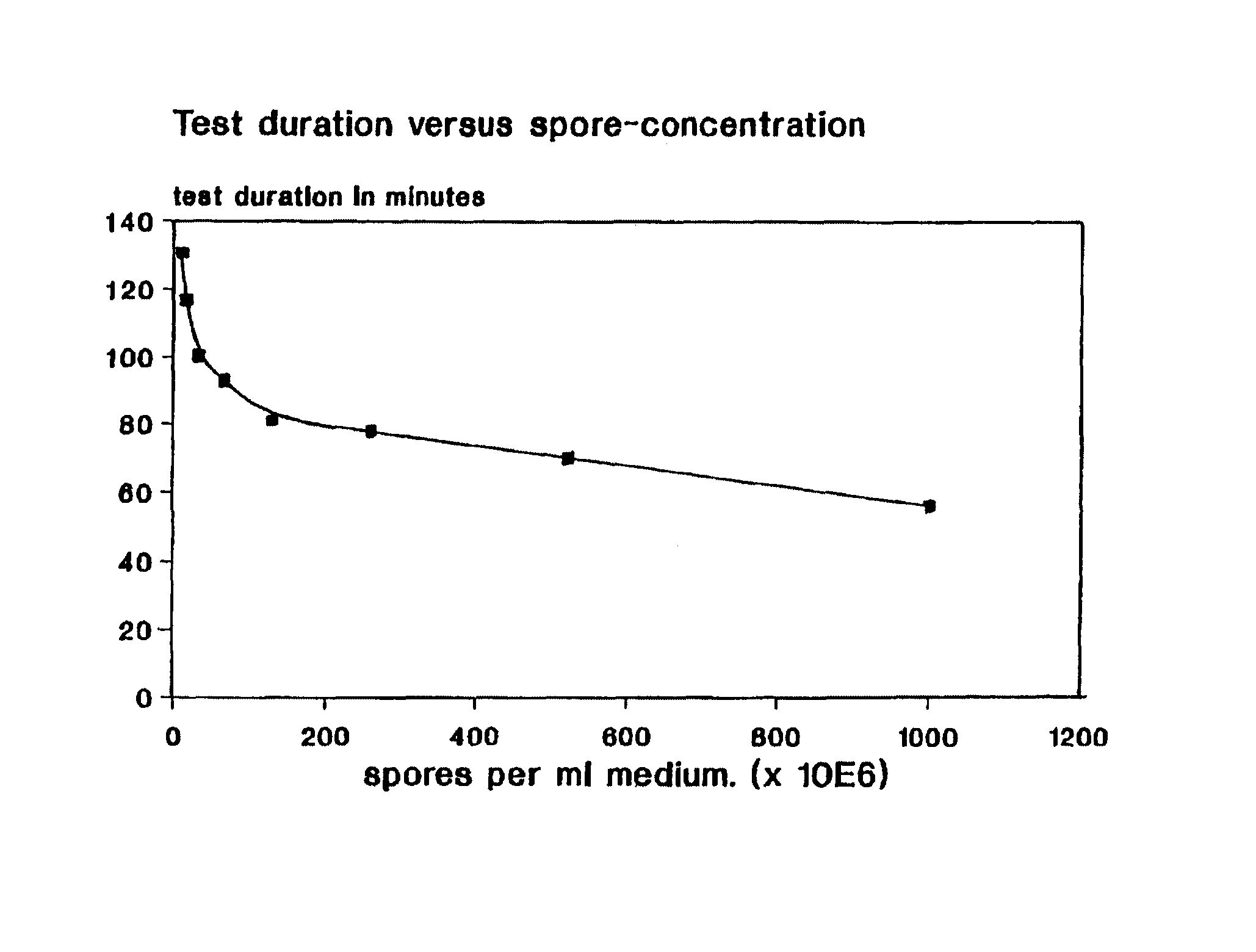
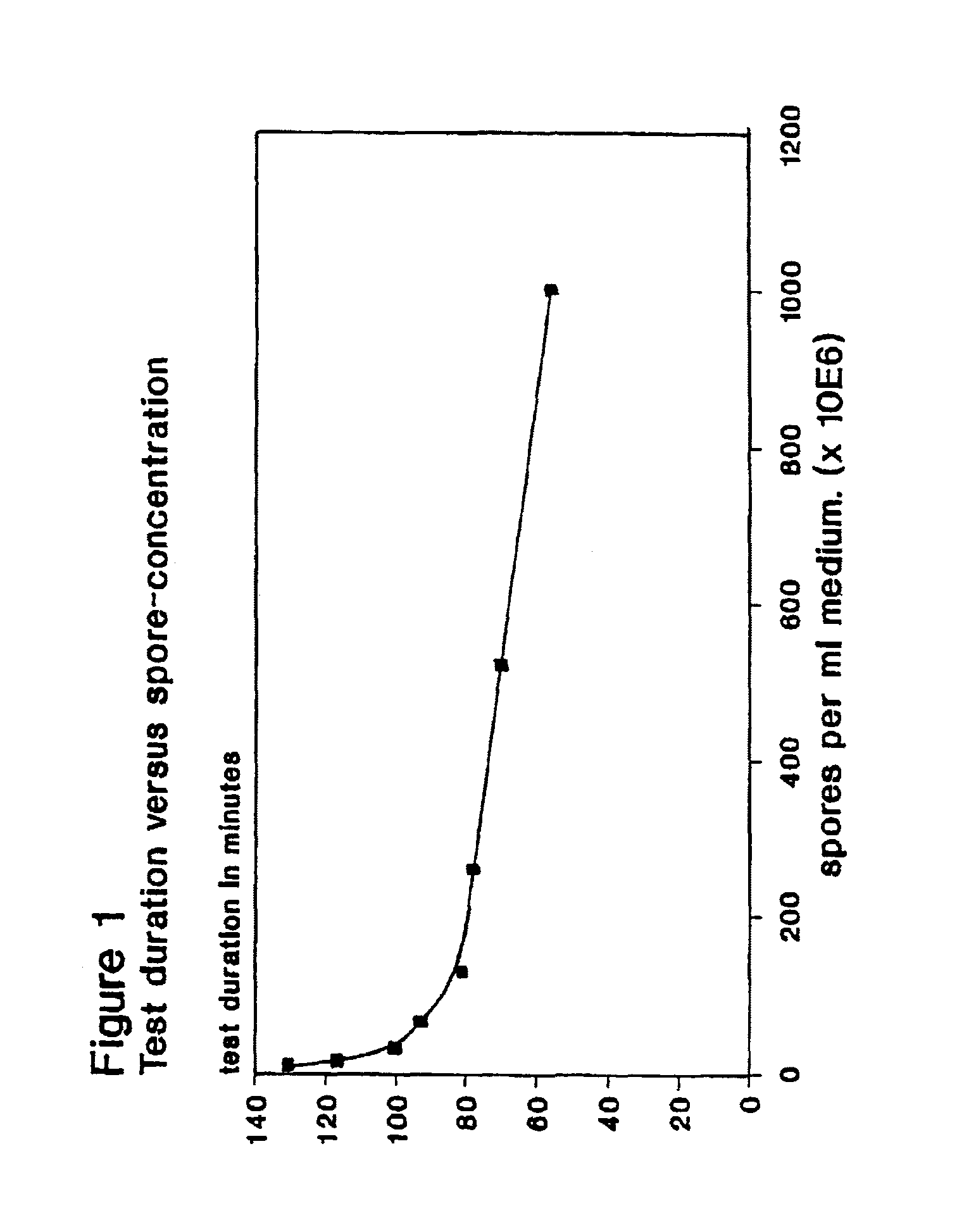
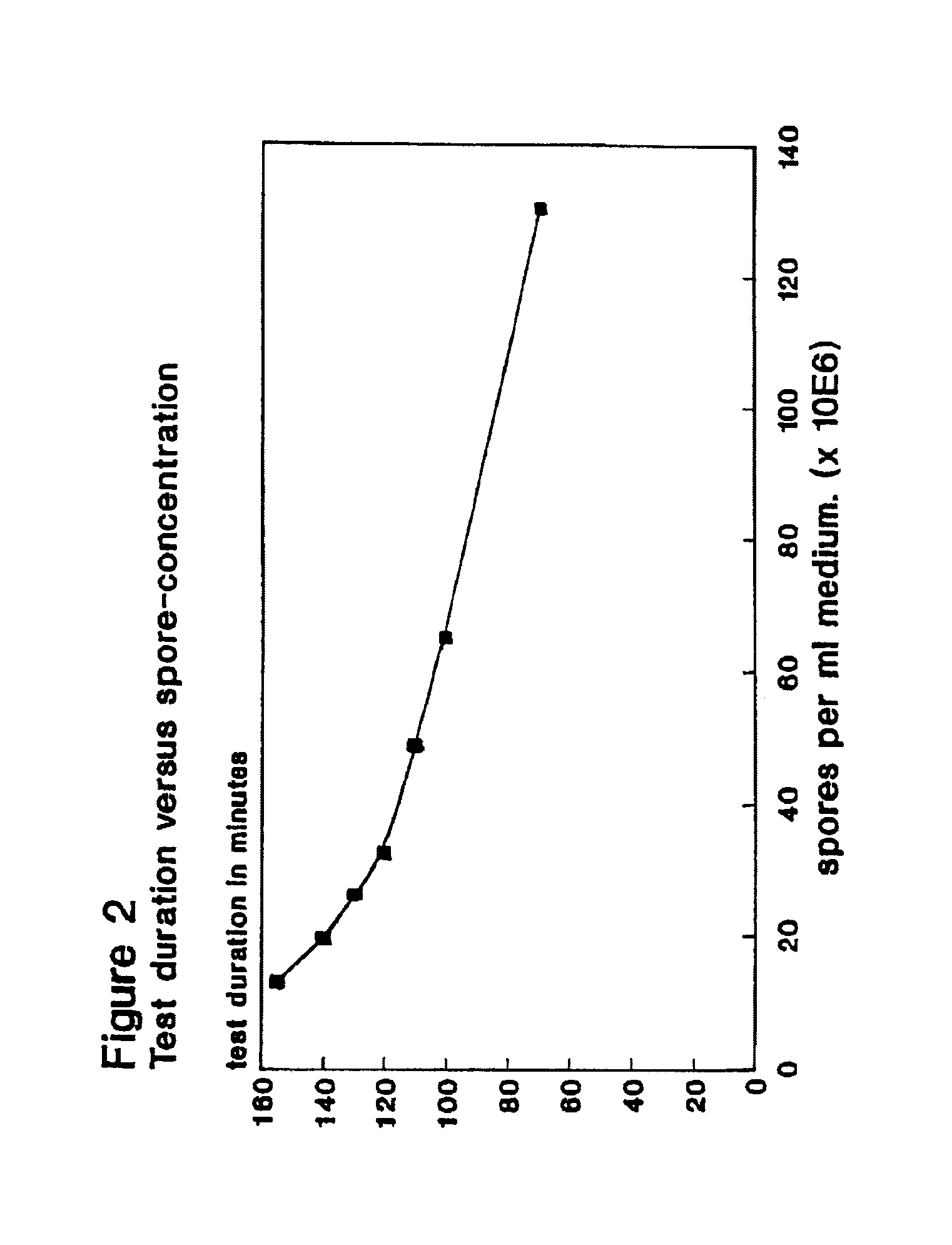
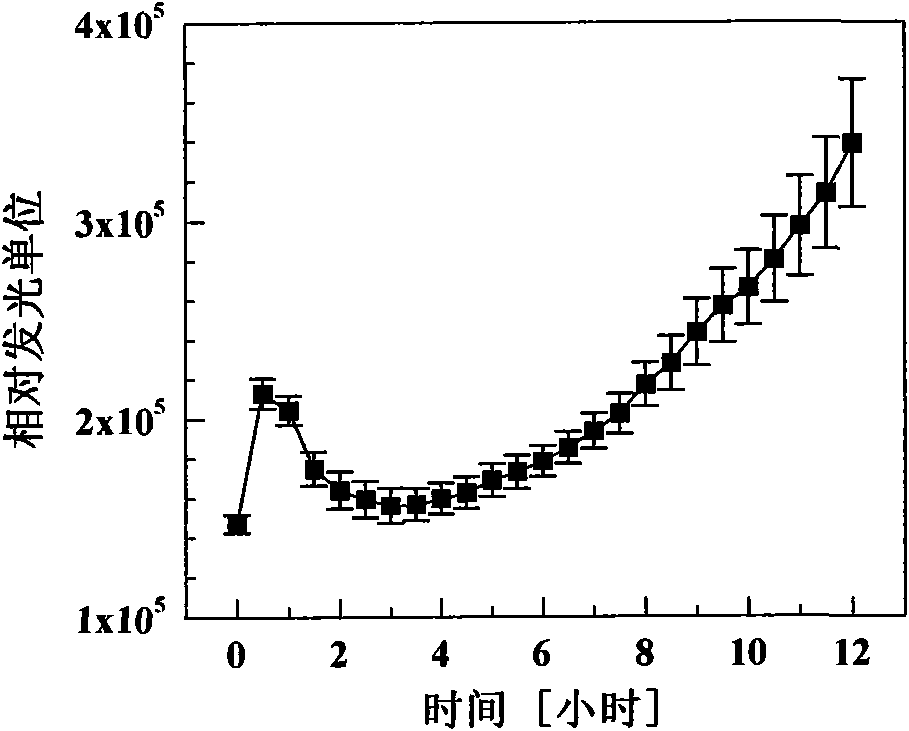
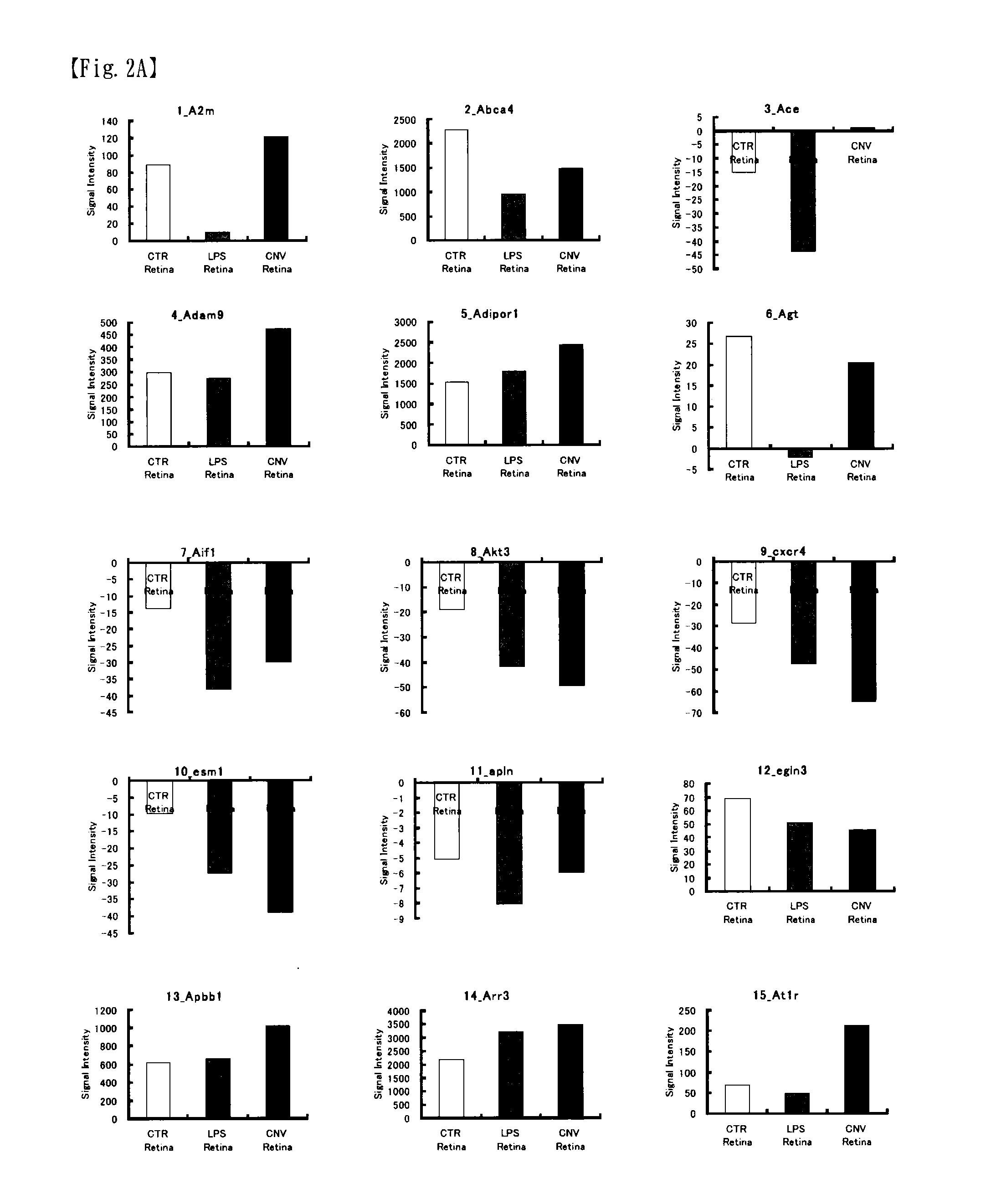
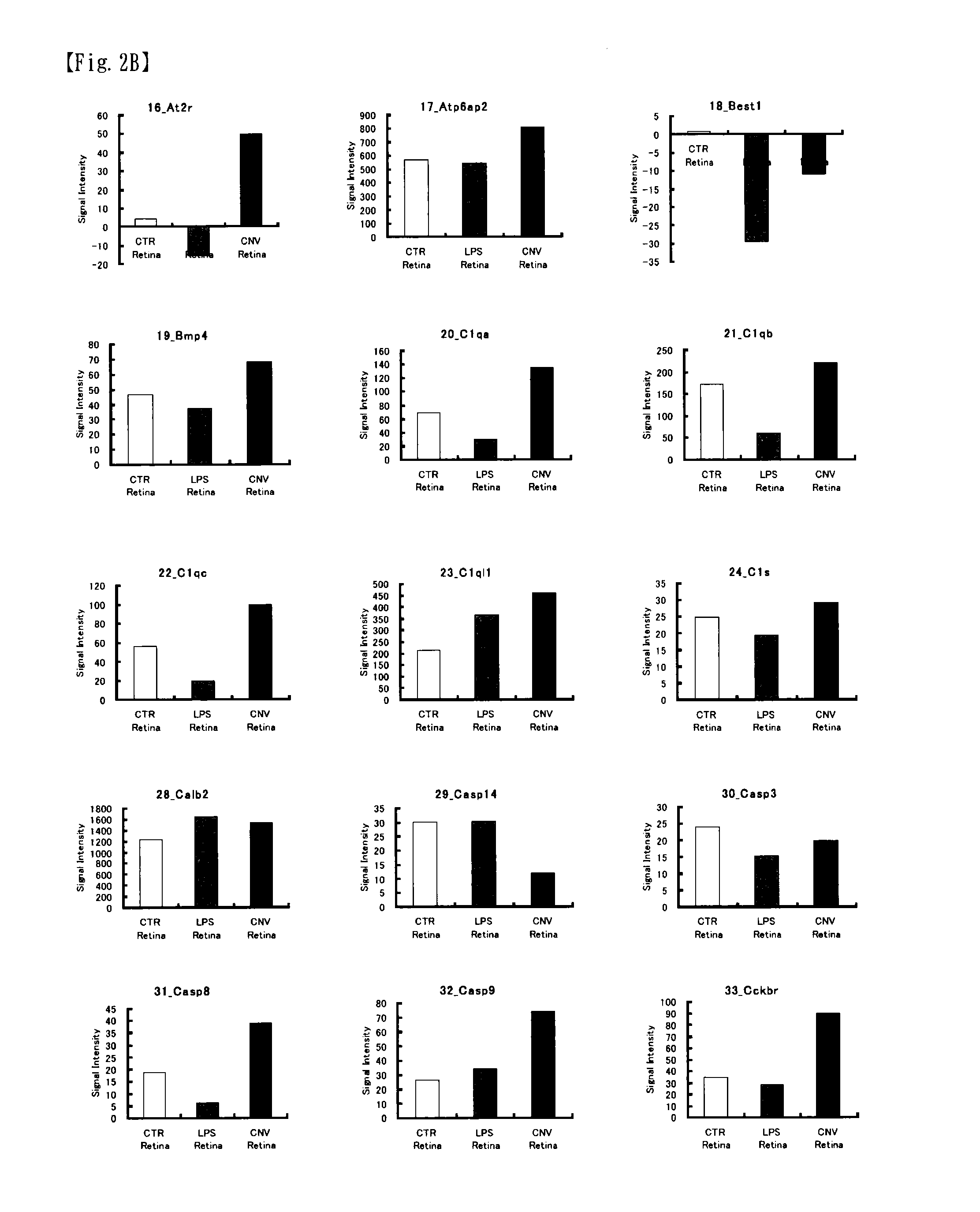
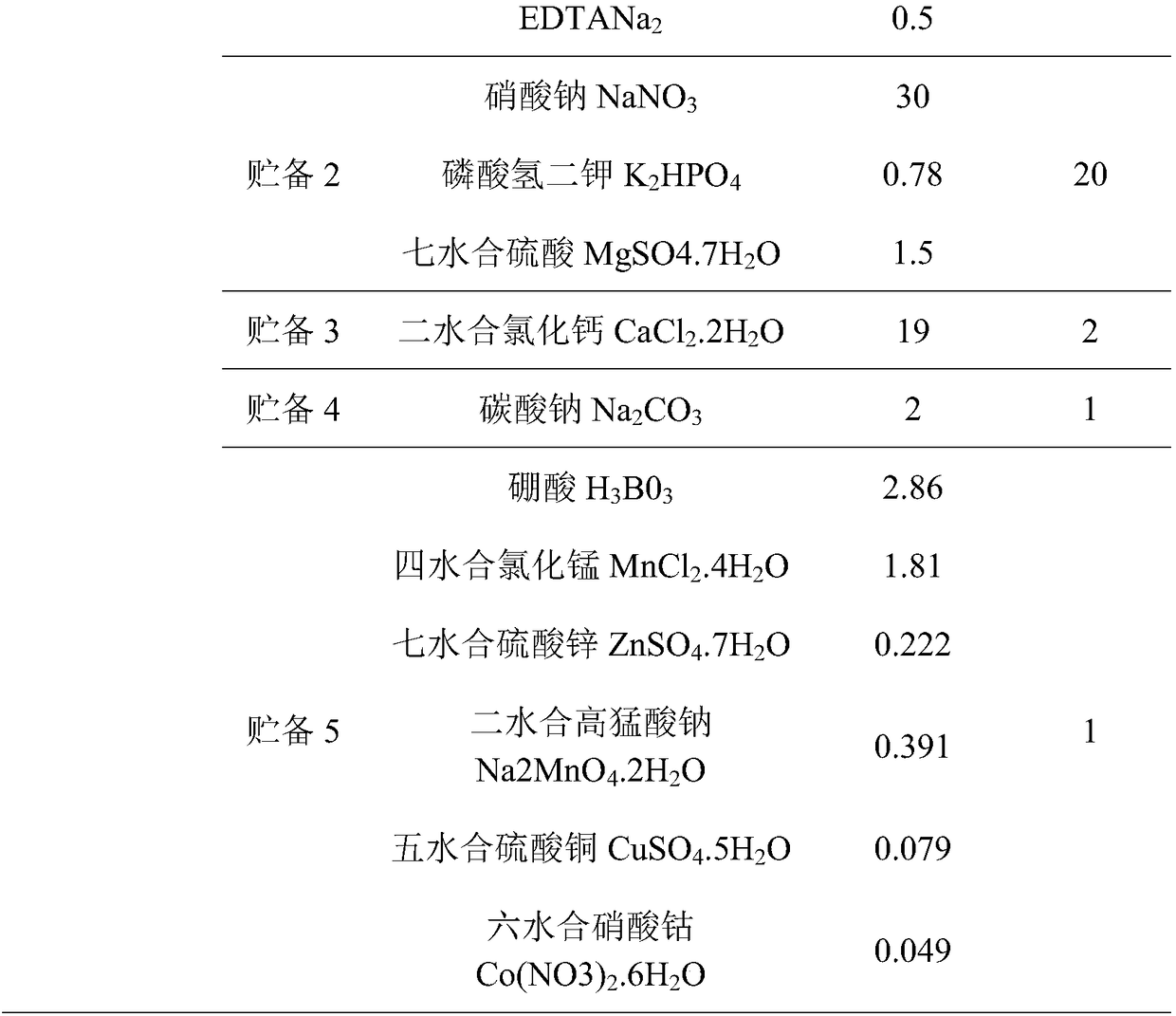
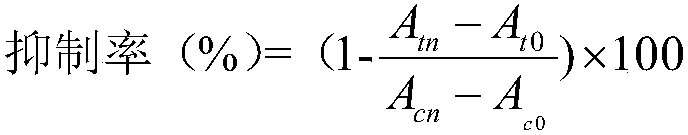Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
119 results about "Test organism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
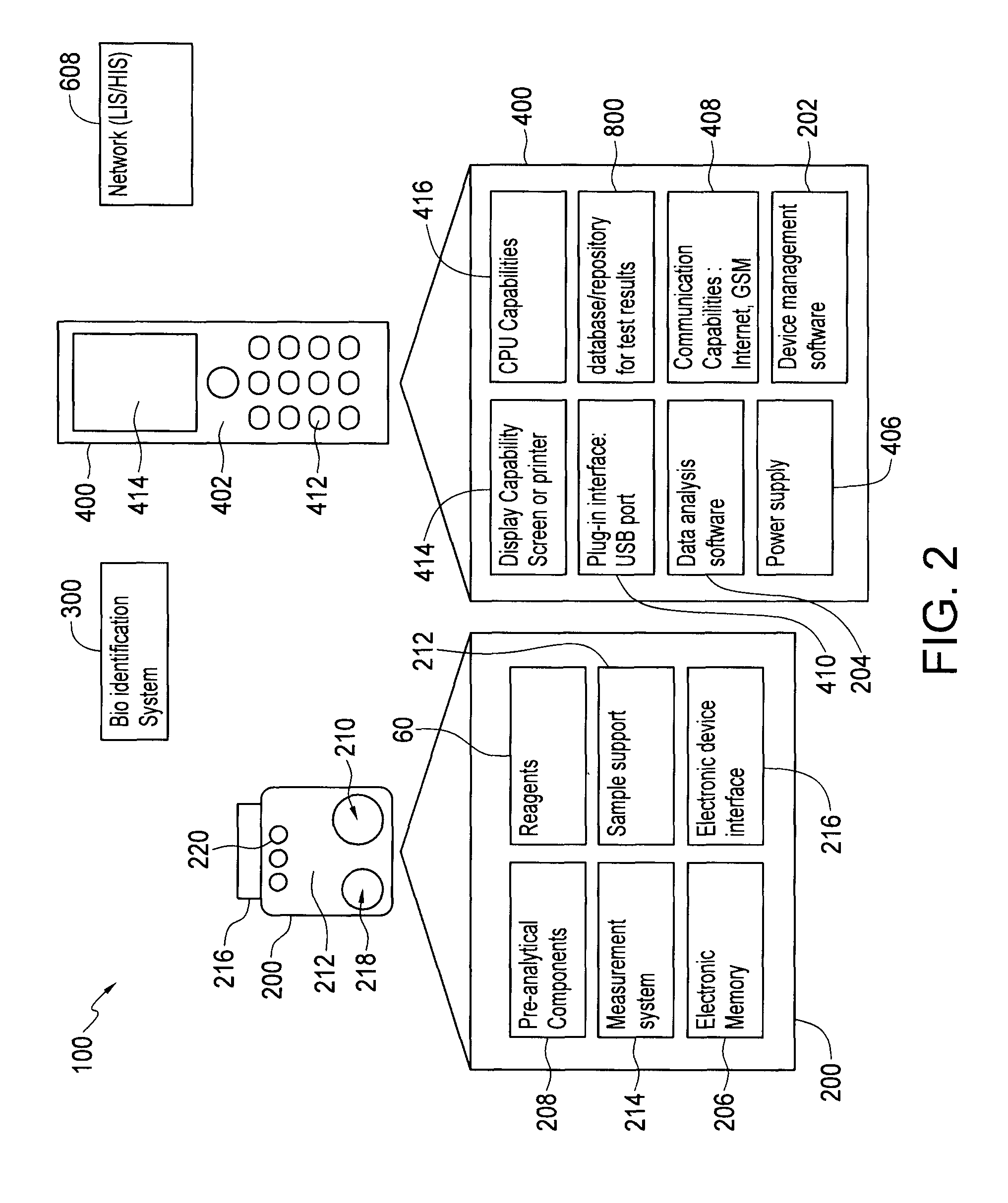
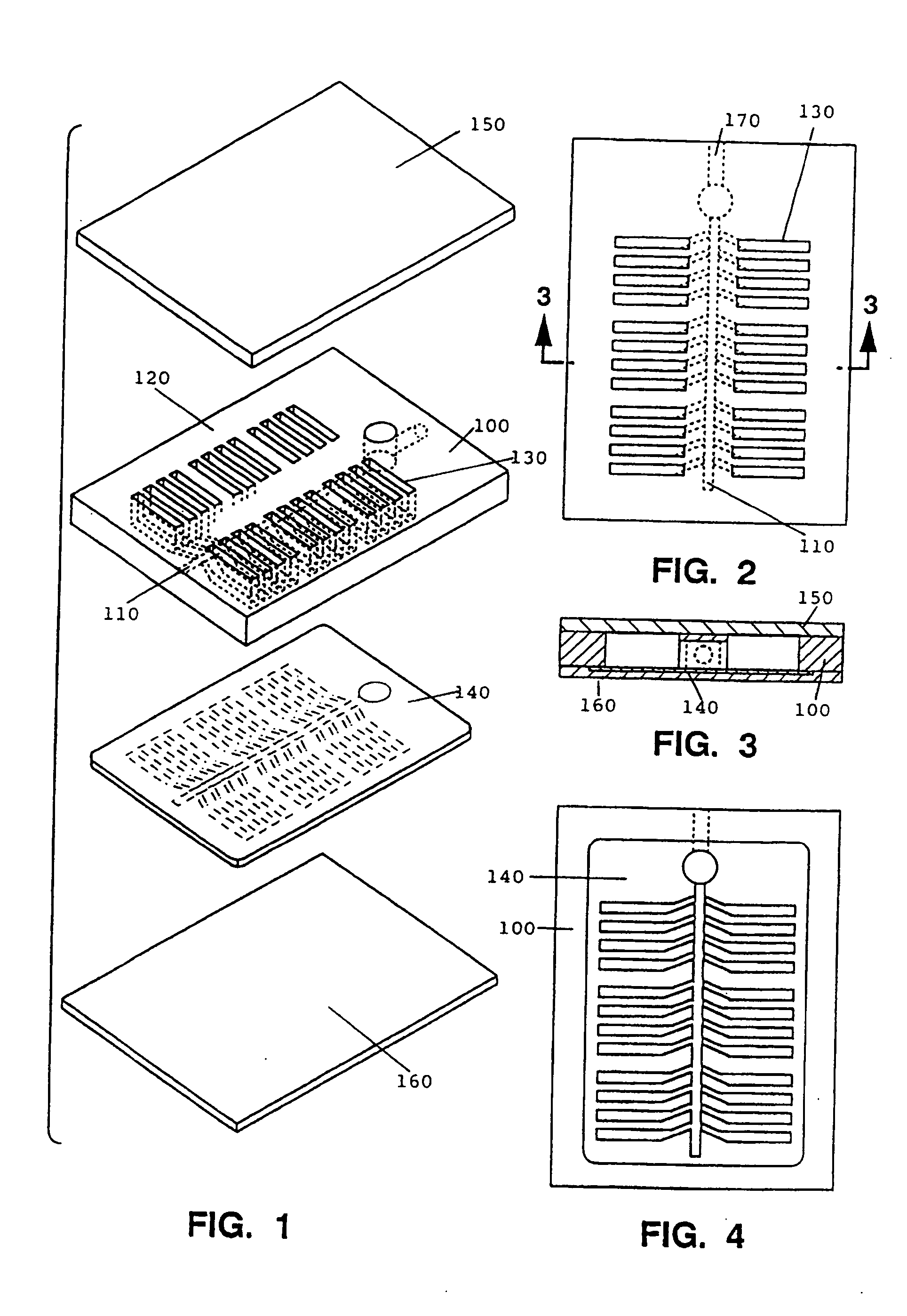
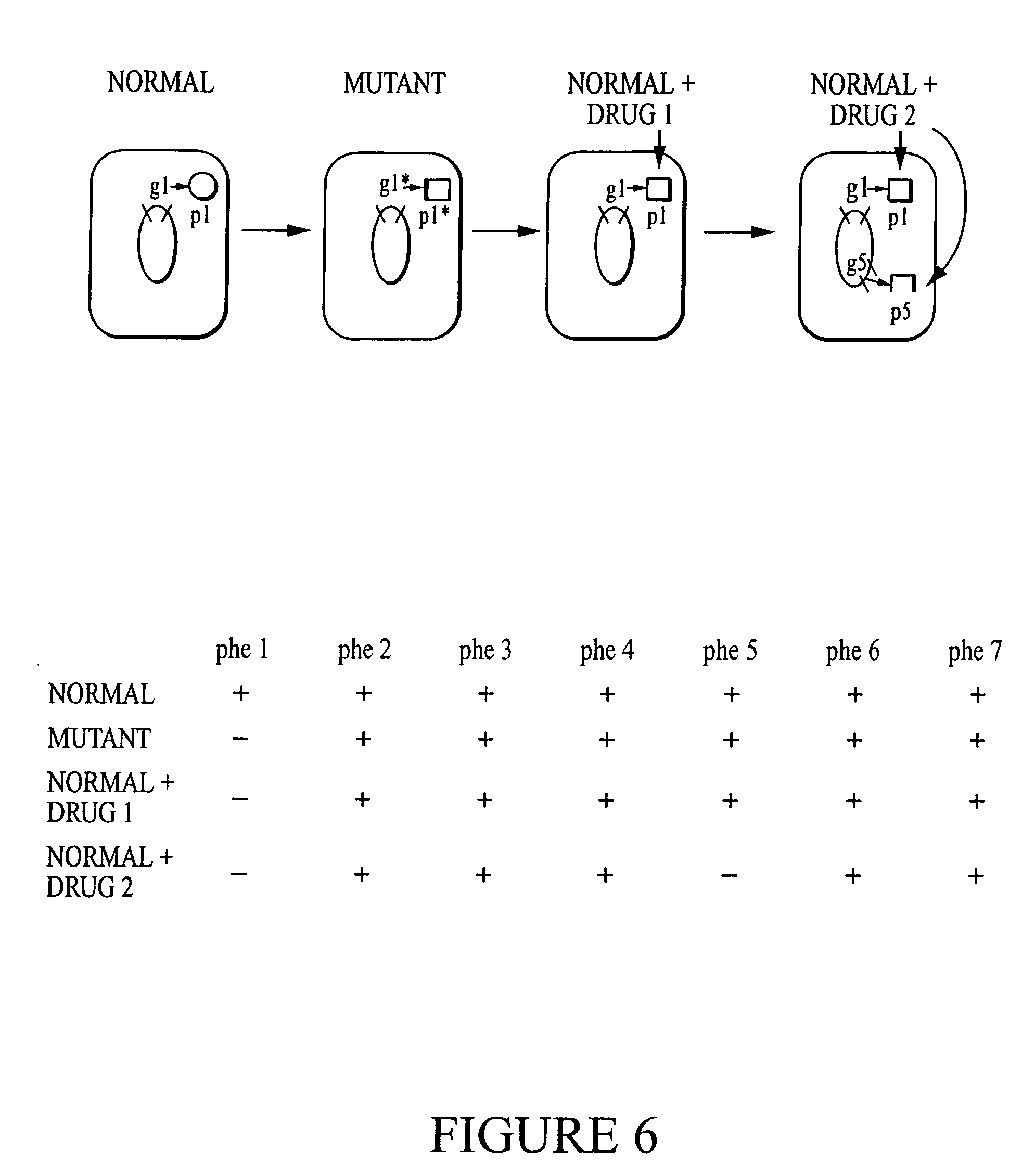
Systems and methods for detecting biological features
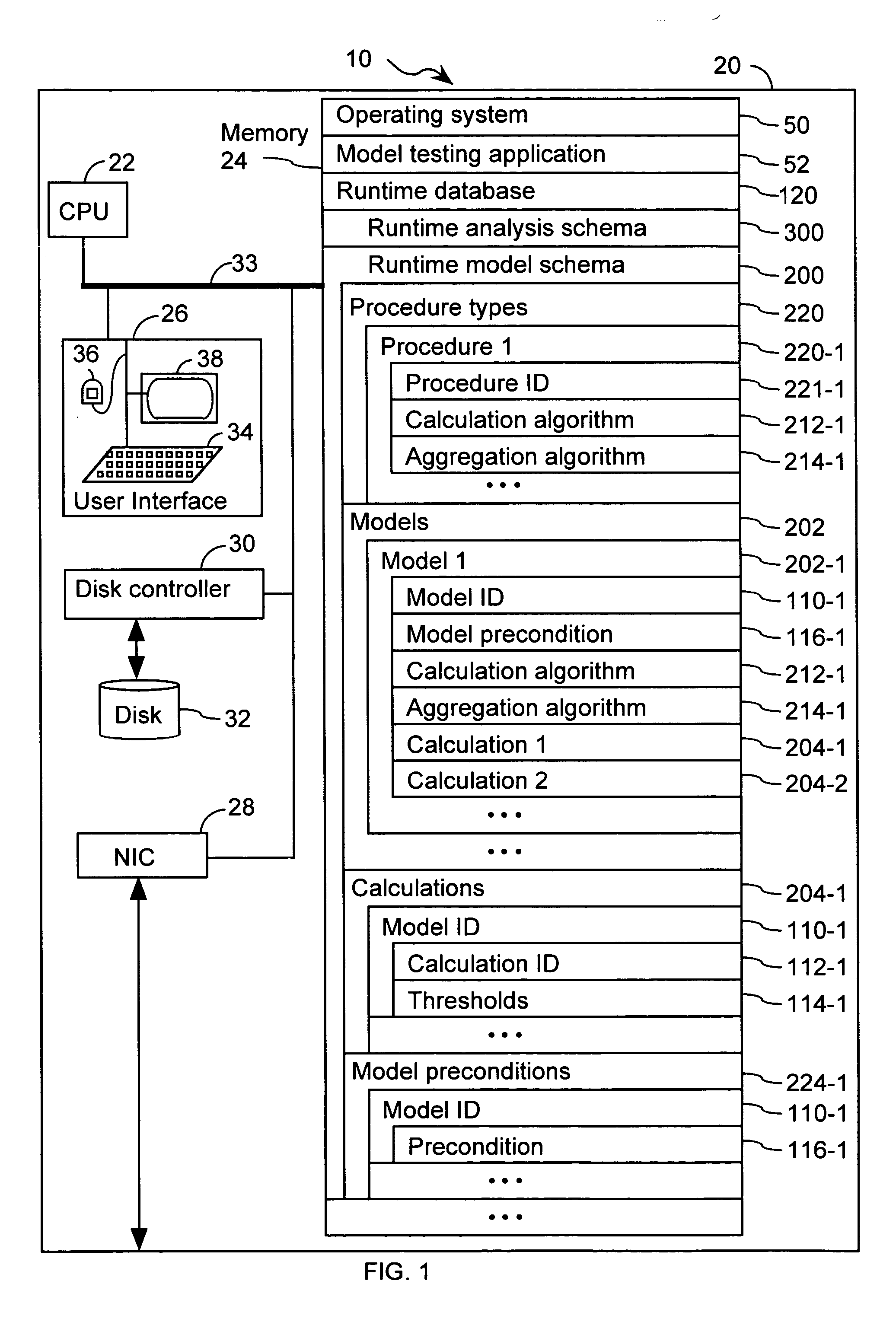
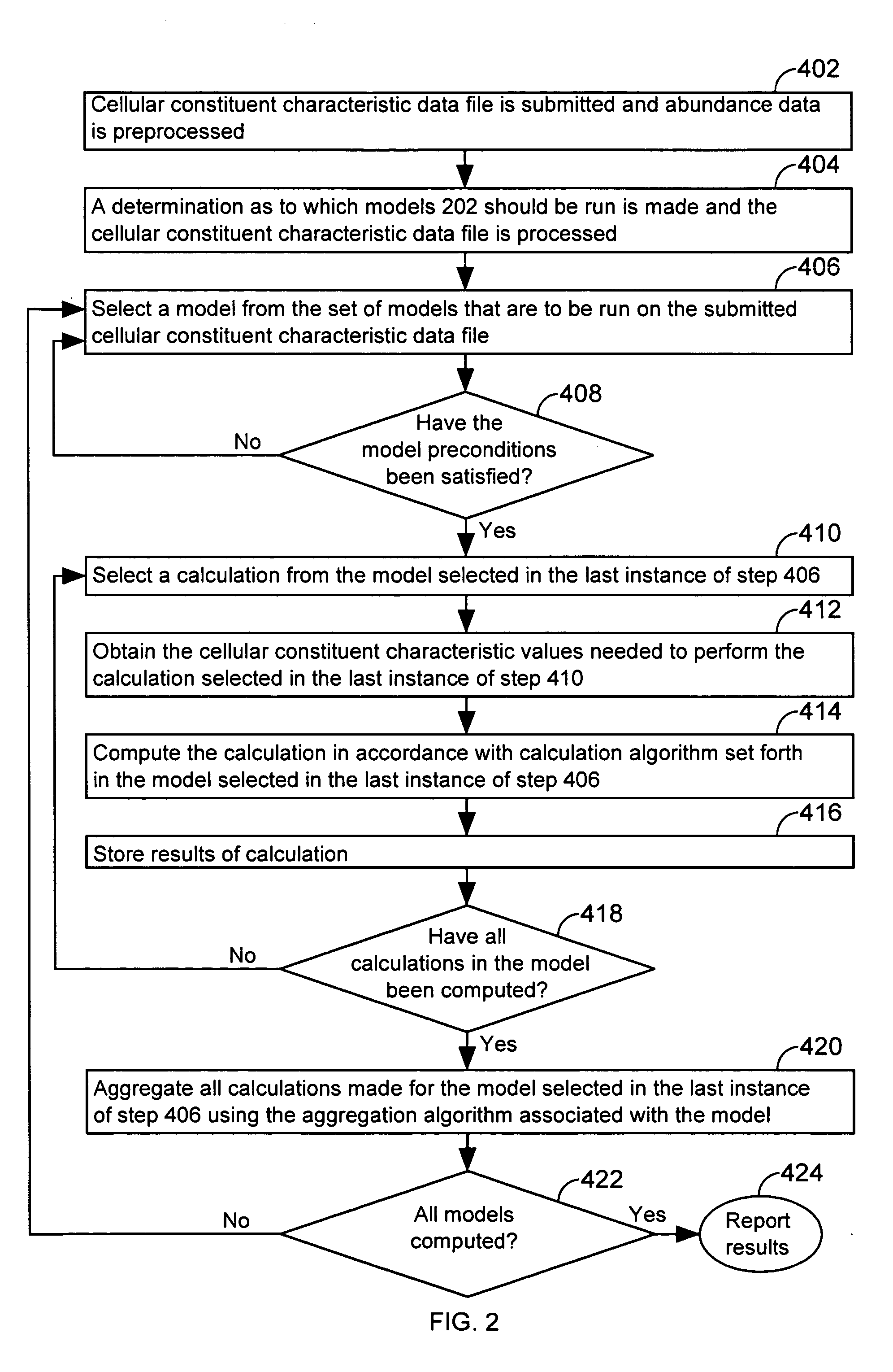
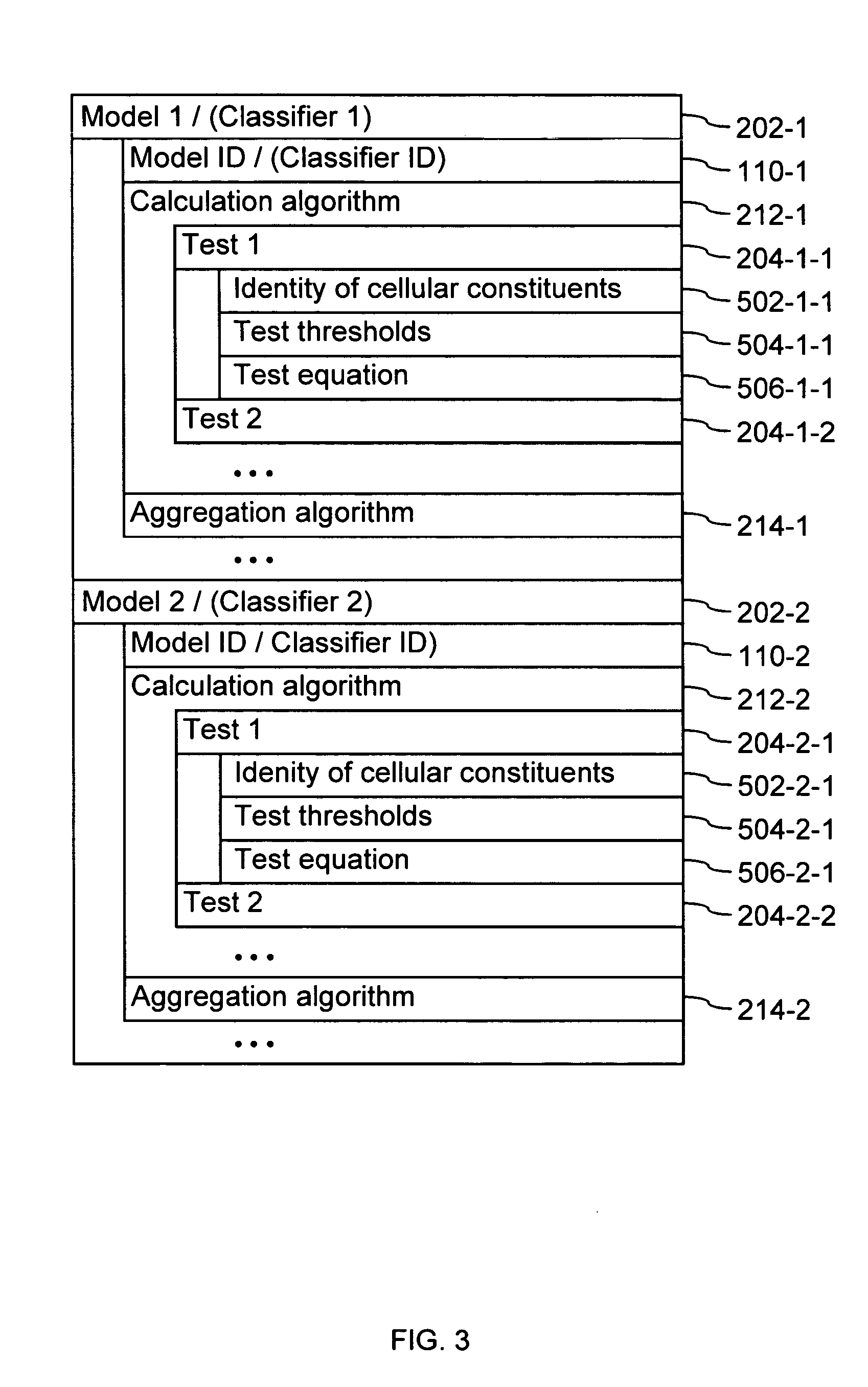
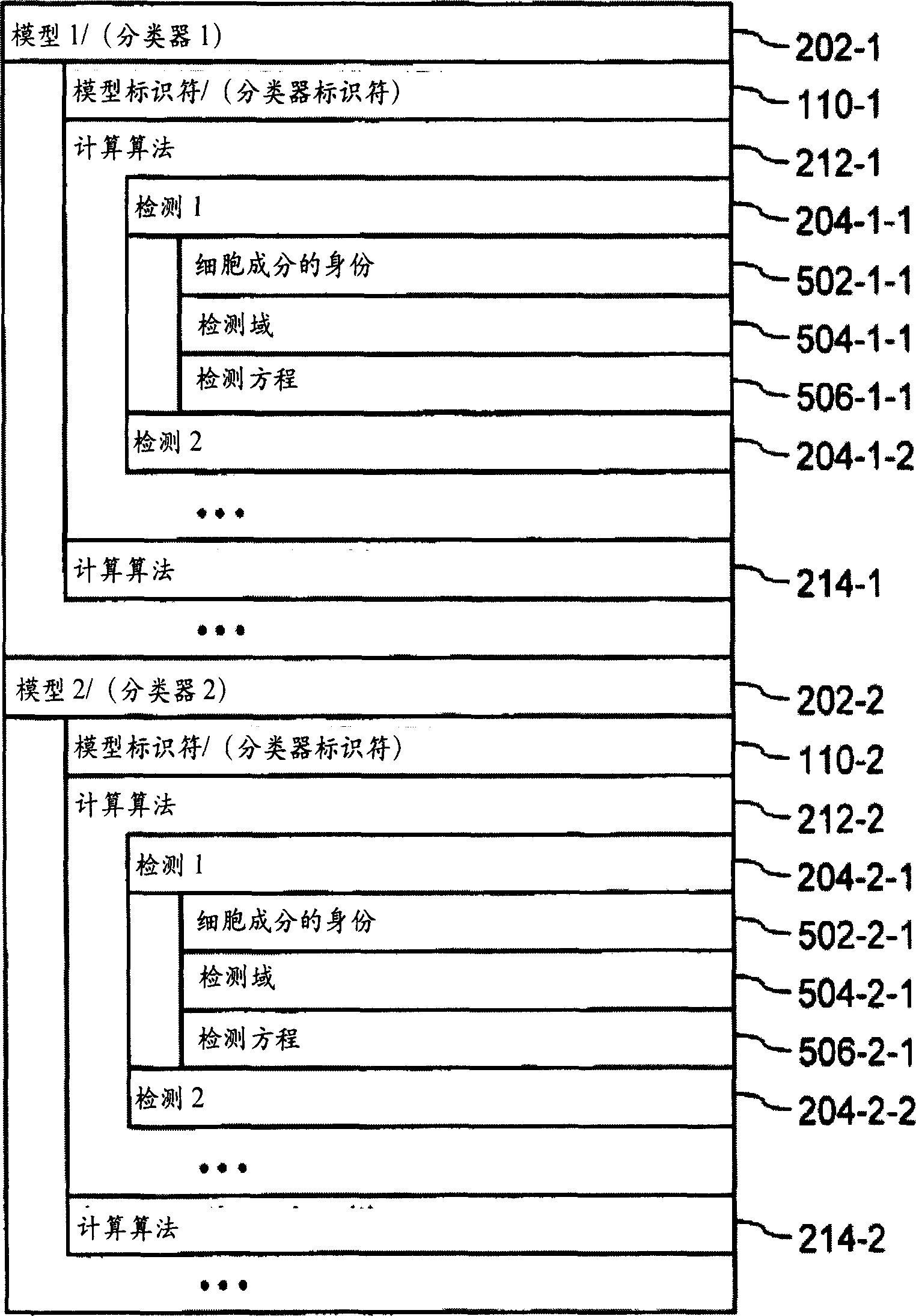
InactiveUS20050071087A1Mathematical modelsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological bodyTest organism
