Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
59 results about "Redox cycle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A redox cycle within the cell cycle that is preserved in the daughter generations. The cell cycle has two distinct growth states: quiescence (G 0) and proliferation (G 1, S, G 2, and M). Progression through the cell cycle is regulated by cell-cycle phase–specific ...
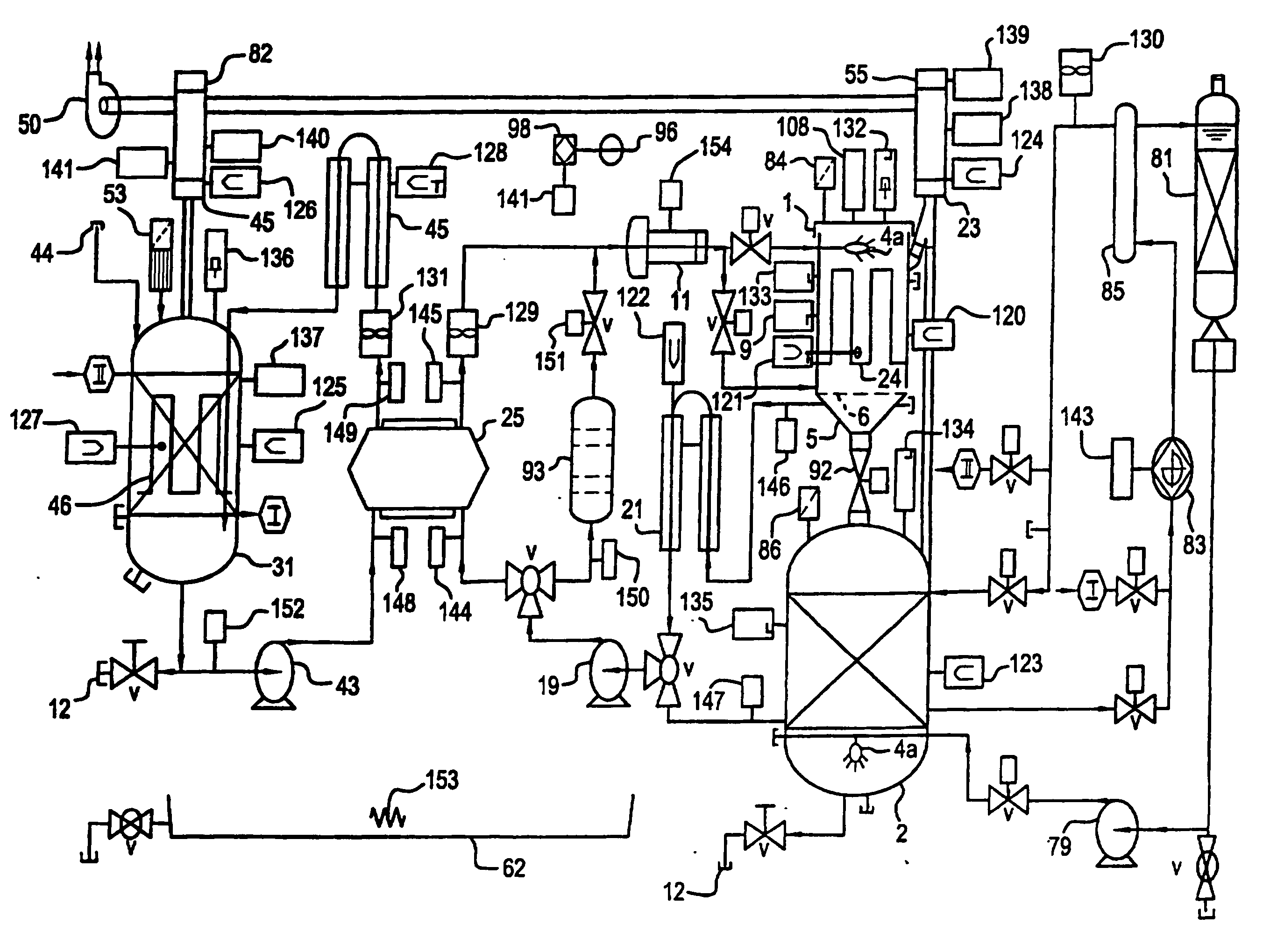
