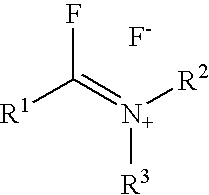
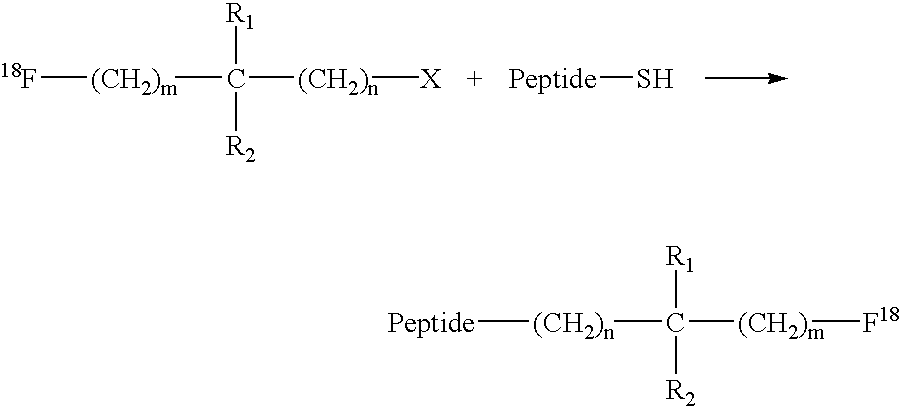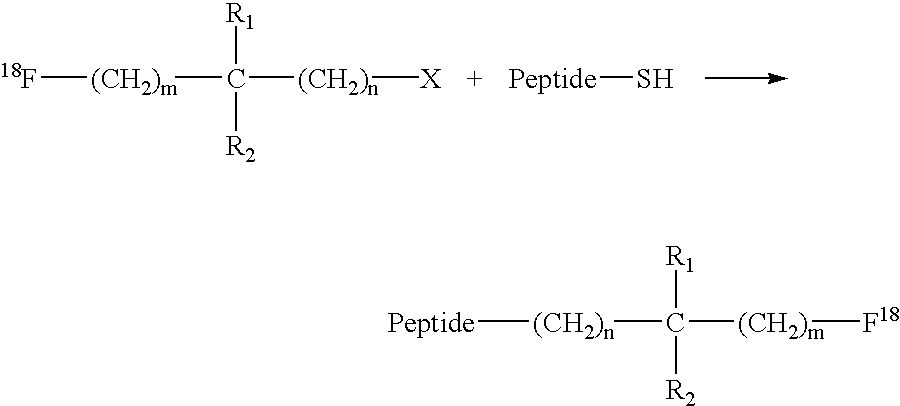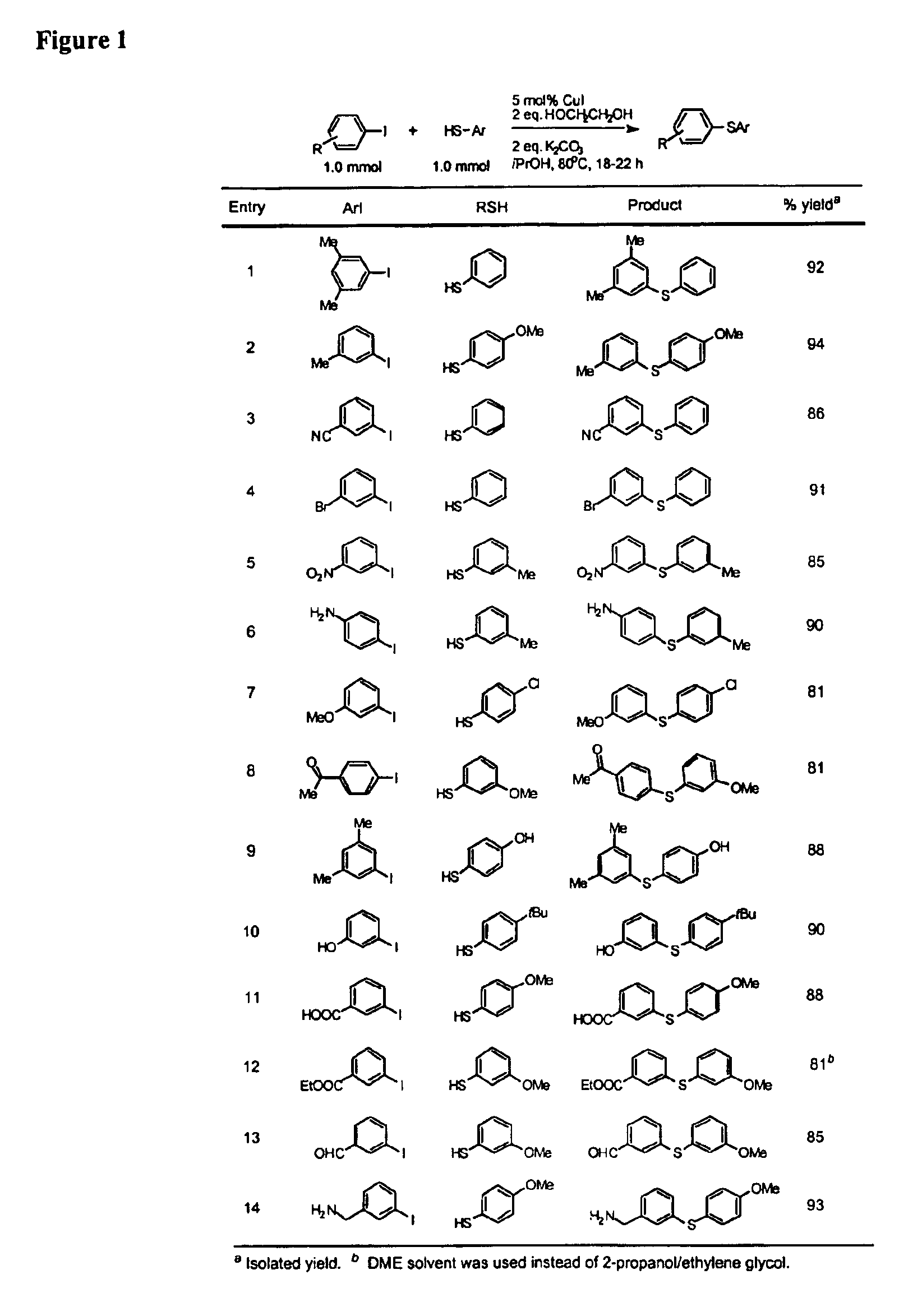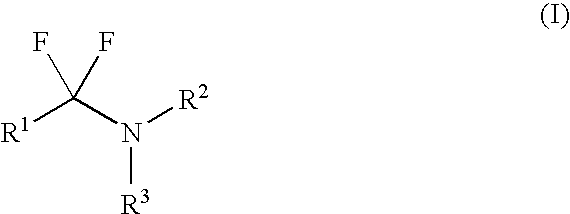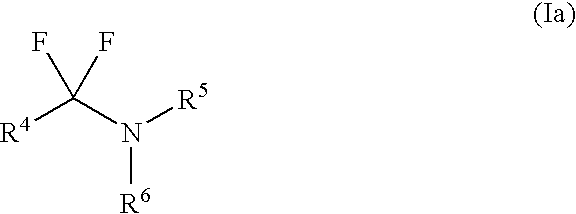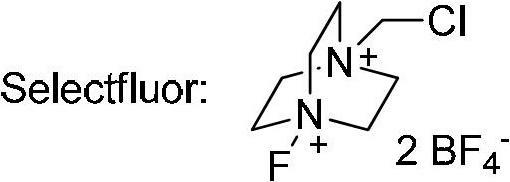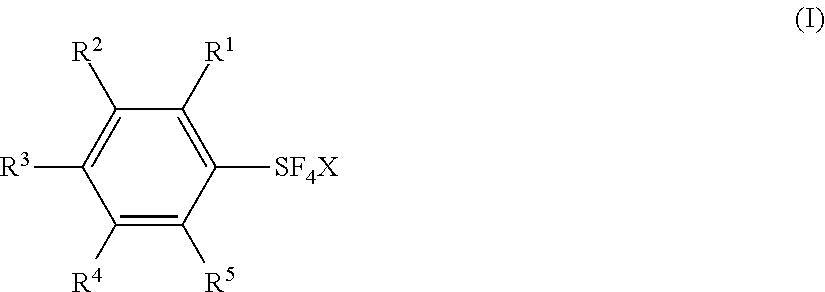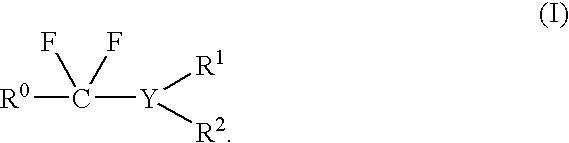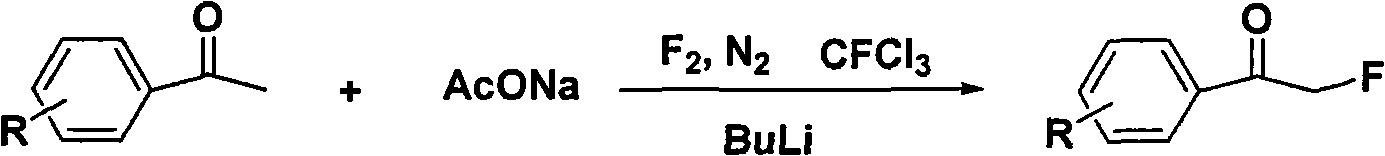Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
469results about "Organic halogenation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
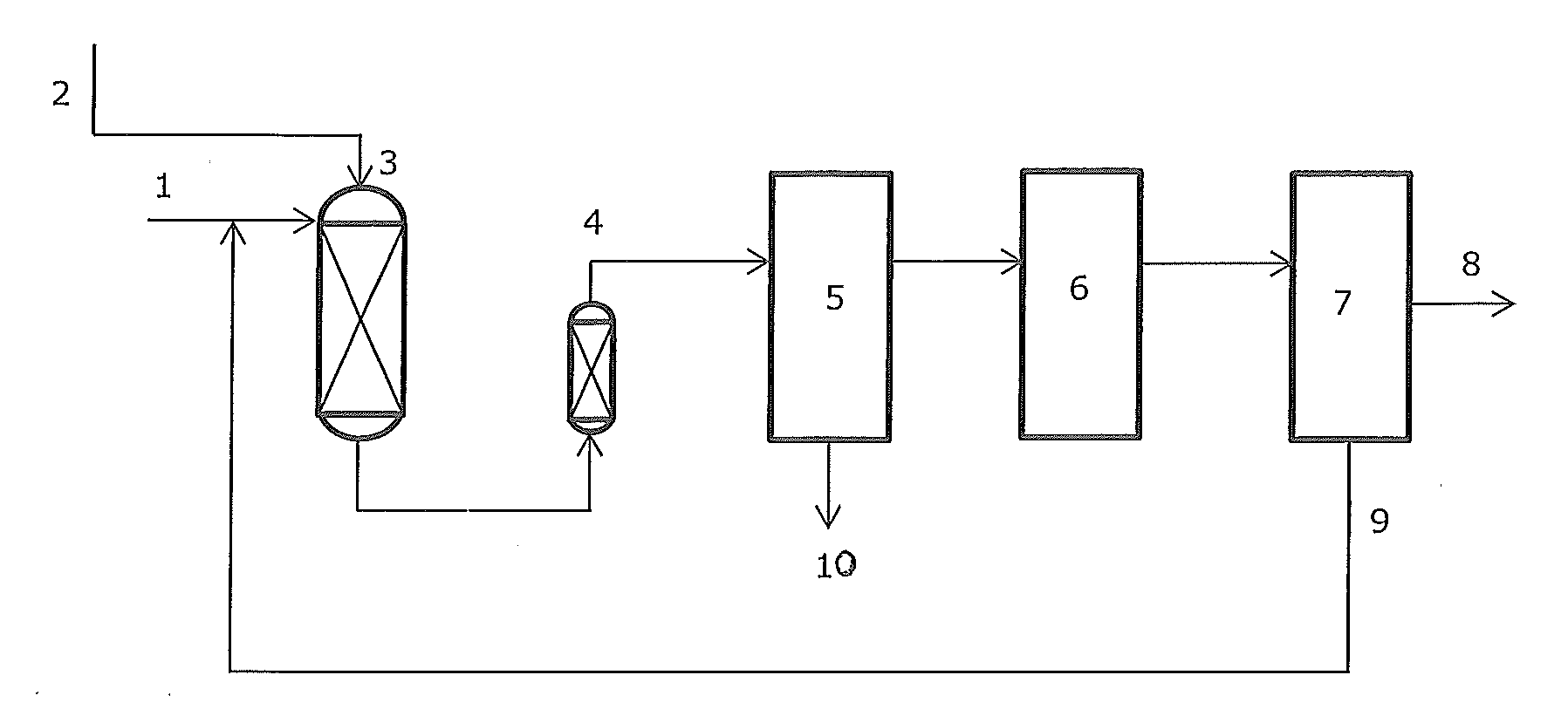
Complex comprising oxidative dehydrogenation unit
ActiveUS20140249339A1Consumes lotThermal non-catalytic crackingSequential/parallel process reactionsAlkaneDehydrogenation
Oxidative dehydrogenation of paraffins to olefins provides a lower energy route to produce olefins. Oxidative dehydrogenation processes may be integrated with a number of processes in a chemical plant such as polymerization processes, manufacture of glycols, and carboxylic acids and esters. Additionally, oxidative dehydrogenation processes can be integrated with the back end separation process of a conventional steam cracker to increase capacity at reduced cost.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
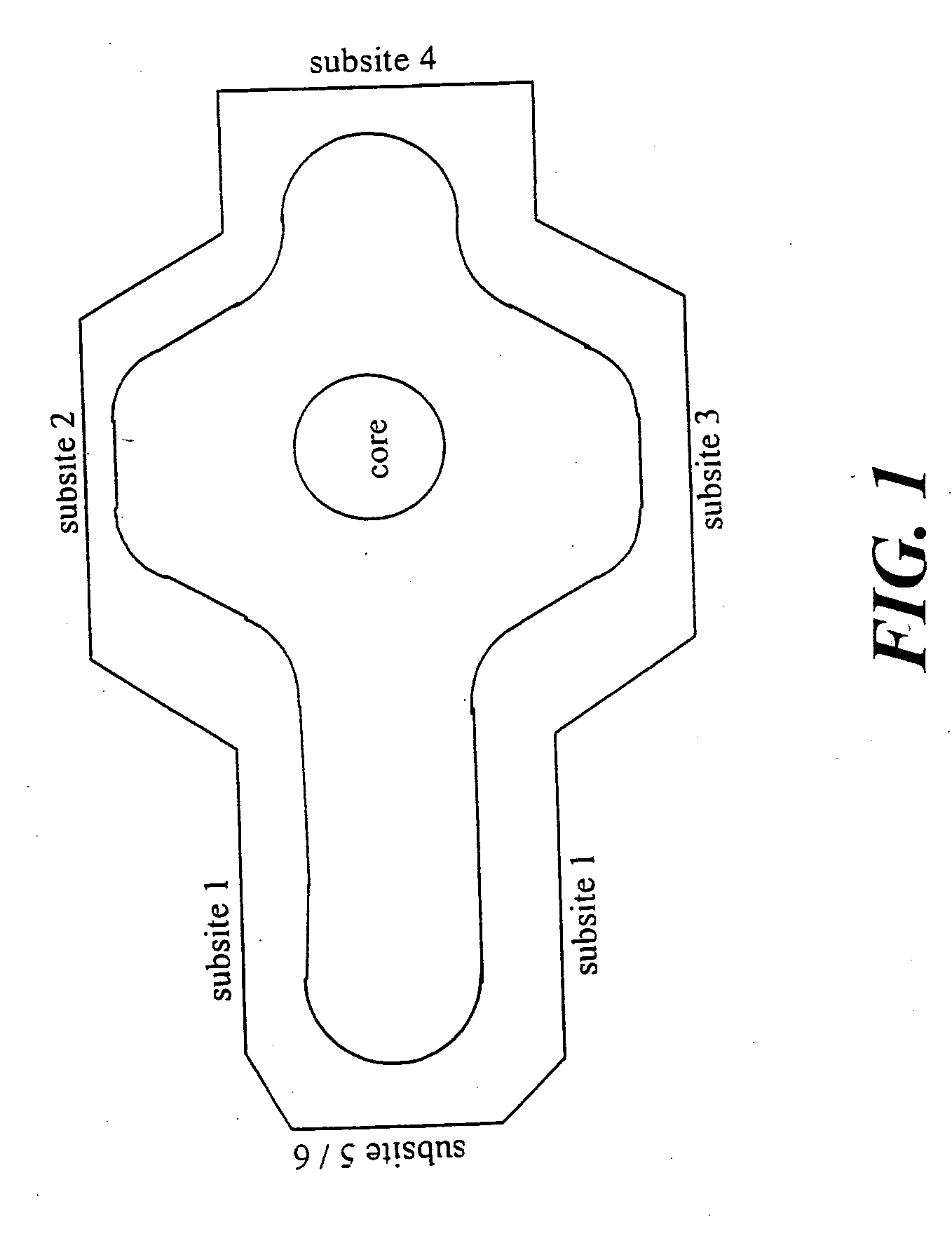
Method of identifying inhibitors of DHODH
ActiveUS20070027193A1Inhibit biological activityBiocideOrganic compound preparationBinding siteUbiquinone binding
The present invention provides a compound capable of binding to the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH which contains a non-aromatic ring system as a core structure, a group capable of interacting with structural elements of subsite 2 or 3 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH and a group capable of interacting hydrophobically with structural elements of subsite 1 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH. Furthermore, the present invention provides a compound capable of binding to the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH which contains an aromatic ring system as a core structure, a group capable of interacting with residues His 56 and / or Tyr 356 of subsite 3 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH and a group capable of interacting hydrophobically with structural elements of subsite 1 of the ubiquinone binding site of DHODH.
