Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121results about "Optical bistable devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
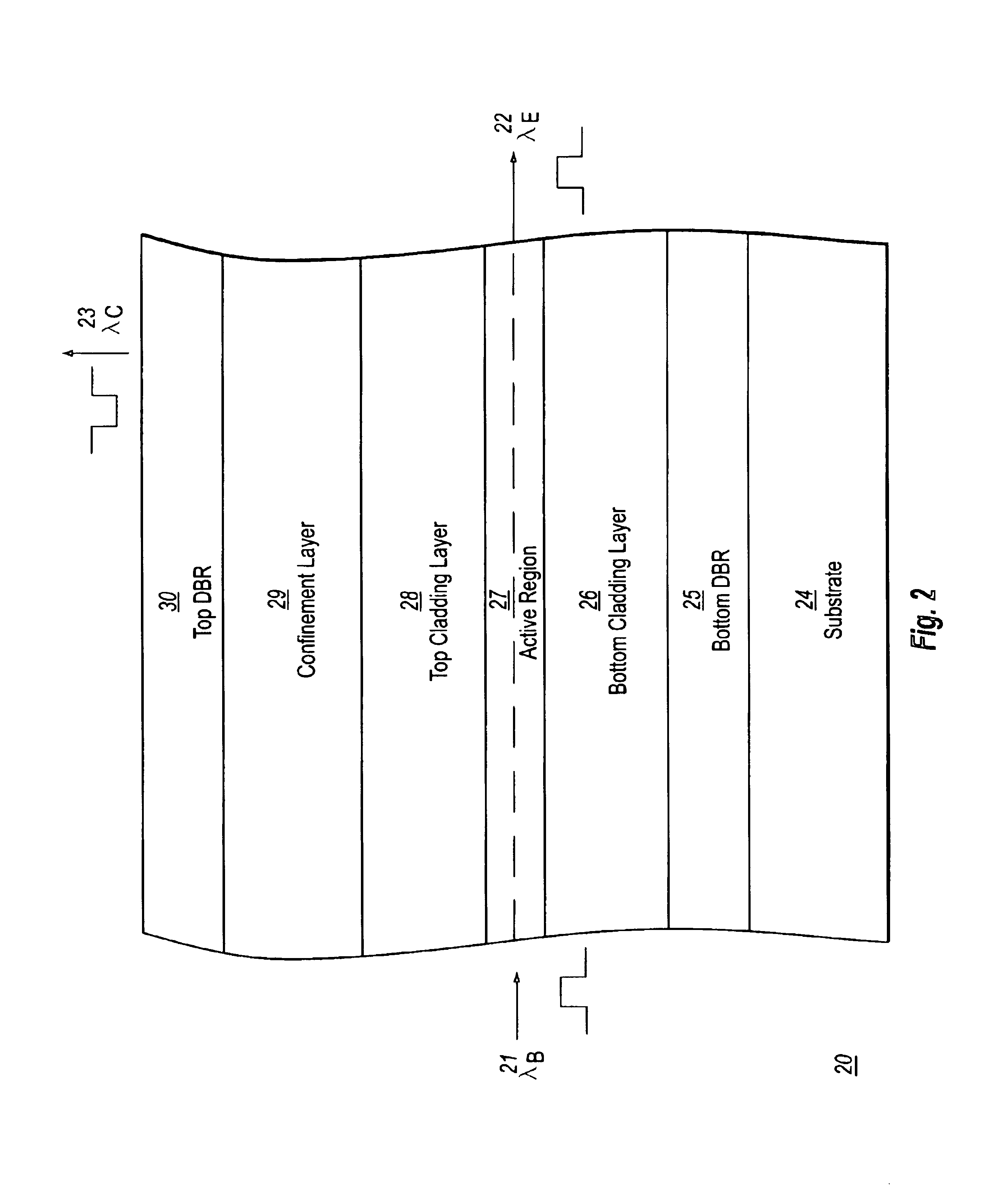
Optical semiconductor device
InactiveUS6043515AEasy population inversionImprove featuresExcitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesMagnetizationContact layer
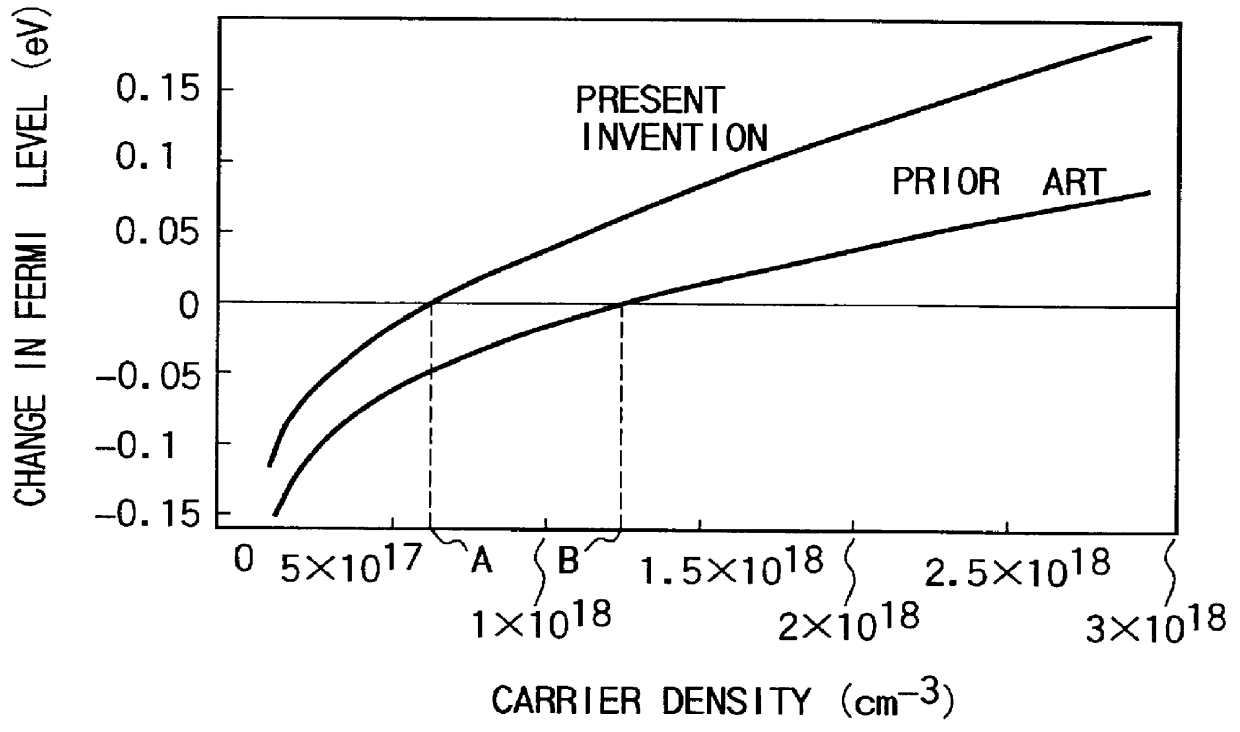
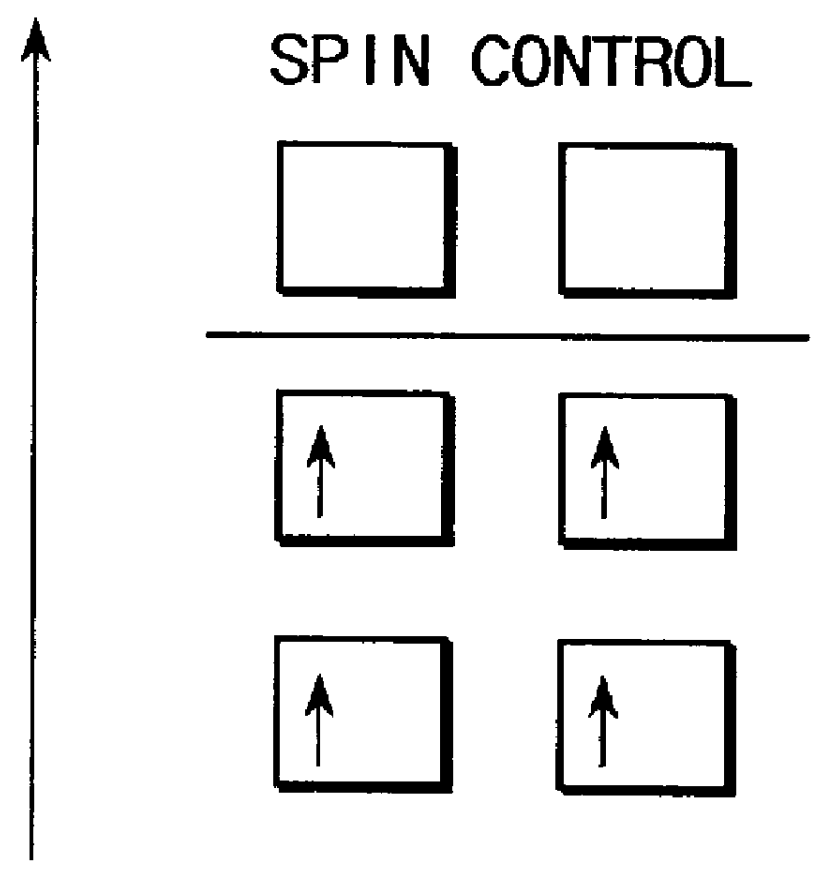
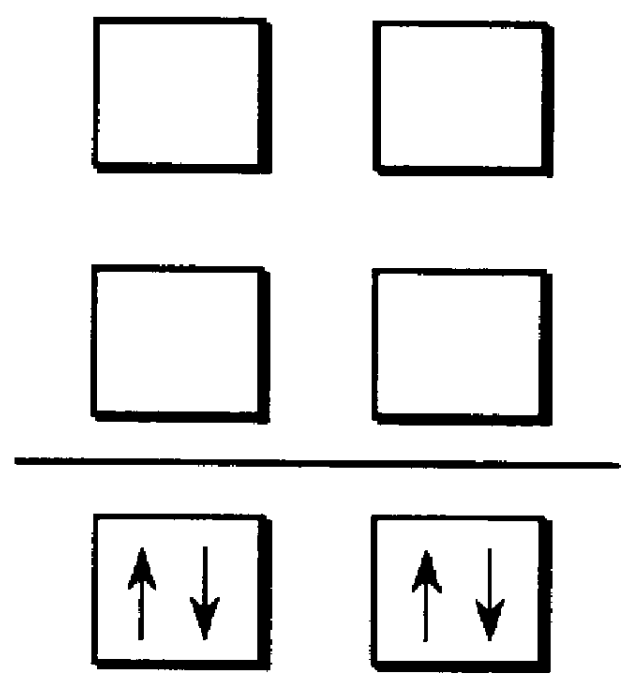
An optical semiconductor device has a structure in which a semiconductor active layer is sandwiched by a p-type semiconductor cladding layer and an n-type semiconductor cladding layer and a p-type contact layer is formed on the p-type semiconductor cladding layer side and an n-type contact layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor cladding layer side, wherein two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the n-type contact layer and two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the p-type contact layer. Magnetization directions of a pair of ferromagnetic layers vertically opposed to each other are set to be parallel to each other, and the magnetization directions of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are inverted to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Bistable all optical devices in non-linear photonic crystals
InactiveUS20060062507A1Reduce input powerIncrease contrastNanoopticsCoupling light guidesPhotonicsEngineering
A bistable photonic crystal configuration comprises a waveguide sided coupled to a single-mode cavity. This configuration can generate extremely high contrast between the bistable states in its transmission with low input power. All-optical switching action is also achieved in a nonlinear photonic crystal cross-waveguide geometry, in which the transmission of a signal can be reversibly switched on and off by a control input, or irreversibly switched, depending on the input power level.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
