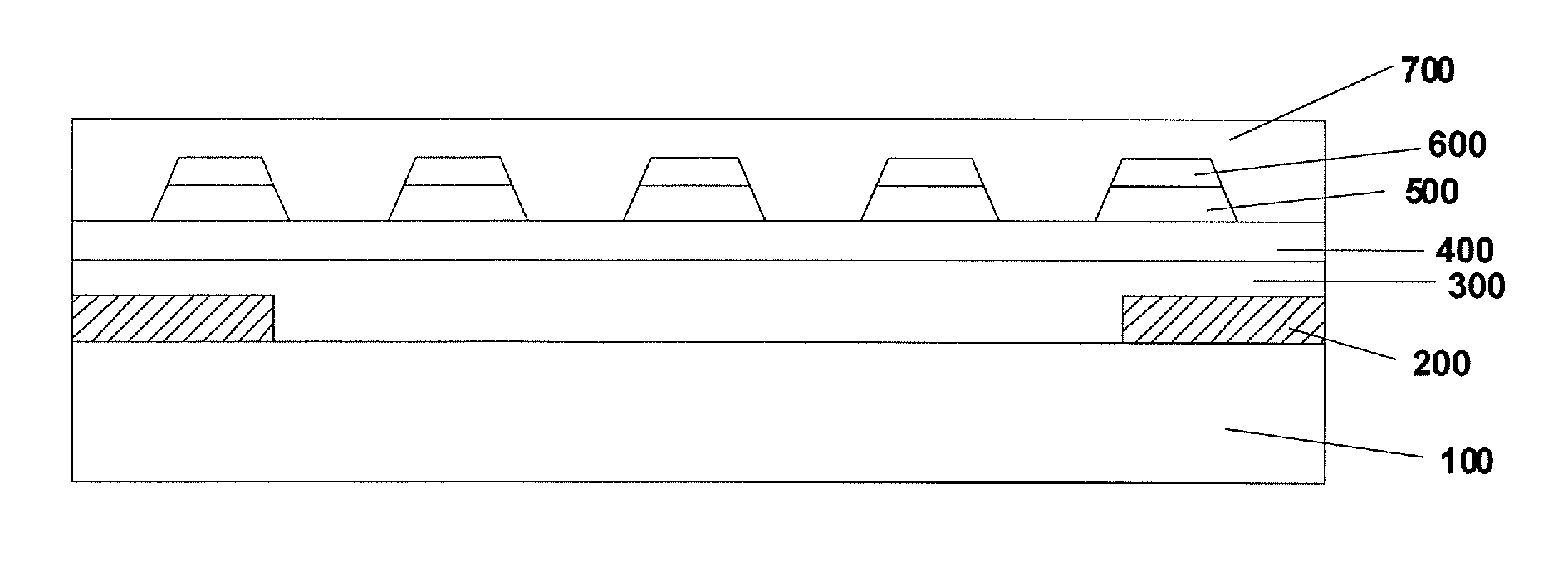
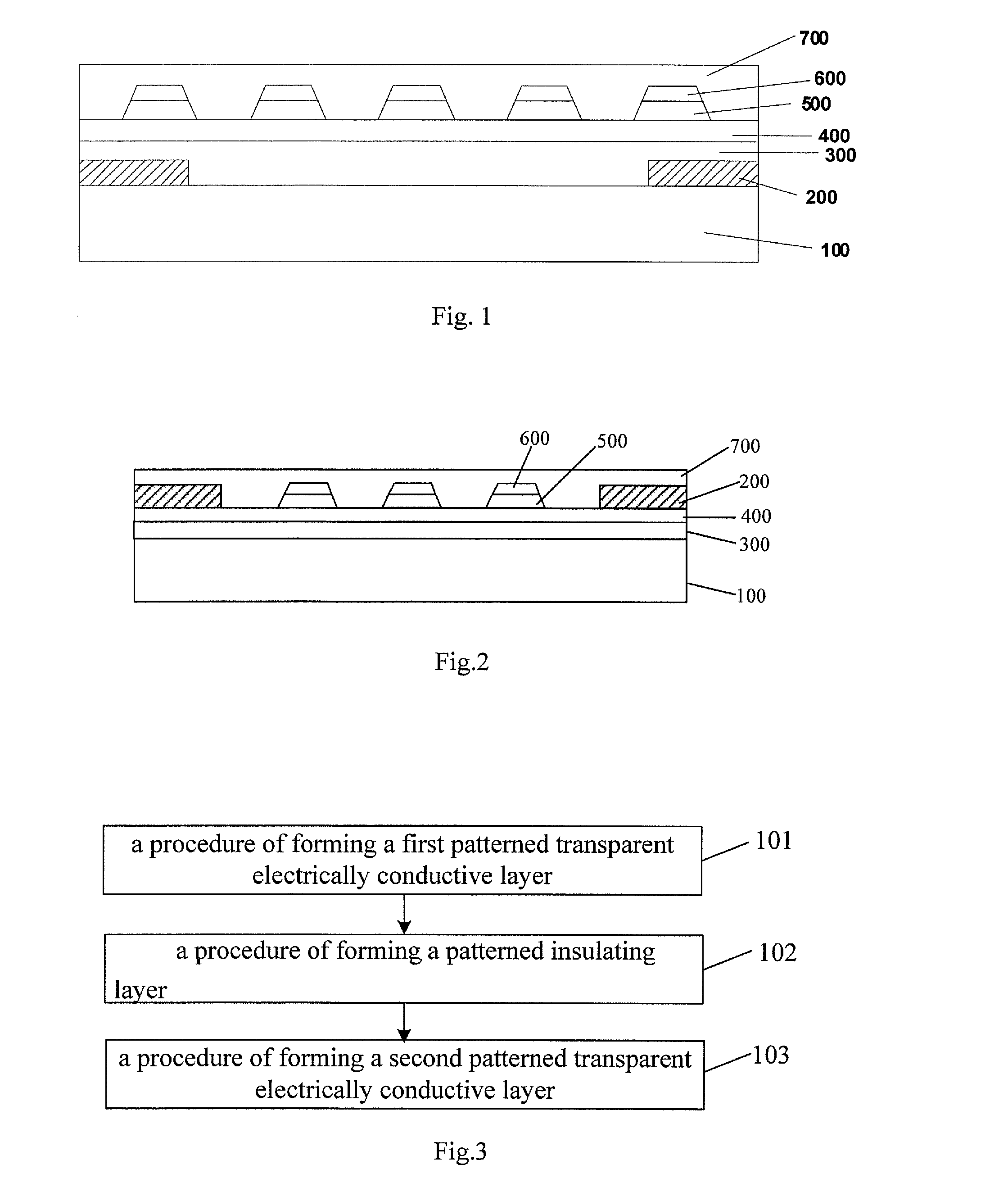
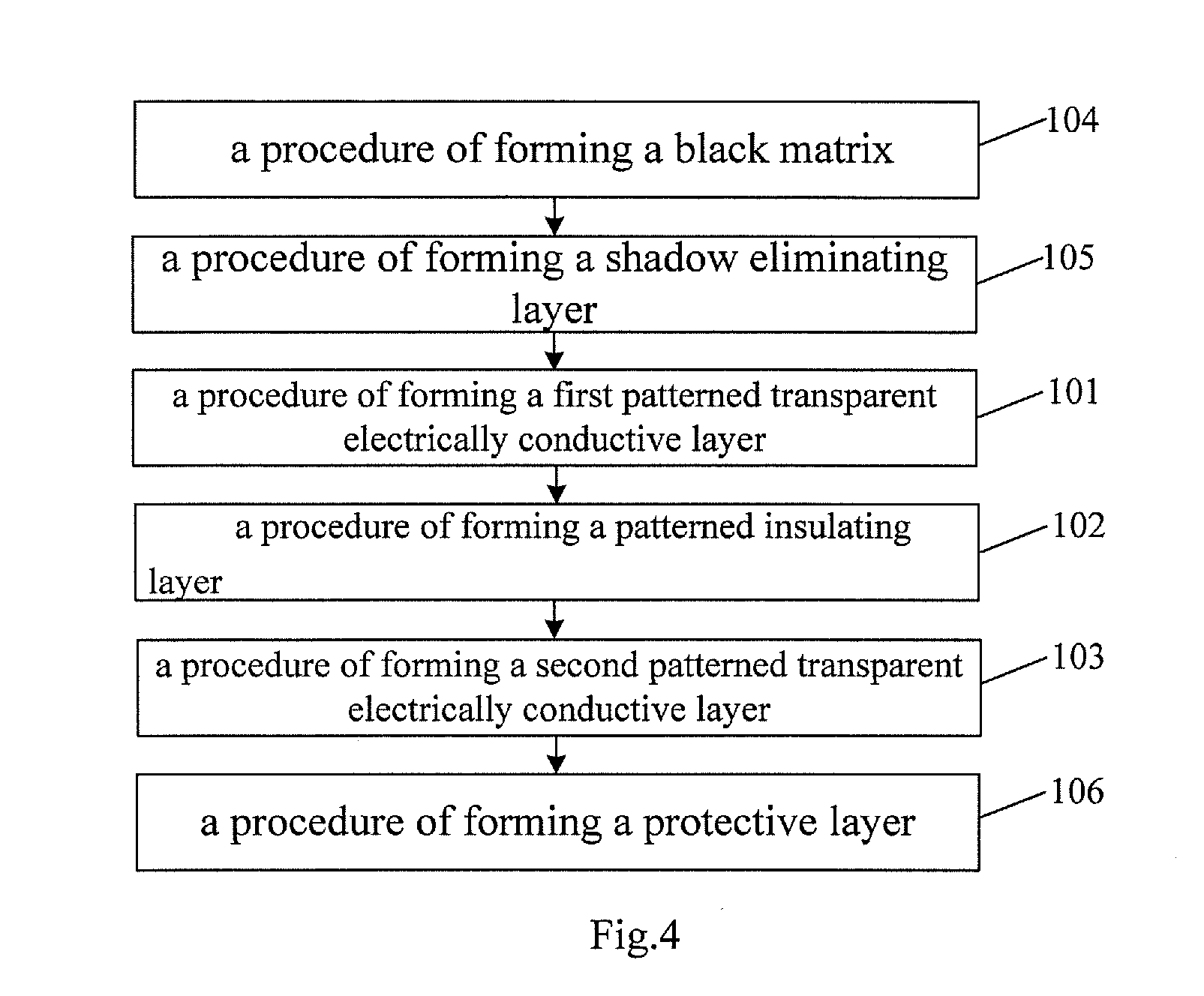
The embodiments of the invention disclose a touch screen, a method for producing a touch screen, and a touch display device, which relate to a field of display. The touch screen does not need bridging, have high transmittance, and are simple in process, which can not only reduce the production cost but also achieve a high yield of mass production. The touch screen as provided in the embodiments of the invention comprises: a transparent substrate; a first patterned transparent eclectically conductive layer; a patterned insulating layer and a second patterned transparent eclectically conductive layer, which are formed above said transparent substrate successively, wherein among said first patterned transparent electrically conductive layer and said second patterned transparent electrically conductive layer, one is formed with a plurality of drive lines, and the other is formed with a plurality of induction lines; the pattern of said insulating layer