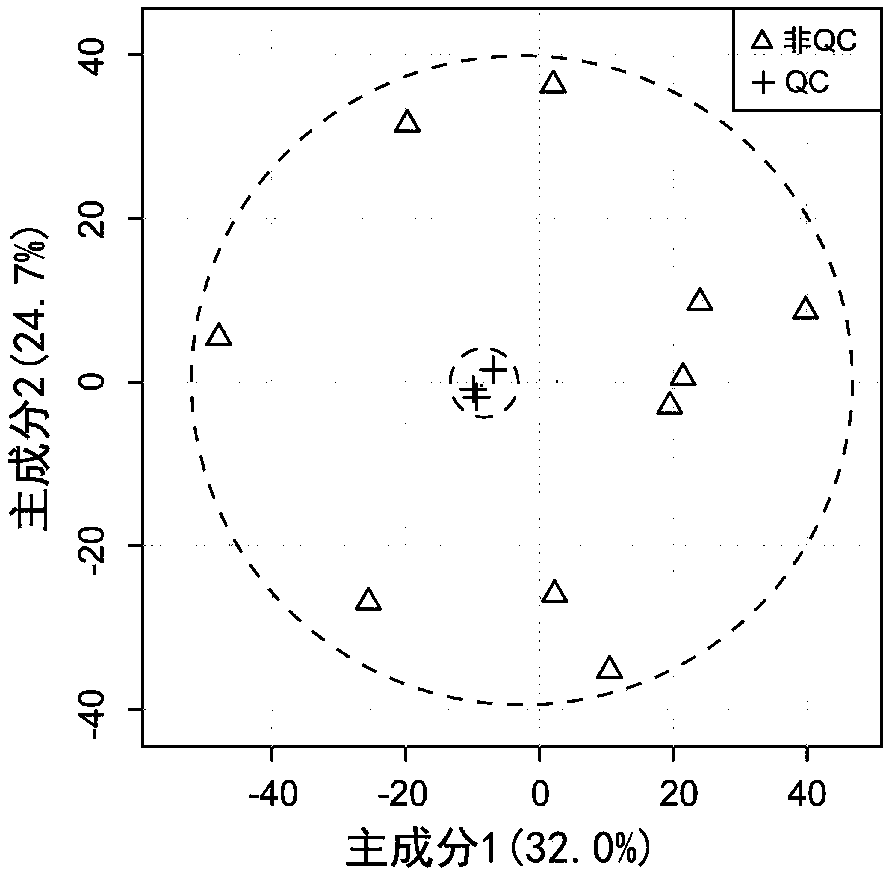
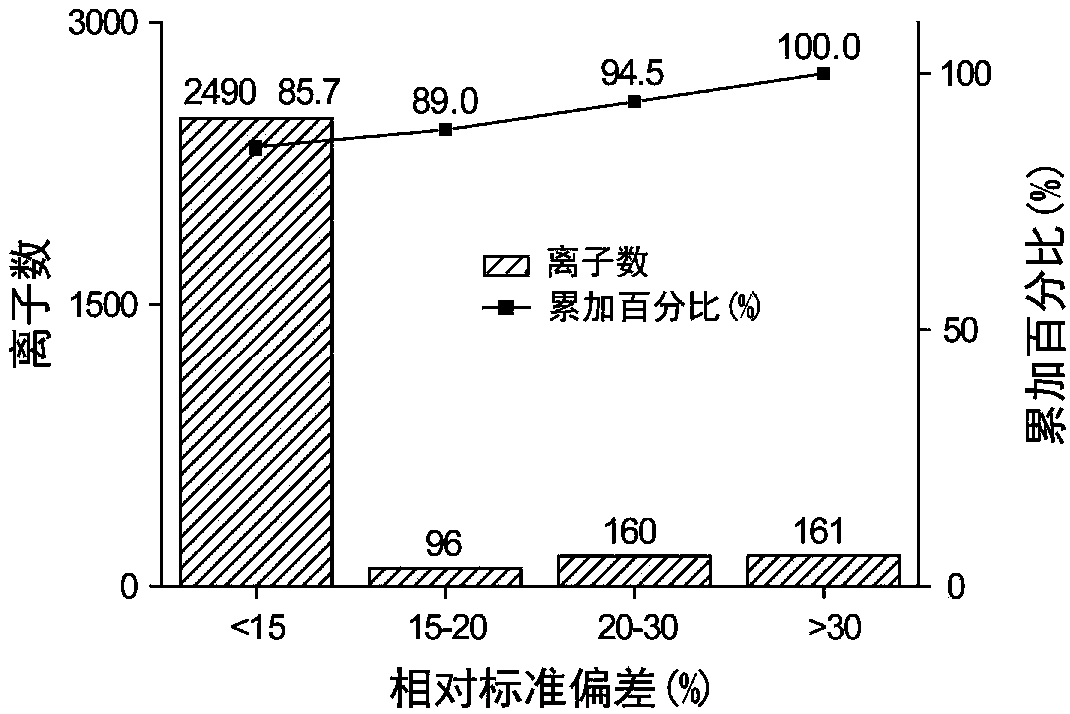
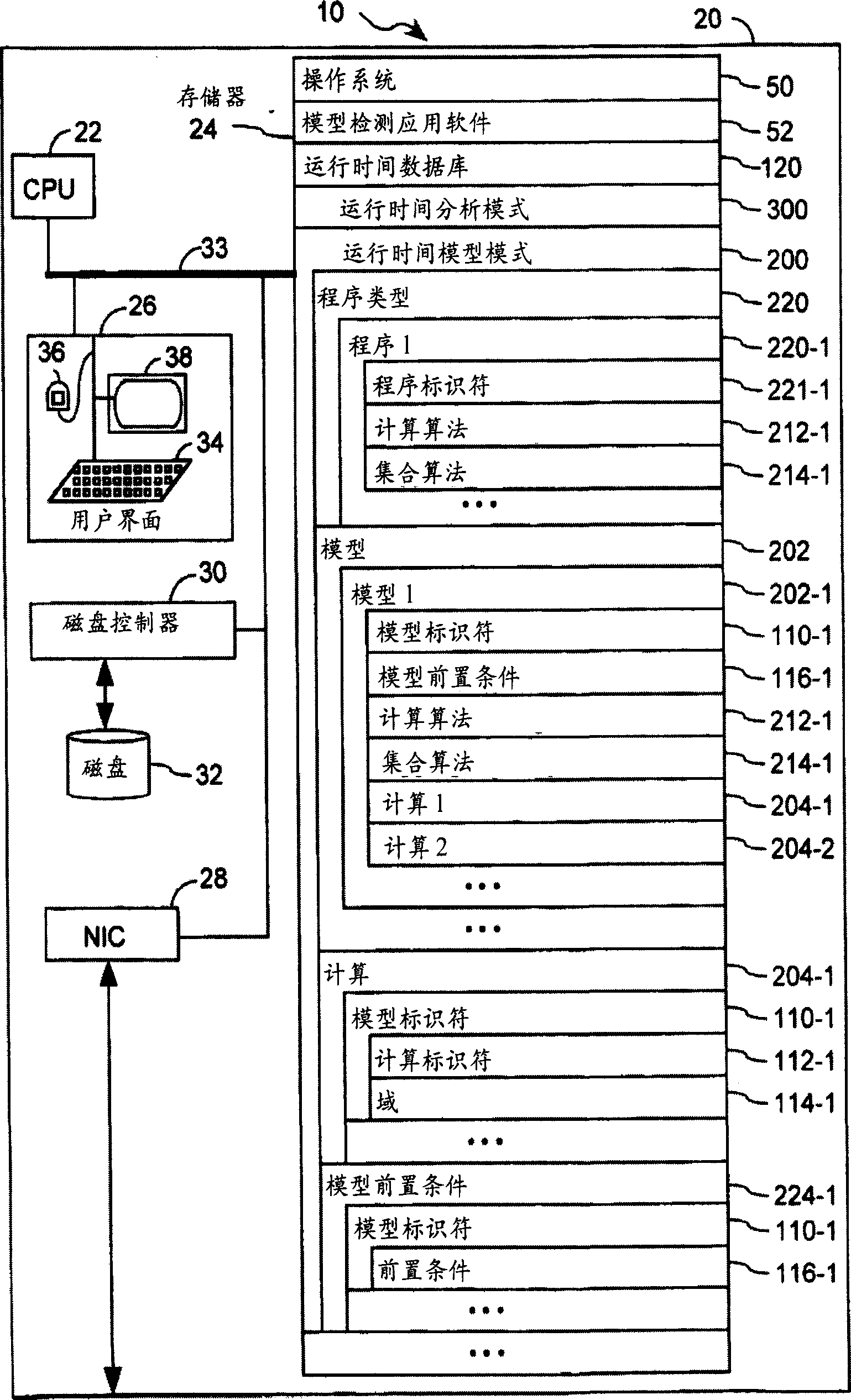
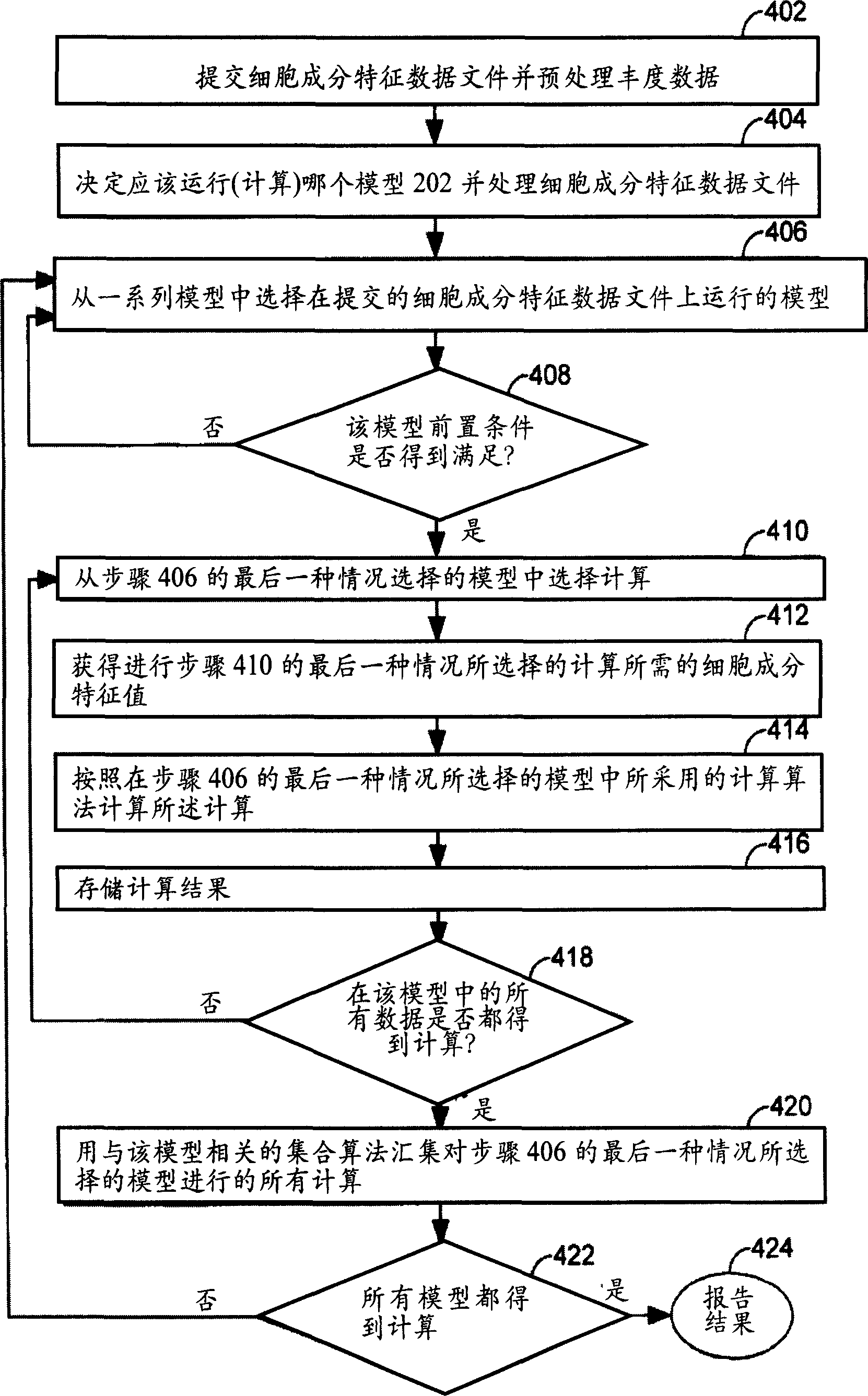
A computer having a memory stores instructions for receiving data. The data comprises one or more characteristics for each cellular constituent in a plurality of cellular constituents that have been measured in a test organism of a species or a test biological specimen from an organism of the species. The memory further stores instructions for computing a model in a plurality of models, wherein the model is characterized by a model score that represents the likelihood of a biological feature in the test organism or the test biological specimen. Computation of the model comprises determining the model score using one or more characteristics for one or more cellular constituents in the plurality of cellular constituents. The