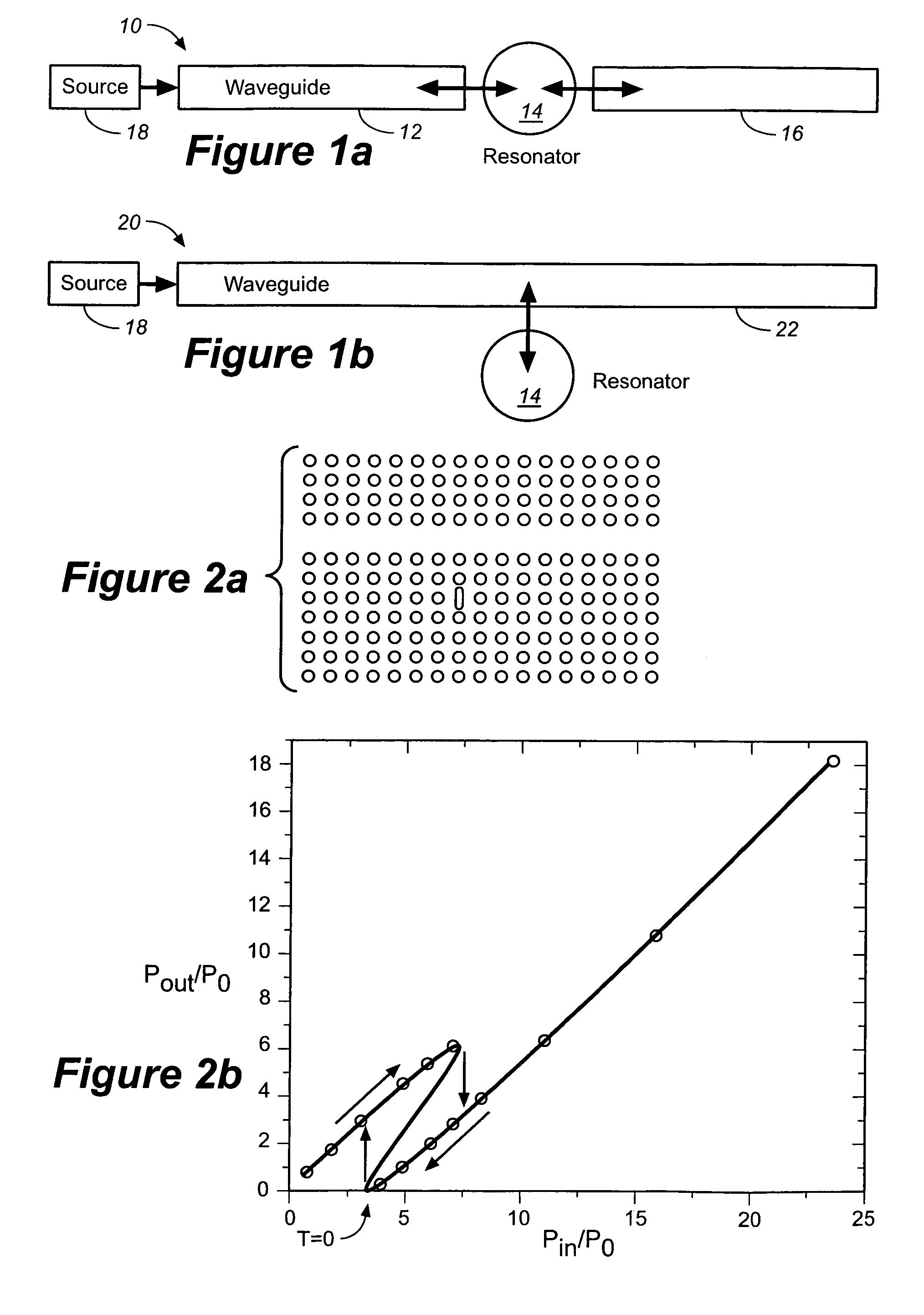
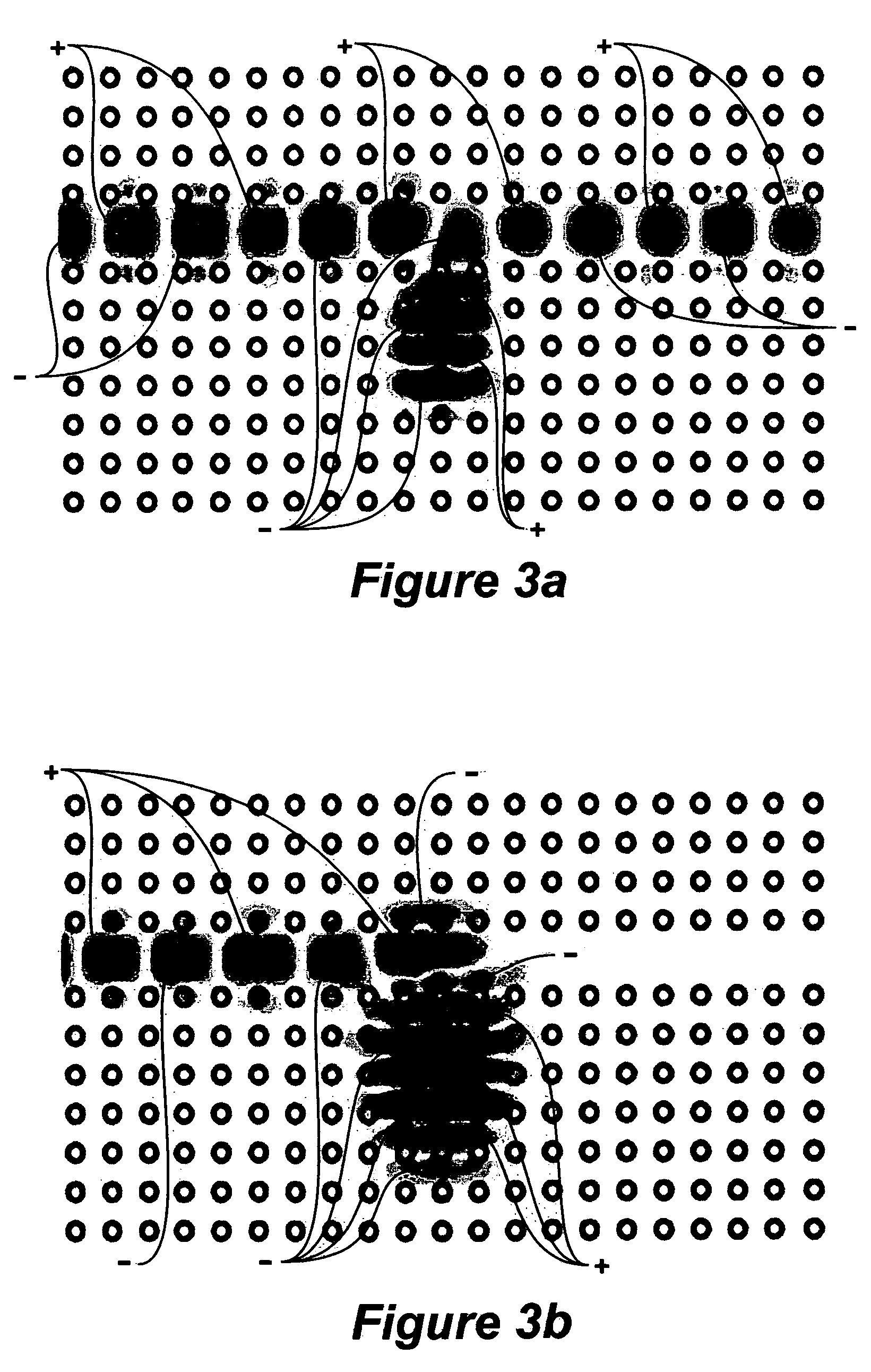
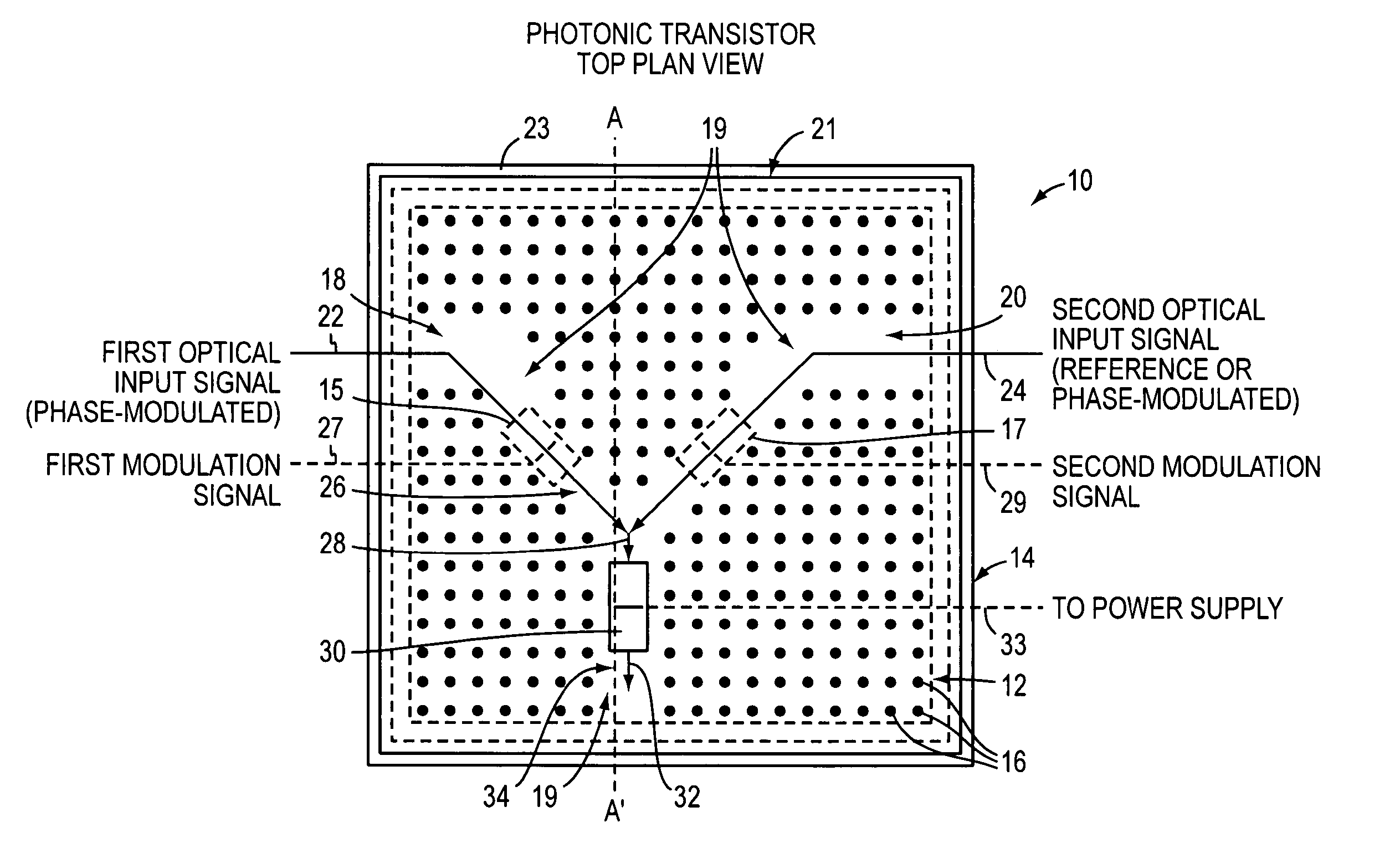
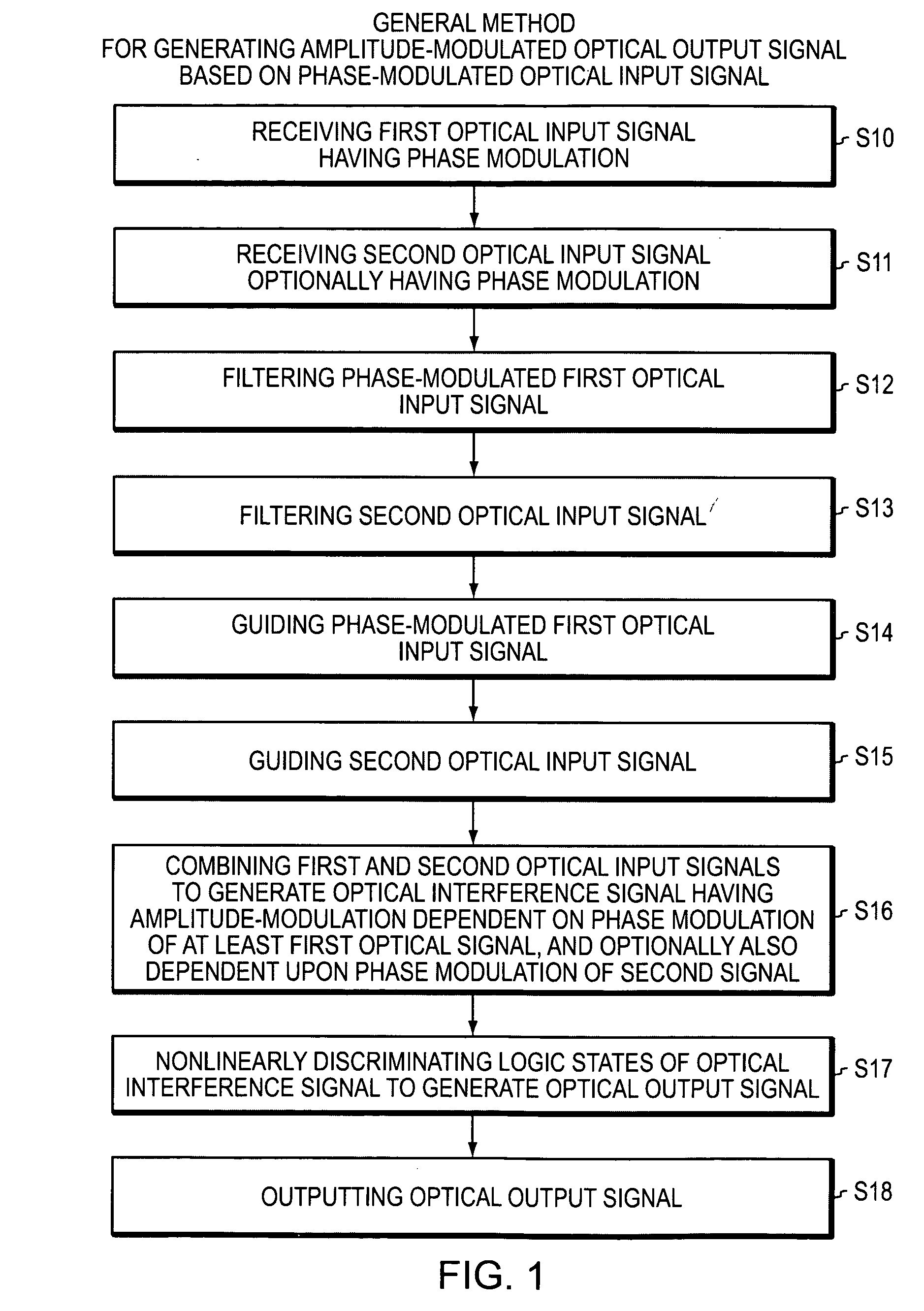
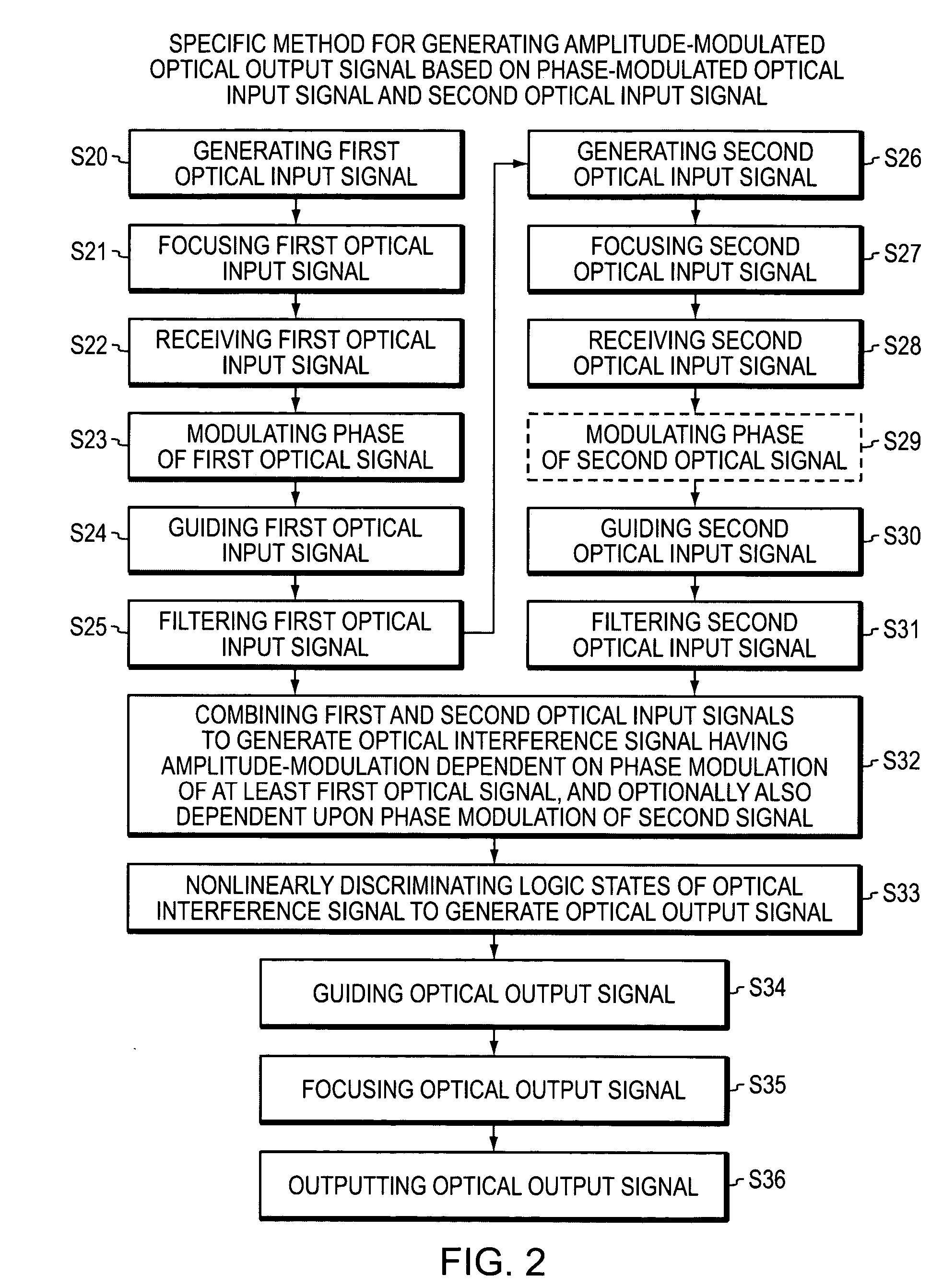
Optical device and circuit using phase modulation and related methods
InactiveUS20050259999A1Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmittersNonlinear elementLogic gate
A disclosed apparatus comprises a guiding element and a nonlinear element. The guiding element guides optical input signals, at least one of which is phase-modulated, to an interference area where such signals meet and interfere. The resulting interference signal is nonlinearly discriminated by the nonlinear element to produce an optical output signal that can be amplitude- or phase-modulated according to the phase modulation of the input signals. The invention also includes related methods and photonic logic gates.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
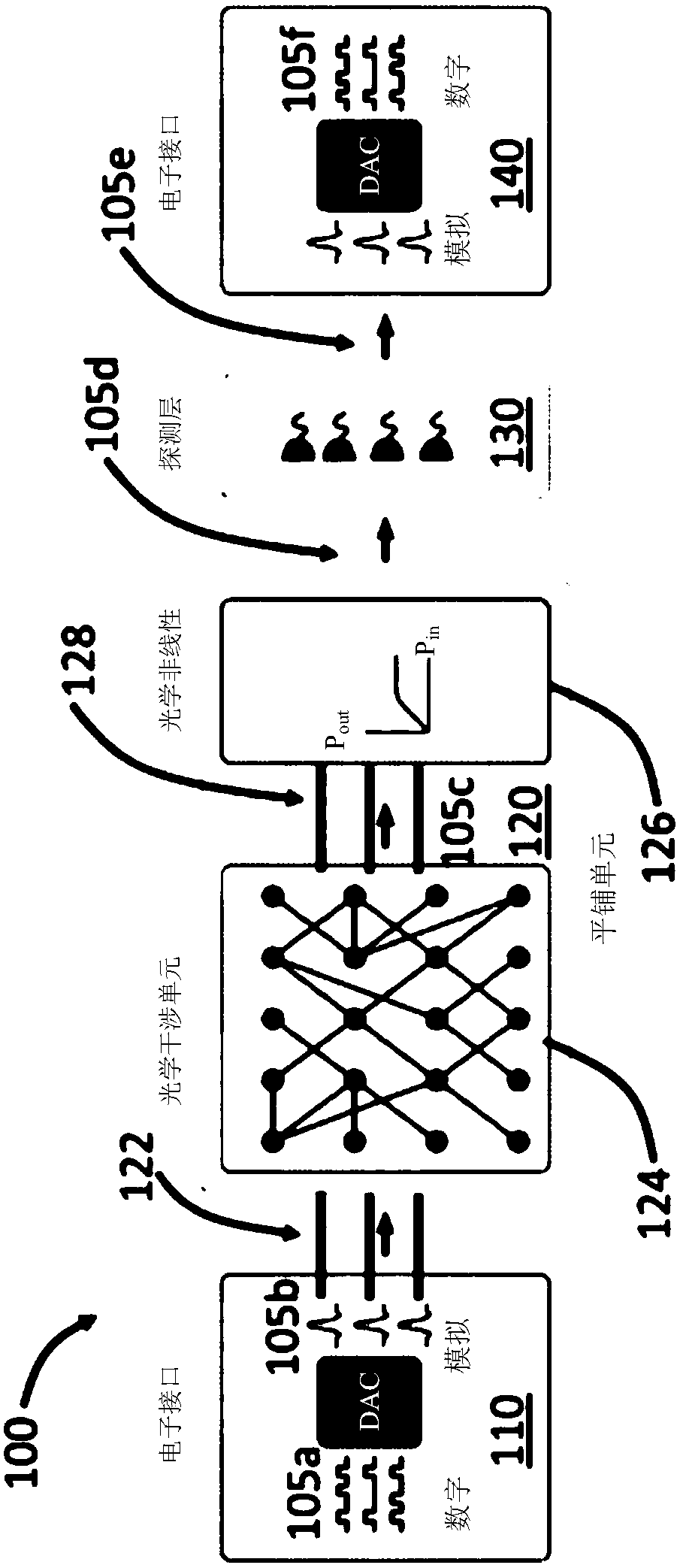
Apparatus and methods for optical neural network
ActiveCN109477938AWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical neural networkOptical nonlinearity
An optical neural network is constructed based on photonic integrated circuits to perform neuromorphic computing. In the optical neural network, matrix multiplication is implemented using one or moreoptical interference units, which can apply an arbitrary weighting matrix multiplication to an array of input optical signals. Nonlinear activation is realized by an optical nonlinearity unit, which can be based on nonlinear optical effects, such as saturable absorption. These calculations are implemented optically, thereby resulting in high calculation speeds and low power consumption in the optical neural network.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
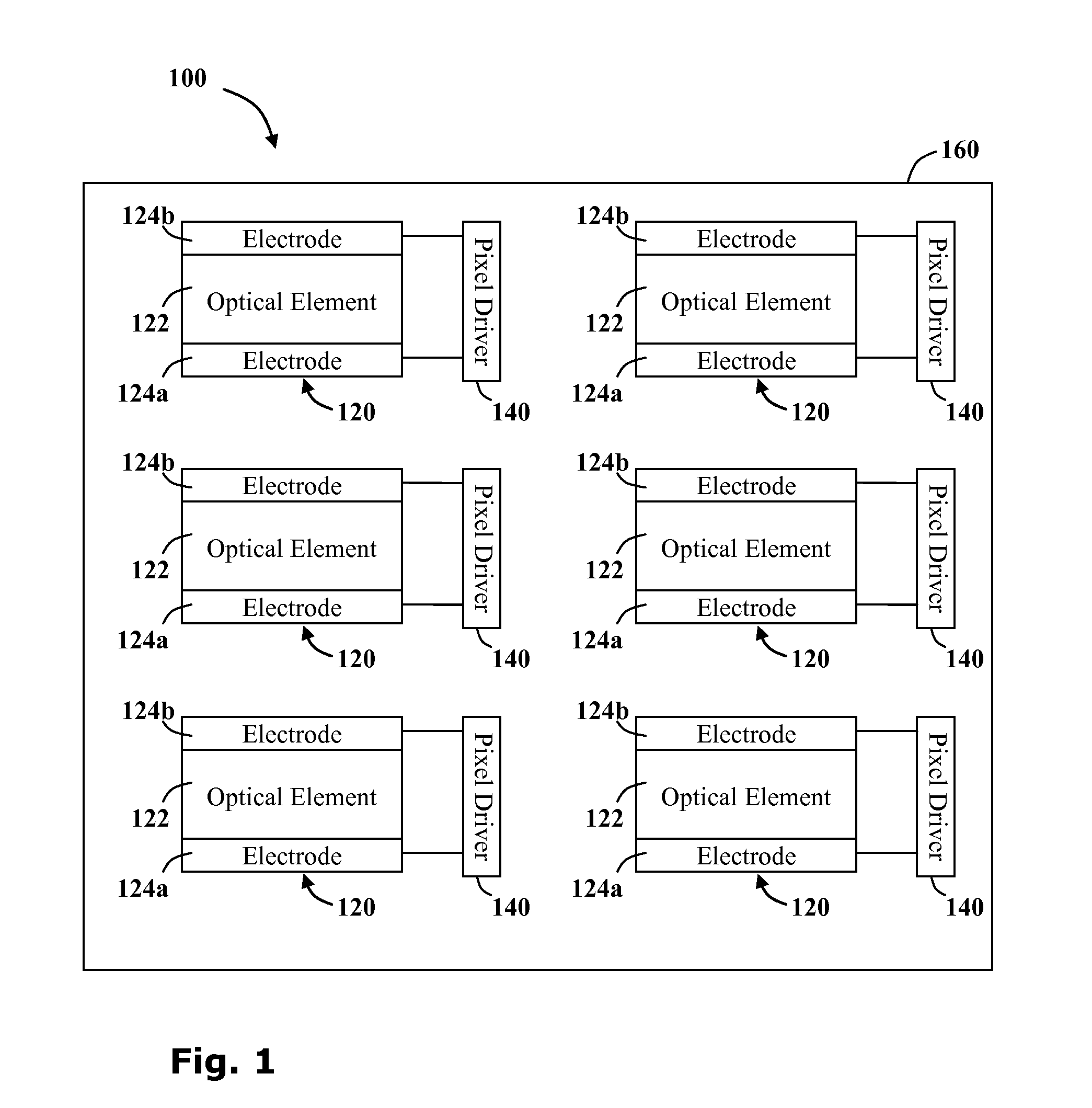