is identical with that of said first patterned transparent electrically conductive layer, or identical with that of said second patterned transparent electrically conductive layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Achromatic Polarization Element, And Polarization Plate
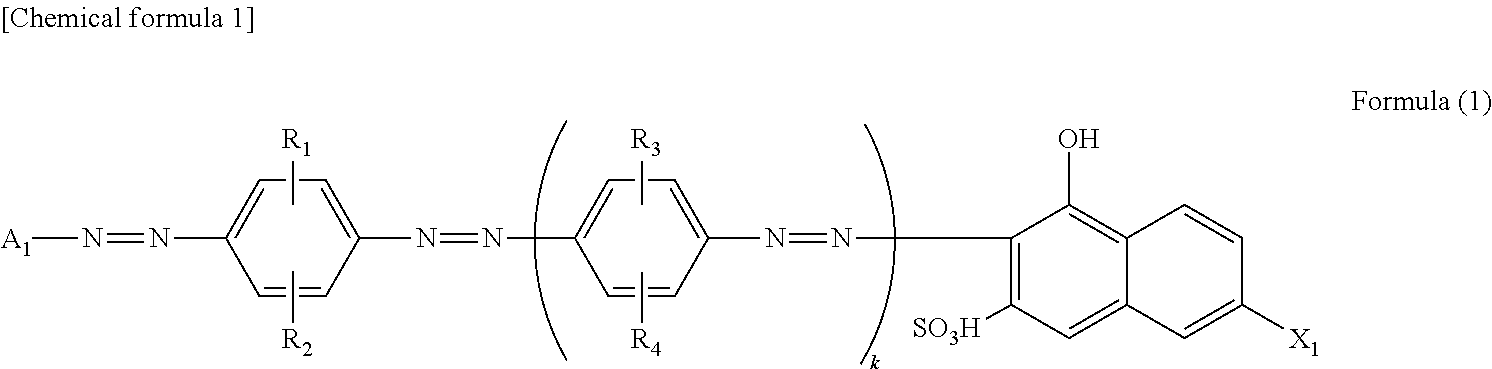
InactiveUS20160041322A1High transmittanceHigh light transmittancePolarising elementsTrisazo dyesPolarizerTransmittance
[Problem] To provide a highly-transmissive polarization plate that can express achromatic white when a polarization element is arranged parallel, to an absorbing axis, and achromatic black when the polarization element is arranged orthogonal to the absorbing axis.[Solution] a* and b* values, which define, the hue of a polarization element or a polarization plate using JIS.Z.8729, are adjusted such that the absolute value of the a* and b* values is: less than 1 during a single-body transmittance measurement; less than 2 when two sheets of a base material are arranged parallel, to the absorbing axis direction and the a* and b* values are measured; and less than 2 when two sheets of the base material are arranged orthogonal to the absorbing axis direction and the a* and b* values are measured.