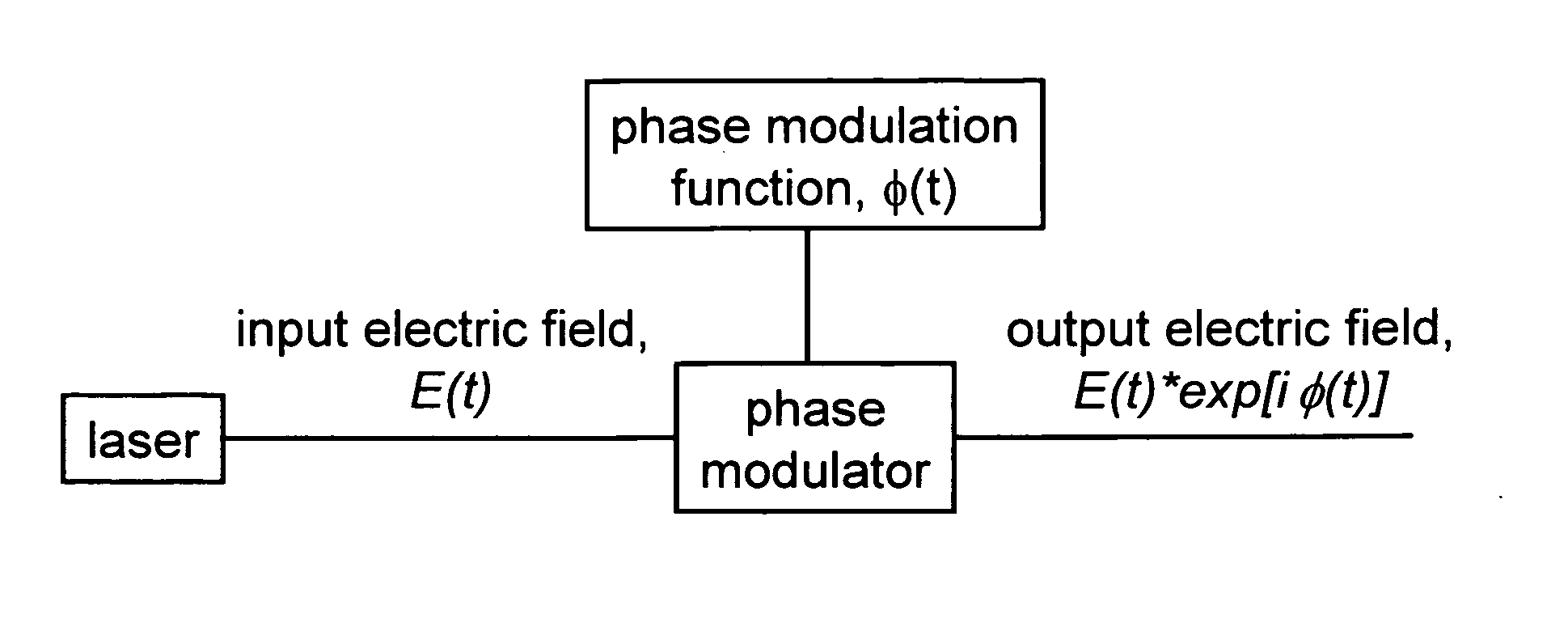
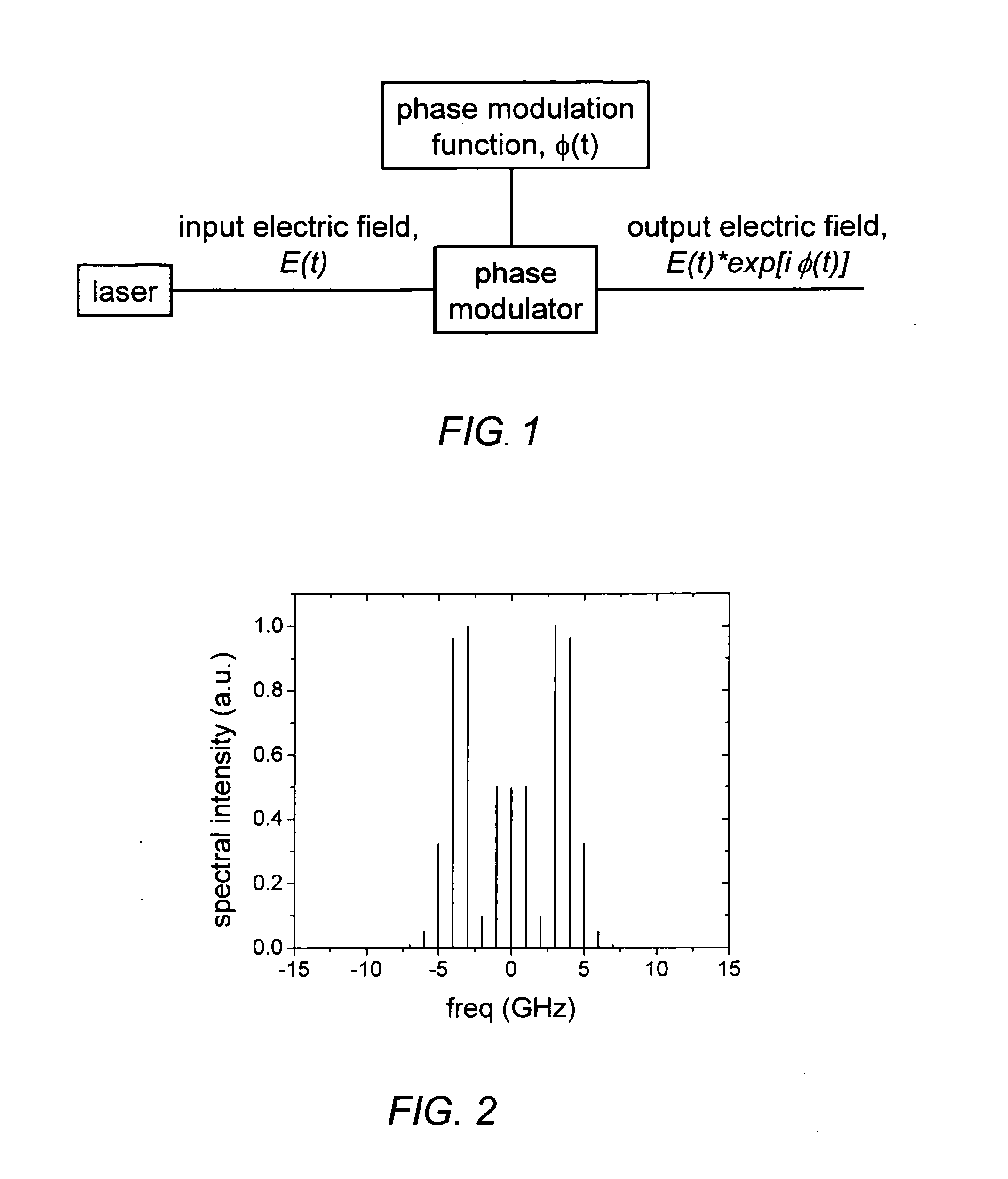
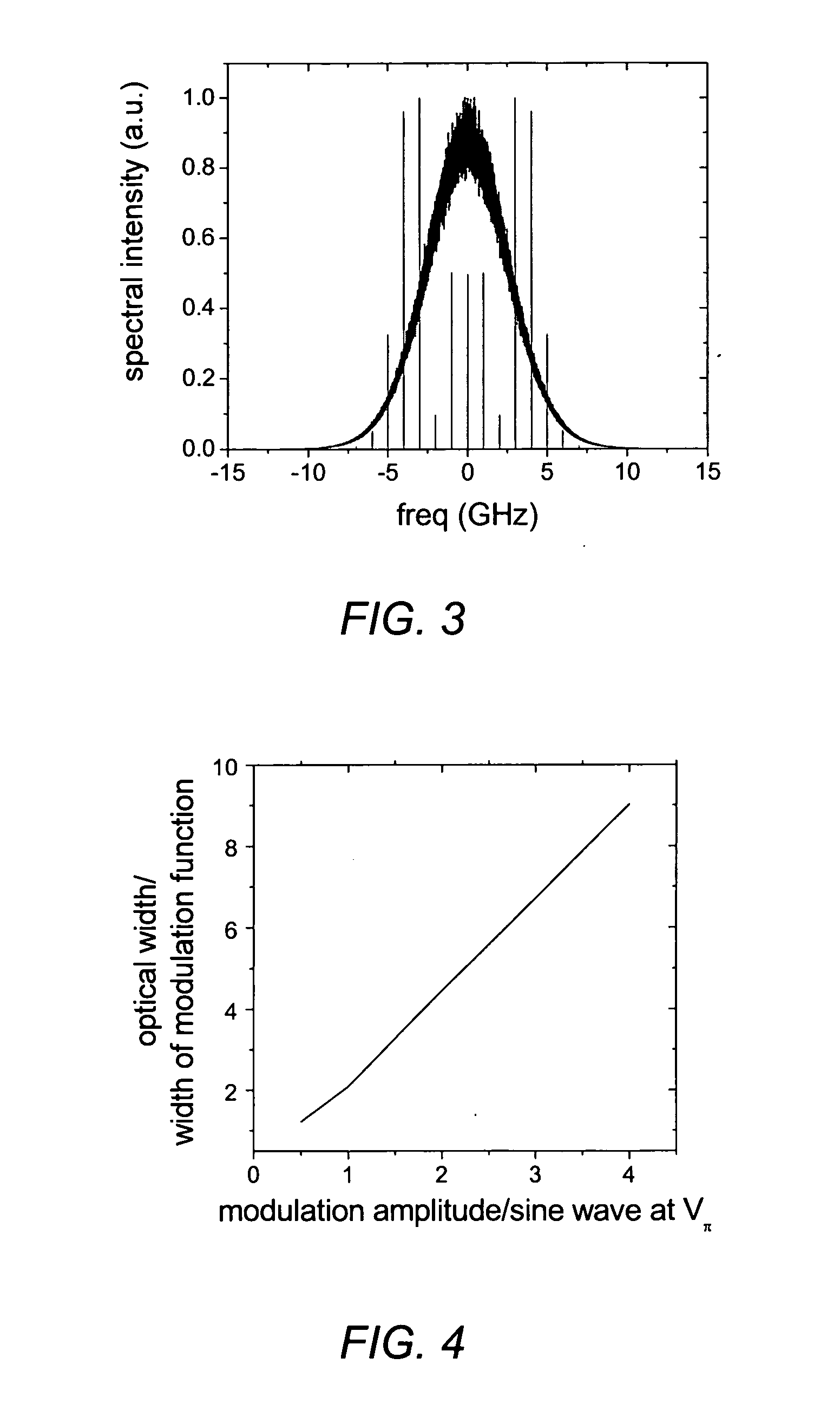
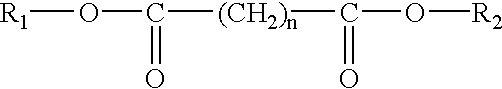Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93results about How to "Cutting can not be obtained" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
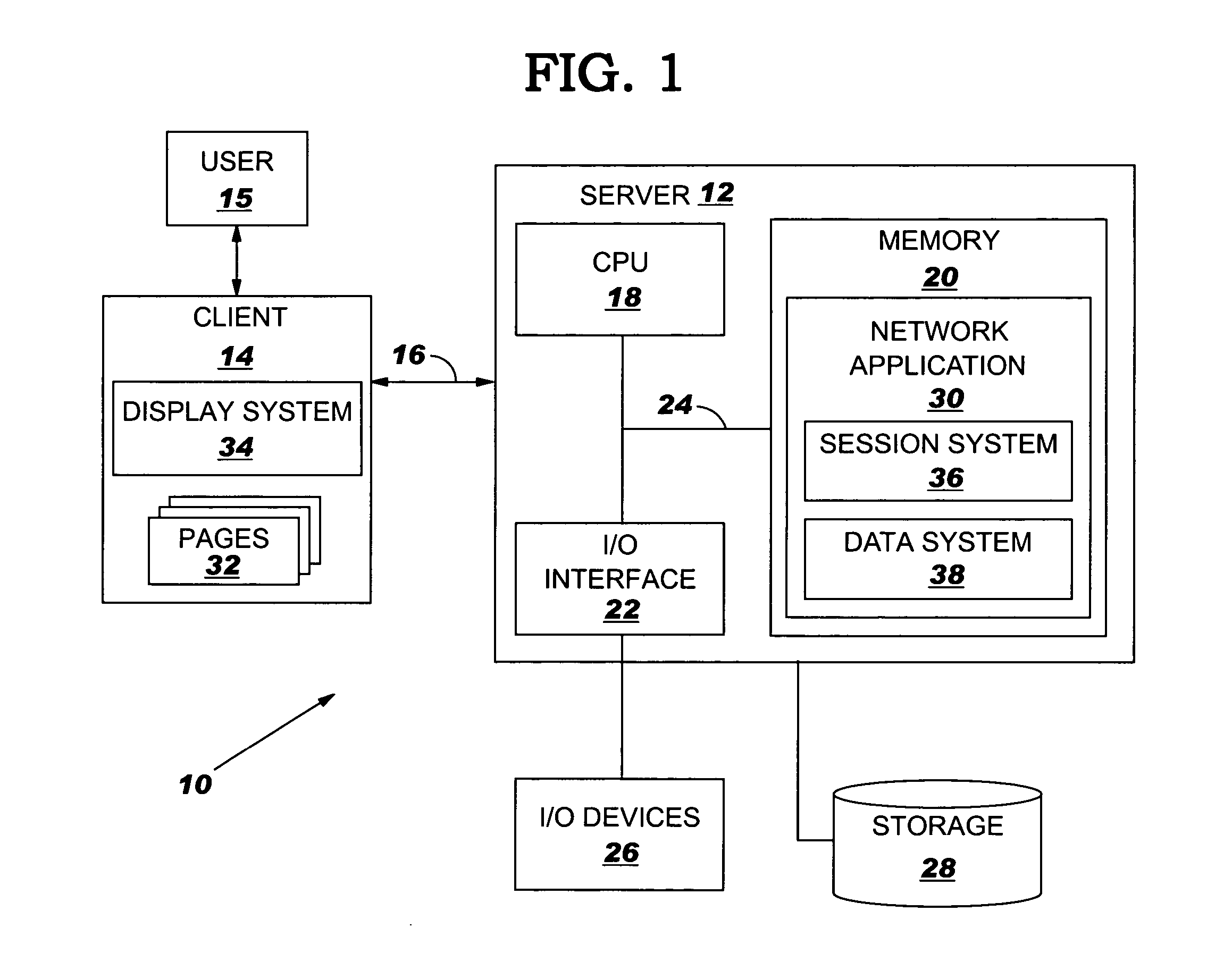
Knowledge-information-processing server system having image recognition system
InactiveUS20140289323A1Improve image recognition rateHigh frequencyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalNetwork terminationInformation processing
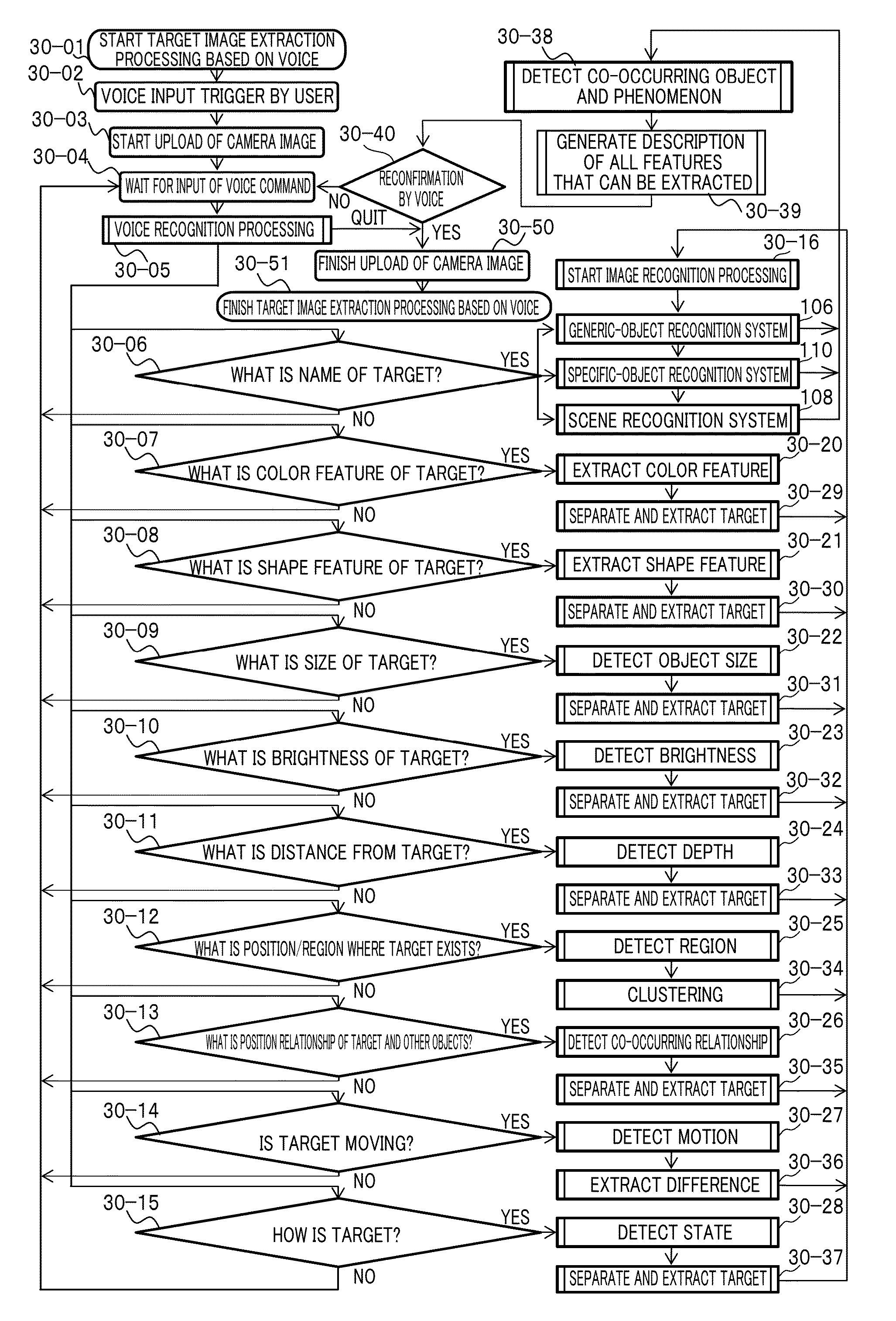
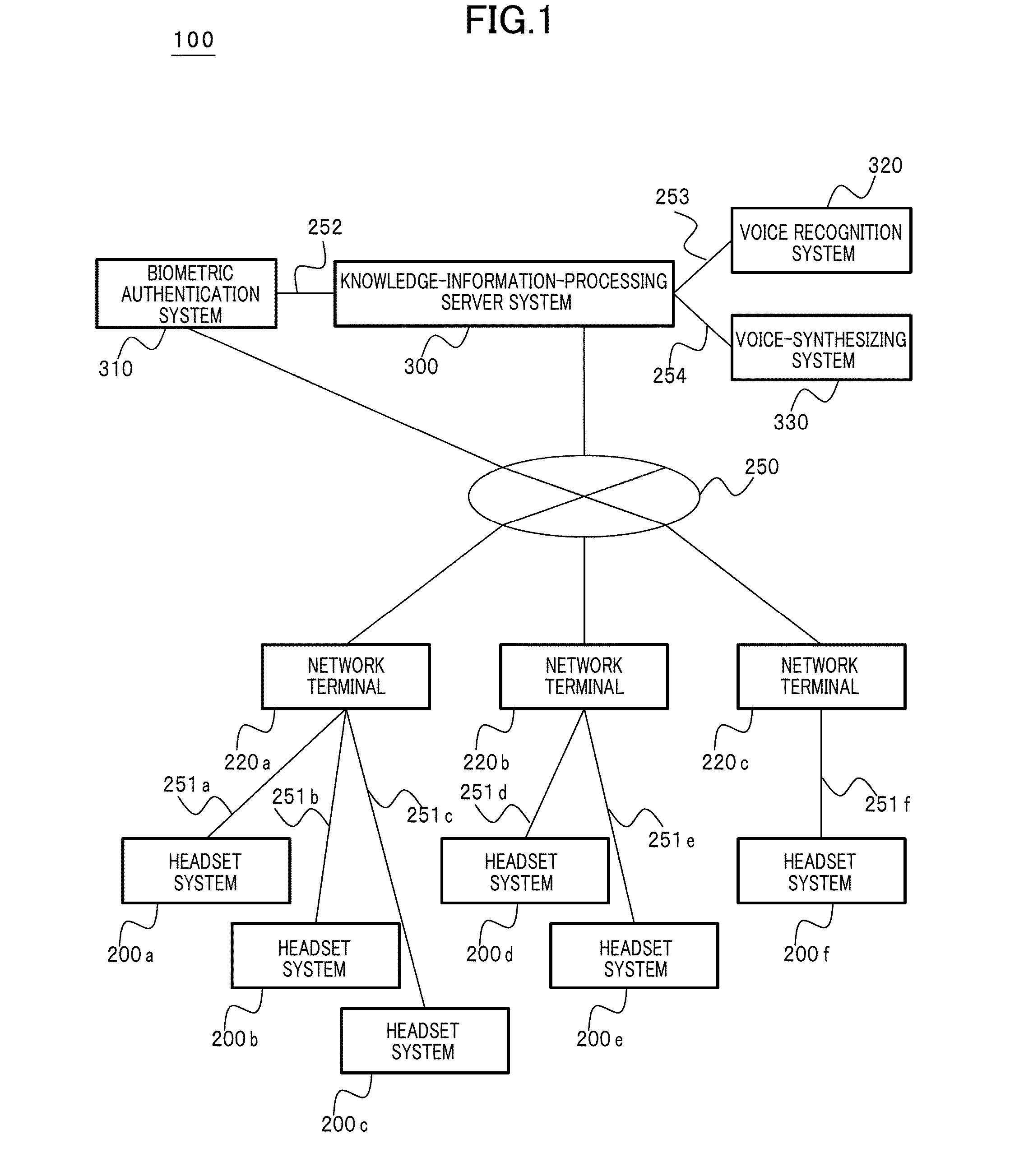
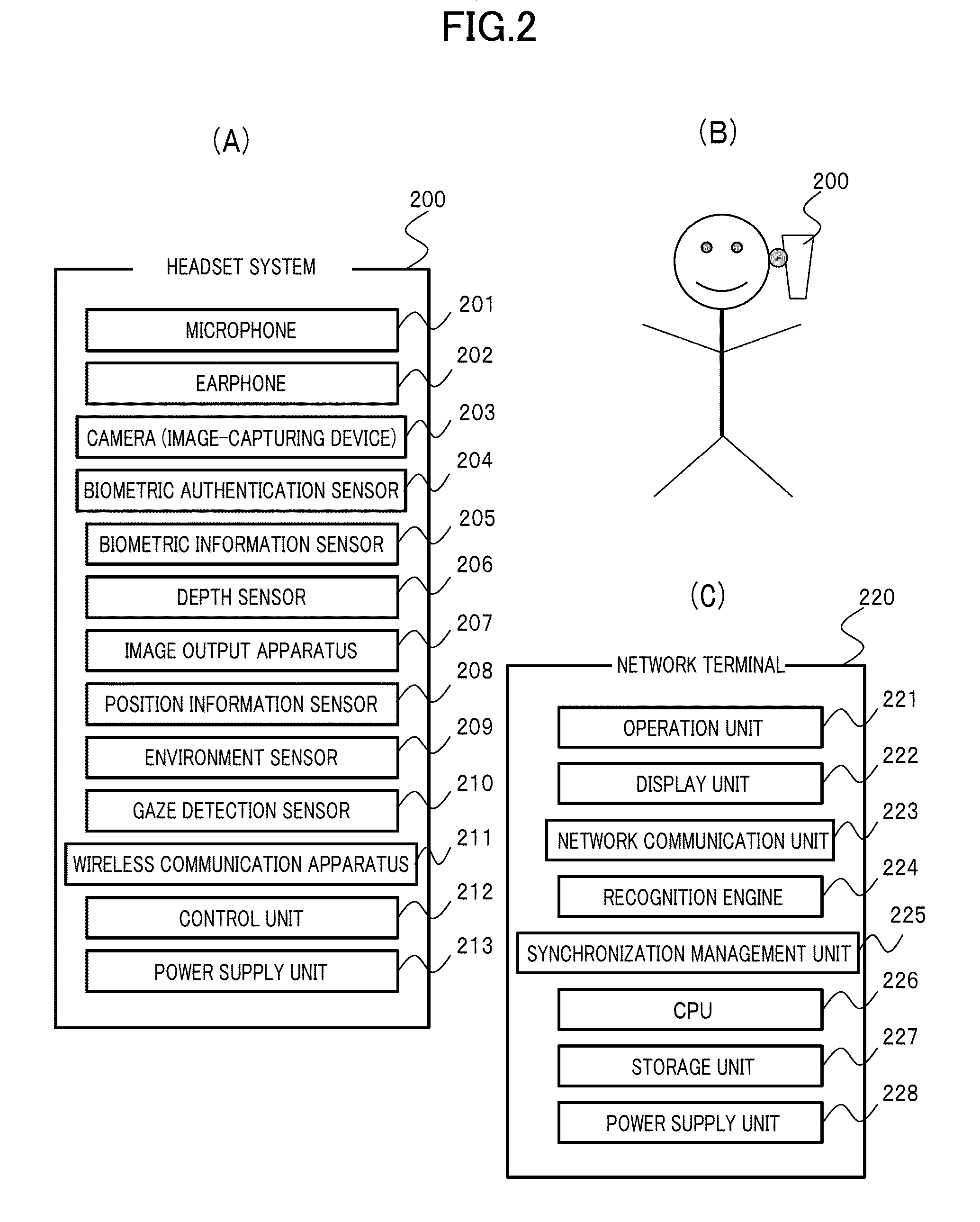
Extensive social communication is induced. Connection is made with a network terminal capable of connecting to the Internet, and an image and voice signal reflecting the subjective visual field of the user and the like which can be obtained from the headset system that can be worn by the user on the head is uploaded via the network terminal to a knowledge-information-processing server system, and specifying and selecting of an attention-given target by the voice of the user himself / herself are enabled on the server system with collaborative operation with the voice recognition system with regard to a specific object and the like to which the user gives attention and which is included in the image, and with regard to the series of image recognition processes and image recognition result made by the user, image recognition result and recognition processes thereof are notified as voice information to an earphone incorporated into the headset system of the user by way of the user's network terminal via the Internet by the server system with collaborative operation with a voice-synthesizing system, so that user's message or tweet can be extensively shared by users.
