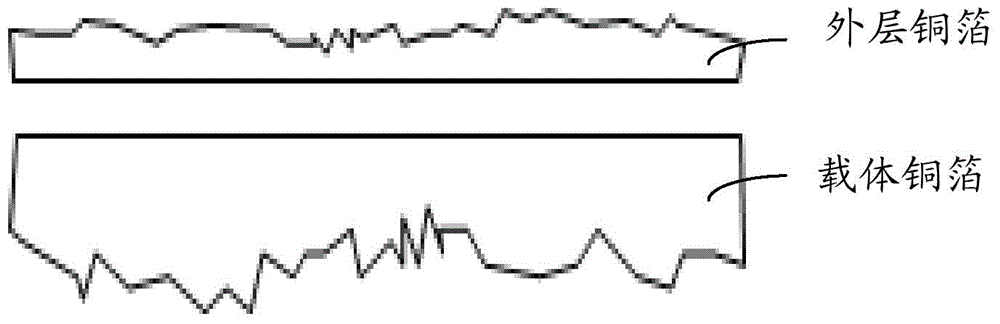
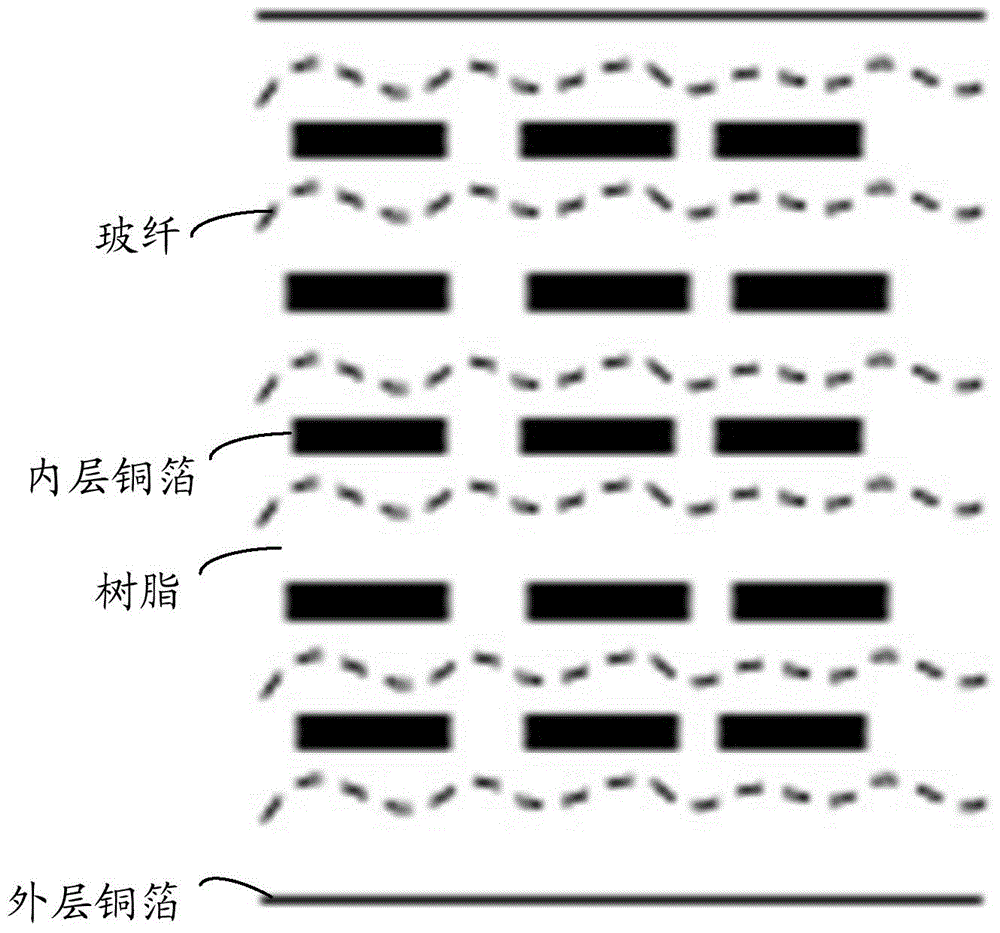
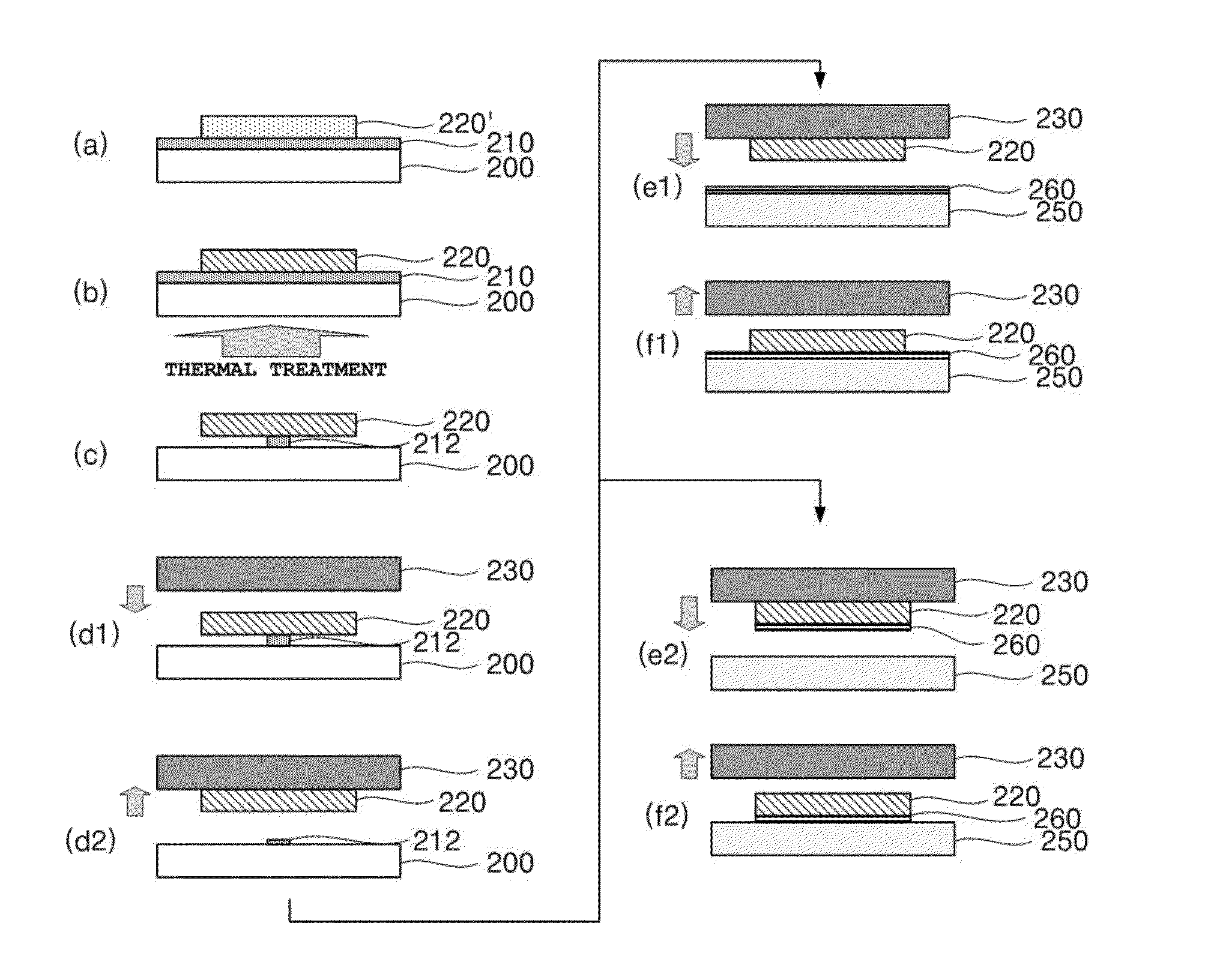
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
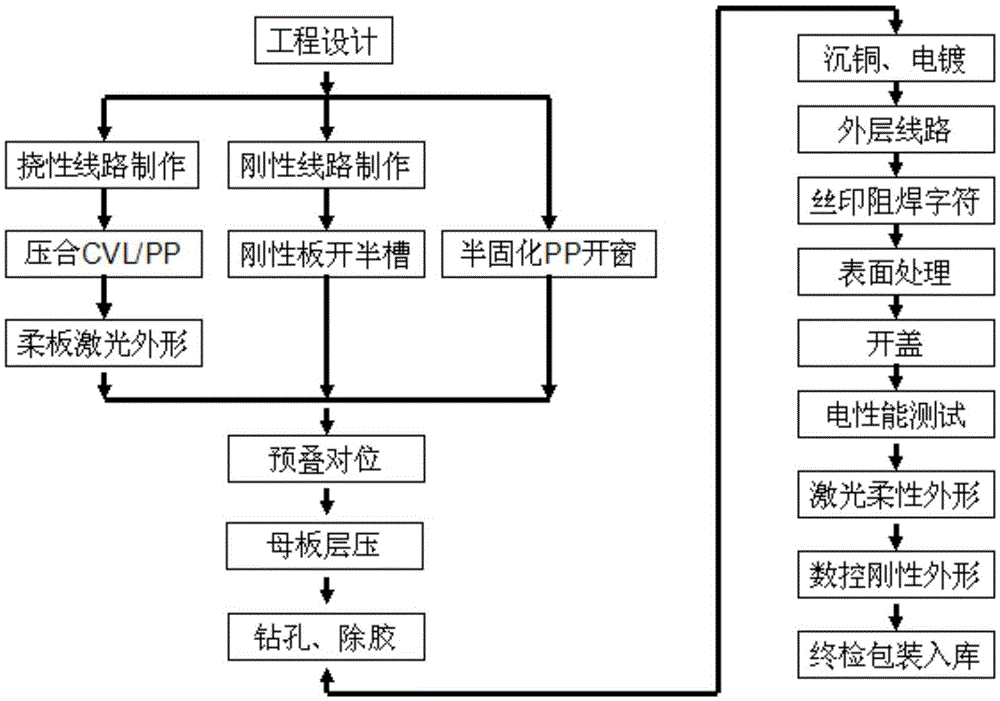
247results about "Circuit lamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
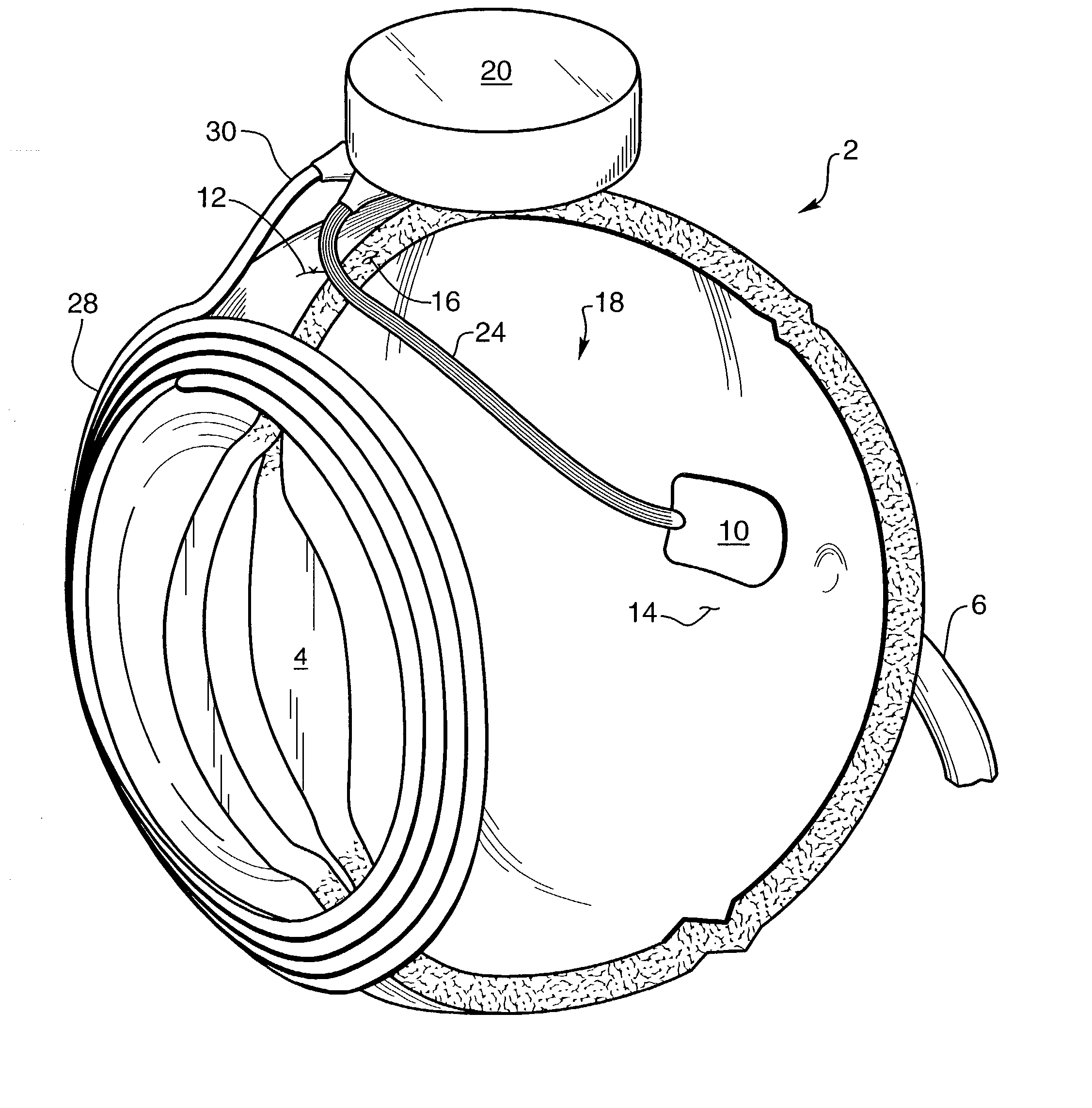
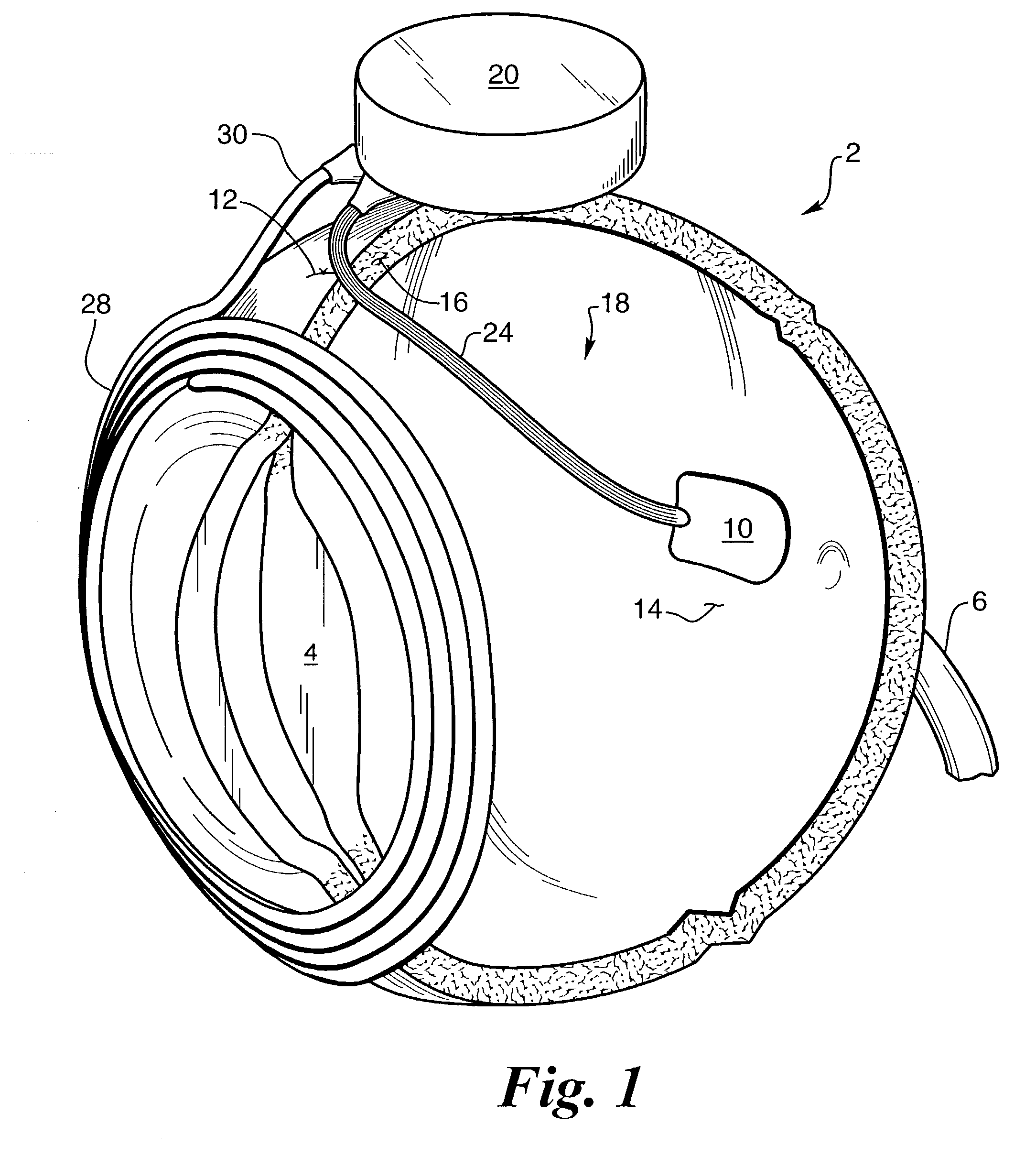
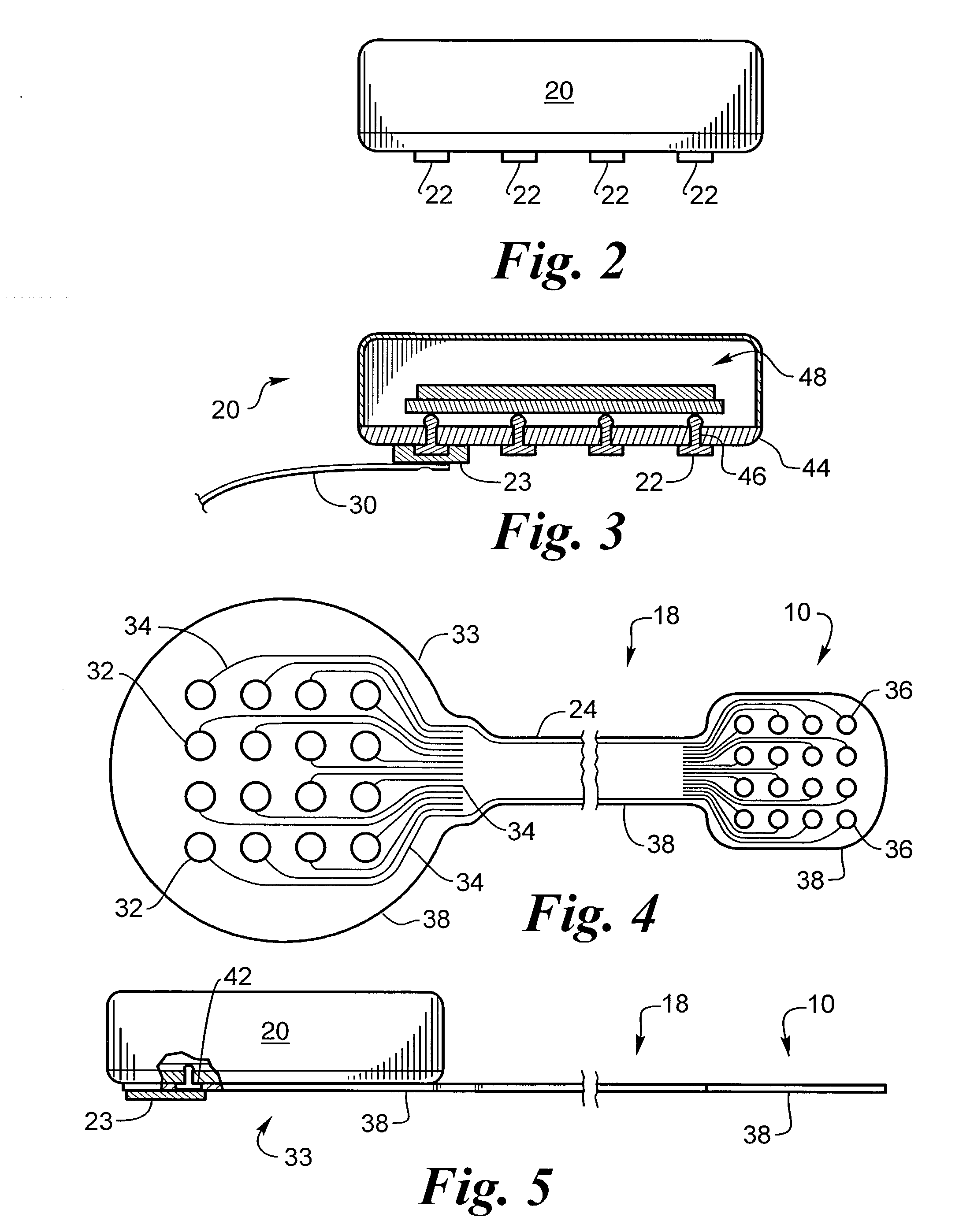
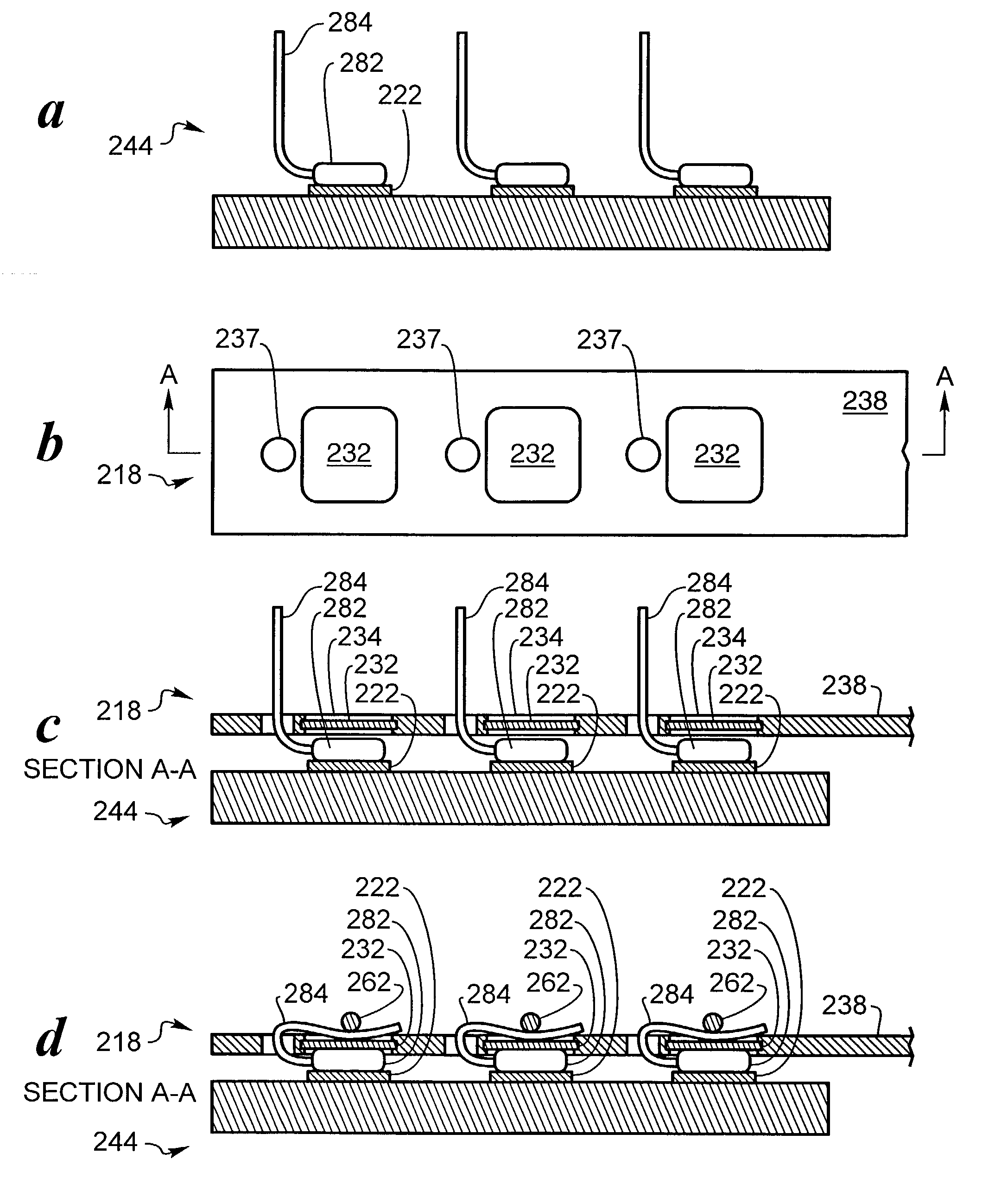
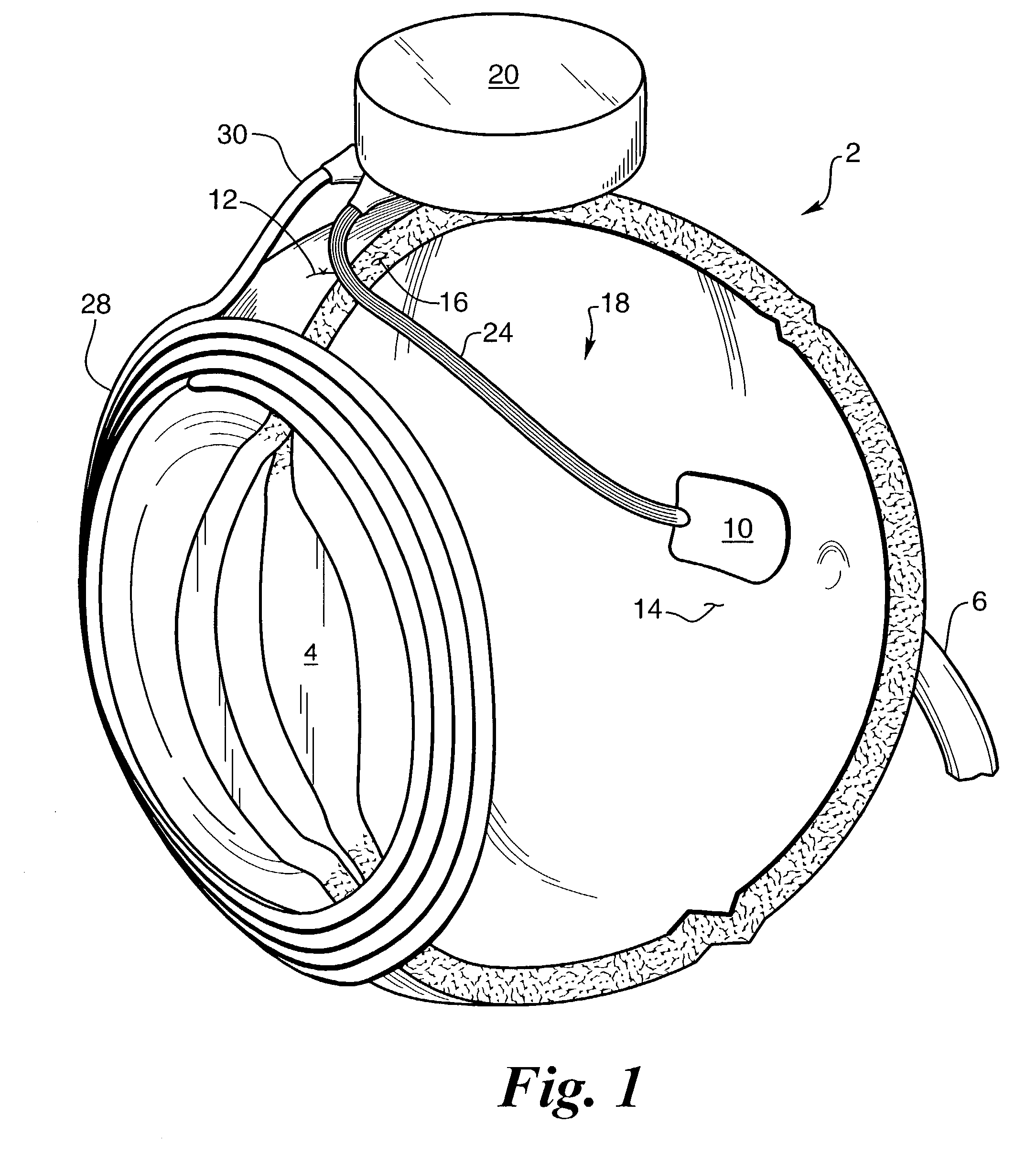
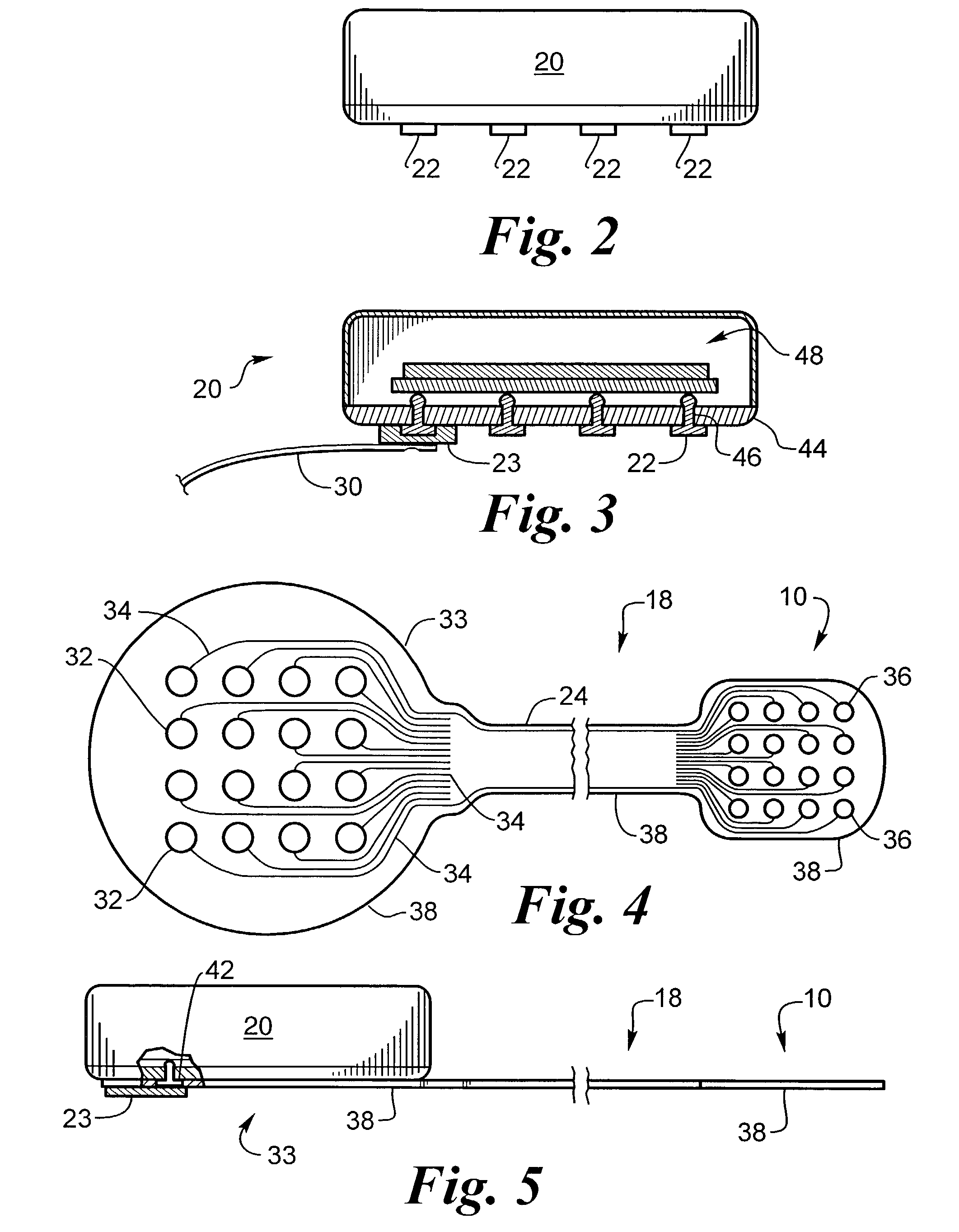
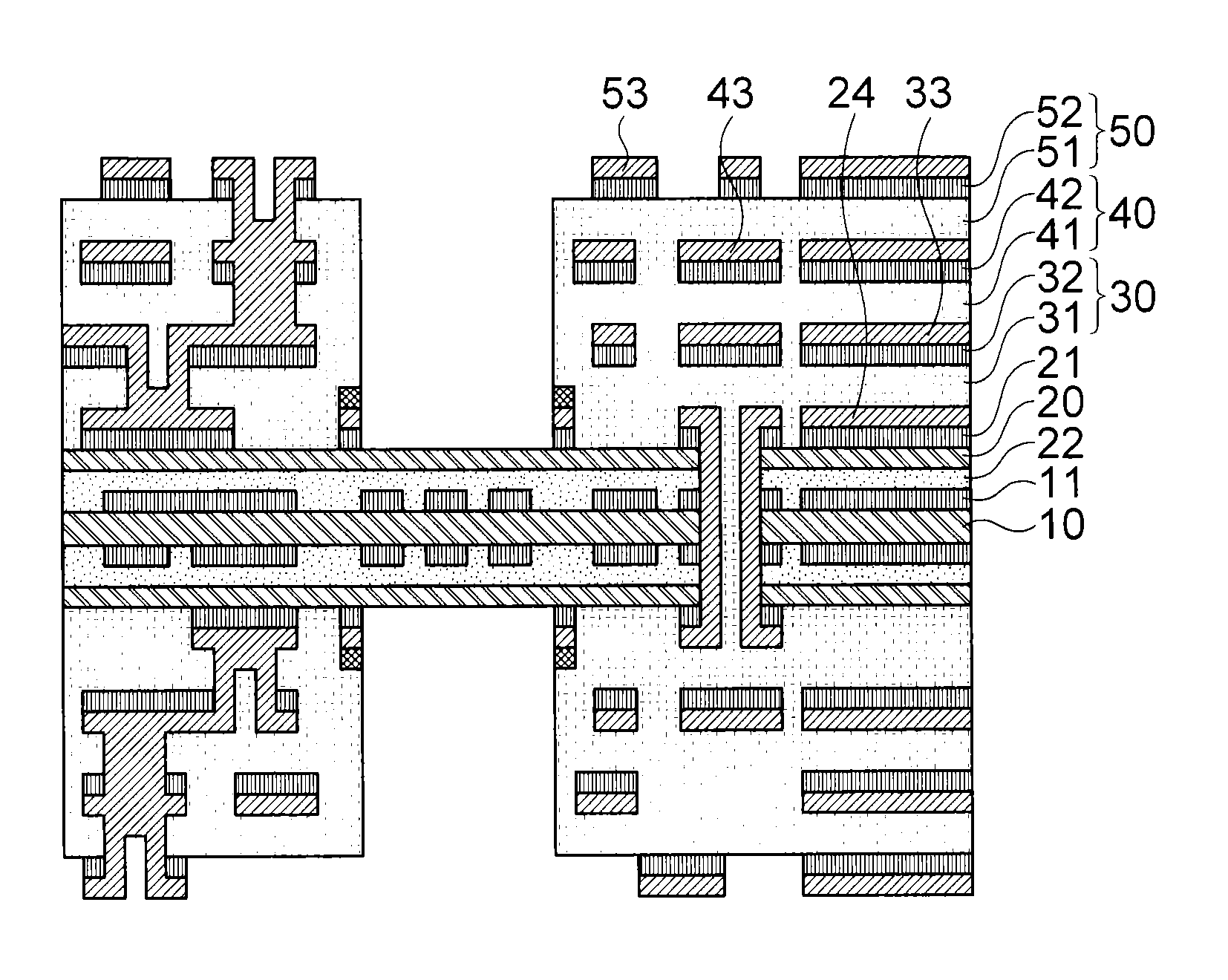
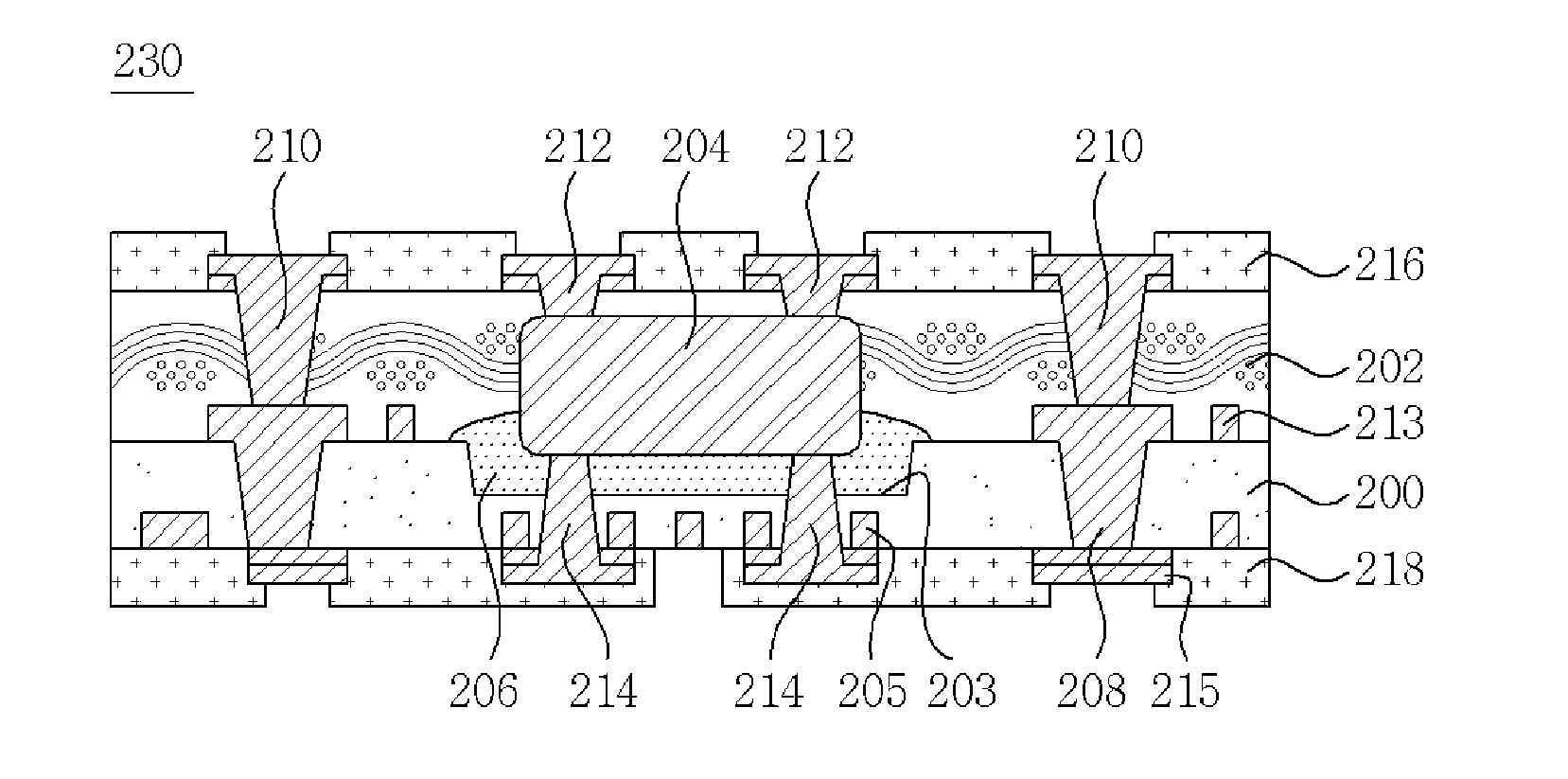
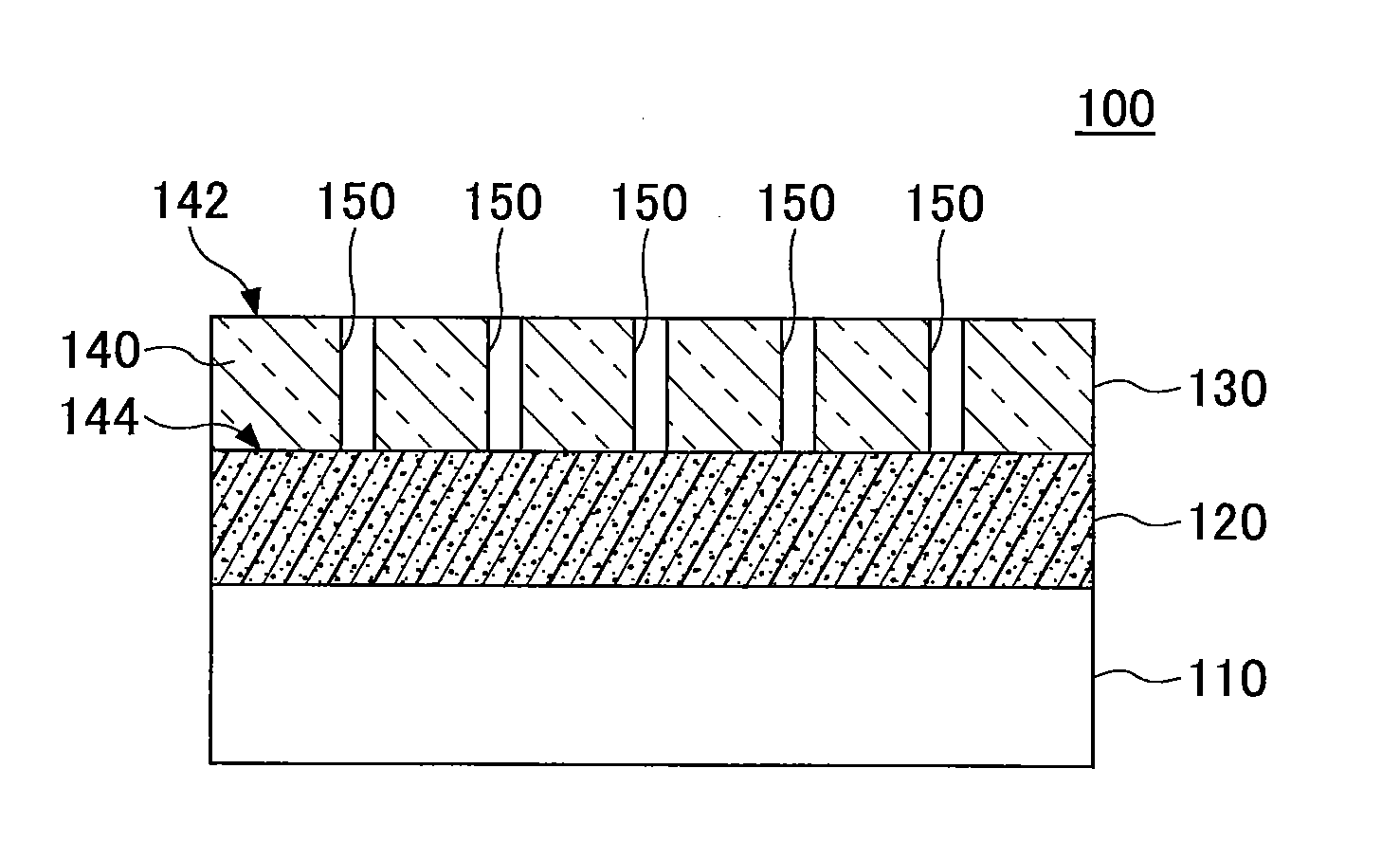
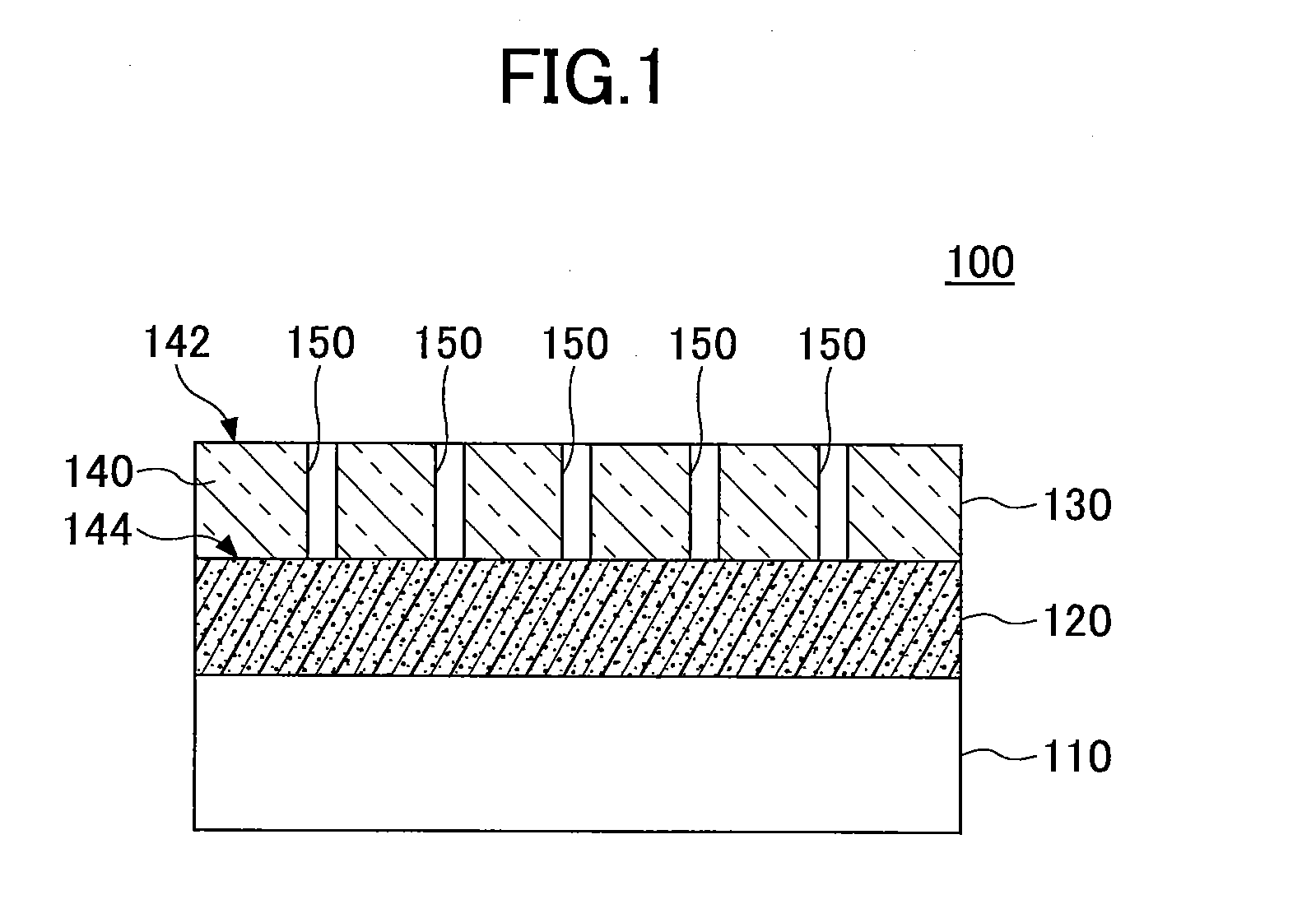
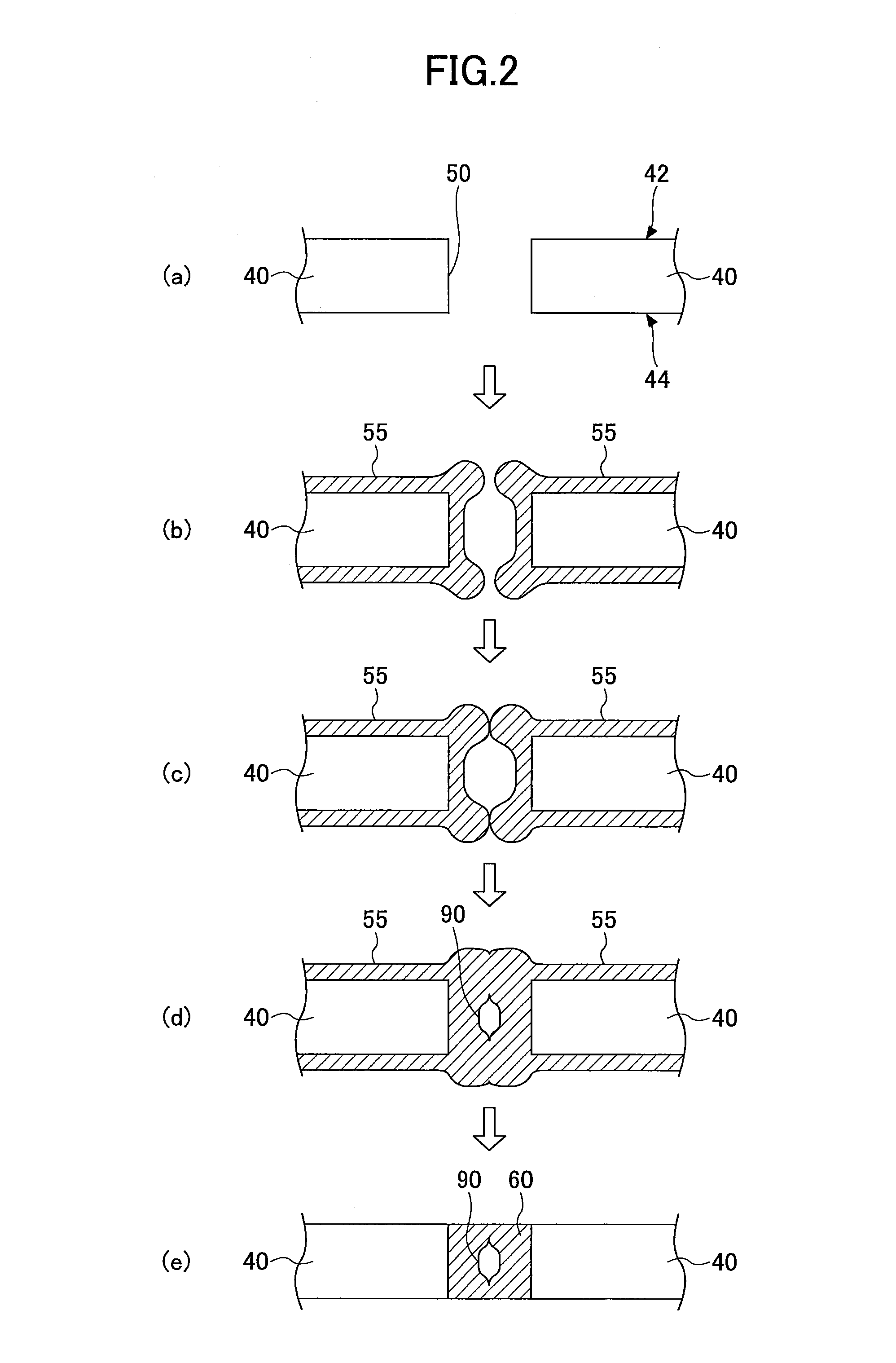
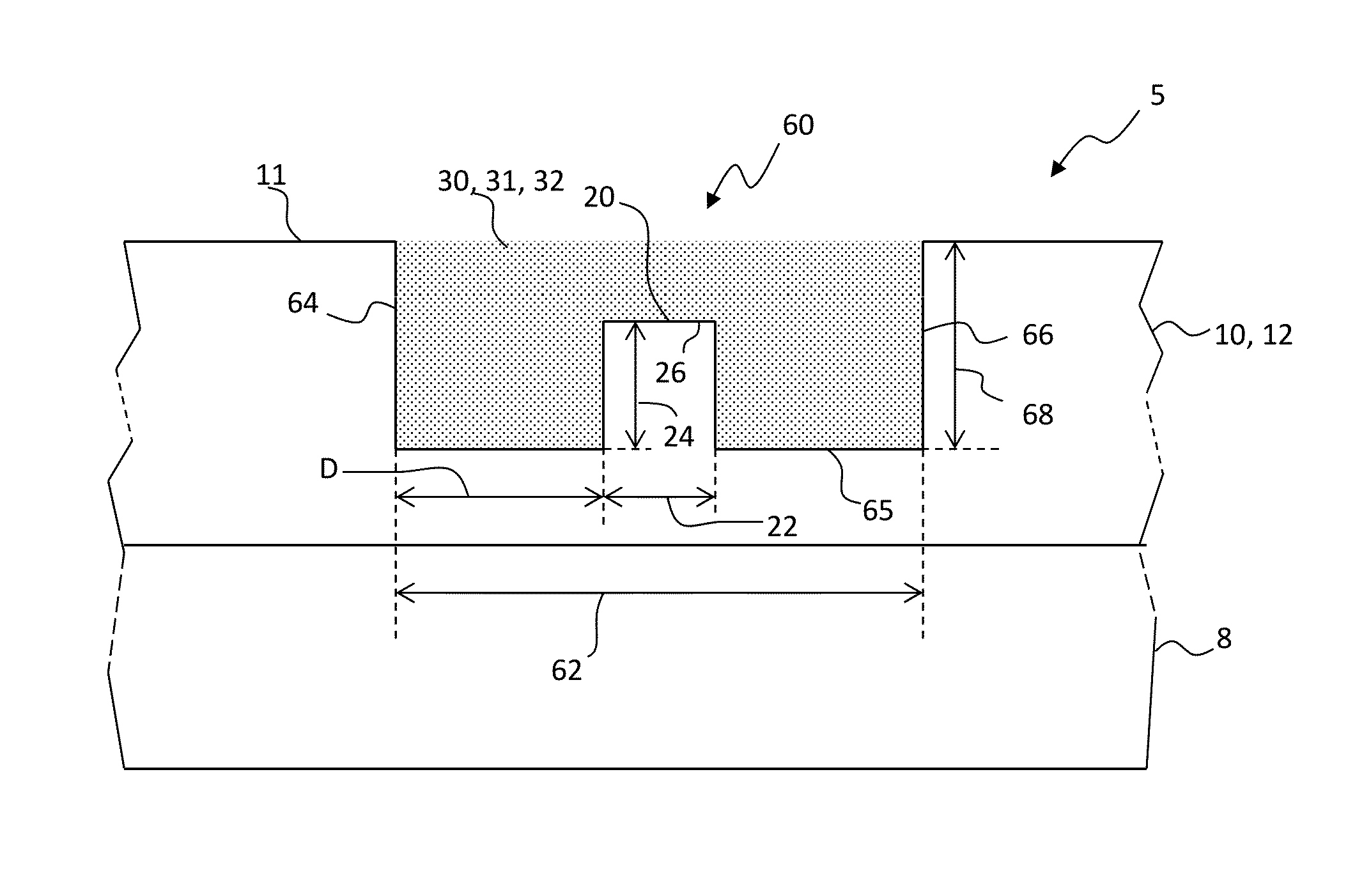
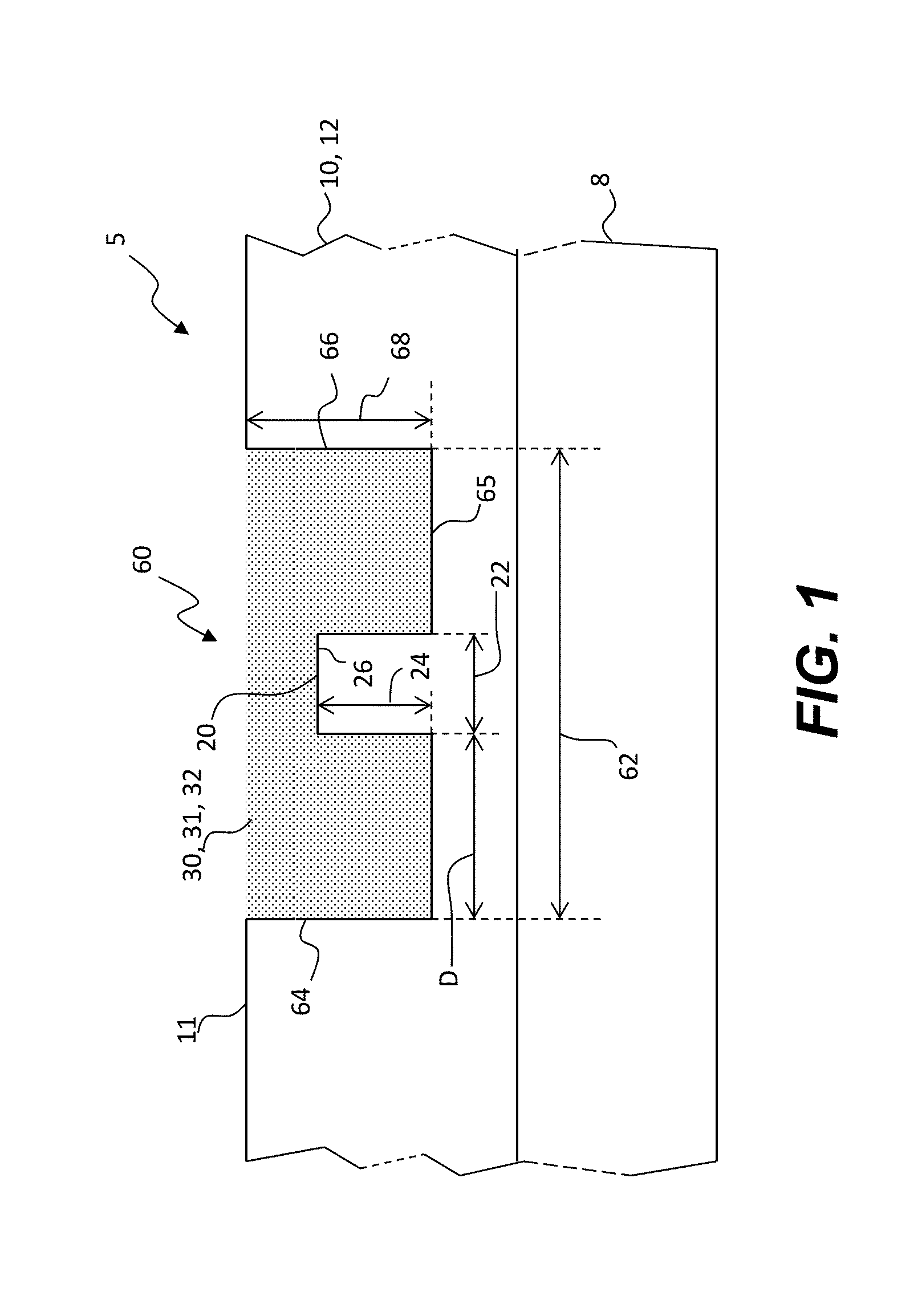
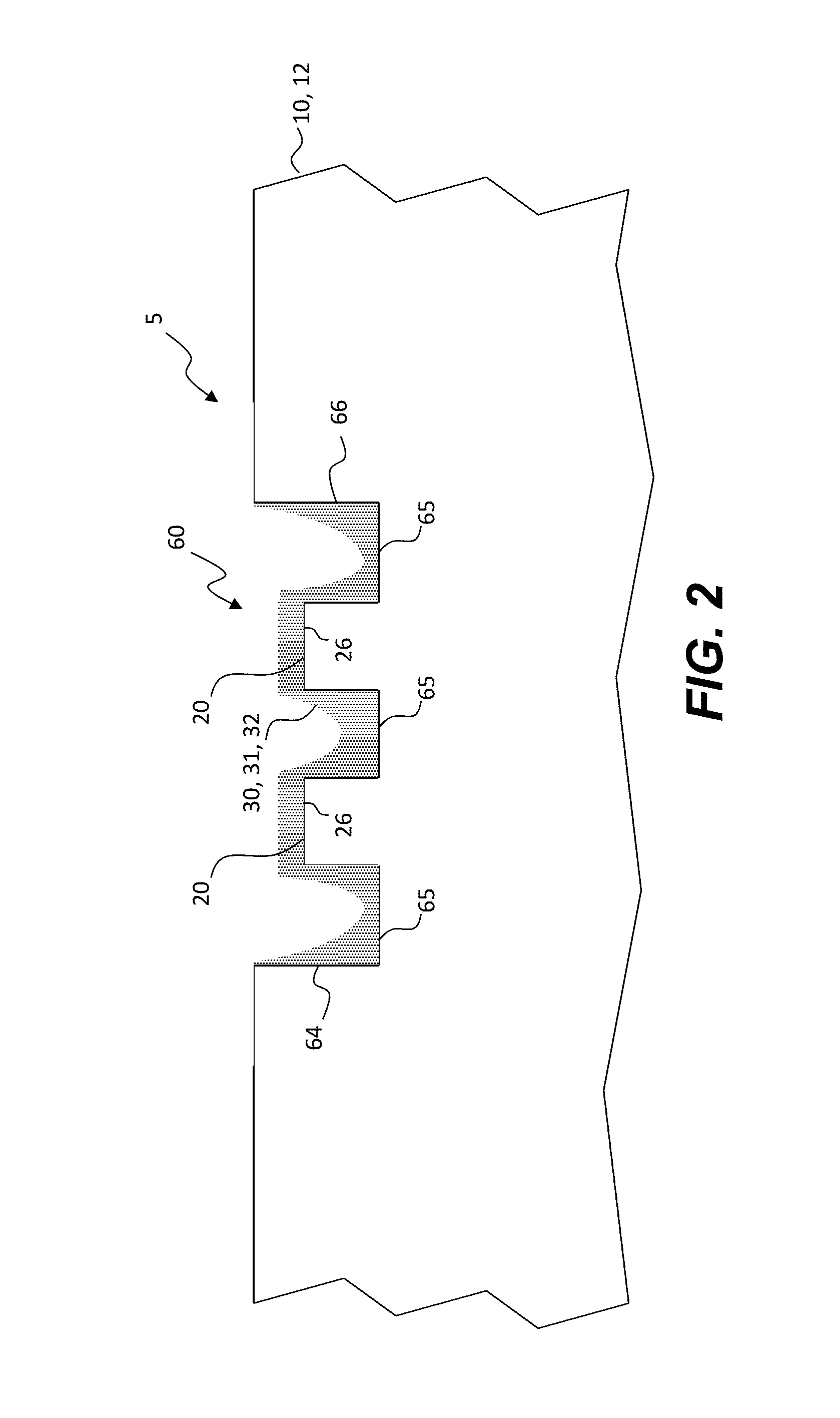
Biocompatible bonding method and electronics package suitable for implantation