Owner:IMMUNIC AG
Catalytic process for regiospecific chlorination of alkanes, alkenes and arenes
InactiveUS6825383B1Save energyOrganic compound preparationPreparation by OH and halogen introductionMetal chlorideAlkene
The present invention provides a process for regiospecific chlorination of an aromatic or aliphatic compound with a chlorine source comprising a metal chloride and other than Cl2 and SO2Cl2 in presence of hypervalent iodine catalyst and in acidic medium.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Fluorination of proteins and peptides for F-18 positron emission tomography
Thiol-containing peptides can be radiolabeled with fluorine-18 (F-18) by reacting a peptide comprising a free thiol group with an F-18-bound labelling reagent which also has a group that is reactive with thiols. The resulting F-18-labeled peptides may be targeted to a tissue of interest using bispecific antibodies or bispecific antibody fragments having one arm specific for the F-18-labeled peptide or a low molecular weight hapten conjugated to the F-18-labeled peptide, and another arm specific to the targeted tissue. The targeted tissue is subsequently visualized by clinical positron emission tomography.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
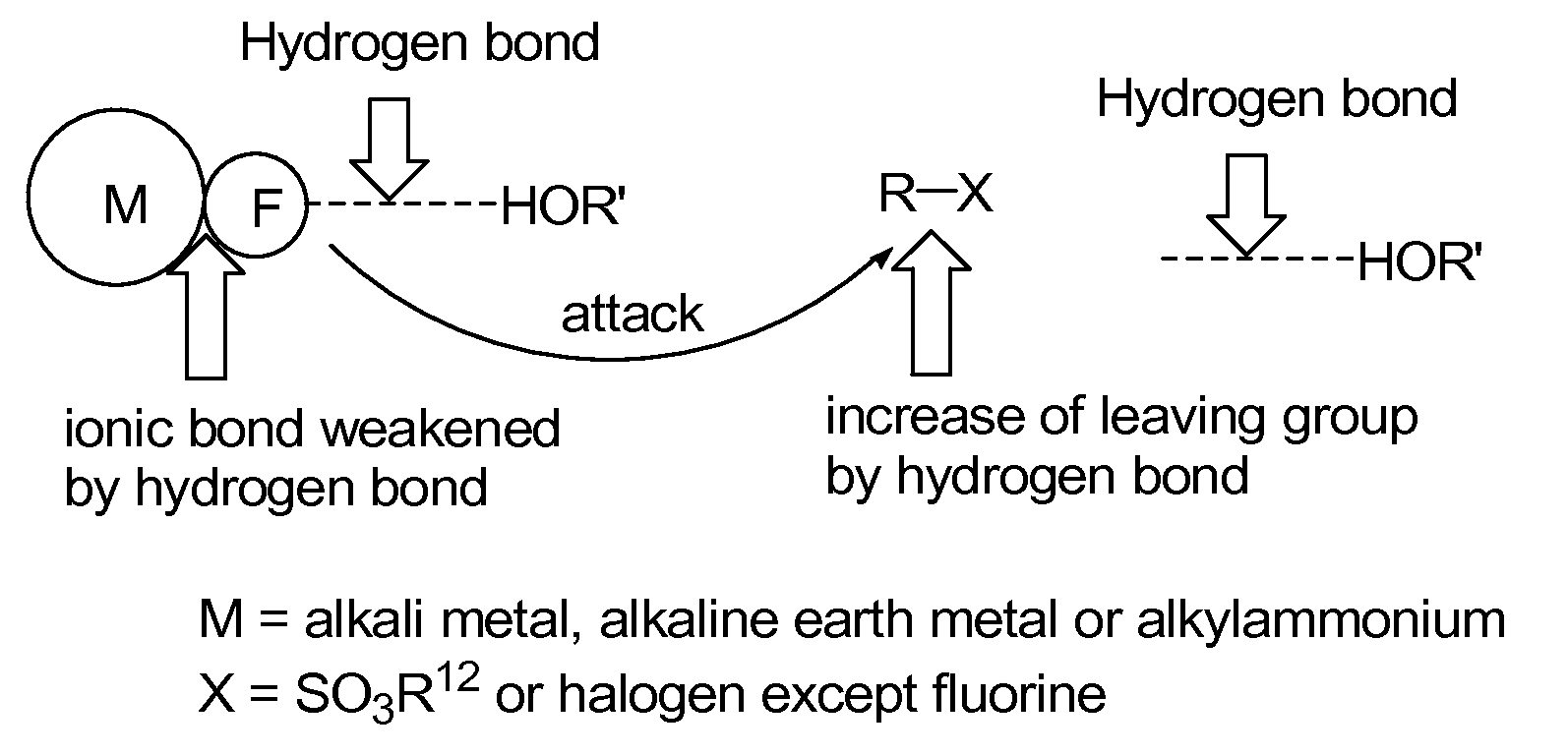
Method for preparation of organofluoro compounds in alcohol solvents
InactiveUS20100113763A1Inhibition formationReduced responseIsotope introduction to heterocyclic compoundsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsAlcoholIsotope
The present invention relates to a method for preparation of organofluoro compounds containing radioactive isotope fluorine-18. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for preparation of organofluoro compound [18F]florbetaben or [18F]AV-45 having <Chemistry Formula 11> and <Chemistry Formula 12>, respectively, by reacting fluorine salt containing radioactive isotope fluorine-18 with alkyl halide or alkyl sulfonate in the presence of alcohol of Chemistry Formula 1 as a solvent to obtain high yield of organofluoro compound. Synthesis reaction according to the present invention may be carried out under mild condition to give high yield of the organofluoro compounds and the reaction time is decreased, and thereby is suitable for the mass production of the organofluoro compounds.
Owner:FUTURECHEM +1
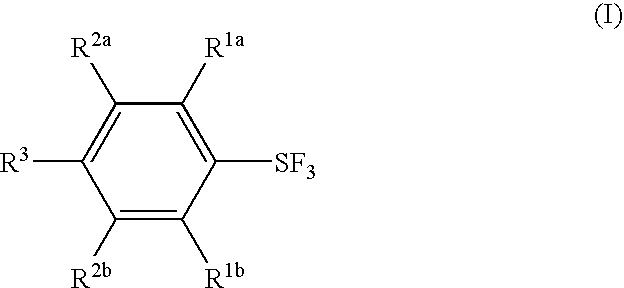
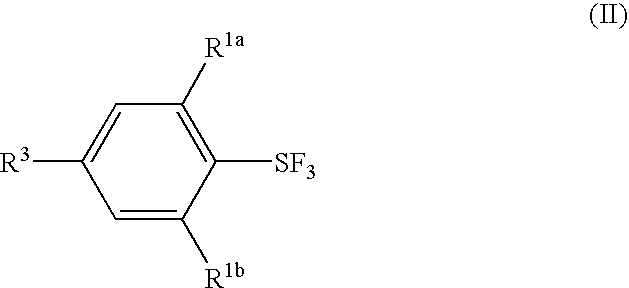
Substituted phenylsulfur trifluoride and other like fluorinating agents
ActiveUS7265247B1Significant comprehensive benefitsOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationTrifluorideCombinatorial chemistry
Novel substituted phenylsulfur trifluorides that act as fluorinating agents are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for their preparation and methods for their use in introducing one or more fluorine atoms into target substrate compounds.
