Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Spatial shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Light detection system and method
ActiveUS20150249496A1Electroluminescent light sourcesClose-range type systemsConsecutive frameRolling shutter
There is provided a method for detecting modulated light comprising: receiving a set of images acquired by means of a rolling shutter camera having image acquisition settings comprising a frame rate, fframe, and a line rate, fline; identifying in consecutive frames of said images—a pattern governed by the ratio between a modulation frequency, fc, of a modulated light source and the line rate, fline, and—between consecutive frames a spatial shift of said pattern governed by the ratio between said modulation frequency fc, and said frame rate, fframe; and providing based on said pattern and spatial shift thereof, an estimate of the modulated light amplitude from said light source.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
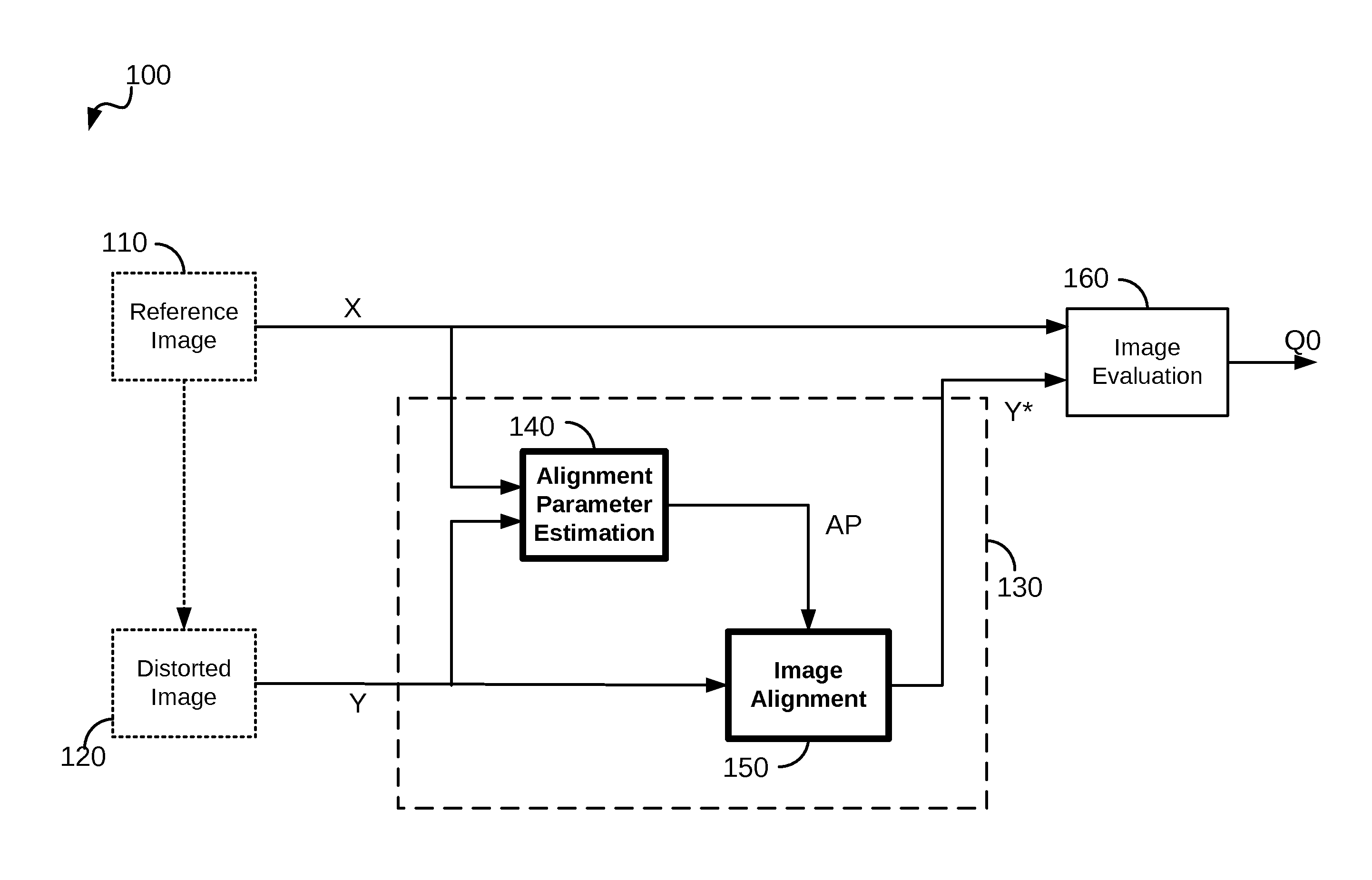
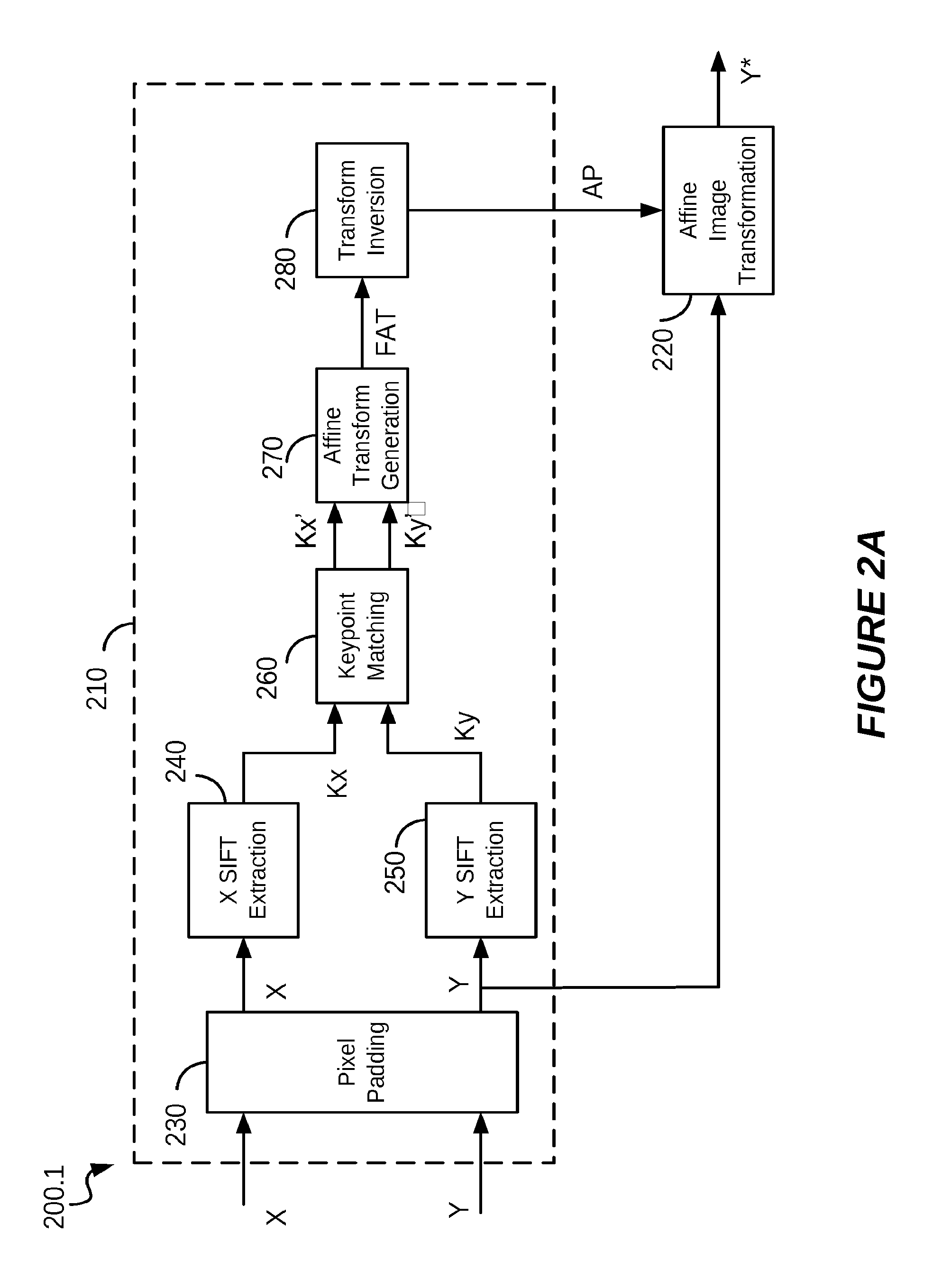
Image registration method and system robust to noise
ActiveUS20130163896A1Improved image registration methodStrengthen the systemImage analysisGeometric image transformationFast Fourier transformComputer graphics (images)
An image registration method is disclosed for processing a distorted image into a registered image that is aligned with reference to an original image. Distortions from the original image may include scaling, rotation, and noise. The method is based on correlating Radon transforms of both images to determine the rotation angle, and the scaling factor is determined by dividing averages of the overall luminance of each image on the assumption that any added noise will cancel. The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to estimate global spatial shifts. In one embodiment, the distorted image is first scaled to the size of the original image before being rotated. In another embodiment, the original image is first scaled to the size of the distorted image before rotating the distorted image, and finally scaling it to match the original image. A corresponding system for image registration is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
Method for providing a stabilized video sequence
ActiveUS20120218427A1Without usingQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoVideo sequence
A method for providing a stabilized digital video sequence, comprising: analyzing a set of image frames captured at different times to determine one-dimensional image frame representations; combining the one-dimensional frame representations to form a two-dimensional spatiotemporal representation of the video sequence; identifying a set of trajectories corresponding to structures in the two-dimensional spatiotemporal representation; identify a set of foreground trajectory segments and a set of background trajectory segments; analyzing the background trajectory segments to estimate a motion pattern for the digital video camera; analyzing the motion pattern for the digital video camera to determine a undesired motion portion corresponding to an unintended camera shaking motion; applying spatial shifts to at least some of the image frames of the digital video sequence to provide a stabilized digital video sequence.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
Methods, systems and computer program products for calibration of microscopy imaging devices
An imaging system on which a calibration method is practiced includes: a light source; a substrate for supporting an object; a patterning mask that generates a substantially periodic spatial pattern on the object; a phase shifter that adjusts the relative position of the patterning mask and object to shift the position of the pattern on the object; a detector that detects images of the object; and an analyzer that analyzes at least three images of the object, each of which represents a different spatial shift of the pattern, the analyzer being configured to remove the spatial pattern from the images to generate an optically sectioned image of the object. The calibration method includes: calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a phase-voltage technique; calibrating the position of the mask relative to the substrate via a merit function technique; and operating the calibrated imaging system.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and apparatus for regional image quantification verification
A method and apparatus are disclosed for testing the accuracy of digital test images generated by a computer graphics program executed on a computer graphics system. A test program is utilized to compare a test image with a reference image. Regional image quantification verification aims at an image comparison test that accepts minor color value differences and spatial shifts in rendered pixel values. The test image and reference image are divided into corresponding sub-regions. The average color value for each sub-region of the test image is compared to the average color value of the corresponding reference image sub-region and also to other nearby reference image sub-regions. A test image is unacceptably different from a reference image, if for any sub-region of the test image, no reference image sub-region is found with an average color value difference and spatial shift less than specified maximums.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method of Changing Fluid Flow by Using an Optical Beam
ActiveUS20120273054A1Positional shiftCircuit elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansComputational physicsMicro fluidic
The application of an optical beam redirects sheathed micro-fluidic flow without direct interaction with the sample. The hydrodynamic properties of the sheath are locally modified due to optical absorption and heating, resulting in a spatial shift of the sample flow. The technique can result in up to 100 μm shift at peak flow velocities of 19 mm / sec.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Apparatus and method employing multilayer thin-film stacks for spatially shifting light