ActiveUS20030233134A1Uniform propertySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFlexible circuitsHermetic seal
The invention is directed to a method of bonding a hermetically sealed electronics package to an electrode or a flexible circuit and the resulting electronics package, that is suitable for implantation in living tissue, such as for a retinal or cortical electrode array to enable restoration of sight to certain non-sighted individuals. The hermetically sealed electronics package is directly bonded to the flex circuit or electrode by electroplating a biocompatible material, such as platinum or gold, effectively forming a plated rivet-shaped connection, which bonds the flex circuit to the electronics package. The resulting electronic device is biocompatible and is suitable for long-term implantation in living tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
Biocompatible bonding method and electronics package suitable for implantation
ActiveUS7142909B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFlexible circuitsEngineering
The invention is directed to a method of bonding a hermetically sealed electronics package to an electrode or a flexible circuit and the resulting electronics package, that is suitable for implantation in living tissue, such as for a retinal or cortical electrode array to enable restoration of sight to certain non-sighted individuals. The hermetically sealed electronics package is directly bonded to the flex circuit or electrode by electroplating a biocompatible material, such as platinum or gold, effectively forming a plated rivet-shaped connection, which bonds the flex circuit to the electronics package. The resulting electronic device is biocompatible and is suitable for long-term implantation in living tissue.