Owner:CYBER AI ENTERTAINMENT
System and method for automatic identification of vehicle identification number
ActiveUS7421322B1Simplifies and automates identificationEasy transferVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesInformation systemAutomotive engineering
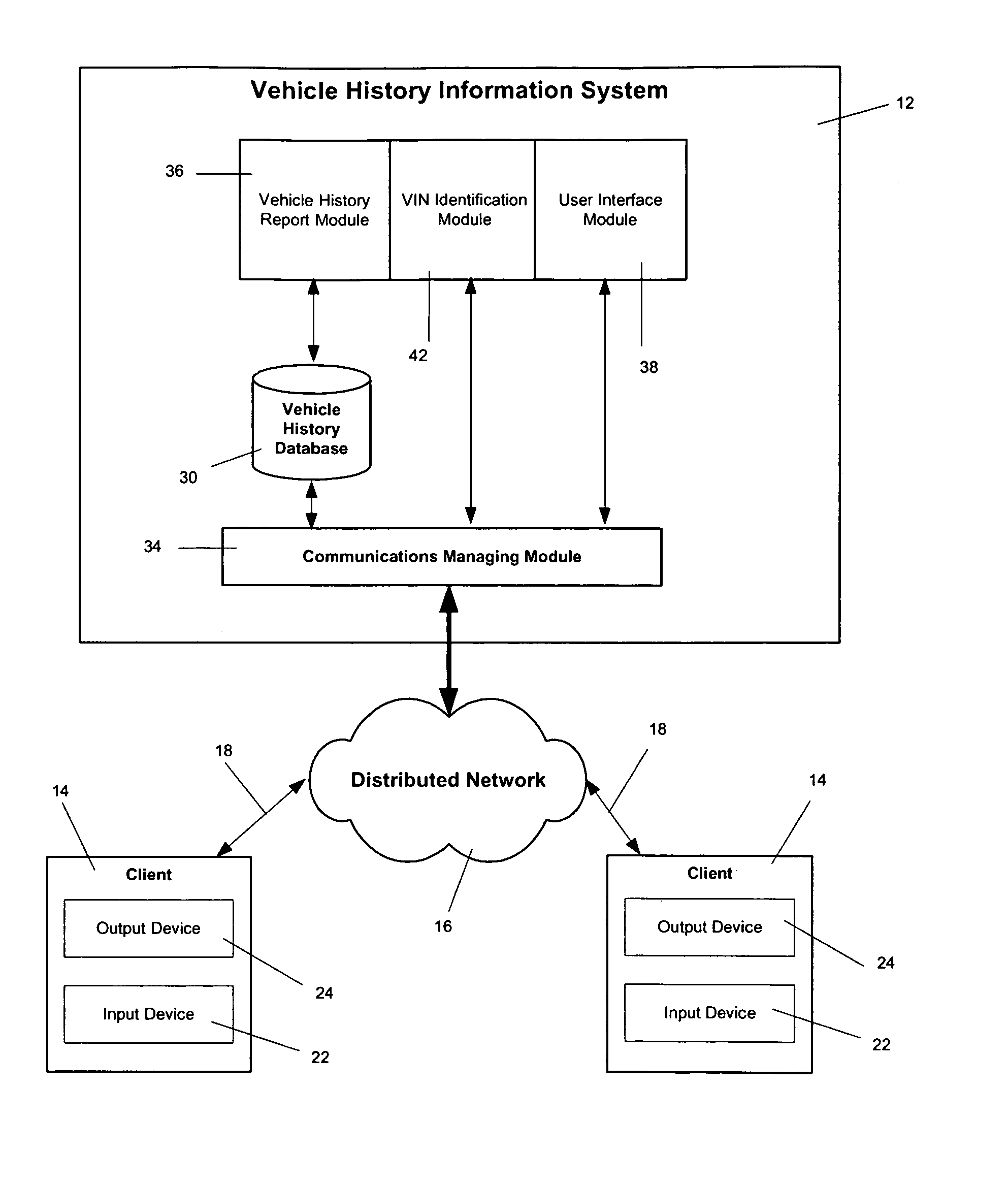
A vehicle history information system is provided for obtaining vehicle history information associated with a vehicle identification number (VIN). The vehicle history information system includes a VIN identification module adapted to identify at least one VIN in an electronic file, a database having vehicle history records relating to vehicle history of one or more vehicles, and a vehicle history report module adapted to retrieve vehicle history records associated the VIN identified. A method and a computer readable storage medium having instructions for obtaining vehicle history information are also provided.
Owner:CARFAX
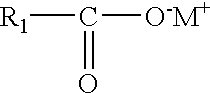
Stable, homogeneous natural product extracts containing polar and apolar fractions
InactiveUS6485756B1Cutting can not be obtainedEfficient killingCosmetic preparationsBiocideLipid formationNatural product
Disclosed are stable, homogeneous dispersions, comprising (a) from about 20 to 90% by weight of a first composition comprising (i) about 60-95% by weight of a first polar solvent, (ii) about 0-40% by weight of one or more second polar solvents, and (iii) water soluble components of a first natural product; and (b) from about 10 to 60% by weight of a second composition comprising: (i) one or more apolar solvents, and (ii) oil soluble organic components of a second natural product; and (c) from about 0.01 to 80% by weight of a non-surface active lipid phosphate or a surface active agent. Also disclosed are methods of forming the stable, homogeneous dispersions of the invention, comprising forming a first composition comprising water soluble components of a first natural product; forming a second composition comprising oil soluble organic components of a second natural product; mixing the compositions and subjecting the mixture to high pressure high shear processing to form a stable, homogeneous dispersion.
Owner:ENGELHARD CORP
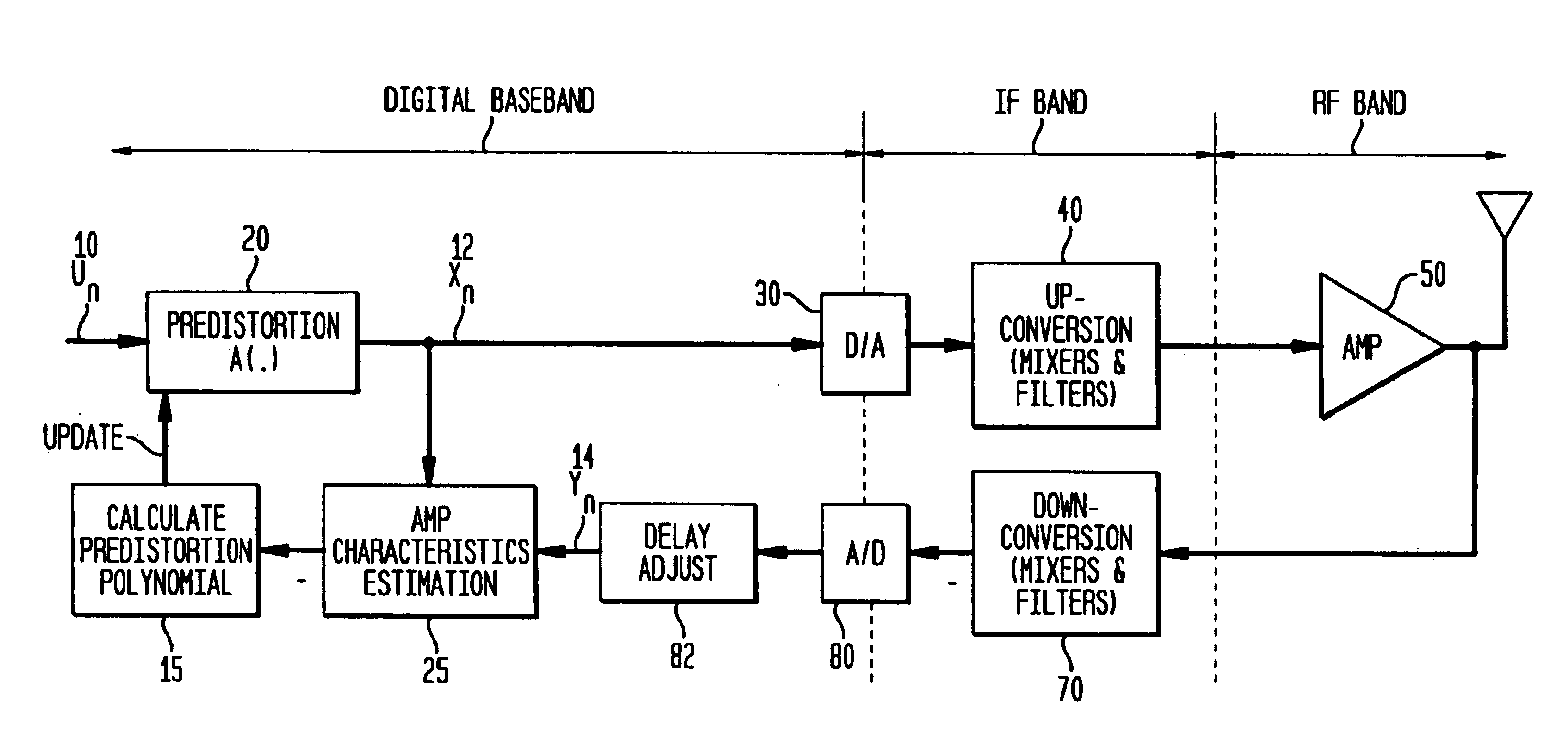
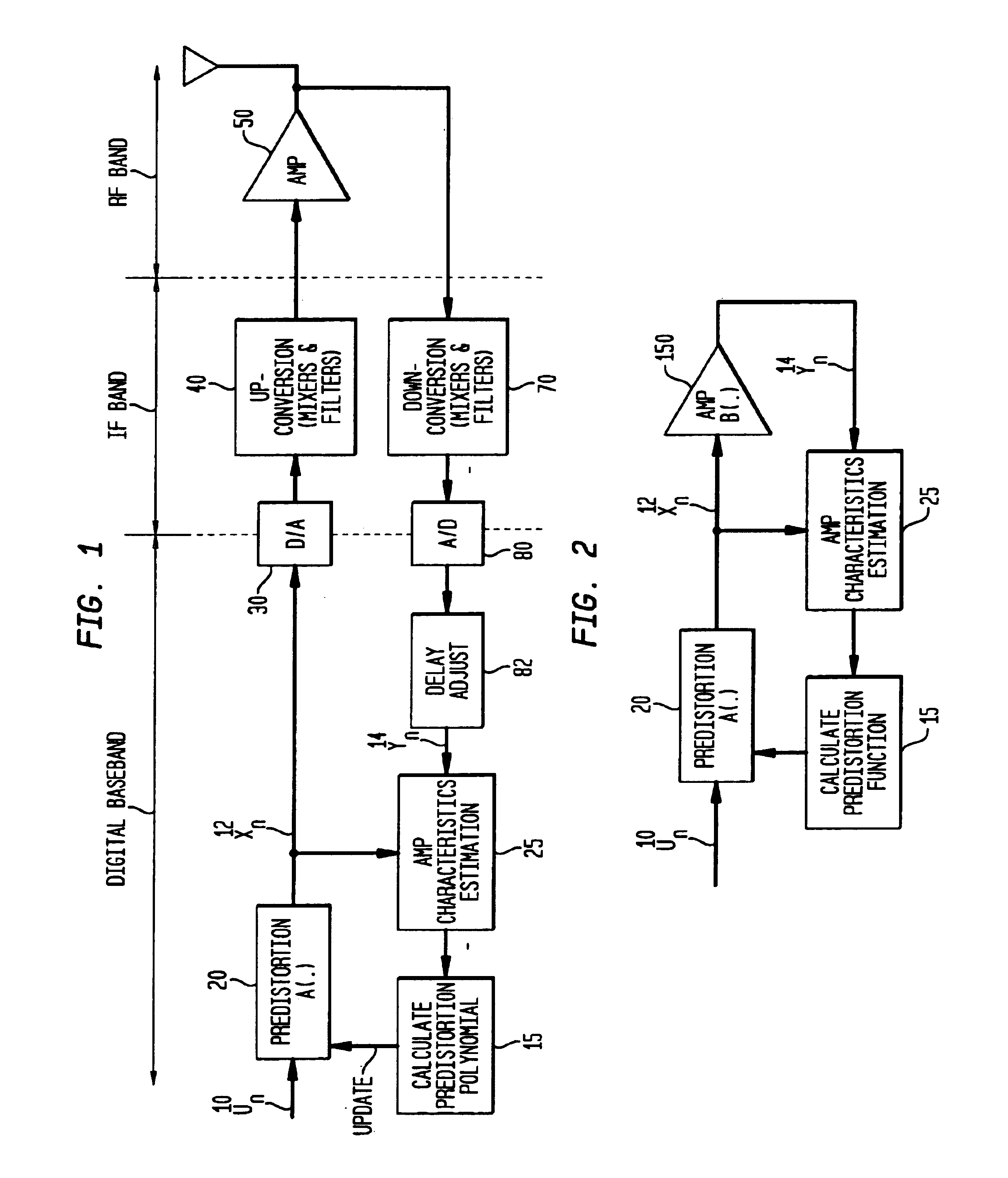
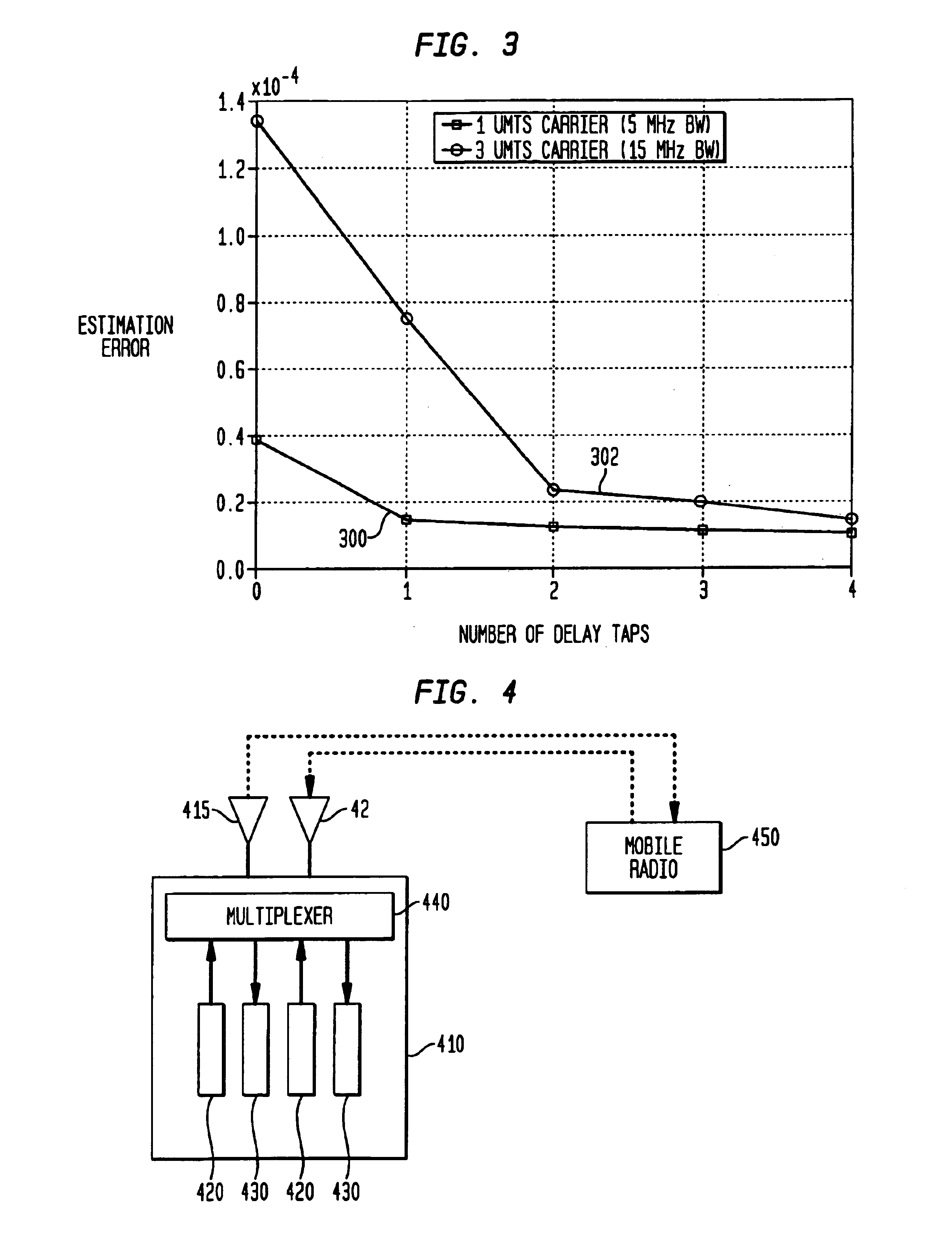
Method and apparatus for modeling and estimating the characteristics of a power amplifier
ActiveUS6903604B2Fast and efficient implementationImprove abilitiesPower amplifiersMemory effect compensationCurrent sampleAudio power amplifier
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for modeling and estimating the characteristics of a power amplifier with memory. A predistortion module generates a predistorted signal in response to coefficients of a complex polynomial representative of the amplifier and to an input signal. A power amplifier receives time-spaced samples of the predistorted signal and generates an output signal. A polynomial module updates the coefficients of the complex polynomial in response to a current sample of the output signal and to the time-spaced samples of the predistorted signal. In particular, the complex polynomial is implemented with both even and odd terms.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
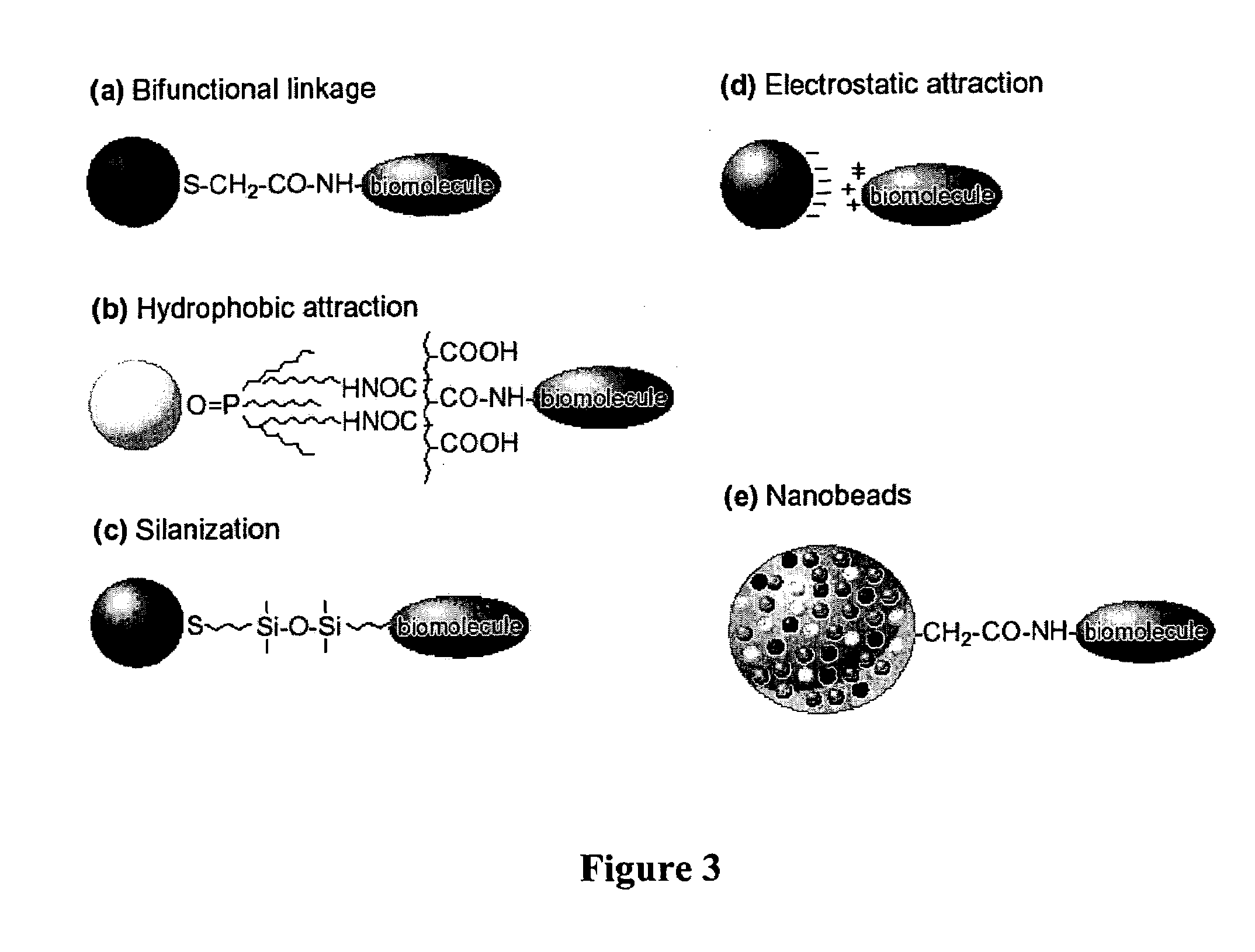
Use of particulate labels in bioanalyte detection methods
InactiveUS7413868B2Maintain their viabilitySimple methodBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsParticulatesCellular component
New applications for the use of distinguishable particulate labels available in a variety of hues and sized in the submicron range are described. These applications include profiling of cellular components, obtaining secretion patterns, identifying a multiplicity of components in chromatographic or electrophoretic techniques and identification of desired immunoglobulin secreting cells.
Owner:TRELLIS BIOSCIENCE LLC
System for determining the position of a sound source
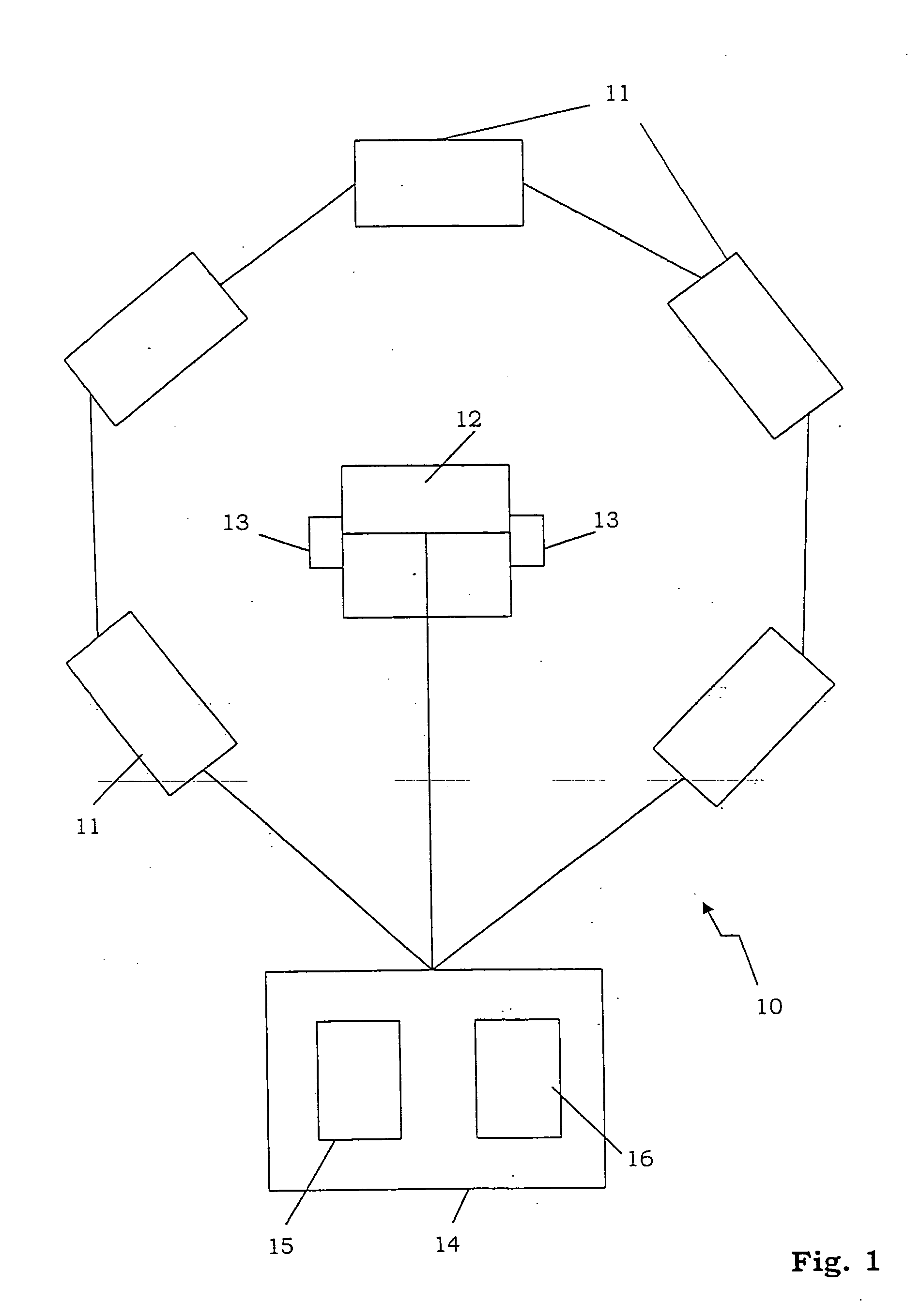
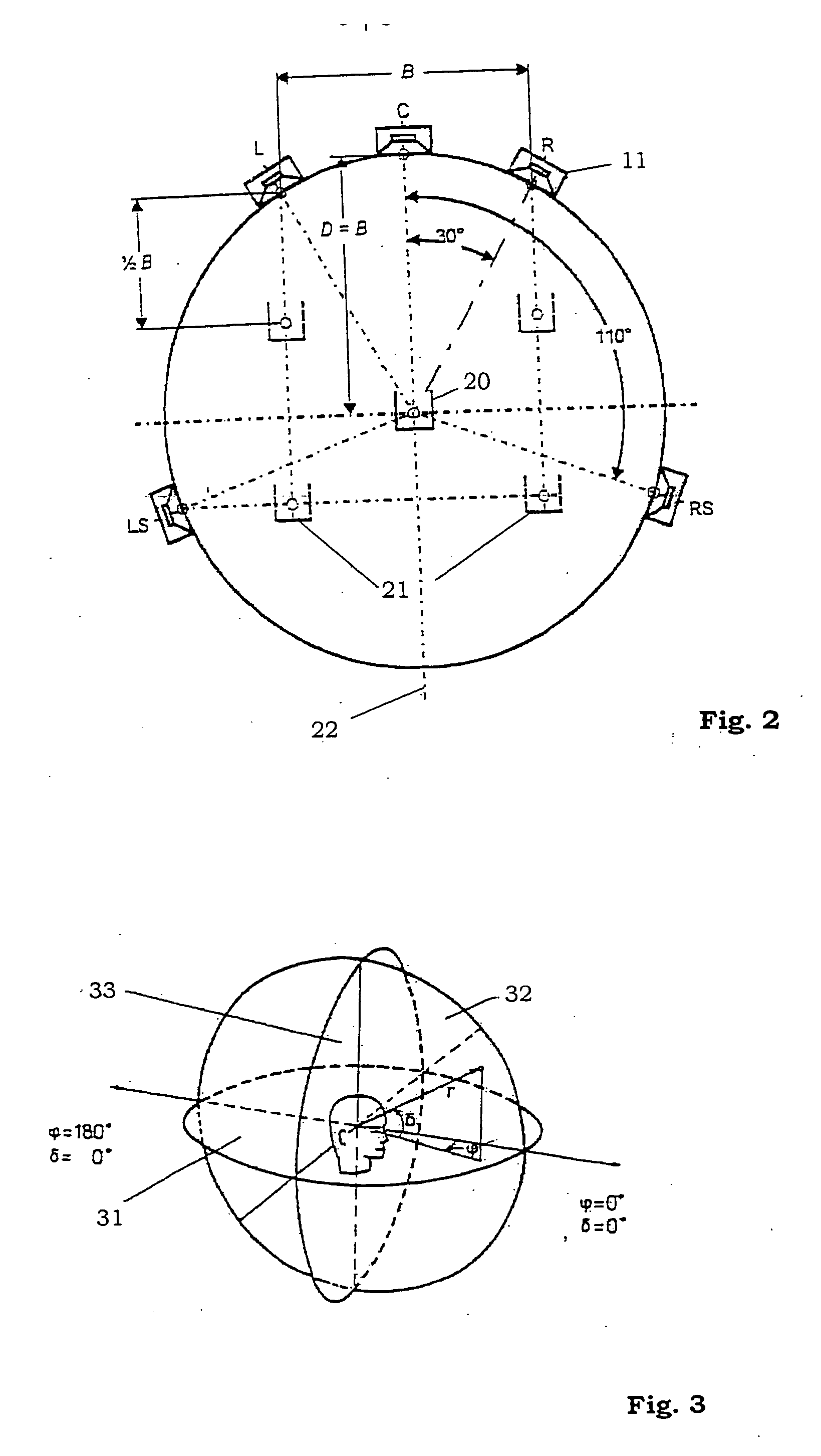
ActiveUS20050078833A1Cutting can not be obtainedPosition fixationDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesTime delays
A method and system for determining the position of a sound source in relation to a reference position, comprising the steps of generating a sound signal emitted from the sound source, detecting the emitted sound signal, processing the sound signal by the use of a physiological model of the ear, deducing at least one of lateral deviation in relation to the reference position, time delay of the sound signal from the sound source to the reference position, and the sound level of the detected sound signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
