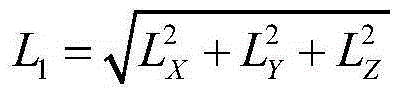Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
145 results about "Spatial Displacement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
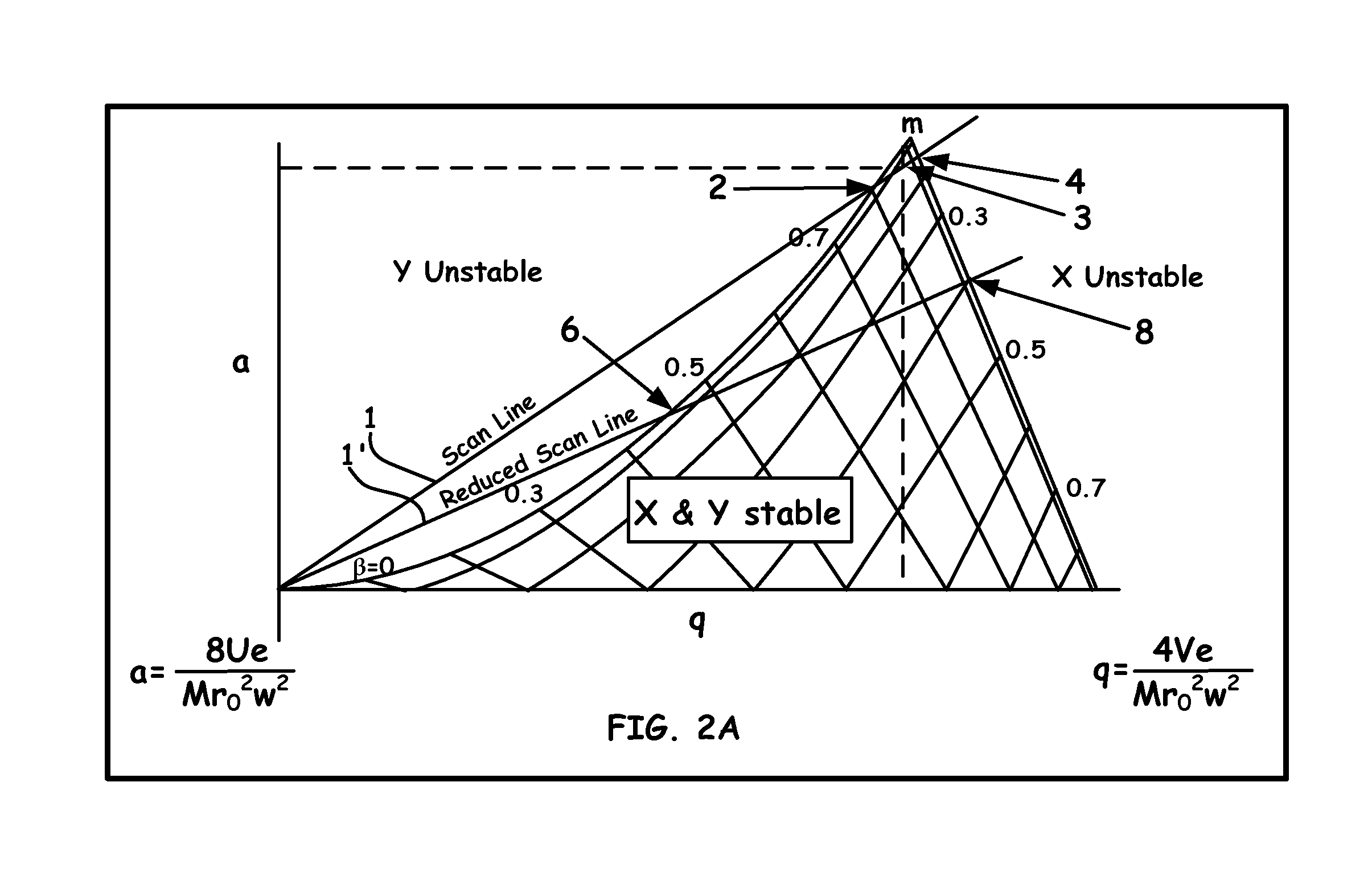
Spatial displacement was an ability built into the improved DeLorean time machine, which allowed for the time traveler to travel through space instantaneously as would make the jump through time.
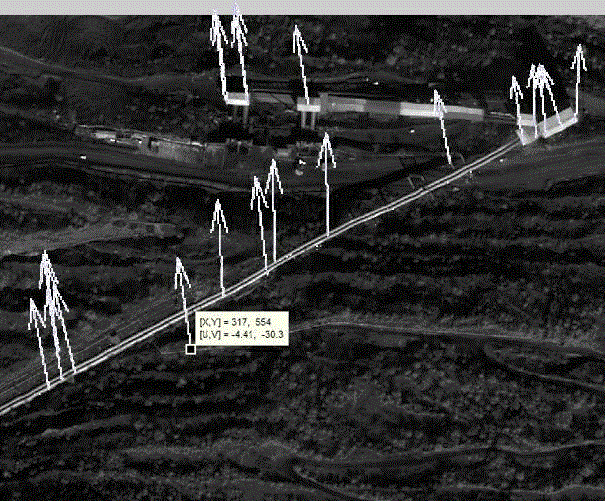
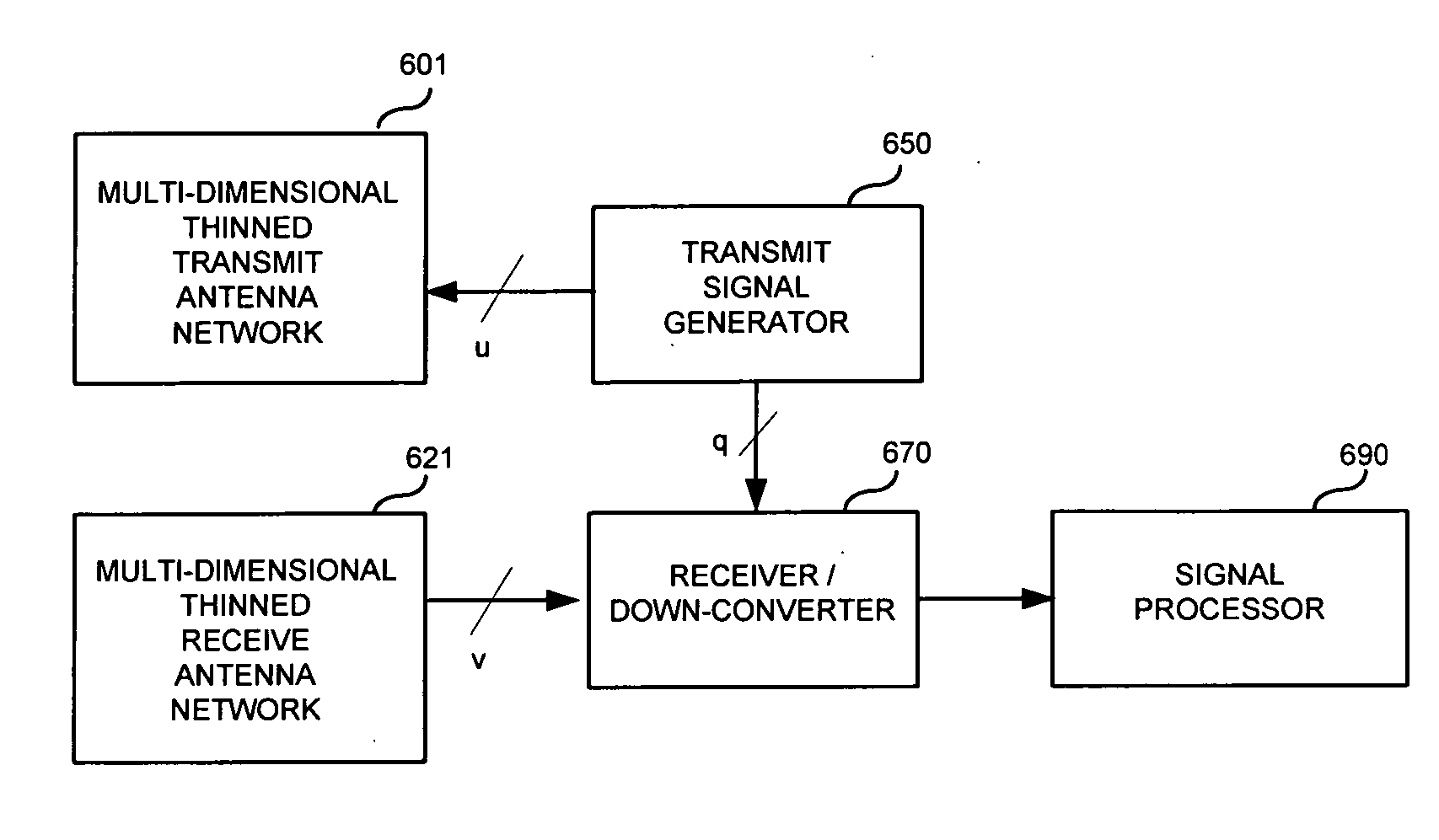
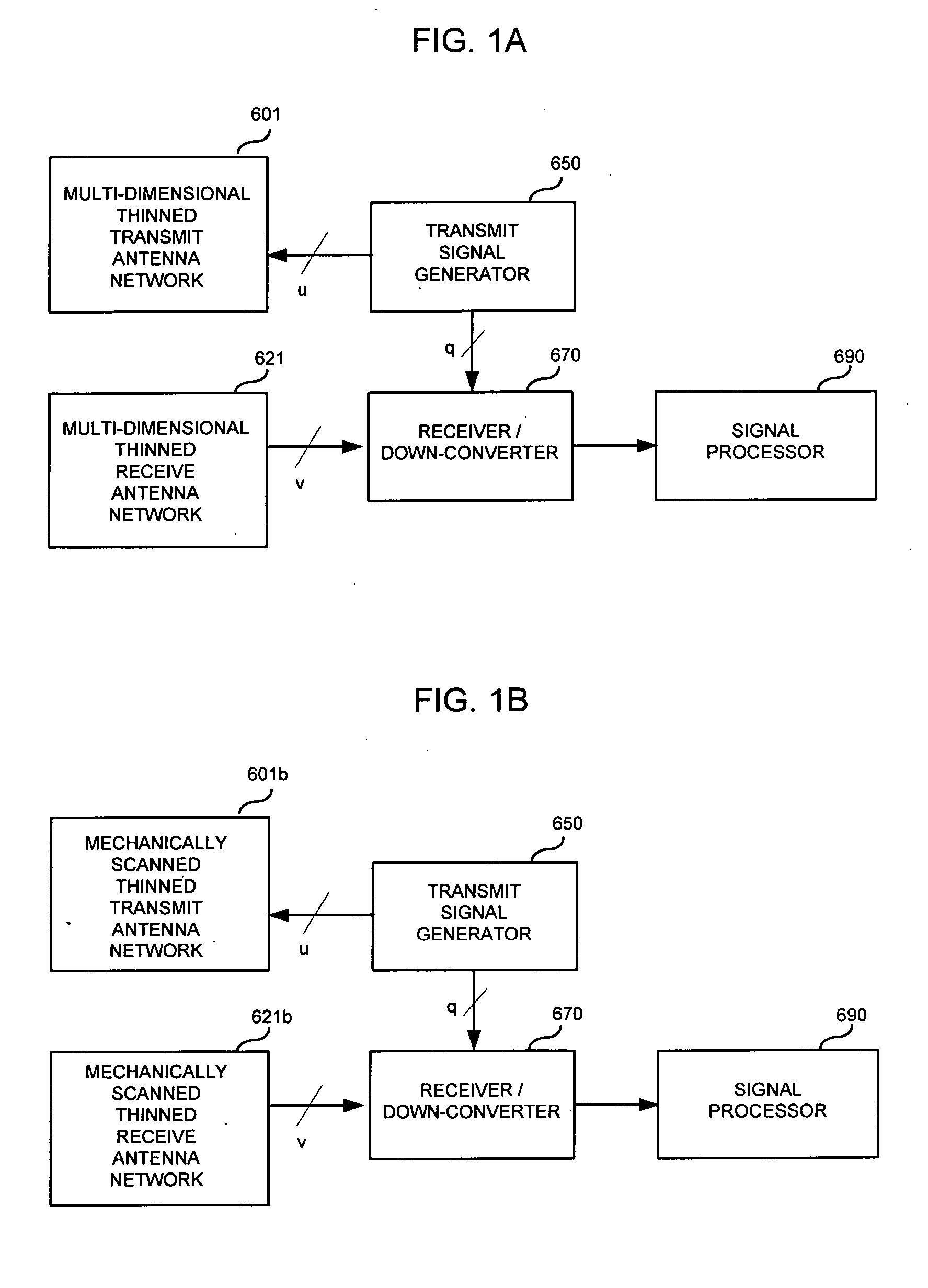
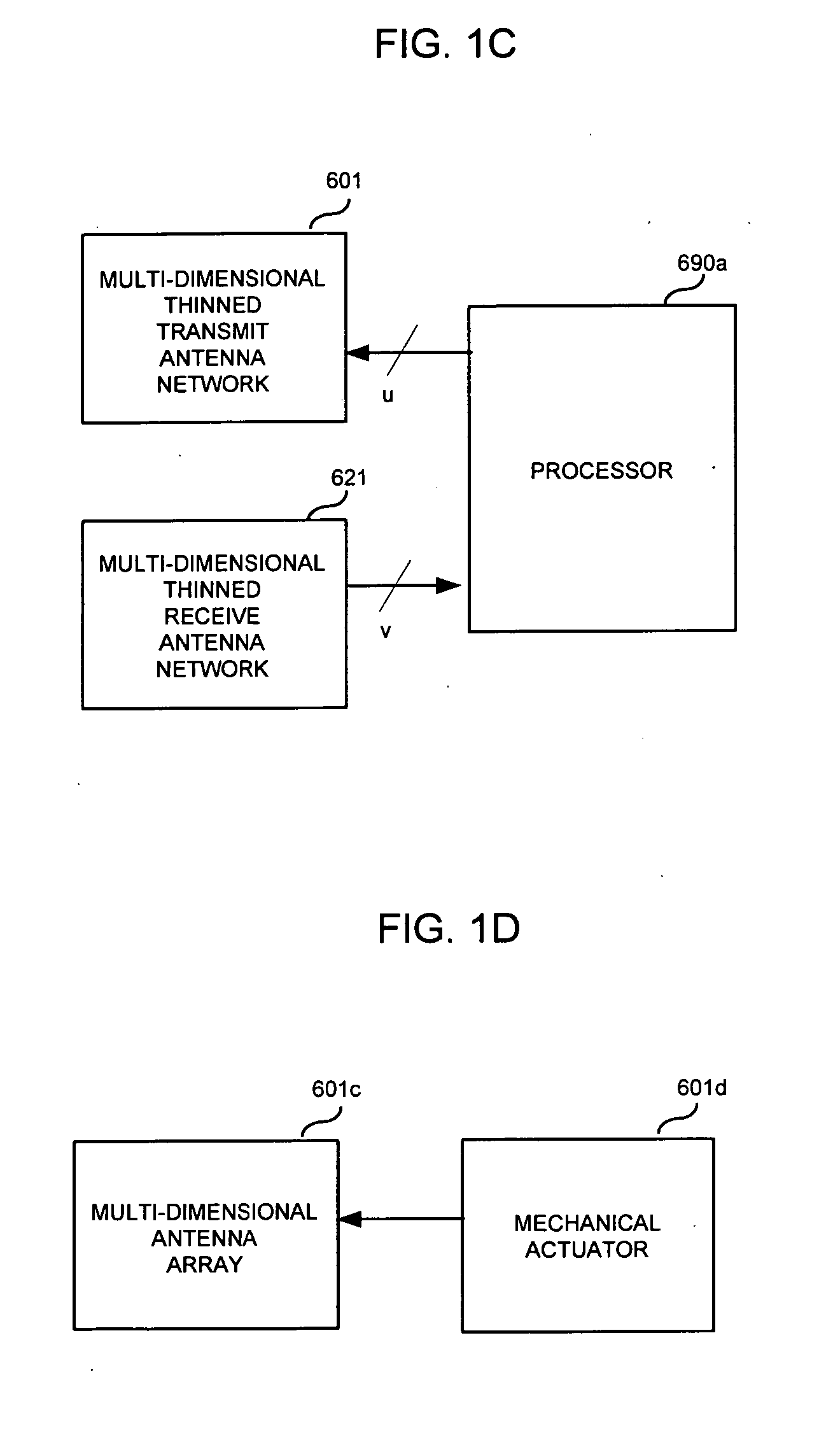
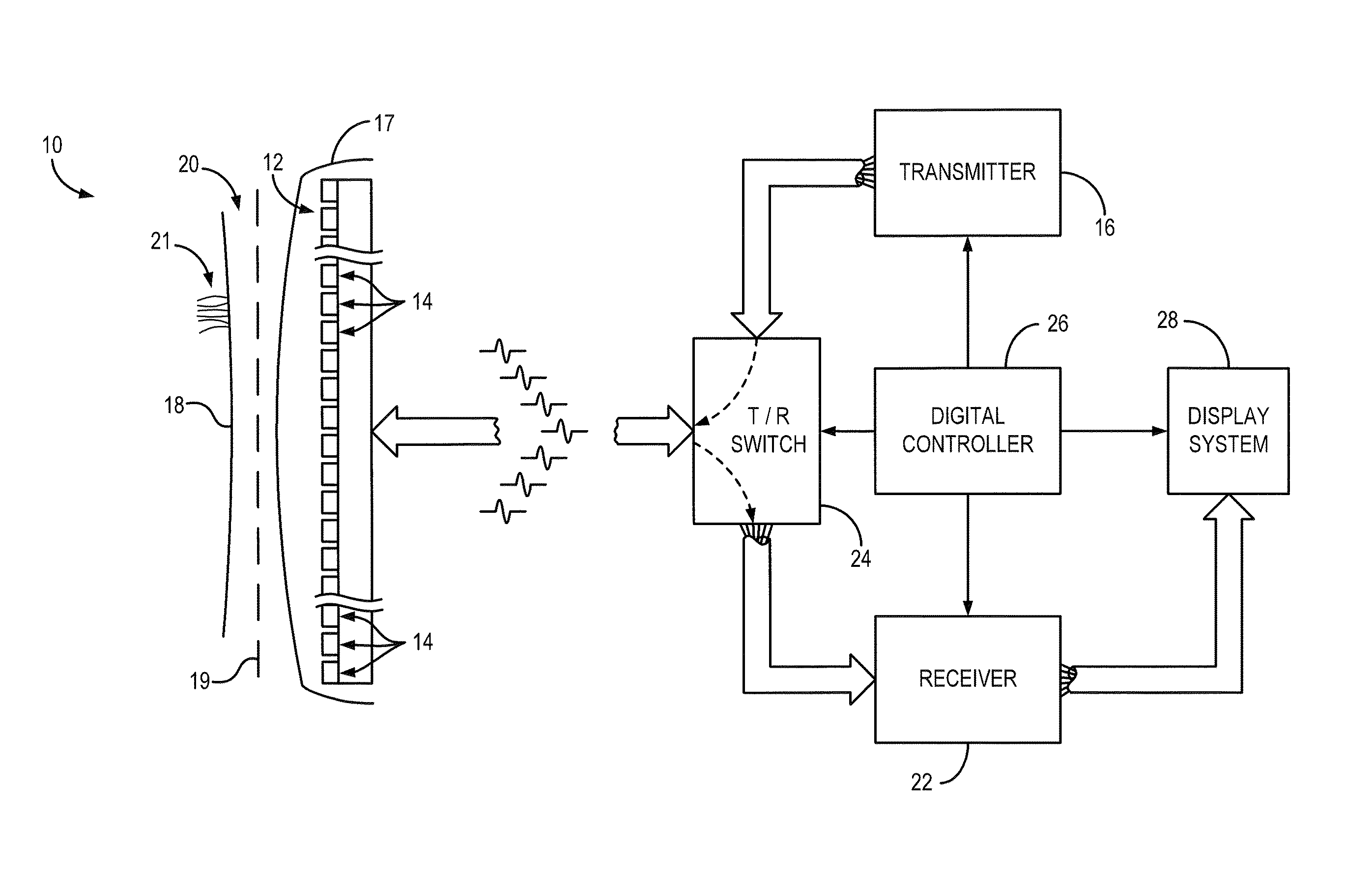
Method and apparatus for microwave and millimeter-wave imaging
InactiveUS20080100510A1Differential interacting antenna combinationsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringMillimetre wave
An antennae system for a detector. The antennae system includes a two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter array that has an x number of transmitter elements, and a two-dimensional electro-magnetic receiver array that has a y number of receiver elements. The two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter and receiver arrays have a spatial relationship such that at least one subset of the two-dimensional electro-magnetic transmitter and receiver arrays forms a regular array of spatial displacements of z pairwise combinations of transmitter and receiver elements, where z is greater than the sum of x and y.
