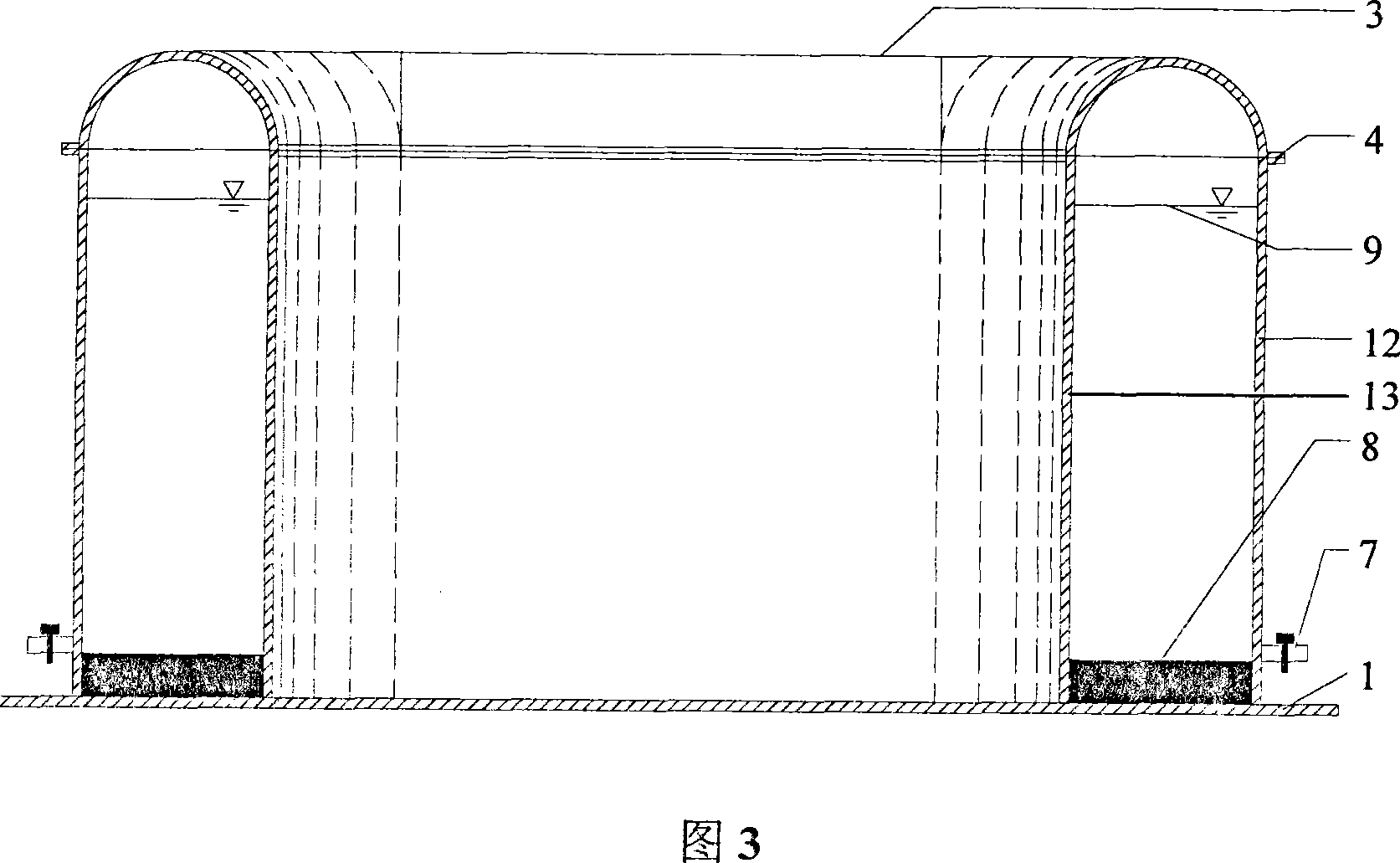
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Wave disturbance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Wave disturbance. In synoptic meteorology, the same as wave cyclone, but usually denoting an early state in the development of a wave cyclone, or a poorly developed one.
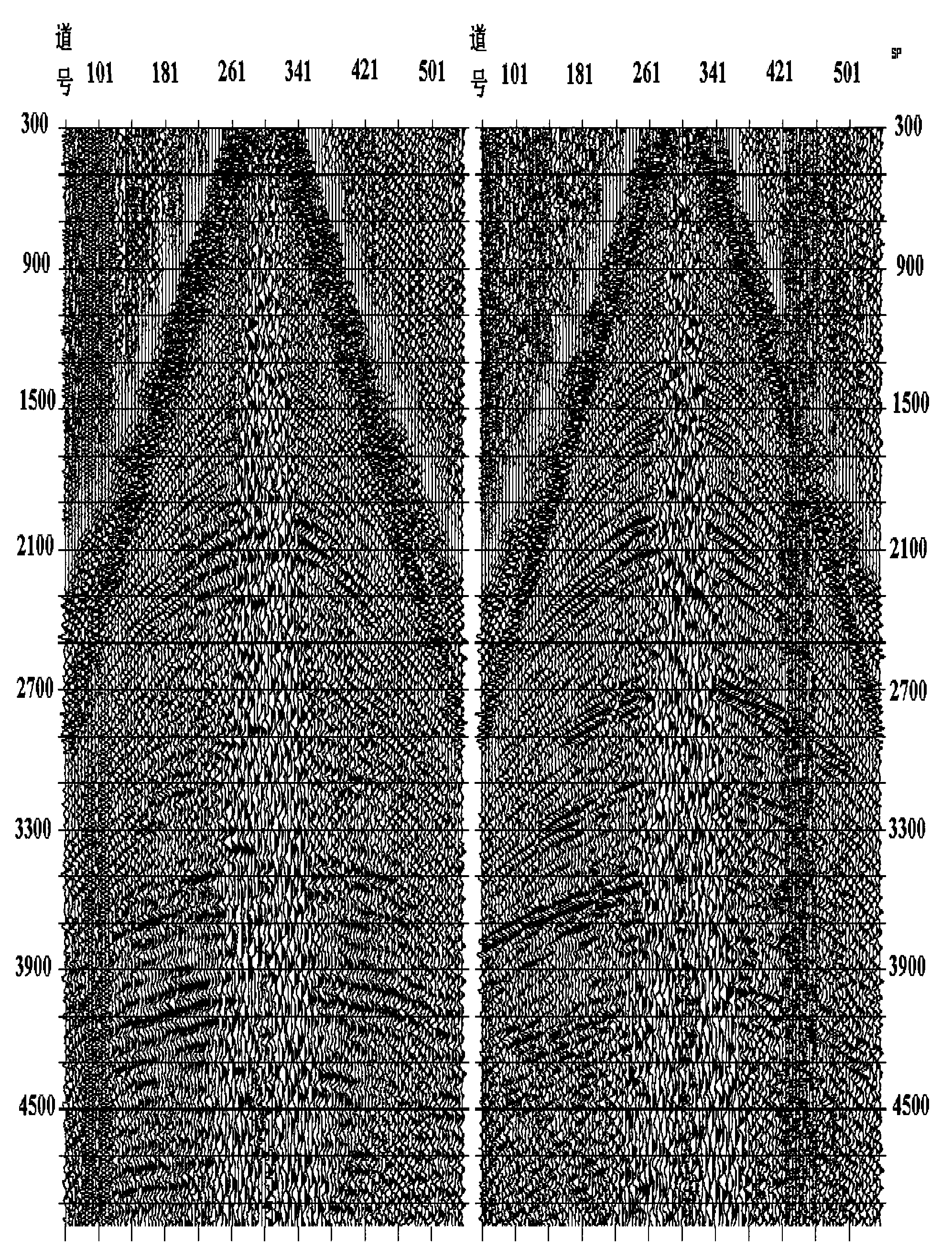
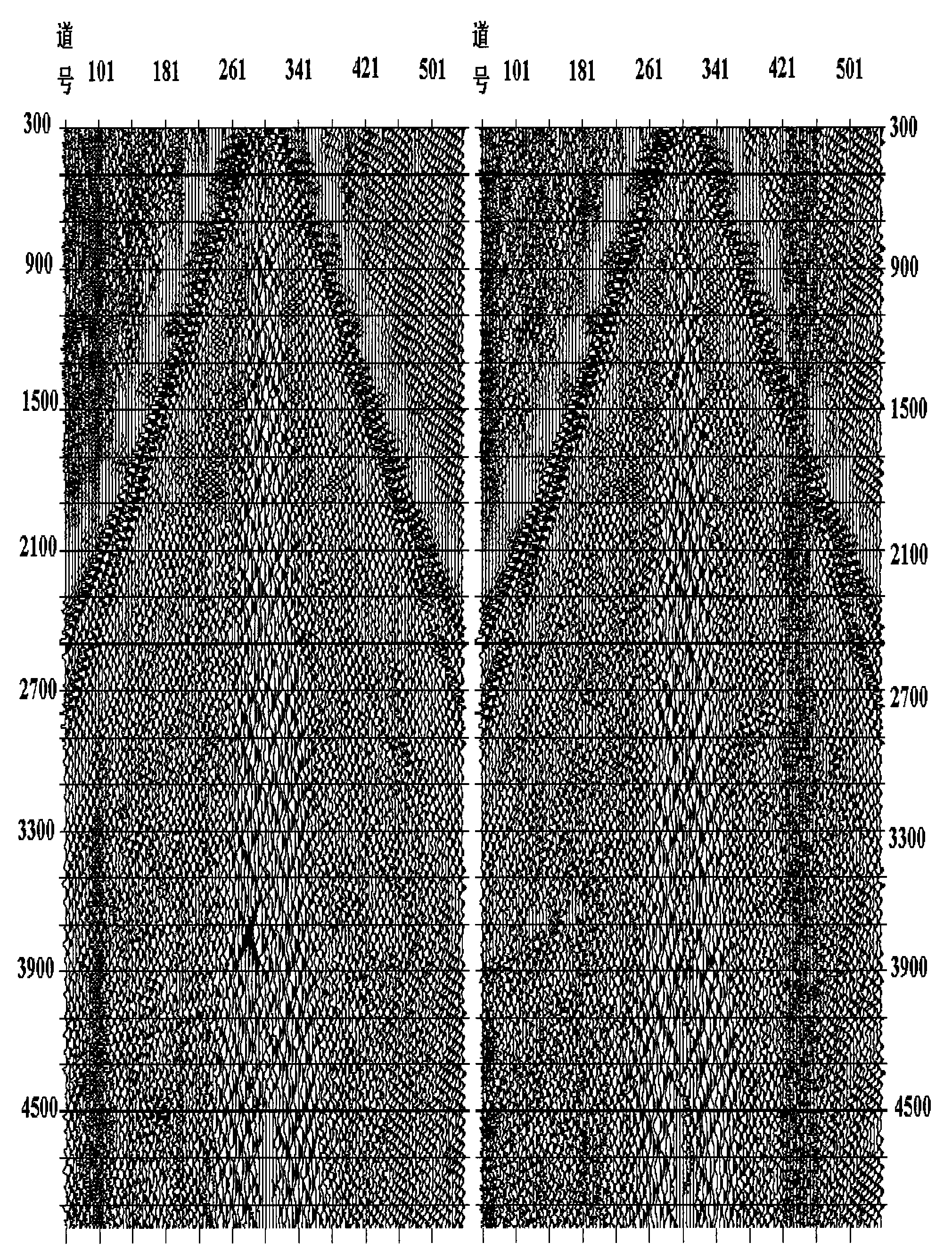
Method for eliminating linear regular noise and multiple wave disturbance in self-adapting mode
InactiveCN101598809AEliminate interference wavesDoes not harm frequency componentsSeismic signal processingGraphicsData set
The invention relates to a method for eliminating linear regular noise of seismic prospecting and multiple wave disturbance in a self-adapting mode, aiming to provide seismic figures with high resolution for the exploration of oil fields. The method comprises the following steps: transforming seismic data sets in a field according to regular disturbance linear event virtual inclination; subtracting a seismic trace and a noise model trace to obtain a current signal value; determining the receiving probability of the noise by utilizing a probability density function and a threshold value; subtracting the separated noise from an original record to eliminate a regular interference wave; carrying out linear inverse transform on the seismic data to obtain a data set; carrying out linear inverse transform on the record with the regular interference wave being eliminated to obtain a seismic record; and carrying out separate frequency processing and noise suppressing processing. The invention dose not damage the frequency components of effective waves and has the advantages of fast operation speed, good effect for suppressing noise, suitability for pre-stack seismic data and post-stack seismic data, and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
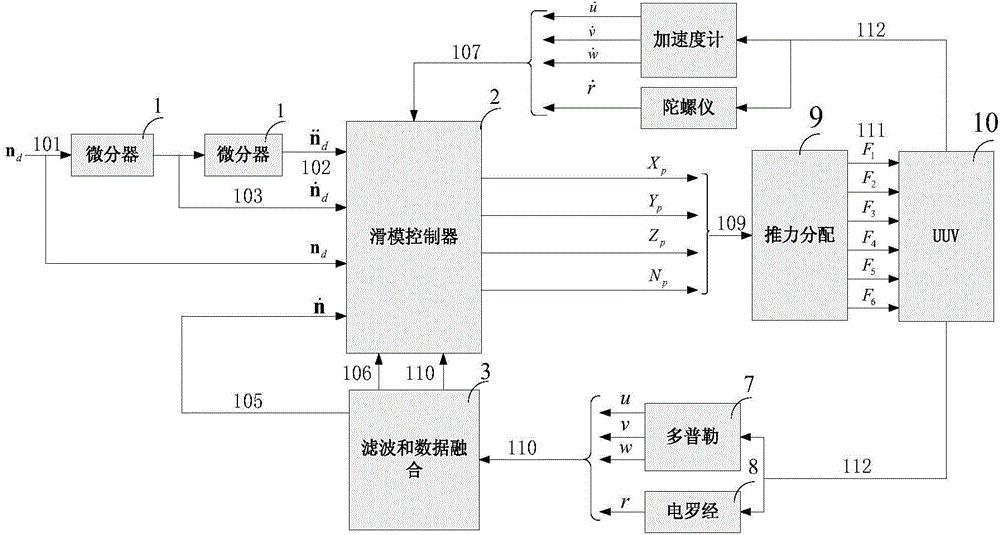
UUV four degree-of-freedom dynamic positioning adaptive anti-interference sliding mode control system and control method
ActiveCN104898688AGuaranteed stabilityImprove robustnessPosition/course control in three dimensionsAdaptive controlDifferentiatorGyroscope
The invention discloses an UUV four degree-of-freedom dynamic positioning adaptive anti-interference sliding mode control system and a control method. The system comprises a first differentiator, a second differentiator, an adaptive anti-interference sliding mode controller, a filter and data fusion unit, a Doppler sensor, an electric gyrocompass, a thrust allocation unit, an UUV, an accelerometer and a gyroscope , wherein the adaptive anti-interference sliding mode controller comprises a sliding mode controller, an adaptive disturbance compensation controller and a data processing unit; the sliding mode controller is used for realizing UUV four degree-of-freedom dynamic positioning variable structure control and eliminating pose errors; and the adaptive disturbance compensation controller is used for estimating uncertainty errors of an actually controlled object model and wave disturbance effects in an online mode. A dynamic process during which the system state approaches to the sliding mode surface is improved, steady-state anti-interference performance is improved, and compared with a common sliding mode control method, dynamic performance is better, and buffet of the system under disturbance effects can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
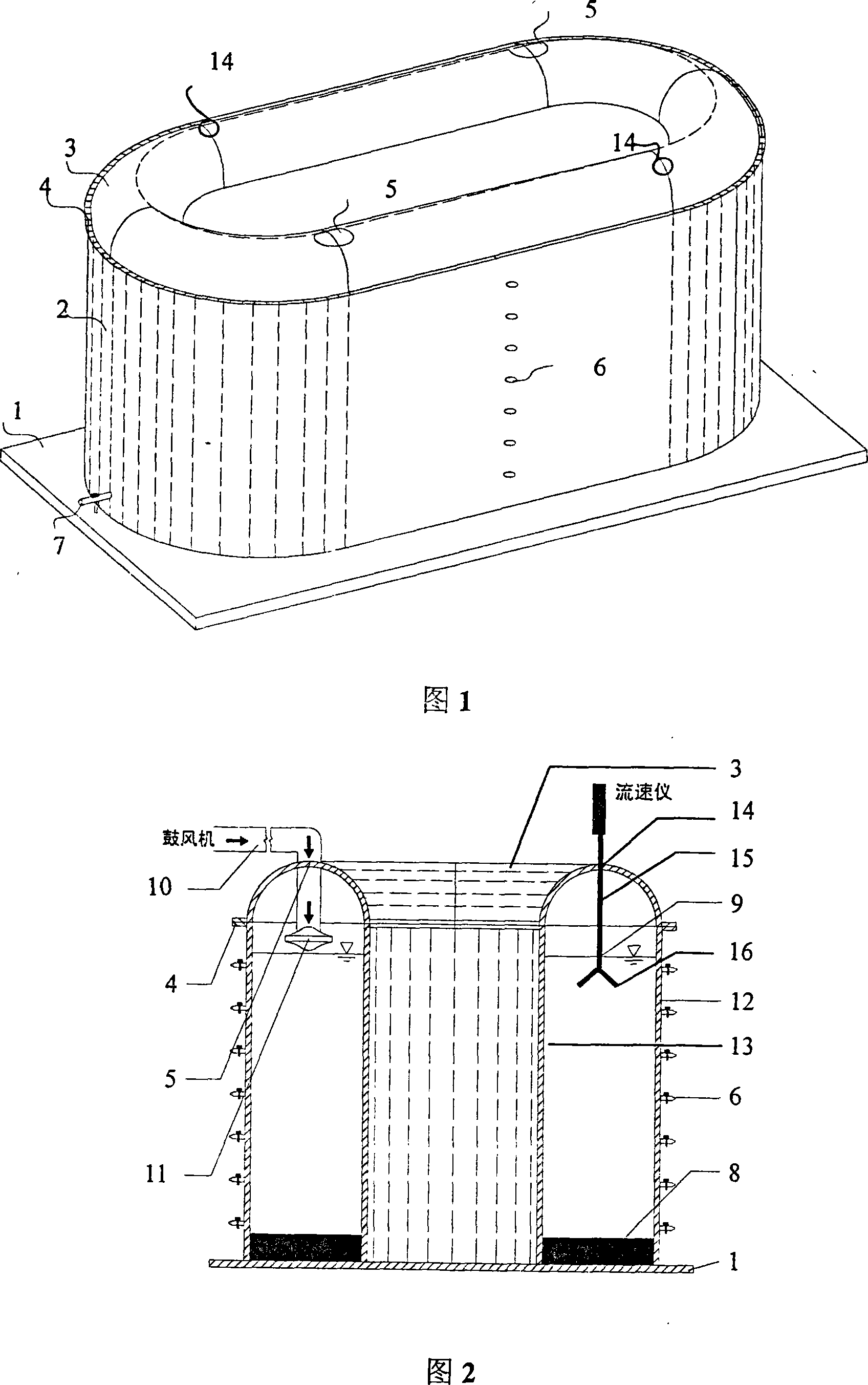
Method for re-suspending underwater deposit under simulated wave disturbance in annular water tank and device thereof
InactiveCN101110174AImprove sampling accuracyStable resuspension conditionsEducational modelsUnderwater explosionEngineering
The invention discloses a method for disturbing and resuspending underwater sediments with simulated wave in circular sink, which is characterized in that: place the sediments collected without disturbance at the bottom of the circular sink; plant submerged plant over the sediments and overlaying water; use a plurality of blowers to simulate different wind forces and apply it on the overlaying water, so as to generate water flow; adjust the position of the blower port and its included angle with the overlay water surface to make basically even flow field in the sink; the sediments at the bottom of the sink is resuspended under the action of hydrodynamic force, so as to realize the simulation for the resuspension of sediments under the disturbance of wave with different forces in the water body of lake and river where submerged plant grows. The invention has the flowing advantages: simulate the resuspension process of sediments due to the motion of flow field under the disturbance of wave with different forces in natural water body of lake and river where submerged plant grows; realize the collection of samples in water body of different depths under relative stable condition for the resuspension of sediments; meet the requirements for the study over the ration relations among wave disturbance-motion of flow field-resuspension of sediments; simple structure, low cost and convenient application of relevant device.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Electromagnetic wave absorber, method of manufacturing the same and appliance using the same