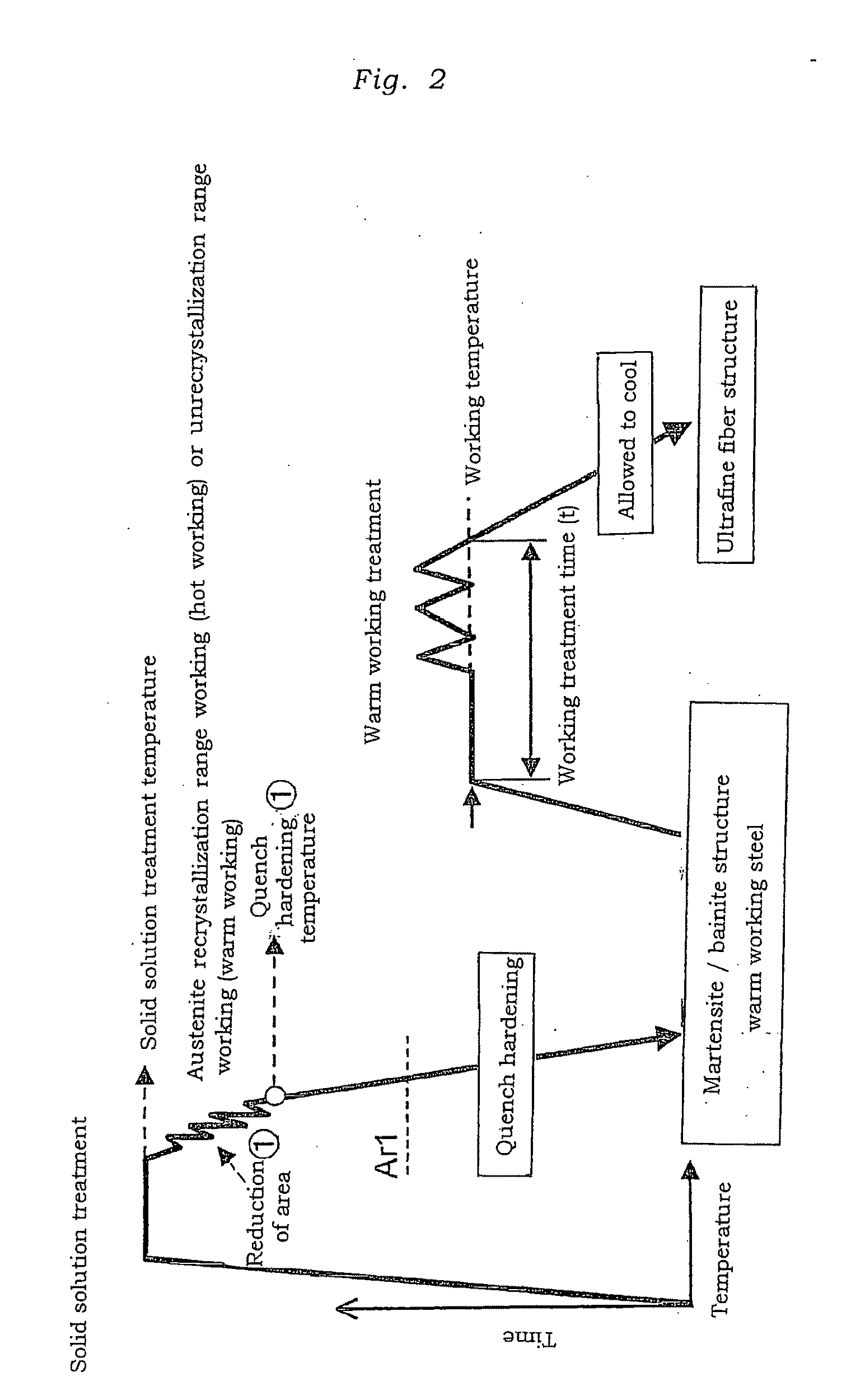
Steel for Warm Working, Warm Working Method Using the Steel, and Steel Material and Steel Component Obtainable Therefrom
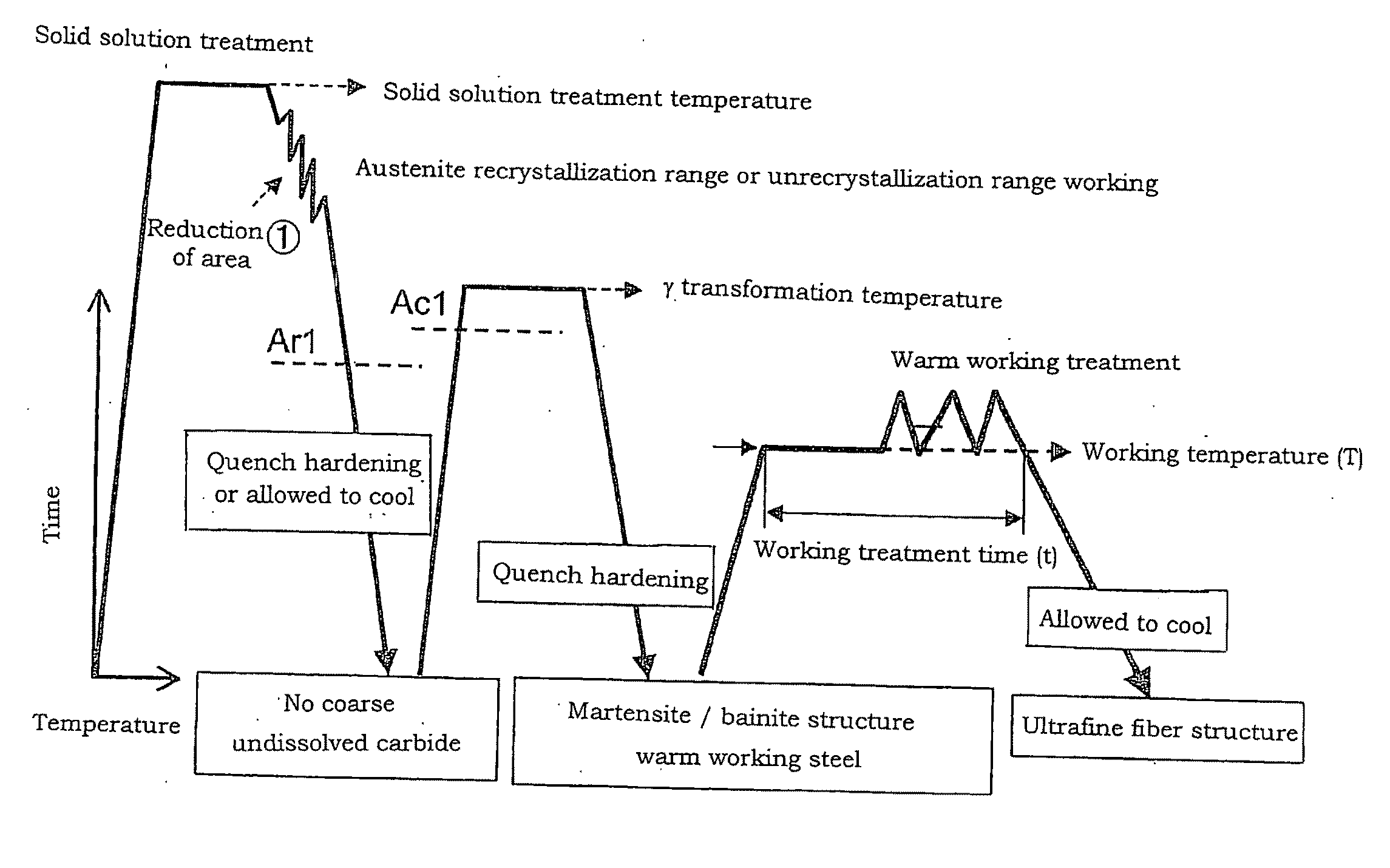
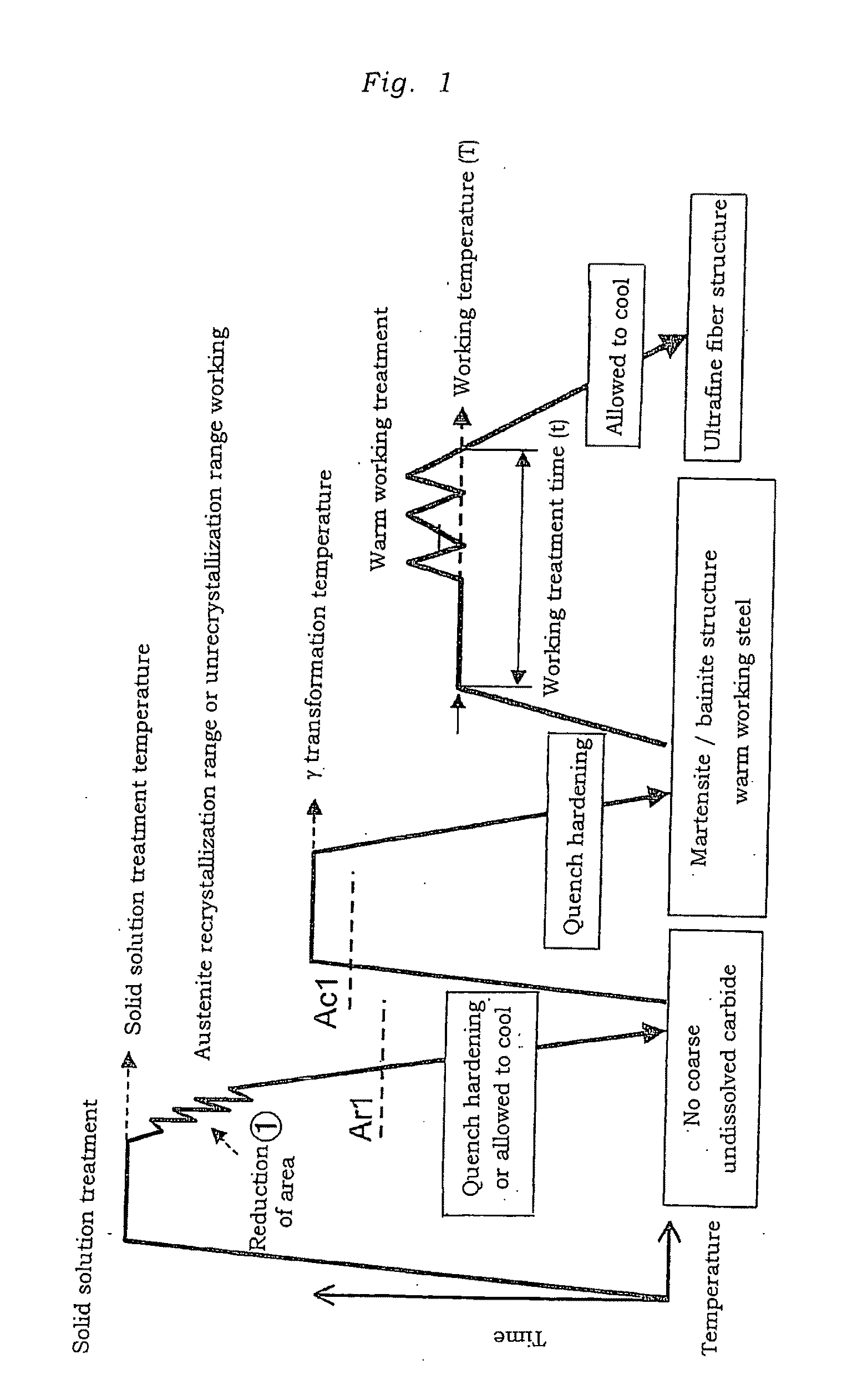
InactiveUS20090277539A1Improve toughnessImproved delayed fracture resistanceFurnace typesHeat treatment process controlRoom temperatureHardness
There are provided a steel for warm working, to be subjected to warm working as various structures, components of cars, and the like, a warm working method thereof, and a steel material and a steel component obtainable from the warm working method.[Solving Means] A steel is to have a particle dispersion type fiber structure formed in the matrix by warm working. The steel is characterized in that the total amount of the dispersed second-phase particles at room temperature is 7×10−3 or more in terms of volume fraction, and the Vickers hardness (HV) is equal to or larger than the hardness H of the following equation (2):H=(5.2−1.2×10−4λ)×102 (2)when the steel is subjected to any of annealing, tempering, and aging treatments in the as-unworked state under conditions such that a parameter λ expressed by the following equation (1):λ=T(log t+20)(T; temperature(K), t; time(hr)) (1)is 1.4×104 or more in a prescribed temperature range of 350° C. or more and Ac1 point or less. This steel is taken as the steel for warm working.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
Dielectric slit die for in-line monitoring of liquids processing
InactiveUS7143637B1Cutting can not be obtainedUniform sizeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIndirect flow property measurementElectricityDielectric
The dielectric slit die is an instrument that is designed to measure electrical, rheological, ultrasonics, optical and other properties of a flowing liquid. In one application, it is connected to the exit of an extruder, pump or mixing machine that passes liquefied material such as molten plastic, solvents, slurries, colloidal suspensions, and foodstuffs into the sensing region of the slit shaped die. Dielectric sensing is the primary element of the slit die, but in addition to the dielectric sensor, the die contains other sensing devices such as pressure, optical fiber, and ultrasonic sensors that simultaneously yield an array of materials property data. The slit die has a flexible design that permits interchangeability among sensors and sensor positions. The design also allows for the placement of additional sensors and instrumentation ports that expand the potential data package obtained.
Owner:MCBREARTY MICHAEL +1
Colouring agents
InactiveUS20050039271A1Shorten the dissolution timeCutting can not be obtainedCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsFiberColoring agents
A shaped body for coloring keratinous fibers consisting of at least one dissolution accelerator and at least one oxidation dye precursor of the secondary intermediate type, contained within a cosmetically acceptable carrier. The shaped body is free from oxidation dye precursors of the primary intermediate type. Also disclosed are a method for coloring keratin fibers and a kit containing these ingredients.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
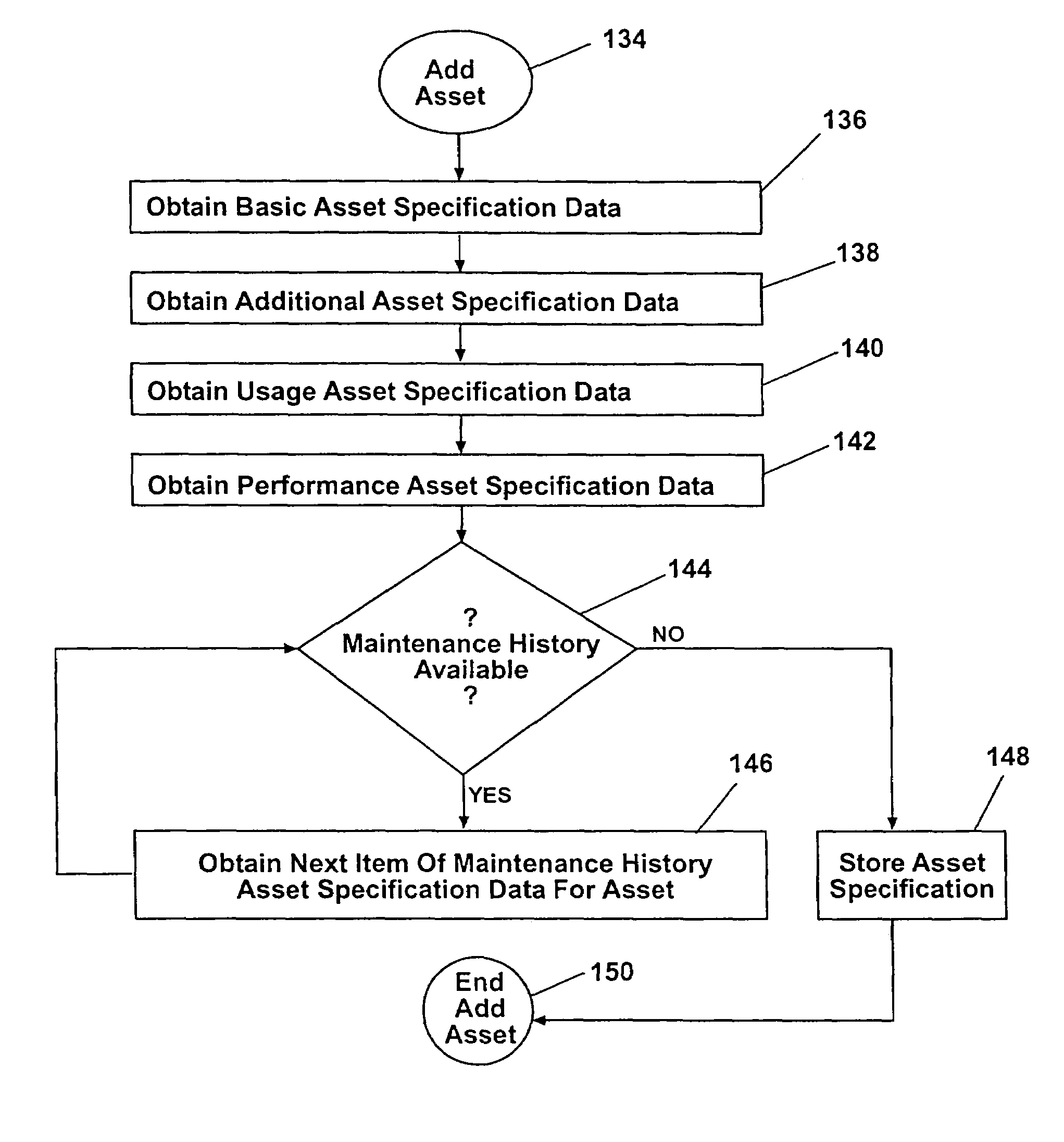
System and method for disposing of assets
InactiveUS7395275B1Maximizes value extractionMinimize and eliminate costBuying/selling/leasing transactionsSpecial data processing applicationsThe InternetE-commerce
A system for managing assets, and facilitating electronic commerce respecting the assets includes a computerized database for storing asset profiles for a plurality of assets. The asset profiles, each include an asset specification and a bid definition. The asset specification includes maintenance history data for the asset and the bid definition outlines the bounds for one of sale, rental or lease of the asset. Users of the system may search the database remotely over the Internet for desired assets, and retrieve detailed information, such as maintenance history, and then bid on the asset for purchase, rental, or lease. Users can also add their own assets to the database for search by others. The system also includes a fantasy fleet feature for conducting “what if” analyses of a simulated fleet containing existing assets and proposed assets.