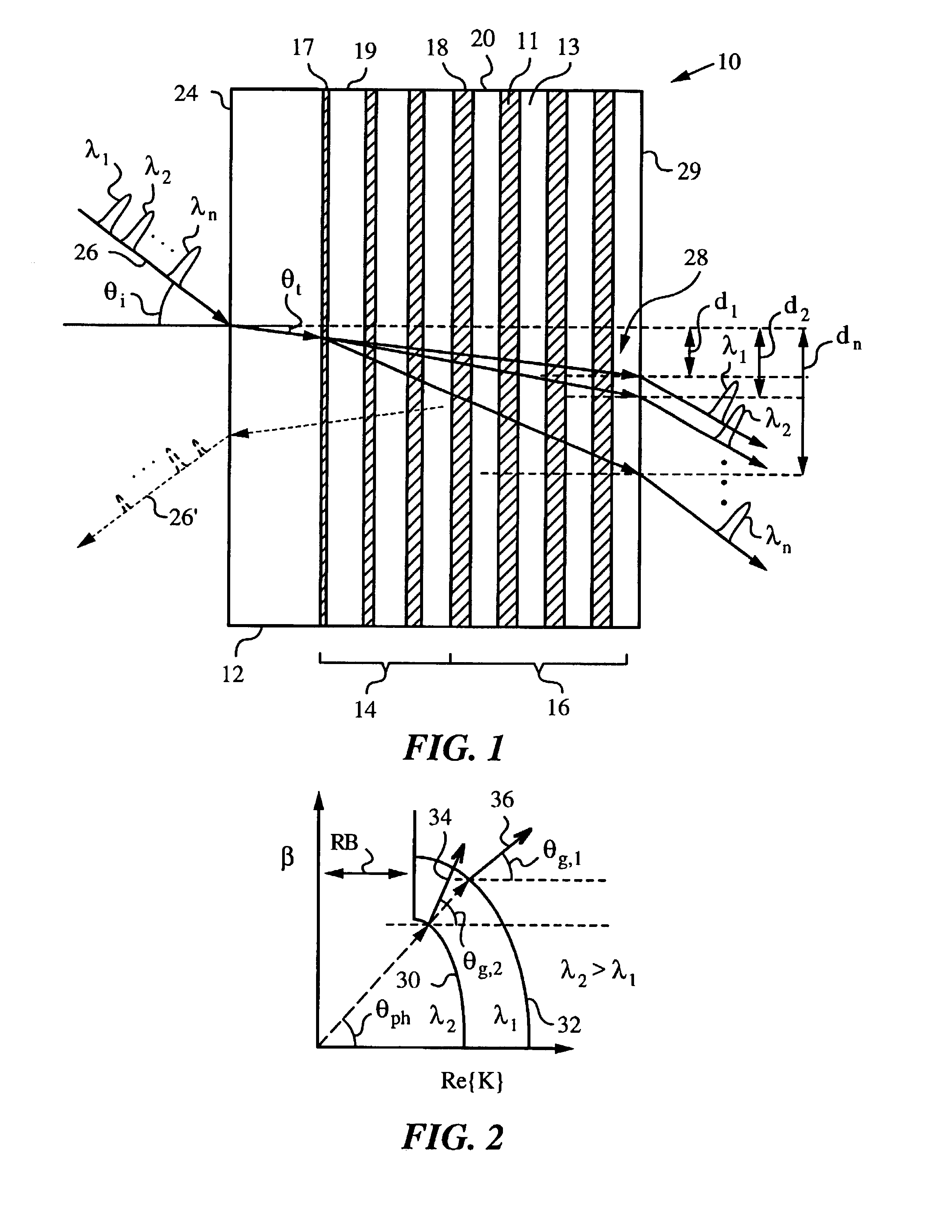
InactiveUS7088884B2Improve spatial resolutionEasy to makeCoupling light guidesOptical propertyCoupling
An apparatus and method for spatially shifting a light using a multilayer thin-film stack of at least two materials having unequal optical properties, such as indices of refraction and absorption coefficients. The apparatus has an input face for admitting the light into the apparatus and an impedance matching mechanism for maximizing the in-coupling of the light into the multilayer thin-film stack at a non-normal incidence. The non-normal incidence is sufficient to generate a spatial shift of the light in the multilayer thin-film stack as a function of at least one light parameter, such as wavelength and / or polarization of the light, thereby separating the light into light components. The spatial shift is achieved by any one or any combination of effects including superprism, turning point and energy confinement. These effects are achieved in the multilayer thin-film stack by appropriately engineering its layer sequence.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Methods and systems for processing a first image with reference to a second image
ActiveUS20130272627A1PowerfulImage analysisGeometric image transformationFast Fourier transformComputer graphics (images)
An image registration method is disclosed for processing a distorted image into a registered image that is aligned with reference to an original image. Distortions from the original image may include scaling, rotation, and noise. The method is based on correlating Radon transforms of both images to determine the rotation angle, and the scaling factor is determined by dividing averages of the overall luminance of each image on the assumption that any added noise will cancel. The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is used to estimate global spatial shifts. In one embodiment, the distorted image is first scaled to the size of the original image before being rotated. In another embodiment, the original image is first scaled to the size of the distorted image before rotating the distorted image, and finally scaling it to match the original image. A corresponding system for image registration is also provided.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
Magnetic resonance imaging method and apparatus to correct distortions due to inhomogeneities of the basic magnetic field
InactiveUS20130076356A1Low costQuality improvementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsData setMeasurement point
In a magnetic resonance method and system to correct spatial shifts in MR data, at least two measurement data sets are acquired, the additional measurement data set or sets being acquired while switching an additional gradient relative to acquisition of the first measurement data set. For respective corresponding measurement points of the measurement data sets, a phase difference is initially determined from the first measurement data set and at least one additional measurement data set acquired with the additional gradient, with a spatial shift of the measurement points of the first measurement data set being determined from the spatial shift. The magnitude values of the initially measured measurement points are distributed to their correct spatial position corresponding to the determined spatial shifts, so a corrected image data set is created.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method and apparatus for regional image quantification verification
ActiveUS7092571B2Reduce in quantityEffectively blurredImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionImage Quantification
A method and apparatus are disclosed for testing the accuracy of digital test images generated by a computer graphics program executed on a computer graphics system. A test program is utilized to compare a test image with a reference image. Regional image quantification verification aims at an image comparison test that accepts minor color value differences and spatial shifts in rendered pixel values. The test image and reference image are divided into corresponding sub-regions. The average color value for each sub-region of the test image is compared to the average color value of the corresponding reference image sub-region and also to other nearby reference image sub-regions. A test image is unacceptably different from a reference image, if for any sub-region of the test image, no reference image sub-region is found with an average color value difference and spatial shift less than specified maximums.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Fast deconvolution method for solid sphere array three-dimensional sound source recognition
ActiveCN106483503APrecise positioningReduce computing timePosition fixationDistribution matrixSolid sphere
The invention discloses a fast deconvolution method for solid sphere array three-dimensional sound source recognition. The method comprises the following steps: 1, a sound pressure output formula is used for calculating the sound pressure output amount of each focusing grid point; 2, an output matrix is constructed by using the output amount of each point obtained through calculation; 3; a PSF function is used for calculating a PSF matrix A-tilde at the center focusing point; and 4, a sound source strength distribution matrix S-tilde is solved iteratively. The spatial shift immovability feature is used in the fourth step, a huge A matrix does not need to be calculated, a small-dimension matrix A-tilde only needs to be calculated, A<C>-tilde is obtained through A-tilde deformation, Fourier transform is carried out on the A<C>-tilde, based on FFT acceleration, the calculation time is greatly shortened, the calculation efficiency is improved, a good spatial resolution can be kept, and each sound source can be positioned accurately.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for providing a stabilized video sequence