InactiveUS6919387B2Excellent electromagnetic wave absorbing characteristicIncrease heightMagnetic/electric field screeningRoad vehicles traffic controlElectromagnetic wave absorberElectromagnetic absorbers
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Linear structured light pavement surface detection system-based pavement depth image production method
InactiveCN105133471AAvoid interferenceThere is no grayscale jumpImage analysisRoads maintainenceVertical vibrationImage extraction
The present invention discloses a linear structured light pavement surface detection system-based pavement depth image production method, a light strip image containing three-dimensional information of a to-be-tested pavement is collected by a vehicle-mounted linear structured light pavement surface detection system, section surface contour lines are extracted from the light strip image, the section surface contour lines are spliced and converted into a pavement surface three-dimensional depth image by selection linear fitting and difference calculation method so as to realize pavement distress detecting free of vehicle wave disturbance. Beneficial effects are that: compared with surface fitting method in the prior art, disturbance caused by a variety of pavement fluctuations and detection system vertical vibration in the actual road detection process can be effectively overcome, so that the obtained pavement depth image is relatively flat, and is free of gray transition, detect effect is better, response is rapid, processing is efficient, and the result is reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electromagnetic wave absorber, method of manufacturing the same and appliance using the same
InactiveUS20050140539A1Suppress noise interferenceExcellent electromagnetic wave absorption characteristicMagnetic/electric field screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionElectromagnetic wave absorberElectromagnetic absorbers
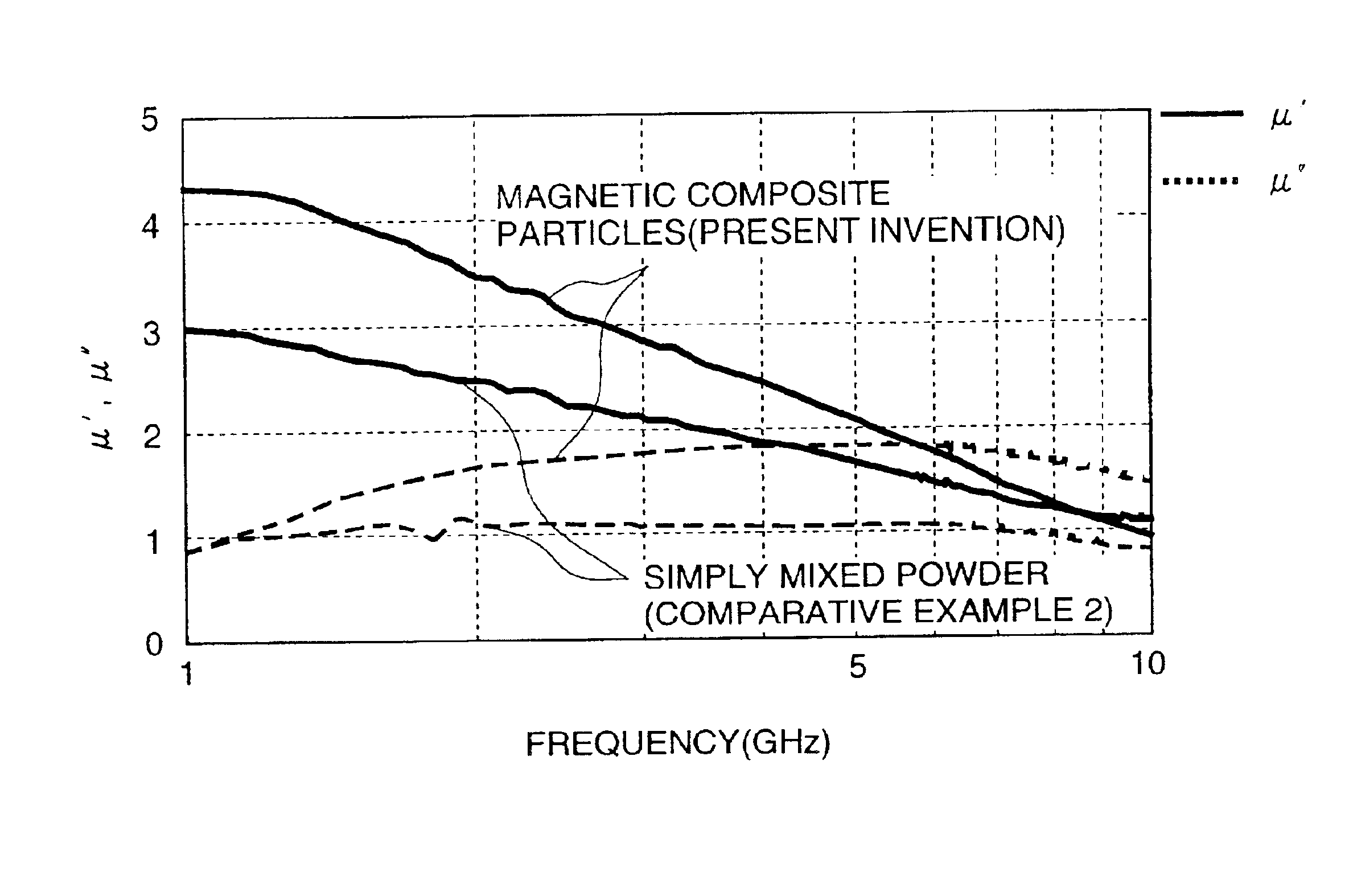
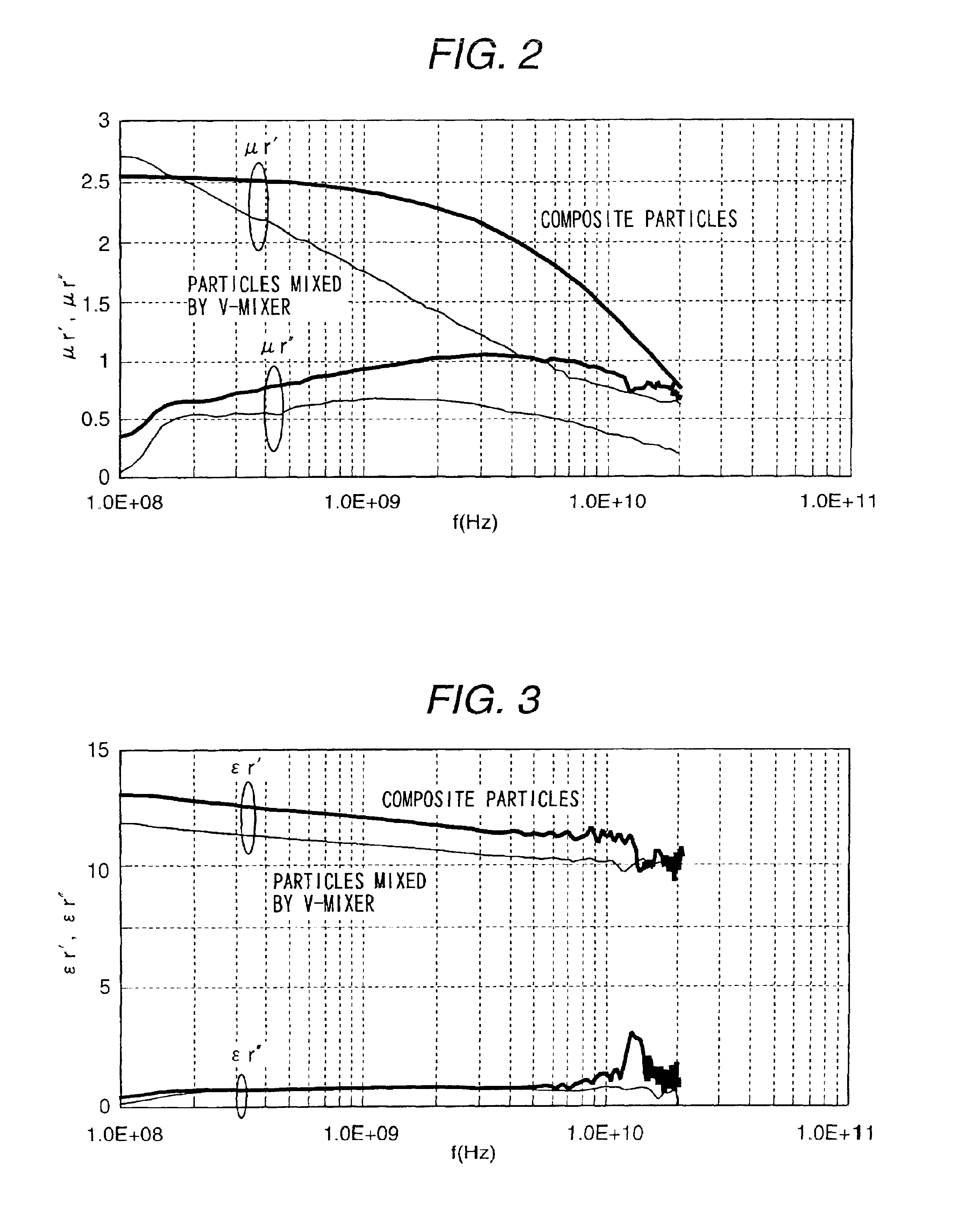
An electromagnetic wave absorber for use in the high frequency range above 1 Ghz and a composite member are characterized by the fact that magnetic metal grains are covered with ceramic above 20 volume %. Further, a method of manufacturing the electromagnetic absorber and the composite member is characterized by the fact that composite magnetic particles, in which a plurality of magnetic metal grains and ceramic are unified, are formed through a mechanical alloying method applied to a composite powder composed of magnetic metal powder and ceramic powder. The electromagnetic wave absorber can be used in a semiconductor device, an optical sending module, an optical receiving module, an optical sending and receiving module, an automatic tollgate in which erroneous operation due to electromagnetic wave disturbance is provided by use of the electromagnetic wave absorber.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Electromagnetic wave absorber, method of manufacturing the same and appliance using the same
InactiveUS7218266B2Excellent electromagnetic wave absorbing characteristicIncrease heightMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectromagnetic wave absorberElectromagnetic absorbers
An electromagnetic wave absorber for use in the high frequency range above 1 Ghz and a composite member are characterized by the fact that magnetic metal grains are covered with ceramic above 20 volume %. Further, a method of manufacturing the electromagnetic absorber and the composite member is characterized by the fact that composite magnetic particles, in which a plurality of magnetic metal grains and ceramic are unified, are formed through a mechanical alloying method applied to a composite powder composed of magnetic metal powder and ceramic powder. The electromagnetic wave absorber can be used in a semiconductor device, an optical sending module, an optical receiving module, an optical sending and receiving module, an automatic tollgate in which erroneous operation due to electromagnetic wave disturbance is provided by use of the electromagnetic wave absorber.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Pulse gas laser intracavity flow field measurement device based on four-quadrant detector
InactiveCN102980739AOvercoming complexityOvercome the disadvantages of expensive equipmentLaser detailsAerodynamic testingShock waveMeasurement device