Owner:BONTHRON ANDREW J +1
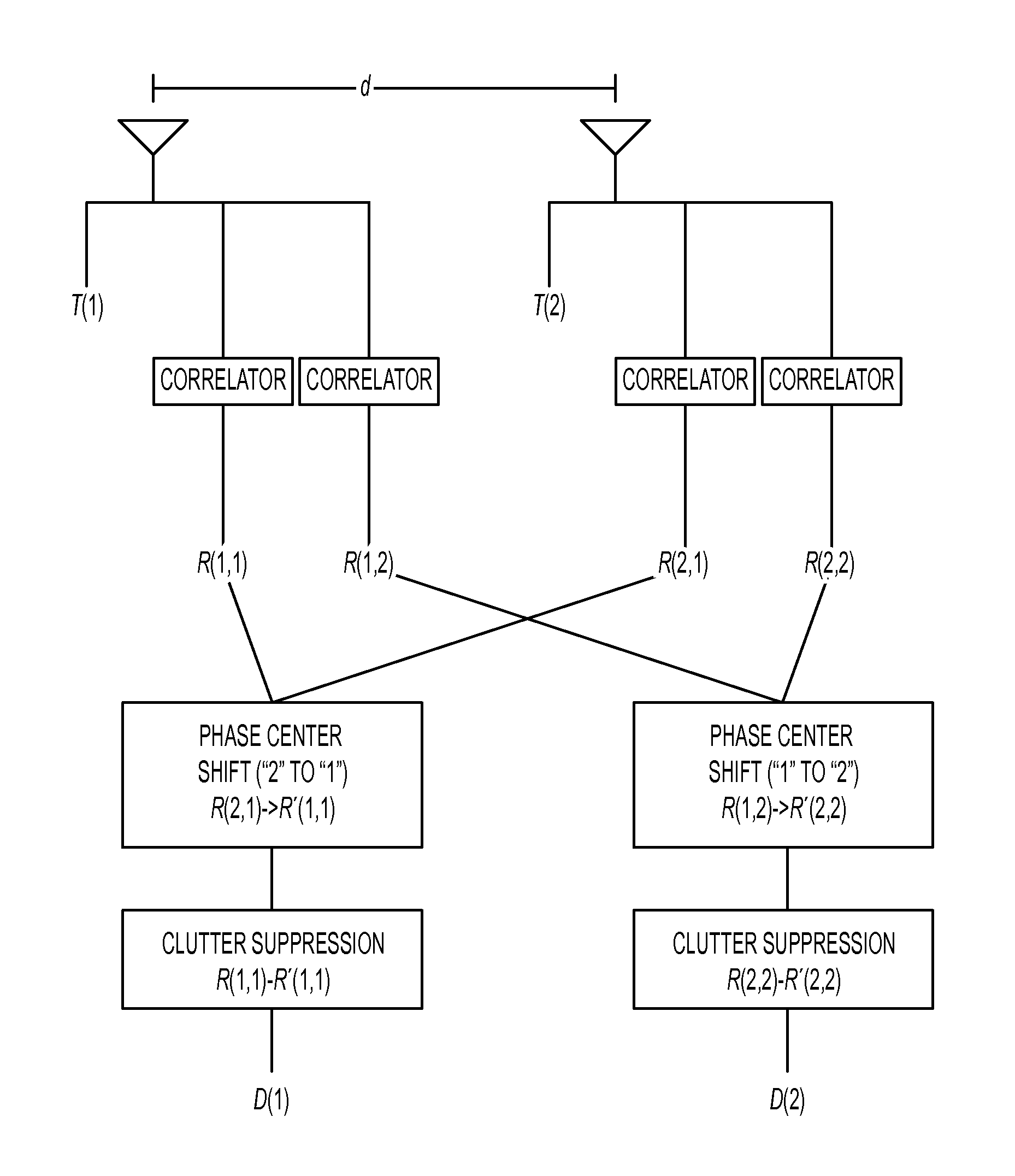
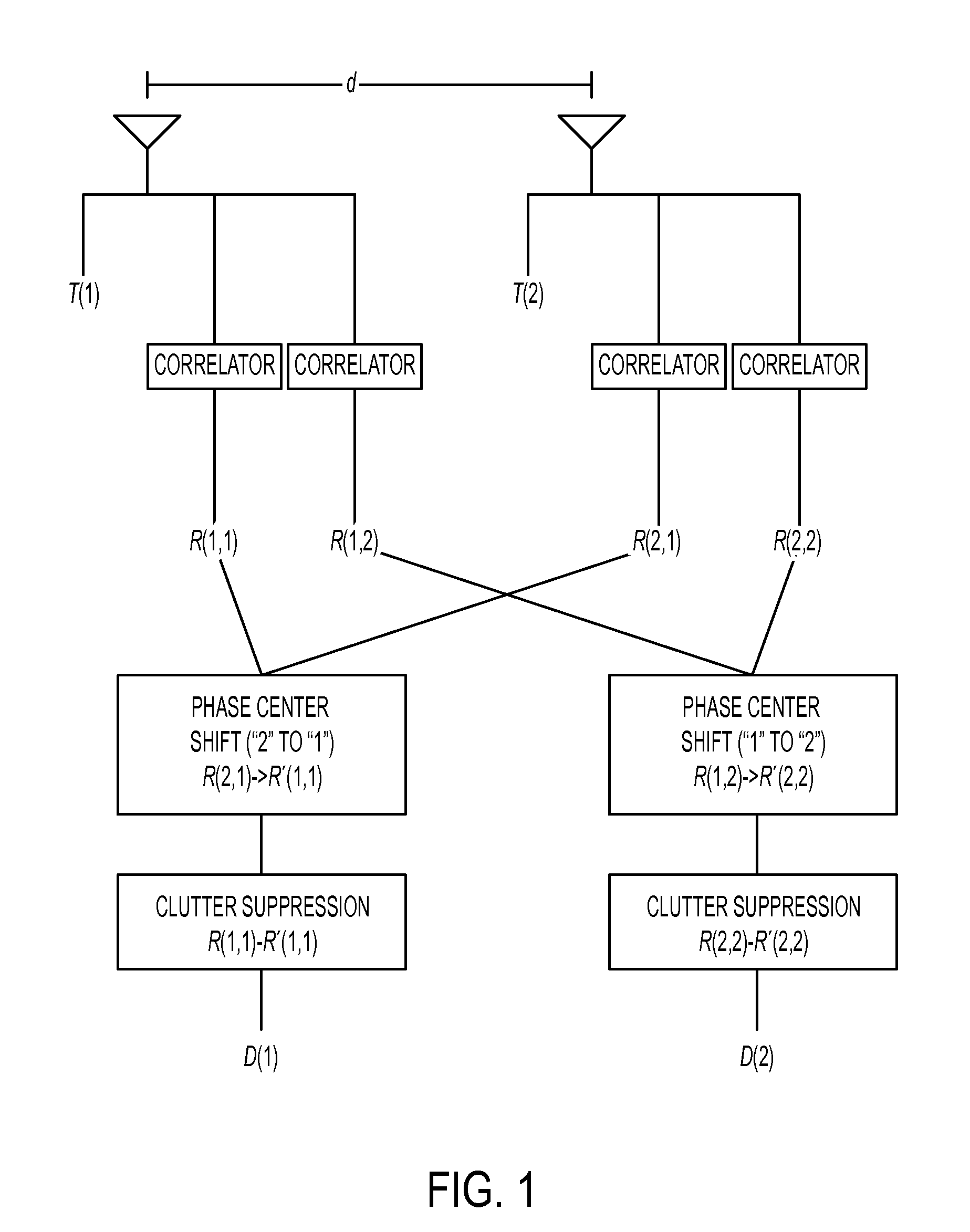
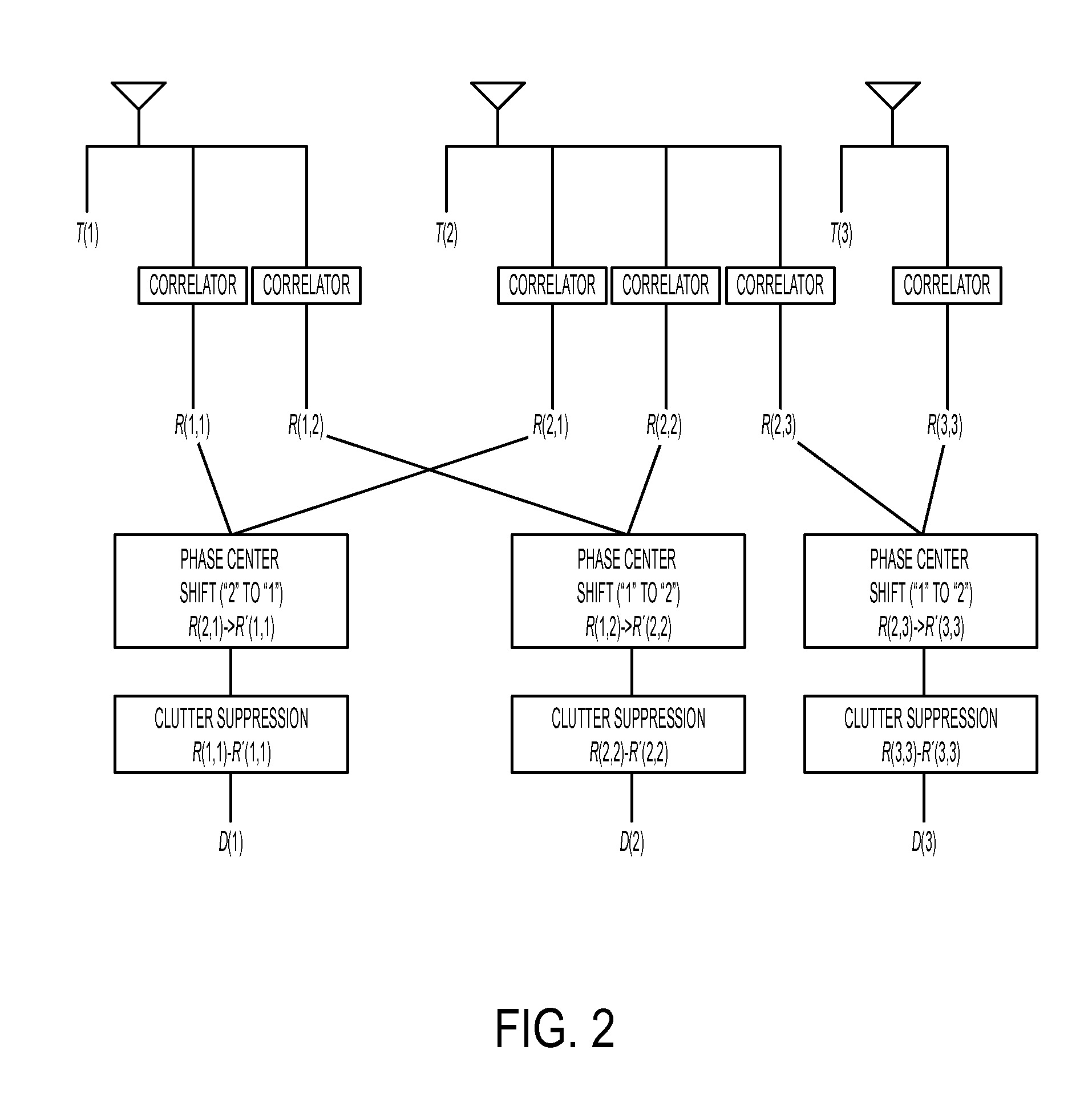
Methods And Systems For Multiple Input Multiple Output Synthetic Aperture Radar Ground Moving Target Indicator
A multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system. The radar system includes spatially offset transmitting antennas simultaneously transmitting at least two distinguishable waveform signals and receiving antennas receiving incoming waveform returns for each of the distinguishable waveform signals. The radar system also includes a displaced phase center antenna (DPCA) processing unit adapted to perform processing on the incoming waveform returns, and a synthetic aperture radar processing unit adapted to produce a plurality of spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. The radar system also generates a plurality of clutter-suppressed signals using the spatially-coincident SAR-processed signals. For each of two MIMO transmissions from spatially displaced transmitters, clutter is cancelled simultaneously in at least two spatially displaced receive channels via DPCA processing. This results in at least two spatially displaced but simultaneous clutter cancelled complex SAR images, which are combined in a monopulse processor to enhance target detection and unambiguously determine target angle.
Owner:SRC INC
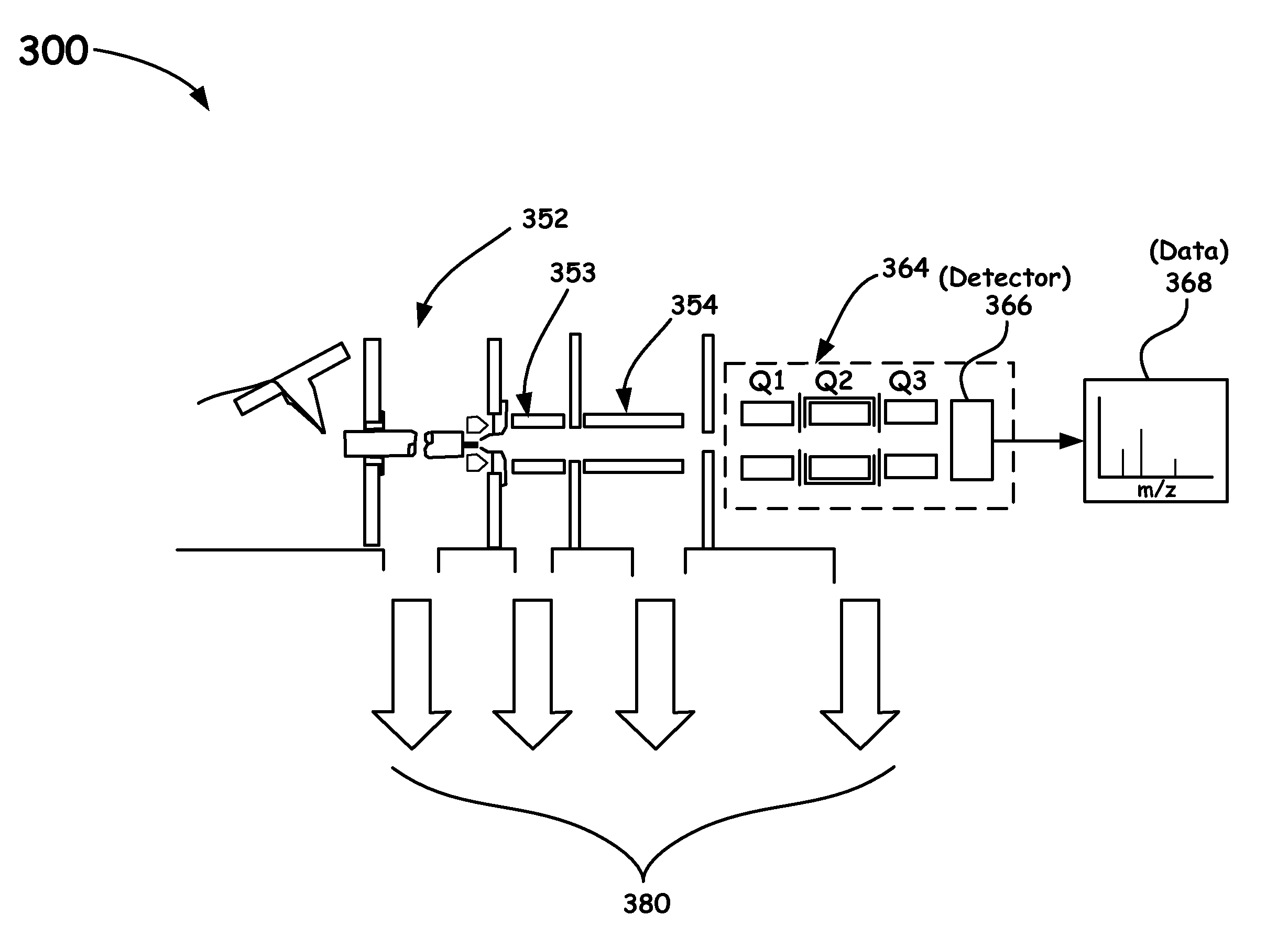
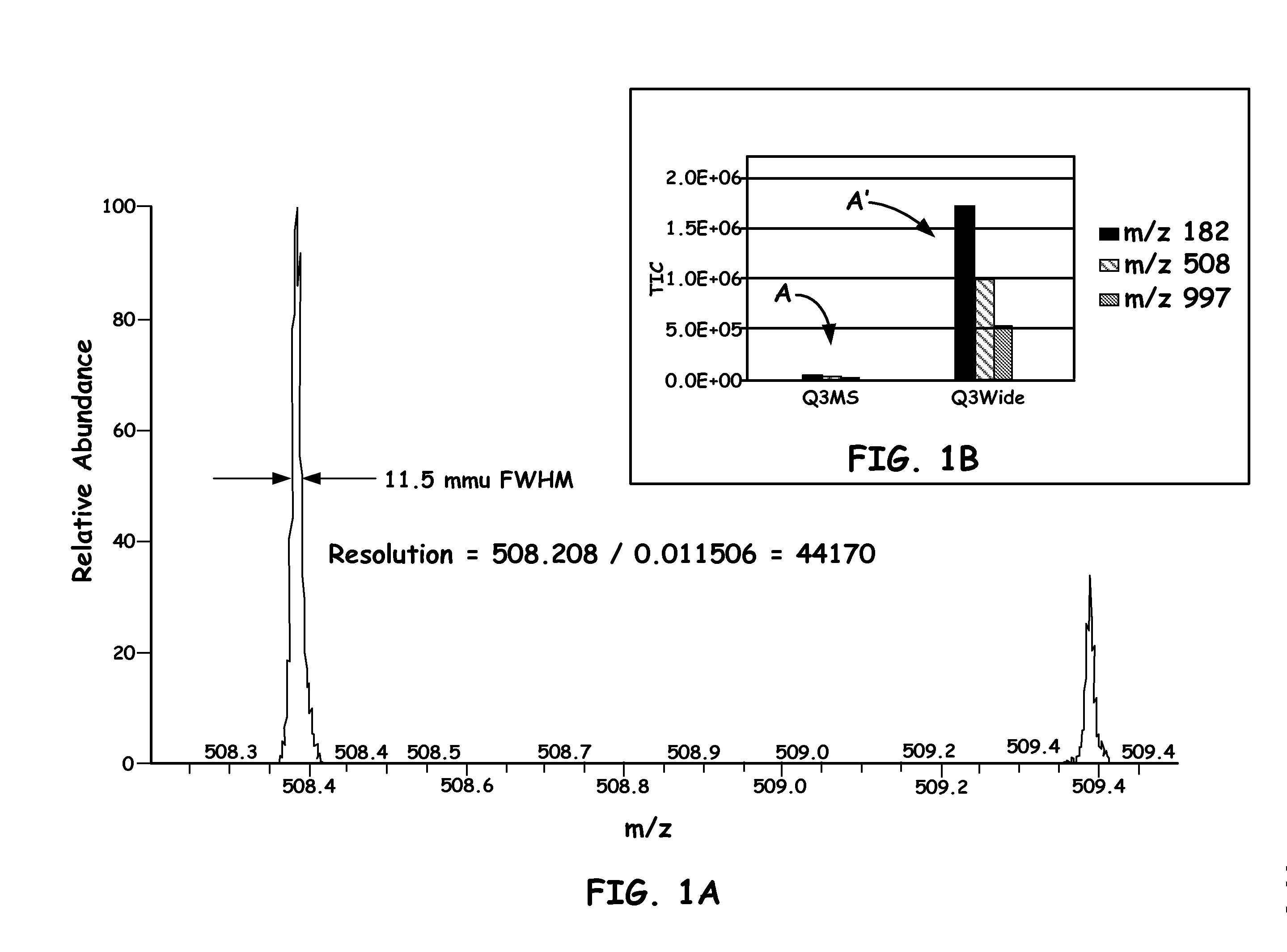
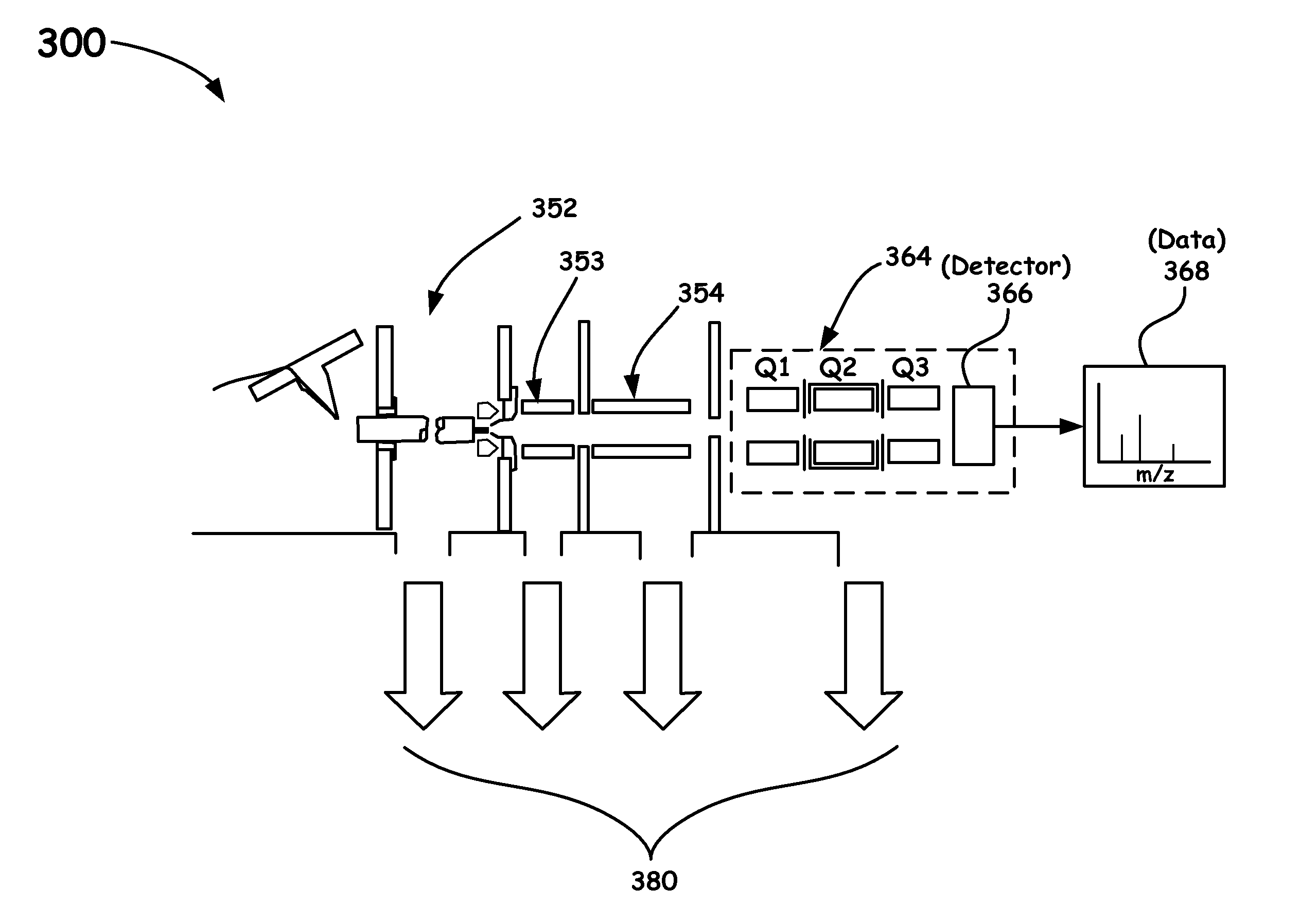
Quadrupole mass spectrometer with enhanced sensitivity and mass resolving power
ActiveUS8389929B2Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
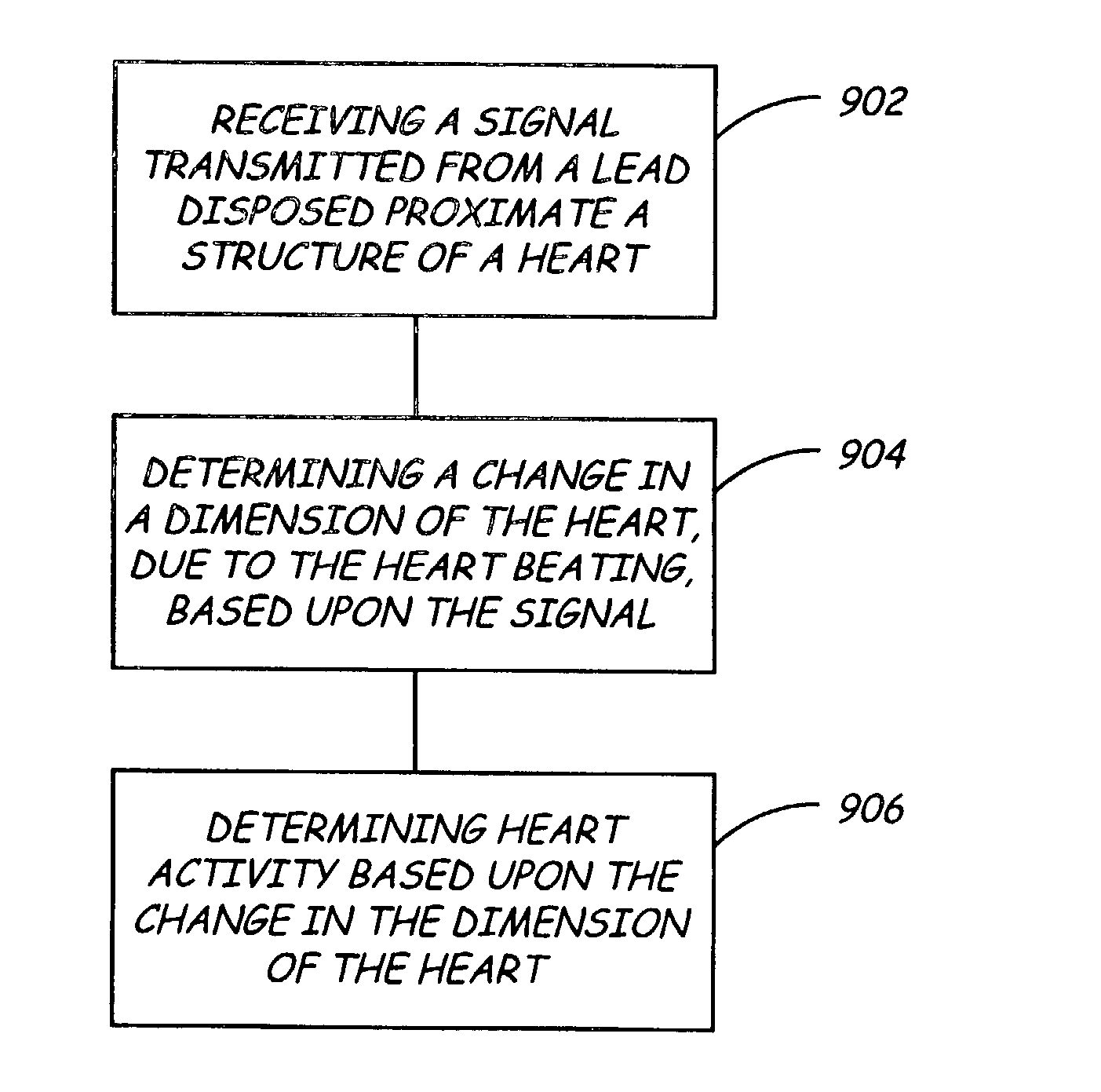
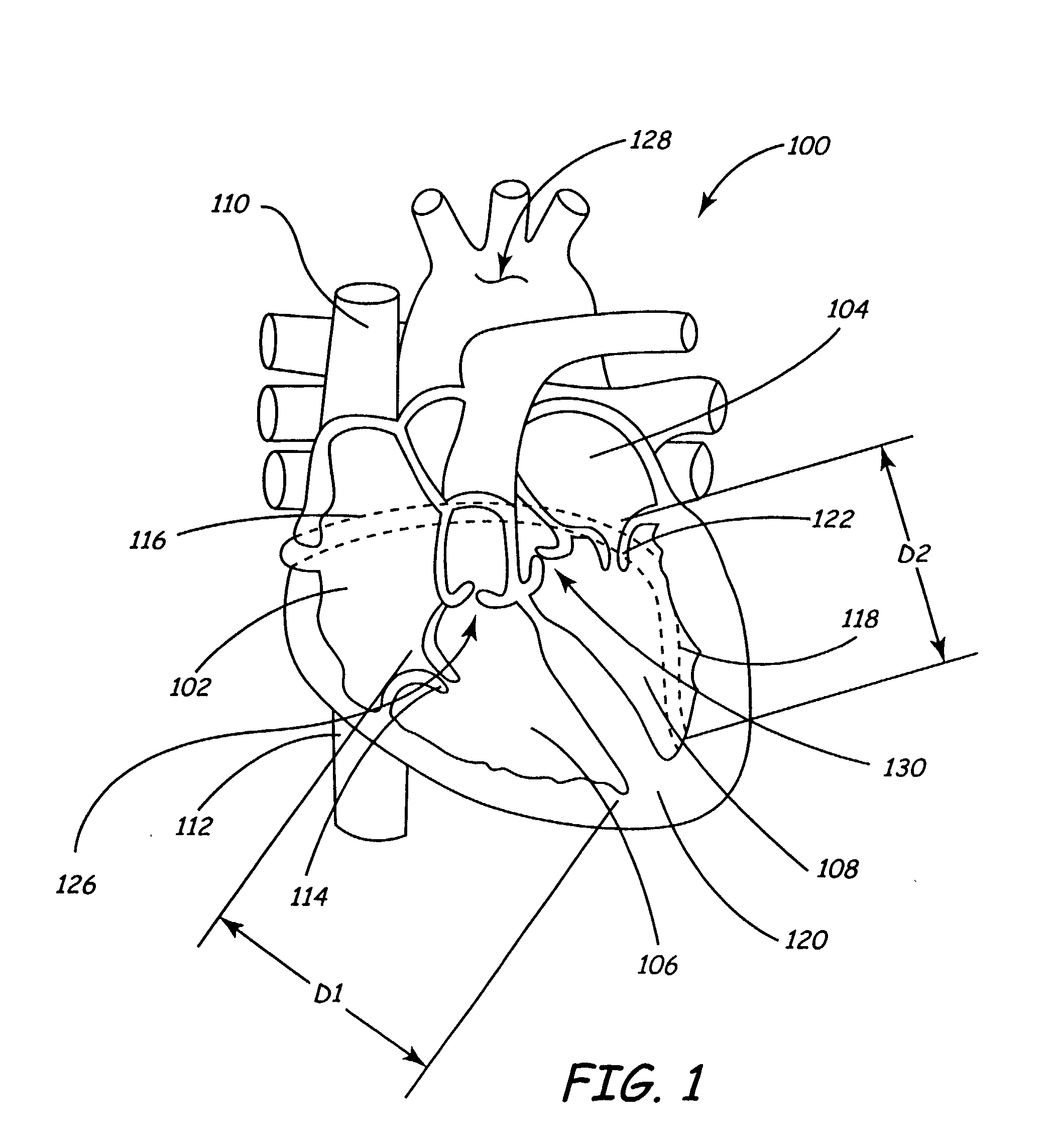
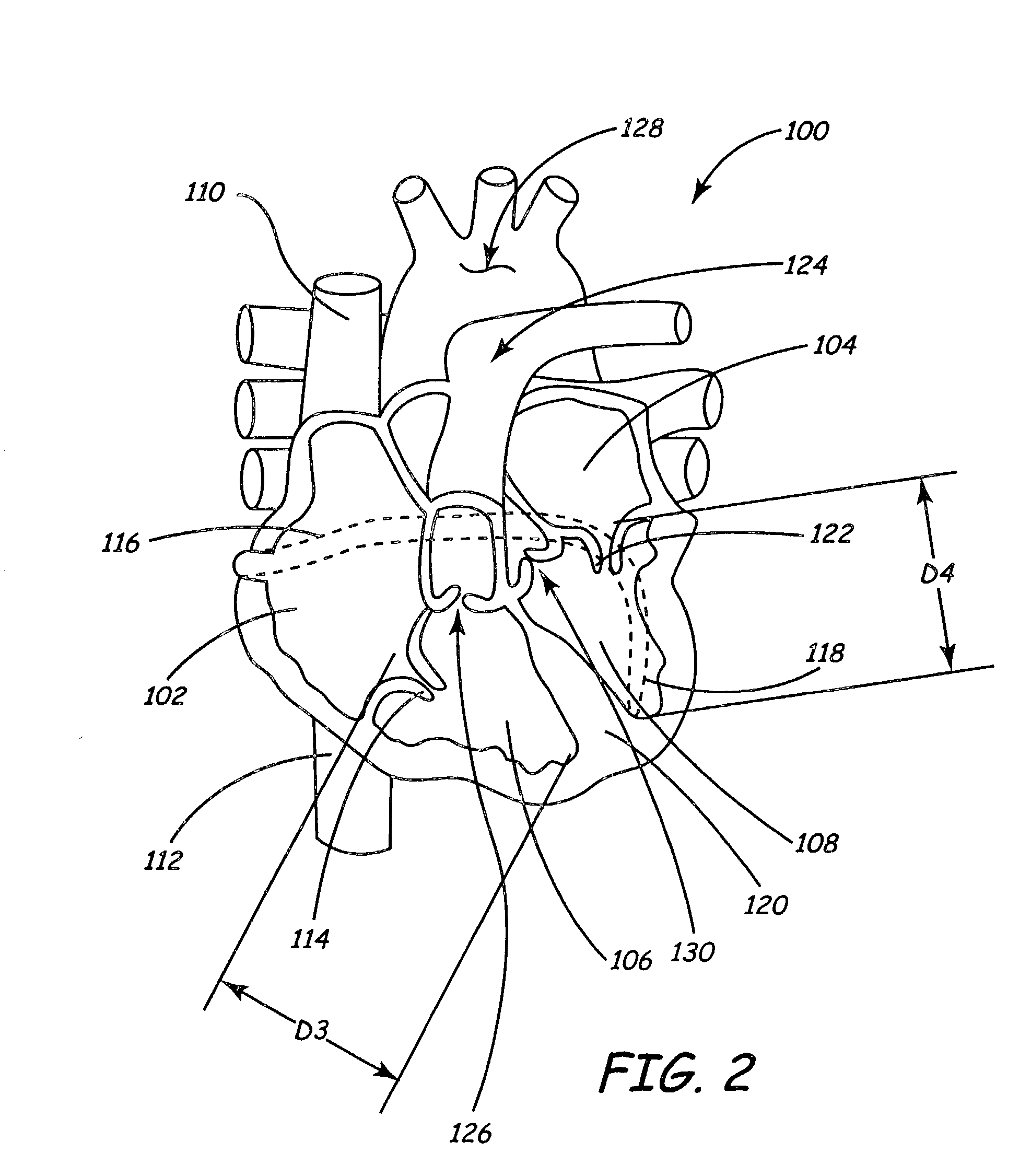
Apparatus and method for sensing spatial displacement in a heart
InactiveUS20030158494A1Organ movement/changes detectionTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectricityEngineering
An electrical lead includes an elongate body having a proximal end, and a sensing unit capable of resolving a change in a spatial configuration of the electrical lead. A medical device includes a control unit, an elongate body having a proximal end coupled with the control unit, and a sensing unit capable of resolving a change in a spatial configuration of the electrical lead and relating it to the amount of blood ejected from the heart. A method includes receiving a signal transmitted from a lead disposed within a heart and determining a change in a dimension of the heart, due to the heart beating, based upon the signal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer With Enhanced Sensitivity And Mass Resolving Power
ActiveUS20110215235A1Low costImprove robustnessStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsMass analyzerQuadrupole
A novel method and mass spectrometer apparatus is introduced to spatially and temporally resolve images of one or more ion exit patterns of a multipole instrument. In particular, the methods and structures of the present invention measures the ion current as a function of time and spatial displacement in the beam cross-section of a quadrupole mass filter via an arrayed detector. The linearity of the detected quadrupole ion current in combination with it reproducible spatial-temporal structure enables the deconvolution of the contributions of signals from individual ion species in complex mixtures where both sensitivity and mass resolving power are essential.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