memory also stores instructions for repeating the instructions for computing one or more times, thereby computing the plurality of models. The memory also stores instructions for communicating computed model scores.
Owner:CANCER GENETICS
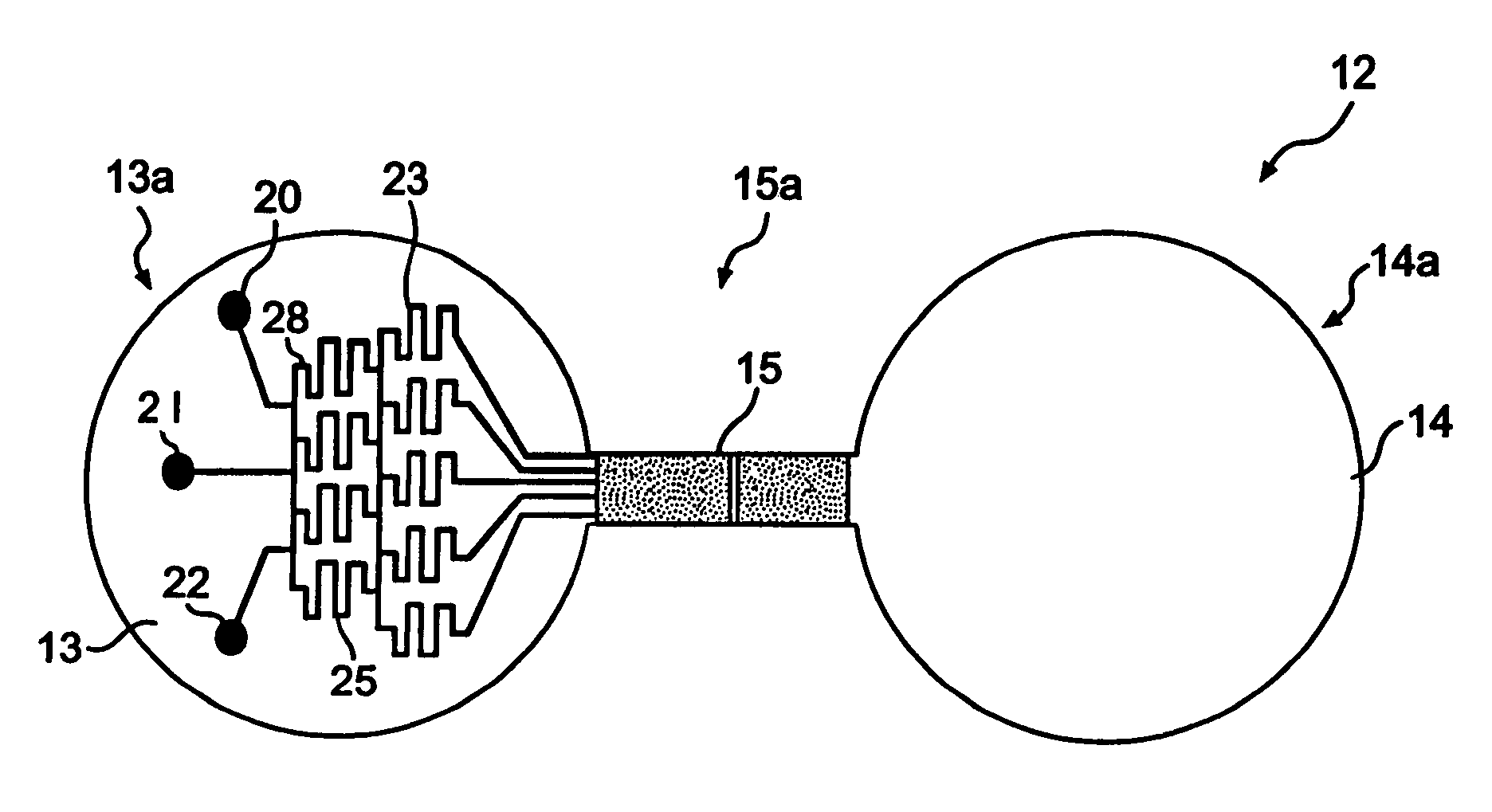
Biological assays using gradients formed in microfluidic systems
InactiveUS7374906B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAssayBiological interaction
The present invention discloses a device for monitoring chemotaxis or chemoinvasion. The present invention further provides a flexible assay system and numerous assays that can be used to test biological interactions and systems. Laminar flow gradients are employed that mimic gradient situations present in vivo.
Owner:SURFACE LOGIX INC
Comparative phenotype analysis of cells, including testing of biologically active compounds
InactiveUS20030162164A1Easy to atomizeReduce chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest organismPlant cell
The present invention relates to growing and testing any cell type in a multitest format. The present invention is suited for the characterization of microorganisms, as well as animal and plant cells. The present invention is also particularly suited for analysis of phenotypic differences between strains of organisms, including cultures that have been designated as the same genus and species. The present invention is also suited for the analysis of phenotypic differences between cell lines. In some embodiments, a gel forming matrix is used. The present invention provides methods and compositions for the phenotypic analysis and comparison of eukaryotic, as well as prokaryotic cells. The present invention further provides novel methods and compositions for testing the effect(s) of biologically active chemicals on various cells.
