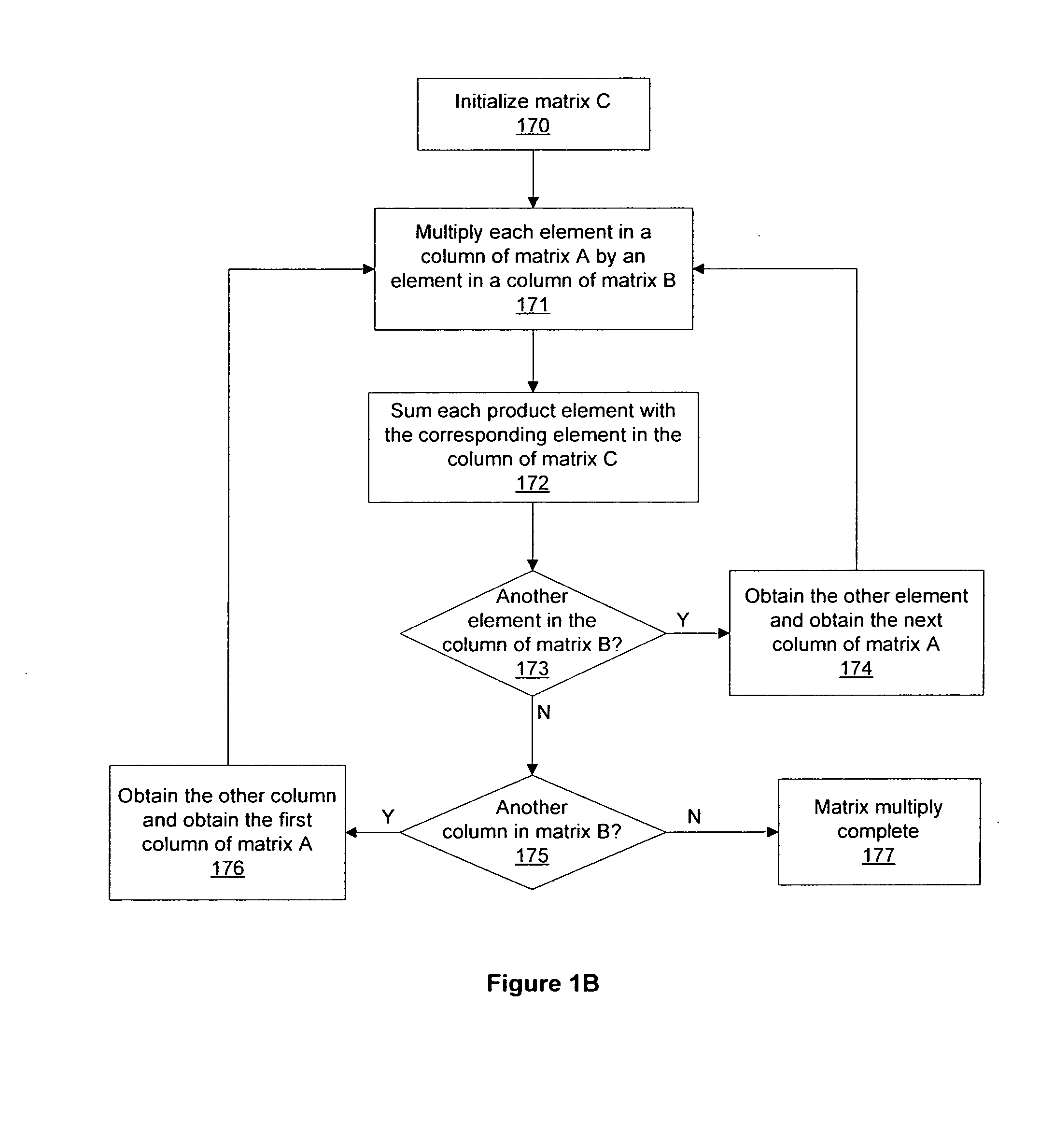
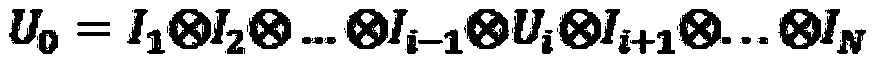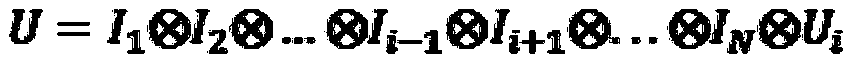Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
835 results about "Matrix element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
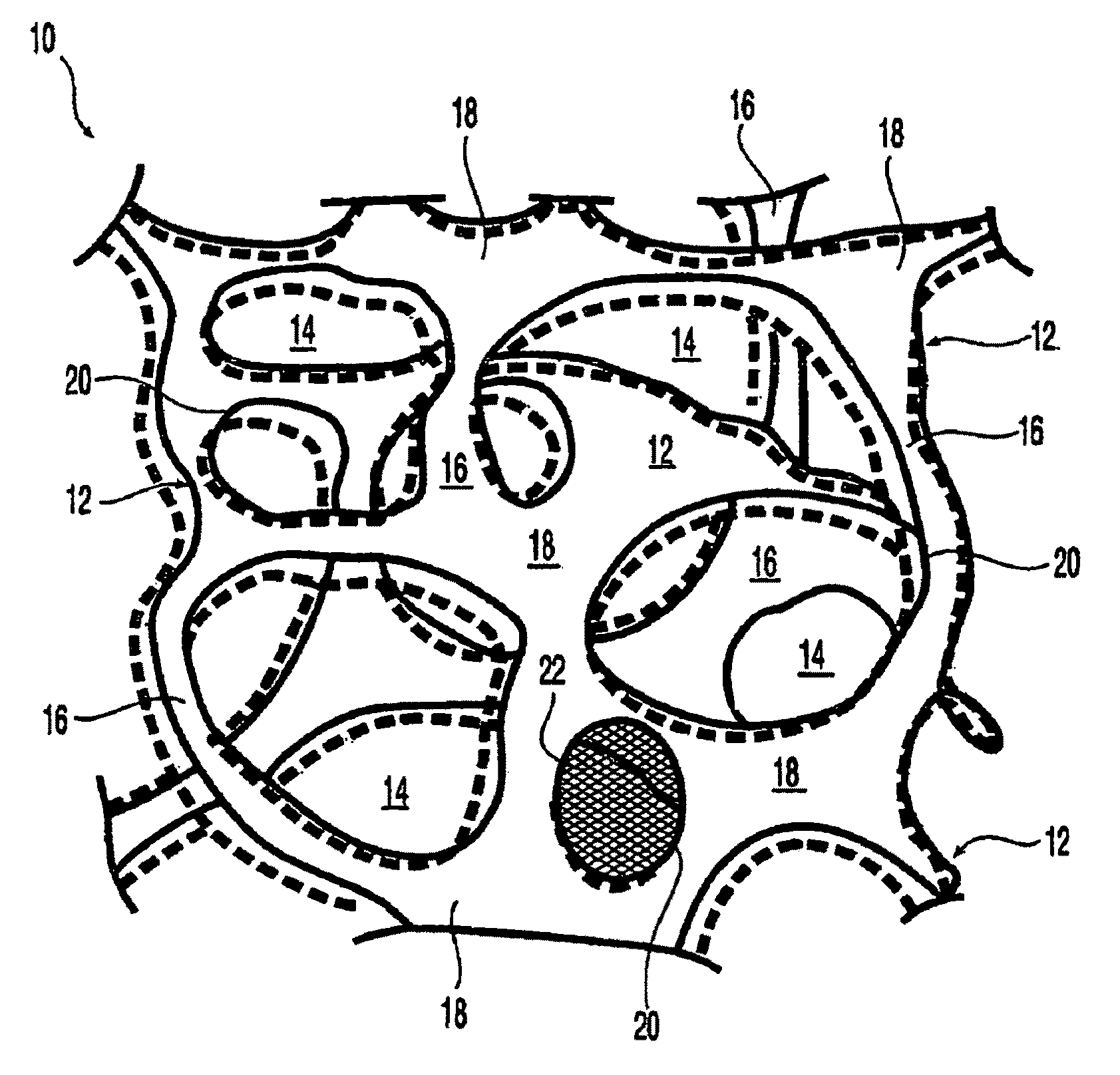
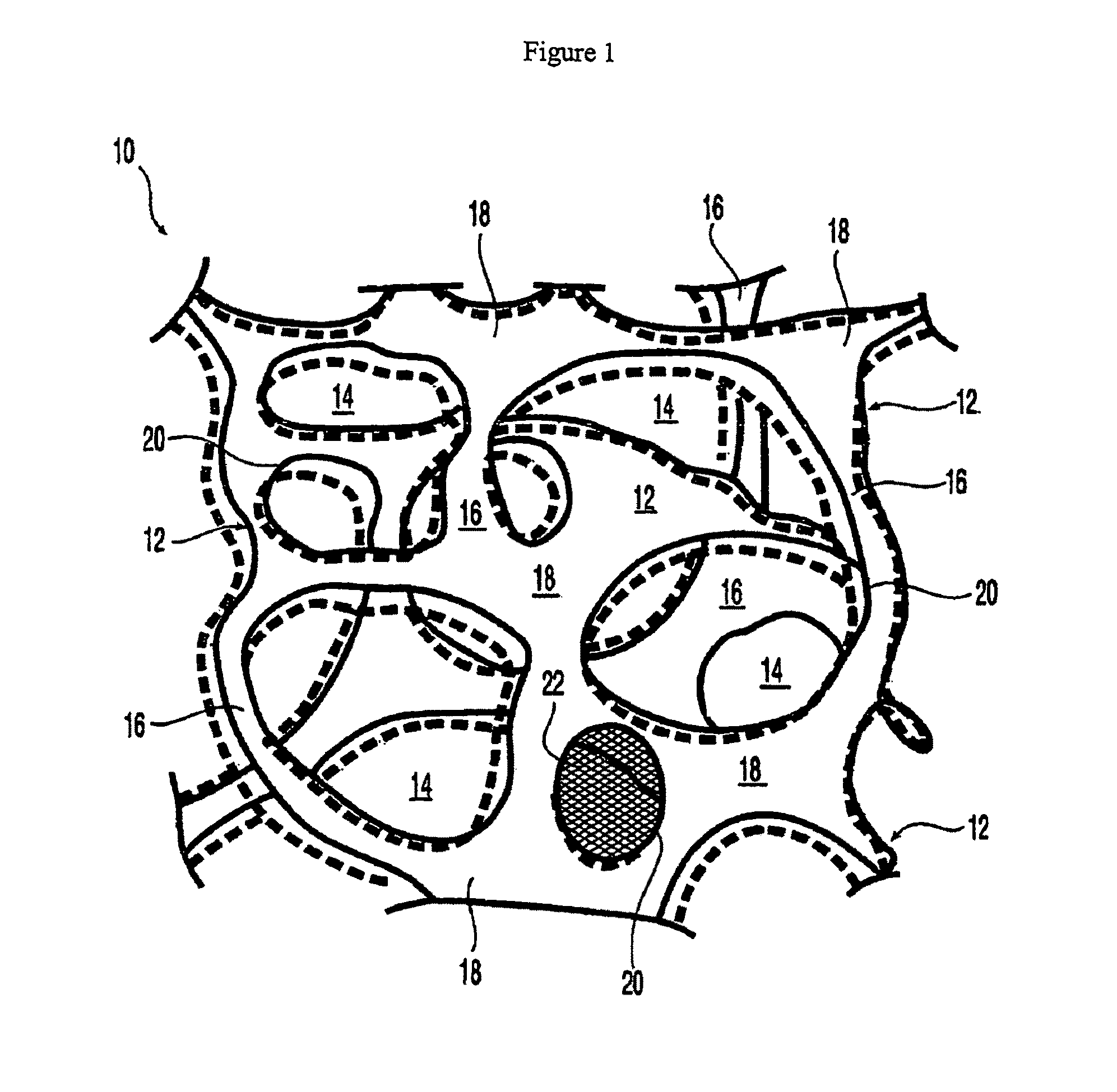
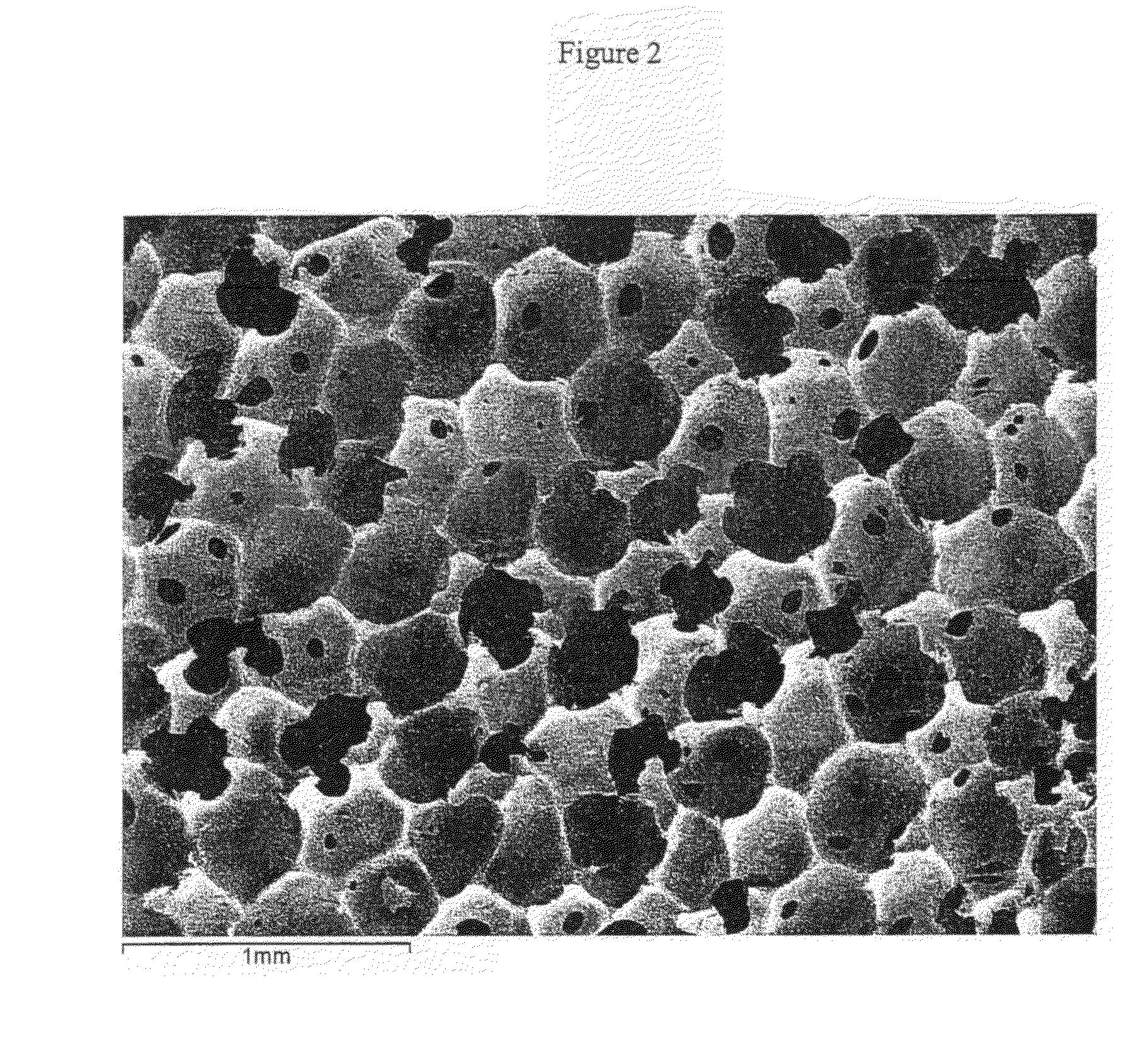
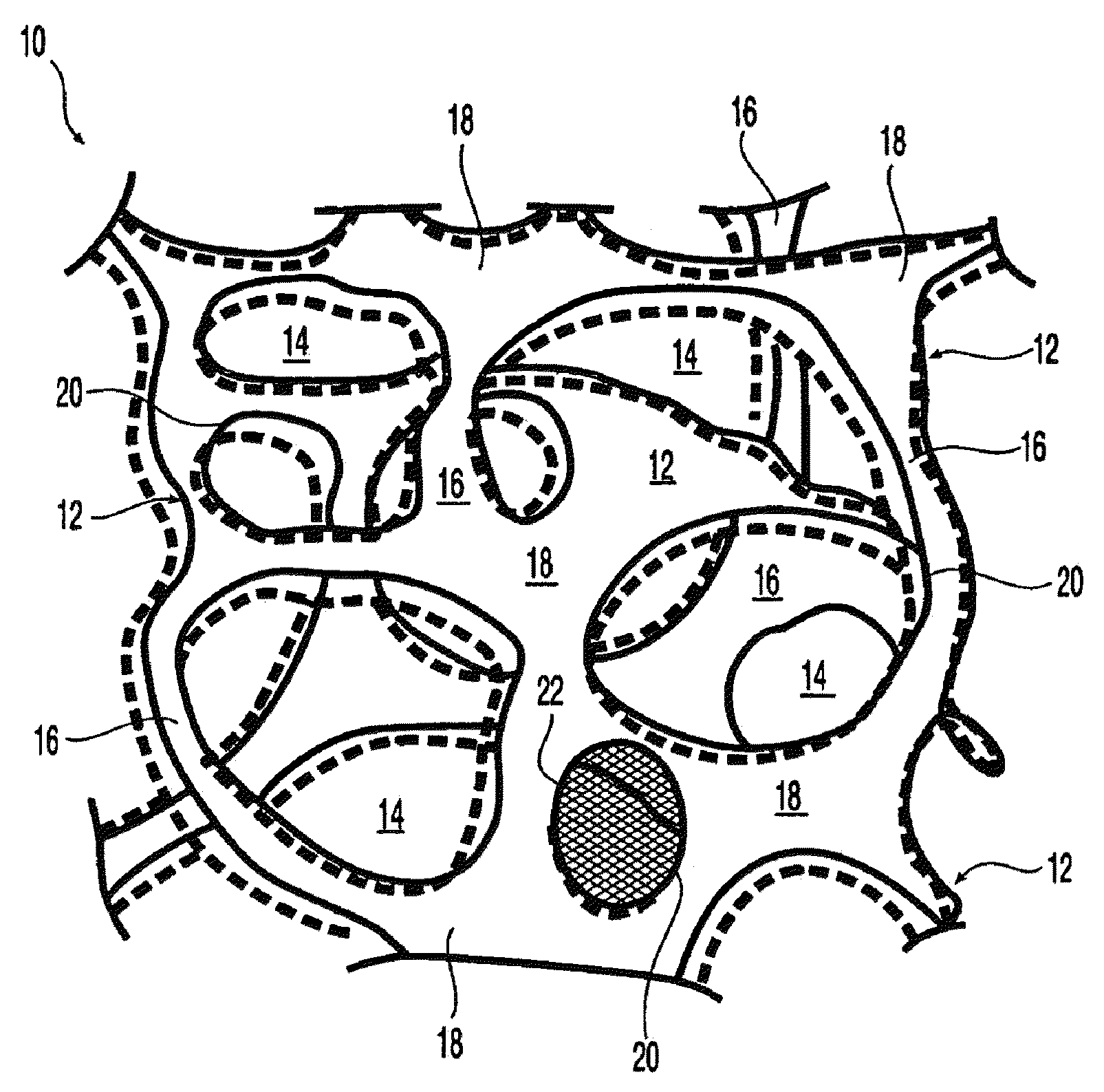
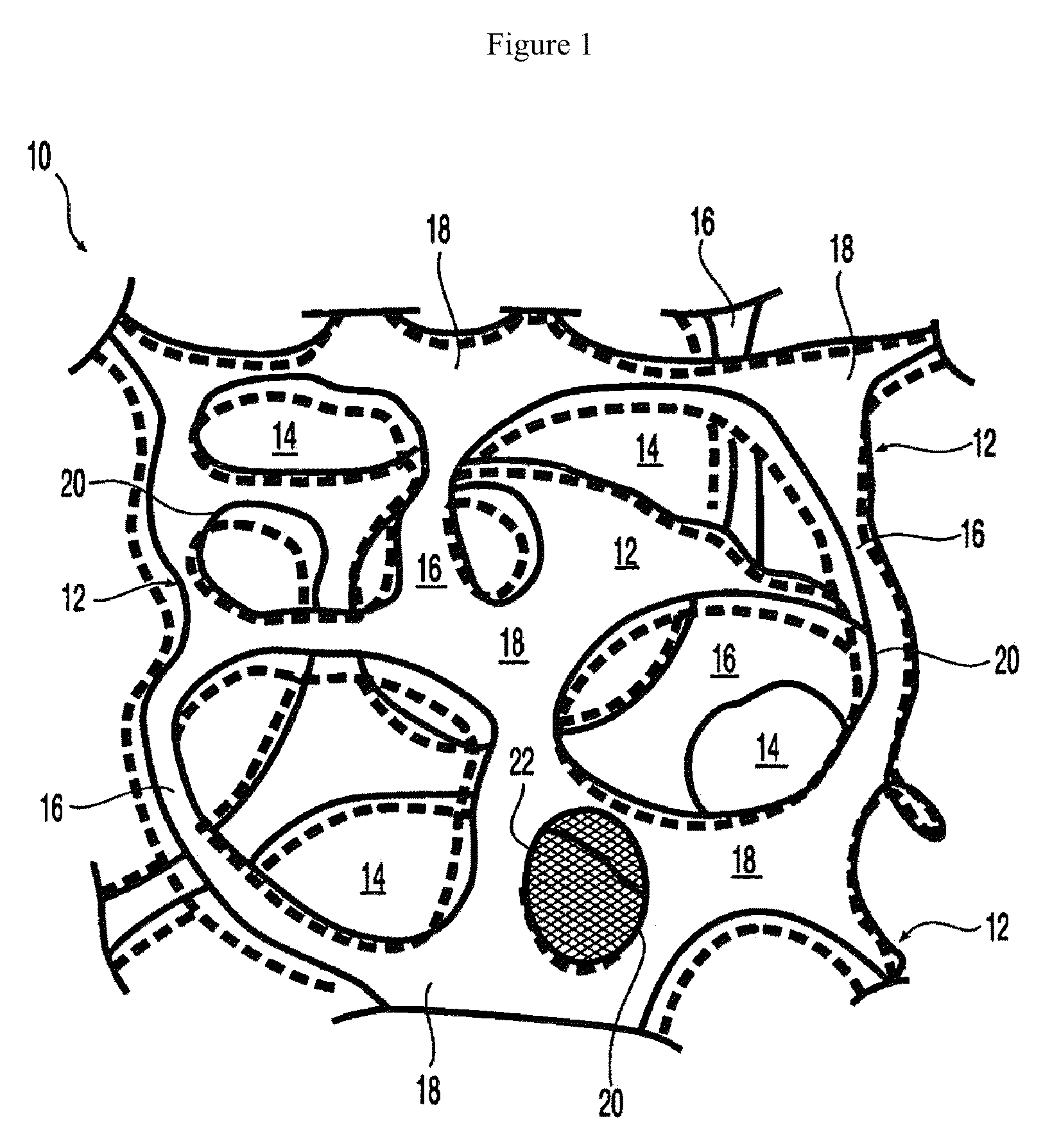
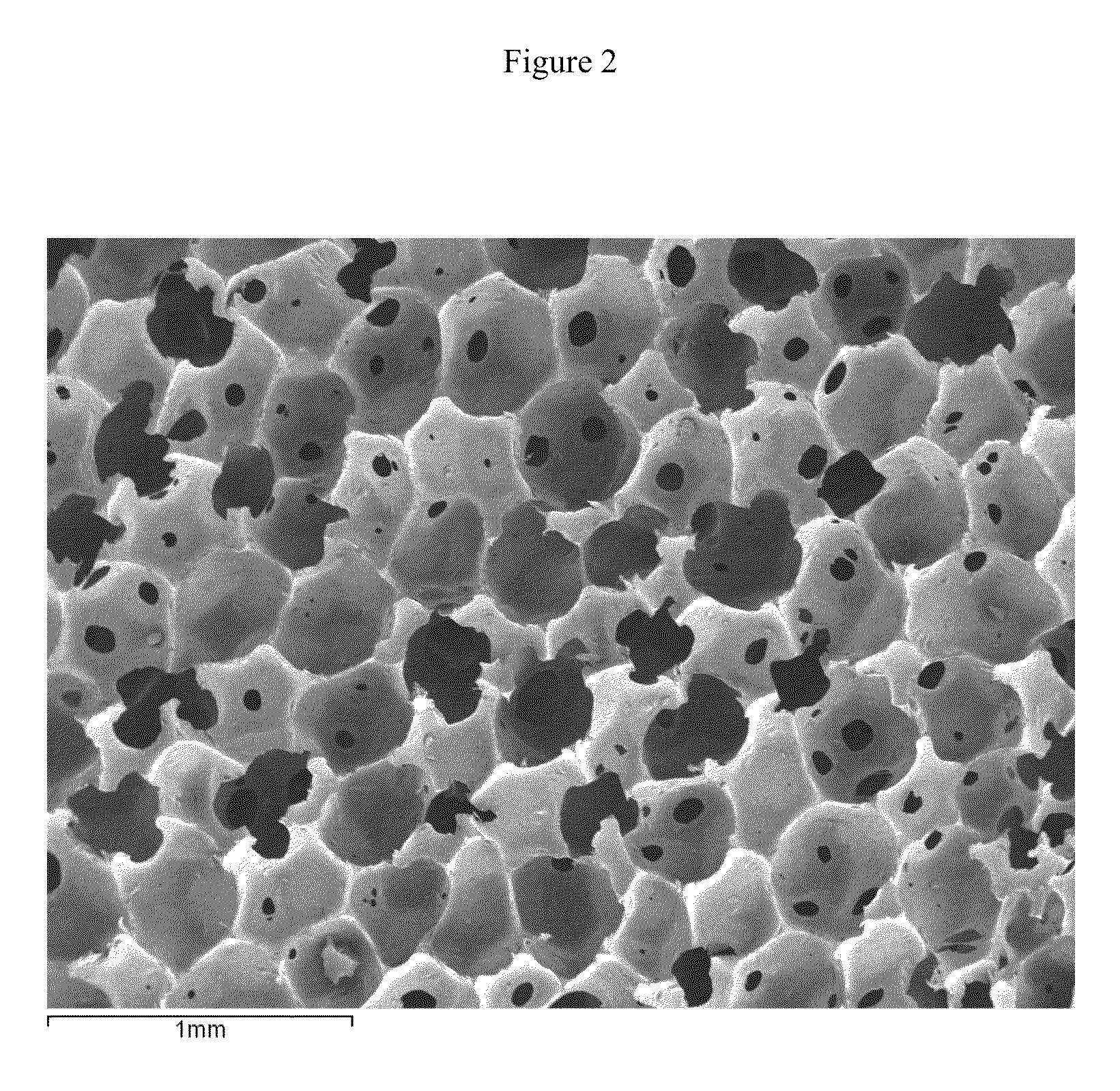
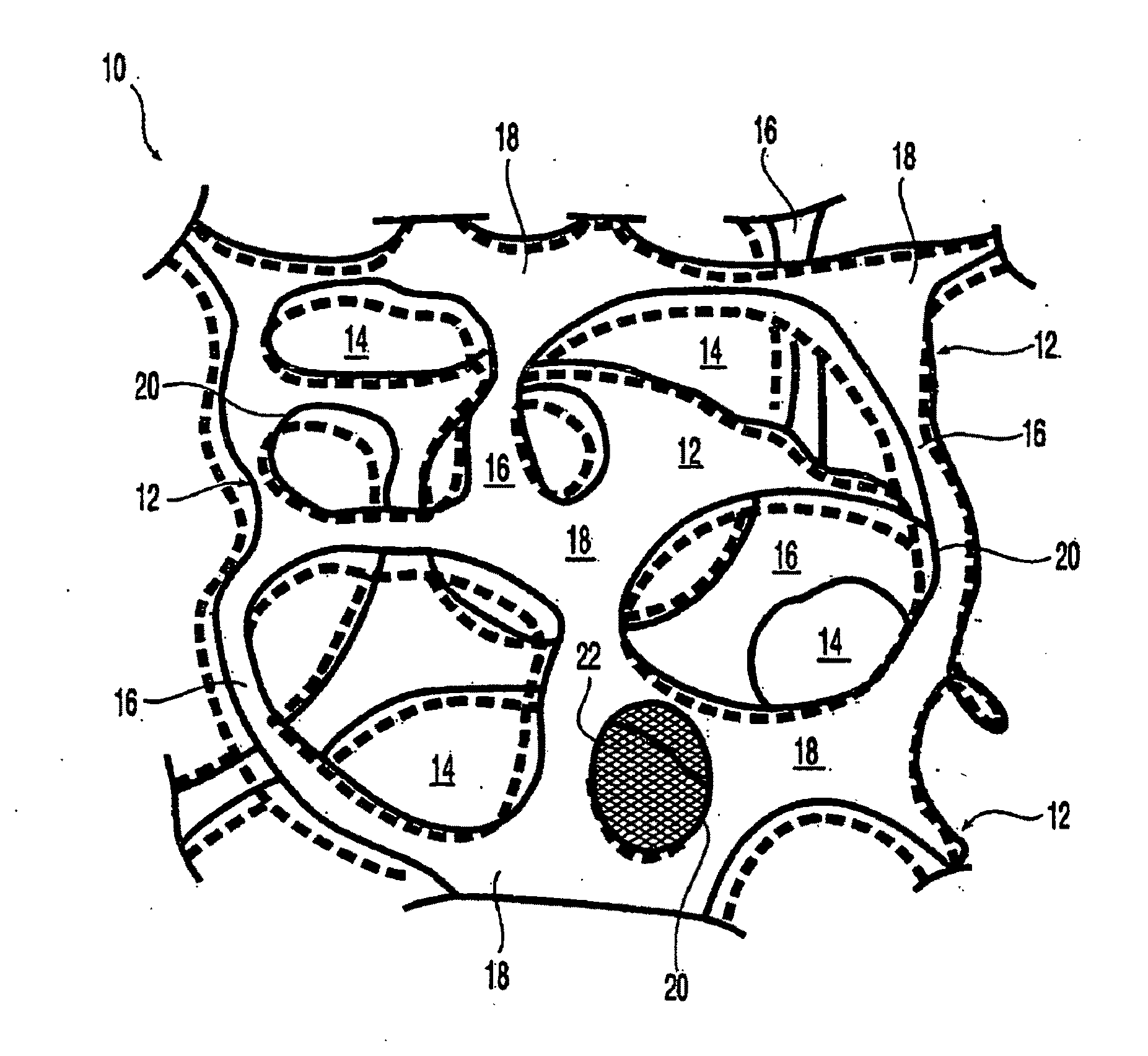
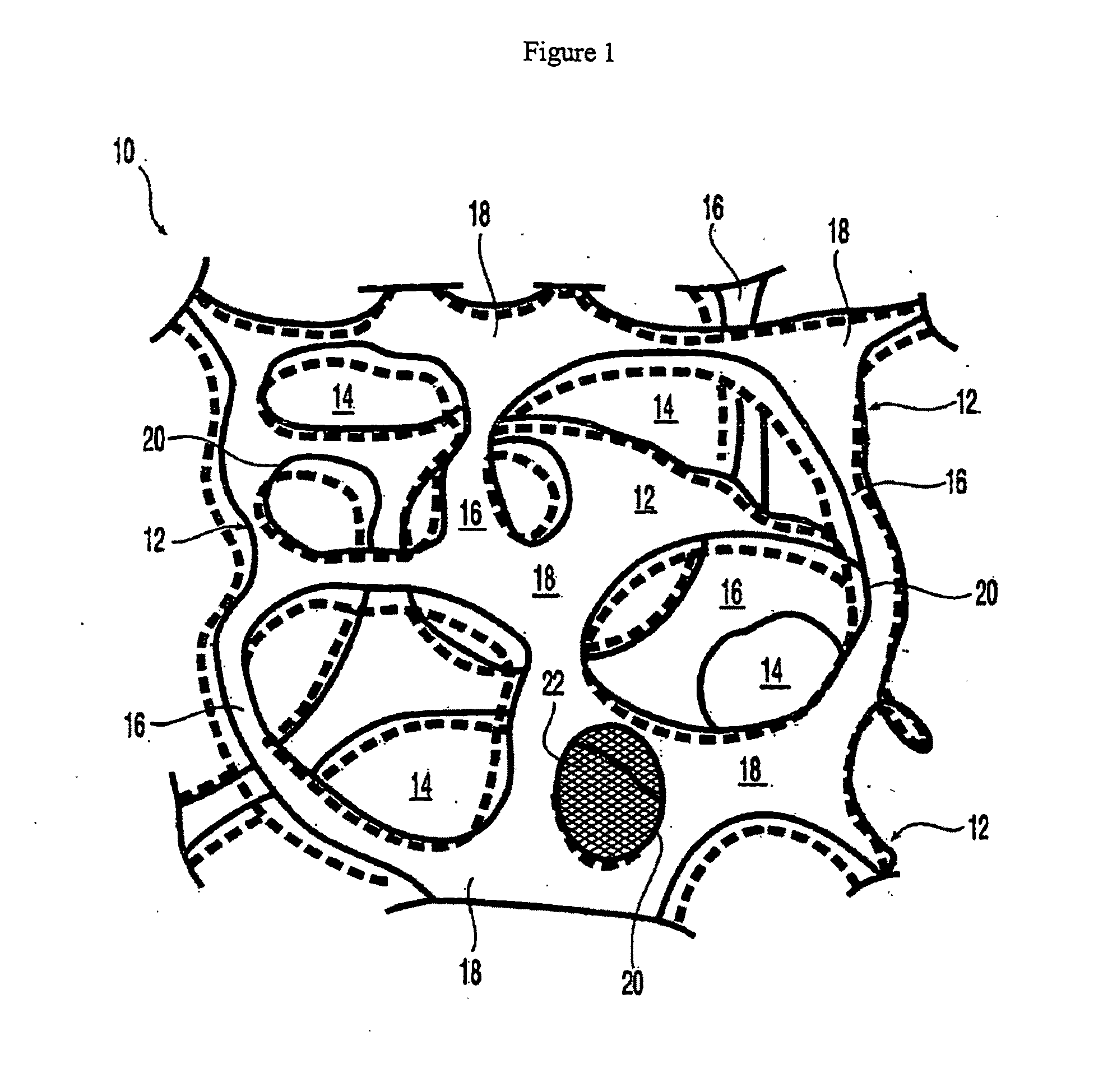
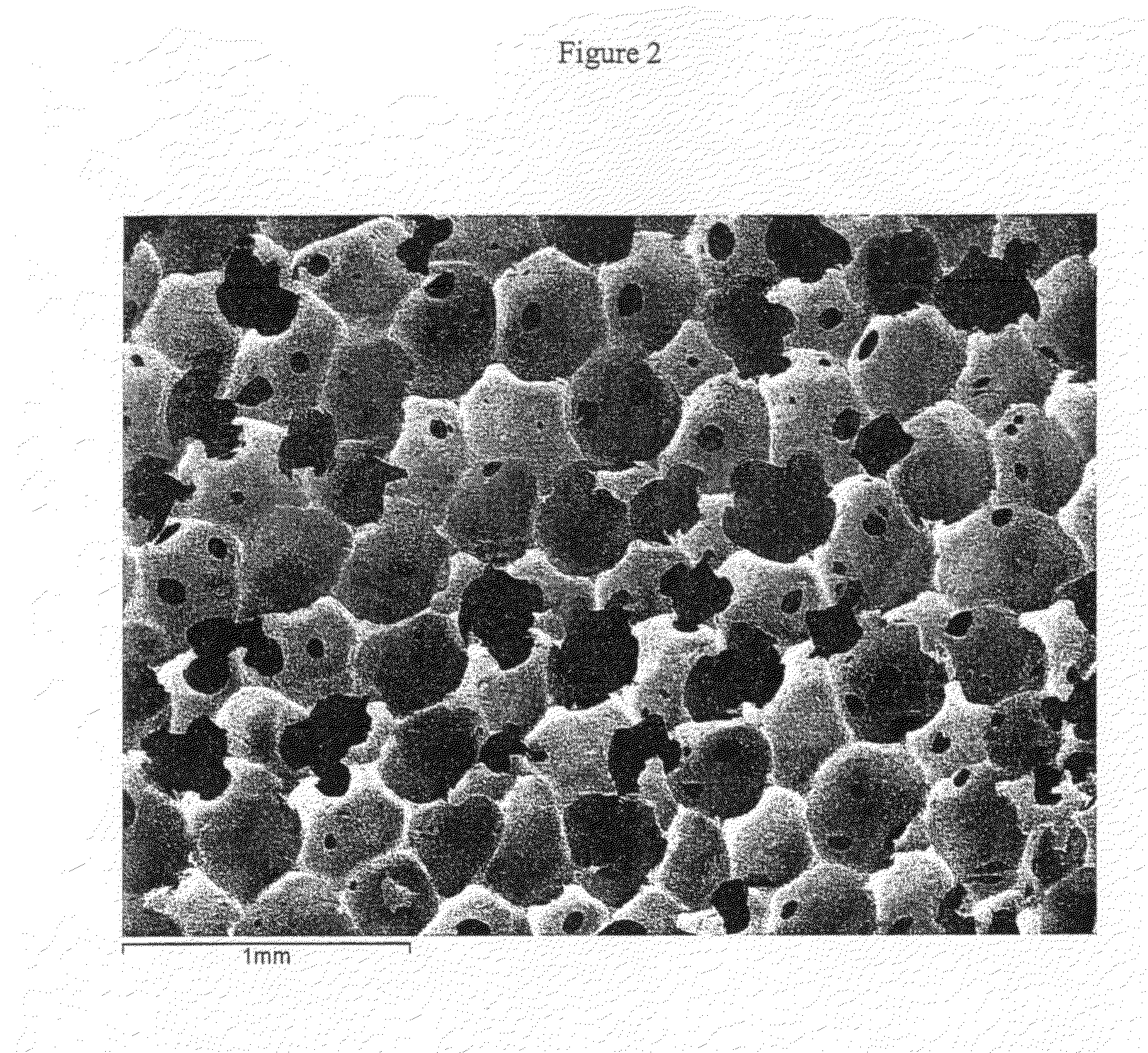
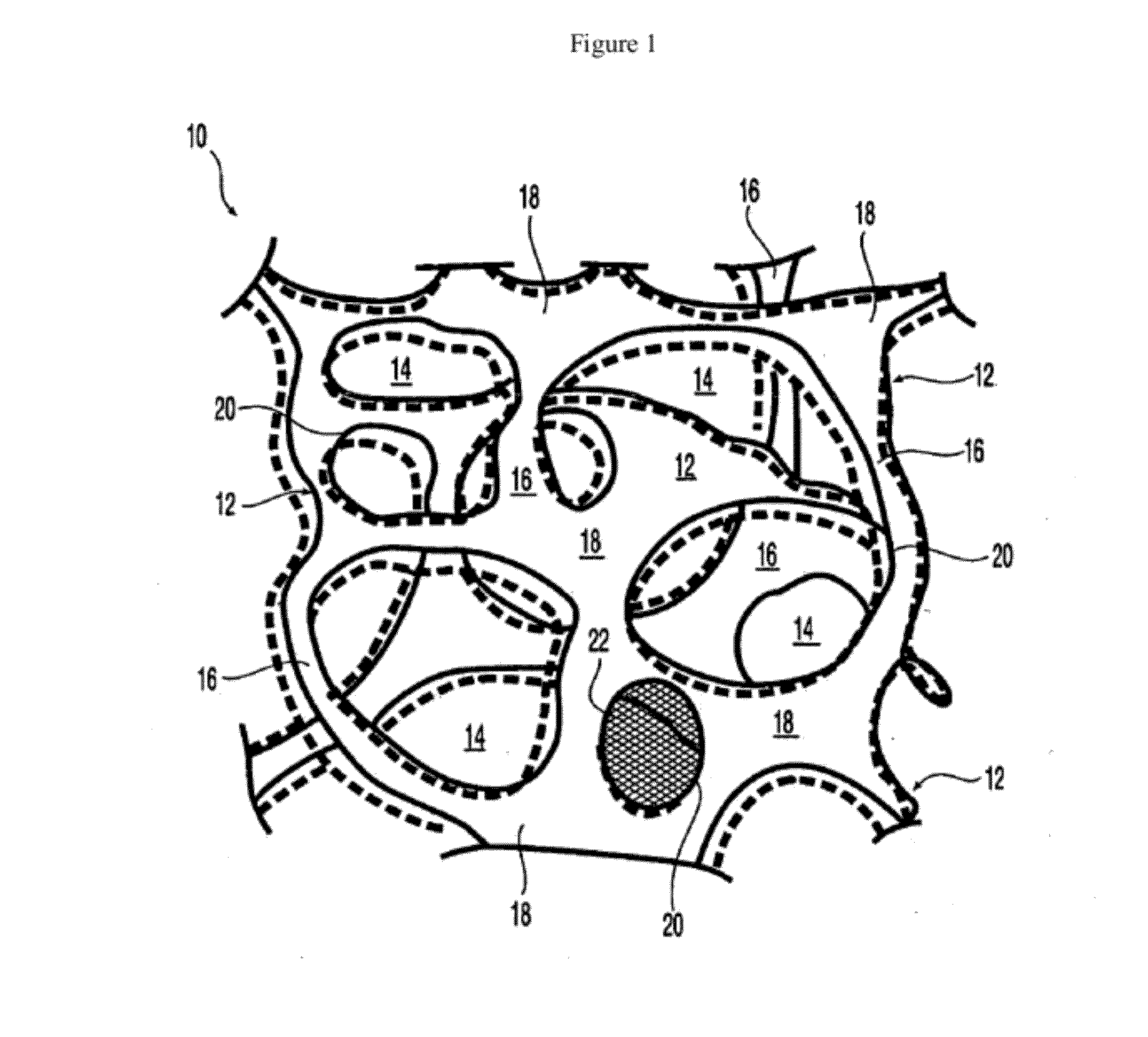
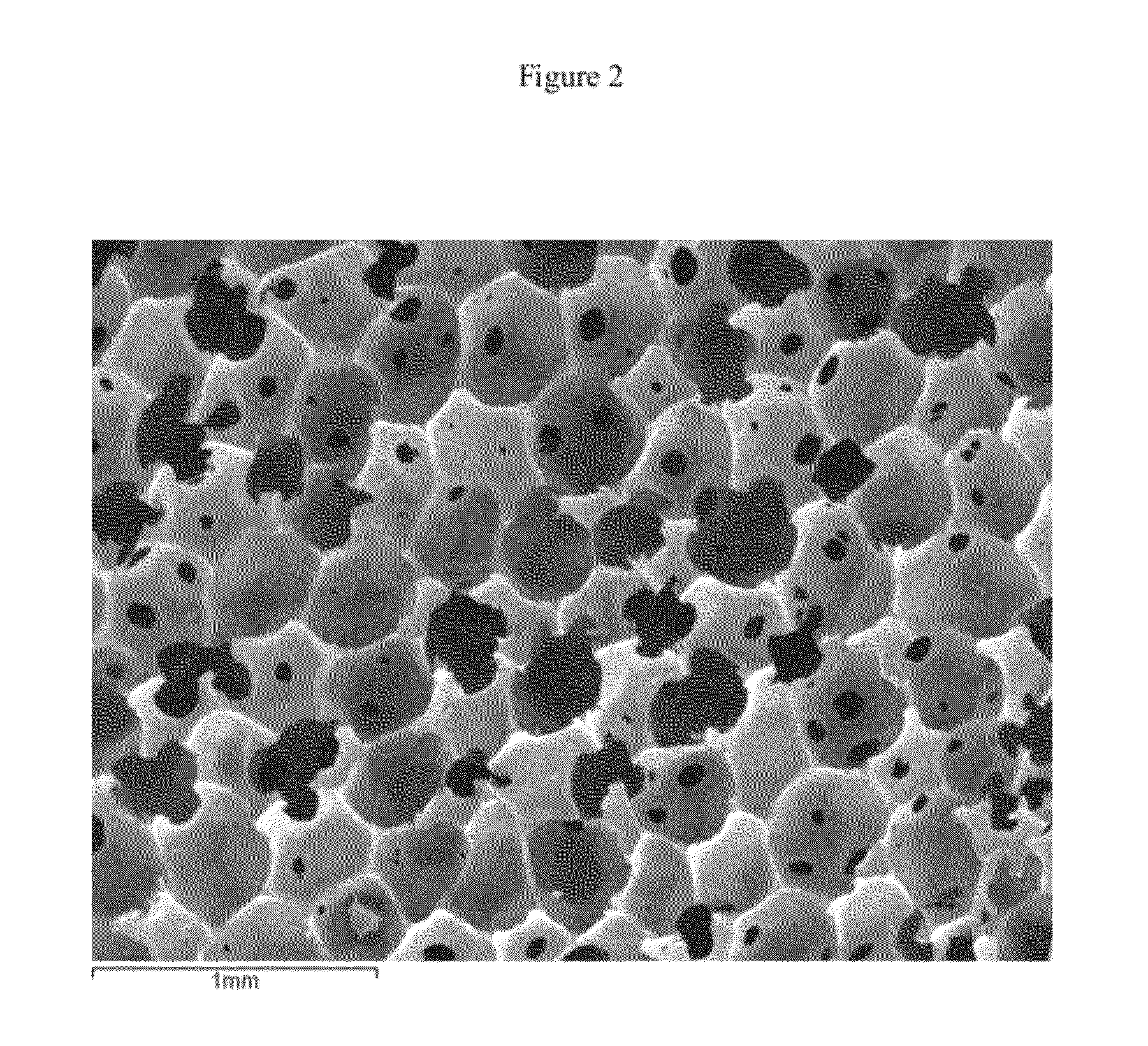
At least partially resorbable reticulated elastomeric matrix elements and methods of making same
ActiveUS8801801B2Small volumeIncrease in sizePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsProsthesisElastomerBiomedical engineering
The present disclosure relates to reticulated elastomeric matrices, and more particularly to at least partially degradable elastomeric elements that are compressible and exhibit resilience in their recovery and that can be employed in diverse applications including, without limitation, biological implantation, especially in humans.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