The invention discloses a pulse gas laser intracavity flow field measurement device based on a four-quadrant detector. The pulse gas laser intracavity flow field measurement device comprises a detection light source, a detection light receiving system and a signal processing system. A light beam sent out by the detection light source is parallel to the optical axis direction of a pulse gas laser. The detection light receiving system comprises a four-quadrant photoelectric detector, a photosensitive face faces towards a detection area and is perpendicular to a detection light beam to be used for receiving the detection laser light beam, and signals of the four-quadrant photoelectric detector can be processed by a signal processing system to obtain laser wave transmission characteristic parameters. The pulse gas laser intracavity flow field measurement device is simple in structure and convenient to operate. The four-quadrant photosensitive sensor simplifies an experiment device. Laser wave disturbance and transmission direction of the laser wave can be judged according to movement of the center of a light spot of the four-quadrant photosensitive detector to improve detection flexibility. Simultaneously, a dichroic mirror is used to separate the detection light beam form laser of the pulse gas laser. The laser oscillation can simultaneously obtain real-time test results to overcome the defect that thermal deposition in non-laser resonant cavity test discharging area is high.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
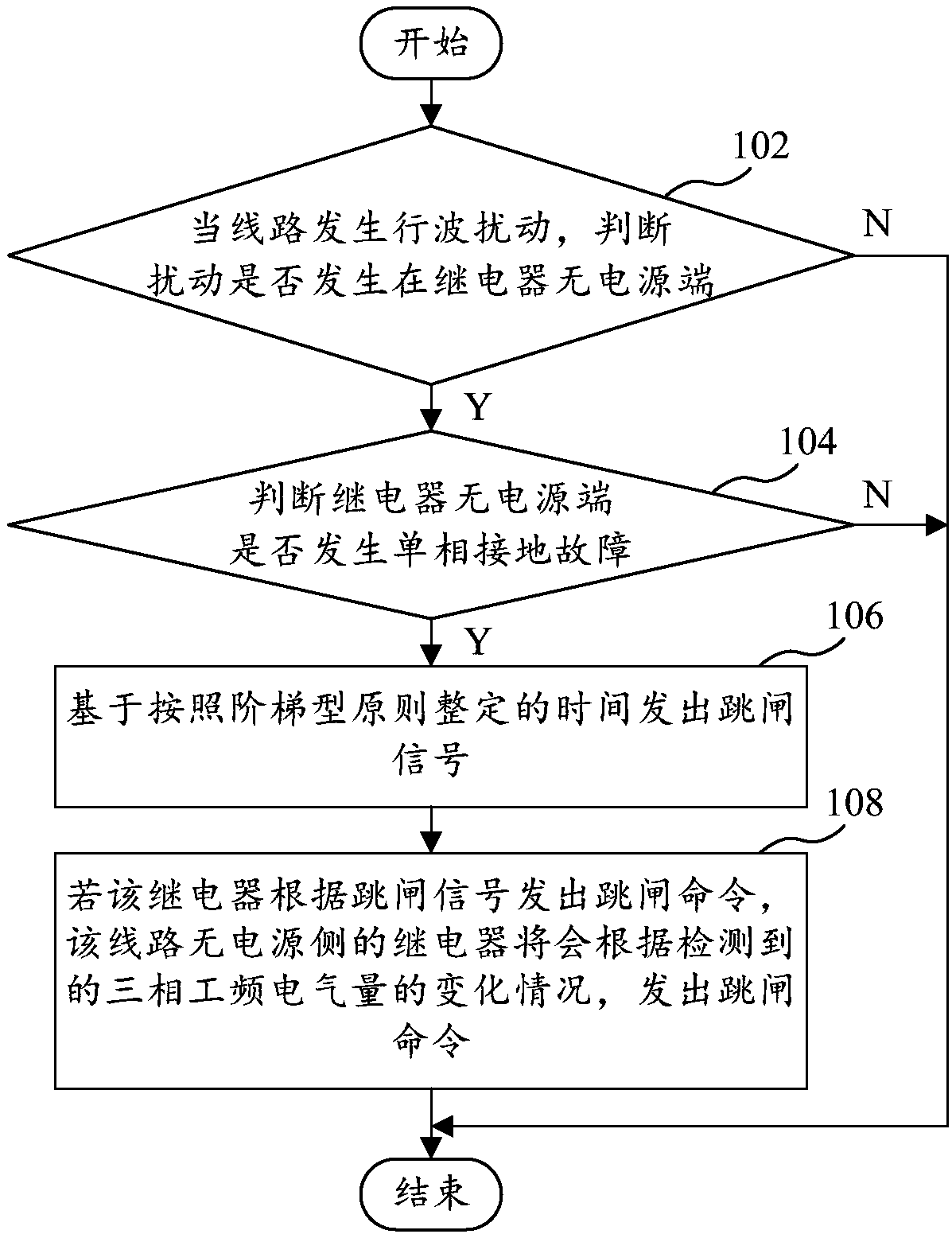
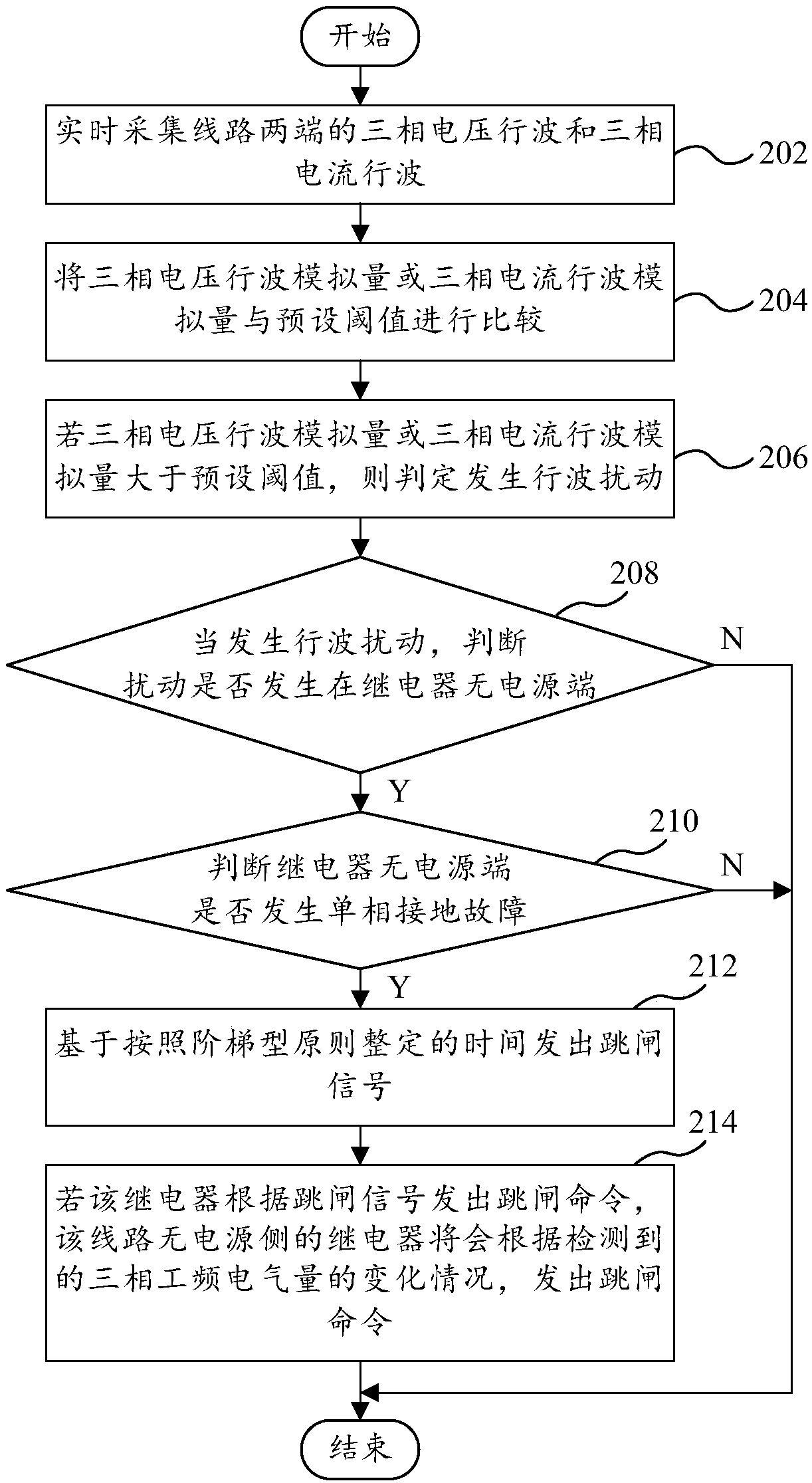
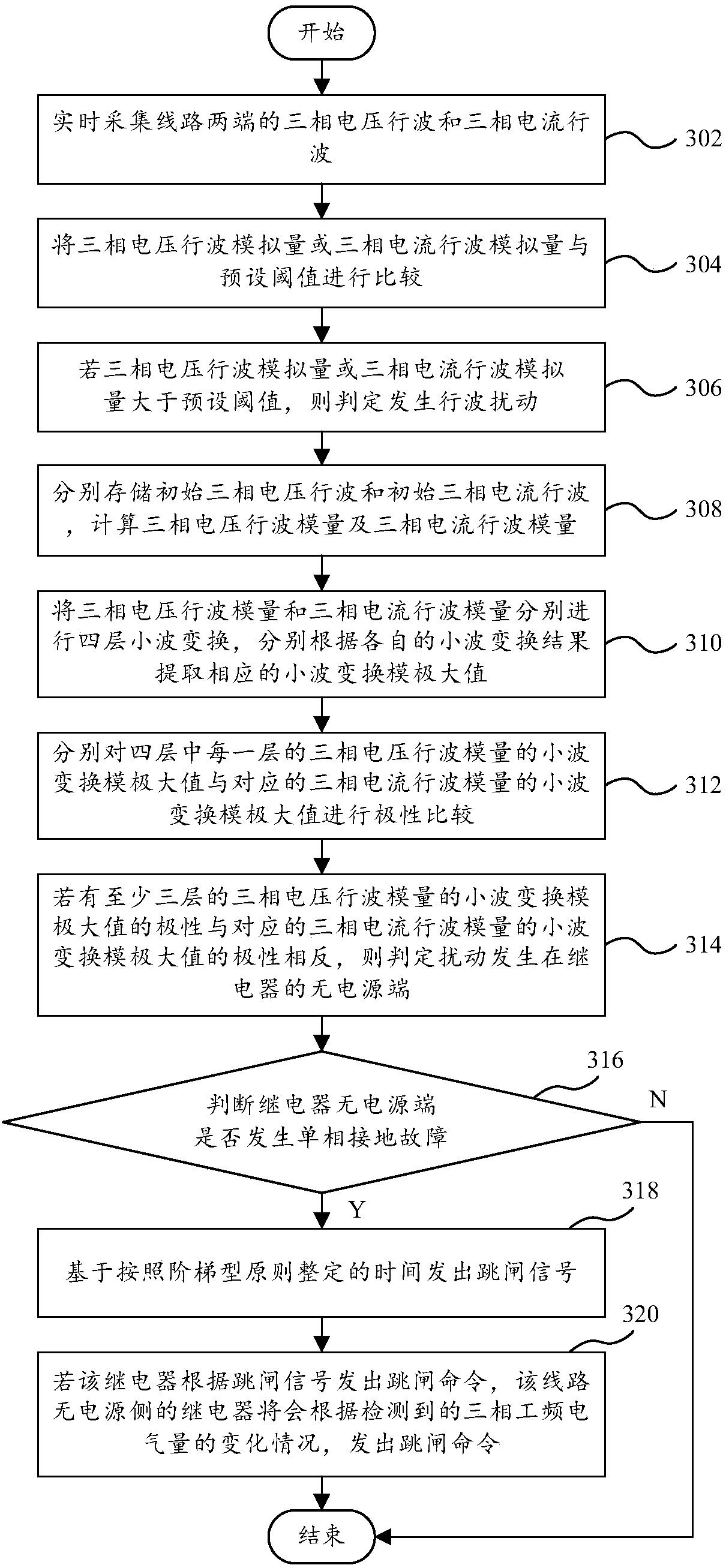
Single-phase grounding travelling wave protection method and device and computer equipment
ActiveCN108336720AImprove operational reliabilityHigh-precision detectionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical testingTime delaysEngineering
The invention provides a single-phase grounding travelling wave protection method and device and computer equipment. The method comprises the steps of judging whether disturbance occurs in a non-powersupply end of a relay in a circuit or not when travelling wave disturbance occurs in the circuit; judging whether a single-phase grounding fault occurs in the non-power supply end of the relay or notwhen that disturbance occurs in the non-power supply end of the relay is judged; giving out a trip signal according to time delay set on the basis of a stepped principle when the single-phase grounding fault is judged; and giving out a trip command by the relay at a non-power supply side of the circuit according to the detected change condition of three-phase power frequency electrical quantity if the relay gives out the trip command according to the trip signal. By the technical scheme, power circuit protection is achieved, full-line trip acceleration is achieved, the single-phase groundingfault is rapidly and selectively removed from two ends of the circuit, a condition is provided for rapid recovery of normal power supply of the circuit, the running reliability of the power circuit isimproved, a communication passage is not needed, and the method has favorable economy and practicability.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
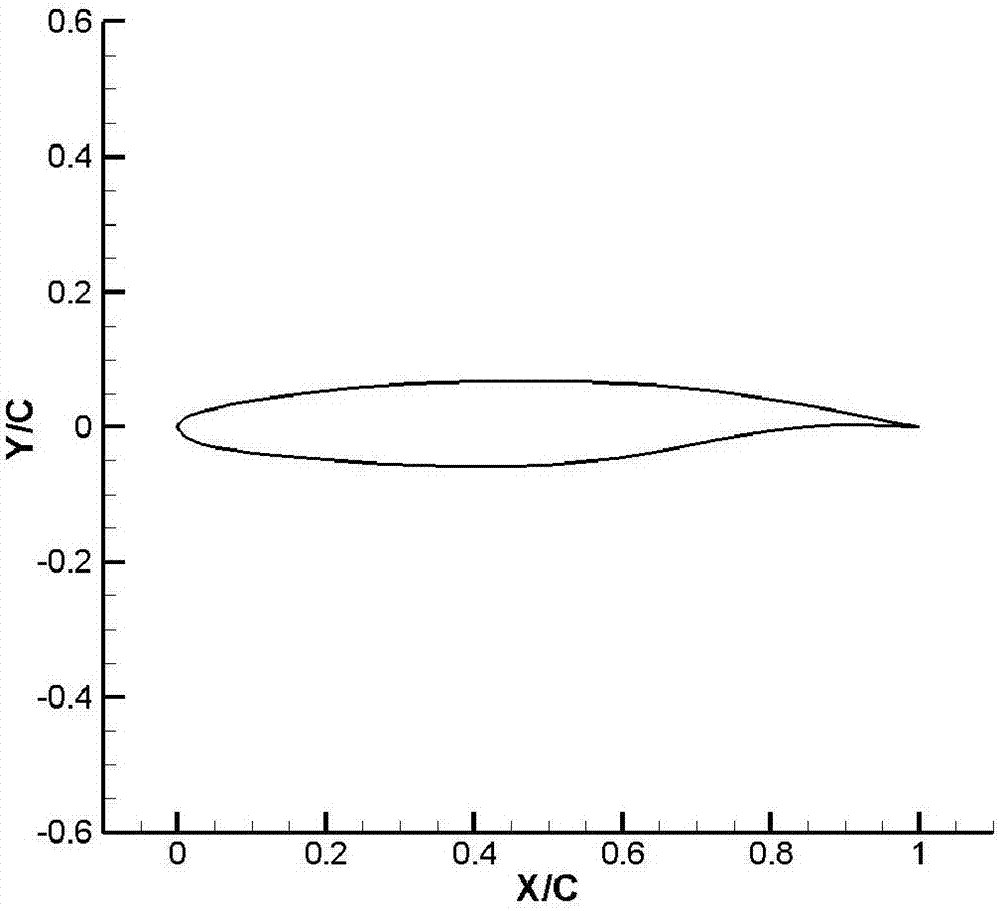
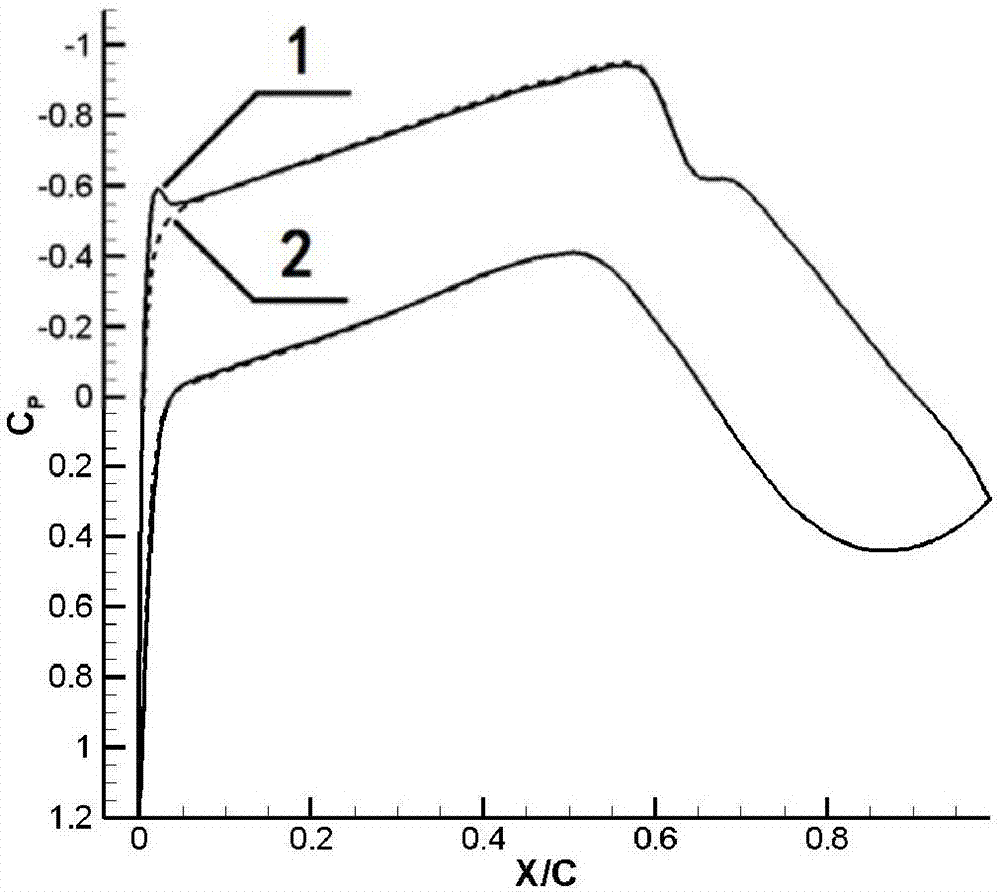
Natural laminar-flow supercritical wing section applied to sweepback wing of intermediate range civil airplane
ActiveCN107284650AInhibition transitionReduce resistanceWing shapesHeat reducing structuresShock waveJet aeroplane
The invention provides a natural laminar-flow supercritical wing section applied to a sweepback wing of an intermediate range civil airplane. The natural laminar-flow supercritical wing section has the following pressure distribution form: a bump appears in a front edge area of an upper surface, i.e., an area with a chordwise range of 0 to 5 percent C, a pressure coefficient height of the bump is 0.05, a bump area accounts for 0.3 percent of a whole pressure distribution area, which is used for inhibiting the unstable disturbance development of a three-dimensional cross-flow CF wave; and a favorable pressure gradient is kept in an area from the back of the bump to a shock wave position, which is used for inhibiting the unstable disturbance development from a two-dimensional flow to a TS wave. The natural laminar-flow supercritical wing section has the advantages that the development of the two-dimensional TS wave disturbance and the three-dimensional cross-flow CF wave disturbance can be simultaneously inhibited, the transition of boundary laminar flow occurring in the front edge area when the wing section is arranged on the sweepback wing can be avoided, so that a relatively large-scale natural laminar flow can still be maintained on the surface of the sweepback wing, the resistance of a whole airplane can be reduced, the cruise efficiency is increased, and the consumption of fuel oil and carbon dioxide discharging can be reduced.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