Encapsulated pixels for display device
ActiveUS20110157137A1Improving inductive couplingManufacture of electrical instrumentsCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectric power transmissionPotential difference
A display device comprising an array of encapsulated pixels. The encapsulating pixel includes an optical element which is altered from a first optical state to a second optical state upon when a potential difference is generated across it. The optical element is in contact with two electrodes which are connected to a pixel driver for generating the potential difference. The encapsulated pixel is hermetically sealed from the environment by a sealing layer and the driver receives power wirelessly via an inductive power transmission system.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
Non-linear photonic switch and method of making the same
InactiveUS6937804B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicrocontact printingPhotonics
A photonic switch according to the present invention may be formed using one of a selected group of non-linear optical materials. Each of the materials within this group has a refractive index that demonstrates a substantial peak as a function of wavelength, where the peak occurs at a wavelength distinct from the wavelength of the input signal. A method of producing a photonic switch according to the present invention includes fabricating source and drain waveguides using micro-molding or micro-contact printing processes, or MIMIC (micro-molding in capillaries) of a UV-curable polymer. If desired, a gate waveguide may also be formed in part by these processes. The photonic switch also includes a photonic crystal formed from non-linear optical material, which may be formed, for example, using a block copolymer and nanoparticle composite in a MIMIC or μfluidics process. Such a process may employ a functionalized mold material to align the blocks.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
