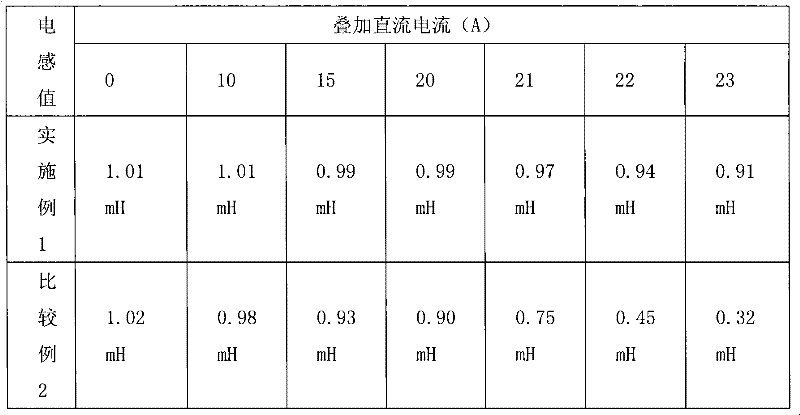
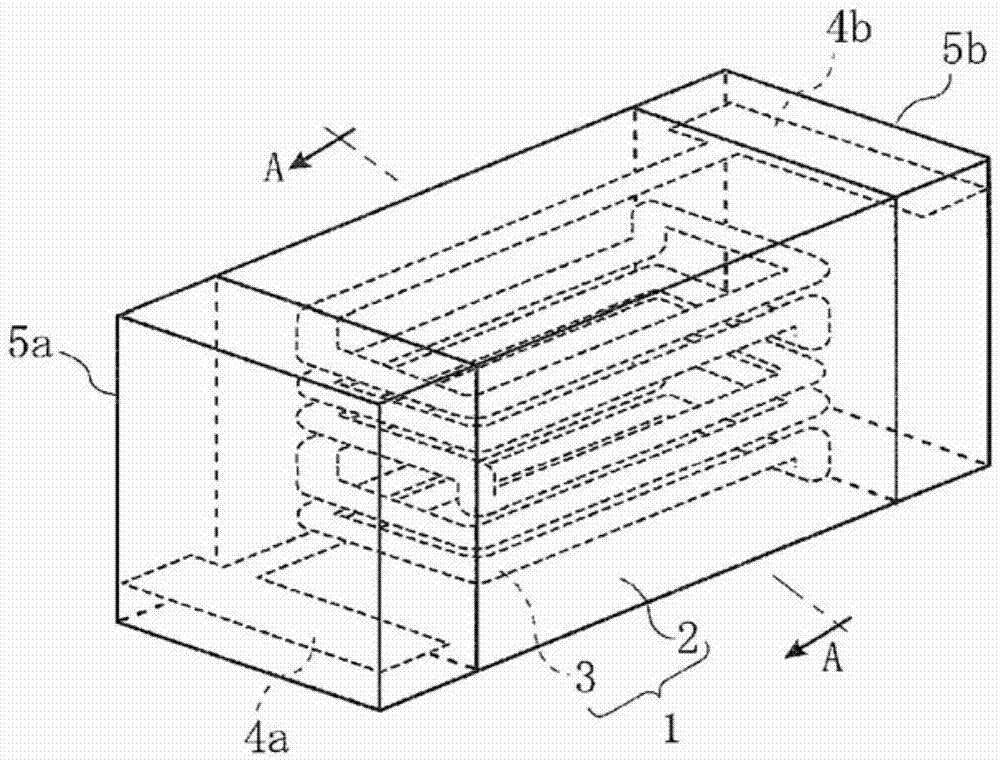
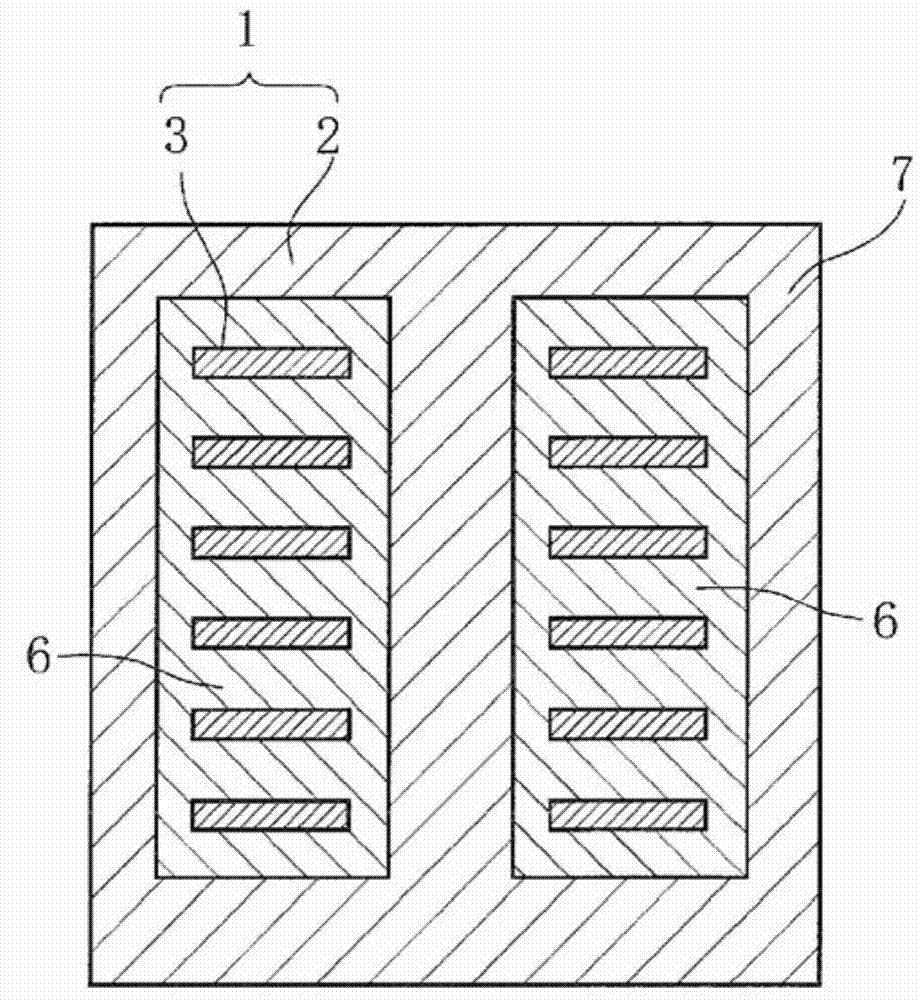
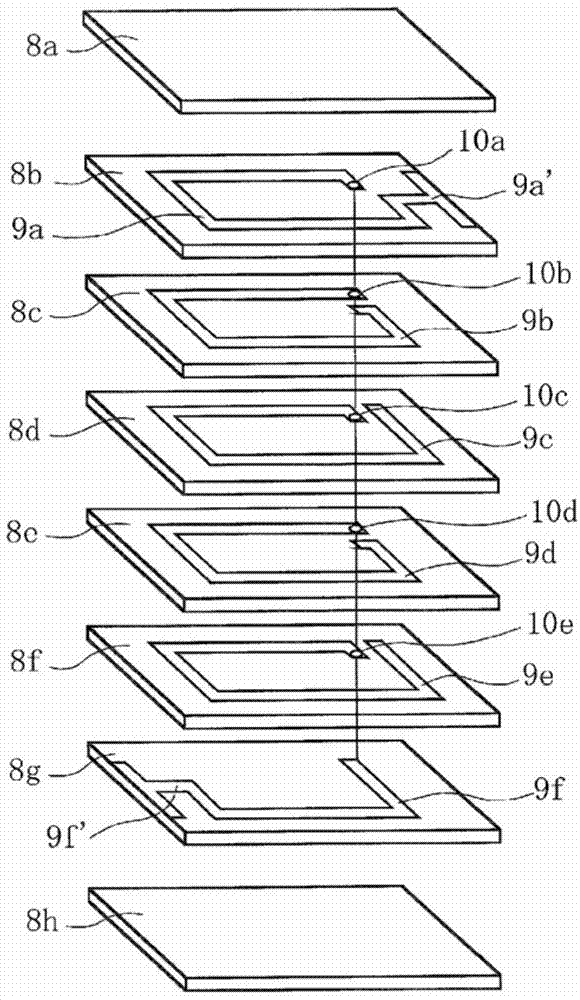
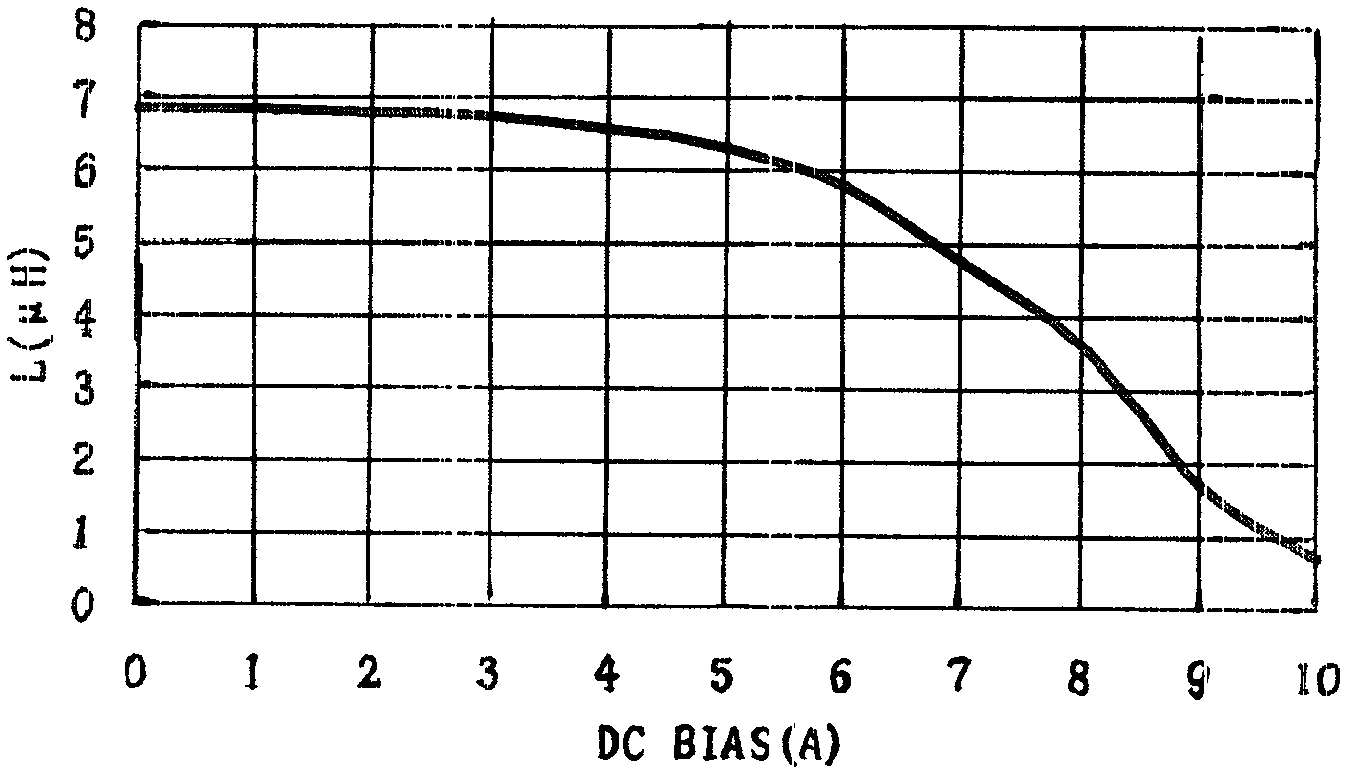
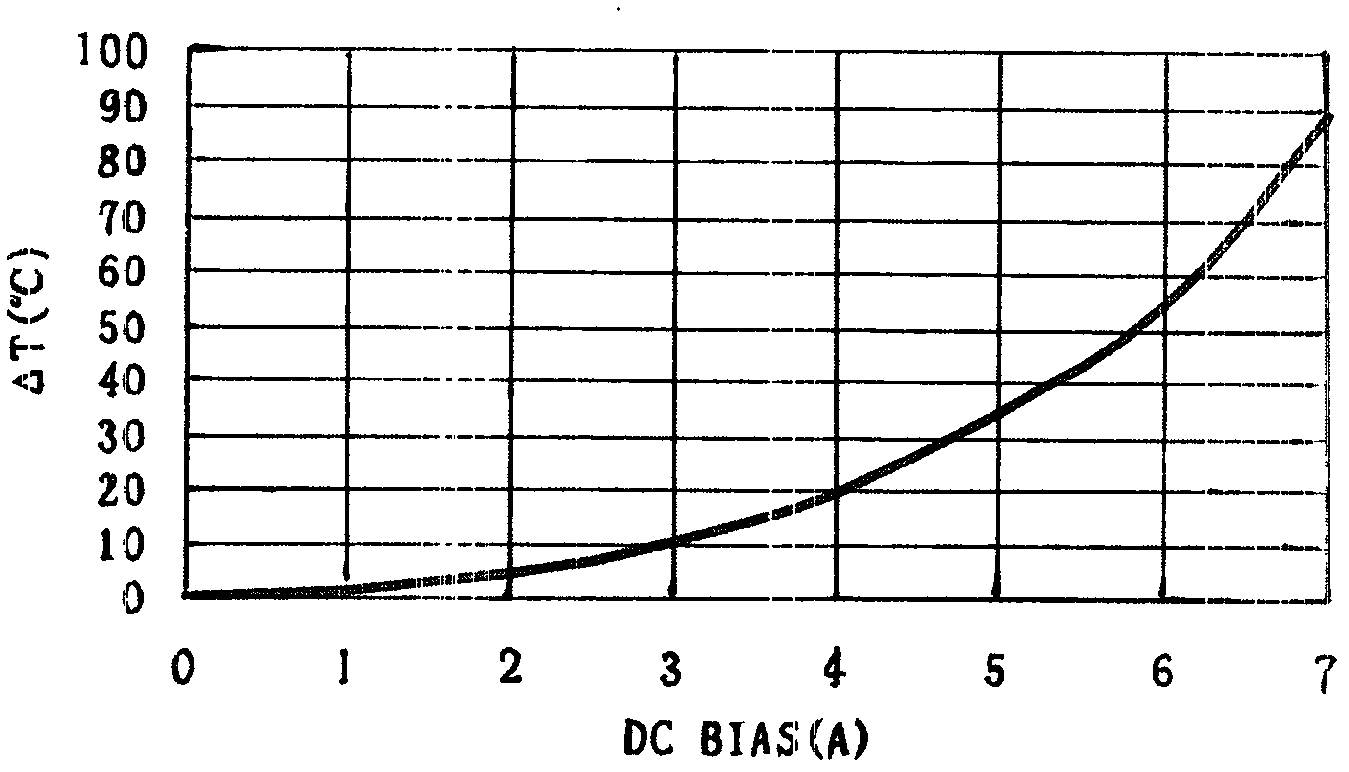
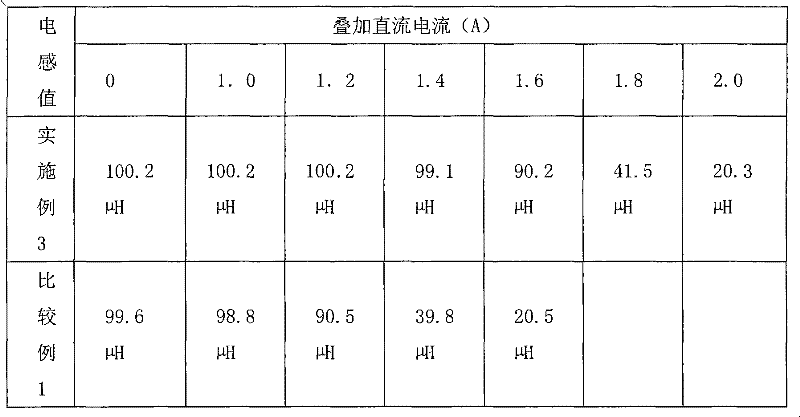
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169results about How to "High saturation flux density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composite magnetic core for switch-mode power converters
ActiveUS6980077B1Avoid Core SaturationLower average currentTransformers/inductances magnetic coresCores/yokesEddy currentConductor Coil
A composite magnetic core formed of a high permeability material and a lower permeability, high saturation flux density material prevents core saturation without an air gap and reduces eddy current losses and loss of inductance. The composite core is configured such that the low permeability, high saturation material is located where the flux accumulates from the high permeability sections. The presence of magnetic material having a relatively high permeability keeps the flux confined within the core thereby preventing fringing flux from spilling out into the winding arrangement. This composite core configuration balances the requirements of preventing core saturation and minimizing eddy current losses without increasing either the height or width of the core or the number of windings.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Fe-based amorphous alloy ribbon
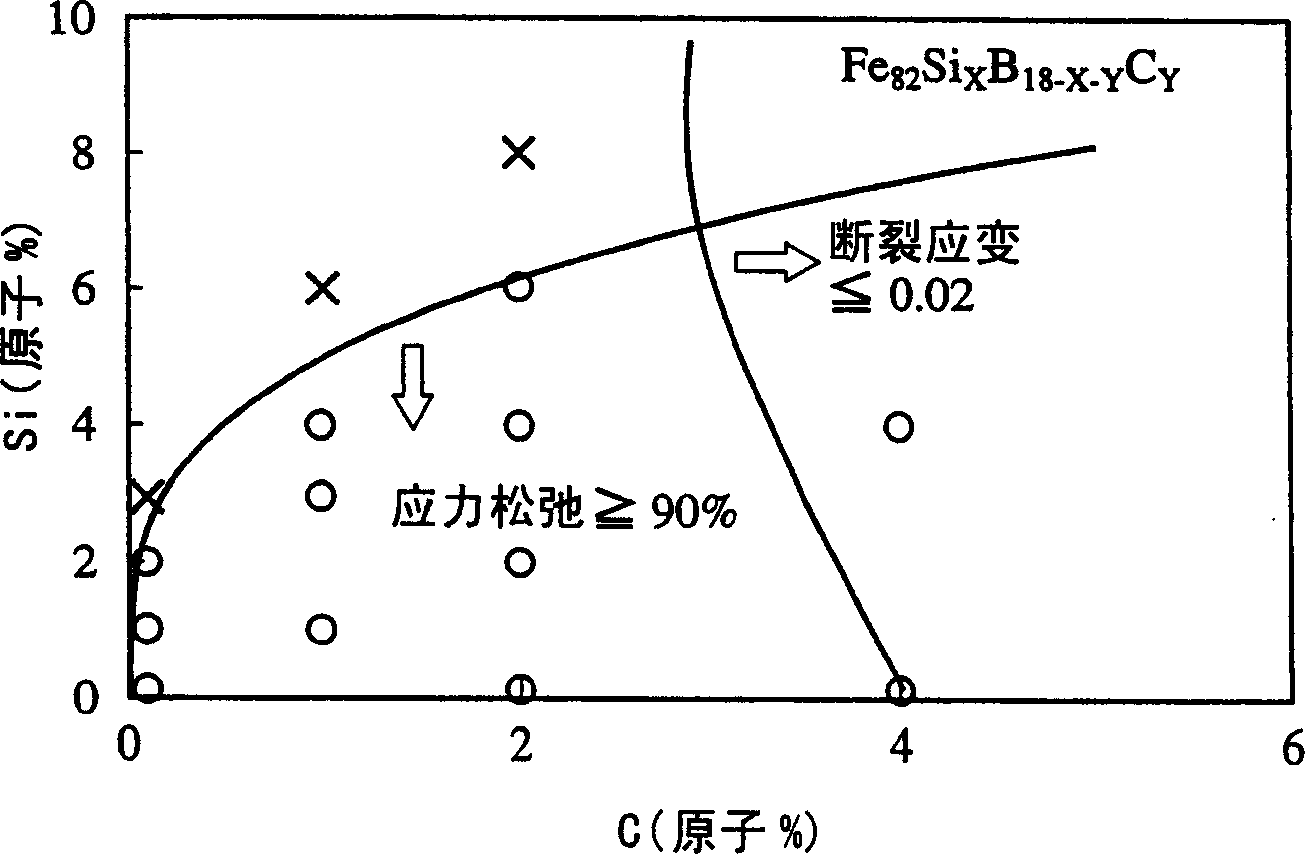
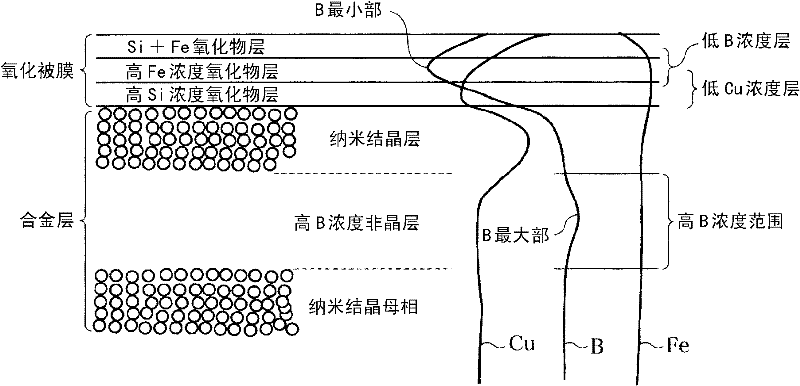
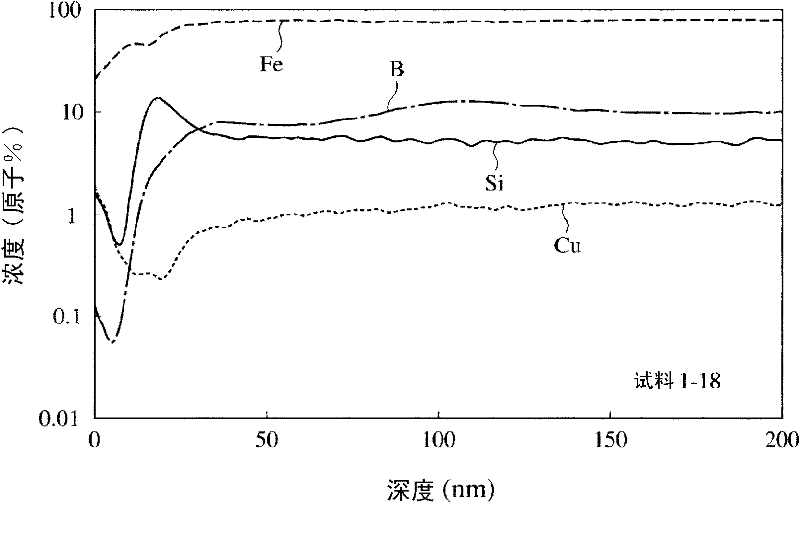
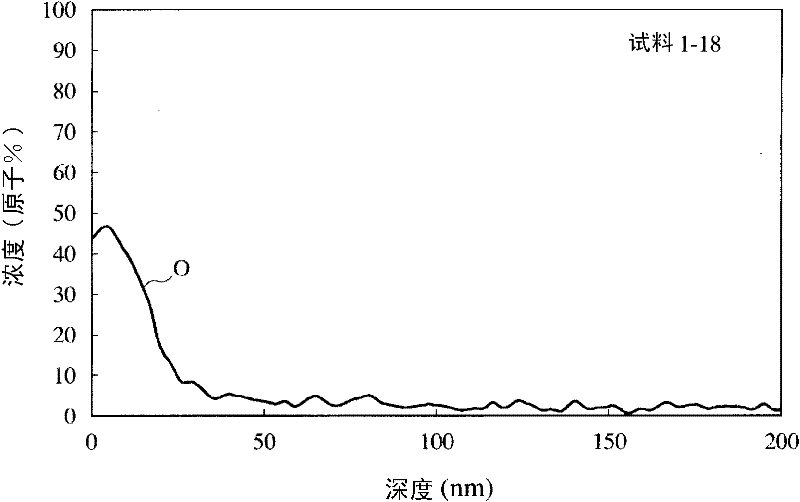