System for measuring booster noise
InactiveCN102937478AWide range of changesAccurate measurementSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFrequency spectrumDisplay device
The invention provides a system for measuring booster noise. The system comprises a turbine air inlet simulation device, a semi-anechoic room, a booster, a frequency spectrum generator, a controller and a display device, wherein the booster is communicated with an air outlet of the turbine air inlet simulation device and placed in the semi-anechoic room, the frequency spectrum generator is internally installed in the semi-anechoic room, the controller is used for controlling the turbine air inlet simulation device, and the display device is used for displaying air inlet parameters of the turbine air inlet simulation device and indoor sound decibels of the semi-anechoic room. The system for measuring the booster noise has the advantages that the turbine air inlet simulation device can set the air inlet parameters close to the turbine through the simulation of the turbine air inlet, so that the measurement is accurate; and the semi-anechoic room can eliminate external acoustic disturbance and indoors reflected noise wave disturbance, the noise spectrum measured by the frequency spectrum generator is used as the acoustic spectrum of the booster, namely, the acoustic spectrum of the booster can be independently measured, and the basis is provided for reducing the noise of the booster.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDE MASCH CO LTD
Multi-direct-current feed-in city power transmission network harmonic wave amplification characteristic analysis method
ActiveCN106340876AAccurate descriptionEase of evaluationHarmonic reduction arrangementAc network to reduce harmonics/ripplesCapacitanceHigh pressure
The invention discloses a multi-direct-current feed-in city power transmission network harmonic wave amplification characteristic analysis method. Through an established high-voltage long-cable distribution parameter model and a direct-current power-transmission droppoint harmonic wave emission frequency scope, a city power transmission network node admittance matrix is acquired. And then a harmonic wave amplification inductance and capacitance coupling relationship is decoupled so as to determine a harmonic wave amplification key modal. Based on the above condition, a node observation factor, a harmonic wave source excitation factor and sensitivity of a modal impedance to a network component parameter are calculated. In the invention, a harmonic wave amplification frequency scope of a multi-infeed city power transmission network can be accurately determined, a node which is greatly influenced by harmonic wave amplification can be accurately determined too, and an effect of each direct-current droppoint harmonic wave disturbance source can be well assessed. An idea of reducing the harmonic wave amplification through reversely adjusting a component parameter according to a component modal sensitivity is provided, which is good for searching a solution scheme of restraining the harmonic wave amplification.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANXI ELECTRIC POWER
Defrosting judgment method
ActiveCN106052021AInterfering with accurate judgmentMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsFrostTemperature difference
A defrosting judgment method comprises the following steps that a temperature difference starting point is selected, specifically, a temperature difference average value is calculated, the temperature difference variation rate is calculated, and if the sum of k1 times of temperature difference variation rates is larger than a first set threshold value or smaller than a second set threshold value, the temperature difference starting point is calculated again, otherwise whether frosting occurs or not is judged; the temperature of an evaporator and an outdoor environment temperature are continuously collected for k2 times, and if the k2 times of temperature difference variation rates exceed the temperature difference variation rate of the set proportion and are larger than a frosting judgment threshold value, whether deforesting is needed or not is judged, otherwise the temperature difference starting point is calculated again; and the temperature of the evaporator and the outdoor environment temperature are continuously collected for k3 times, and if the continuous k3 times of temperature difference variation rates are smaller than the standard temperature difference variation rate, it is considered that frost layers are accumulated thickly, a defrosting step is executed, otherwise calculation is conducted again. According to the defrosting judgment method, wave disturbance caused by changing system working states can be removed, and the defrosting condition can be judged accurately.
