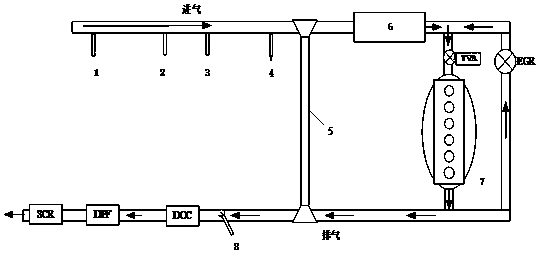
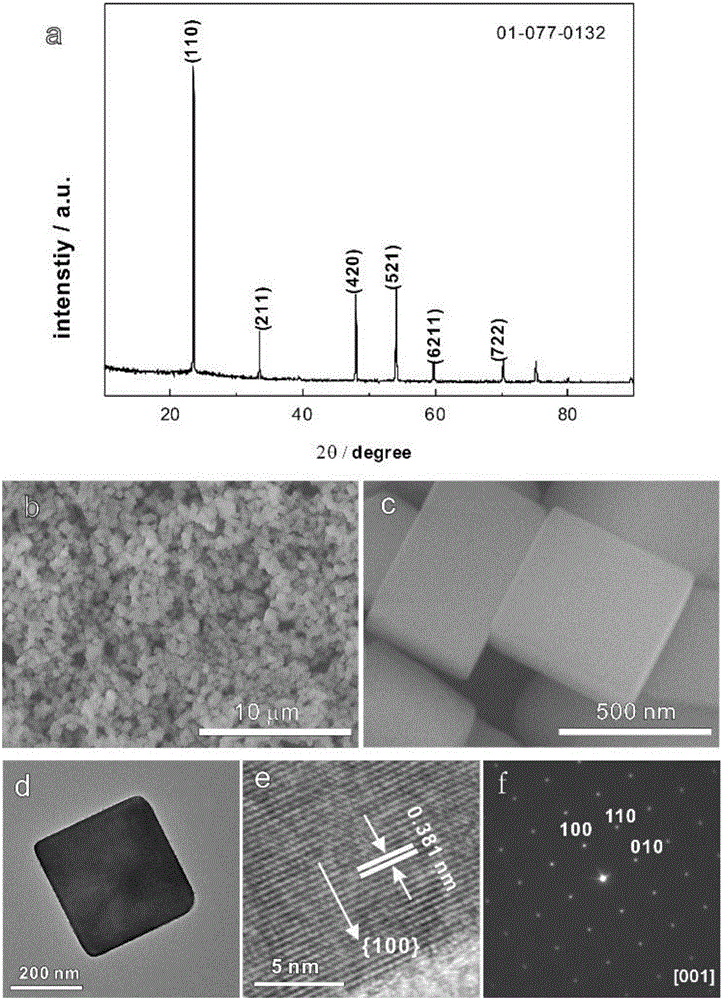
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "Urea decomposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
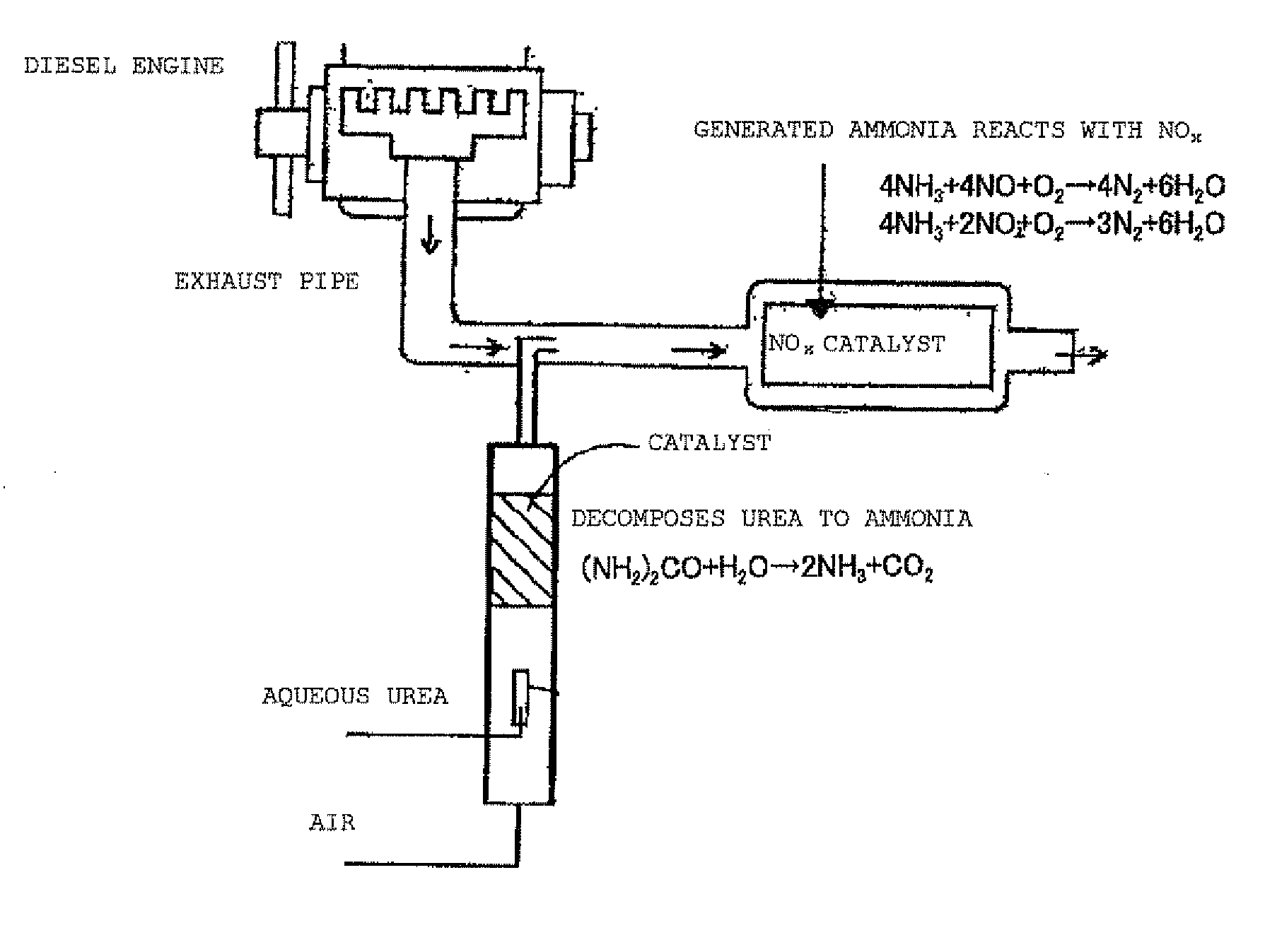
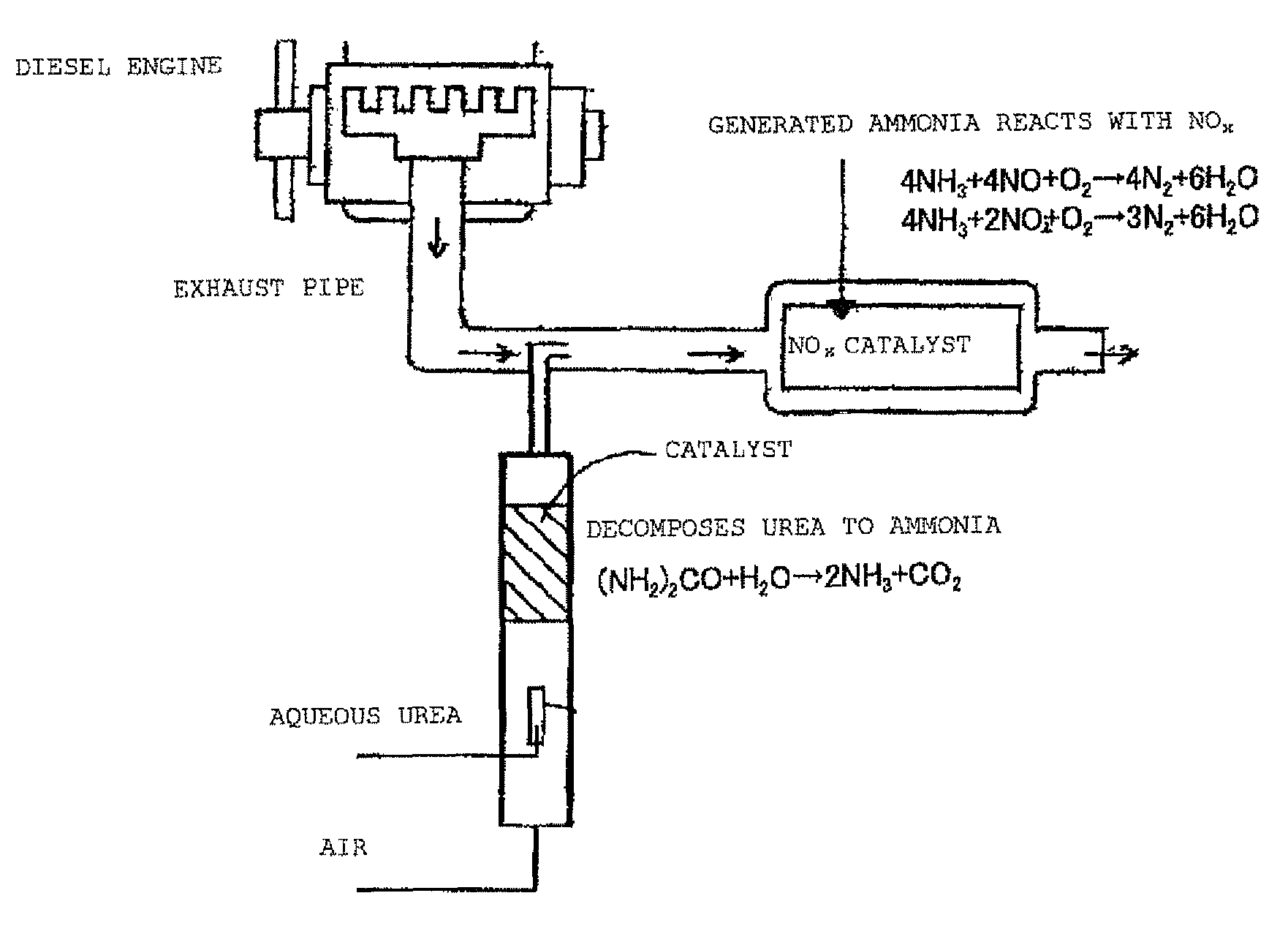
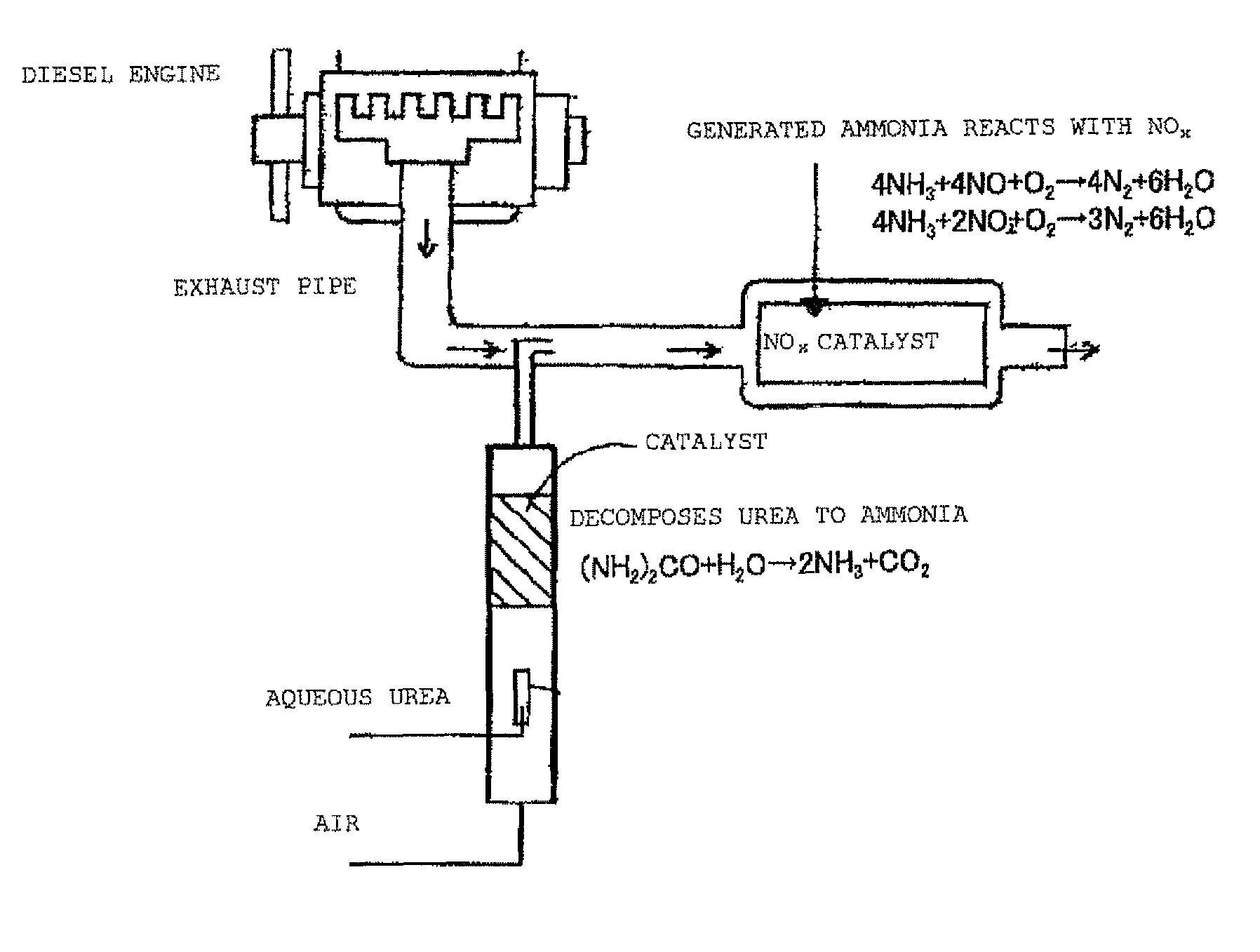
Urea is a stable product that some animals produce as a nitrogenous waste product. However, it can also be decomposed when a suitable catalyst and thermal condition is applied. In a scientific paper published on Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research[1], authors have mentioned that urea decomposes into NH3 and HNCO.
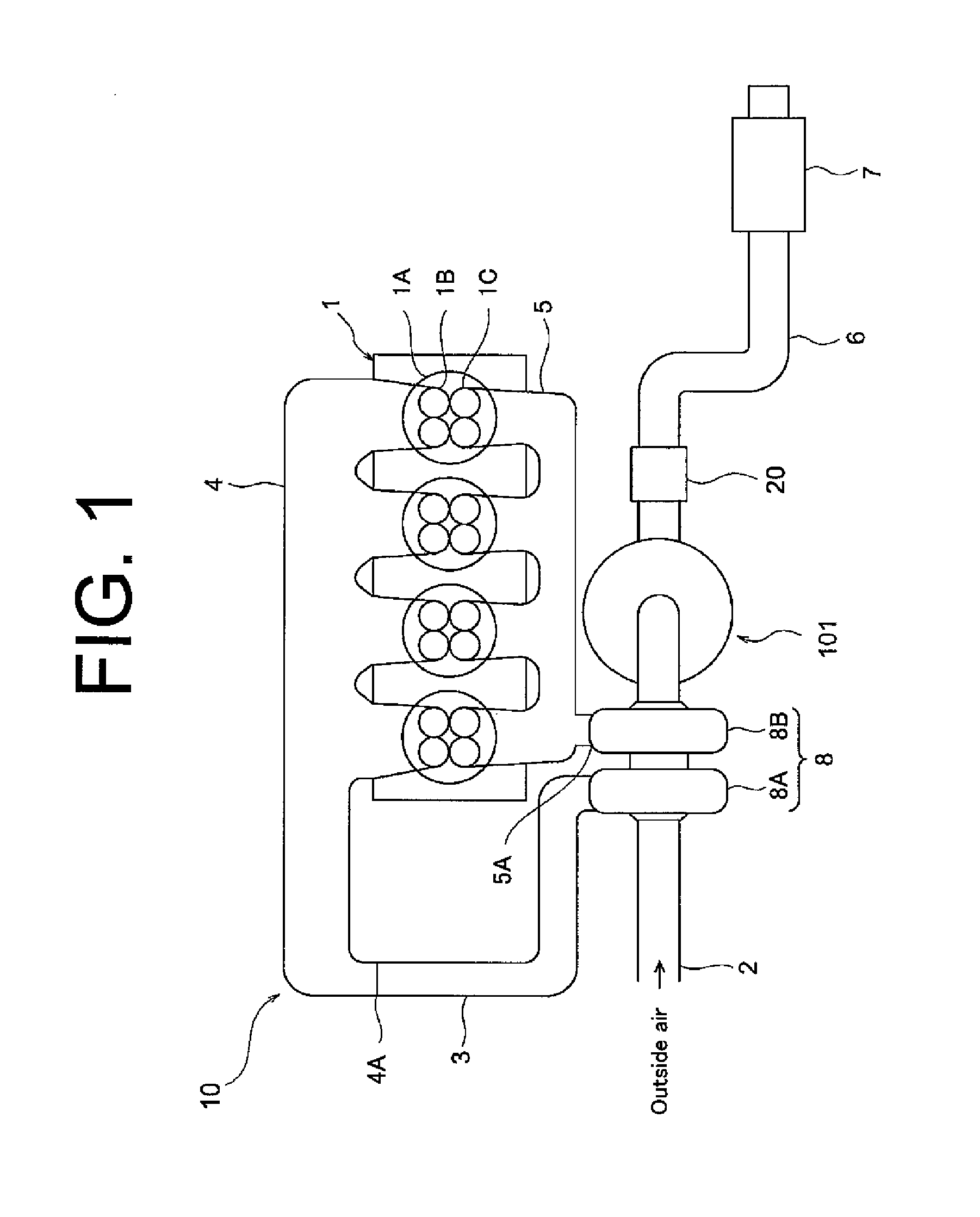
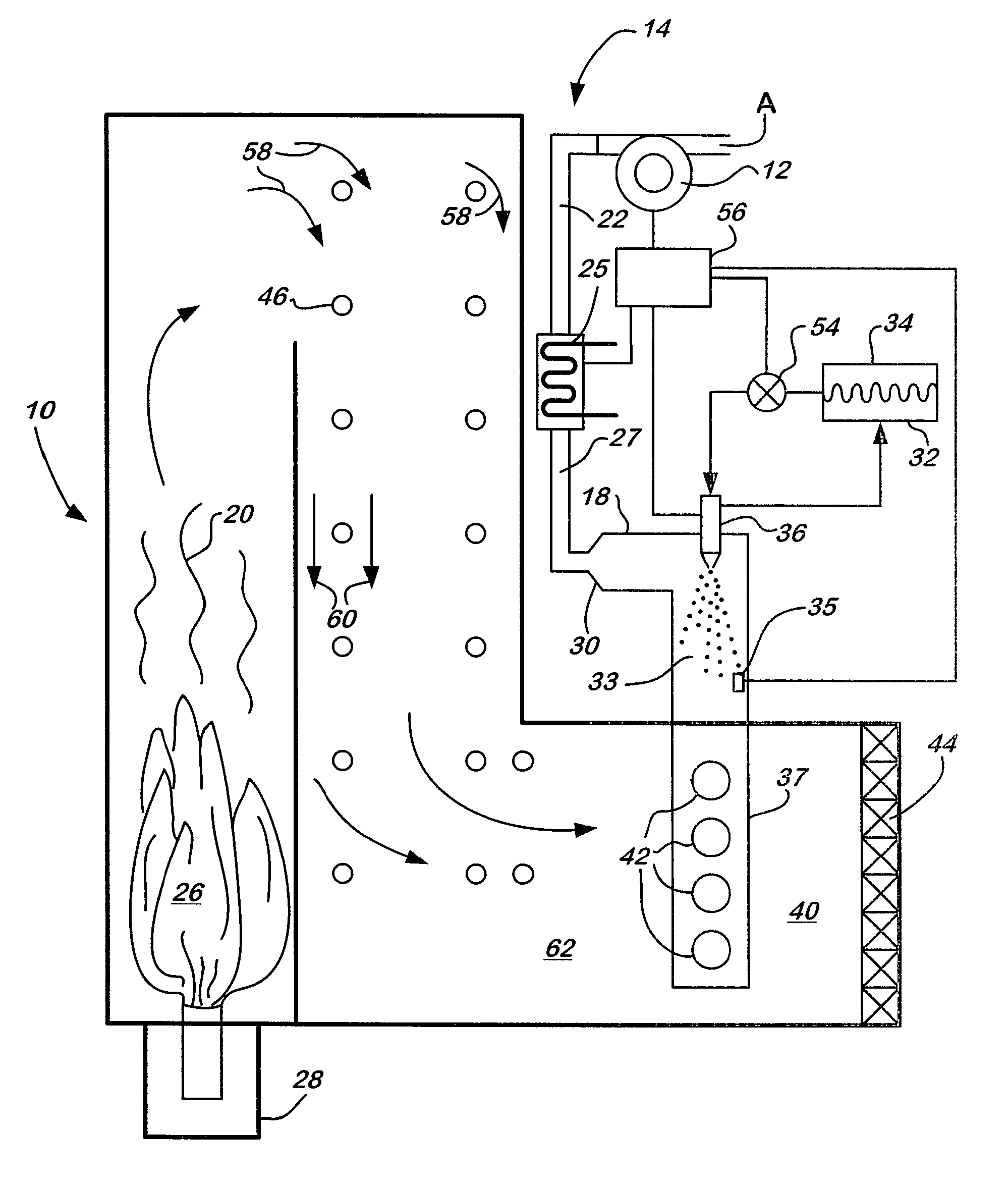
Selective catalytic reduction of nox enabled by sidestream urea decomposition
InactiveUS7090810B2Well mixedAccurate temperatureNitrogen compoundsInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesSuperheater
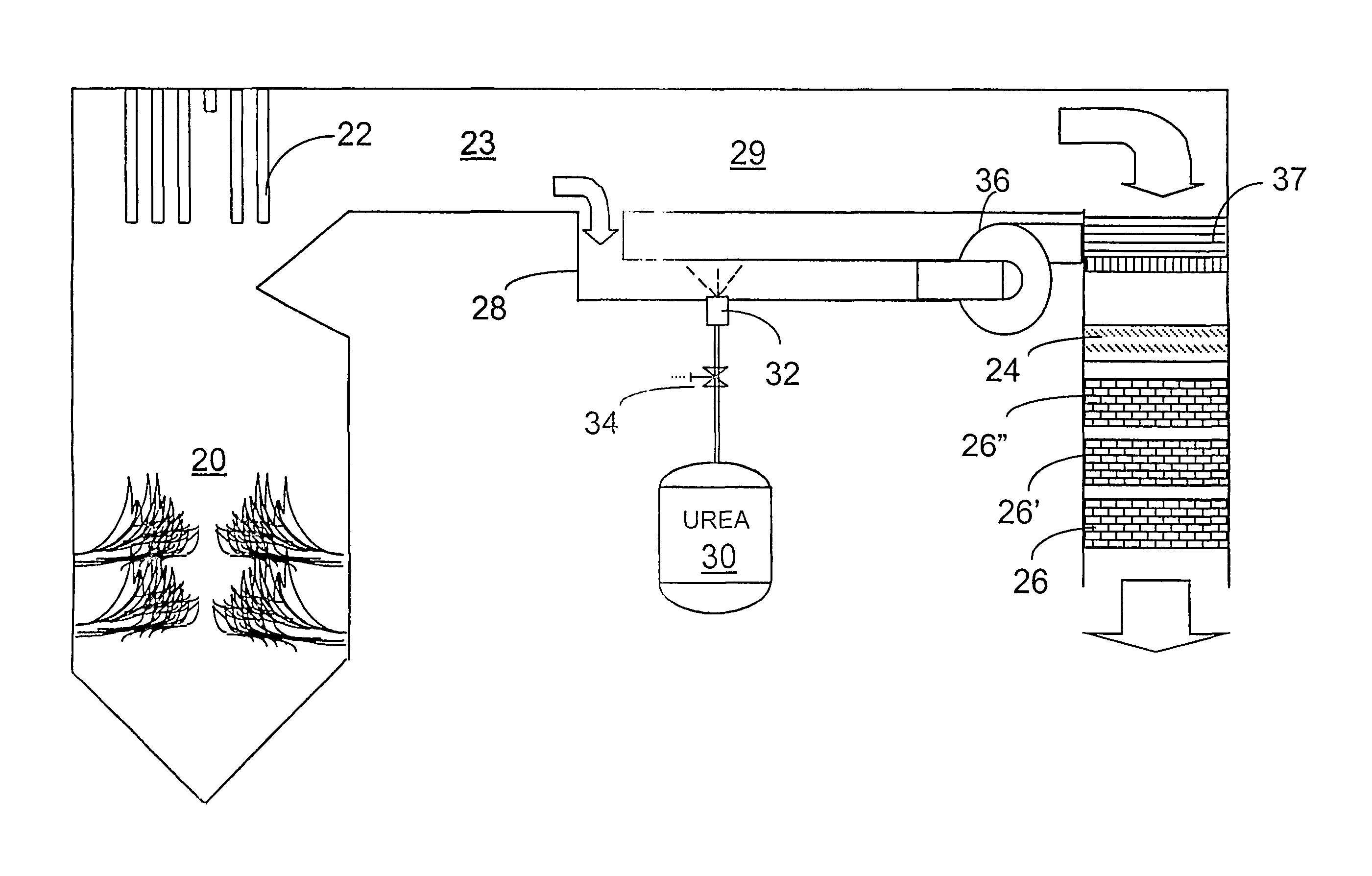
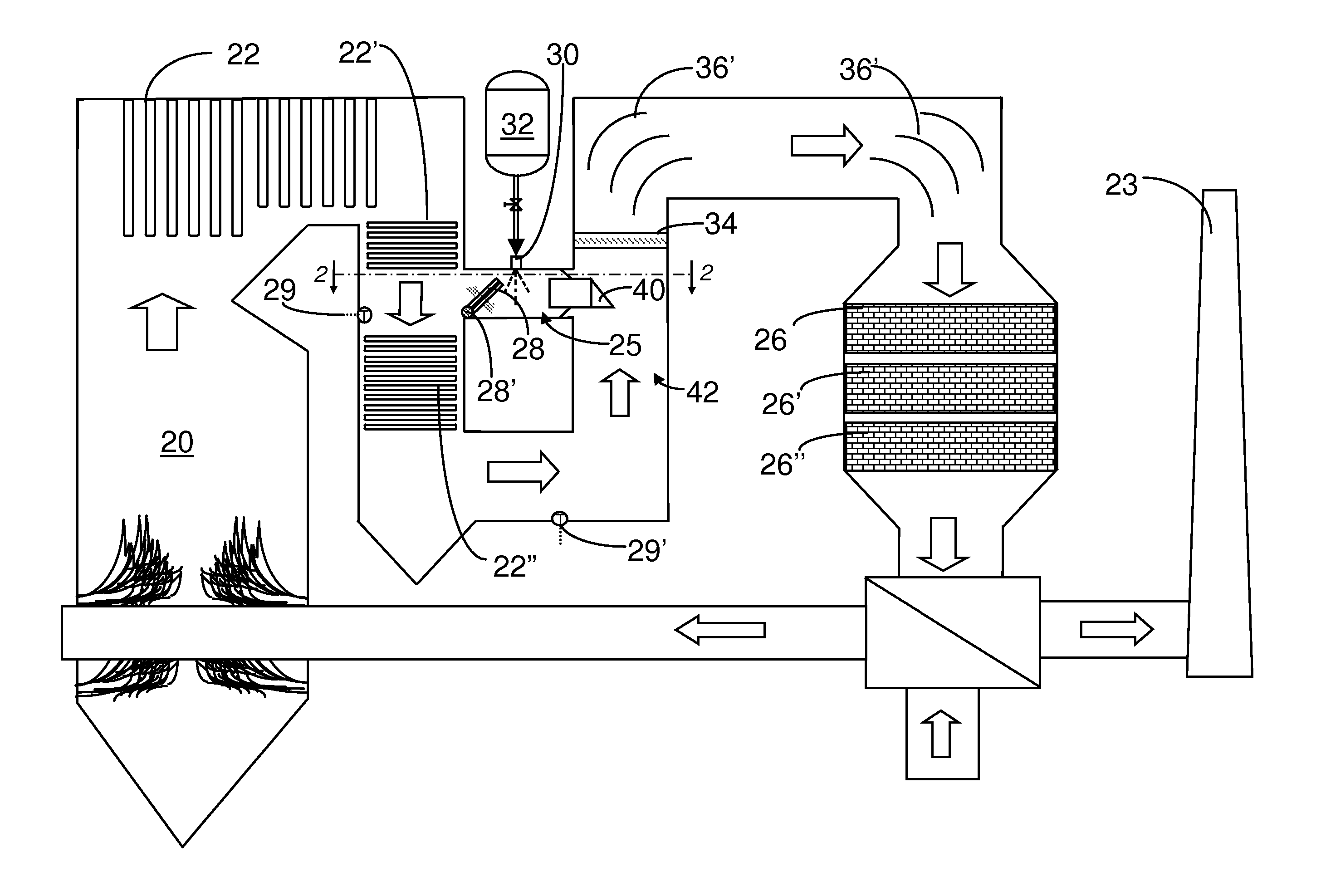
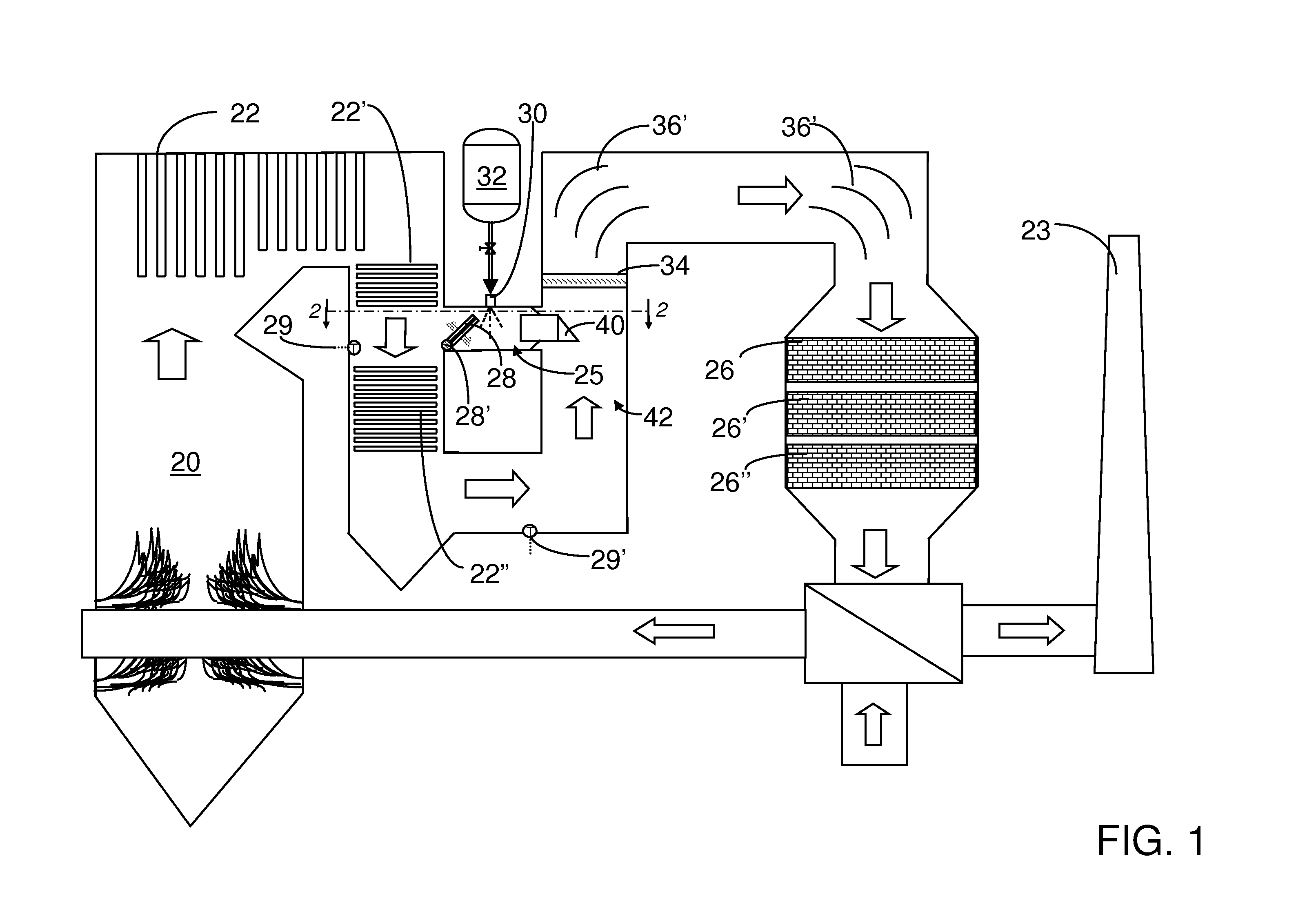
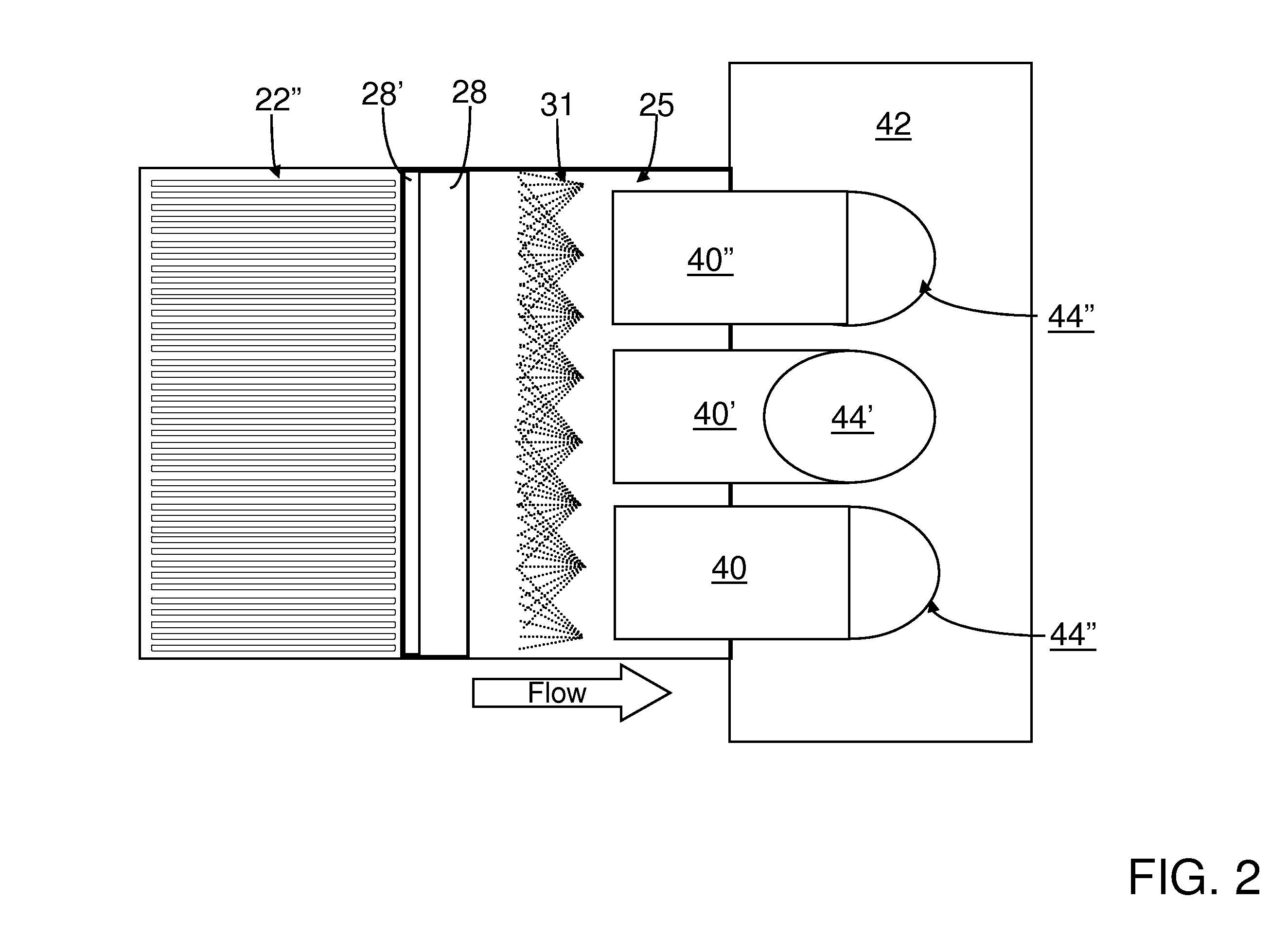
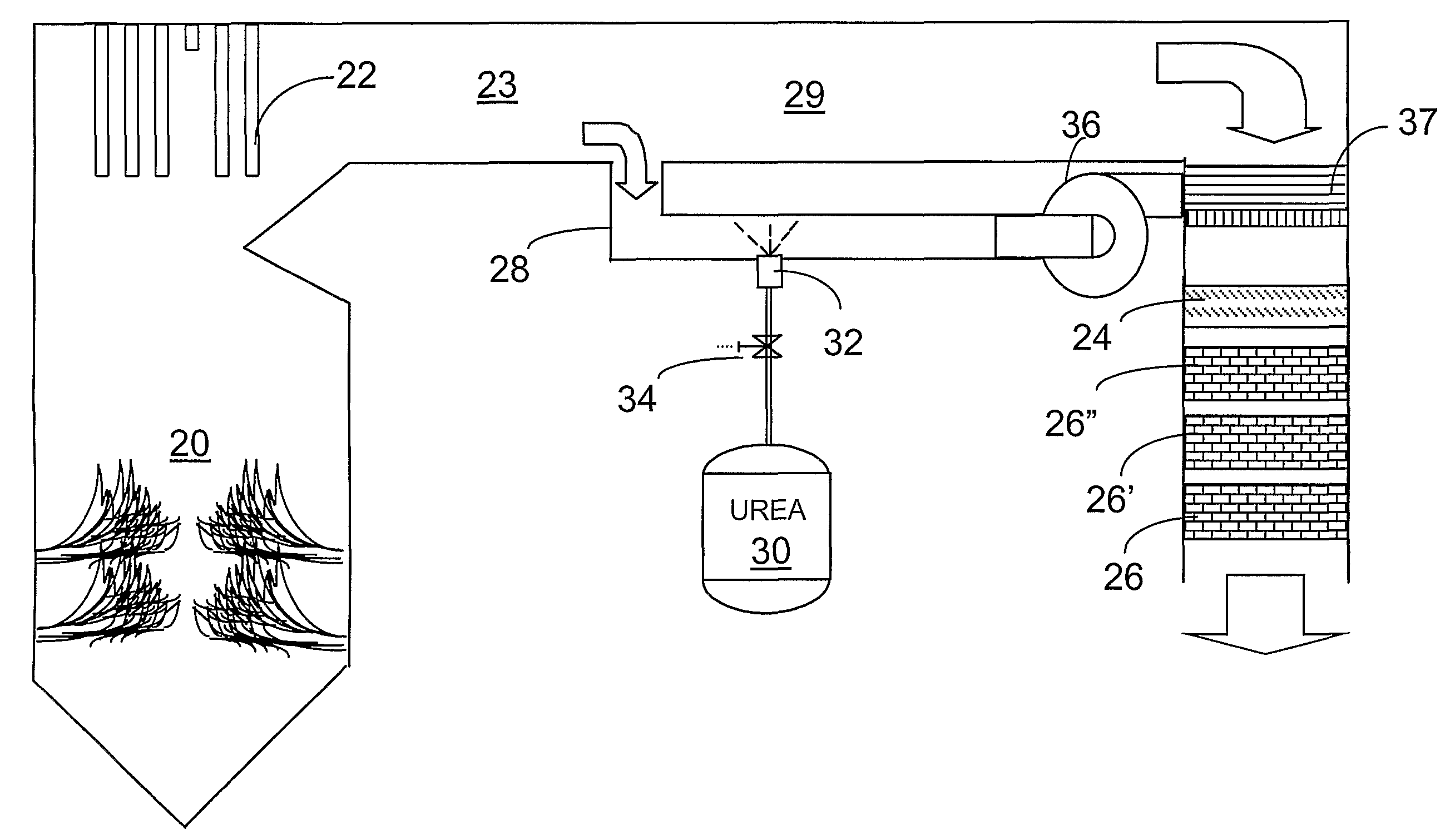
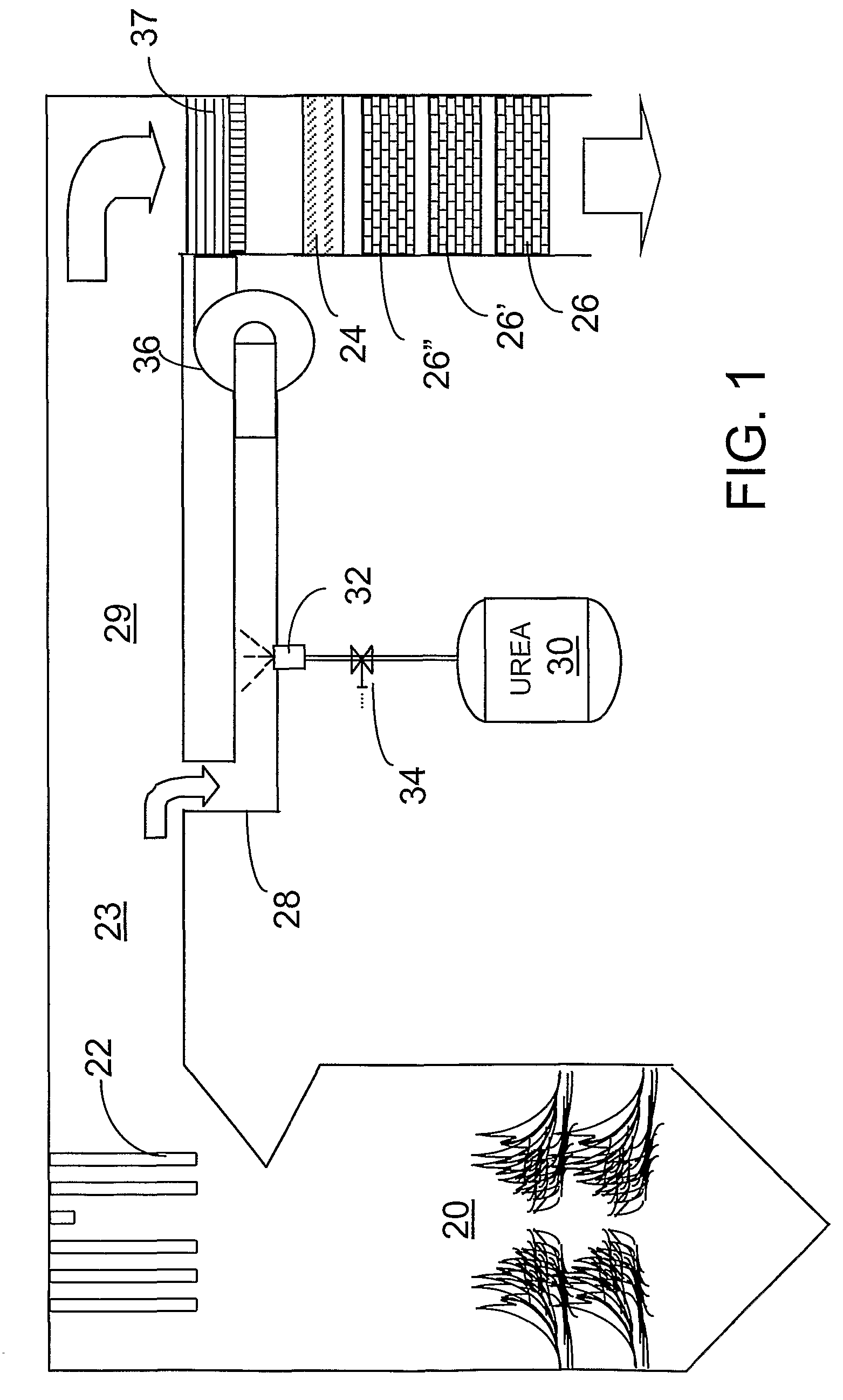
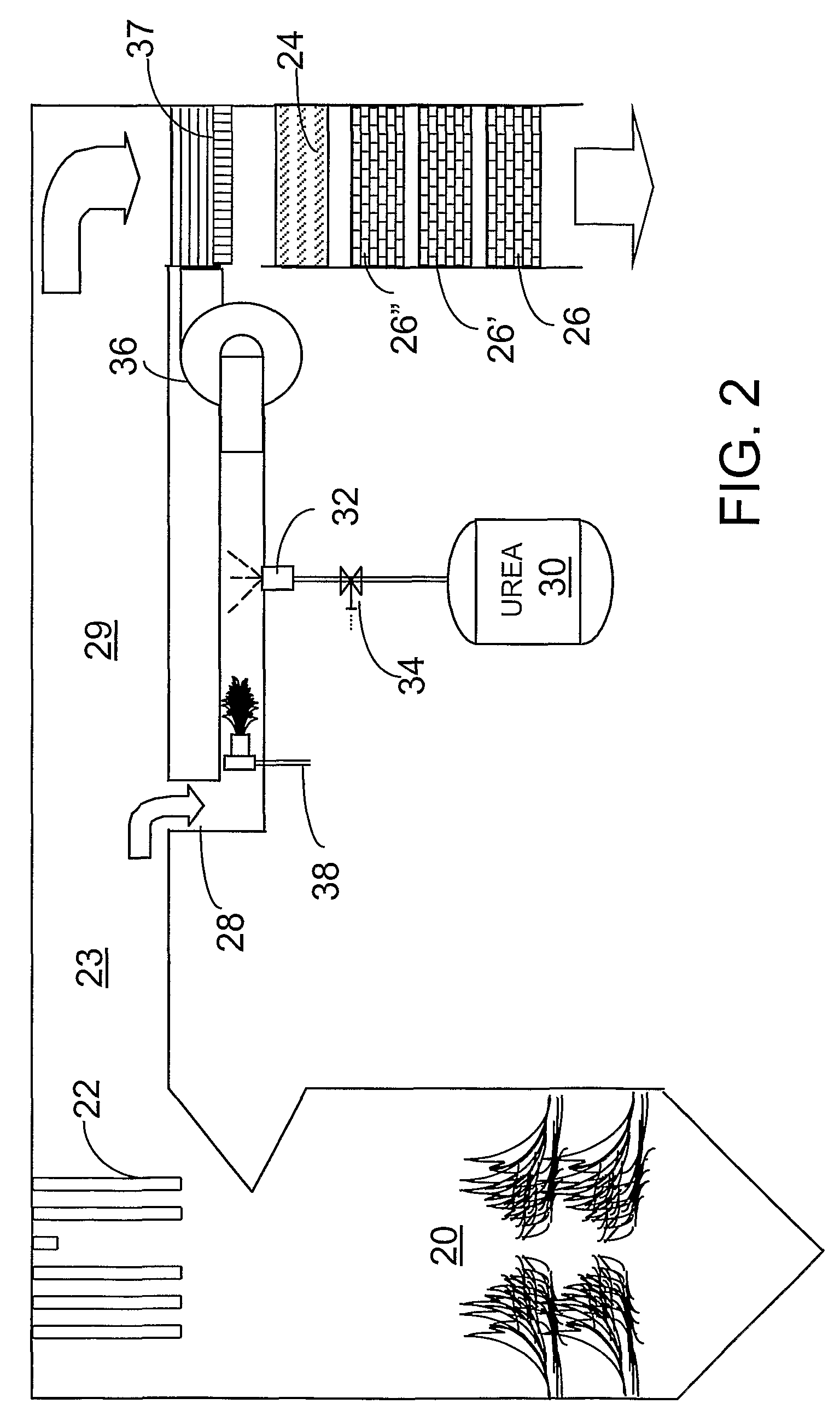