Owner:UBE CORP
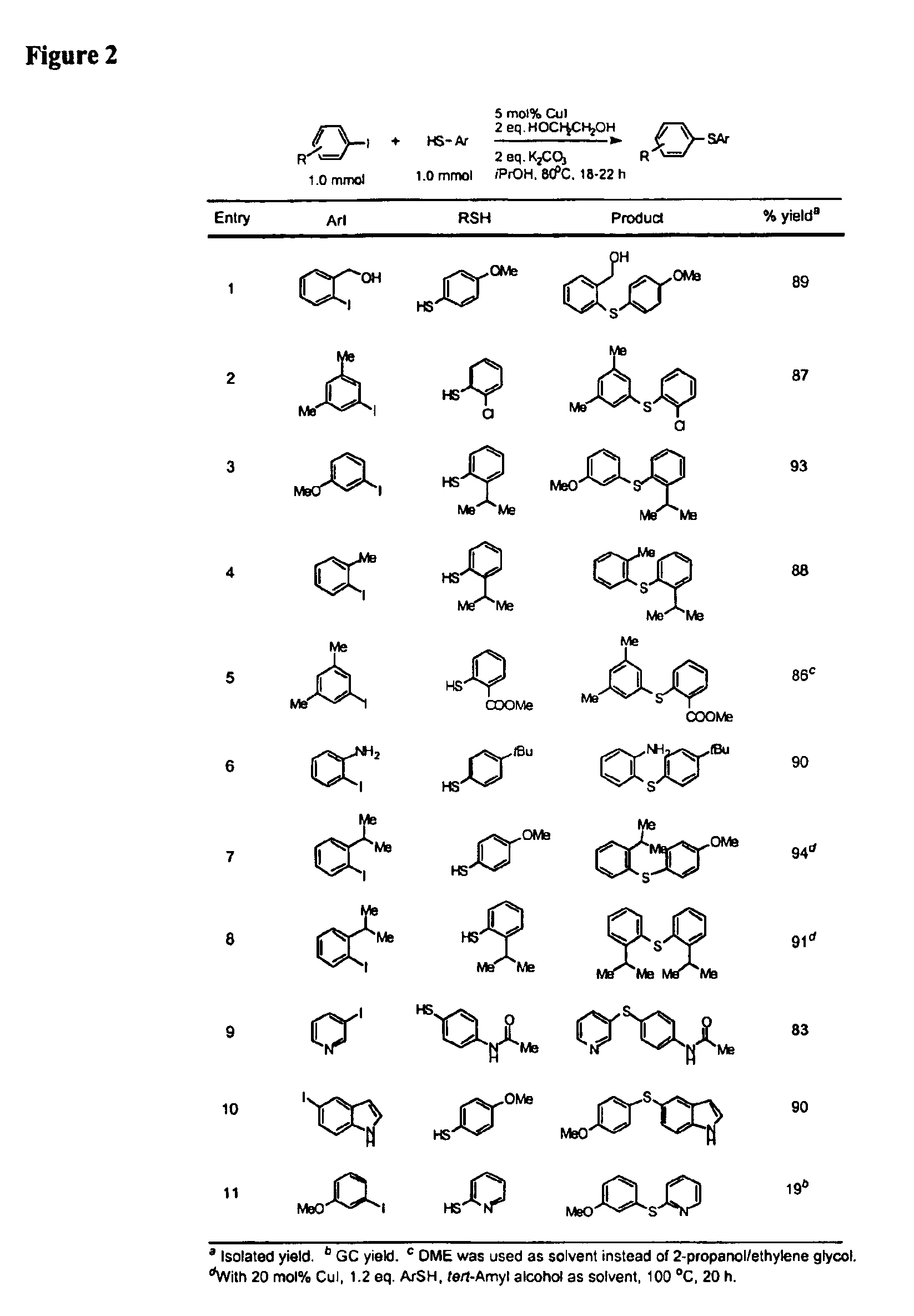
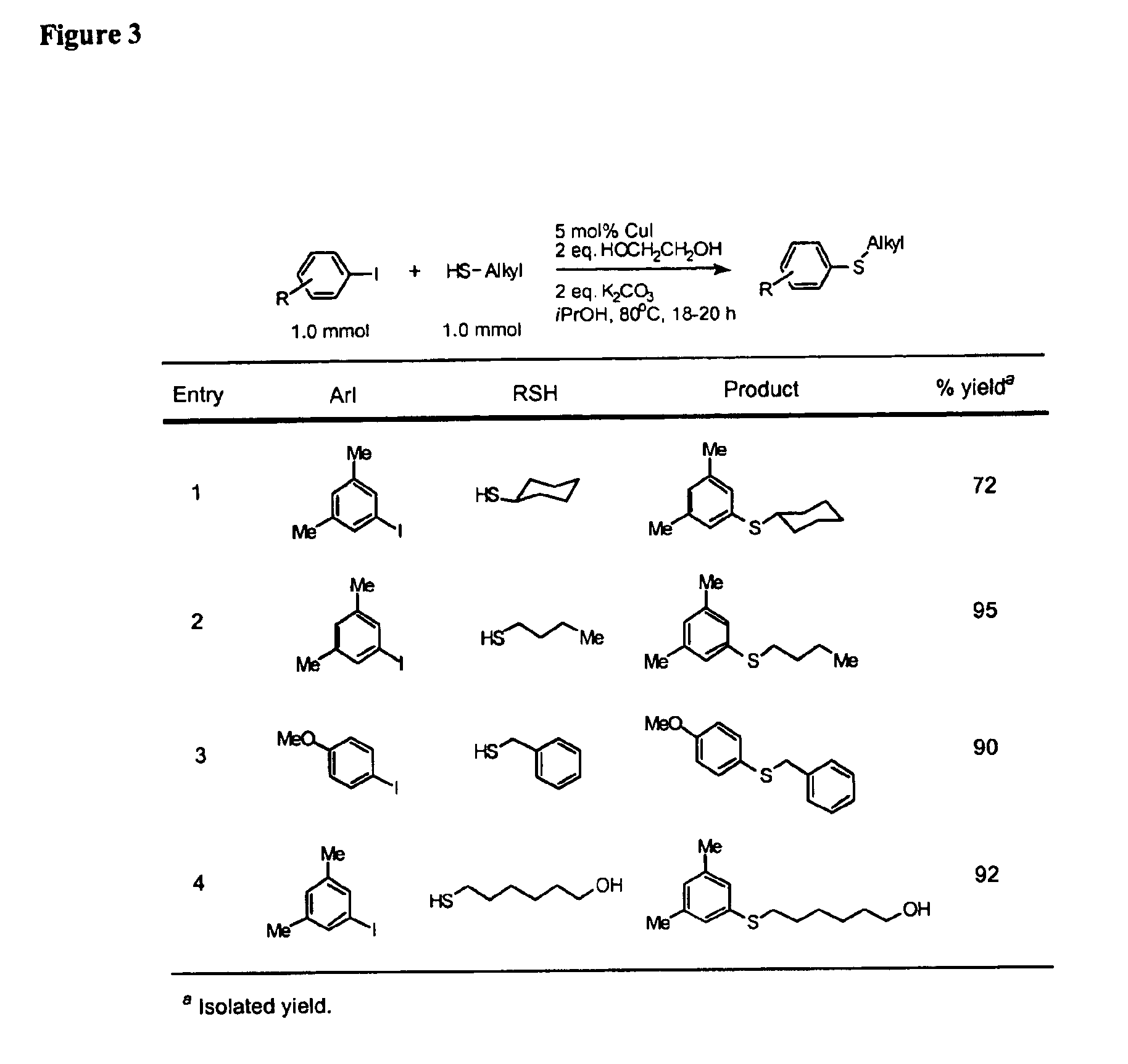
Copper-catalyzed formation of carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bonds
InactiveUS6888032B2Cheap and practicalLow costOrganic compound preparationThiol preparationCarbon–carbon bondSulfide
One aspect of the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed carbon-heteroatom and carbon-carbon bond-forming methods. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-sulfur bond between the sulfur atom of a thiol moiety and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In other embodiments, the present invention relates to copper(II)-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-nitrogen bond between the nitrogen atom of an amide and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In certain embodiments, the present invention relates to copper-catalyzed methods of forming a carbon-carbon bond between the carbon atom of cyanide ion and the activated carbon of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl halide or sulfonate. In another embodiment, the present invention relates to a copper-catalyzed method of transforming an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl chloride or bromide into the corresponding aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide. Yet another embodient of the present invention relates to a tandem method, which may be practiced in a single reaction vessel, wherein the first step of the method involves the copper-catalyzed formation of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide from the corresponding aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl chloride or bromide; and the second step of the method involves the copper-catalyzed formation of an aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl nitrile, amide or sulfide from the aryl, heteroaryl, or vinyl iodide formed in the first step.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Process for converting an alcohol to the corresponding fluoride
InactiveUS6248889B1Good choiceLow costOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationAlcoholOrganic base
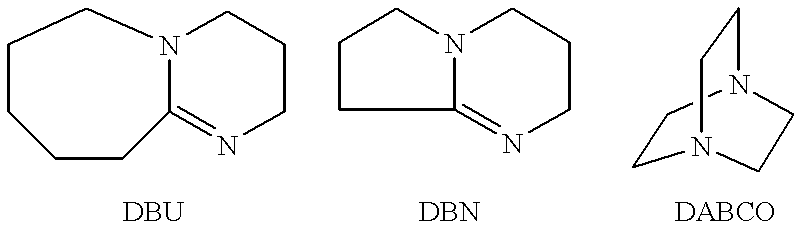
A process for preparing a fluoride from its corresponding alcohol comprises the steps of (a) forming a mixture comprising (i) at least one fluorinated, saturated aliphatic or alicyclic sulfonyl fluoride (for example, perfluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride) and (ii) at least one primary or secondary alcohol; and (b) adding a molar excess of at least one strong, aprotic, non-nucleophilic, hindered, double bond-containing, organic base (for example, 1,8-diazabicyclo[5.4.0]undec-7-ene (DBU)) to the mixture.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Microporous zirconium silicate for the treatment of hyperkalemia
ActiveUS8877255B2Reducing serum potassium levelPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsSide effectPotassium ions
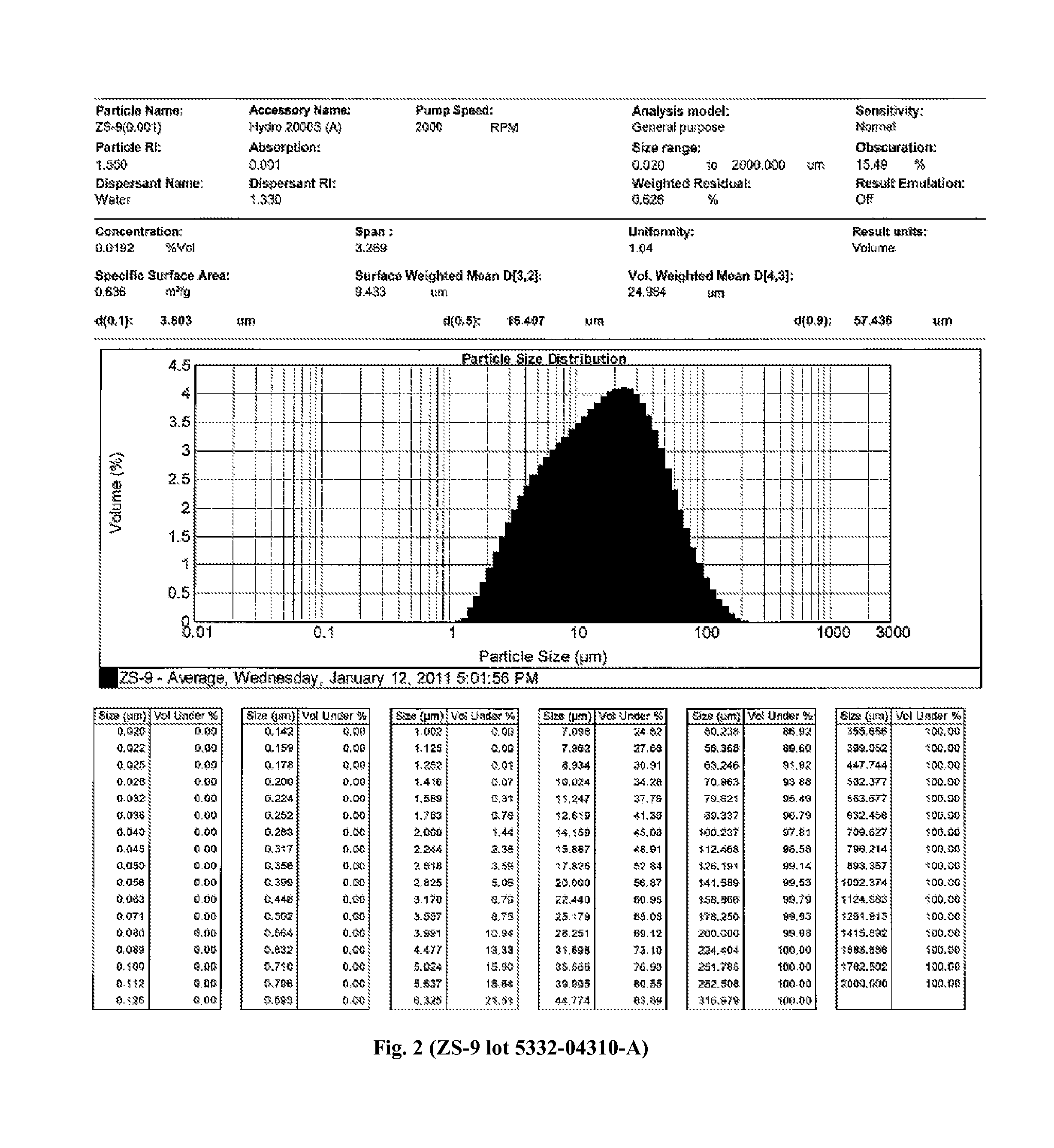
The present invention relates to novel microporous zirconium silicate compositions that are formulated to remove toxins, e.g. potassium ions, from the gastrointestinal tract at an elevated rate without causing undesirable side effects. The preferred formulations are designed avoid increase in pH of urine in patients and / or avoid potential entry of particles into the bloodstream of the patient. Also disclosed is a method for preparing high purity crystals of ZS-9 exhibiting an enhanced level of potassium exchange capacity. These compositions are particularly useful in the therapeutic treatment of hyperkalemia.
Owner:ZS PHARMA
Method of fluorinating a halogenated organic substance
InactiveUS20010049457A1High fluorine contentPreparation by halogen replacementOrganic halogenationFluorideOrganic matter
A method of fluorinating a halogenated organic substance comprising the steps of: introducing a germanium fluoride compound to a halogenated organic substance at a temperature between 250 and 320° C. to increase the fluorine content of the halogenated organic substance, thereby forming a fluorinated organic substance and a halogenated germanium compound, and separating the fluorinated organic substance and the halogenated germanium compound.
Owner:STEPHENS MATTHEW D
Method of fluorination
InactiveUS20060014972A1Short timeProcess safetyEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesLipid formationPolyol
A method of fluorination comprising reacting monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, composite saccharides formed by bonding of these saccharides with proteins and lipids and saccharides having polyalcohols, aldehydes, ketones and acids of the polyalcohols, and derivatives and condensates of these compounds with a fluorinating agent represented by general formula (I) thermally or under irradiation with microwave or an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength around the microwave region. In accordance with the method, the fluorination at a selected position can be conducted safely at a temperature in the range of 150 to 200° C. where the reaction is difficult in accordance with conventional methods. The above method comprising the irradiation with microwave or an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength around the microwave region can be applied to substrates other than saccharides. When a complex compound comprising HF and a base is reacted under irradiation with microwave, fluorination at a specific position which is difficult in accordance with conventional methods proceeds highly selectively, efficiently in a short time and safely.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
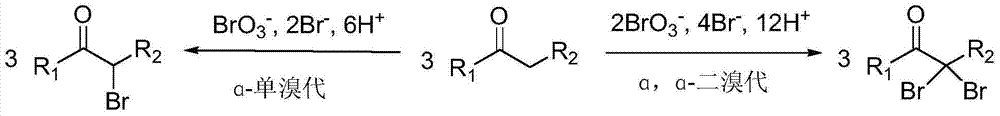
Method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds
InactiveCN104119211AIncrease profitHigh selectivity for brominationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationKetoneSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing alpha-monobrominated ketone and alpha, alpha-dibrominated ketone compounds by selectively brominating ketone compounds. The method comprises the steps of by taking ketone compounds as reactants, taking bromated and metal bromides in the presence of bromic acid or inorganic acid as brominating reagents and taking alcohol as a solvent, selectively brominating the ketone compounds into corresponding alpha-monobrominated ketone. The reaction has effects of high brominating selectivity, gentle reaction condition, high reaction velocity and high yield; the selected brominating reagents are cheap, easily available and low in toxicity; moreover, the method is high in bromine rate which is close to requirements of green chemistry, and therefore, the method is easy for industrial production and has good application prospect.