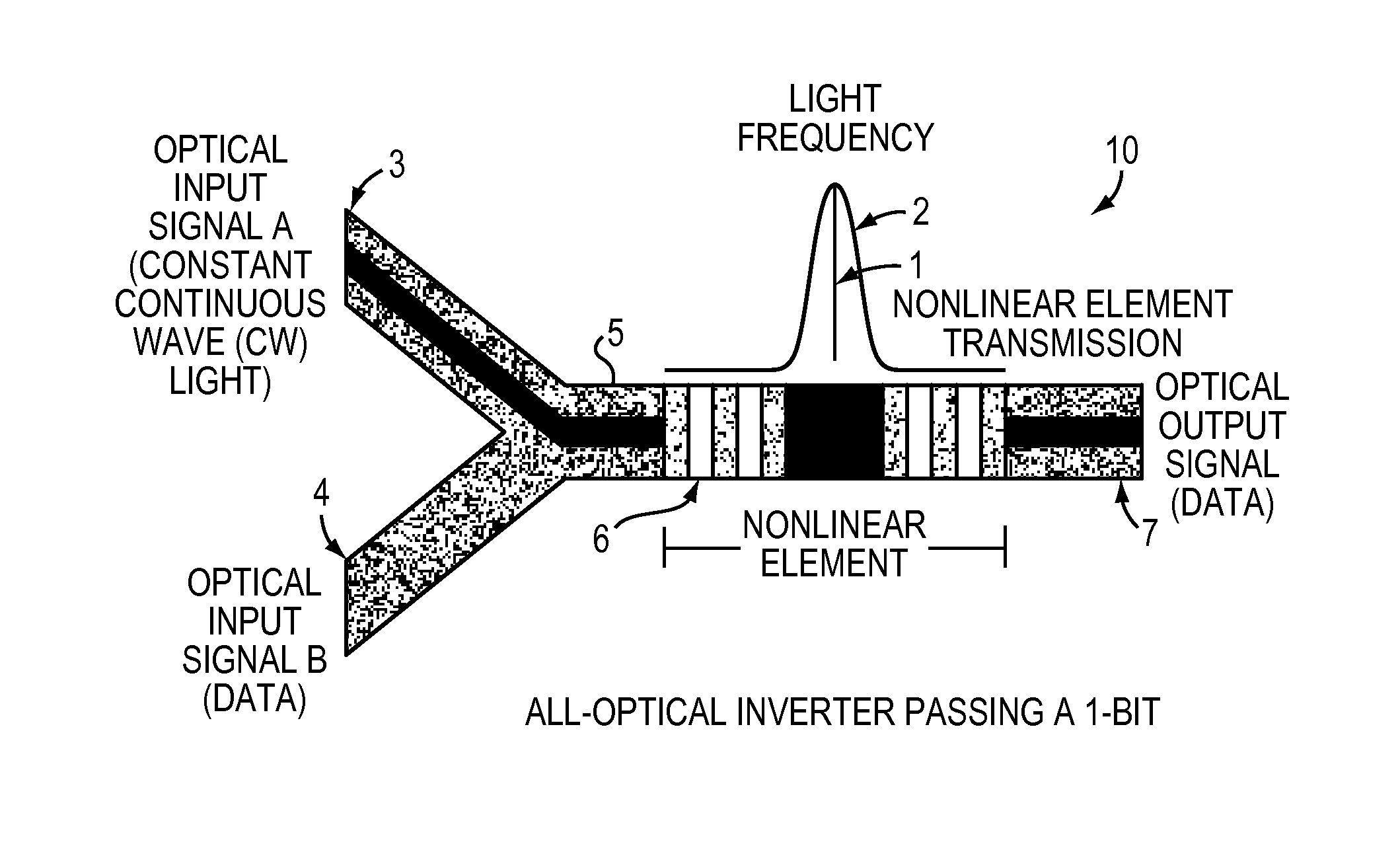
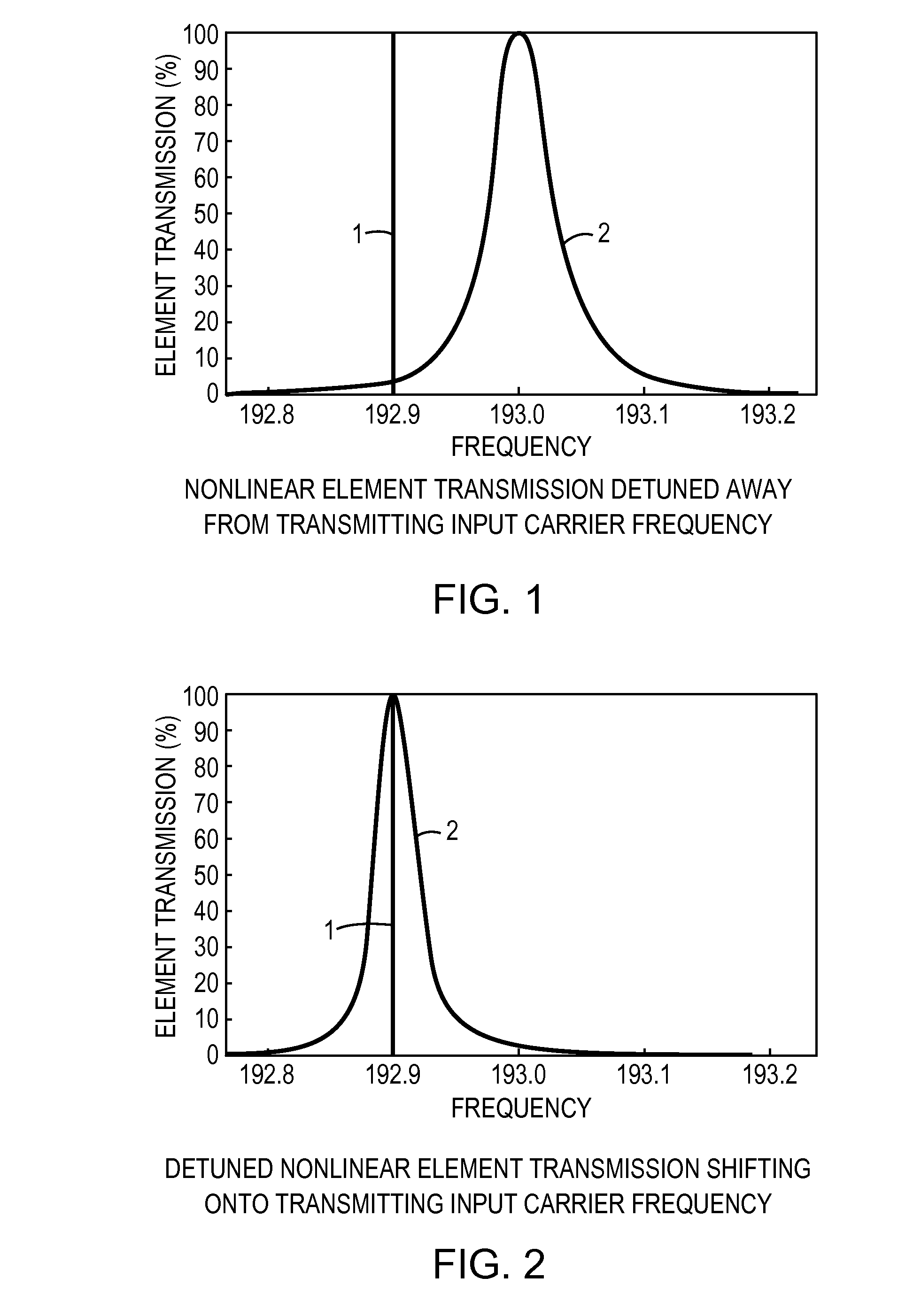
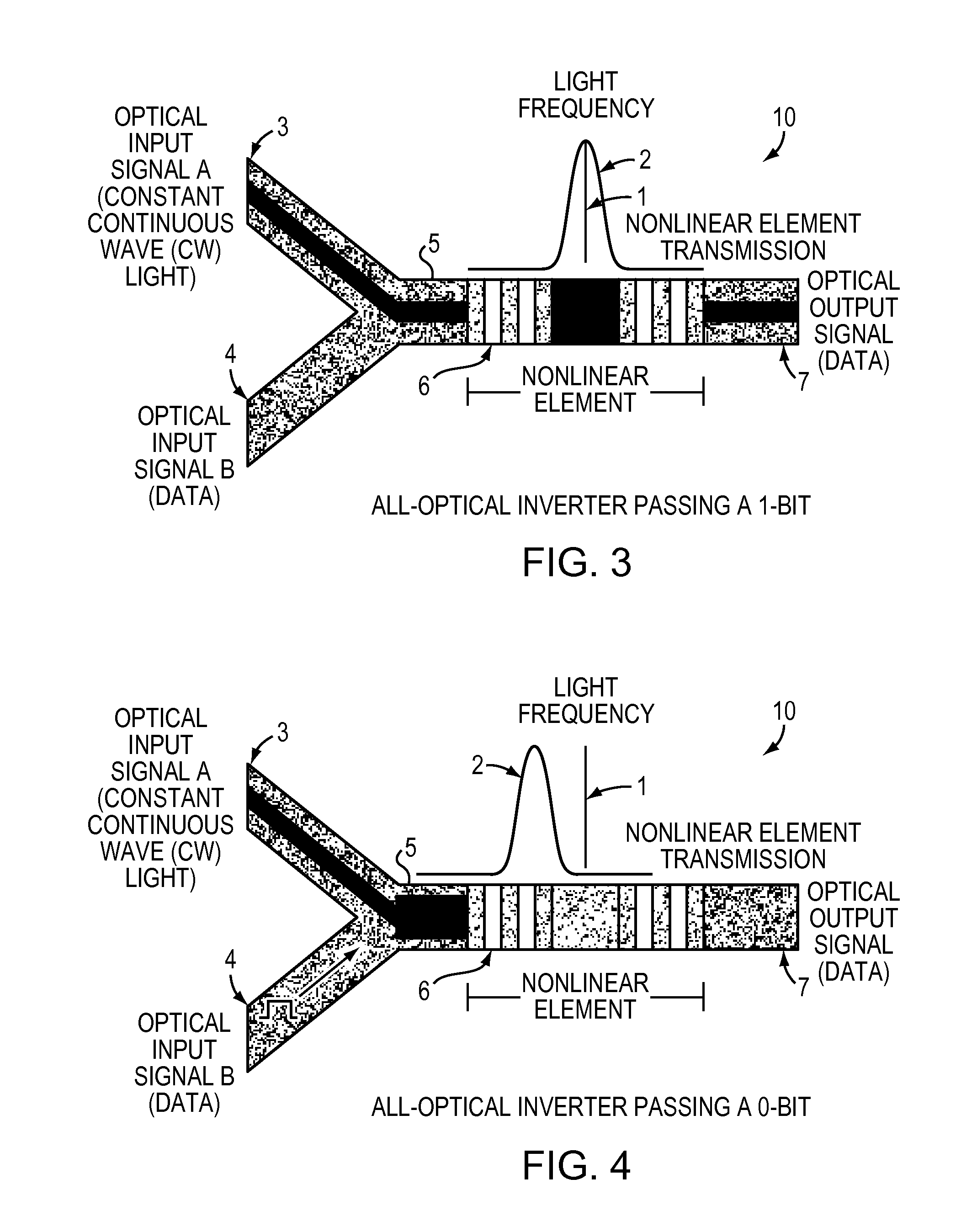
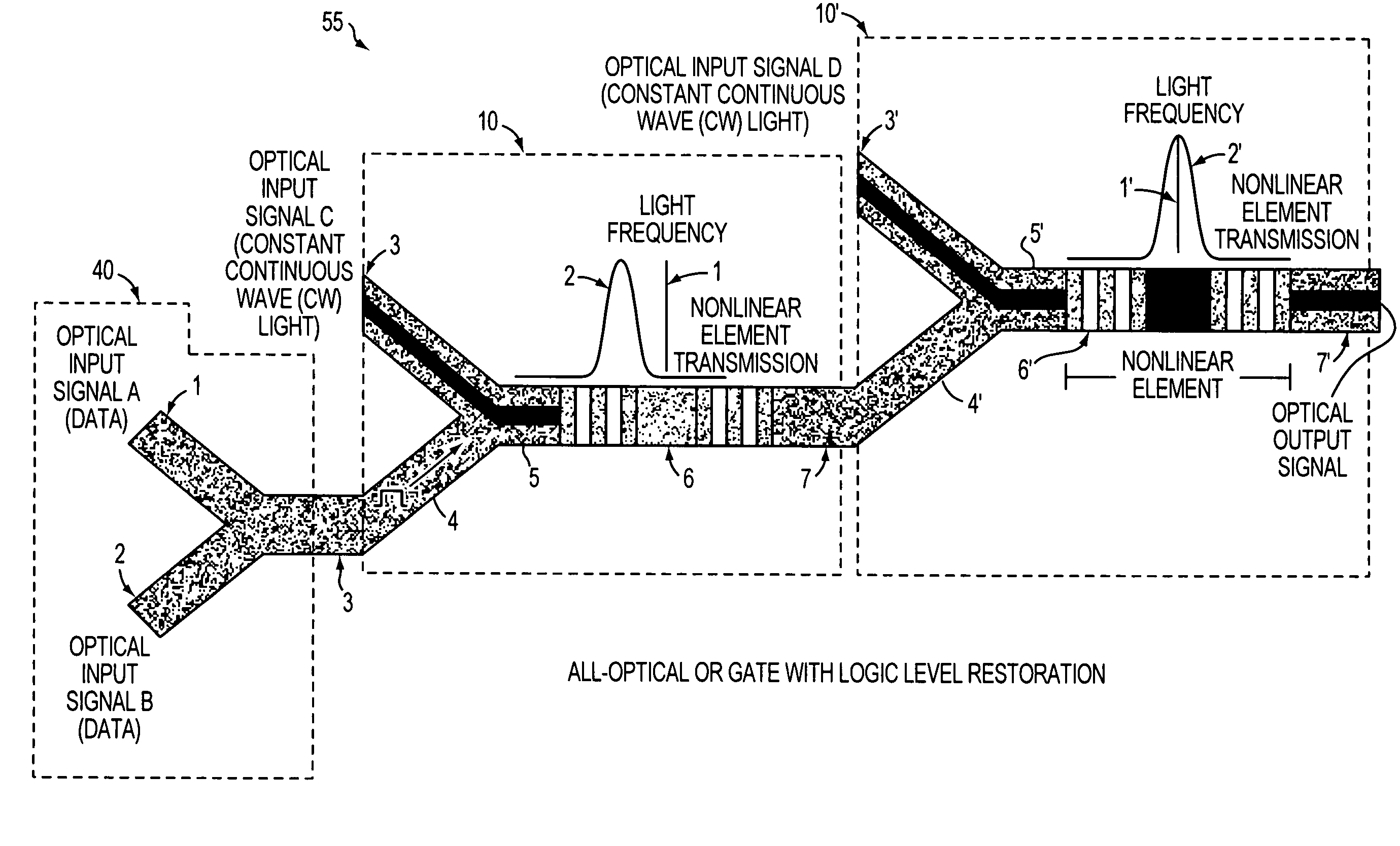
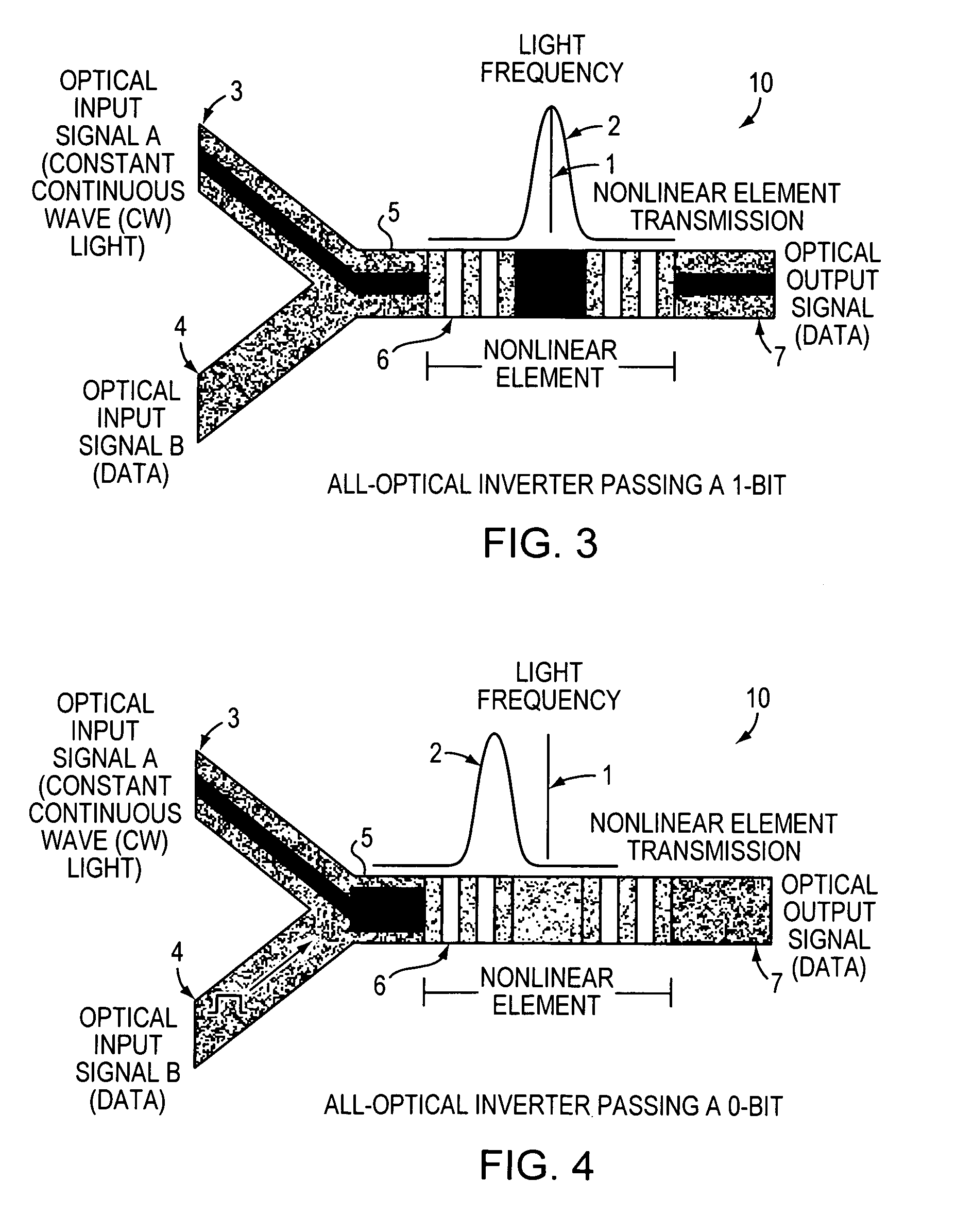
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements-claim set VI
InactiveUS7263262B1Change quantityPrecise arrangementCoupling light guidesOptical bistable devicesNonlinear elementLogic gate
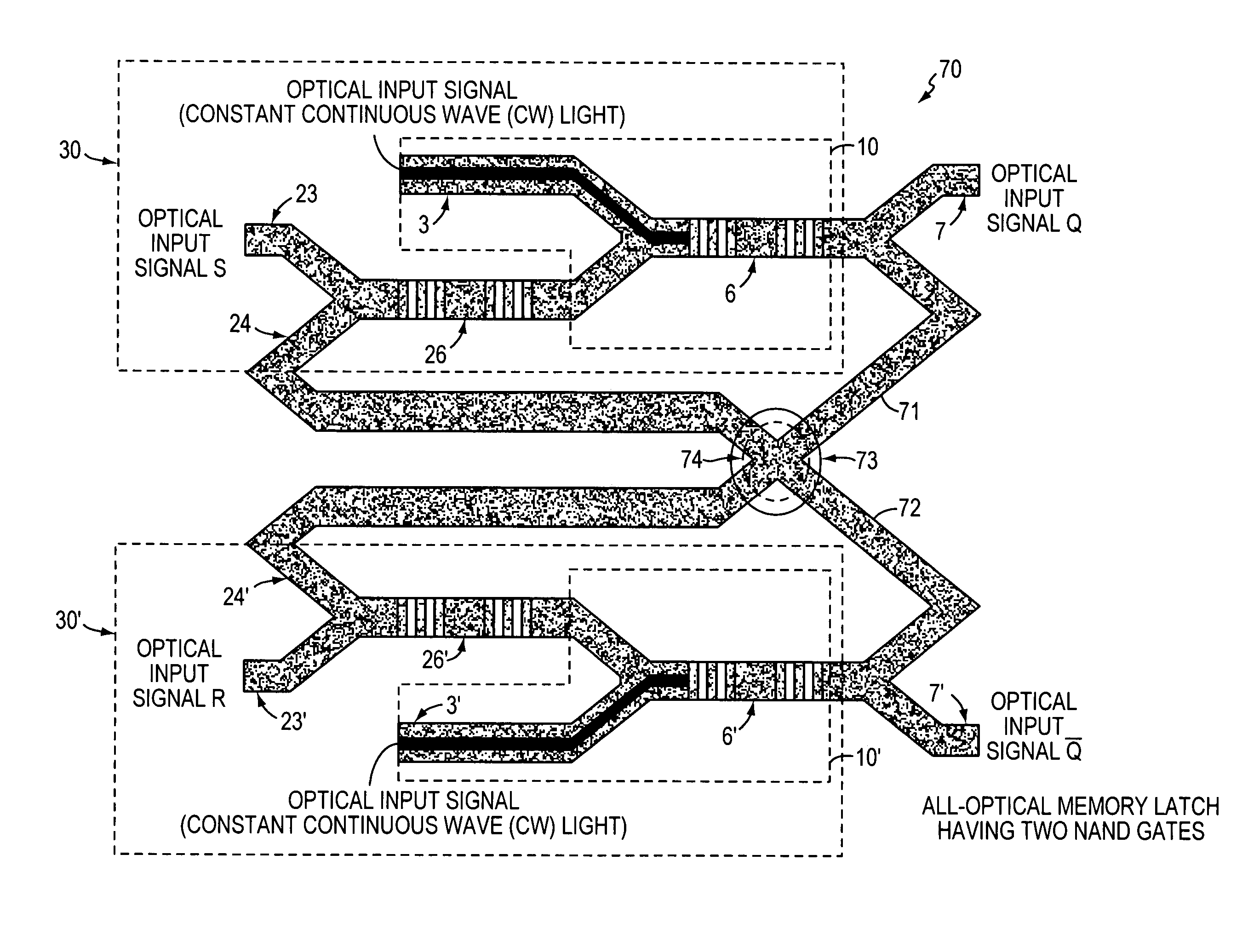
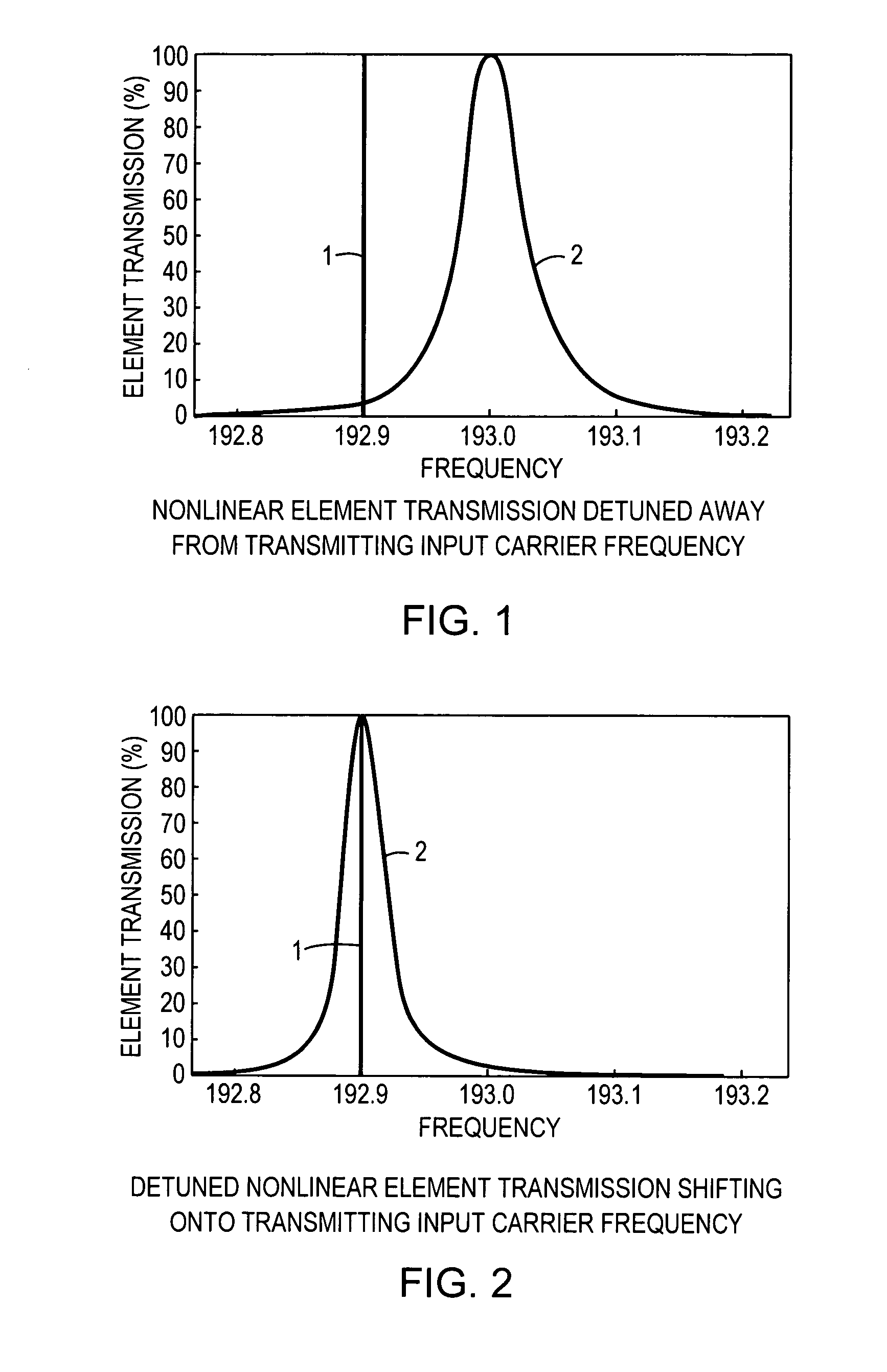
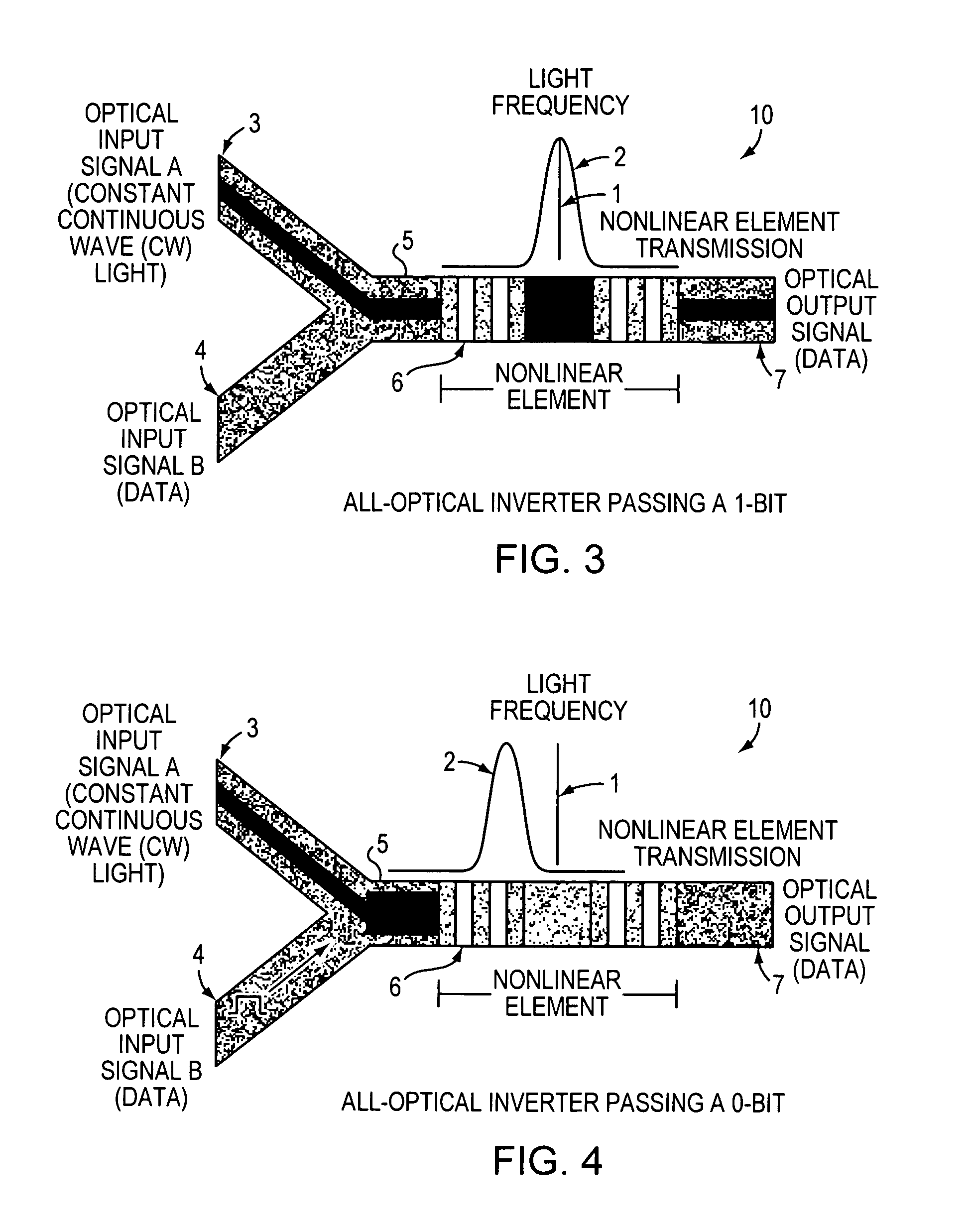
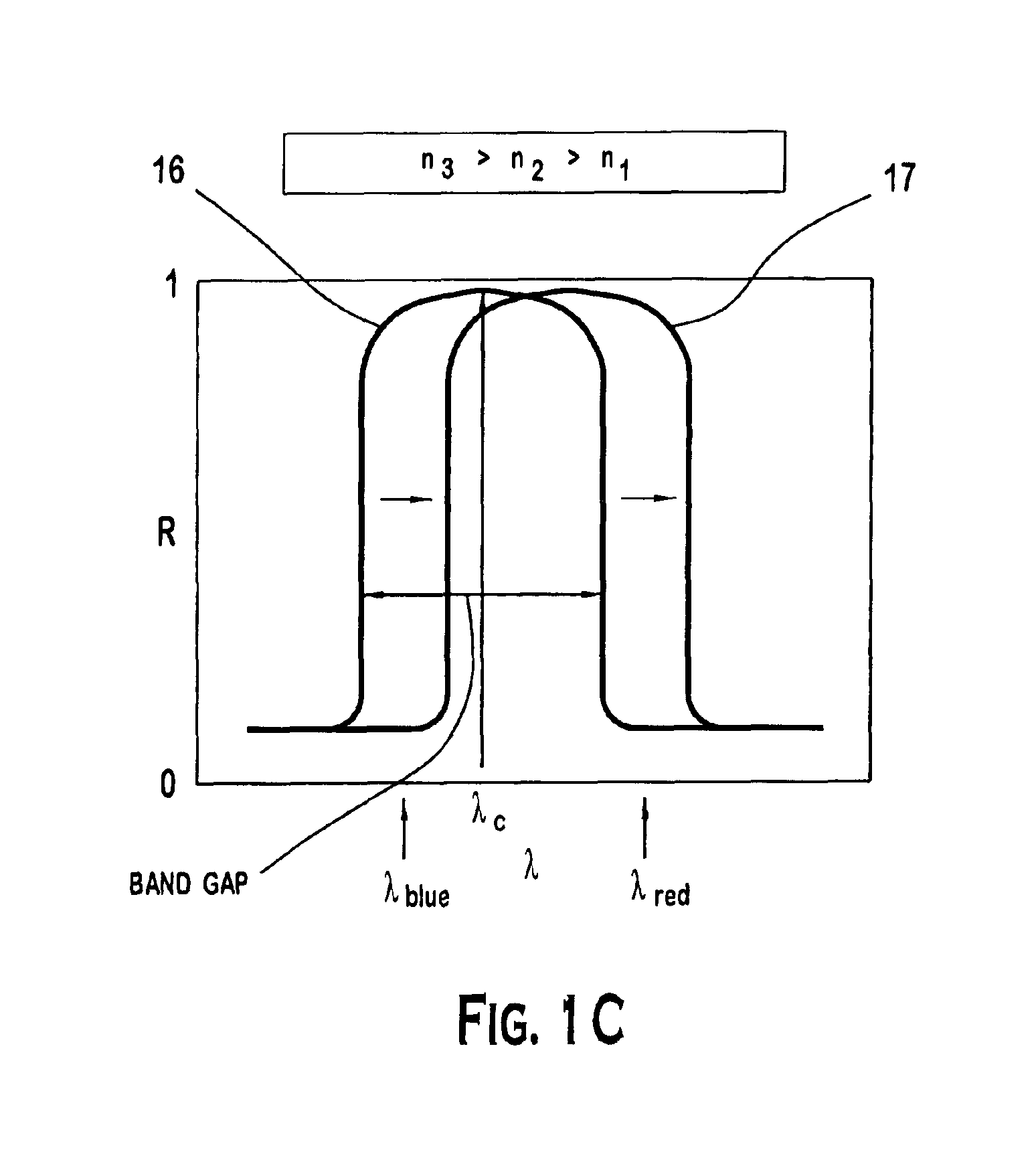
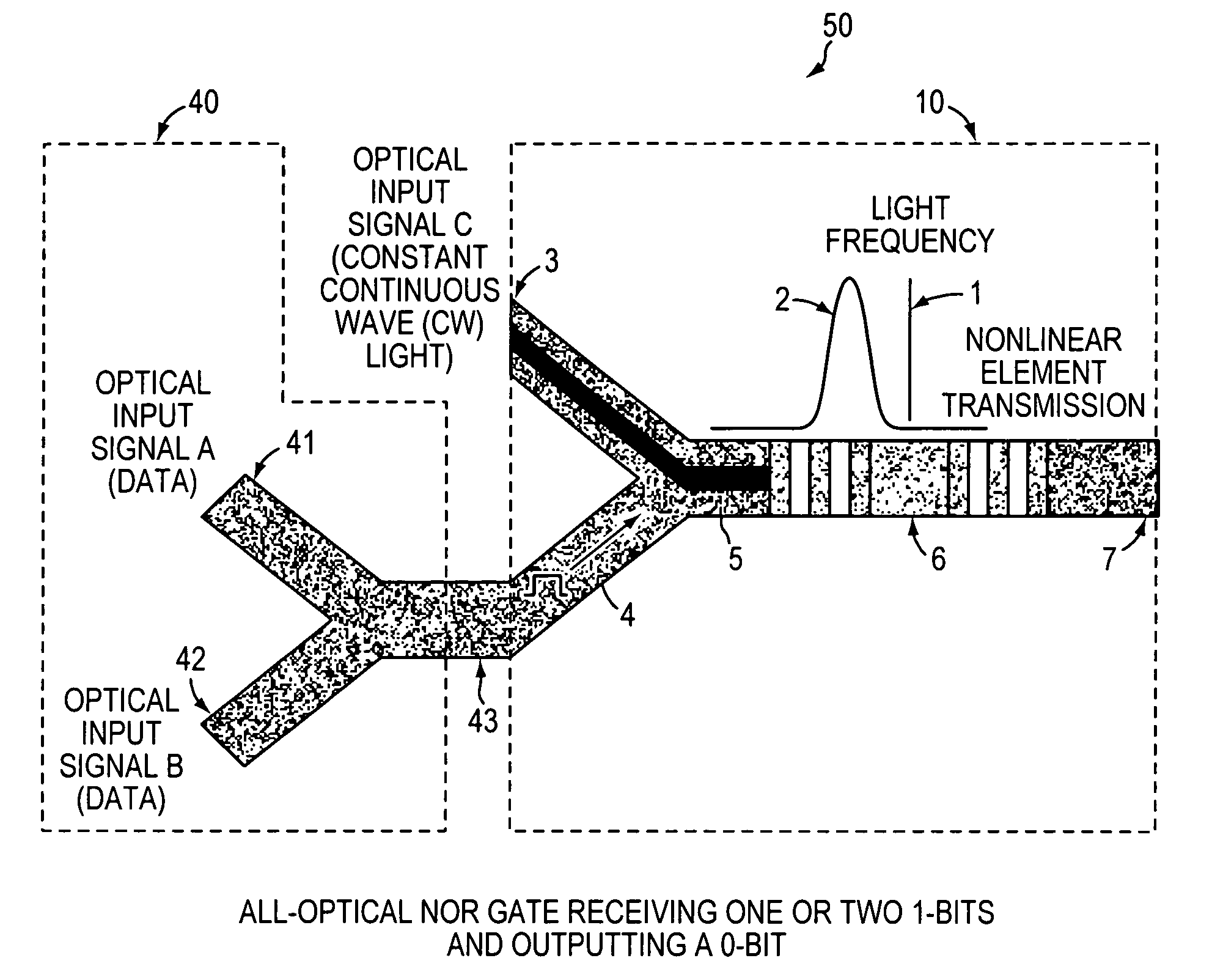
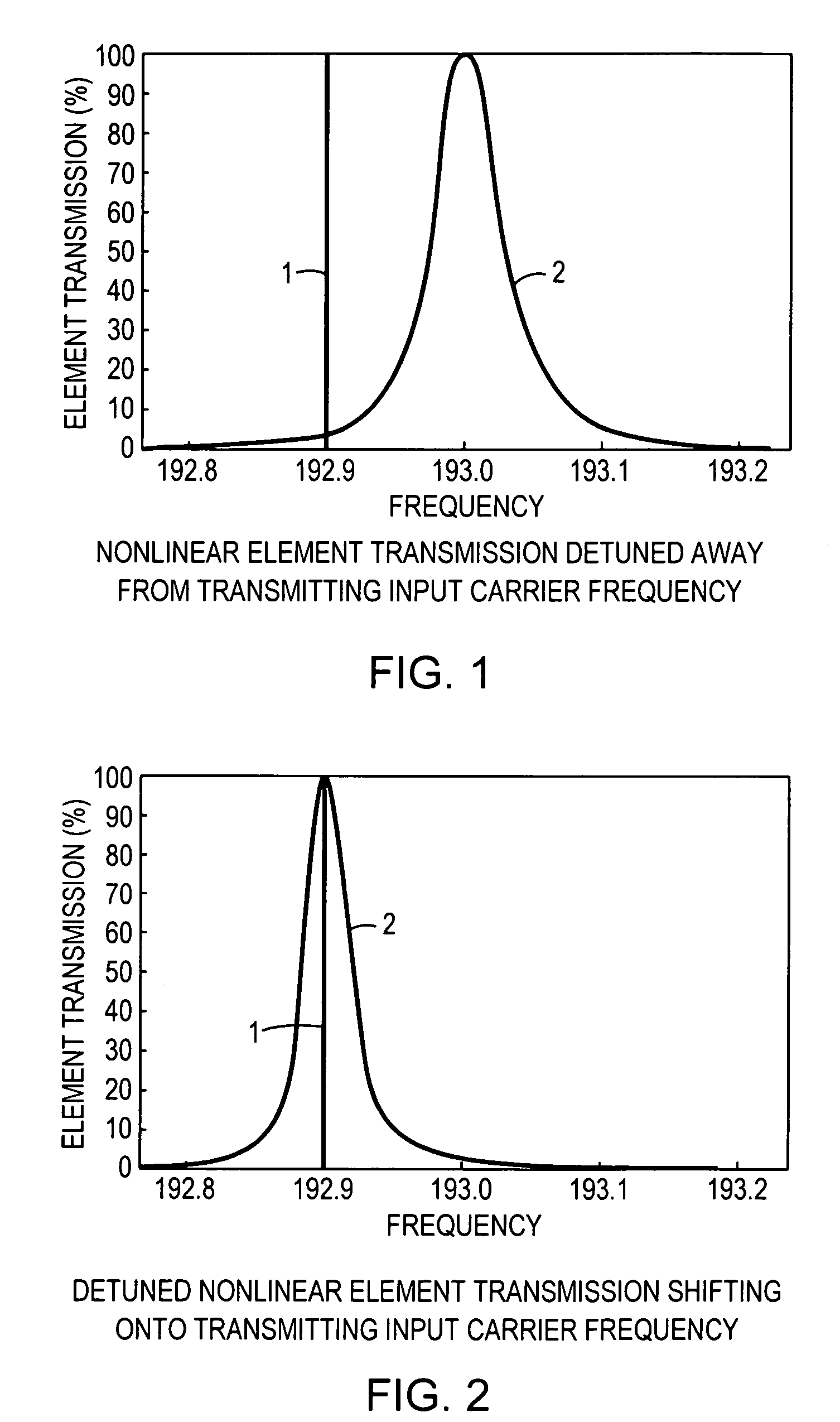
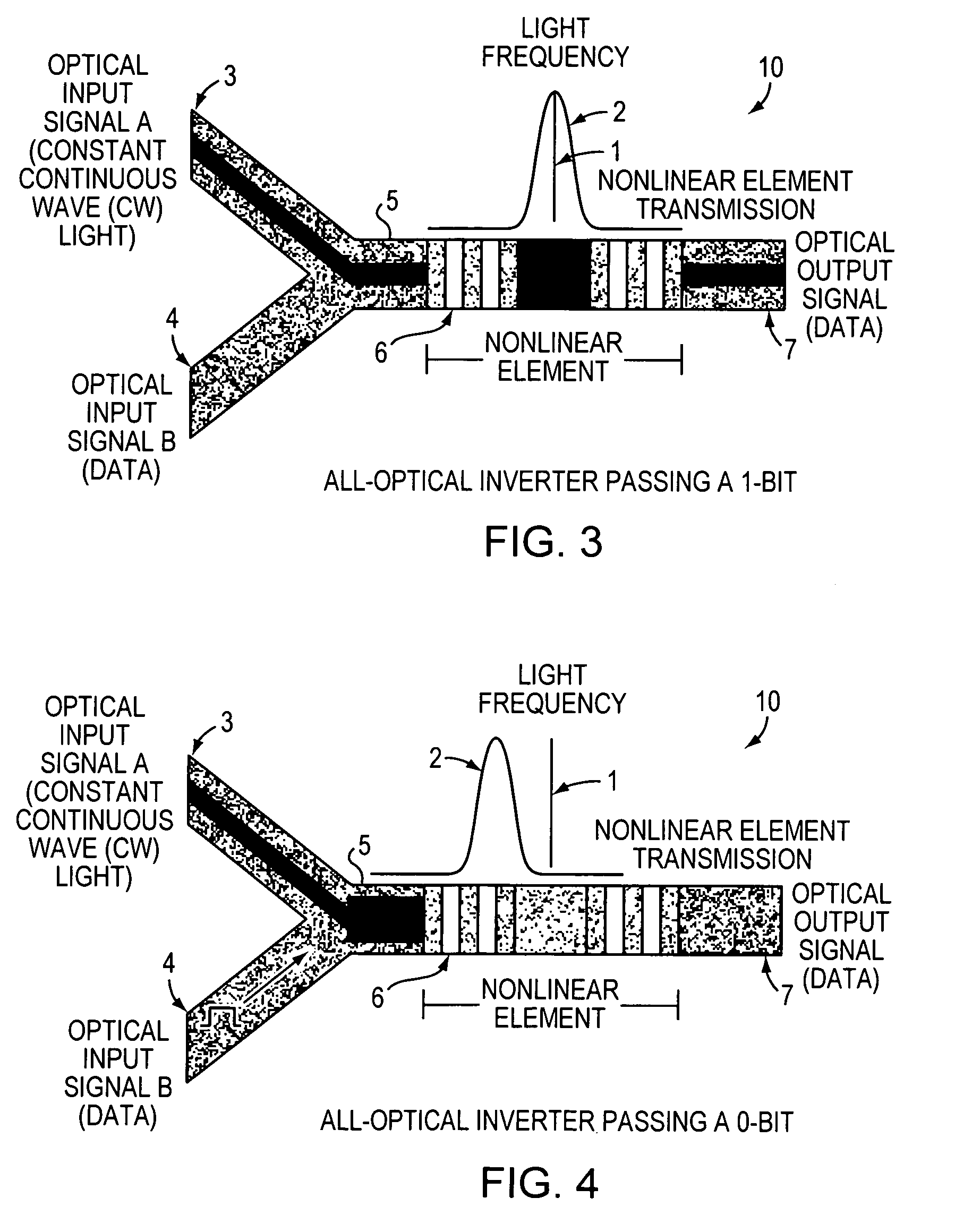
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
Optical switching device
InactiveUS6101298AIncrease chanceLayer structure is simpleElectronic switchingCoupling light guidesChemical compoundDisplay device
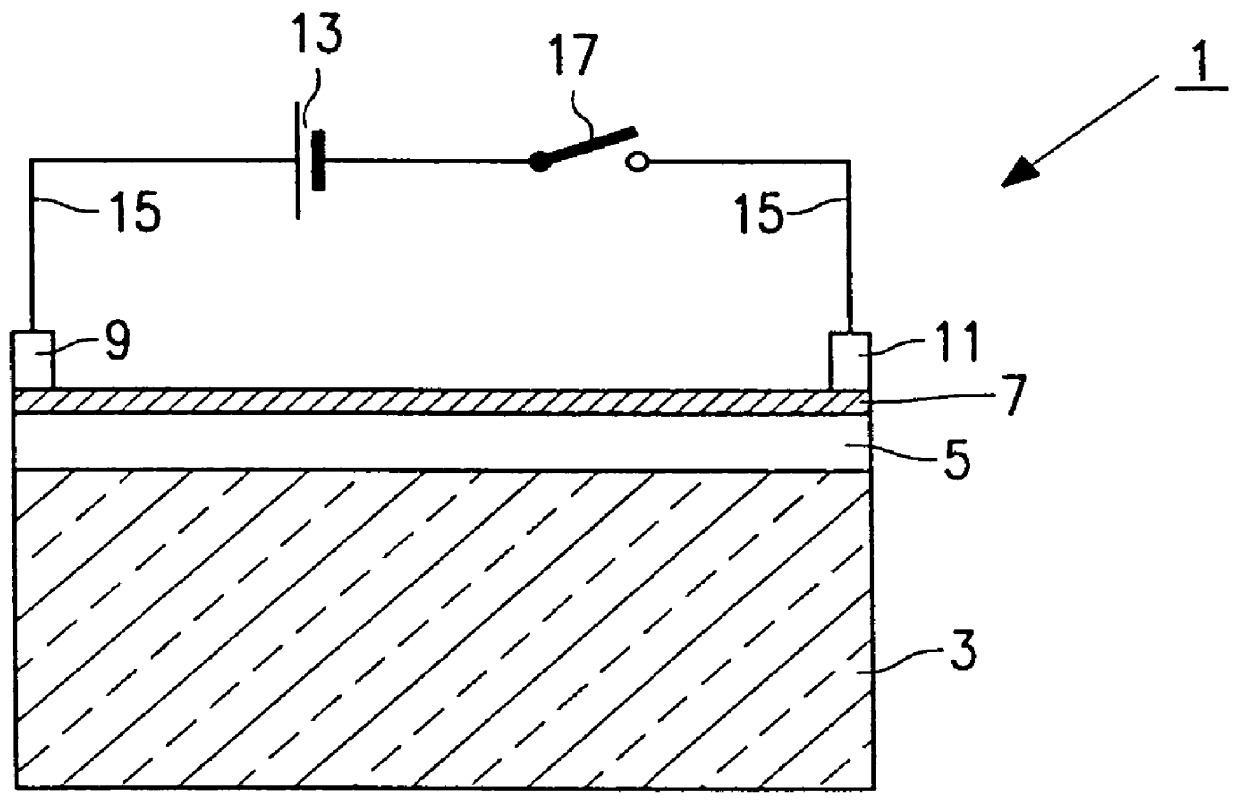
A description is given of an optical switching device (1) comprising a transparent substrate (3), a switching film (5) of a hydride compound of a trivalent transition or rare earth metal having a thickness of 300 nm, and a palladium capping layer (7) having a thickness of 30 nm. The capping layer is in contact with hydrogen. An electric current through the switching film (5) can be switched on and off between the terminals (9, 11). Joule heating of the switching film (5) causes a rapid transition from the transparent trihydride state to the absorbing dihydride state. By switching off the current, the switching film (5) cools down, which results in the formation of the absorbing dihydride state. The conversion between both states is reversible and can be repeated many times. The device can be used for controlling light beams, or it can be used in or for a display. Optionally, cooling of the switching film (5) is obtained with a Peltier element in thermal contact with the switching film (5).