Owner:SHENZHEN ENVICOOL TECH
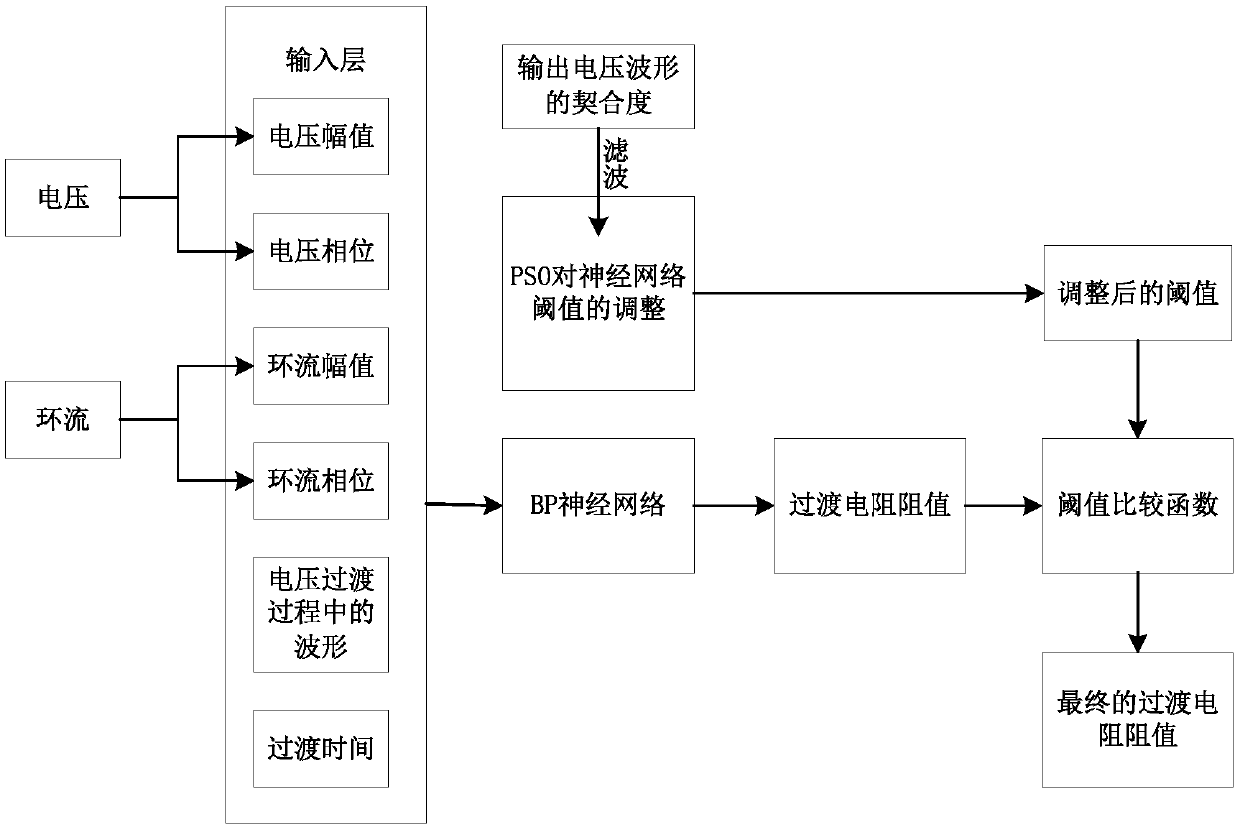
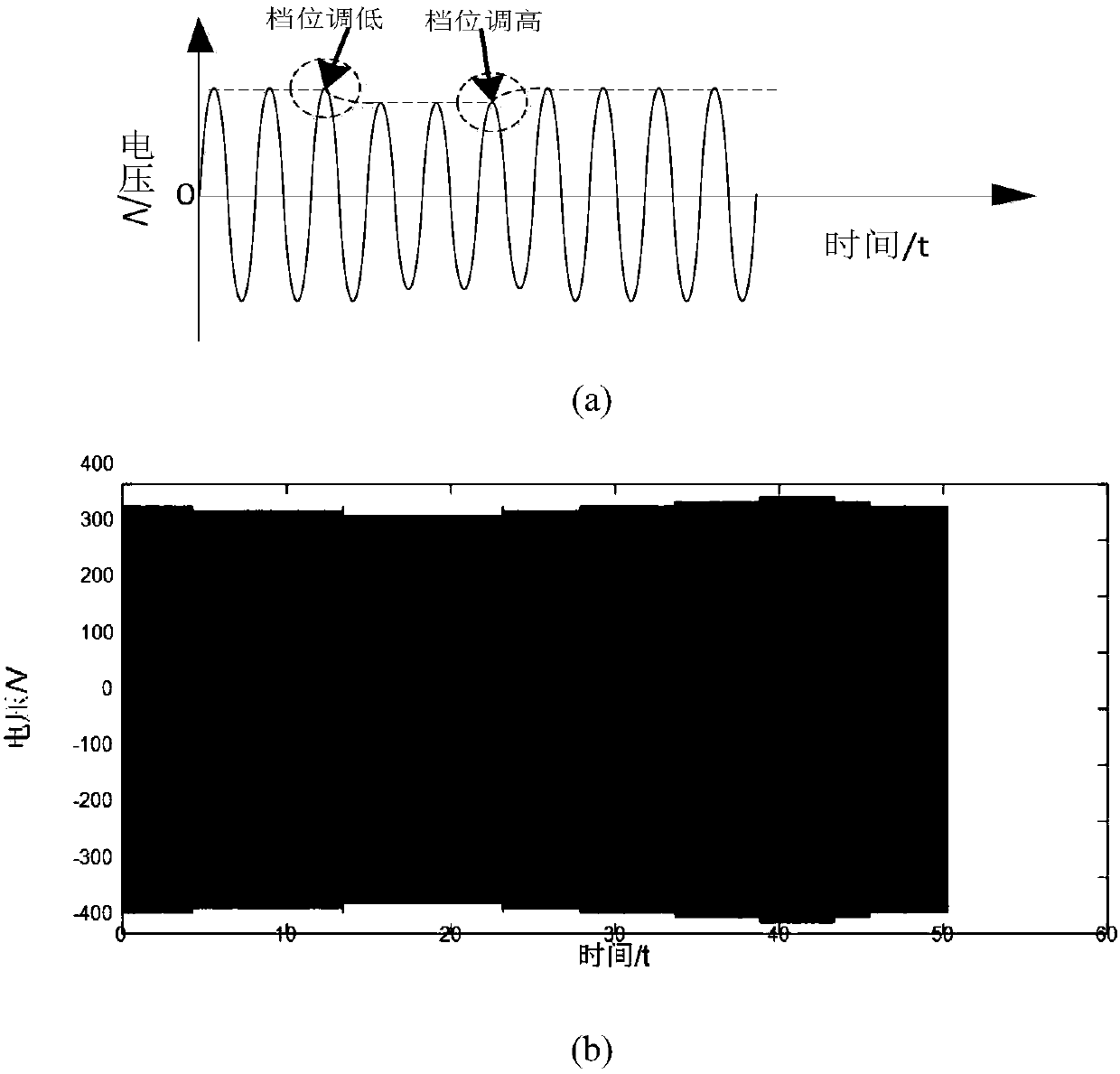
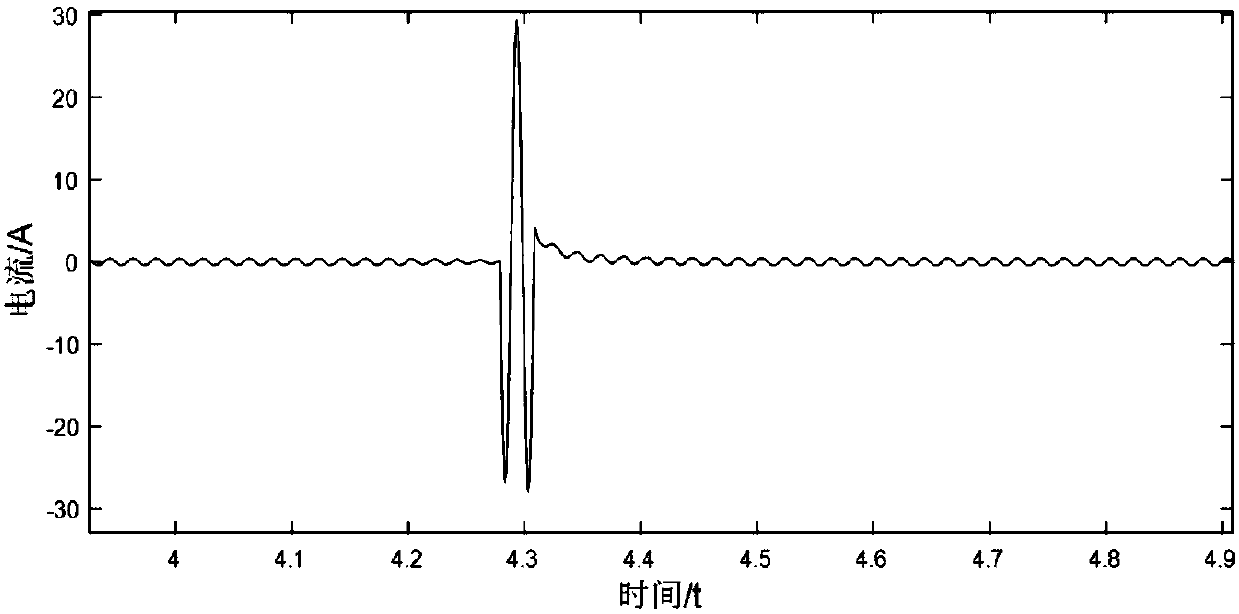
Selection method of transition resistance during automatic voltage regulation of distribution transformer
ActiveCN107681665AImprove approximationAccurate Transition Resistance ValueAc network voltage adjustmentElectrical resistance and conductanceDistribution transformer
The invention discloses a selection method of transition resistance during automatic voltage regulation of a distribution transformer. The selection method comprises the following steps: starting fromvoltage waveforms and the circulation waveform characteristics in the transition process, filtering the output voltage waveforms and then taking the filtered output voltage waveforms as input of a particle swarm PSO algorithm through BP neural network training and approaching, calculating an optimal threshold value suitable for a BP neural network, then comparing the resistance value of the transition resistance calculated by the neural network with the optimal threshold value by using a threshold value comparison function, and if a BP threshold value selection function is met, outputting a final transition resistance value after repeated calculation. According to the selection method, simulating calculation is carried out on the transition resistance of the distribution transformer system by using the particle swarm PSO algorithm and a BP neural network algorithm, the resistance value of the transition resistance can be solved simply and effectively, and the method is more reliable compared with a manner that the resistance value of the transition resistance is obtained through experience, so that the value of the transition resistance is more scientific, the output voltage of the distribution transformer is stabler, the wave disturbance on a power grid is smaller, and little harmonic pollution is also caused.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
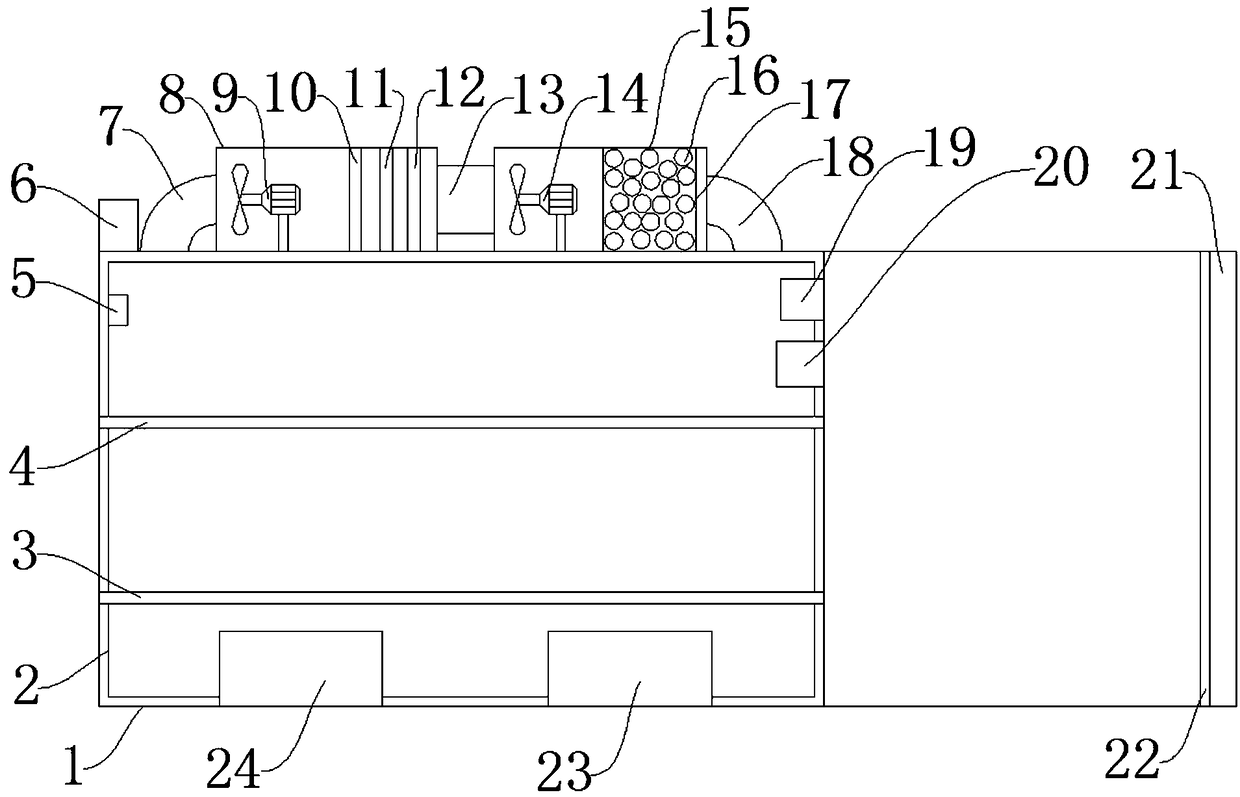
Dustless storage device for communication equipment and application method thereof
InactiveCN109319305AAvoid damageExtended service lifePackaging vehiclesContainers for machinesAir purifiersElectric machine
The invention discloses a dustless storage device for communication equipment and an application method thereof. The device comprises a box body, an air purifier and a dehumidifier; a controller is arranged on one side above the box body; a first connecting pipe is arranged on the side, far from the controller, above the box body; the air purifier is arranged on the side, far from the controller,of the first connecting pipe; a first fan is arranged on the side, near the first connecting pipe, in the air purifier; the first fan comprises blades, a motor and a support rod; and the motor is arranged above the support rod. The device has the following beneficial effects: dust particles in air can be thoroughly removed through the air purifier; a dehumidifier can be provided for dehumidifyingthe air to prevent damage of the communication equipment due to moisture; an electromagnetic wave shielding paint layer is provided for preventing damage caused by electromagnetic wave disturbance; and a heater and a semiconductor refrigerator are provided for guaranteeing a proper storage temperature to prolong the service life of the communication equipment.
Owner:芜湖市传世信息技术有限公司
Coaxial resonant microwave discharge plasma large-scale high-efficiency combustion-supporting device
PendingCN109310003AEmission reductionAdjustable temperatureCombustion apparatusPlasma techniqueHigh energyPulse microwave
The invention discloses a coaxial resonant microwave discharge plasma large-scale high-efficiency combustion-supporting device in the technical field of coaxial resonant microwave discharge plasma large-scale high-efficiency combustion supporting. The device includes a pulse microwave generator, a power display and a plasma generator; and the pulse microwave generator includes a microwave signal generator, a pulse modulation generator and a power amplifier. Through the utilization of microwave pulse resonance as a discharge driver, the tip of the tungsten filament of a U-shaped tungsten filament electrode can generate a locally enhanced electric field, so that gas discharge can be generated, plasma can be generated, particles having chemical activity can be massively generated, and the plasma and the combustion state in adjacent areas of the plasma can be changed; and gas turbulence levels can be enhanced by the wave disturbance formed by the diffusion of high-energy particles, so thatthe atomization, gasification and the mixing with air of fuel oil can be promoted, the contact area of flame front and fuel can be increased, and therefore, the purposes of enhancing combustion stability, rising combustion efficiency and reducing exhaust pollution can be achieved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Remote control decoding and fault tolerance method