An Fe-based amorphous alloy ribbon having a composition comprising FeaSibBcCd and inevitable impurities, wherein a is 76 to 83.5 atomic %, b is 12 atomic % or less, c is 8 to 18 atomic %, and d is 0.01 to 3 atomic %, the concentration distribution of C measured radially from both surfaces to the inside of said Fe-based amorphous alloy ribbon having a peak within a depth of 2 to 20 nm.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
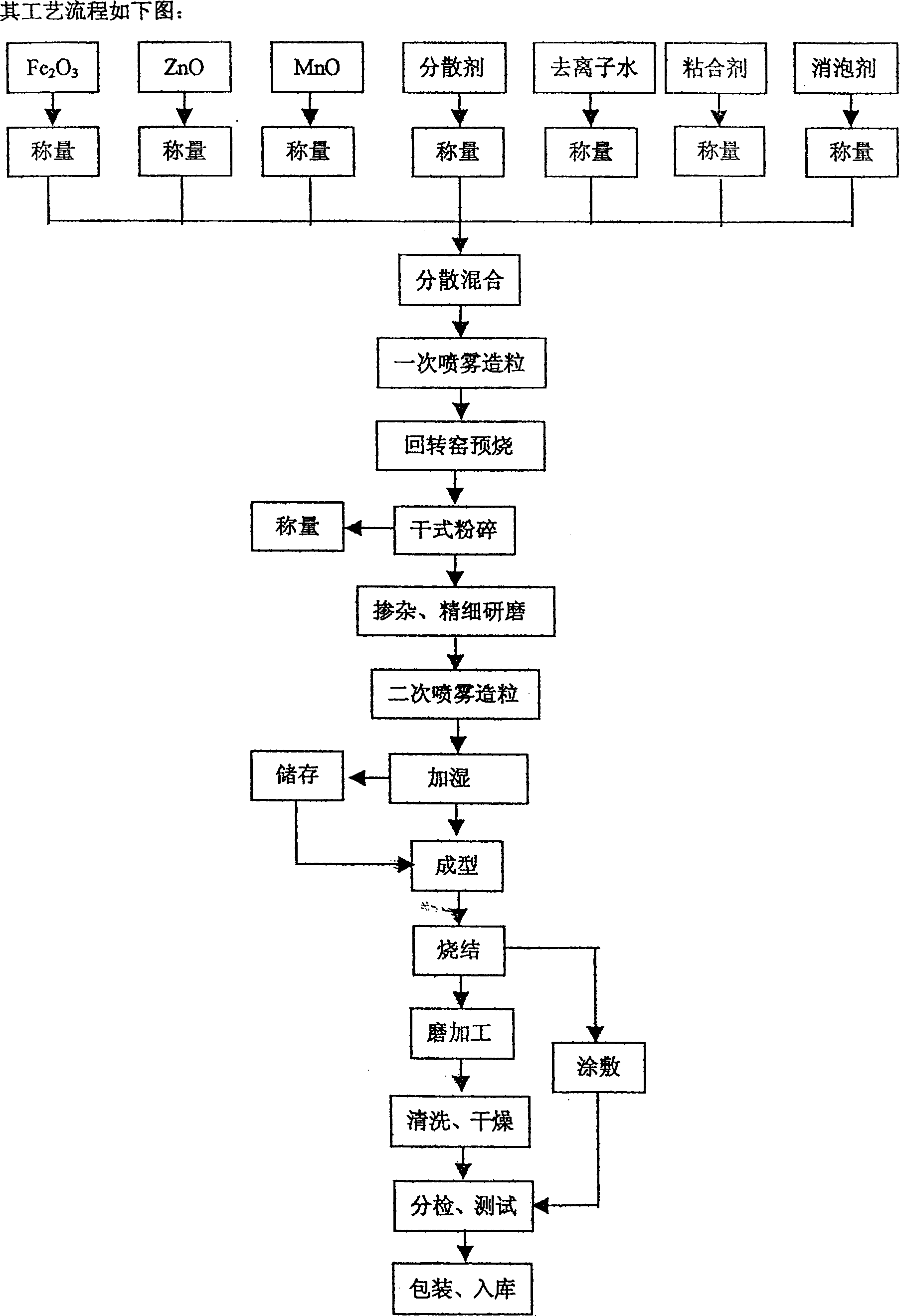
Method for producing Mn-Zn ferrite
InactiveCN1649039AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismIron compoundsMetallurgy
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
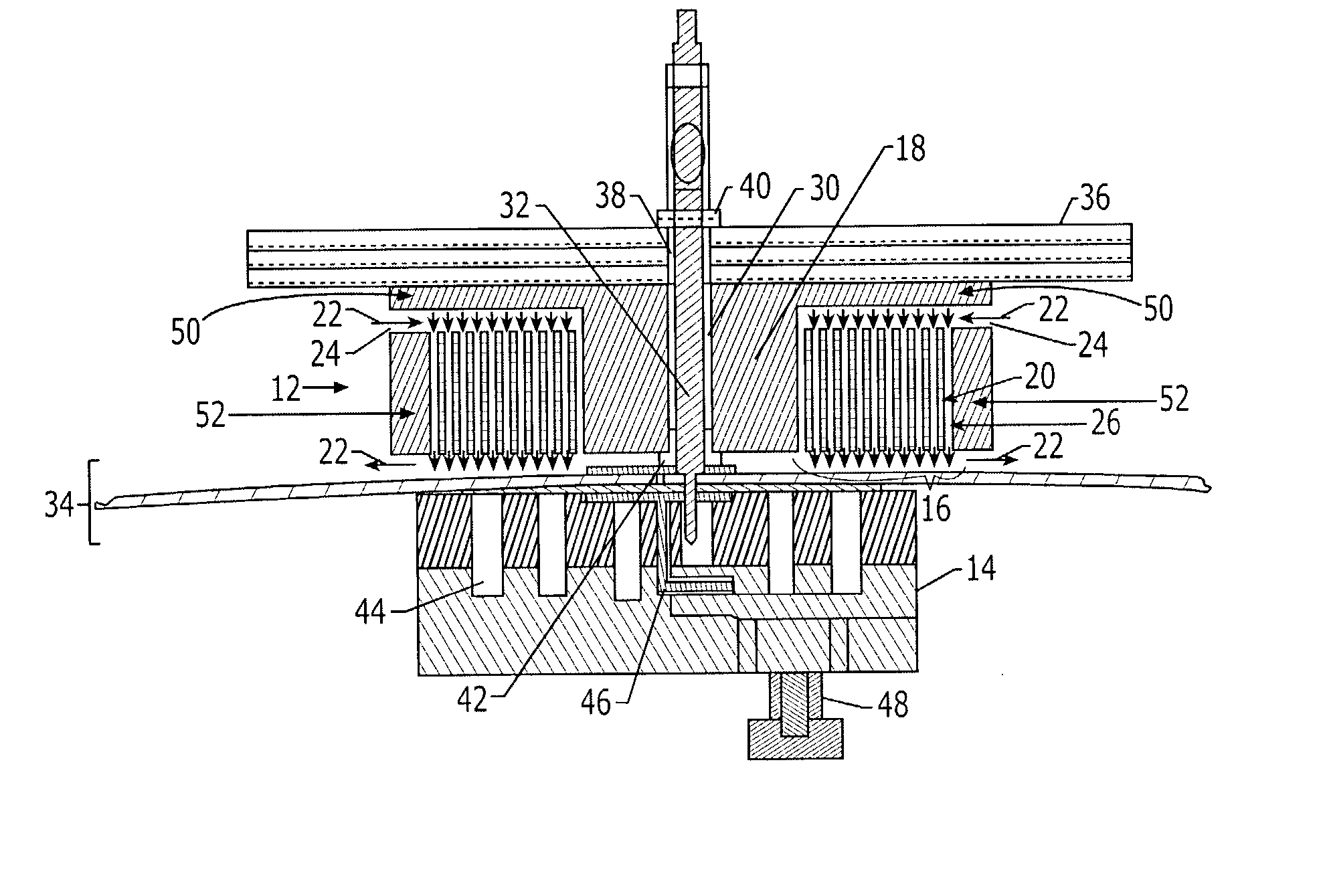
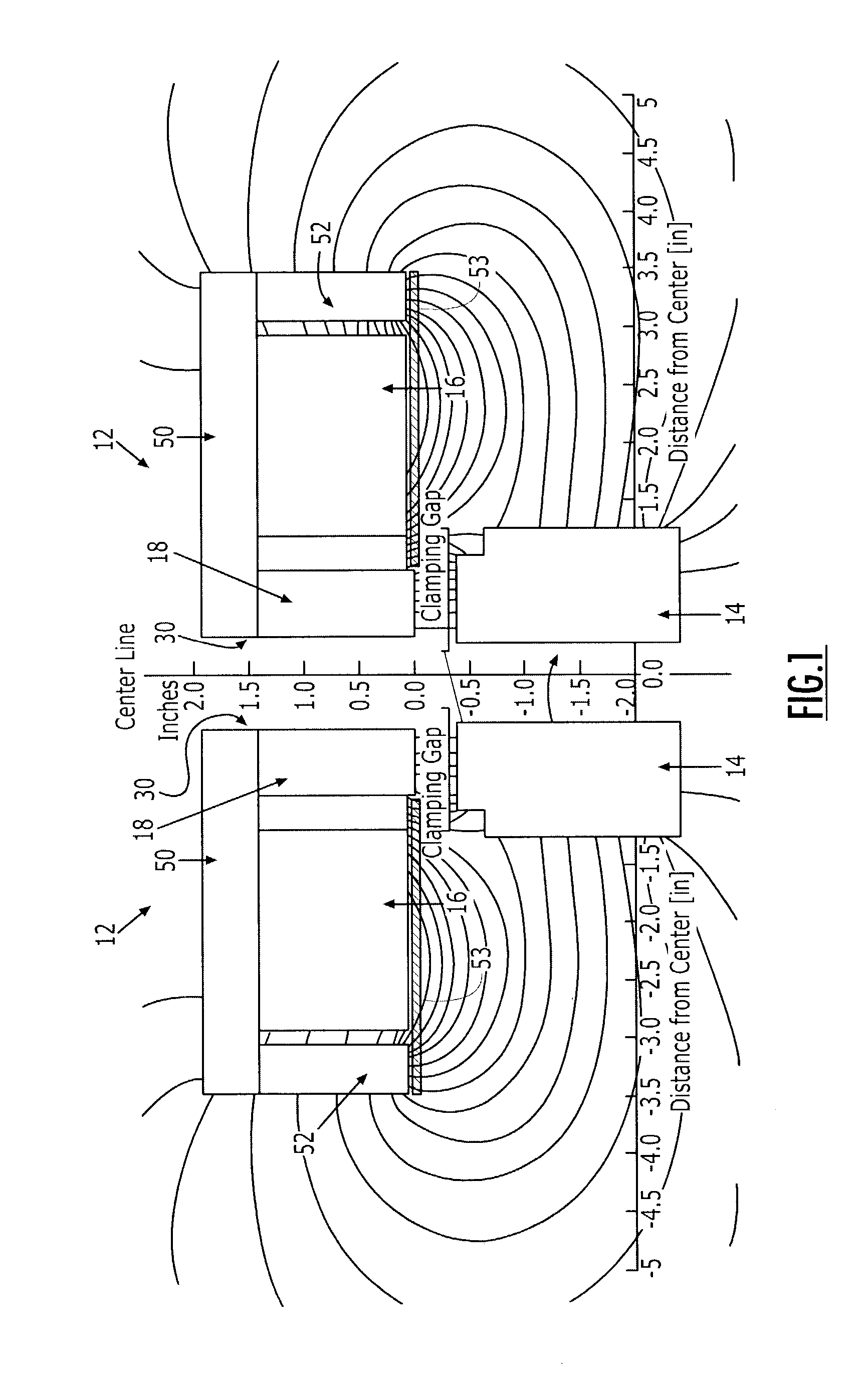
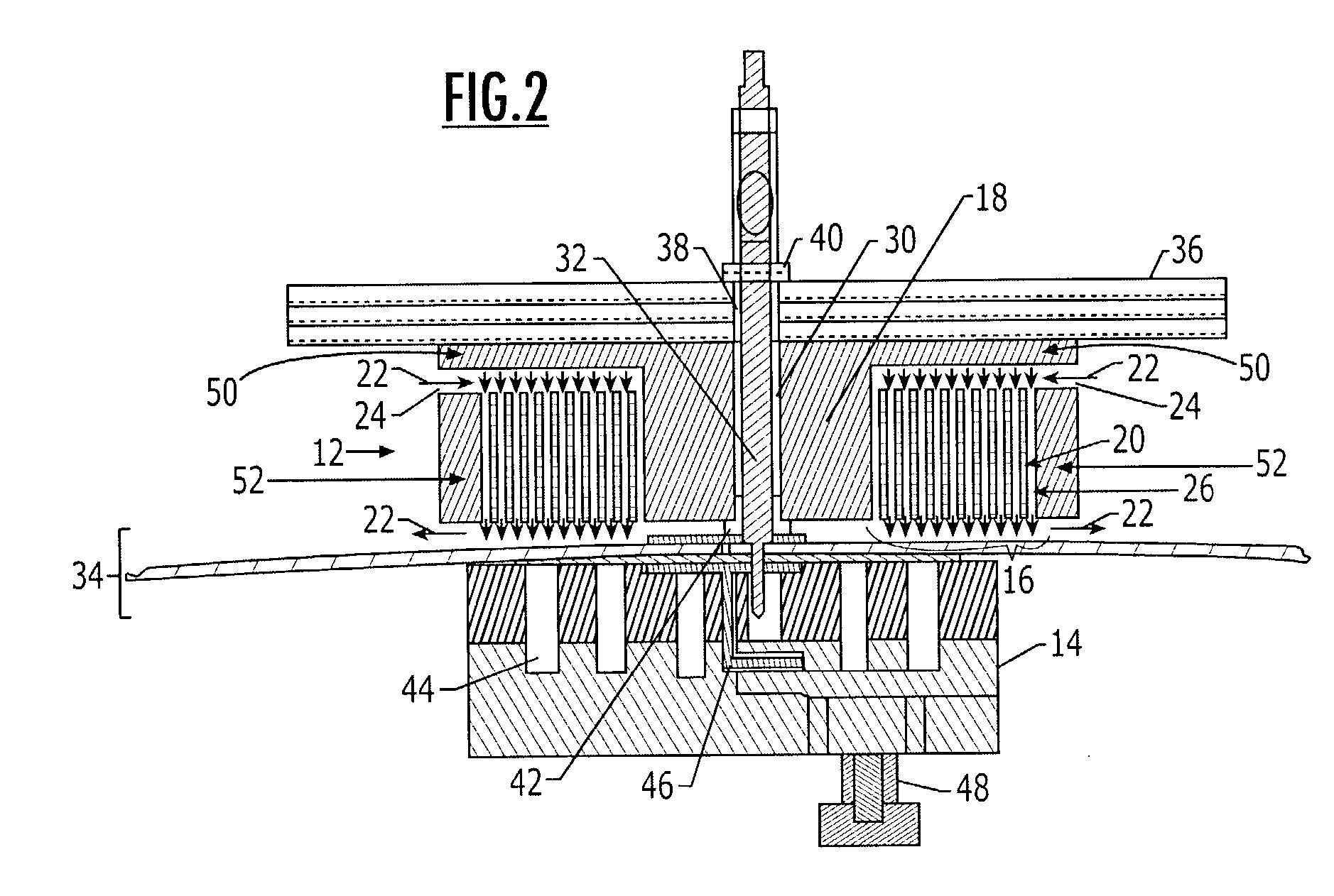
Electromagnetic clamp and method for clamping a structure
ActiveUS7148776B2Low costShorten the timeElectromagnets without armaturesWork holdersEngineeringElectromagnet
The electromagnetic clamp and method includes an electromagnet and a clamping piece located on opposite sides of a structure to clamp the structure. The electromagnet attracts the clamping piece through the structure when the electromagnet is energized, such that the electromagnet and clamping piece exert force on the structure, and an operation, such as drilling and / or fastener installation, may be performed on the structure. The configuration of the electromagnet creates the force necessary to securely clamp the structure. The electromagnet includes a coil and a core, and the core of the electromagnet is located within a longitudinal aperture that extends through the coil. The smallest lateral dimension of the core is chosen to maximize the flux density between the core and the clamping piece. As such, the smallest lateral dimension of the electromagnet may be greater than the distance between the clamping piece and the electromagnet.