Owner:CORTIGENT INC +1
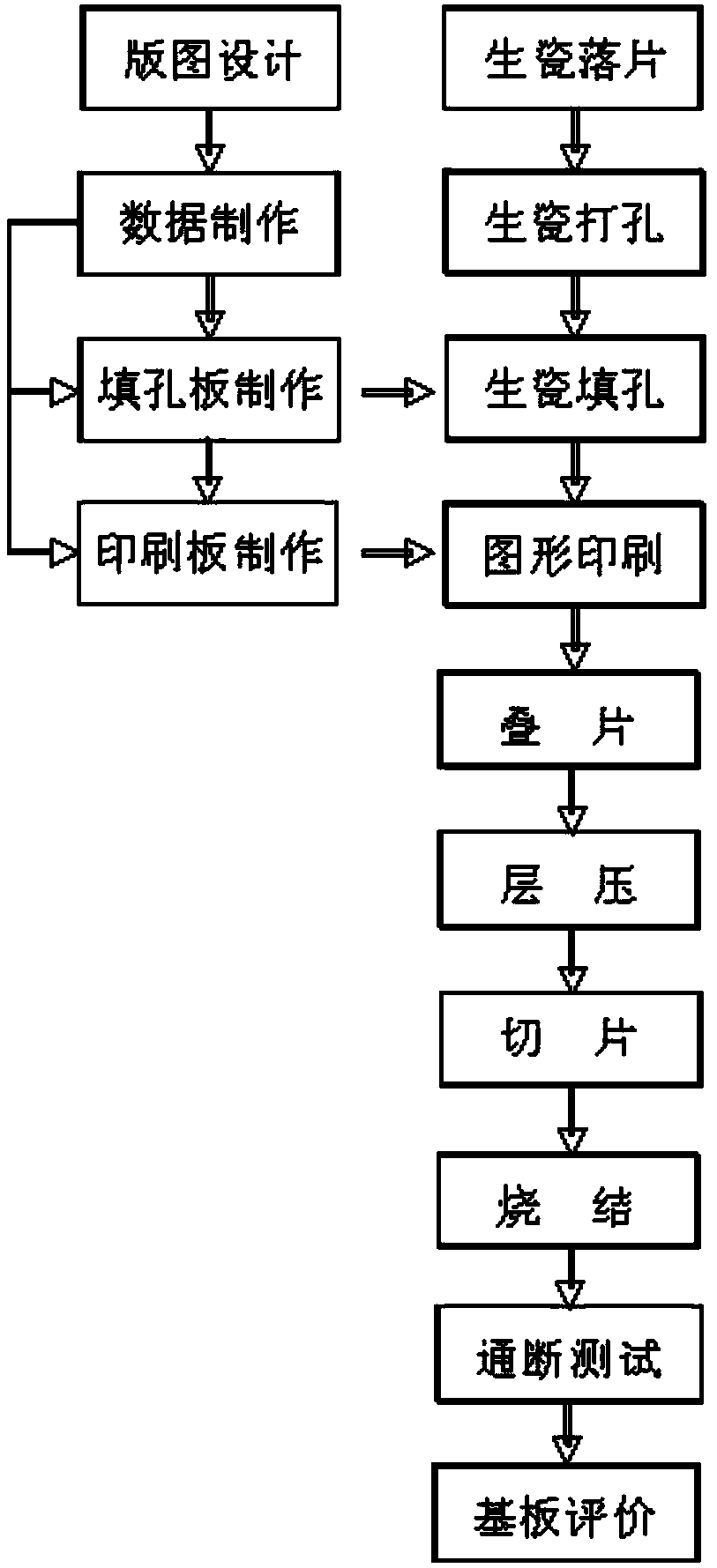
Ultra-multi-layer ultra-deep-cavity LTCC substrate manufacturing technology
ActiveCN104284534AAchieve preparationEasy to operateMultilayer circuit manufacturePrinted element electric connection formationScreen printingManufacturing technology
The invention discloses an ultra-multi-layer ultra-deep-cavity LTCC substrate manufacturing technology. A conventional solid flat plate LTCC substrate machining technology is broken through, after hole filling and screen printing, a cavity window in an unglazed porcelain layer is formed in a laser-cutting-up mode, the non-operability problem of hole filling and screen printing technologies on a large-size window unglazed porcelain piece is avoided, and the contraction amount and the unevenness of an unglazed porcelain piece obtained after filling and printing before piece stacking are lowered. After cofiring, an abrasive wheel cuts a ripe porcelain plate in a rotating mode, and the fact that an LTCC substrate which is regular in shape, accurate in size, thin in wall and ultra-deep in cavity is machined is guaranteed. Network multi-through-hole connecting is used in an ultra-deep-cavity ultra-multi-layer unglazed porcelain side wall, and the connecting pass rate is guaranteed through redundancy. Through a lamination tool set and an optimized overlying technology method, the lamination and stacking technology of the deep-large-cavity ultra-thick LTCC substrate is guaranteed. An abrasive wheel dicing saw is used for opposite cutting of a ripe porcelain body LTCC substrate from the bottom face and the top face of the ultra-thick substrate, and the problem that the maximum thickness can only reach 5 mm during blade unglazed porcelain hot cutting and abrasive wheel ripe porcelain rotating cutting is solved.
Owner:EAST CHINA INST OF OPTOELECTRONICS INTEGRATEDDEVICE
Method of manufacturing rigid-flexible printed circuit board
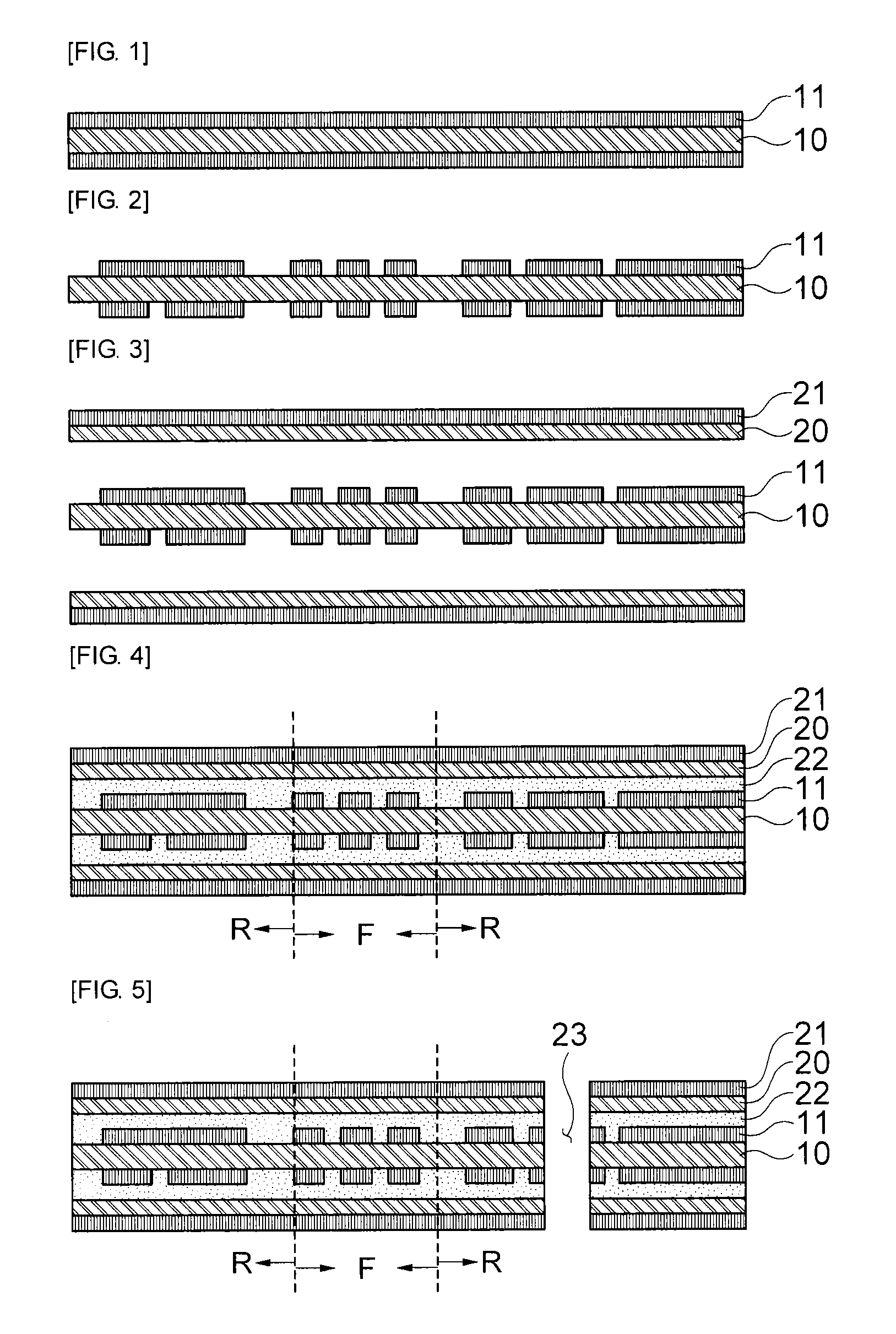
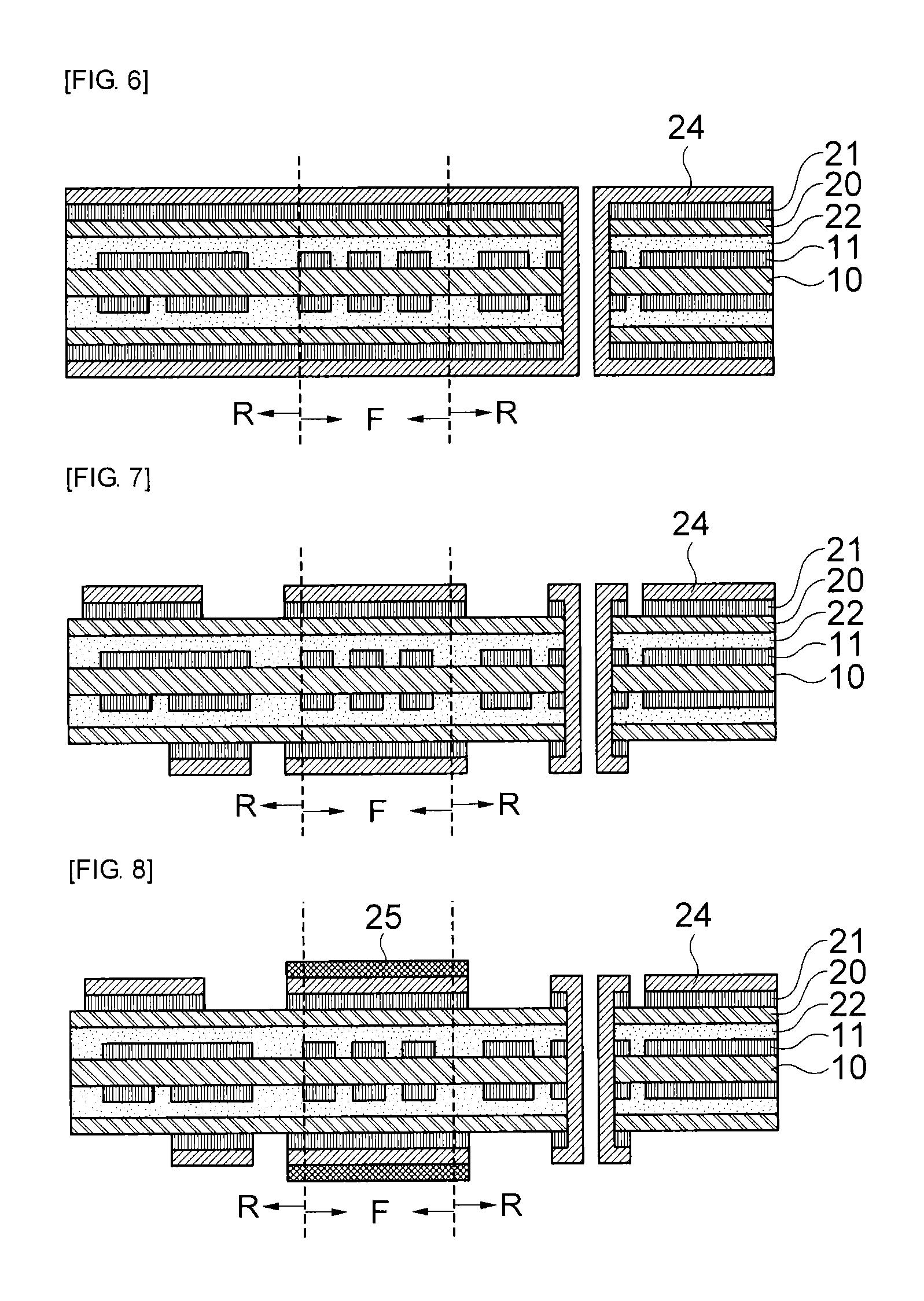
ActiveUS20130220535A1Circuit bendability/stretchabilityLamination ancillary operationsOxidation resistantEngineering
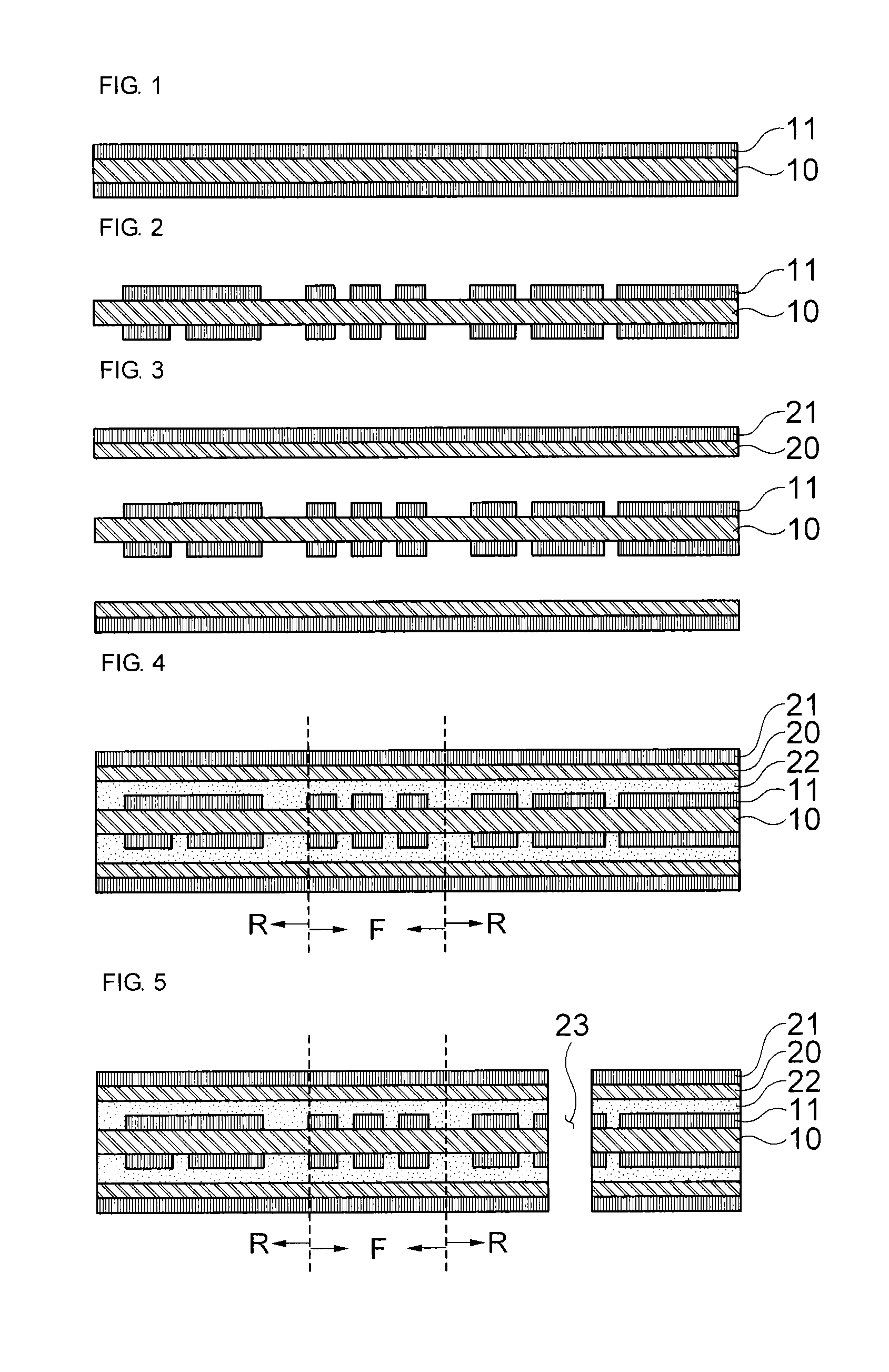
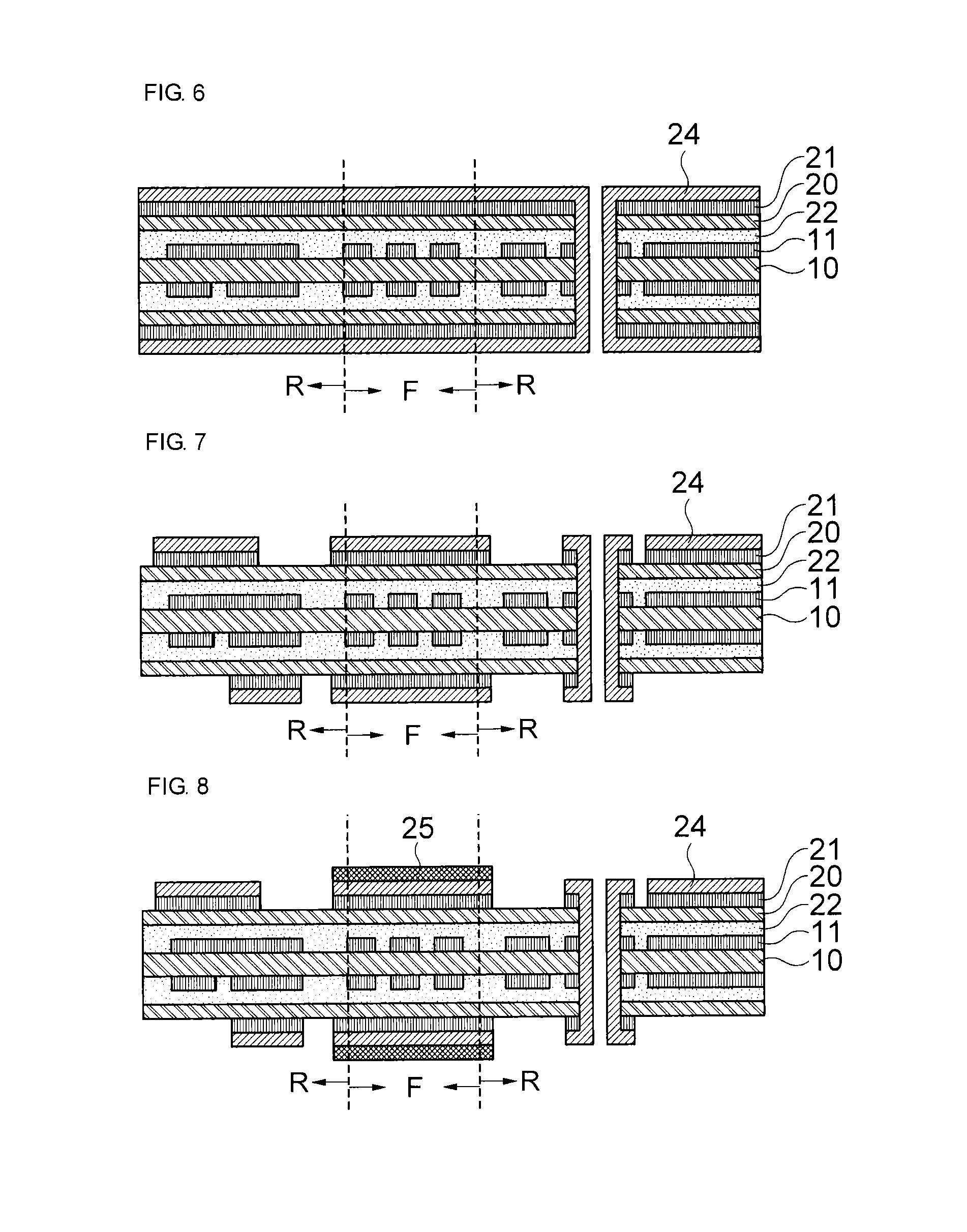
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a rigid-flexible printed circuit board including: providing a first flexible film having a first metal layer on one or both surfaces; forming a circuit pattern by patterning the first metal layer; forming a second flexible film, which has a second metal layer on one surface, on one or both surfaces of the first flexible film; forming a circuit pattern by patterning the second metal layer in a rigid domain R; providing an anti-oxidation protective layer on the second metal layer in a flexible domain F; laminating at least one circuit layer on the second flexible film; and removing the circuit layer in the flexible domain F.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Buried and embedded copper block PCB manufacturing method
InactiveCN104853523AReduce offsetReduce friction damageMultilayer circuit manufacturePrinted circuit non-printed electric components associationMetallurgyEngineering
The invention discloses a buried and embedded copper block PCB manufacturing method, which comprises steps of laminating treatment of a buried copper block, groove milling, gold immersion, laminating treatment of an embedded copper block and the like. The step of lamination of the buried copper block comprises a buried copper block lamination pre-treatment process. The buried copper block lamination pre-treatment process comprises groove treatment on the edge of the bottom part of the copper block, round corner treatment on the edge of the copper block, and chamfer treatment on the edge corner of the copper block. The step of lamination of the embedded copper block comprises an embedded copper block lamination pre-treatment process, which comprises groove treatment on the edge of the bottom part of a groove hole into which the copper block needs to be embedded, round corner treatment on the edge of the groove hole into which the copper block needs to be embedded and chamfer treatment on the edge corner of the groove hole into which the copper block needs to be embedded. The buried and embedded copper block PCB manufacturing method has the advantages of high product yield, high production efficiency, good quality consistency and simple operation.
Owner:HUIZHOU KING BROTHER CIRCUIT TECH +2
Embedded printed circuit board and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20160174381A1Well formedSolid-state devicesElectrical connection printed elementsInsulation layerElectronic component
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Press fit method for high-voltage-resistant PCB with thick copper plate
InactiveCN105472912AMeet reliabilityImprove liquidityMultilayer circuit manufactureCircuit laminationHigh resistanceVitrification