At least partially resorbable reticulated elastomeric matrix elements and methods of making same
ActiveUS9050176B2Small volumeIncrease in sizePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsElastomerBiomedical engineering
The present disclosure relates to reticulated elastomeric matrices, and more particularly to at least partially degradable elastomeric elements that are compressible and exhibit resilience in their recovery and that can be employed in diverse applications including, without limitation, biological implantation, especially in humans.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
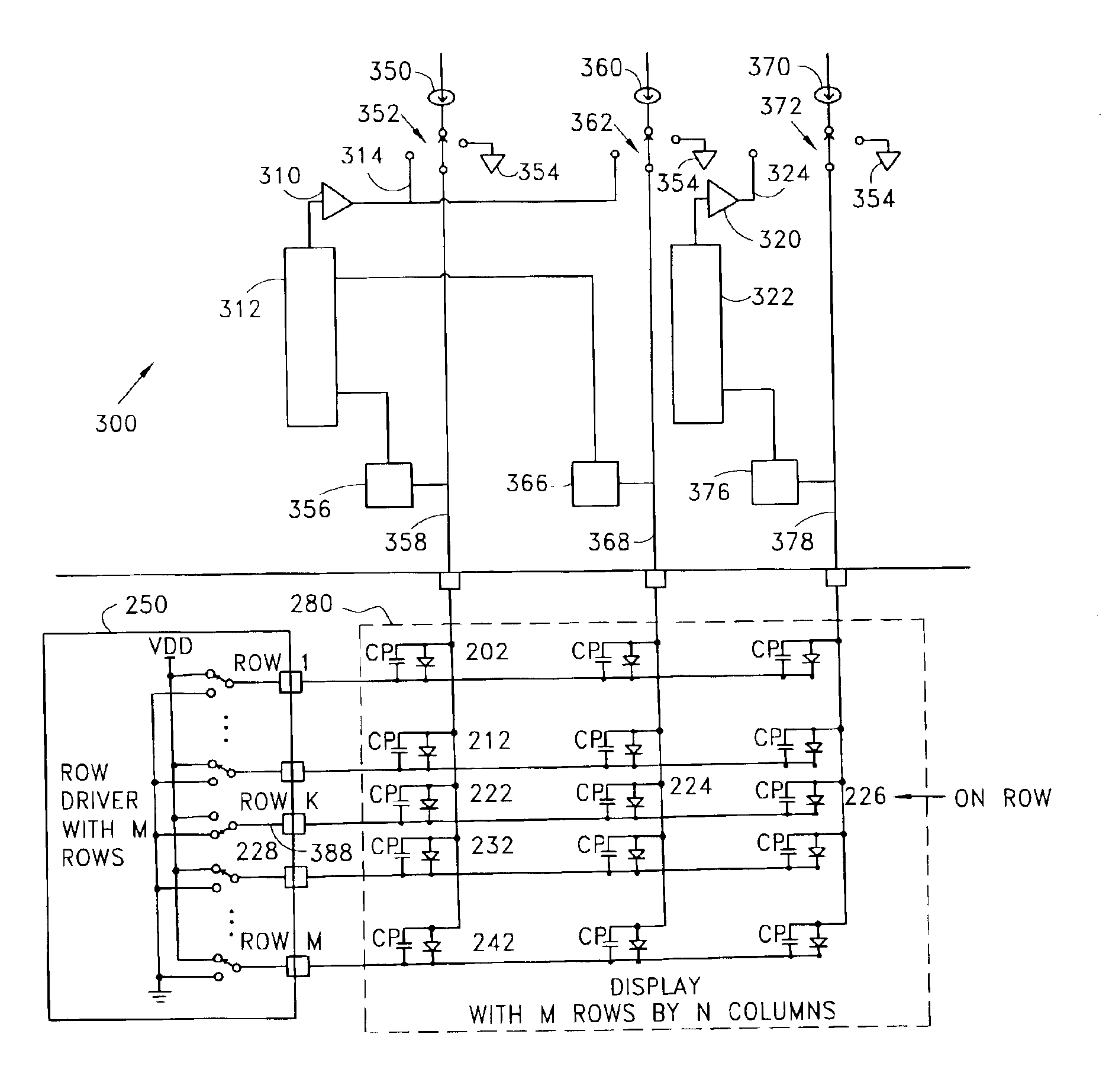
Matrix element precharge voltage adjusting apparatus and method
An apparatus for establishing and applying a voltage to precharge current-driven elements in a matrix. During ordinary scan cycles, a conduction voltage is sensed while the elements conduct a selected current. One or more such sensed conduction voltages are combined to provide a basis for a precharge voltage. Conduction and transient errors are determined, and are compensated for by offsetting the final precharge voltage from the conduction voltage basis. The final precharge voltage is provided to one or more columns during a precharge period of the scan cycle.