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Soft magnetic alloy thin strip, manufacturing method thereof, and magnetic component having soft magnetic alloy thin strip
ActiveCN102282633AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismAmorphous phaseOxygen
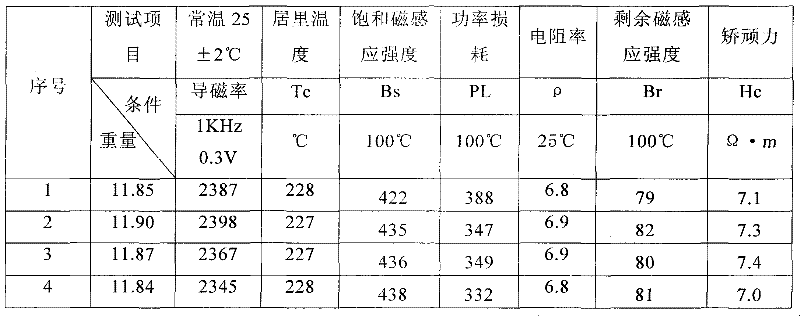
Disclosed is a method for producing a soft magnetic alloy thin strip which has a composition represented by Fe100-x-y-zAxByXz (wherein A represents Cu and / or Au; X represents at least one element selected from among Si, S, C, P, Al, Ge, Ga and Be; and x, y and z respectively represent the numbers expressing the atom% of the elements and satisfying 0 < x = 5, 10 = y = 22, 1 = z = 10 and x + y + z = 25), and comprises a matrix wherein fine crystal grains having an average grain size of 60 nm or less are dispersed at a volume fraction of 50% or more. In the soft magnetic alloy thin strip, a part of the oxide coating film formed on the surface is a layer that has a B concentration lower than the average B concentration of the matrix. In the method for producing a soft magnetic alloy thin strip, (1) an initial microcrystalline alloy thin strip, which has a matrix wherein fine crystal nuclei having an average grain size of 30 nm or less are dispersed in an amorphous phase at a volume fraction of more than 0% but less than 30%, is formed by jetting and quenching an alloy melt having the above-described composition on a rotating cooling roll, and then (2) the initial microcrystalline alloy thin strip is subjected to a heat treatment in an atmosphere having an oxygen concentration of 6-18%.