Owner:DANA AUTOMOTIVE SYST GRP LLC
Method, system and program product for obtaining application data
InactiveUS20050108570A1Cutting can not be obtainedDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsOperating systemNetwork application
An improved solution for obtaining application data for a network application. The application data is received using a data page displayed to a user during a session with the network application. Prior to submitting the application data to the network application, it is first ensured that the session is valid. In particular, if the session remains valid, then the application data is submitted. However, if the session is no longer valid, then a new session is established prior to the application data being submitted.
Owner:IBM CORP
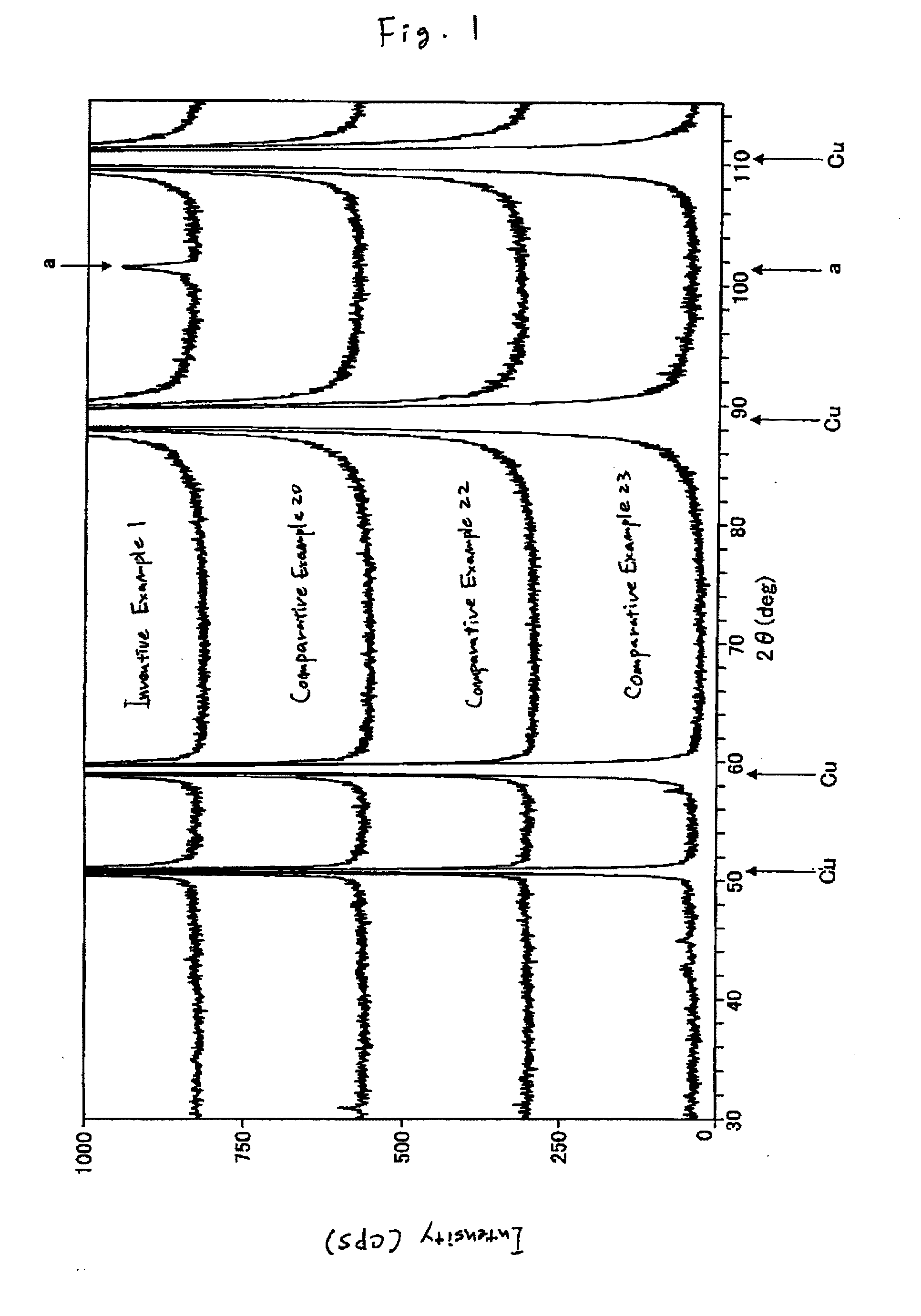
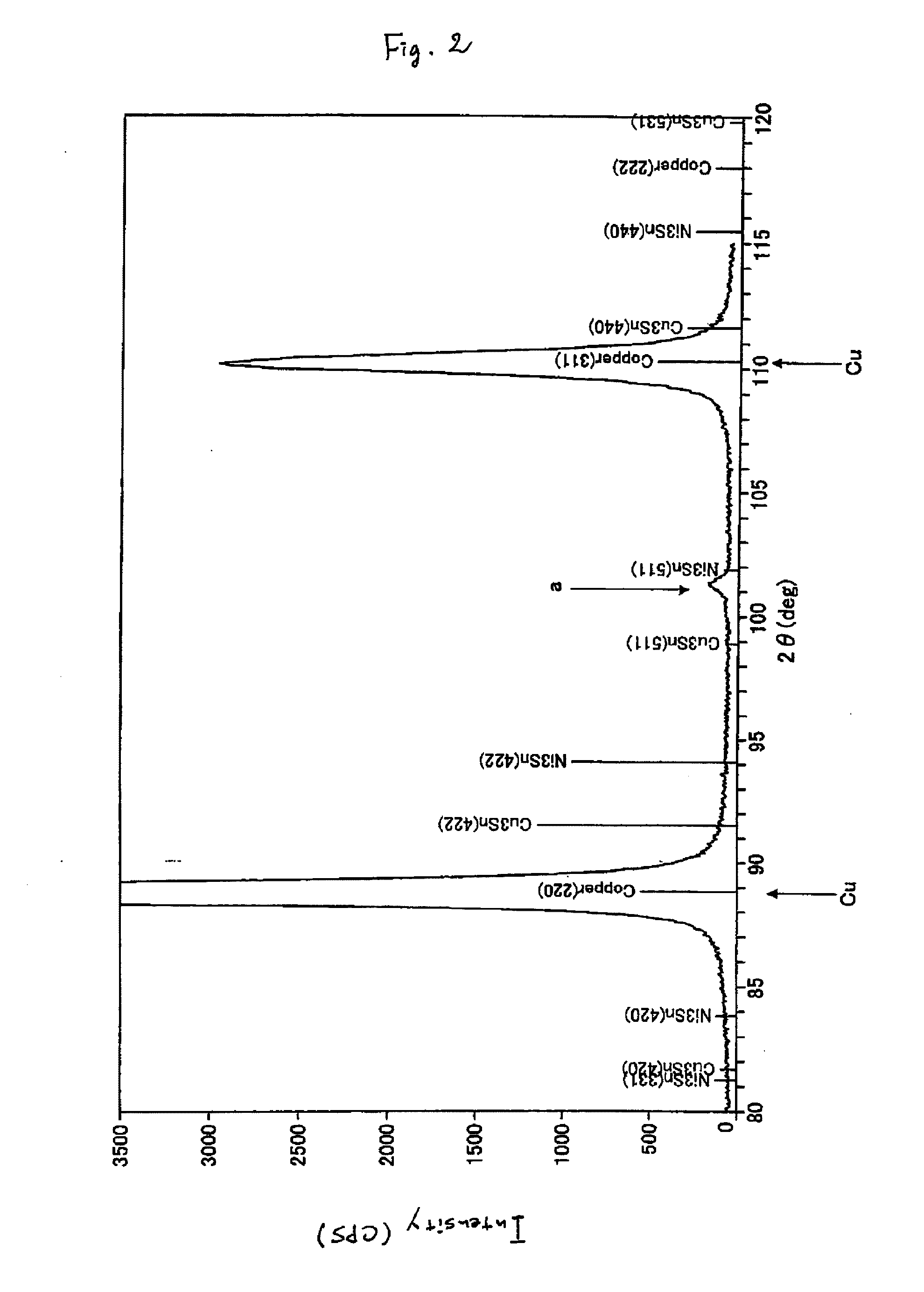
Copper alloy sheet
InactiveUS20110223056A1Reduce intensityMaintaining stress relaxation resistance characteristicContact member manufacturingCoupling contact membersX-rayStress relaxation
The present invention relates to a Cu—Ni—Sn—P-based copper alloy sheet having a specific composition, where (1) the copper alloy sheet is set to have an electrical conductivity of 32% IACS or more, a stress relaxation ratio in the direction parallel to the rolling direction of 15% or less, a 0.2%-proof stress of 500 MPa or more and an elongation of 10% or more; (2) the X-ray diffraction intensity ratio I(200) / I(220) in the sheet surface is set to be a given value or less and at the same time, anisotropy in the stress relaxation resistance characteristic is reduced by fining the grain size; (3) the texture of the copper alloy sheet is set to a texture such that the distribution density of B orientation and the sum of distribution densities of B orientation, S orientation and Cu orientation each is set to fall in a specific range and bendability is thereby enhanced; or (4) the dislocation density measured using the value obtained by dividing the half-value breadth of the X-ray diffraction intensity peak from {200} plane in the copper alloy sheet surface by the peak height is set to a given value or more and press punchability is thereby enhanced. The Cu—Ni—Sn—P-based copper alloy sheet of the present invention is excellent in the properties required for a terminal or connector and further (1) has excellent strength-ductility balance, (2) satisfies the stress relaxation resistance characteristic in the direction orthogonal to the rolling direction, (3) has excellent bendability, or (4) has excellent press punchability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
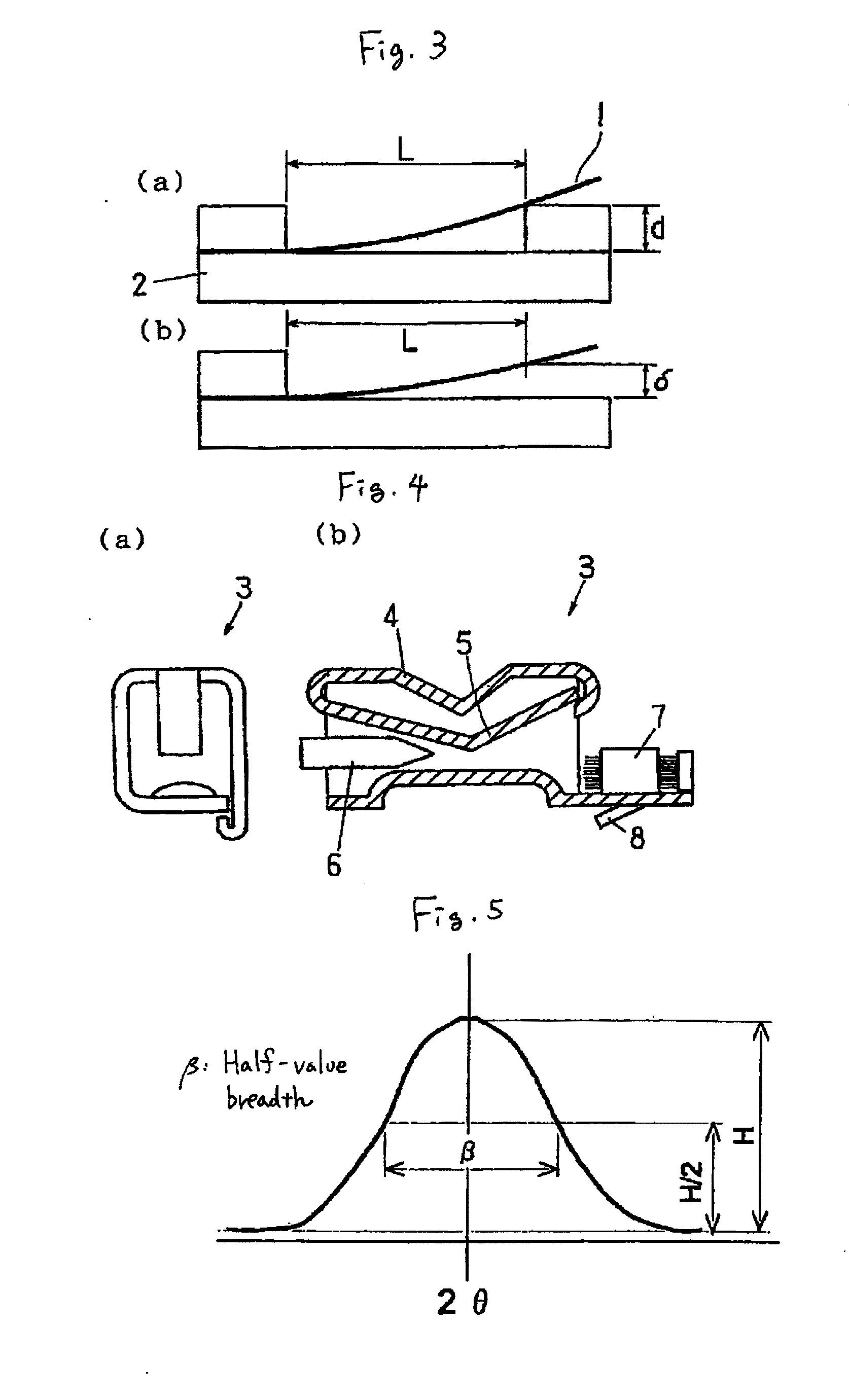
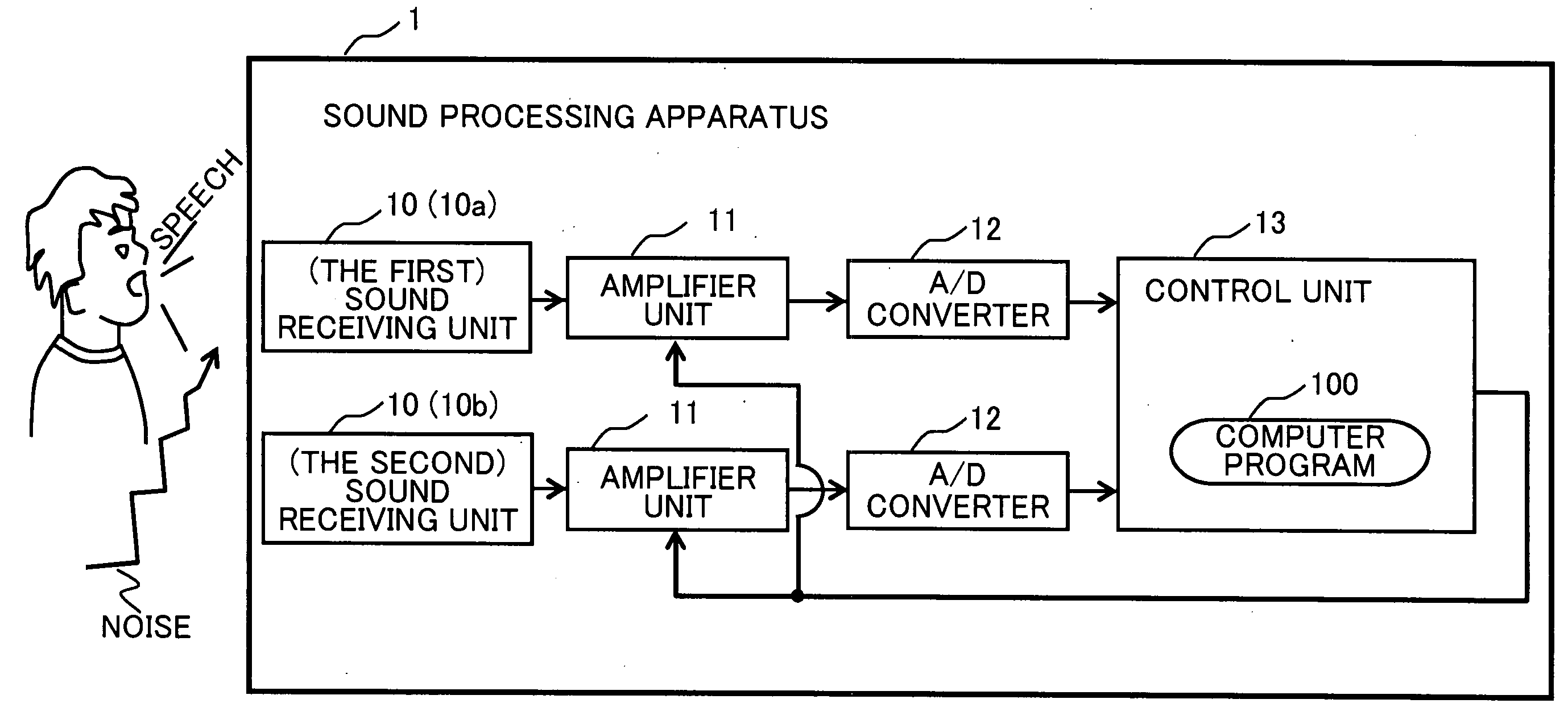
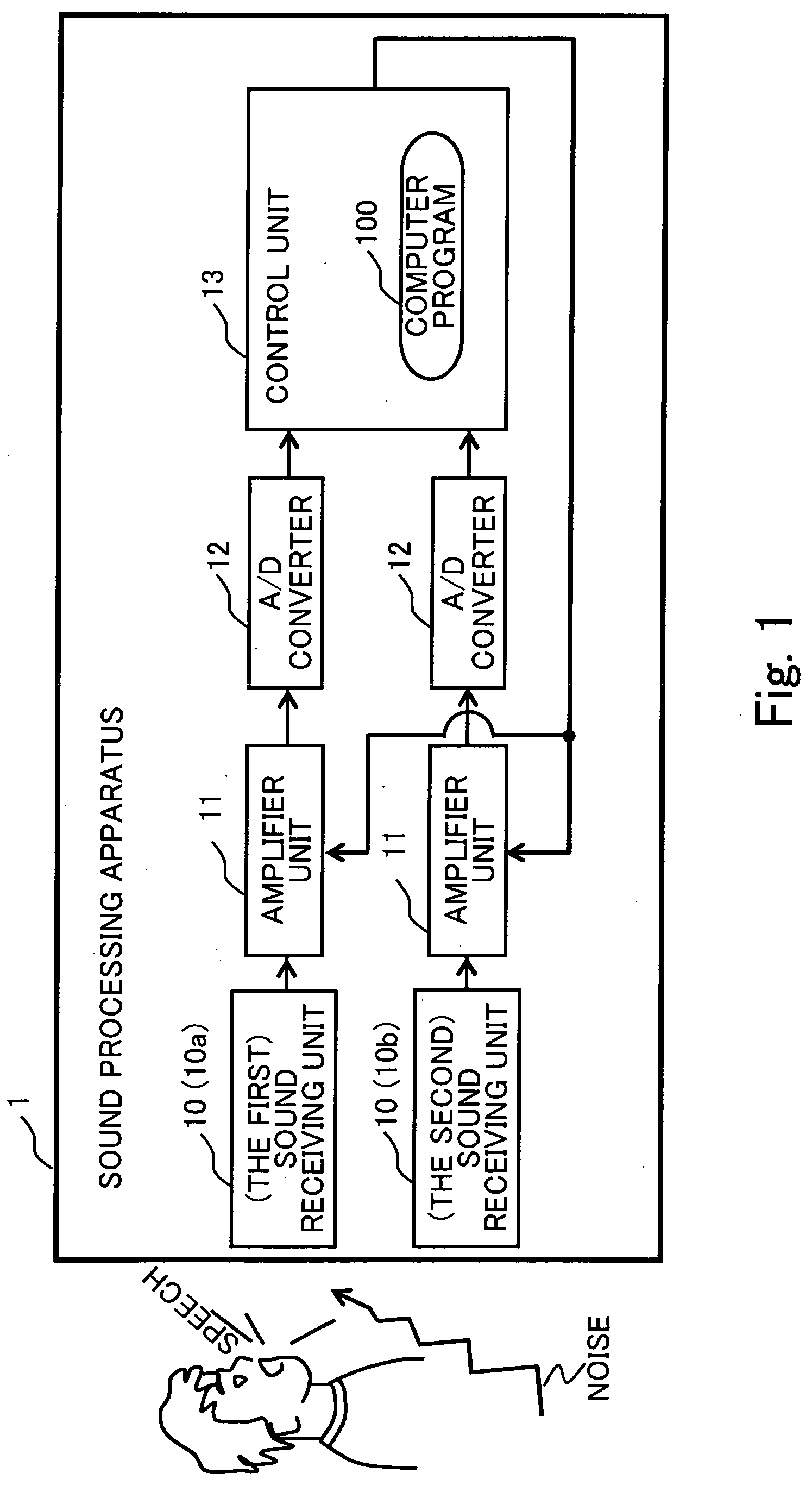
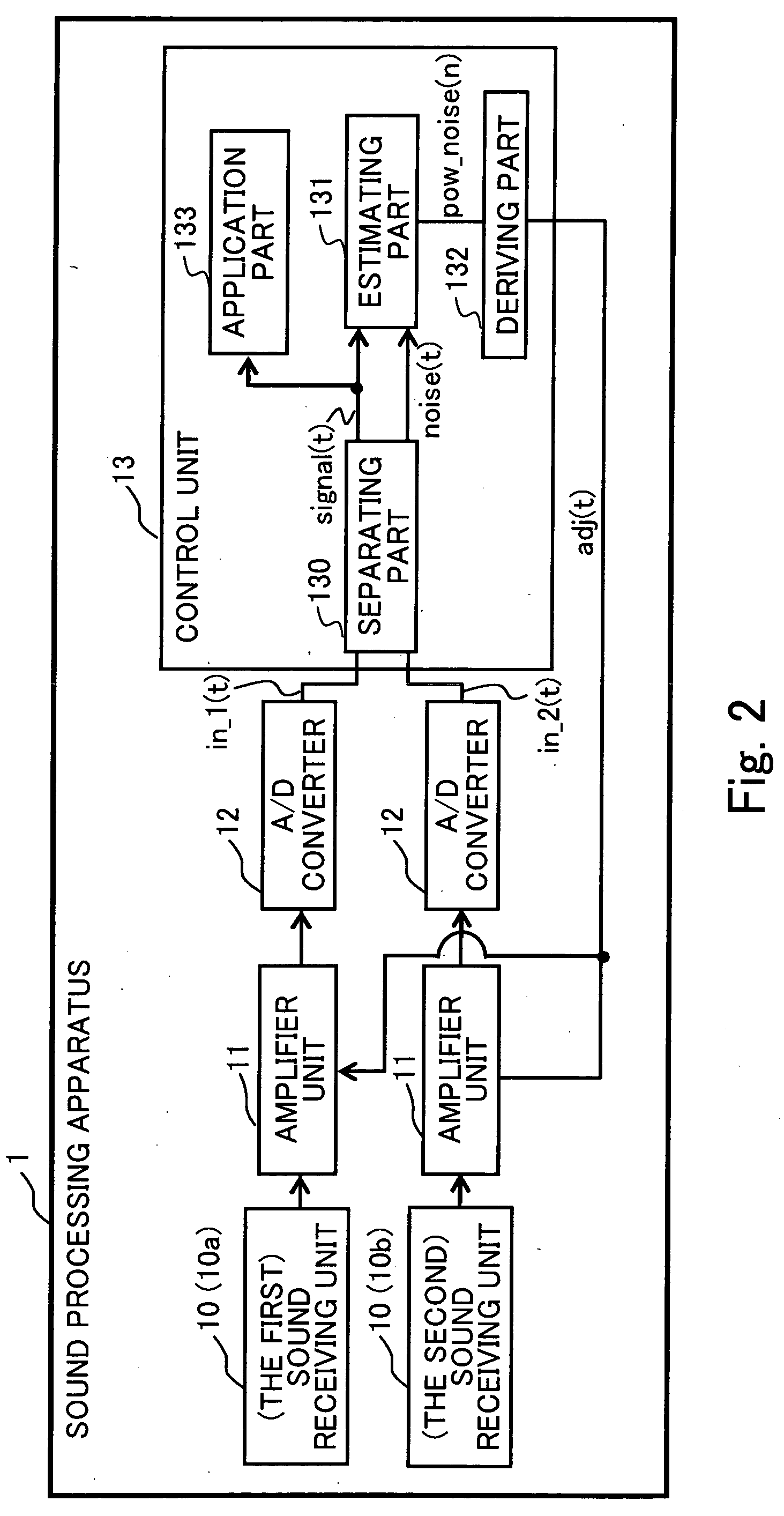
Sound processing apparatus, apparatus and method for cotrolling gain, and computer program
ActiveUS20090076810A1Degraded voice qualityHigh correlationGain controlSpeech recognitionVoice communicationDirectional sound
A sound processing apparatus is provided for estimating the power of background noise using a directional sound receiving technology using a plurality of sound receiving units, computing a gain control value on the basis of the estimated power of background noise and a predetermined power target value, and outputting the gain control value, so that a delay time of starting gain control can be reduced, and a slow response of a speech recognition application program or degradation of the speech quality of a voice communication program can be prevented.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
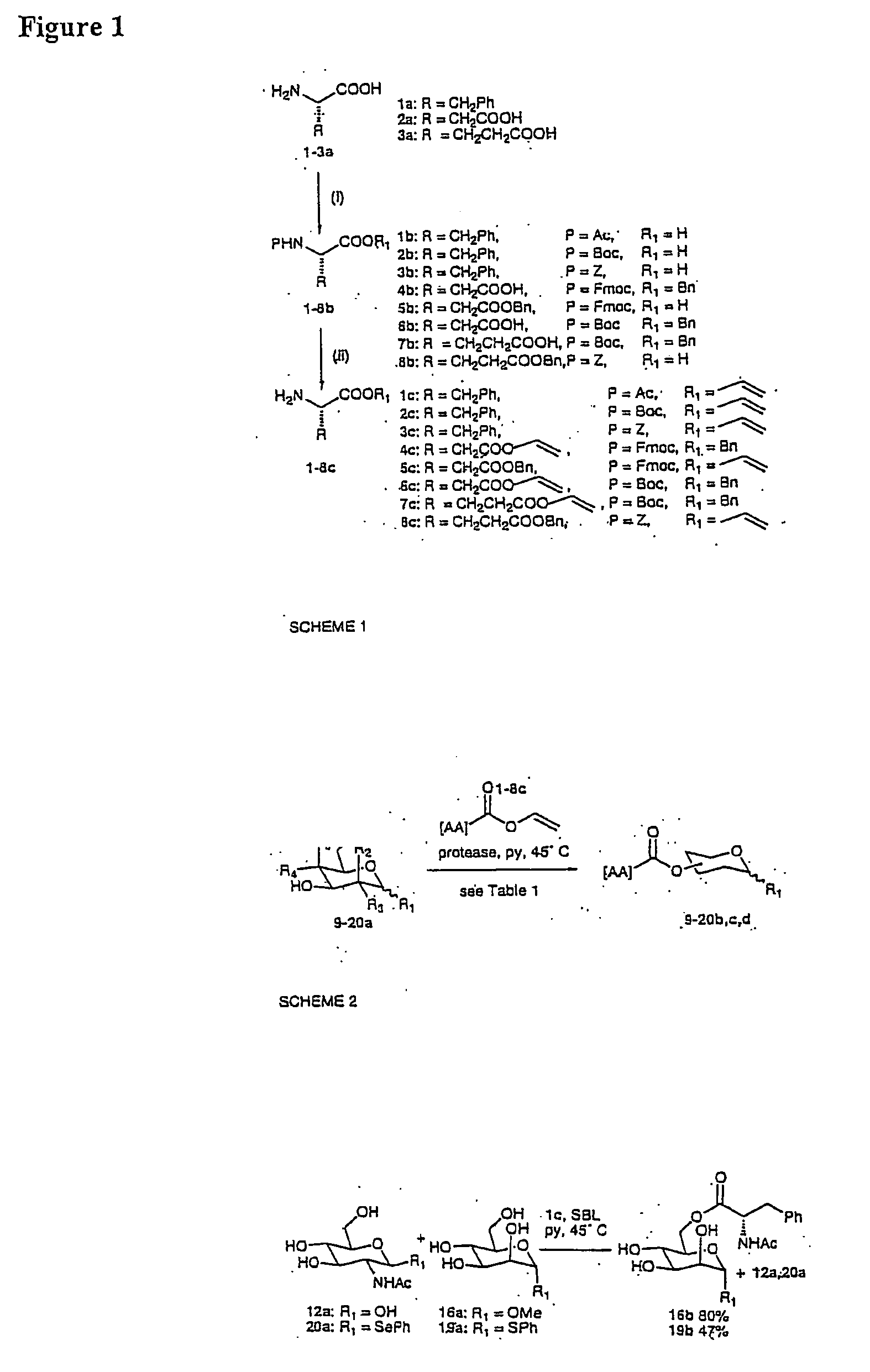
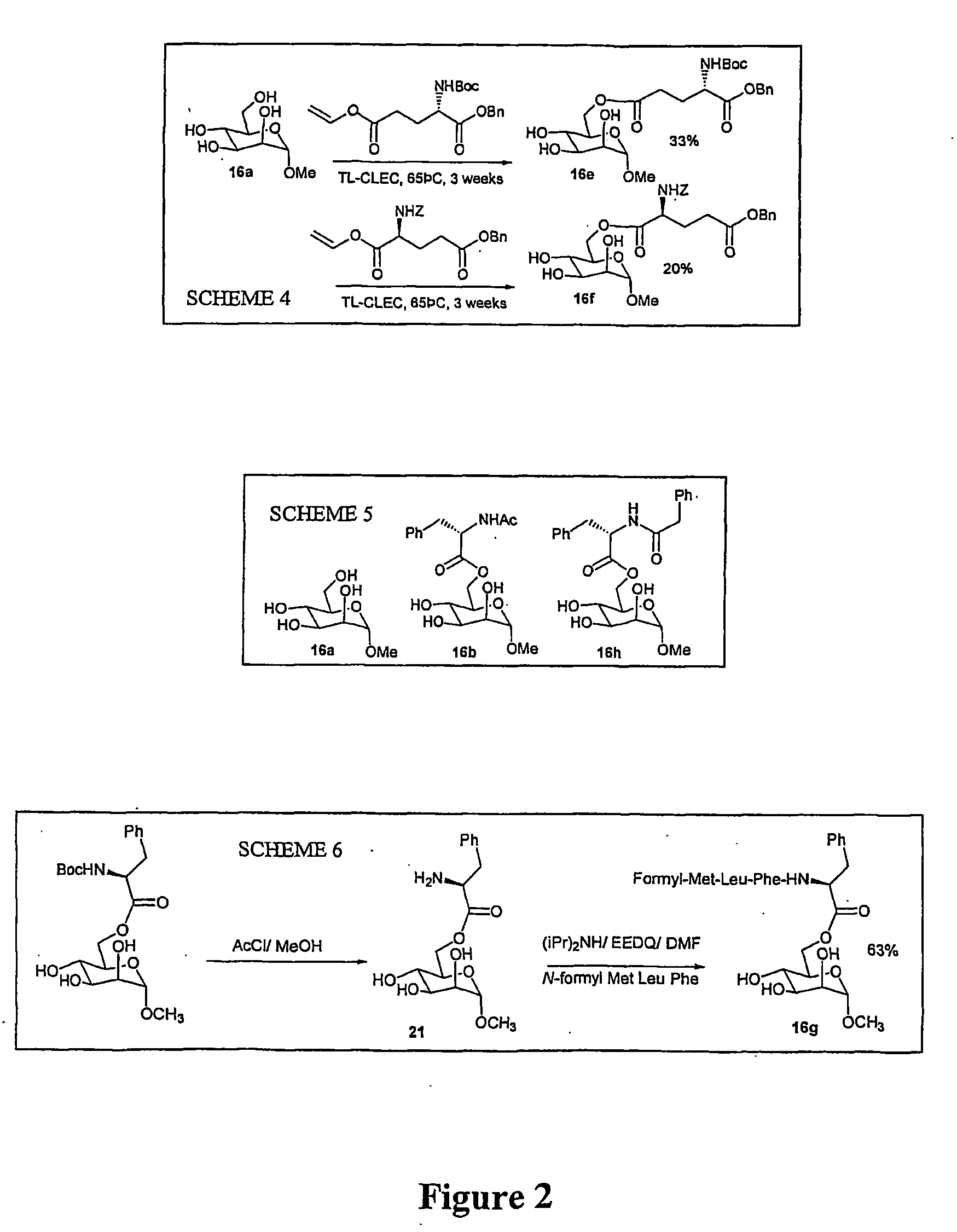
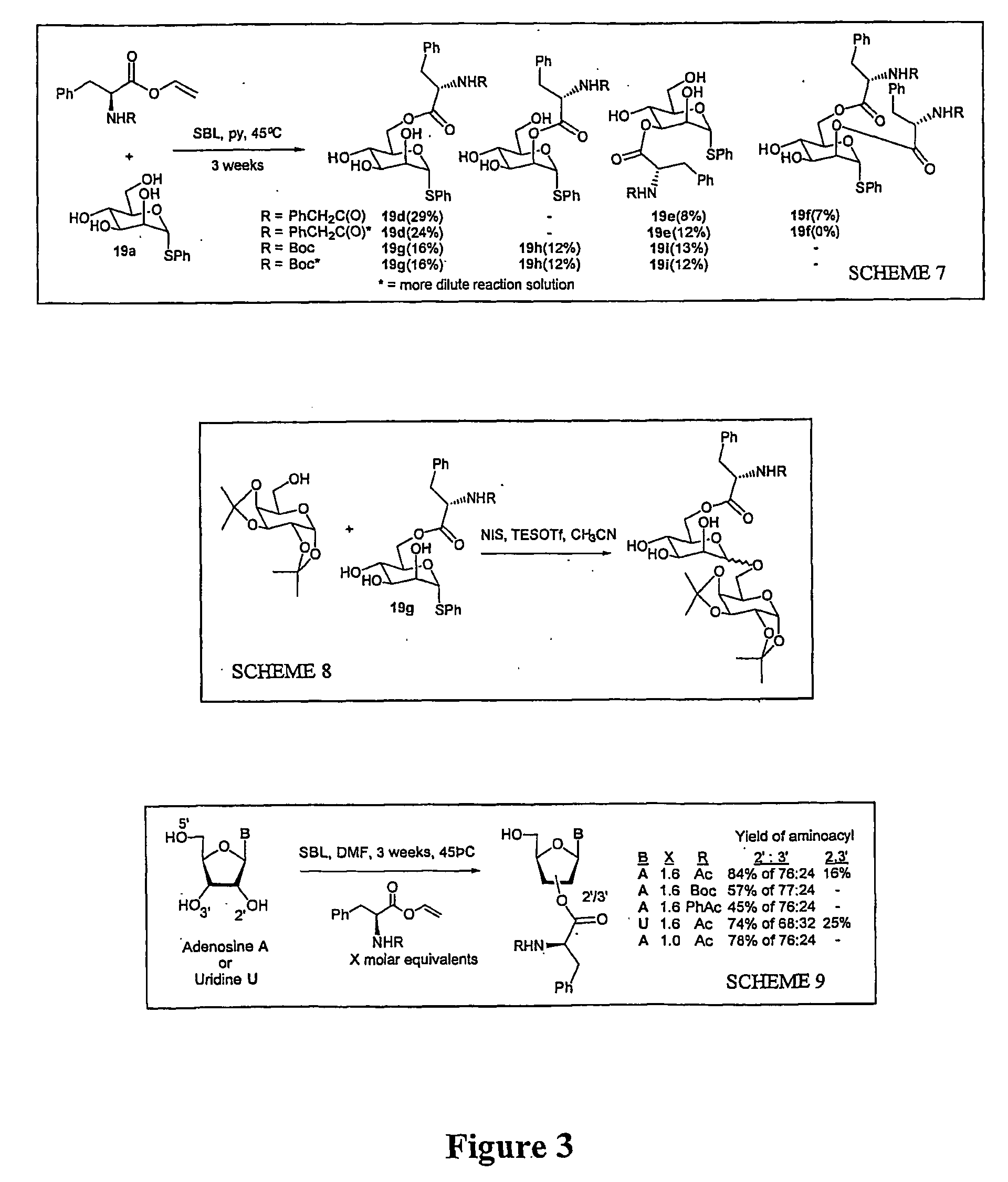
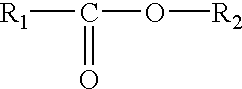
Method for preparing ester linked peptide-carbohydrate conjugates
InactiveUS20040208883A1Cutting can not be obtainedPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesAcyl groupVinyl ester
A method of producing an ester linked carbohydrate-peptide conjugate is provided comprising: (a) providing a vinyl ester amino acid group, and (b) reacting the vinyl ester amino acid with a carbohydrate acyl acceptor in the presence of an enzyme, to produce thereby an ester-linked carbohydrate-peptide conjugate. Also provided are ester linked carbohydrate-peptide conjugates obtainable by such methods.