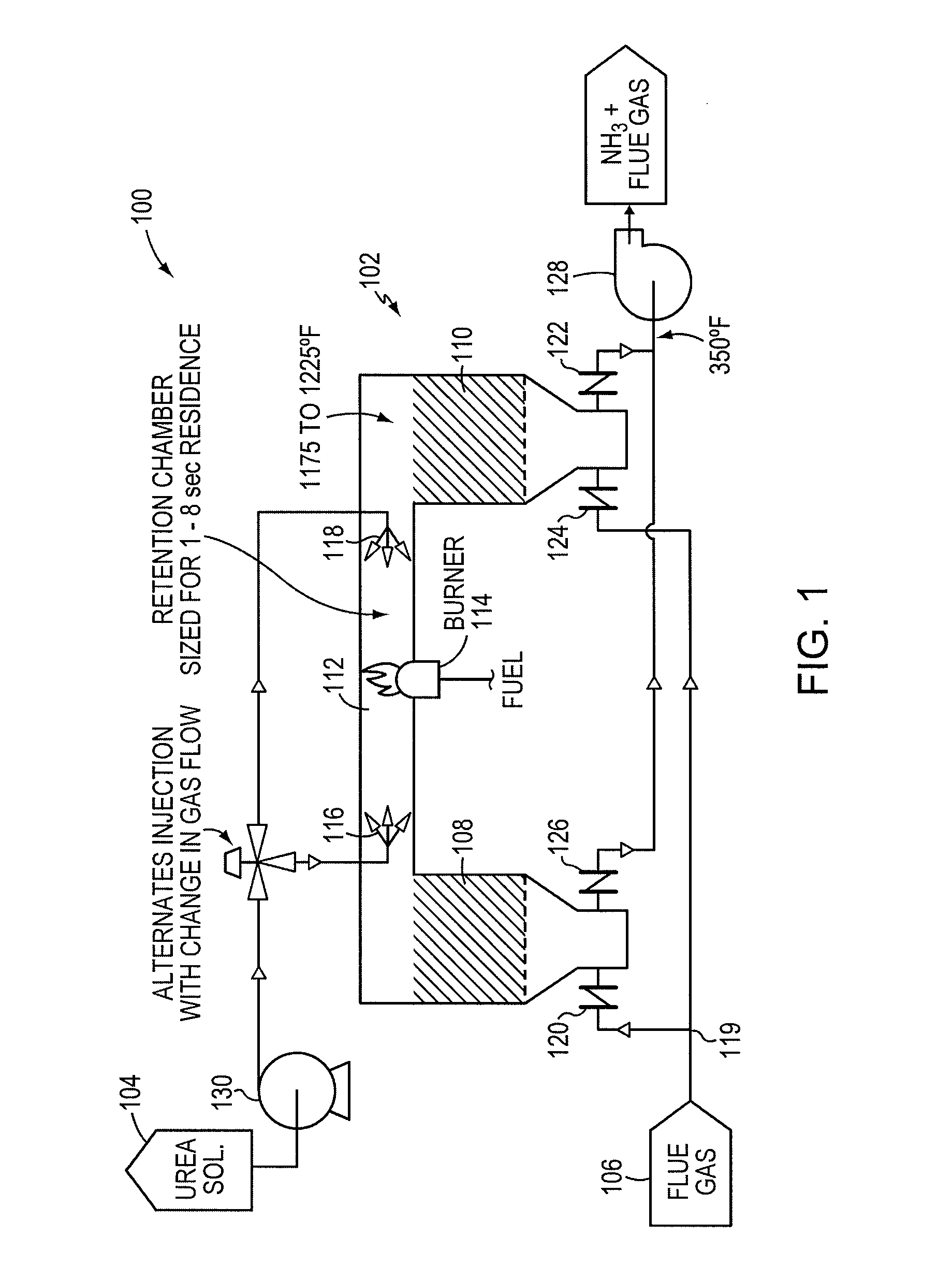
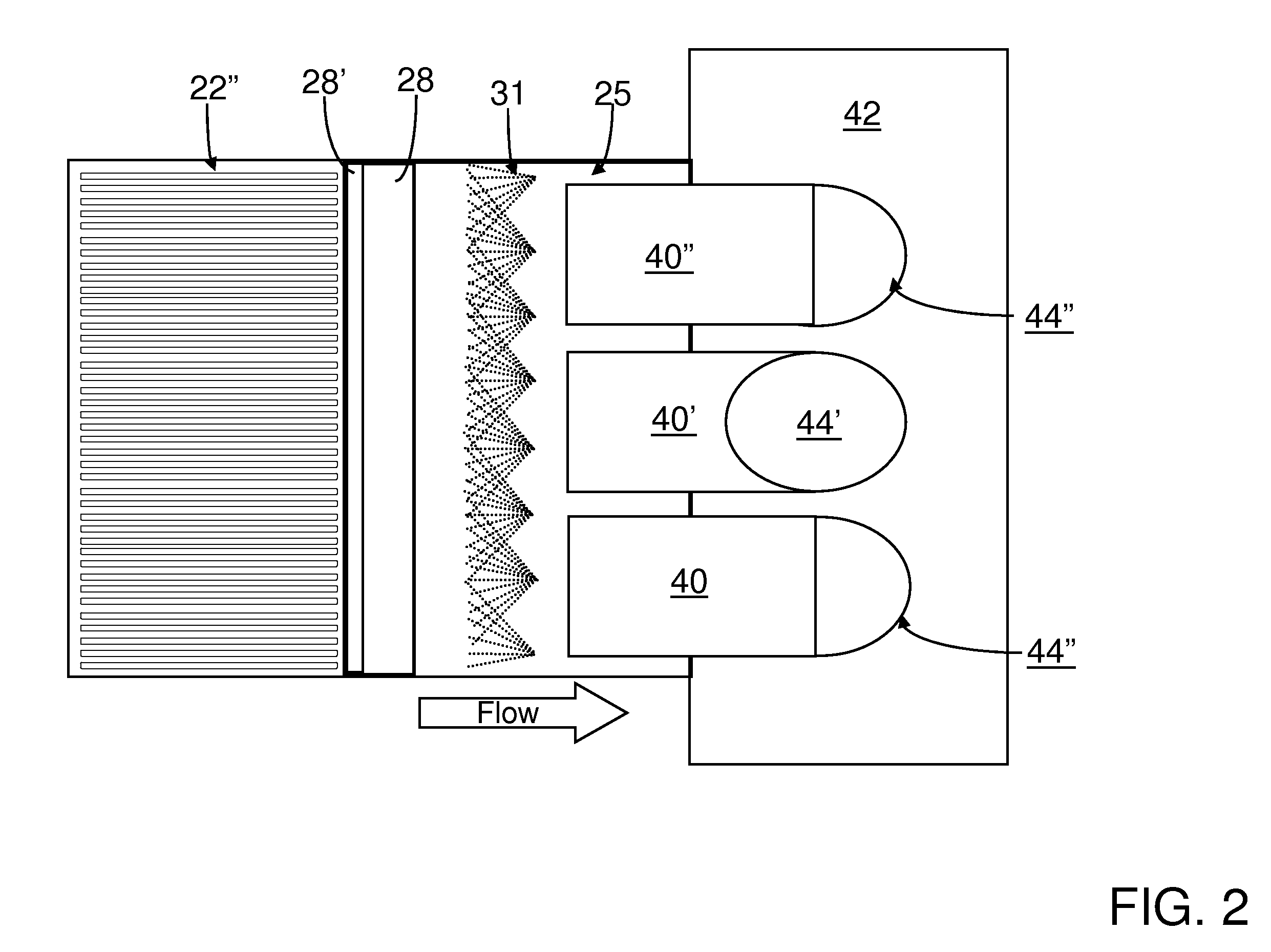
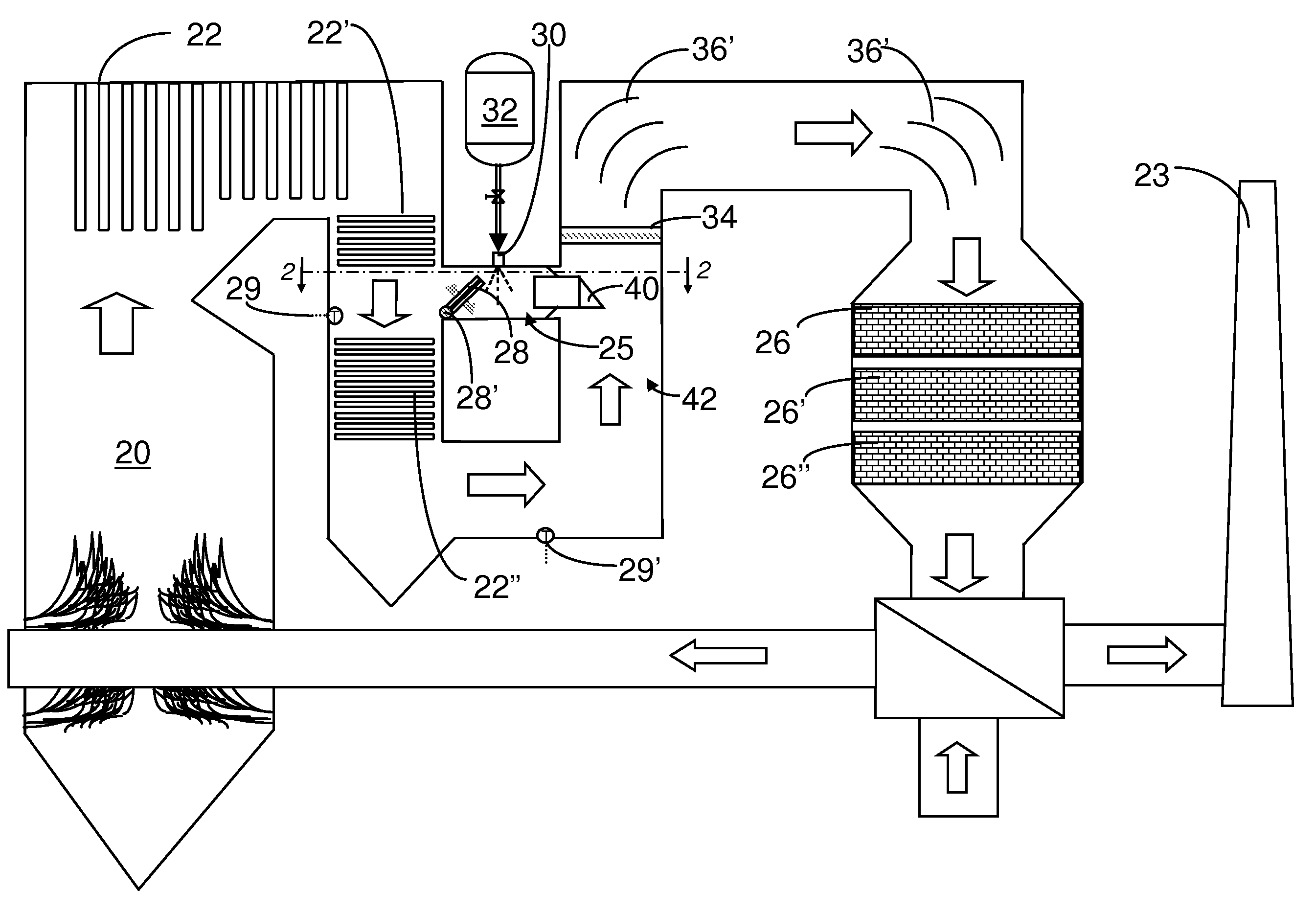
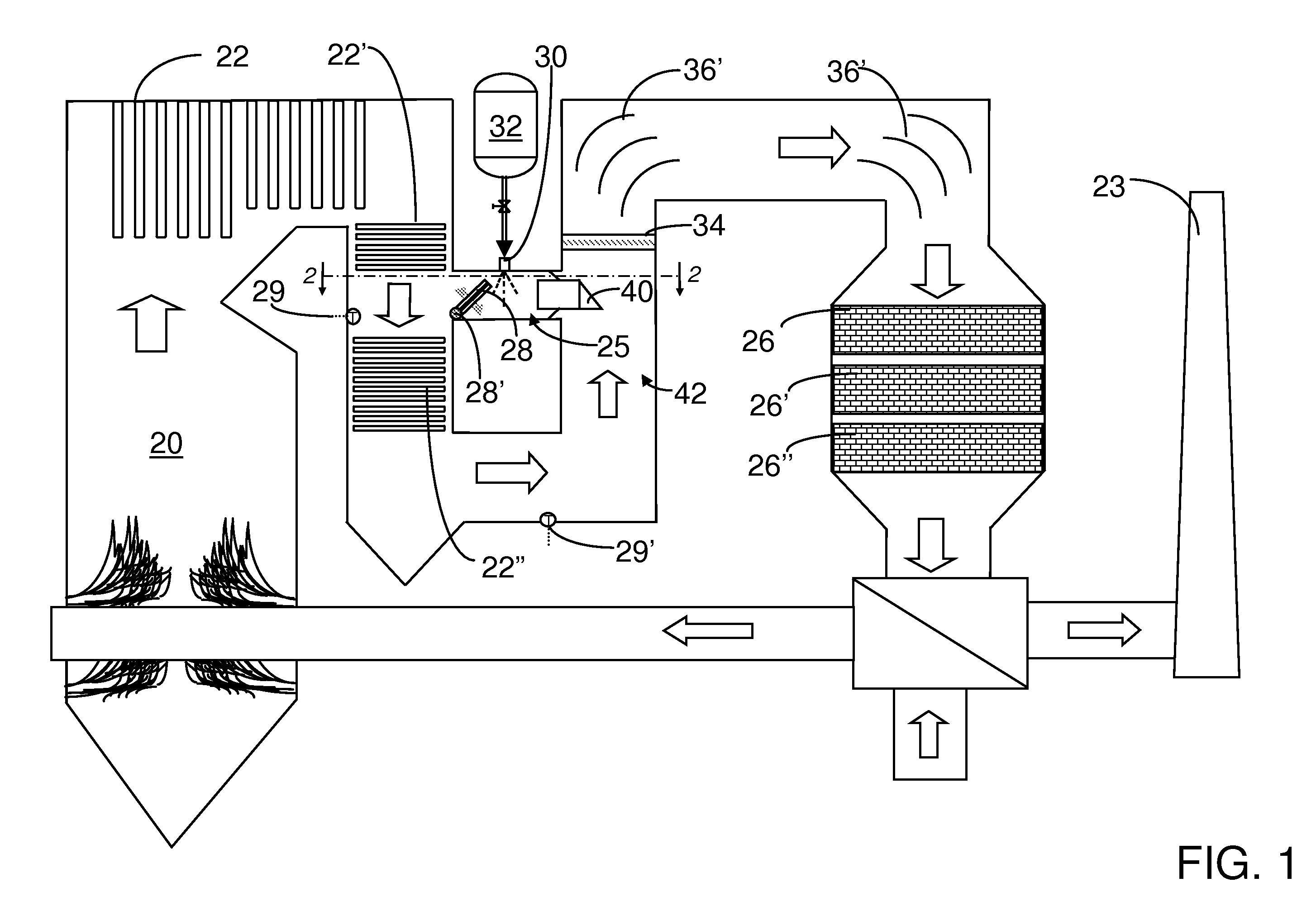
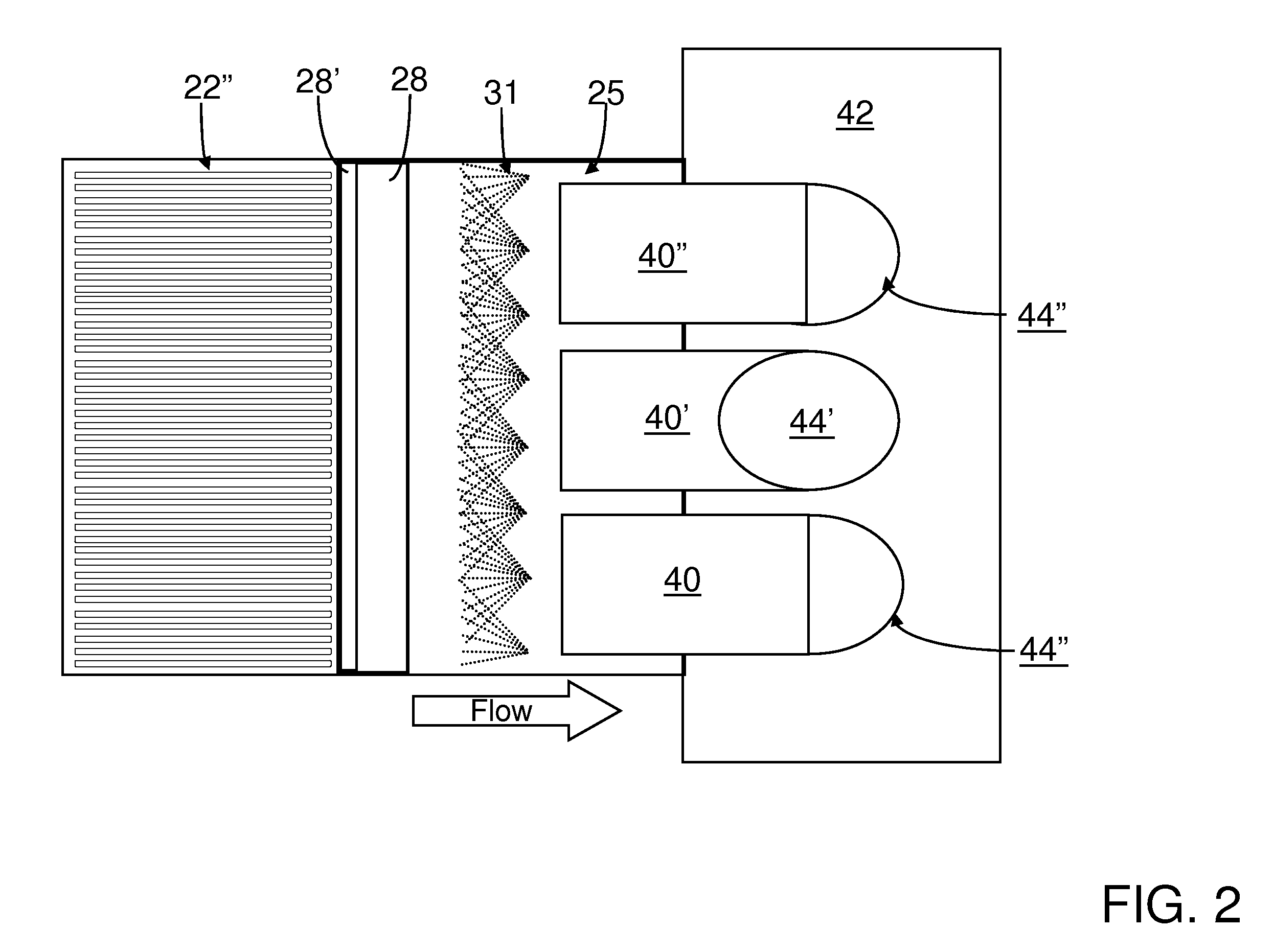
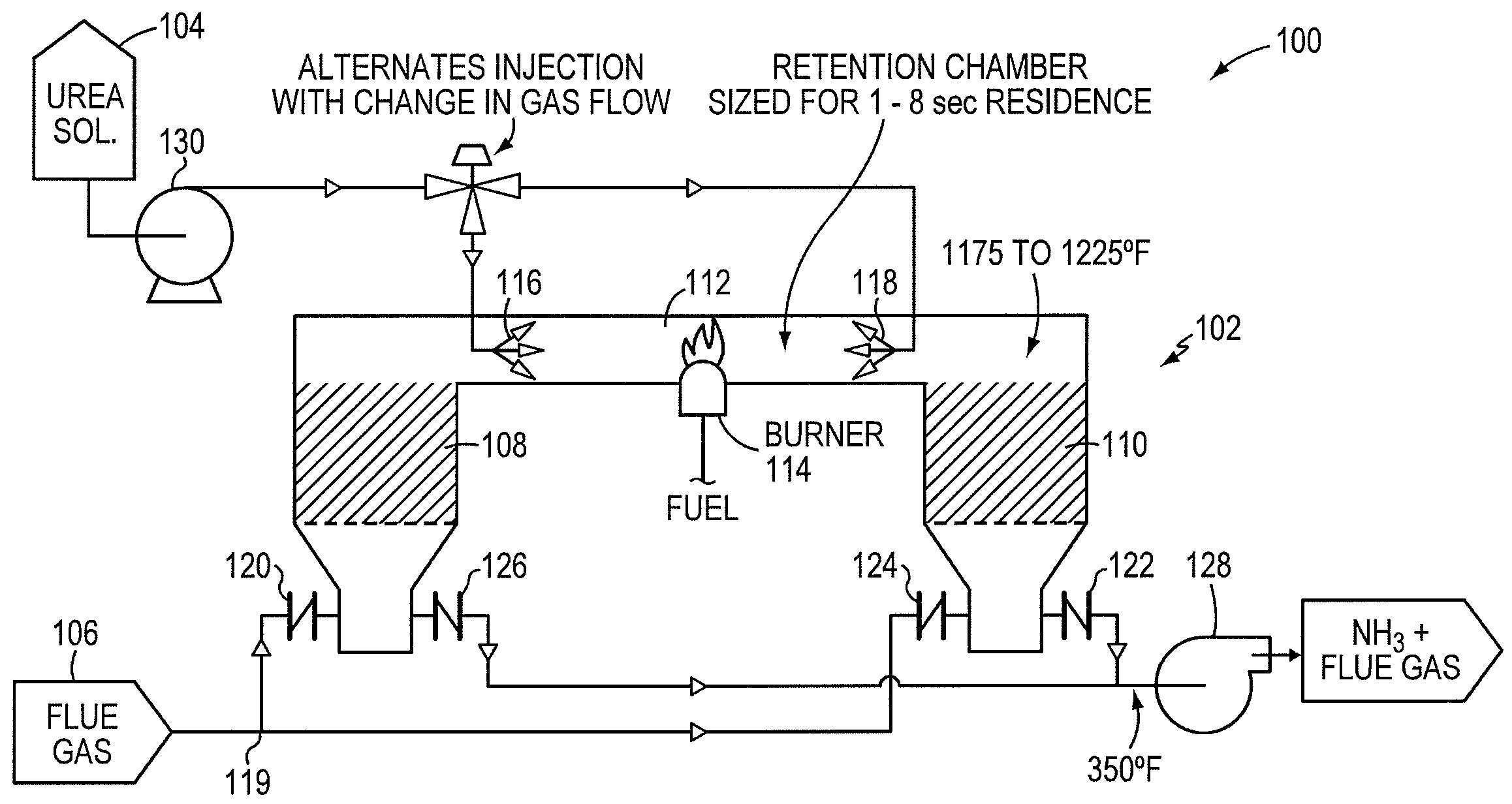
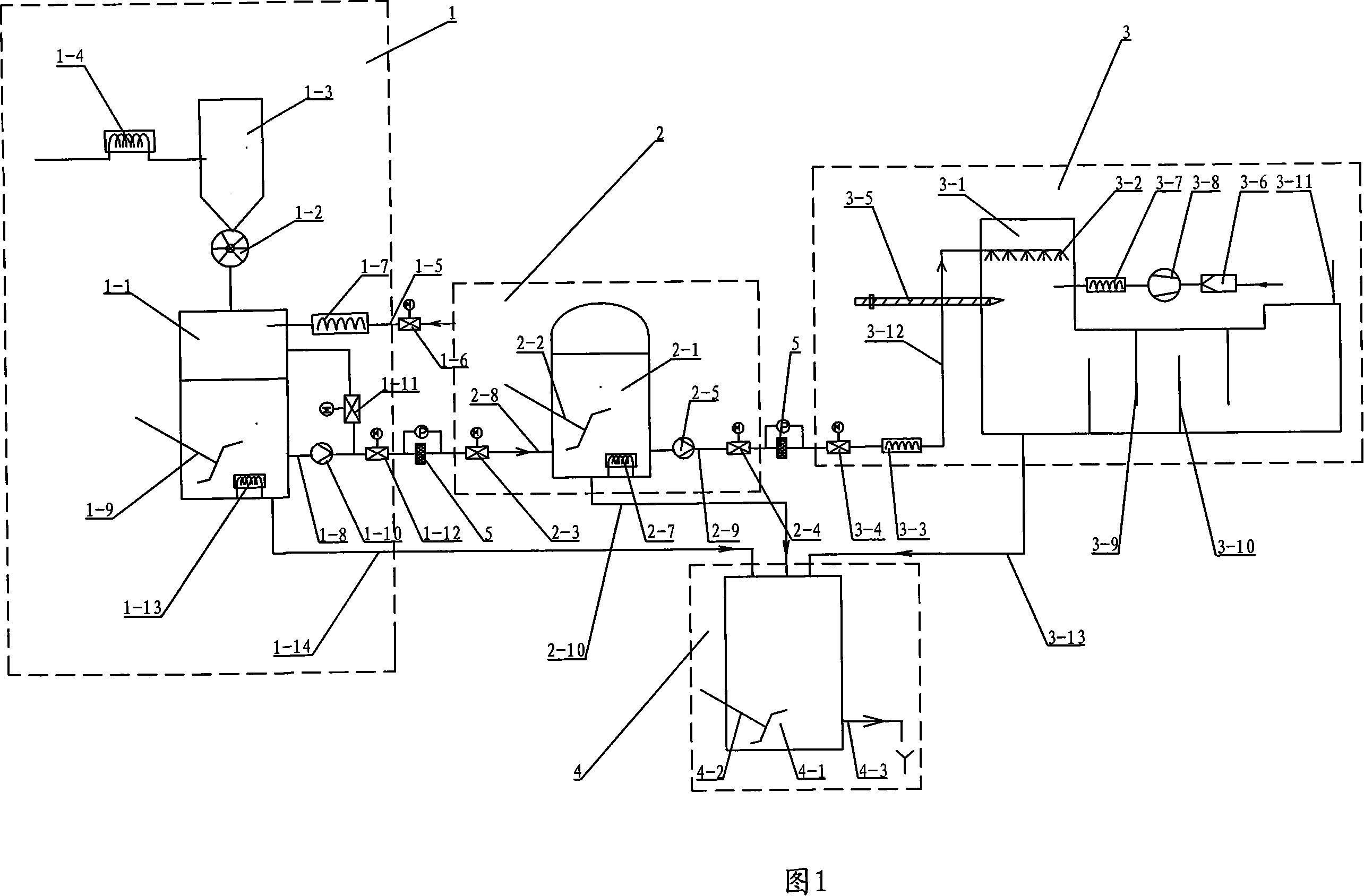
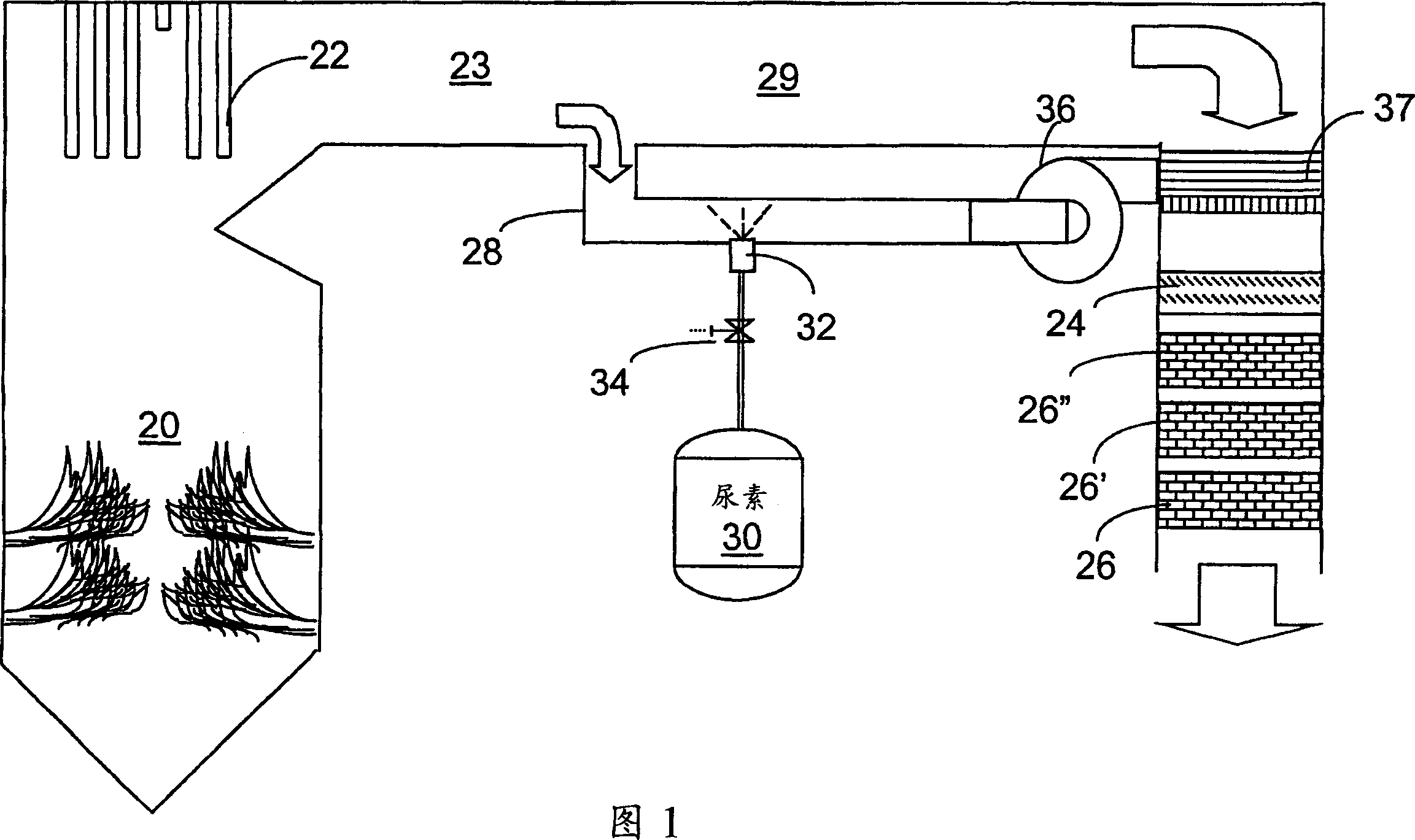
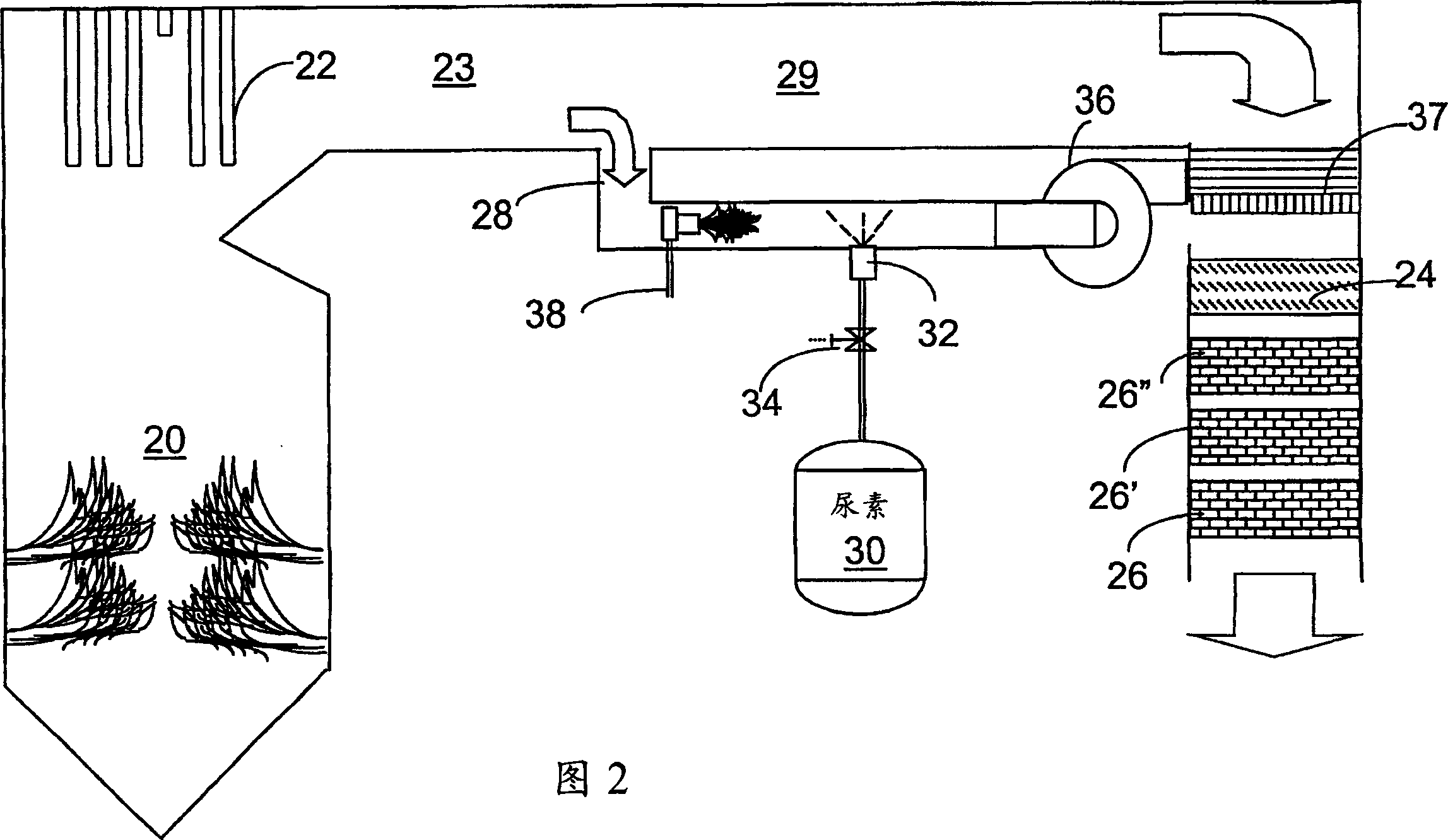
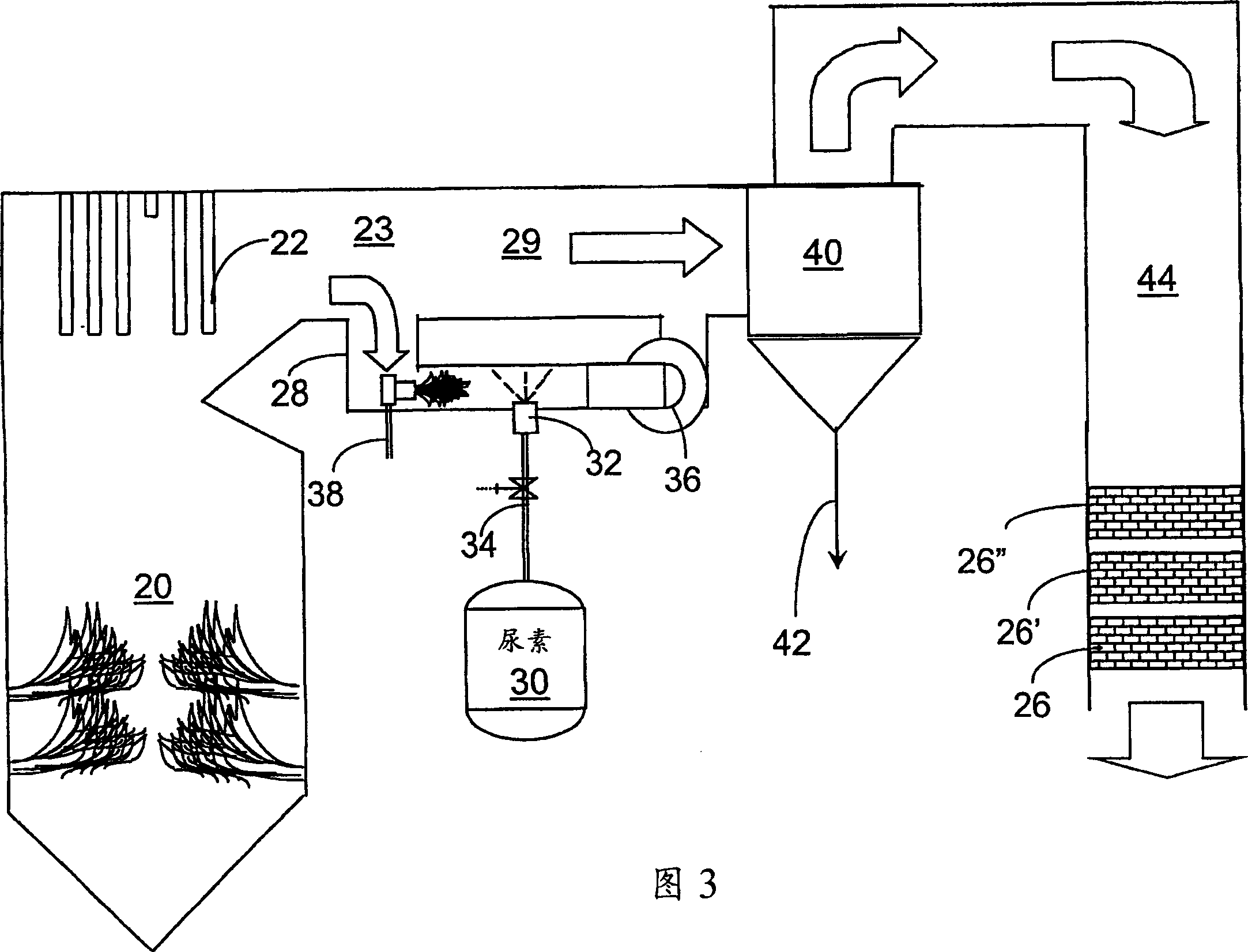
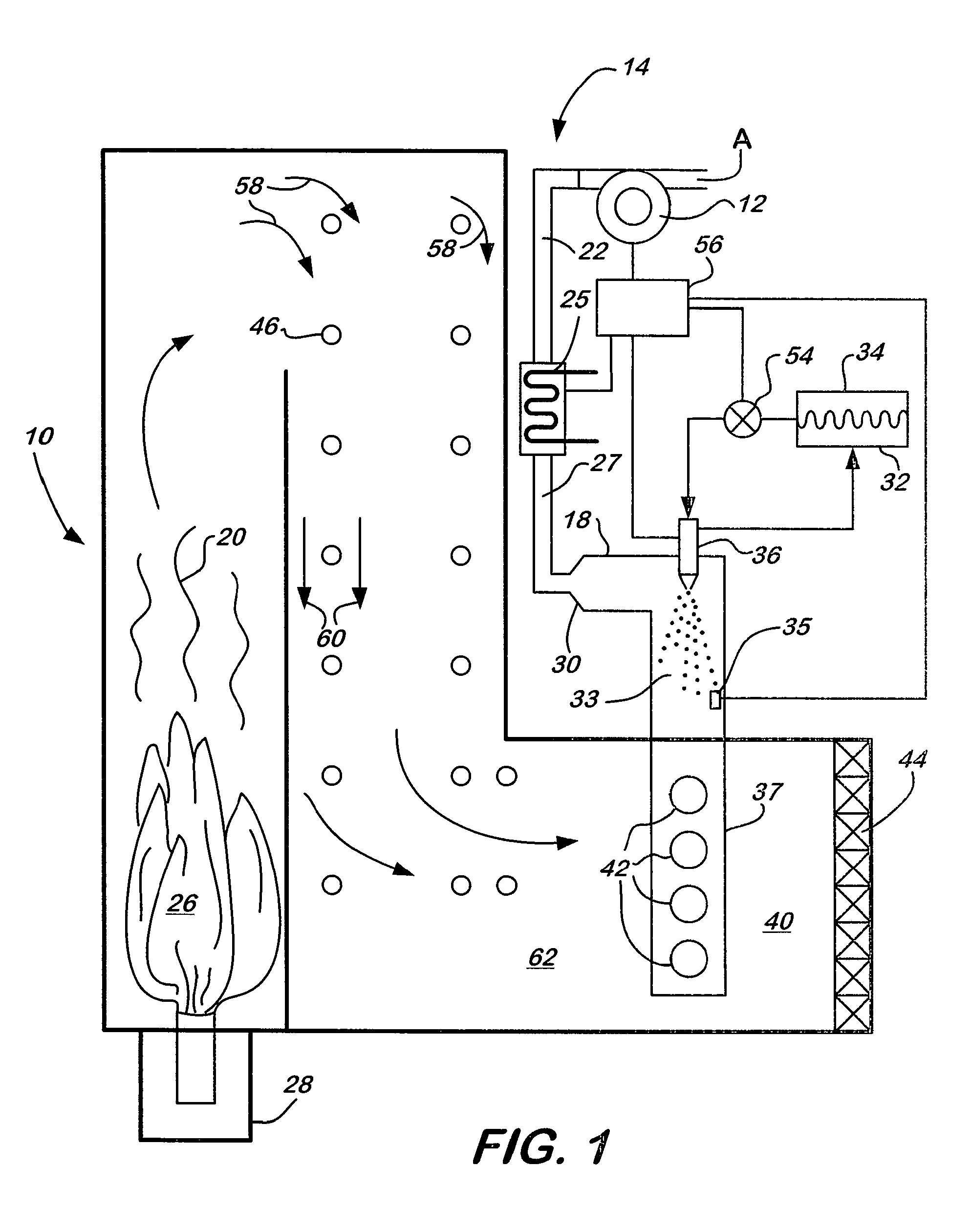
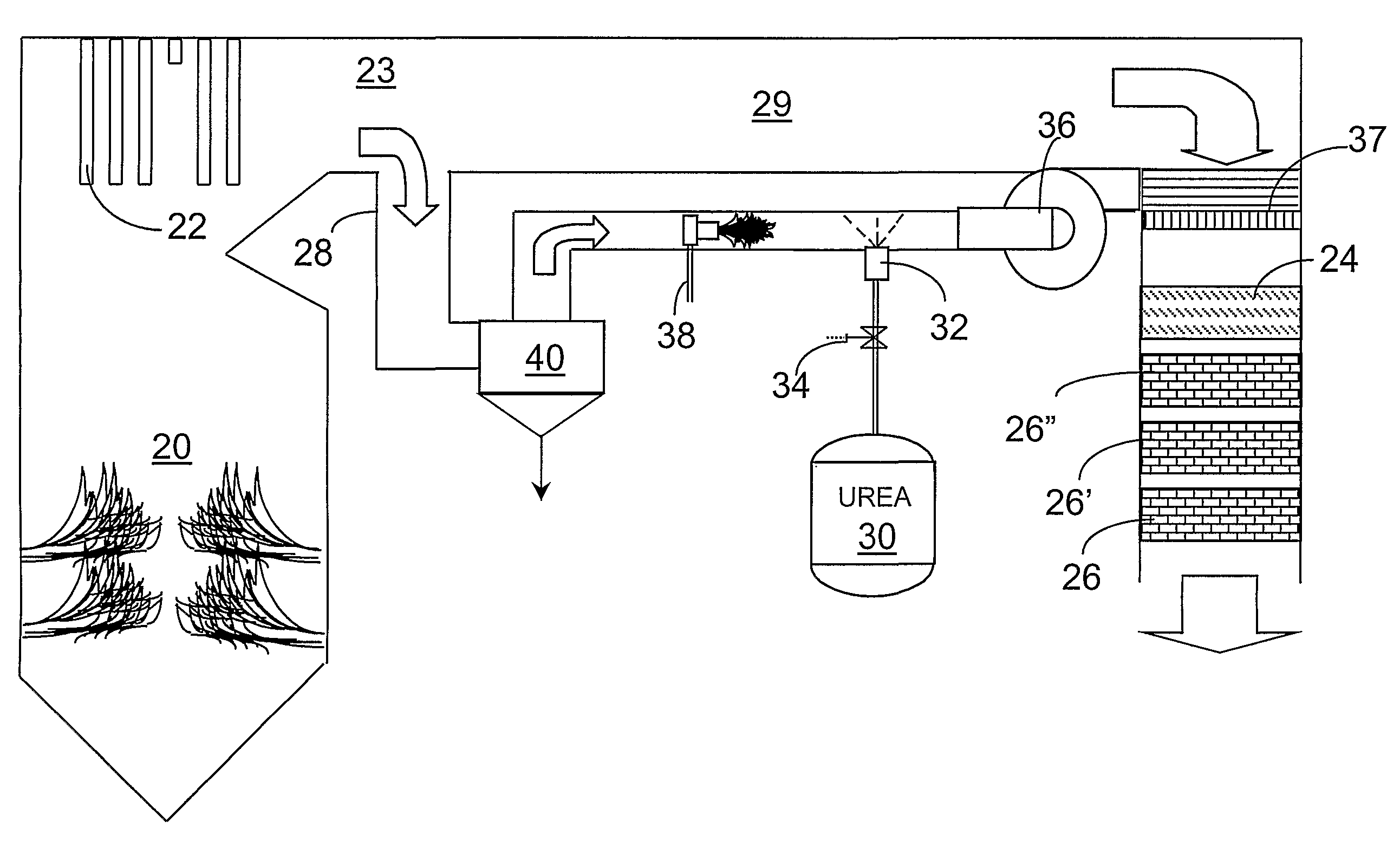
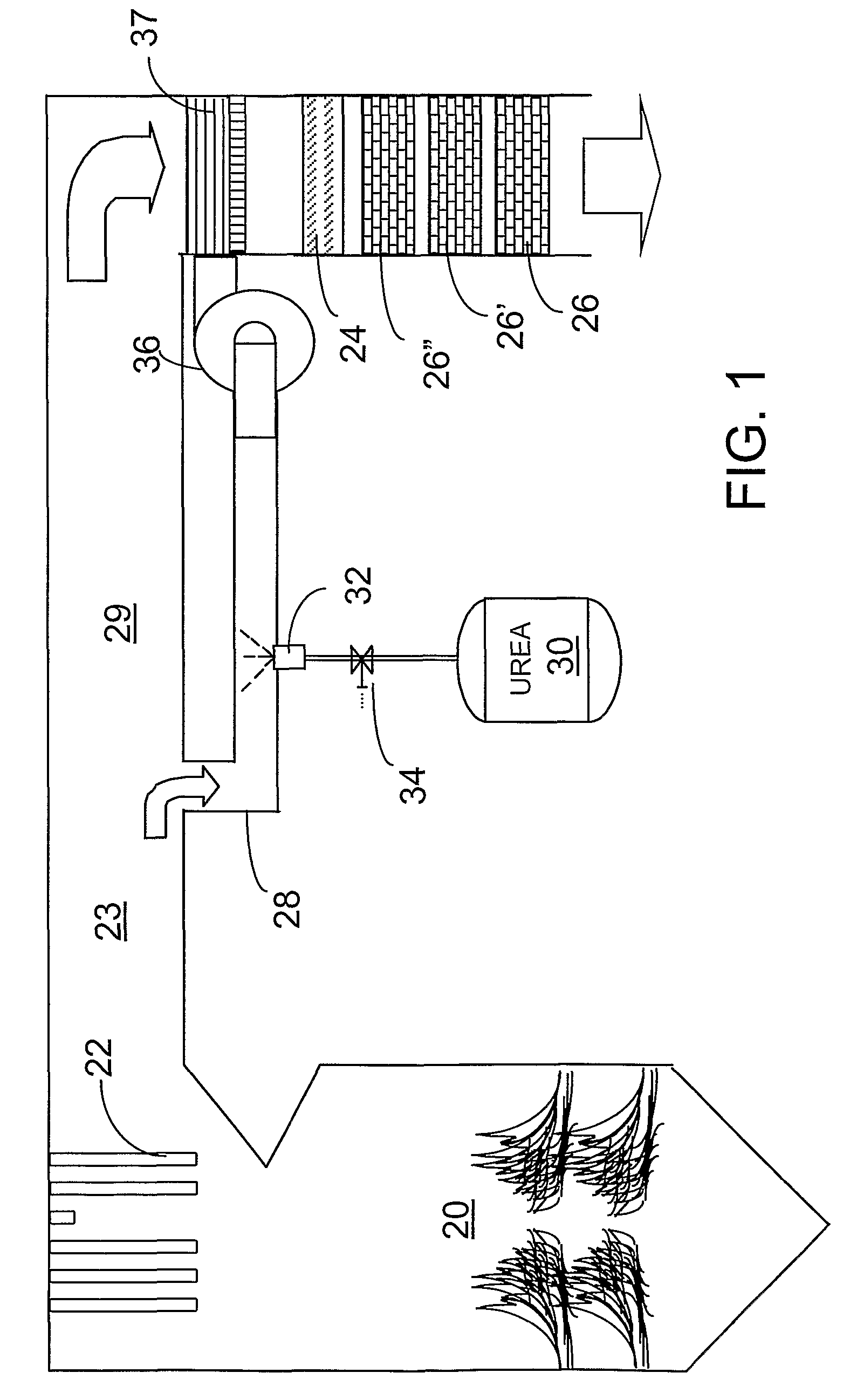
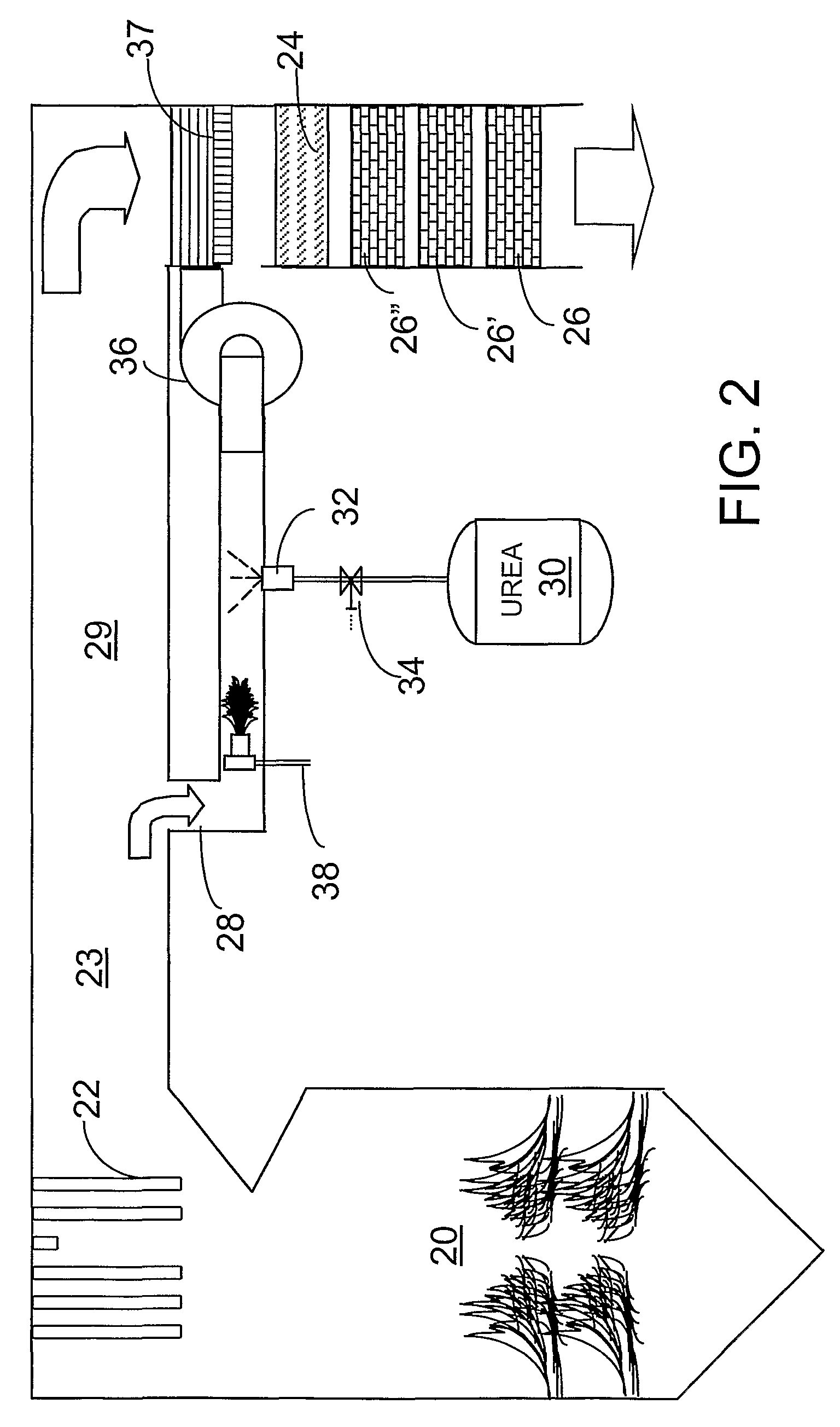
A preferred process arrangement utilizes the enthalpy of the flue gas, which can be supplemented if need be, to convert urea (30) into ammonia for SCR. Urea (30), which decomposes at temperatures above 140 ° C., is injected (32) into a flue gas stream split off (28) after a heat exchanger (22), such as a primary superheater or an economizer. Ideally, the side stream would gasify the urea without need for further heating; but, when heat is required it is far less than would be needed to heat either the entire effluent (23) or the urea (30). This side stream, typically less than 3% of the flue gas, provides the required temperature and residence time for complete decomposition of urea (30). A