The invention discloses a press fit method for a high-voltage-resistant PCB with a thick copper plate. The method includes the following steps: S1, cutting, i.e., cutting an outer-layer copper foil, a polyimide medium, pure-glue prepreg and a polyimide copper-clad plate according to required dimensions; S2, inner-layer pattern making; and S3, conducting press fit after plate lamination, the press fit including the first heating stage at the temperature of 100-140 DEG C, the second heating stage at the temperature of 140-180 DEG C, the third heating stage at the temperature of 180-220 DEG C, a warm-keeping stage, the first cooling stage at the temperature of 220-150 DEG C and the second cooling stage at the temperature of 150-100 DEG C. Conventional FR-4 prepreg is replaced by a polyimide material that has higher glass transition temperature and exhibits higher resistance to voltage, so a PCB with a thick copper plate is made to have the excellent resistance to voltage, and polyimide having high glass transition temperature can effectively ensure that resin is fully filled among lines during press fit. Moreover, press fit parameters can be adjusted and the operating time of a high-temperature and high-voltage stage can be prolonged, thus helping polyimide materials to fully fill line gaps in a high-temperature and high-voltage condition.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNTAK MULTILAYER PCB
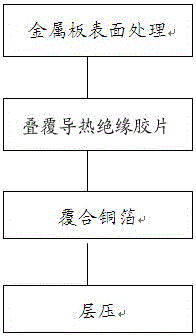
Manufacturing method of metal-based circuit board of LED
ActiveCN106132098AChange the traditional formStrong adhesionConductive material chemical/electrolytical removalCircuit precursor manufacturePunchingHigh volume manufacturing
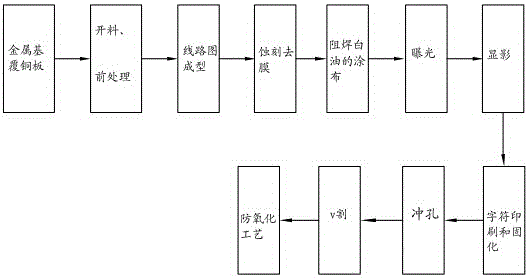
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of a metal-based circuit board of an LED. A finished product is obtained through a metal plate surface treatment step, a heat-conducting insulating film superimposing step, a combined copper foil laminating step, a cutting step, a location hole drilling step, a pretreatment step, a circuit diagram forming step, an etching and stripping step, a solder resist white oil coating step, an exposure step, a developing step, a character printing and solidifying step, a punching step, a v cutting step and an anti-oxidation process. PP glue is combined on a metal-based base plate; and a printing technology or an exposure technology is adopted for circuit diagram forming. Through the technical scheme provided by the invention, the metal-based circuit board integrating a drive power supply and a light source can be massively produced; and the manufactured LED and power supply have good heat dissipation performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LEUCHTEK ELECTRONICS
Surface-Treated Metal Material, Metal Foil With Carrier, Connector, Terminal, Laminate, Shielding Tape, Shielding Material, Printed Wiring Board, Processed Metal Member, Electronic Device, And Method For Manufacturing Printed Wiring Board
InactiveUS20160212836A1Good heat absorbency heatGood heat absorbency and heat releasabilityPrinted circuit aspectsRecord information storageMetal foilMetallic materials
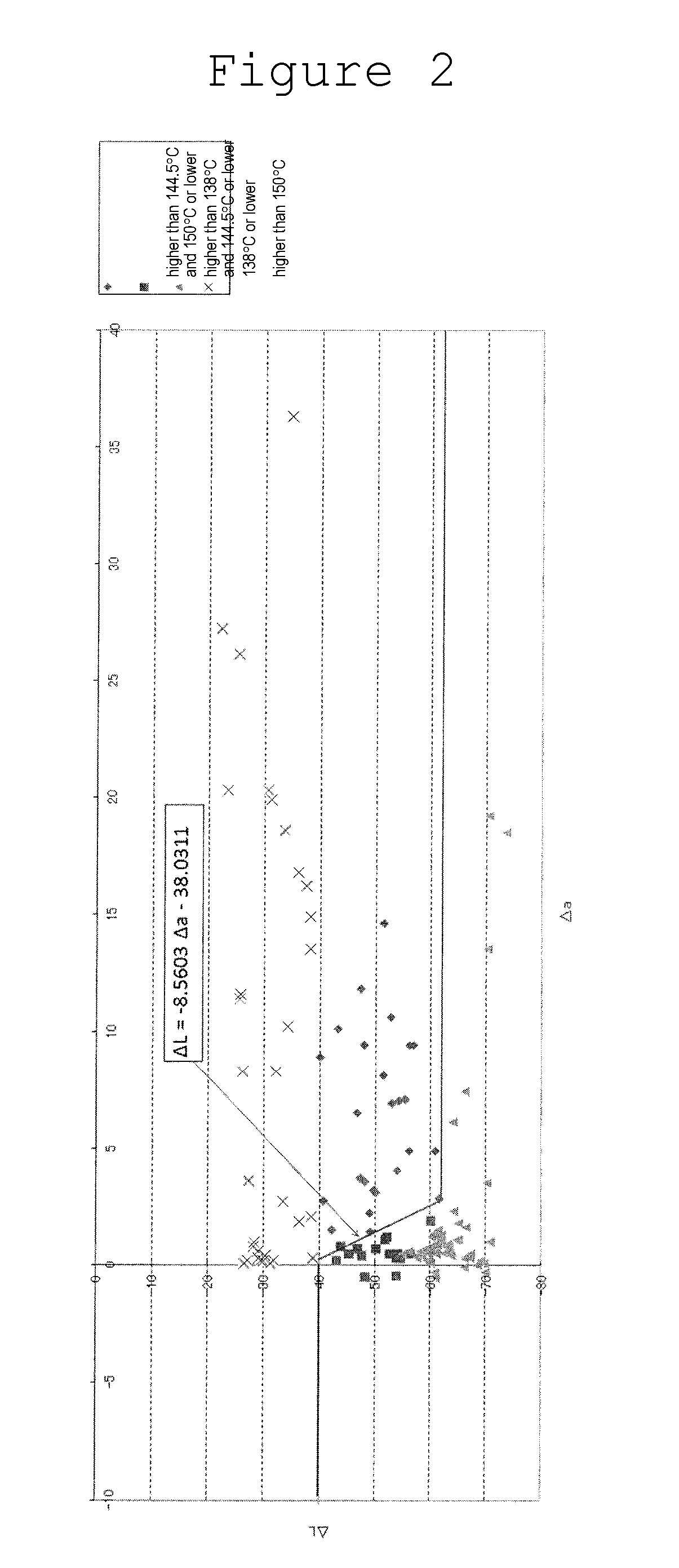
A surface-treated metal material good in heat absorbency and heat releasability is provided. The surface-treated metal material has a heat conductivity of 32 W / (m·K) or higher; and a color difference ΔL based on JIS Z8730 of the surface thereof satisfying ΔL≦−40.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
Method of manufacturing rigid-flexible printed circuit board
ActiveUS8882954B2Paper/cardboard articlesLaminating printed circuit boardsEngineeringOxidation resistant
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing a rigid-flexible printed circuit board including: providing a first flexible film having a first metal layer on one or both surfaces; forming a circuit pattern by patterning the first metal layer; forming a second flexible film, which has a second metal layer on one surface, on one or both surfaces of the first flexible film; forming a circuit pattern by patterning the second metal layer in a rigid domain R; providing an anti-oxidation protective layer on the second metal layer in a flexible domain F; laminating at least one circuit layer on the second flexible film; and removing the circuit layer in the flexible domain F.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing flexible-embedded electrode film using heat-pressure welding transcription
InactiveUS20150216057A1Well formedLower resistanceConductive layers on insulating-supports3D rigid printed circuitsThin membraneEngineering
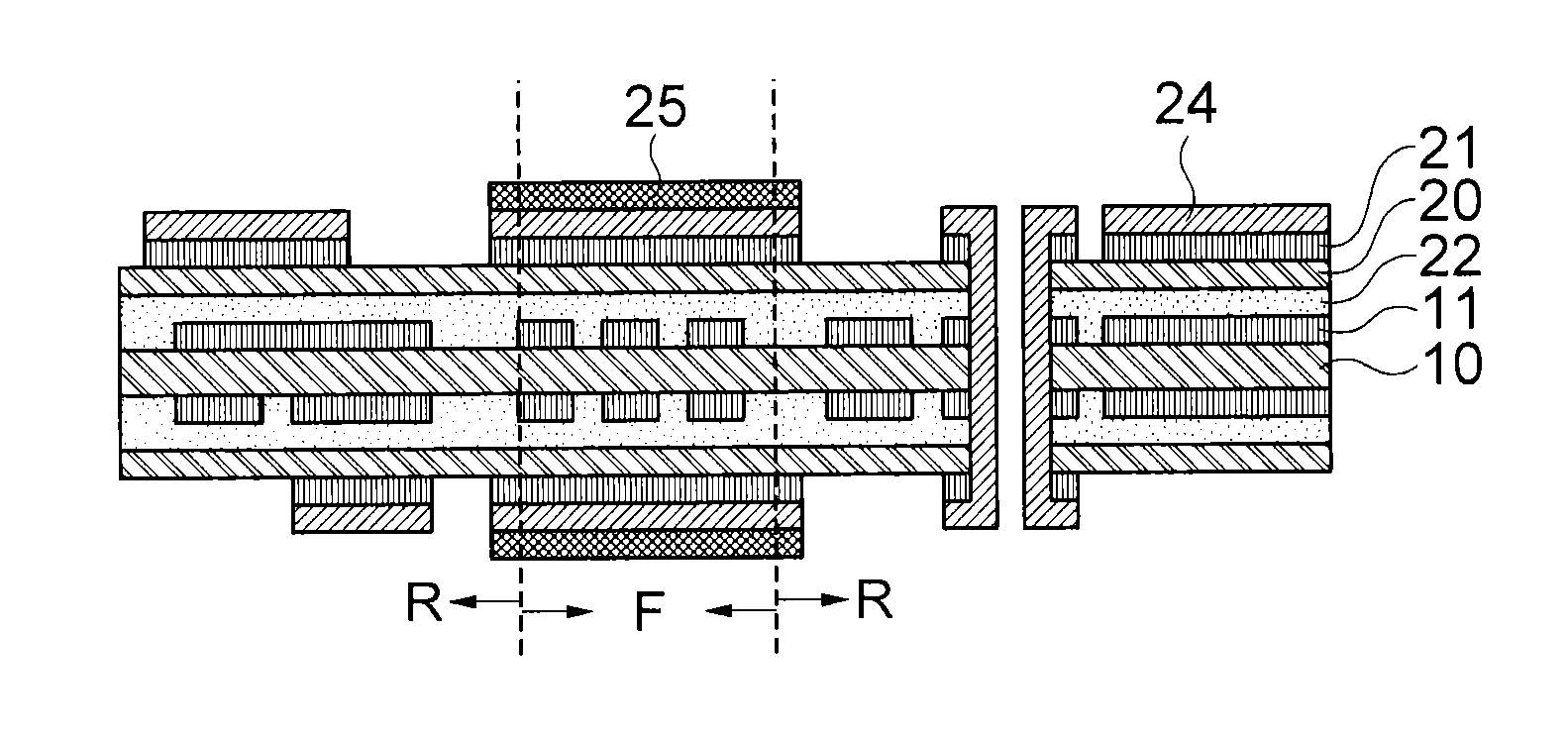
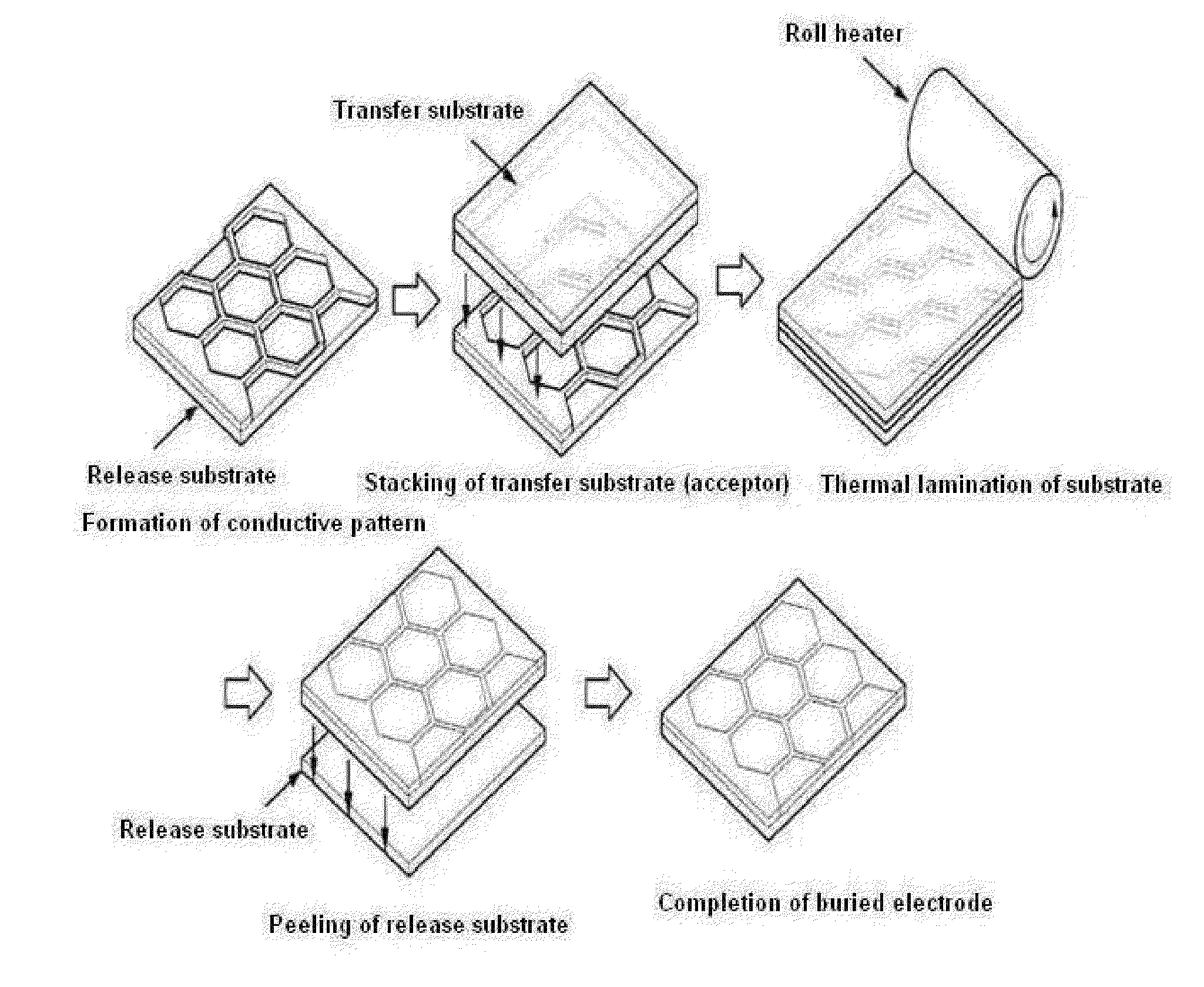
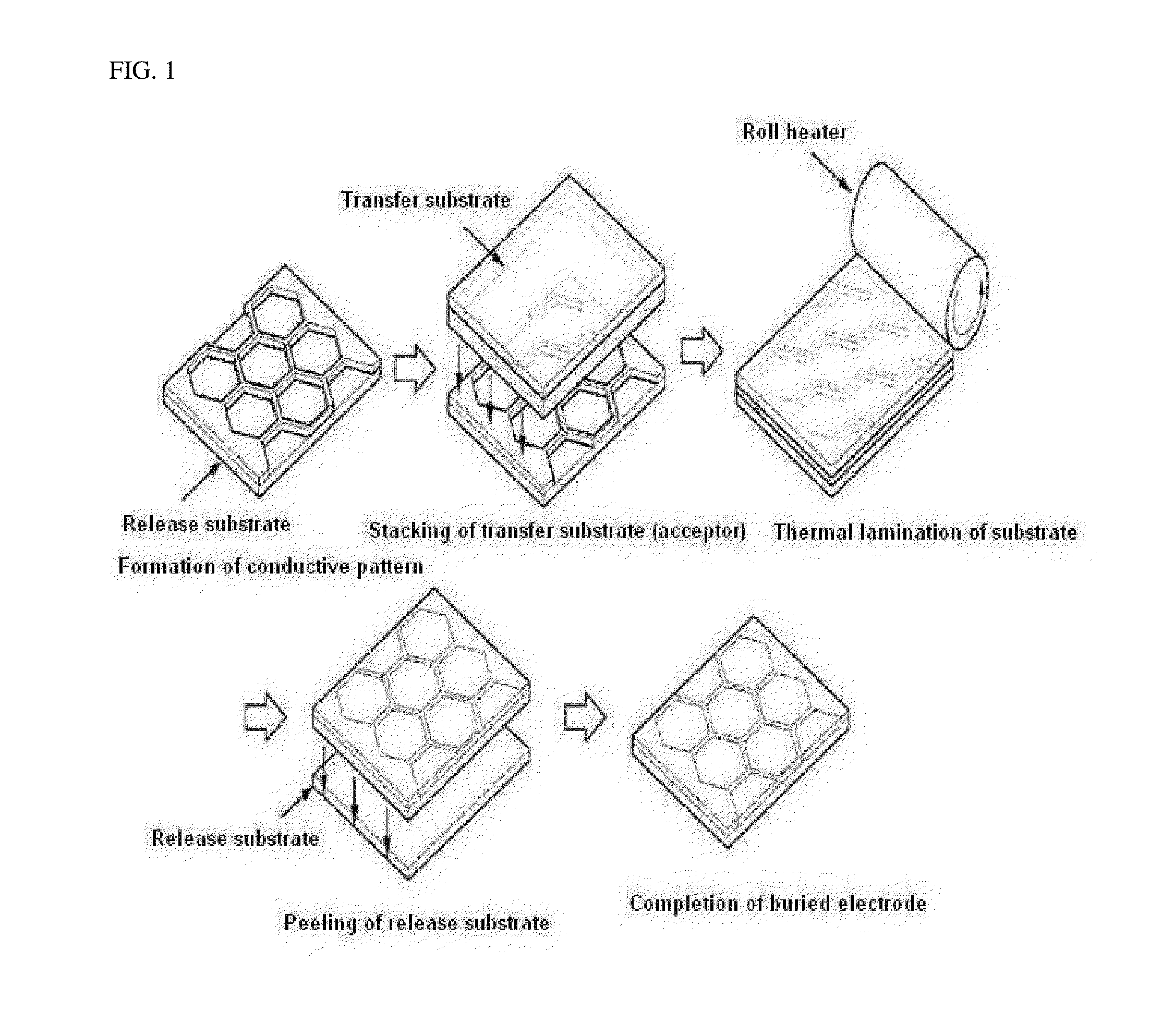
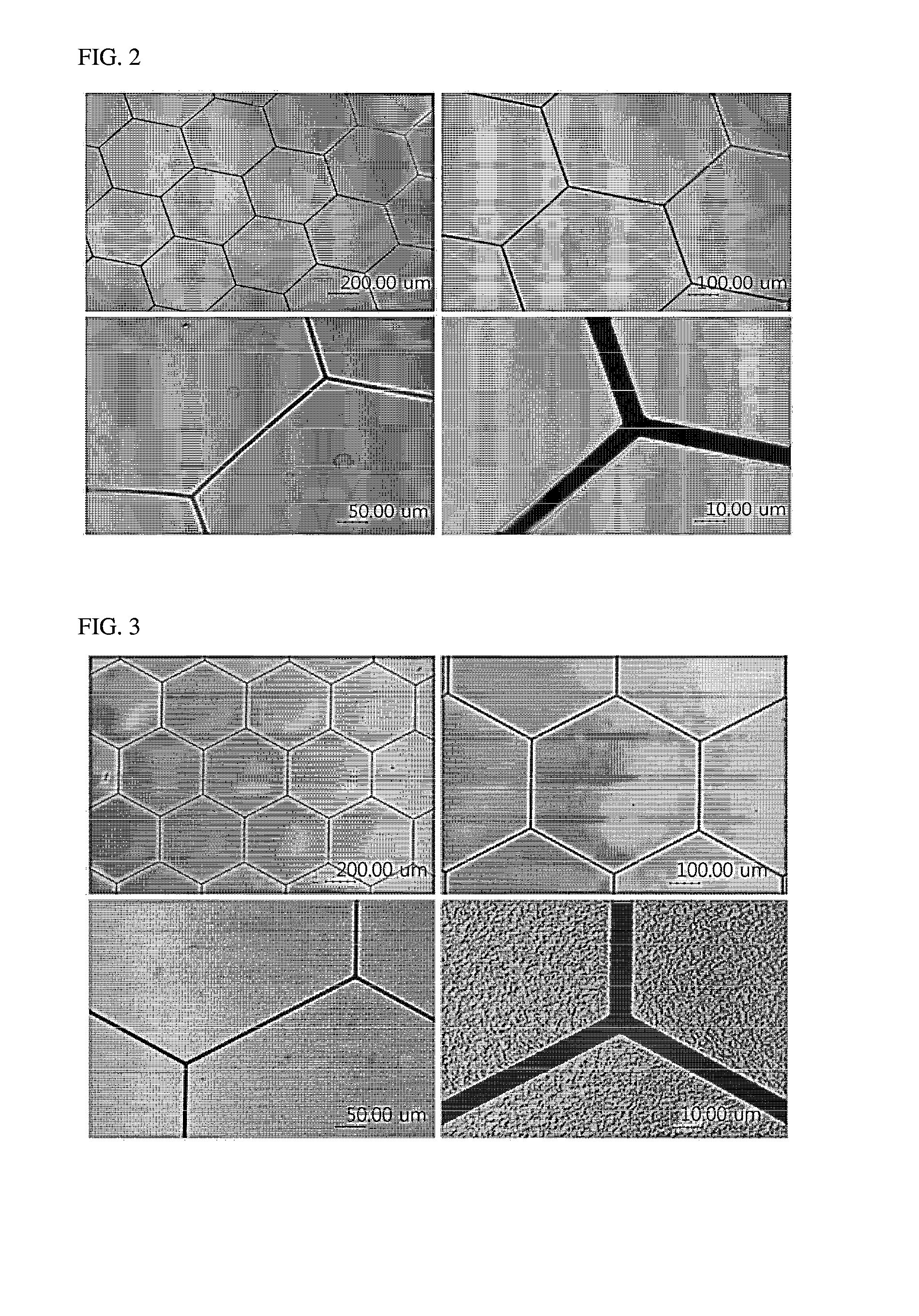
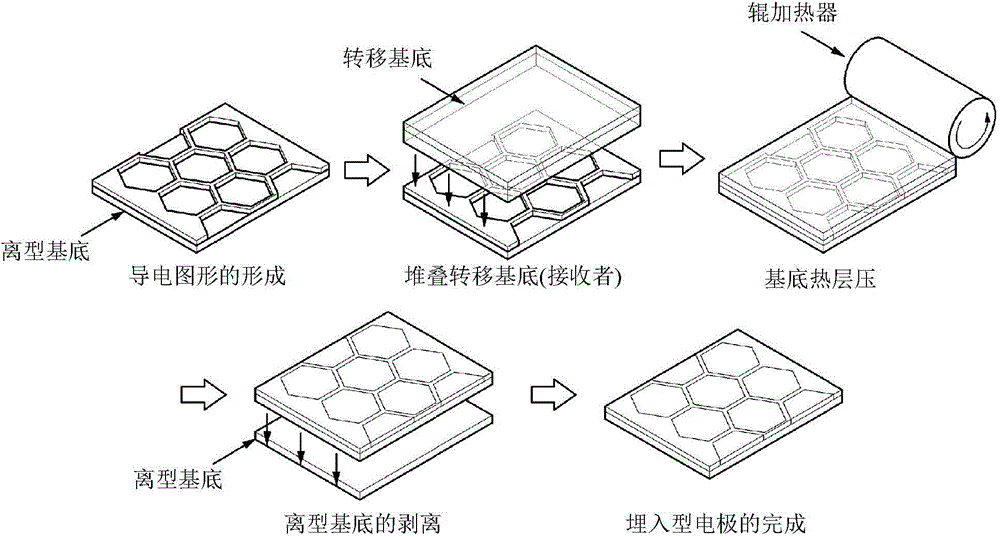