Owner:CLARE MICRONIX INTEGRATED SYST
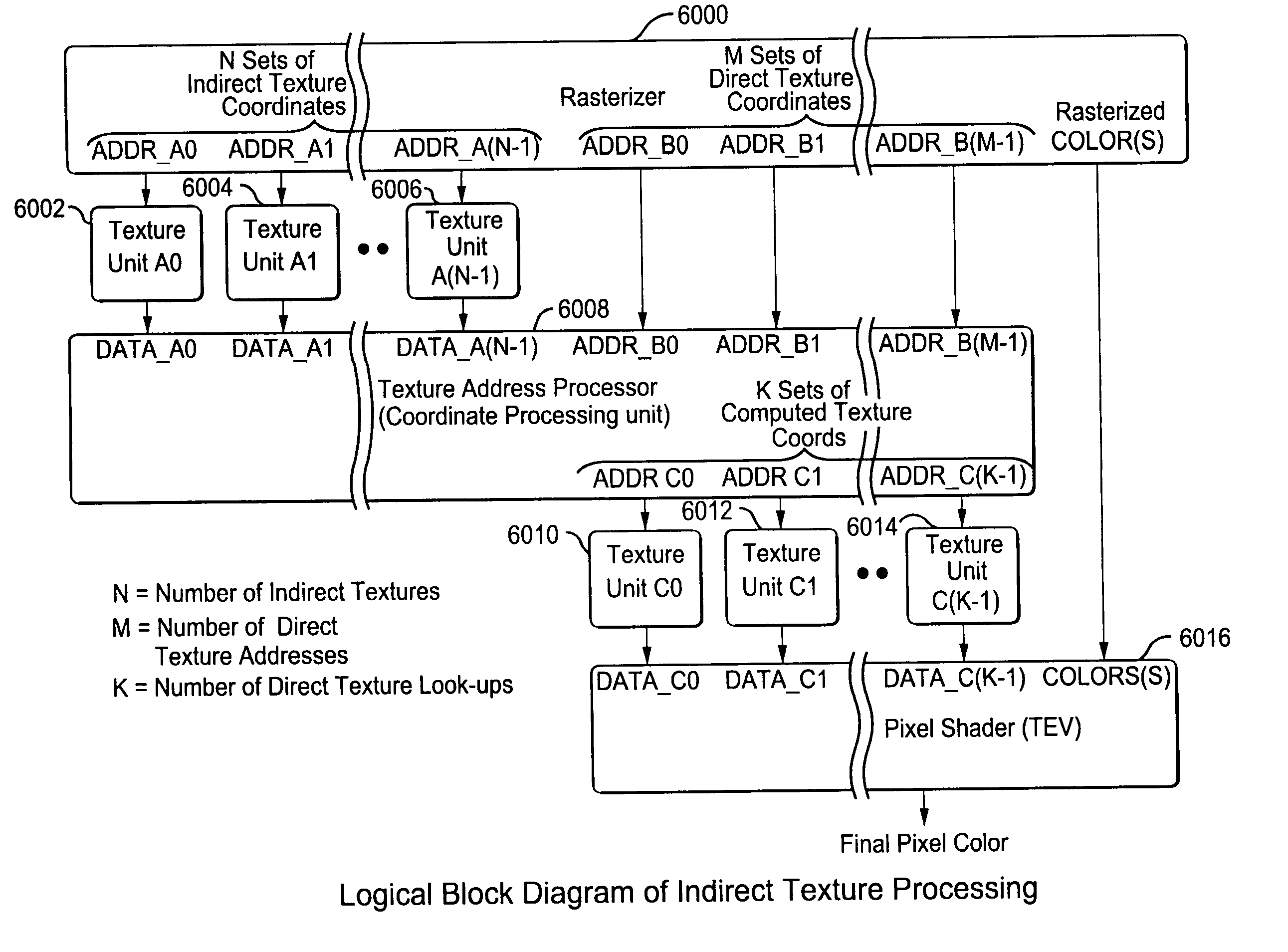
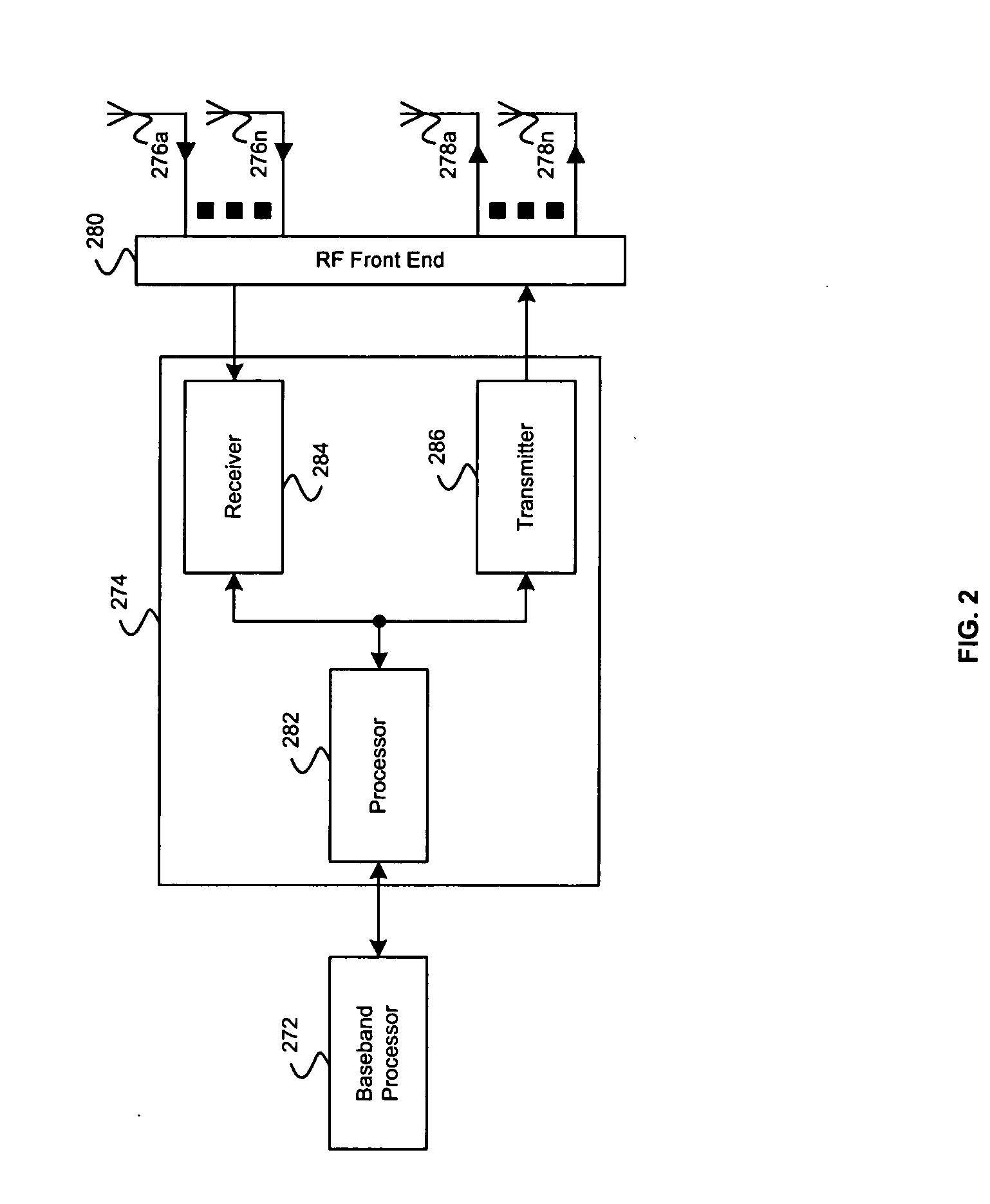
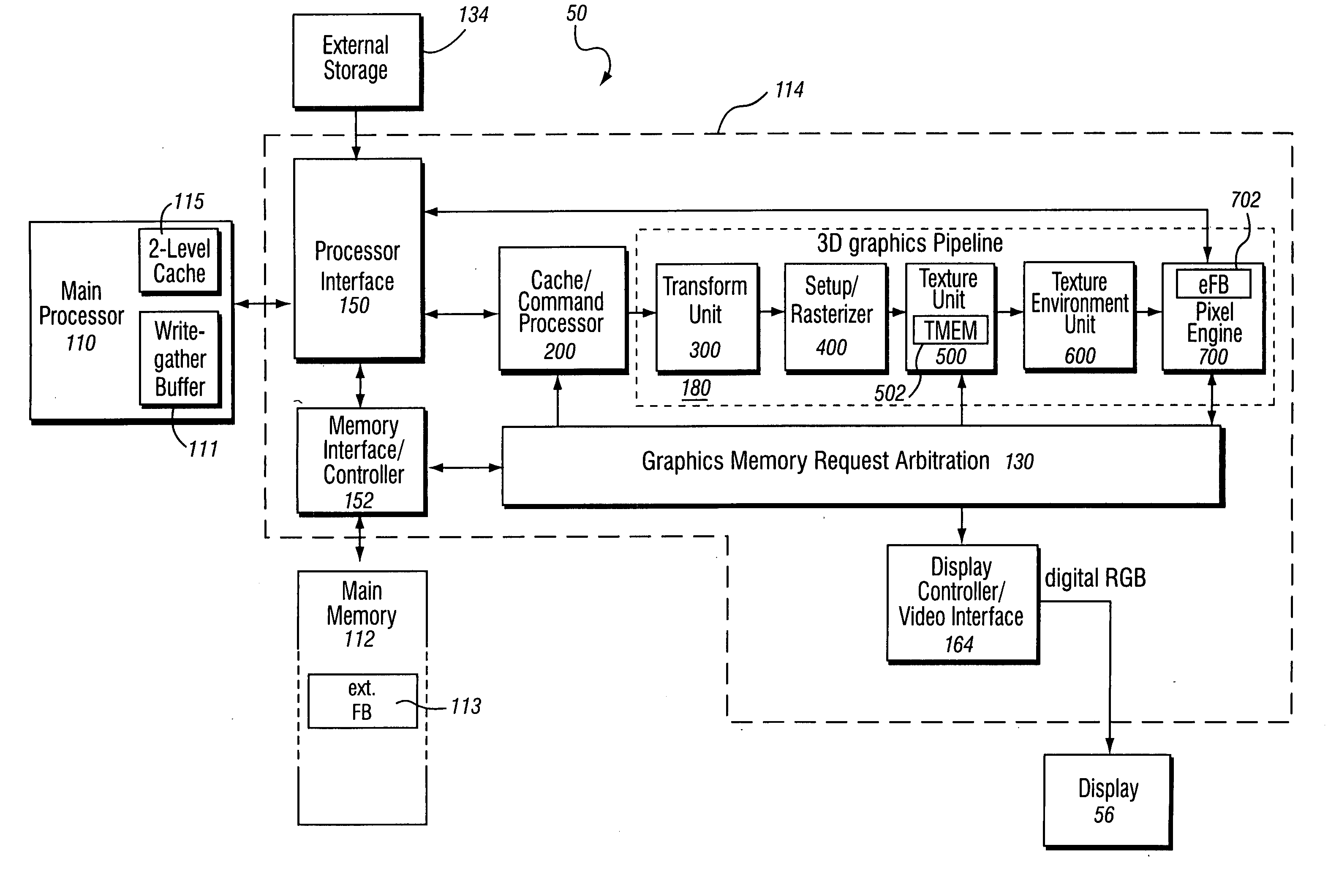
Method and apparatus for interleaved processing of direct and indirect texture coordinates in a graphics system
InactiveUS7002591B1Efficient implementationIncrease in texture mapping hardware complexityCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingPattern recognitionProcessing
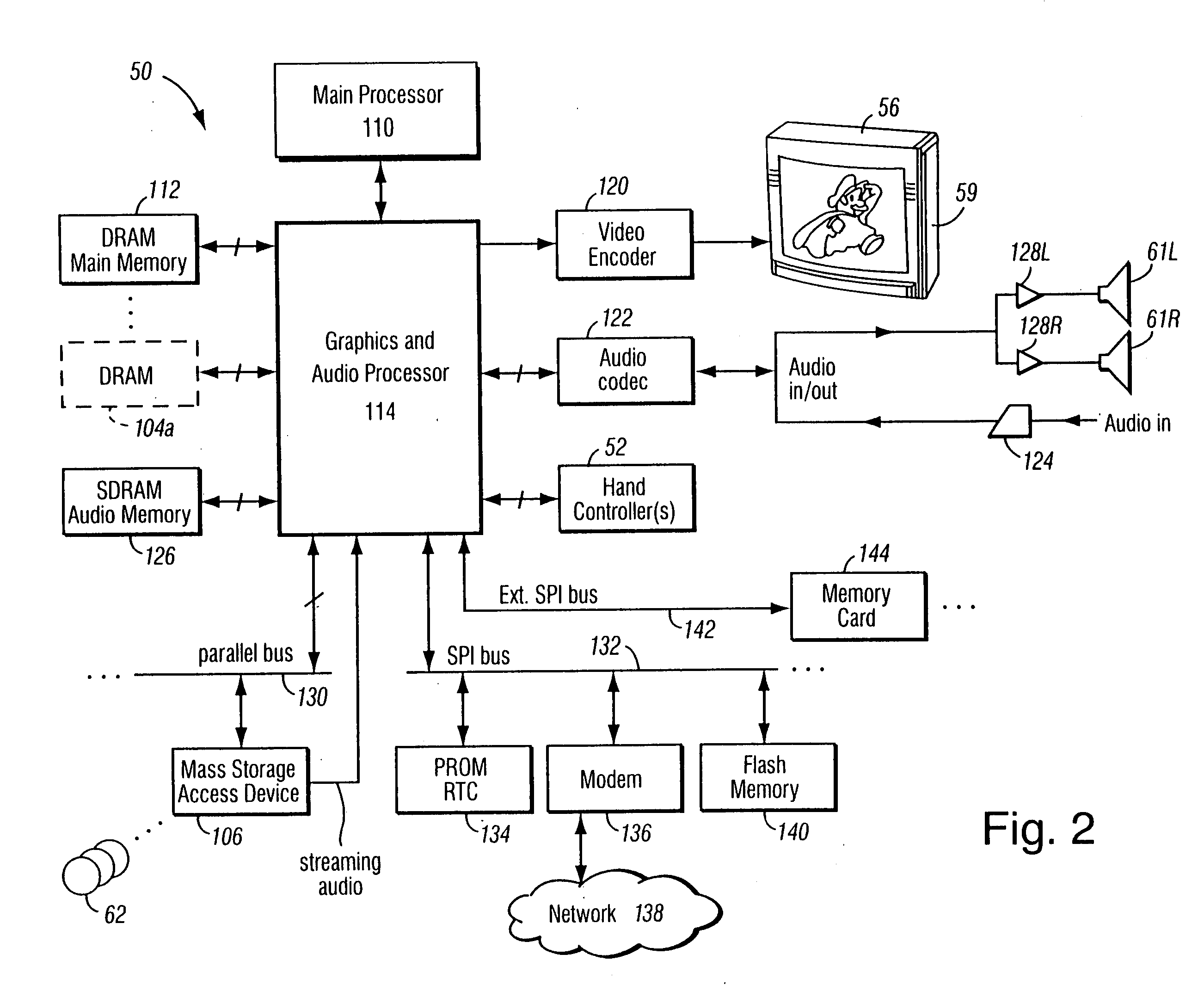
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics pipeline renders and prepares images for display at least in part in response to polygon vertex attribute data and texel color data stored as a texture images in an associated memory. An efficient texturing pipeline arrangement achieves a relatively low chip-footprint by utilizing a single texture coordinate / data processing unit that interleaves the processing of logical direct and indirect texture coordinate data and a texture lookup data feedback path for “recirculating” indirect texture lookup data retrieved from a single texture retrieval unit back to the texture coordinate / data processing unit. Versatile indirect texture referencing is achieved by using the same texture coordinate / data processing unit to transform the recirculated texture lookup data into offsets that may be added to the texture coordinates of a direct texture lookup. A generalized indirect texture API function is provided that supports defining at least four indirect texture referencing operations and allows for selectively associating one of at least eight different texture images with each indirect texture defined. Retrieved indirect texture lookup data is processed as multi-bit binary data triplets of three, four, five, or eight bits. The data triplets are multiplied by a 3×2 texture coordinate offset matrix before being optionally combined with regular non-indirect coordinate data or coordinate data from a previous cycle / stage of processing. Values of the offset matrix elements are variable and may be dynamically defined for each cycle / stage using selected constants. Two additional variable matrix configurations are also defined containing element values obtained from current direct texture coordinates. Circuitry for optionally biasing and scaling retrieved texture data is also provided.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
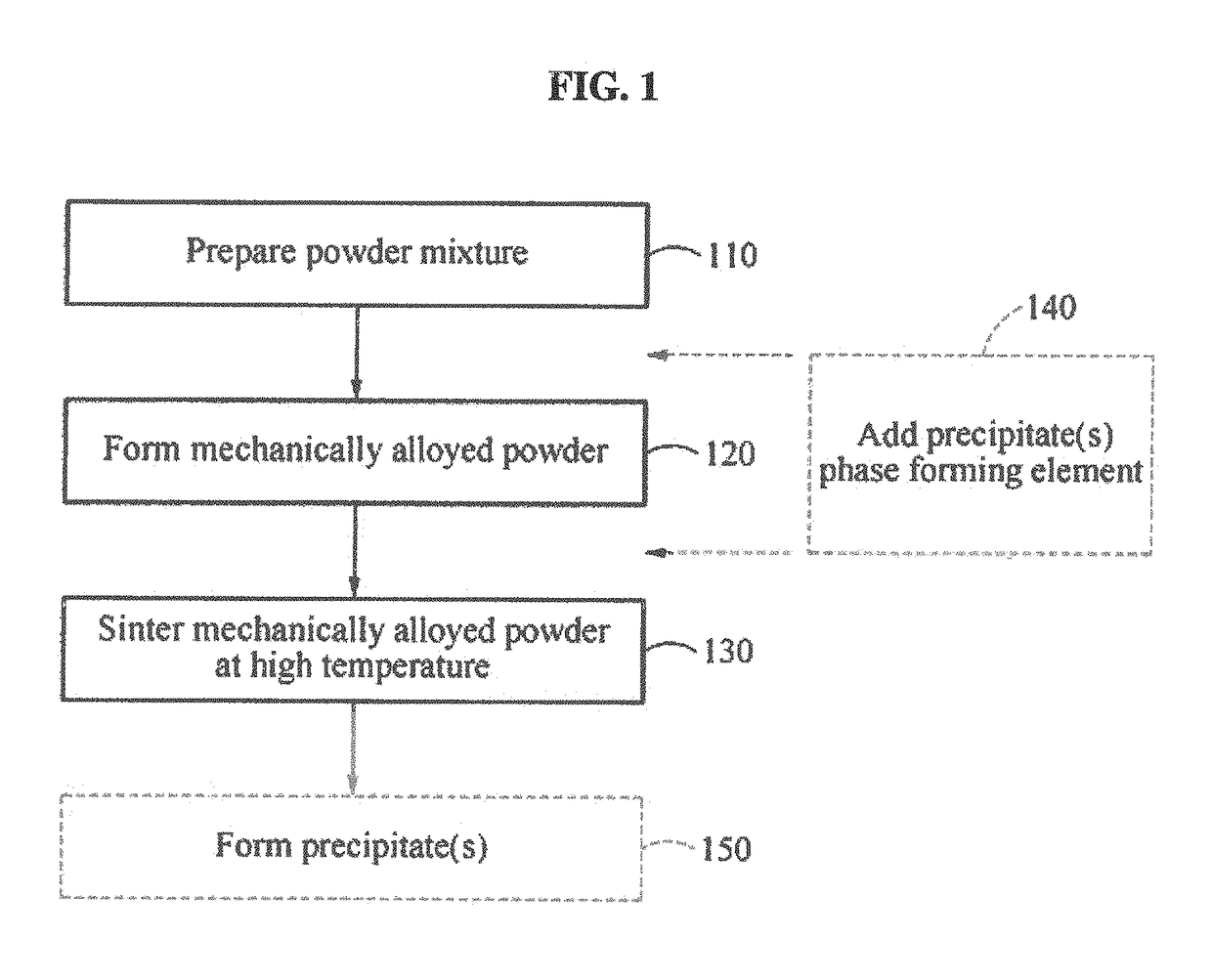
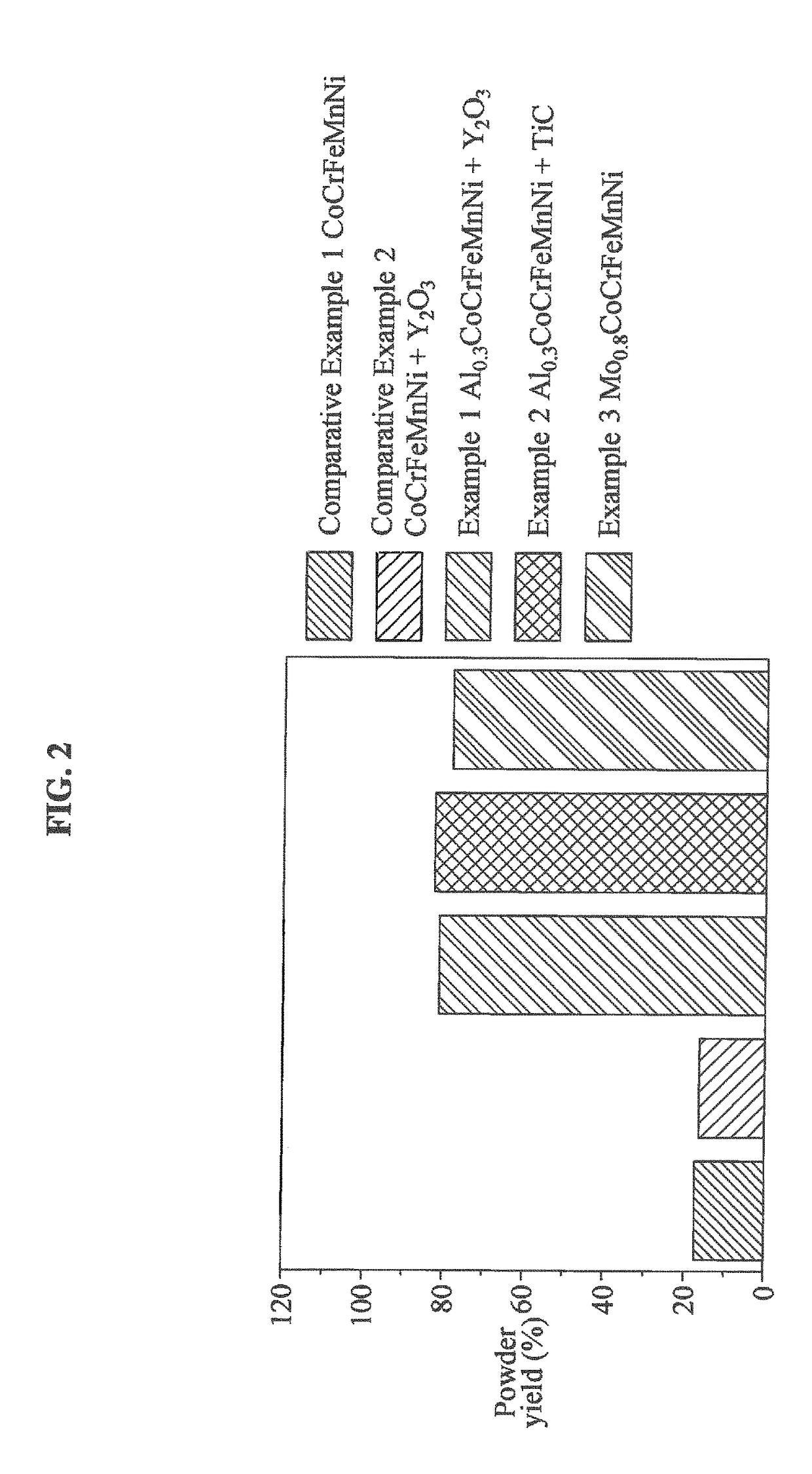
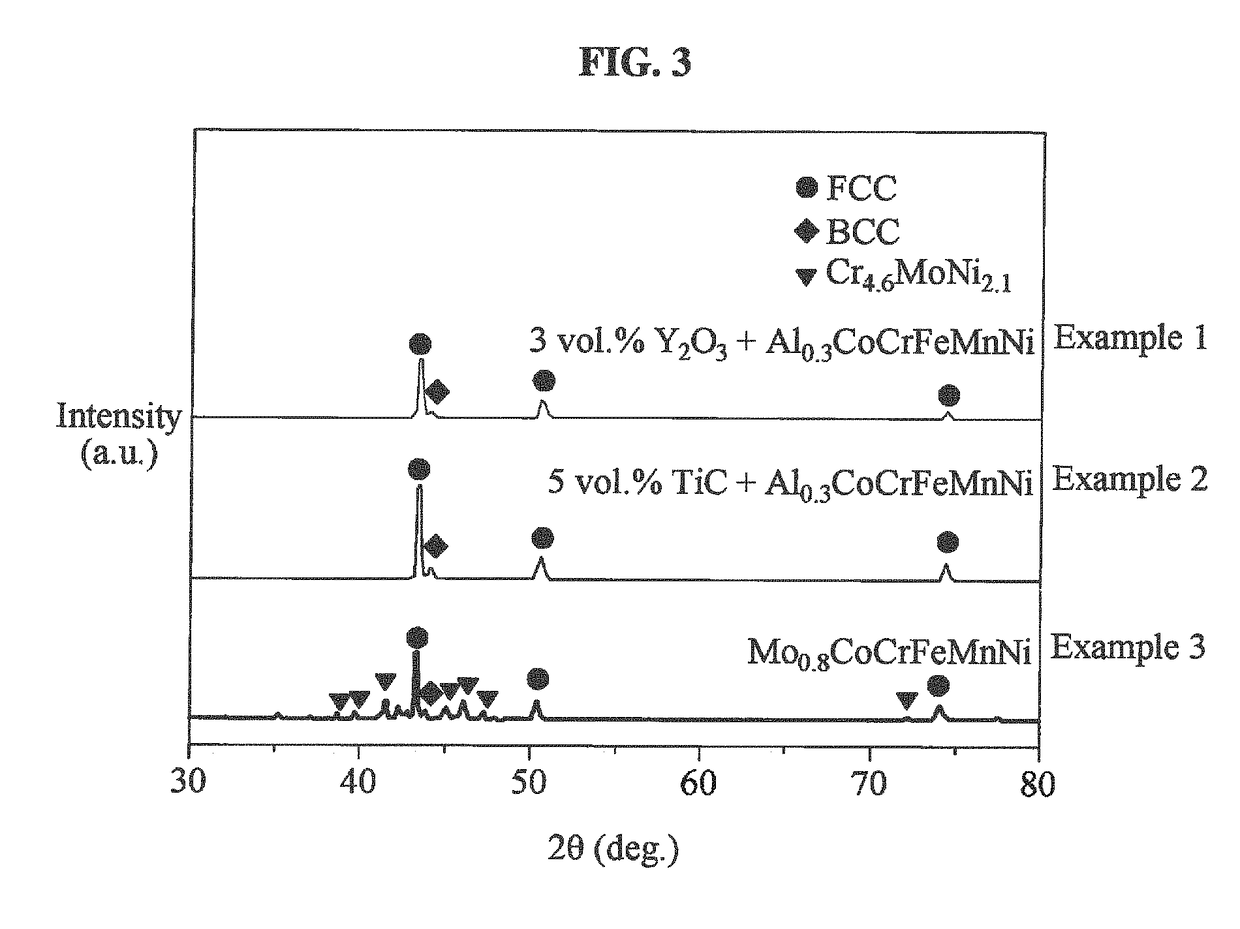
High-strength and ultra heat-resistant high entropy alloy (HEA) matrix composites and method of preparing the same
A high-strength and ultra heat-resistant high entropy alloy (HEA) matrix composite material and a method of preparing the HEA matrix composite material are provided. The HEA matrix composite material may include at least four matrix elements among Co, Cr, Fe, Ni, Mn, Cu, Mo, V, Nb, Ta, Ti, Zr, W, Si, Hf and Al, and a body-centered cubic (BCC) forming alloy element.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
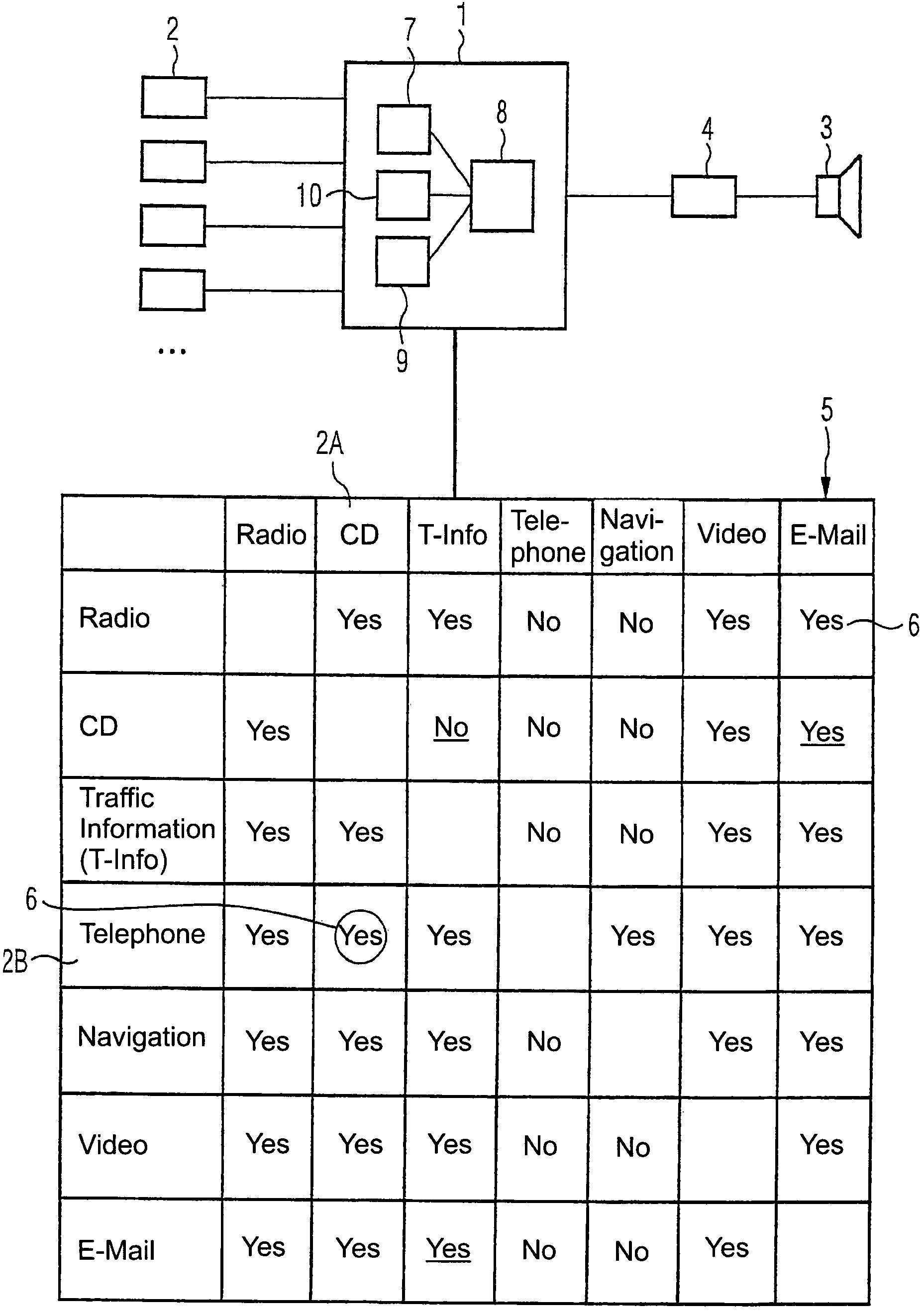
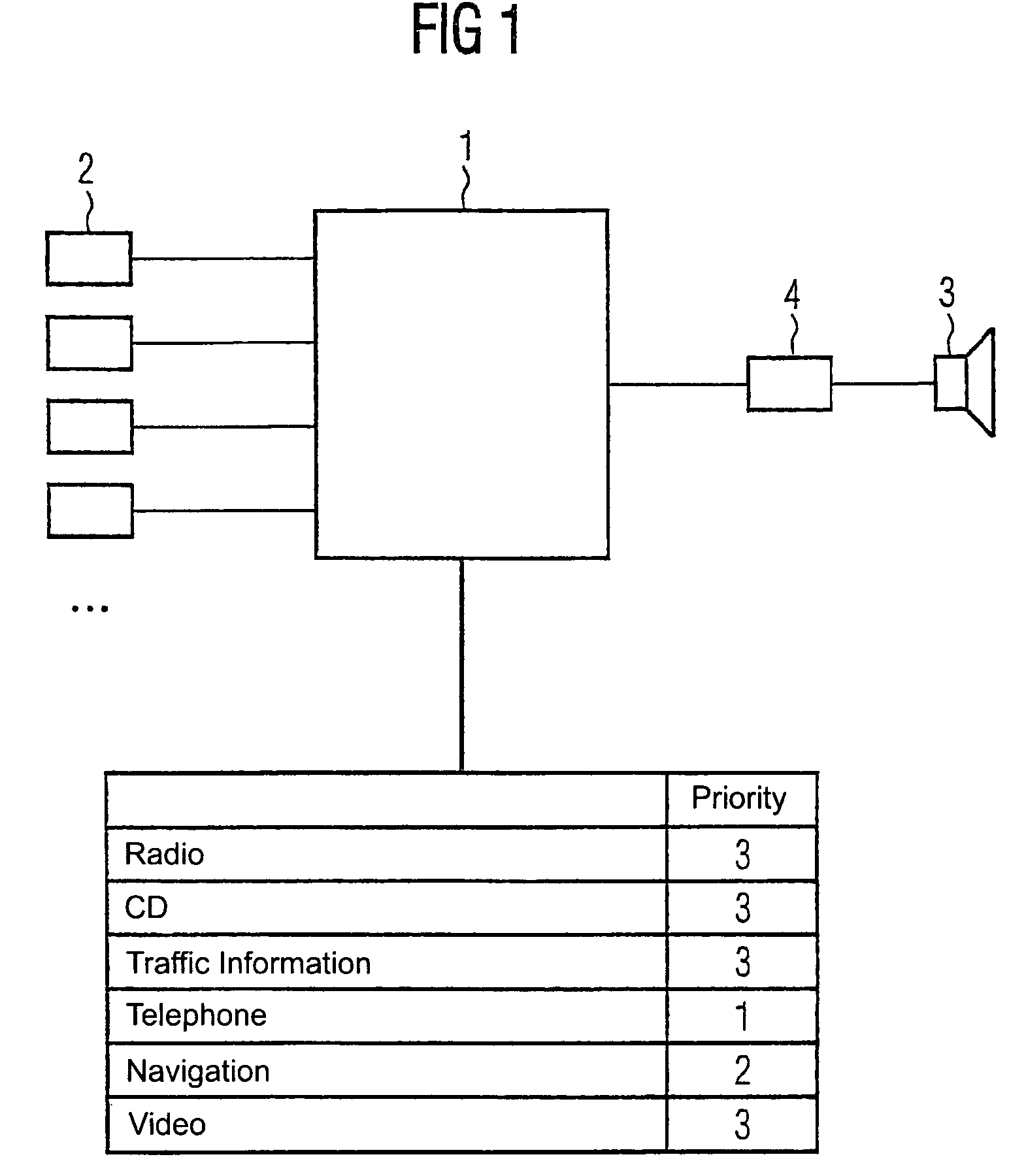
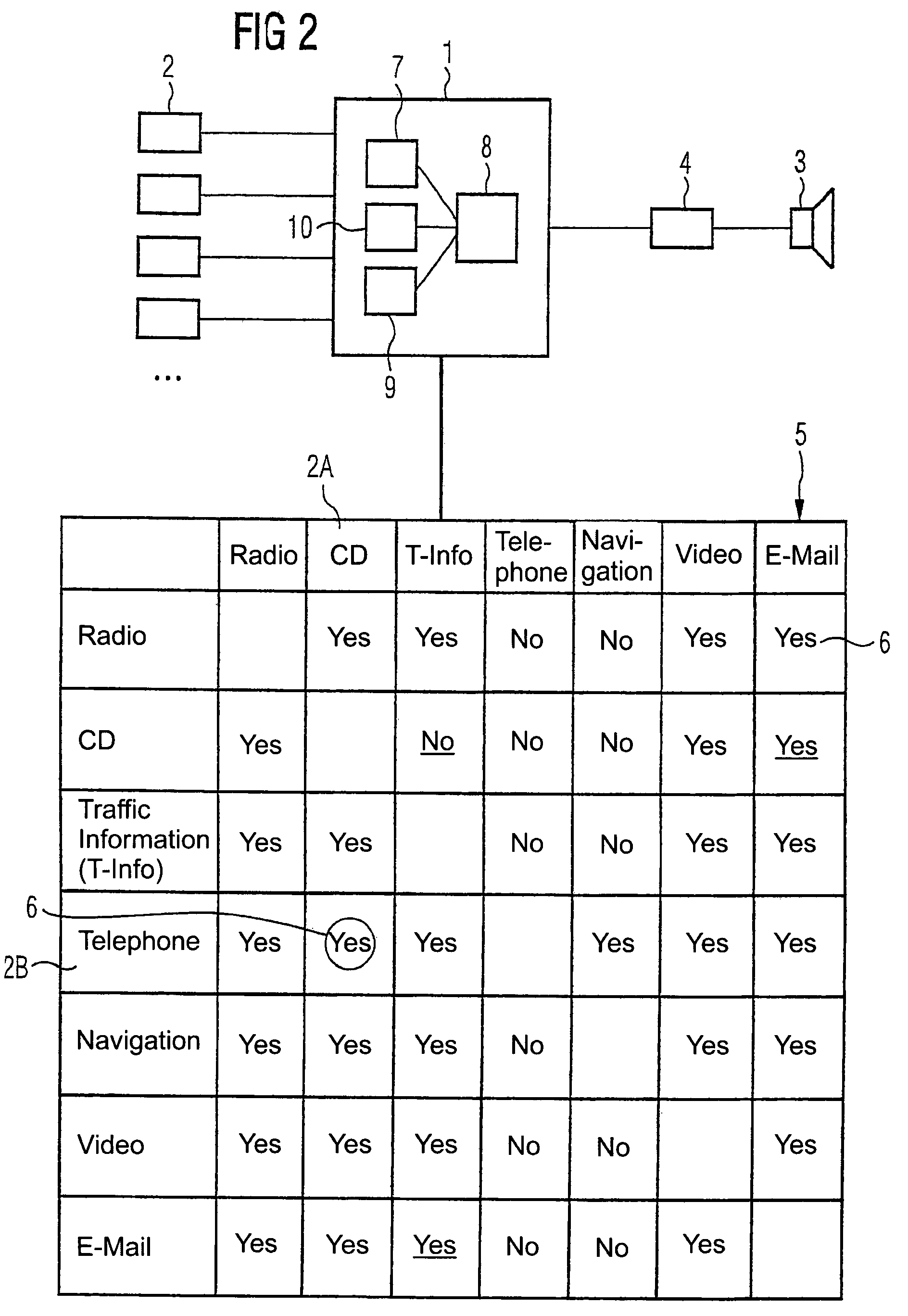
Control device and control method for fixing an information output order for several information sources, especially audio sources
InactiveUS7558635B1Easy to seeEasy to specifyInstruments for road network navigationArrangements for variable traffic instructionsAlgorithmRanking