Owner:PROTERIAL LTD
Method for preparing metal soft magnetic compound material by tape casting
ActiveCN104073660AHigh saturation flux densityHigh resistivityMagnetic materialsOrganic solventPlasticizer
The invention discloses a method of preparing a metal soft magnetic compound material by tape casting. The method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) mixing a passivant and a solvent according to a mass fraction of the passivant being 0.1-0.5% to obtain a passivation liquid, mixing the passivation liquid with magnetic metal powder according to a mass ratio of 0.01-1, stirring and drying to obtain passivation powder; 2) mixing the passivation powder with an organic solvent, a dispersant, a binder and a plasticizer, uniformly stirring, filtering through a screen and defoaming to prepare uniformly dispersed slurry; 3) tape casting; and 4) drying and curing. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the metal soft magnetic compound material prepared by tape casting has the characteristics of high electrical resistivity and higher saturation flux density than conventional ferrite. By means of a mature tape casting process, the production process of the metal soft magnetic compound material is simplified and the cost is lowered; and the metal soft magnetic compound material has a wide application prospect in preparation of electron devices such as thin-film inductors.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Soft magnetic ferrite material and preparation process thereof
ActiveCN102194561AHigh saturation flux densityReduce magnetic lossInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyMaterials science
The invention discloses a soft magnetic ferrite material and a preparation process thereof. The soft magnetic ferrite material comprises the following components: 52 to 55 mol of Fe2O3, 39 to 42 mol of Mn3O4, 5-8 mol of ZnO, 0.1 to 0.6 mol of additive 1, 0.1 to 0.2 mol of additive 2 and 0.006 to 0.06 mol of ZrO2, wherein the additive 1 is one or more of SnO2, CaCO3 and V2O5; and the additive 2 isone or more of Nb2O5, K2CO3, CaCO3, Ta2O5, SnO2 and V2O5. The soft magnetic ferrite material prepared by the process overcomes defects of the prior art and has the advantages of high frequency, high saturation magnetic flux density and low magnetic loss.
Owner:WUXI SPINEL MAGNETICS
Soft magnetic thin strip, process for production of the same, magnetic parts, and amorphous thin strip
InactiveCN101663410AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismAmorphous phaseVolumetric Mass Density
The invention provides a soft magnetic thin strip which contains nanoscale fine grains and exhibits a high saturation magnetic flux density and excellent soft magnetic characteristics; a process for production of the same; magnetic parts; and an amorphous thin strip to be used in the production. In the invention, an amorphous thin strip is used, which is represented by the composition formula: Fe100-x-y-zAxMyXz-aPa (wherein A is at least one element selected from between Cu and Au; M is at least one element selected from among Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Mo, W and Mn; X is at least one elementselected from between B and Si; and x, y, z and a (in terms of atomic percentage) satisfy the relationships: 0.5<=x<=1.5, 0<=y<=2.5, 10<=z<=23, and 0.35<=a<=10 respectively) and permits 180 DEG bending. The amorphous thin strip can give through heat treatment a soft magnetic thin strip having a structure wherein grains of body-centered cubic structure having an average grain size of 60nm or beloware distributed in an amorphous phase with a grain volume fraction of 30% or above.
Owner:PROTERIAL LTD
Soft magnetic ferrite material and preparation process thereof
The invention discloses a soft magnetic ferrite material. Raw materials for preparing the soft magnetic ferrite material comprise composite materials and auxiliary materials. The composite materials comprise iron oxide, manganese oxide and zinc oxide. The auxiliary materials comprise 0-6000 ppm of nickel oxide, 100-800 ppm of calcium carbonate, 0-500 ppm of lithium carbonate, 20-120 ppm of silicon dioxide, 0-230 ppm of magnesium oxide, 0-180 ppm of niobium oxide, 700-2000 ppm of cobalt oxide, 0-350 ppm of bismuth oxide, 100-600 ppm of vanadium oxide, 0-2500 ppm of titanium dioxide, 0-500 ppm of copper oxide, and 100-500 ppm of zirconium oxide. The invention also discloses a preparation process of the soft magnetic ferrite material. The soft magnetic ferrite material has high initial magnetic permeability and low magnetic core loss.
Owner:ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS
Method for making nano-scale metal powder and method for making high-frequency soft magnetic core using same
InactiveCN1579682AImprove economyReduce lossNanostructure manufactureTransportation and packagingMetal powderAmorphous metal
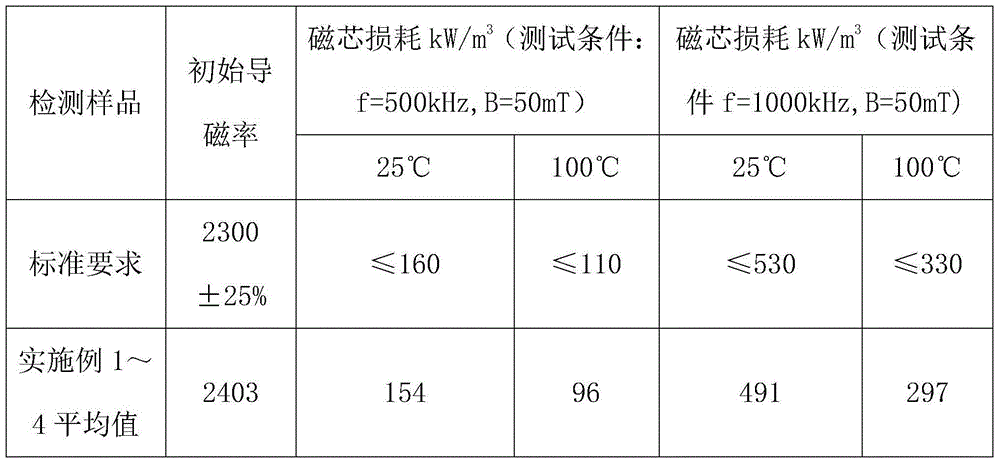
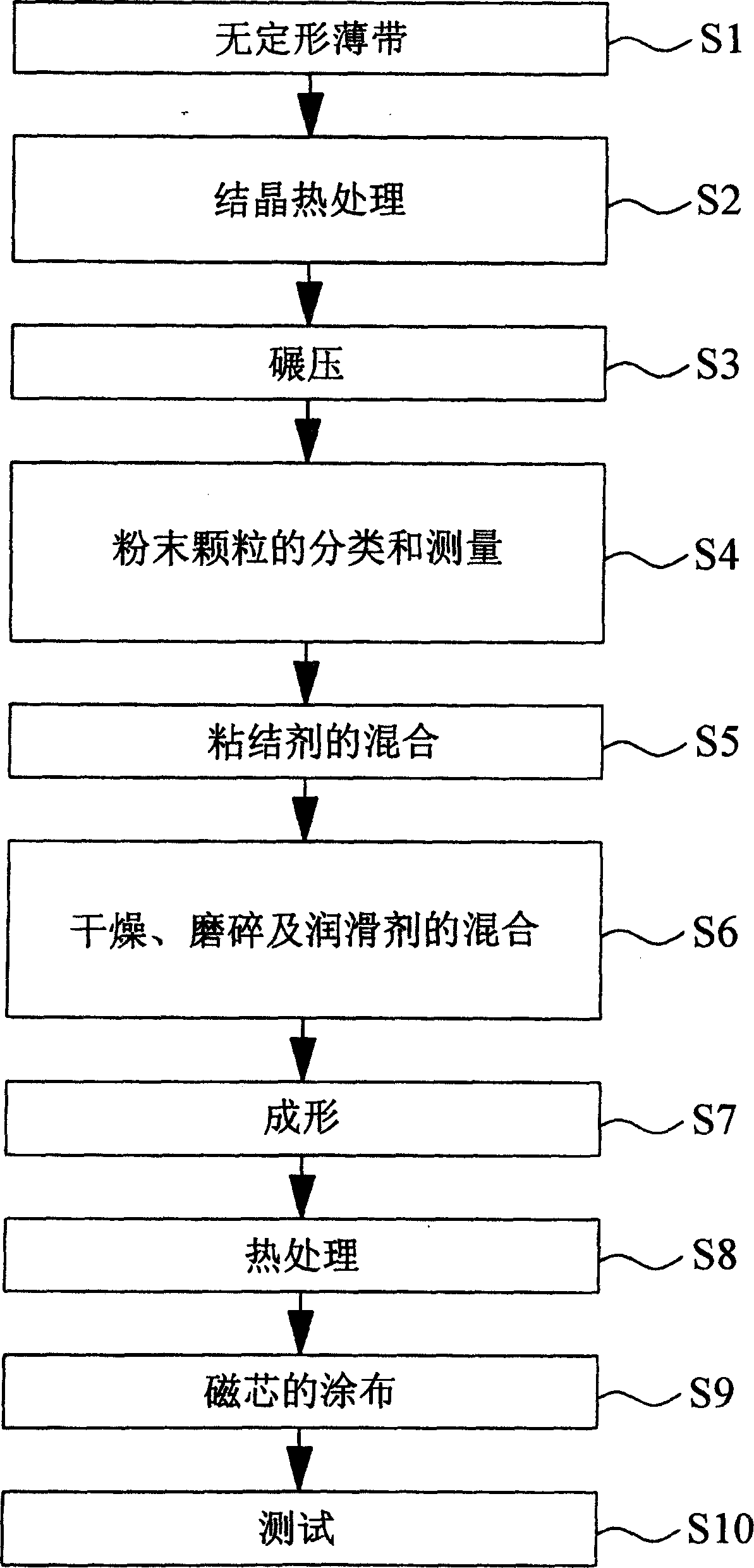
A method for making a nano-scale amorphous soft magnetic powders obtained by thermally processing and crystallizing amorphous ribbons produced using a rapid solidification process (RSP) and crushing the same. The amorphous soft magnetic core having an excellent high-frequency characteristic is obtained by performing a preliminary thermal treatment of Fe-based amorphous metal ribbons produced by using RSP to then be converted into nano-scale grain metal ribbons, crushing the metal ribbons to thereby obtain nano-scale grain metal powders, classifying the nano-scale grain metal powders to then be mixed into a distribution of powder particles having an optimal uniform composition, mixing the mixed powder with a binder, and then forming a core, and annealing the formed core to then coat the core with an insulating resin.