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Fast quantum gates with ultrafast chirped pulses
ActiveUS7899092B2Laser using scattering effectsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesTime domainPulse shaper
Apparatus and methods of performing fast single-qubit quantum gates using ultrafast femtosecond frequency chirped laser pulses are disclosed. The use of chirped pulses removes the demanding restrictions of prior art approaches and allows for the construction of fast quantum gates that operate at speeds on the of order several picoseconds. The apparatus includes two synchronized lasers (pump and Stokes) used to manipulate a qubit wave function in a select manner. Each laser system generates a train of optical pulses. Pulse pickers choose pump and Stokes pulses, which propagate though respective pulse shapers that apply necessary time-dependent phases. To achieve complete overlap between the pulses in time domain, necessary adjustments can be made by using an additional time delay line, which can be located in any path or in both paths.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Non-volatile programmable optical element employing F-centers
ActiveUS8054669B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRecord information storageElectromagnetic radiationF-Center
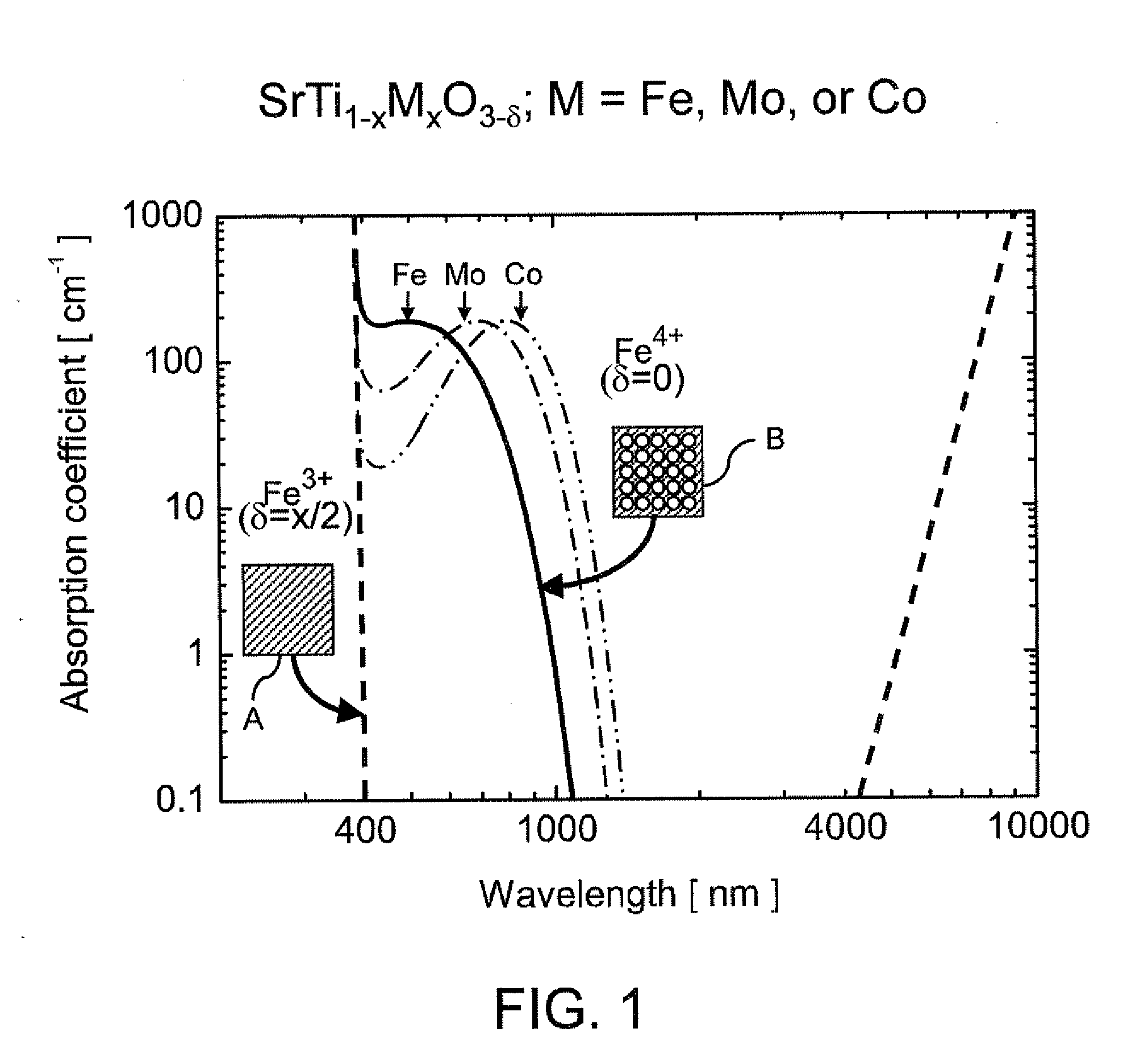
A non-volatile programmable electro-optical element alters absorption characteristics of an optical medium that comprises a doped transition metal oxide material including F-centers. The F-centers are electrostatically moved into or out of the regions containing a wavefunction of an optical beam. A specific F-center profile in the transition metal oxide material may be programmed into the optical medium. The F-center profile alters an absorption profile within the optical medium. The spectral range for transmission of electromagnetic radiation in the optical medium may be tailored by the F-centers. Once the absorption profile is set by an electrical signal, the optical element maintains its state even when the electrical signal is turned off. Thus, the programming node may be disconnected from a power supply network, thereby enabling a low power operation of the electro-optical element. The inventive electro-optical element may be employed for both the visible and the infrared wavelength spectrum.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements - claim set vi
InactiveUS20070248124A1Change quantityPrecise arrangementLaser using scattering effectsCoupling light guidesLogic gateNonlinear element
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements - claim set V
InactiveUS20070189665A1Change quantityPrecise arrangementCoupling light guidesLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesLinear elementLogic gate
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
Phase wavelength and polarization insensitive optical devices
InactiveUS20070103684A1Light polarisation measurementOptical bistable devicesPulse-code modulationContinuous beam
An optical chopper includes an optical loop having first and second terminals and includes first and second nonlinear elements. The optical loop is arranged to receive, at the first and the second terminals, a pulse-modulated signal and a continuous beam, respectively. The optical loop is arranged to cause the pulse-modulated signal and the continuous beam to counter-propagate in the loop and to produce in the first nonlinear element an inverted pulse-modulated signal having modulation which is inverted with respect to the pulse modulation of the pulse-modulated signal and to cause the inverted pulse-modulated signal to chop the pulse-modulated signal in the second nonlinear element.
Owner:SHAHAR ARIE
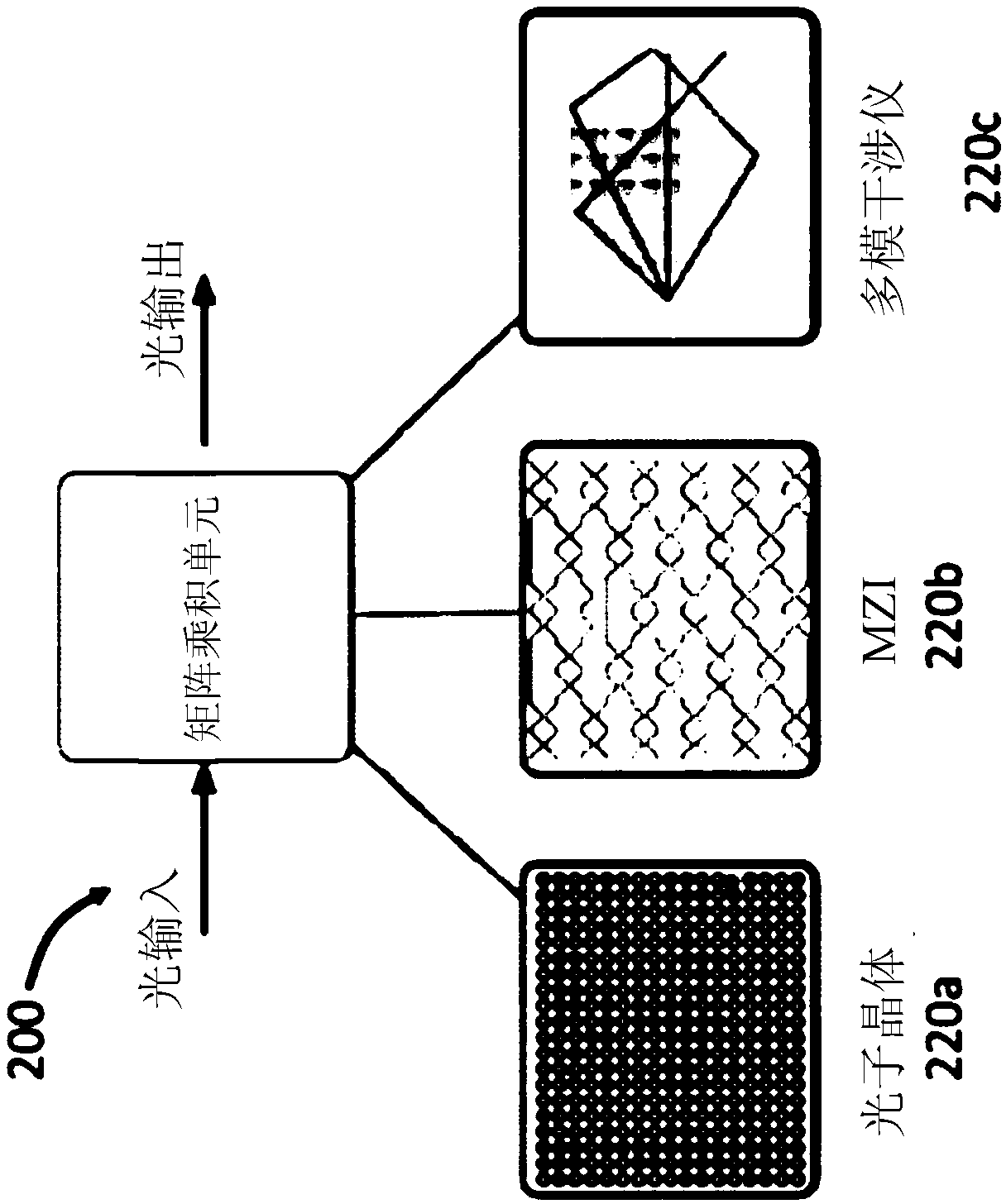
Optoelectronic computing systems
Systems and methods that include: providing input information in an electronic format; converting at least a part of the electronic input information into an optical input vector; optically transforming the optical input vector into an optical output vector based on an optical matrix multiplication; converting the optical output vector into an electronic format; and electronically applying a non-linear transformation to the electronically converted optical output vector to provide output information in an electronic format. In some examples, a set of multiple input values are encoded on respective optical signals carried by optical waveguides. For each of at least two subsets of one or more optical signals, a corresponding set of one or more copying modules splits the subset of one or moreoptical signals into two or more copies of the optical signals. For each of at least two copies of a first subset of one or more optical signals, a corresponding multiplication module multiplies theone or more optical signals of the first subset by one or more matrix element values using optical amplitude modulation. For results of two or more of the multiplication modules, a summation module produces an electrical signal that represents a sum of the results of the two or more of the multiplication modules.
Owner:ライテリジェンスインコーポレイテッド
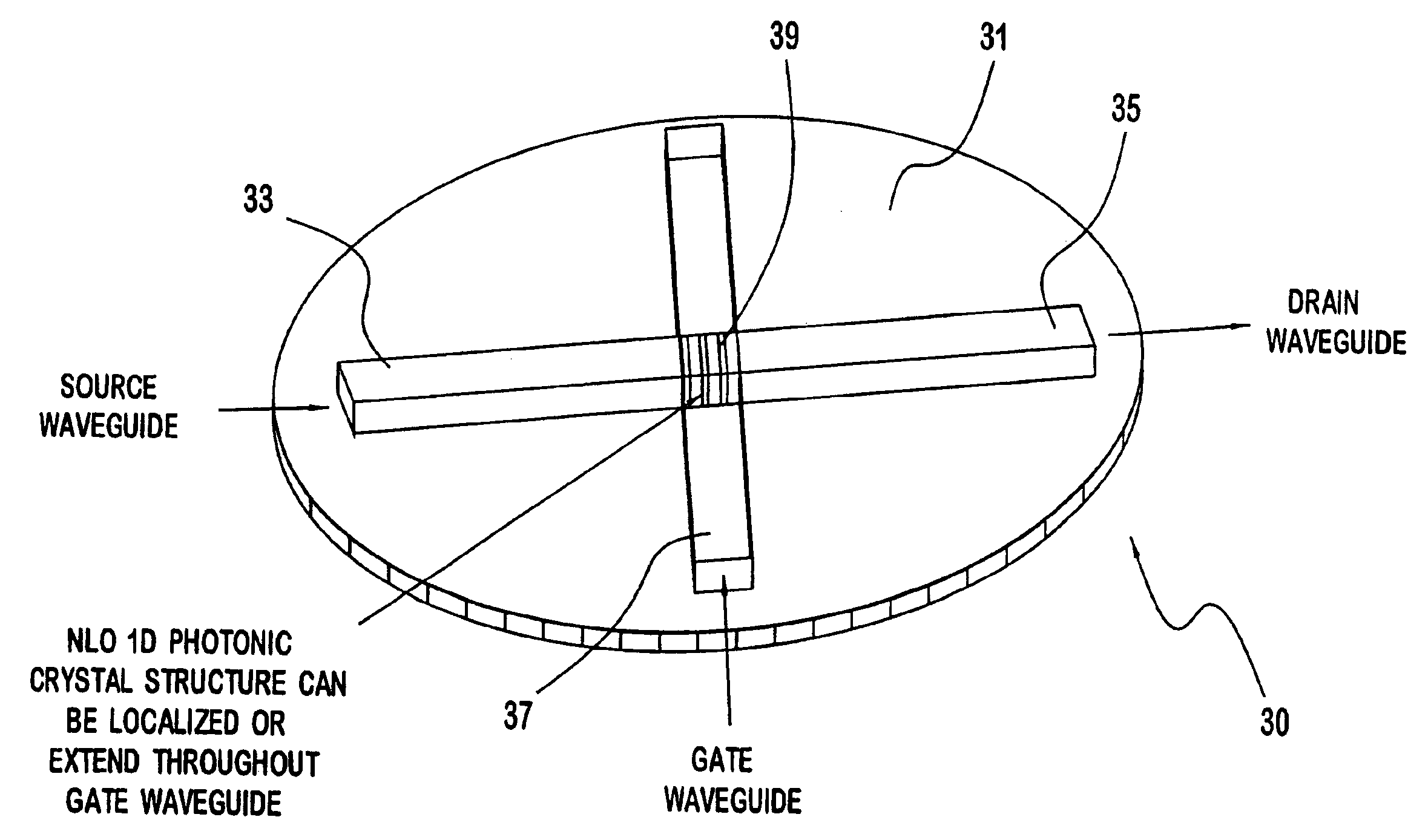
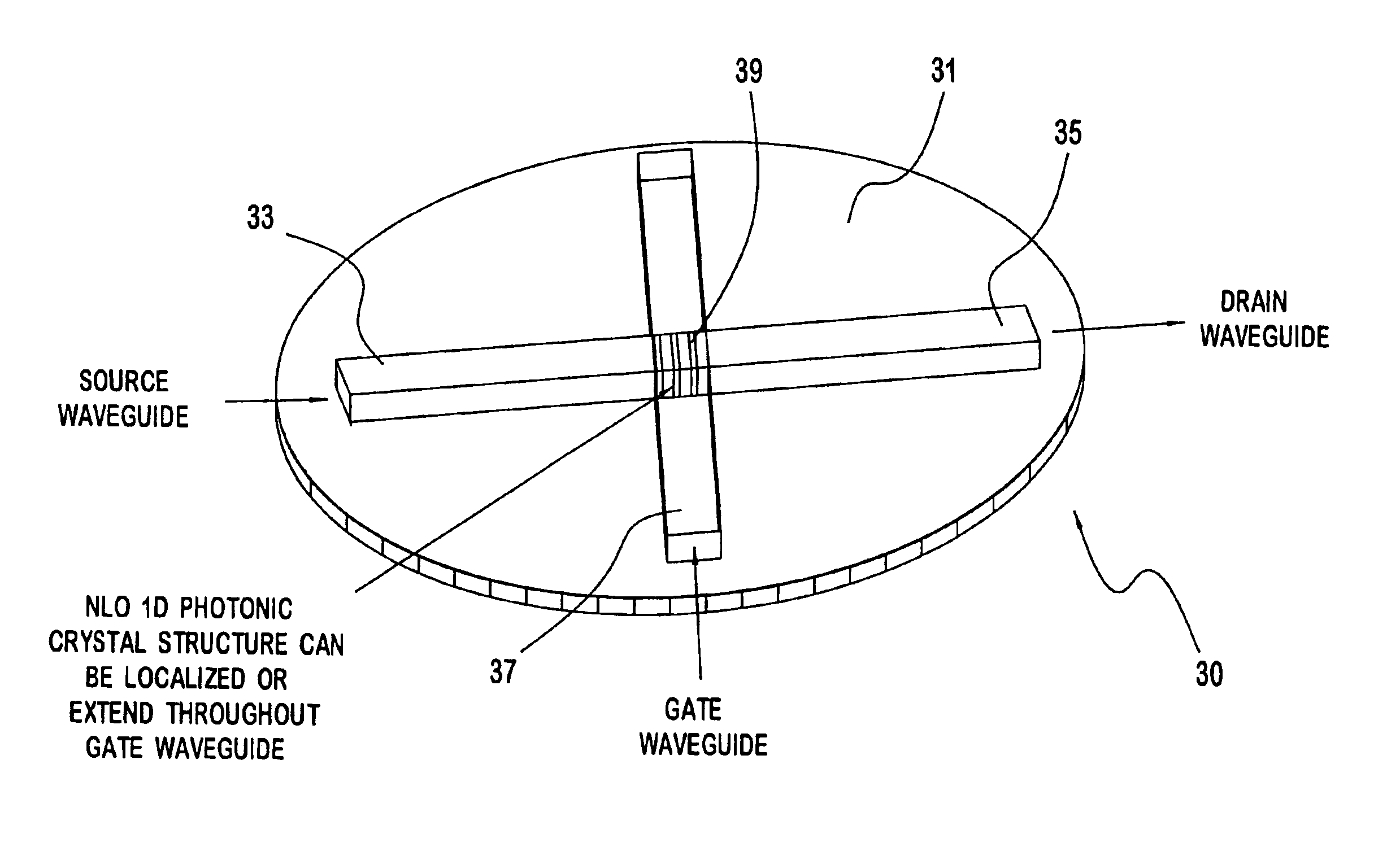
Non-linear photonic switch
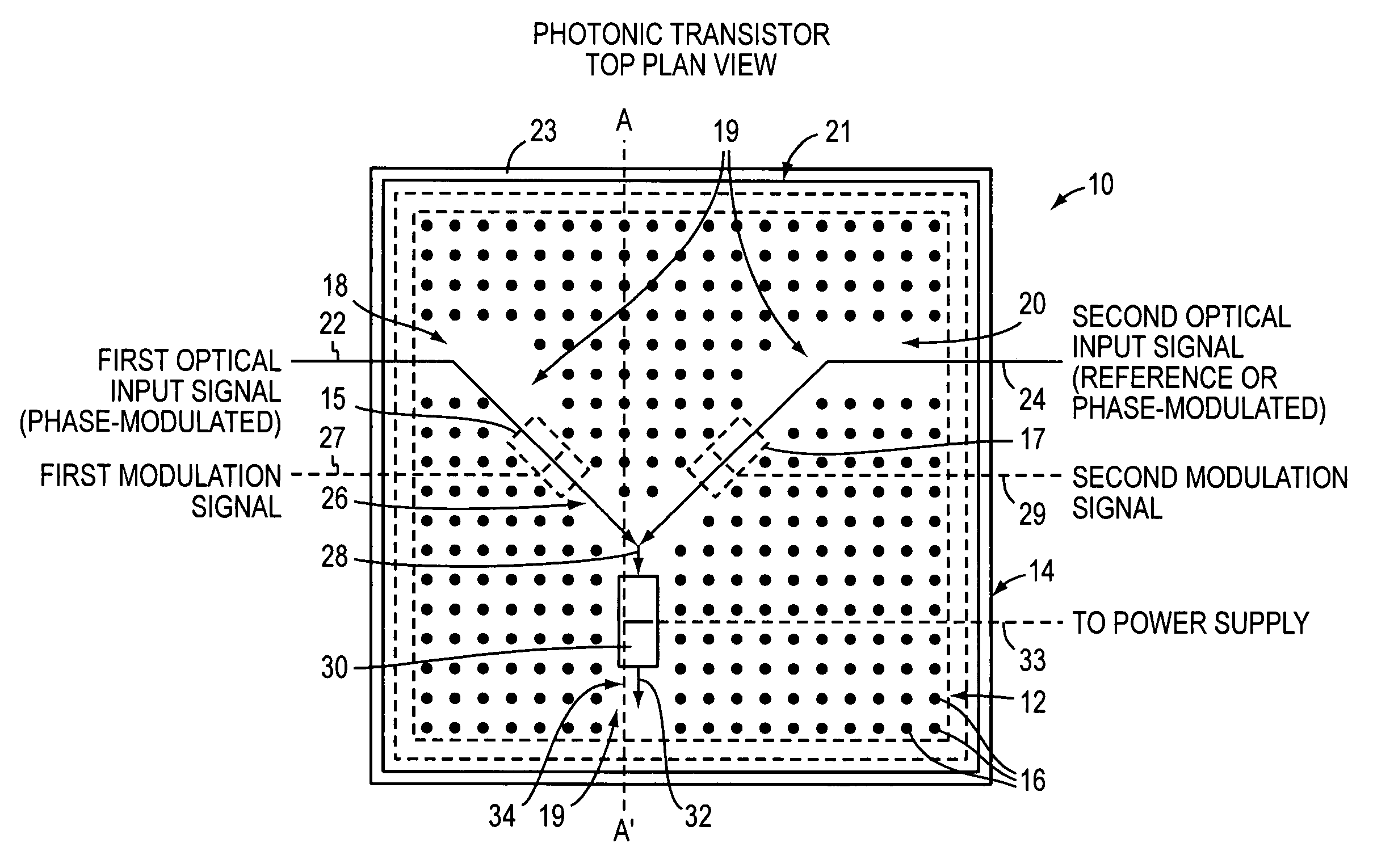