Owner:ISIS INNOVATION LTD
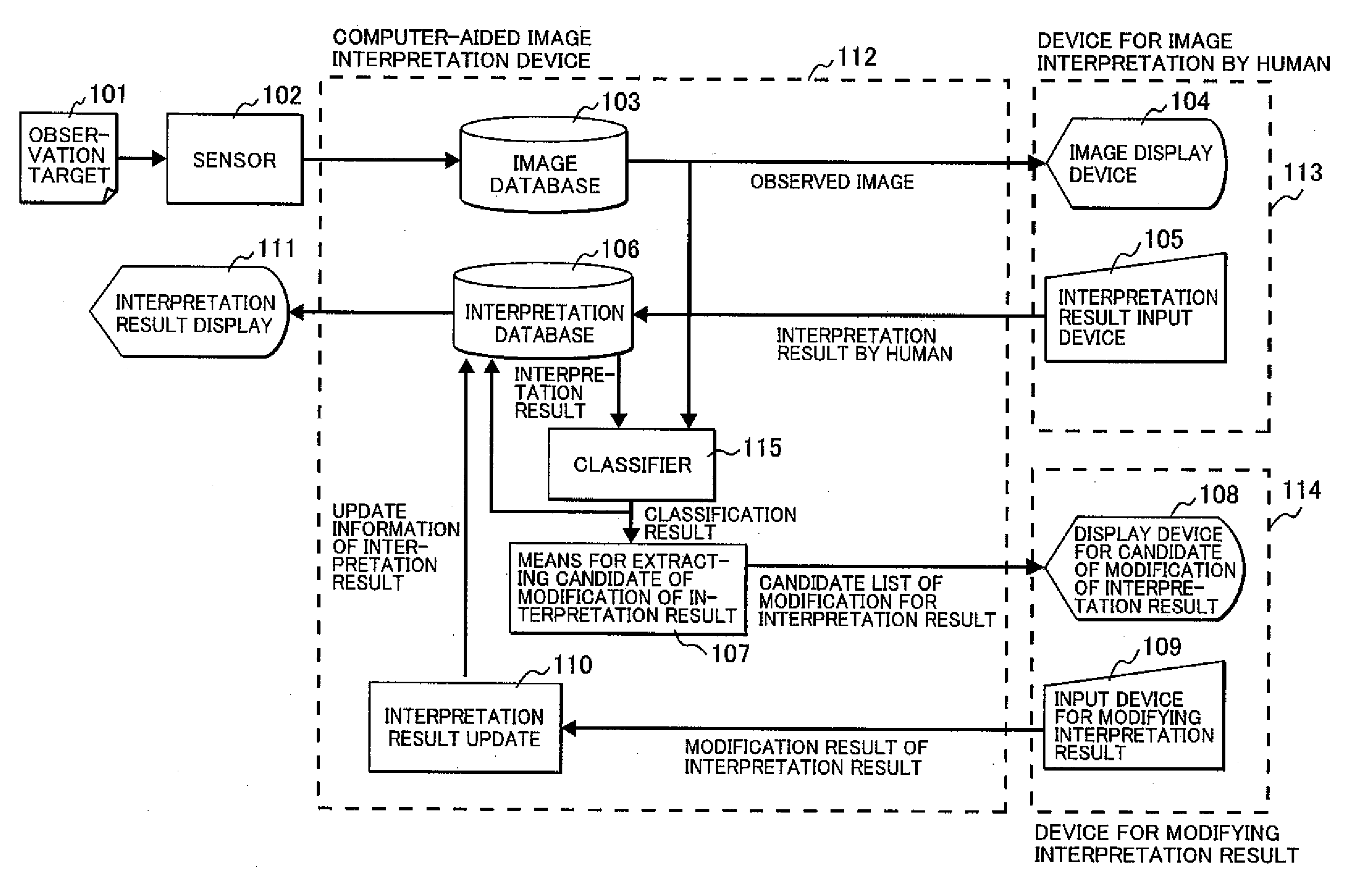
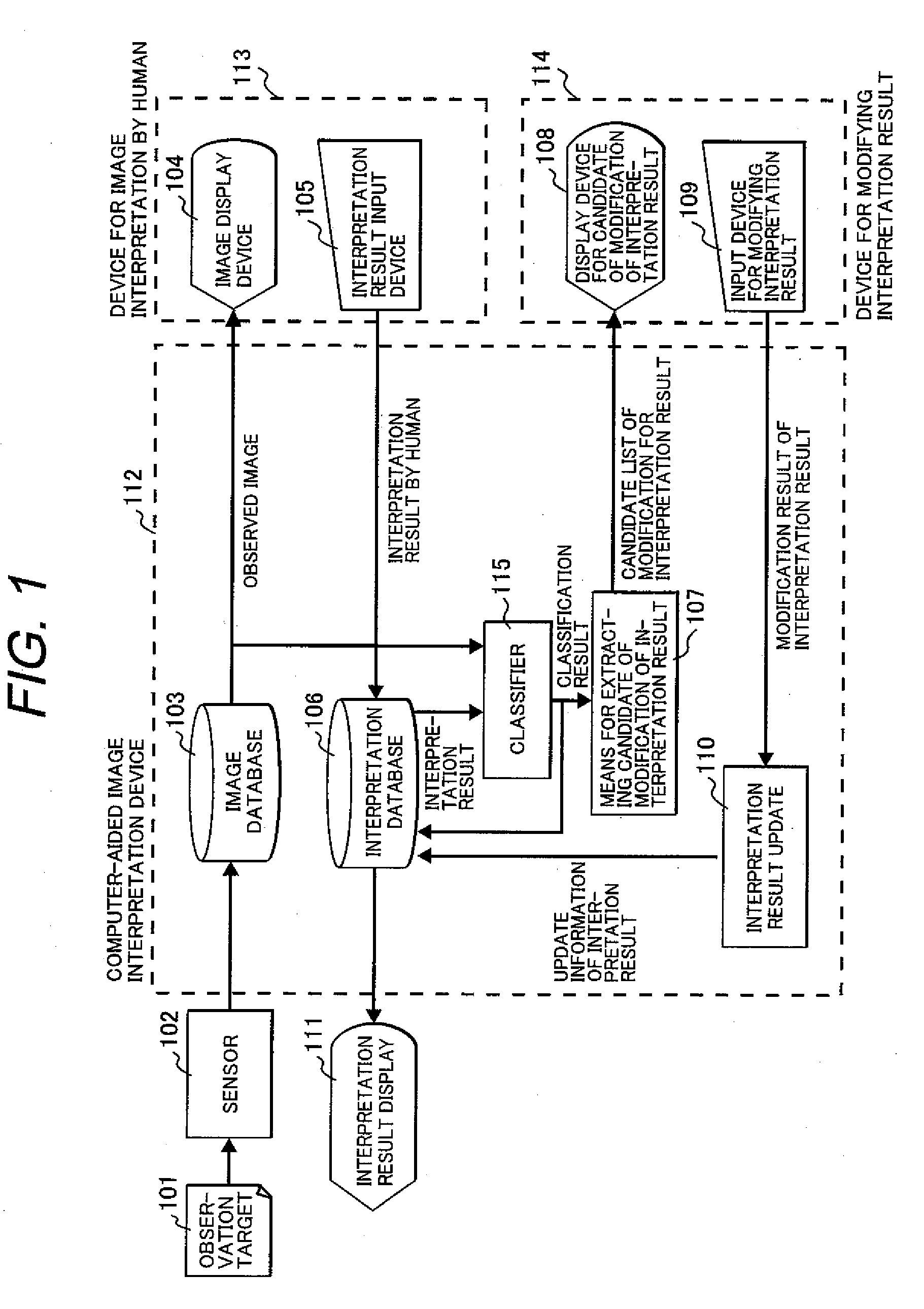
Computer-aided image interpretation method and device
A computer-aided image interpretation method and a device thereof to easily obtain an accurate image interpretation result are provided. An automatic classification means of the image interpretation device performs automatic classification by one of spectral characteristics, radiometric characteristics, diffuse characteristics, textures and shapes, or combinations thereof and accumulates data to an interpretation result database, for plural features of the same kind obtained by interpreting a remote sensing image obtained with an observation sensor. A means for extracting candidate of modification of interpretation result extracts the candidate of modification of interpretation result by comparing likelihoods that are the automatic classification results. A reinterpretation is performed for the candidate of modification of interpretation, and an interpretation result database is updated by an interpretation result update means. As a result, modification of the interpretation work can be efficiently performed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for reducing crystal defects in transistors with re-grown shallow junctions by appropriately selecting crystalline orientations
ActiveUS7763505B2Enhance re-crystallization processAvoid undue crystalline defectTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSide effectSemiconductor materials
By appropriately adapting the length direction and width directions of transistor devices with respect to the crystallographic orientation of the semiconductor material such that identical vertical and horizontal growth planes upon re-crystallizing amorphized portions are obtained, the number of corresponding stacking faults may be significantly reduced. Hence, transistor elements with extremely shallow PN junctions may be formed on the basis of pre-amorphization implantation processes while substantially avoiding any undue side effects typically obtained in conventional techniques due to stacking faults.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Device for blowing gas onto a face of a traveling strip of material
InactiveUS20100269367A1Vibration minimizationMinimizing offsetDrying gas arrangementsFurnace typesEngineeringProduct gas
Owner:COCKERILL MAINTENANCE & INGIE
Stable, homogeneous natural product extracts containing polar and apolar fractions
InactiveUS20030026856A1Cutting can not be obtainedCosmetic preparationsBiocideLipid formationNatural product
Disclosed are stable, homogeneous dispersions, comprising (a) from about 20 to 90% by weight of a first composition comprising (i) about 60-95% by weight of a first polar solvent, (ii) about 0-40% by weight of one or more second polar solvents, and (iii) water soluble components of a first natural product; and (b) from about 10 to 60% by weight of a second composition comprising: (i) one or more apolar solvents, and (ii) oil soluble organic components of a second natural product; and (c) from about 0.01 to 8% by weight of a non-surface active lipid phosphate or a surface active agent. Also disclosed are methods of forming the stable, homogeneous dispersions of the invention, comprising forming a first composition comprising water soluble components of a first natural product; forming a second composition comprising oil soluble organic components of a second natural product; mixing the compositions and subjecting the mixture to high pressure high shear processing to form a stable, homogeneous dispersion.
Owner:COLLABORATIVE TECH
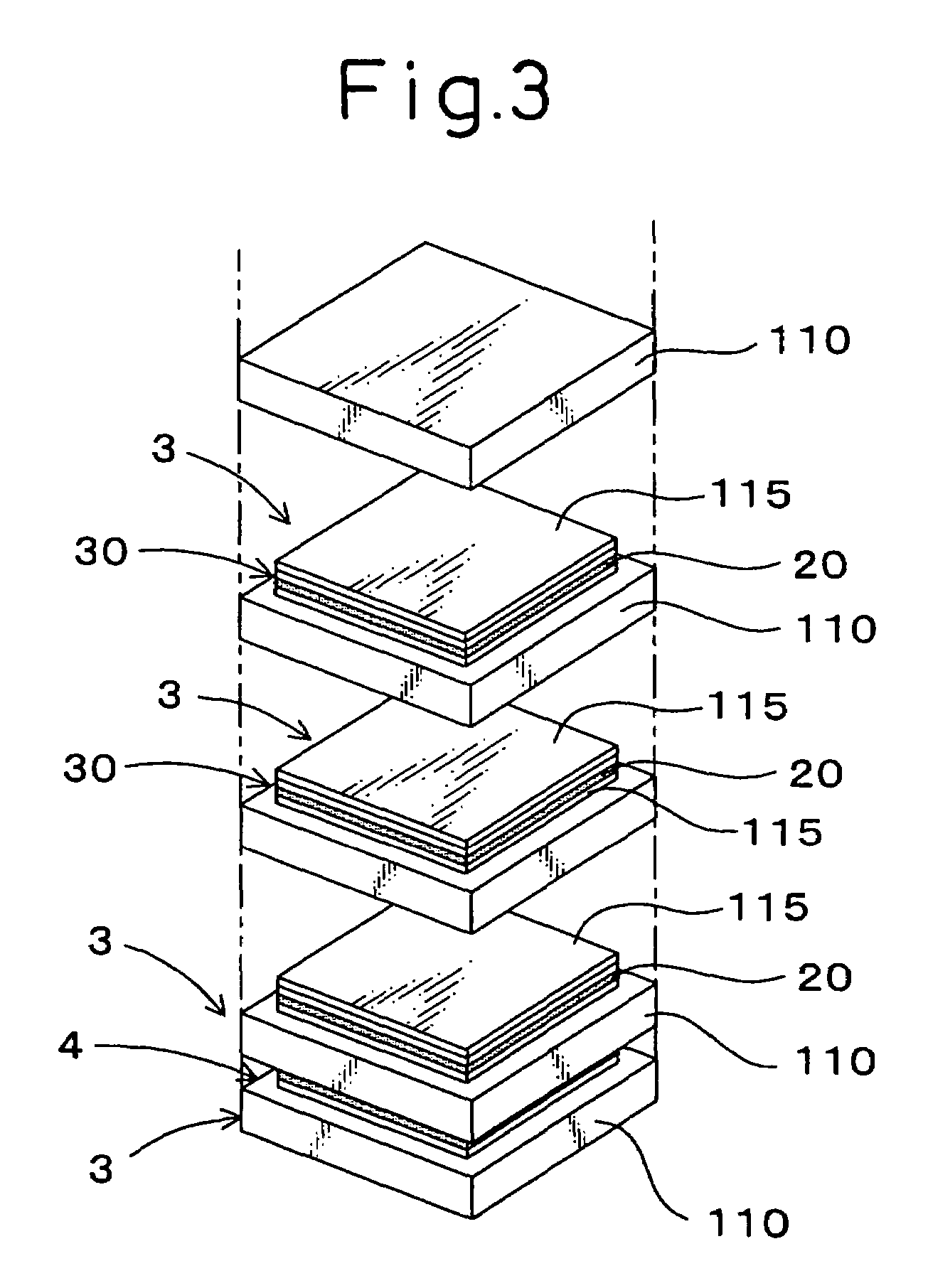
Production method of stacked piezoelectric element
InactiveUS7225514B2Cutting can not be obtainedCoating state can be stablePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringMechanical engineering
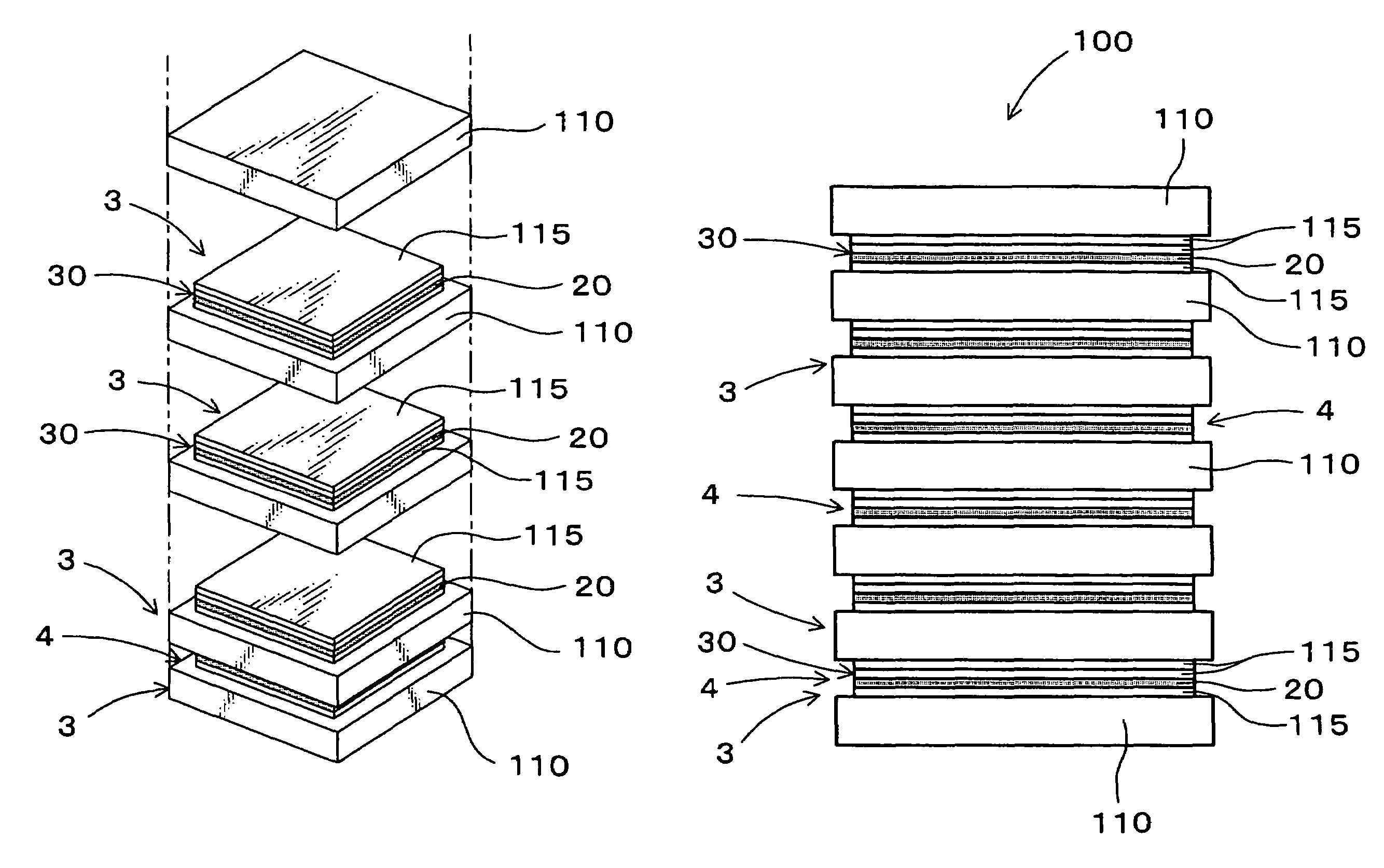
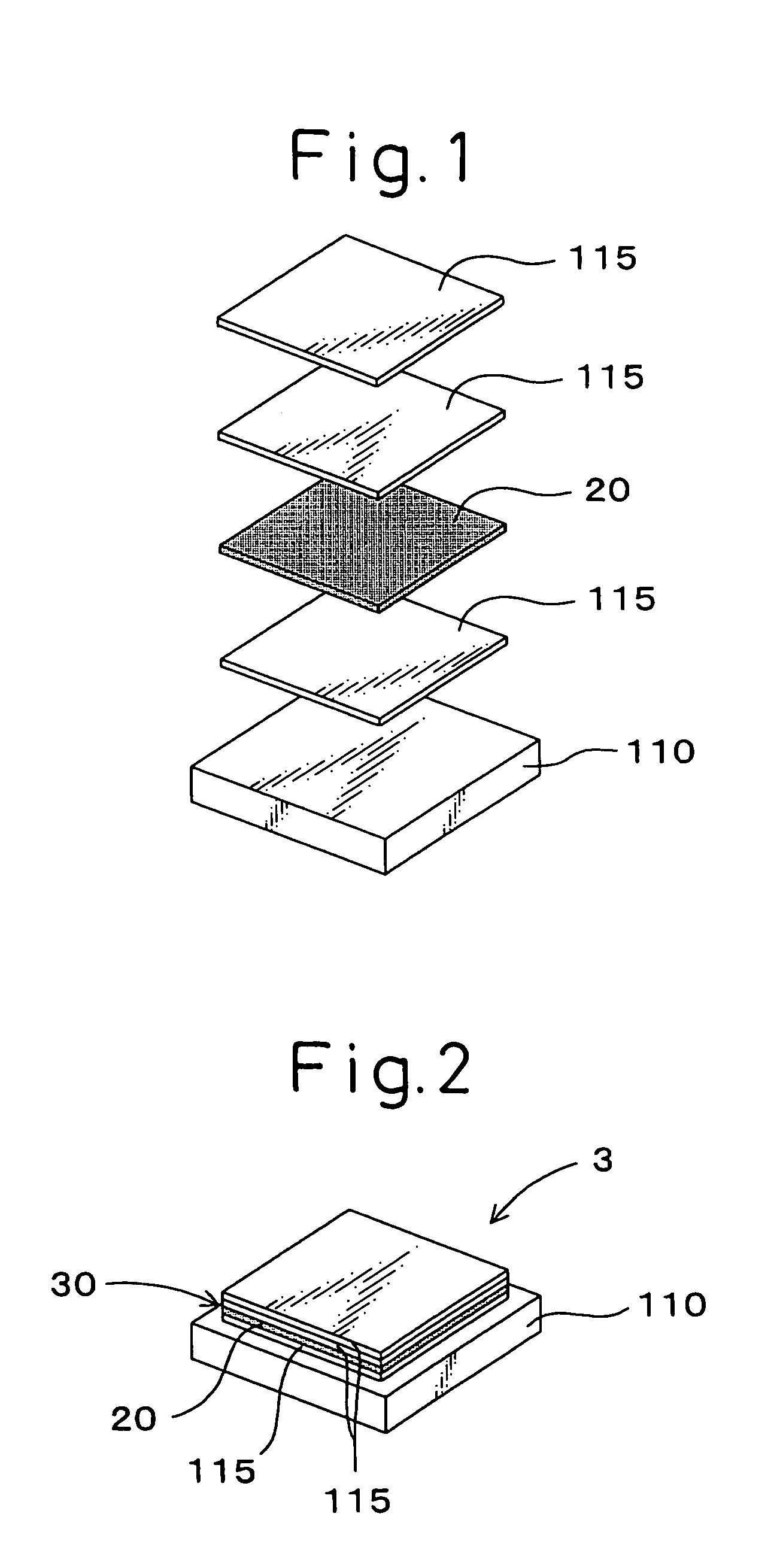
A stacked piezoelectric element is produced by alternately stacking a piezoelectric layer and an inner electrode layer. The method includes producing a green sheet 110 for a base, forming a unit body 3 having a narrow stacked part 30 where a narrow piezoelectric material layer 115 having an area smaller than the green sheet 110 for base and an electrode material layer 20 having an area smaller than the green sheet 110 for base are stacked, the unit body being formed by disposing the narrow stacked part 30 on the green sheet 110 for base; forming a stacked body having groove parts by stacking a plurality of the unit bodies 3, the groove part having the bottom being defined by the side face of the narrow stacked part 30; and firing the stacked body.
Owner:DENSO CORP
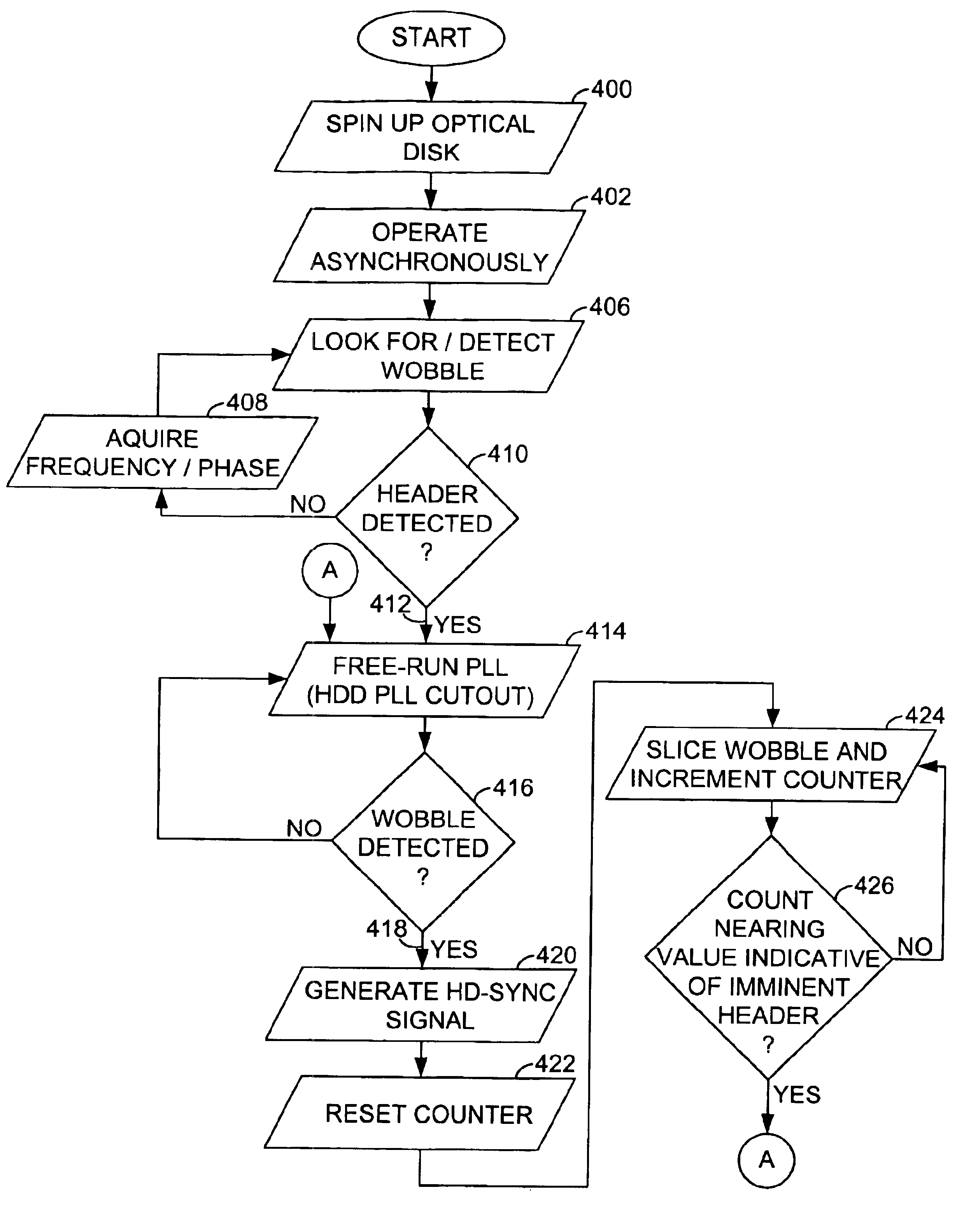
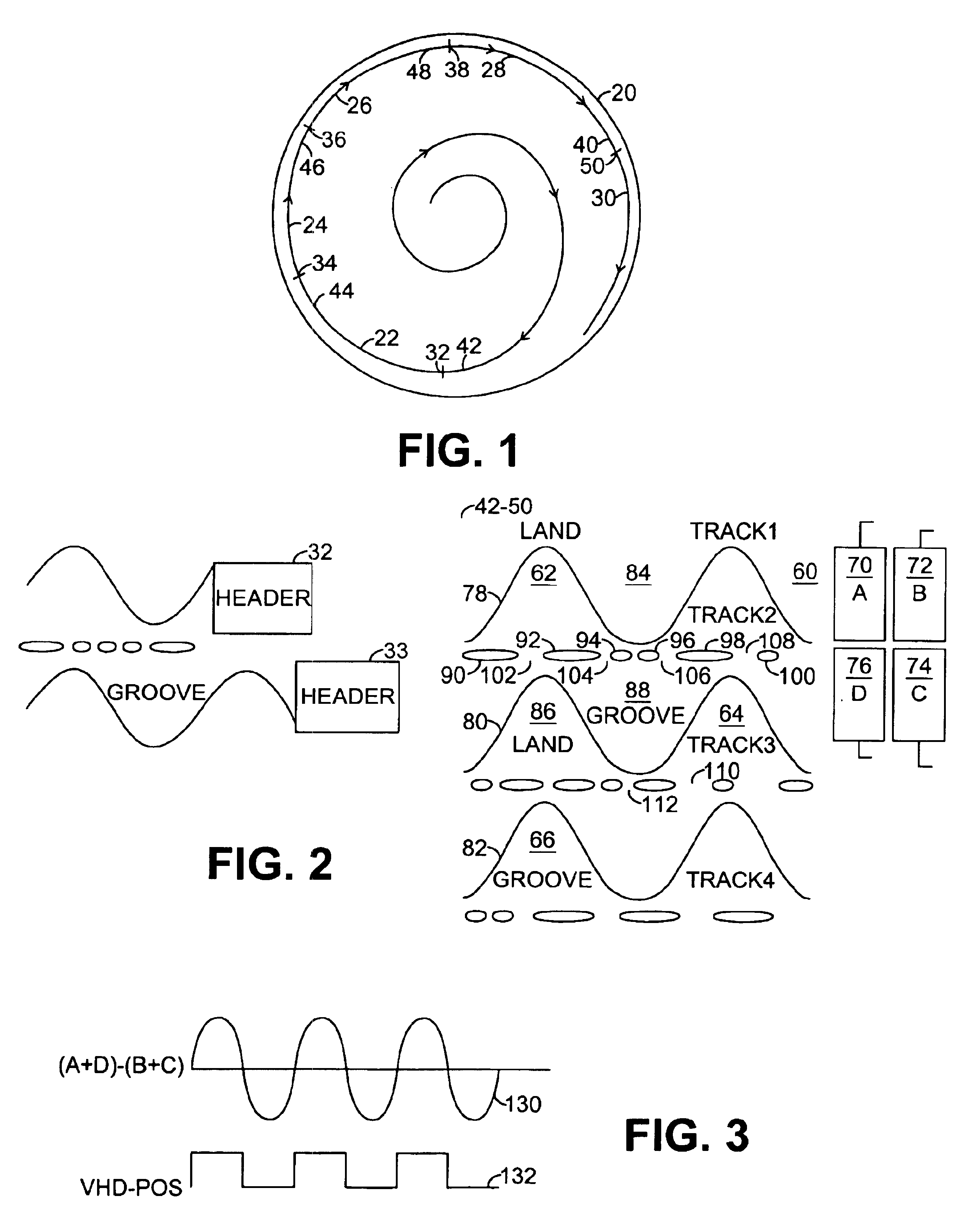
Header detect configuration within a DVD-RAM read device and methods of acquiring and maintaining phase lock in a wobble phase lock loop
InactiveUS6882609B2Increase ratingsEasy to useCombination recordingTelevision system detailsBandpass filteringVoltage spike