A control device and a corresponding control method are provided for establishing an information-output ranking of a plurality of information sources, in particular audio sources. In order to output the information of the information sources to a common information-output device, the information-output ranking is established in pairs for the audio sources which is in the form of an audio-output matrix having a nonlinear order with respect to the matrix elements, and wherein each matrix element of the information-output matrix is used to determine the priority of a corresponding information source with respect to another information source. A conflict among competing information outputs is solved in this manner.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
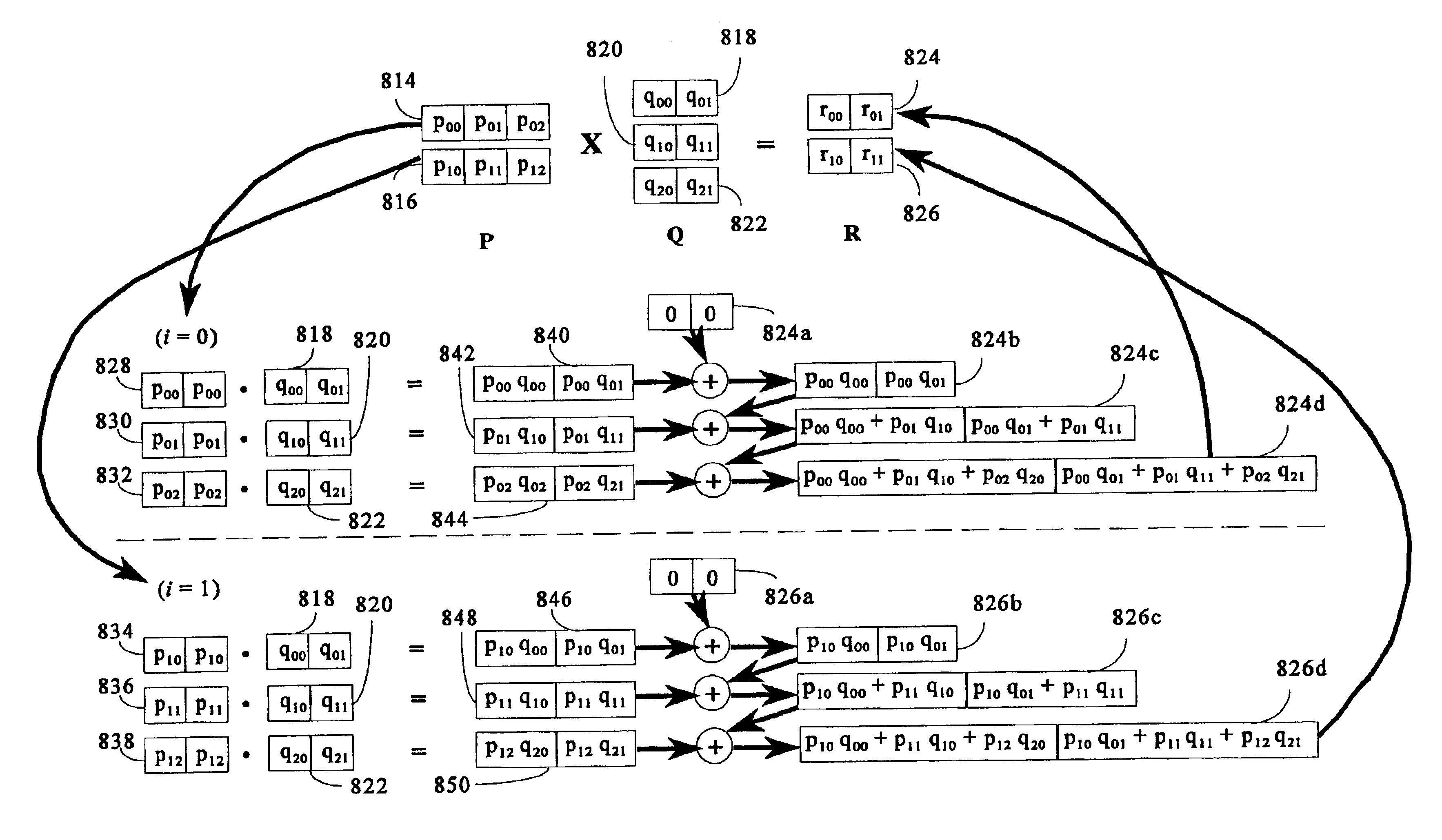
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
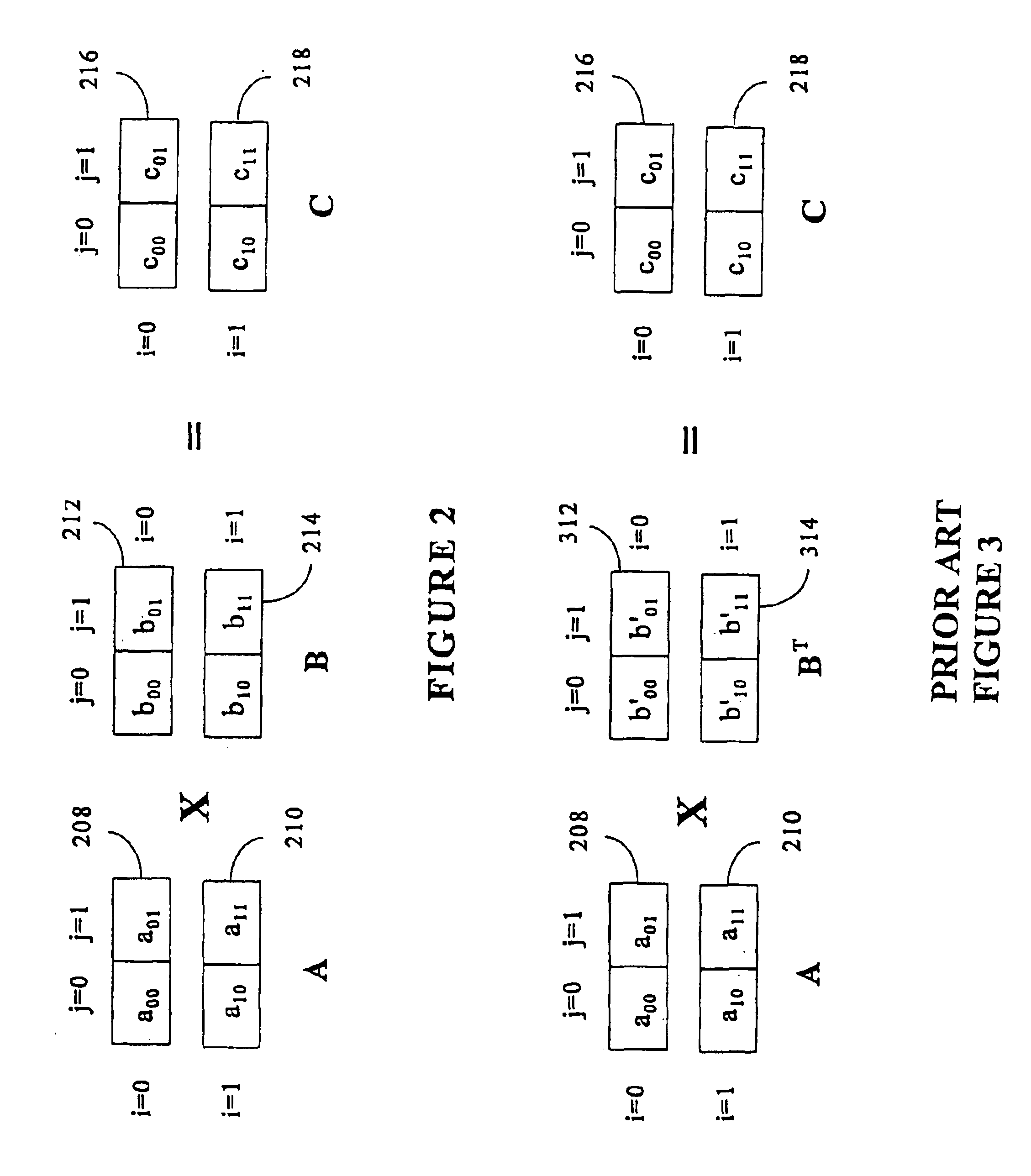
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
Efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates on classical computer based on fast algorithm
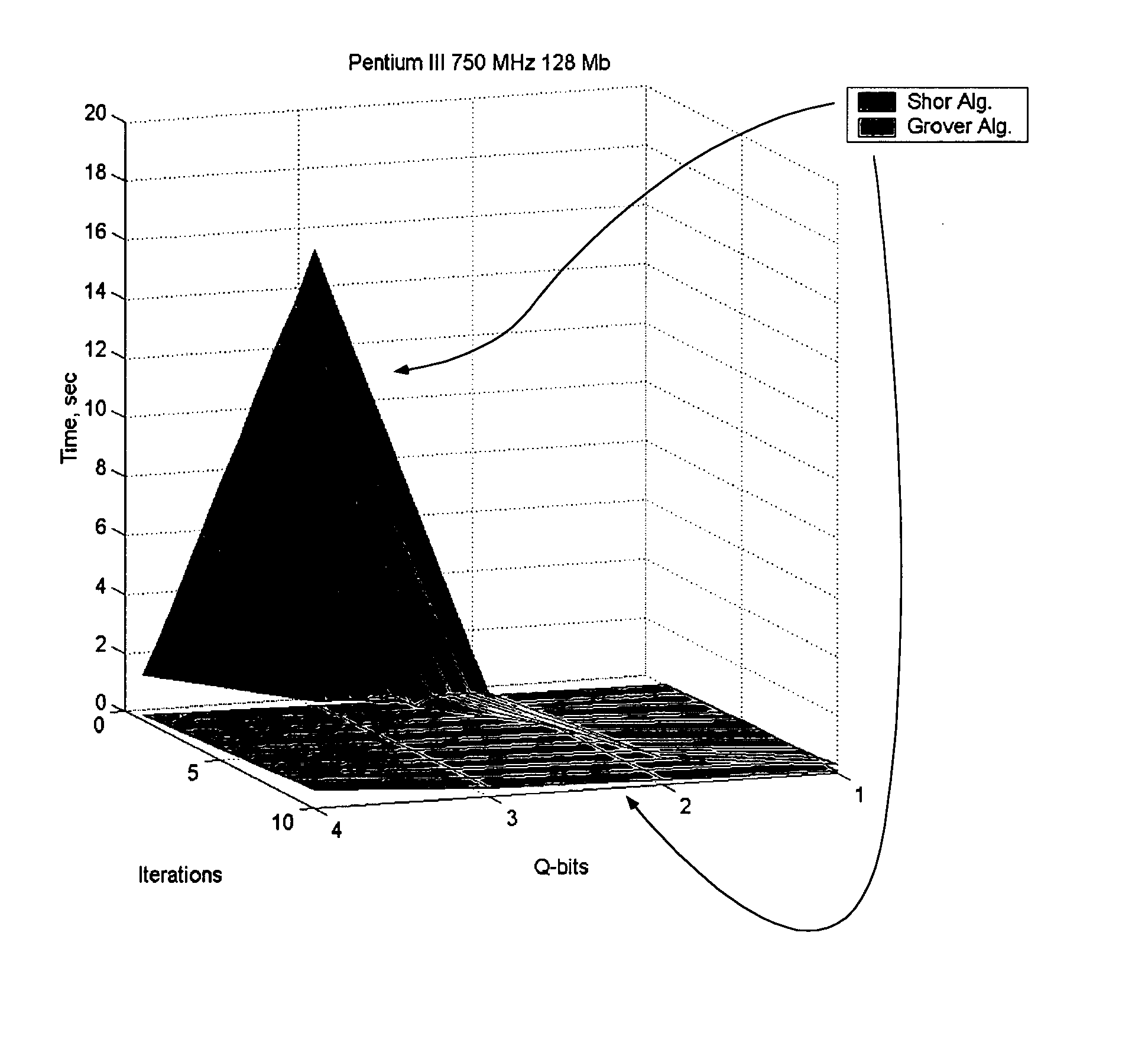
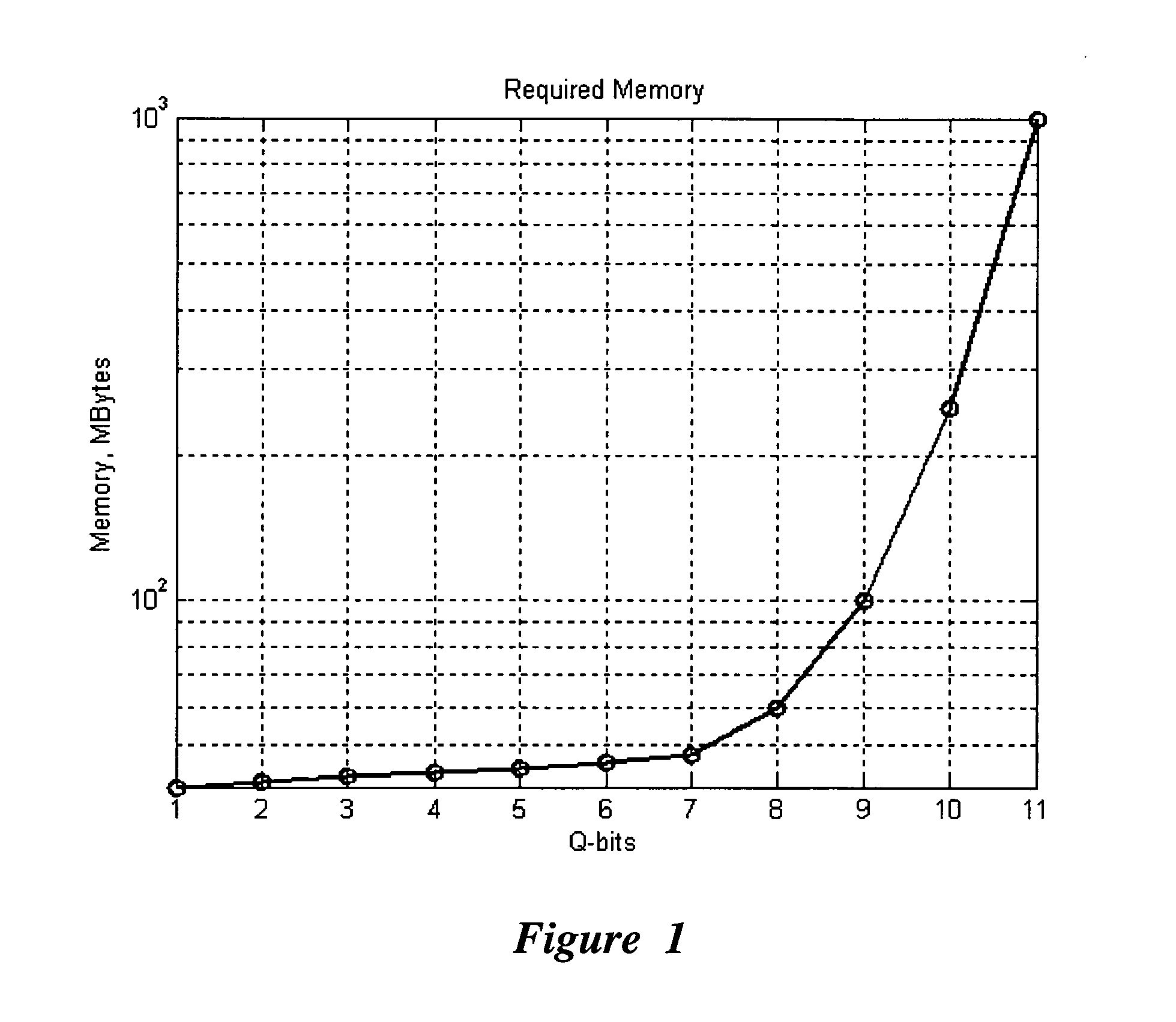
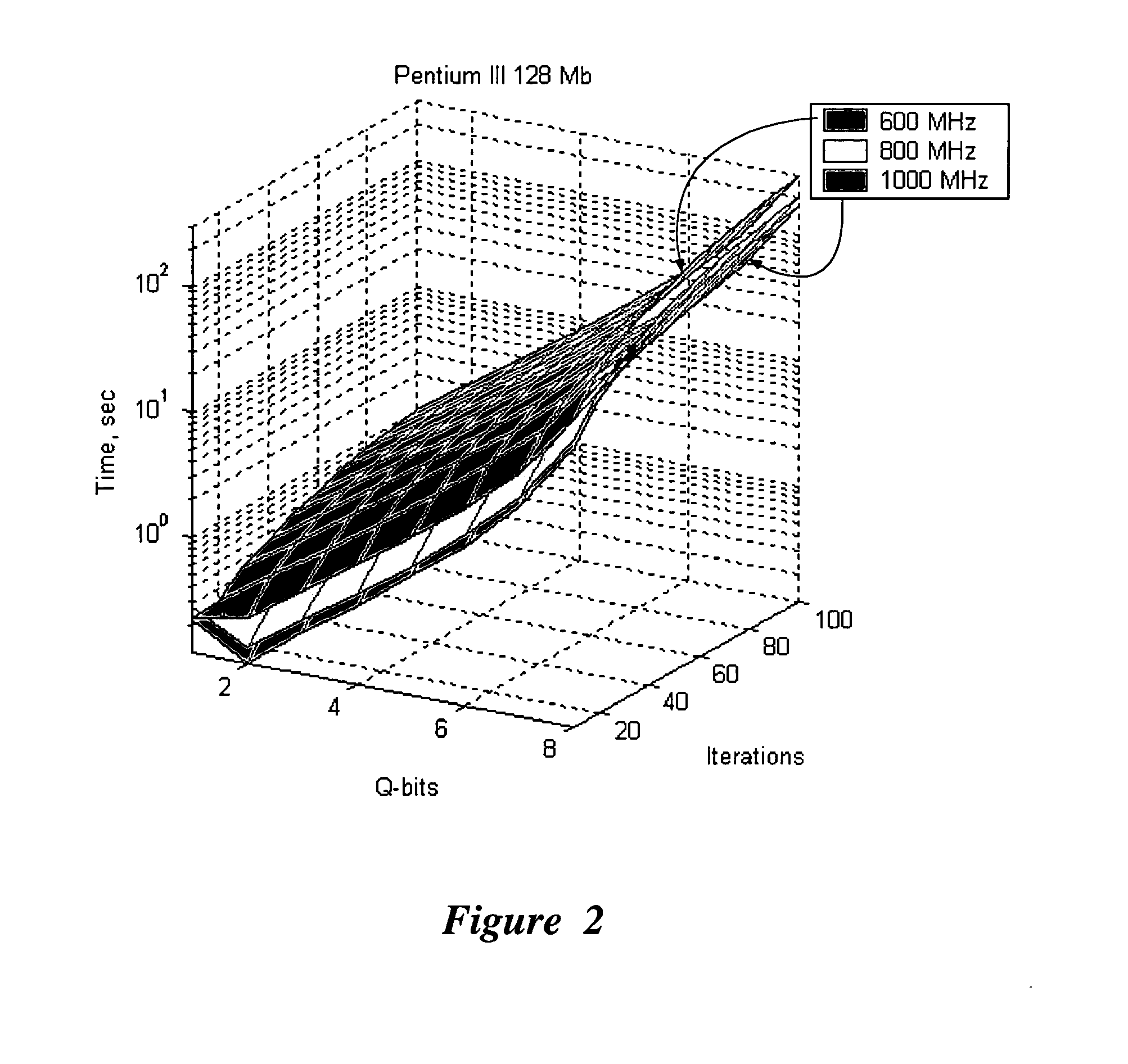
InactiveUS20060224547A1Effective simulationReduce in quantityQuantum computersNanoinformaticsFast algorithmMinimum entropy
An efficient simulation system of quantum algorithm gates for classical computers with a Von Neumann architecture is described. In one embodiment, a Quantum Algorithm is solved using an algorithmic-based approach, wherein matrix elements of the quantum gate are calculated on demand. In one embodiment, a problem-oriented approach to implementing Grover's algorithm is provided with a termination condition determined by observation of Shannon minimum entropy. In one embodiment, a Quantum Control Algorithm is solved by using a reduced number of quantum operations.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
System and method for content management
InactiveUS20050108619A1Extend cycle timeExtension of timeMetadata multimedia retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDocumentation procedureDocument preparation
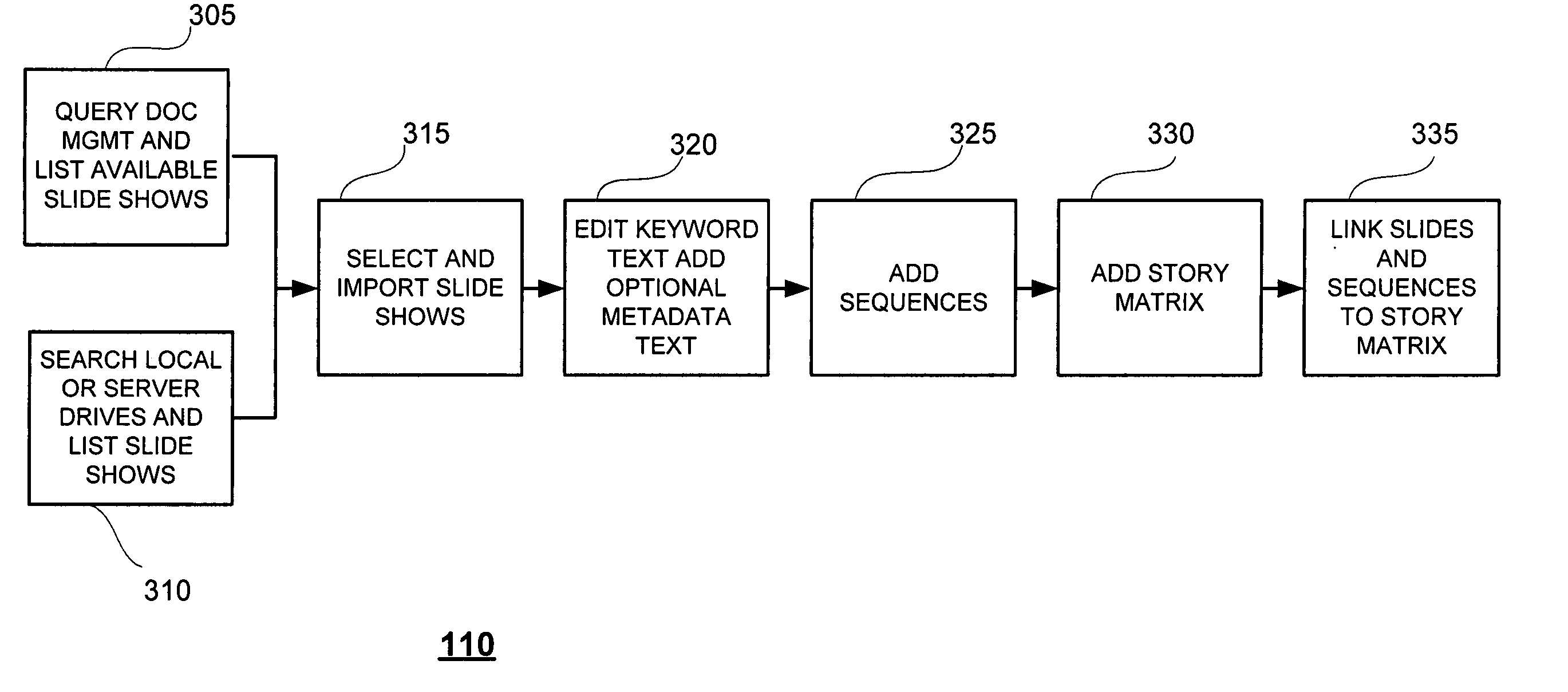
Embodiments of the invention provide an administrative utility for associating keywords or other metadata, sequence information, and / or one or more elements of a story matrix with a presentation slide, document page, or other portion of a document. Embodiments of the invention provide a search utility for identifying and / or importing a presentation slide, document page, or other portion of a pre-existing document based on one or more of keyword(s) and / or other metadata. Embodiments of the invention provide a utility for ordering presentation slides, document pages, or other portions of documents based on one or more of sequence information and / or one or more story matrix elements. Embodiments of the invention provide a utility for identifying and / or correcting slide or page formatting errors that may be associated with the reuse of presentation slides, document pages, or other portions of documents in a new presentation or other document. Any one or combination of the foregoing features may advantageously improve the cost and / or cycle time associated with creating a new presentation or other document.