Owner:HUANGSHAN UNIV
Preparation of non-hazardous brominating reagents
InactiveUS6740253B2Easy to handleStable storageDispersed particle filtrationOrganic compound preparationAqueous sodium hydroxideBromate
The present invention relates to a non-hazardous brominating reagent from an aqueous alkaline bromine byproduct solution obtained from bromine recovery plant and containing 25 to 35% bromine dissolved in aqueous lime or sodium hydroxide containing alkali bromide and alkali bromate mixture having bromide to bromate stoichiometric ratio in the range of 5:1 to 5.1:1 or 2:1 to 2.1:1 and a pH ranging between 8-12 and also relates to a method for borminating aromatic compounds by using the above brominating agent.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Fluorinating reagents and their preparation
Owner:LANXESS DEUTDCHLAND GMBH
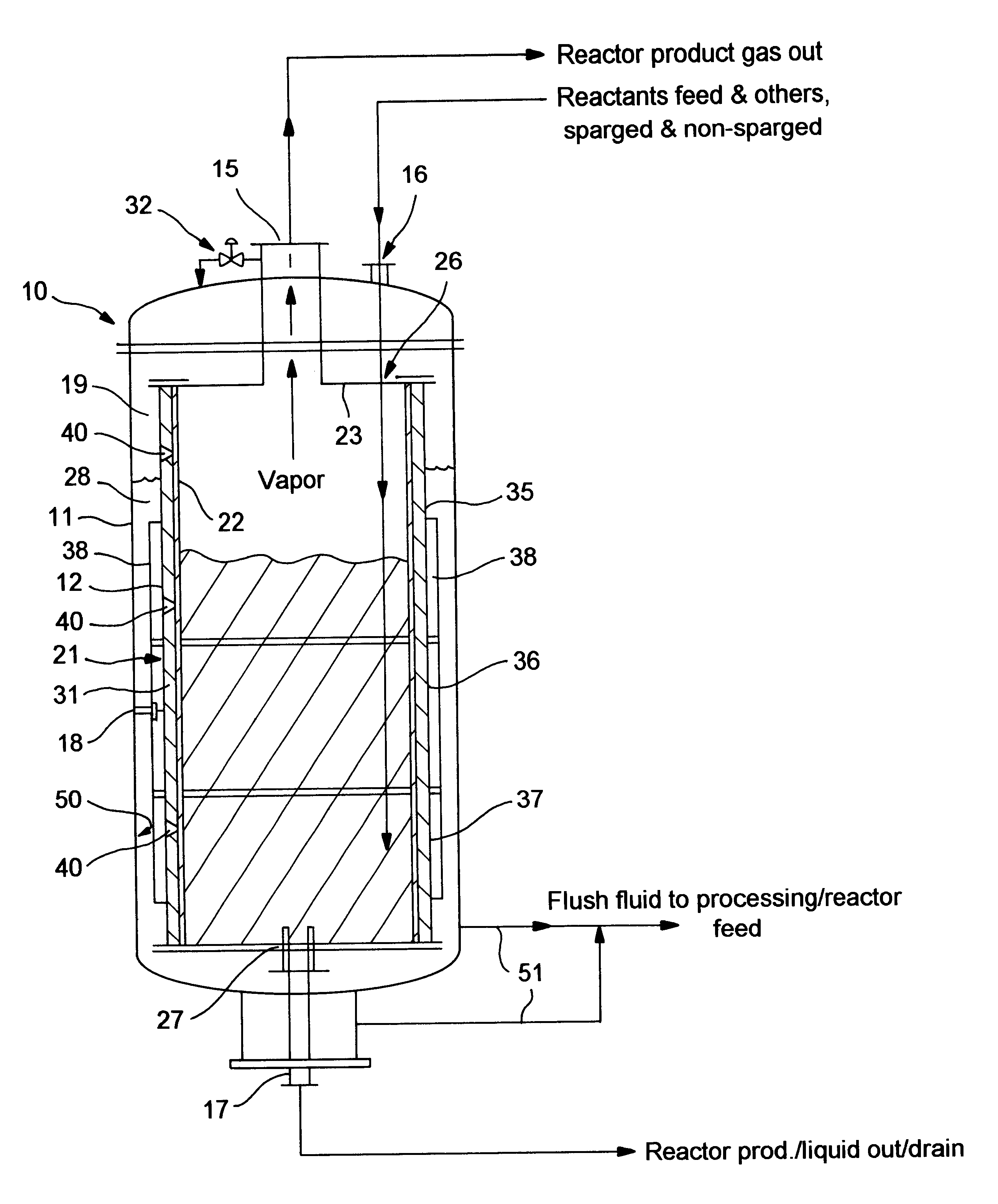
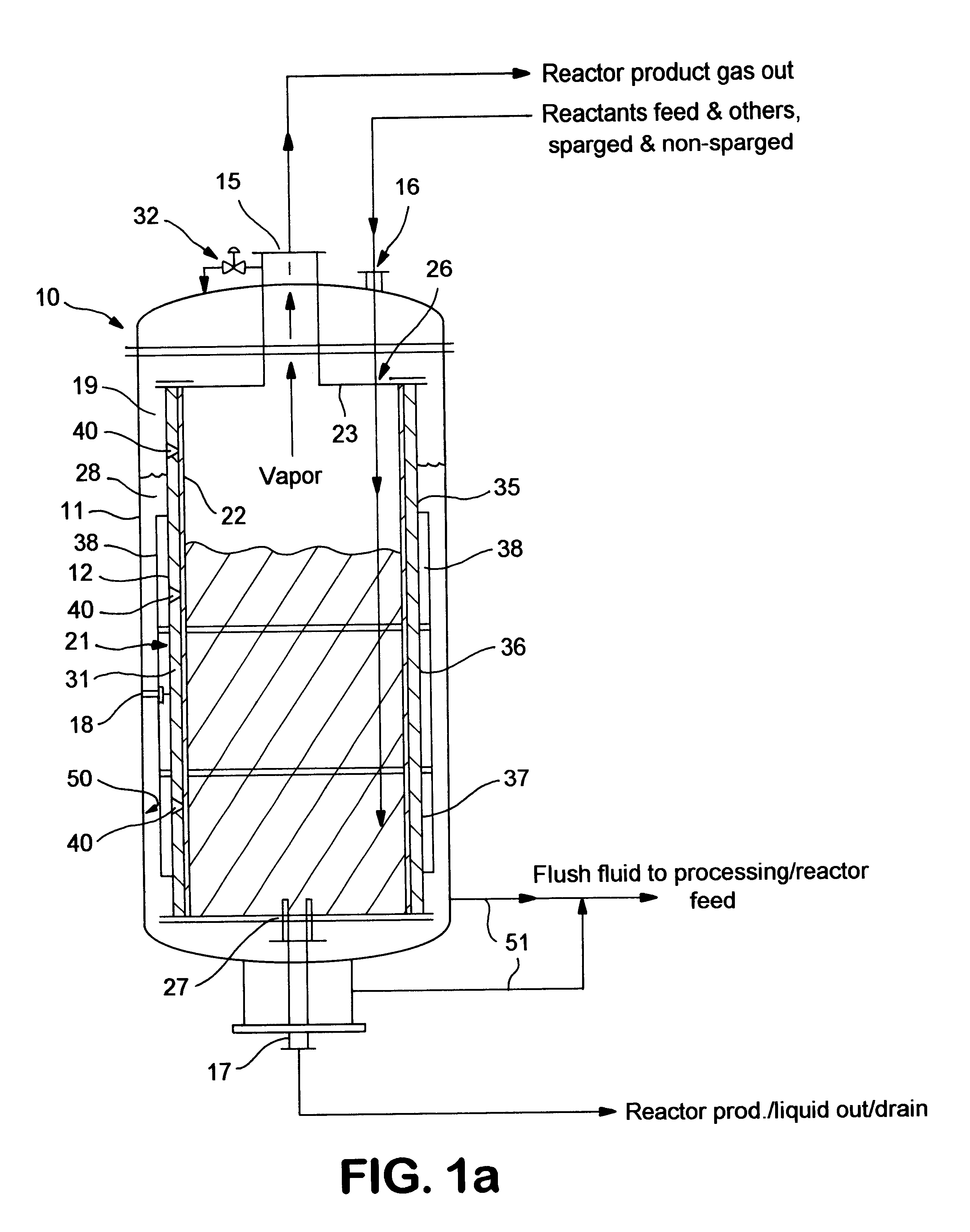
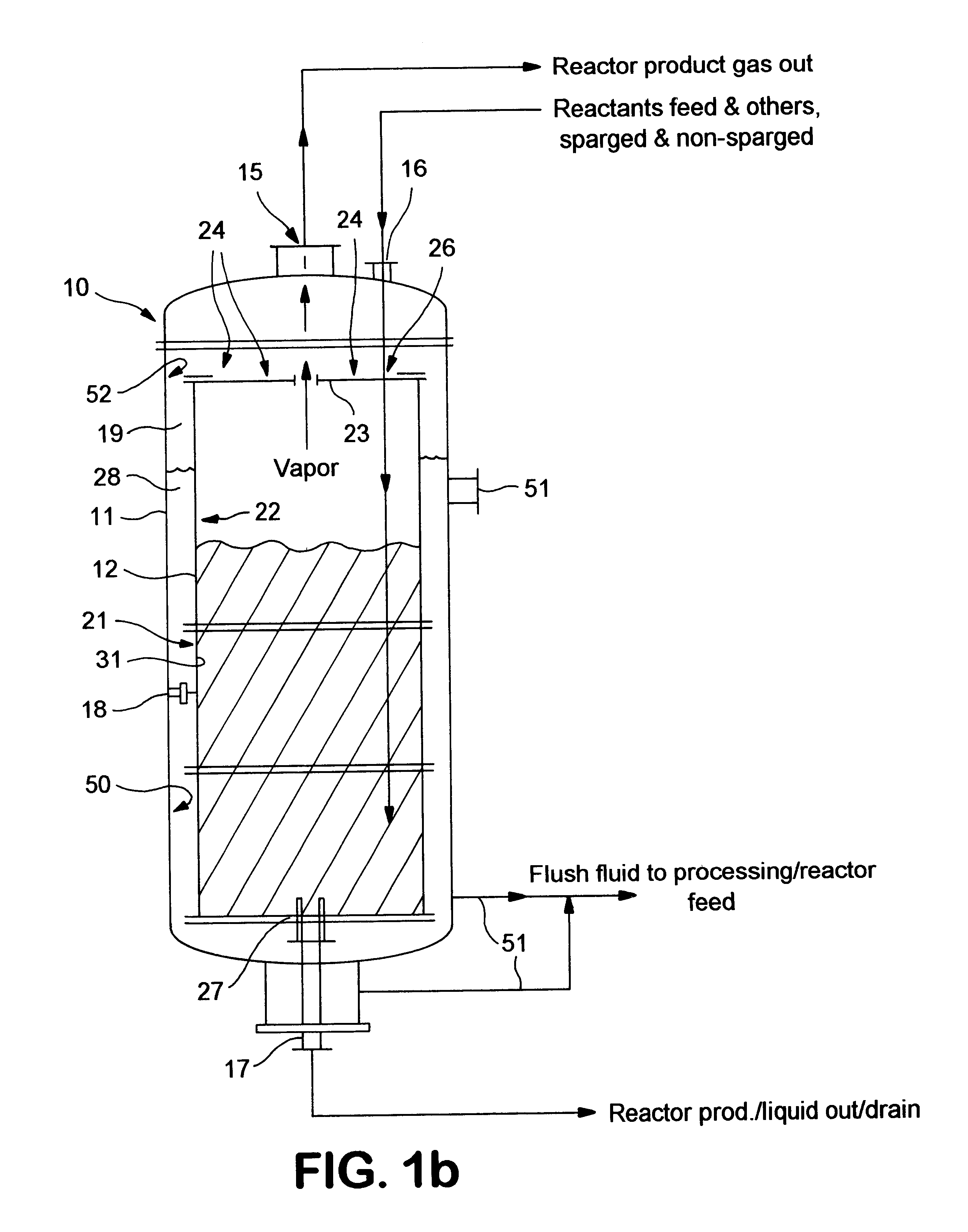
Fluoropolymer reactor with heat exchange jacket
InactiveUS6939521B1Improve heat transfer performanceIncrease heatPreparation by halogen replacementOrganic halogenationNuclear engineeringFluoropolymer
A reactor for fluorinating an organic compound comprising (a) an outer vessel; (b) a reactor vessel being disposed within said outer vessel to define an annular space, said reactor vessel at least partially comprising a fluoropolymer, said annular space being adapted to receive a fluid; (c) at least one pathway for introducing said heating fluid into said annular space; (d) at least one pathway for inputing reaction materials into said reactor vessel; and (e) at least one pathway for ouputing a product stream from said reactor vessel.