In the context of a DVD-RAM read-type architecture in which an optical storage medium (20) makes use of an eccentric wobble (164) to attain synchronisation information, a wobble PLL (179) is held in an acquired state whenever header regions (32, 33) embossed at regular intervals across the optical storage medium (20) are detected. More specifically, large dc variations associated with voltage spikes caused by header regions (32, 33) are scaled (260) relative to a dynamically varying amplitude envelope of the extracted wobble signal (164), such as to identify a start location (300) for each header region. The wobble PLL (179) is effectively allowed to free-run and hold state during periods of header, thereby mitigating the likelihood that the wobble PLL will loose lock during the header regions. Also, with suspension of the wobble PLL triggered by a first spike (300), a counter is initiated to over-sample wobble clock periods to pre-empt a successive header and such that the PLL can be disabled immediately prior to the successive header region. Use of a bandpass filter (156) to extract the wobble signal (164) benefits from generation of a spike at each transition of the header dc level, which spike can be used as a definitive marker for a header region.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System for determining the position of a sound source
ActiveUS7386133B2Cutting can not be obtainedPosition fixationDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesPhysiological model
A method and system for determining the position of a sound source in relation to a reference position, comprising the steps of generating a sound signal emitted from the sound source, detecting the emitted sound signal, processing the sound signal by the use of a physiological model of the ear, deducing at least one of lateral deviation in relation to the reference position, time delay of the sound signal from the sound source to the reference position, and the sound level of the detected sound signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
High power amplifiers
InactiveUS20070201880A1Limited effectivenessBroaden spectrumLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmittersBroadband noiseFrequency spectrum
The specification describes an improved seed laser source for high power MOPA applications. Improvement is obtained by modulating the seed laser with a broadband noise function, for example, a Guassian noise function. A broadband noise function is one in which, in contrast to a sine wave function for example, has an RF spectrum with a bandwidth comparable in value to the mean frequency. Use of a broadband noise modulator allows effective tuning of the output of the modulated laser.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
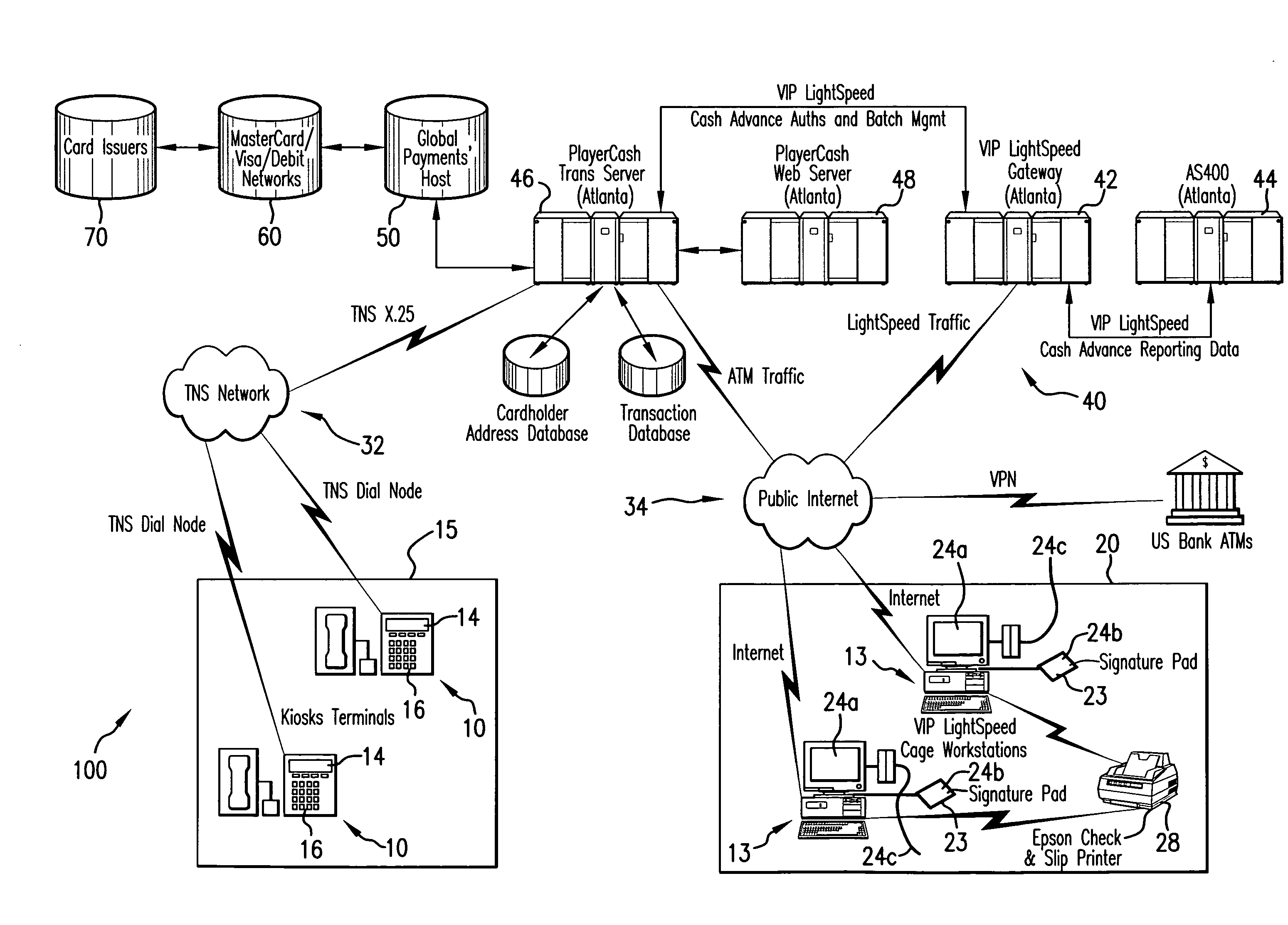
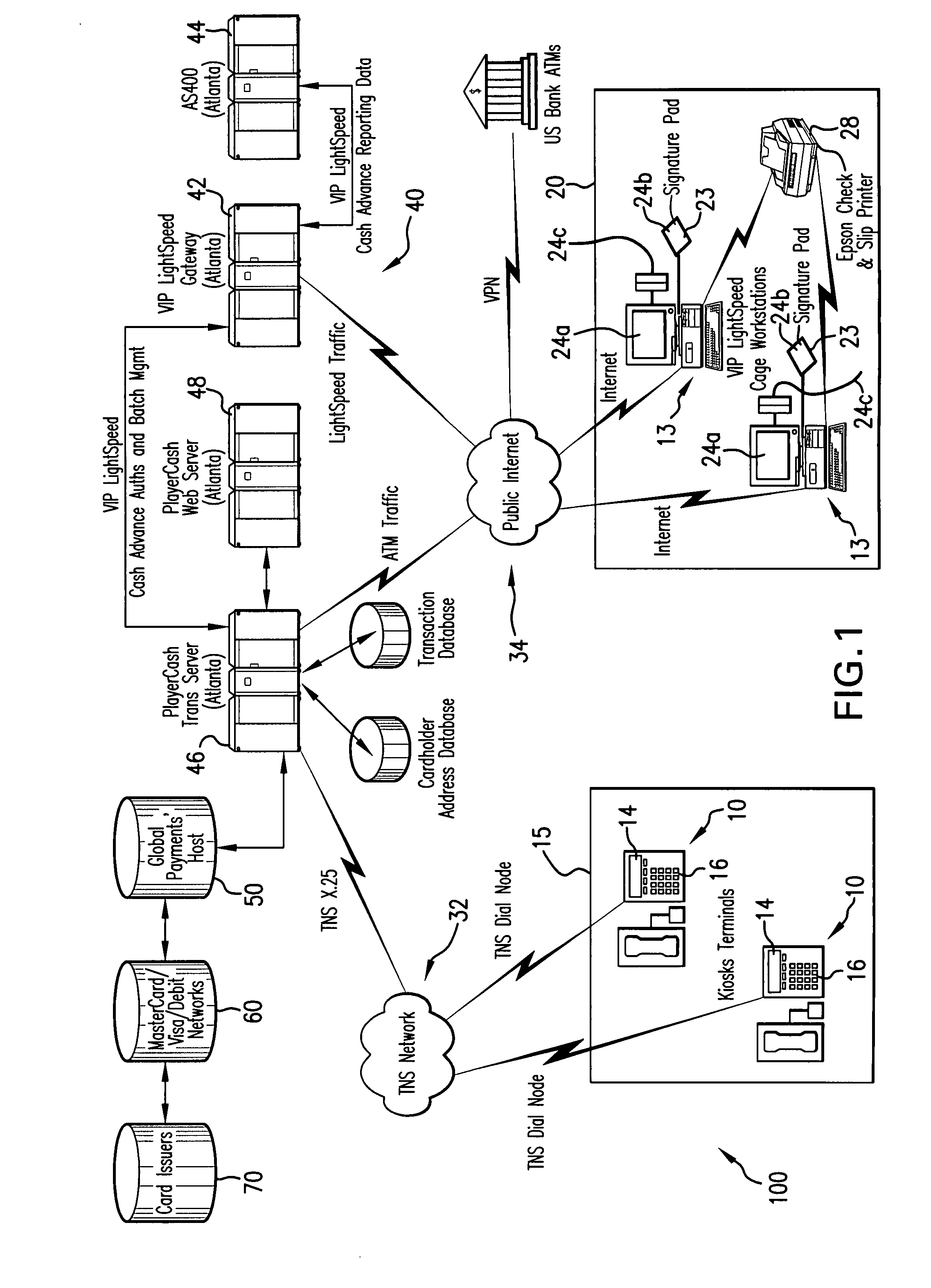
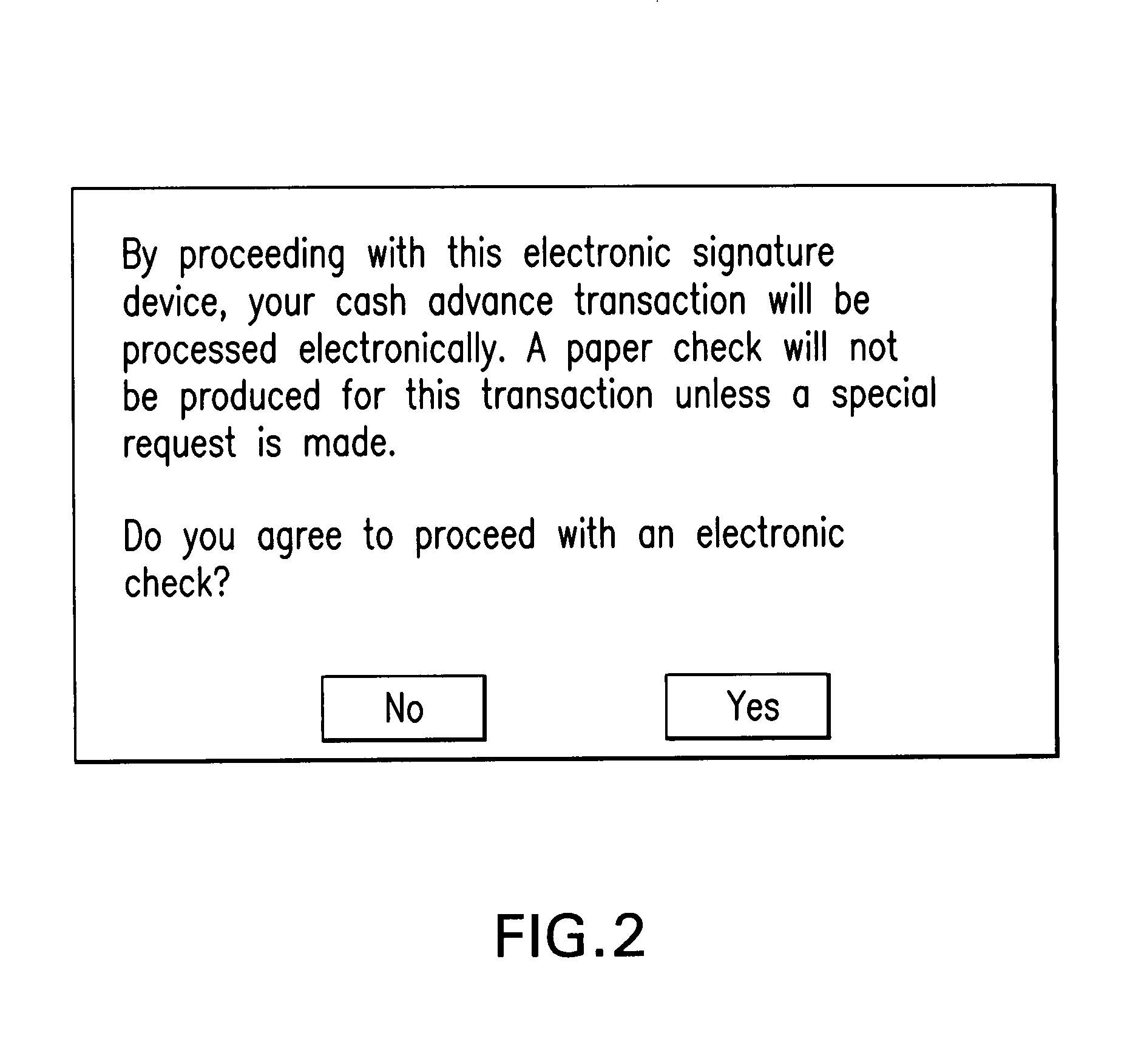
System for making funds available for gaming
A system for making funds available for gaming which includes a terminal which is configured to read customer information from a card. The terminal includes an input / output unit configured to allow the customer to select a quasi-cash transaction and to generate an order authorizing the quasi-cash transaction. The system also includes a station which is configured to retrieve the order and information verifying the identity of the customer and, when the identity of the customer is verified, is configured to, at the customer's option (1) obtain an electronic endorsement from the customer and place the electronic endorsement in an electronic image or (2) print out a hard copy of a check for endorsement by the customer.
Owner:GLOBAL PAYMENTS GAMING SERVICES INC
Information processing apparatus, image enlargement processing method, and program
InactiveUS20110102467A1Improve processing efficiencyEnhance the imageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingInformation processingComputer graphics (images)
An information processing apparatus includes a display section, a generation section, a determination section, and a control section. The display section includes a screen. The generation section generates an image of content data including visible data. The determination section determines an area surrounding an area in which the visible data is arranged in the generated image and corresponding to a shape of the screen, as a visible data area. The control section generates, by the generation section, an enlarged image obtained by enlarging the image so that a size of the screen and a size of the visible data area become close to each other, determines, by the determination section, the visible data area in the enlarged image, and extracts the visible data area from the enlarged image to display the visible data area on the screen.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Apparatus and methods for recovery of variational wind energy
InactiveUS9366234B2Maximize electrical energyIncreased turbulenceBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCommunications systemMechanical energy
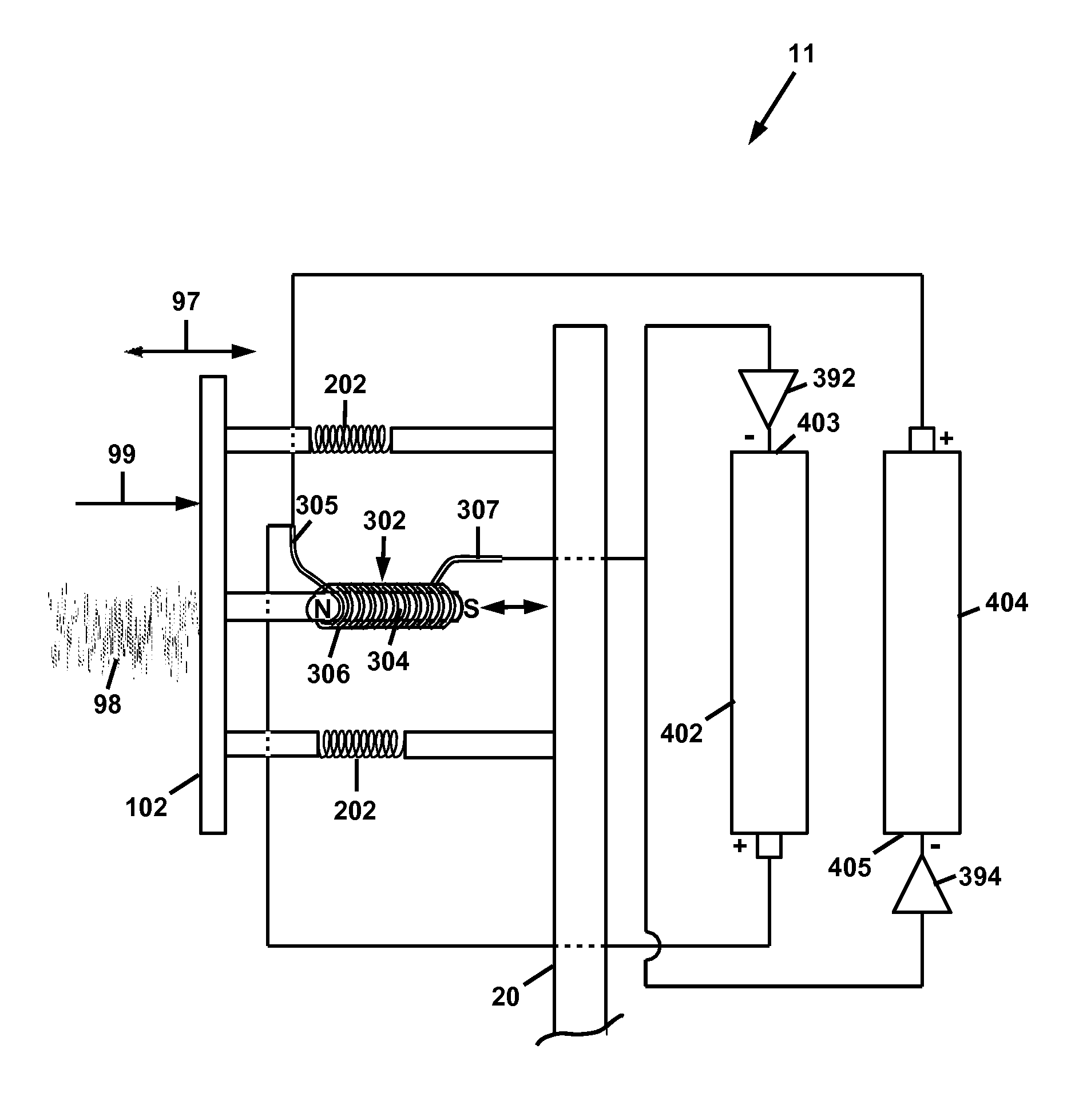
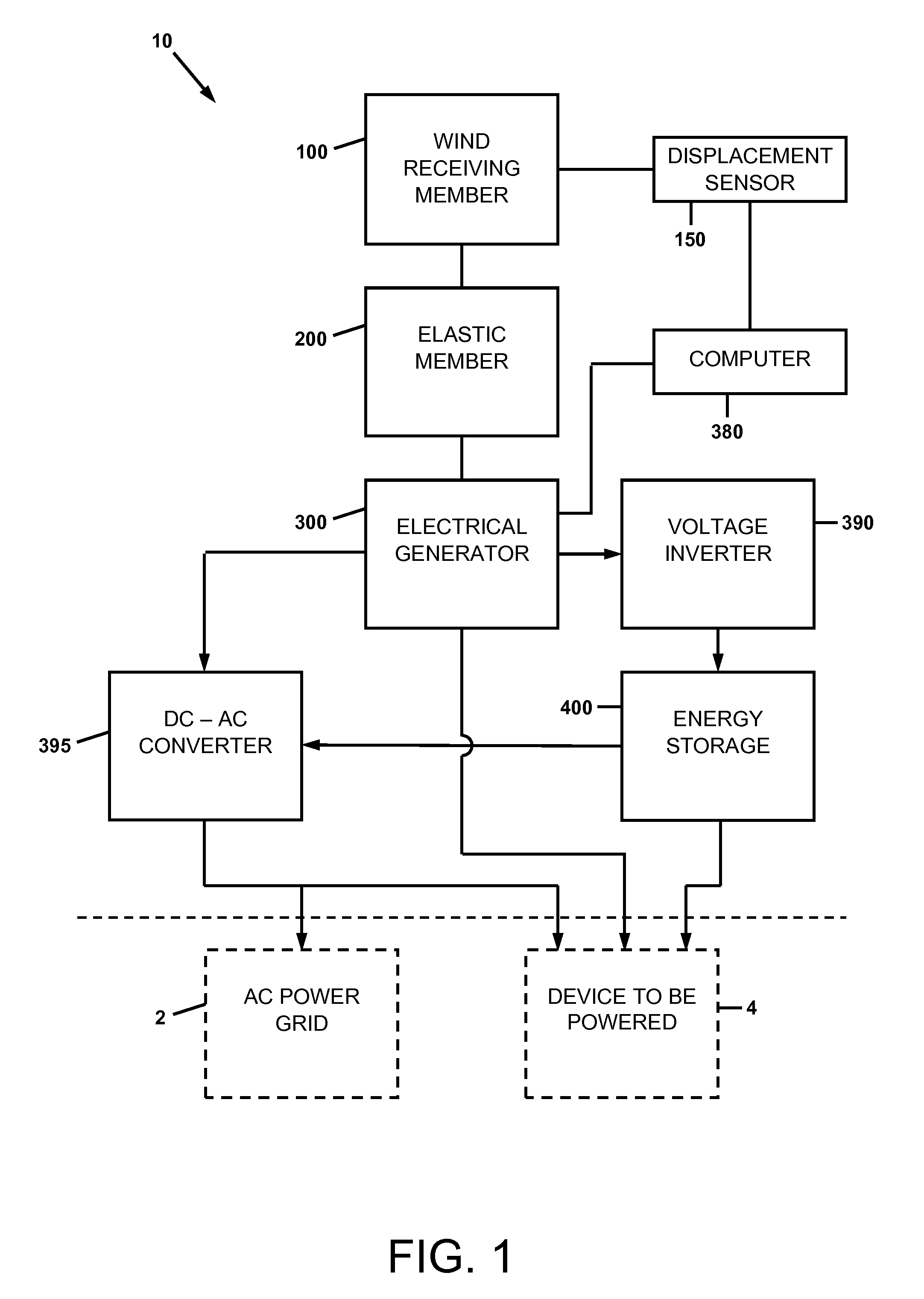
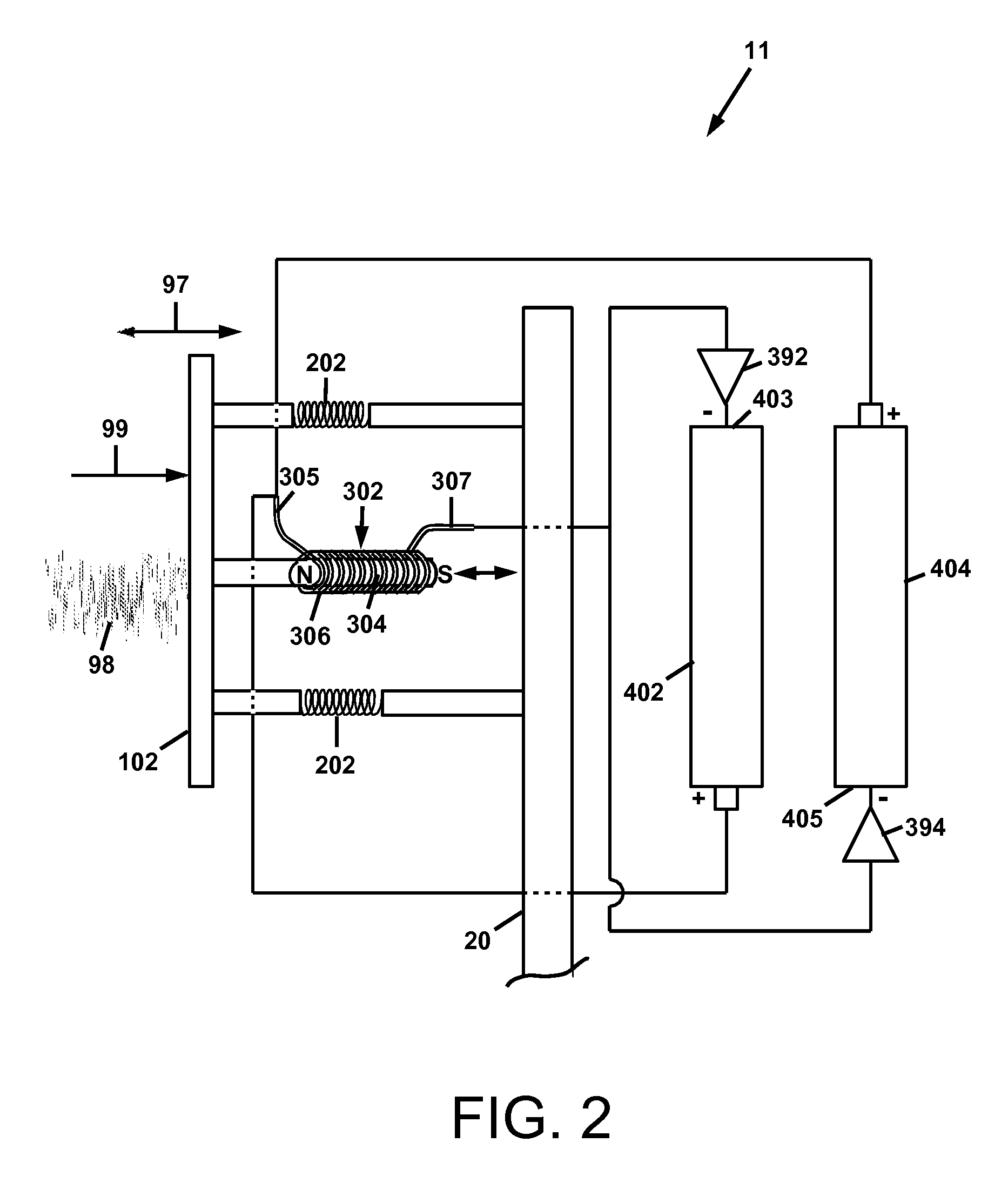
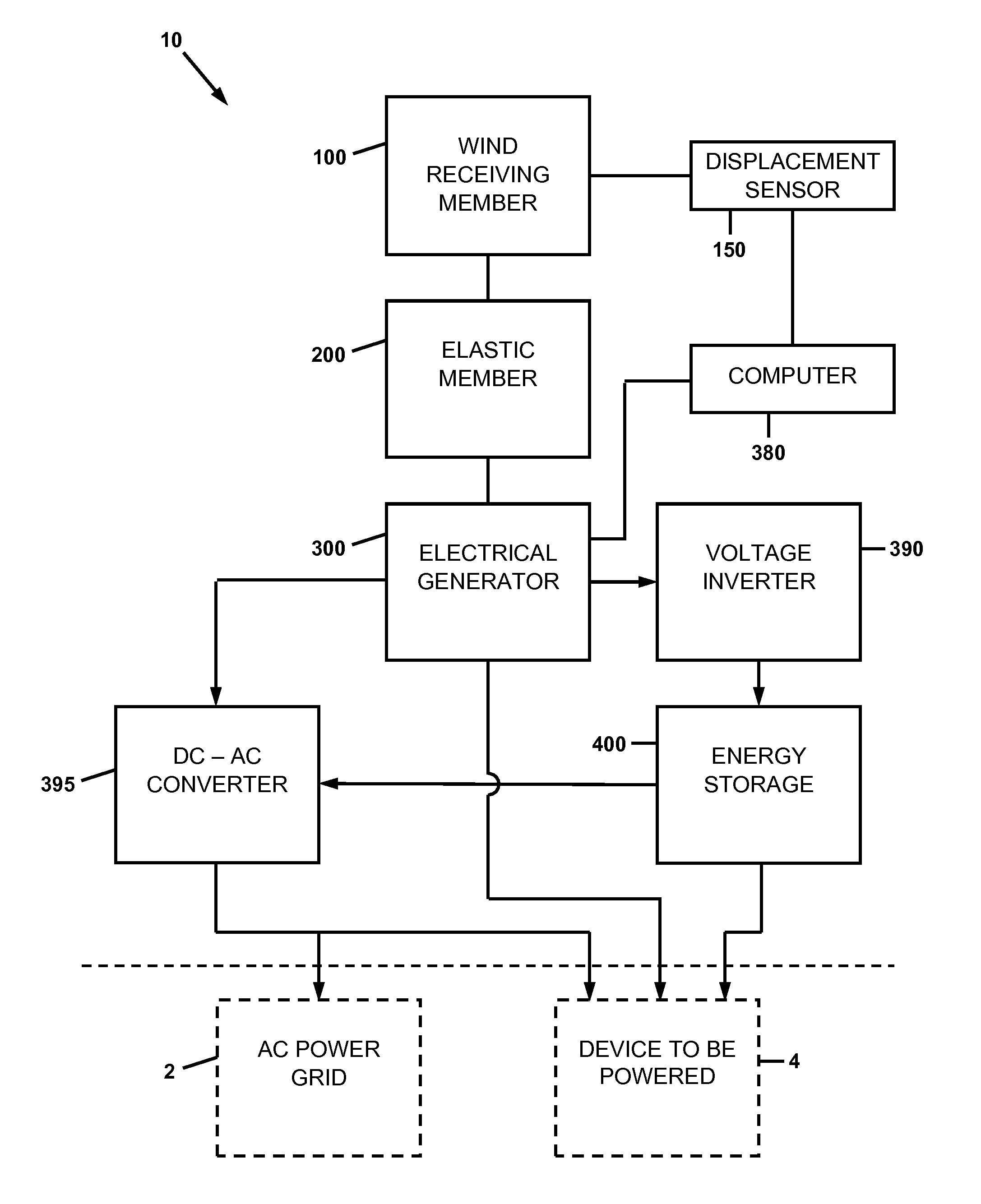
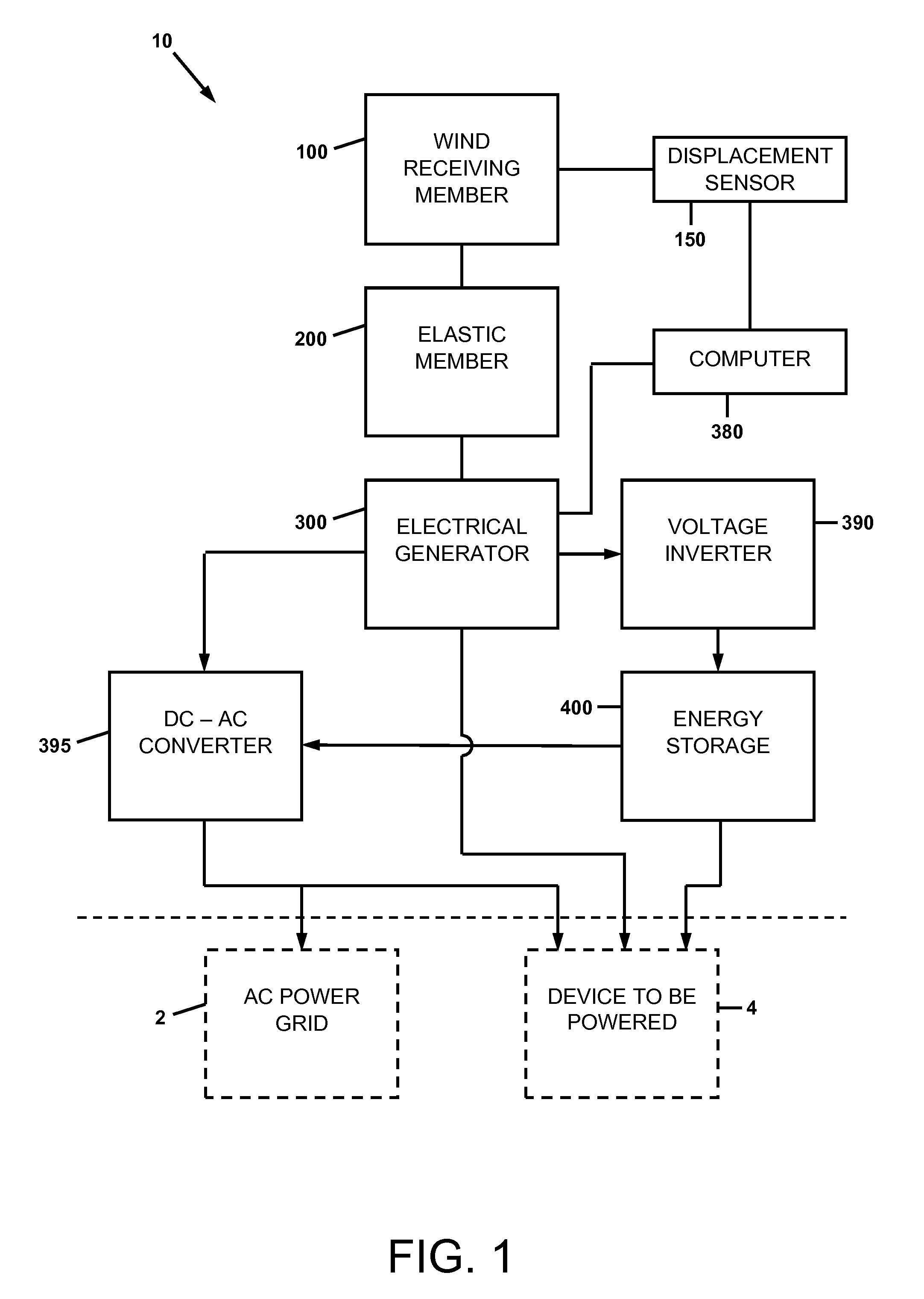
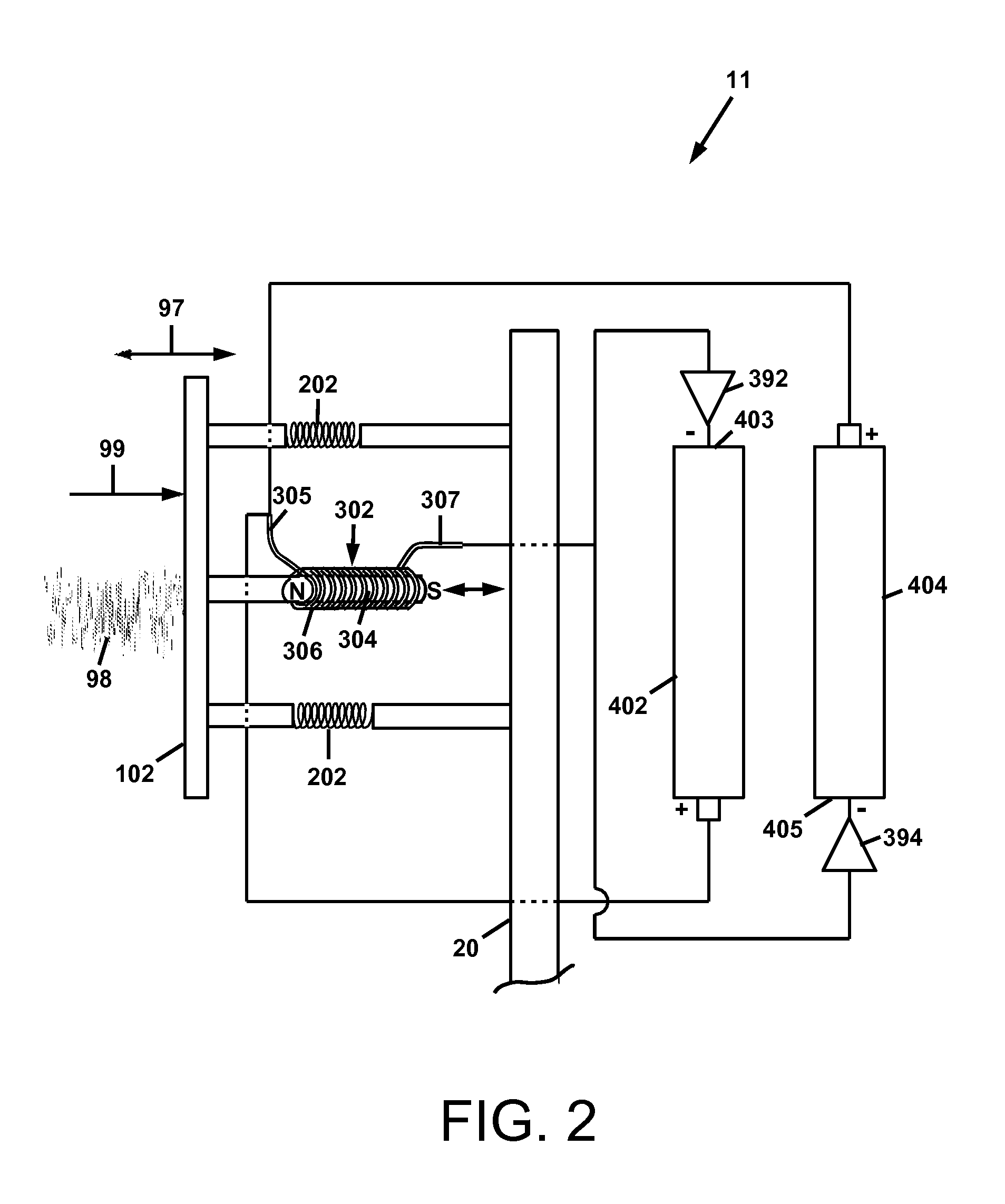
A wind energy recovery apparatus and related methods are disclosed. The apparatus is comprised of a first wind receiving member displaceable by a wind having a variable velocity, a first elastic member coupled to the first wind receiving member, and an electrical generator operatively connected to the first wind receiving member and configured to convert mechanical energy of the first wind receiving member to electrical energy. An energy storage device may be provided in communication with the electrical generator. A self-powered signal communications system including the apparatus is also disclosed. A method of identifying a site for recovering variational wind energy is also disclosed.