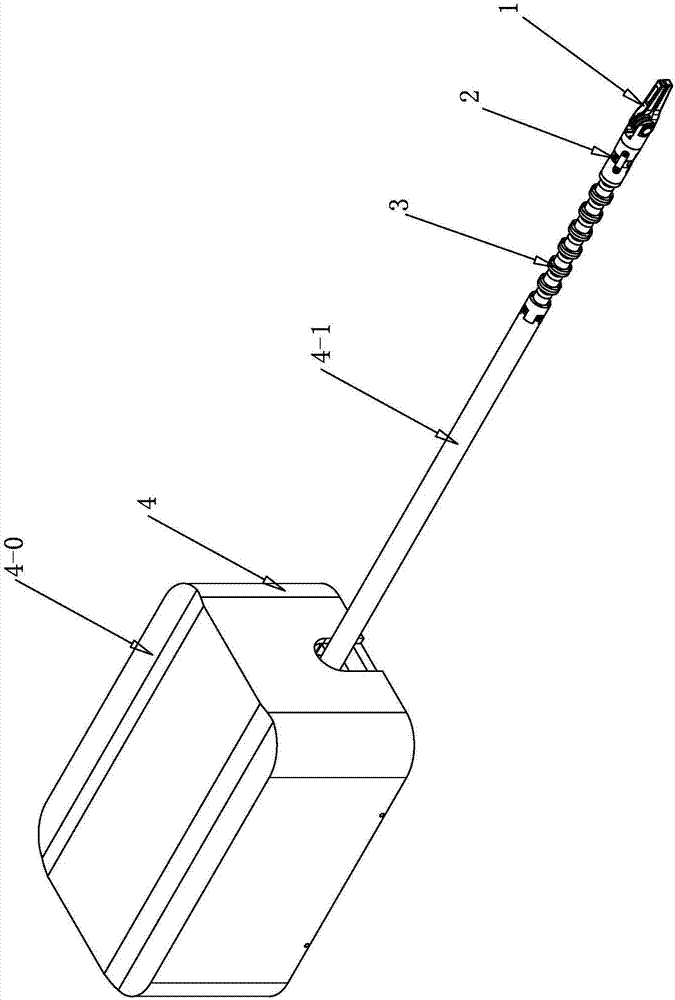
Flexible multi-joint surgical instrument for robot assisted minimally invasive surgery
ActiveCN107468339ARealize opening and closing movementAchieve bending motionSurgical manipulatorsSurgical robotsSurgical operationForceps
The invention discloses a flexible multi-joint surgical instrument for robot assisted minimally invasive surgery, and relates to the technical field of enterocoelia minimally invasive surgery department medical facilities. The instrument can achieve spatial displacement and positioning of tail end operating forceps by itself inside a patient, the tail end gesture adjusting capability of the surgical instrument is enhanced, the good flexibility is achieved, and the tissue surgical operation is completed inside the small space; by means of a self-rotation joint designed between the wrist of the surgical instrument and the tail end operating forceps, and the problem that joint restoration is needed during autorotation is avoided; the instrument comprises the tail end operating forceps mechanism, the autorotation joint, the wrist flexible joint and a power driving box; the power driving box comprises a wiring pipe, a shell, an upper base plate, a lower base plate, five sets of motor rope sheave devices, a rope guiding wheel set and a rope guiding column set; one end of the wiring pipe is connected with the tail end ball hinge structure of the wrist flexible joint, and the other end of the wiring pipe is fixed to the lower base plate. The instrument is used for the robot assisted minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
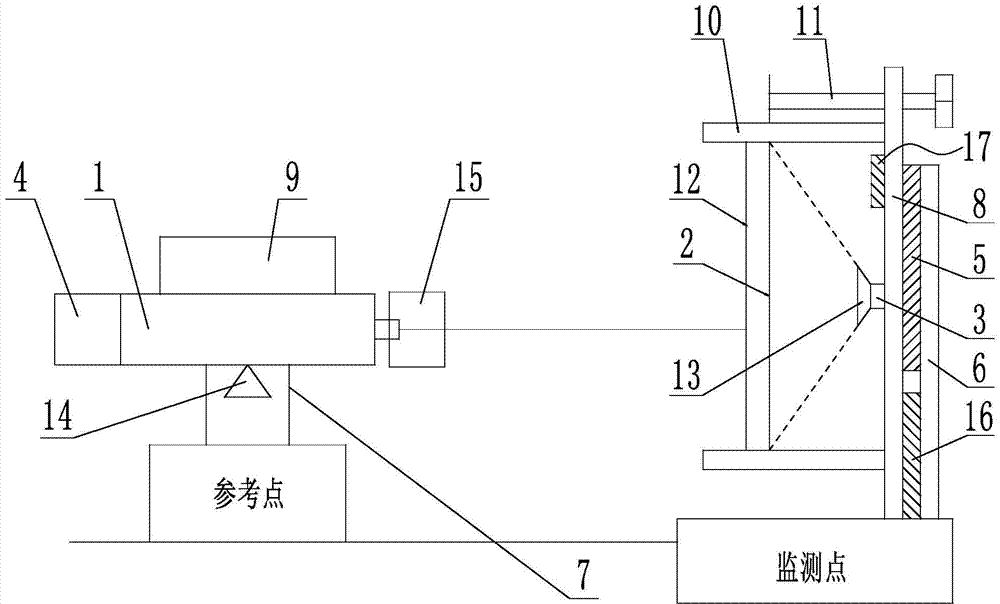
Non-contact spatial displacement measurement device
InactiveCN103940357AReduce energy consumptionReduce the impactUsing optical meansLaser rangingMeasurement device
The invention discloses a non-contact spatial displacement measurement device. The non-contact spatial displacement measurement device comprises a laser range finder arranged on the reference point, an imaging transmitting plate arranged on the monitoring point, an image collection device arranged on the side, with the back to the laser range finder, of the imaging transmitting plate, a drive module and a control module. The imaging transmitting plate is used for receiving light emitted by the laser range finder and forming light spots. The image collection device is used for collecting the light spots formed on the imaging transmitting plate and connected with the drive module, and the drive module is connected with the control module. The non-contact spatial displacement measurement device is large in measuring range, high in measurement accuracy, small in power consumption and capable of measuring prostration and hypsokinesis from front to back and forward and reverse rotation deformation, relative to a laser device, of a position sensor, solves the problems in the prior art and can be widely used for monitoring deformation of engineering buildings under the condition of geological disasters, and the measuring range is convenient to adjust.