Owner:ALLIEDSIGNAL INC
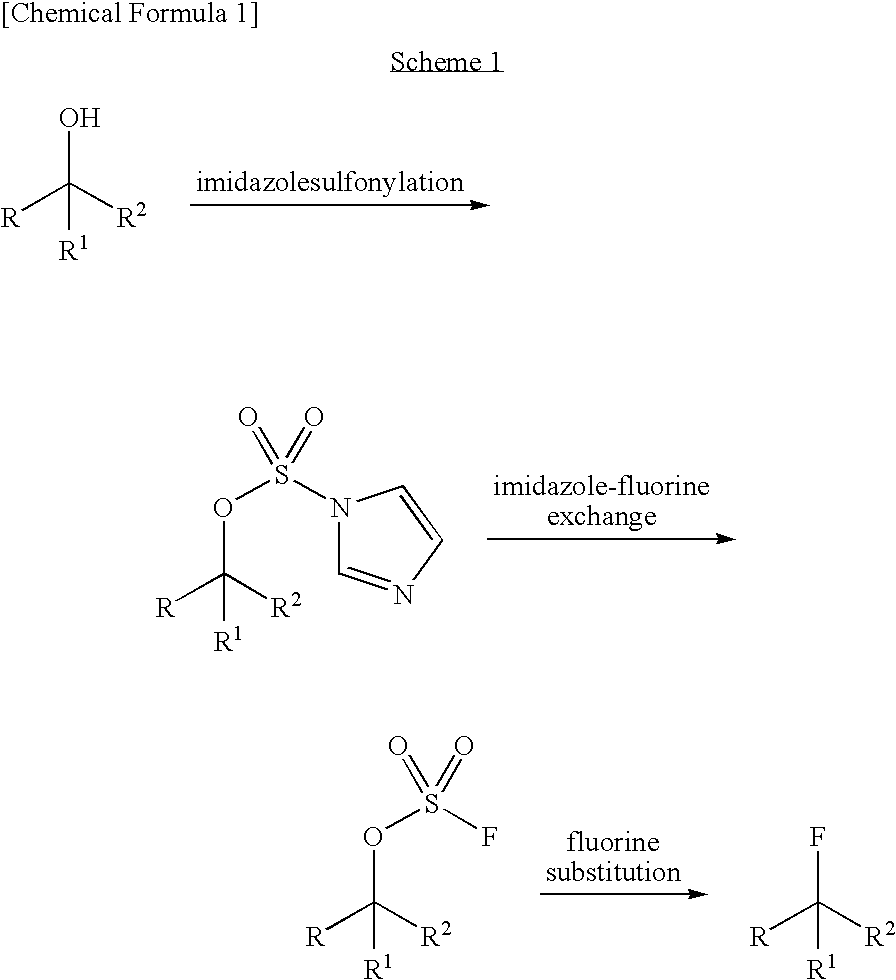
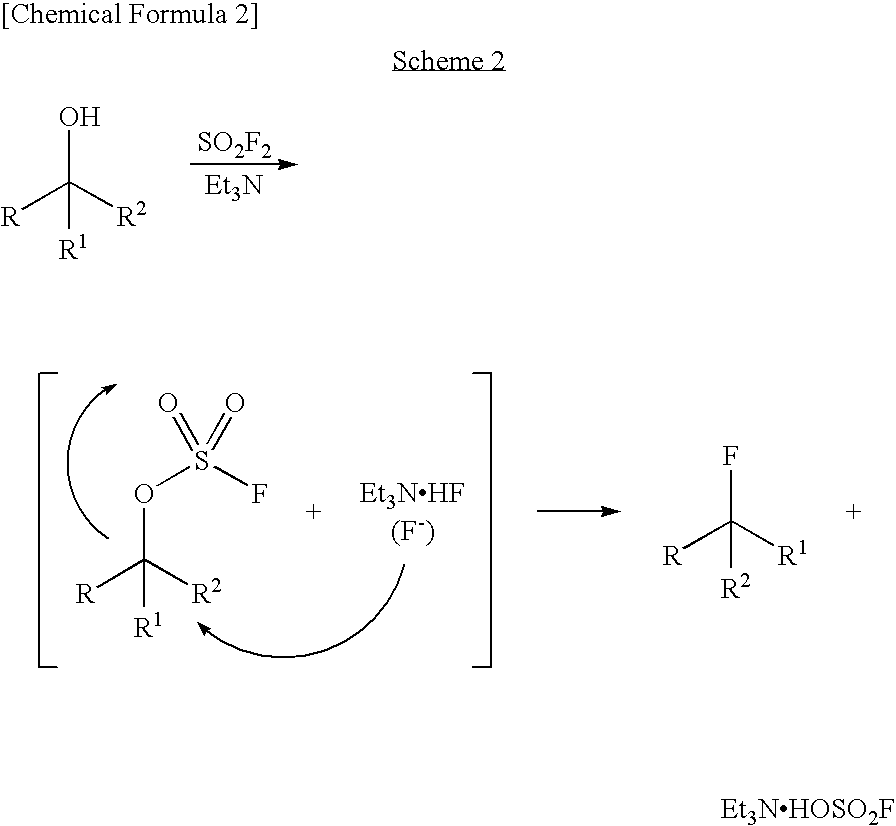
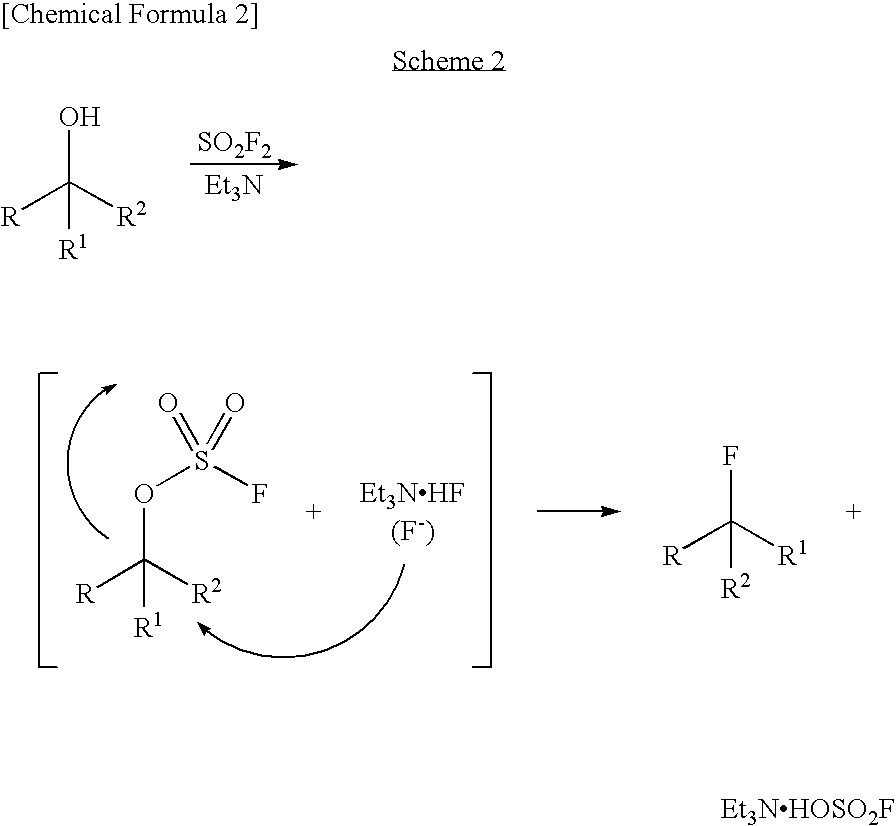
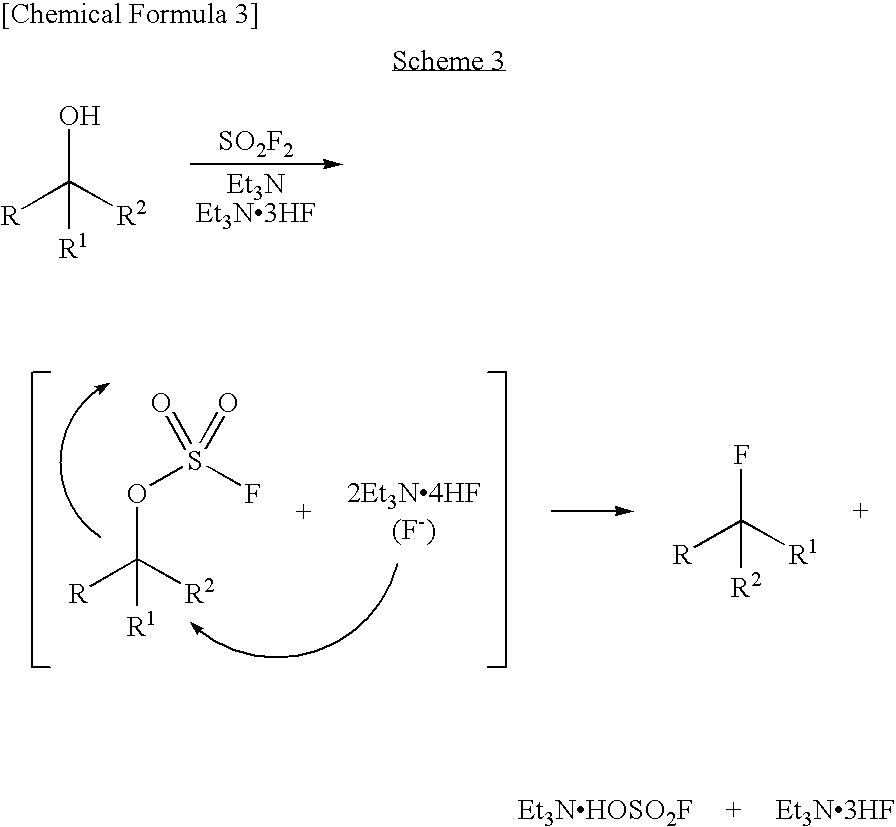
Process for Production of Fluoro Derivative
InactiveUS20080125589A1High selectivityEfficient productionSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationHydrogen fluorideOrganic base
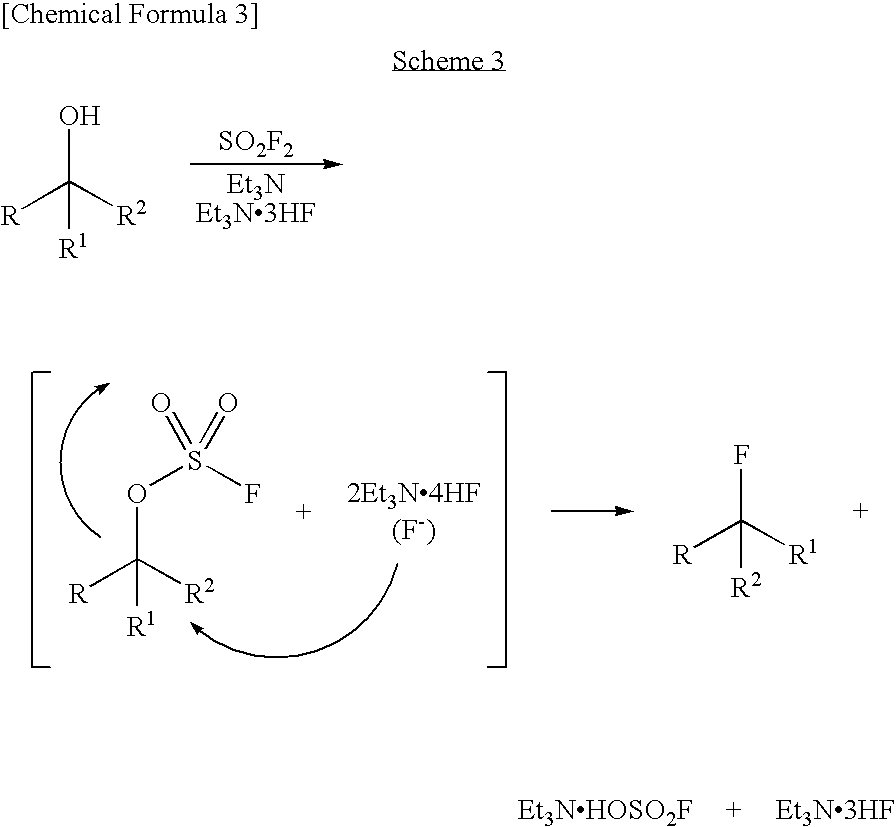
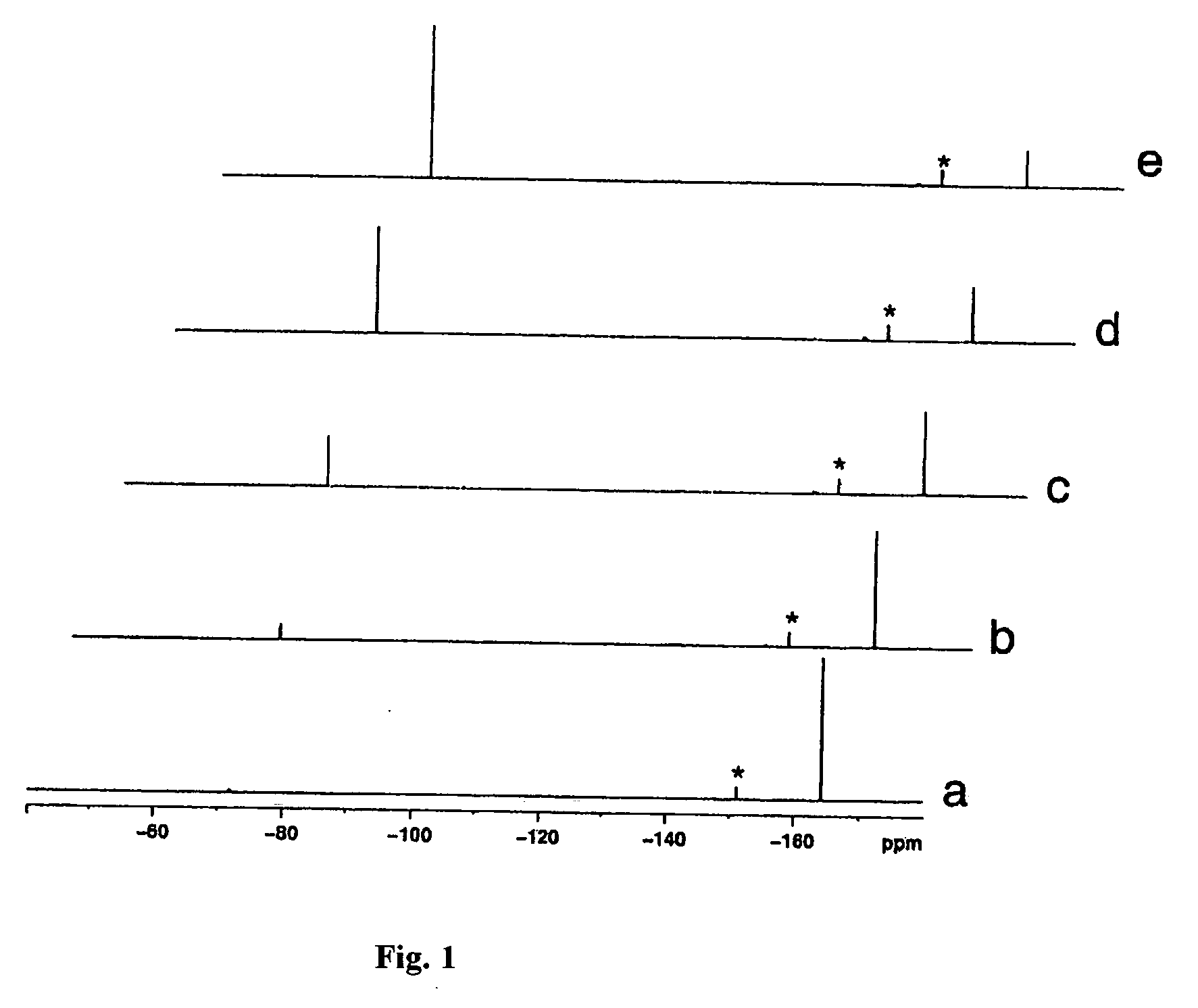
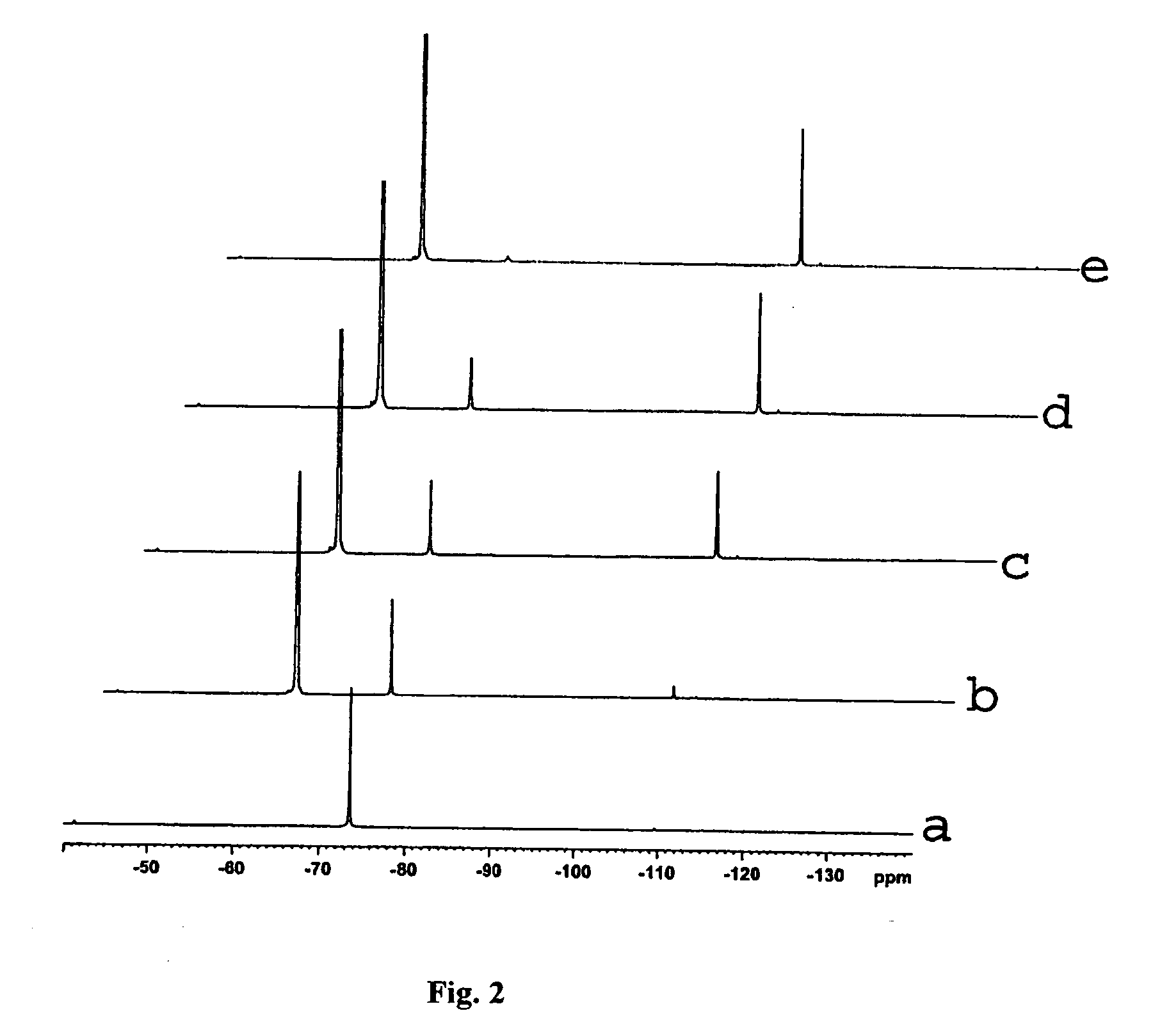
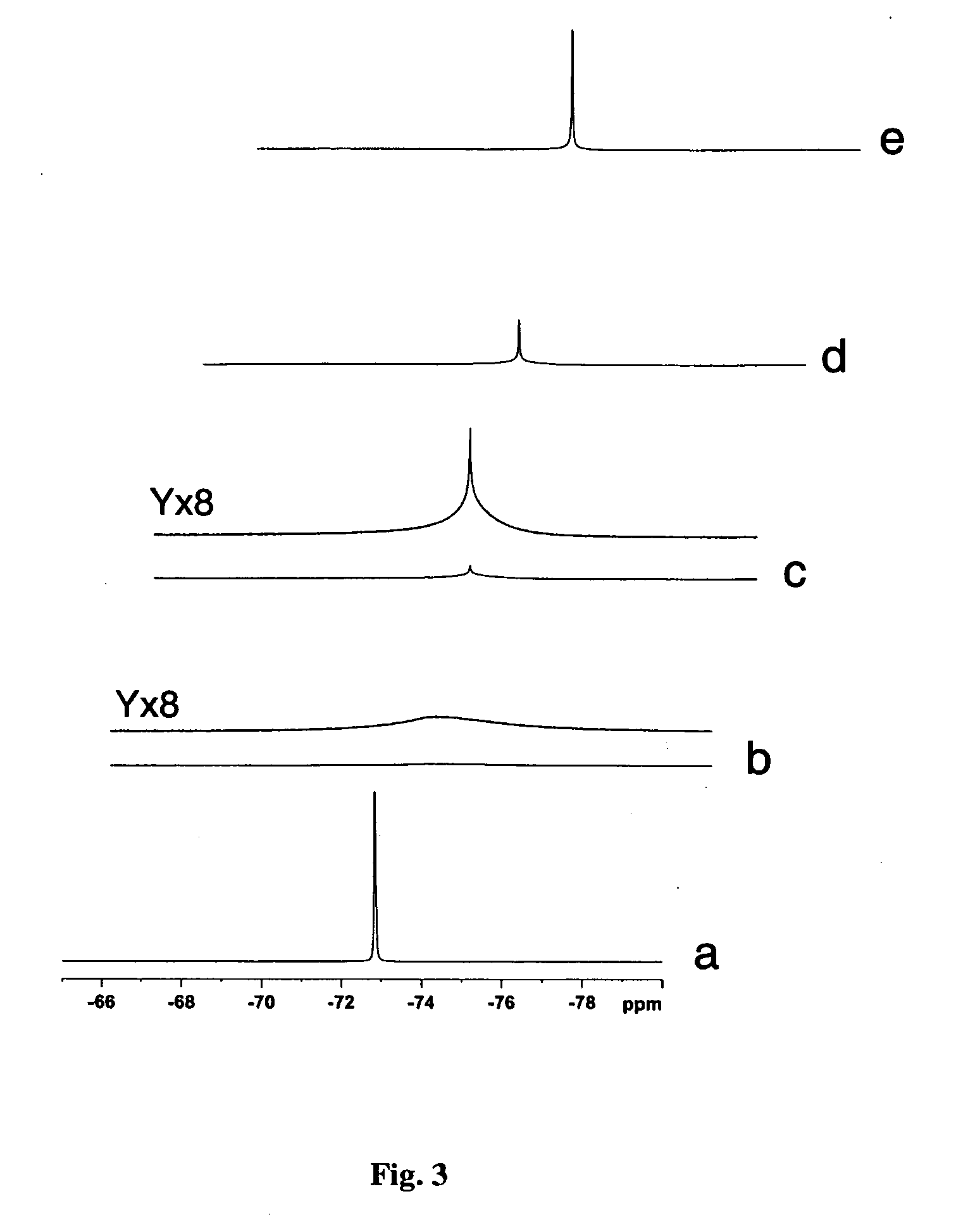
It was found that a fluoro derivative can be produced by reacting a hydroxy derivative with sulfuryl fluoride (SO2F2) in the presence of an organic base or in the presence of an organic base and “a salt or complex comprising an organic base and hydrogen fluoride”. According to the present production process, it is not necessary to use perfluoroalkanesulfonyl fluoride, which is not preferable in industrial use, and it is possible to advantageously produce optically-active fluoro derivatives, which are important intermediates of medicines, agricultural chemicals and optical materials, specifically 4-fluoroproline derivatives, 2′-deoxy-2′-fluorouridine derivatives, optically-active α-fluorocarboxylate derivatives, and the like, even in a large scale.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Anhydrous flouride salts and reagents and methods for their production
ActiveUS20060089514A1Organic compound preparationOrganic halogenationSimple Organic CompoundsIsotope