ActiveUS8384787B2High motion estimateLess processing timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoVideo sequence
A method for providing a stabilized digital video sequence, comprising: analyzing a set of image frames captured at different times to determine one-dimensional image frame representations; combining the one-dimensional frame representations to form a two-dimensional spatiotemporal representation of the video sequence; identifying a set of trajectories corresponding to structures in the two-dimensional spatiotemporal representation; identify a set of foreground trajectory segments and a set of background trajectory segments; analyzing the background trajectory segments to estimate a motion pattern for the digital video camera; analyzing the motion pattern for the digital video camera to determine a undesired motion portion corresponding to an unintended camera shaking motion; applying spatial shifts to at least some of the image frames of the digital video sequence to provide a stabilized digital video sequence.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
Method and apparatus for adaptive local image quantification verification
ActiveUS6961468B2Reduce in quantityEffectively blurredImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImage QuantificationGraphics
A method and apparatus are disclosed for testing the accuracy of digital images generated by a computer graphics program executed on a computer graphics system. A test program is utilized to compare test images with a set of reference images. Adaptive local image quantification verification aims at an image comparison that allows specified color value and spatial shifts. The color value for each pixel of a specified portion of the test image is compared to the average color value of an offset array of pixels in a reference image. A test image region may be unacceptably different from a reference image, if for any pixel of the test image region an offset reference image array is not found that has an array size, absolute color value difference, and spatial shift less than specified maximums.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Volume holographic data recording media
ActiveUS20100119957A1Photomechanical apparatusRecord information storageRefractive indexRecording layer
There is provided volume holographic data recording media having a recording layer which is capable of recording interference fringes generated by interference of light having excellent coherence as fringes having different refractive indexes and undergoes holographic data recording by an amount of spatial shift distance of not more than 3 μm which is smaller than that of conventional media.
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
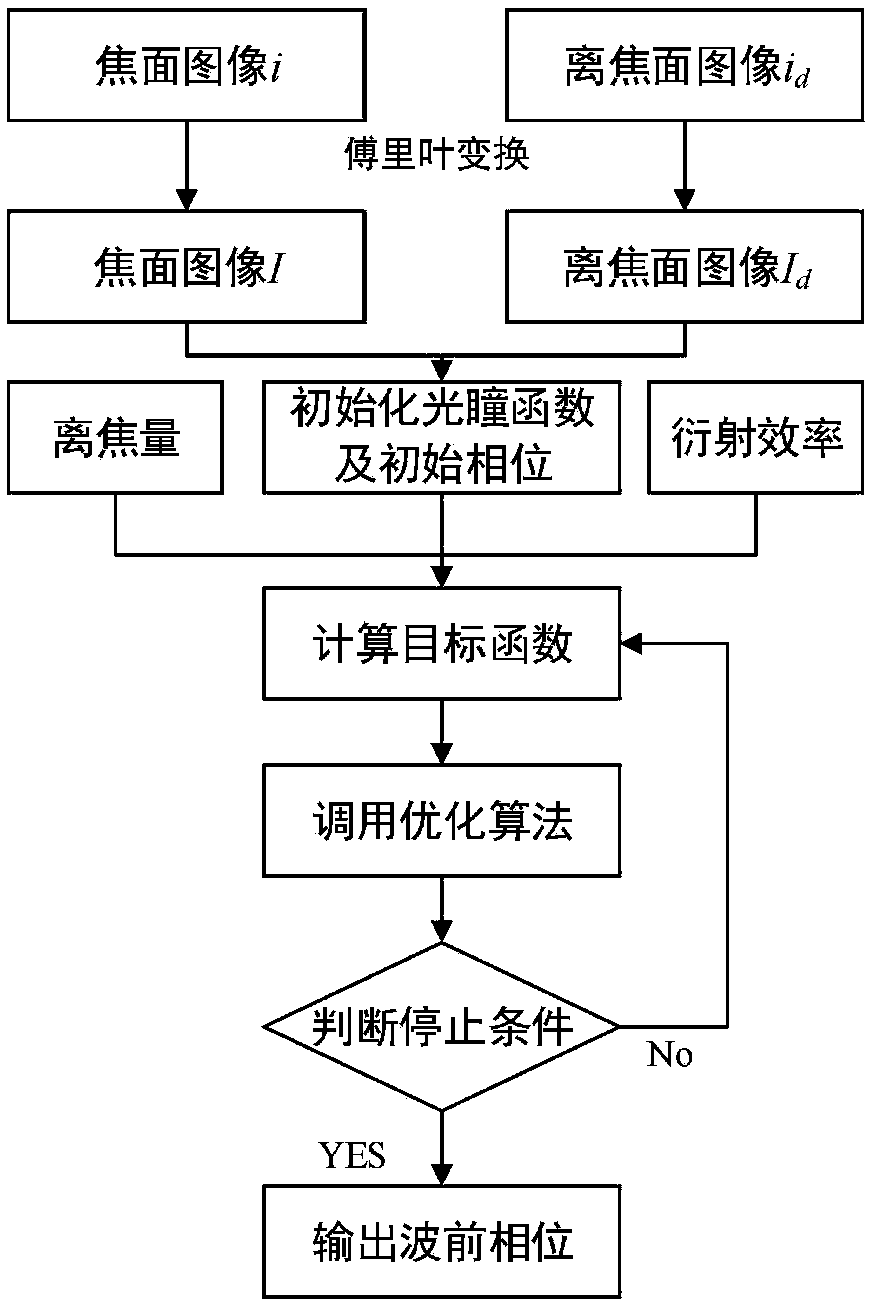
Diffractive optical imaging system wavefront inversion algorithm based on phase difference method
ActiveCN109407311AImprove adaptability to spatial changesAccurate adaptabilityOptical elementsPhase differenceGlobal optimization
The invention discloses a diffractive optical imaging system wavefront inversion algorithm based on a phase difference method. The algorithm comprises the following steps: 1, a diffractive optical imaging feature characterization model containing the diffractive efficiency and the spatial shift characteristics of the diffractive optical imaging system is built; 2, based on a maximum likelihood method, a phase difference wavefront inversion model for the diffractive optical imaging system is built; 3, based on a scalar diffraction theory, a defocusing diffractive phase expression and a defocusing diffractive efficiency characterization model are deduced; 4, according to the spatial shift characteristics of the diffractive imaging, based on an isoplanatic region blocking idea, a focus surface space-variant degraded image and a defocus plane space-variant degraded image are subjected to blocking processing; and 5, a simulated annealing-based particle swarm algorithm is used to carry out global optimization solution on the phase difference wavefront inversion model, and the wavefront information corresponding to different view fields is outputted. A support is provided for the space application of a future super large aperture thin film diffractive optical imaging system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Distortion correction method, magnetic resonance apparatus, program product and data medium
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Memory control apparatus and efficient search pattern for block-matching motion estimation
InactiveUS7072395B2Avoid searchingSave powerTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationMemory addressMemory bank
A memory control apparatus for block-matching motion estimation and an associated search pattern for processing video sequence in real-time are described in this disclosure. The motion estimation subsystem utilizes a set of memory banks to store a section of the reference picture used for computing the differences between an underlying block and a spatially shifted reference block. The memory control apparatus derives the memory addresses for storing the reference picture region in the memory banks in such a way that a row or a column of data from the reference block can be accessed in parallel without wait. The row- or column-data are then made available to the parallel computation unit for computing the block difference in a single processing cycle. An associated spiral search pattern that covers the whole search region is also described that minimizes the required data access and consequently saves power consumption. Combined with a search-stop criterion, the search pattern will result in early search termination during the block-matching motion estimation process and consequently conserves more power.