A photonic switch may be formed using one of a selected group of non-linear optical materials. Each of the materials within this group has a refractive index that demonstrates a substantial peak as a function of wavelength. The photonic switch includes a positive gain, and thus acts as a photonic transistor. In addition, a photonic switch is formed so that a gate signal is applied in a direction that is substantially perpendicular to the direction of the input signal so that there is no effective contamination of the input signal by the gate signal affecting the output signal.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
All-optical logic gates using nonlinear elements-claim set V
InactiveUS7409131B2Change quantityPrecise arrangementCoupling light guidesLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesLogic gateNonlinear element
An all-optical logic gates comprises a nonlinear element such as an optical resonator configured to receive optical input signals, at least one of which is amplitude-modulated to include data. The nonlinear element is configured in relation to the carrier frequency of the optical input signals to perform a logic operation based on the resonant frequency of the nonlinear element in relation to the carrier frequency. Based on the optical input signals, the nonlinear element generates an optical output signal having a binary logic level. A combining medium can be used to combine the optical input signals for discrimination by the nonlinear element to generate the optical output signal. Various embodiments include all-optical AND, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR, XOR, and XNOR gates and memory latch.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
Non-volatile programmable optical element employing f-centers
ActiveUS20100039848A1Low power operationCharacteristic can be alteredSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRecord information storageElectromagnetic radiationF-Center
A non-volatile programmable electro-optical element alters absorption characteristics of an optical medium that comprises a doped transition metal oxide material including F-centers. The F-centers are electrostatically moved into or out of the regions containing a wavefunction of an optical beam. A specific F-center profile in the transition metal oxide material may be programmed into the optical medium. The F-center profile alters an absorption profile within the optical medium. The spectral range for transmission of electromagnetic radiation in the optical medium may be tailored by the F-centers. Once the absorption profile is set by an electrical signal, the optical element maintains its state even when the electrical signal is turned off. Thus, the programming node may be disconnected from a power supply network, thereby enabling a low power operation of the electro-optical element. The inventive electro-optical element may be employed for both the visible and the infrared wavelength spectrum.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
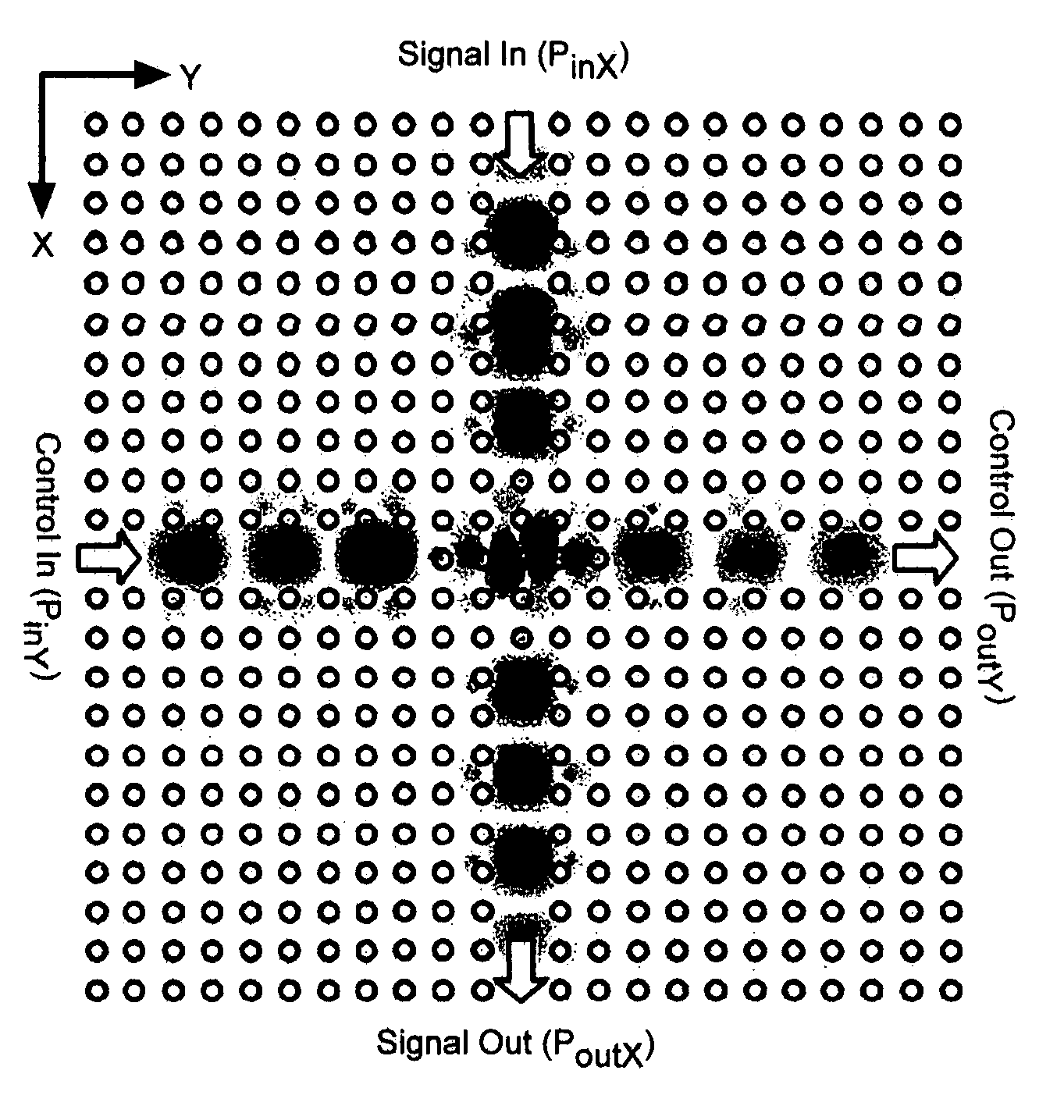
Rapidly reconfigurable all-optical universal logic gate
InactiveUS20080130084A1Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesOptical bistable devicesJoystickLaser light
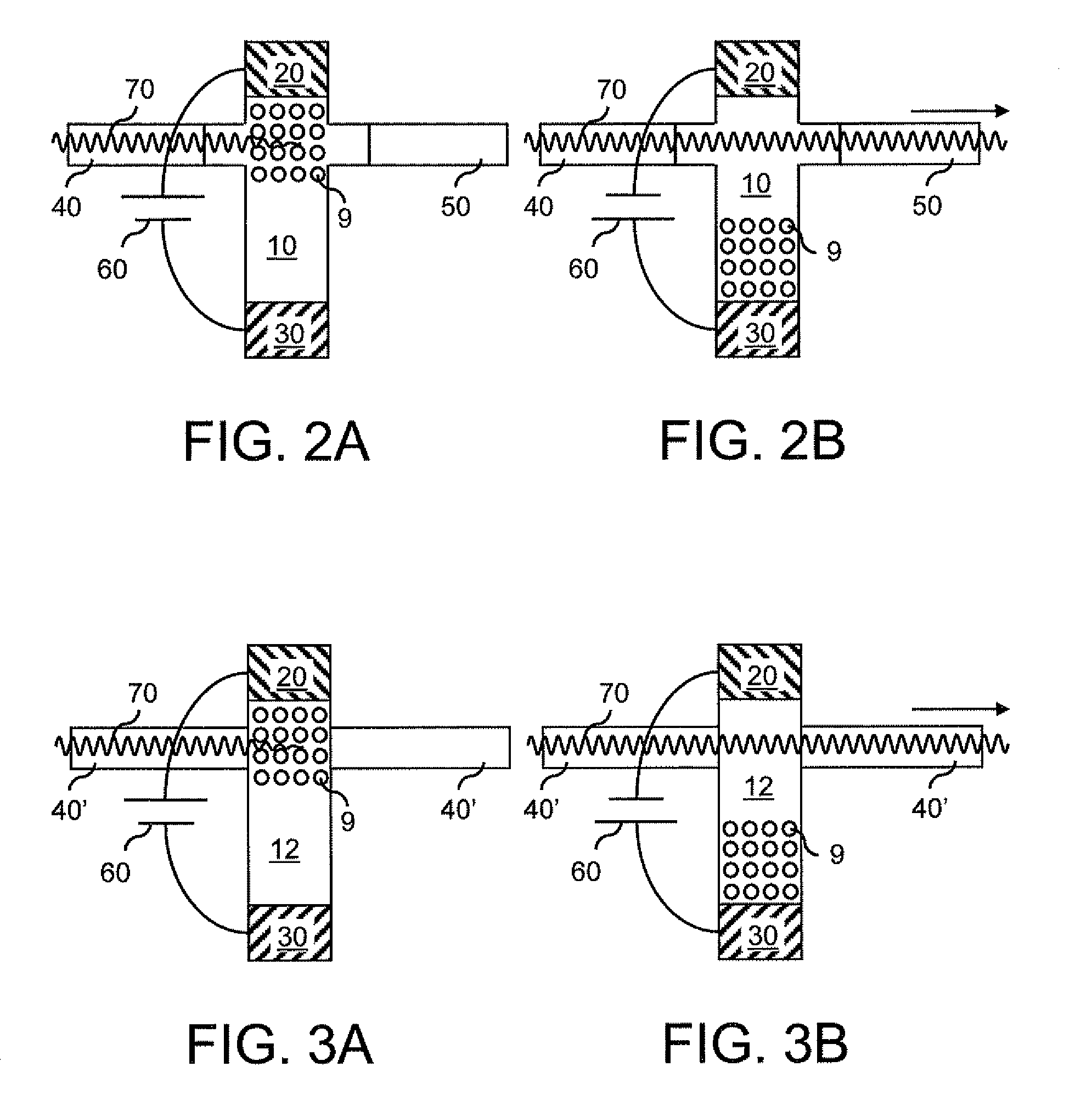
A new reconfigurable cascadable all-optical on-chip device is presented. The gate operates by combining the Vernier effect with a novel effect, the gain-index lever, to help shift the dominant lasing mode from a mode where the laser light is output at one facet to a mode where it is output at the other facet. Since the laser remains above threshold, the speed of the gate for logic operations as well as for reprogramming the function of the gate is primarily limited to the small signal optical modulation speed of the laser, which can be on the order of up to about tens of GHz. The gate can be rapidly and repeatedly reprogrammed to perform any of the basic digital logic operations by using an appropriate analog optical or electrical signal at the gate selection port. Other all-optical functionality includes wavelength conversion, signal duplication, threshold switching, analog to digital conversion, digital to analog conversion, signal routing, and environment sensing. Since each gate can perform different operations, the functionality of such a cascaded circuit grows exponentially.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Reconfigurable dynamic full light chaos logic gate
InactiveCN107065392AAchieve conversionRealize mutual conversionOptical bistable devicesSecuring communicationBeam splitterOptical isolator
The invention relates to the field of photon equipment and especially relates to a reconfigurable dynamic full light chaos logic gate which comprises a tunable distribution-feedback laser device, a beam splitter, a vertical chamber surface emission laser device, an optical isolator, a polarization beam splitter, a first subtracter and a second subtracter. The reconfigurable dynamic full light chaos logic gate provided by the invention has the advantages that conversion between a full light chaos logic gate operation and each logic gate operation is achieved; specifically, operations of ''AND'' gate, ''NAND'' gate, ''OR'' gate, ''NOR'' gate, ''XOR'' gate, and ''XNOR'' gate operations as well as mutual conversion can be achieved; and the reconfigurable dynamic full light chaos logic gate can be generalized and applied to logic operations of a full light digital chaos combination.