Owner:SANHE WENKONG COMP TECH CO LTD
Lens coupling system and method
PendingCN110045465AGrab smoothly and accuratelyHigh degree of automationMaterial gluingCoupling light guidesEngineeringCoupling system
The invention relates to the field of optical device installation, and discloses a lens coupling system and method. The system comprises the following parts of a grasping mechanism for grasping a lensin a tray; a space displacement mechanism connected to the grasping mechanism for driving the lens to move to contact a dispensing mechanism for dispensing and for moving the dispensed lens to fit achip; a curing mechanism disposed above the chip for curing the glue between the lens and the chip; and a positioning subsystem comprising a first image detecting mechanism, which is disposed above the tray for obtaining position information of the lens in the tray. The lens coupling system and method provided by the invention can automatically couple the lens and the chip, and can obtain preciseposition information of the lens on the tray by providing the first image detecting mechanism, so that the grasping mechanism can smoothly and accurately grasp the lens. The system is highly automated, and can reduce labor intensity, position the lens and improve efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Five-axis machine tool cutter posture and cutter point position error synchronous detection mechanism
InactiveCN104625880AGuaranteed measurementAvoid interferenceMeasurement devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsNumerical controlMeasurement device
The invention discloses a five-axis machine tool cutter posture and cutter point position error synchronous detection mechanism. The five-axis machine tool cutter posture and cutter point position error synchronous detection mechanism comprises a tilt angle measurement device, a spatial displacement measurement device, a rotating angle measurement device, an installation device and a follow-up platform, wherein the tilt angle measurement device, the spatial displacement measurement device, the rotating angle measurement device and the follow-up platform are all installed on the installation device, the spatial displacement device is used for measuring the three-axial-direction micrometric displacement of a cutter point when the rotating center of a cutter of the machine tool to be detected moves along a set track, and the tilt angle measurement device and the rotating angle measurement device are used for measuring the tilt angle and the rotating angle of the cutter of the machine tool to be detected respectively. By the adoption of the five-axis machine tool cutter posture and cutter point position error synchronous detection mechanism, real-time synchronous measurement of the tilt angle and the rotating angle of the cutter of the five-axis machine tool and the three-axial-direction micrometric displacement of the cutter point is achieved. The five-axis machine tool cutter posture and cutter point position error synchronous detection mechanism has positive significance in detecting high-precision machine tools.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for demarcating large-deformation landslide displacement field based on high-resolution remote sensing image
The invention discloses a method for demarcating a large-deformation landslide displacement field based on a high-resolution remote sensing image. The method is that two geometric models are utilized to perform ortho-rectification for the high-resolution remote sensing image and corresponding DEM at different time phases in a search area; after the preprocessing and high-precision image matching, a vector set model is created based on the accurately matched feature points with the same feature points; the space displacement field of a landslide body can be demarcated according to the model. With the adoption method for early warning of large landslide disaster, in particular the landslide disaster under a complex terrain, the sliding landslide can be automatically found out and subjected to macroscopic monitoring, so that the macroscopic displacement direction and displacement of the large deformation landslide body at some time quantum can be obtained, and the sliding range can be determined; the basic data and basis can be provided to accurately monitor the landslide displacement and early warn the landslide disaster. The system and the method are mature in technology, low in cost, convenient to operate, quick to calculate, and high in accuracy; the scientific basis can be provided to monitor and evaluate the landslide disaster, and the safety in fire preventing and reduction can be ensured.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
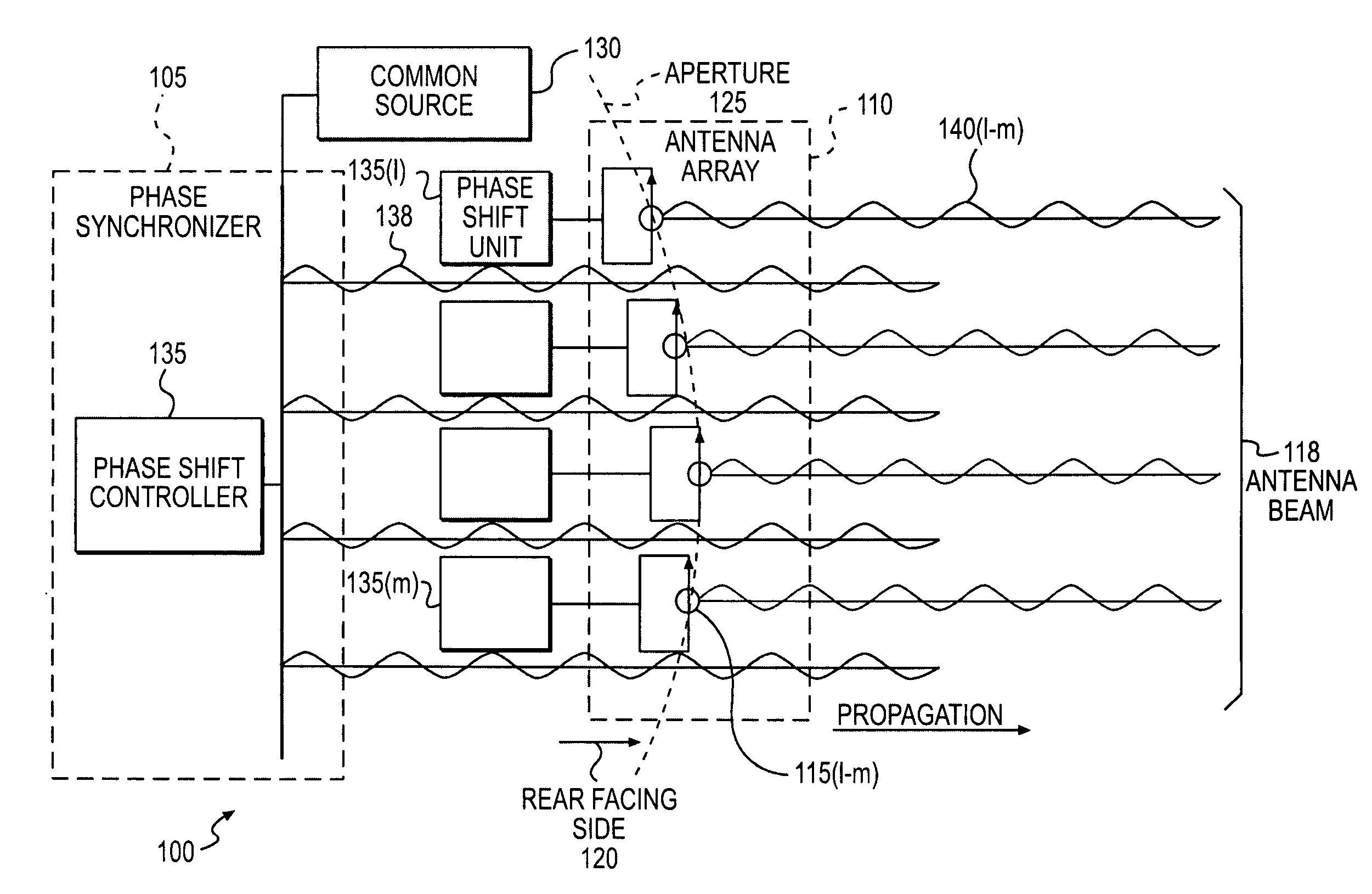
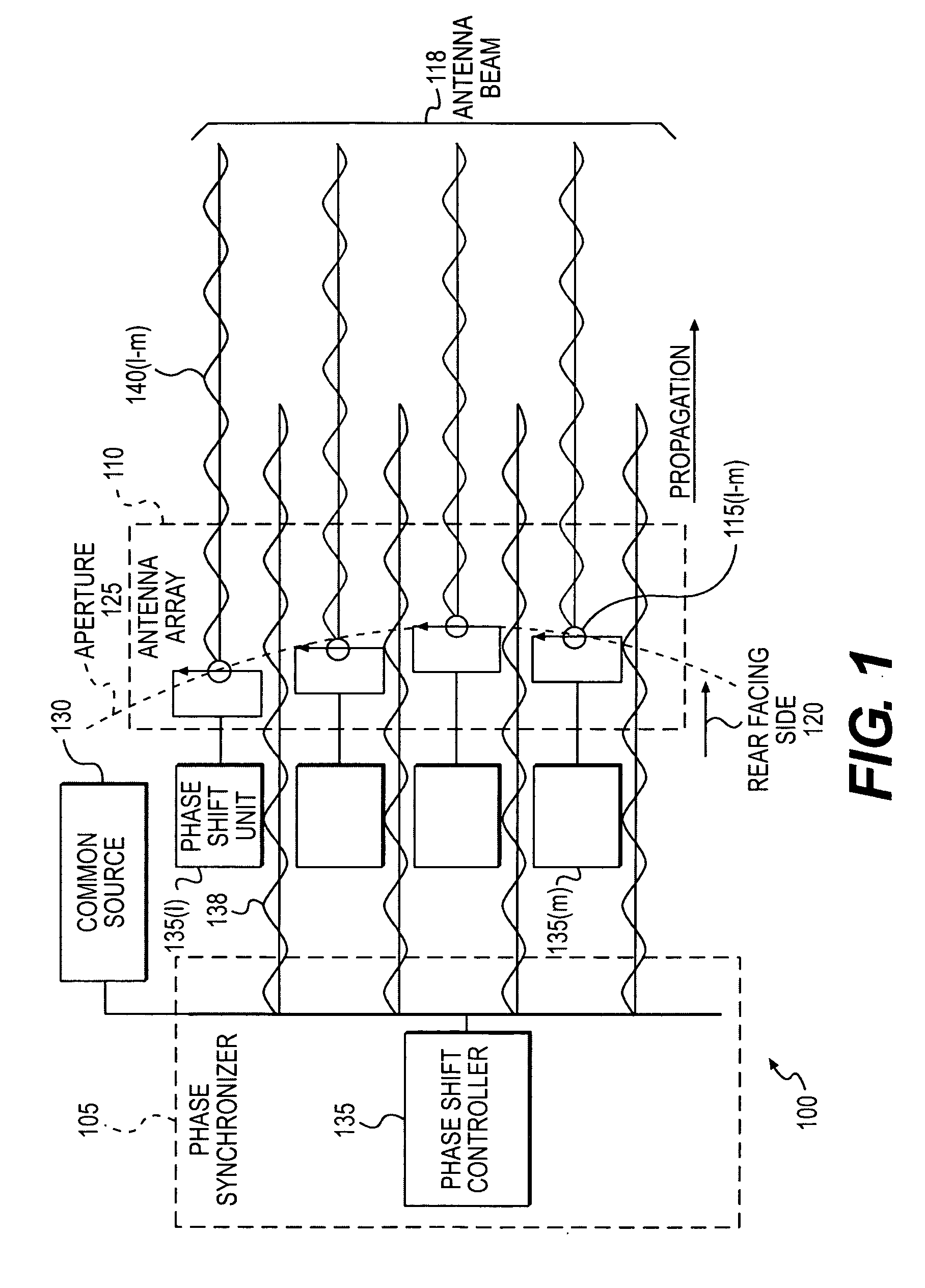
Forming an antenna beam using an array of antennas to provide a wireless communication
The present invention provides a method and an apparatus for forming an antenna beam from an array antenna having a rear facing side, an aperture, and including a first and a second radiating element. The method comprises injecting a synchronization signal wirelessly from a common source at the rear facing side of the array antenna to provide an initial calibration of the array antenna that synchronizes phase of an output signal from the first and second radiating elements to the common source. The method further comprises compensating a change in phase of the synchronization signal at the first radiating element based on a spatial displacement to synchronize phase of a first portion of the output signal from the first radiating element to the phase of the synchronization signal at the second radiating element in response to the spatial displacement of the first radiating element after the initial calibration of the antenna array. A synchronization source may couple to the phased array antenna wirelessly, such as optically or using radio frequency based coupling. To synchronize a portion of an output signal from a plurality of radiating elements, a phase shift unit and / or a time delay unit at each radiating element may lock its phase to a synchronization signal from a common or a point source regardless of a location thereof relative to the synchronization source. In this way, a synchronization source may synchronize the phase of the phased array antenna even if one or more radiating elements may move from an original spatial location to any arbitrary position.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
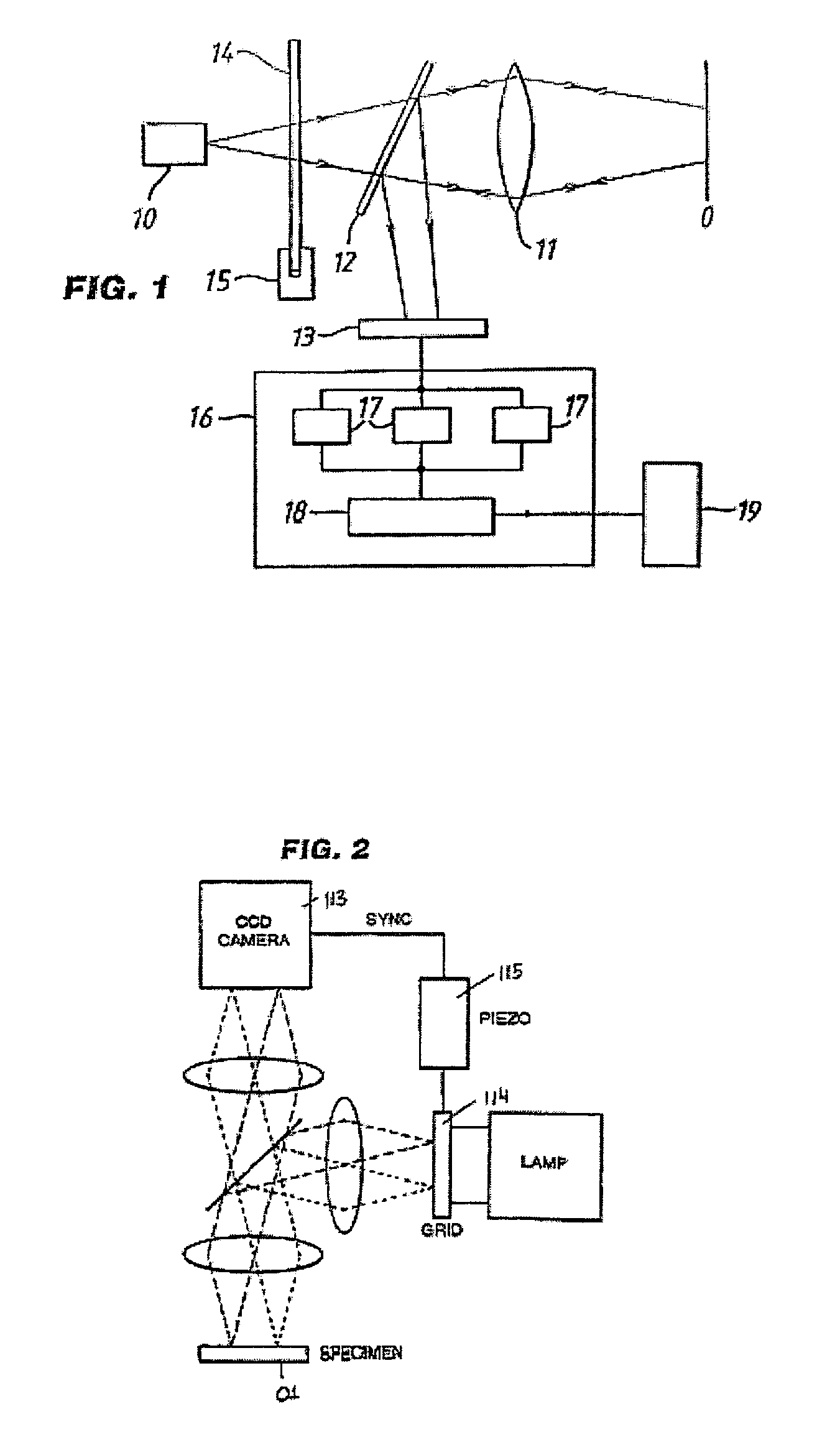
Methods, systems and computer program products for calibration of microscopy imaging devices
An imaging system on which a calibration method is practiced includes: a light source; a substrate for supporting an object; a patterning mask that generates a substantially periodic spatial pattern on the object; a phase shifter that adjusts the relative position of the patterning mask and object to shift the position of the pattern on the object; a detector that detects images of the object; and an analyzer that analyzes at least three images of the object, each of which represents a different spatial shift of the pattern, the analyzer being configured to remove the spatial pattern from the images to generate an optically sectioned image of the object. The calibration method includes: calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a phase-voltage technique; calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a merit function technique; and operating the calibrated imaging system.