Anhydrous organic fluoride salts and reagents prepared by a method comprising the nucleophilic substitution of a fluorinated aromatic or fluorinated unsaturated organic compound with a salt having the formula: [QnM]x+Ax−in an inert polar, aprotic solvent; wherein M is an atom capable of supporting a formal positive charge, the n groups Q are independently varied organic moieties, n is an integer such that the [QnM] carries at least one formal positive charge, x is an integer defining the number of formal positive charge(s), +, carried by the [QnM], A− is an anionic nucleophile capable of substituting for F in the fluorinated compound and F represents fluorine or a radioisotope thereof.
Owner:NUTECH VENTURES
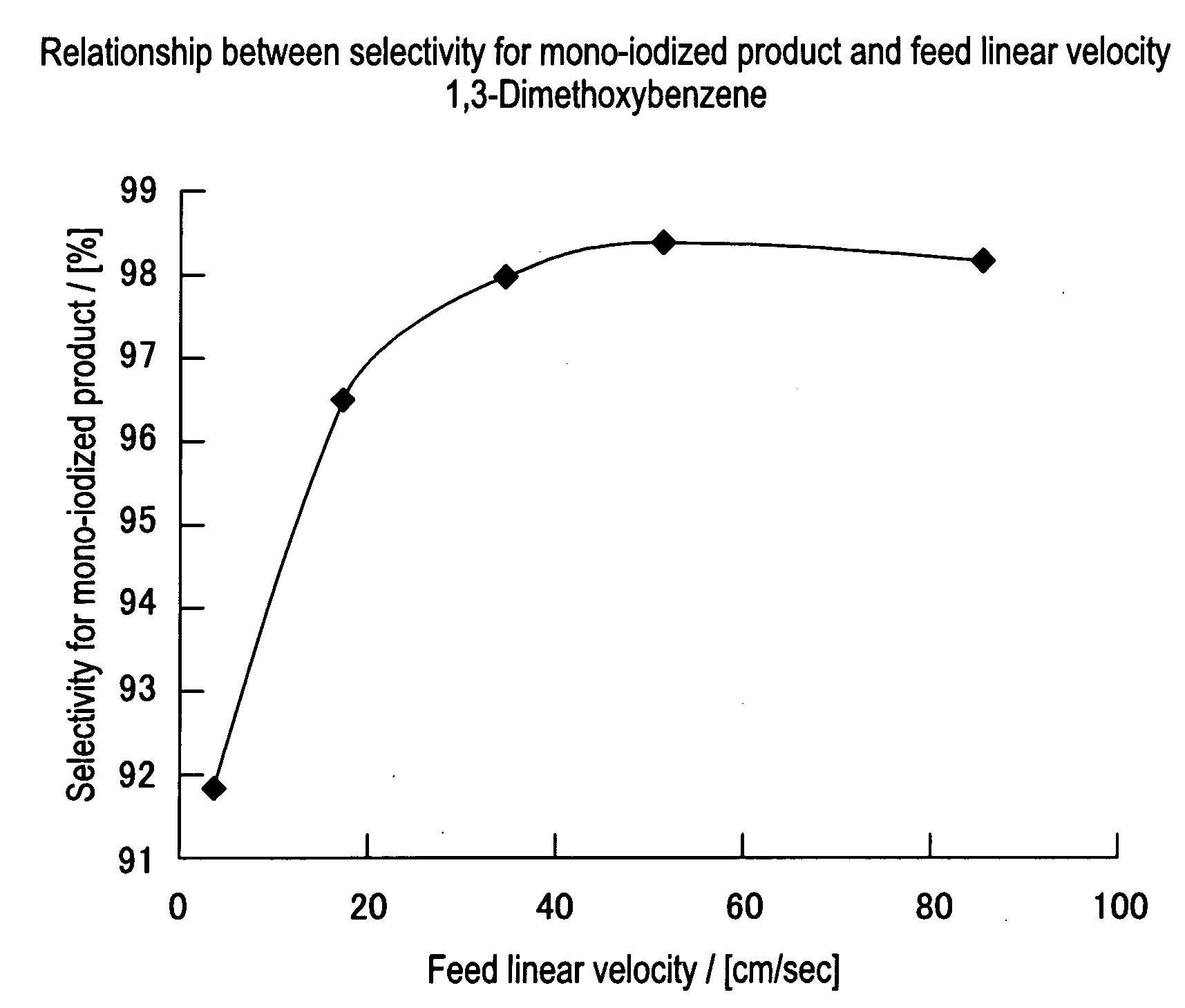
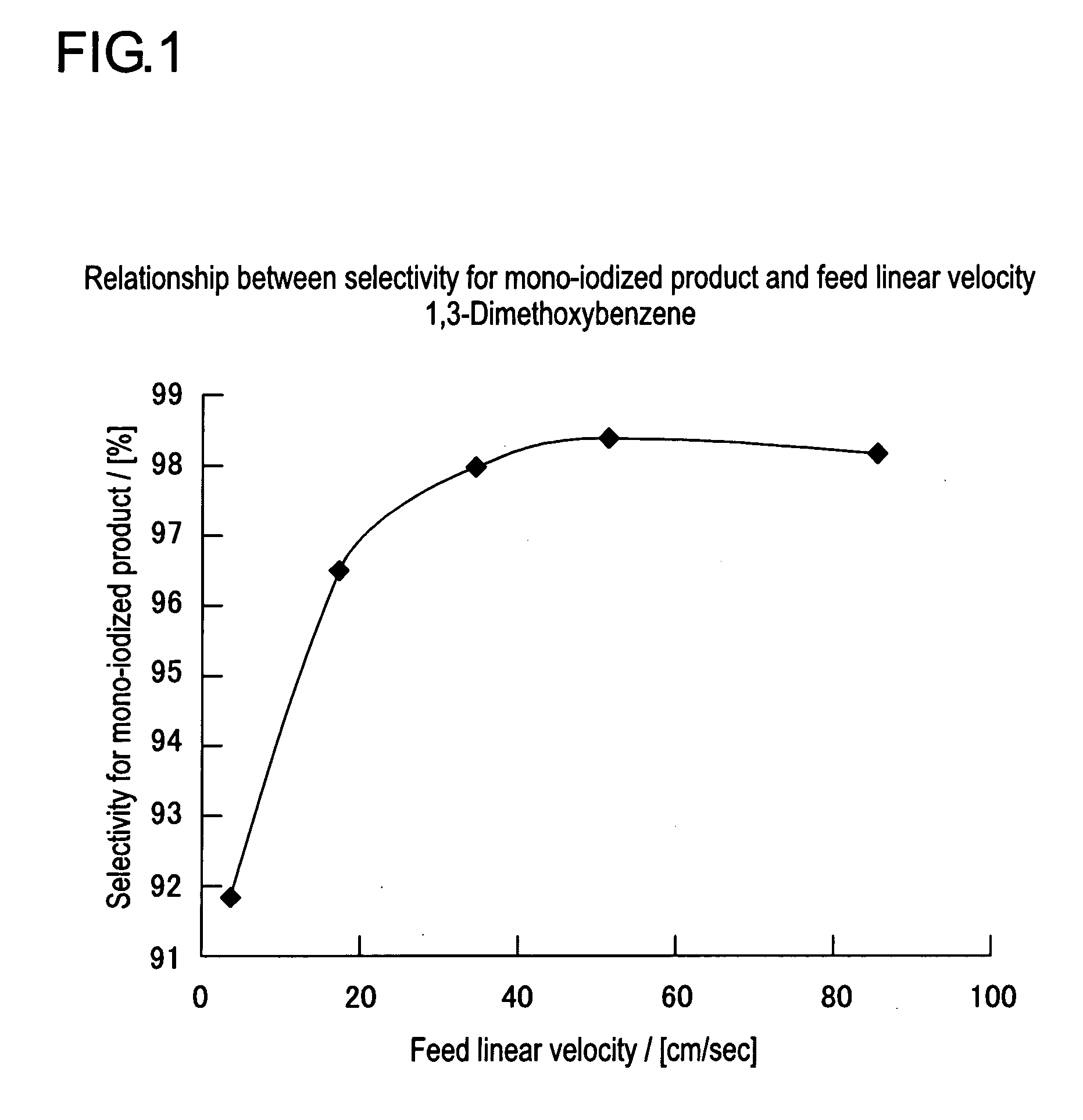
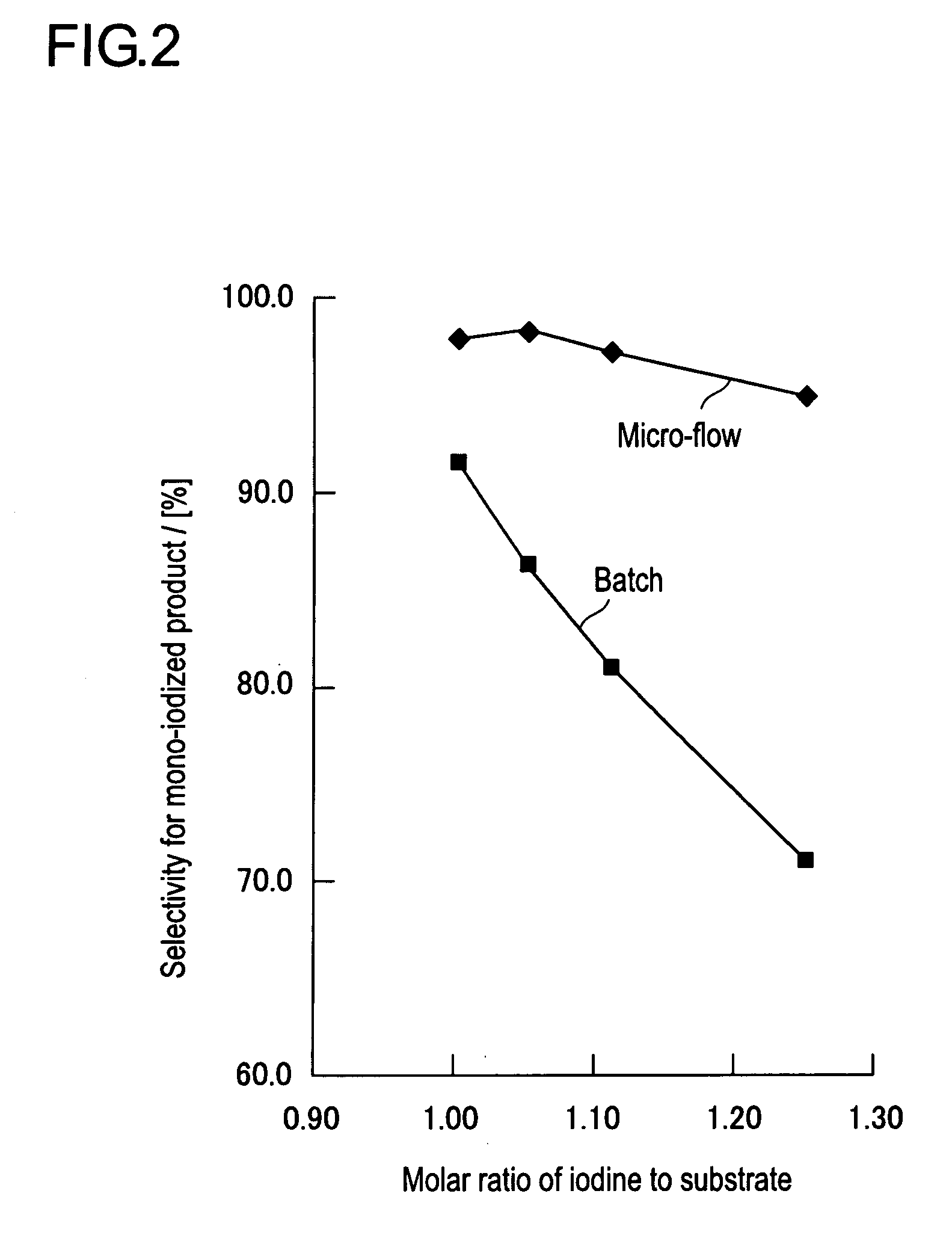
Method for Producing Aromatic Iodides
InactiveUS20080146853A1Excellent toneHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationIodideChemistry
The present invention is directed to provide a means, which enables production of a product superior in color tone in high yield by using an easy-to-handle and highly safe technique, in a method for producing an aromatic iodide. The present invention relates to a method for producing an aromatic iodide, characterized in that an aromatic compound and an active iodinating agent are fed into a flow reactor equipped with a high-speed mixer and hydrogen atom on the aromatic ring of said aromatic compound is continuously substituted by iodine atom.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