Owner:MEDIA MARKETING MATERIALS
Method and device for localization of sound source by microphone
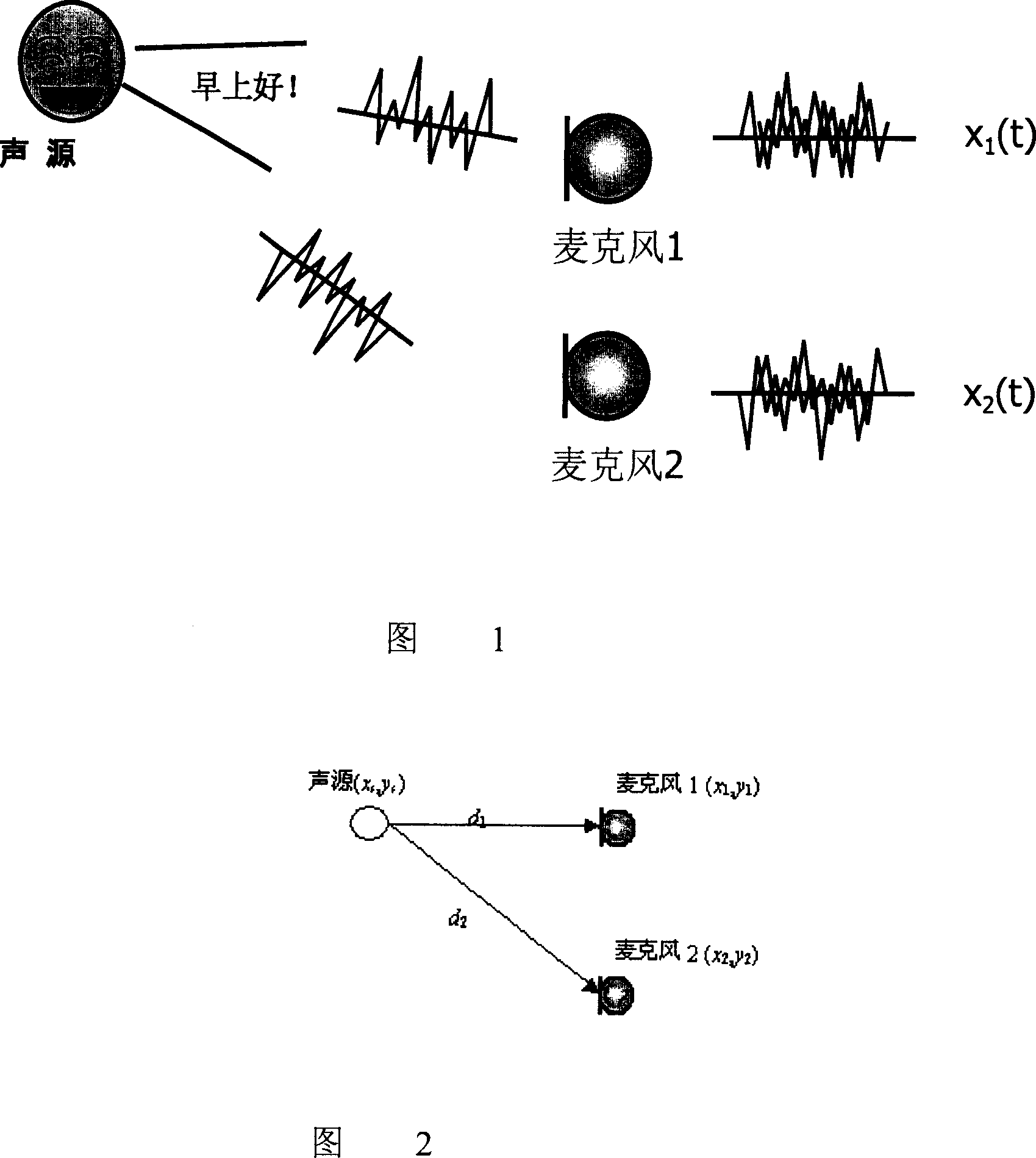
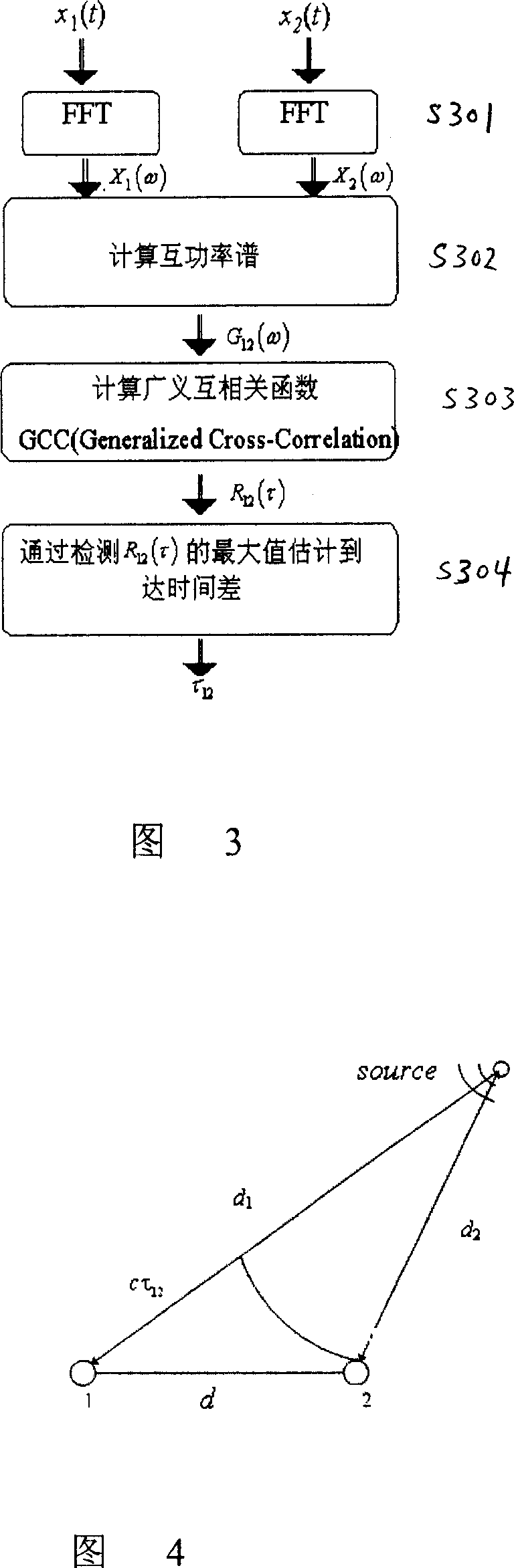
A method for positioning the location of sound source is disclosed that includes steps: the receiving device receives the sound signal generated by the sound source; provisional estimates the time difference of said sound signals reaching the receiving device; provisional estimates the receiving device separately receives the energy ratio of said sound signals; ascertains the location of the sound source by the time difference and the energy ratio. The method of double micro sound localization is compared to people's double ears position mechanism; the position is located by the sound energy and the time-delay information simultaneously, it can reach the aim of reducing the number of matrix element, and doesn't need to send and receive the type-specific reference signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and system for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information
ActiveUS20070160011A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFormation matrixSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Aspects of a method and system for utilizing Givens rotation expressions for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information. In one aspect of the invention, feedback information is computed at the receiving MIMO wireless device based on a geometric mean decomposition (GMD) method. The feedback information may include a matrix that describes a wireless medium. The matrix may represent a multiplicative product of at least one rotation matrix and at least one diagonal phase rotation matrix. Each of the rotation matrices may include at least one matrix element whose value is based on Givens rotation angle. The transmitting MIMO wireless device may subsequently transmit a plurality of signals via the wireless medium based on the received matrix information. The signal strength and / or signal to noise ratio (SNR) measurement (as measured in decibels, for example) associated with each of the transmitted plurality of signals may be about equal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
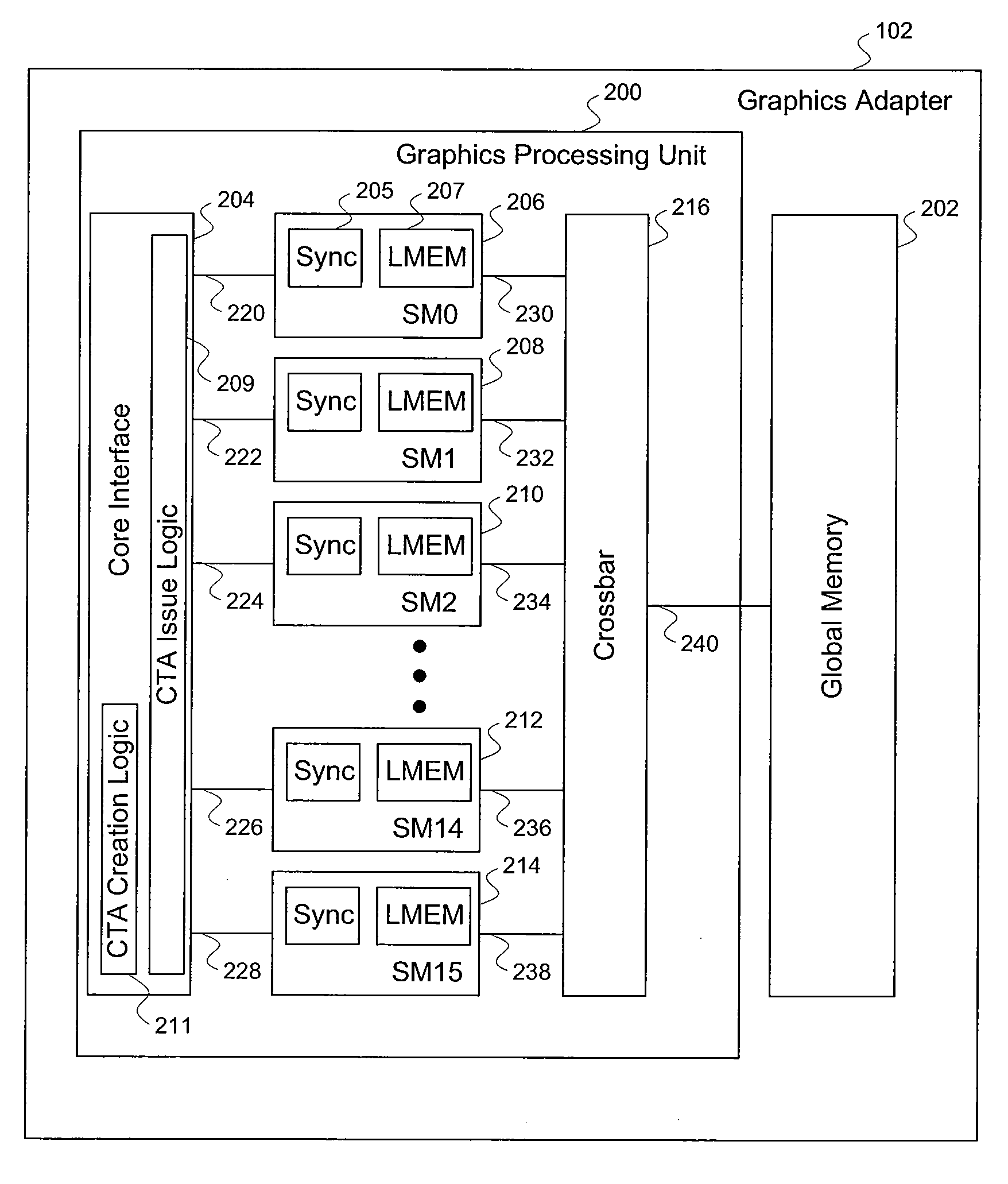
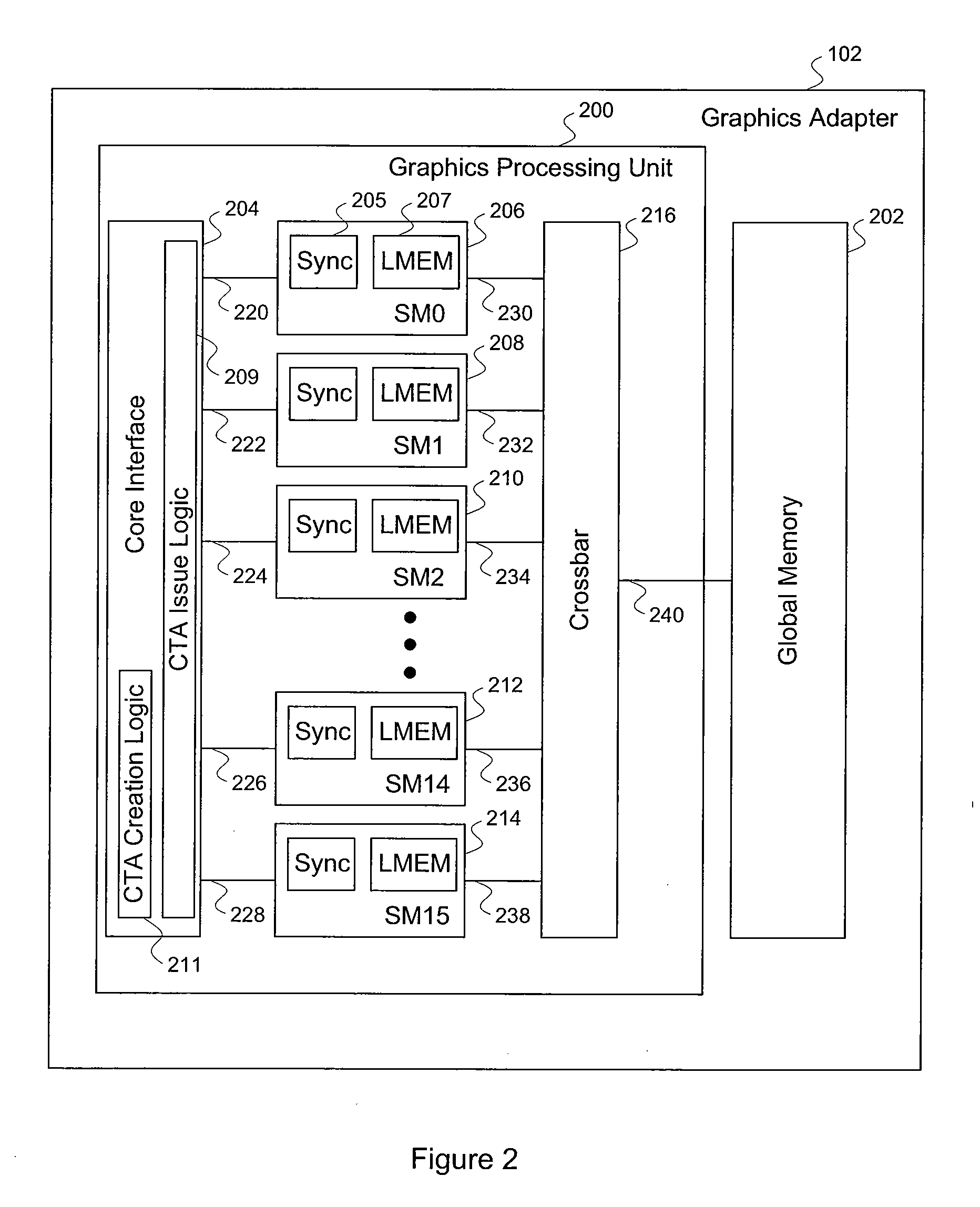
Efficient matrix multiplication on a parallel processing device
ActiveUS20100325187A1Significant processing efficiencyReduce the number of timesComputation using non-contact making devicesData mergingMulti processorParallel processing
The present invention enables efficient matrix multiplication operations on parallel processing devices. One embodiment is a method for mapping CTAs to result matrix tiles for matrix multiplication operations. Another embodiment is a second method for mapping CTAs to result tiles. Yet other embodiments are methods for mapping the individual threads of a CTA to the elements of a tile for result tile computations, source tile copy operations, and source tile copy and transpose operations. The present invention advantageously enables result matrix elements to be computed on a tile-by-tile basis using multiple CTAs executing concurrently on different streaming multiprocessors, enables source tiles to be copied to local memory to reduce the number accesses from the global memory when computing a result tile, and enables coalesced read operations from the global memory as well as write operations to the local memory without bank conflicts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
At least partially resorbable reticulated elastomeric matrix elements and methods of making same
ActiveUS20100256777A1Small volumeIncrease in sizePolyurea/polyurethane coatingsProsthesisElastomerBiomedical engineering
The present disclosure relates to reticulated elastomeric matrices, and more particularly to at least partially degradable elastomeric elements that are compressible and exhibit resilience in their recovery and that can be employed in diverse applications including, without limitation, biological implantation, especially in humans.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
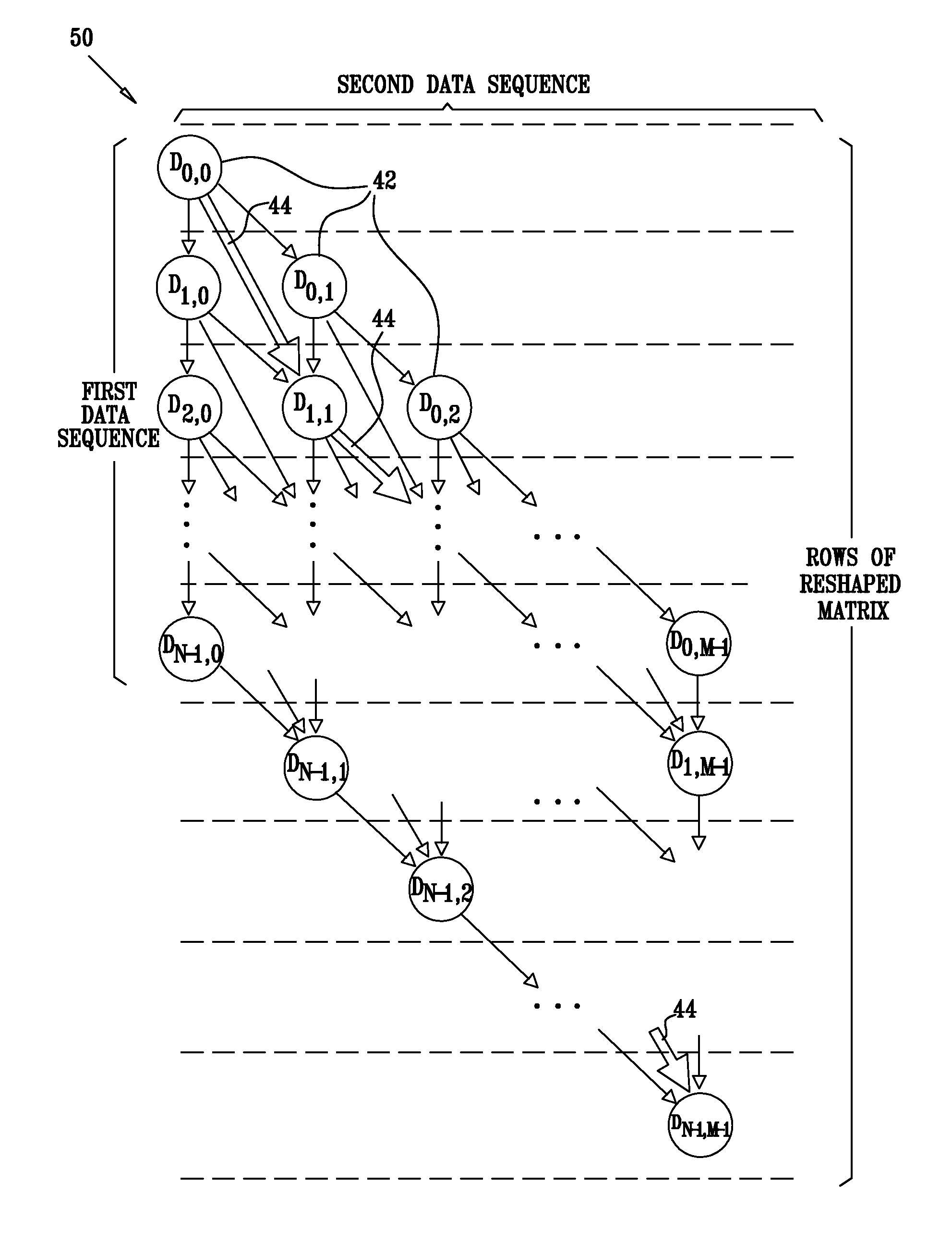
Vectorization of dynamic-time-warping computation using data reshaping
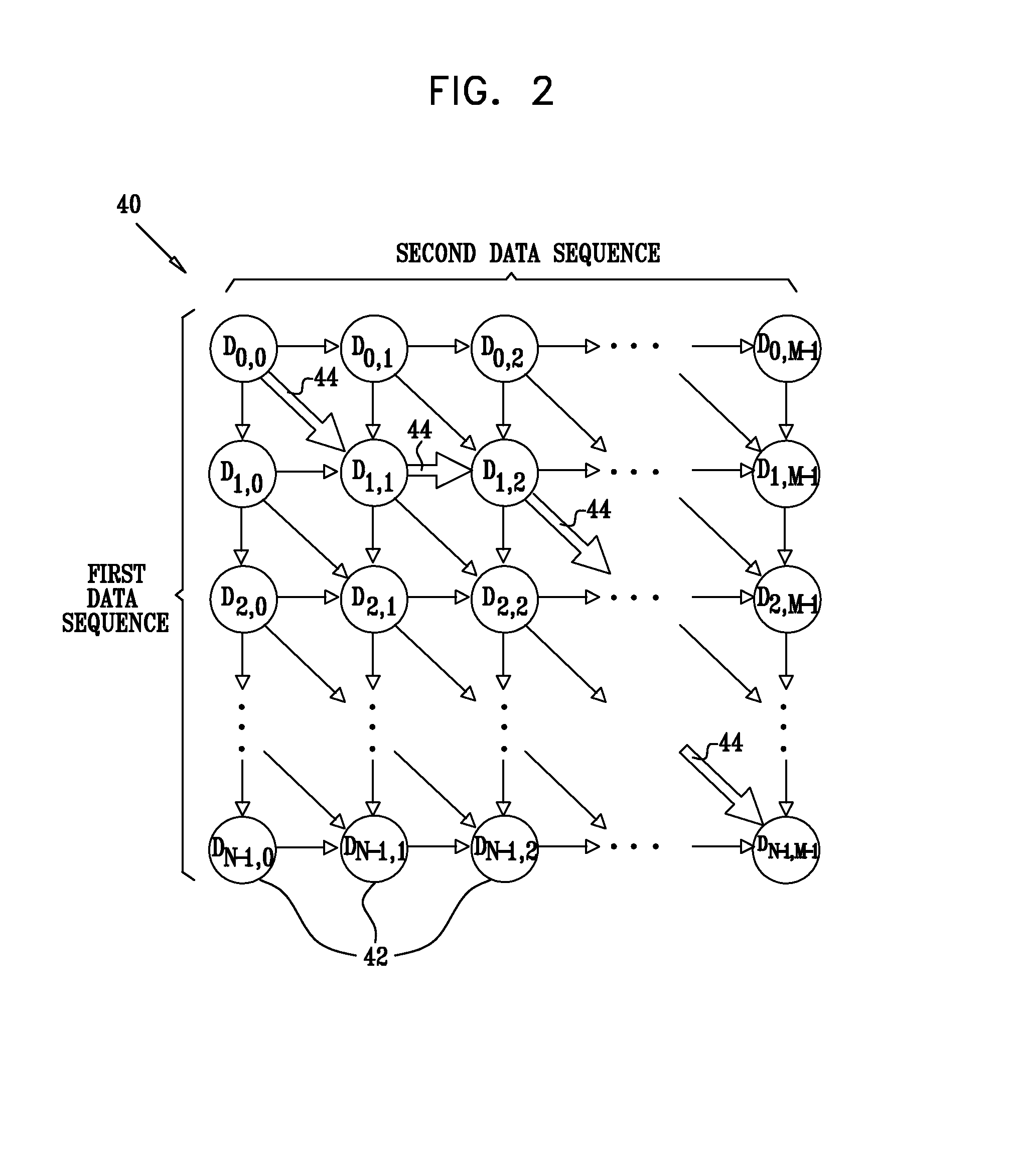
InactiveUS20090150313A1Removing data dependencyGenetic modelsDigital computer detailsDistance matrixAlgorithm