cyclonic separator can be used to remove particulates and completely mix the reagent and flue gas. This stream can then be directed to an injection grid (37) ahead of SCR using a blower (36). The mixing with the flue gas is facilitated due to an order of magnitude higher mass of side stream compared to that injected through the AIG in a traditional ammonia-SCR process.
Owner:FUEL TECH
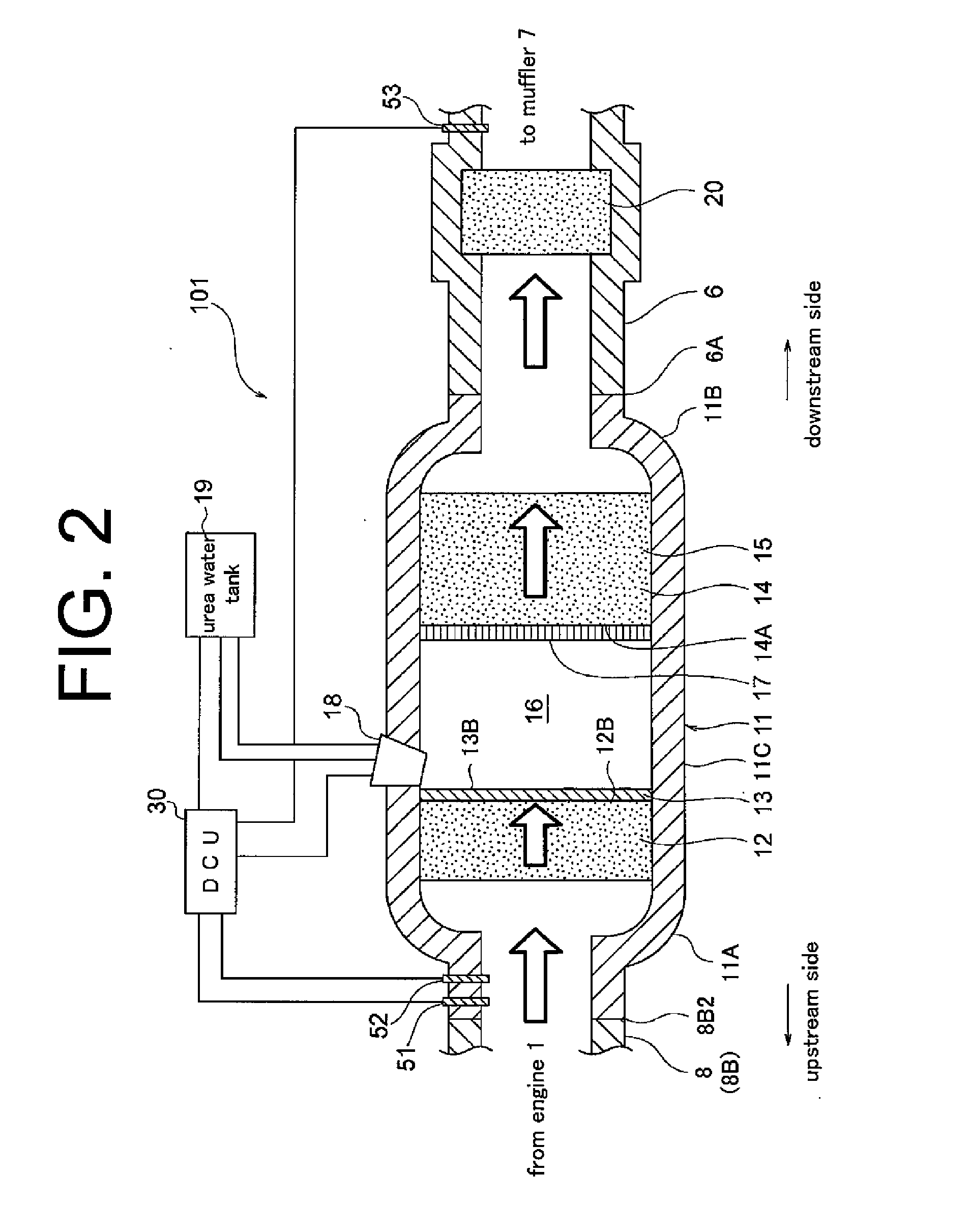
Exhaust Gas Treatment Apparatus
InactiveUS20090214397A1Improve adhesionIncrease resistanceCombination devicesGas treatmentParticulatesHoneycomb
An exhaust gas treatment apparatus includes a device (A) which is provided in an exhaust system and which selectively reduces NOx in an exhaust gas and a device (B) which is disposed upstream of the device (A) and which decomposes urea and supplies ammonia as a NOx reducing gas, the device (B) including a urea decomposition catalyst. The catalyst is [1] a zeolite catalyst which is composed of granular molded bodies including zeolite particles or which includes a catalyst layer composed of zeolite particles disposed on a support, or [2] a honeycomb catalyst or a membranous catalyst in which metal oxide particulates adhere to a conductive honeycomb substrate or netlike support, and