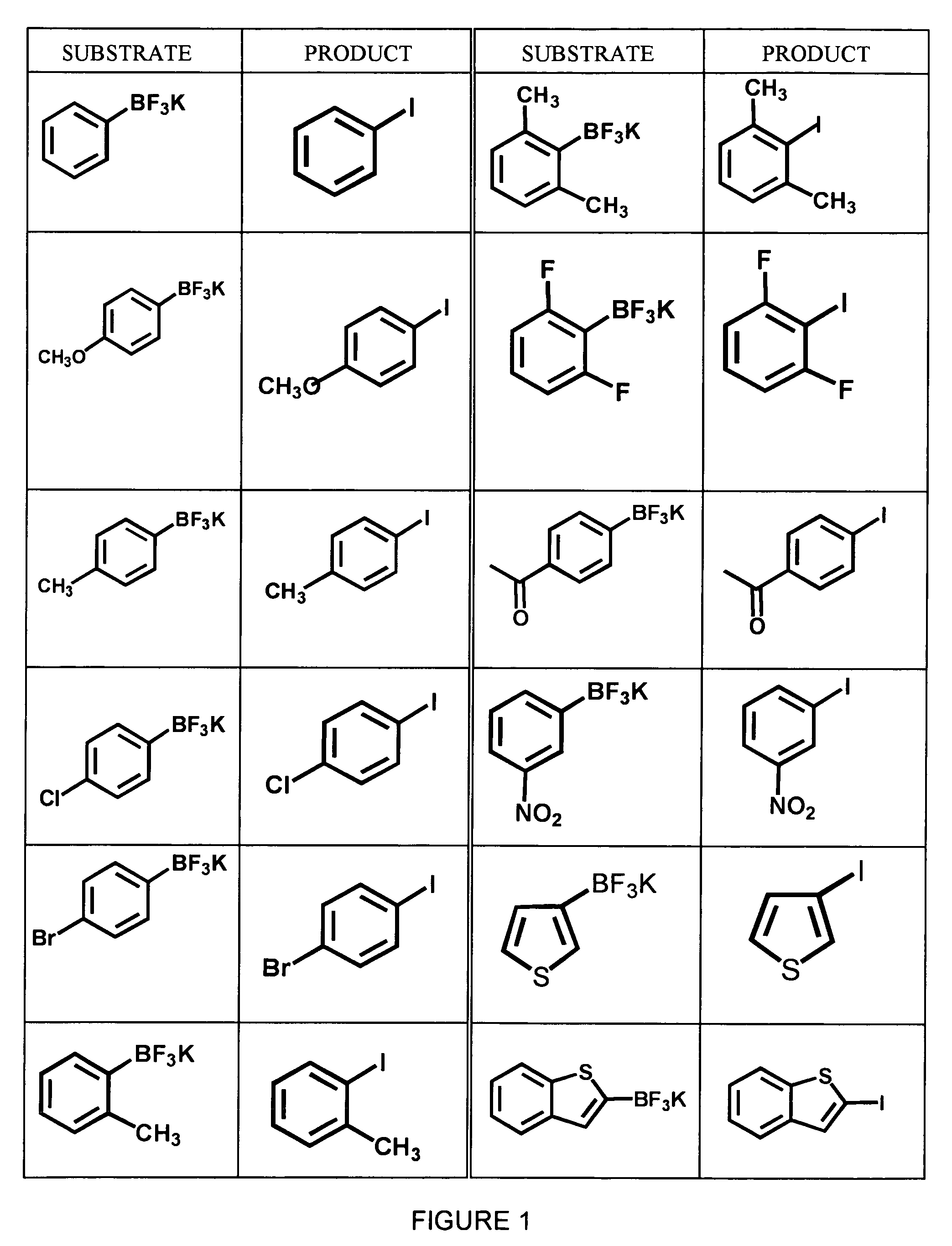
Method for halogenating or radiohalogenating a chemical compound
InactiveUS7041859B1Avoid error introductionCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationChemical compoundOrganic compound
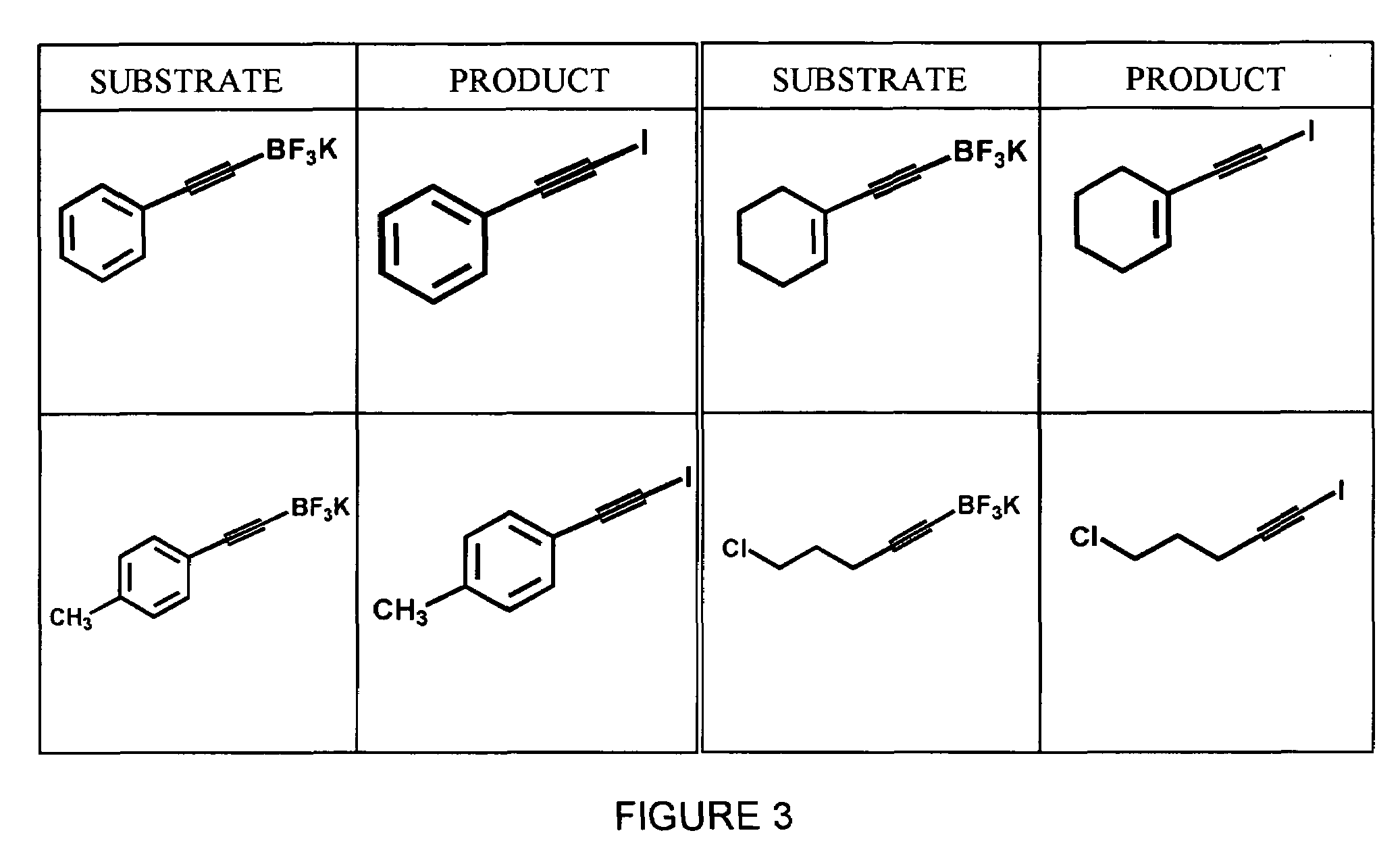
A method for obtaining a halogenated organic compound, whereby an organotrifluoroborate compound is reacted with a halide ion in the presence of an oxidizing agent to produce the corresponding halogenated organic compound. The method may be used for producing radiohalogenated organic compounds.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Decarboxylation and fluorination method for carboxylic acid
ActiveCN102675015AOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarbon–fluorine bondRoom temperature
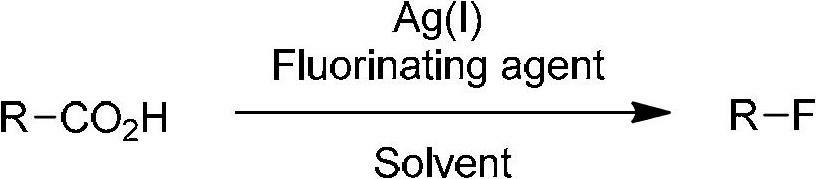
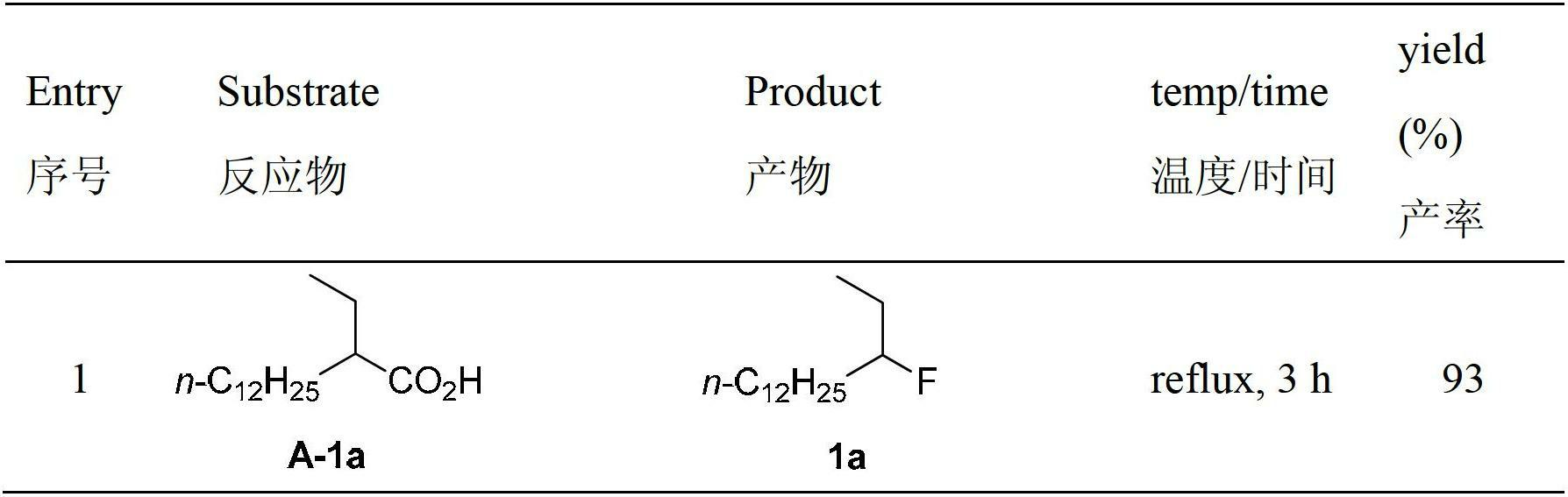
The invention relates to a decarboxylation and fluorination method for carboxylic acid. According to the method, fatty acid RCOOH, monovalent silver salt catalyst and fluorinated reagent Selectfluor or hexafluorophosphate derivative thereof are reacted in a solvent at the temperature of between room temperature and 80 DEG C to obtain RF; and by adopting the method, the carboxylic acid is efficiently converted into corresponding decarboxylated and fluorinated product in an aqueous phase. The method is mild in reaction conditions and easy to operate, has good chemical selectivity and functional group compatibility, and is a very practical sp<3> carbon-fluorine bond synthesizing method.