Owner:SANCHEZ JAMES MICHAEL +1
Apparatus and methods for recovery of variational wind energy
InactiveUS20150285223A1Maximize electrical energyAdditional electrical energyBatteries circuit arrangementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCommunications systemMechanical energy
A wind energy recovery apparatus and related methods are disclosed. The apparatus is comprised of a first wind receiving member displaceable by a wind having a variable velocity, a first elastic member coupled to the first wind receiving member, and an electrical generator operatively connected to the first wind receiving member and configured to convert mechanical energy of the first wind receiving member to electrical energy. An energy storage device may be provided in communication with the electrical generator. A self-powered signal communications system including the apparatus is also disclosed. A method of identifying a site for recovering variational wind energy is also disclosed.
Owner:SANCHEZ JAMES MICHAEL +1
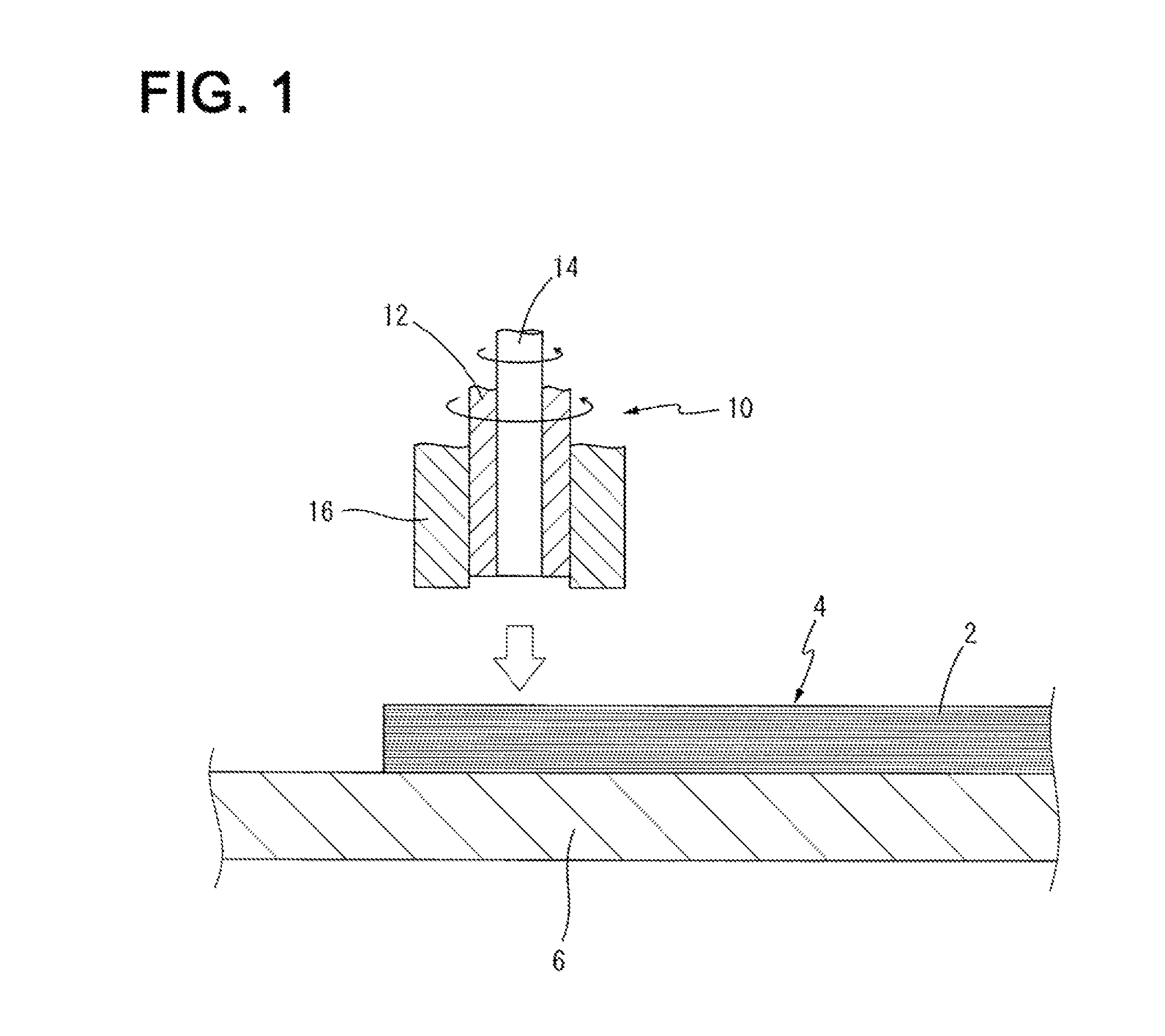
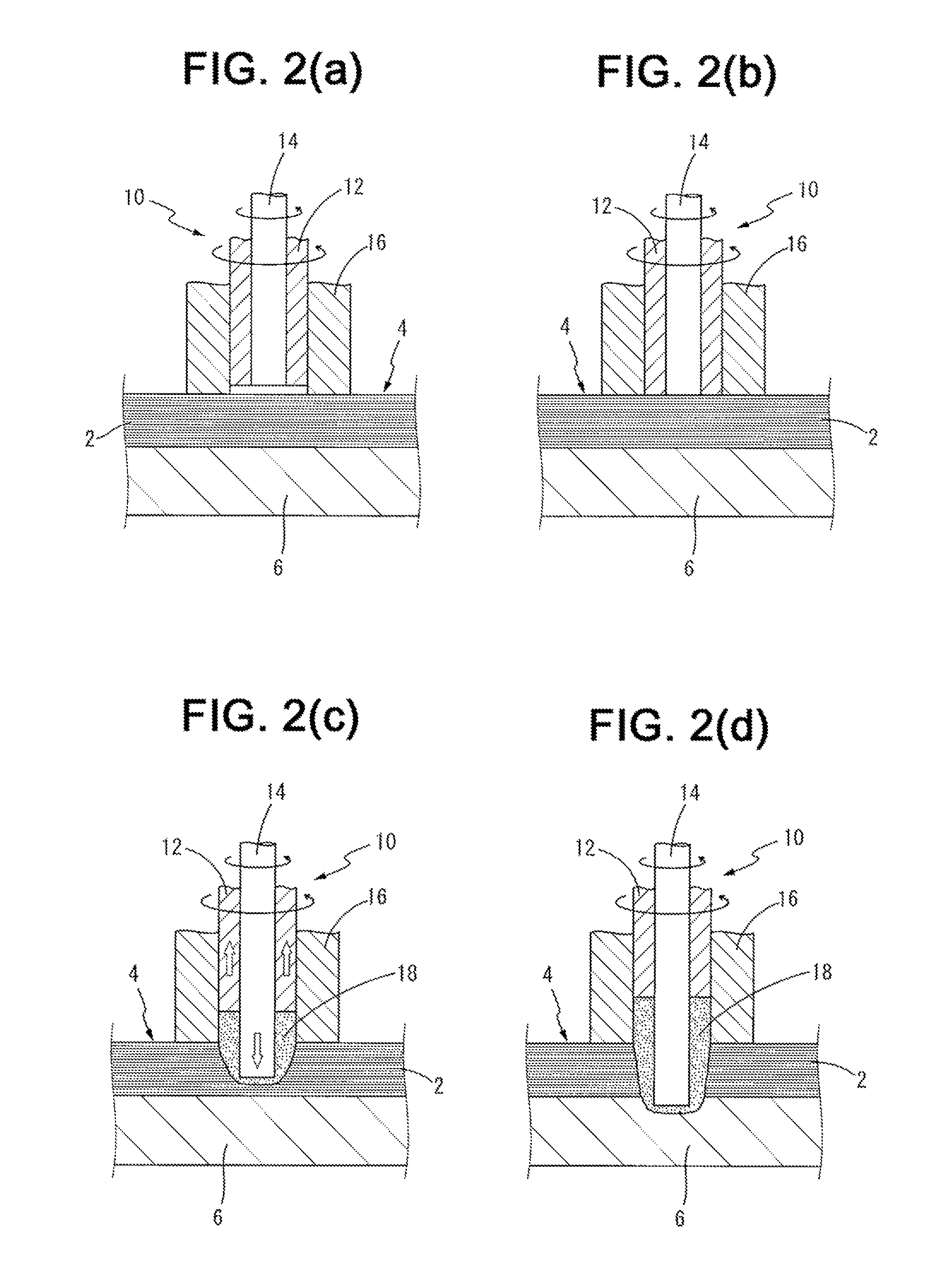
Process for spot-joining stacked metal foils
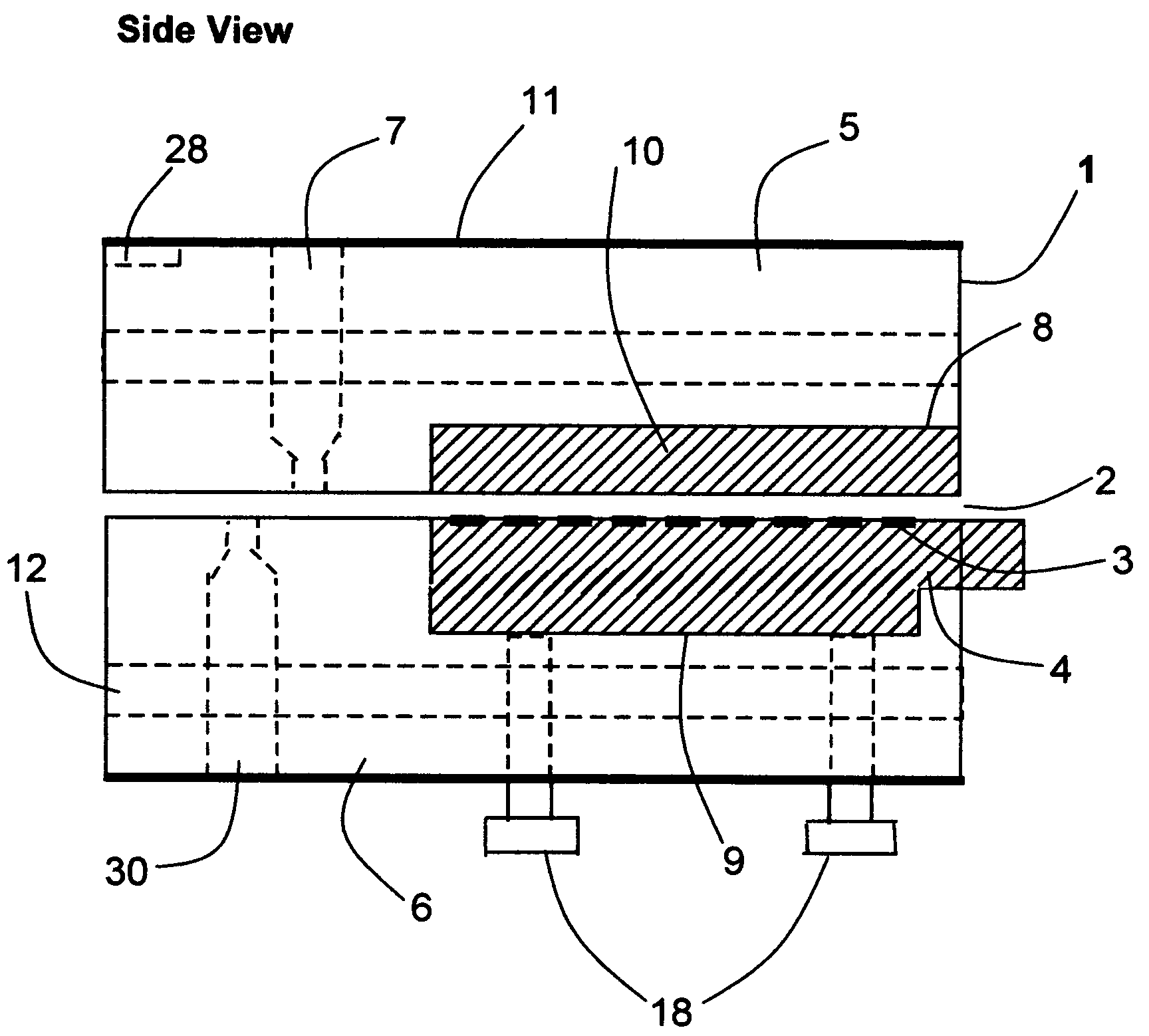
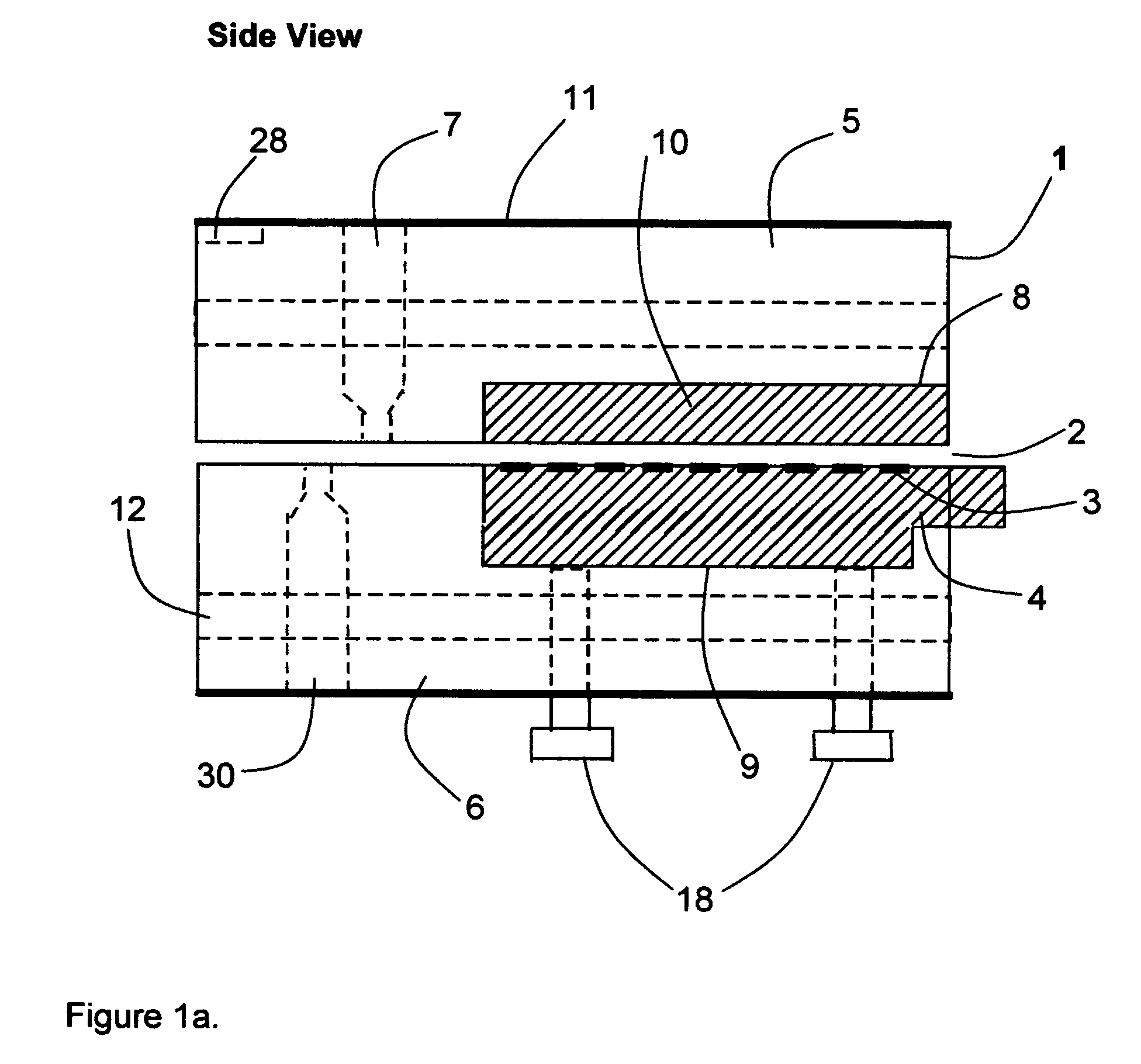
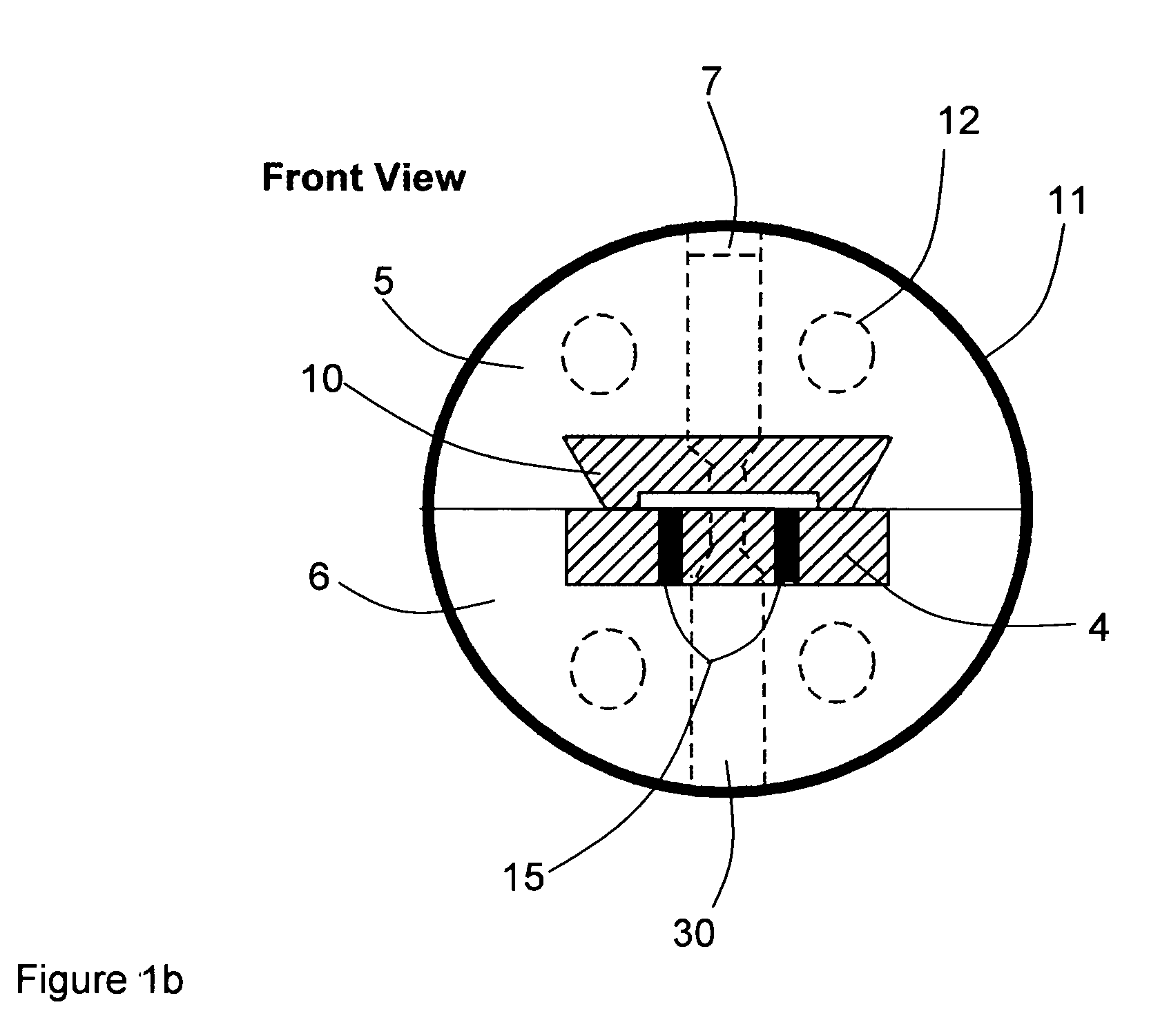
ActiveUS9302343B2Cutting can not be obtainedRestricting and preventing problemNon-electric welding apparatusMetal foilEngineering
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD +1
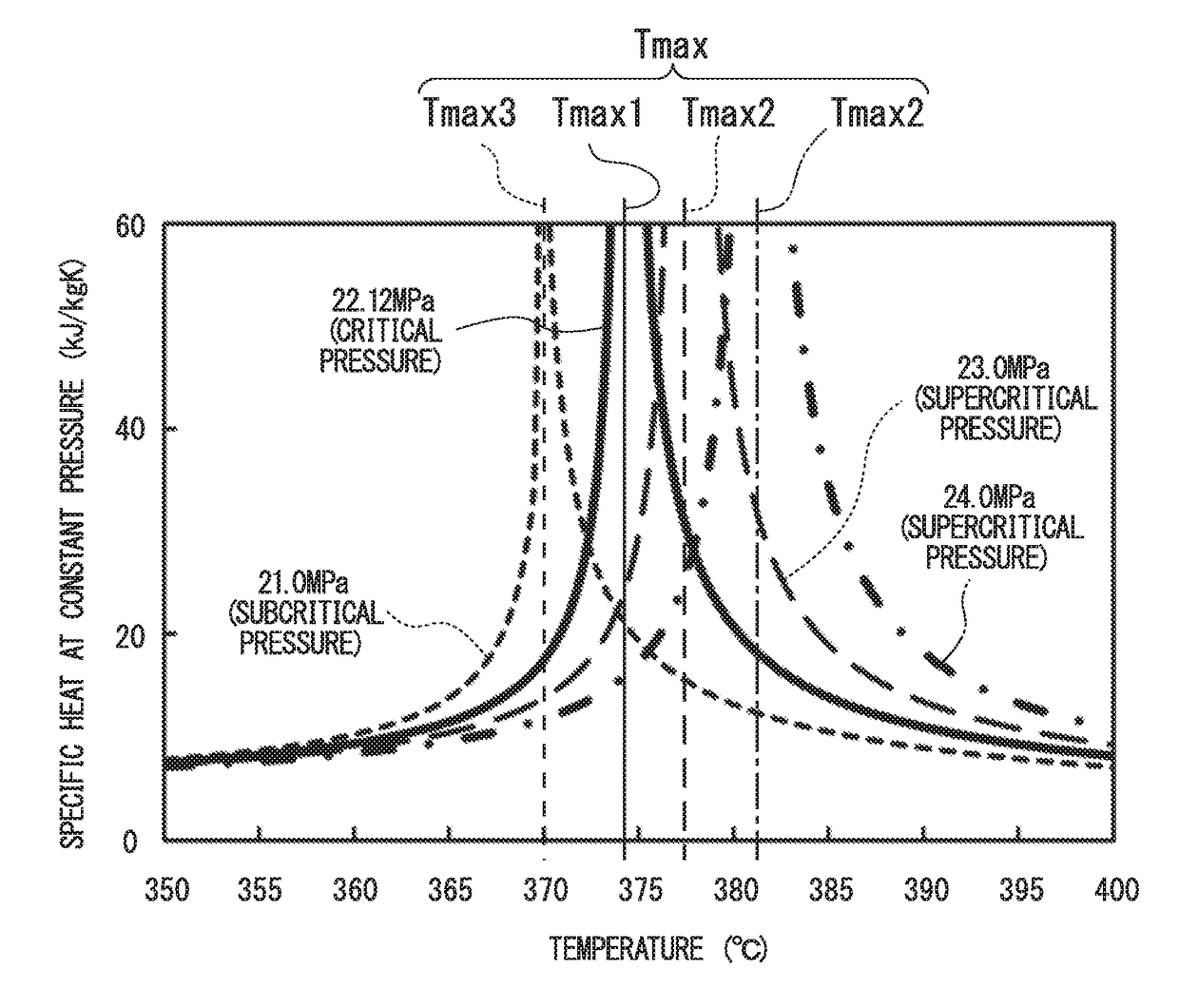
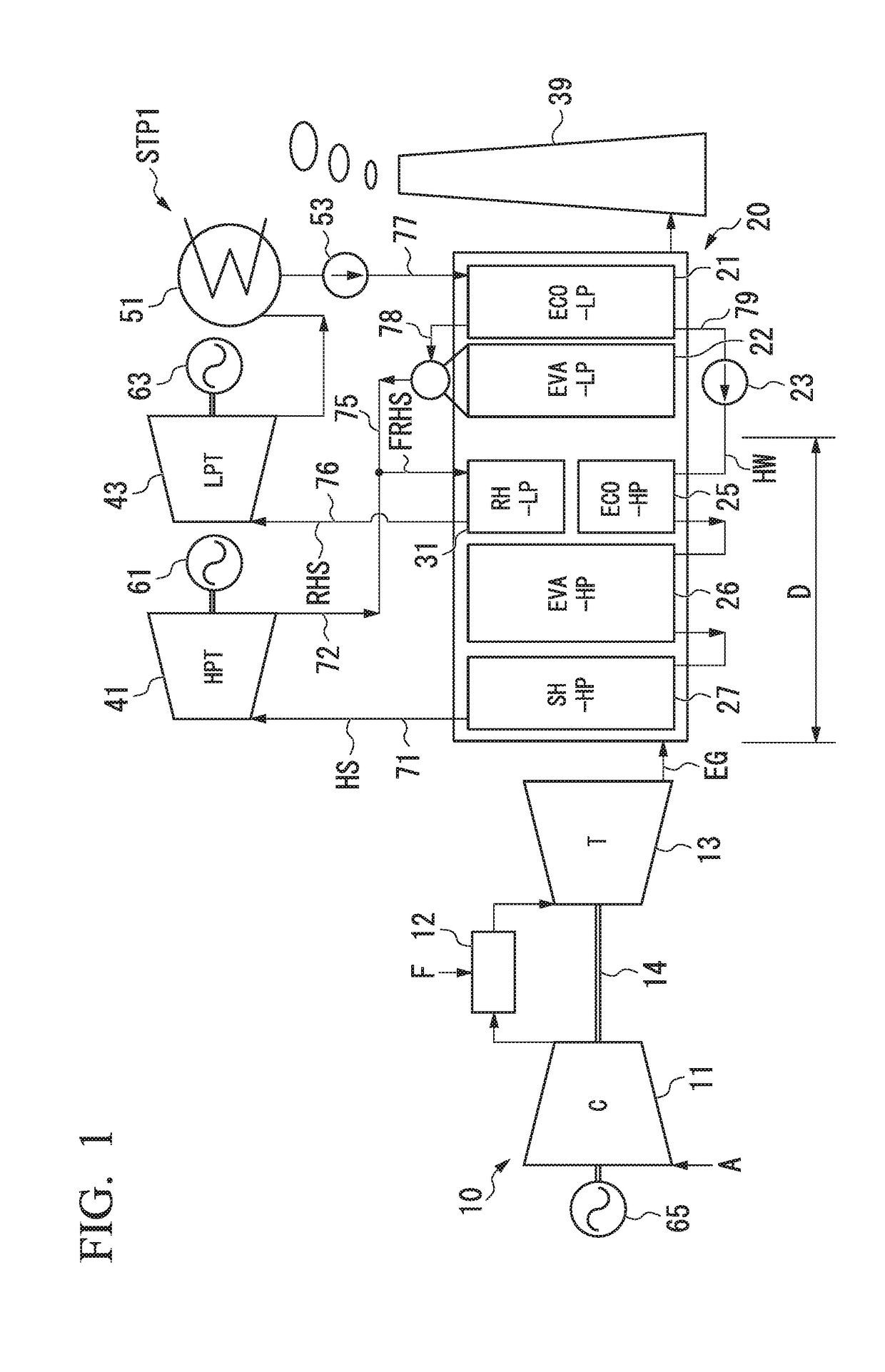
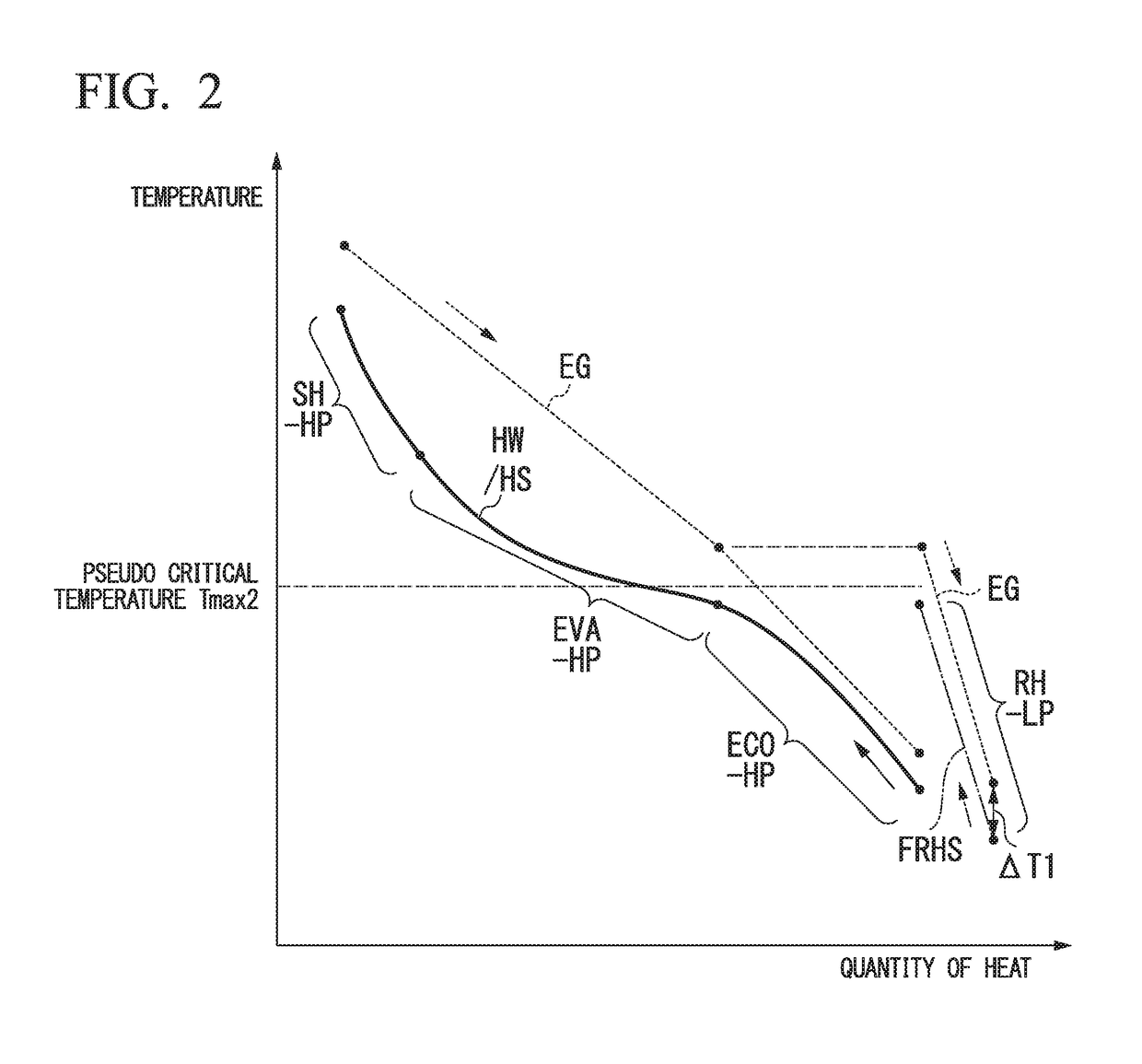
Steam turbine plant, combined cycle plant provided with same, and method of operating steam turbine plant
ActiveUS20180003085A1Cutting can not be obtainedImprove steaming efficiencyEngine componentsSteam engine plantsEngineeringHigh pressure