ActiveCN101193194AImprove reliabilityAvoid misuseTelevision system detailsNon-electrical signal transmission systemsKey pressingRemote control
The invention discloses a remote control decoding fault-tolerance method. When the received remote control key-pressing code is a repeated key-pressing code, a tolerance value is given. When the code error rate of the remote control decoding is lower than the tolerance value, the key-pressing value with code error is set as the key-pressing value corresponding to the last key-pressing. When the code error rate of the remote control decoding is higher than the tolerance value, the key-pressing value with code error is set as the key-pressing value corresponding to no operation of key-pressing. Thus false action of the TV set can be prevented. In the invention, the fault-tolerance design is added to the remote control decoding software, namely, certain tolerance for code error is provided. When the code error rate is lower than the tolerance value, the key-pressing is considered as repeated; when the code error rate is higher than the tolerance value, no key-pressing is believed to occur until the key is released. The tolerance value is determined according to the light or electromagnetic wave disturbance degree in the environment, thus the remote control reliability of the TV set is effectively improved and false action of the TV set is prevented, which is good for promoting the whole quality of the TV set.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
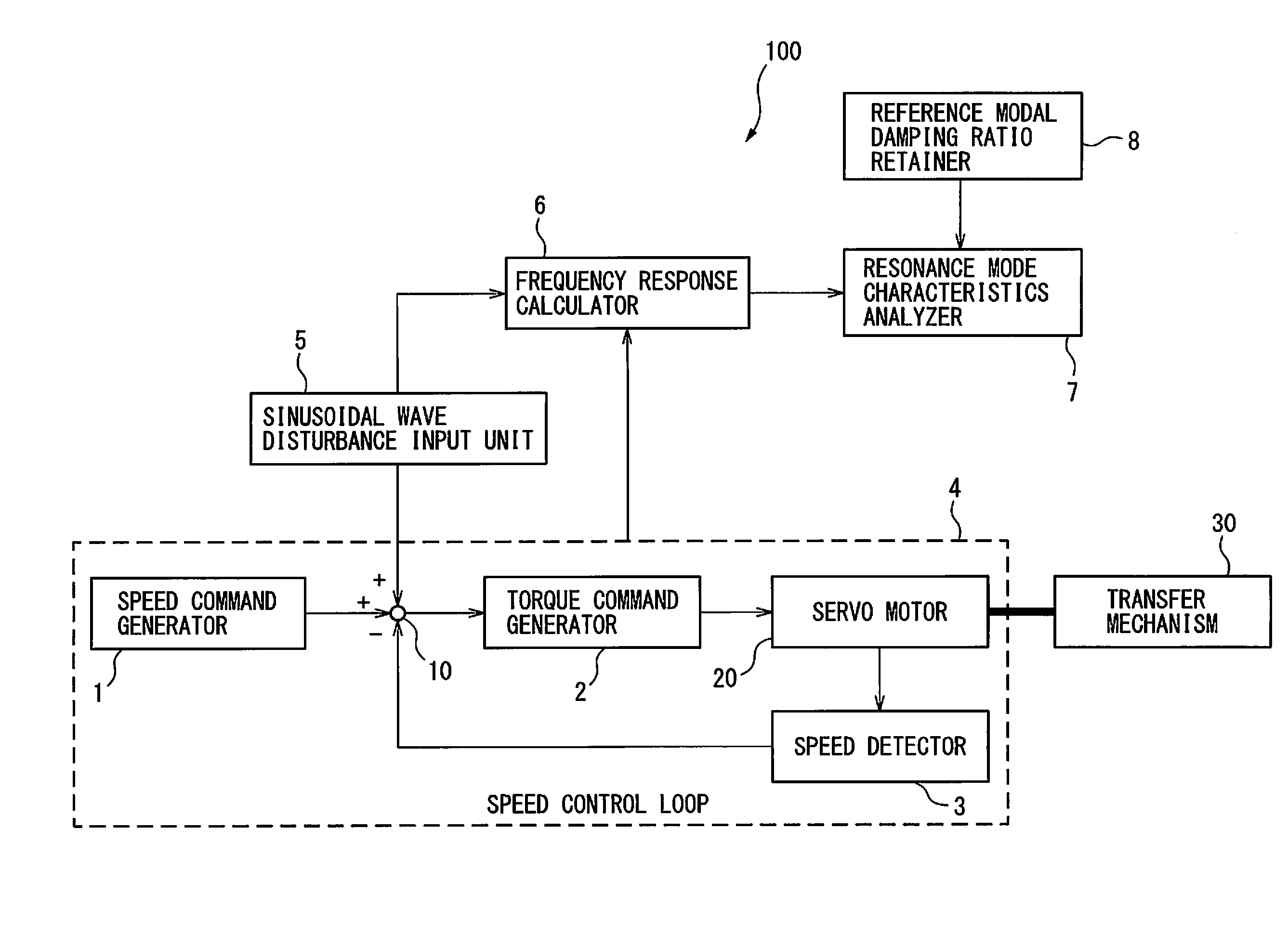
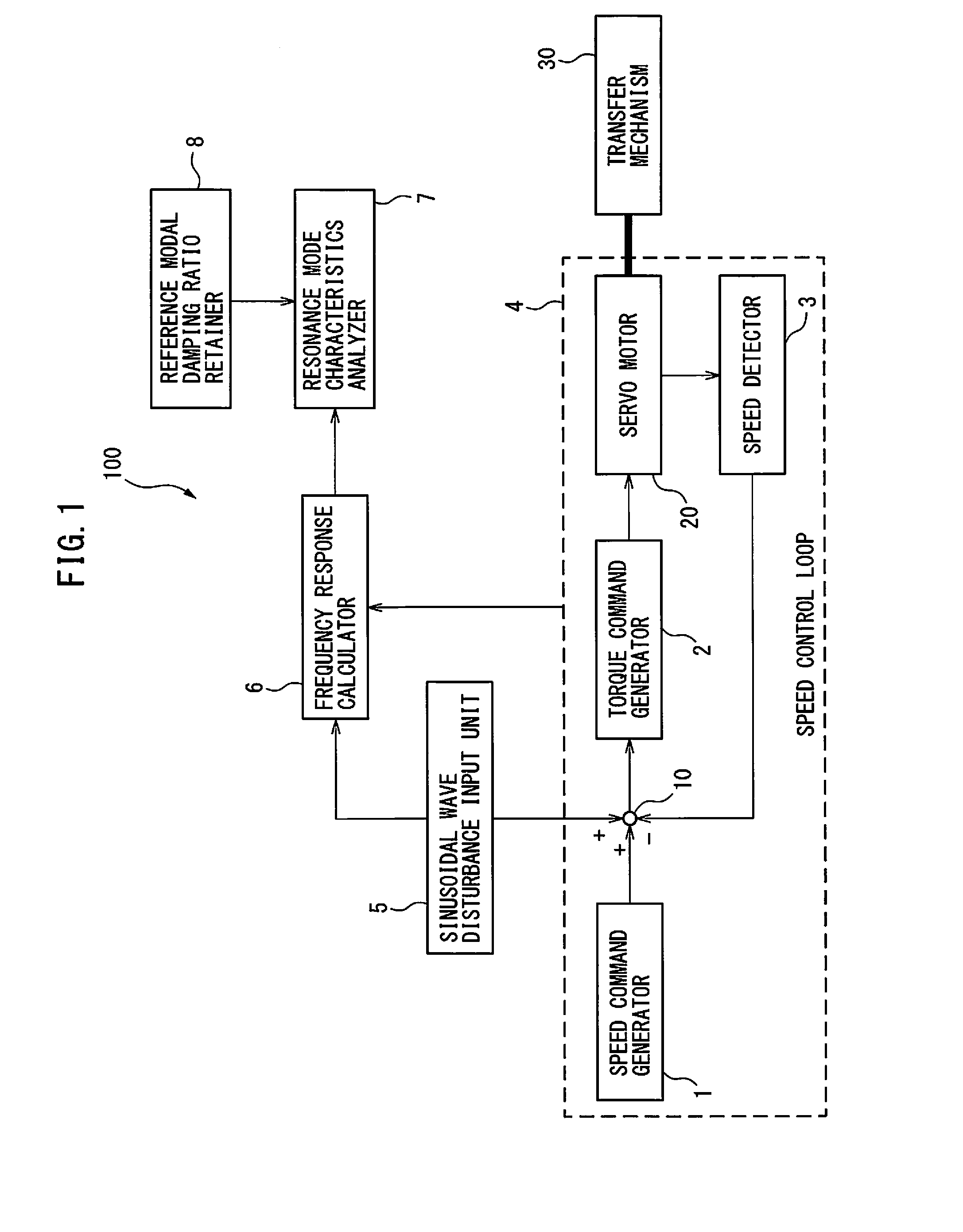
Servo controller for measuring lubrication characteristics of a machine by experimental modal analysis
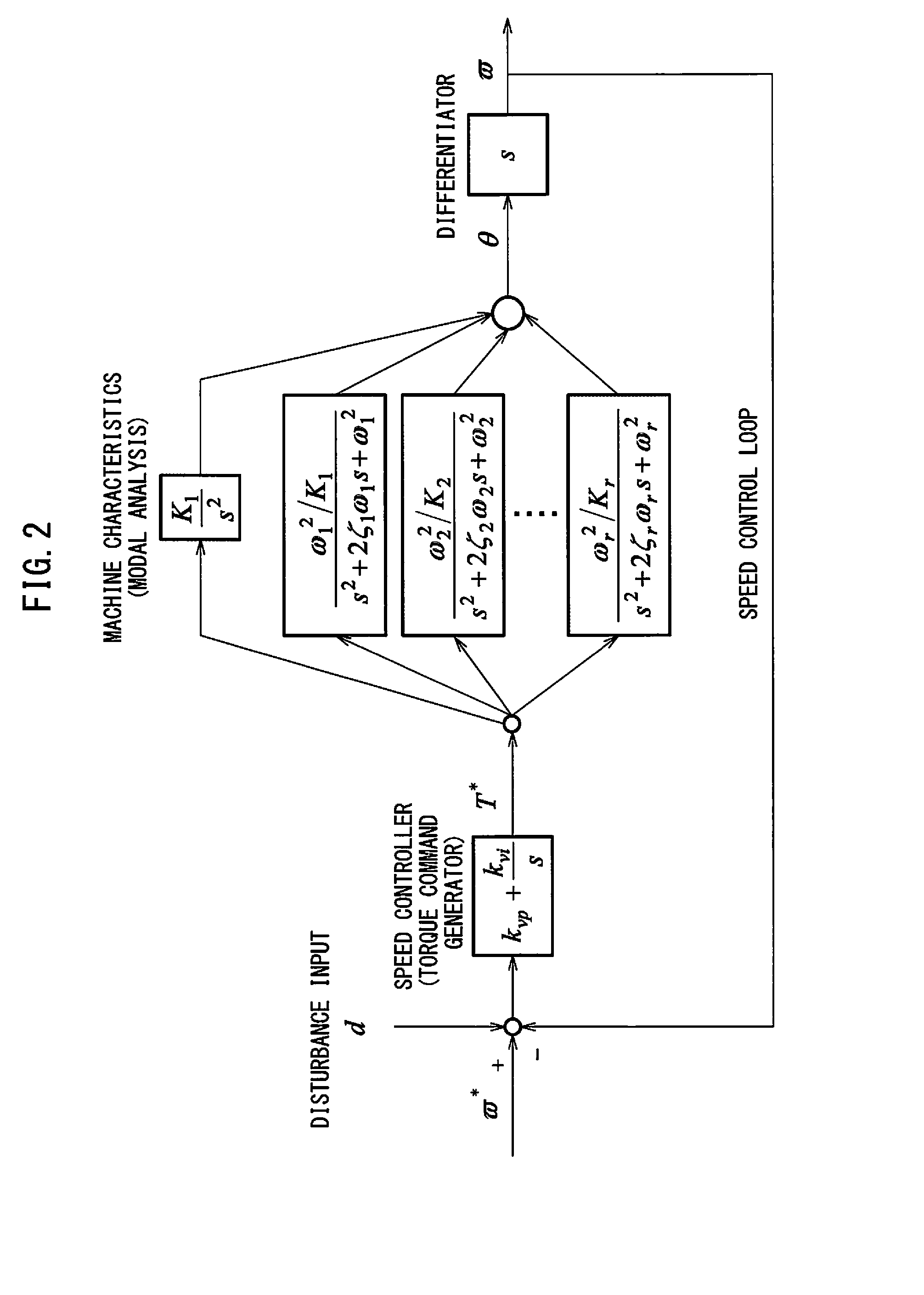
A servo controller includes: a sinusoidal wave disturbance input unit for supplying a sinusoidal wave disturbance to a speed control loop including a speed command generator, a torque command generator and a speed detector; a frequency response calculator for estimating the gain and phase from the output of the speed control loop; a resonance frequency detector for detecting resonance frequencies at which the gain becomes maximum; a resonance mode characteristics analyzer for estimating resonance characteristics from the frequency response; and, a reference modal damping ratio retainer for retaining a reference modal damping ratio as a resonance characteristic corresponding to the reference lubricating condition, and the resonance mode characteristics analyzer calculates lubrication characteristics on the basis of the reference modal damping ratio and the measured modal damping ratio at the resonance frequency corresponding to the reference modal damping ratio.
Owner:FANUC CORP
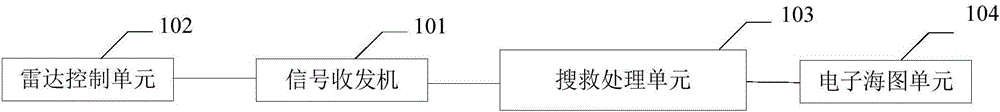
Maritime peril target search system and method based on marine radar
InactiveCN106199598AImplement searchImprove search and rescue capabilitiesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverRandom noise
The invention provides a maritime peril target search system and method based on marine radar. The system comprises a signal transceiver, a radar control unit, a search and rescue processing unit and an electronic chart unit; the signal transceiver is used for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves and echo signals of the electromagnetic waves; the electronic chart unit is used for providing sea surface geographic coordinates; the search and rescue processing unit is used for converting the electromagnetic spectrum echo signals received by the signal transceiver into digital signals, the digital signals are subjected to filter processing, random noise and wave disturbance from the surroundings are removed, data obtained after filtering is subjected to image processing, and the processed image is subjected to feature extraction, target recognition and classification. Through the maritime peril target search system and method, the ability in searching and rescuing peril targets on the sea surface of deep and far sea can be improved.
Owner:天威英利
Apparatus for reducing electromagnetic wave interference and method thereof
InactiveCN1567989AReduce distractionsTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesElectromagnetic interferenceWave disturbance
The invention is a device and method for decreasing electromagnetic wave disturbance. The invention generates frequency-expanded pulse according to original pulse, and receives the data bit stream according to original pulse, and outputs data bit stream according to frequency expanded pulse. The invention includes: frequency expanded buffer, which is used to store data bit stream temporarily; frequency generator, which generates frequency expanding pulse according to the frequency rising signal and the frequency decreasing signal; frequency expanding controller, which is used to decide the frequency rising signal and the frequency decreasing signal according to the storage of the frequency expanding buffer.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Jam-proof intelligent valve positioner