Owner:AMOXIANSI ELECTRONICS & ELECTRICAL CO LTD
Ferrite core and producing method thereof
InactiveCN1404076AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismIron compoundsMagnetic stabilityVolumetric Mass Density
To provide a soft ferrite which has a high saturation magnetic flux density of Bs at a high temperature of 100 DEG C or higher, especially at a temperature of 150 DEG C or so and deteriorates its magnetic properties less (even if sacrificing its low power loss property to some extent) at the above high temperature, especially deteriorates its core loss less, and is superior in magnetic stability. The major composition of ferrite core contains 56 to 57 mol% iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3, 5 to 10 mol% zinc oxide in terms of ZnO, 3 to 6 mol% in terms of NiO, and the residual mol% manganese oxide in terms of (MnO). When the major composition is expressed by: (Zn<2+>a, Ni<2+>b, Mn<2+>c, Mn<3+>d, Fe<2+>e, Fe<3+>f)O4+delta equation (1) (in the equation (1), a+b+c+d+e+f=3, and the relationship delta=a+b+c+(3 / 2)d+e+(3 / 2)f-4) the delta value in the equation (1) is in the range 0 <= delta <= 0.001.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Sintering method for high saturated flux density MnZn ferrite
ActiveCN101090016AHigh saturation flux densityLow costInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyPartial pressure
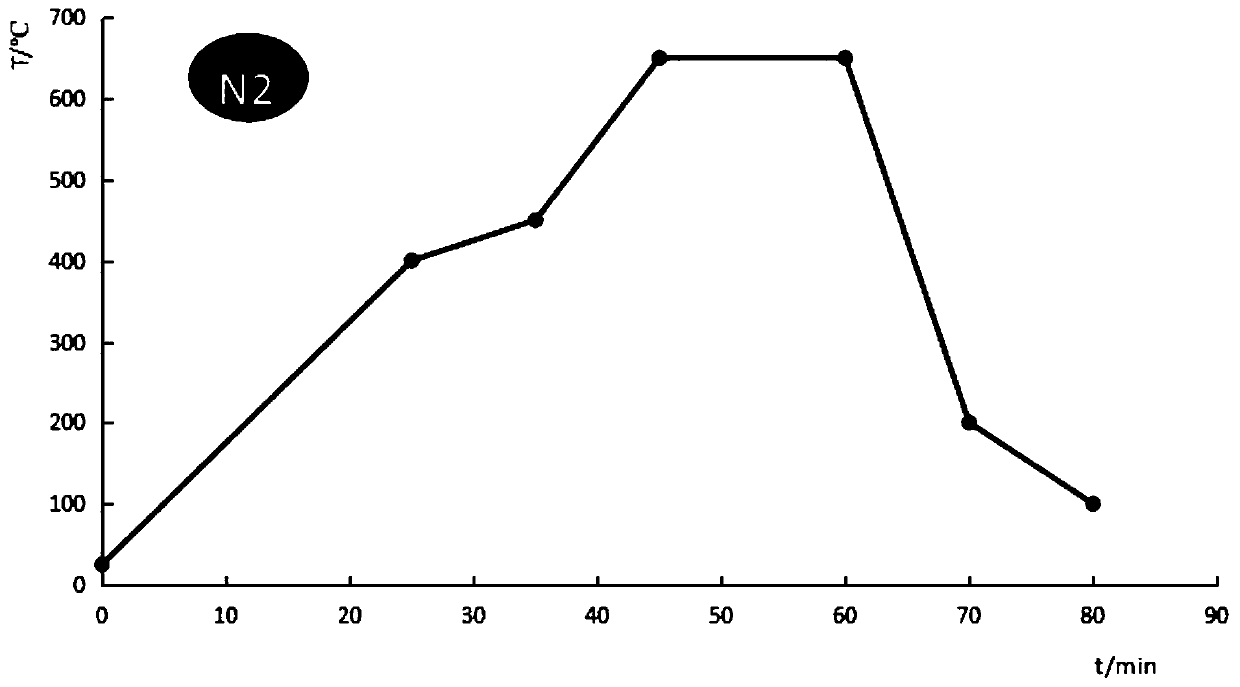
This invention provides a sintering method for a high-saturated flux density MnZn ferrite including the following steps: a, a first temperature-rising stage, b, a second temperature-rising stage, c, a heat preservation stage, d, temperature-reducing, which can increase the saturated flux density of MnZn ferrite greatly by controlling the temperature and oxygen partial pressure during the sintering process, besides, no expensive asistant components are needed in the preparation process.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Manganese-zinc ferrite magnetic core mfg. method
InactiveCN1402265AReduce lossHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureManganese oxideNitrogen gas
A MnZn ferrite core is prepared from high-Si iron oxide (52.6-54 mol%), zinc oxide (8-12 mol%), manganese oxide (35.4-38 mol%) and calcium oxide (0.02-0.12 wt.%) through sintering in the oxygen partial pressure controlled nitrogen gas or vacuum atmosphere. Its advantages are low cost, low magnetic loss, high saturated magnetic flux density, and short sinter time (20 hr).
Owner:无锡晶石磁性电子器件有限公司
Magnetic powder core and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109545537AImprove performanceHigh saturation flux densityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAfter treatmentIron powder
The invention provides a preparation method of magnetic powder cores. The preparation method comprises the steps: mixing carbonyl iron powder with a phosphating solution, and phosphating to obtain iron powder after treatment; drying the iron powder after treatment, sieving and then mixing and coating with an insulating coating agent to obtain powder after coating, wherein the insulating coating agent comprises organic resin, inorganic coating material, coupling agent and curing agent; and granulating, pressing and solidifying the coated powder to obtain a magnetic powder core. The preparationmethod of magnetic powder cores achieves the best performance of the magnetic powder core by selecting a specific insulating coating agent, and combines the remaining operations, thus having the magnetic properties such as higher saturation magnetic flux density and stable magnetic permeability, and having strong resistance to breakdown. The preparation method of magnetic powder cores is excellentin molding performance, can meet molding of the complex structure of one-piece inductors, and can satisfy the industrial requirement for mechanical properties. The preparation method of magnetic powder cores enables the insulating coating of the magnetic powder core to be more stable by combination of multi-element coatings, so that the prepared product has stronger working stability during the service life of the product.
Owner:DONGGUAN MENTECH OPTICAL & MAGNETIC CO LTD
High saturation magnetic flux density low loss soft magnetic ferrite material and producing method thereof
ActiveCN101483092AHigh saturation flux densityReduce lossInorganic material magnetismVolumetric Mass DensityMagnetic flux
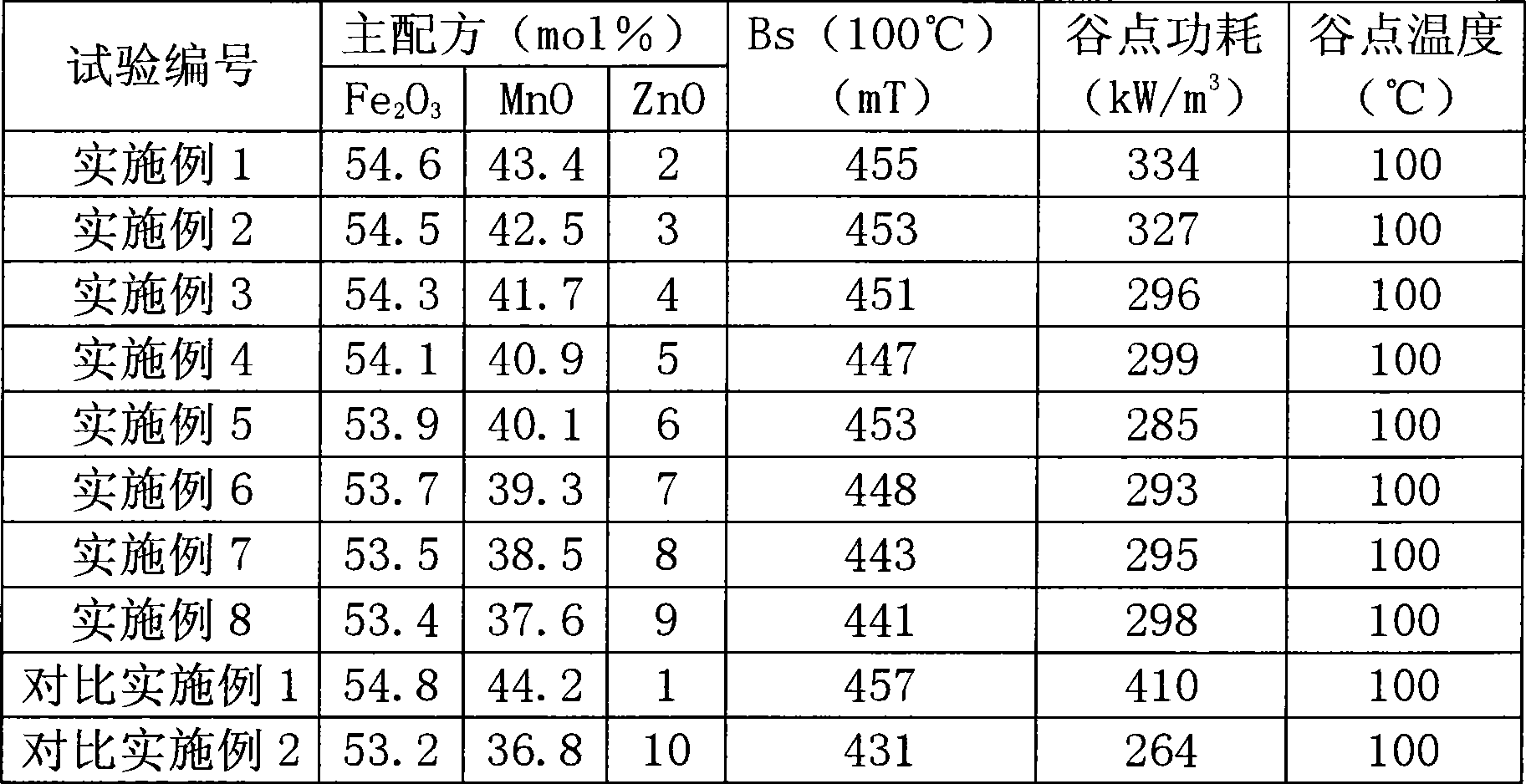
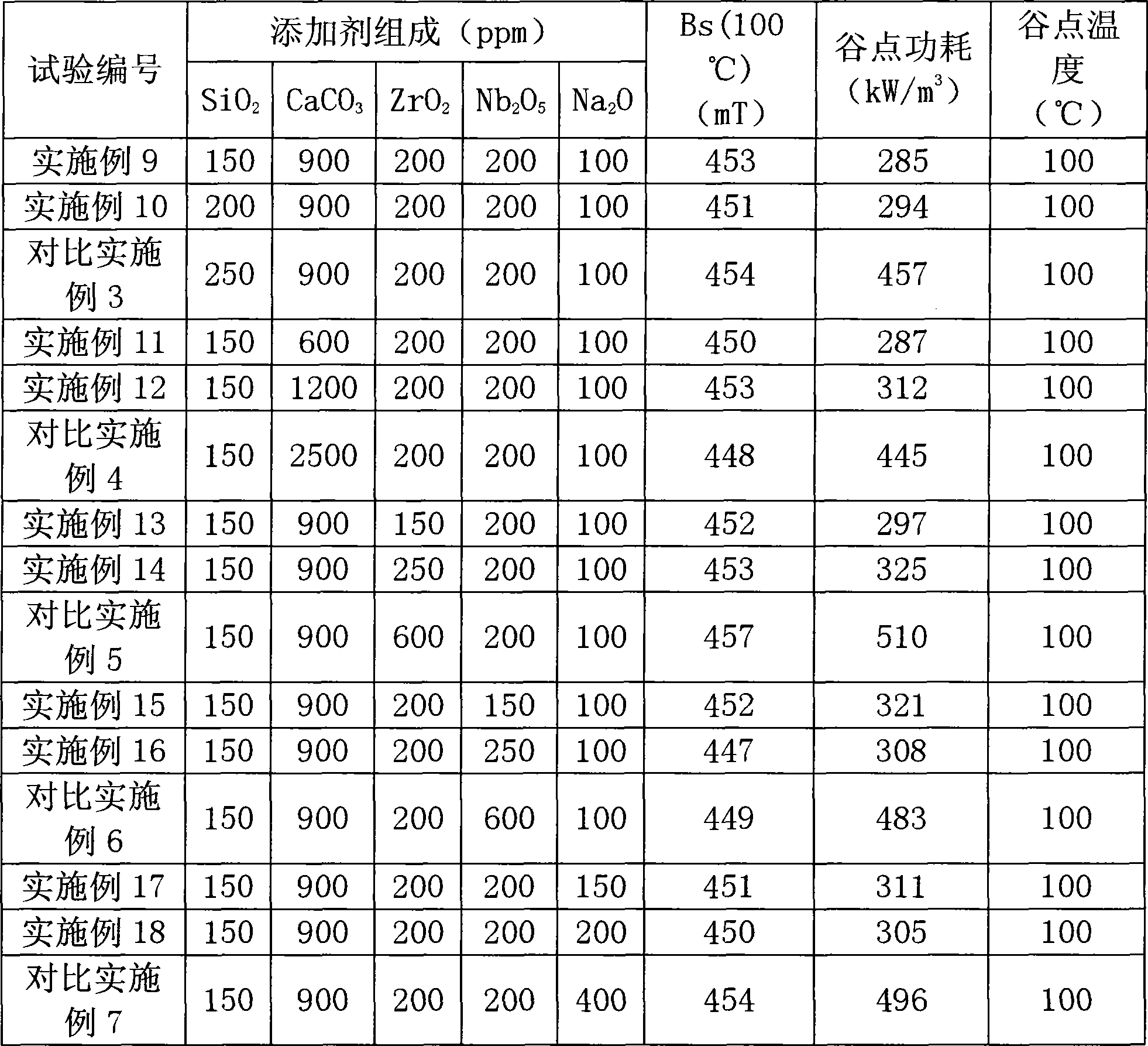
The present invention relates to a soft magnetic ferrite material and preparation method, specifically to a highly saturated magnetic flux density low-loss soft magnetic ferrite material and preparation method thereof. The present invention is mainly directed to resolve low saturated magnetic flux density and large loss and the like problems existing in the prior art, the invention provides highly saturated magnetic flux density low-loss soft magnetic ferrite material which has high saturation magnetic flux density, low loss and adaptation to the prior large-scale production and preparation method thereof by the improvement of composition. The main technical program of this invention as follows: the principal components are 53.4 - 54.6mol% of Fe2O3, 2 - 9mol% of ZnO and 37.6 - 43.4mol% of MnO; the vice components are 150 - 200ppm of SiO2, 600 - 1200ppm of CaCO3, 150 - 250ppm of ZrO2, 150 - 200ppm of Nb2O3, and 100 - 200ppm of Na2O.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Soft-magnetic ferrite with low loss and high saturation flux density and preparation method therefor
The invention discloses a soft-magnetic ferrite with low loss and a high saturation flux density. The raw materials comprise materials A and materials B. The materials A comprise, by mole, 56-60 parts of iron oxide, 40-45 parts of manganese oxide, 7-10 parts of zinc oxide and 2-4 parts of copper oxide. With the total weight of the materials A as a base, the materials B comprise 2500-3000ppm, 300-700ppm of calcium oxide, 100-300ppm of niobium oxide, 400-800ppm of zirconium oxide, 1500-2000ppm of nickel oxide, 300-800ppm of bismuth oxide, 300-500ppm of molybdenum oxide, 200-500ppm of silicon oxide and 2000-2500ppm of bonding agents. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the soft-magnetic ferrite with low loss and a high saturation flux density.