Owner:ESS TECH INT INC
Method and device for producing height images of technical surfaces with microscopic resolution
InactiveUS6943823B2Easy accessMaterial analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionControl mannerUltimate tensile strength
A method for producing height images of technical surfaces with microscopic resolution uses a confocal measuring microspace. The sample to be measured is displaced in the direction (Z direction) towards the microspace in a controlled manner and images are produced at defined distances with a digital camera. The digitized images recorded are transmitted to a controller (PC) for further processing and evaluation and the light intensity maximum for every pixel is detected, the position of the maximum indicating the height of the sample to be measured. The sample is displaced in a continuous manner and that the image exposures are triggered at discrete localized distances. The intensities of the N individual images recorded and digitized in the above manner are stored in the PC in such a manner that a number N of subsequent storage locations is occupied for every pixel.
Owner:NANOFOCUS
Light detection system and method
ActiveUS9479251B2Electroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementConsecutive frameRolling shutter
There is provided a method for detecting modulated light comprising: receiving a set of images acquired by means of a rolling shutter camera having image acquisition settings comprising a frame rate, fframe, and a line rate, fline; identifying in consecutive frames of said images—a pattern governed by the ratio between a modulation frequency, fc, of a modulated light source and the line rate, fline, and—between consecutive frames a spatial shift of said pattern governed by the ratio between said modulation frequency fc, and said frame rate, fframe; and providing based on said pattern and spatial shift thereof, an estimate of the modulated light amplitude from said light source.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
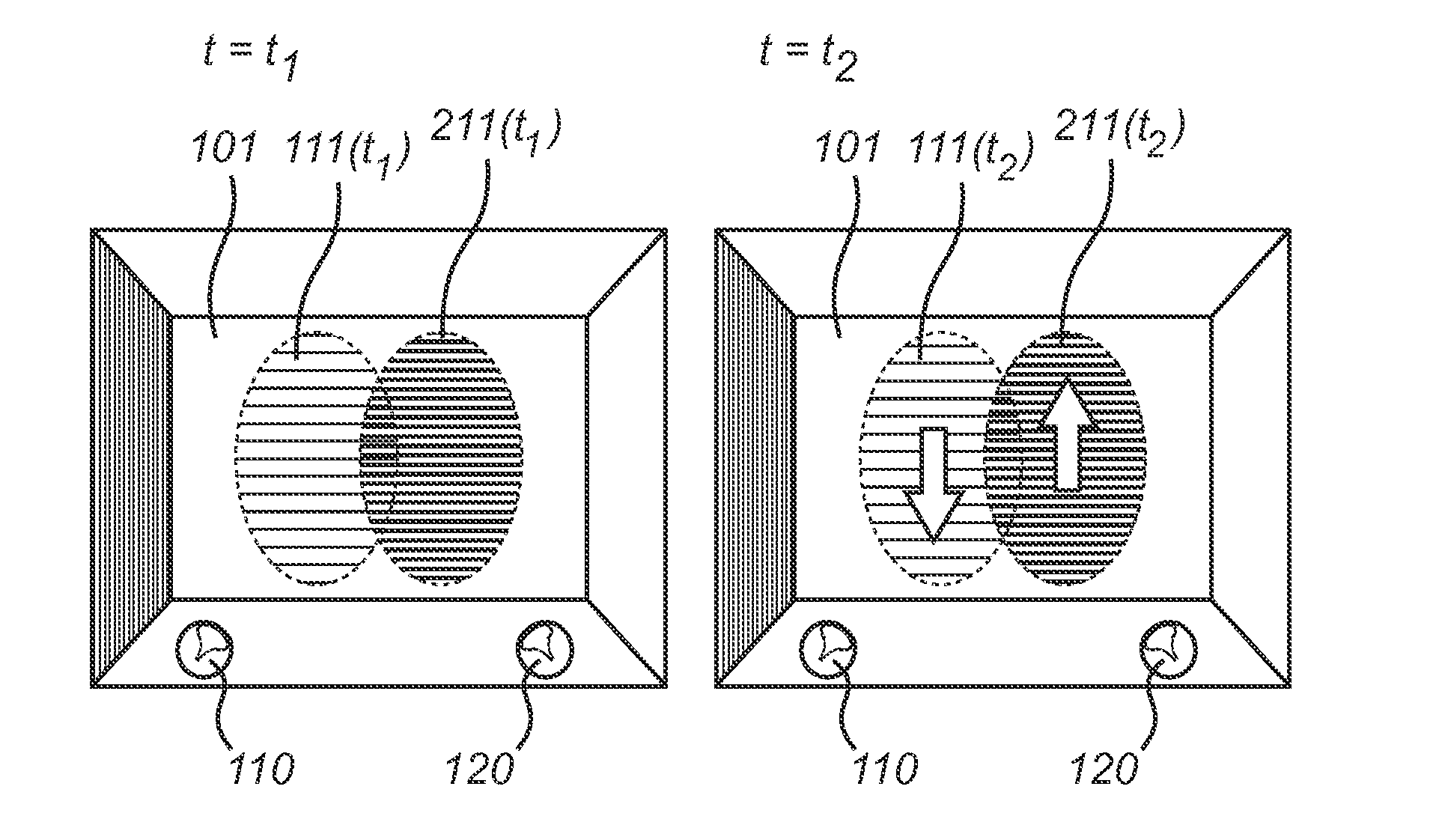
Heart activity measurement
ActiveUS20160242698A1Reduce the impactReduce impactElectrocardiographyDiagnostics using lightImage processingImage based
A method includes: obtaining, by an apparatus, instantaneous images from an optical heart activity sensor, wherein the instantaneous images characterize a heart activity data of a user; obtaining information about spatial shifts of a measuring area of the optical heart activity sensor in relation to a body tissue of the user; determining effect of the spatial shifts in the instantaneous images based on the information about the spatial shifts; enhancing the instantaneous images by decreasing the effect of the spatial shifts in the instantaneous images; and processing the enhanced instantaneous images into the heart activity data of the user.