Owner:上海睿瓦科技有限公司
Fluorination Processes with Arylsulfur Halotetrafluorides
InactiveUS20110160488A1Improve stabilityPrevent degradationOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationTrifluorideCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:UBE IND LTD
Method of fluorination
A method of fluorination comprising reacting monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, composite saccharides formed by bonding of these saccharides with proteins and lipids and saccharides having polyalcohols, aldehydes, ketones and acids of the polyalcohols, and derivatives and condensates of these compounds with a fluorinating agent represented by general formula (I) thermally or under irradiation with microwave or an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength around the microwave region. In accordance with the method, the fluorination at a selected position can be conducted safely at a temperature in the range of 150 to 200° C. where the reaction is difficult in accordance with conventional methods. The above method comprising the irradiation with microwave or an electromagnetic wave having a wavelength around the microwave region can be applied to substrates other than saccharides
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
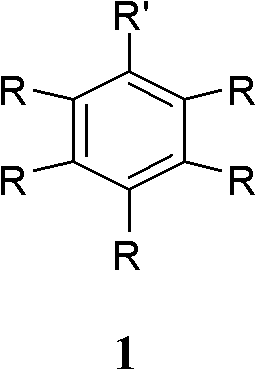
Green synthesizing method of aryl bromide
ActiveCN101857518AReduce usageImprove economyCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationArylHalogen
The invention discloses a green synthesizing method of aryl bromide. The synthesizing method comprises the step of carrying out bromination on an aromatic compound of which the structure is shown as a formula (1) to prepare the aryl bromide by using hydrogen bromide as a brominating agent, using copper nitrate as a catalyst and using molecular oxygen as an oxidant, wherein in the formula (I), R is hydrogen; substituent groups R1, R2, R3, R4 and R5 are respectively independently selected from hydrogen, hydroxy, amino, C1 to C8 alkoxy, single C1 to C8 alkyl amino, double C1 to C8 alkyl amino, C1 to C12 alkyl, C6 to C12 aryl, C1 to C8 acyloxy, C1 to C8 acylamino, halogen, nitryl, cyan, carboxyl and C1 to C8 acyl or C1 to C8 carbalkoxyl group; and at least one substituent group of R1, R2, R3,R4 and R5 is hydroxy, amino, C1 to C8 alkoxy, single C1 to C8 alkyl amino, double C1 to C8 alkyl amino, C1 to C8 acyloxy, C1 to C8 acylamino or C1 to C12 alkyl. The synthesizing method of the invention has the advantages of wide application range and high atom utilization, avoids using an organic solvent and has the characteristics of economy and environment protection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
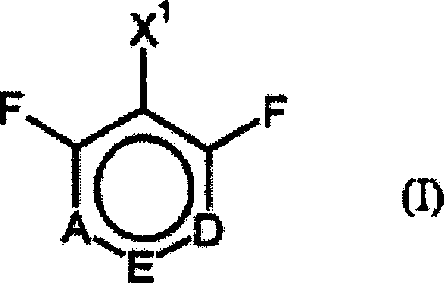
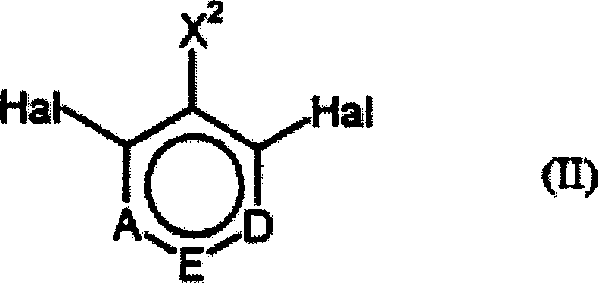
Process for preparing ring-fluorinated aromatics
The invention is directed to an improved process for preparing a ring-fluorinated aromatic compound of a general formula (I), which is performed by a halogen conversion reaction (Halex reaction) of various halogen substituents in a one-step reaction and in the presence of a catalyzer.
Owner:SALTIGO GMBH
A kind of method that adopts oxidative halogenation method to prepare haloaryl compound
InactiveCN102260127AGood choiceHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationPtru catalystOrganosolv
The invention discloses a method for preparing halogenated aryl compounds through oxidation and halogenation. In the method, chlorine gas, bromine water or elementary iodine are prevented from serving as a halogenating agent, and in an aqueous phase or ionic liquid reaction medium, bidirectional ionic liquid is taken as a catalyst, hydrogen peroxide (commercial 30 percent aqueous solution) is taken as an oxidant, aryl compounds and halogeno salt (or haloid acid) are subjected to oxidation and halogenation to form the halogenated aryl compounds. The method is a green synthesis method; and the prepared halogenated aryl has high selectivity and yield, reaction conditions are mild, volatile organic solvents are not needed in the reaction, and the catalyst can be recycled.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
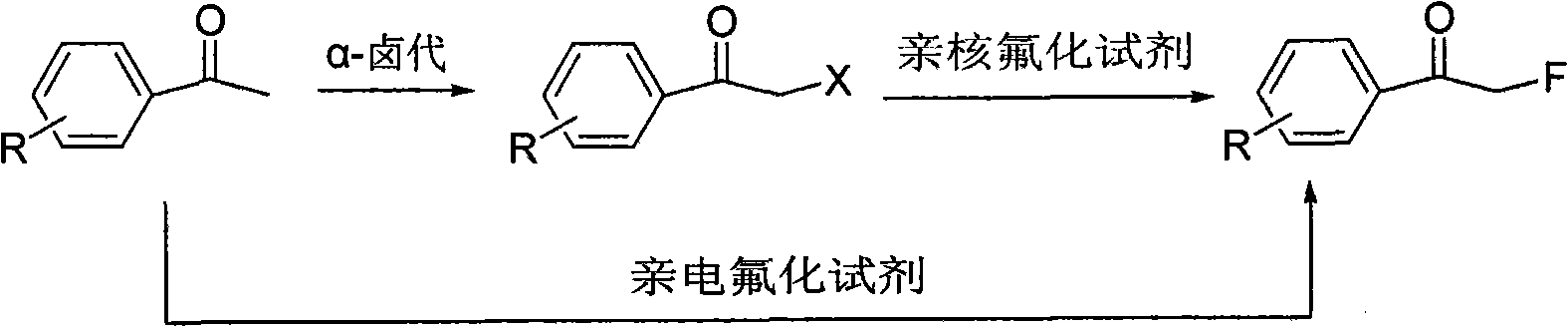
Method for directly preparing alpha-fluoro acetophenone by acetophenone one-pot method
InactiveCN101665394ALower synthesis costEfficiently obtainedCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationAcetophenoneReagent
The invention discloses a method for directly preparing alpha-fluoro acetophenone by an acetophenone one-pot method, comprising the following steps: firstly preparing eutectic mixture, and sequentially adding acetophenone compound and alpha-halogenated reagent to react for 3-5h under the condition of 10-100 DEG C; and then, adding nucleophilic fluorinating agent to react for 5-10h under the condition of 50-150 DEG C, wherein the using quantity of the alpha-halogenated reagent is 0.5-2.0 times molar weight of the acetophenones compound, the using quantity of the nucleophilic fluorinating agentis 1-10 times molar weight of the the acetophenones compound, and the molar weight ratio between the eutectic mixture and the acetophenones compound is 5:1-1:1. The method directly utilizes various easily obtained acetophenones compounds as raw material, and the alpha-halogenation reaction is combined with nucleophilic fluorination reaction to realize the one-pot method for effectively obtaining the alpha-fluoro acetophenones compound; furthermore, the method has mild reaction condition and simple method, reduces the cost for synthesizing the alpha-fluoro acetophenones compound and has betterindustrialization prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Continuous neutralizer mixer reactor and a continuous process for quenching chlorination reaction mixture in production of chlorinated sucrose
An improved process of production of a chlorinated sugar is described comprising chlorination of a partially protected sugar, wherein quenching as well as neutralization of chlorinated reaction mass is carried out concurrently and continuously in a reactor which is a continuous mixer as well as quencher providing continuous mixing of chlorination reaction mixture and pH adjusting solution and also provides for continuous quenching and continuous removal of quenched chlorinated reaction mixture.
Owner:V B MEDICARE PVT LTD
Method for synthesizing alpha-brominated aromatic ketones compound
ActiveCN102503751AAvoid pollutionAvoid harmOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationOrganic solventHazardous substance
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing an alpha-brominated aromatic ketones compound. The method comprises the following steps: taking an aromatic ketones compound as a substrate, hydrogen bromide as a brominating agent, copper nitrate as a catalyst, oxygen or air as an oxidizing agent and water as a solvent; performing brominating reaction at 25-100 DEG C; and after finishing the reaction, post-processing the reaction solution, thereby obtaining the alpha-brominated aromatic ketones compound. According to the method, water is taken as the solvent, so that the pollution and harm to the environment during a producing, recycling or discharging process caused by an organic solvent are avoided; the method is an environment-friendly green synthesizing technology; the hydrogen bromide is taken as the brominating agent, so that the operation is conveniently and easily controlled, the final reaction products are only alpha-bromoketone and water, no other harmful matter is generated and the defects of the prior art are eliminated; the oxygen or air is taken as the oxidizing agent, so that the price is low and the oxidizing agent is easily obtained; and the method provided by the invention is characterized by convenience in operation, safety, environmental protection, low cost, high economic benefit, and the like, and belongs to a green chemical technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for production of fluoro derivative
InactiveUS7807858B2Improve solubilityEfficient removalSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationHydrogen fluorideOrganic base
It was found that a fluoro derivative can be produced by reacting a hydroxy derivative with sulfuryl fluoride (SO2F2) in the presence of an organic base or in the presence of an organic base and “a salt or complex comprising an organic base and hydrogen fluoride”. According to the present production process, it is not necessary to use perfluoroalkanesulfonyl fluoride, which is not preferable in industrial use, and it is possible to advantageously produce optically-active fluoro derivatives, which are important intermediates of medicines, agricultural chemicals and optical materials, specifically 4-fluoroproline derivatives, 2′-deoxy-2′-fluorouridine derivatives, optically-active α-fluorocarboxylate derivatives, and the like, even in a large scale.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD
Method for synthesizing trifluoromethyl amine
ActiveCN102875270ARaw materials are easy to getShort processOrganic compound preparationOrganic halogenationHydrofluoric acidSulfur tetrafluoride
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing trifluoromethyl amine. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing amino acid, anhydrous hydrofluoric acid and sulfur tetrafluoride in a molar ratio of 1:(3-20):(1.8-3.2), and reacting at temperature of between 50 and 150 DEG C for 2 to 10 hours; and cooling, neutralizing, extracting and rectifying to obtain a trifluoromethyl amine product. According to the method, a process is short; and the product is easy to separate, high in yield and stable in quality, the highest yield is 88 percent, and the content of the product is over 97.5 percent.
Owner:JUHUA GRP
Popular searches
Hydrocarbon purification/separation Ethylene production Gaseous mixture working up Refining by selective hydrogenation Bulk chemical production Hydrocarbon oils treatment products Refining with oxygen compounds Treatment with plural serial stages only Hydrocarbons Carboxylic preparation by oxidation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com