Owner:THALES SA
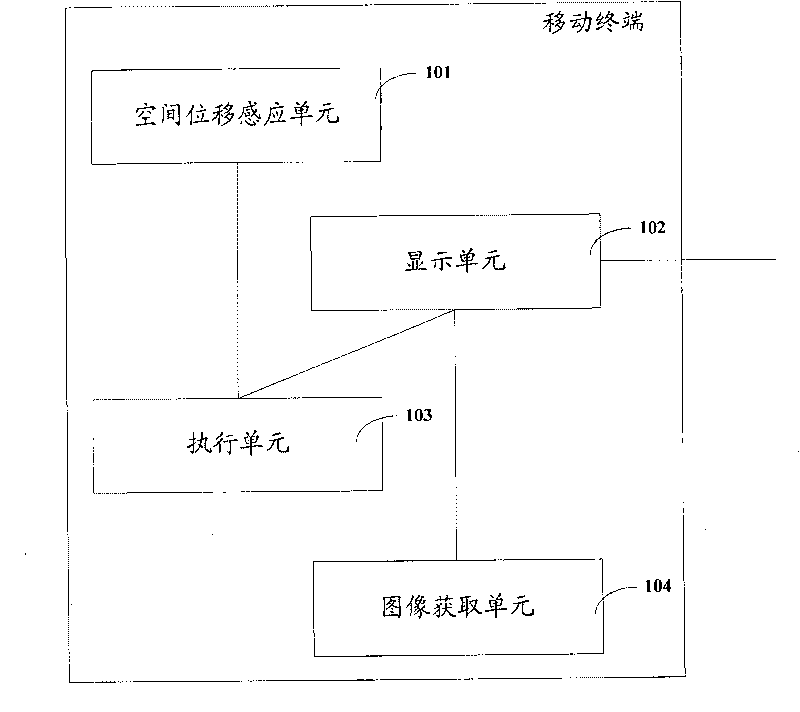
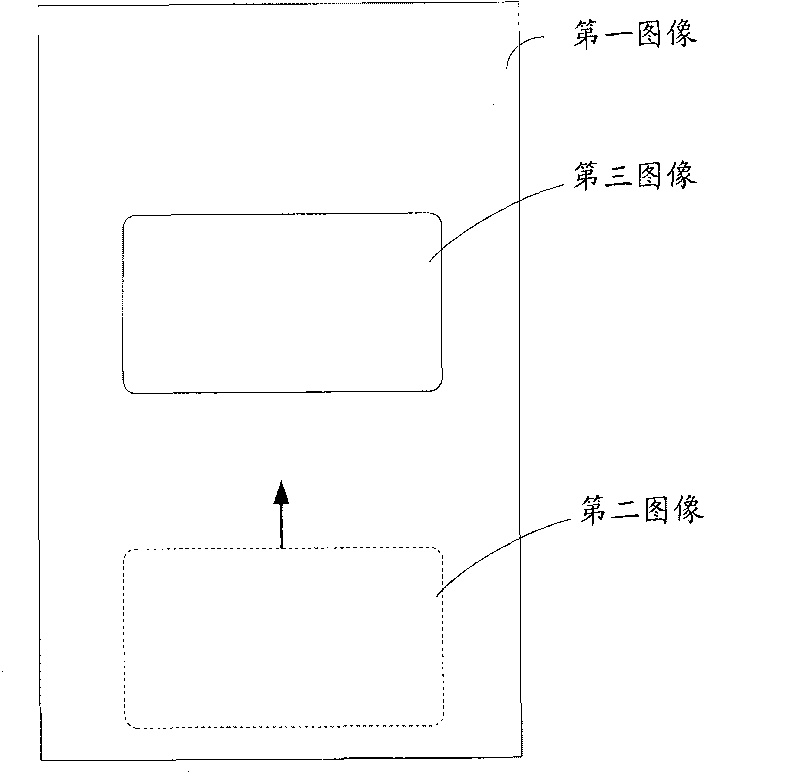
Mobile terminal and method for displaying images
InactiveCN101739199AEasy to browseInput/output processes for data processingComputer graphics (images)Execution unit
The invention provides a mobile terminal and a method for displaying images, wherein the mobile terminal stores a first image, the display area of the first image is larger than the area of a display region, and the mobile terminal comprises a spatial displacement sensing unit, an actuating unit, an image acquisition unit and a display unit, wherein the spatial displacement sensing unit is used for obtaining spatial position adjustment parameters; the actuating unit is used for obtaining image translation parameters correspondingly according to the spatial position adjustment parameters; the image acquisition unit is used for acquiring a second image, the second image is the part for constituting the first image, the area of the second image is equal to the area of the display region, and a third image is obtained according to the image translation parameters and the relative position between the translation display region and the first image; and the display unit is used for displaying the second image and displaying the third image. The embodiment of the invention has the following benefits: a user can conveniently and rapidly browse information of the image out of the display region without a touch screen and buttons.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
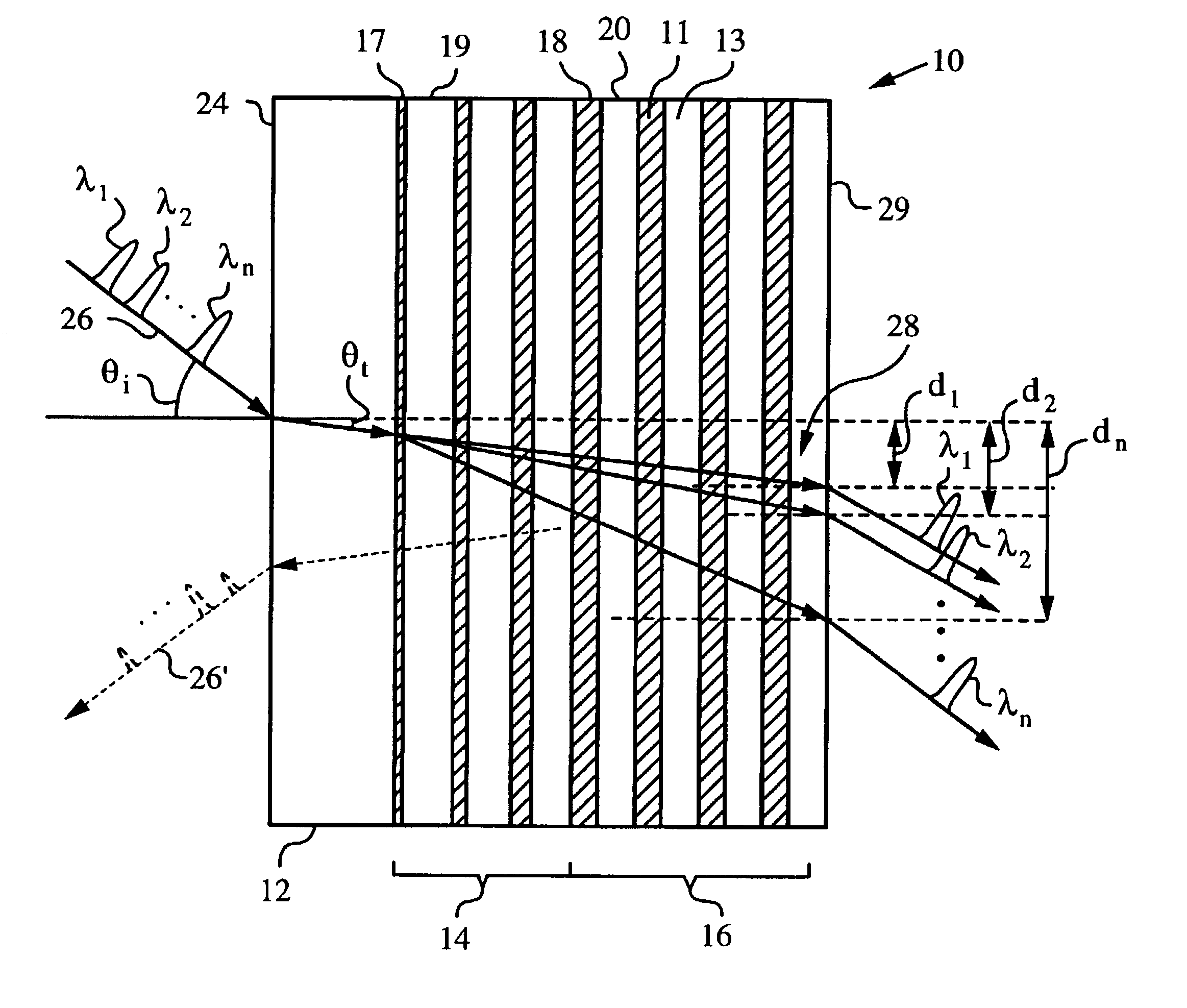
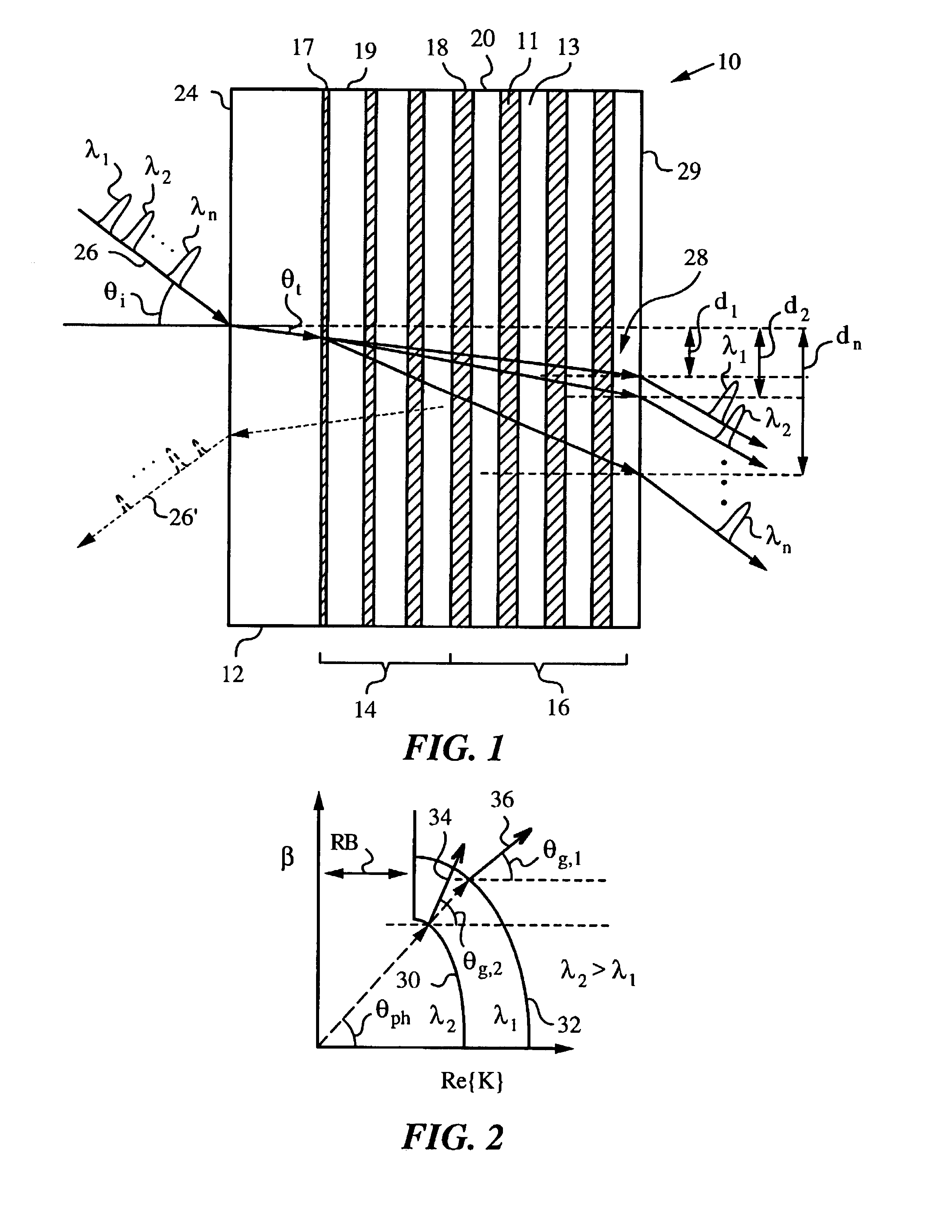
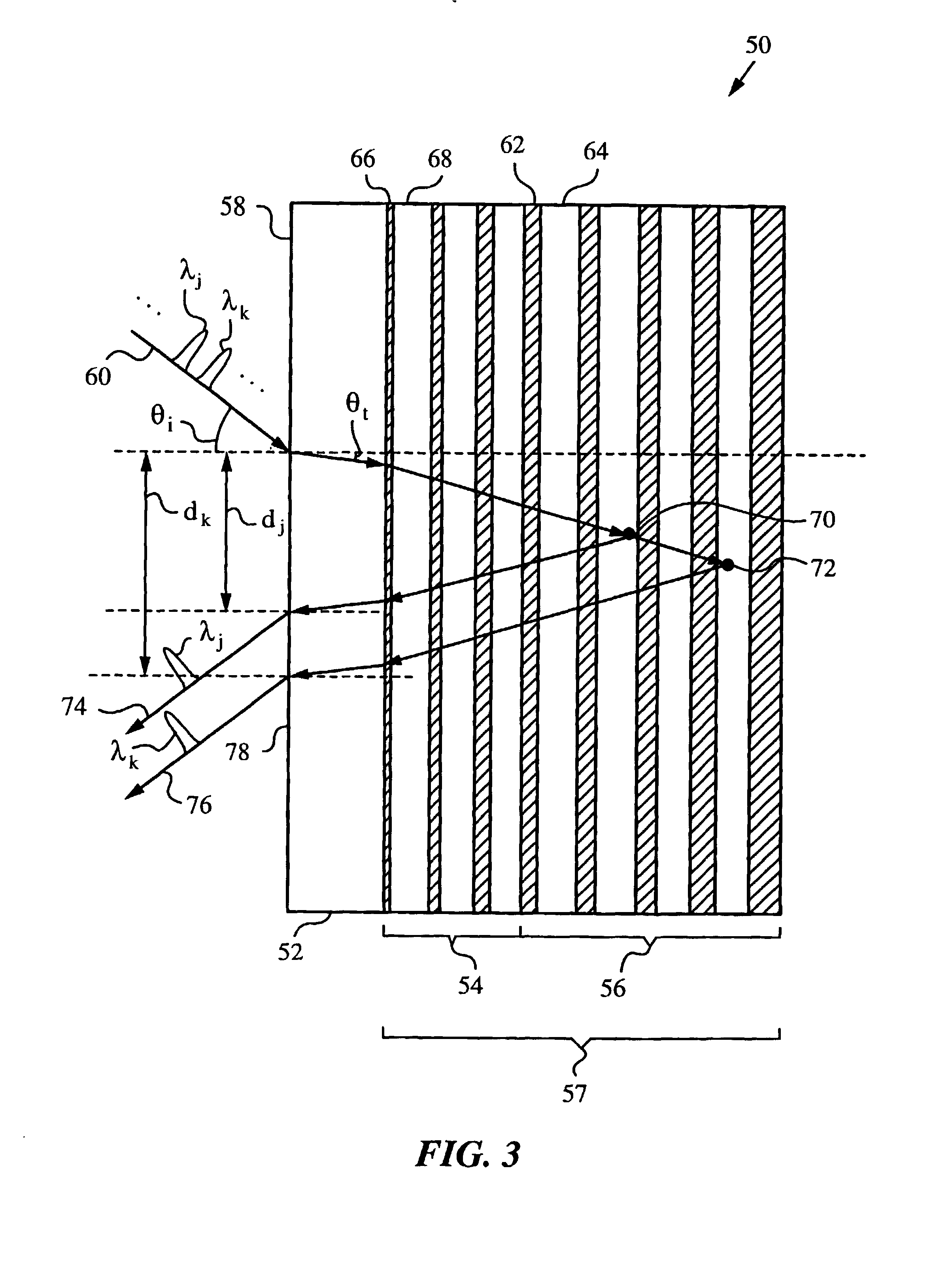
Apparatus and method employing multilayer thin-film stacks for spatially shifting light
InactiveUS7088884B2Improve spatial resolutionEasy to makeCoupling light guidesOptical propertyCoupling
An apparatus and method for spatially shifting a light using a multilayer thin-film stack of at least two materials having unequal optical properties, such as indices of refraction and absorption coefficients. The apparatus has an input face for admitting the light into the apparatus and an impedance matching mechanism for maximizing the in-coupling of the light into the multilayer thin-film stack at a non-normal incidence. The non-normal incidence is sufficient to generate a spatial shift of the light in the multilayer thin-film stack as a function of at least one light parameter, such as wavelength and / or polarization of the light, thereby separating the light into light components. The spatial shift is achieved by any one or any combination of effects including superprism, turning point and energy confinement. These effects are achieved in the multilayer thin-film stack by appropriately engineering its layer sequence.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
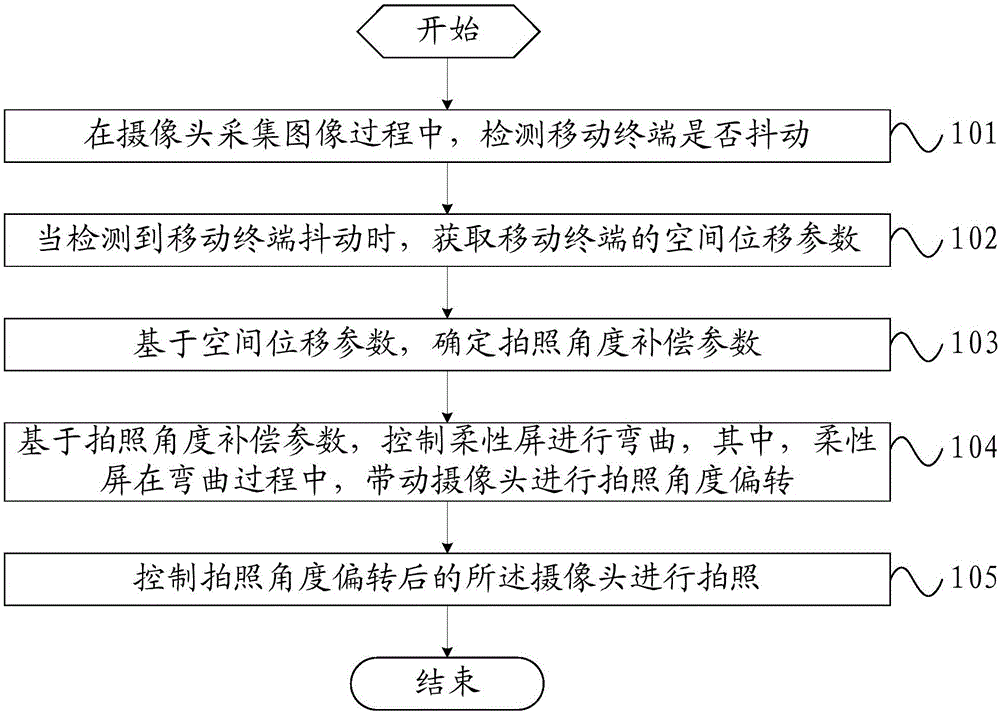
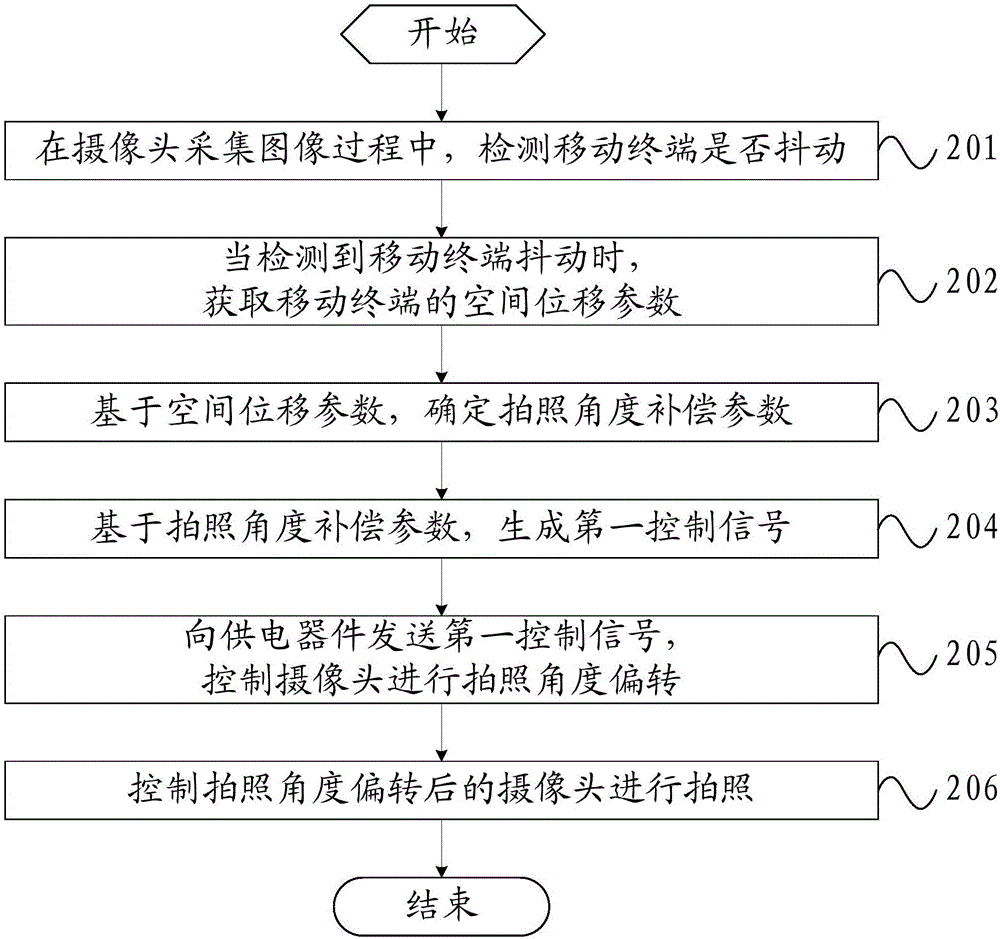
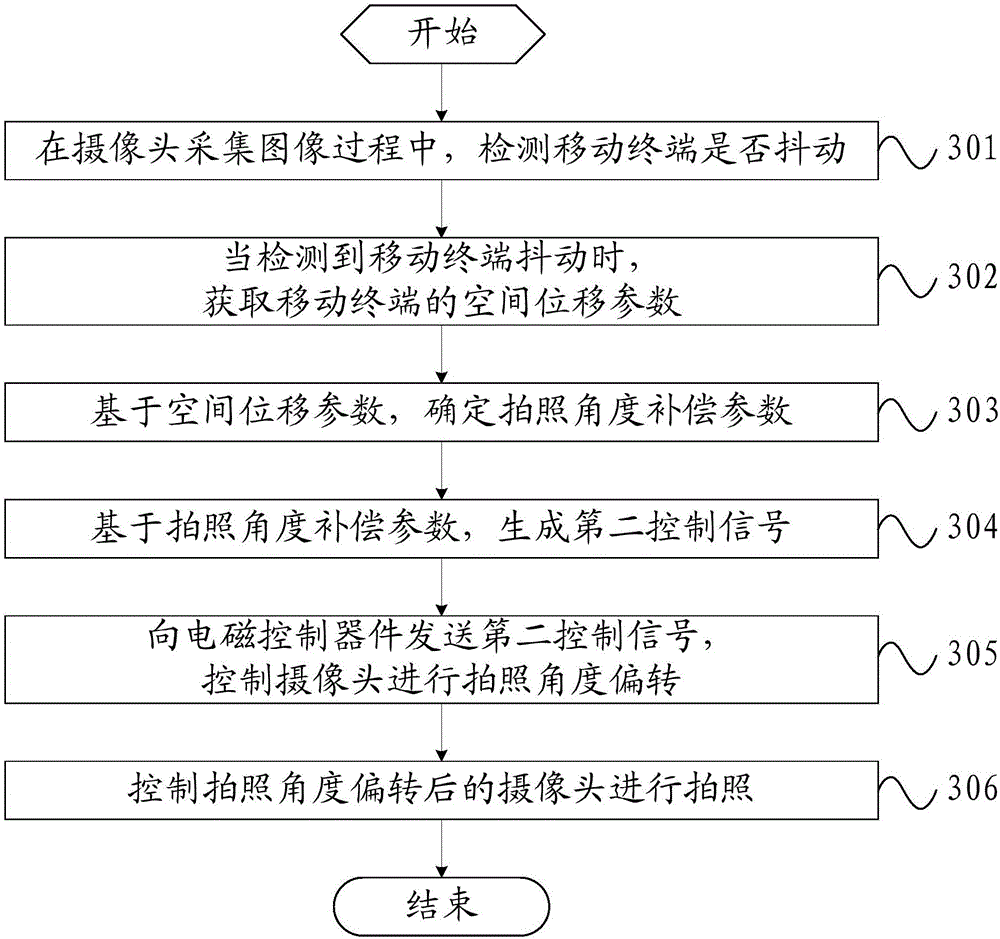
Photographing method and mobile terminal
ActiveCN106791450AMake up for the impact of photo qualityGuaranteed photo effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer graphics (images)Computer terminal
The invention provides a photographing method and a mobile terminal. whether the mobile terminal shakes or not is detected when a camera acquires an image; when the mobile terminal is detected to shake, a spatial displacement parameter of the mobile terminal is acquired; a photographing angle compensation parameter is determined on the basis of the spatial displacement parameter; a flexible screen is controlled to bend on the basis of the photographing angle compensation parameter, wherein the flexible screen drives the camera to deflect a photographing angle in the bending process; the camera with the photographing angle deflected is controlled to photograph. Thus, the effect of shaking of the mobile terminal on the photographing quality can be reduced, the photographing effect can be guaranteed, and the photographing method has the characteristics of low cost and high response speed.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
Fan speed-increasing gearbox test bed capable of achieving pose controlling and spindle loading
InactiveCN103323234AImprove carrying capacityGood sports characteristicsMachine gearing/transmission testingElectricityContact type
The invention belongs to the technical field of the dynamic property and the reliability of a speed-increasing gearbox transmission system of wind power equipment, and particularly relates to a fan speed-increasing gearbox test bed capable of achieving pose controlling and spindle loading. The test bed comprises a pose simulation platform and a spindle loading simulation platform. According to the pose simulation platform, six post loading driving devices simulate the spatial displacement variations of six degrees of freedom of the test bed in an actual wind load. According to the spindle loading simulation platform, six magnetic field loading devices simulate alternating bending loads and axial thrust loads, and the alternating bending loads and the axial thrust loads are borne by a spindle in an actual wind load. A parallel mechanism basic structure is used, the position and the pose of the six degrees of freedom of the wind power speed-increasing gearbox can be simulated under the action of the wind loads, the non-contact type spindle is used for achieving electromagnetic loading, and the axial thrust loads and the alternating bending loads borne by the spindle in an actual working condition can be truly simulated.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Plane wheel space displacement measuring system of landing gear lowering shock test