Owner:POLAR ELECTRO
Tunable dispersion compensator
A tunable dispersion compensator includes a collimating unit that collimates an incident light to output a parallel light, a parallel shifting unit that spatially shifts the parallel light from the collimating unit within a predetermined range, and an optical-path-length providing unit that provides optical path length of light corresponding to a position at which light output from the parallel shifting unit is input.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Demodulation method for bidirectional relay spatial shift key modulation signal
InactiveCN104079331ATroubleshoot two-way relay communication issuesImprove throughputSpatial transmit diversityRadio relay systemsComputation complexityComputer science
The invention provides three signal demodulation schemes for adopting spatial shift key modulation specific to source nodes and adopting an amplifying-forwarding way specific to single-antenna relay nodes in a bidirectional relay communication scene. The first scheme is maximum-likelihood demodulation. The first scheme has optimal performance, but the computation complexity increases along with the third-power speed of the number of receiving antennas. The second scheme is zero-forcing equalization. The second scheme has the worst performance, but the computation complexity is low, and each transmitting antenna is modulated independently. The third scheme is maximal ratio combination. The performance of the third scheme is approximate to the performance of maximum-likelihood demodulation, and the computation complexity is low. By using any of the three schemes, bidirectional relay communication can be supported.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Grinding device with spatial displacement
PendingCN111644963ASimple structureEasy to manufactureGrinding drivesGrinding feed controlControl systemEngineering
The invention discloses a grinding device with spatial displacement. The grinding device comprises a support frame. A spatial displacement mechanism is arranged on the support frame. A grinding head identification device is movably arranged on the spatial displacement mechanism. A clamping and adjusting mechanism for workpiece positioning is arranged below the grinding head identification device.The spatial displacement mechanism and the clamping and adjusting mechanism both are connected with a control system. The grinding device with spatial displacement adopts the frame type structure andhas the beneficial effects of being easy to manufacture, low in cost and stable and reliable; the arranged matched spatial displacement mechanism is simple in structure, high in moving precision and high in space flexibility and is suitable for multi-azimuth grinding operation; the grinding head identification device can accurately identify the position needing to be polished on the surface of a workpiece, the surface-repaired workpiece is identified and ground, the grinding efficiency is improved, and working hours are saved; and the clamping and adjusting mechanism can quickly adjust the position and the height of the workpiece, and the problems that the grinding workpiece is not easy to clamp and is easy to deflect when clamped are solved.
Owner:宝鸡云智造科技有限公司
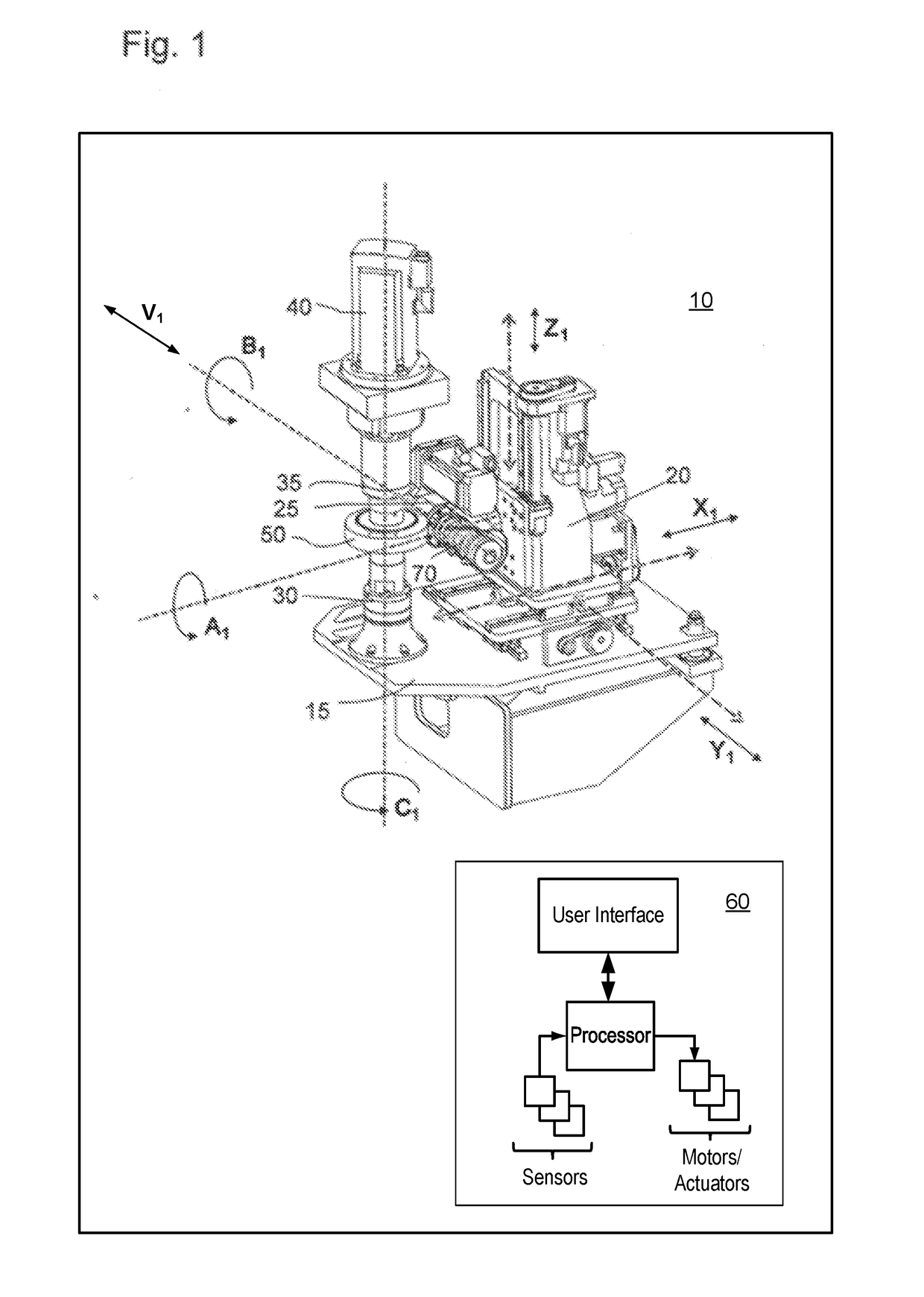
Method for deburring a gear blank
ActiveUS20170087653A1Automatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsControl theoryMachine tool
A method for deburring a gear blank includes correcting chamfer sizes, chamfer shapes and chamfer symmetry at tooth edges which were produced with a deburring cutter with a strongly asymmetric tooth shape (ChamferCut). The chamfers are semi-automatically corrected by coupling the movement of several axes of a gear cutting machine, including a workpiece axis of rotation C1, spatial shifting axes of a machine column Z1, X1, and Y1, and a V1-axis corresponding to the tool axis. The method further includes specifying a correction in the axial direction in one of the axes Z1, V1 and C1, and calculating the correction amount of further axes by the controller depending on the specified axis.