A boiler includes one or more evaporators configured to heat water which has flowed therein to a specific heat maximum temperature at constant pressure or more in which a specific heat at constant pressure is maximized using a heated fluid and one or more reheaters configured to heat the steam which has come from the boiler using the heated fluid. All the reheaters configured to supply steam to a low-pressure steam turbine are disposed only at a downstream side of the high-pressure evaporator. All the reheaters heat reheating steam (FRHS) containing steam which has passed through a high-pressure steam turbine configured to receive steam supplied from the high-pressure evaporator and having a temperature lower than a specific heat maximum temperature at constant pressure in the high-pressure evaporator to less than the specific heat maximum temperature at constant pressure.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
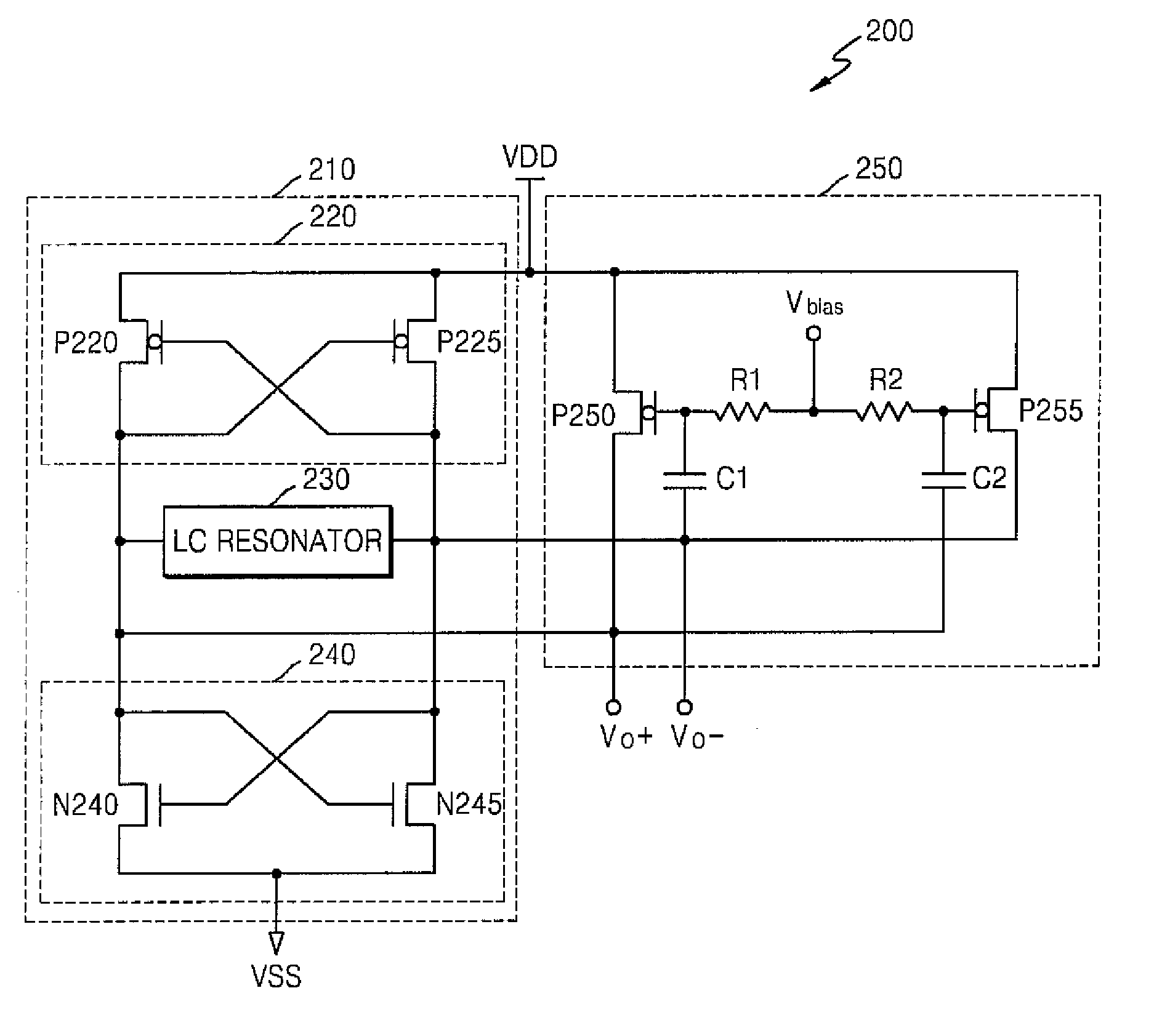
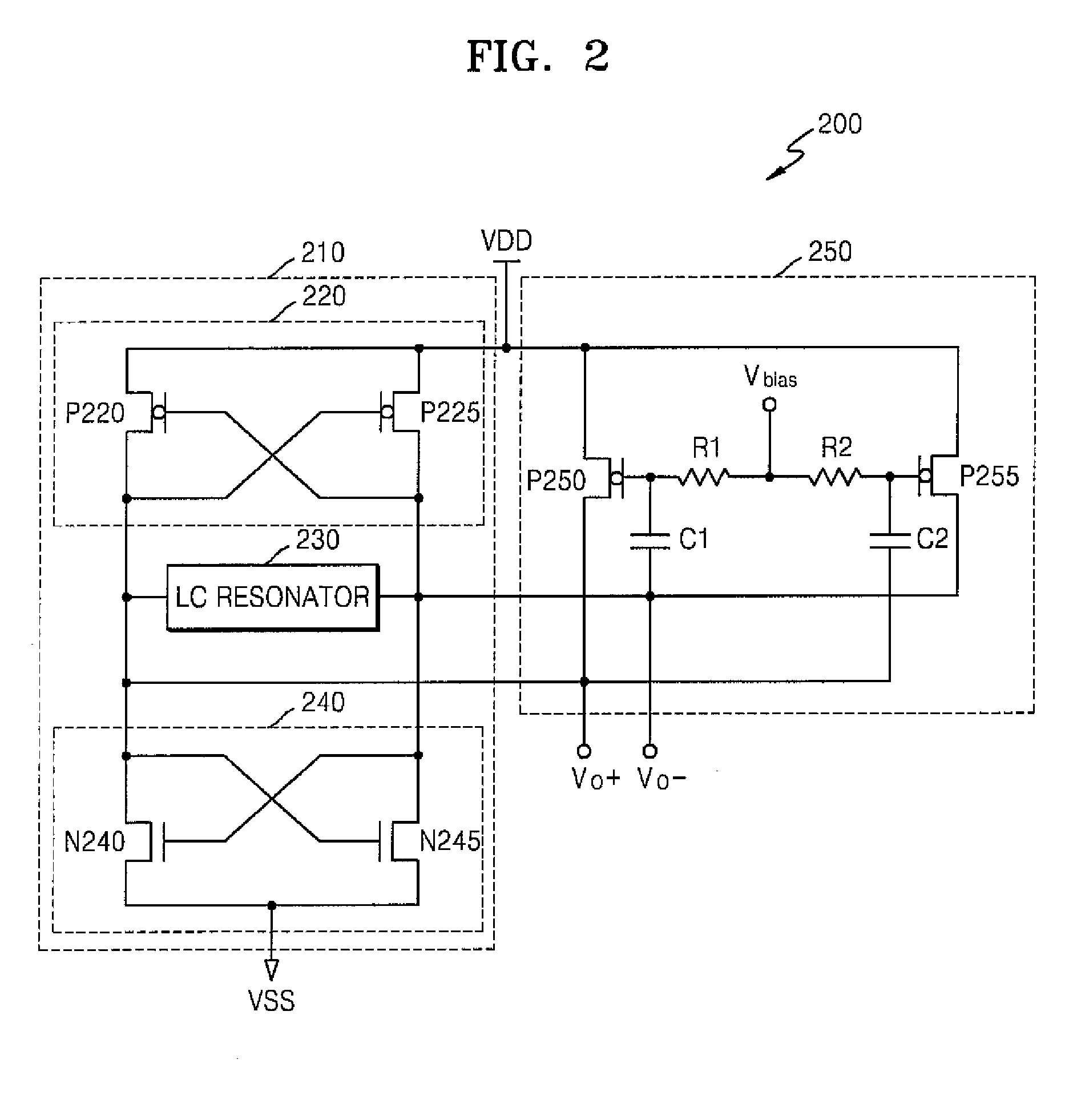
Voltage controlled oscillator for controlling phase noise and method using the same
InactiveUS20080164954A1Reduce phase noiseSteep slopePillowsSleeping rugPhase noiseAudio power amplifier
A voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) includes a VCO unit having multiple VCO unit output terminals and an amplifier having multiple amplifier output terminals respectively connected to the VCO unit output terminals. The VCO unit generates first output signals having an oscillation frequency corresponding to a supply voltage. The amplifier amplifies a value obtained by performing n-th differentiation on a transconductance component of each first output signal (n being a natural number). Second output signals, corresponding to the first output signals, are output through the amplifier output terminals. Each second output signal includes the amplified value of the corresponding first output signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
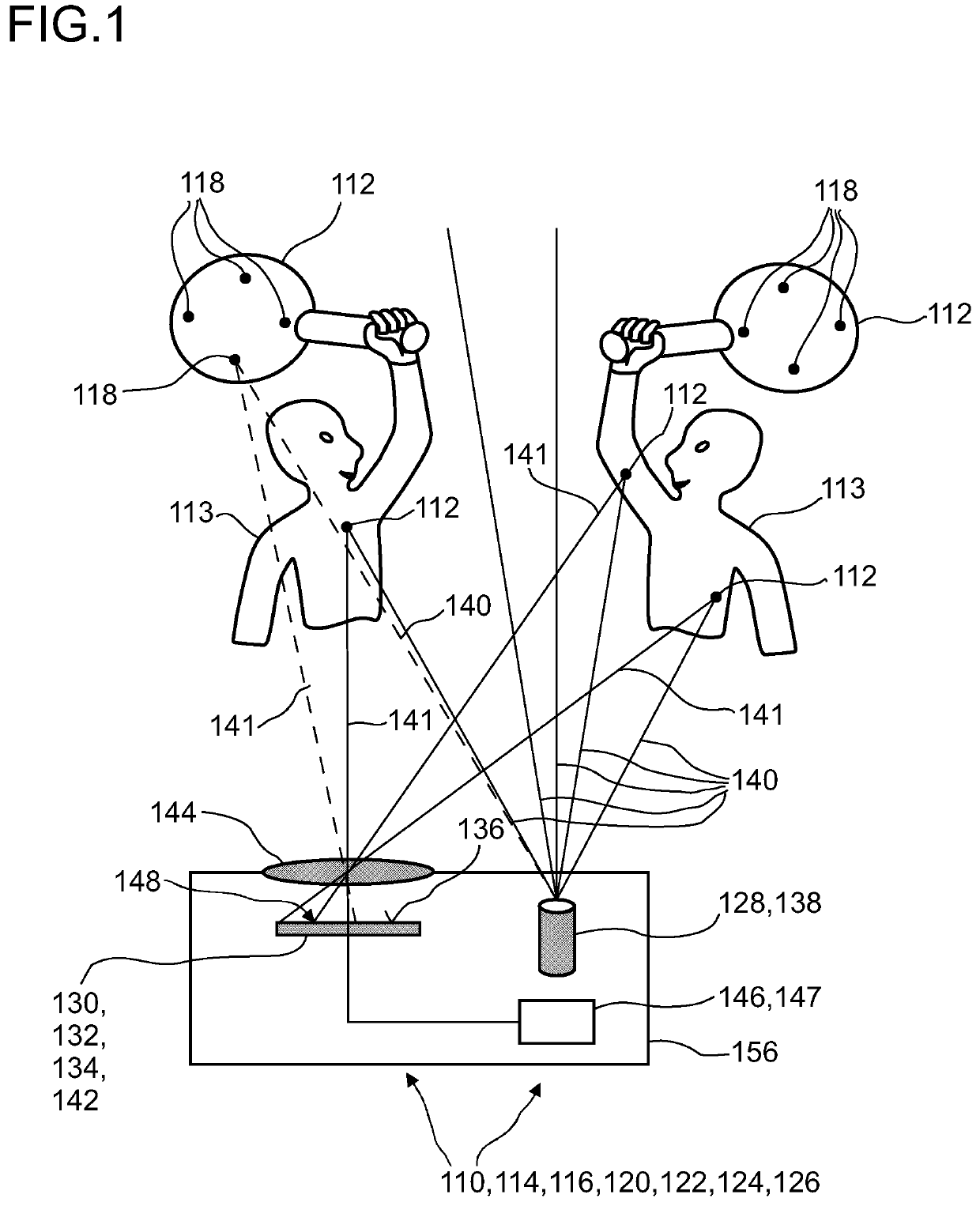
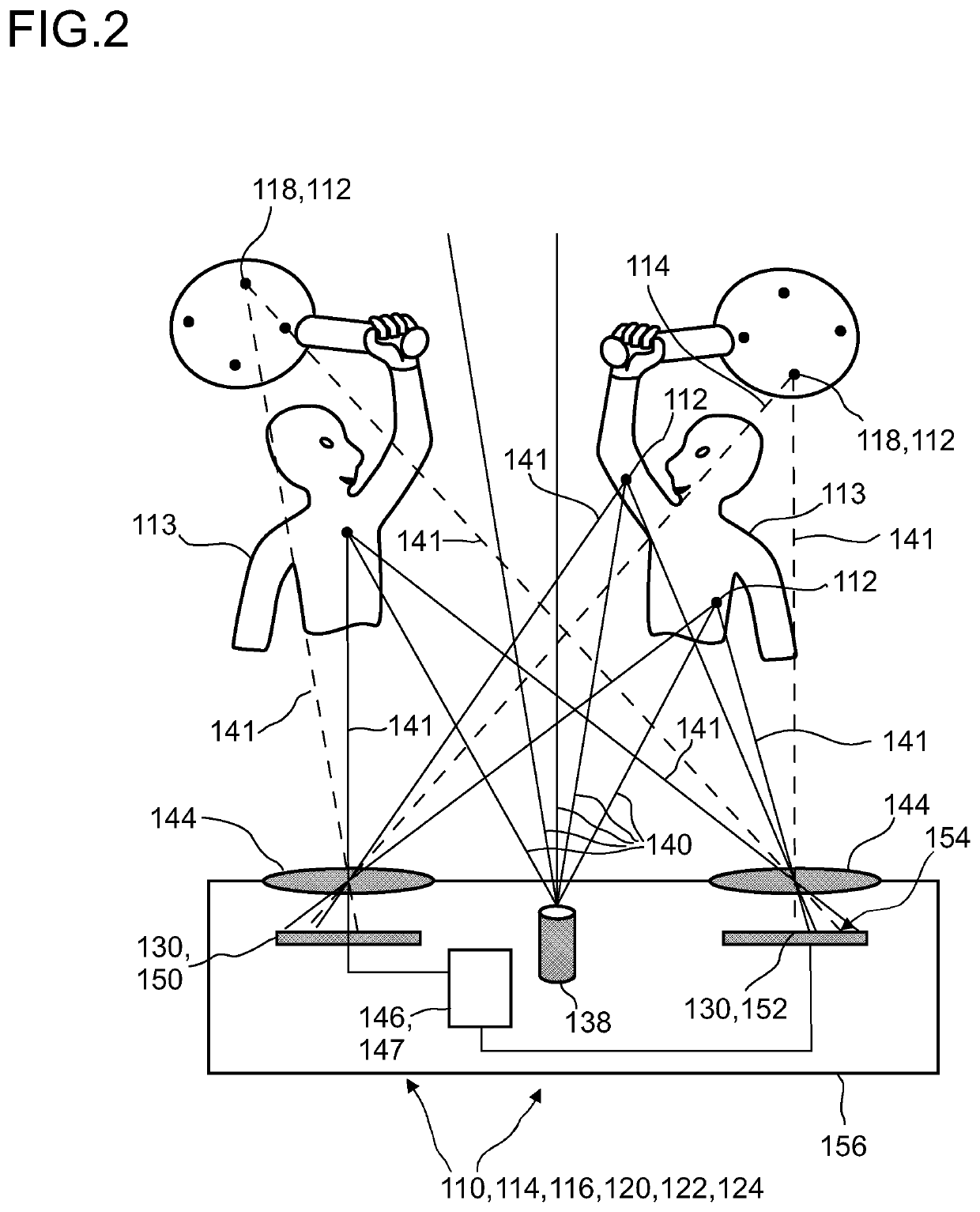
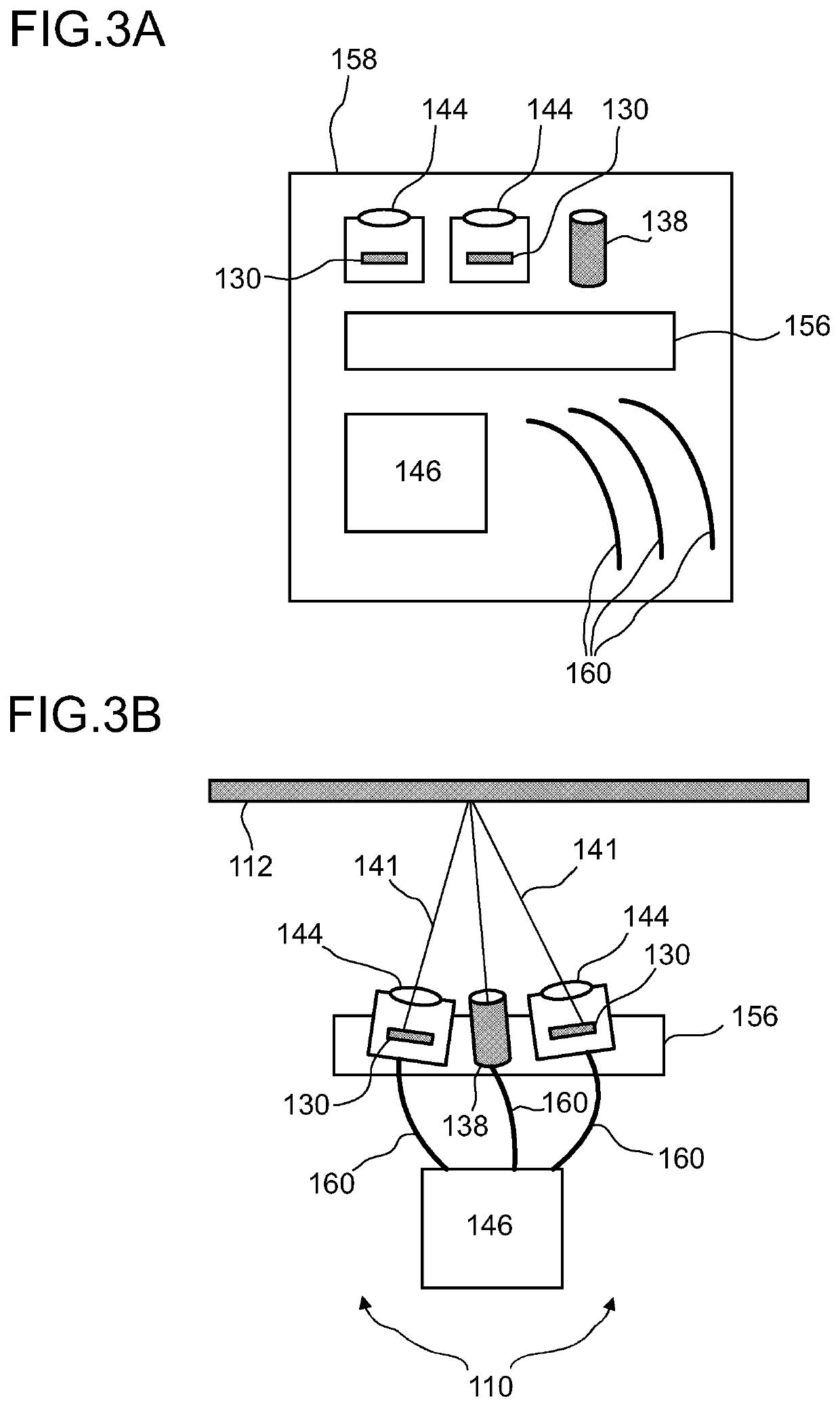
Detector for determining a position of at least one object
ActiveUS20200348385A1Reduce possible numberReduce computing needsImage analysisDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsLight beamReference image
Owner:TRINAMIX GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com