Owner:BIOLOG
Rapid microbiological test for the detection of antibacterial compounds
InactiveUS6867015B1Reduce testingQuality of the sample liquid is known more quicklyMicrobiological testing/measurementRedox indicatorTest organism
The present invention relates to a microbioligcal test method for detecting antibacterial compounds in liquid samples such as milk, meat juice, serum and urine. The method employs an acid-base or redox indicator to detect growth of a test organism and is characterised in that a thermophilic strain of Bacillus or Streptococcus, e.g. Bacillus stearothermophilus var. calidolactis C953, is employed at a concentration of above 107 CFU / ml, preferably between 2×107 and 3×108 CFU / ml.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV
Vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 based long-term microplate toxicity analyzing method of environmental pollutant
InactiveCN101915759AMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTest organismAntibiotic Y
The invention discloses a vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 based long-term microplate toxicity analyzing method of environmental pollutants. The long-term microplate toxicity analyzing method is established by using the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 as a tested organism and introducing time factors into the toxicity concentration-effect relationship of the traditional compound on the basis of a microplate toxicity analyzing method. The vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 based long-term microplate toxicity analyzing method of the environmental pollutants is characterized by adopting a specific microplate design and sampling scheme and a microplate culture medium suitable for the growth of the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67, measuring the long-term toxicity effect of the environmental pollutants on the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67 and repeatedly measures the toxicity of the same pollutant through multiple plates to ensure the statistical significance of an experimental result. By measuring the long-term toxicity of a part of the environmental pollutants on the vibrio qinghaiensis Q67, compared with short-term toxicity, the long-term toxicity of the tested environmental pollutants is discovered to be obviously higher than the short-term toxicity of the tested environmental pollutants, wherein the difference of the long-term toxicity and the short-term toxicity of antibiotics is most significant. The invention can actually reflect the toxicity of a site compound having specific action on compounds and more reasonably evaluate the toxicity of the pollutants.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
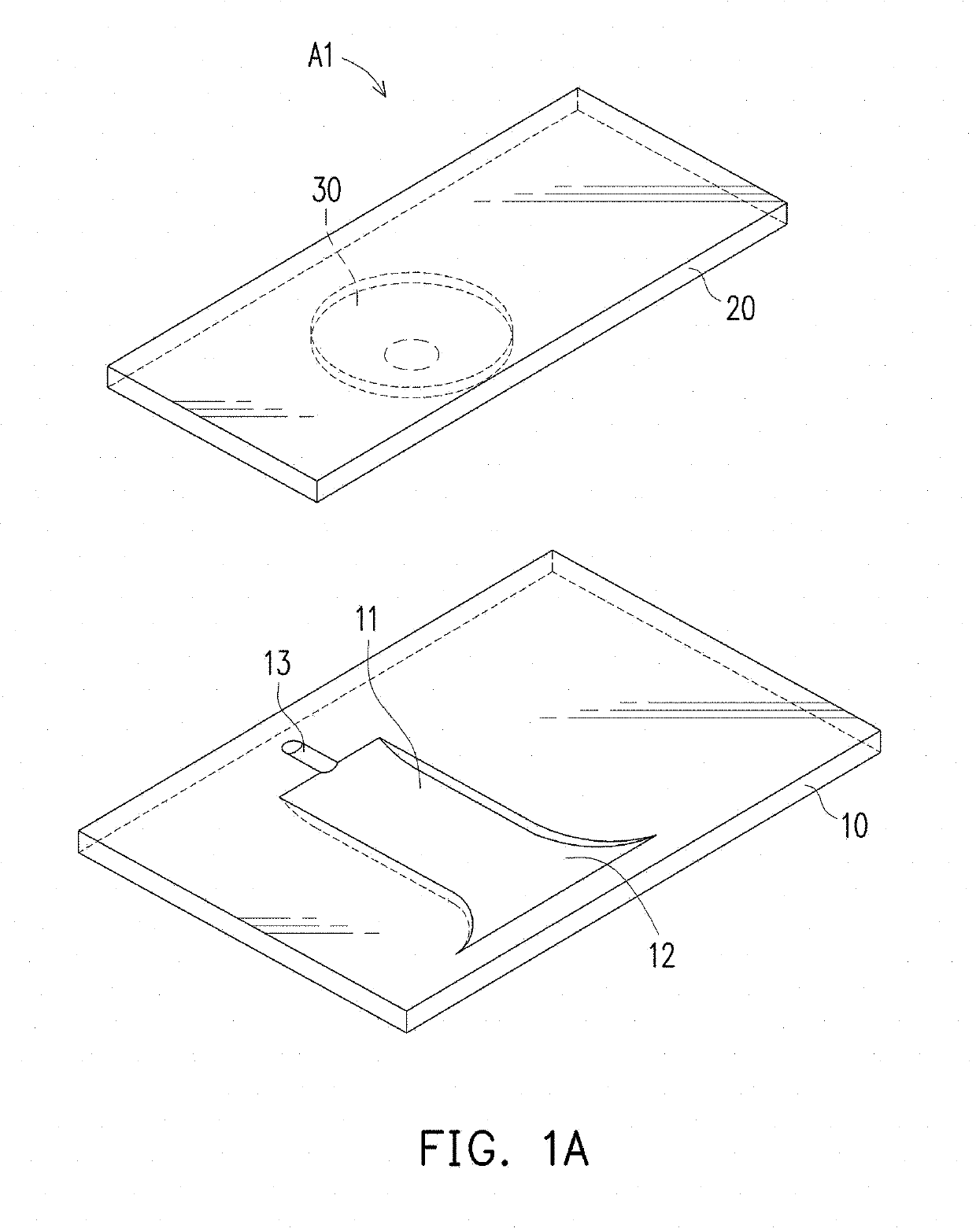
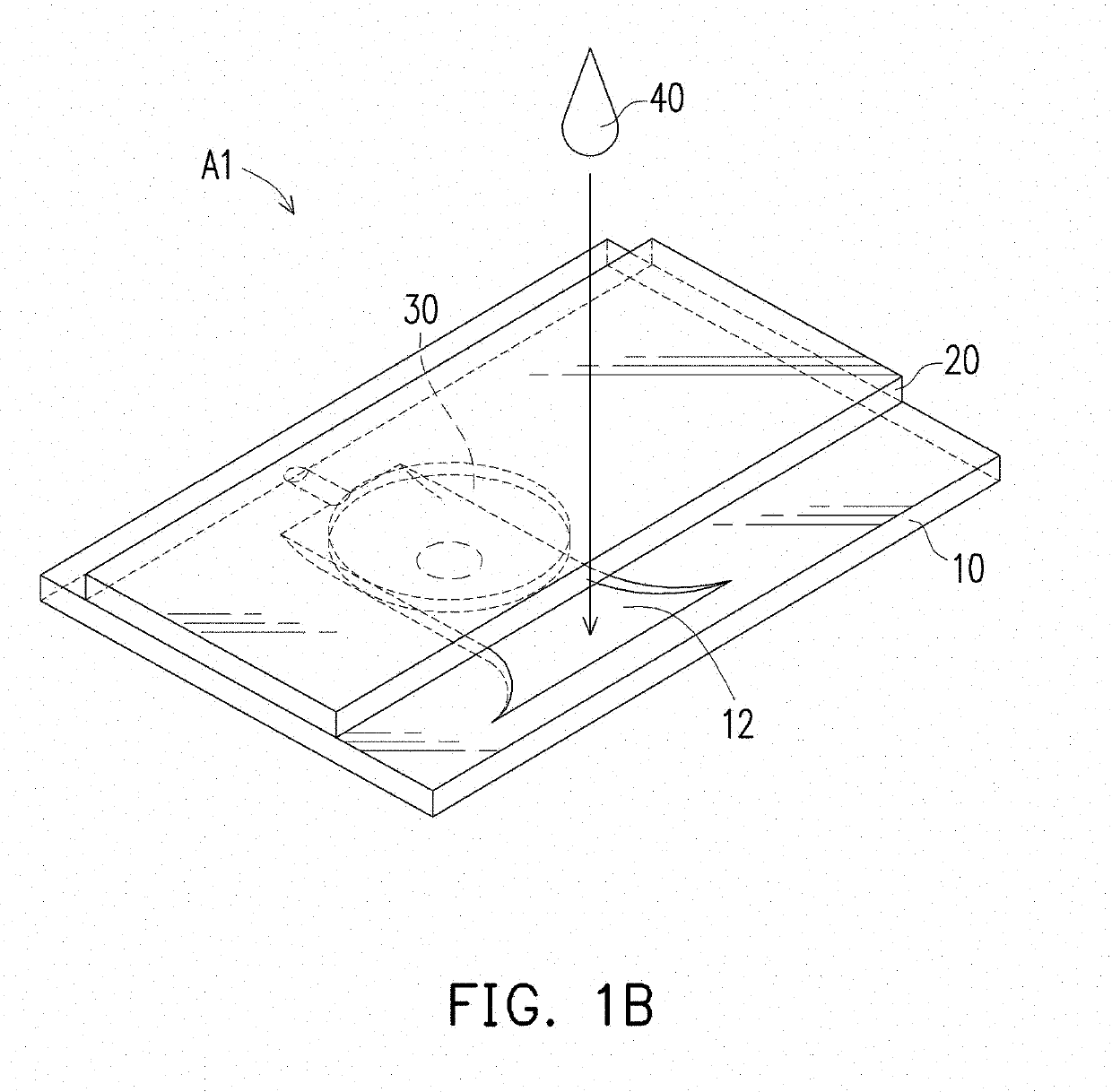
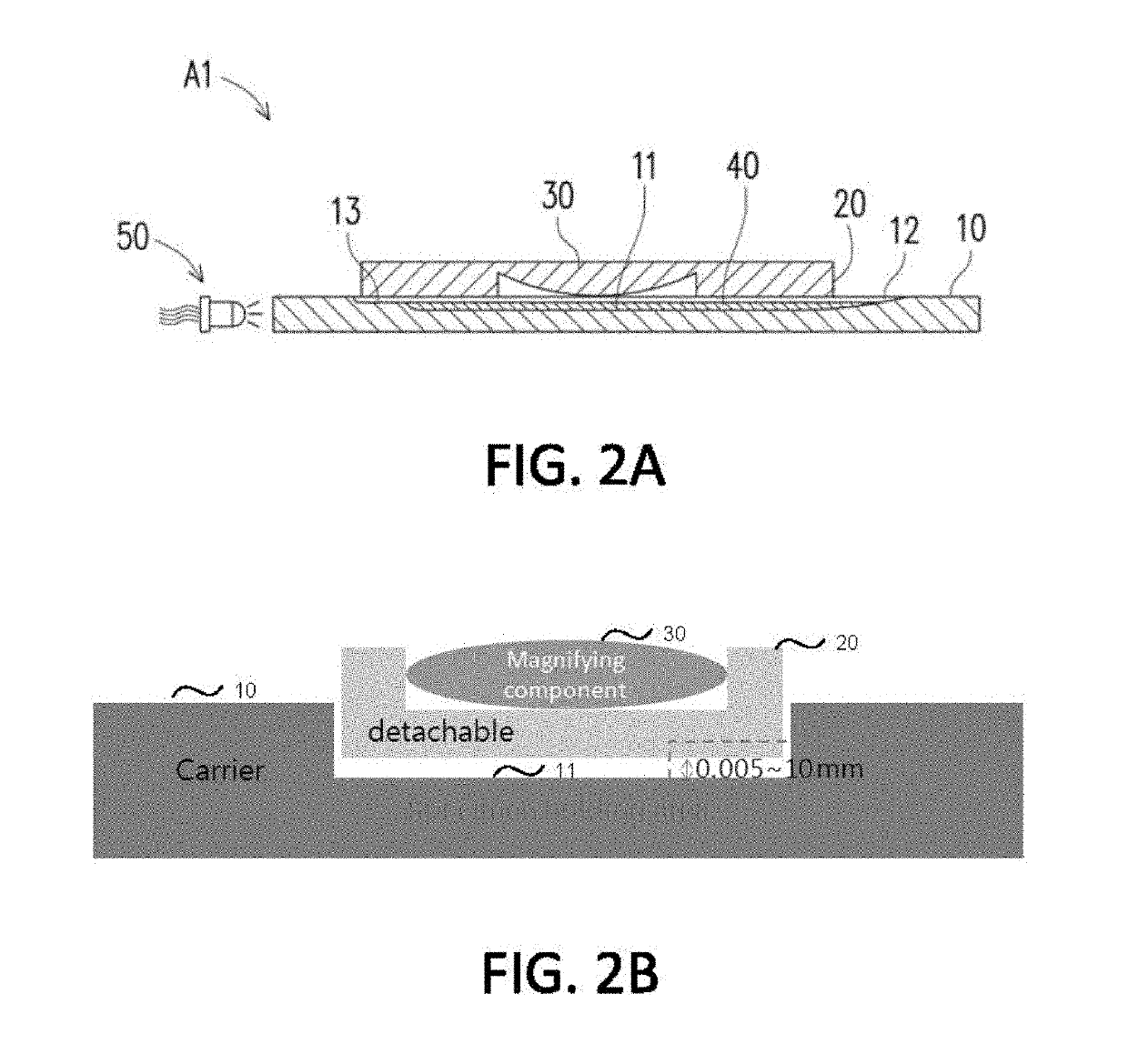
Automated testing apparatus
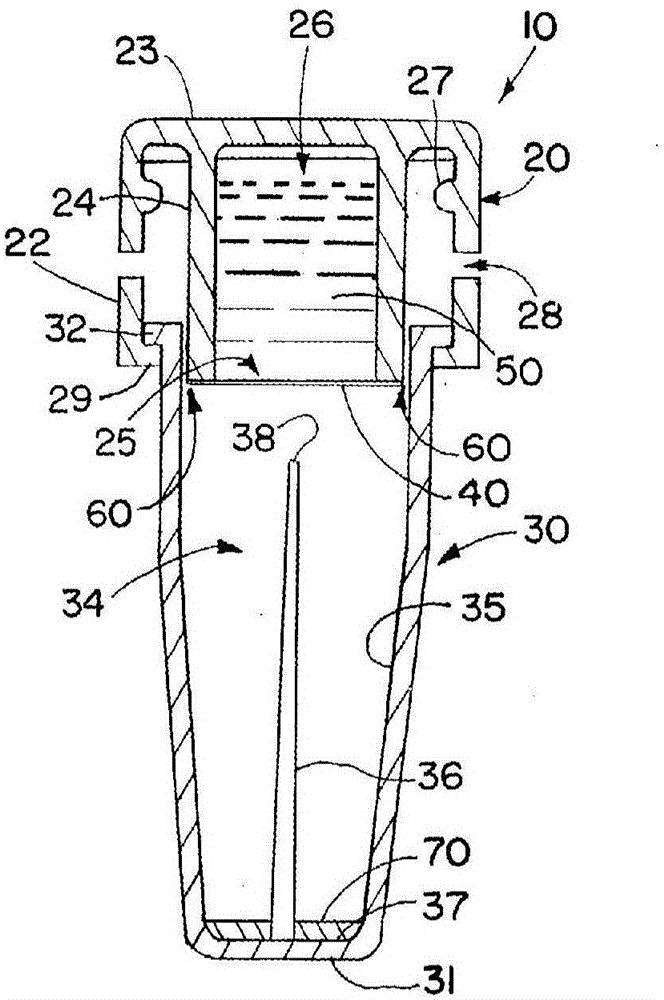
ActiveUS10281386B2Less expensiveEasy to useMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSurgeryTest organismEngineering
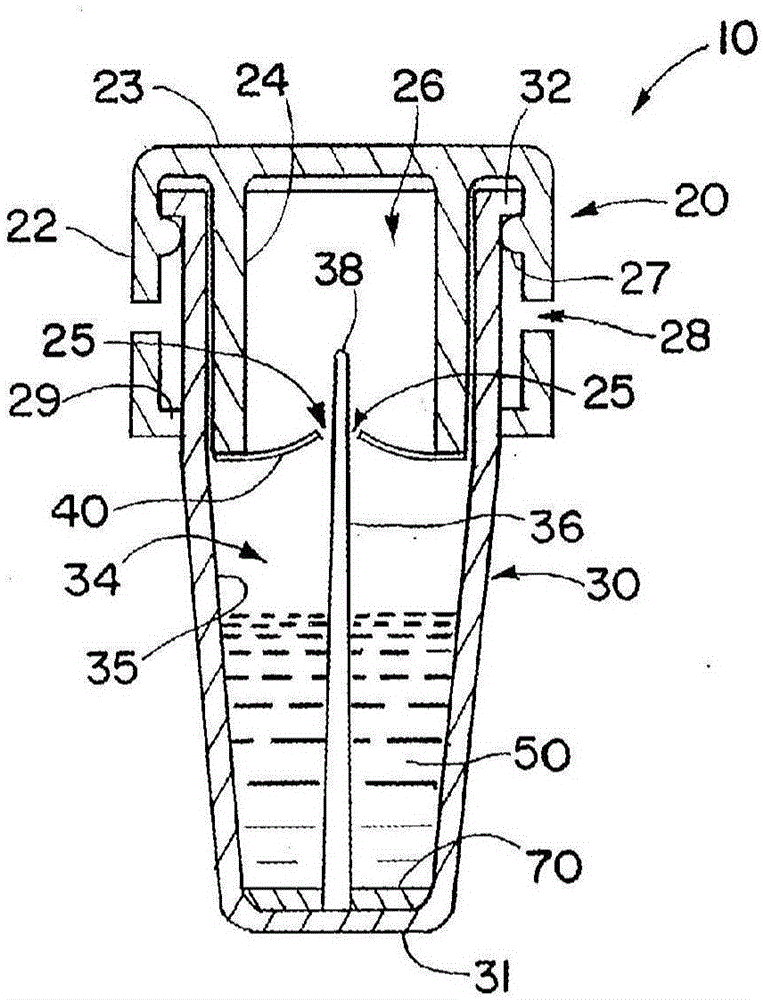
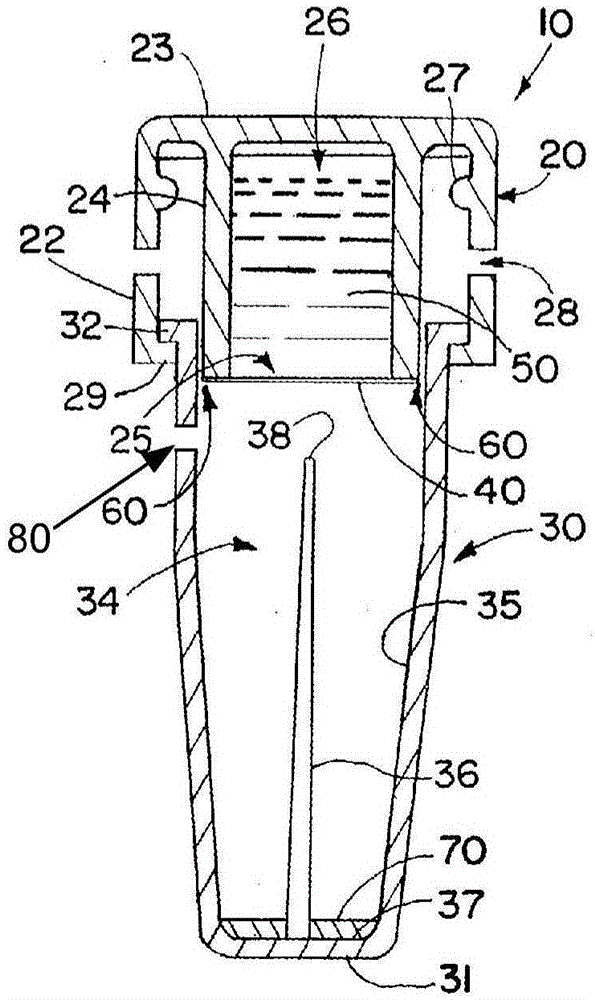
Embodiments disclose a device for testing biological specimen. The device includes a sample carrier and a detachable cover. The sample carrier includes a specimen holding area. The detachable cover is placed on top of the specimen holding area. The detachable cover includes a magnifying component configured to align with the specimen holding area. The focal length of the magnifying component is from 0.1 mm to 8.5 mm. The magnifying component has a linear magnification ratio of at least 1. Some embodiments further include a multi-camera configuration. These embodiments include a first camera module and a second camera module arranged to capture one or more images of the first holding area and the second holding area, respectively. The processor may perform different analytic processes on the captured images of different holding areas to determine an outcome with regard to the biological specimen.