Owner:LIEBHERR VERZAHNTECHNIK GMBH
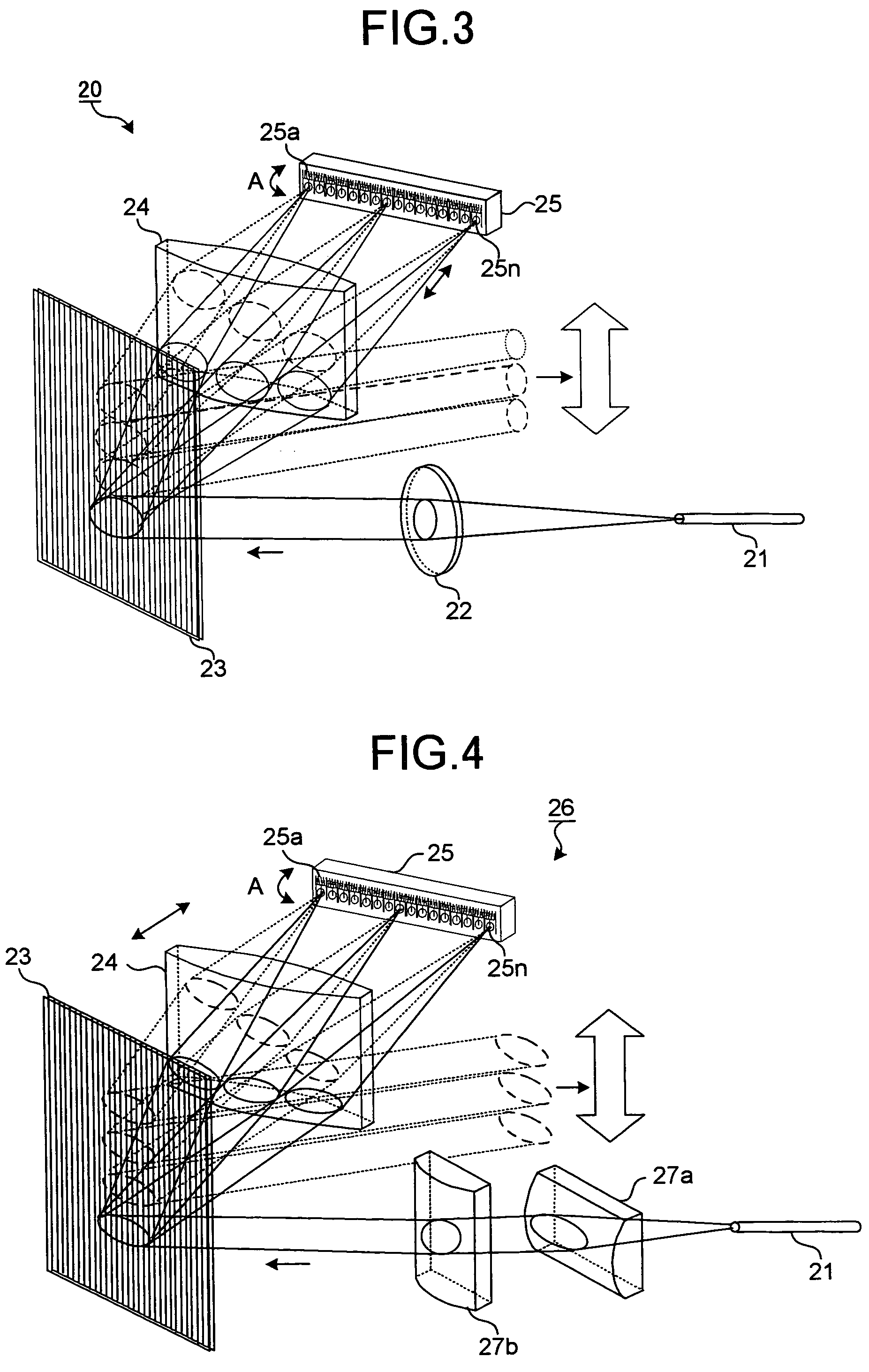
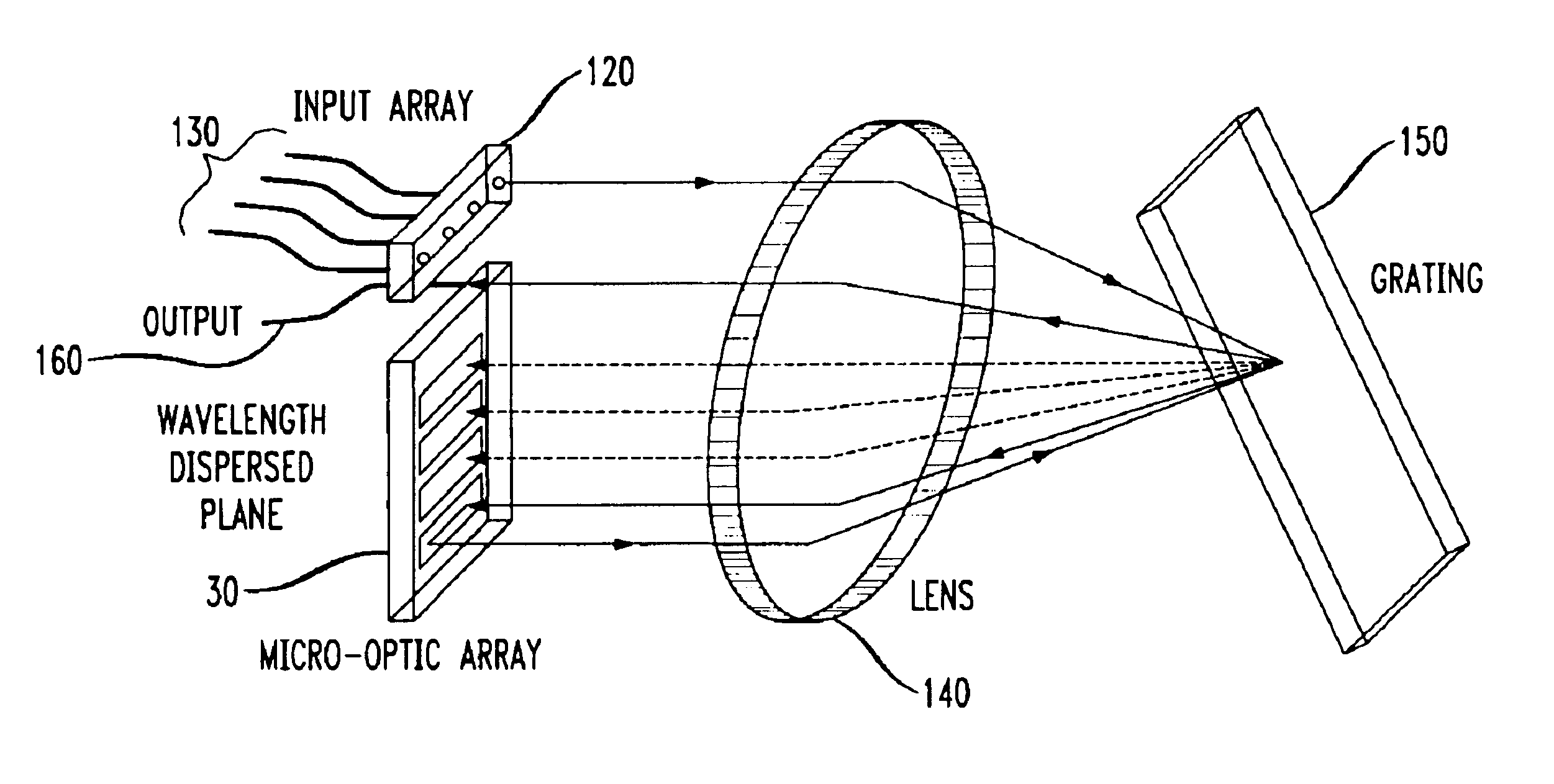
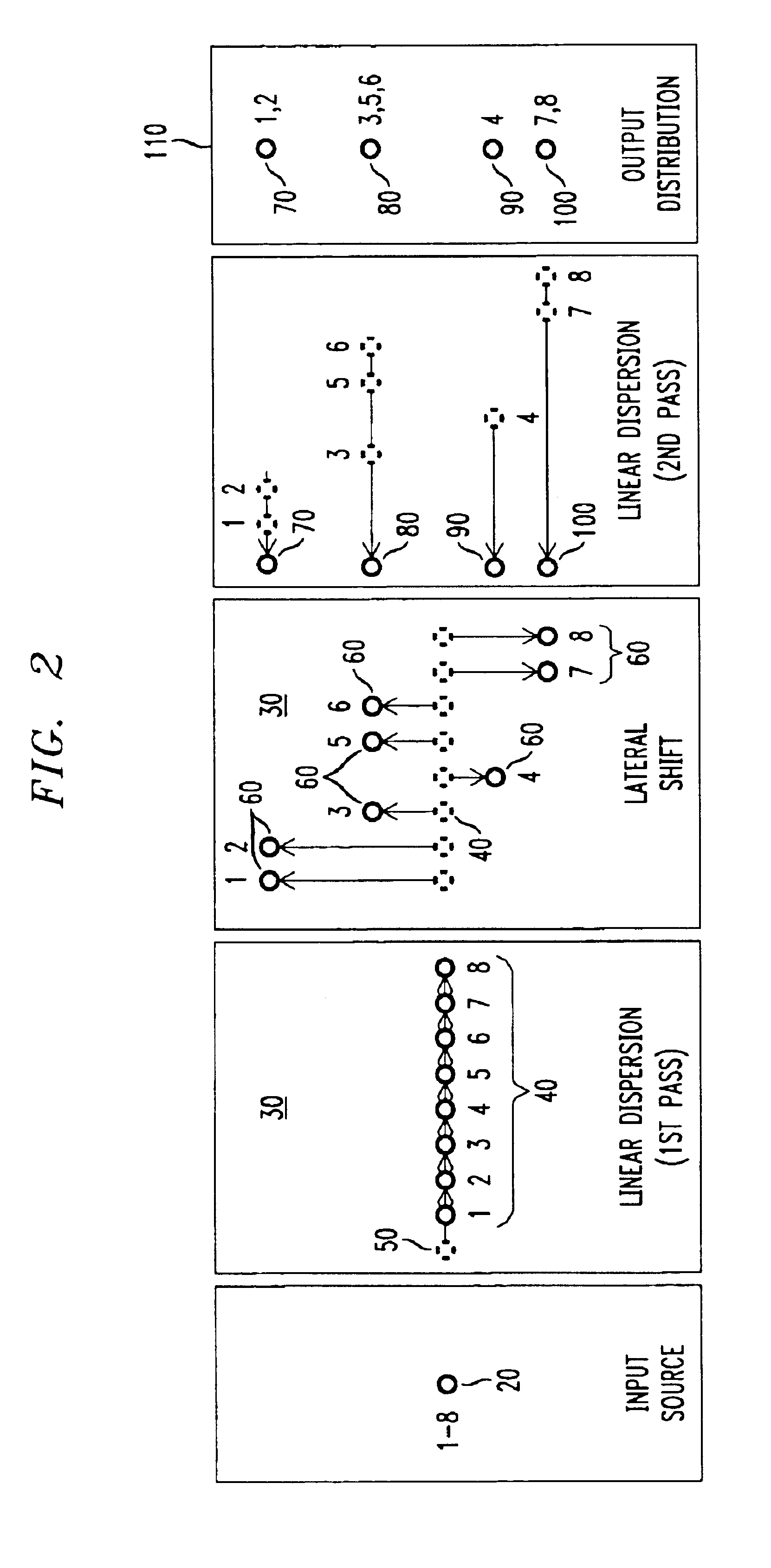
Method and apparatus for spatial-shift wavelength multiplexing in communication systems
InactiveUS6763163B1Efficient spatial shiftingProcess economyCoupling light guidesMultiplexingLinear dispersion
Methods and apparatus for spatially-shifting and multiplexing optical signals for transmission in a wavelength division multiplexed or dense wavelength division multiplexed optical communication system linearly disperse the optical signals and then spatially, laterally shift the signals. The spatially shifted, dispersed signals are thereafter re-imaged to remove the linear dispersion so that the spatially shifted signals can then be transmitted through the optical communication system. The spatially-shifted, multiplexed signals have a flat passband with sharp transition points so that the transmitted signals are routed through the optical communication system with low loss and high integrity.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
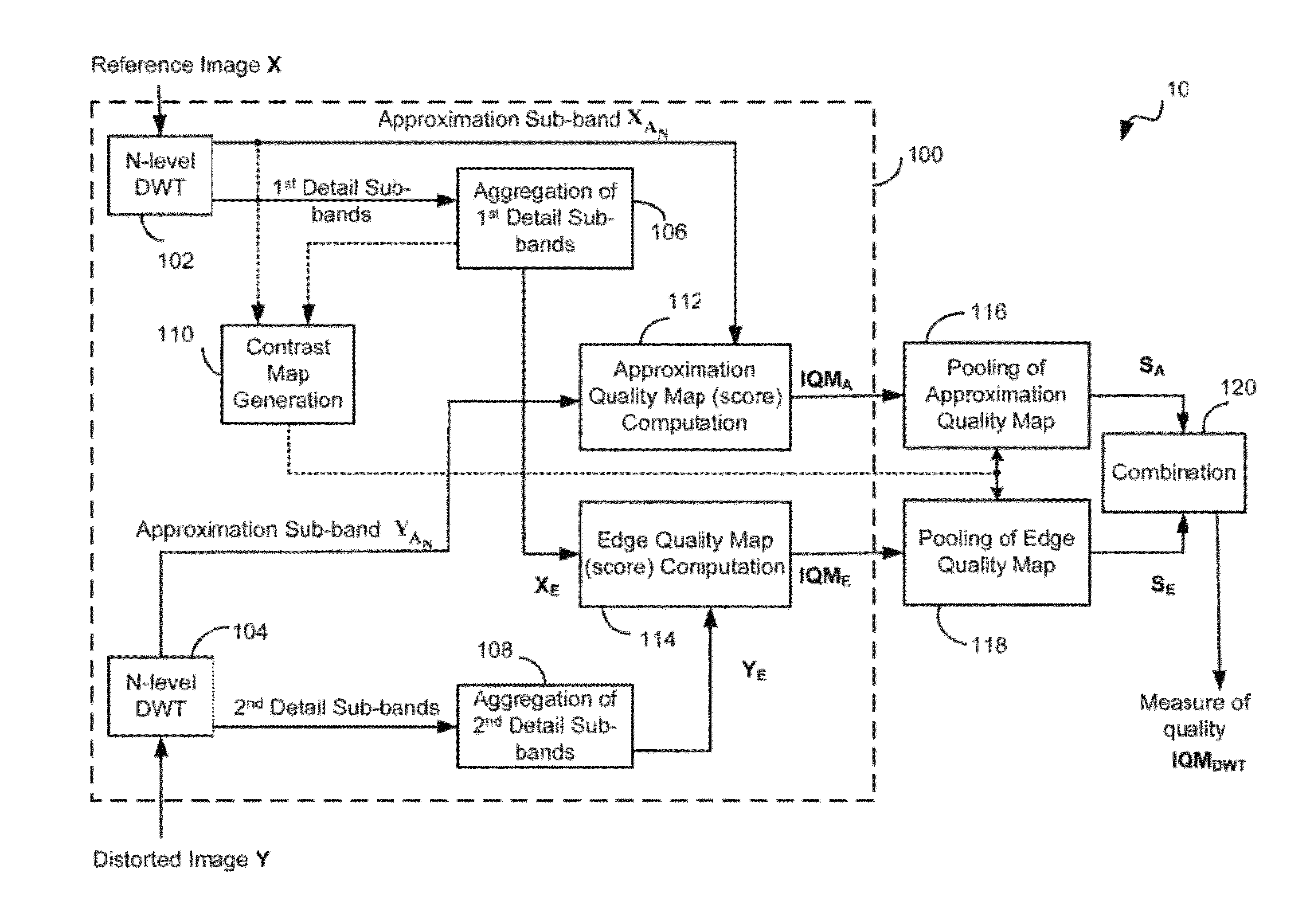
Method and system for increasing robustness of visual quality metrics using spatial shifting
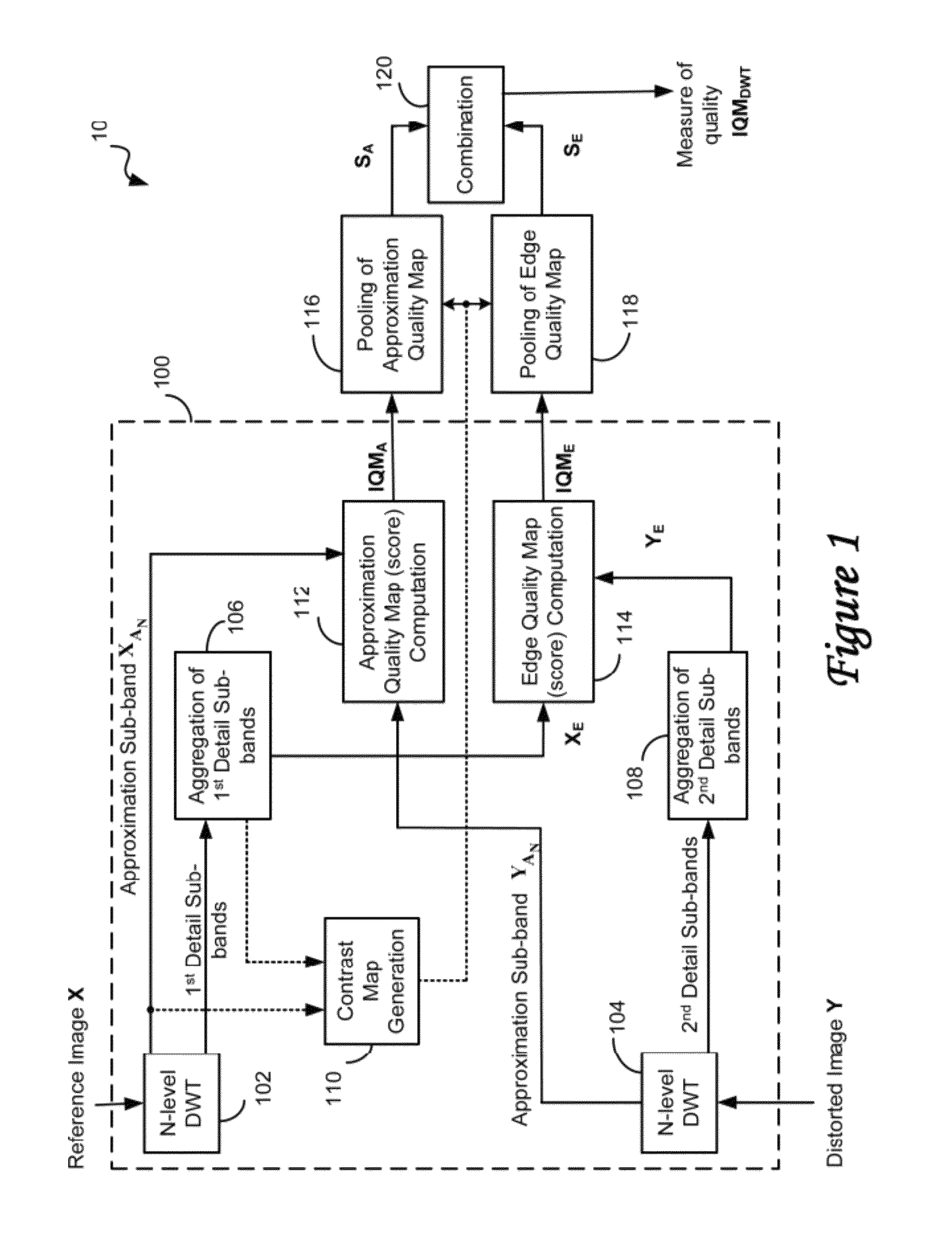
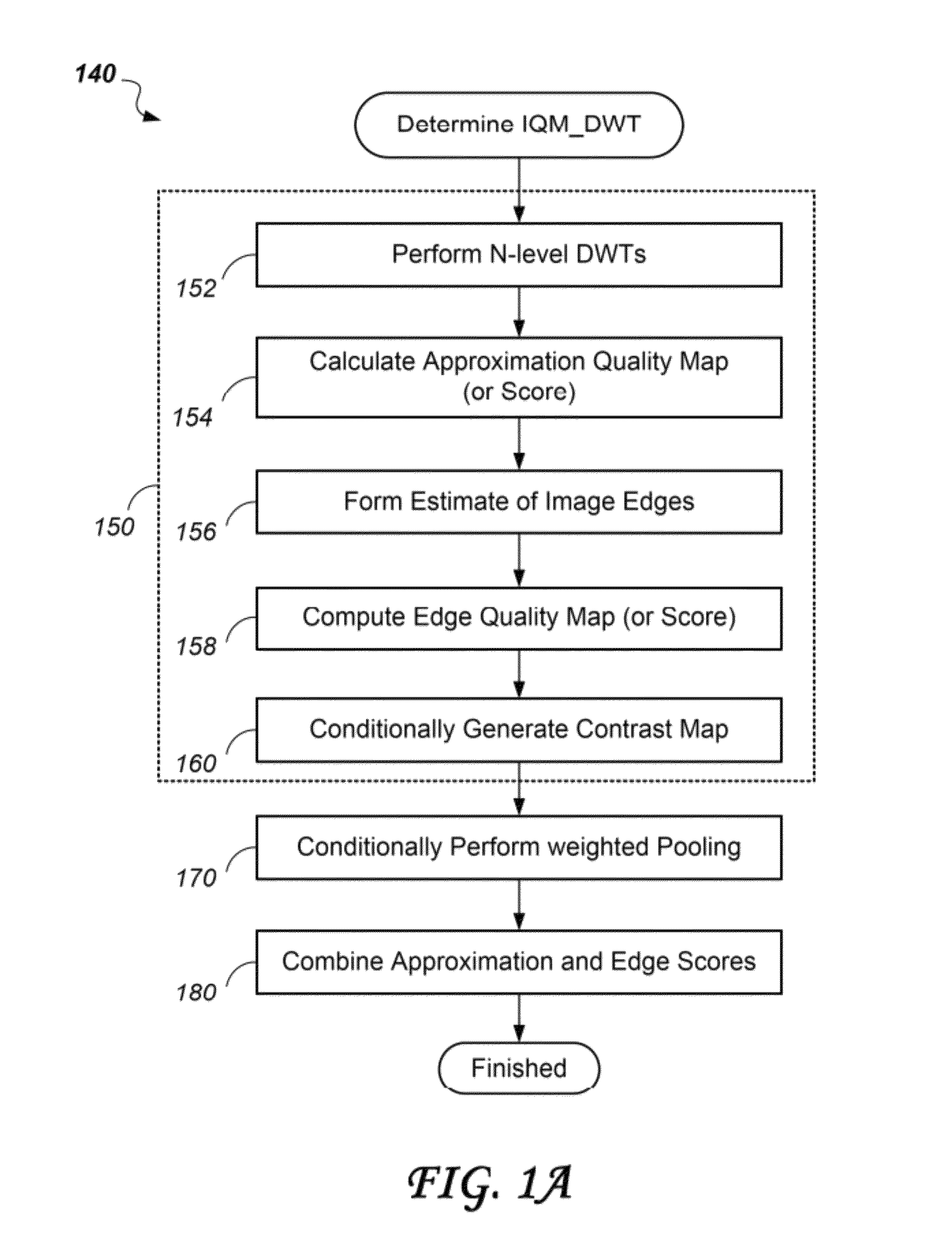
ActiveUS8983206B2Improve robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisQuality assessmentWavelet transform
A visual quality assessment method and system are based on deriving a quality metric by comparing sub-band approximations of a distorted image and an undistorted version of the same image, providing a good compromise between computational complexity and accuracy. The sub-band approximations are derived from Discrete Wavelet (Haar) transforms of small image blocks of each image. Due to inherent symmetries, the wavelet transform is “blind” to certain types of distortions. But the accuracy of the method is enhanced, and the blindness of the transform is overcome, by computing quality metrics for the distorted image as well as computing quality metrics for a shifted version of the distorted image and combining the results.