Owner:WUYI UNIV
Unidirectional optical transmitting method and apparatus for photonic crystal based all-optical diode
ActiveCN105720475AWide bandwidth in the bistable rangeImprove working bandwidthOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical bistable devicesContinuous wave signalPulsed laser
The invention discloses a unidirectional optical transmitting method for a photonic crystal based all-optical diode. A direct coupling micro cavity and a side coupling micro cavity of the photonic crystal are pumped by two ultra-short pulse laser with adjustable power respectively, wherein the direct coupling micro cavity is taken as a variable transmission unit while the side coupling micro cavity is taken as a variable reflection unit; multiple combinations of optical dual stable states, including a high-energy state and a low-energy state, of the two micro cavities can be realized by choosing proper pulse pumping power based on a nonlinear Kerr effect; and the incident continuous wave signal is subjected to the dual regulation and control by the two micro cavities, so that the forward high transmission or backward high transmission of the all-optical diode can be realized. The invention also discloses a unidirectional optical transmitting apparatus for the photonic crystal based all-optical diode. The pass-through directions of the signal light can be freely controlled by adjusting the pumping power of the ultra-short pulse laser; and extremely high forward transmission and backward transmission contrast ratio and relatively high operating bandwidth can be obtained.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
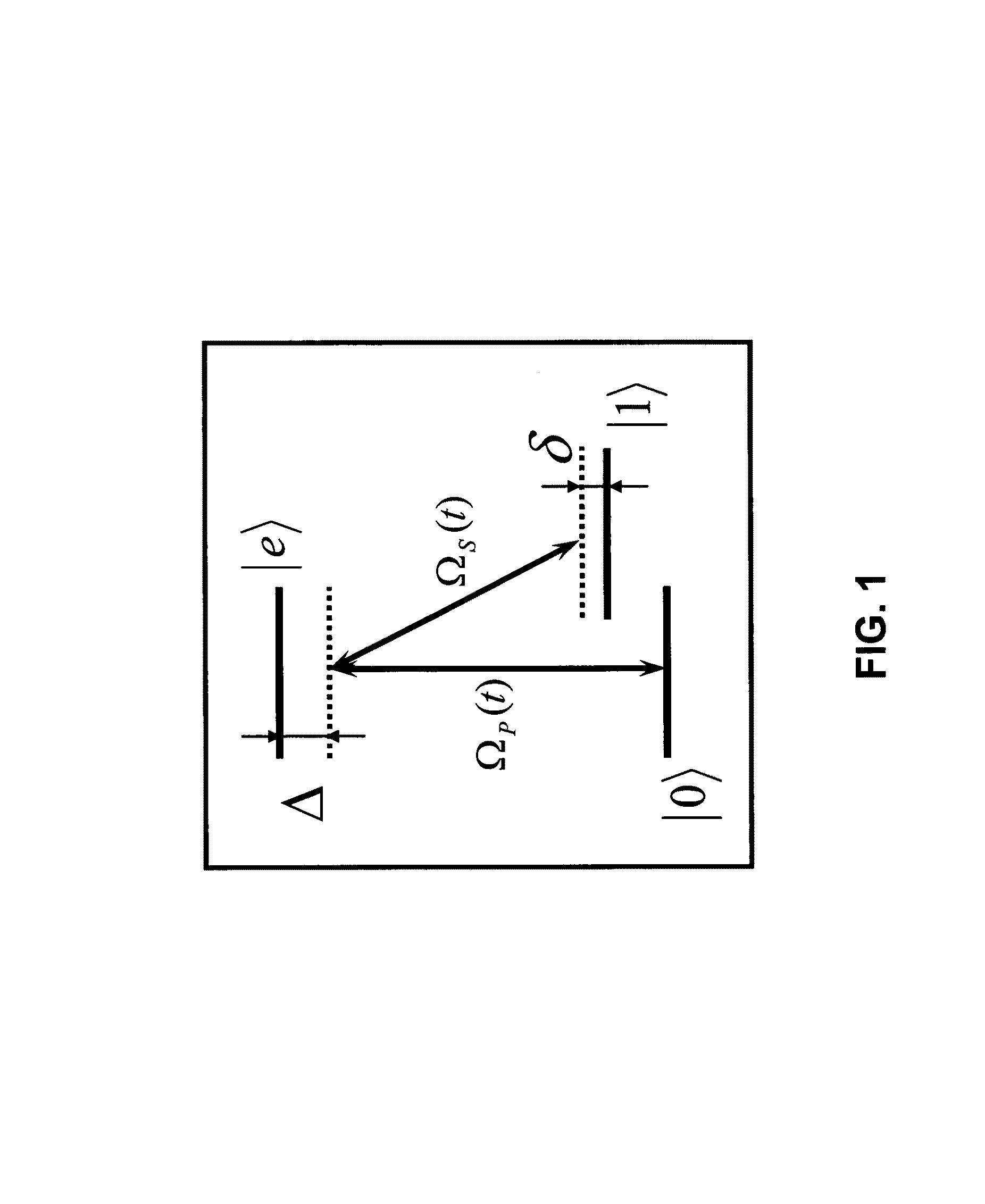
Phase-Switched Optical Flip-Flops Using Two-Input Bistable Resonators and Methods
A two-input bistable resonator that can be switched in a robust way by phase modulation of the input beams is presented. An optical flip-flop of the present invention may be embodied as a two-input Kerr resonator. The disclosed switching mechanism is compatible with cross-phase modulation induced by set and reset pulses for realization of an ultrafast, passive, all-optical memory element.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
All-optical flip-flop
The present invention provides a set-reset flip-flop operating in an all-optical manner. In this invention, a set pulse is inputted from the setting port. In doing so, only oscillation in set mode is generated at the multi-mode interference portion in a waveguide. As a result, a non-inverting output Q is obtained from the non-inverting output port. This state is then continued even if the set pulse input goes off. Next, a reset pulse is inputted to the resetting port. In doing so, at the multi-mode interference portion, oscillation of light in the set mode is halted, and oscillation in the reset mode occurs. As a result, it is possible to obtain an inverting output Q-bar from the inverting output port. This state is then continued even if the reset pulse goes off.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
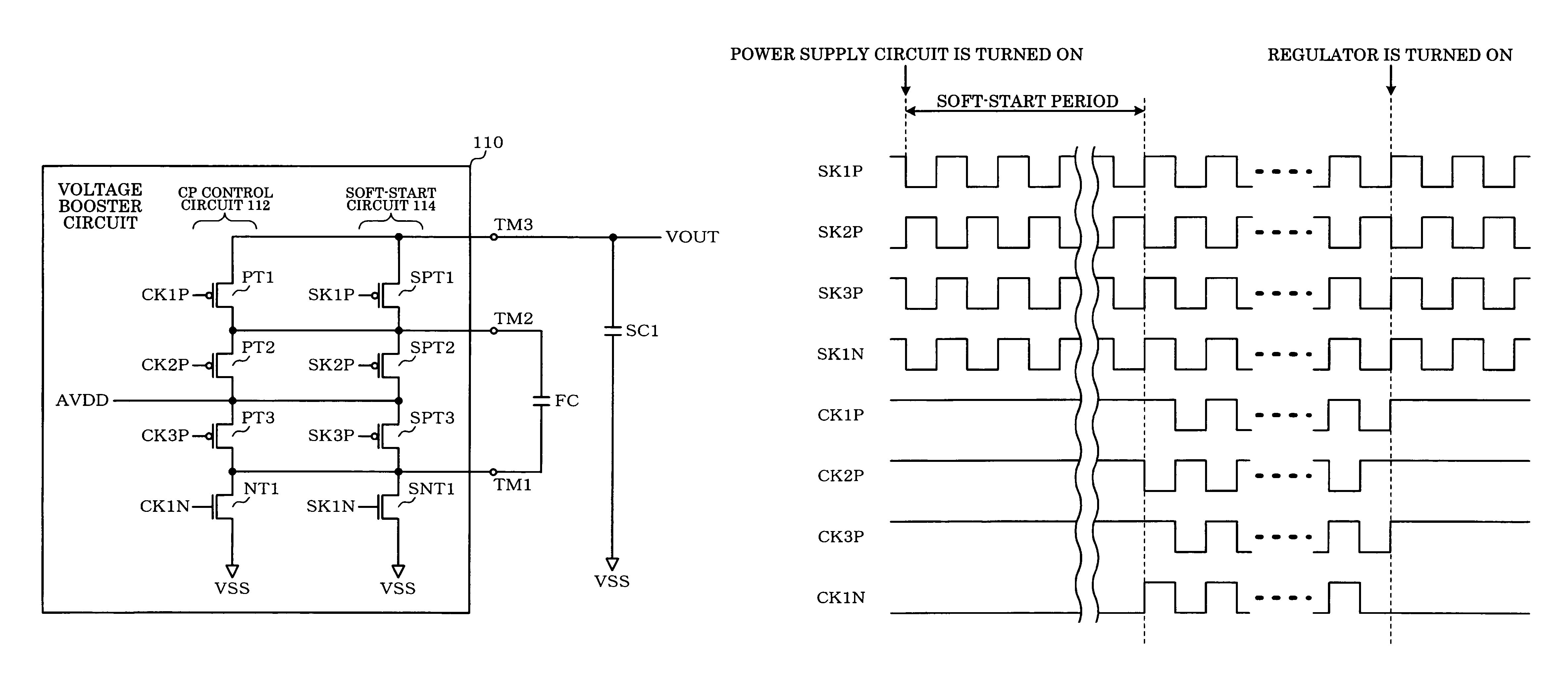
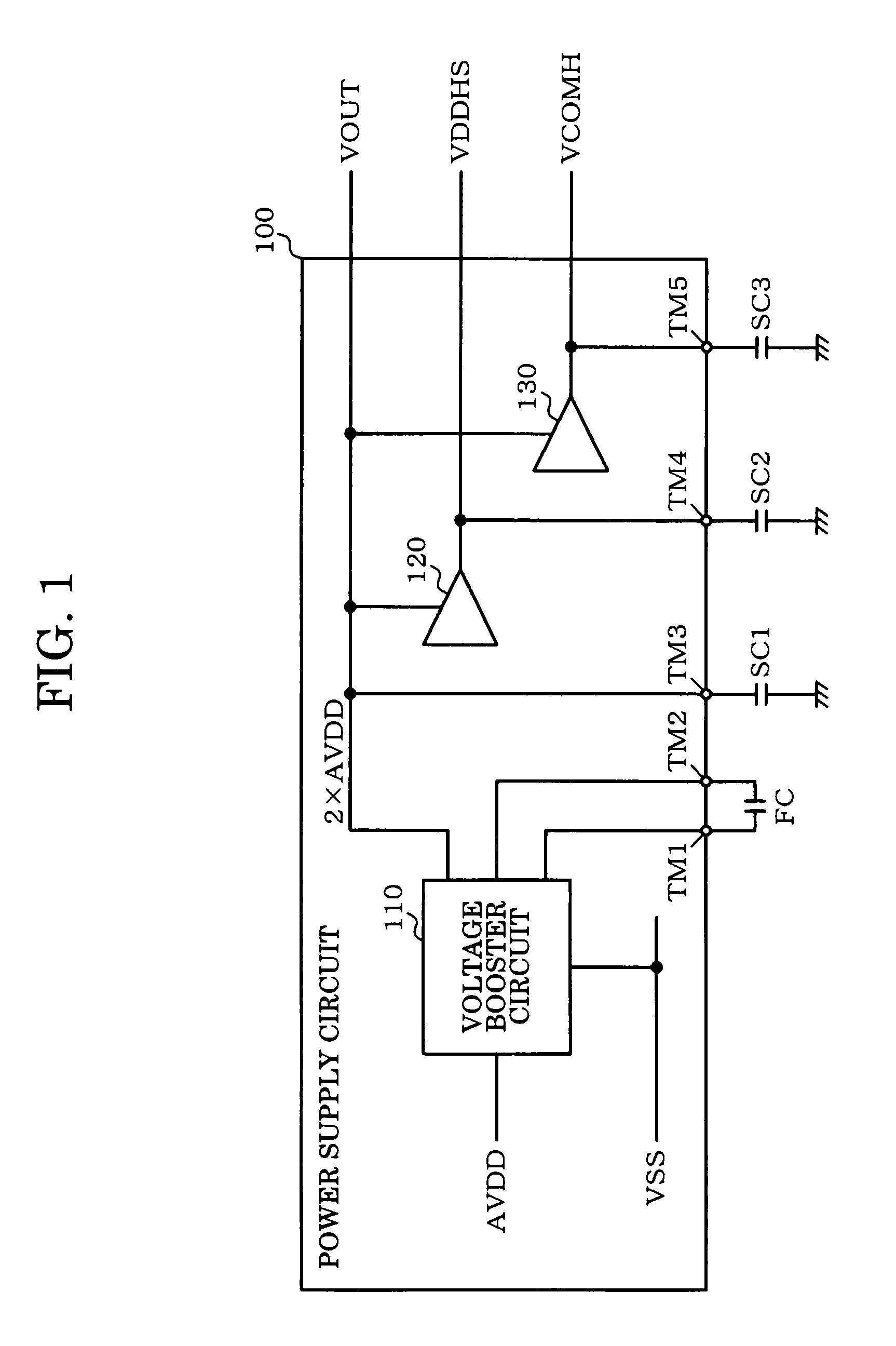
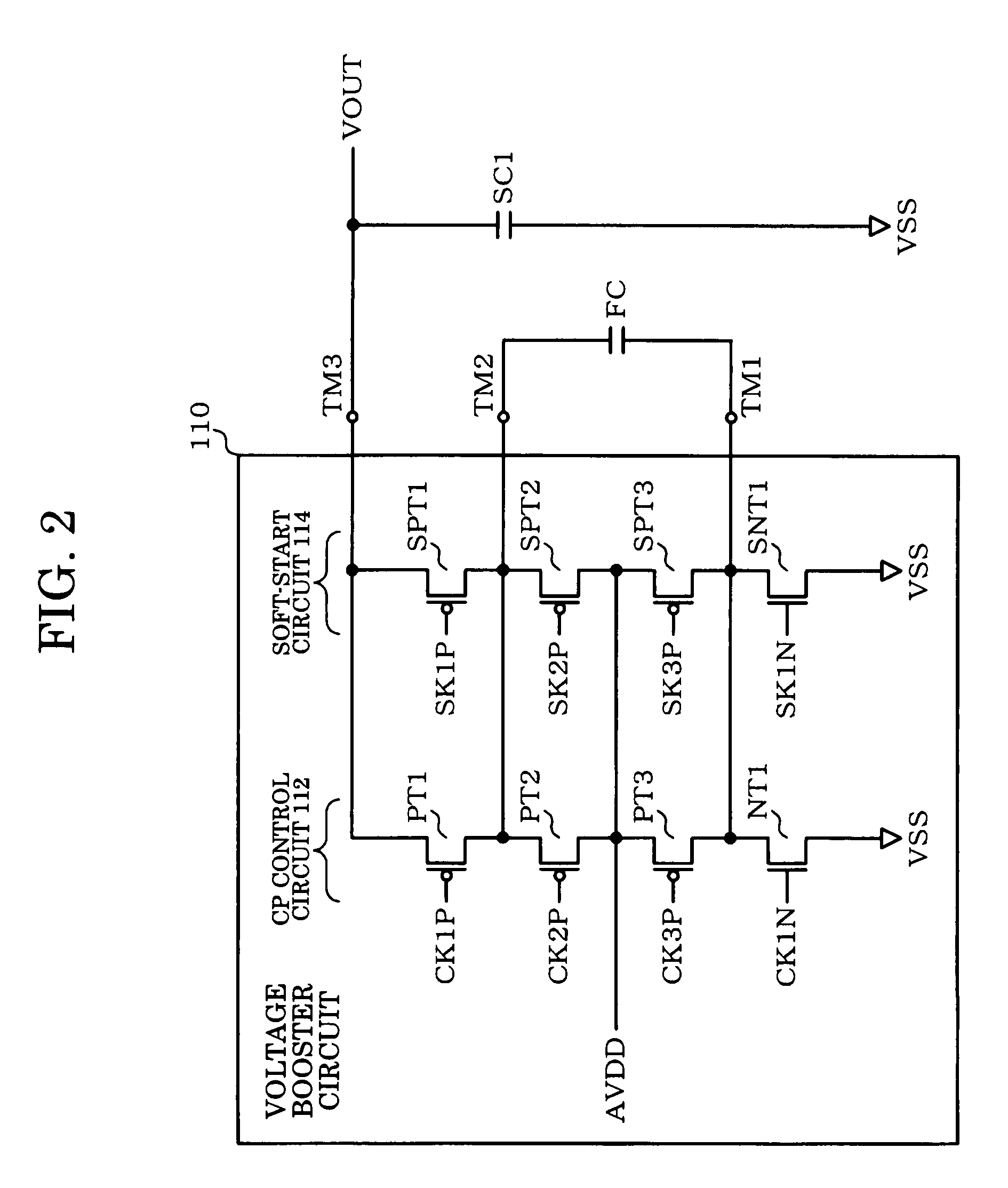
Power supply circuit, display driver, electro-optical device, and electronic instrument
InactiveUS7880530B2Avoid flowAc-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringElectron
A power supply circuit which boosts a given voltage to generate one or more power supply voltages includes a charge-pump control circuit including switching elements for generating a boost voltage by a charge-pump operation using charge stored in a flying capacitor, a soft-start circuit which prevents a rush current toward the flying capacitor, and a power supply generation circuit which is connected with a stabilization capacitor and generates a power supply voltage using the boost voltage as a power supply. After the power supply generation circuit has been turned ON in a state in which the charge-pump control circuit generates the boost voltage by the charge-pump operation, the switching elements are turned OFF, and the soft-start circuit generates the boost voltage by a charge-pump operation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical bistable device applied to all-optical switch and optical memory
ActiveCN109634025ALarge third-order nonlinear coefficientRaise the thresholdOptical bistable devicesCommunications systemOptical communication
The invention provides an optical bistable device applied to an all-optical switch and an optical memory, which belongs to the technical field of all-optical communication systems. The optical bistable device has a multilayer structure formed by eight first dielectric layers, eight second dielectric layers and fifteen graphene layers, specifically from the upper surface to the lower surface in sequence, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a first dielectric layer, agraphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a first dielectric layer, a graphene layer, a second dielectric layer, a graphene layer and a first dielectric layer. The optical bistable device applied to the all-optical switch and the optical memory has the advantages of reducing the optical bistable threshold.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electro-optical logic techniques and circuits