the metal oxide particulates are composed of at least one oxide of a metal selected from the group consisting of Na, Mg, Ca, Ba, La, Ce, Ti, Zr, V, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Zn, Al, Si, P, Sb, Cu, Fe, Ru, Co, and Re.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
SELECTIVE CATALYTIC REDUCTION OF NOx ENABLED BY UREA DECOMPOSITION IN HEAT-EXCHANGER BYPASS
InactiveUS20070231232A1Well mixedAccurate temperatureCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsLow loadActive component
Disclosed are a process and apparatus for selective catalytic reduction of NOx. The process is enabled by passing a heat exchanger section, such as an economizer, of the boiler in advance of an SCR unit at low load conditions to enable NOx reduction even at low loads using urea instead of ammonia. In a preferred form, under high load conditions, the bypass can be almost fully closed and the economizer can be operated normally without excessively cooling the combustion gases, using only a portion of bypassed gases which are hot enough to decompose the urea into its active components including ammonia.
Owner:FUEL TECH
SELECTIVE CATALYTIC REDUCTION OF NOx ENABLED BY SIDESTREAM UREA DECOMPOSITION
ActiveUS20060115402A1Well mixedAccurate temperatureCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsParticulatesSuperheater
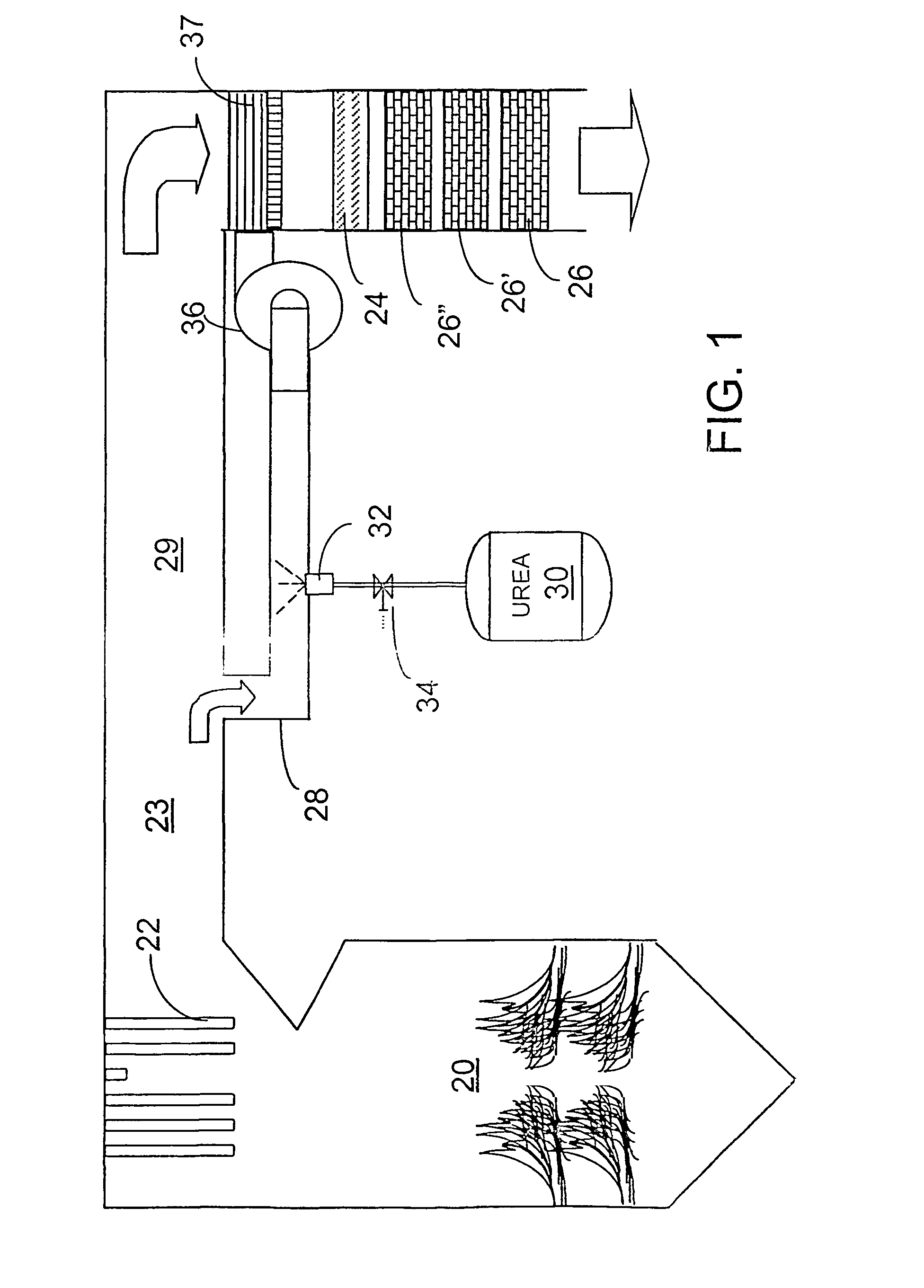
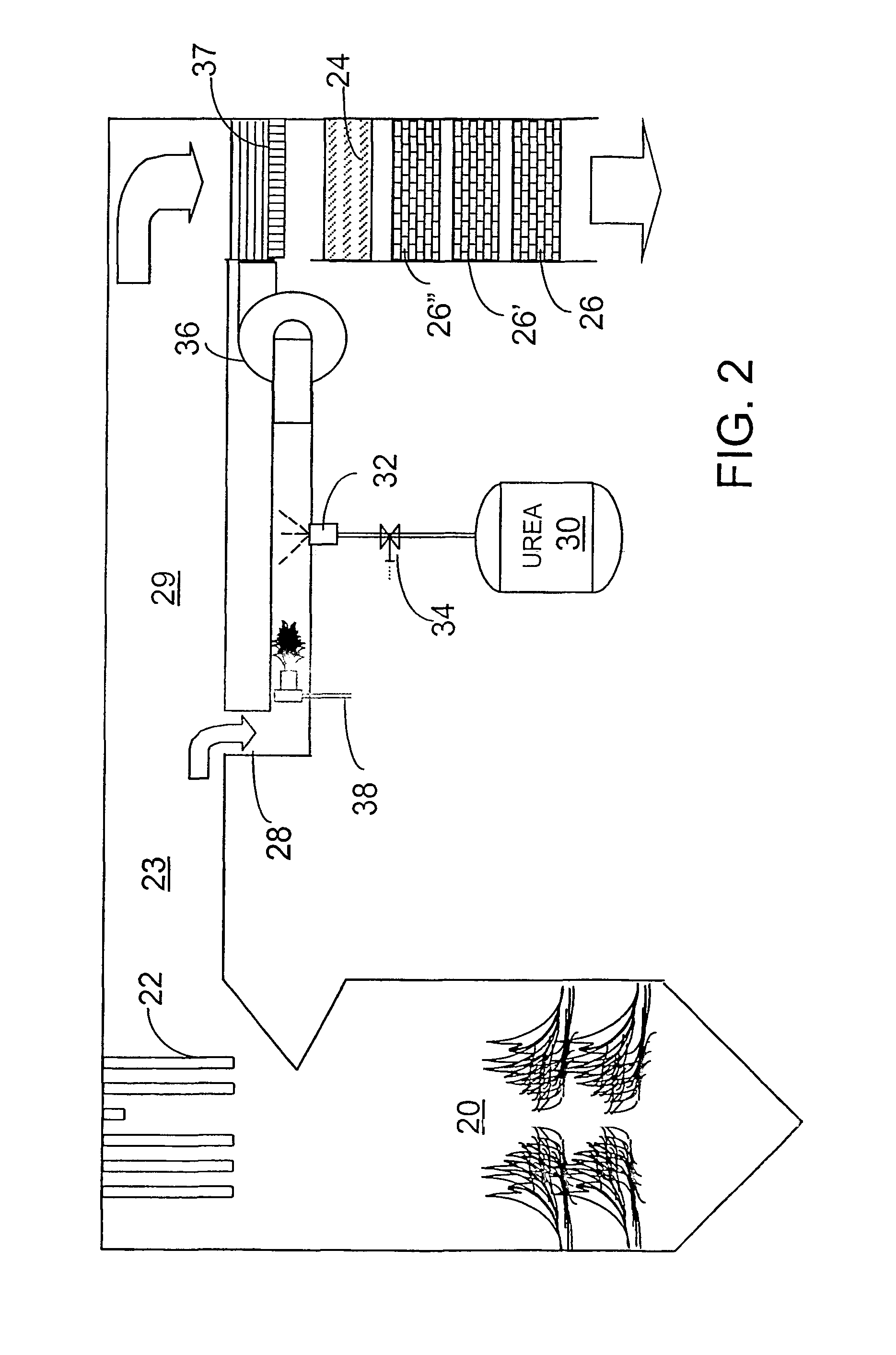
A preferred apparatus arrangement utilizes the enthalpy of the flue gas, which can be supplemented if need be, to convert urea (30) into ammonia for SCR. Urea (30), which decomposes at temperatures above 140.degree. C., is injected (32) into a flue gas stream split off (28) after a heat exchanger (22), such as a primary superheater or an economizer. Ideally, the side stream would gasify the urea without need for further heating; but, when heat is required it is far less than would be needed to heat either the entire effluent (23) or the urea (30). This side stream, typically less than 3% of the flue gas, provides the required temperature and residence time for complete decomposition of urea (30). A cyclonic separator can be used to remove particulates and completely mix the reagent and flue gas. This stream can then be directed to an injection grid (37) ahead of SCR using a blower (36). The mixing with the flue gas is facilitated due to an order of magnitude higher mass of side stream compared to that injected through the AIG in a traditional ammonia-SCR process.