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD +1
Preparing method for hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose crosslinked membrane
The invention discloses a preparing method for a hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose crosslinked membrane. According to the method, collected corn stigmas are subjected to air drying, clipping, grinding and screening, powdery raw materials are obtained, the screened corn stigmas are scattered in a TBAA / DMAc ionic solution, cellulose nanocrystalline is dissociated and subjected to the esterification reaction with dripped acetic anhydride, and cellulose acetate nanocrystalline is prepared; the above modified cellulose nanocrystalline and the hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose DMAc dissolving solution are mixed, glutaric anhydride is added, after forming in a die and low-temperature drying film forming, the heating esterification cross-linking reaction is conducted, a product is cleaned, and after cold drying, the corn stigma modified cellulose blended film is obtained. A mulching film prepared through the method is a transparent film, high tensile performance and pull-up performance are achieved, and good waterproof performance and oxygen isolation performance are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Glutamic acid fermentation method and monosodium glutamate production method
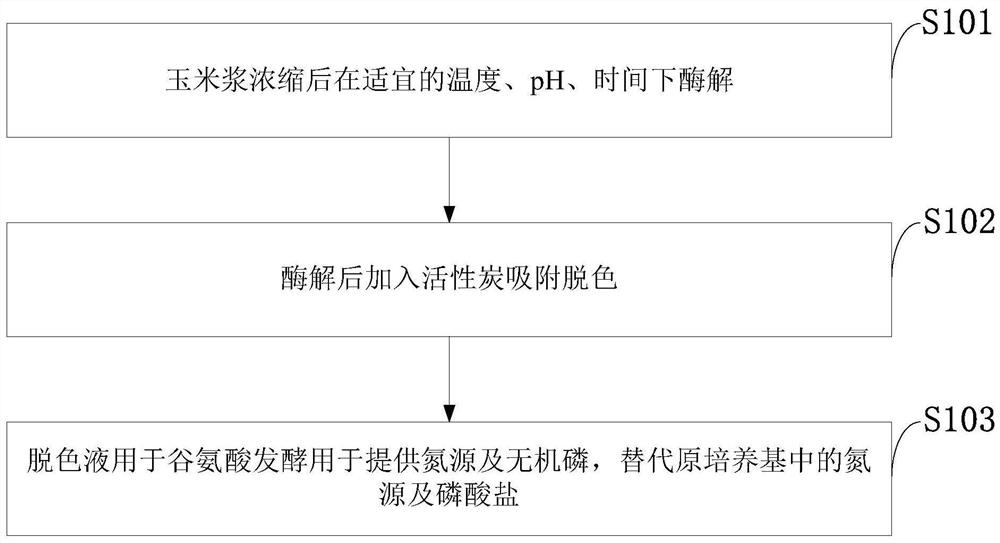
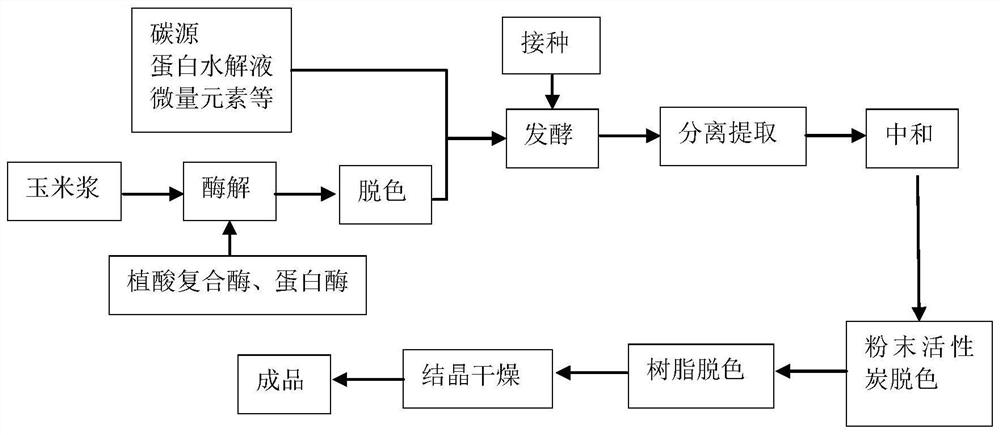
PendingCN111961694AIncrease free phosphorusImprove small proteinOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
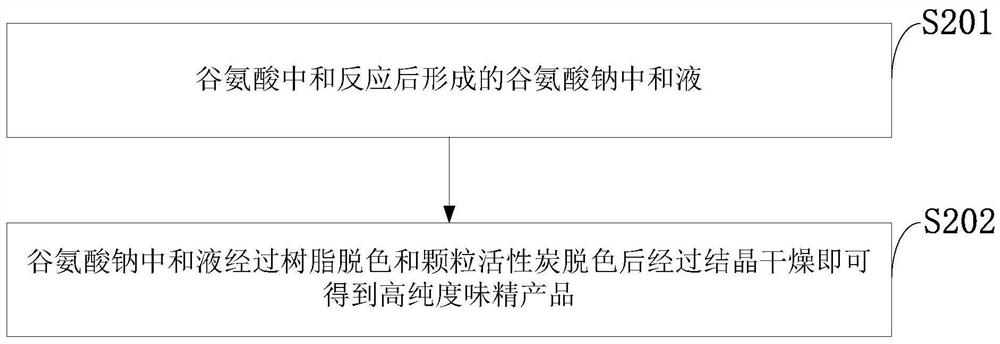
The invention belongs to the technical field of glutamic acid fermentation, and discloses a glutamic acid fermentation method and a monosodium glutamate production method. Corn steep liquor is concentrated and is subjected to enzymolysis at proper temperature, pH value and time; and activated carbon is added for adsorption decoloration, and a decolorizing liquid is used for glutamic acid fermentation to provide a nitrogen source and inorganic phosphorus so as to replace the nitrogen source and phosphate in an original culture medium. The baume degree of the concentrated corn steep liquor is 20-25. The hydrolase comprises phytic acid complex enzyme and protease. The corn steep liquor is subjected to enzymolysis, so that the content of available free phosphorus and amino acid is increased, inorganic phosphorus and part of protein hydrolysate in glutamic acid fermentation ingredients are completely replaced, the resource utilization rate is increased, the production cost is reduced, dipotassium phosphate is saved by 9.09 kg / ton in unit glutamic acid, and 1.5 kg / ton defoaming agent is saved. Resin decoloration replaces decoloration of granular activated carbon in the original process,the light transmittance of a neutralization solution can be improved to 93%-98%, and 75% of washing sewage can be reduced compared with the original process.
Owner:BAOJI FUFENG BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com