This invention relates to a method of manufacturing a buried flexible electrode film, including 1) preparing a release-substrate; 2) forming a conductive pattern layer on the release-substrate; 3) positioning a transfer-substrate on the conductive pattern layer and then performing thermal and pressure lamination so that the conductive pattern layer formed on the release-substrate is inserted or buried in the surface of the transfer-substrate; and 4) separating the release-substrate and the conductive pattern layer from each other, and to a buried flexible electrode film manufactured thereby.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Manufacturing method of flexible buried electrode film using thermal lamination transfer
InactiveCN104662619AWell formedMeet the height limit requirementsConductive layers on insulating-supportsCable/conductor manufactureEngineeringElectrode
The present invention relates to a method for manufacturing a flexible buried electrode film and a flexible buried electrode film manufactured by the same. The method includes the steps of: 1) preparing a release base material; 2) forming a conductive pattern layer on the release base material; 3) locating a transfer base material on the conductive pattern layer and then inserting into or burying in the surface of the transfer base material the conductive pattern layer formed on the release base material by thermal and pressure fusion; and 4) separating the release base material from the conductive pattern layer.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Making multi-layer micro-wire structure
InactiveUS20150271930A1Few manufacturing stepFew stepsCapacitance measurementsLaminationEngineeringSecondary layer
A method of making a multi-layer micro-wire structure includes providing a substrate with a micro-wire layer having first and second areas. The micro-wire layer includes first and second micro-wire electrodes and first and second connection pads in the first and second areas, respectively. Each micro-wire electrode includes one or more electrically connected micro-wires and is electrically connected to a connection pad. The micro-wires are located in a common step. The first area is separated from the second area and the first area of the substrate and the second area of the micro-wire layer are located between the first micro-wires and the second area of the substrate so that a second layer edge extends at least partly beyond a first layer edge and one or more of the second connection pads is located between at least a portion of the first layer edge and the second layer edge.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Lamination method for multi-layer flexible board and multi-layer flexible board
InactiveCN105578802ASolve wrinkleGood shapeMultilayer circuit manufactureCircuit laminationFlexible circuitsCopper foil
The invention discloses a lamination method for a multi-layer flexible board and the multi-layer flexible board. The method disclosed by the invention is wide in application range, and can well solve the problem of wrinkling of copper foil for lamination of the multi-layer board with the copper foil outside; meanwhile, the flexible circuit board can be relatively well coated and combined through combination of an aluminum sheet and a PE film; the reliability is relatively well guaranteed; and the product yield is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN KINWONG ELECTRONICS
Method of manufacturing an intermediate product for an interposer and intermediate product for an interposer
ActiveUS20150173191A1Reduce riskSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterposerMechanical engineering
A method of manufacturing an intermediate product for an interposer including a glass substrate having a plurality of through holes is provided. The method includes a step of forming a resin layer on a support substrate, and a step of forming a laminated body by adhering the glass substrate having the plurality of through holes on the resin layer. The glass substrate having the plurality of through holes has a thickness within a range of 0.05 mm to 0.3 mm.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
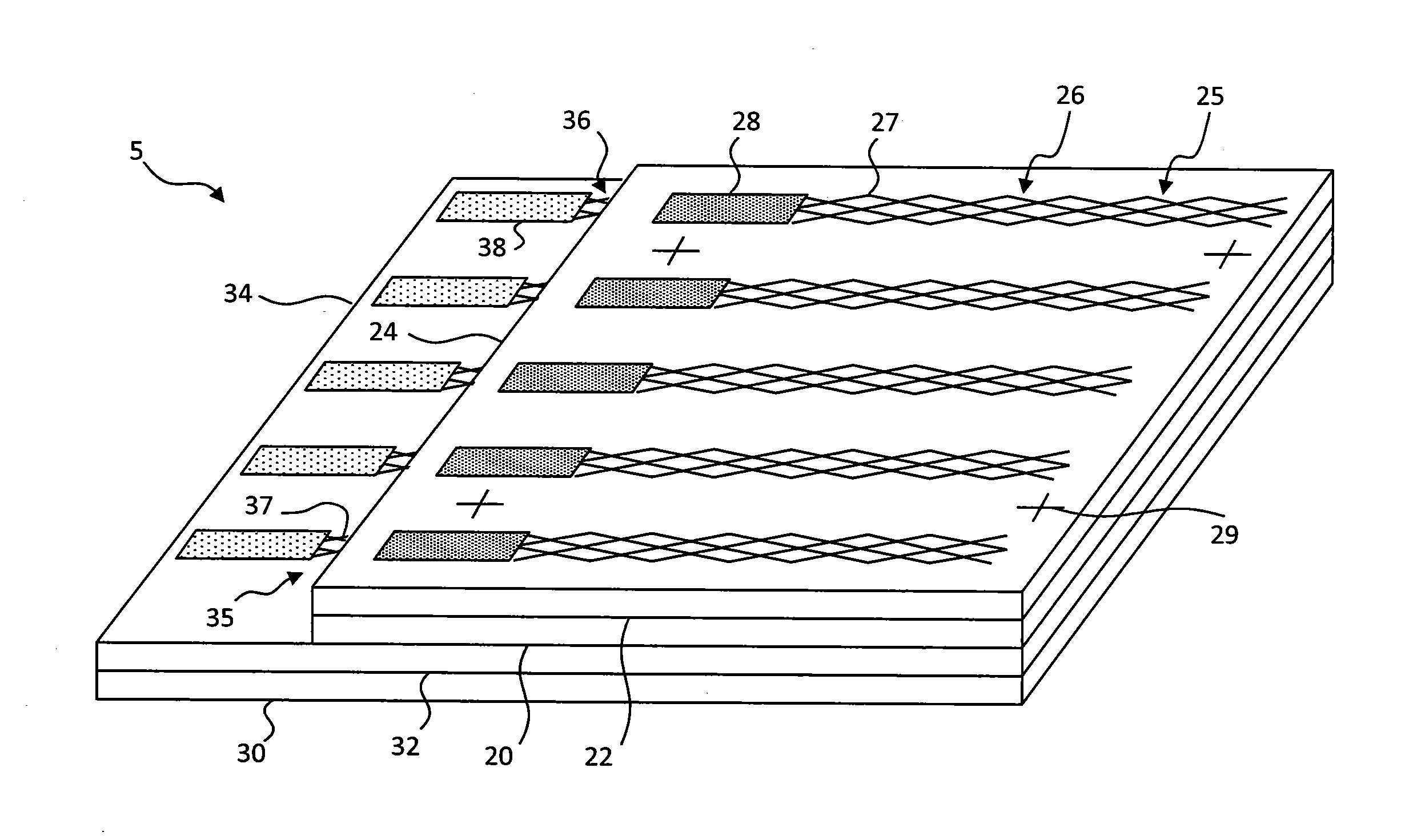
Circuit board with embedded passive component and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20160150651A1Printed circuit assemblingPrinted electric component incorporationEngineeringElectronic component
The present disclosure relates to a semiconductor device substrate and a method for making the same. The semiconductor device substrate includes a first dielectric layer, a second dielectric layer and an electronic component. The first dielectric layer includes a body portion, and a wall portion protruded from a first surface of the body portion. The wall portion has an end. The second dielectric layer has a first surface and an opposing second surface. The first surface of the second dielectric layer is adjacent to the first surface of the body portion. The second dielectric layer surrounds the wall portion. The end of the wall portion extends beyond the second surface of the second dielectric layer. The electronic component includes a first electrical contact and a second electrical contact. At least a part of the electronic component is surrounded by the wall portion.