Owner:BONRAYBIO
Quick acquiring method for multi-frequency-point bioelectrical impedance
ActiveCN104146709AAddressing the Impact of Analytical AccuracyReduce computationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBiological bodyElectrical resistance and conductance
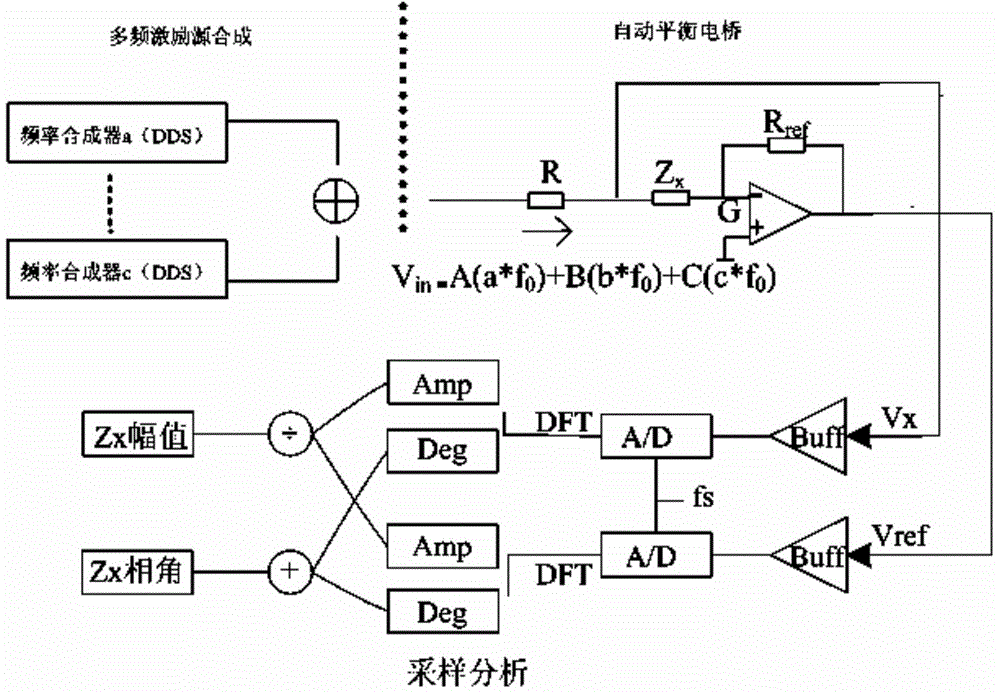
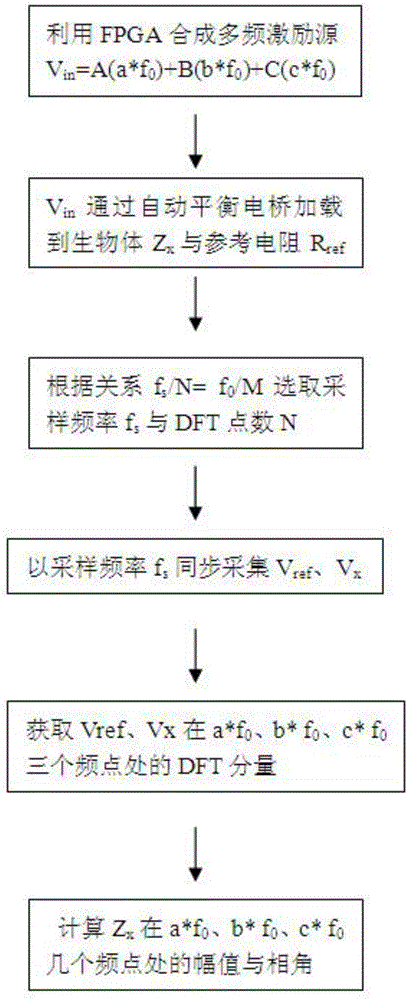
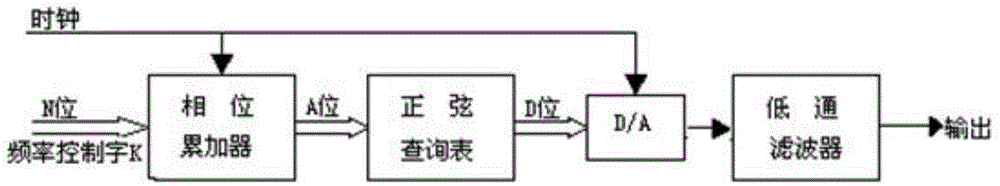
The invention discloses a quick acquiring method for multi-frequency-point bioelectrical impedance. A multi-frequency-point composite excitation source Vin is realized based on a DDS (direct digital synthesizer) principle by means of FPGA (field-programmable gate array) programming, the composite excitation source Vin is loaded onto reference resistance Rref and to-be-tested organism electric impedance Zx simultaneously, corresponding amplitudes Ampref and Ampx and phase angles Degref and Degx of the Vref and Vx on frequency points can be acquired accurately by reasonably selecting sampling frequency fs and points N of DFT (digital Fourier transform) and by only performing DFT on the Vref and Vx on the several needed frequency points, and further amplitudes of the to-be-tested organism electric impedance Zx on the frequency points are acquired. The quick acquiring method has the advantages of high impedance acquisition accuracy, small operation amount, high anti-jamming capability, short scanning time and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
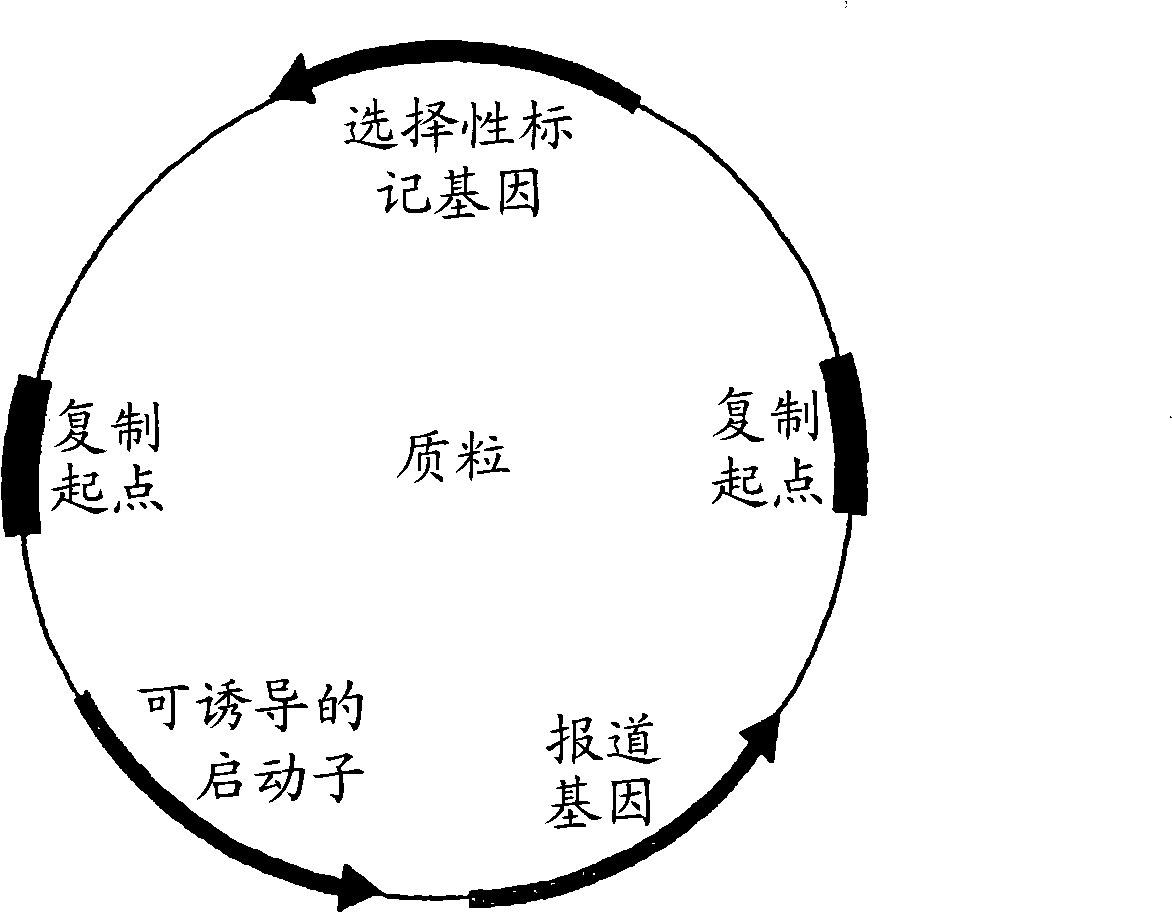
Genetically engineered biological indicator
ActiveCN101535496ADesensitizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBiological body
The disclosed technology relates to a genetically engineered biological indicator, comprising: at least one test organism and at least one reporter gene suitable for producing an indicator enzyme, the reporter gene being taken up by the test organism; and at least one repressor gene that inhibits expression of the reporter gene until the reporter gene is exposed to at least one inducer. A process and an apparatus for using the biological indicator are disclosed.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Microfluid system and method to test for target molecules in a biological sample
ActiveUS20100151443A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSludge treatmentFluorescent spectraTest sample
A system and method to test for the presence of target molecules in a biological test sample includes test molecules, a microfluidic chip, and irradiating and detection devices. The test molecules include bio-recognition molecules conjugable with the target molecules, and the corresponding conjugates. The microfluidic chip includes sample channels and flow focusing channels adjoining the sample channels. A buffer exiting from the focusing channels directs a single-file stream of the test molecules through one of the sample channels. The irradiating device delivers radiation for absorption by the test molecules in the single-file stream. After absorption, the test molecules emit fluorescence of a distinct fluorescent spectrum for each of the conjugates. The detection device monitors identifies the presence of the conjugates by monitoring for the distinct fluorescent spectrum. Thus, the test system and method identifies the presence of the target molecules in the test sample.
Owner:FIO CORP
Flow-through system and method for toxicity testing
InactiveUS6093566ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest organismToxic material
A method and apparatus for evaluating the effects of toxic substances in the environment on aquatic organisms is disclosed. The apparatus allows for exposure of test organisms, placed in test chambers made of partially submerged sieves, to water that is pumped from an urban creek at preset time intervals. The invention also allows for maintenance of cool temperatures in the exposure chambers, both for the treatment (i.e., creek water) and the experimental control.
Owner:KATZNELSON REVITAL
Microarray for evaluating eye disease, and evaluation method of eye disease
InactiveUS20160024582A1Inhibit functioningSenses disorderNucleotide librariesBiological bodyTest organism
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for objectively evaluating the state of eye disease in a test organism. Provided is a microarray for evaluating the state of eye disease. Further, this method for evaluating the state of eye disease in a test organism is characterized by detecting, from a sample taken from the test organism, at least one gene from a prescribed gene group and comparing the obtained detection result with a control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI RAYON CO LTD
Monitoring and identifying evaluation method for group biotoxicity in printing and dyeing wastewater
InactiveCN108120812ASolve unrepresentative problemsImprove securityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTesting waterToxicity reductionResearch Object
The invention discloses a monitoring and identifying evaluation method for group biotoxicity in printing and dyeing wastewater and belongs to the field of biotoxicity identification. The method comprises the following steps: screening photogenic bacteria, zebrafish larvae, zebrafish embryos and chlorella as test organisms; and performing risk and toxicity reduction evaluation on the printing and dyeing wastewater by adopting group biotoxicity tests and combining with a toxicity evaluation method, and constructing a toxicity identification evaluation system by combining with a TIE technology according to the wastewater contamination characteristics and results. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the group biotoxicity tests comprising three trophic levels such as decomposer,producer and consumer are performed for characterizing toxicities of the printing and dyeing wastewater, and the problem that a single biotoxicity test does not have representativeness is solved. Themethod has the advantages of being comprehensive, simple, high-efficiency, capable of controlling from the source, high in safety and the like, can be widely applied to researching and evaluating influences of toxic pollutants on the ecological environment, and provides a certain basis for ecological risk assessment.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Ecological risk evaluation method of PPCPs (pharmaceutical and personal care products) in water environment
InactiveCN106841431ALow costEasy to operateComponent separationPredicted no-effect concentrationTest organism
The invention discloses an ecological risk evaluation method of PPCPs (pharmaceutical and personal care products) in a water environment. The method comprises the following steps: (1) detection of PPCPs concentration in a water environment: water sample pretreatment, solid-phase extraction and quantitative detection by a high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy combined technique; (2) by using bacteria, algae, invertebrates, fish and other aquatic organisms as test organisms, determining the predicted no effect concentration (PNEC) by using toxicological data 50% effective concentration (EC50); (3) calculating the risk quotients (RQ) according to the formula RQ=MEC / PNEC, wherein MEC is the measured environmental concentration; and (4) evaluating the ecological risk degree of the target compounds PPCPs by an RQ process. The method is low in cost, friendly to the environment and convenient for operation. The detection method of PPCPs is simple to operate and easy to implement, has the advantages of high selectivity for target compounds, high sensitivity, high enrichment multiple and favorable reproducibility, and can simultaneously separate and determine multiple compounds.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Rapid test method of toxicity in marine oil spill organisms
InactiveCN101551336AMeet the living conditionsReduce mistakesBacteriaChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTest organismSolvent
The invention relates to a rapid test method of toxicity in marine oil spill organisms. The method takes photobacteria as tested organisms for testing the toxicity in the marine oil spill organisms and simultaneously utilizes artificial seawater for preparing water accommodation friction (WAF), thus avoiding the experiment error caused by the reduction of the salinity of marine photobacteria and the changes of living conditions of the photobacteria due to the application of pure water as solvent for preparing the WAF in previous photobacteria experiments.
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE
Reagent or kit for evaluating intestinal lipid accumulation and its intervention, and application and detection method thereof
ActiveCN107632084ADistinguish ability to accurately distinguishStrong resolutionComponent separationGas chromatography–mass spectrometryTest organism