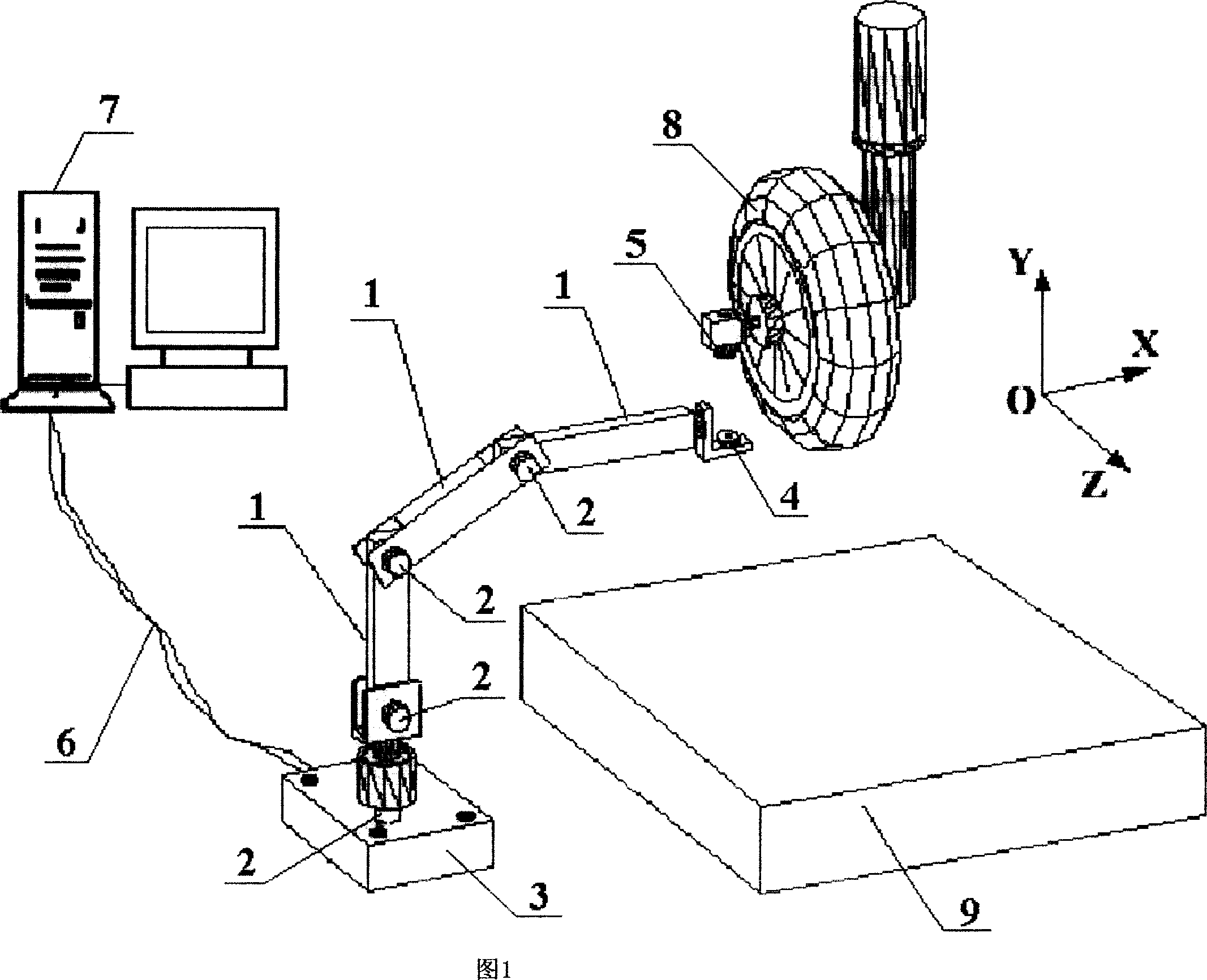
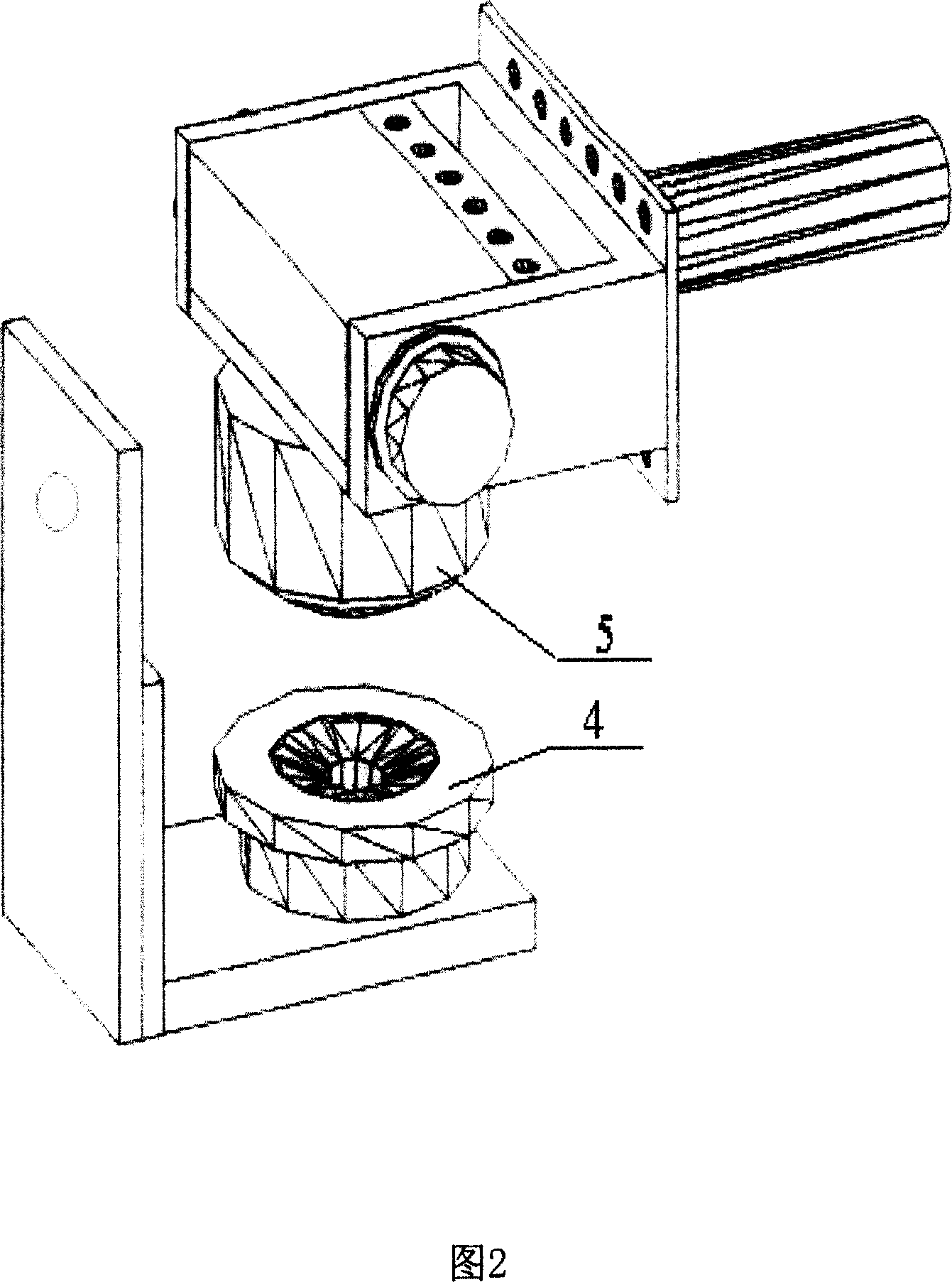
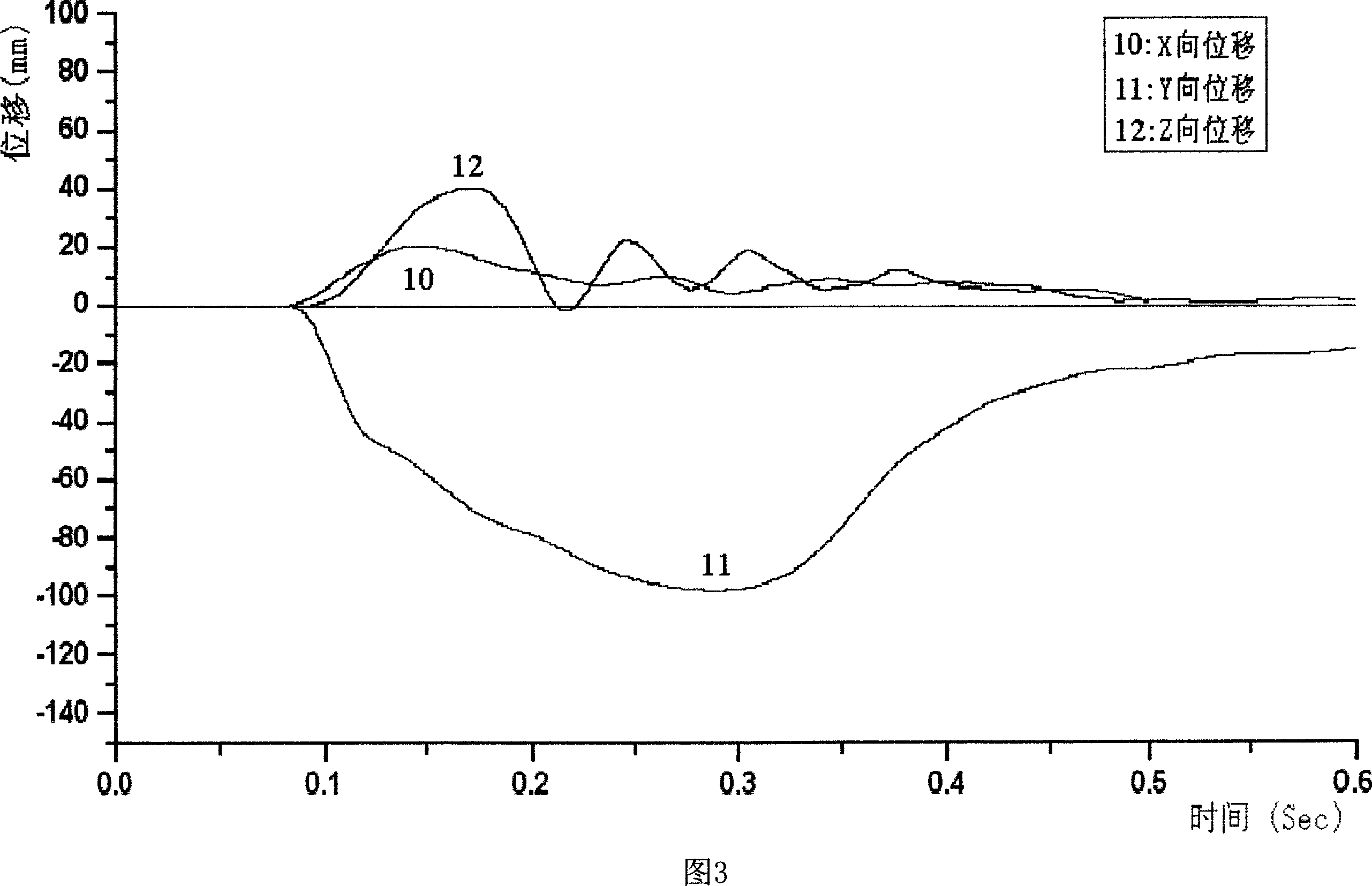
InactiveCN101000238ADoes not damage the structureIndestructible strengthMeasurement devicesJet aeroplaneTransducer
The invention relates to undercarriage shock test airplane wheel space displacement measuring system. It is made up of three space locating machine arms, four corner transducers, support, two magnetic attracting components, and computer. The three space locating machine arms are connected with each other by connecting fitting on which three corner transducers are set. The forth one is set on the support. Each of them is connected with the computer by lead. One magnetic attracting component is connected with the free end of the third space locating machine arm. Another one is fixed on the principal axis of the airplane wheel. While measuring three directions displacement, the invention can ensure expensive undercarriage run normally after shock test without drilling to set displacement transducer and destroying its structure and strength.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
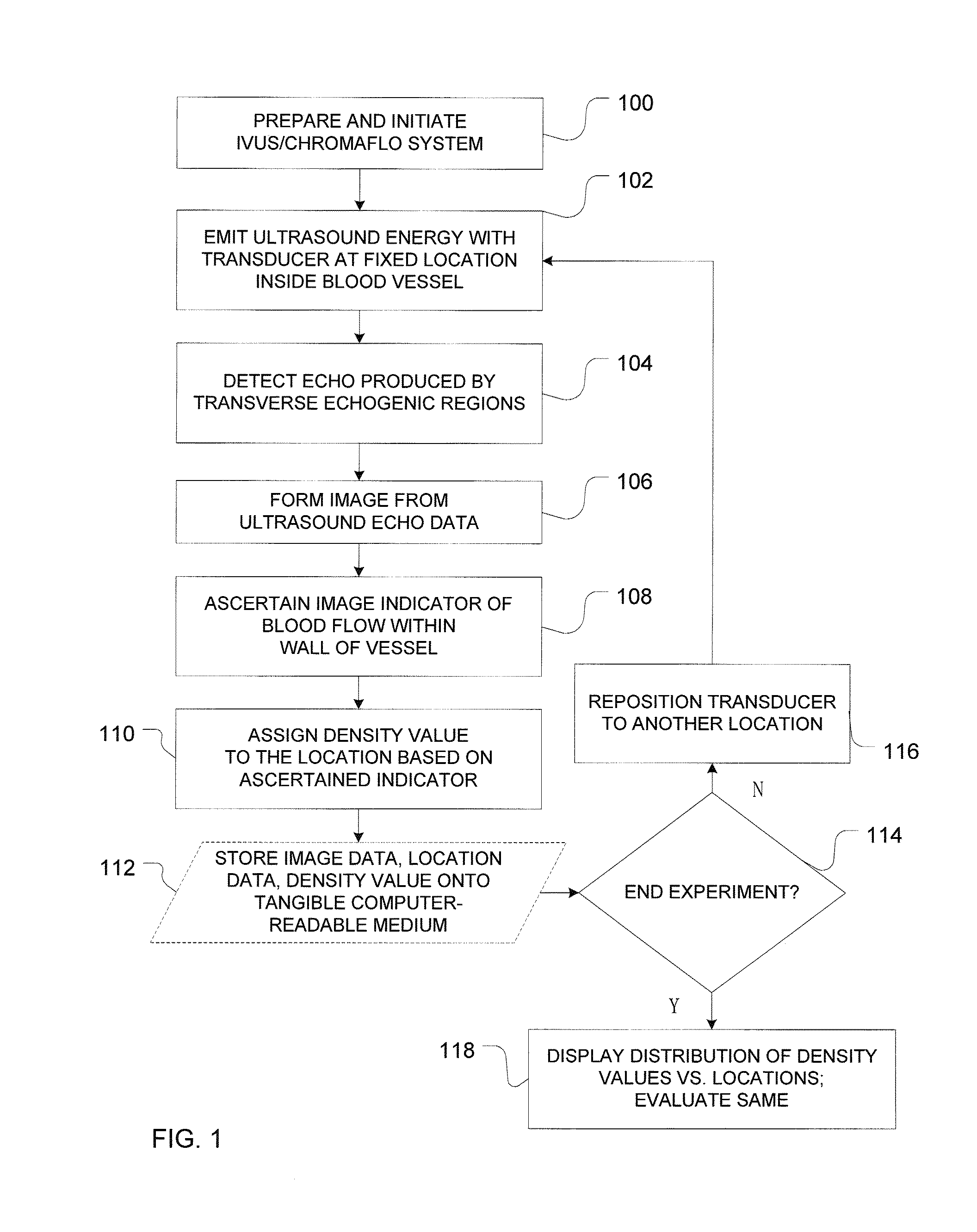
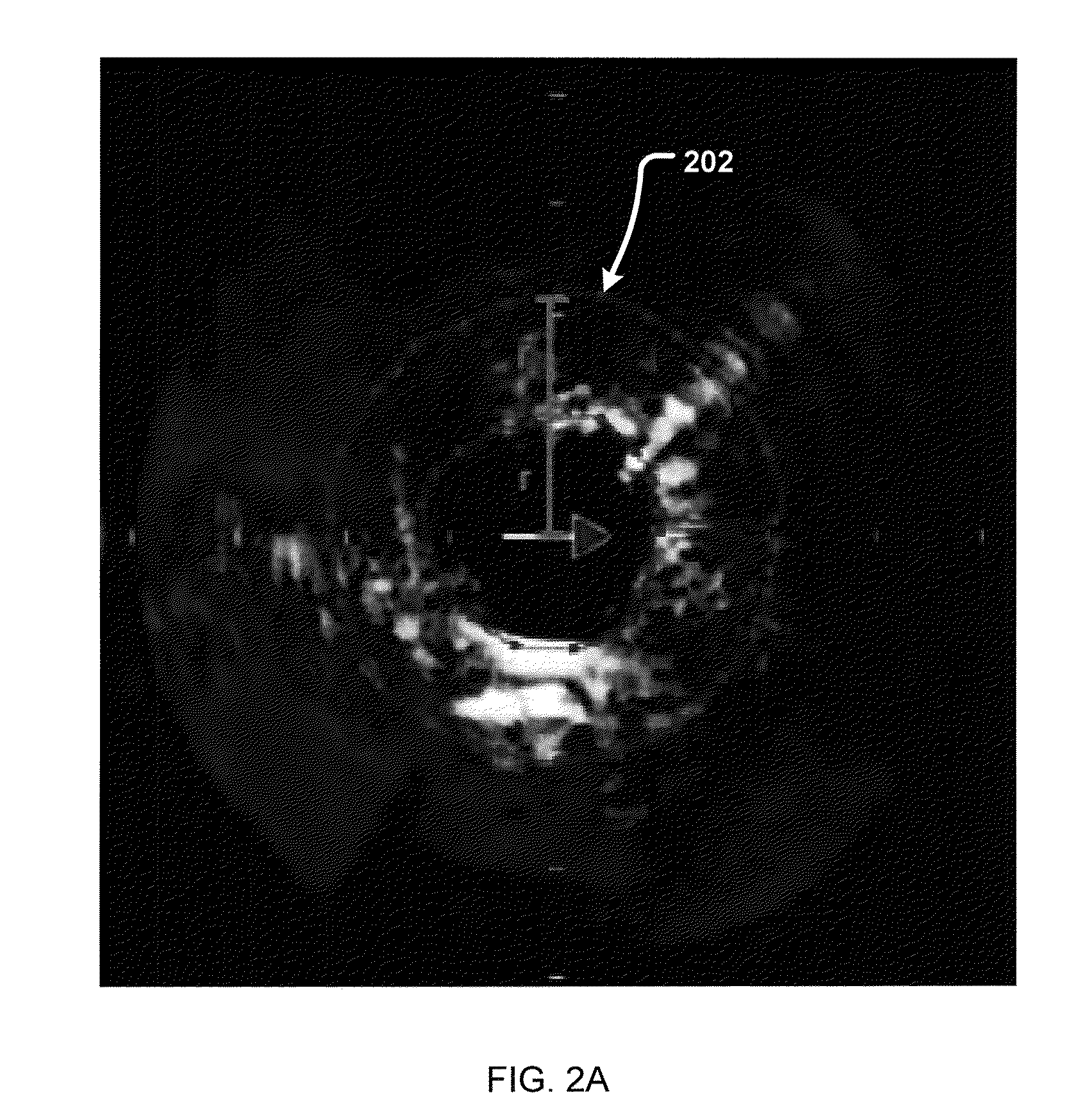
Intravascular ultrasound detection of blood-flow distribution in an arterial wall
A system and method for quantitative determination of density of vasa vasorum in an arterial wall that utilizes a detection of temporal and / or spatial displacement of blood-flow with the use of intravascular ultrasound system. Locations of extrema in the spatial distribution can be identified to detect vascular defects. The system and method support a clinically-useful application for early detection of indicators of diseases, such as coronary atherosclerosis.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
High temperature probe
ActiveUS20160169749A1Avoid displacementThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThermocoupleSpatial Displacement
High temperature probes and methods for assembling high temperature probes are disclosed. The high temperature probes may include a rod with a thermocouple embedded within the rod, and a ceramic matrix composite sheath substantially surrounding the rod. The high temperature probes may also include an outer metal tube surrounding a portion of the rod, and an inner metal tube positioned between the alumina rod and the outer metal tube, the inner metal tube being configured to prevent the rod from spatial displacement with respect to the outer metal tube.
Owner:AMETEK INC
Method for measuring end face spatial displacement and angular variation of shafting engineering member on the basis of stay-supported displacement sensors
ActiveCN105258662AReduce cost of measurementEasy to use and flexibleMeasurement devicesRelative displacementMeasurement cost
The invention discloses a method for measuring the end face spatial displacement and the angular variation of a shafting engineering member on the basis of stay-supported displacement sensors. The method comprises a step 1 of installing a stay-supported displacement sensor A, a stay-supported displacement sensor B, and a stay-supported displacement sensor C on three points with measurable distance, wherein the three points are arbitrarily selected from both end faces of a measurable shafting, and installing a stay-supported displacement sensor D, a stay-supported displacement sensor E, and a stay-supported displacement sensor F on three points with measurable relative distance, wherein the three points are selected from the end faces of the measurable shafting; a step 2 of measuring three displacement values on the measurable end faces and measuring nine measurable relative displacement values on the two end faces; a step 3 of after displacement generates, repeating the step 2 and computing spatial displacement and angular variation. The method may measure the end face spatial displacement and the angular variation of the shafting engineering member as required, is low in measurement cost, flexible and convenient to use, and good in applicability.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Planar two-dimensional time grating displacement sensor