Owner:ADVANCED SEMICON ENG INC
Method for press fitting thick copper printed circuit board
InactiveCN105007696AIncreased residual copper rateGood filling effectProcessing steps orderMultilayer circuit manufactureCopper foilEngineering
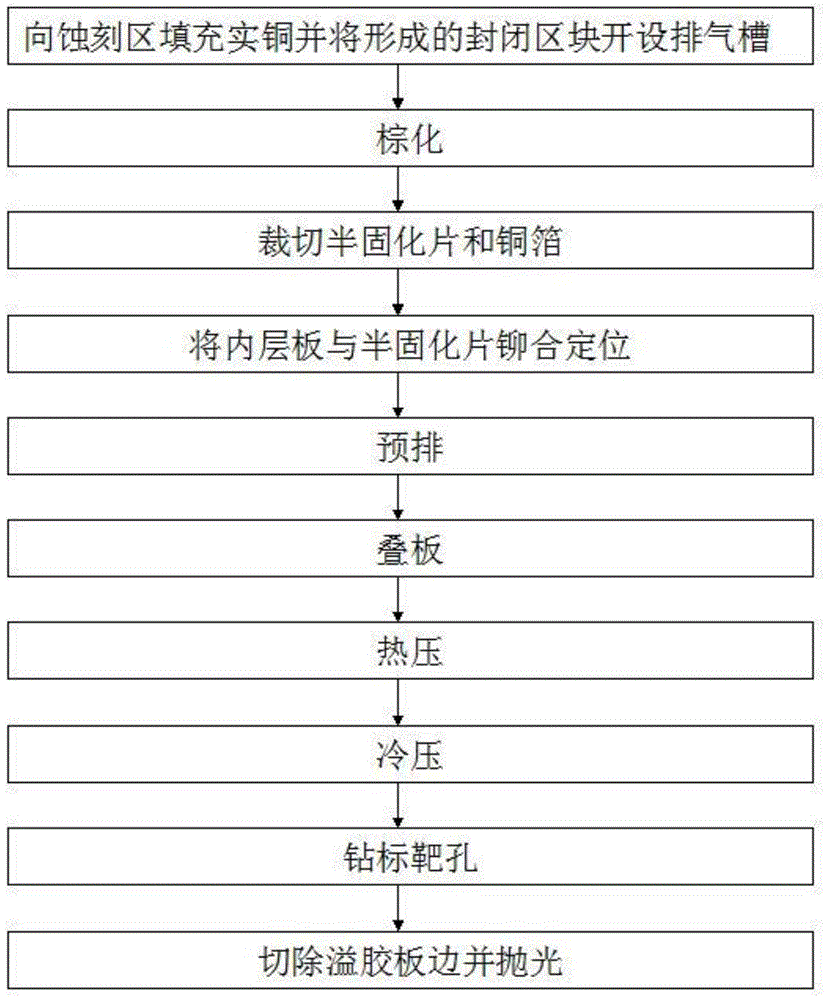
The invention belongs to the field of circuit board processing and discloses a method for press fitting a thick copper printed circuit board. The method comprises the following steps of: filling an etched area of the inner-layer board of the printed circuit board with copper and arranging an air discharge duct on an enclosed block formed by filling the copper; performing brown oxide; cutting a prepreg and a copper foil and riveting the inner-layer board and the prepreg by using rivets in an overlapped manner to achieve laminated positoning; prearranging the inner-layer board; stacking boards; performing hot pressing and cold pressing treatment; and drilling a mark hole. After the etched area is filled with the copper, the residual copper rate of the inner-layer board is at least increased by 5 to 10%. Thus, the filling effect of the inner-layer board is obviously enhanced; a technology problem of press fit cavities is effectively relieved, and a decrease in the voltage withstand capability of a product is prevented. The air discharge duct arranged after the copper is filled guarantees good flow of the prepreg in a press fitting production process.
Owner:SHENZHEN SUNTAK MULTILAYER PCB
Method of manufacturing polymer printed circuit board
ActiveUS20180199441A1Improve conductivityConductive pattern formationCircuit susbtrate materialsOptoelectronicsGraphene
Owner:BGT MATERIALS
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104349613AImprove product qualityOvercome residualPrinted circuit detailsMultilayer circuit manufactureSurface layerEngineering
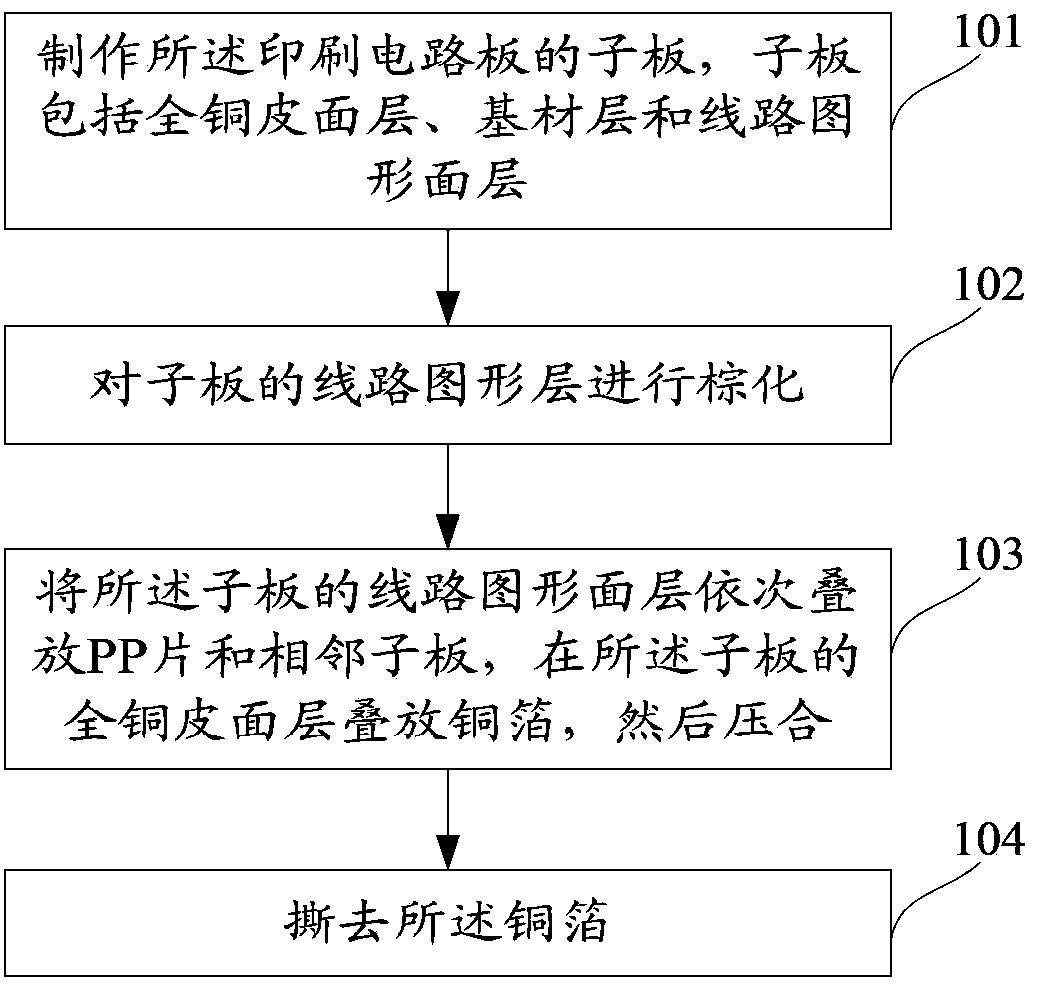
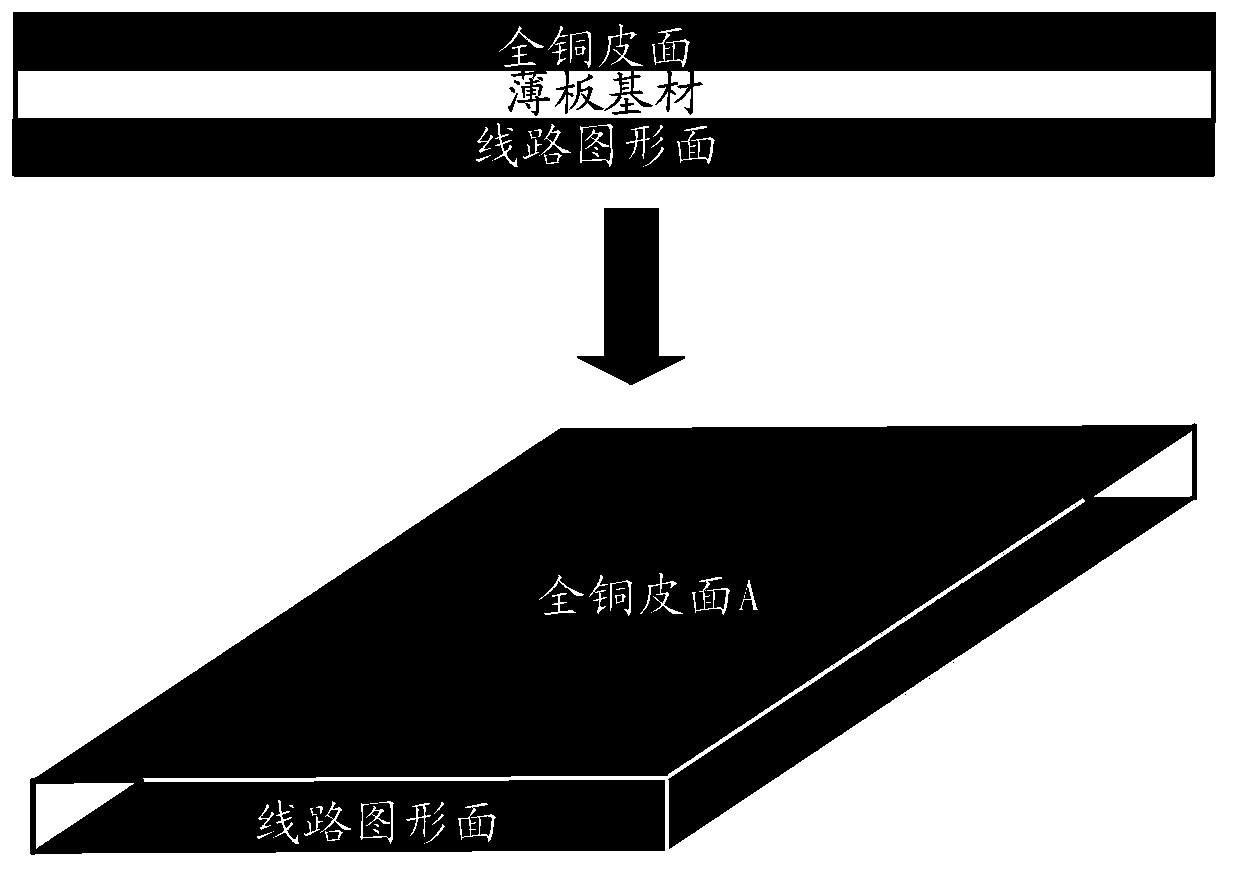
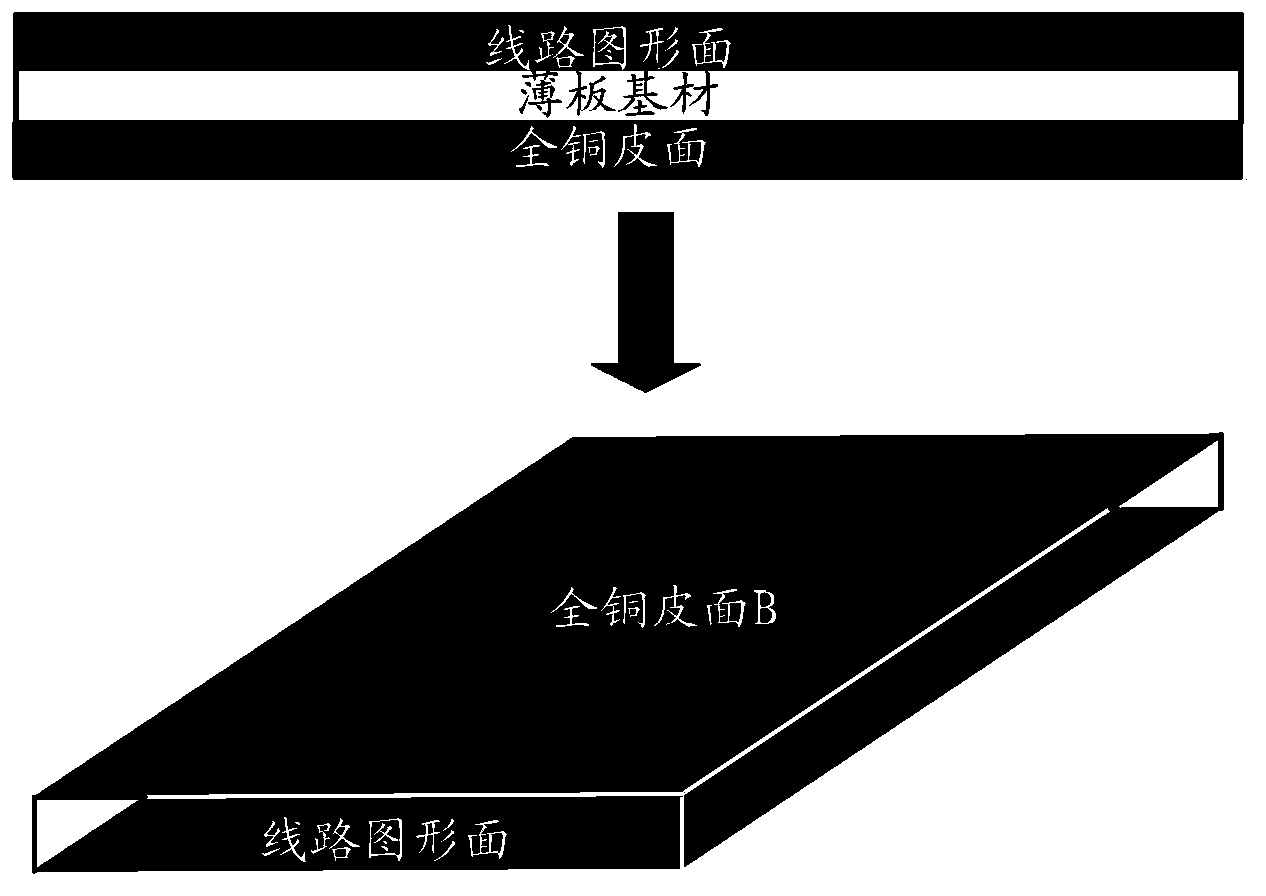
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board). The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: manufacturing sub-boards of the PCB, wherein each sub-board comprises a full-copper sheet surface layer, a substrate layer and a circuit pattern surface layer; performing brown oxidation on the circuit pattern surface layers of the sub-boards; sequentially stacking a PP (Propene Polymer) sheet and adjacent sub-boards on the circuit pattern surface layers of the sub-boards, stacking copper foils on the full-copper sheet surface layers of the sub-boards and then laminating; tearing off the copper foils The invention also provides a PCB which is manufactured by use of the method. The method can be used for improving the PCB manufacturing quality.