Owner:ECOLE DE TECH SUPERIEURE
Extensible method of spatial shift keying modulation mode
InactiveCN105939171ABoost bitIncrease capacitySpatial transmit diversityMultiple carrier systemsData streamChannel capacity
The invention discloses an extensible method of spatial shift keying (SSK) modulation based on transmitting antenna selection. The method is characterized in comprising the steps of carrying out orthogonal code group binding on each antenna at a transmitting end; grouping data streams according to a specific length; carrying out spatial modulation mapping, and mapping the data streams to corresponding transmitting antenna combination, thereby obtaining a sequence of activated antennas and corresponding binding code groups; and transmitting the corresponding code groups by the activated antennas; and judging the sequence number and corresponding orthogonal codes of the transmitting antennas at a receiving end, and carrying out information restoration. The method is the technique for extending the simplest spatial modulation mode--spatial shift keying (SSK). Through reference of the method of a subcarrier density modulation technique in light communication, the application of the antenna sequence combination number in the spatial shift keying mode is increased; therefore, the information bits capable of being processed each time by the spatial shift keying is improved; the processing capability of the transmitting end to the information streams is improved; and the channel capacity is improved greatly.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Image series alignment system and method
A system and method involve receiving a sequence of images of an object with at least two consecutive images of the sequence being spatially shifted relative to each other. Each image is transformed into a Fourier domain using a Fourier transform to generate a corresponding plurality of Fourier transformed images. An amplitude filtered pattern is calculated in the Fourier domain based on amplitude components of the plurality of Fourier transformed images. Spatial shifts for pairs of consecutive images in the sequence of images are determined using the amplitude filtered pattern. Images in the sequence of images are aligned based on the determined spatial shifts and the aligned images are summed to form an image-shift-corrected summed image.