Owner:FUEL TECH
Thermal Decomposition of Urea in a Side Stream of Combustion Flue Gas Using a Regenerative Heat Exchanger
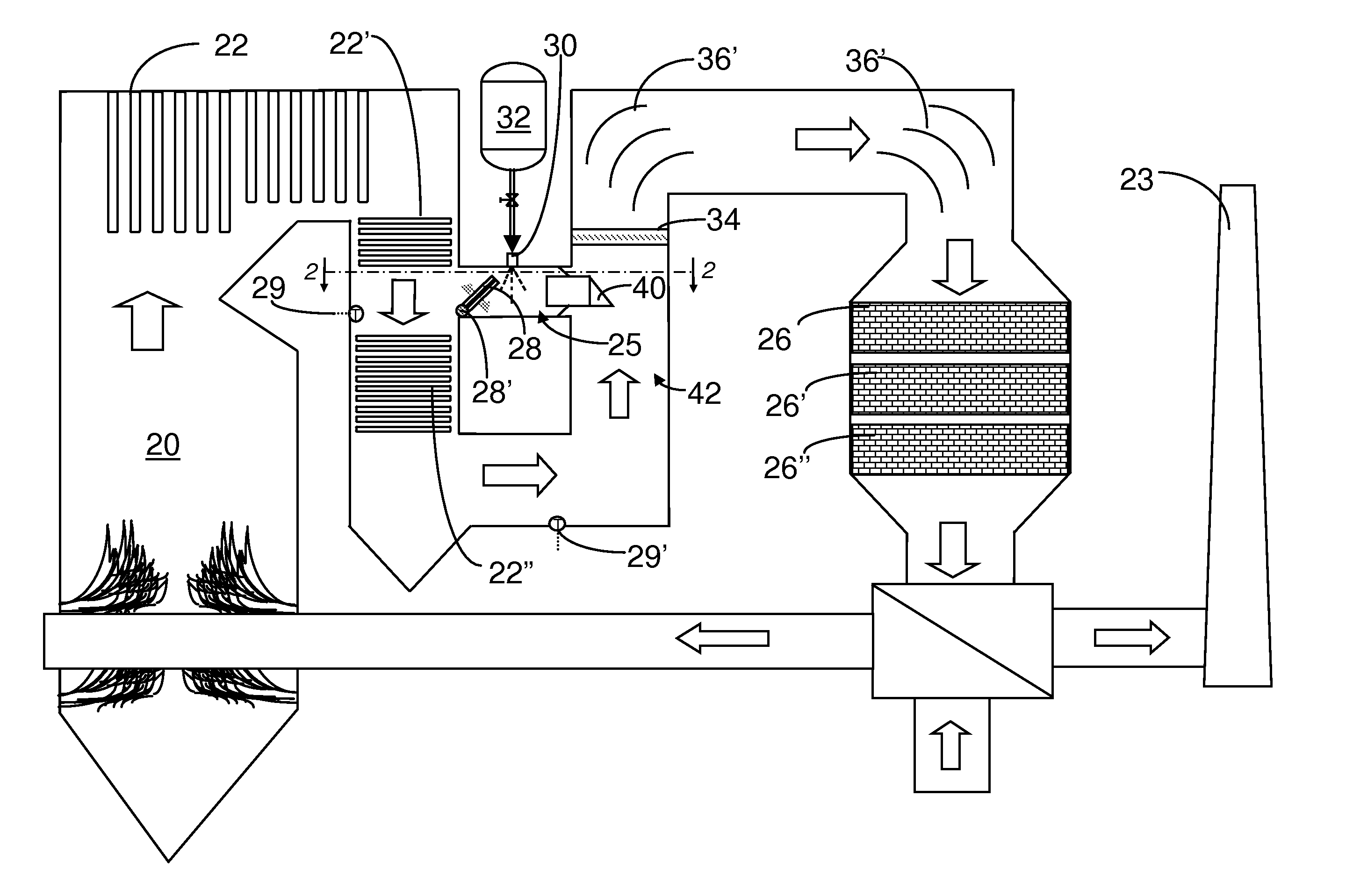
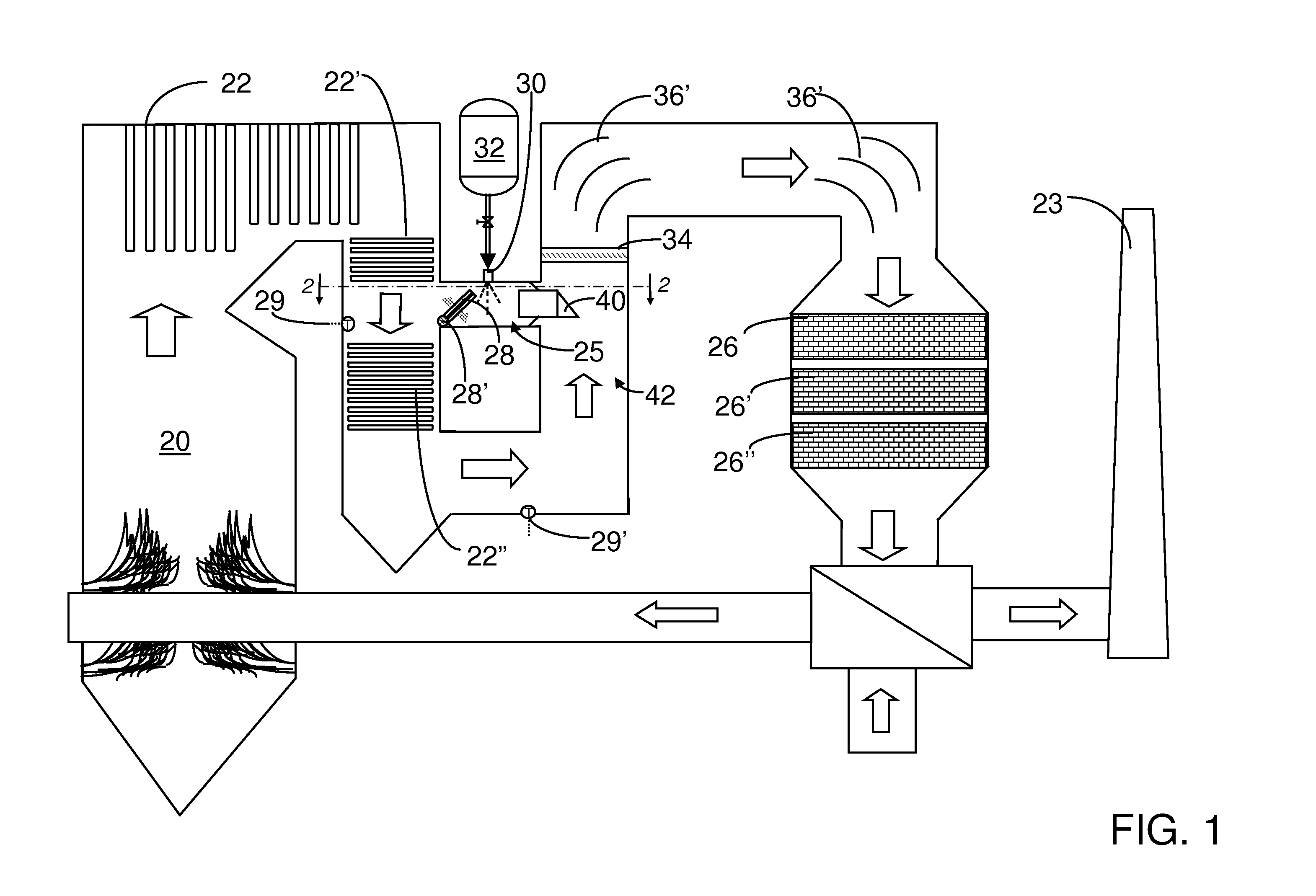
InactiveUS20080050297A1Avoid insufficient temperatureImprove thermal efficiencyNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusFlue gasThermal efficiency
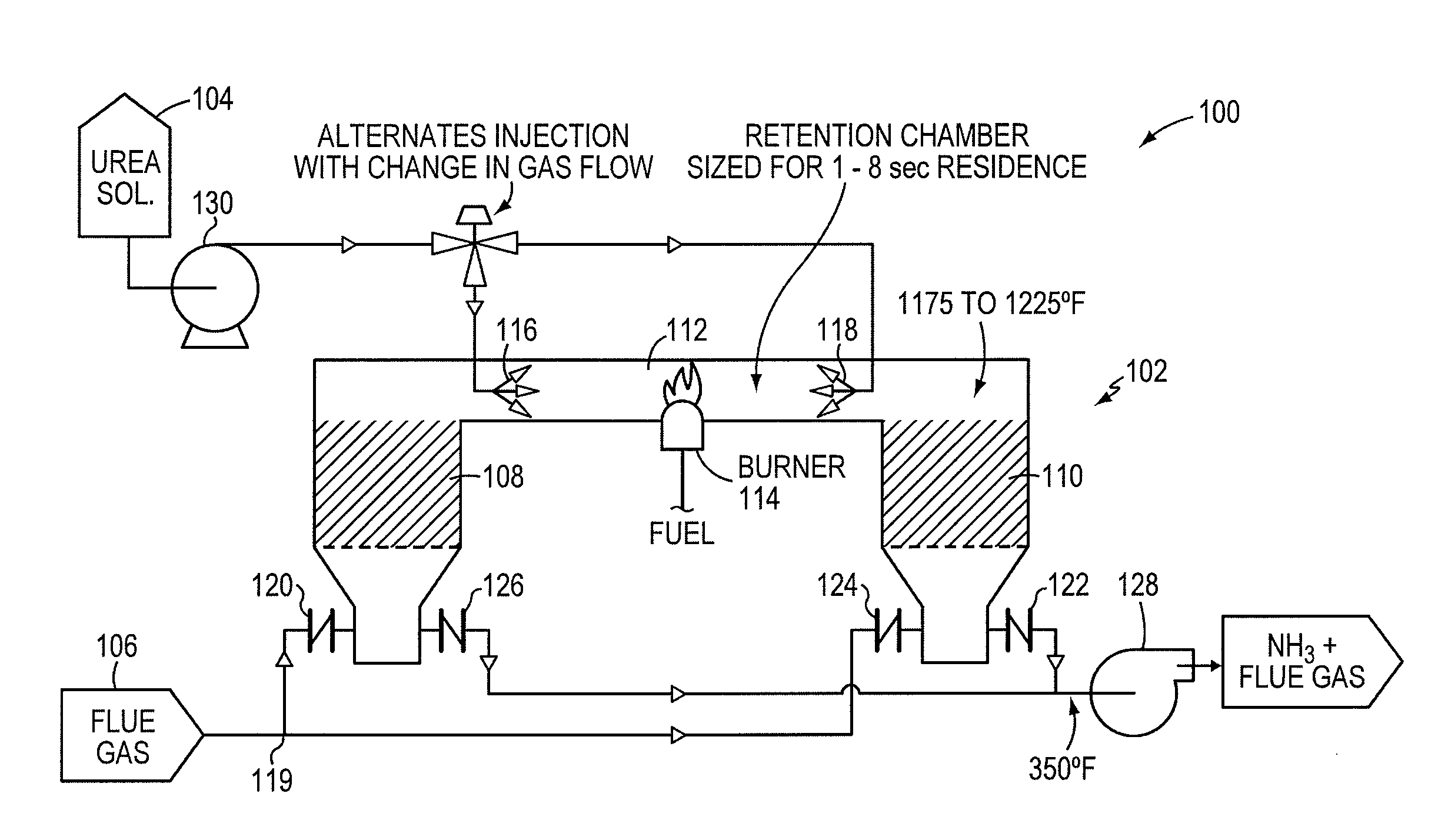
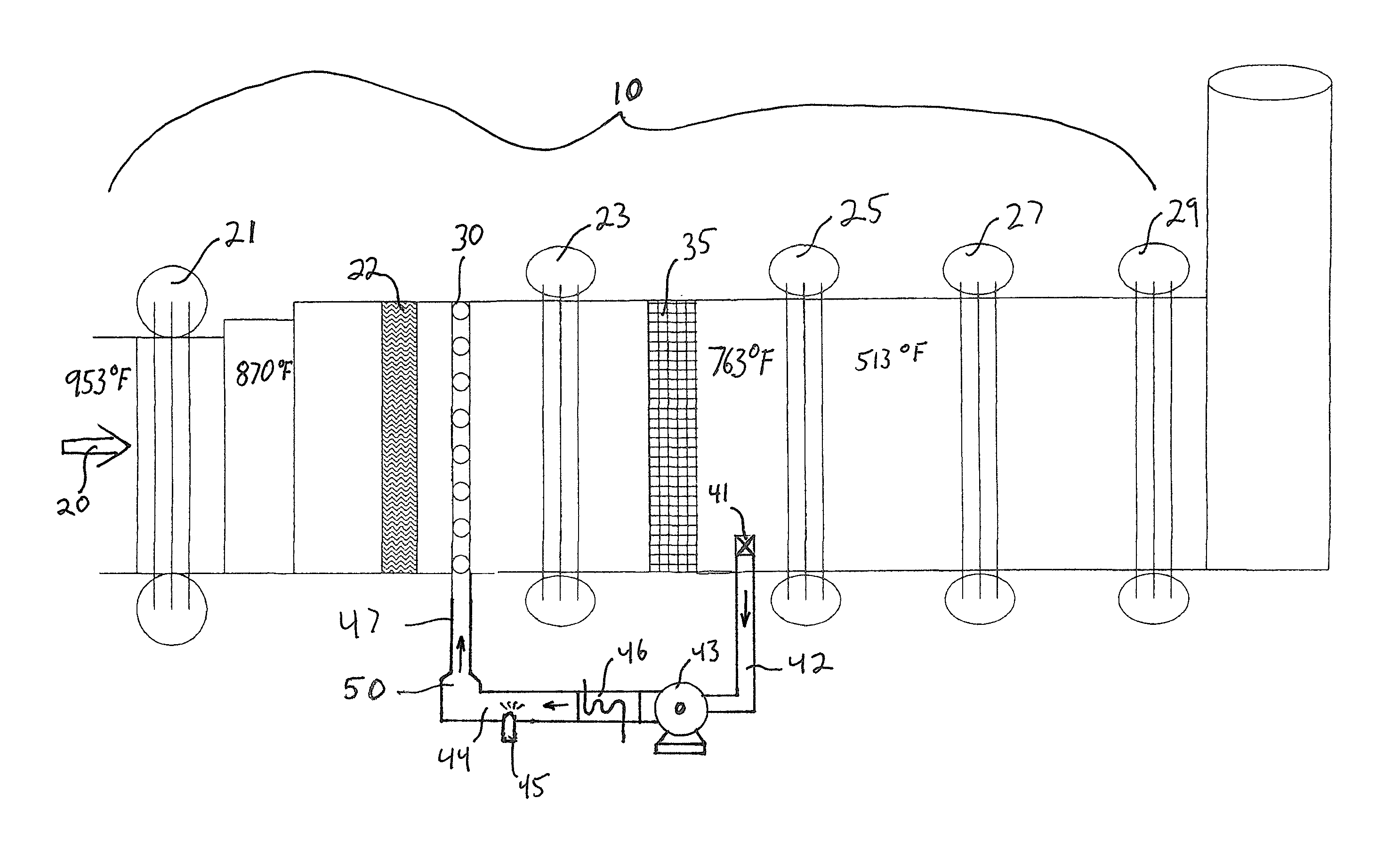
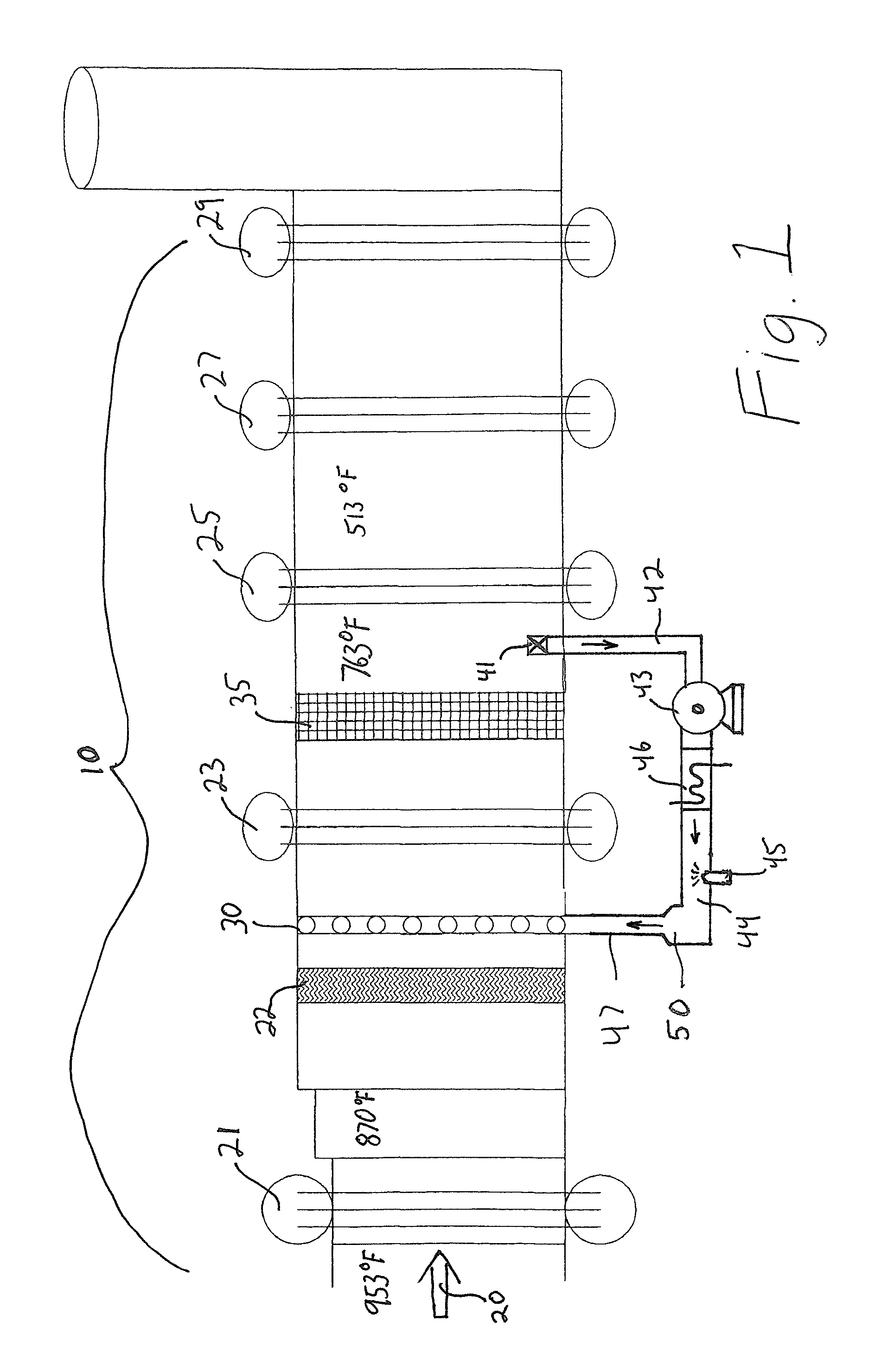
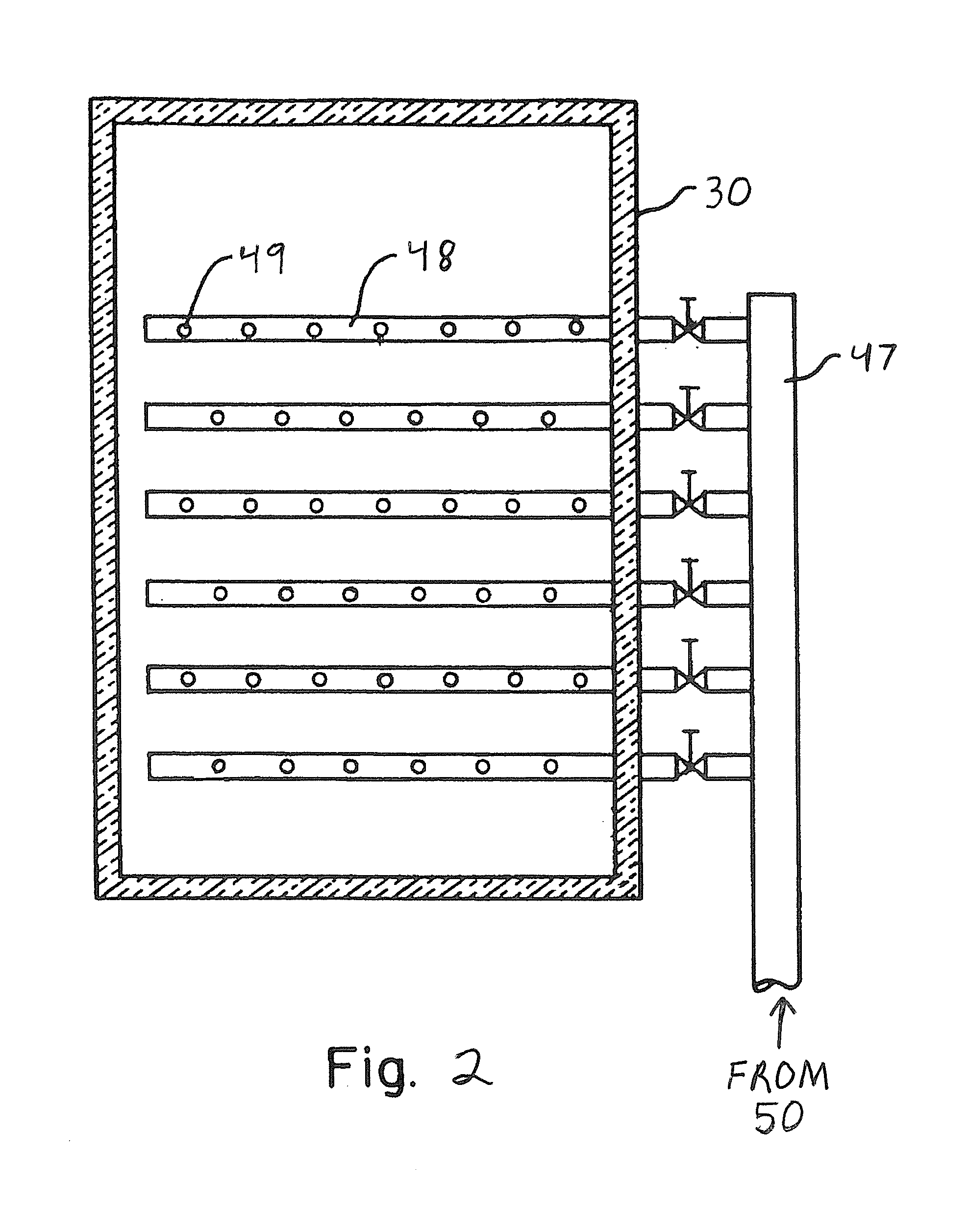
This invention relates generally to the treatment of NOx in combustion flue gas. In certain embodiments, the invention relates to the use of a regenerative heat exchanger (RHE) to convert urea to ammonia in a side stream of flue gas. Ammonia and / or other urea decomposition products exit the heat exchanger, are mixed with the rest of the flue gas, and enter a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) unit for reduction of NOx in the flue gas. The use of an RHE significantly improves the thermal efficiency of the overall process. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the regenerative heat exchanger is a dual chamber RHE.
Owner:BABCOCK POWER ENVIRONMENTAL INC (US)
Hydrotalcite type hydrocracking catalyst and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101181686AHigh reactivityHigh selectivityHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsReaction temperatureCrystallinity
The invention relates to a houghite hydrocracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof, and component of the houghite hydrocracking catalyst is Ni / Me-Mg-Al-O, wherein, Me is one or two elements of Co, Fe, Mn, Zn and Cu. The catalyst is used for hydrocracking tar component in coke-oven gas at high temperature to transform the coke-oven gas to rich hydrogenous permanent gas, pertaining to coke-oven gas hydrocracking process and catalyst technology field. The invention has the advantages that: urealysis-homogeneous co-precipitation is adopted, Al, Me, Ni and correspondent divalent metal salt are dissolved in aqueous urea solution, and urealysis speed is controlled by reaction temperature and reaction time; reactive precipitate is filtered, washed and dried, and after roasting for 15 to 20 hours at 500 to 600 DEG C and 3 to 5 hours at 750 to 850 DEG C, and 20 to 40 meshes of particle is obtained after grinding and screening, which is houghite hydrocracking catalyst. The catalyst prepared by the method of the invention has the advantages of high crystallinity, good dispersivity, large specific surface and long service life, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Selective catalytic reduction of NOx enabled by urea decomposition in heat-exchanger bypass
InactiveUS7615200B2Well mixedAccurate temperatureCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsLow loadActive component
Disclosed are a process and apparatus for selective catalytic reduction of NOx. The process is enabled by passing a heat exchanger section, such as an economizer, of the boiler in advance of an SCR unit at low load conditions to enable NOx reduction even at low loads using urea instead of ammonia. In a preferred form, under high load conditions, the bypass can be almost fully closed and the economizer can be operated normally without excessively cooling the combustion gases, using only a portion of bypassed gases which are hot enough to decompose the urea into its active components including ammonia.
Owner:FUEL TECH
Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx Enabled by Urea Decomposition Heat-Exchanger Bypass
InactiveUS20100055014A1Well mixedAccurate temperatureCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsLow loadActive component
Disclosed are a process and apparatus for selective catalytic reduction of NOx. The process is enabled by bypassing a heat exchanger section, such as an economizer, of the boiler in advance of an SCR unit at low load conditions to enable NOx reduction even at low loads using urea instead of ammonia. In a preferred form, under high load conditions, the bypass can be almost fully closed and the economizer can be operated normally without excessively cooling the combustion gases, using only a portion of bypassed gases which are hot enough to decompose the urea into its active components including ammonia.