A method for comparing data sequences includes accepting first and second data sequences of data elements. A distance matrix is computed. The matrix includes rows and columns of matrix elements, describing distances between the data elements of the first sequence and the data elements of the second data sequence. The distance matrix is reshaped by applying successive, incremental shifts to the rows or columns so as to produce a reshaped matrix. A best-score path through the reshaped matrix is calculated using vector operations, so as to quantify a similarity between the first and second data sequences. Due to vectorization, a significant increase in computation speed is achieved in both software and hardware implementations.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for matrix data processing
InactiveUS20060101245A1Easy to handleImprove performanceRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisDigital signal processingParallel computing
Owner:GEMTECH SYST
Code calculating device
A code computing apparatus with an error detection code (CRC) generating function and an elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) function, comprising a matrix element computation part 30 for generating matrix elements from parameter values set in first and second registers 201 and 202, a matrix element register 51 for holding the matrix elements generated by the matrix element computation part, and an inner product calculation part 40 for executing inner product calculation between the matrix elements held by the matrix element register and data set in a third register. The matrix element computation part selectively generates matrix elements for error detection and matrix elements for encryption by changing the parameters to be set in the first and second registers, and the inner product calculation part is shared to error control code generation and data encryption by altering the matrix elements to be held in the matrix element register.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
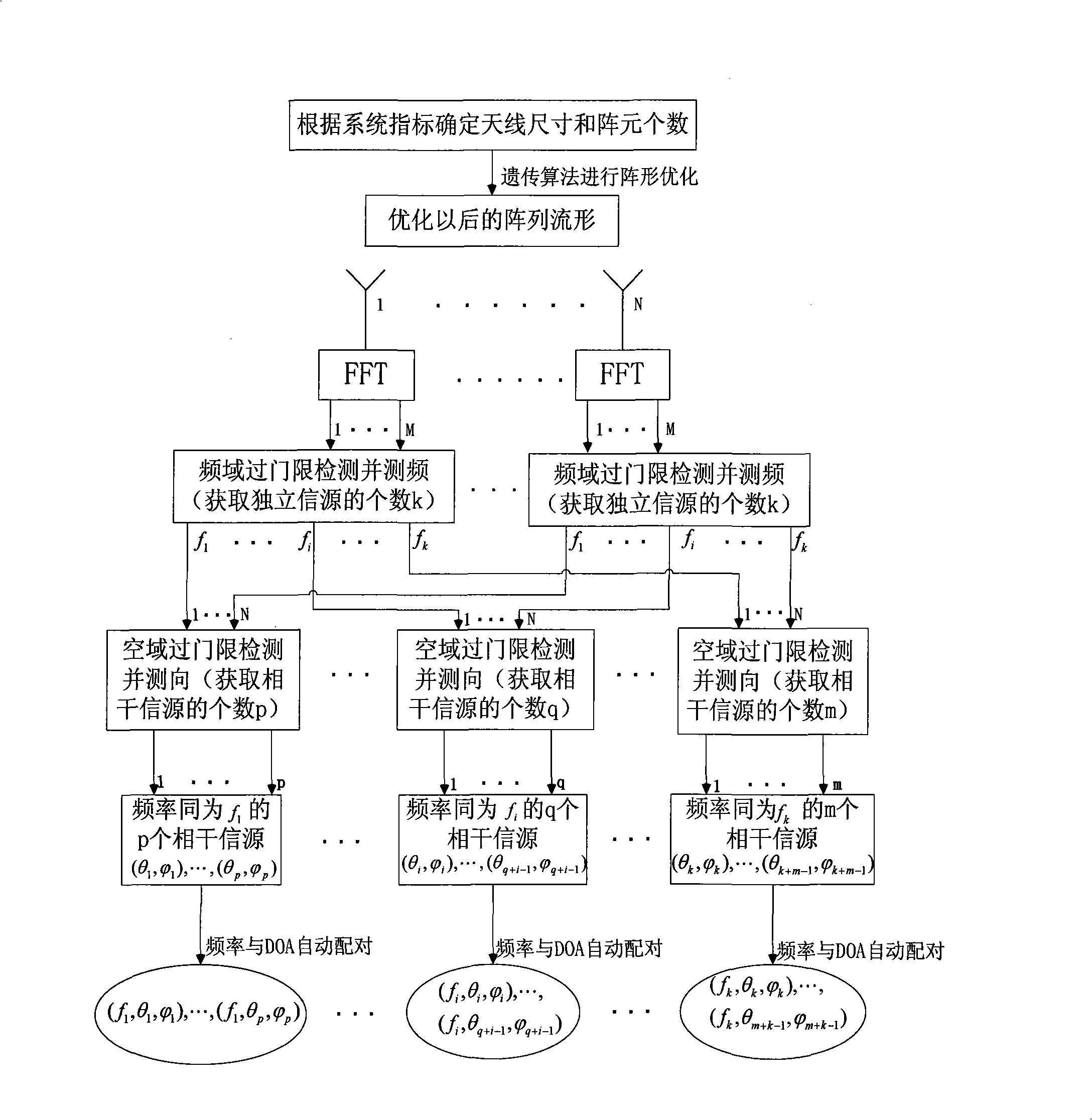
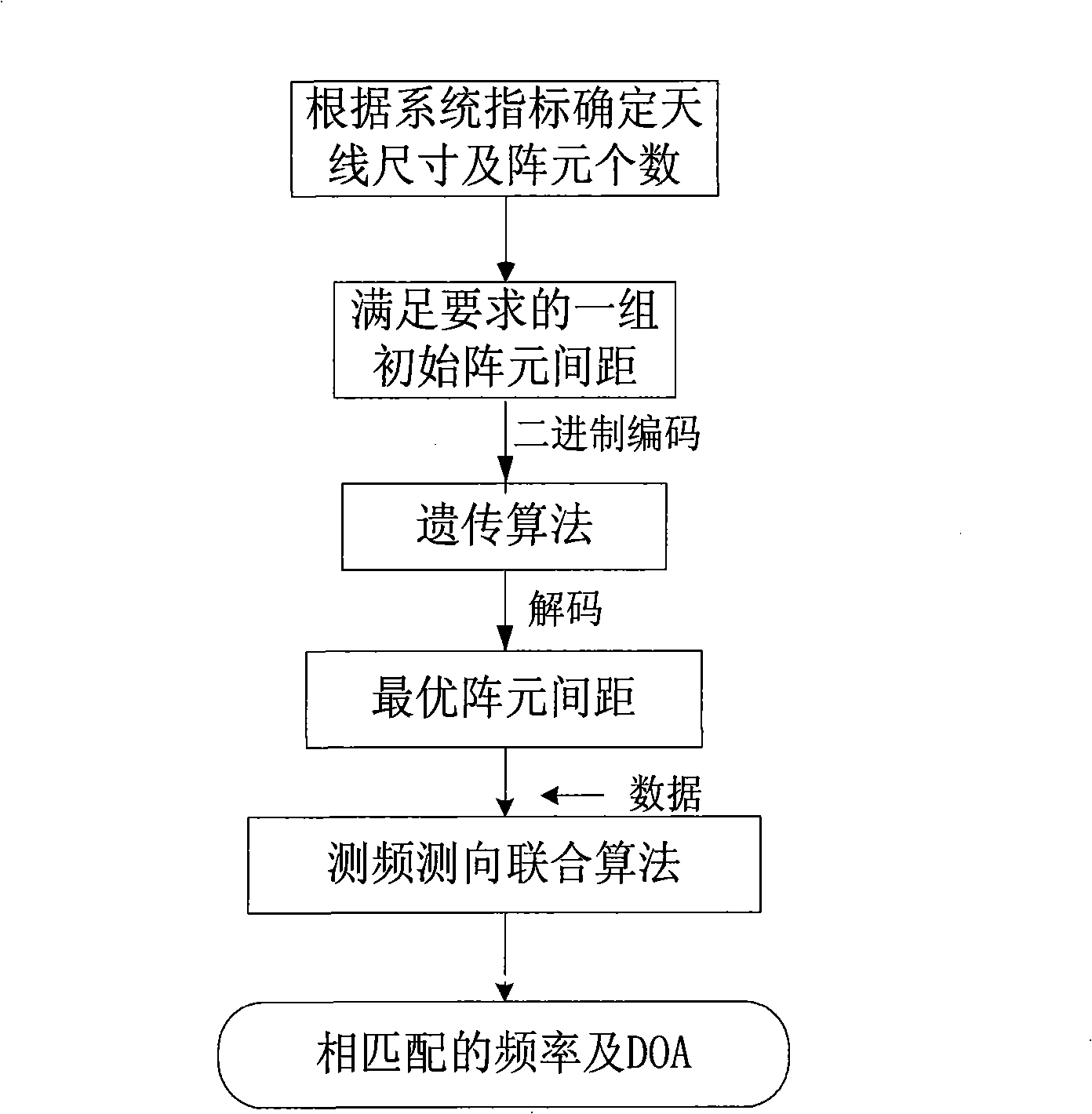
Method for optimizing space between broad band phased array elements and measuring frequency and direction of frequency domain multiple targets
InactiveCN101349742AImproved DF resolutionSolve the direction finding ambiguity problemRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency measurementsArray element
The invention discloses a method for matrix element distance optimization and frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement of wideband phased arrays, for realizing the direction measurement of multiple targets having narrow band coherence and irrelevance of a wideband receiver, resolving the contradiction between the direction measurement resolution and unambiguous direction measurement of sparse array, and realizing more accurate target detection under a certain channel error. The method comprises the steps of: first using uneven array, using genetic algorism to optimize the distance of array elements to satisfy the higher direction measurement resolution and high direction measurement accuracy of spatial unambiguous condition; based on the optimized array, realizing the frequency domain multi target frequency and direction measurement algorism as a DOA evaluation algorism which processes frequency domain accumulation, frequency domain check and frequency measurement for the data of each array element channel and realizes frequency automatic match. The algorism adopts array optimization, frequency domain peak snapshot frequency and direction measurement joint algorism. The invention can be applied for the multi narrow band target accurate frequency and direction measurement of wideband receivers in the airborne and satellite-borne electronic reconnaissance.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
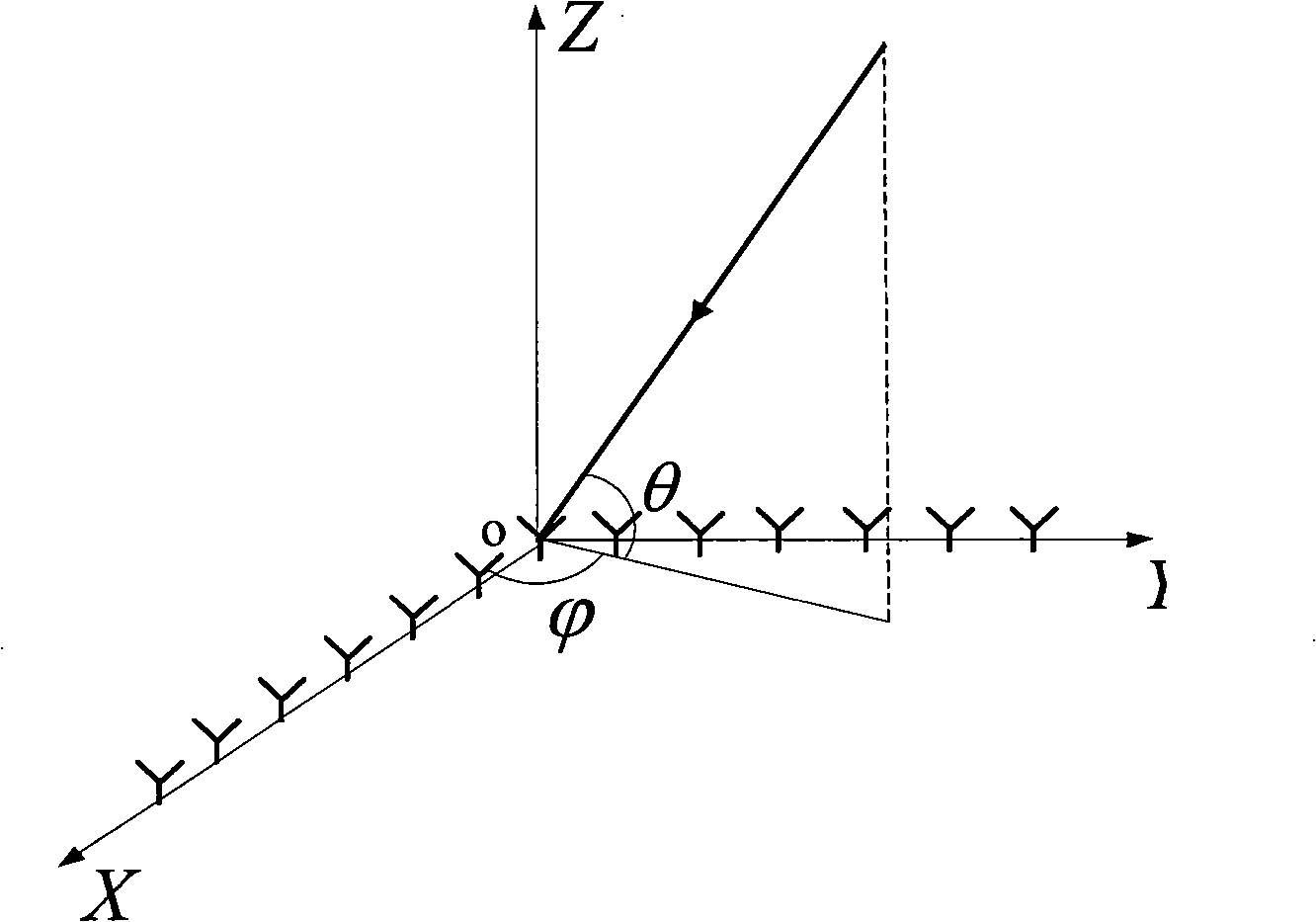
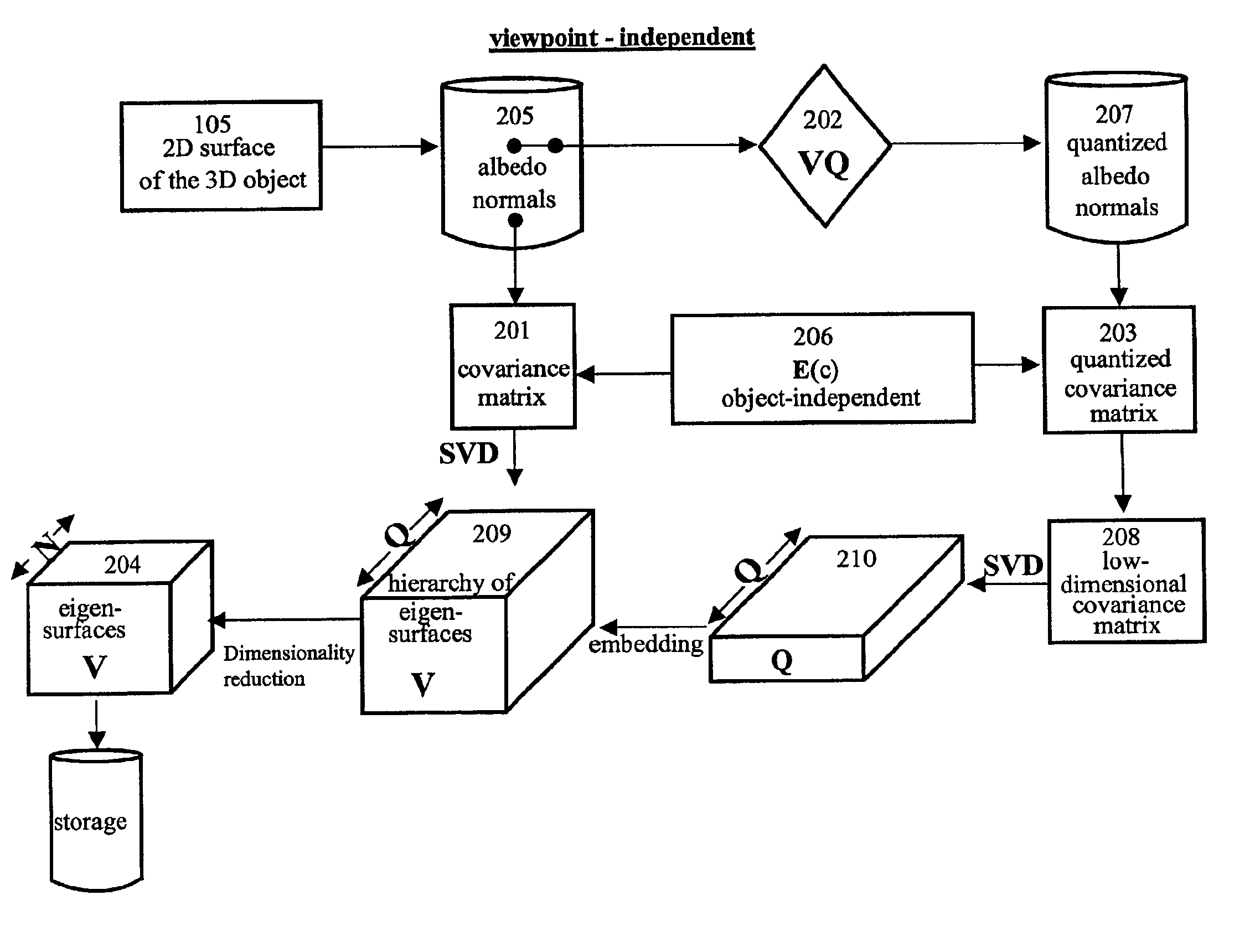
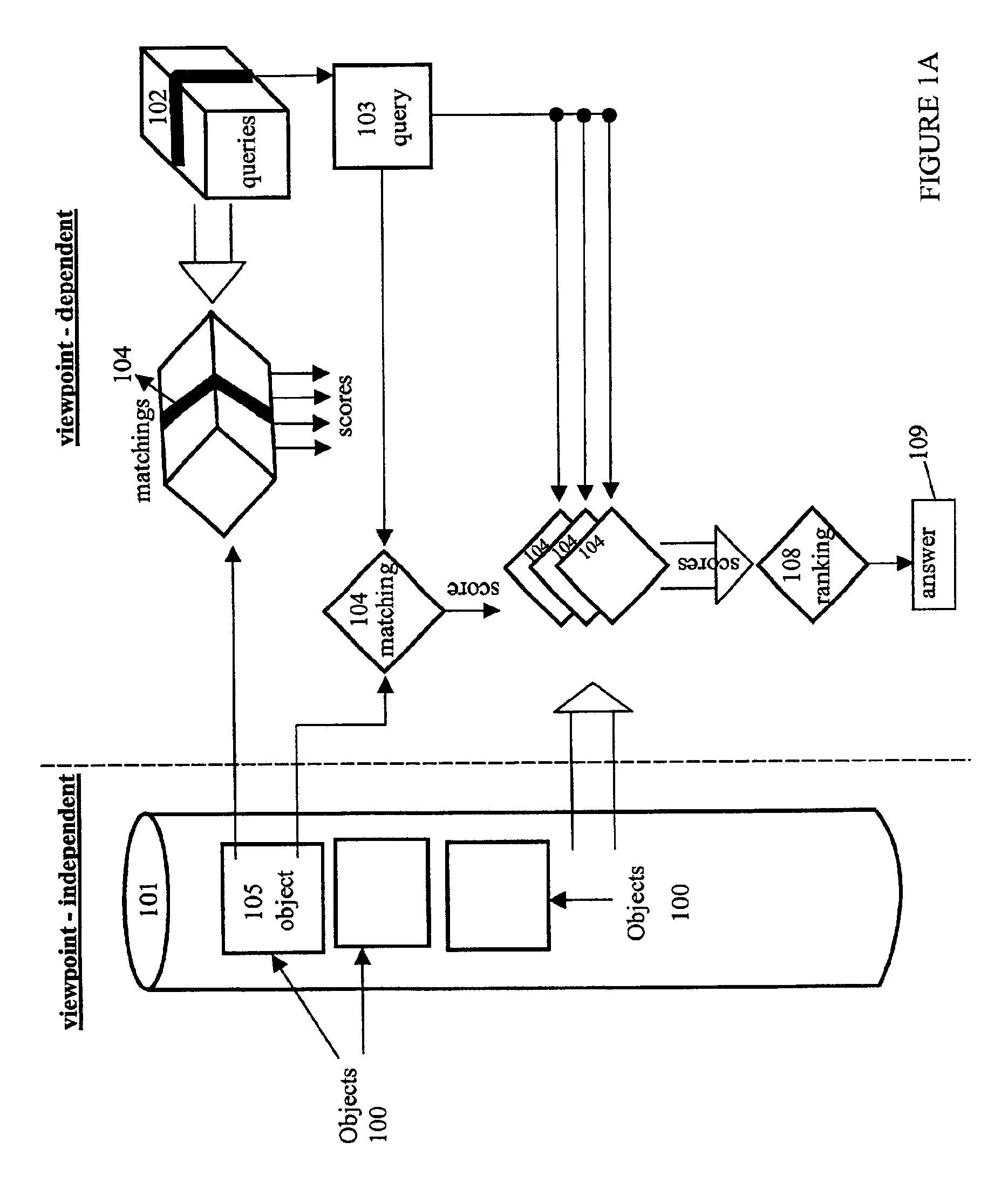
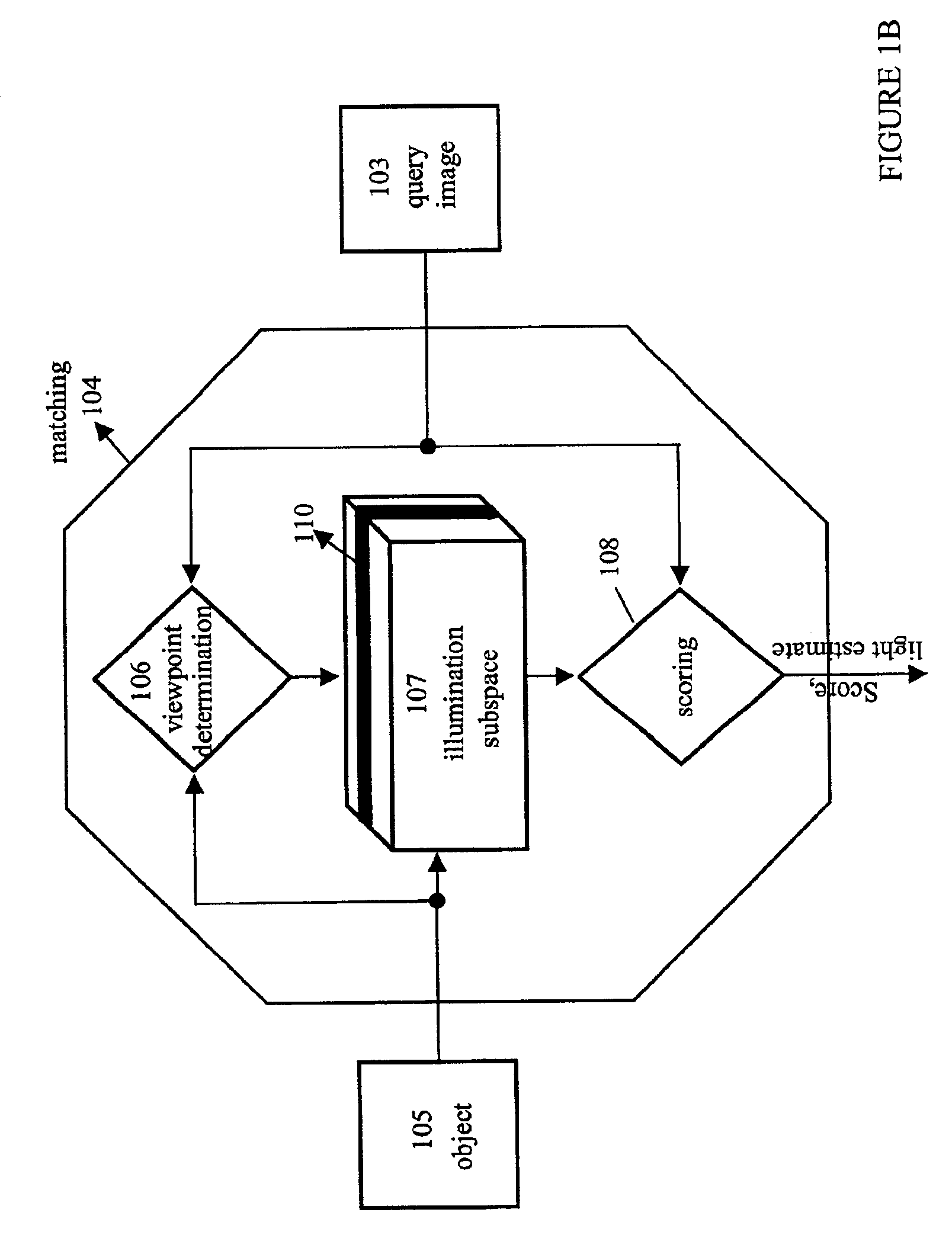
Fast optimal linear approximation of the images of variably illuminated solid objects for recognition
InactiveUS6888960B2Solve the lack of precisionComputationally efficientImage analysisImage codingViewpointsView camera
An efficient computation of low-dimensional linear subspaces that optimally contain the set of images that are generated by varying the illumination impinging on the surface of a three-dimensional object for many different relative positions of that object and the viewing camera. The matrix elements of the spatial covariance matrix for an object are calculated for an arbitrary pre-determined distribution of illumination conditions. The maximum complexity is reduced for the model by approximating any pair of normal-vector and albedo from the set of all such pairs of albedo and normals with the centers of the clusters that are the result of the vector quantization of this set. For an object, a viewpoint-independent covariance matrix whose complexity is large, but practical, is constructed and diagonalized off-line. A viewpoint-dependent covariance matrix is computed from the viewpoint-independent diagonalization results and is diagonalized online in real time.