The invention relates to a new application of oleic acid and glycerol 1-monooleate in the preparation of a kit for evaluating the intestinal lipid accumulation in a tested organism and its intervention effect, and a detection method of the oleic acid and the glycerol 1-monooleate. A reagent and the method are used to detect the content of the oleic acid and the glycerol 1-monooleate in the intestinal tissues of the tested organism. The invention further provides the method for detecting the content of the oleic acid and the glycerol 1-monooleate in the intestinal tissues of the tested organismthrough gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The content can be used for evaluating the intestinal lipid accumulation and its intervention effect. The kit and the detection method have the characteristics of simplicity in operation, good reliability, fastness, high sensitivity, high specificity, and easiness in promotion.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and methods for detecting biological features
A computer having a memory stores instructions for receiving data. The data comprises one or more characteristics for each cellular constituent in a plurality of cellular constituents that have been measured in a test organism of a species or a test biological specimen from an organism of the species. The memory further stores instructions for computing a model in a plurality of models, wherein the model is characterized by a model score that represents the likelihood of a biological feature in the test organism or the test biological specimen. Computation of the model comprises determining the model score using one or more characteristics for one or more cellular constituents in the plurality of cellular constituents. The memory also stores instructions for repeating the instructions for computing one or more times, thereby computing the plurality of models. The memory also stores instructions for communicating computed model scores.
Owner:传道生物有限公司
Waste water online biological monitoring method and device
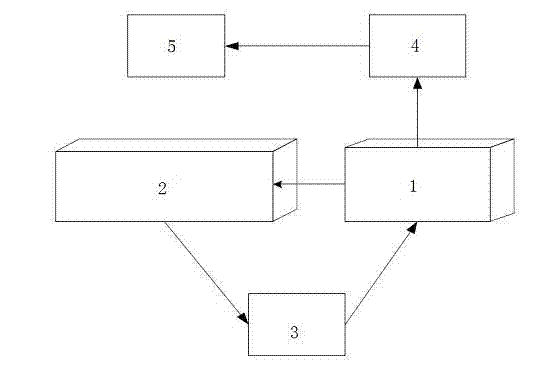
InactiveCN102207485AEfficient managementSimple structureMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEnvironmental resistanceTest organism
The invention discloses a waste water online biological monitoring method and a waste water online biological monitoring device, and belongs to the field of waste water online monitoring. The device consists of a circulating pump (3), a liquid storage chamber (2), a circulation chamber (1), an inductive electrode (4) and a multimeter (5); the circulating pump is arranged at the lateral bottom of the liquid storage chamber away from the circulation chamber, and is connected with the circulation chamber via a plastic pipe; the sidewall of the circulation chamber is connected with side surface of the liquid storage chamber at the equal height to realize flow exposure of the whole course. Two pairs of copper electrodes with nuts are arranged on the inner side of the circulation chamber, wherein one pair of the electrodes functions as an input end of an electrical signal, and the other pair of the electrodes is connected with the multimeter to form an output end of the electrical signal. The distribution of an electric field in the circulation chamber can be influenced by swimming of the tested organism daphnia, namely the change of output current or voltage. By the invention, whether the quality of the discharged water is safe can be intuitively reflected; meanwhile, an 'electronic eye' is provided for the pollution incident monitoring and the dispute resolution monitoring of an environmental monitoring department. The device disclosed by the invention is simple in structure and strong in mobility and can be used indoors and outdoors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
Sterilization indicator including a simplified genetically engineered biological indicator
InactiveCN105143452AHigh sensitivityIncrease signal strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiological bodyBiotechnology
A sterilization indicator, including a first compartment containing a genetically engineered biological indicator, and a second compartment containing an enzyme substrate, the second compartment adapted to maintain the enzyme substrate separate from the biological indicator during sterilization, and to permit the enzyme substrate to contact the biological indicator after the biological indicator has been exposed to the sterilization medium; in which the genetically engineered biological indicator comprises at least one test organism and at least one reporter gene suitable for producing an indicator enzyme, the reporter gene being taken up by the test organism; and the test organism is free of any active or activatable repressor gene that would inhibit expression of the reporter gene if present in the test organism or sterilization indicator, and the indicator enzyme and the enzyme substrate are selected such that enzymatic action of the indicator enzyme upon the enzyme substrate yields a detectable signal.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Single-use handheld diagnostic test device, and an associated system and method for testing biological and environmental test samples
ActiveUS9459200B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial thermal conductivityTest fixtureElectron
Owner:FIO CORP
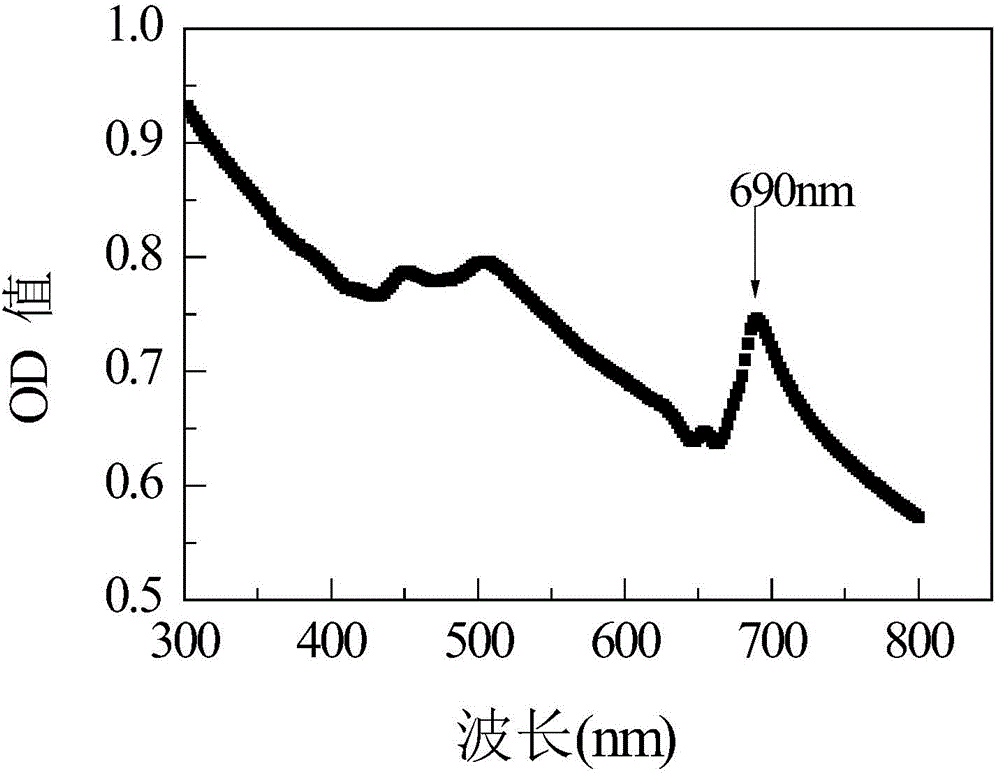
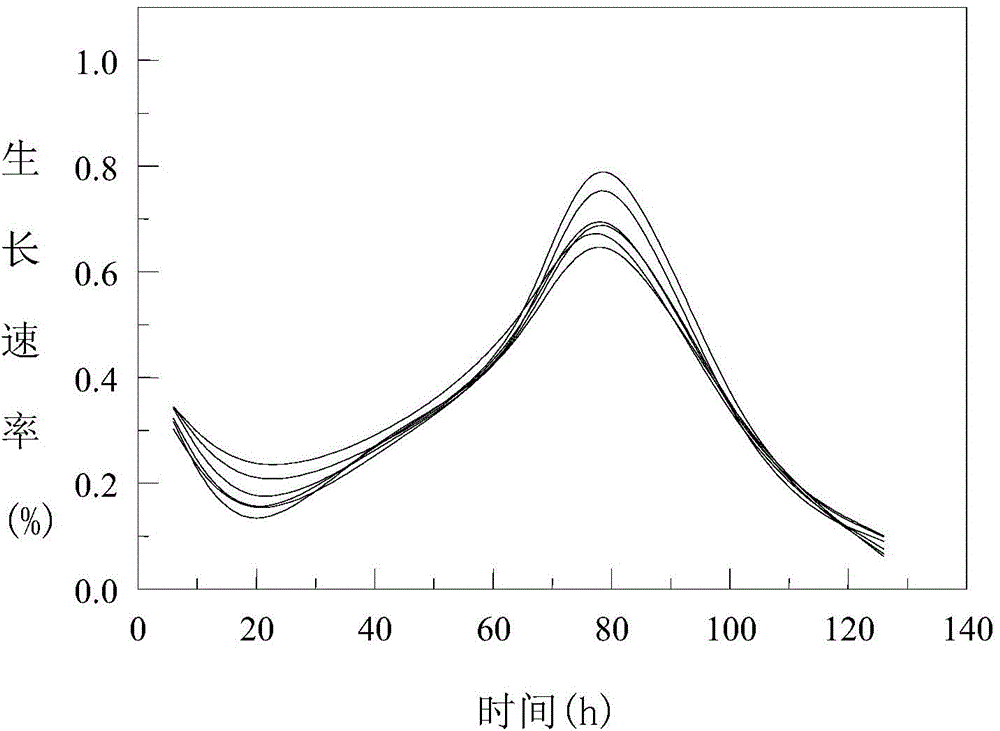
Microplate analysis method for time toxicity of environmental pollutants on basis of chlorella pyrenoidosa
InactiveCN104390920AUnderstand the mechanism of toxicological actionWays to understandColor/spectral properties measurementsFresh water organismTest organism
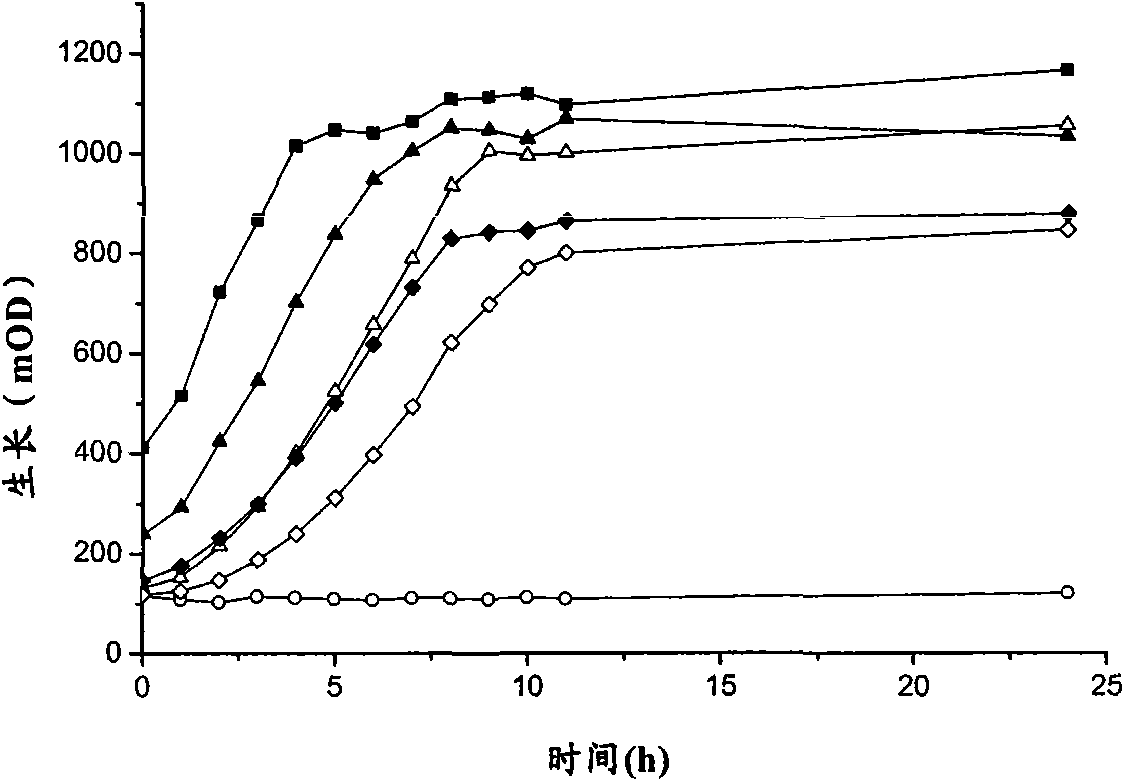
The invention discloses a microplate analysis method for the time toxicity of environmental pollutants on the basis of chlorella pyrenoidosa. The microplate analysis method comprises the following steps: with chlorella pyrenoidosa in freshwater green algae as a tested organism and a 96-hole transparent microplate as a carrier, introducing a time factor into a traditional compound concentration-effect relation, determining the time dependent toxicity of partial environmental pollutants on the chlorella pyrenoidosa, thereby discovering that all the determined pollutants have obvious time dependent characteristic, and then establishing a concentration-time-effect curve surface by utilizing a least-square spline function approximation method, thereby knowing the dynamic toxicity effect of the pollutants along with change of the concentration and the time. The microplate analysis method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the defect that a traditional toxicity analysis method can only analyze the accumulation effect of pollutants for exposed organisms at a certain exposure time endpoint is overcome, the toxicity effect of the pollutants can be learned comprehensively, the mechanism and the means of the toxicological effect of the pollutants can be known deeply, and further, the phenomenon and information of exposure of the pollutants in actual environments can be embodied.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
Compound function fabric and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104328664AImprove waterproof performanceImproves UV protectionVegetal fibresTest organismStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a compound function fabric and a preparation method thereof. The compound function fabric is prepared from a gray fabric padding water-proofing agent, an anti-ultraviolet finishing agent and an antibacterial agent, wherein the water-proofing agent is a non-fluorine water-proofing agent, the non-fluorine water-proofing agent is composed of the following components by mass percent: 5-35% of non-fluorine polymer with a hydrophobic group, 5-20% of modified polyethylene wax, 1-10% of self-crosslinking polyacrylic acid emulsion, 1-10% of polyacid ester emulsion and the balance of water. The non-fluorine water-proofing agent which has good compatibility with the anti-ultraviolet finishing agent and the antibacterial agent is used for synergetically treating the fabric in combination with the anti-ultraviolet finishing agent and the antibacterial agent so as to obtain the compound function fabric. The waterproof level of the obtained compound function fabric is the third or above, the ultraviolet protection coefficient UPF average value is greater than 160, the test organism reduction percentage of the colibacillus is 96% and more, the test organism reduction percentage of the staphylococcus aureus is 96% and more, the test organism reduction percentage of the candida albicans is 96% and more, and the fabric has good antibacterial performance.
Owner:东莞市中纺化工有限公司
Adhesive force testing device and adhesive force testing method thereof
ActiveCN110865026ATest adhesionTest frictionUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisAdhesion forceRotational axis
The invention discloses an adhesive force testing device and an adhesive force testing method thereof. A device and a method for detecting the adhesion and friction of organisms with strong adhesion capability are absent in the prior art. The adhesive force testing device comprises a test bed support, a reversible platform, a motor, an angle sensor, a rotating shaft, a sliding table, a sliding block, a sliding rod, a camera bracket, a camera and a substrate. The device not only can test the adhesive force of organisms with the adhesion capability, but also can conduct friction force and adhesive test on a bionic attachment device. The device does not cause any damage to the organisms or non-organisms tested in the test. According to the device, a substrate with different surface roughnesscan be replaced, so that the influence of roughness on the adhesive force is tested. According to the device, the friction force and the adhesive force of the organisms can be tested through the reversible platform.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method for measuring content of ayfivin and its preparations by nephelometry