Owner:PEKING UNIV FOUNDER GRP CO LTD +3
Resin composition, prepreg, resin sheet, and metal foil-clad laminate
InactiveUS20150017449A1High peel strengthImprove performancePretreated surfacesCoatingsMetal foilThermal expansion
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Press-fitting method and lamination structure for flexible circuit board
InactiveCN105555032ALess clean upEnsure consistencyFlexible printed circuitsLaminating printed circuit boardsFlexible circuitsKraft paper
The invention discloses a press-fitting method and a lamination structure for a flexible circuit board. The press-fitting method comprises the steps of laying a buffer layer on the lower carrier plate of a press-fitting machine; paying a lamination layer on the buffer layer, wherein the lamination layer comprises brown paper, a filling layer, a release layer, a circuit board to be press-fit, and a release layer, a filling layer and brown paper stacked on the circuit board; repeatedly laying a number of lamination layers in the step S20 from the bottom up; laying a buffer layer on the topmost lamination layer; and starting the press-fitting machine for hot-pressing, wherein each lamination layer and the corresponding buffer layer, as well as each two adjacent lamination layers are separated by a thermal-conductive rigid pressure plate, and the filling layers can be melted after heating to fill the gaps between the brown paper and the release layers. According to the press-fitting method, the melted PE liquid can be adsorbed, thus the cleanup work after press-fitting is reduced; the consistency of different batches of products can be effectively ensured, thus control on the product precision is facilitated; the layer number of the circuit boards in one time of press-fitting is increased, thus the production efficiency is greatly enhanced.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINYU TENGYUE ELECTRONICS
Making imprinted micro-wire rib structure
ActiveUS9161456B1Less spaceReduced material requirementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTransparent dielectricsConductive materialsMechanical engineering
A method of making a micro-wire rib structure includes providing a substrate and locating a curable layer on or over the substrate. The curable layer is imprinted and cured to form a cured layer including a cured-layer surface and a micro-channel having a micro-channel depth, a micro-channel bottom, first and second micro-channel sides, and one or more ribs having opposing rib sides and a rib top defining a rib height less than the micro-channel depth. Each rib is located between the first and second micro-channel sides and extends from the micro-channel bottom toward the cured-layer surface. A curable conductive material is located in the micro-channel and cured to provide a cured electrical conductor forming a micro-wire in the micro-channel. The micro-wire extends continuously from the first micro-channel side, over the micro-channel bottom, the rib side(s) and rib top(s), to the second micro-channel side forming a continuous electrical conductor from the first micro-channel side to the second micro-channel side.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
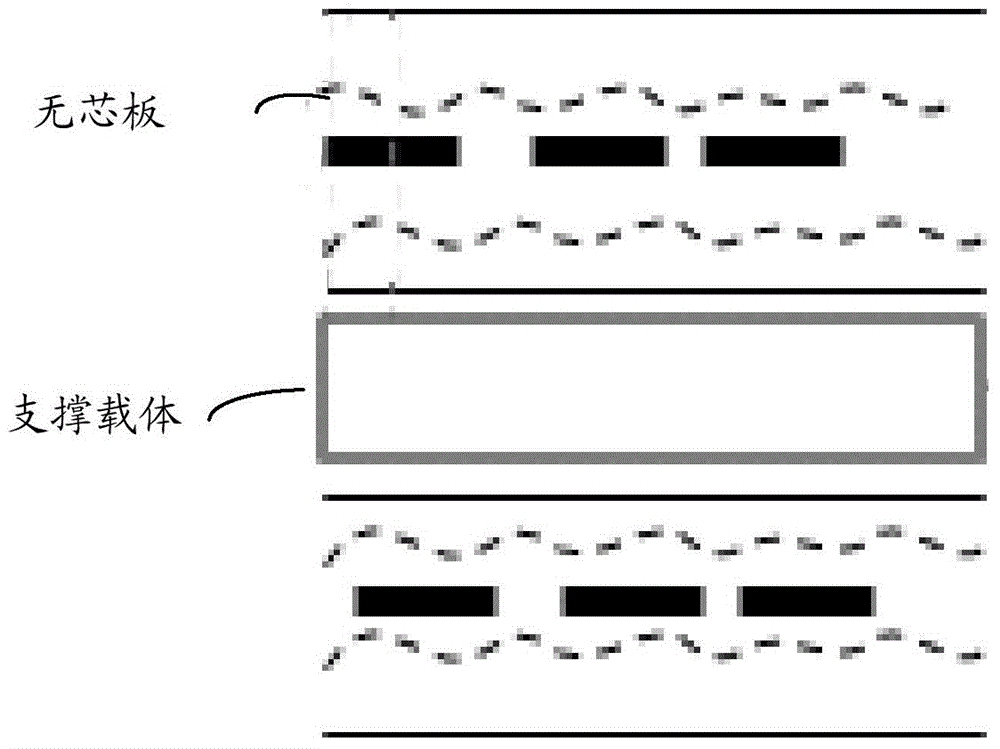
Core-less board manufacturing method
ActiveCN104538320AReduce warpageReduce residual stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMultilayer circuit manufactureCopper foilResidual stress
A core-less board manufacturing method comprises the steps that a supporting carrier is provided, inner copper foil layers are laminated on an upper accumulation layer of the supporting carrier, inner prepregs are arranged between all the inner copper foil layers, and outer copper foil layers are arranged outside outer prepregs to form a core-less board, wherein the highest temperature for laminating the inner copper foil layers and the inner prepregs ranges from 140 DEG C to 180 DEG C; the core-less board is separated from the supporting carrier. By the adoption of the core-less board manufacturing method, in the laminating process, pre-laminating is adopted for the inner prepregs and the inner copper foil layers, full-laminating is adopted for outer layers, and laminating temperature and laminating time are both improved. Compared with conventional laminating, the curing degree of the inner prepregs laminated through the laminating parameters of the method is only 70-95 percent of that of inner prepregs laminated through conventional parameters, full laminating parameters are adopted for laminating in the final laminating process of the outer layers, the residual stress on all the inner prepregs is lowered, and buckling of the core-less board is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FASTPRINT CIRCUIT TECH +2
Method of forming metal lines having high conductivity using metal nanoparticle ink on flexible substrate
InactiveUS20150173200A1Improve heat resistanceImprove conductivityMicrostructural device assemblyConductive pattern formationOptoelectronicsSolvent
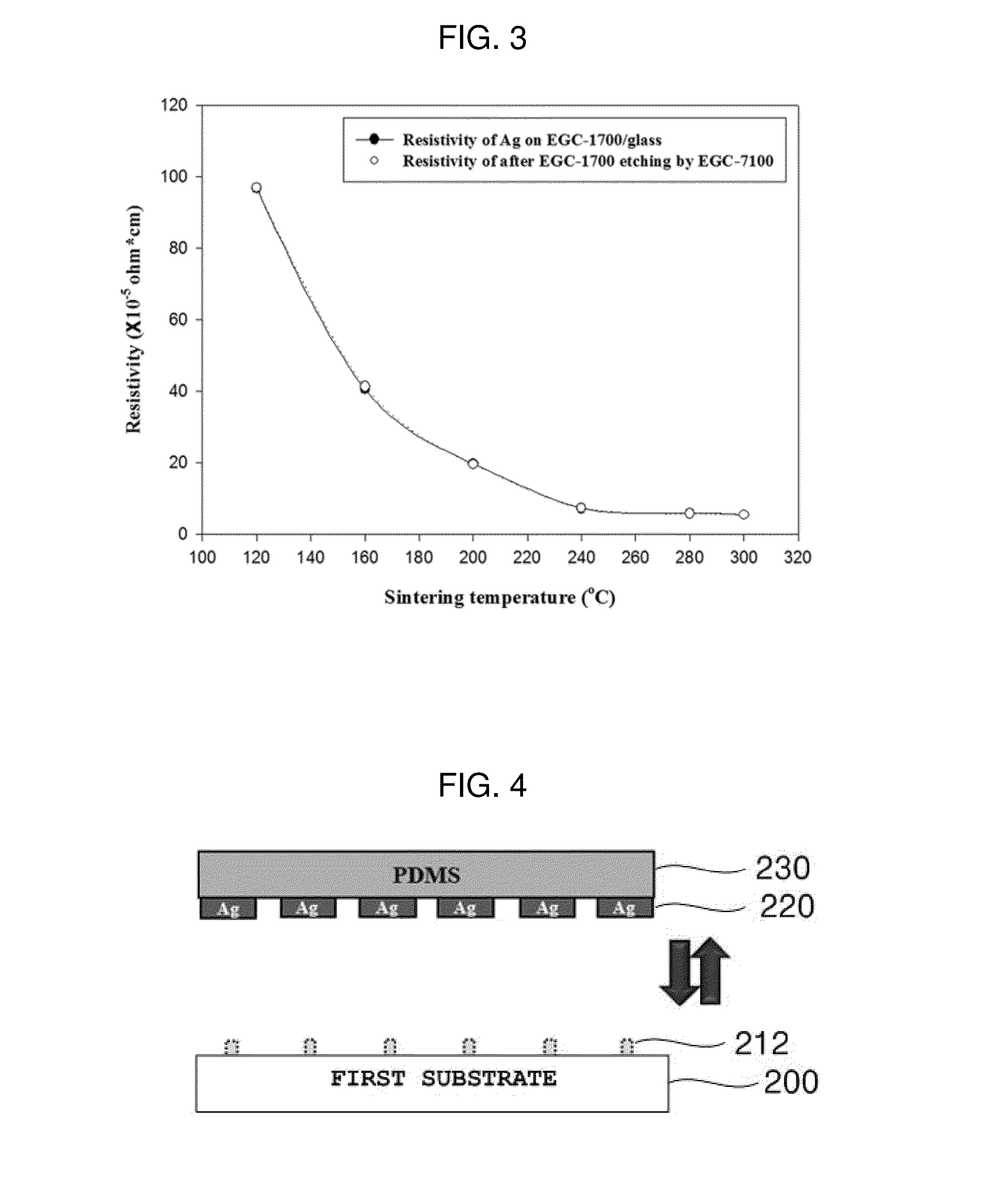
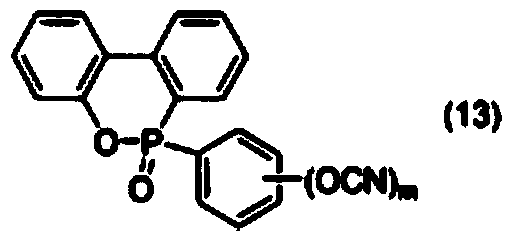
Provided is a method of forming metal-lines having high conductivity on a flexible substrate, including (a) forming a buffer layer on a first substrate, (b) forming metal-lines by printing a metal-nanoparticle-ink on the buffer layer, (c) sintering the metal-nanoparticle-ink through thermal treatment, (d) forming supporting-members between the metal-lines and the first substrate by etching the buffer layer by using a etching solvent and controlling an etching time so that a portion of the buffer layer is not etched, (e) picking up the metal-lines from the first substrate by using a stamp in the state where a pattern of the metal-lines is fixed and arranged by the supporting-members, and (f) transferring the picked-up metal-lines to a second substrate, wherein the first substrate is a heat resistant substrate which is not deformed at a sintering temperature of the metal-nanoparticle-ink, and the second substrate is a flexible substrate.
Owner:KYUNGPOOK NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Resin composition, prepreg, resin sheet, and metal foil-clad laminate
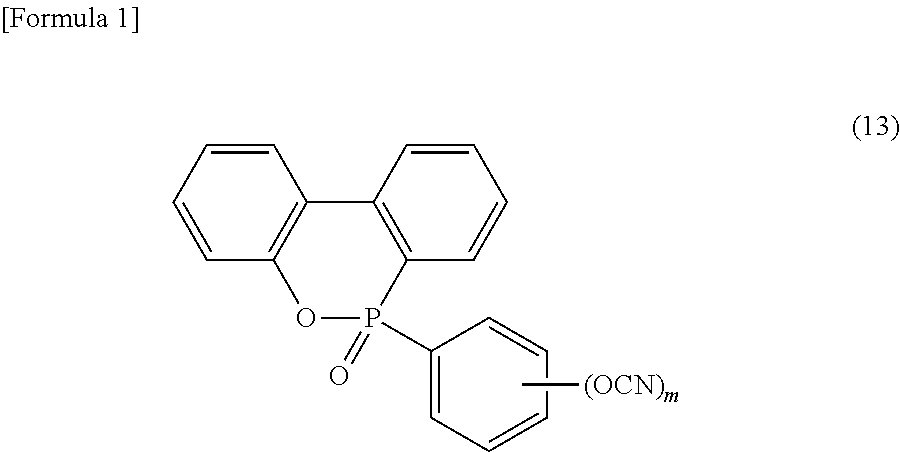
InactiveCN104271671AHigh peel strengthImprove performanceSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsMetal foilThermal expansion
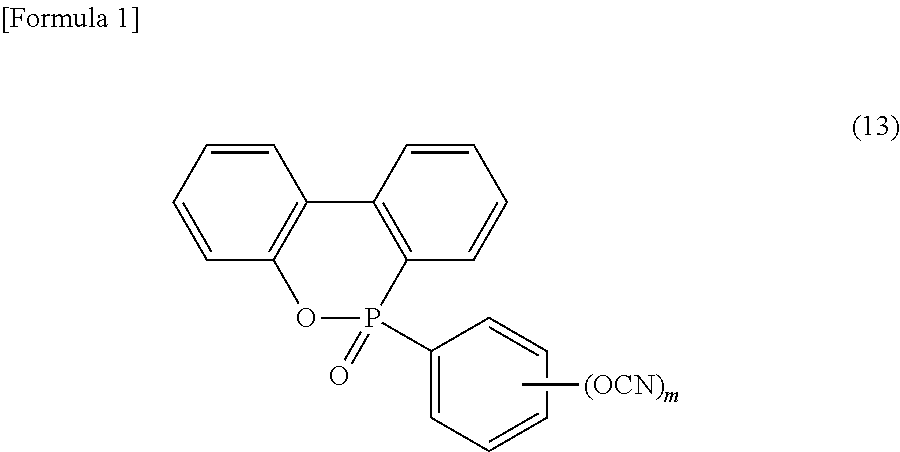
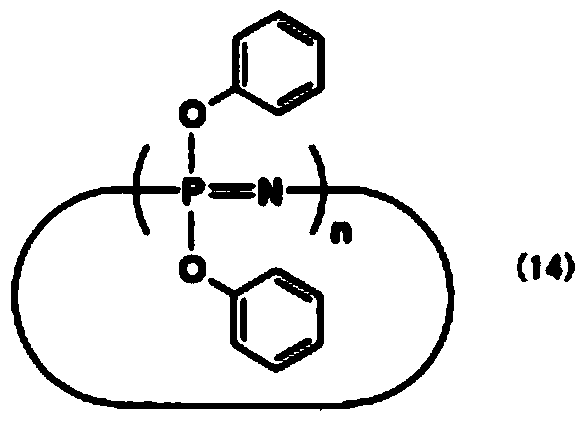
A resin composition has high flame retardancy and excellent heat resistance, peel strength with copper foil, thermal expansion coefficient, heat resistance property upon moisture absorption, and electrical properties, a prepreg and single-layer or laminated sheet, a metal foil-clad laminate using the prepreg, and the like. The resin composition has polyphenylene ether (A) having a number average molecular weight of 500 to 5000, a phosphorus-containing cyanate ester compound (B) represented by formula (13), a cyclophosphazene compound (C), a halogen-free epoxy resin (D), a cyanate ester compound (E) other than the phosphorus-containing cyanate ester compound (B), an oligomer (F) of styrene and / or substituted styrene, and a filler (G), wherein a content of the phosphorus-containing cyanate ester compound (B) is 1 to 10 parts by mass based on 100 parts by mass of a total of the (A) to (F) components. wherein m represents an integer of 1 to 3.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Fabrication method of covering film and protective electromagnetic wave shielding film rigid-flex printed circuit board
ActiveCN106102351ANo problems with peeling damageLow costMultilayer circuit manufactureCircuit laminationEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The invention discloses a fabrication method of a covering film and protective electromagnetic wave shielding film rigid-flex printed circuit board. The method comprises the steps of laminated stack design, flexible board circuit pattern fabrication, flexible board electromagnetic wave shielding film quick pressing, rigid board circuit pattern fabrication, rigid board covering film fast pressing, press-forming, subsequent procedure processing and the like. The fabrication method of the covering film and protective electromagnetic wave shielding film rigid-flex printed circuit board of the of the invention has the advantages of low cost, stable performance and strong processability.
Owner:HUIZHOU KING BROTHER CIRCUIT TECH +1
Carrier-Attached Copper Foil, Laminate, Method For Producing Printed Wiring Board, And Method For Producing Electronic Device
ActiveCN106455342AFormation effect is goodSynthetic resin layered productsPrinted circuit aspectsCopper foilTriazine
Provided herein is a carrier-attached copper foil having desirable fine circuit formability. The carrier-attached copper foil includes a carrier, an interlayer, and an ultrathin copper layer in this order, wherein D2-D1 is 0.30 to 3.83 [mu]m, where D1 is the gravimetrically measured thickness of the carrier-attached copper foil excluding the carrier and the interlayer, and D2 is the maximum thickness of the layer remaining on a bismaleimide-triazine resin substrate in case of detaching the carrier after the carrier-attached copper foil is laminated to the resin substrate from the ultrathin copper layer side by being heat pressed under a pressure of 20 kgf / cm2 at 220 DEG C for 2 hours.
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING & METALS CORP
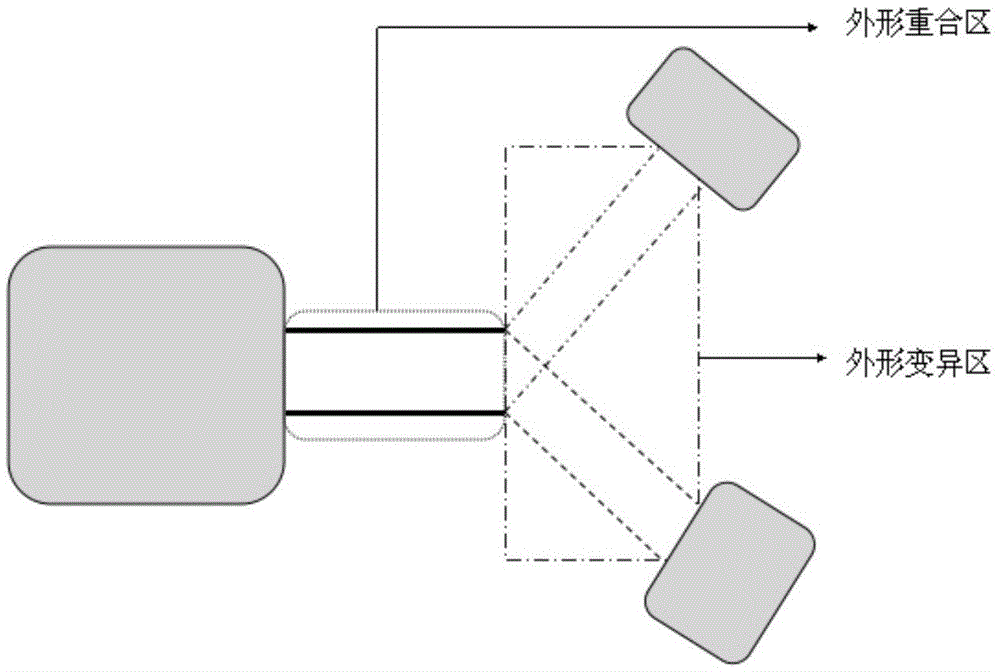
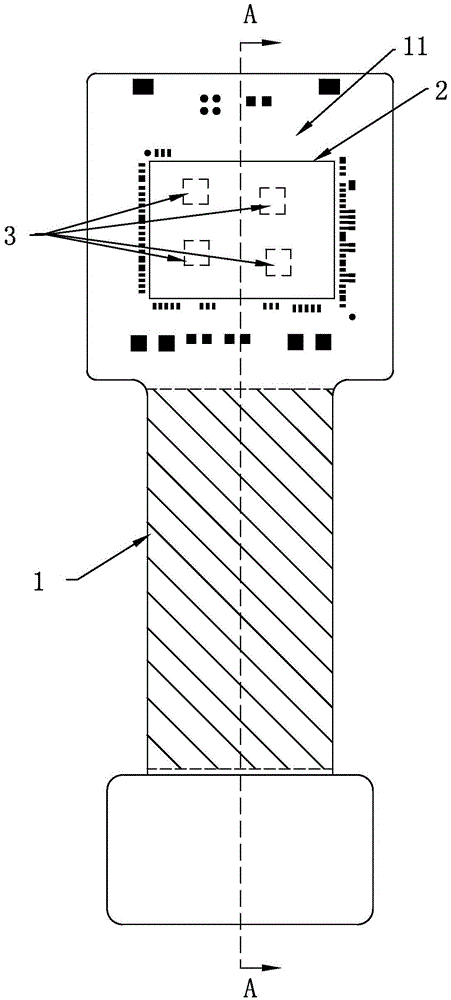
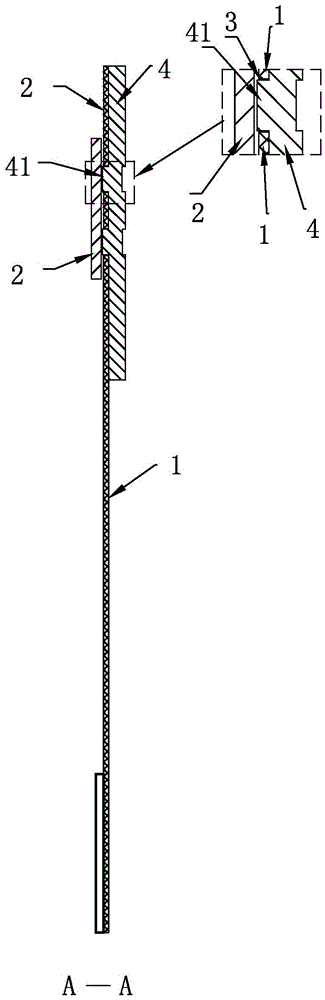
Rigid-flex board with different flexible appearances and preparation method of rigid-flex board
ActiveCN105491819AMeet the InternetMeet bendabilityMultilayer circuit manufactureCircuit laminationEngineeringLayered structure
The invention relates to a rigid-flex board with different flexible appearances and a preparation method of the rigid-flex board. The preparation method comprises the following steps: fabricating flexible core boards, rigid core boards and prepregs; stacking all flexible core boards and rigid core boards in a set order; carrying out laminating, drilling, degumming, copper deposition, electroplating, outer line fabrication, screen-printing and resistance welding procedures; conventionally carrying out surface treatment; carrying out uncapping operation on a circuit board which is subjected to surface treatment and exposing a flexible region; and carrying out laser appearance operation on the uncapped circuit board, so as to obtain the rigid-flex board with different flexible appearances. According to the method, appearance treatment is carried out on a flexible substrate overlapping region before lamination, so that the randomness in a hierarchical structure design on the rigid-flex board can be improved; multi-branch interconnection requirements are met; multi-branch current wiring space can also be saved; the bending performance of branch circuits is met; and the space of the printed board is saved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU FASTPRINT CIRCUIT TECH +2
High-cooling-efficiency FPC board used for camera module group and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN105578736AStable jobReduce heat accumulationFlexible printed circuitsPrinted circuit non-printed electric components associationStable stateEngineering
The invention provides a high-cooling-efficiency FPC board used for a camera module group and a manufacturing method thereof. The high-cooling-efficiency FPC board used for the camera module group is simple in structure, low in cost and quick in effect realization. The vacant positions in a circuit board area corresponding to mounted chip on the FPC board are provided with multiple window holes capable of penetrating through the FPC board. The positions, which are opposite to the window holes, of a steel reinforced piece arranged at the other surface opposite to the mounted chip on the FPC board are provided with bosses capable of inserting in the window holes. The mesa of the bosses is contacted with the heat-radiating surface of the mounted chip. The mesa of the bosses stretches out of the window holes to be contacted with the heat-radiating surface of the chip fit on the FPC board so that a part of heat generated by the chip is conducted to the whole steel reinforced piece through the bosses and guided away by the other surface of the steel reinforced piece in working of the chip. The phenomenon of heat accumulation caused by long time of working of the chip can be reduced so that the chip is enabled to work in the more stable state.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUALIN CIRCUIT TECH
Grooved PCB structure used for bare chip testing and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106793495ASimple structureLow costPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringDielectric layer
The invention provides a grooved PCB structure used for bare chip testing and a manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: firstly machining a PCB, forming a groove of which the area and the shape are the same as those of a bare chip in the PCB, and machining a diversion trench and a bonding pad; then adding an insulating dielectric layer between two PCBs, and laminating the two PCBs, wherein no bonding pad is machined on the surface opposite to the two PCBs; using a drilling tool to form connecting through holes in the laminated PCBs; finally adhering a bare chip at the position of the groove, and adopting an ultrasonic-thermocompression welding bonding technology to complete golden wire bonding between metal PAD of the bare chip and the bonding pad on the PCBs. The structure is simple, low in cost and easy to machine, the design difficulty of the PCB is reduced, and the pollution for the metal PAD of the bare chip when a conducting resin overflows can be preferably avoided.
Owner:NO 20 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com