Owner:ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS
Soft magnetic composite material with high saturation magnetic flux density and high strength and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110277238AImprove temperature resistanceHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureNitrogen gasFriction force
The invention relates to a soft magnetic composite material with high saturation magnetic flux density and high strength and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of soft magnetic composite material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: 1, carrying out phosphating treatment on iron powder; 2, washing, filtering and drying the powder, and then obtaining coated powder through screening; 3, mixing the coated powder with calcium carbonate through mechanical ball milling; 4, premixing the coated iron powder obtained at step 3 with a lubricant; 5, heating a mold, and adding the mixture obtained at step 4 for compression molding; 6, placing a pressed magnetic ring in a vacuum sintering furnace for nitrogen atmosphere annealing heat treatment. The warm-pressing molding of the insulated coated powder is performed through the heating of the mold, thereby effectively reducing the friction force between the powder; and then the residual stress of the material is removed through annealing heat treatment, so the composite material is obtained and the use requirements under complex stress conditions are met.
Owner:山东精创磁电产业技术研究院有限公司
Magnetic material for photovoltaic inverter
ActiveCN102173767AReduce power consumptionHigh frequencyInorganic material magnetismThermal expansionEnergy consumption
The invention discloses a magnetic material for a photovoltaic inverter. The magnetic material is characterized by being a MnZn ferrite material and comprising 51.5 to 57.5 molar percent of Fe2O3, 4.5 to 15.5 molar percent of ZnO and the balance of MnO which serve as main components and 0.05 to 0.15 weight percent of Eu2O3 and 0.008 to 0.10 weight percent of Al2O3 which serve as auxiliary components, and one or more of 0 to 0.15 weight percent of CaO, 0 to 0.035 weight percent of SiO2, 0 to 0.50 weight percent of MgO, 0 to 0.06 weight percent of Nb2O5 and 0 to 0.055 weight percent of ZrO2 which also serve as auxiliary components. The magnetic material is characterized in that: the thermal expansion coefficient is less than 8*10<-6>; the magnetostrictive coefficient is less than -0.3*10<-6>; the magnetic conductivity at the temperature of 25 DEG C is 2,100+ / -25 percent; the saturation magnetic flux density at the temperature of 25 DEG C is more than 530mT and the saturation magnetic flux density at the temperature of 100 DEG C is more than 430mT; and at the temperature of 100 DEG C, under the conditions of 25KHz*200mT and 100KHz*200mT, the energy consumption is less than 65mW / cm<3>and 320mW / cm<3> respectively.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGRUI ELECTRONICS
Multilayer coil part
ActiveCN103597558AInhibit growthReduced sinterabilityTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInorganic material magnetismElectrical conductorSize ratio
This multilayer coil part has a magnetic body section (2) that is made of an Ni-Zn system ferrite material and a Cu-based coil conductor (3) that has been wound into a coil shape. The coil conductor (3) is buried inside the magnetic body section (2) to form a part element body (1). The part element body (1) is divided into a first region (6) that is located close to the coil conductor (3) and a second region (7) that comprises the region other than the first region (6). The grain size ratio (D1 / D2) between the average crystal grain size (D1) of the magnetic body section (2) in the first region (6) and the average crystal grain size (D2) of the magnetic body section (2) in the second region (7) is equal to or lower than 0.85. The molar quantity of CuO content in the ferrite material is set to 6 mol% or less, and the ferrite material is baked in a reductive atmosphere with the oxygen partial pressure being equal to or lower than the Cu-Cu2O equilibrium oxygen partial pressure. Thus, a multilayer coil part that exhibits not only little fluctuation of inductance and excellent thermal shock resistance when subjected to a thermal shock or an external stress but also excellent direct-current superposition characteristics can be obtained without requiring any complicated step.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Insulator-coated powder for magnetic member
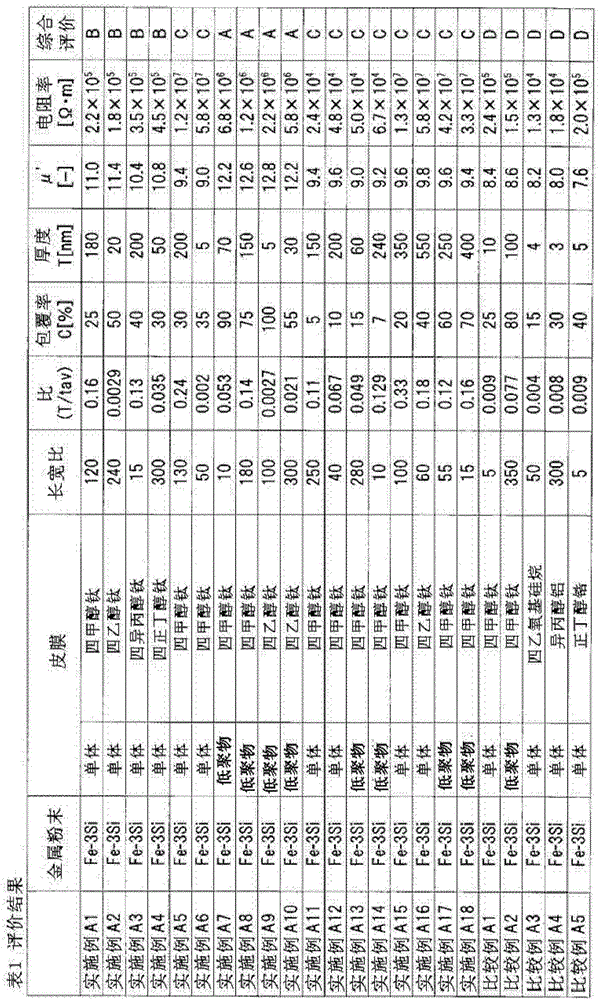
ActiveCN105474334AHigh saturation flux densityDecrease the real part permeability μ’Magnetic/electric field screeningInorganic material magnetismElectromagnetic wave absorberOligomer
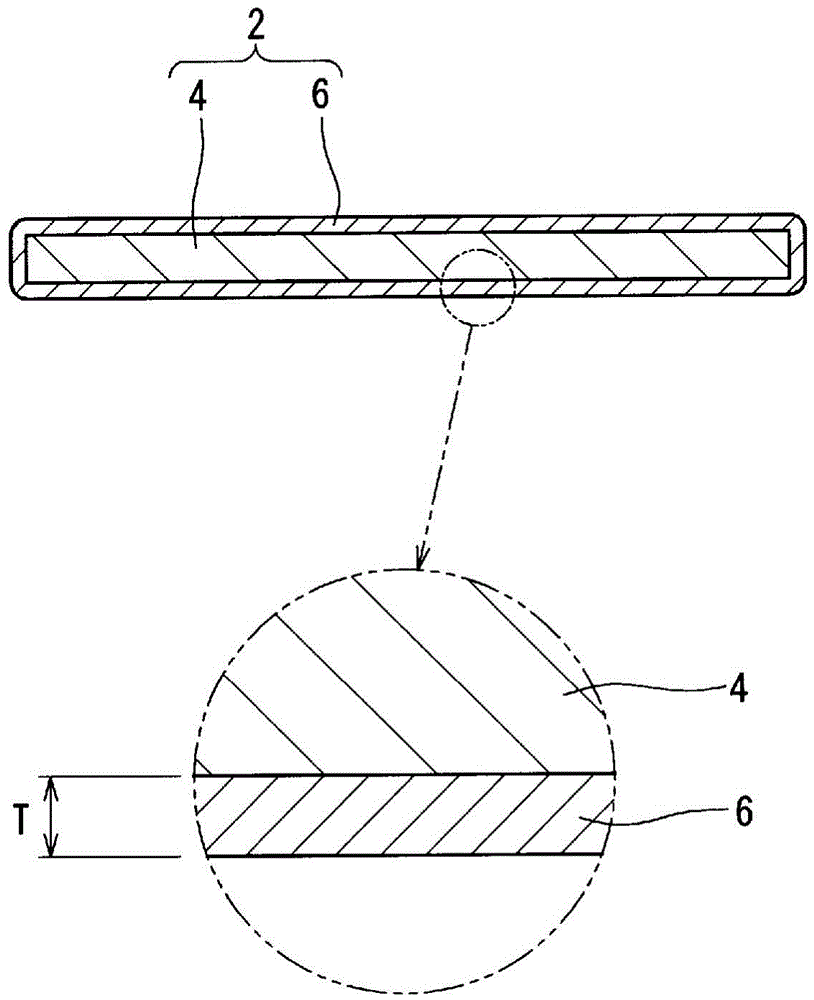
Provided is an insulator-coated flat powder (2) that is for a magnetic member such as an electromagnetic wave absorber that is effective in blocking or absorbing electromagnetic waves in a frequency range of 1 MHz-50 GHz. The insulator-coated flat powder (2) is provided with flattened metal particles (4) and an insulating film (6) that is attached to the surface of the metal particles (4). The aspect ratio of the metal particles (4) is 10-300. The film (6) is a polymer that contains a titanium alkoxide. It is preferable that the ratio of the thickness of the film (6) to the thickness of the metal particles (4) in the powder (2) be 0.002-0.2. It is preferable that the titanium alkoxide in the powder (2) be an oligomer of a titanium alkoxide. It is preferable that the coverage rate of the metal particles (4) by the film (6) in the powder (2) be 20% or higher. It is preferable that the thickness of the film (6) in the powder (2) be 1 nm to 200 nm, and that the film (6) be an oxide of titanium.