The invention provides a planar two-dimensional time grating displacement sensor. The planar two-dimensional time grating displacement sensor is composed of fixed array planes and a movable array plane, wherein the fixed array planes are arranged relatively in parallel in an up-down mode. Each fixed array plane is composed of a fixed array plane base body and exciting coils arranged on the surface of the fixed array plane base body. The movable array plane is composed of a movable array plane base body and induction coils arranged on the surface of the movable array plane base body. The single movable array plane is adopted to obtain magnetic signals at different positions of the fixed array planes according to the electromagnetic induction principle, and the magnetic signals (space information) are converted into electric signals (time information) and then processed according to the space-time coordinate transformation theory, so that the planar two-dimensional space displacement is obtained. Two linear displacement sensors do not need to be installed perpendicularly, a binary optical device prepared in a complex process is not needed, a complex optical path design is not needed, the fixed array planes and the movable array plane are prepared in a common semiconductor machining process, and consequently the planar two-dimensional time grating displacement sensor has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in cost, resistant to oil fouling and dust and high in impact vibration capacity.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Method for grouping 3D models to classify constitution
ActiveUS20110116707A1Reduce riskSimple compositionCharacter and pattern recognition3D modellingClassification methodsColor table
Provided is a three-dimensional model classification method of classifying constitutions. The method includes correcting color values of a frontal image and one or more profile images to allow a color value of a reference color table in the images to equal a predetermined reference color value, through obtaining the frontal image and one or more profile images of a subject including the reference color table by a camera, the reference color table including one or more sub color regions, generating a three-dimensional geometric model of the subject by extracting feature point information from the frontal image and the profile image, matching the corresponding feature point information to extract spatial depth information, after removing the reference color table region from the frontal image and the profile image, and classifying a group of the three-dimensional geometric model of the subject by selecting a reference three-dimensional geometric model having a smallest sum of spatial displacements from the three-dimensional geometric model of the subject from a plurality of reference three-dimensional geometric models stored in the database and setting the group which the selected reference three-dimensional geometric model represents as the group where the three-dimensional geometric model of the subject belongs.
Owner:KOREA INST OF ORIENTAL MEDICINE
Scanning data correction method and system of two-dimensional scanning type laser radar
ActiveCN105572679AImprove reliabilityHigh precisionElectromagnetic wave reradiationCurrent velocityRadar
The invention discloses a scanning data correction method and system of a two-dimensional scanning type laser radar. According to the method, the current angle of an i-th laser beam relative to a scanning environment is obtained based on scanning parameters of the laser radar and the distance information of the i-th laser beam in a scanning period; the current speed and current distance of the laser radar are obtained based on a sensor, so that the correction value and real scanning value of the i-th laser beam of the laser radar can be calculated. The attitude of the laser radar in movement is obtained in real time, error calculation and compensation are performed on environmental data in a laser radar scanning period, and therefore, the error correction of scanning data of the two-dimensional scanning type laser radar can be realized, and the accuracy of environment detection and the reliability of the navigation of a robot can be improved when the robot moves relative to the environment. With the method and system adopted, errors caused by spatial displacement which is accumulated in time difference in a detection period can be eliminated. The method and system are of great significance for solving the problem of data scanning errors on the laser radar in a motion state.
Owner:重庆大学溧阳智慧城市研究院
Nonmechanical wavelength-independent beam steerer
Methods and devices are provided for steering an electromagnetic beam. The device includes a reflective element, a polarizer, a relay focusing element, and a modulation element. The polarizer is configured to transmit light of a specified polarization and to reflect light having other than the specified polarization. The relay focusing element is disposed to provide optical paths for the electromagnetic beam from a first spot position to a second spot position spatially displaced from the first spot position such that the optical paths encounter the reflective element and the polarizer. The modulation element is configured for selectively transforming a polarization of the electromagnetic beam to include a component of the specified polarization at a spatially localized position along the optical paths.