Owner:FUEL TECH INC
Thermal decomposition of urea in a side stream of combustion flue gas using a regenerative heat exchanger
InactiveUS7682586B2Avoid insufficient temperatureHeat produced by the burner is conservedNitrogen compoundsExhaust apparatusFlue gasThermal efficiency
This invention relates generally to the treatment of NOx in combustion flue gas. In certain embodiments, the invention relates to the use of a regenerative heat exchanger (RHE) to convert urea to ammonia in a side stream of flue gas. Ammonia and / or other urea decomposition products exit the heat exchanger, are mixed with the rest of the flue gas, and enter a selective catalytic reduction (SCR) unit for reduction of NOx in the flue gas. The use of an RHE significantly improves the thermal efficiency of the overall process. More particularly, in certain embodiments, the regenerative heat exchanger is a dual chamber RHE.
Owner:BABCOCK POWER ENVIRONMENTAL INC (US)
System and method for urea decomposition to ammonia in a side stream for selective catalytic reduction
ActiveUS20140096532A1Reduce nitrogen oxide emissionsReduce NOxExhaust apparatusEmission preventionRecovery boilerAmmonia gas
A method for reducing NOx emissions in the exhaust of a combined cycle gas turbine equipped with a heat recovery boiler and a catalyst effective for NOx reduction, wherein a slip stream of hot flowing exhaust gases is withdrawn from the primary gas flow after the catalyst at a temperature of 500° F. to 900° F. and directed through a fan to a continuous duct into which an aqueous based reagent is injected for decomposition to ammonia gas and the outlet of the continuous duct is connected to an injection grid positioned in the primary exhaust for injection of ammonia gas into the primary exhaust stream at a location upstream of the catalyst.
Owner:CECO ENVIRONMENTAL IP INC
Technique for preparing ammonia from urea by pyrolysis method
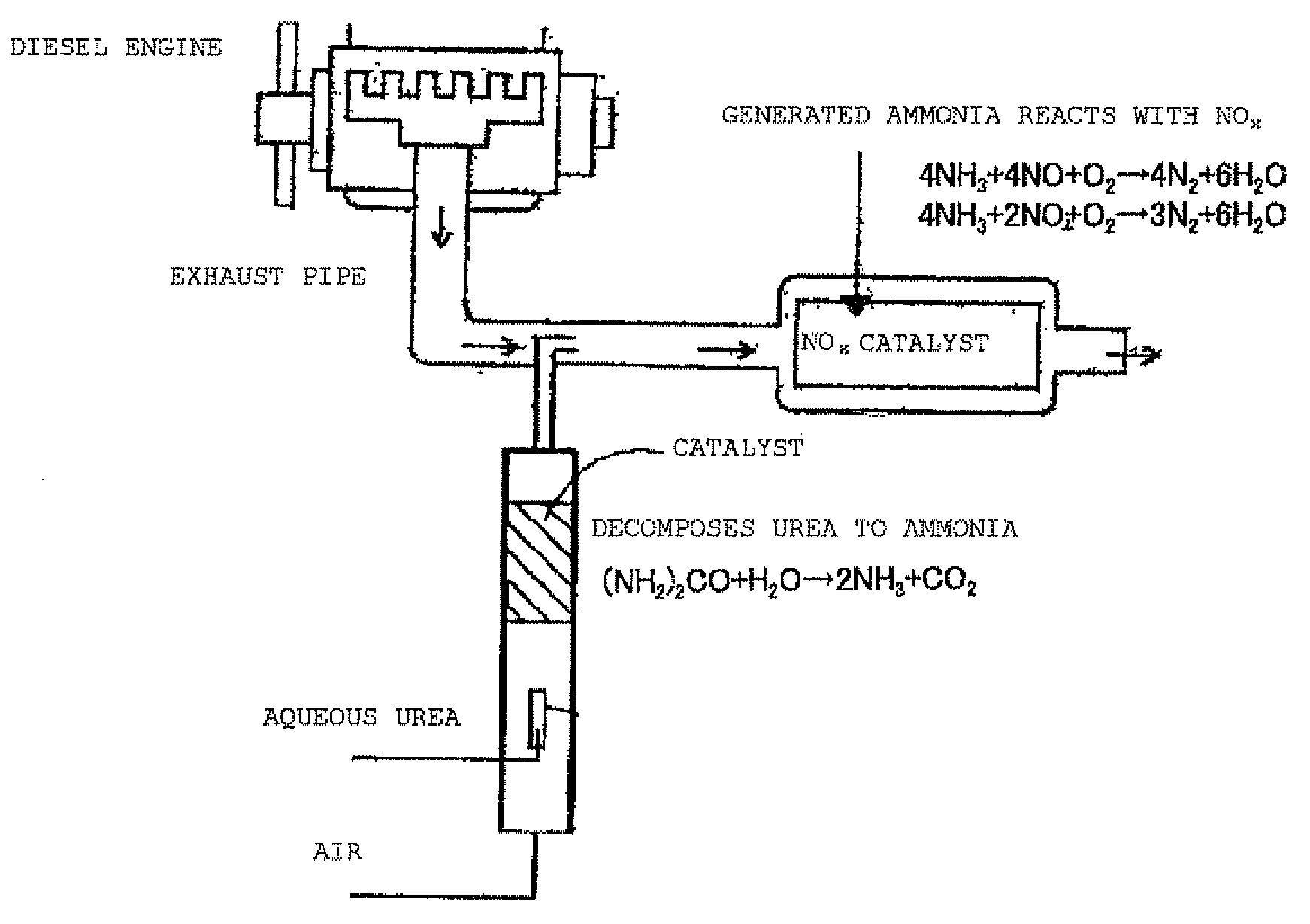
The invention discloses a technique to prepare ammonia from urea through thermolysis, comprising the steps that: step 1: a storage and dissolution system (1) for urea particles is set; step 2: a storage system (2) for urea solution is set; step 3: an urea thermolysis system is set; step 4: a waste liquid treatment system (4) is set; step 5: all systems of the whole technique are communicated; step 6: urea particles are stored and dissolved; step 7: urea is cleaved and ammonia is acquisited; and step 8: waste liquid is treated. The preparation method of ammonia of the invention has the advantages of low cost, simple operation, needing not high pressure, quick respond (the reaction can begin in 5 to 30 sec.), various heating means, and gas fuel or diesel and so on can be used.
Owner:CPI YUANDA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG +1
Selective catalytic reduction of NO, enabled by side stream urea decomposition
A preferred process arrangement utilizes the enthalpy of the flue gas, which can be supplemented if need be, to convert urea ( 30 ) into ammonia for SCR. Urea ( 30 ), which decomposes at temperatures above 140 ° C., is injected ( 32 ) into a flue gas stream split off ( 28 ) after a heat exchanger ( 22 ), such as a primary superheater or an economizer. Ideally, the side stream would gasify the urea without need for further heating; but, when heat is required it is far less than would be needed to heat either the entire effluent ( 23 ) or the urea ( 30 ). This side stream, typically less than 3% of the flue gas, provides the required temperature and residence time for complete decomposition of urea ( 30 ). A cyclonic separator can be used to remove particulates and completely mix the reagent and flue gas. This stream can then be directed to an injection grid ( 37 ) ahead of SCR using a blower ( 36 ). The mixing with the flue gas is facilitated due to an order of magnitude higher mass of side stream compared to that injected through the AIG in a traditional ammonia-SCR process.
Owner:FUEL TECH
Preparation of loaded bimetallic nano-catalyst
InactiveCN102773097AHigh catalytic activityStrong alkalineOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationNano catalystNanoparticle
The invention relates to a kind of Mg-Al hydrotalcite loaded bimetallic nano-catalyst and its preparation method, and relates to application of the catalyst system in oxidation of alcohol into corresponding carbonyl compounds. The catalyst preparation method consists of: 1) preparing an Mg-Al hydrotalcite carrier through a urea decomposition method; 2) loading the precursors of metal Pd and Au on the Mg-Al hydrotalcite surface; and 3) then reducing Pd (II) and Au (III) through NaBH4, thus obtaining the bimetallic nanometer particle catalyst. The catalyst provided in the invention has the advantages of high catalytic activity, good stability, separability, and easy recovery, thus being applicable to alcohol oxidation reactions in aqueous phases.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
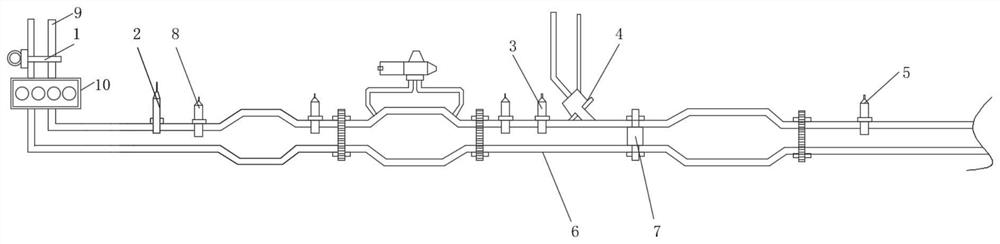
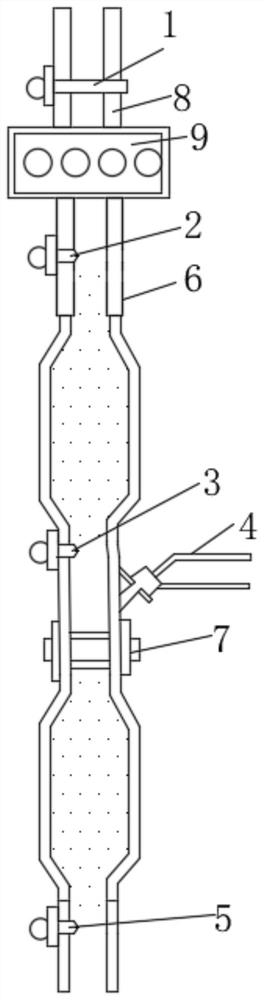
Two-way rotational flow cylinder type urea mixing device
PendingCN110273734AGuaranteed mixing effectReduced risk of crystallizationExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusRotational flowMetal mesh
The invention relates to a two-way rotational flow cylinder type urea mixing device which comprises a nozzle base, a base supporting cover, a rotational flow pipe, a metal mesh ring, a supporting plate, a back rotational flow plate, a front rotational flow plate and a cylinder; the supporting plate is arranged inside the cylinder, a hole is formed in the front part of the supporting plate, the front rotational flow plate is installed inside the hole, the back rotational flow plate is installed at the rear part of the supporting plate, and the front rotational flow plate, the supporting plate and the back rotational flow plate form a mixing cavity inside the cylinder; the nozzle base, the base supporting cover, the rotational flow pipe and the metal mesh ring are sequentially fixedly connected from top to bottom, the base supporting cover penetrates through the hole in the cylinder and is fixedly connected with the cylinder, and the rotational flow pipe runs into the hole in the middle of the supporting plate to be fixedly connected with the supporting plate; the metal mesh ring stretches into the mixing cavity; the nozzle base, the base supporting cover, the rotational flow pipe and the metal mesh ring are inclined. On the condition of ensuring urea mixing uniformity, the crystallization problem that the urea decomposition efficiency is not high in an SCR system is solved.
Owner:WUXI WEIFU LIDA CATALYTIC CONVERTER
Exhaust gas purifying apparatus
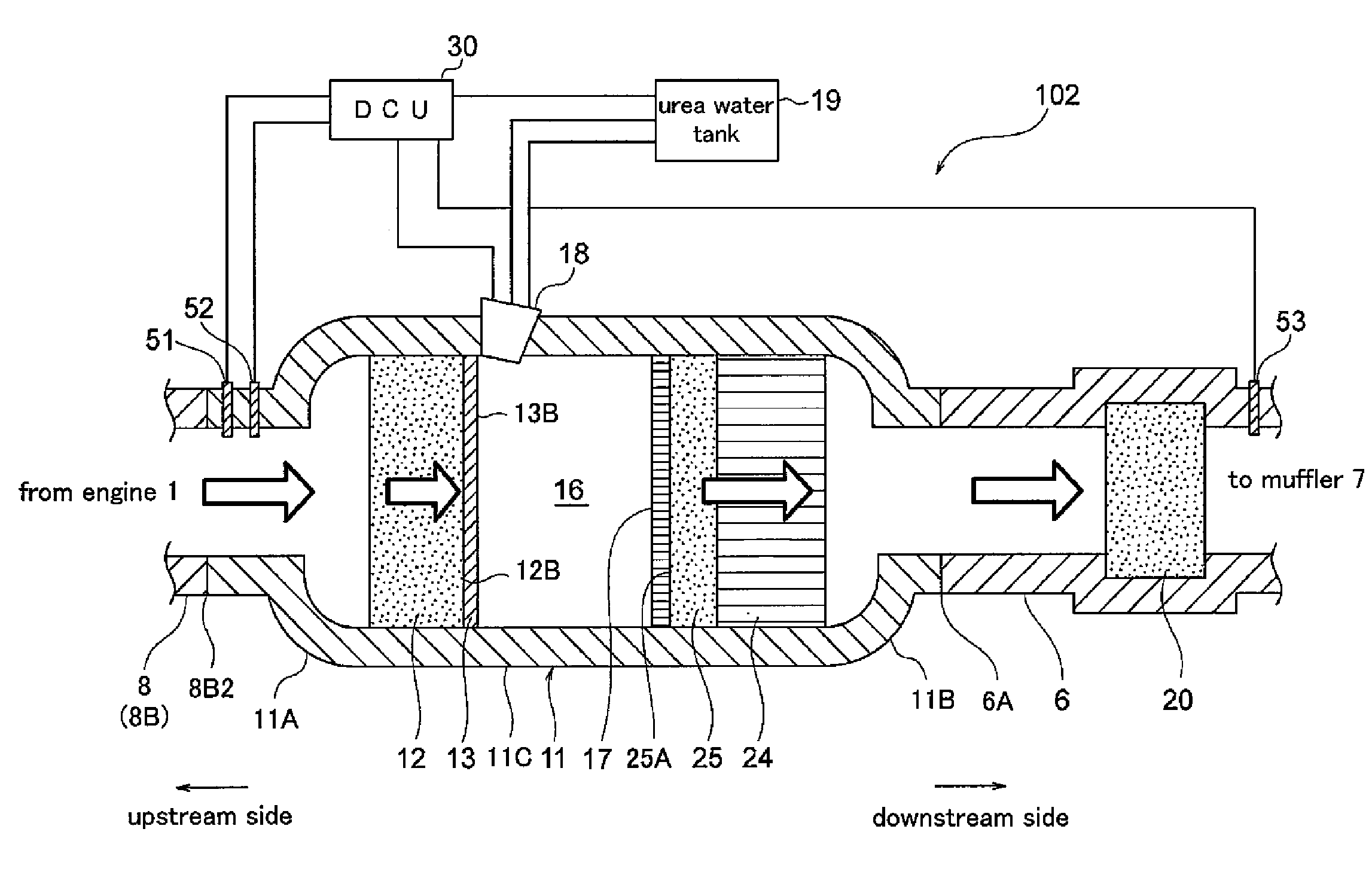
An exhaust gas purification apparatus includes an oxidation catalyst provided in a passage through which exhaust gas flows, a urea decomposition accelerator, a selective catalytic reduction catalyst provided downstream of the urea decomposition accelerator and a urea water supplying device for supplying urea water to the urea decomposition accelerator. The urea decomposition accelerator is provided downstream end surface of the oxidation catalyst and has at least one of hydrophilic function and hydrolytic catalytic function.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
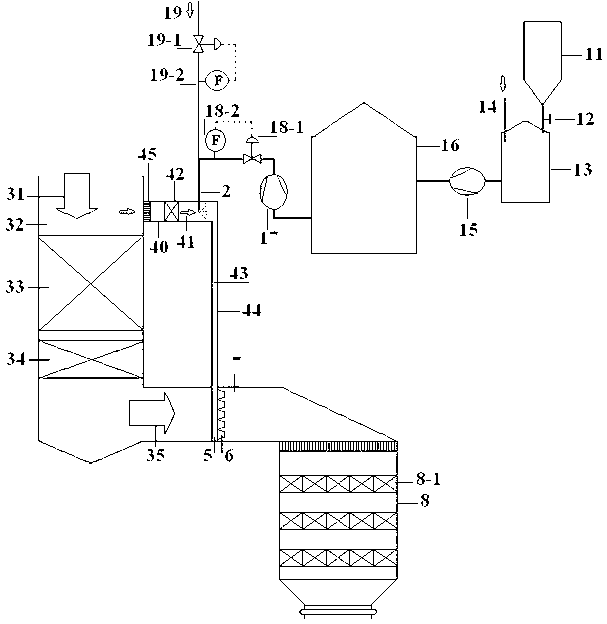
Method and device for spraying reducing agent used for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx
InactiveCN102794106AReduce operating energy consumptionSave investment costDispersed particle separationFlue gasPressure difference
The invention discloses a method and a device for spraying a reducing agent used for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NOx and belongs to the field of SCR of NOx. The method comprises the following steps of self-extracting out a small amount of flue gas in an area having a temperature of 500 to 900 DEG C in a boiler by a pressure difference, wherein the small amount of the extracted flue gas is used as urealysis flue gas, spraying a urea solution to the flue gas so that the urea solution is decomposed into ammonia and the ammonia is mixed with the flue gas, feeding back the mixed gas to a reactor for SCR of NOx, and carrying out denitration. The device comprises a denitration reducing agent channel of which one end is communicated with the area having a temperature of 500 to 900 DEG C in the boiler and the other end is communicated with an inlet flue gas channel of the reactor for SCR of NOx. The denitration reducing agent channel comprises a urealysis pipe, an ammonia / flue gas mixed gas pipe and an ammonia injection pipe, wherein the urealysis pipe, the ammonia / flue gas mixed gas pipe and the ammonia injection pipe are communicated orderly. The urealysis pipe is provided with a urea solution spray gun. The method and the device for spraying a reducing agent used for SCR of NOx have the advantages of low investment and operation costs, low energy consumption, high safety, high reliability and complete urealysis.
Owner:DONGFANG BOILER GROUP OF DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP
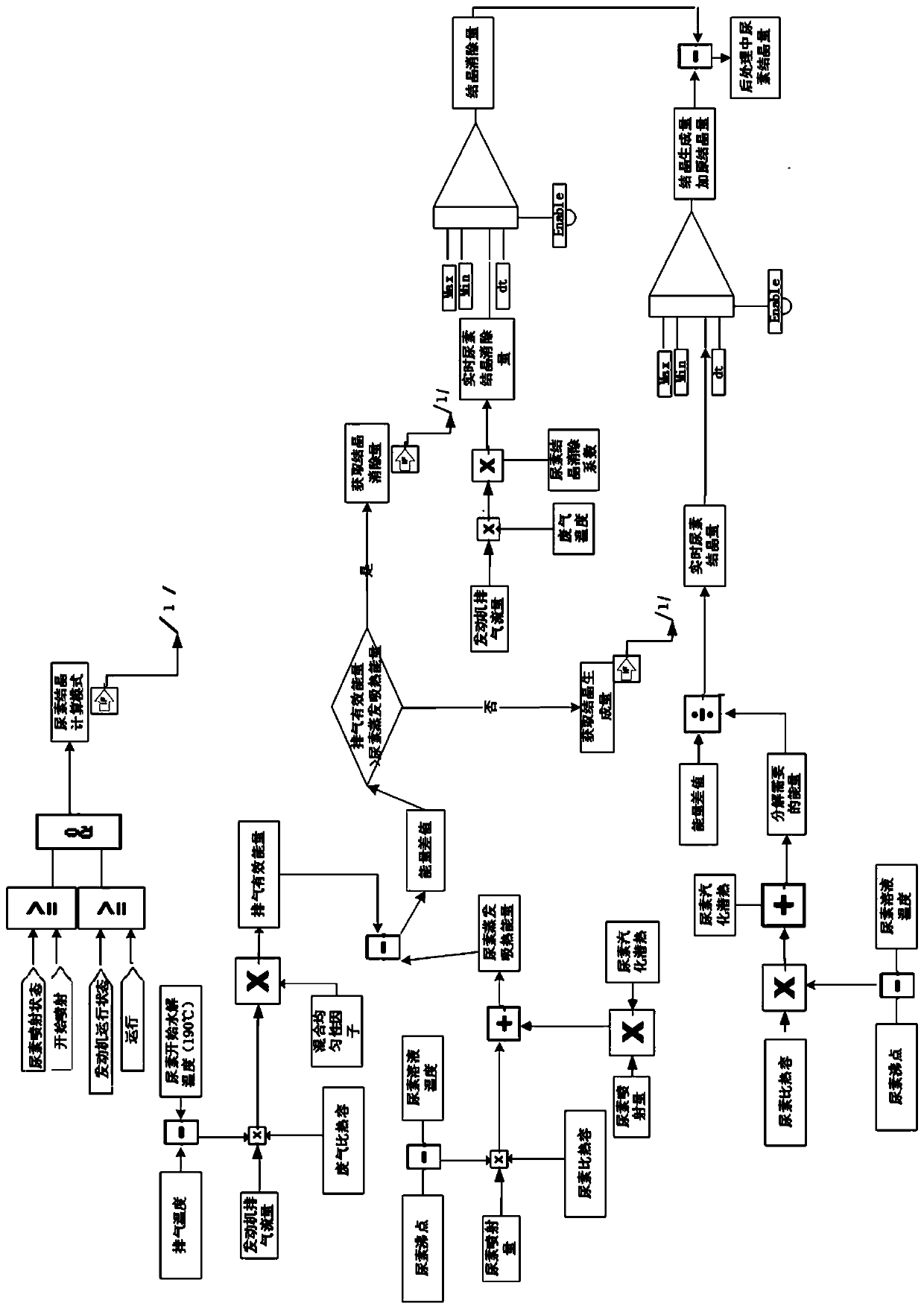
Urea crystallization state monitoring method of catalytic reduction reaction device and storage medium
ActiveCN110725737AImprove conversion efficiencyAvoid the risk of corrosionInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusChemical reactionPhysical chemistry
The application discloses a urea crystallization state monitoring method of a catalytic reduction reaction device and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps: obtaining exhaust effective energy and obtaining urea evaporation heat absorption energy; if the exhaust effective energy is greater than the urea evaporation heat absorption energy, obtaining a crystal elimination amount; otherwise, obtaining a crystal generation amount; obtaining the urea crystallization amount in the post-treatment according to the original crystallization amount, the crystal elimination amount and the crystal generation amount of the catalytic reduction reaction device; and if the urea crystallization amount in the post-treatment is greater than or equal to the urea crystallization amount limit value, triggering a de-crystallization treatment mode. According to the method provided by the invention, the crystallization state is judged on the basis of the difference between the real-time energy of thewaste gas and the energy required by urea decomposition, and when the crystallization amount of urea exceeds a threshold value, the de-crystallization treatment mode can be triggered in time, so thatcrystals are prevented from being further chemically reacted into stones, the conversion efficiency of the catalytic reduction reaction device is improved, and the risk of corrosion of an exhaust pipeis avoided.