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for deburring a gear blank
ActiveUS10421136B2Automatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsControl theoryMachine tool
A method for deburring a gear blank includes correcting chamfer sizes, chamfer shapes and chamfer symmetry at tooth edges which were produced with a deburring cutter with a strongly asymmetric tooth shape (ChamferCut). The chamfers are semi-automatically corrected by coupling the movement of several axes of a gear cutting machine, including a workpiece axis of rotation C1, spatial shifting axes of a machine column Z1, X1, and Y1, and a V1-axis corresponding to the tool axis. The method further includes specifying a correction in the axial direction in one of the axes Z1, V1 and C1, and calculating the correction amount of further axes by the controller depending on the specified axis.
Owner:LIEBHERR VERZAHNTECHNIK GMBH
Optical information recorder (reflection holographic memory device)
InactiveUS8120826B2Lower performance requirementsPoor consistencyRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsHolographic storageHolographic memory
A holographic memory device is described which records and reproduces binary image data by irradiating a holographic recording medium with signal light and reference light. The holographic memory device includes a system for aligning polarization of the signal light and reference light on the holographic recording medium by guiding the signal light and the reference light to be coaxially opposed. The holographic memory device further includes a random-phase modulation multiplex recorder and spatial-shift multiplex recorder that, together with the system for aligning polarization, significantly enhances recording density and improves recording capacity.
Owner:KOBE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com