ActiveCN106763977AAnti-gas source fluctuation interferenceWith anti-vibration interferenceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPower flowControl signal
The invention discloses a jam-proof intelligent valve positioner which comprises an electric pneumatic converter, a circuit control component and a displacement detection feedback unit, wherein the electric pneumatic converter comprises a pneumatic amplifier, a nozzle arranged at the backpressure opening of the pneumatic amplifier, a baffle covering the nozzle and an electromagnetic drive mechanism for driving the baffle to control the cover degree of the baffle and the nozzle; the electromagnetic drive mechanism is controlled by a current control signal emitted from the circuit control component; a micro pressure reduction valuator is arranged at the air inlet of the pneumatic amplifier; the micro pressure reduction valuator comprises a constant throttling screw, a pressure relief spring sleeving the constant throttling screw and a sealing ring; the constant throttling screw is matched with a constant throttling orifice formed in the pneumatic amplifier. The jam-proof intelligent valve positioner provided by the invention has the characteristics of resisting air source wave disturbance and vibrating disturbance and preventing electromagnetic interference, is stable and reliable in property and beneficial to marketing promotion, and can effectively ensure the reliability and positioning stability in complex disturbance conditions.
Owner:博流控制技术(浙江)有限公司
Hybrid multilayer circuit board and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN1960597AImprove flexibilityMagnetic/electric field screeningMultilayer circuit manufactureElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
The present inveniton provides a hybrid multilayer circuit board and a manufacture method thereof to further enhance a bending property of a cable when a conductive layer is formed in an outside of a hybrid multilayer circuit board which extends at least one cable from a multilayer mounting part obtained by laminating an outer layer material on a circuit board serving as an inner layer and a shield layer is formed for electromagnetic wave disturbance. In the hybrid multilayer circuit board, at least one cable (b) extends from a layer except an outermost layer in a multilayer mounting part (a). The hybrid multilayer circuit board contains a shield layer for electromagnetic interference in an outside, and the shield layer (4) is arranged to have an opening gap between the shield layer and the cable at a location corresponding to the cable in the outermost layer. The hybrid multilayer circuit board has: 1) a base film (11) shared with a circuit layer of the outermost layer in the part mounting part; 2) a conductive layer 12 formed on the base film; and (3) a cover layer 13 for insulating and protecting the conductive layer.
Owner:NIPPON MEKTRON LTD
Packing component for decreasing electromagnetic-wave disturbance
ActiveCN101030569ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesShadowingsElectrical conductor
The invention is concerned with encapsulation component to reduce the disturb of electromagnetic wave, relating to base plant, shadowing structure and insulating-layer under the base plant one by one, and there is crossing-hole filled with conductor to guide the base plant and shadowing structure. Some lead frame with leading foot set on the base plant, and the second base plant is at front of two lead frames. Some the first components set on lead frame, the second component set on front of the second base plant, and the said components connect with each other by lead. The local base plant, the first and the second component and local lead frame are airproofed with molding compound, thus the encapsulation component releases electromagnetic wave / radio frequency to the outside of encapsulation component to reduce interfering to other components in the system, through lead frame, conductor inside of base plant, shadowing structure and grounding end.
Owner:CYNTEC
Improved structure of circuit anti-interference device
InactiveCN1414824AThe production process is simpleIncrease productivityMagnetic/electric field screeningPrinted circuit manufactureFit frequencyInterference resistance
A structural improvement for antidisturbance device of line uses a number of frame lines to form a number of frequency domain zone blocks according to the requirement by dividing in the design to seteach related circuit element belonging to oscillation source to the fitted frequency domain zone block as per the magnitude of the frequency so that the copper frame body independent to each other being formed on the circuit board by using frequency domain zone blocks divided in advance after the surface being processed with catching. The effective isolation of external impurity message and internal disturbance to each other can be realized by using the copper line frame body to lead the individual / message to the ground end so as to prevent the mixed wave disturbance to each other from oscillation source in different property frequency.