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
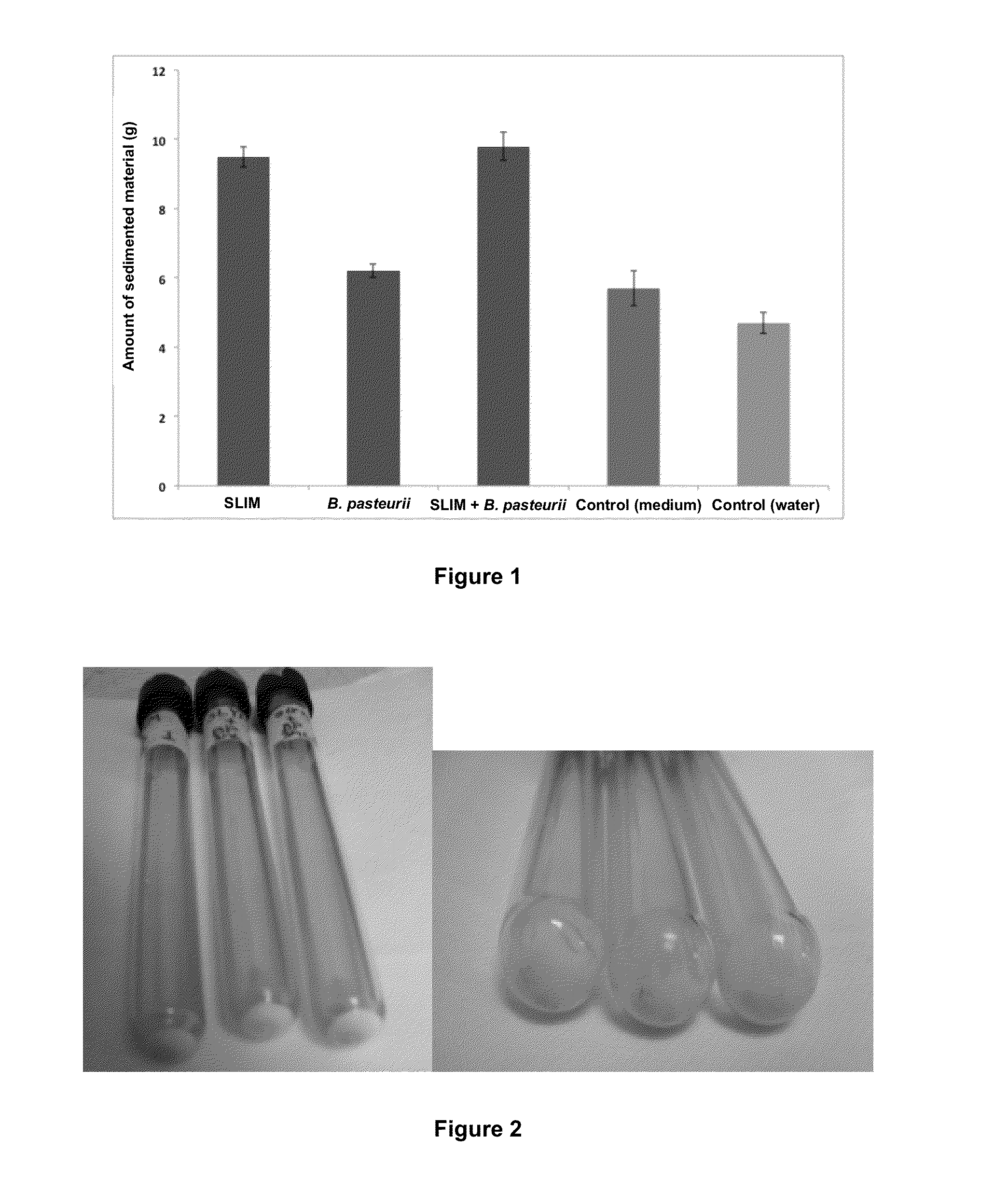
Biocementation of particulate material in suspension
The present invention is directed to a composition and method to decrease the amount of particulate material in suspension, both in a liquid or in air, especially in industrial processes that generate suspended particulate material. In particular, the invention is directed to a composition and method to decrease the amount of particulate material in suspension in air or a liquid through agglomeration and subsequent biocementation, by application of an exopolysaccharide (EPS) source that can be direct or through inoculation with microorganisms that produce said EPS. This allows in a first step to settle the particulate material and subsequently the cementation of the material when there are calcium containing compounds in the particulate material that has been settled in the first step, by means of the inoculation of a second class of microorganisms that have ureolytic activity.
Owner:CULTIVOS HIDROBIOLOGICOS Y BIOTECHA AGUAMARINA
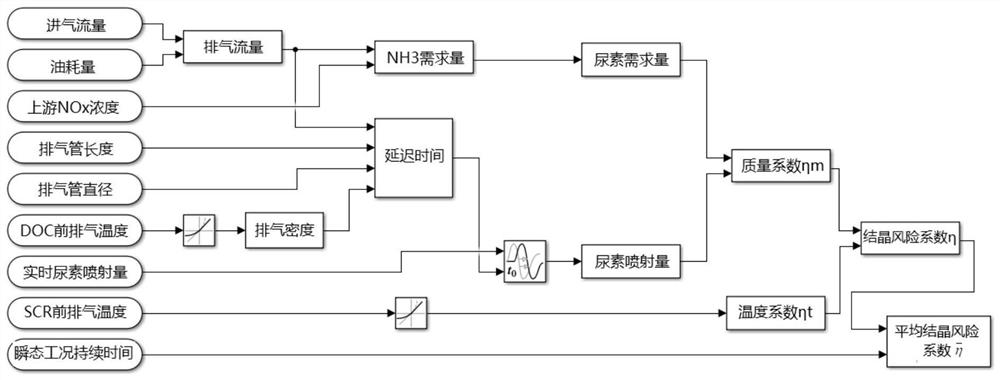
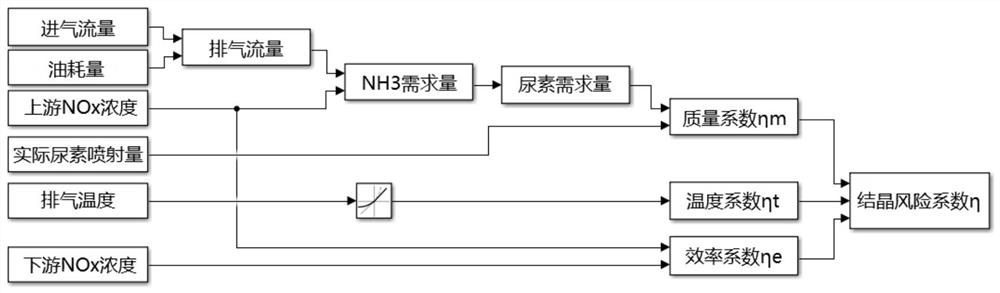
Method and device for evaluating urea crystallization risk based on transient working condition
ActiveCN112879136AImprove reliabilityWide versatilityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusChemical physicsChemical reaction
The invention discloses a method for evaluating urea crystallization risk based on a transient working condition. The evaluation method uses two most important coefficients influencing urea crystallization, namely a quality risk coefficient and a temperature risk coefficient; the crystallization risk coefficient eta is calculated according to a quality coefficient eta m and a temperature coefficient eta t, and the average crystallization risk coefficient is obtained by integrating the crystallization risk coefficient eta in the transient working condition duration t and then averaging; the urea crystallization risk coefficient is calculated from the aspects of quality and temperature which have the maximum influence on crystallization; the urea crystallization risk is quantized by using a mathematical method; a threshold value of urea crystallization can be obtained through calibration; a urea decomposition detailed mechanism is fused into a model; a chemical reaction path is expressed in the form of a mathematical equation; the influence of exhaust pipeline arrangement on the urea crystallization risk under the transient working condition is considered; the urea crystallization risk coefficient is not a fixed formula and can be calibrated according to a bench transient test; the reliability is high; and the universality is wide.
Owner:天津市津聿动力科技有限公司
Method for urea decomposition and ammonia feed to a selective catalytic reduction system
ActiveUS8815197B2Reduce the temperatureLow costNitrogen compoundsDispersed particle separationAqueous solutionSide stream
Owner:CECO ENVIRONMENTAL IP INC
Spinel-supported catalyst for dry reforming of coke oven gas and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103599785AHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a spinel-supported catalyst for dry reforming of coke oven gas and a preparation method of thereof and belongs to the technical fields of comprehensive utilization of metallurgical resources and preparation of catalysts. The spinel-supported catalyst is characterized in that large-specific surface area MgAl2O4 spinel with a mesoporous structure serves as a carrier, rare earth or a rare earth oxide solid solution serves as an aid, and one or two in Ni, Co, Ru, Pt and Pd are taken as active metal components, wherein the mass percent of the active metal components is 5-11 percent, and the mass percent of the aid is 0-5 percent. The large-specific surface area MgAl2O4 spinel with the mesoporous structure is prepared by adopting a uniform urea decomposition-template method, and the aid and the active metal components are impregnated step by step according to an impregnation method. By the catalyst prepared by the method, the carbon deposition tendency in the dry reforming reaction process of the coke oven gas can be effectively reduced; and the catalyst has the advantages of large specific surface area, high active metal dispersibility, high catalytic activity, high product selectivity and long service life.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Composite unit of automobile exhaust catalytic reduction postprocessor
InactiveCN102032030AAchieve hybridAchieve decompositionExhaust apparatusDispersed particle separationSurface layerCeramic coating
The invention relates to a composite unit of an automobile exhaust catalytic reduction postprocessor. The composite unit is characterized in that: ceramic coatings are coated on the inner wall and the outer wall of the composite unit, and nano-scale TiO2 granules are uniformly and densely distributed on the surface layer of the composite unit; and the catalytic reduction postprocessor is a square box, ceramic coatings are coated on the inner sides of a cavity partition plate and an end plugging plate of the catalytic reduction postprocessor, and nano-scale TiO2 granules are uniformly and densely distributed on the surface layer of the catalytic reduction postprocessor. The structure of the catalytic reduction postprocessor applied on a commercial automobile, the structural parameters are optimized, the effect of the urea mixing unit is improved, the ceramic coatings are increased, and the nano-scale TiO2 granule uniformly and densely distributed on the surface layer strengthen the urea decomposition function and have de-noising effect, certain heat insulation effect and high practical value.
Owner:FAW GROUP
Selective catalytic reduction of NOx enabled by sidestream urea decomposition
ActiveUS7829033B2Well mixedAccurate temperatureCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsParticulatesSuperheater
A preferred apparatus arrangement utilizes the enthalpy of the flue gas, which can be supplemented if need be, to convert urea (30) into ammonia for SCR. Urea (30), which decomposes at temperatures above 140 .degree. C., is injected (32) into a flue gas stream split off (28) after a heat exchanger (22), such as a primary superheater or an economizer. Ideally, the side stream would gasify the urea without need for further heating; but, when heat is required it is far less than would be needed to heat either the entire effluent (23) or the urea (30). This side stream, typically less than 3% of the flue gas, provides the required temperature and residence time for complete decomposition of urea (30). A cyclonic separator can be used to remove particulates and completely mix the reagent and flue gas. This stream can then be directed to an injection grid (37) ahead of SCR using a blower (36). The mixing with the flue gas is facilitated due to an order of magnitude higher mass of side stream compared to that injected through the AIG in a traditional ammonia-SCR process.
Owner:FUEL TECH INC
Selective urea decomposition catalyst taking honeycomb metal alloy as carrier and preparation method for catalyst
InactiveCN102658184AImprove aging resistanceGood low temperature ignitionPhysical/chemical process catalystsBulk chemical productionCerium(IV) oxideBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
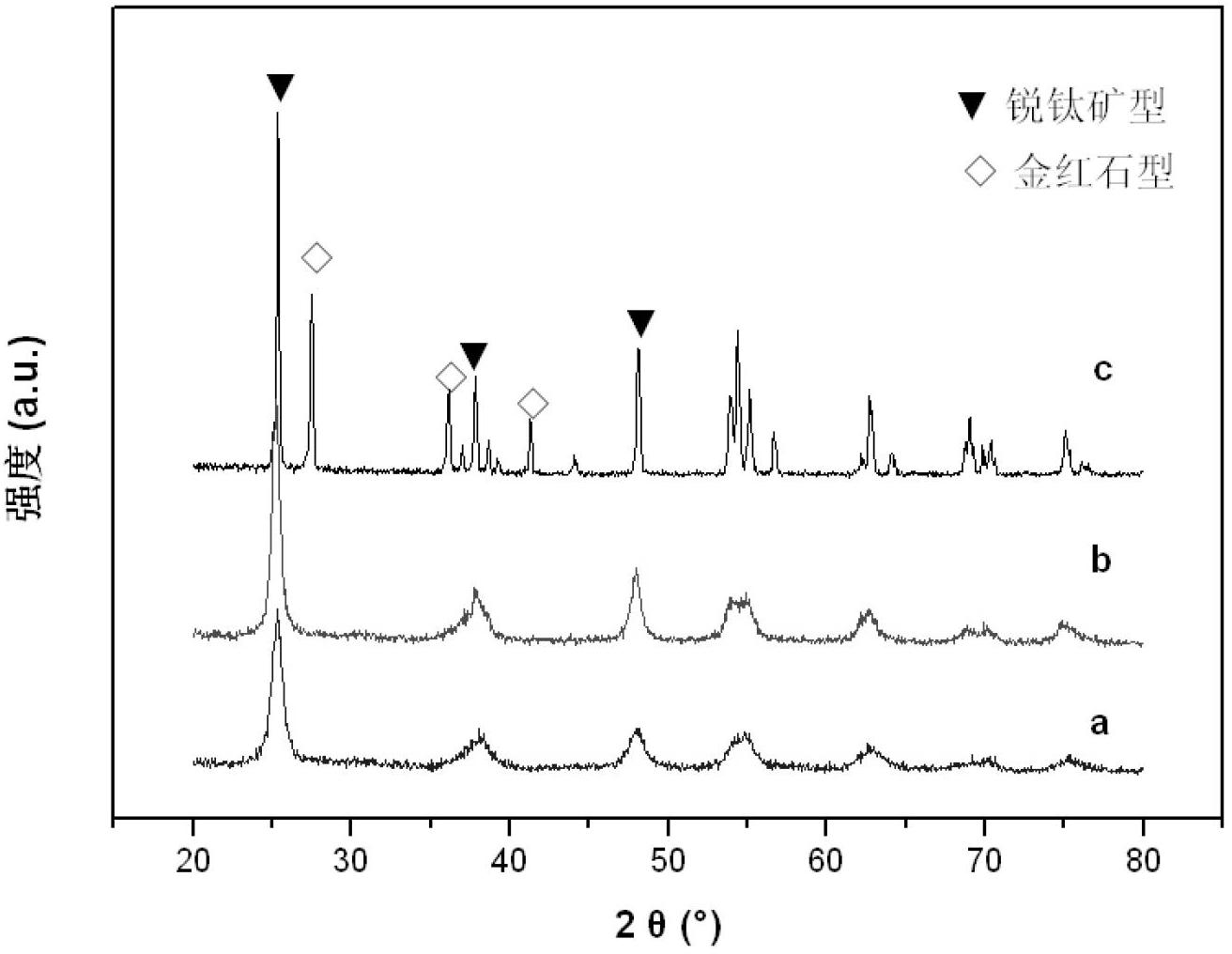
The invention belongs to the field of purification of NOx in tail gas of diesel engines, and in particular relates to a selective urea decomposition catalyst taking a honeycomb metal alloy as a carrier and a preparation method for the catalyst. The catalyst consists of titanium dioxide, cerium dioxide and a phosphorus-containing compound; the mass / volume ratio of the catalyst to the carrier is 50-150g / L; and the catalyst comprises 5 to 25 mass percent of cerium dioxide, 70 to 90 mass percent of titanium dioxide and 1 to 10 mass percent of phosphorus-containing compound, namely CePO4. The catalyst can be firmly adhered to the metal alloy carrier; the titanium dioxide component in the catalyst has high ageing resistance, and when the temperature is lower than 600DEG C, the anatase crystalline phase cannot be converted to the rutile crystalline phase; and moreover, due to the metal alloy carrier, the active ingredients of the catalyst have low light-off temperature.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for in-situ remediation of arsenic-polluted soil by arsenic-resistant bacteria with induction and solidification effects
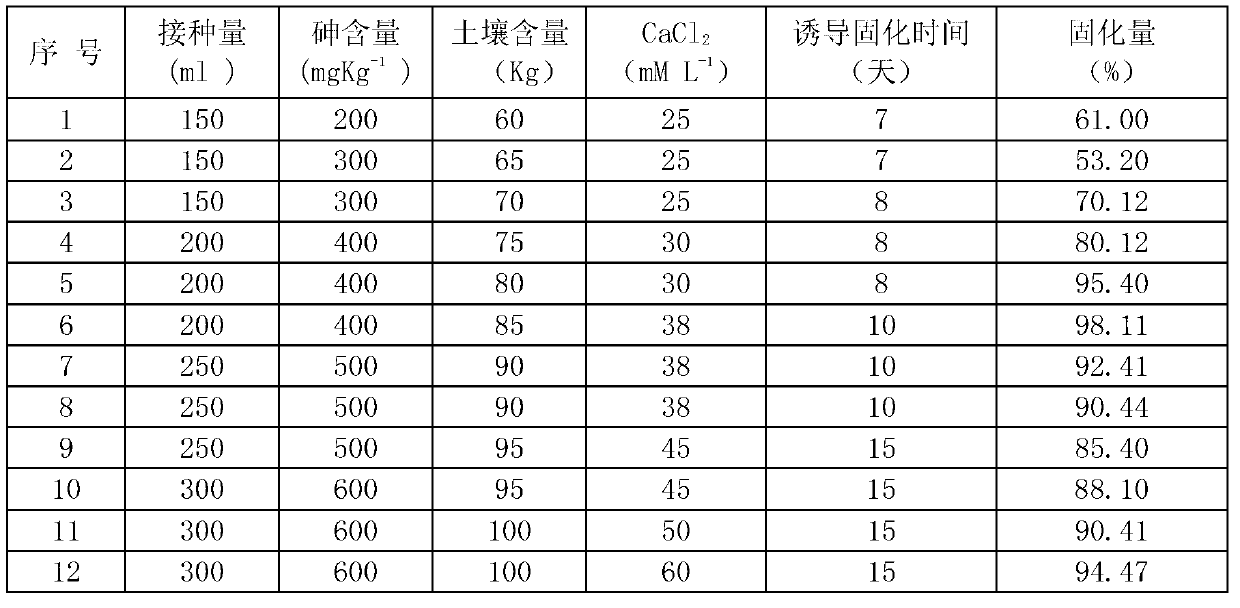
InactiveCN103121033AWide range of repair applicationsAvoid secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationCalcification
The invention relates to a method for in-situ remediation of arsenic-polluted soil by arsenic-resistant bacteria with induction and solidification effects. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, separating arsenic-resistant bacteria which can generate more urea decomposition enzymes under an environment of resisting high-concentration arsenic by gradually increasing the arsenic content in a nutrient bouillon culture medium; putting the arsenic-resistant bacteria in the nutrient bouillon culture medium containing urease and CaC12; gathering to obtain the arsenic-resistant bacteria with calcification; mixing the gathered arsenic-resistant bacteria CR5 bacteria solution with calcification with the polluted soil containing arsenic to form a mixed solution, so that the pH of the mixed solution displays a weak alkaline environment until the pH is 8-9; cultivating the mixed solution in a wet environment; and fixing the arsenic in the polluted soil containing arsenic by the arsenic-resistant bacteria with calcification by inducing calcification, so that the arsenic-polluted soil is subjected to in-situ remediation. The method is simple and convenient to operate, easy to control, and low in cost, and can be widely applied to repairing of heavy metal soil pollution.
Owner:XINJIANG INST OF ECOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Exhaust gas treatment apparatus
InactiveUS8080209B2Improve adhesionIncrease resistanceCombination devicesGas treatmentParticulatesHoneycomb
An exhaust gas treatment apparatus includes a device (A) which is provided in an exhaust system and which selectively reduces NOx in an exhaust gas and a device (B) which is disposed upstream of the device (A) and which decomposes urea and supplies ammonia as a NOx reducing gas, the device (B) including a urea decomposition catalyst. The catalyst is [1] a zeolite catalyst which is composed of granular molded bodies including zeolite particles or which includes a catalyst layer composed of zeolite particles disposed on a support, or [2] a honeycomb catalyst or a membranous catalyst in which metal oxide particulates adhere to a conductive honeycomb substrate or netlike support, and the metal oxide particulates are composed of at least one oxide of a metal selected from the group consisting of Na, Mg, Ca, Ba, La, Ce, Ti, Zr, V, Cr, Mo, W, Mn, Zn, Al, Si, P, Sb, Cu, Fe, Ru, Co, and Re.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Method and device for evaluating urea crystallization risk based on steady-state working condition
ActiveCN112879137AImprove reliabilityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusChemical physicsChemical reaction
Owner:天津市津聿动力科技有限公司
Preparation method of alpha-Fe2O3 magnetic nano-powder material
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of an inorganic non-metal magnetic nano-powder material and in particular relates to a preparation method of an alpha-Fe2O3 magnetic nano-powder material. The preparation method takes inorganic iron salt and urea as raw materials and comprises the following steps: dissolving Fe<3+> and the urea into water according to the mol ratio of no more than 5 to 1; controlling the concentration of the Fe<3+> to be 0.5mol / L to 3.0mol / L and stirring; raising the temperature to 85 DEG C to 98 DEG C and reacting; after reacting, centrifuging and separating; washing with distilled water and precipitating; drying sediment and grinding; putting the sediment into a program temprature controlling resistor furnace and calcining at 500 DEG C to 700 DEG C to obtain the alpha-Fe2O3 magnetic nano-powder material. The alpha-Fe2O3 magnetic nano-powder material is prepared by adopting the urea to uniformly disperse an iron source and carrying out urea decomposition reaction; the preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process, easy to operate, low in cost, low in equipment requirements and environmentally friendly; a product has uniform structure and shape and stable performances.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for preparing nitrogen-doped TiO2 hollow nano material
ActiveCN106732724ANitrogen dopingAchieving Visible Light ResponsePhysical/chemical process catalystsReaction temperatureSolvent
The invention discloses a method for preparing a visible-light-responsive nitrogen-doped TiO2 hollow nano material by adopting a TiOF2 nanocube as a template and urea as a nitrogen source. The TiOF2 nanocube with a cubic structure is obtained by using a solvothermal method. The method comprises the steps that the TiOF2 nanocube powder and different amount of urea are put together in a sealed tubular furnace for heating treatment, NH3 generated from urea decomposition participates in the process that the TiOF2 is heated for decomposition to cause reconstruction of crystal lattices and generate TiO2, so that the N doping is realized; and the products form a hollow cubic box structure, and the surface is formed by TiO2(001) crystal surfaces. According to the method, the doping amount of nitrogen in products can be simply controlled by controlling the use amount of the urea, so that the absorption range and the absorption intensity of the products in a visible-light area can be regulated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the operation is simple, the applicable reaction temperature is wider, and the use amount and the proportion of the materials can be regulated in a larger range, so that the controllability is good and the universality is very strong.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Nonprotein nitrogen feed additive suitable for ruminant and its producing process
InactiveCN101077126ASolve the problem that the decomposition speed is too fastDecomposition will not causeAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsRumenFeed additive
The present invention discloses one kind of non-protein nitrogen feed additive for ruminant and its production process. The non-protein nitrogen feed additive has reasonable recipe, easy production, low cost, high decomposition speed, urea decomposing speed matching the utilization speed of rumen to avoid ammonia accumulation in blood and good taste. The non-protein nitrogen feed additive consists of urea 35-50 wt%, corn starch 35-48 wt%, and coating material 2-20 wt%, and its production process includes the steps of dispersing urea and corn starch in coating material solution, grinding in a colloid mill to form emulsion, and spray drying at normal temperature to form microspherical feed additive. It may be also produced into powder, granule, tablet or capsule.
Owner:史义林 +1
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com