Owner:SANYO SPECIAL STEEL COMPANY
Soft magnetic amorphous alloy
InactiveCN101802240AImprove featuresReduce productionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureAlloy
Disclosed is a soft magnetic amorphous alloy represented by the following composition formula: {Fea(SixByPz)1-a}100-bLb. In the composition formula, L represents one or more elements selected from Al, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta and W, and a, b, x, y and z satisfy the following relations: 0.7 <= a <= 0.82, 0 < b <= 5 atom%, 0.05 <= x <= 0.6, 0.1 <= y <= 0.85, 0.05 <= z <= 0.7 and x + y + z = 1.
Owner:TOKIN CORP +1
Mn-Zn soft magnetic ferrite and production method
InactiveCN101241793ALittle change in initial permeabilityHigh saturation flux densityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureInitial permeabilityMetallurgy
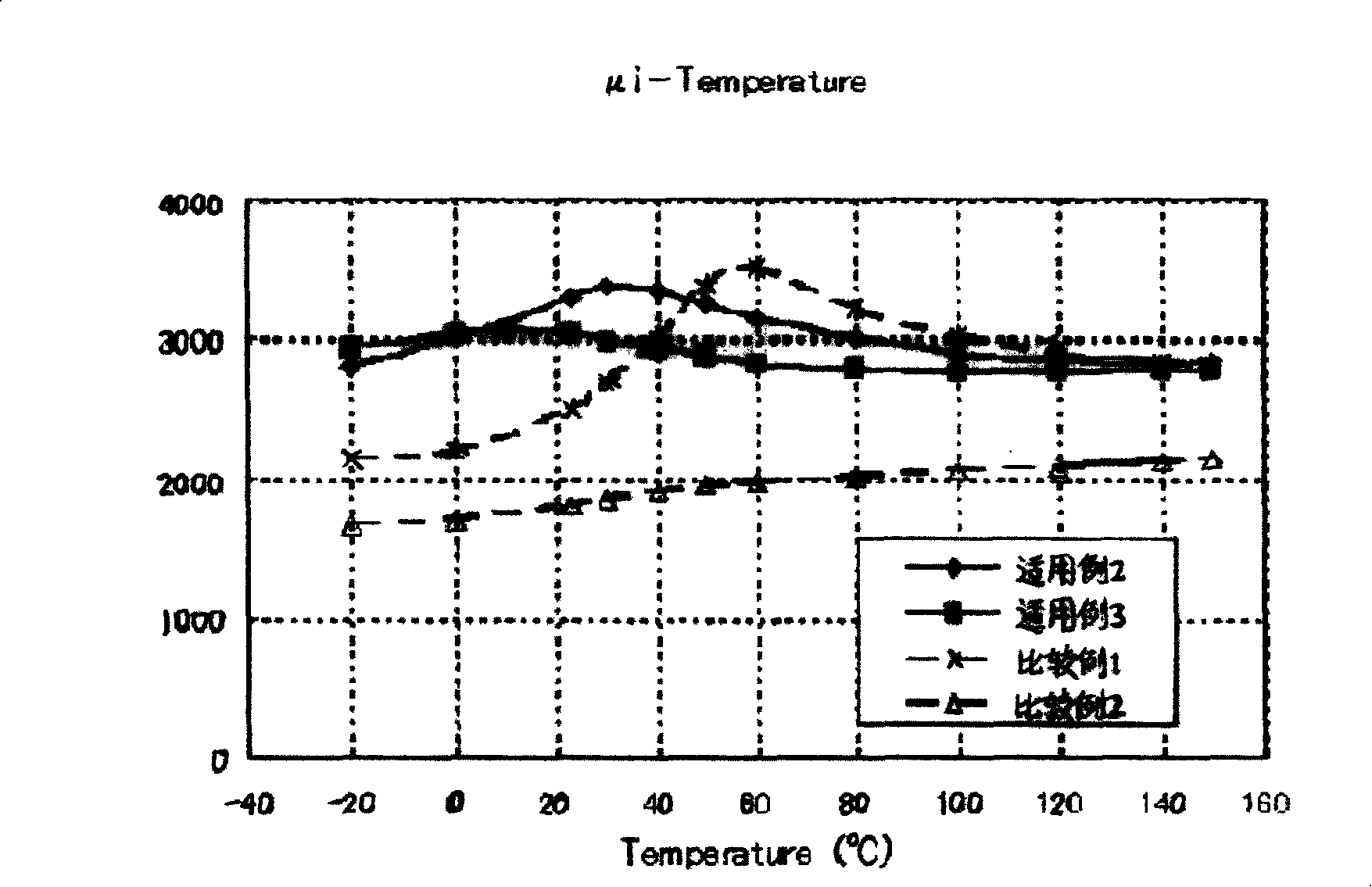
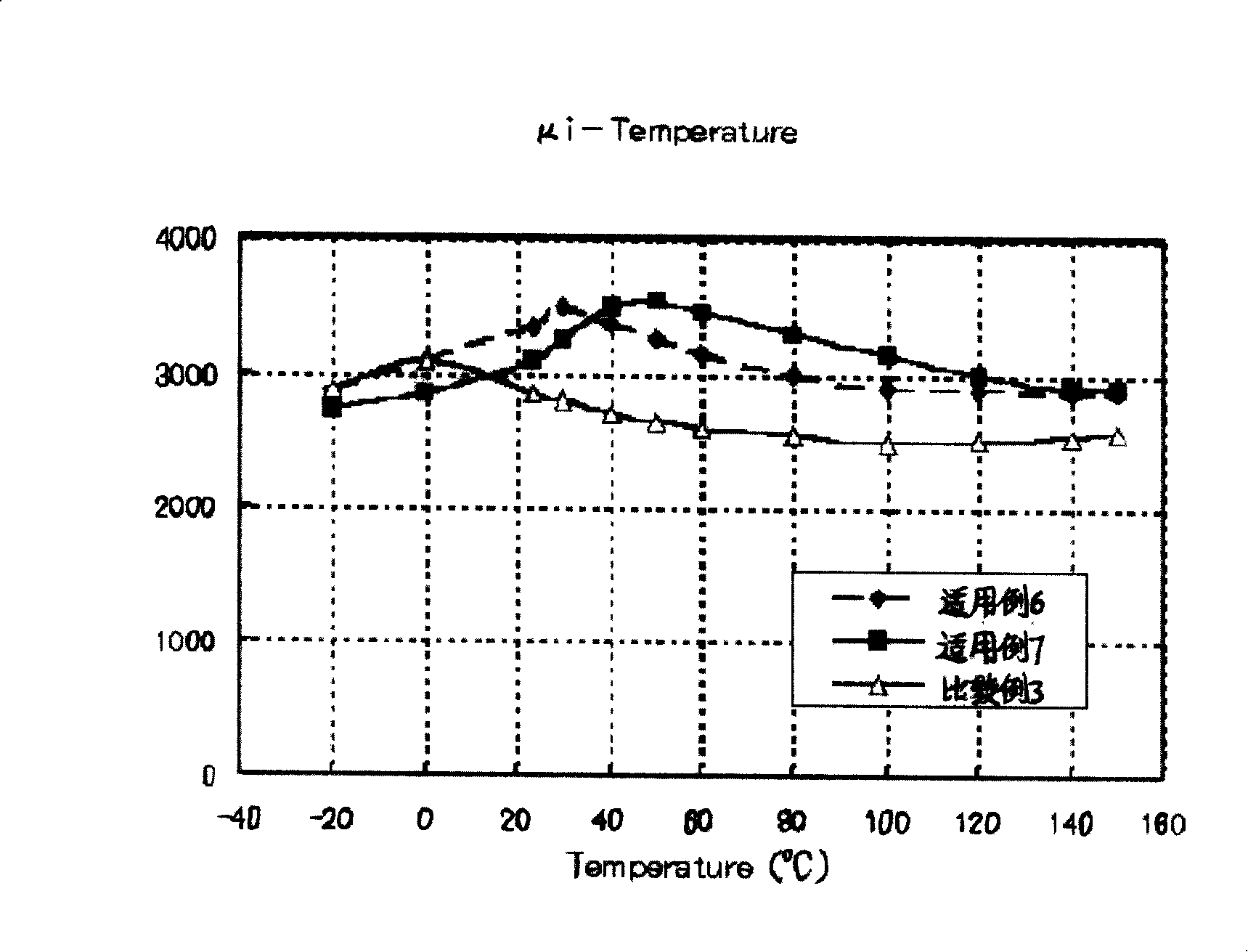
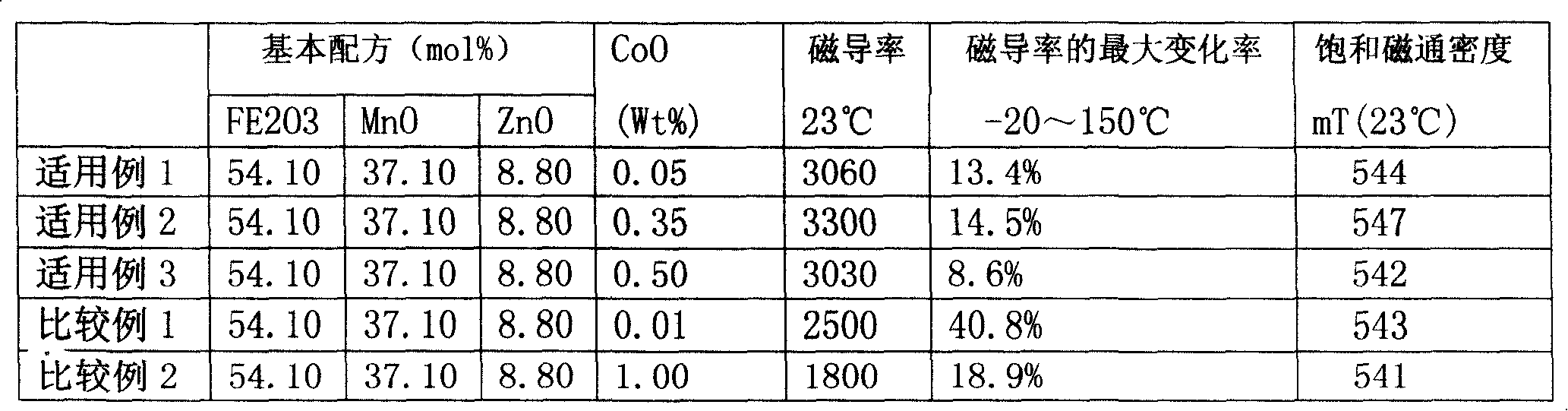
The present invention discloses a Mn-Zn series ferrite and the preparing technique thereof. The raw material is prepared with the adjusting of the main formula and the adjusting of the kind and dosage of the adulterant (especially CoO is used). When the raw material is provided higher magnetic conductivity and stable magnetic conductivity change rate in broad temperature range, the raw material is provided with high saturation flux density. The range of the main formula of the material is as follows: Fe2O3 for 53.7-54.4mol, MnO for 36-38mol, and ZnO for 8-10mol The invention is mainly characterized in that the adding amount of CoO is 0.05-0.6wt Therefore the invention has the advantages of small initial permeability variation in broad temperature range and high saturation flux density. The technique of the invention is simple and can be actualized with generalization.
Owner:KUSN NICERA ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
Low-consumption soft magnet ferrite material
ActiveCN107200574ALow melting pointHigh resistivityInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureHigh frequencySoft magnet
The invention discloses a low-consumption soft magnet ferrite material which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 100 parts of a main material, 0.8-0.9 part of an auxiliary material and 6-8 parts of aids, wherein the main material comprises the following raw materials in parts by mole: 56-58 parts of Fe2O3, 30-33 parts of MnO, 8-9 parts of ZnO and 3-4 parts of NiO; the auxiliary material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 2.5-3.5 parts of CaO, 0.8-1.2 parts of V2O5, 0.9-1.1 parts of SnO2, 0.25-0.35 part of TiO2, 0.5-1 part of Co2O3, 0.15-0.25 part of Nb2O5, 0.9-1.1 parts of MoO3, 0.2-0.4 part of Bi2O3 and 0.3-0.5 part of Ta2O5. The low-consumption soft magnet ferrite material has properties of high frequency, high initial magnetic conductivity and low consumption.