InactiveCN101271117AIncrease supplyPromote growthMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingTurbidityTest organism
The invention discloses a method for measuring bacitracin and the content of the preparation thereof by the turbidity method, and the method contains the following steps: the preparation of standard solution, the preparation of test solution, the preparation of test organism suspension, the content measurement, etc. The antibiotics-microbial test and multi-dose turbidity method of the invention are adopted for measuring the bacitracin and the content of the preparation thereof, thus the test method is accurate and effective and has low cost, and test results can truly reflect antibacterial activity of the bacitracin and the preparation thereof; the method has stronger practicality and operability in the production and the quality control of the drug and the preparation thereof.
Owner:高燕霞
Automated Concentration System
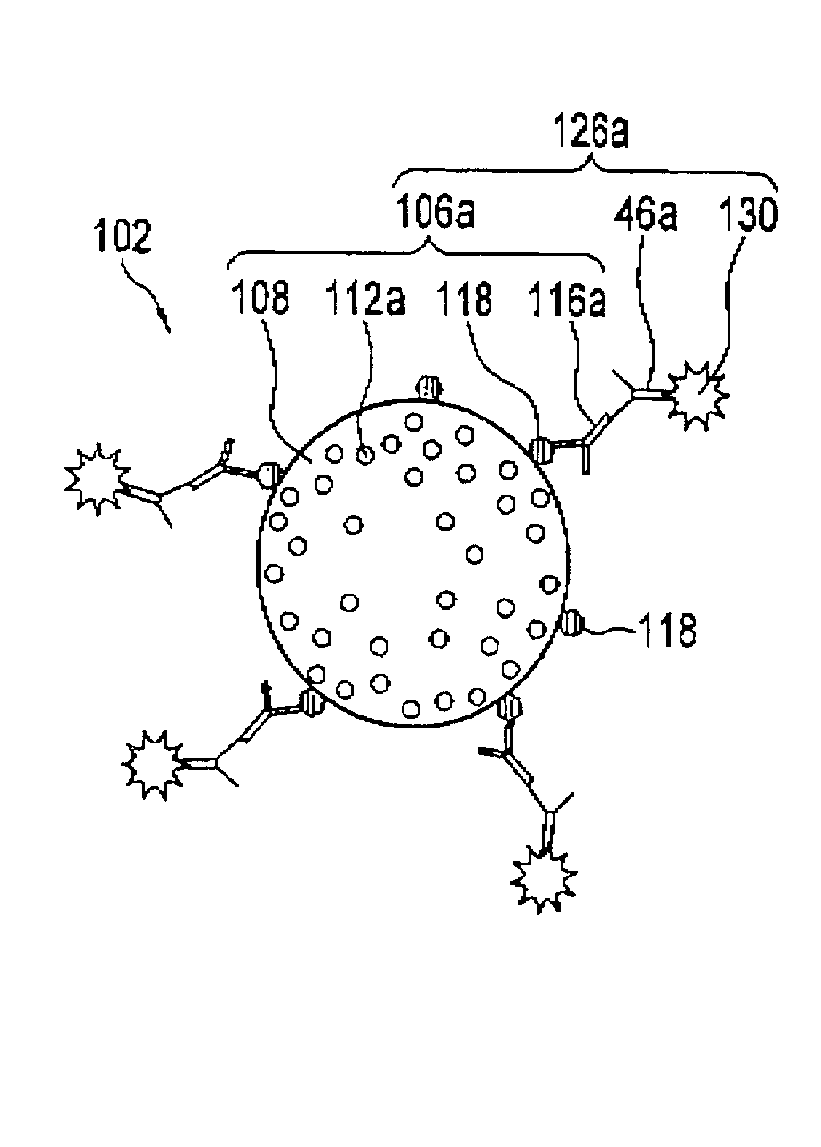
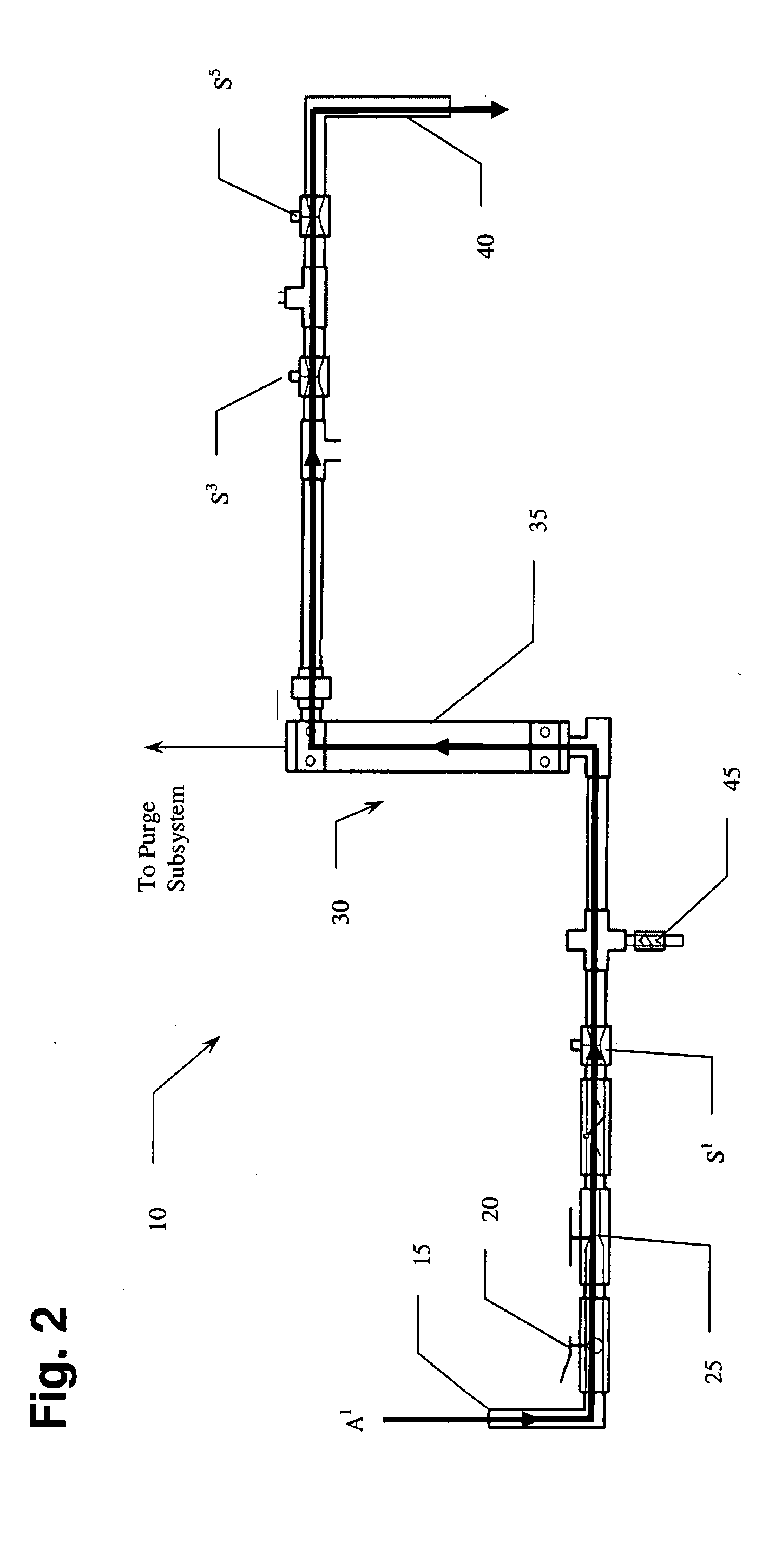
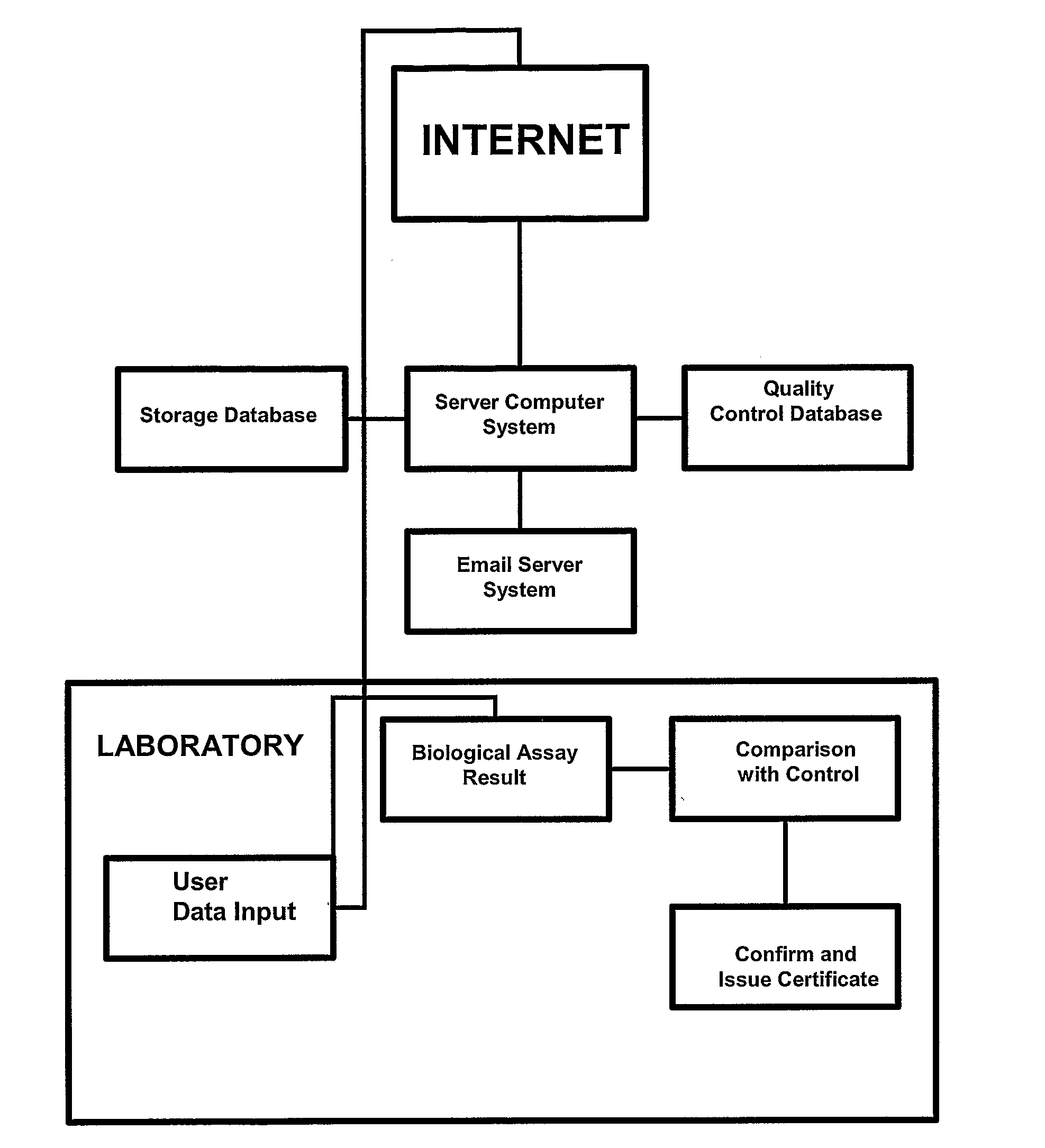
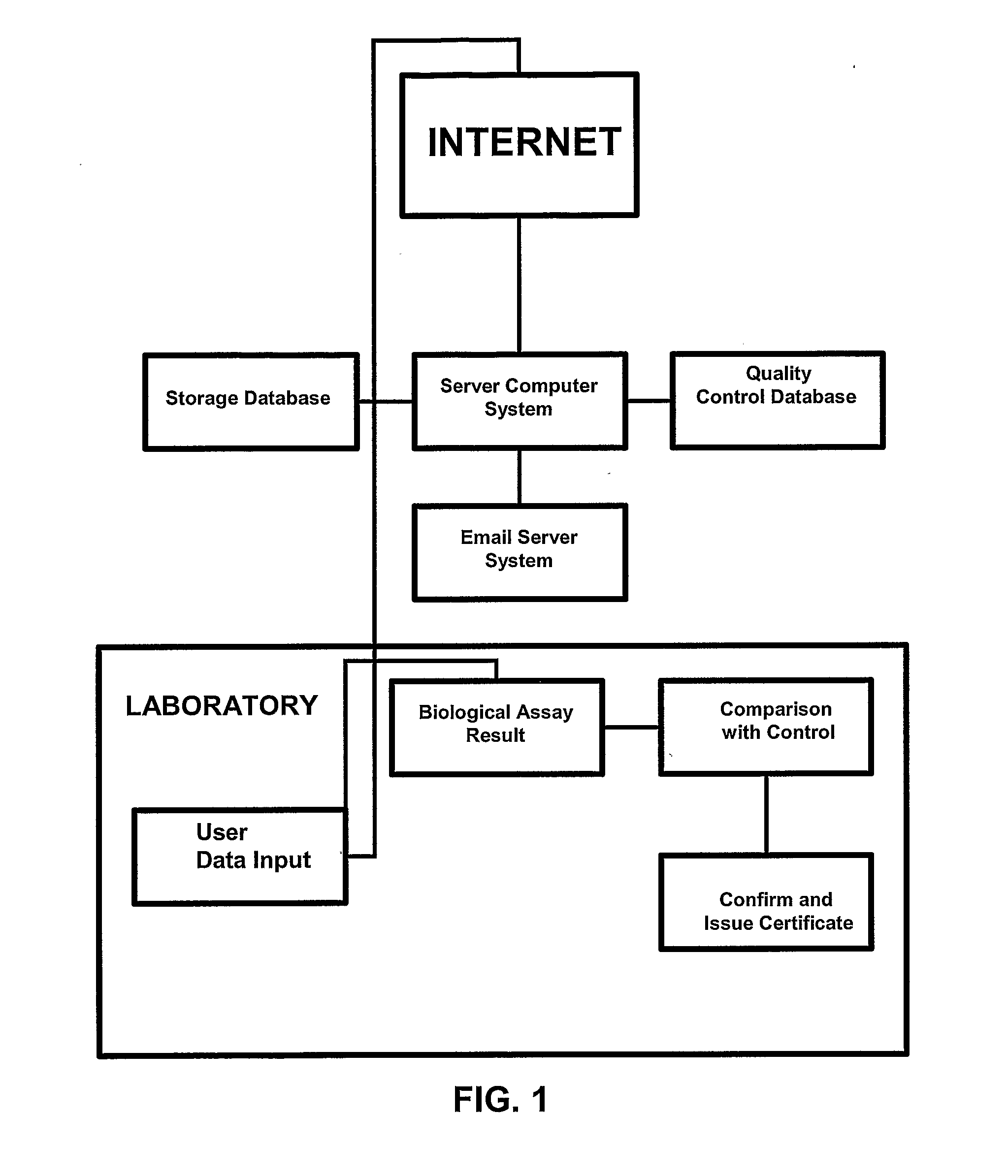
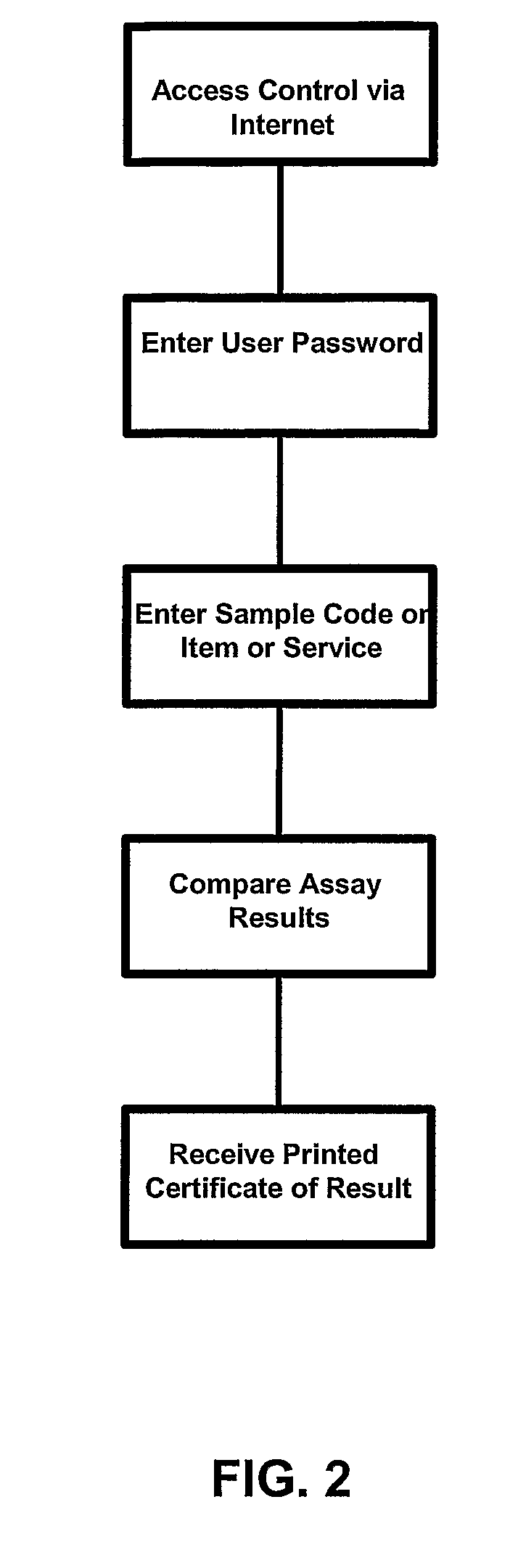
An in-line water monitoring system for the detection of the accidental or intentional introduction of potentially harmful substances. The automated system comprises a water pressure driven concentration unit that filters drinking water through a hollow-fiber filter. Material collected on the filter is backflushed into a collection vessel by passing a sterile solution through the filter in the reverse direction. An electronic signal at the end of the backflush sequence triggers a sensor such as an array biosensor to begin processing and analyzing the sample. The array biosensor houses a slide prepared with antibodies to the test organism. The array biosensor is programmed to automatically run sample and detection reagents over the slide, analyze the resulting pattern for positive and negative data, and report the results.
Owner:CONSTELLATION TECH +1
Method for screening drugs for targeting synthesis and assembly of bacillus tubercle cell wall core
ActiveCN101906461ASimple and fast operationImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismHigh flux
The invention relates to a method for screening drugs for targeting bacillus tubercle, in particular to a method for screening drugs for targeting synthesis and assembly of a bacillus tubercle cell wall. The invention comprises the following steps of establishing a screening model for targeting the synthesis and the assembly of the bacillus tubercle cell wall core by adopting Corynebacterium glutamicum as a test organism and an BHI (Brain-Heart Infusion) and BHIS (Brain-Heart Infusion Supplemented) medium as a screening medium, and screening novel anti-tuberculous drugs and lead compounds of different enzyme systems and target spots, which act on the synthesis and assembly process of the bacillus tubercle cell wall core, from microorganism metabolic products and samples of other sources. The anti-tuberculous drugs for targeting the whole synthesis and assembly process of the bacillus tubercle cell wall core can be screened by the screening model of the invention. The model is a cell-level high-flux screening model.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Comparative phenotype analysis of cells including testing of biologically active chemicals
InactiveUS20050260558A1Improve effectivenessImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingPlant cellTest organism
The present invention relates to growing and testing any cell type in a multitest format. The present invention is suited for the characterization of microorganisms, as well as animal and plant cells. The present invention is also particularly suited for analysis of phenotypic differences between strains of organisms, including cultures that have been designated as the same genus and species. The present invention is also suited for the analysis of phenotypic differences between cell lines. In some embodiments, a gel forming matrix is used. The present invention provides methods and compositions for the phenotypic analysis and comparison of eukaryotic, as well as prokaryotic cells. The present invention further provides novel methods and compositions for testing the effect(s) of biologically active chemicals on various cells.
Owner:BIOLOG
Thin-layer chromatography coloration method
InactiveCN1743842AObserve the separation effectGood effectComponent separationBiotechnologyTest organism
This invention refers to thin layer chromatography color development method, which contains 1, laying the dissolved biological color development culture medium on chromatography thin board air dried by normal method, 2, preparing test organism into bacteria suspension liquid and coating on biological color development culture medium, 3, putting the bacteria coated board in culture box to culturing color development.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
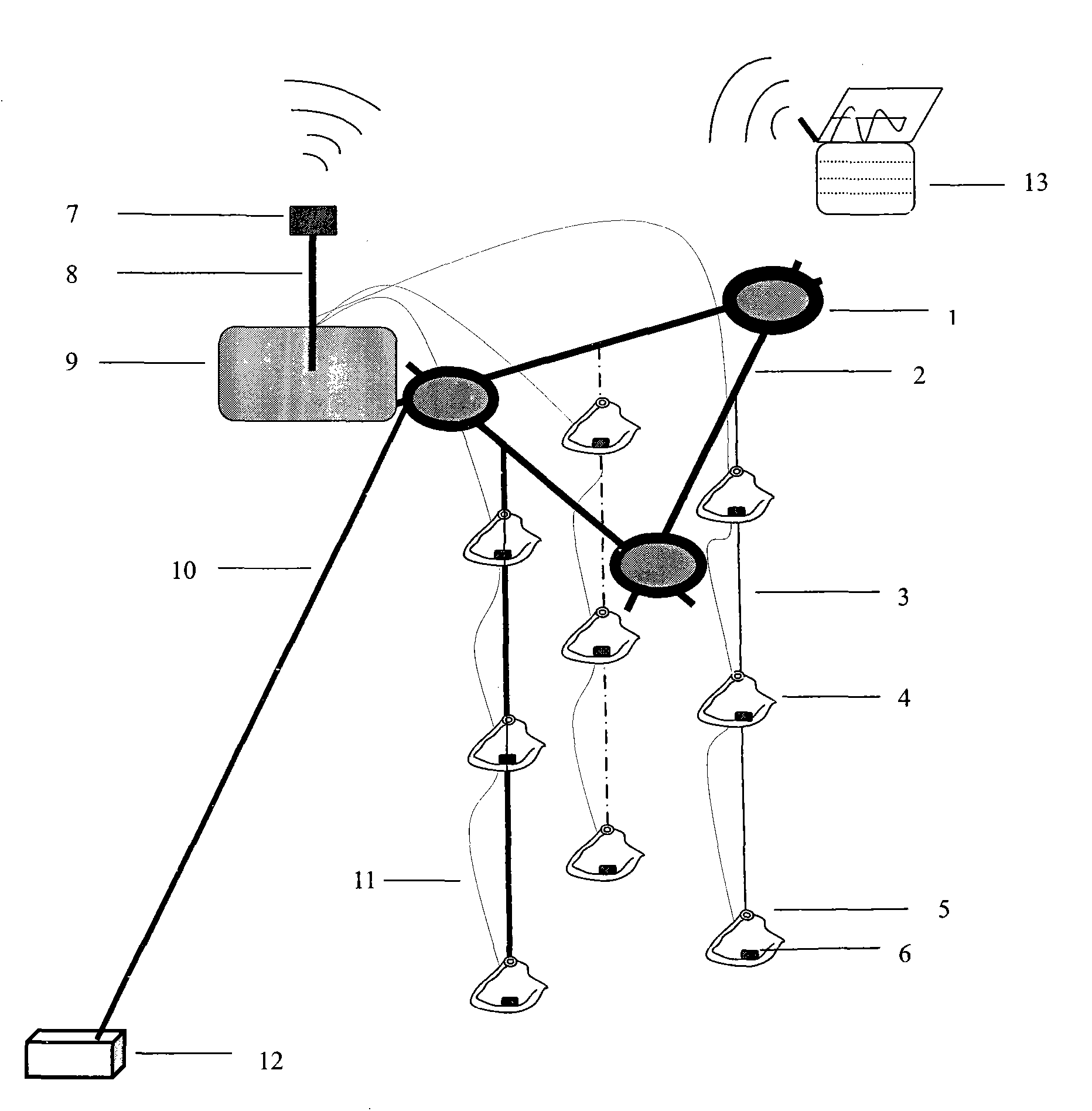
Field device for biologically monitoring water quality online
The invention discloses a field device for biologically monitoring water quality online. The defects that tested organisms need to be fed by foods, the tested organisms need to be replaced periodically, monitoring is limited to a specific monitoring site and medium / long-term online biological monitoring cannot be realized in the conventional online water quality biological monitoring are overcome. The scientific requirements of medium / long-term biological monitoring early warning which reflects water toxicity change in a natural water body can be met. According to the device, a rule that hyriopsis cumingii can be subjected to hanging culture in lakes and reservoirs for ingesting plankton and a physiological phenomenon that the shell of the hyriopsis cumingii is tightly closed after the hyriopsis cumingii is stressed are fully utilized, and the shell motion of the hyriopsis cumingii is induced by using a sensor fixed on the shell of the hyriopsis cumingii, so that the biological toxicity monitoring of the water quality is performed. According to the device, a floating platform and a floating ball are fixed on a monitoring site by utilizing a mooring anchor, a signal emitter is supported by buoyancy supporting the floating platform, and the hyriopsis cumingii and the sensor are supported by utilizing buoyancy of the floating ball, so that the hyriopsis cumingii and the sensor are suspended in the water body. The shell closing response of the hyriopsis cumingii is induced by utilizing the sensor, a signal is transmitted to the signal emitter through a wire, the signal is received by utilizing a signal receiver arranged ashore for performing analytical processing, and the water quality is subjected to scientific early warning and monitoring.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
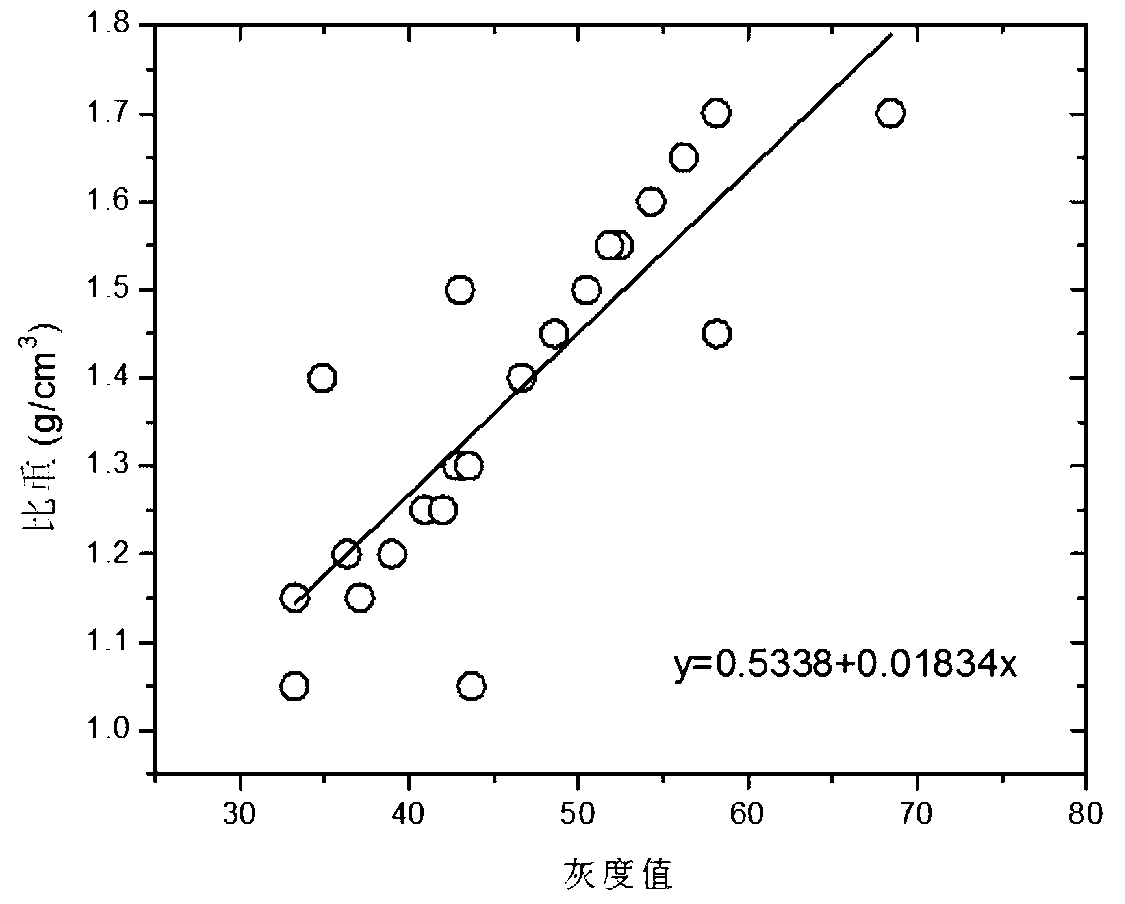
Microbial aggregate quantitative microscopic imaging testing and evaluating method
InactiveCN103234865AThe determination method is simpleThe measurement result is accurateSpecific gravity measurementImage resolutionTest organism
The invention discloses a quantitative microscopic imaging testing and evaluating method of microbial aggregate property. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, demarcating a standard relation curve of grey scale values and specific gravity values of a to-be-tested microbial aggregate sample; then obtaining an image of a to-be-tested slide made of a mixed solution containing to-be-tested microbial aggregates by using a digital microscope, calculating grey scale values and areas of all the to-be-tested microbial aggregates from resolutions, R values, G values and B values of all the microbial aggregates in the image, and calculating specific gravity values from the grey scale values as well as the standard relation curve of grey scale values and specific gravity values; and finally performing comprehensive evaluation on the areas and the specific gravity values of the to-be-tested organism aggregates by using a fuzzy pattern recognition method, to obtain a level characteristic value vector as an evaluation result of the to-be-tested organism aggregates. According to the high-efficiency and precise method, quantitative analysis and comprehensive evaluation on the microbial aggregates are achieved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Compositions and Methods Comprising Biological Samples for Quality Controls
InactiveUS20080177477A1High sensitivityImprove precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingQuality control systemQuality control
A quality control system for testing biological samples is provided, comprising: a support having at least one surface capable of receiving one or more predetermined quantities of a biological sample from one or more known donors. A computerized system for testing biological samples is also provided.
Owner:ORCHID CELLMARK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com