InactiveUS20120038960A1Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesOptical bistable devicesElectricityControl signal
A method for implementing an electro-optical logic function responsive to first and second logical inputs, includes the following steps: providing, as an output stage, a light-emitting transistor having an electrical input port and an optical output port; and providing, as an input stage, a circuit for receiving the first and second logical inputs and producing a control signal that is coupled with the electrical input port of the output stage.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optical device and circuit using phase modulation and related methods
InactiveUS7657188B2Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesElectromagnetic transmittersLogic gateNonlinear element
A disclosed apparatus comprises a guiding element and a nonlinear element. The guiding element guides optical input signals, at least one of which is phase-modulated, to an interference area where such signals meet and interfere. The resulting interference signal is nonlinearly discriminated by the nonlinear element to produce an optical output signal that can be amplitude- or phase-modulated according to the phase modulation of the input signals. The invention also includes related methods and photonic logic gates.
Owner:COVEY JOHN
Optical transistor and method thereof
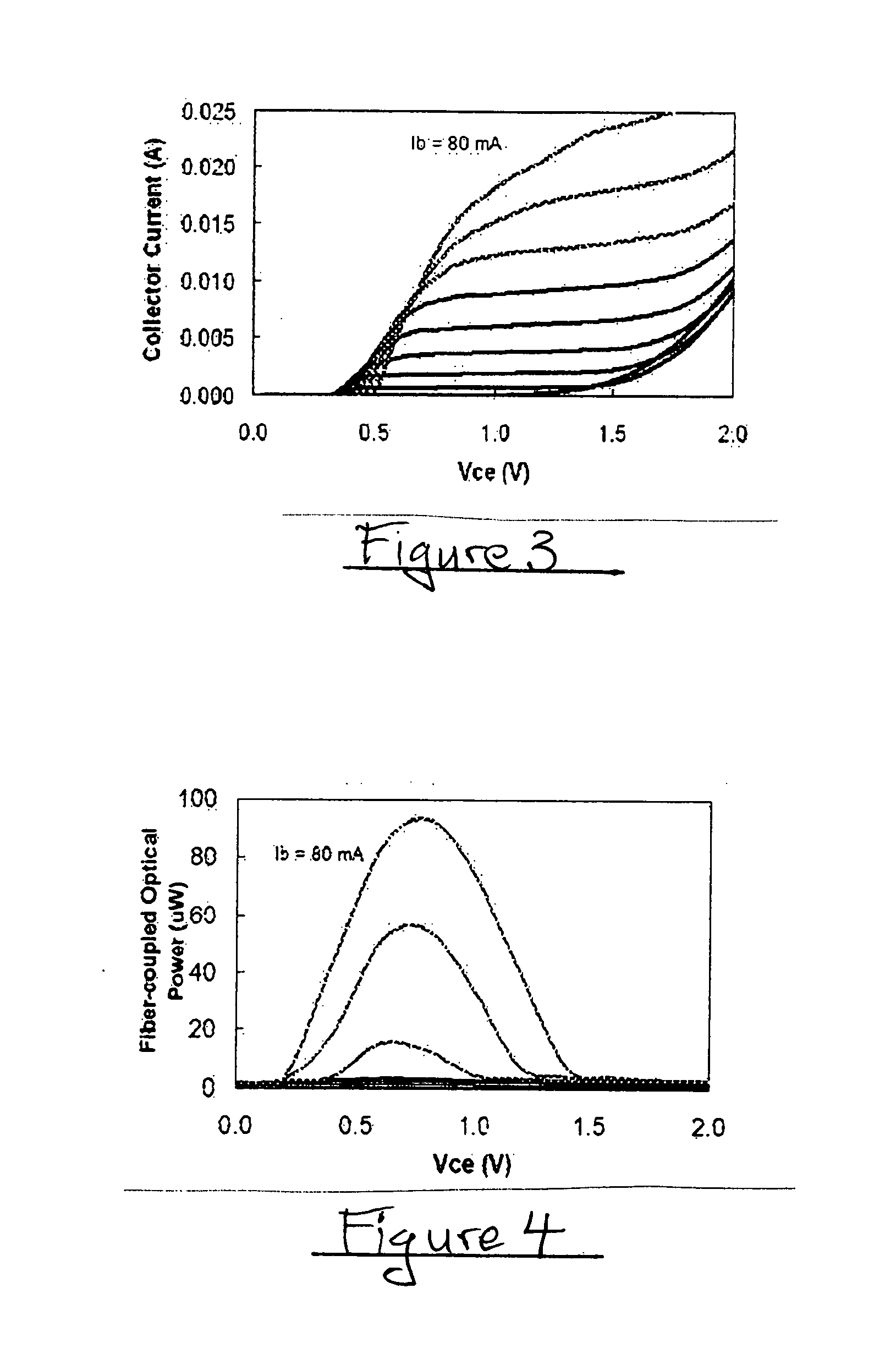
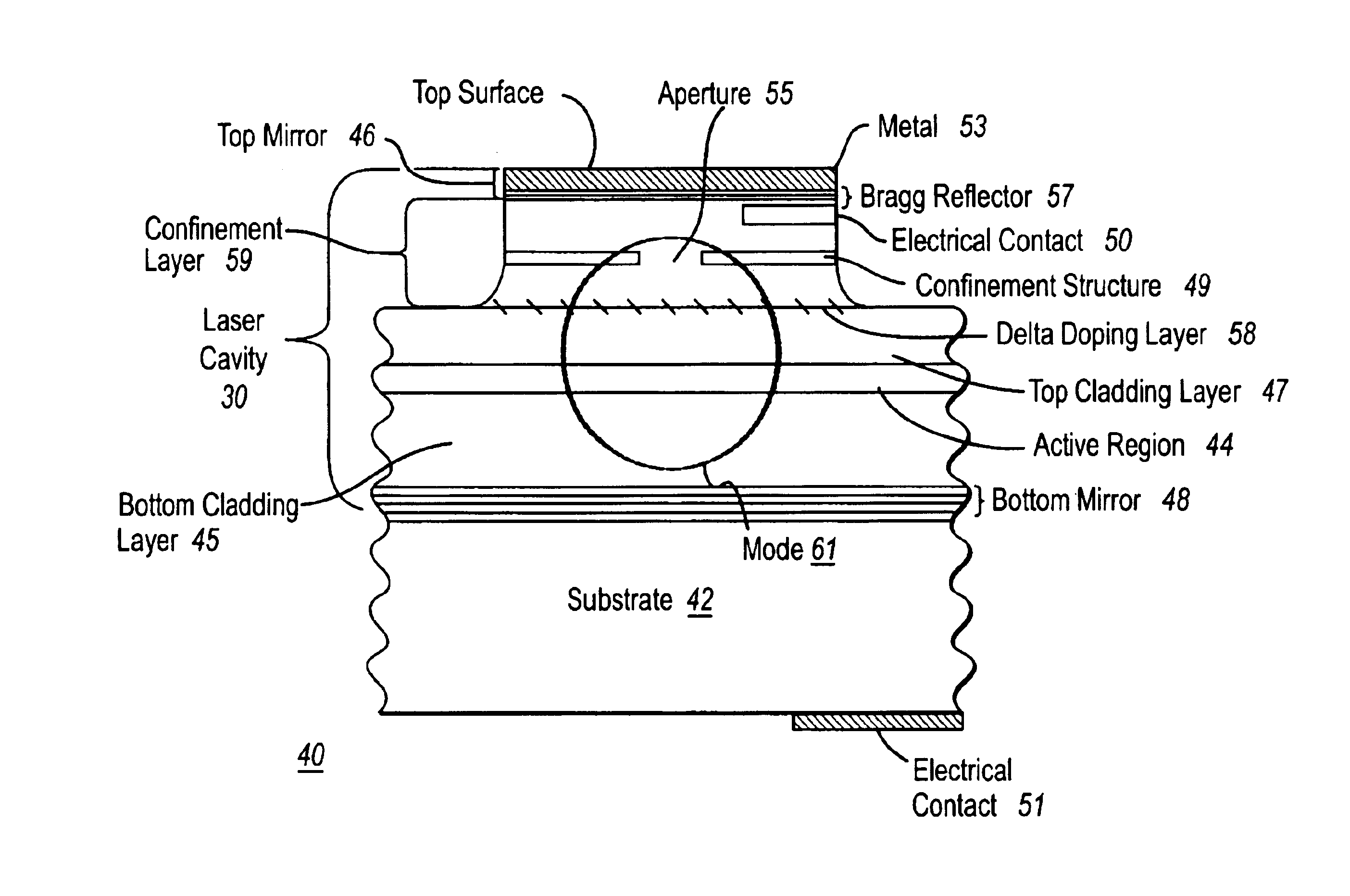
InactiveUS6847054B1Fast switching timeHigh gainSolid-state devicesLight demodulationSemiconductorOptical amplifier
An optical transistor is disclosed that provides a fast switching time, an amplified gain, and isolation. The optical transistor receives a small optical input signal at an optical base port, generates an amplified replica at an optical emitter port, and generates an inverted replica on a vertical light at an collector port. One embodiment of the optical transistor is implemented with a vertical lasing semiconductor optical amplifiers (VLSOA), wherein the ballast light is used a signal for the collector port.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
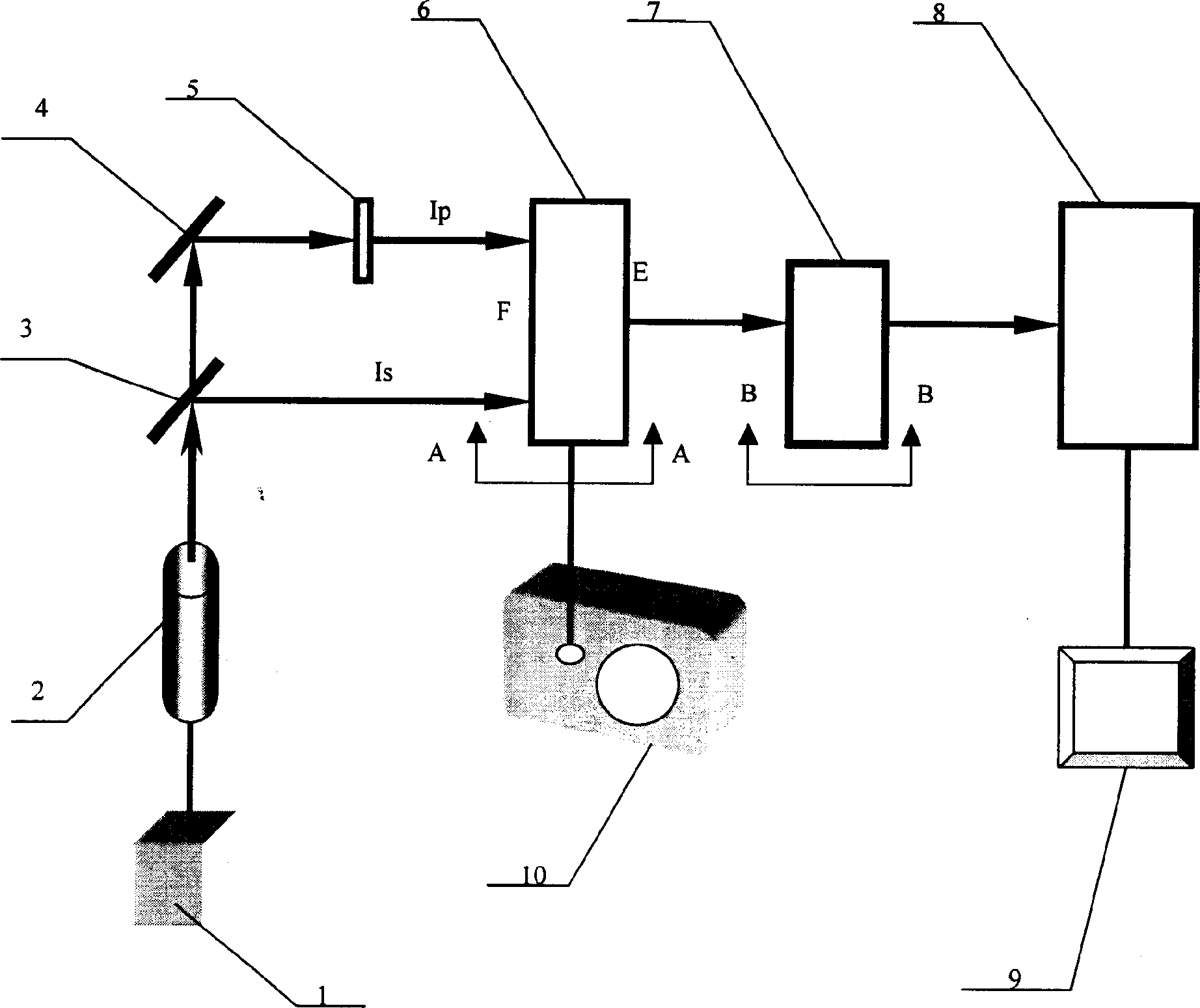
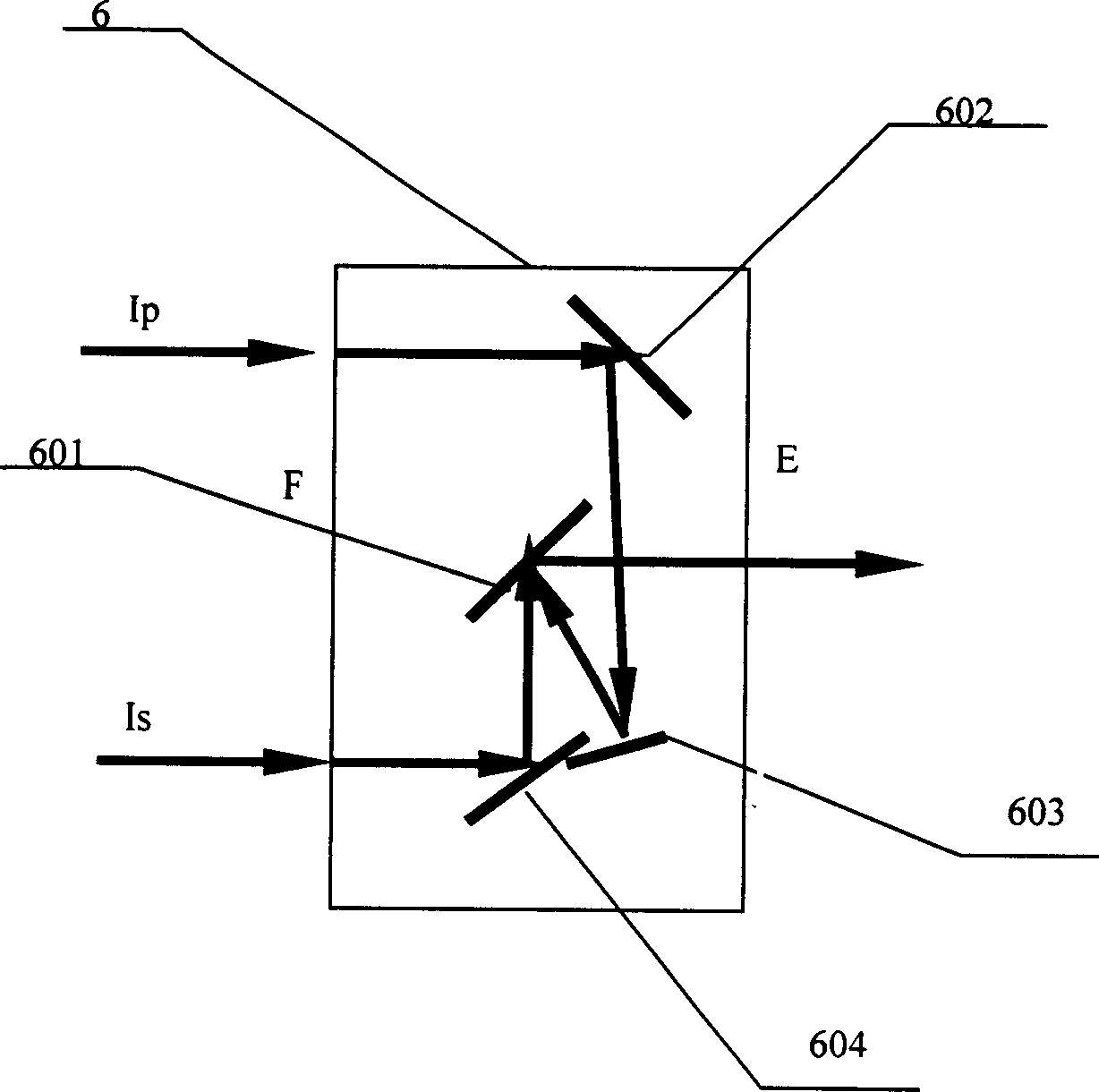
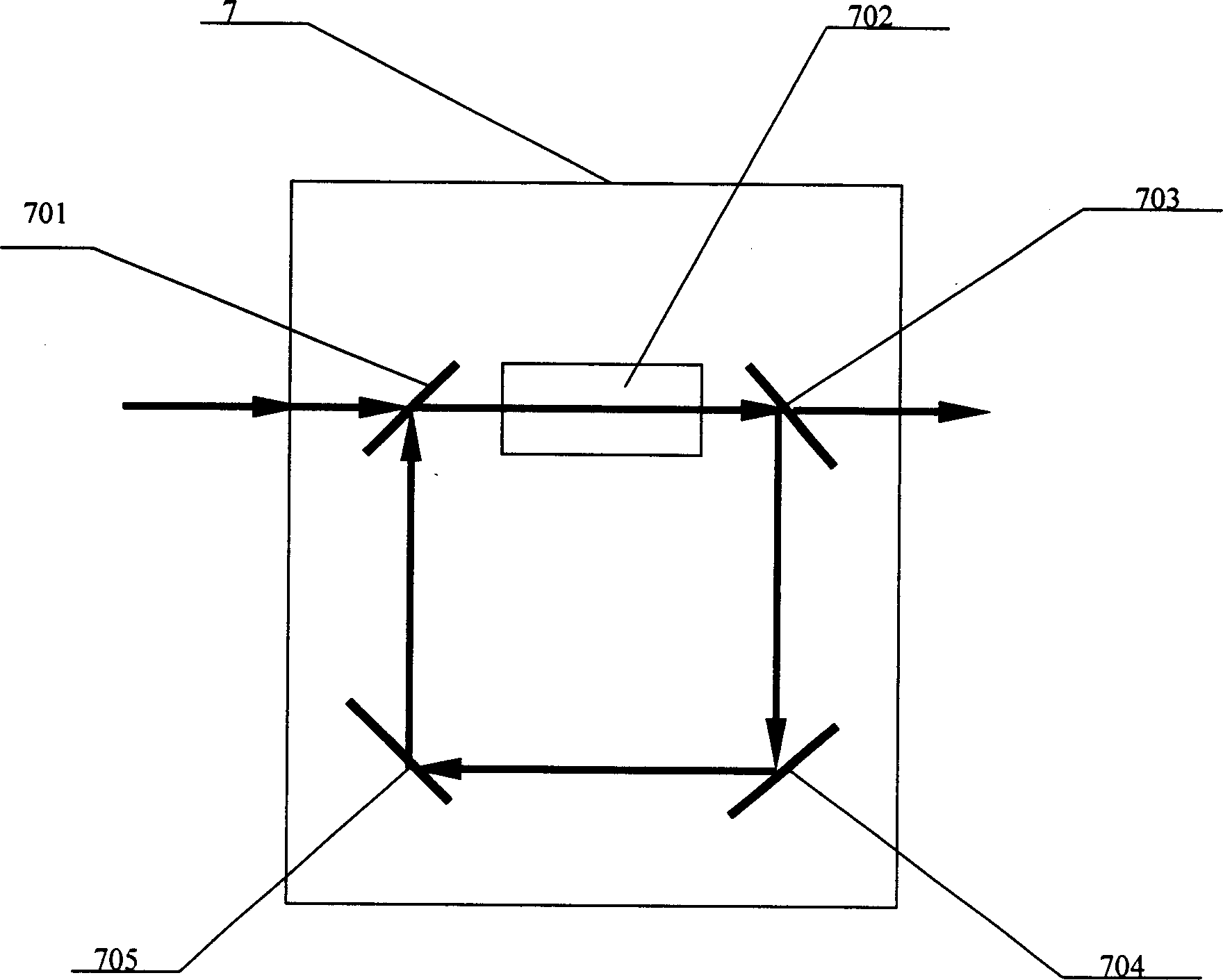
Stark chatter optical bistable high speed switch device
InactiveCN1445581AHigh reverse efficiencyEasy to implementExcitation process/apparatusOptical bistable devicesPolarizerOptoelectronics
A high-speed dual-stable optical stark chirp switch device is composed of laser pump source, laser source, semi-transmitting and semi-reflecting polarizer, polarizing planar reflection plate, frequency-doubling crystal, pulse delay unit, pulse delay monitoring controller, medium cavity and receiver. Its advantages are simple structure, and high switching speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
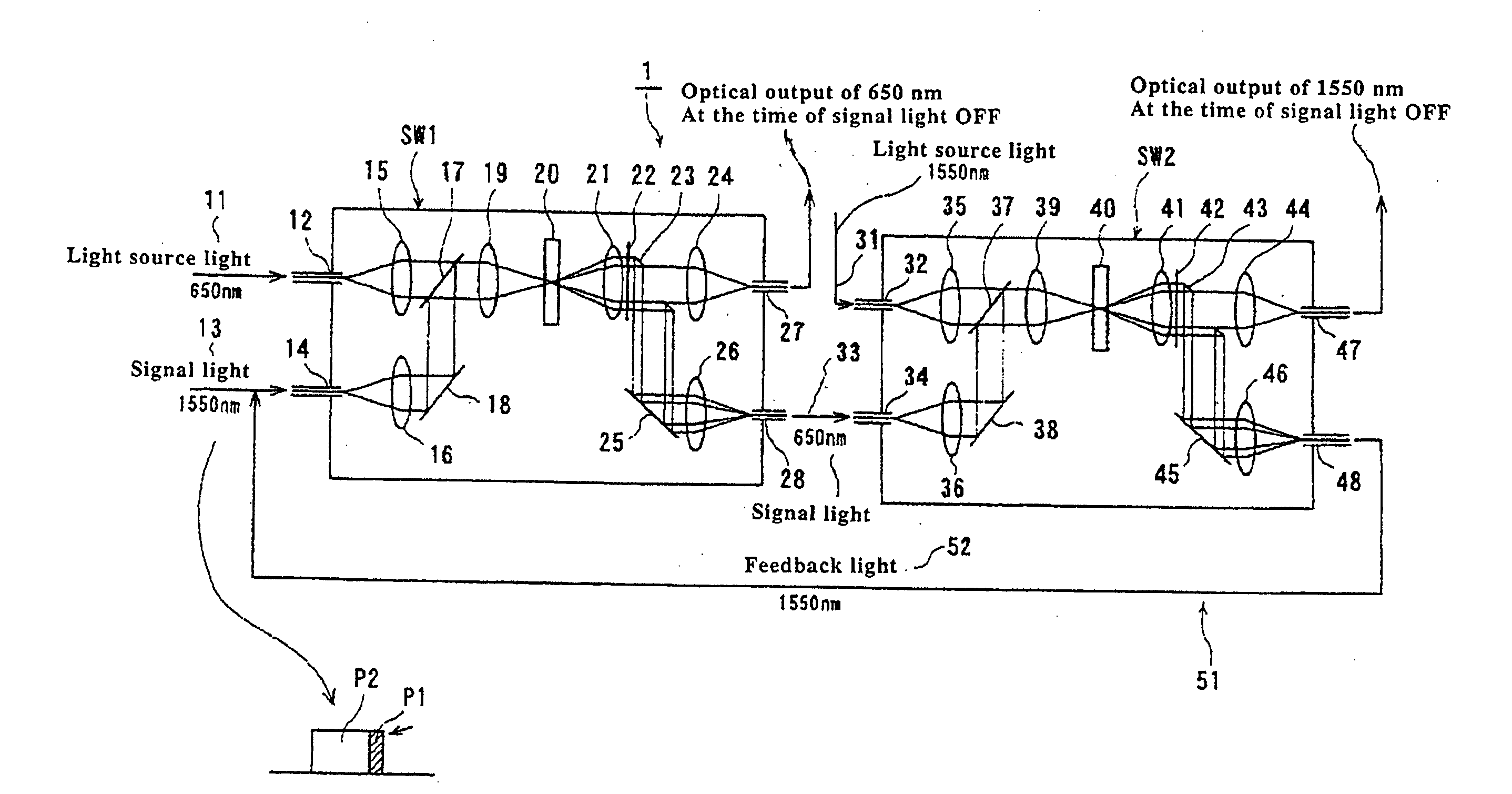
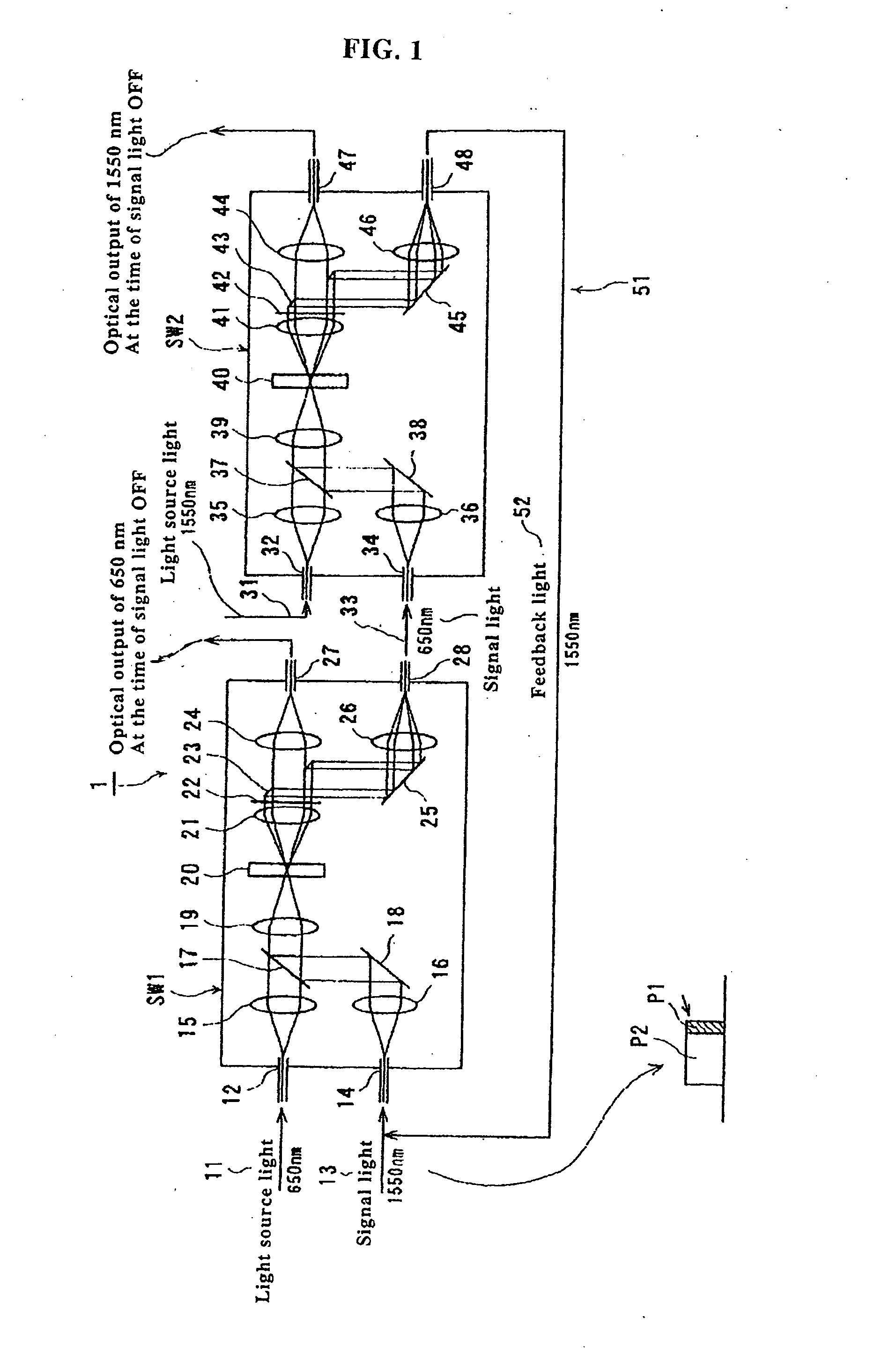
Optical flip-flop circuit
A flip-flop circuit of the present invention includes a first switch and a second switch which are connected in series to each other. The first switch includes: two input ports upon which light source light and signal light are incident; two output ports for outputting an optical output; and a thermal lens forming element for forming a thermal lens in a predetermined optical inputting condition. Although the second switch is composed in the same manner as that of the first switch, a relation between the wave-lengths to be utilized is inverted. When a state is changed from OFF to ON, a pulse signal is inputted for setting and one of the rays of output light of the second switch is fed-back to the first switch so as to maintain the state of ON. When the state is changed from ON to OFF, a pulse of additional signal light is inputted. Due to the foregoing, the two states of ON and OFF can be stably maintained.
Owner:DAINICHISEIKA COLOR & CHEM MFG CO LTD +1
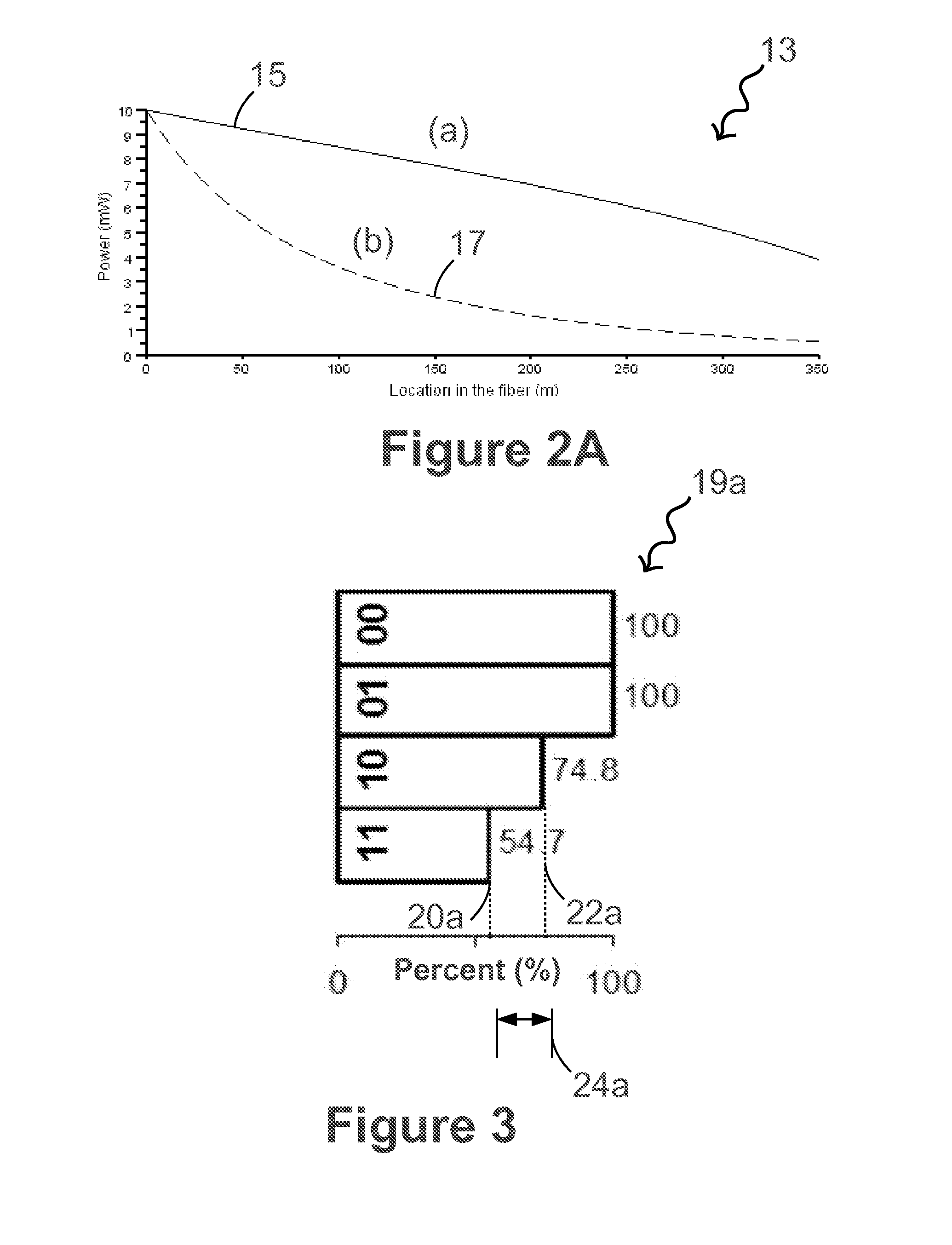
All-optical NAND/not/and/or logic gates based on combined brillouin gain and loss in an optical fiber
ActiveUS20140098408A1Logic circuits using opto-electronic devicesOptical bistable devicesPhysicsBrillouin gain
A combined Brillouin gain and loss process has been created in a polarization maintaining optical fiber to realize all-Optical NAND / NOT / AND / OR logic gates in the frequency domain. A model describing the interaction of a Stokes, anti-Stokes and continuous wave, and two acoustic waves inside a fiber, ranging in length from 350 m-2300 m, was used to theoretically model the gates. Through the optimization of the gain and loss process, switching contrasts of 20-88% have been achieved, under different configurations. Experimental setups for NAND / NOT / AND / OR optical logic gates have been described. A method and system for designing the all-optical logic gates have been also provided.
Owner:WILLIAMS DAISY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com