Owner:ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS
Preparation process of wide-temperature low-power-consumption manganese zinc ferrite powder
InactiveCN105565391AHigh saturation flux densityReduce power lossIron compoundsMetallurgyCurie temperature
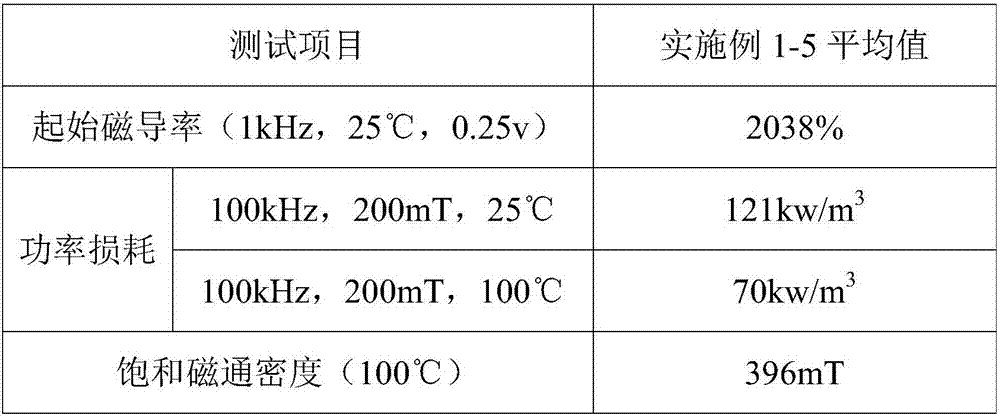
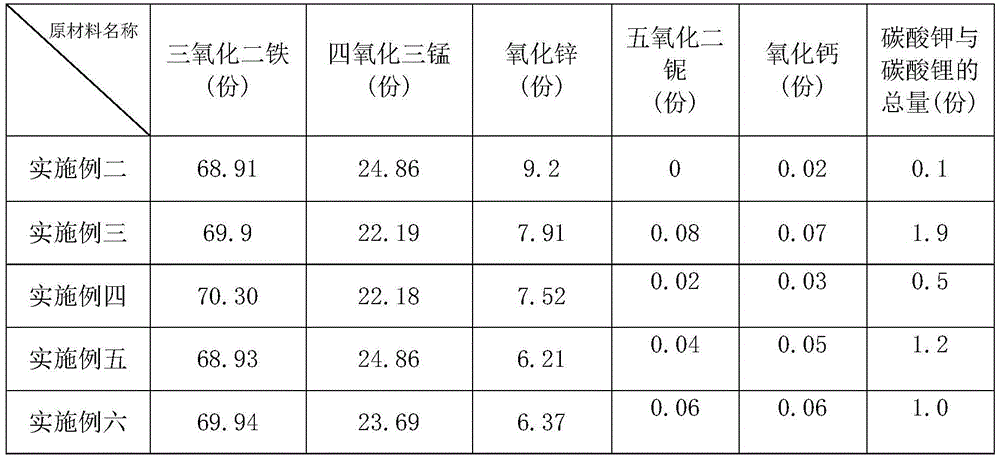
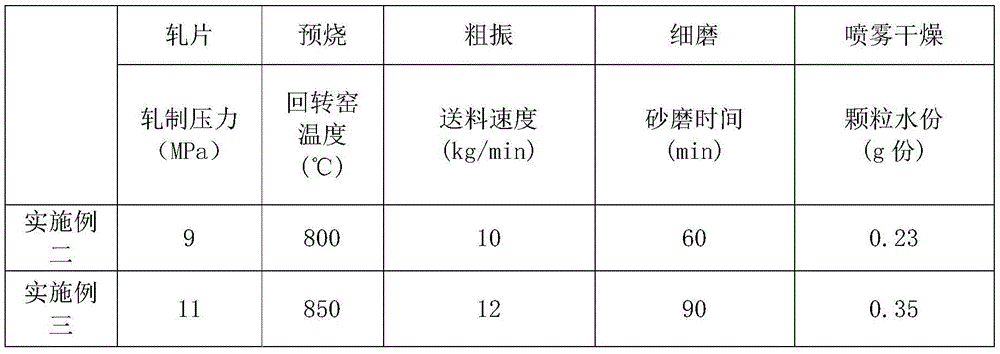
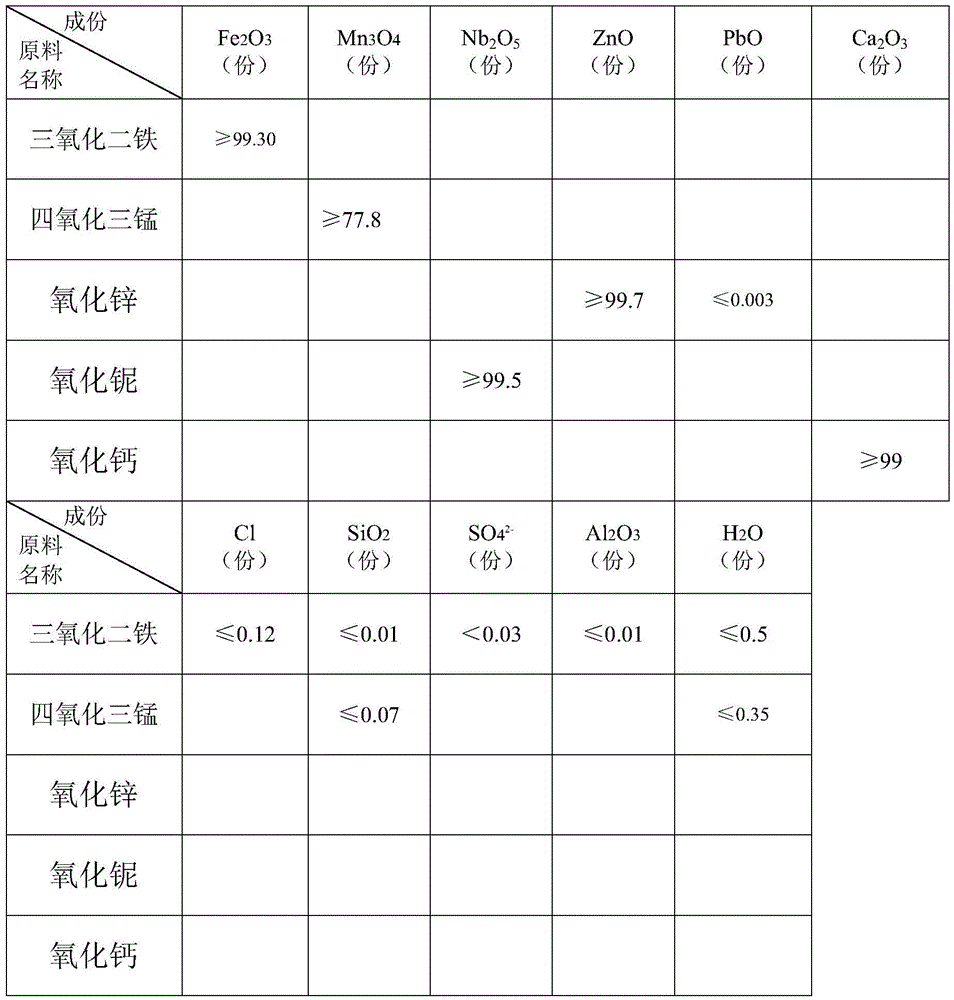
The invention discloses a preparation process of wide-temperature low-power-consumption manganese zinc ferrite powder. The preparation process includes, preparing and mixing materials, sheet rolling, pre-sintering, coarse vibrating, fine grinding, adding PVA and performing component correction, and spray drying. The wide-temperature low-power-consumption manganese zinc ferrite powder prepared by the preparation process is high in saturation flux density, low in power consumption and high in Curie temperature and resistivity in a range of 25-100 DEG C.
Owner:NANTONG HUAXING MAGNETIC MATERIAL
Preparation of soft magnetic thin film
InactiveUS7135103B2Effectively preparing a soft magnetic thin filmHigh saturation flux densityCellsSalt bridgeAlloy
A soft magnetic thin film of CoFe alloy having a high Br and low Hc is prepared by furnishing a plating tank including cathode and anode compartments which are separated by a diaphragm or salt bridge so as to permit charge transfer, but inhibit penetration of Fe ions, feeding a plating solution containing Co ions and divalent Fe ions to the cathode compartment, feeding an electrolyte solution to the anode compartment, immersing a substrate in the plating solution, immersing an anode in the electrolyte solution, electroplating, and heat treating the plated film at 100–550° C.; or by immersing a substrate and a soluble anode in a plating solution containing Co ions and divalent Fe ions, electroplating, and heat treating the plated film at 100–550° C.
Owner:OSAKA TETABUYA
Anti-electromagnetic interference manganese zinc ferrite material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an anti-electromagnetic interference manganese zinc ferrite material and a preparation method thereof. The material comprises main components and auxiliary components, wherein the main components comprise, by mole percent, 43.5-44.5 mol% of Fe2O3, 53-56 mol% of MnO, and 2-3 mol% of ZnO, and the auxiliary components comprise CaCO3, Nb2O5, MgO, and V2O5. The material of the invention overcomes the disadvantage that common manganese zinc ferrite is less in resistivity, and can not be used as anti-EMI materials in high frequency fields; when compared with nickel zinc ferrite, the material of the invention is less in environment pollution, and low in cost, and can substitute for nickel zinc ferrite to be used as an anti-EMI materials in high frequency fields.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Magnetic glue and inductor device using same
InactiveCN106590345AShorten the lengthStrong mechanical impact resistanceMagnetic paintsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectromagnetic interferenceShock resistance
The invention discloses a magnetic glue which is used for a magnetic glue layer of a wire winding inductor device and contains a mixture of a magnetic substrate and an adhesion substrate; the magnetic substrate is a mixture of one or more of NiZn ferrite and MnZn ferrite and one or more of metal series FeNi, carbonyl iron powder, FeSiCr and FeSi. The invention discloses an inductor device which comprises a magnetic core and a coil winding on the magnetic core; and the magnetic glue is coated on the magnetic core, covers the coil winding and forms the magnetic glue layer which is tightly adhered to the magnetic core after being solidified. Compared with an ordinary inductance device, as for the inductor device adopting the magnetic glue, the mechanical shock resistance is stronger, magnetic flux leakage of a formed closed magnetic circuit structure can be reduced, and the electromagnetic interference resistance is strong.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNLORD ELECTRONICS
Nickel zinc ferrite magnetic shielding inductor product and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103000326AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove the ability to withstand DC superpositionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureNickel-zinc ferriteCopper oxide
The invention relates to a nickel zinc ferrite magnetic shielding inductor product and a manufacturing method thereof. A raw material for manufacturing a magnetic shielding inductor mainly comprises ferric oxide, nickel oxide, zinc oxide and copper oxide, and an auxiliary component of the raw material comprises bismuth trioxide, molybdenum trioxide or vanadium pentoxide. The manufacturing method of the magnetic shielding inductor includes that the materials the mixed, sintered and made into powder materials, the powder materials are pressed into a rodlike magnetic core and a square cap-shaped magnetic core blank, the square cap-shaped magnetic core blank is placed in an air kiln to be sintered, the rodlike magnetic core is installed in a sintered square cap-shaped magnetic core after a solenoid coil is installed on the rodlike magnetic core, and the magnetic shielding inductor is manufactured. A special inductor structure and an assembly method are adopted so as to enable the inductor to shield external electromagnetic fields, and anti-interference capacity of the conductor can be improved. Nickel zinc ferrite materials with high saturation magnetic flux density are adopted, tolerance of direct current superposition of the inductor can be improved, and requirements of the inductor for miniaturization, thinning, high frequency, high performance and the like are met.
Owner:DANFENG RONGYI ELECTRONICS
Soft-magnetic ferrite with high saturation magnetic induction and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses soft-magnetic ferrite with high saturation magnetic induction. Raw materials of the soft-magnetic ferrite comprise first group of materials and second group of materials; the first group of materials comprise, in percent by substance amount, 52.0-53.5 mol% of ferric oxide, 38.0-42.0 mol% of manganese oxide, and 6.0-8.0 mol% of zinc oxide; by taking the total mass of the first group of materials as a reference, the second group of materials comprise 25-100 ppm of silicon oxide, 300-800 ppm of calcium oxide, 300-700 ppm of niobium oxide, 300-500 ppm of zirconium oxide, and 2500-3000 ppm of nickel oxide. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the above soft-magnetic ferrite with high saturation magnetic induction. The obtained soft-magnetic ferrite possesses high saturation magnetic induction, relatively high initial magnetic permeability and low magnetic core loss.
Owner:ZHONGDE ELECTRONICS
Magnetic material for light emitting diode (LED) illumination control circuit
ActiveCN102163480AHigh frequencyImprove efficiencyInorganic material magnetismMetallurgyControl circuit
The invention discloses a magnetic material for a light emitting diode (LED) illumination control circuit, and is characterized in that: the magnetic material is MnZn ferrite, which comprises the following main components: 59.5 to 61.8 mol percent of Fe2O3, 9 to 12 mol percent of ZnO and the balance of MnO, and following auxiliary components (based on the total content of the main components): 0.01 to 0.15 weight percent of KCO3, 0.008 to 0.10 weight percent of Y2O3, 0.01 to 0.25 weight percent of CaO, 0.005 to 0.055 weight percent of SiO2, 0.005 to 0.50 weight percent of MgO, 0.005 to 0.06 weight percent of V2O5, 0.01 to 0.50 weight percent of CoO, 0.005 to 0.08 weight percent of Nb2O5 and 0.005 to 0.055 weight percent of ZrO2. The magnetic material is characterized in that: the magneticconductivity at the temperature of 25 DEG C is 1,500+ / -25 percent; the saturated magnetic flux density at the temperature of 100 DEG C is more than 500mT; and the power consumption at the temperatureof 100 DEG C and 100KHz*200mT is less than 620mW / cm<3>.
Owner:SHANDONG ZHONGRUI ELECTRONICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com