Owner:NEC CORP
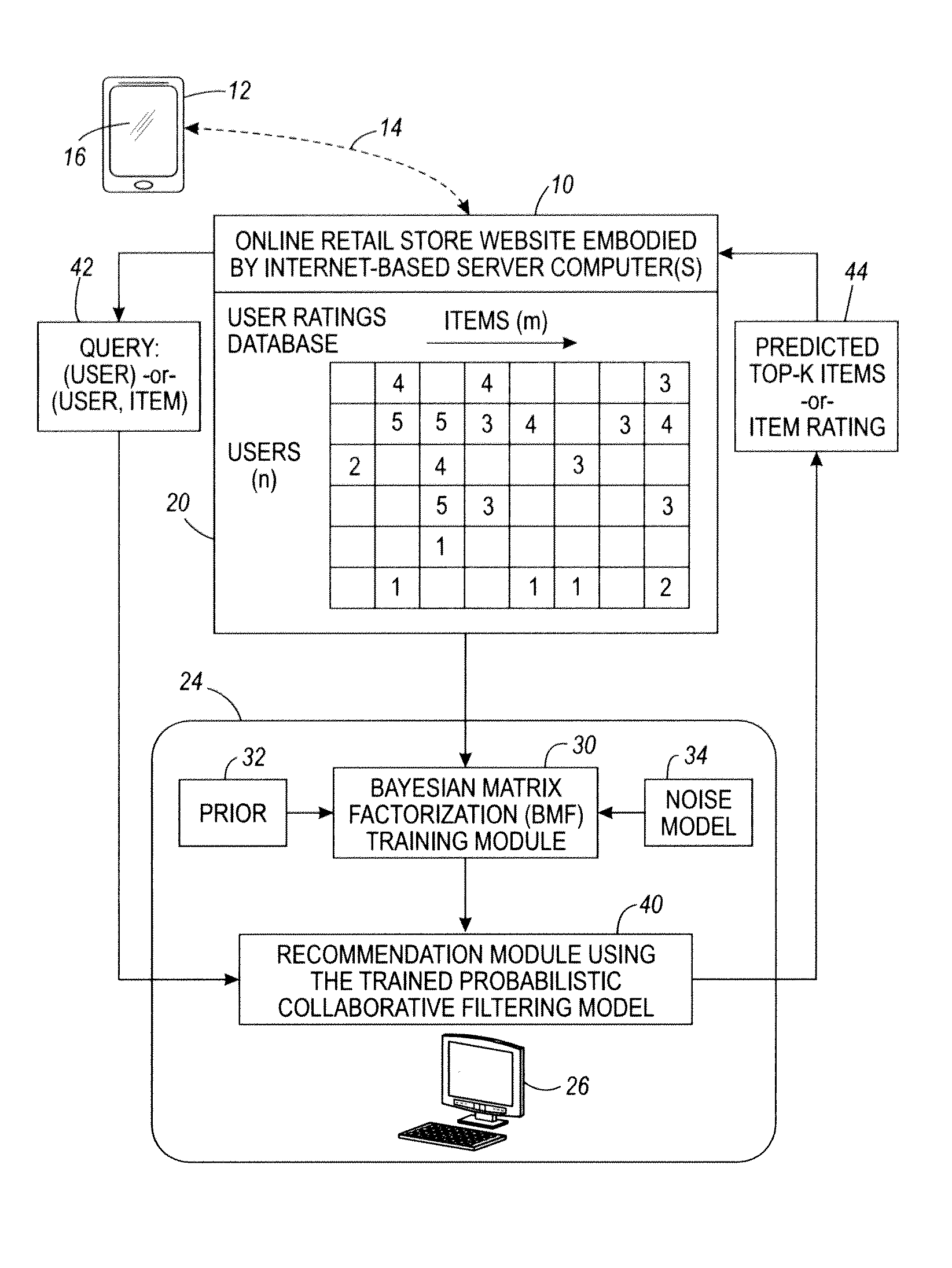
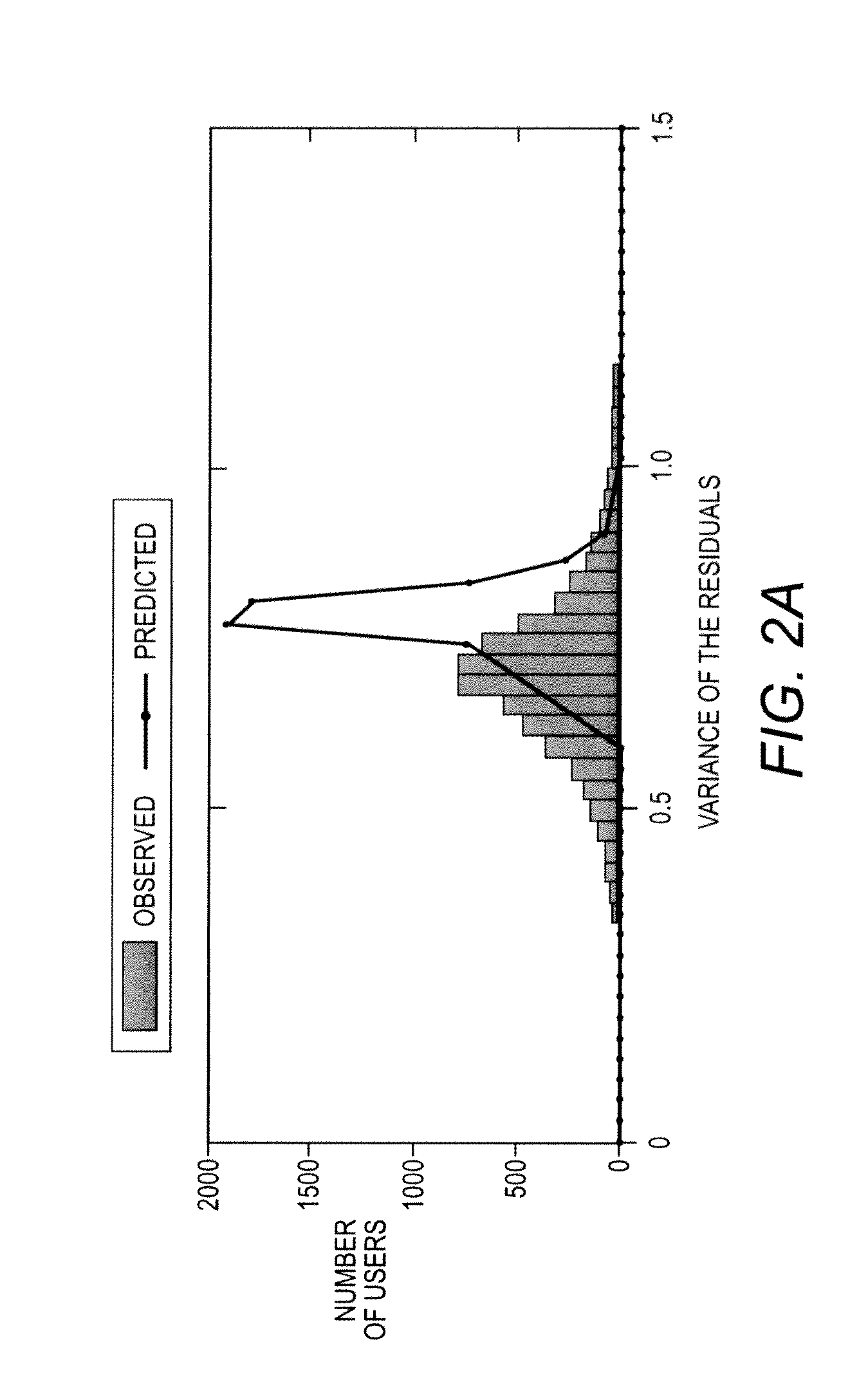
Robust bayesian matrix factorization and recommender systems using same
InactiveUS20130226839A1Kernel methodsDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
In a recommender method, Bayesian Matrix Factorization (BMF) is performed on a matrix having user and item dimensions and matrix elements containing user ratings for items made by users in order to train a probabilistic collaborative filtering model. A recommendation is generated for a user using the probabilistic collaborative filtering model. The recommendation may comprise a predicted item rating, or an identification of one or more recommended items. The recommender method is suitably performed by an electronic data processing device. The BMF may employ non-Gaussian priors, such as Student-t priors. The BMF may additionally or alternatively employ a heteroscedastic noise model comprising priors that include (1) a row dependent variance component that depends upon the matrix row and (2) a column dependent variance component that depends upon the matrix column.
Owner:XEROX CORP
At least partially resorbable reticulated elastomeric matrix elements and methods of making same
ActiveUS20120239161A1High porosityImprove permeabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsElastomerHuman body
The present disclosure relates to reticulated elastomeric matrices, and more particularly to at least partially degradable elastomeric elements that are compressible and exhibit resilience in their recovery and that can be employed in diverse applications including, without limitation, biological implantation, especially in humans.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
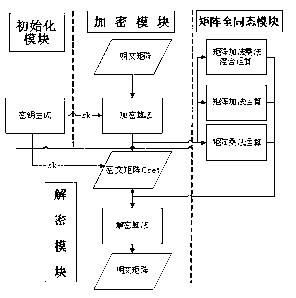
Matrix fully homomorphic encryption method
InactiveCN103259643AInput protectionSatisfy the requirement of full homomorphismSecuring communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
The invention discloses a matrix fully homomorphic encryption method. The matrix fully homomorphic encryption method comprises an initialization module, an encryption module, a decryption module and a matrix fully homomorphic module. The initialization module is used for generating secret keys needed by encryption and decryption according to dimensions of matrices to be encrypted, encryption types and ranges of matrix element values. The encryption module is used for utilizing encryption algorithms and the secret keys to conduct encryption on plaintext matrices and outputting ciphertext matrices according to the given plaintext matrices. The decryption module is used for utilizing the secret keys and decryption algorithms to conduct decryption on ciphertext matrices and outputting the plaintext matrices according to the given ciphertext matrices. According to the matrix fully homomorphic module, additive operation and multiplying operation of the matrices meet homomorphic properties of the matrices, output generated by the additive operation and the multiplying operation of the matrices still meets the homomorphic properties, namely, fully homomorphic properties of the matrices are met. The matrix fully homomorphic encryption method has the advantages of meeting safety requirements, meeting fully homomorphic requirements of the matrices and remarkably increasing the operating rate of the ciphertext matrices.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
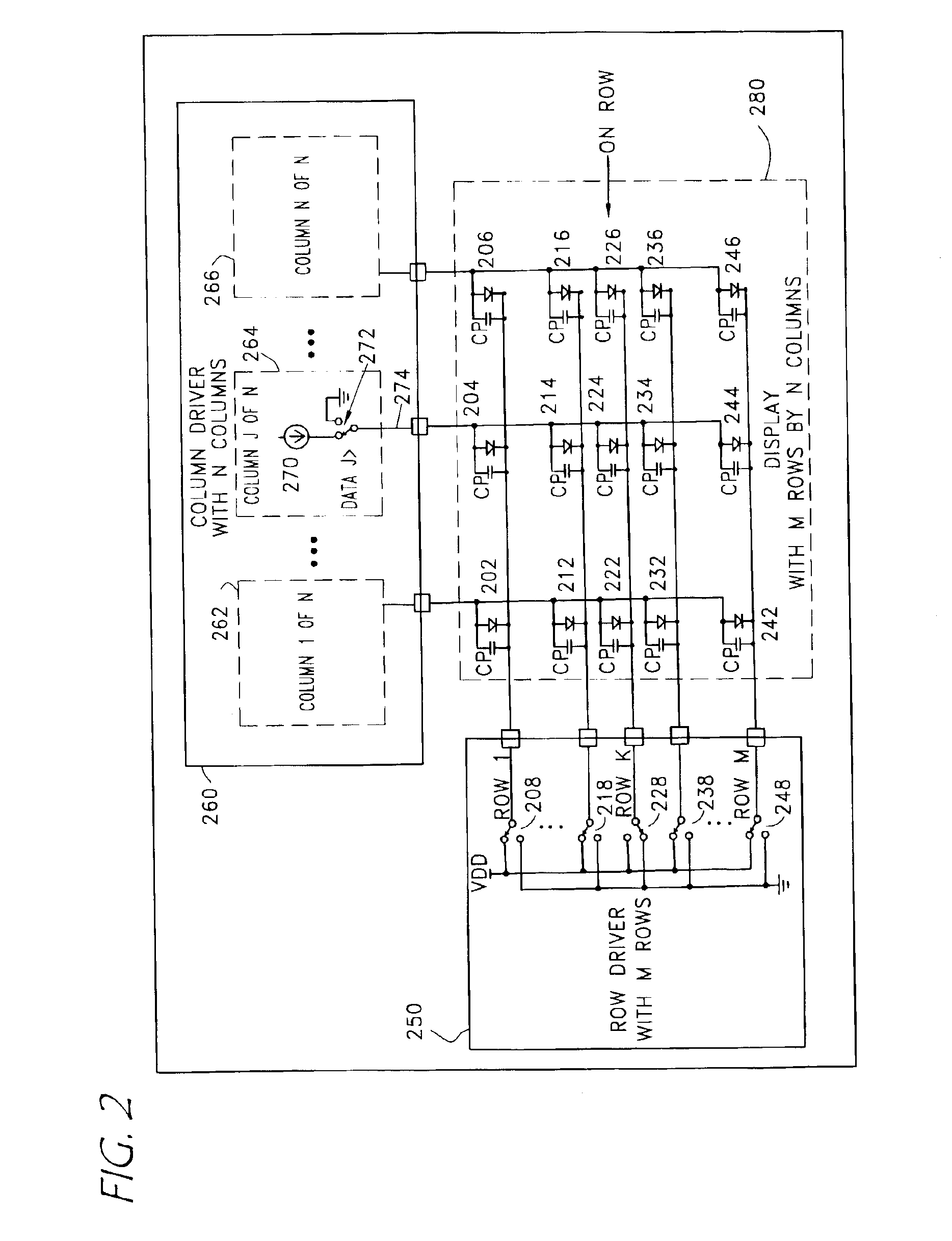
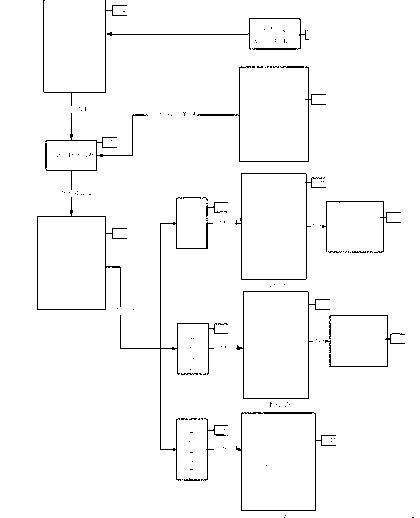
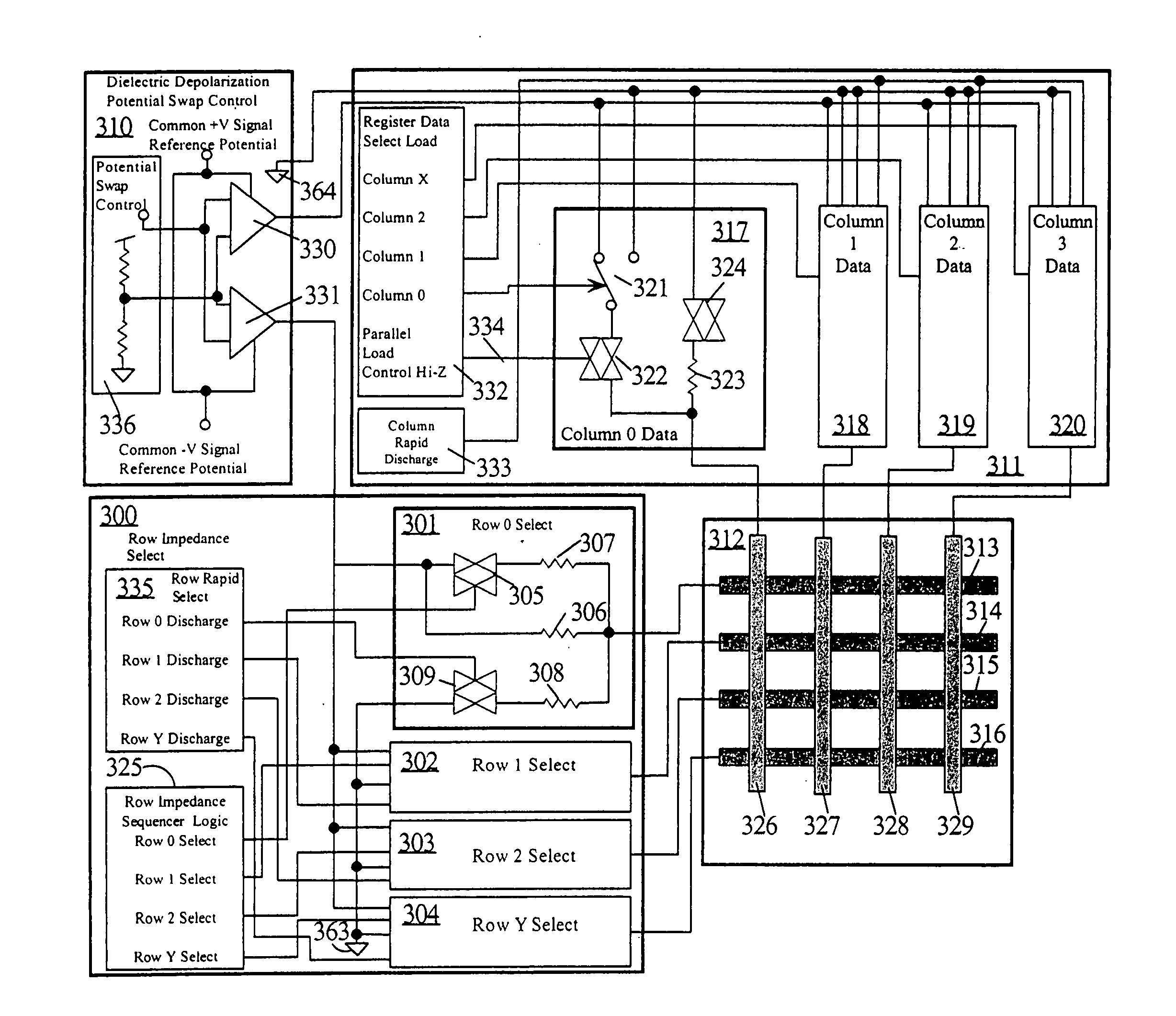
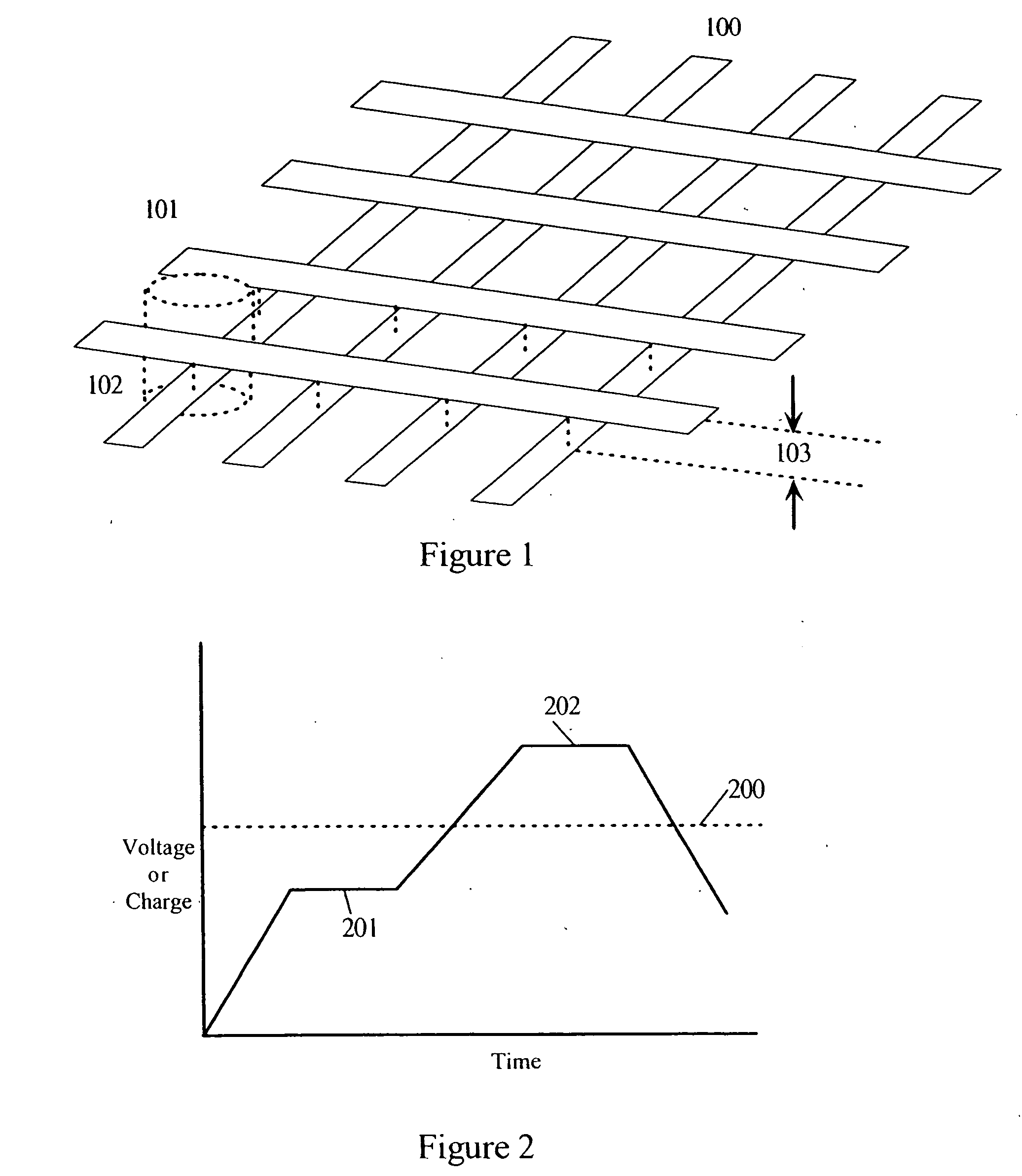
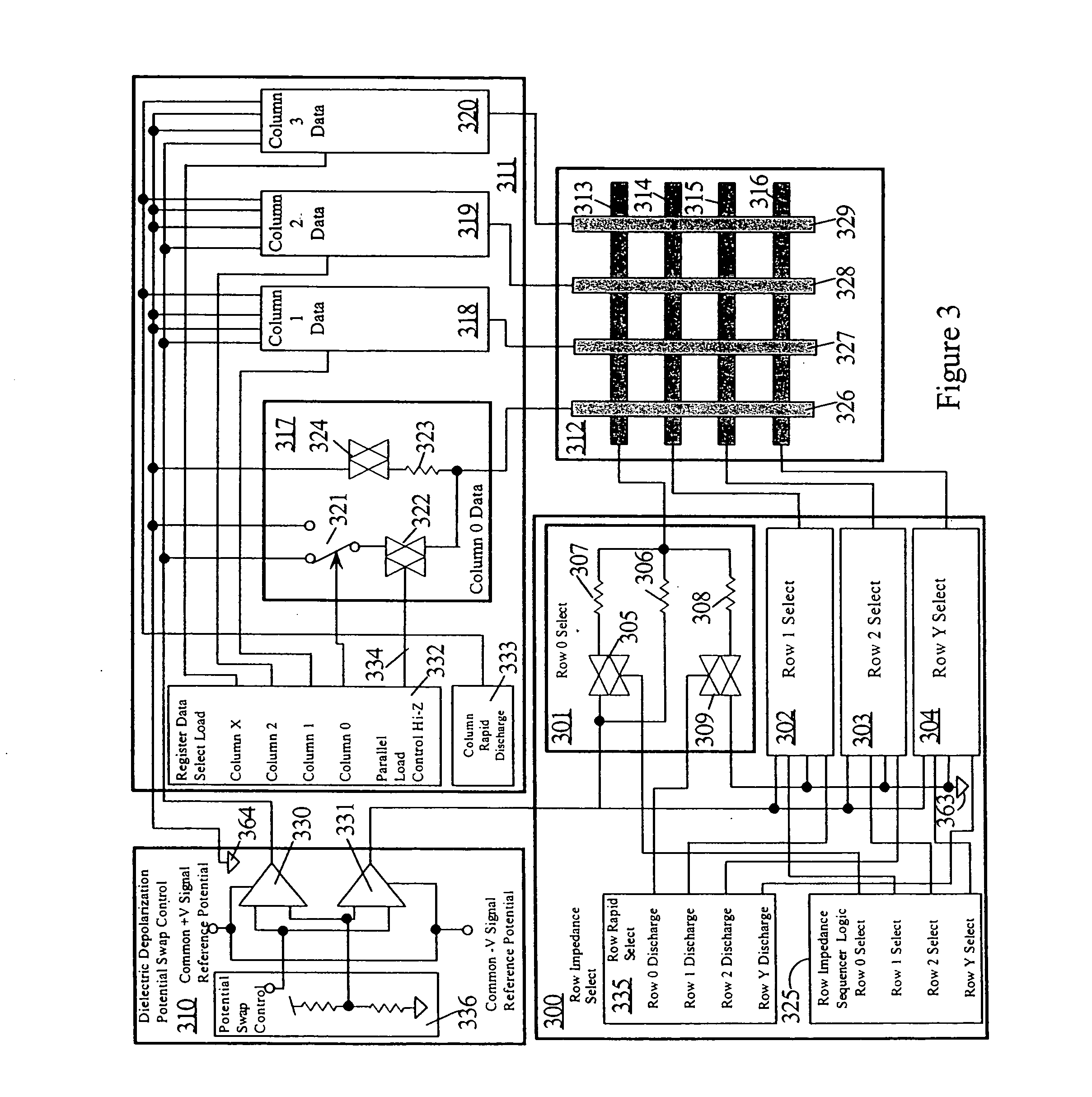
Simple matrix addressing in a display
InactiveUS20060238443A1High resistanceEnsure persistenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCapacitanceHysteresis
An addressing mechanism for charging and discharging quasi-capacitive elements in an X-Y matrix. The addressing mechanism may be configured to toggle a resistor-capacitor (RC) time constant between large and small values such as by opening or closing a circuit path to a low impedance resistor disposed in parallel with a higher impedance in-line resistor. When this occurs, elements in the X-Y matrix can be addressed and controlled. The X-Y matrix may be comprised of multiple “rows” and “columns” of conductors where crosstalk may occur along the columns and rows. Crosstalk may be curtailed by using either hysteresis management or global control of the row's impedance along its entire length. The resulting control obviates the need for active devices at each matrix element to perform the switching functions.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
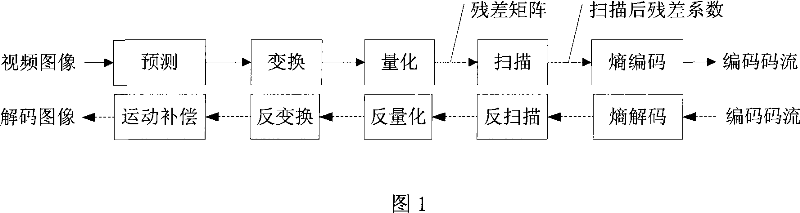
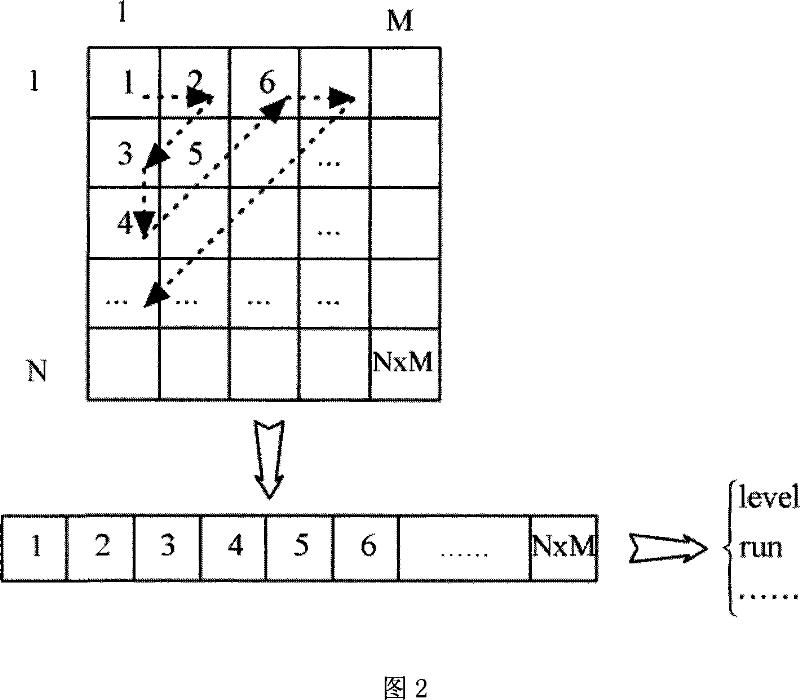
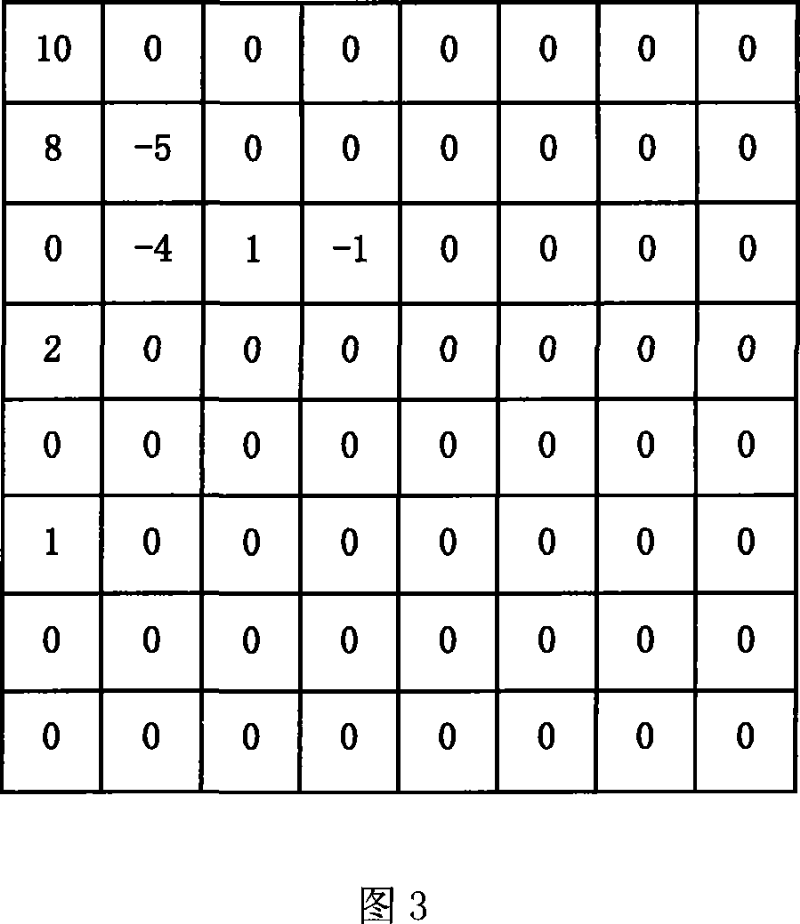
Method for scanning quickly residual matrix in video coding
InactiveCN101039430AReduce the number of clock cyclesTo achieve parallel operationPulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationResidual matrixTime cost
The present invention relates to a quick scanning method for a residual error matrix in video coding process, which belongs to the field of video coding in signal processing. The method comprises: storing elements in a two dimension residual error matrix to a one-dimension serial according to a preset mapping way; extracting the lots of residual error elements gradually and orderly from the one-dimension serial, computing a level value, a map value and a run value of each residual error element, and storing them respectively. In the process of scanning the residual error matrix, the invention can parallelizably and effectively read the residual error element, accomplish parallelizably data computing and information extracting, and can quickly obtain the required scanning results, thereby, the invention greatly reduces the time cost in whole scanning process, enhances the coding rate of a coder, and facilitates the realization of real-time encoding under high distinguishability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
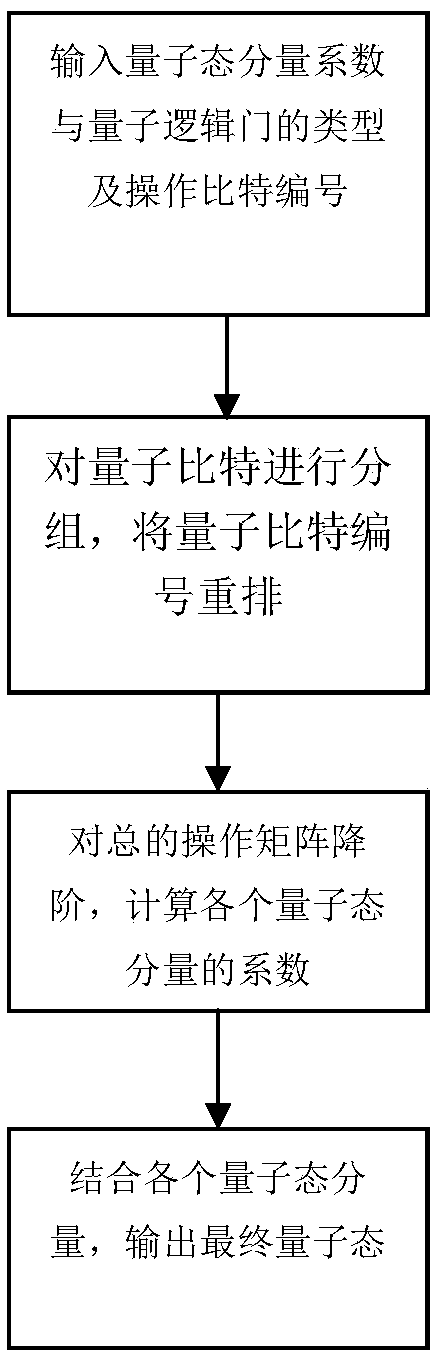
Low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system
ActiveCN108154240AScalableAvoid the disadvantage of too manyQuantum computersSupercomputerQuantum logic
The invention discloses a low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system, and belongs to the field of quantum computing. The low-complexity quantum circuit simulation system overcomes the technicalproblems in the prior art that the quantum circuit simulation storage space is too large and the calculation time is too long. The system comprises an input module, a storage module and an output module, the storage process of the storage module for data is as follows: (1) a mathematical model is established to represent the operation of a quantum state and quantum logic gate; (2) quantum bits aregrouped and the serial numbers of the quantum bits are rearranged; (3) degree reduction is conducted on a total operation matrix U0, and an output state is calculated. According to the system, a matrix element of a quantum state vector is directly operated by using an connotative inherent law of a quantum logic gate, at the same time, the method has expandability, in the future, a supercomputer can be used to simulate a quantum computer with more bits.