Owner:CAMEO COMM
Pumping energy storage model test downstream water tank for simulating wave water level fluctuations
ActiveCN109830168AVerify operational stabilityHydrodynamic testingEducational modelsEngineeringWater level fluctuation
The invention discloses a pumping energy storage model test downstream water tank for simulating wave water level fluctuations. The water tank comprises a traction control system, a flow control system, a water tank main body, an overflow pipeline and a walking corridor. The traction control system consists of a motor support frame, a telescopic device, a PLC controller, a signal line, a flat water tank, a roller, a guide rail and a telescopic bellow. The flow control system consists of the PLC controller, a water pump, a hydration flow regulating valve, a drain flow regulating valve, a hydration drain pipe and a circulating water channel. During the model test, the PLC controller controls the telescopic device to drive the flat water tank to move up and down by a stroke signal so that thewater level of the downstream water tank can conduct sinusoidal fluctuations and random fluctuations with the flat water tank. The water tank is applicable to a seawater pumping energy storage modelpower station and a conventional model pumping energy storage power station with a large water level variation, and performs model test researches of transition processes of large fluctuations, smallfluctuations, hydraulic disturbances and the like and other related problems in a wave disturbance environment.
Owner:SOUTHERN POWER GRID PEAK LOAD & FREQUENCY REGULATION GENERATING CO LTD +2
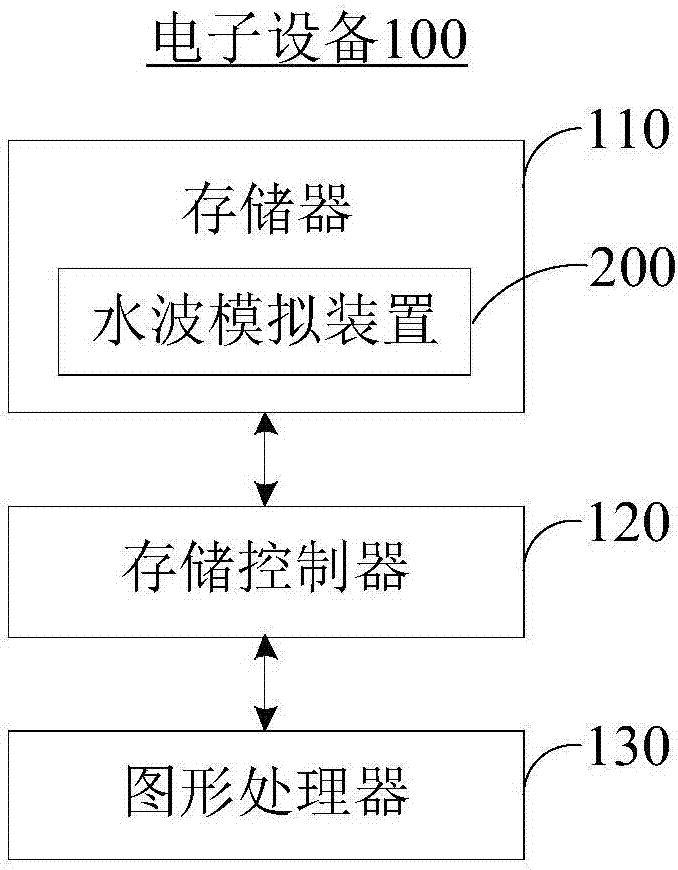
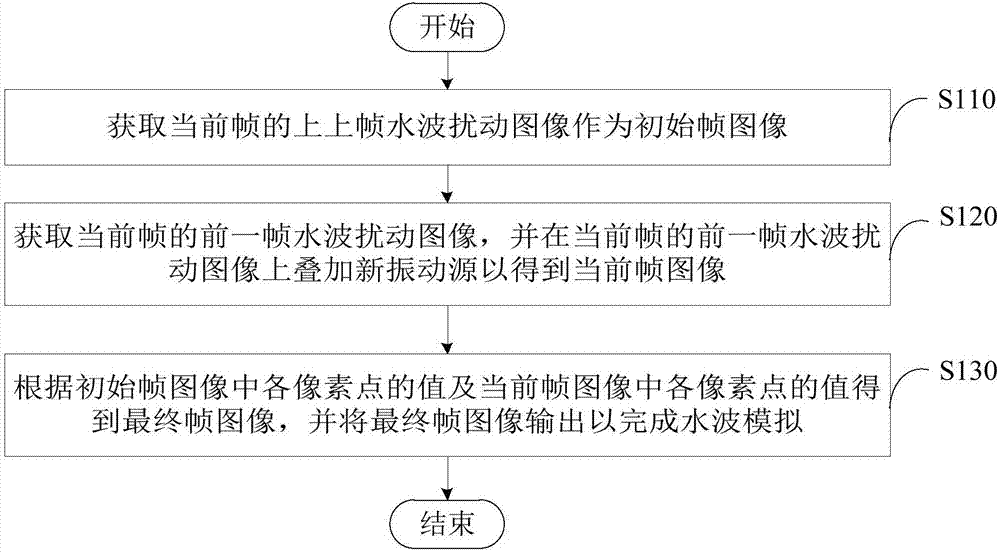
Water wave simulation method and device
The invention provides a water wave simulation method and device. The method applied to a graphics processor of an electronic device comprises: a previous frame before last of the current frame of water wave disturbance image is obtained and the obtained image is used as an initial frame image; a previous frame of the current frame of water wave disturbance image is obtained and a new vibration source is superposed on the previous frame of the current frame of water wave disturbance image to obtain a current frame of image; and a final frame of image is obtained based on values of all pixel points in the initial frame of image and values of all pixel points in the current frame of image and the final frame of image is outputted to complete water wave simulation. With the method provided bythe invention, a water wave can be simulated by a graphic processor vividly and efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING PIXEL SOFTWARE TECH
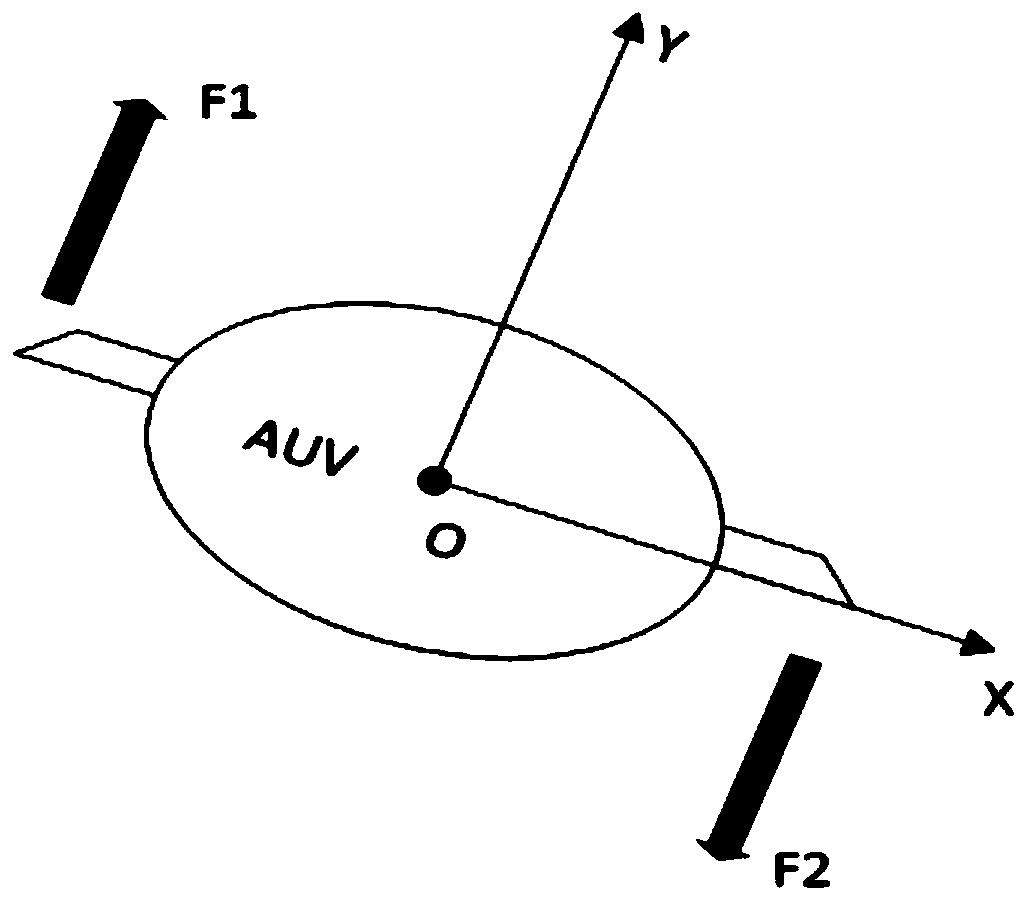
Design method of variable-structure integrated controller for reducing rolling and pitching of AUV
ActiveCN110456809AGood for attitude controlTo achieve the effect of comprehensive anti-rollingAttitude controlLow speedFin stabilizer
The invention belongs to the field of autonomous underwater vehicle navigation control, and particularly relates to a design method of a variable-structure integrated controller for reducing rolling and pitching of an AUV. A hydroplane based on a working principle of a zero-speed fin stabilizer can be used for actively reducing rolling and pitching motions during low-speed navigation. In consideration of six-degree-of-freedom nonlinear and coupling motions of the AUV and the working principle of the hydroplane, an improved variable-structure controller is designed, so that the approaching speed of an approaching process in sliding mode control is further improved, and the buffeting phenomenon of a sliding mode control system is eliminated; and the rolling and pitching interferences under different wave disturbances can be greatly reduced through the improved sliding mode integrated controller. By analyzing a simulation result, the rolling and pitching motions of the AUV can be effectively reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Shock wave enhancement method for shock tube
ActiveCN106777700AHigh strengthSimple analytical formulaGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationWave disturbanceMoving shock
The invention discloses a shock wave enhancement method for a shock tube, and belongs to the field of fluid mechanics. The shock wave enhancement method includes the steps: performing perfect gas equivalent assumption for the enthalpy value of shocked gas to obtain a moving shock wave basic relation after high-temperature gas effect modification; acquiring the shock dynamics theory after high-temperature gas effect modification according to the moving shock wave basic relation after high-temperature gas effect modification; designing a wall surface contraction line of a contraction section of the shock tube according to the shock dynamics theory after high-temperature gas effect modification, and enhancing shock waves by the shock tube with the wall surface contraction line contraction section. The wall surface contraction line after high-temperature gas effect modification is designed, incident plane shock waves with low strength can be continuously enhanced in a contraction duct and finally enter a straight duct with a small section for propagation in a plane form, and planar shock waves with higher strength and without obvious post-wave disturbance are obtained.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel non-destructive testing method for bridge pile foundation
InactiveCN109403395AWithout compromising qualityDoes not damage the structureFoundation testingNon destructiveEngineering
The invention discloses a novel non-destructive testing method for a bridge pile foundation and belongs to the field of bridge pile foundation detection. When analyzing the pile foundation detection data, the pile foundation defect is judged by the average of the health time and twice the standard deviation. According to the half value of the amplitude mean M, whether a lesion occurs in the pile foundation or not is determined. If the pile foundation stress wave changes the peak size and the peak appearance time, the bridge pile foundation may have different degrees of cracks or gaps. If a crack occurs inside the pile foundation, the stress wave propagation characteristics at the crack should be correspondingly changed, so that the reflected wave disturbance may occur. Non-destructive detection will not damage the quality and structure of the pile, especially when detecting the integrity of the bridge pile foundation, and the detection can be used to maximize efficiency. The stress wave method is theoretically mature and can accurately analyze the integrity of the pile foundation.
Owner:TONGREN UNIV
Sealed pneumatic wave energy storage device and power generation device
InactiveCN106321340AExtend working lifeImprove reliabilityMachines/enginesEngine componentsTerrainEngineering
The invention discloses a sealed pneumatic wave energy storage device. The sealed pneumatic wave energy storage device comprises a sealed floater, an anchor chain and an anchor, wherein an inner cavity of the floater comprises an energy storage cavity and an equipment cavity which are sealed and isolated from each other from top to bottom; a main spring, an auxiliary spring, a heavy object and air pumping devices are mounted in the equipment cavity; the heavy object is suspended in the central position of the equipment cavity through the main spring; a plurality of air pumping devices are uniformly articulated between the heavy object and the inner wall of the equipment cavity by taking a vertical central axis of the equipment cavity as a symmetric axis; the air pumping devices are driven by up-and-down vibration motion, left-and-right vibration motion and front-and-back vibration motion of the heavy object under wave disturbance, so that compressed air is continuously pumped into the energy storage cavity and is stored. The invention also discloses a sealed pneumatic wave energy power generation device. The sealed pneumatic wave energy storage device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the motion components are not in contact with seawater, the corrosion resistance is high, the device is conveniently mount and put on the site, and the device can be adapted to any wave direction, tide level, terrain and sea condition.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com