Owner:BOULDER NONLINEAR SYST
A fringe illumination Fourier domain iteration updating super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on total internal reflection
ActiveCN109712072AReduce background levelIncrease contrastGeometric image transformationMicroscopesSignal onFluorescence
The invention discloses a fringe illumination Fourier domain iteration updating super-resolution microscopic imaging method based on total internal reflection. The method comprises the following steps: splitting a parallel illumination laser beam into two parallel beams with equal intensity and consistent polarization direction, and exciting two oppositely propagated evanescent waves to interfereso as to generate a fine evanescent wave fringe illumination fluorescent sample; receiving a fluorescence signal on the imaging image surface by using a detector to obtain a low-resolution image mixedwith high-frequency and low-frequency information of the fluorescence sample; changing the spatial displacement and direction of the evanescent wave illumination fringes for multiple times, and shooting the fluorescence signal modulated by the fringe intensity again to obtain a series of low-resolution images mixed with high-frequency and low-frequency information of the fluorescence sample as original images; and finally, carrying out Fourier domain iteration updating processing on the original image, and carrying out continuous iteration to finally reconstruct a super-resolution image of the fluorescent sample. According to the method, the transverse resolution of about 100 nm can be achieved, the background level can be reduced, the contrast ratio can be improved, the unknown aberration of the system can be corrected, and in-vivo imaging can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
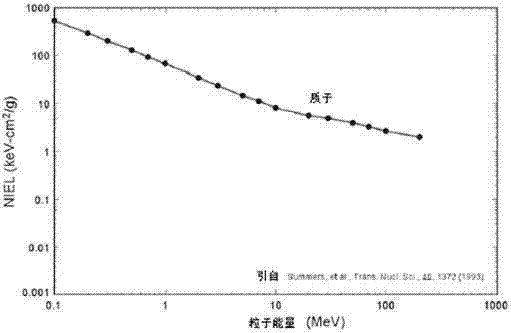
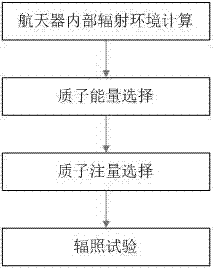
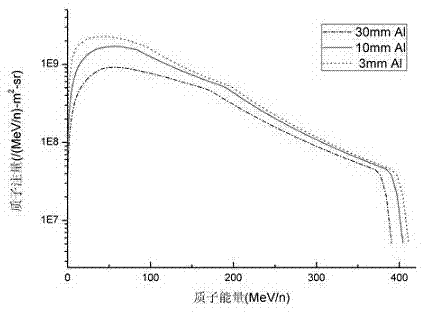
Method for carrying out spatial displacement damage effect evaluation test through high energy protons
InactiveCN104297585AFacilitate engineering developmentThe assessment results are accurateElectrical testingHigh energyPeak value
The invention relates to a method for carrying out a spatial displacement damage effect evaluation test through high energy protons. The method includes the following steps that firstly, internal radiation environment of a spacecraft is calculated, space environment effect calculation software is used, track parameter values of the earth track spacecraft, a space radiation environment model, the shielding thickness of the spacecraft are input, and the internal proton differential energy spectrum of the spacecraft is calculated; secondly, the protons are selected, the worked-out internal proton differential energy spectrum of the spacecraft in the track has a proton fluence peak value as the protons are not evenly distributed along with energy, and the energy proton corresponding to the fluence peak value is selected as the proton for the evaluation test; thirdly, the proton fluence phi(EI) for the test is calculated; fourthly, the radiation test is carried out, and the energy protons determined through calculation are used for radiating an element to the specified fluence. After radiation, the electricity test is carried out according to product standards and requirements.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Multiplatform GMTI radar with enhanced SNR, monopulse
ActiveUS9285469B1Increase electrical sizeReduces MDVRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarClassical mechanics
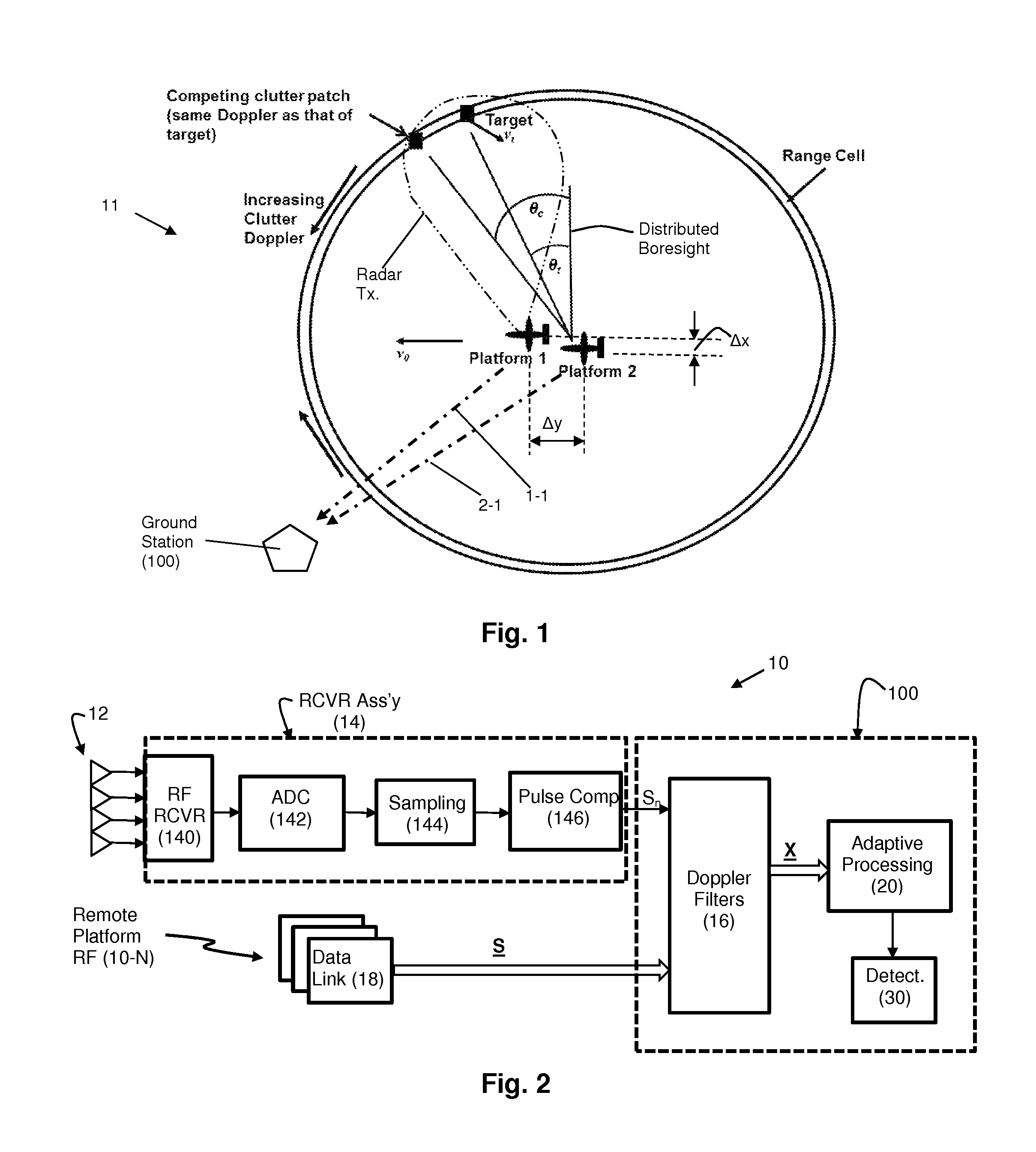
The present invention is directed to a ground moving target (GMTI) radar that can detect targets, including dismounts, with very small minimum detectable velocities by combining signals from antennas on different spatially separated platforms in a main beam clutter-suppressing spatially adaptive process without requiring that the relative positions of the antenna phase centers be accurately tracked. The clutter nulling is in addition to that provided by the Doppler filters. The spatial displacement provides a narrow mainbeam clutter null reducing undesired target suppression. The clutter-suppressing spatially adaptive structure is used in both the sum and delta channels of the monopulse processor so that the beam distortion caused by the spatial nulling is compensated for, and the monopulse look-up process is preserved to maintain angle accuracy. Noncoherent integration is employed to recover signal to noise loss resulting from the uncertain relative locations of the platforms.
Owner:SRC INC
Algorithm for calculating initial rigidity and plastic failure strength of variable-section metal lattice structure
ActiveCN108038318AAccurate section changeCalculate initial stiffnessDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsTangential forceMetal lattice
The invention discloses an algorithm for calculating the initial rigidity and plastic failure strength of a variable-section metal lattice structure. The algorithm includes the steps of s1, building aplane-coordinate system, and using the plane-coordinate system and the section size of a BCC variable-section metal lattice unit cell rod to obtain the radius expression of the section of the BCC variable-section metal lattice unit cell rod; s2, building a space coordinates system, and using the space coordinates system, the Hooke's law and a bending and compression combined deformation formula to obtain the relational expression of spatial tangential force, bending moment and spatial displacement borne by the node of the unit cell rod; s3, using the energy conservation law and the relationalexpression of spatial tangential force, bending moment and spatial displacement to obtain a quadratic equation in one unknown related to the tangential force of the node of the unit cell rod, solvingthe quadratic equation in one unknown to obtain a tangential force expression which does not contain the spatial displacement of the node, and using the tangential force expression and the relation between the tangential force at the node and axial force and the bending moment to obtain the expression of the axial force and the bending moment; s4, using the Hooke's law and the expression of the tangential force, the bending moment and the axial force to obtain the initial rigidity and plastic failure strength of the BCC variable-section metal lattice structure.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
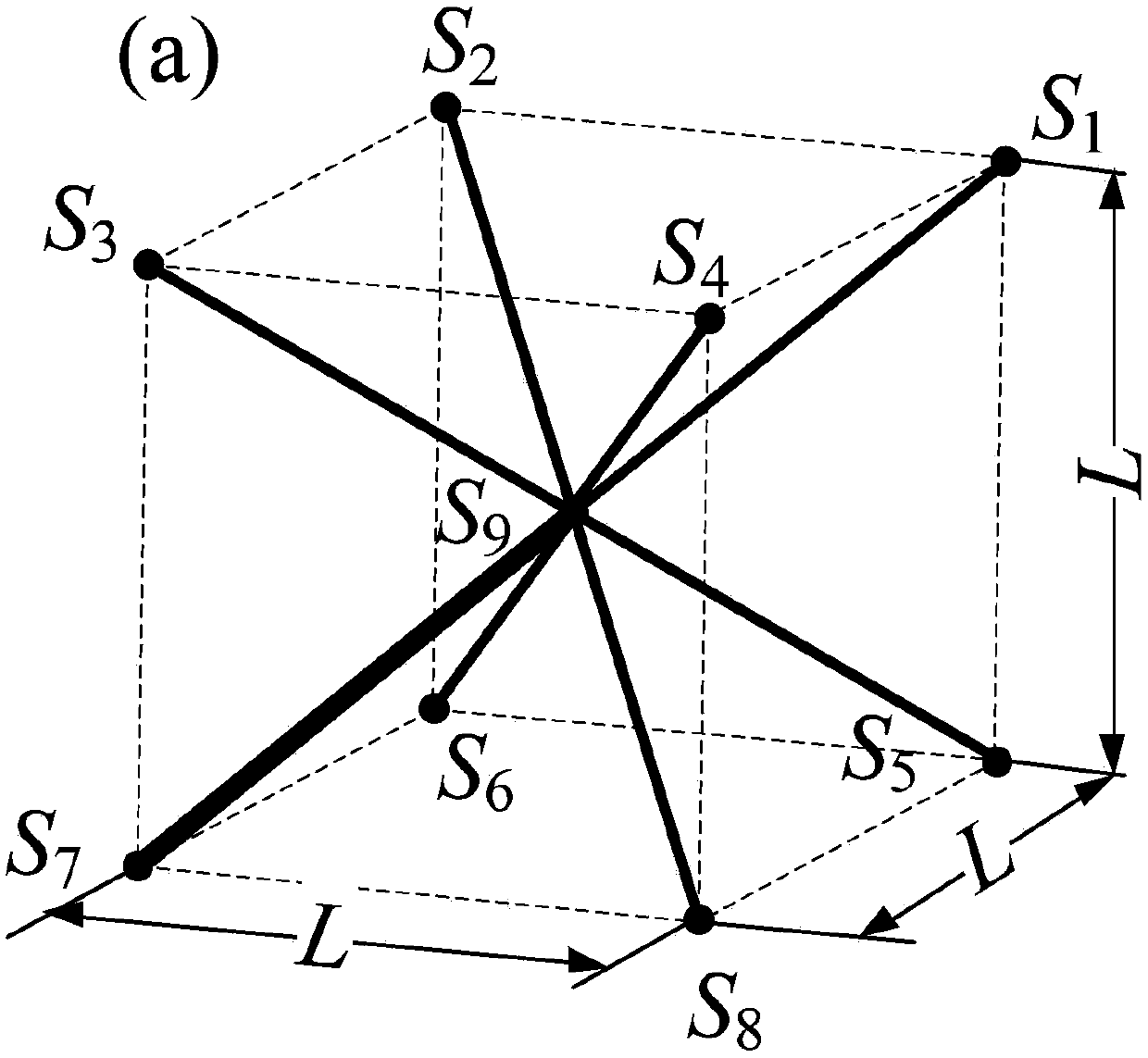
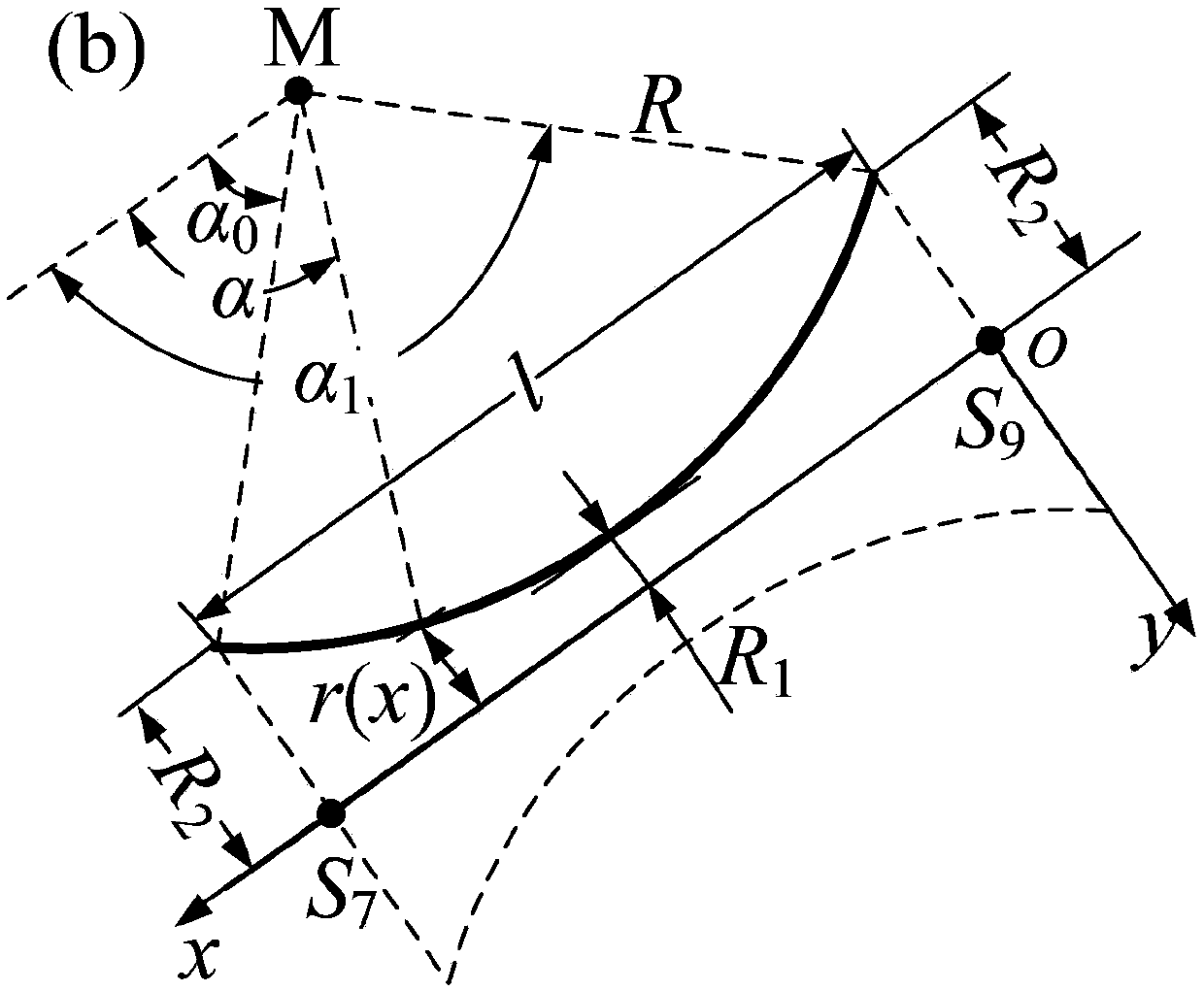
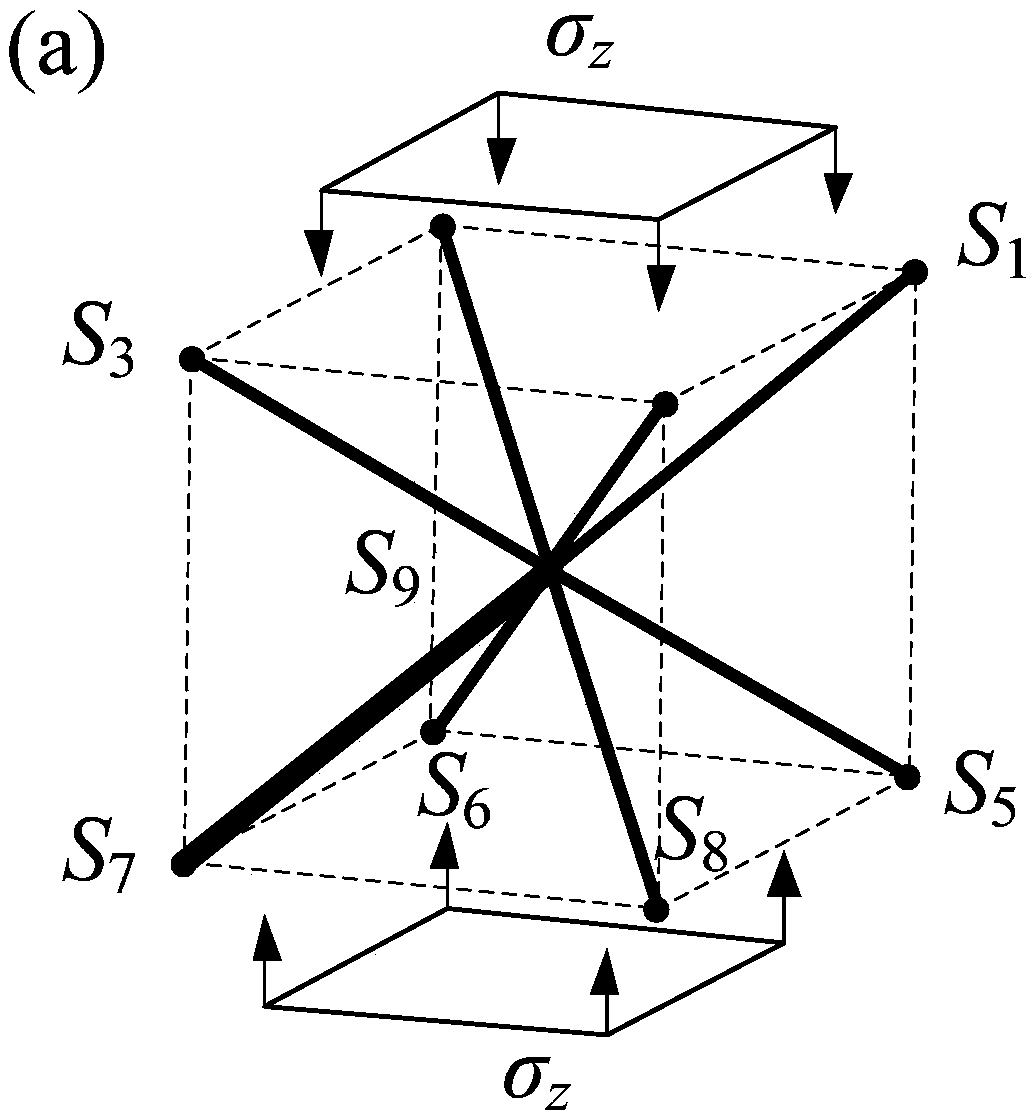
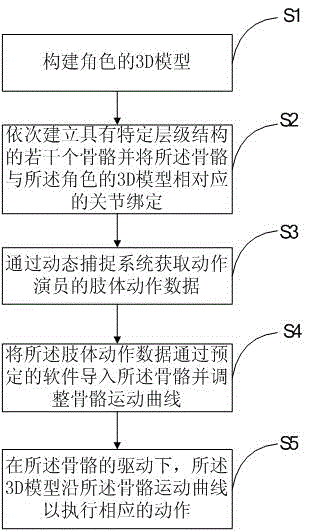
Processing method for dynamically capturing 3D data and 3D model thereof
The invention discloses a processing method for dynamically capturing 3D data and a 3D model thereof. The method comprises the following steps: creating a 3D model of a role; sequentially establishing multiple bones with specific hierarchical structures, and binding the bones with corresponding joints of the 3D model of the role; obtaining body movement data of a motionactor through a dynamic capturing system; introducing the body movement data into the bones through preset software and adjusting a bone movement curve; under the drive of the bones, the 3D model executes corresponding actions along the bone movement curve; and the step of adjusting the bone movement curve specifically comprises: introducing spatial displacement data in the body movement data into displacement bones extending out from the hip bones. The method is used for effectively reducing the errors of action displacement to make the animation of the 3D model be more real and reduce the subsequent displacement modification of an animator, so as to improve the animation making quality and speed of the 3D model.
Owner:SHENZHEN OCT VISION
Time-domain aeroelectromagnetic method receiving coil attitude change suppression device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN108562942ALimited spatial locationImpact of detection resultsElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationTime domainCompensation effect
The invention relates to a time-domain aeroelectromagnetic method receiving coil attitude change suppression device and a manufacturing method thereof. The time-domain aeroelectromagnetic method receiving coil attitude change suppression device is characterized in that connection points are uniformly arranged in a fixed bracket in circumferential manner; the center point of the circular inner surface of the top layer is provided with a receiving coil bearing connection point; a receiving coil is wound in the axial direction of the receiving coil in a differential structure; fixed connection points are uniformly arranged on the outer surface; the center point of the circular outer surface of the top layer is provided with a receiving coil bearing connection point; through flexible or rigidbinding ropes, the connection points are connected in the radial direction of the receiving coil, and through the flexible binding rope, in the axial direction of the receiving coil, the receiving coil bearing points are connected, thus guaranteeing attitude balance of the receiving coil; and the binding rope enables the receiving coil not to generate moment in the pitching and rolling directions,thus suppressing generation of motion fundamentally; and by means of damping fluid, vibration isolation effect is achieved, and at the same time, the mobile resistance of the receiving coil is increased, thus further limiting spatial displacement of the receiving coil, and improving the primary field compensation effect. The time-domain aeroelectromagnetic method receiving coil attitude change suppression device overcomes limitations of application.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com