Owner:ORIGIN QUANTUM COMPUTING TECH (HEFEI) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for interleaved processing of direct and indirect texture coordinates in a graphics system
InactiveUS20050237337A1Efficient implementationIncrease in texture mapping hardware complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsData storeData combination
A graphics system including a custom graphics and audio processor produces exciting 2D and 3D graphics and surround sound. The system includes a graphics and audio processor including a 3D graphics pipeline and an audio digital signal processor. The graphics pipeline renders and prepares images for display at least in part in response to polygon vertex attribute data and texel color data stored as a texture images in an associated memory. An efficient texturing pipeline arrangement achieves a relatively low chip-footprint by utilizing a single texture coordinate / data processing unit that interleaves the processing of logical direct and indirect texture coordinate data and a texture lookup data feedback path for “recirculating” indirect texture lookup data retrieved from a single texture retrieval unit back to the texture coordinate / data processing unit. Versatile indirect texture referencing is achieved by using the same texture coordinate / data processing unit to transform the recirculated texture lookup data into offsets that may be added to the texture coordinates of a direct texture lookup. A generalized indirect texture API function is provided that supports defining at least four indirect texture referencing operations and allows for selectively associating one of at least eight different texture images with each indirect texture defined. Retrieved indirect texture lookup data is processed as multi-bit binary data triplets of three, four, five, or eight bits. The data triplets are multiplied by a 3×2 texture coordinate offset matrix before being optionally combined with regular non-indirect coordinate data or coordinate data from a previous cycle / stage of processing. Values of the offset matrix elements are variable and may be dynamically defined for each cycle / stage using selected constants. Two additional variable matrix configurations are also defined containing element values obtained from current direct texture coordinates. Circuitry for optionally biasing and scaling retrieved texture data is also provided.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
Display driver and method for driving an emissive video display
InactiveUS20050024301A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Control system
Owner:FUNSTON DAVID L
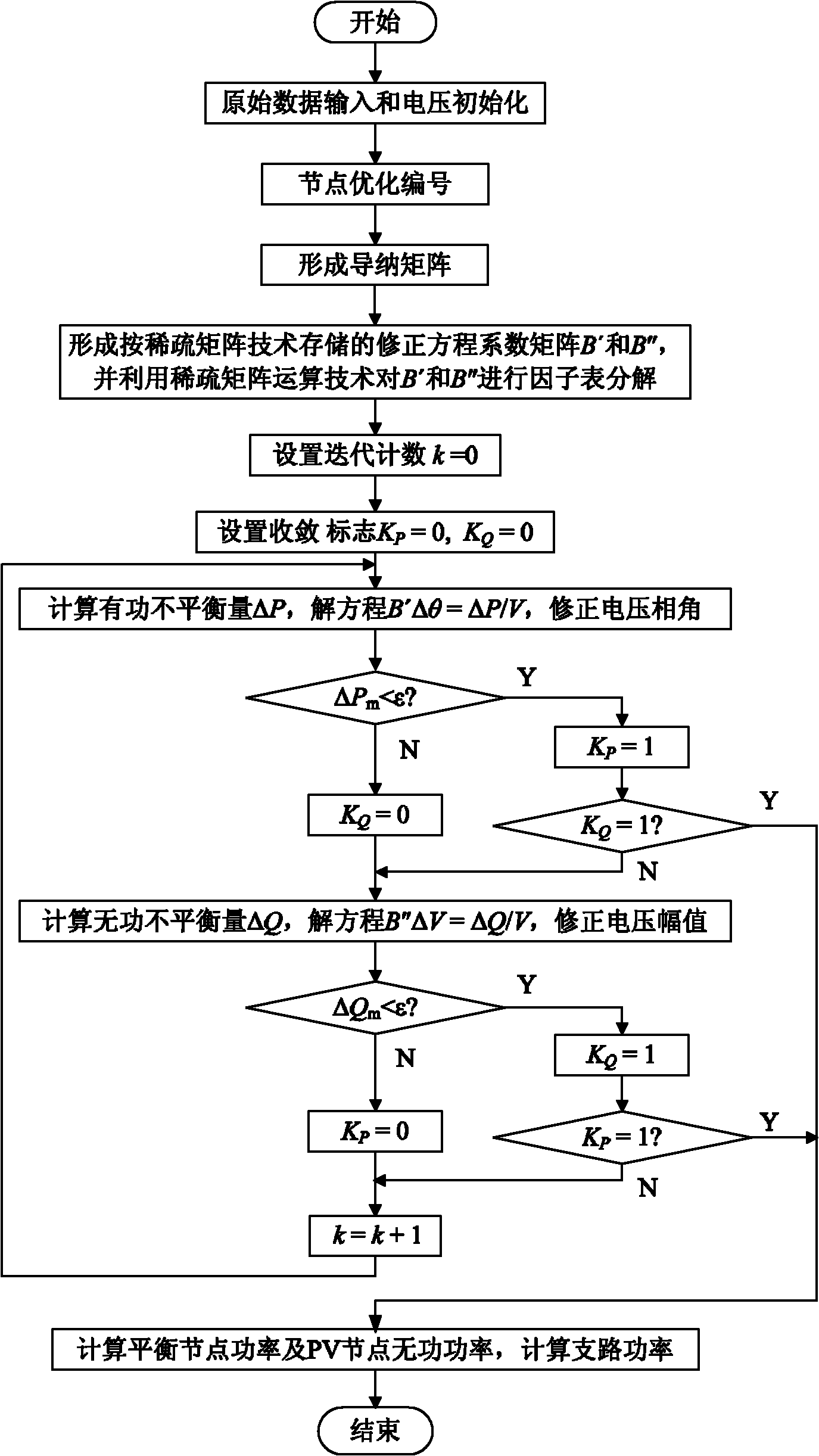
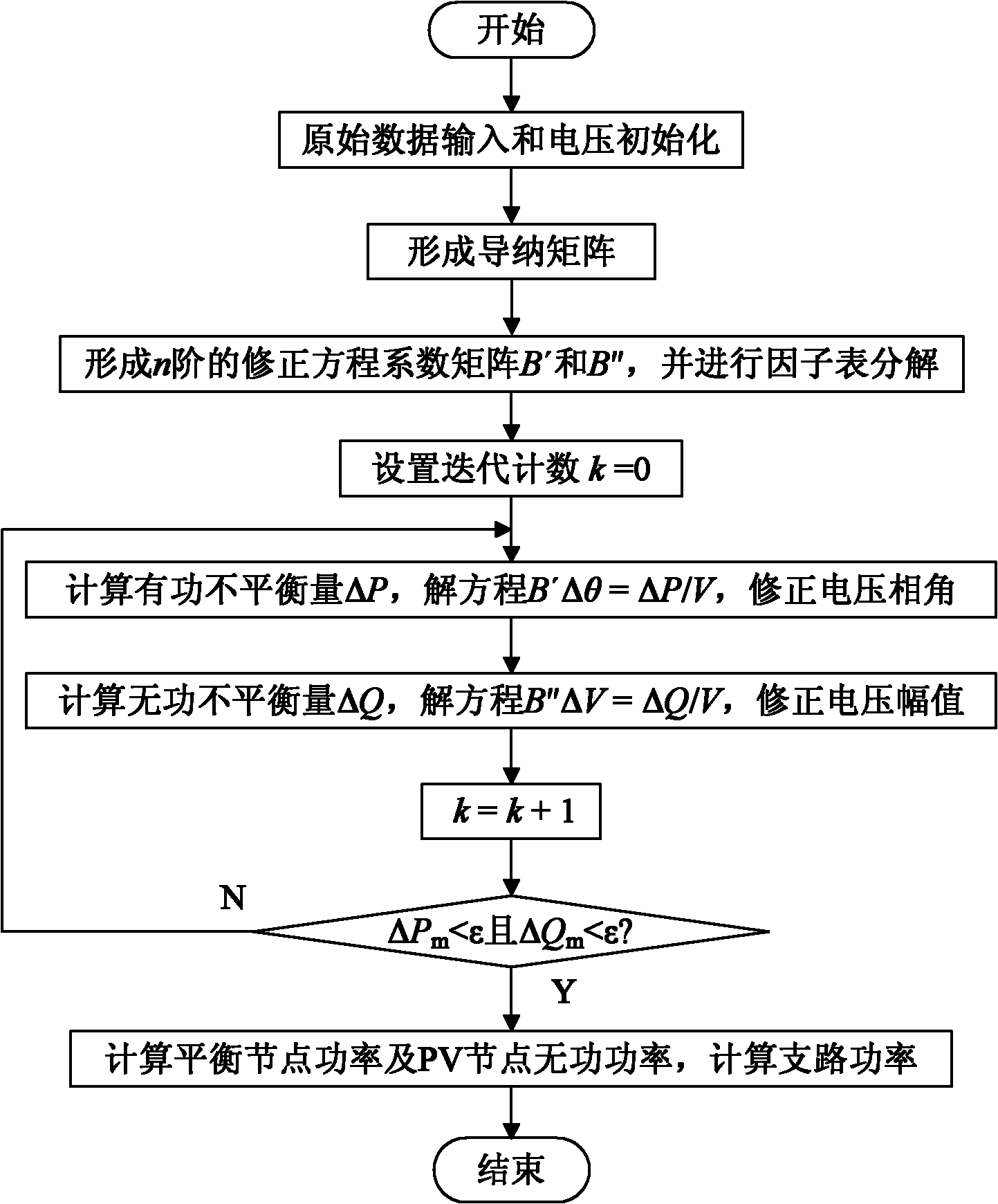
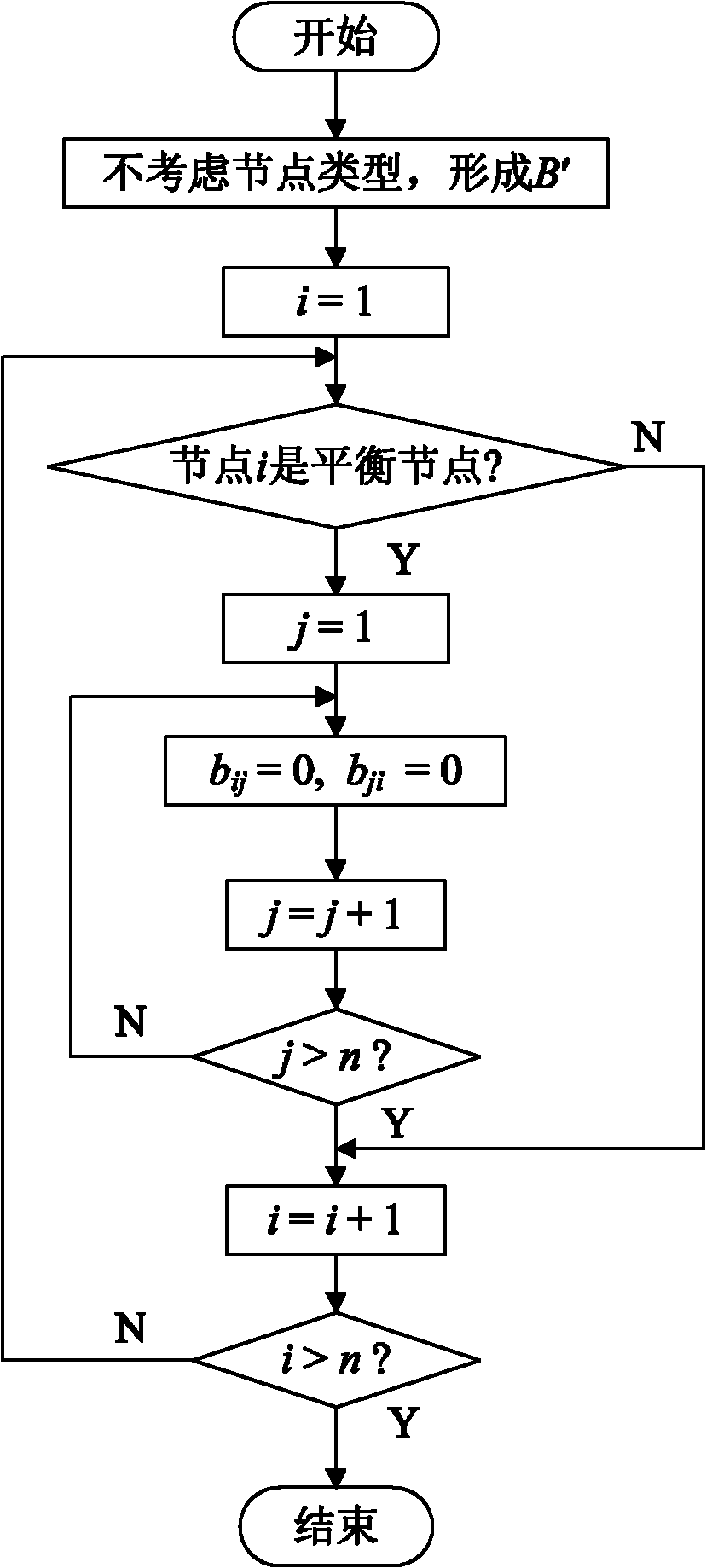
Fast decoupled flow calculation method for power systems
InactiveCN102013680AClear processIntuitive accessAc network voltage adjustmentSpecial data processing applicationsVoltage amplitudeDecomposition
The invention discloses a fast decoupled flow calculation method for power systems, which comprises the following steps of: inputting original data and initializing voltage; forming an admittance matrix; forming correction equation coefficient matrixes B' and B'' and performing factor table decomposition; performing P-theta iteration, and correcting a voltage phase angle; performing Q-V iteration, and correcting voltage amplitude; judging whether the iteration is converged; and calculating node power and branch power. The method requires that the P-theta iteration and the Q-V iteration are all converged in the same iteration and the iteration process is finished, so that the algorithm frame is simpler, and the flow is clearer. The sparse matrix technology is not adopted, so the matrix elements are convenient to access and calculate, and the programming is simple; the correction equation coefficient matrixes are stored according to n order, number change of nodes is avoided, and the programming difficulty is reduced; and the calculation amount is reduced through reasonable logic judgment, the calculation speed is obviously improved and the requirement of scientific research can be completely met. The fast decoupled flow calculation method also can process power systems with a plurality of balance nodes.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
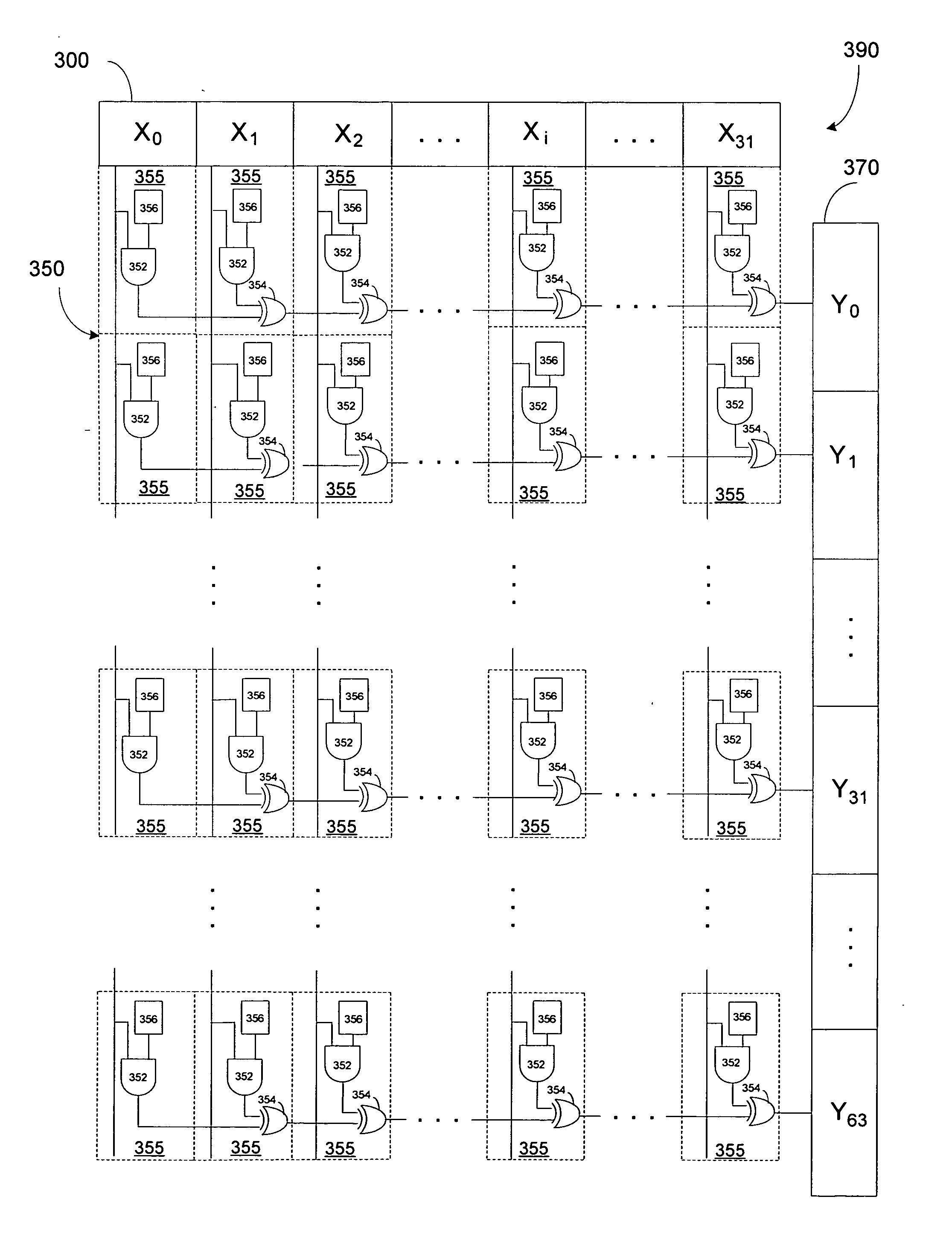
Galois field polynomial multiplication
In one aspect, a multiplier for performing multiplication of a first operand and a second operand is provided. The multiplier comprises a matrix having a plurality of matrix elements arranged in a plurality of columns, a first plurality of storage elements to store at least a portion of the first operand, the first plurality of storage elements connected diagonally to the matrix, and a second plurality of storage elements to store at least a portion of the second operand, the second plurality of storage elements connected vertically to the matrix. In another aspect, a multiplier for computing at least a partial product of a first operand having a first length and a second operand having a second length is provided. The multiplier comprises a first register to store at least a portion of the first operand, a second register to store at least a portion of the second operand, and a logic matrix formed from a plurality of matrix elements that together perform a multiplication operation, the logic matrix connected to the first register and the second register such that each matrix element receives at least one bit from the first register and at least one bit from the second register, wherein a number of the plurality of matrix elements does not exceed a product of the first length and the second length.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Matrix multiply with reduced bandwidth requirements
InactiveUS20070271325A1Reduce memory bandwidth requirementReduce memory bandwidthComputation using non-contact making devicesMultiprogramming arrangementsAlgorithmSingle element
Systems and methods for reducing the bandwidth needed to read the inputs to a matrix multiply operation may improve system performance. Rather than reading a row of a first input matrix and a column of a second input matrix to produce a column of a product matrix, a column of the first input matrix and a single element of the second input matrix are read to produce a column of partial dot products of the product matrix. Therefore, the number of input matrix elements read to produce each product matrix element is reduced from 2N to N+1, where N is the number of elements in a column of the product matrix.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
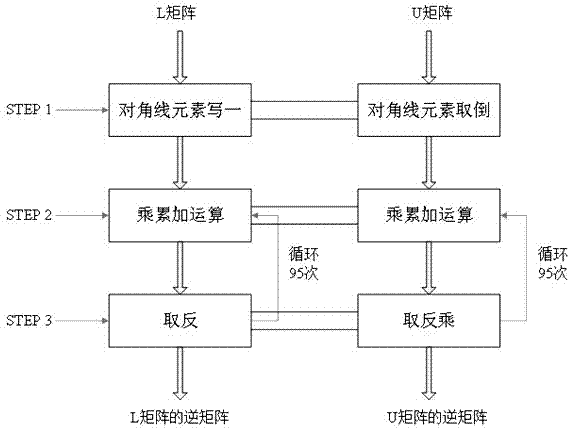
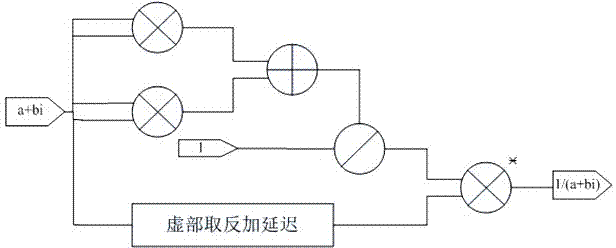
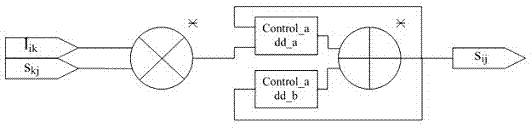
Inverse operation method for lower triangle complex matrix with any order
InactiveCN103927290AImplement the inverse operationSave hardware resourcesComplex mathematical operationsDiagonalComputer science
The invention relates to an inverse operation method for a lower triangle complex matrix with any order. The inverse operation method comprises the following steps that (1) a reciprocal obtaining unit is set, and is used for carrying out reciprocal obtaining operation on a diagonal element of an N-order matrix L, and outputting a matrix obtained after reciprocal obtaining operation is accomplished; (2) a multiplication and accumulation unit is set and is used for receiving the matrix obtained after reciprocal obtaining operation is accomplished, and multiplication and accumulation operation is carried out on the first element to the (i-1)th element in the ith row in the matrix; (3) a reciprocal multiplication obtaining unit is set and is used for receiving the accumulation result corresponding to the elements in the ith row of the matrix, reciprocal obtaining operation is carried out on the accumulation result, and then the accumulation result processed through reciprocal obtaining operation is multiplied by a diagonal element in the ith row so that a matrix element of the ith row of an inverse matrix L-1 can be obtained. In the whole process, a plurality of multiplication and accumulation units are used for carrying out parallel calculation. The inverse operation method for the lower triangle complex matrix with any order has the advantages that the inverse operation of the lower triangle complex matrix with any order can be achieved, and restriction caused by the number of operation units does not exist; only the design of a multiply-accumulator with one plural adder and one plural multiplier is adopted, hardware resources are saved, and operation efficiency is ensured through an effective parallelization mode.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com