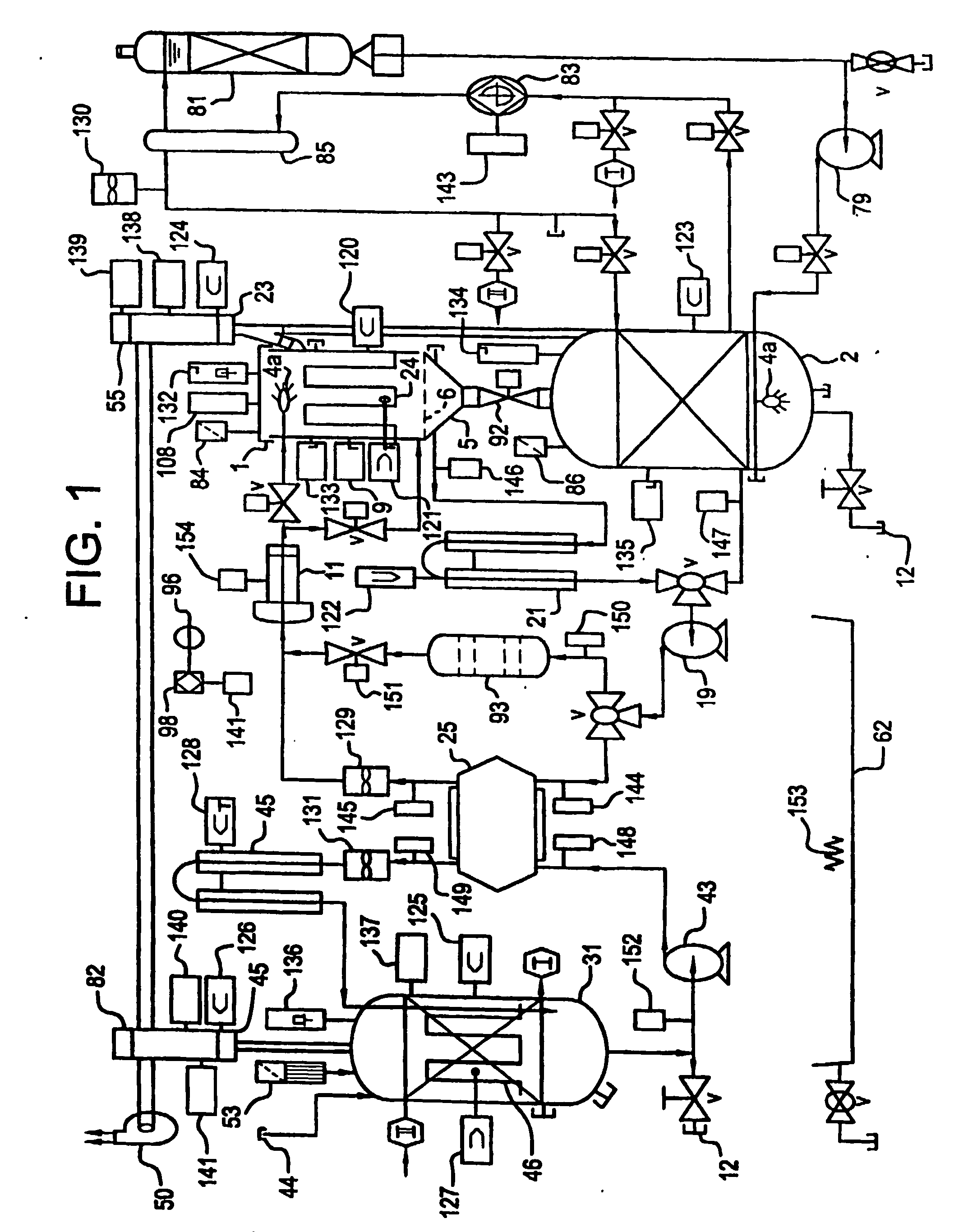
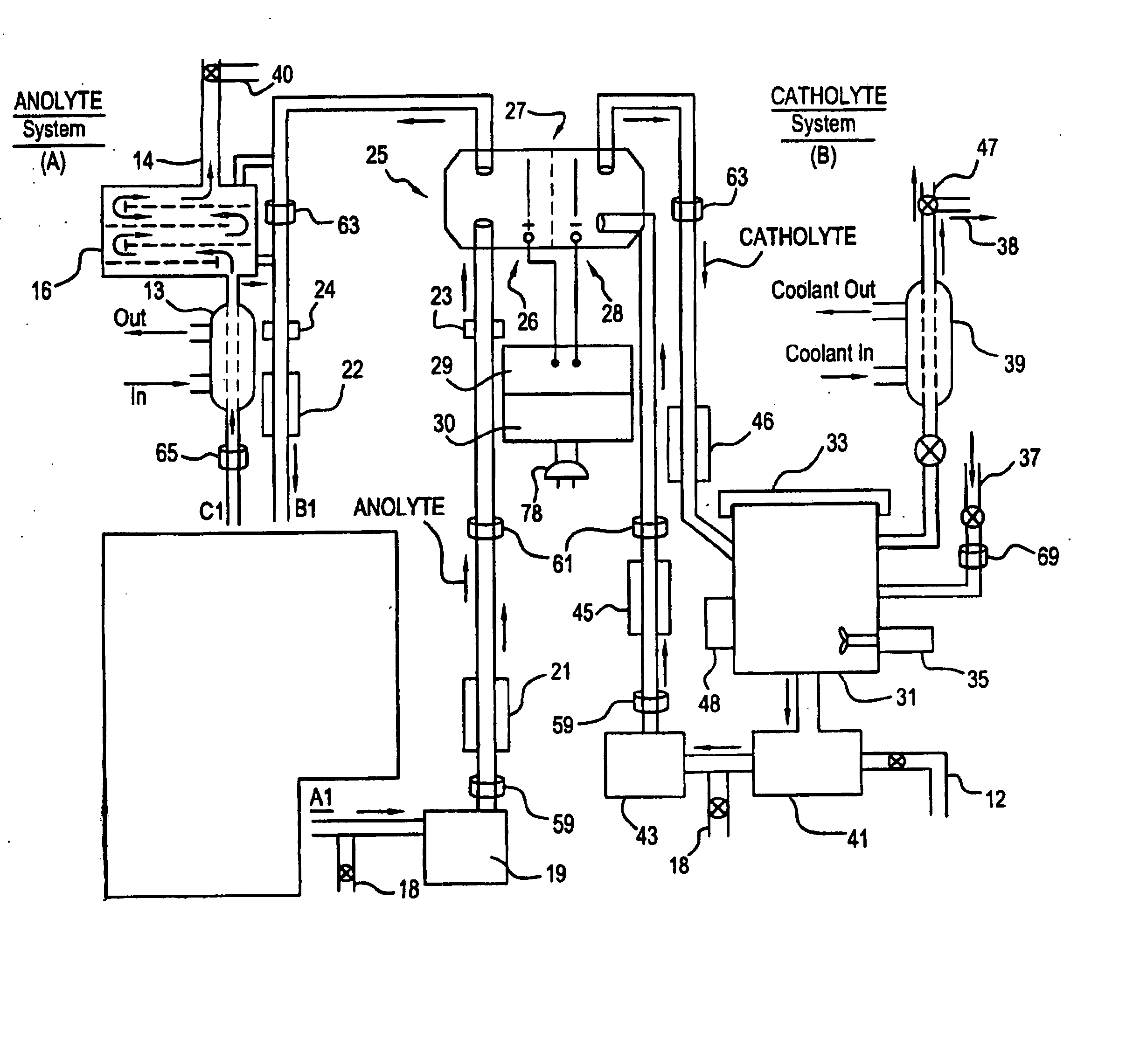
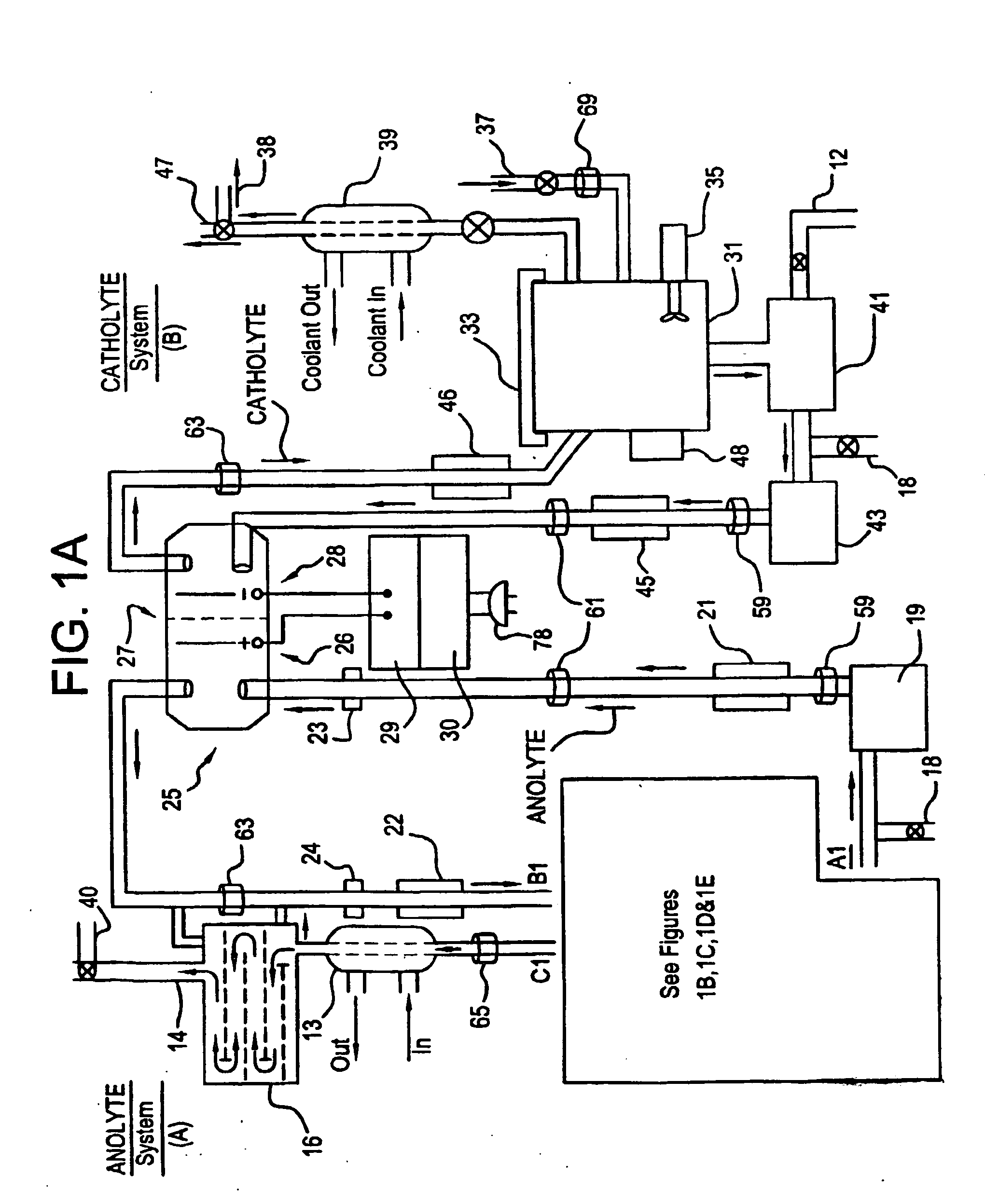
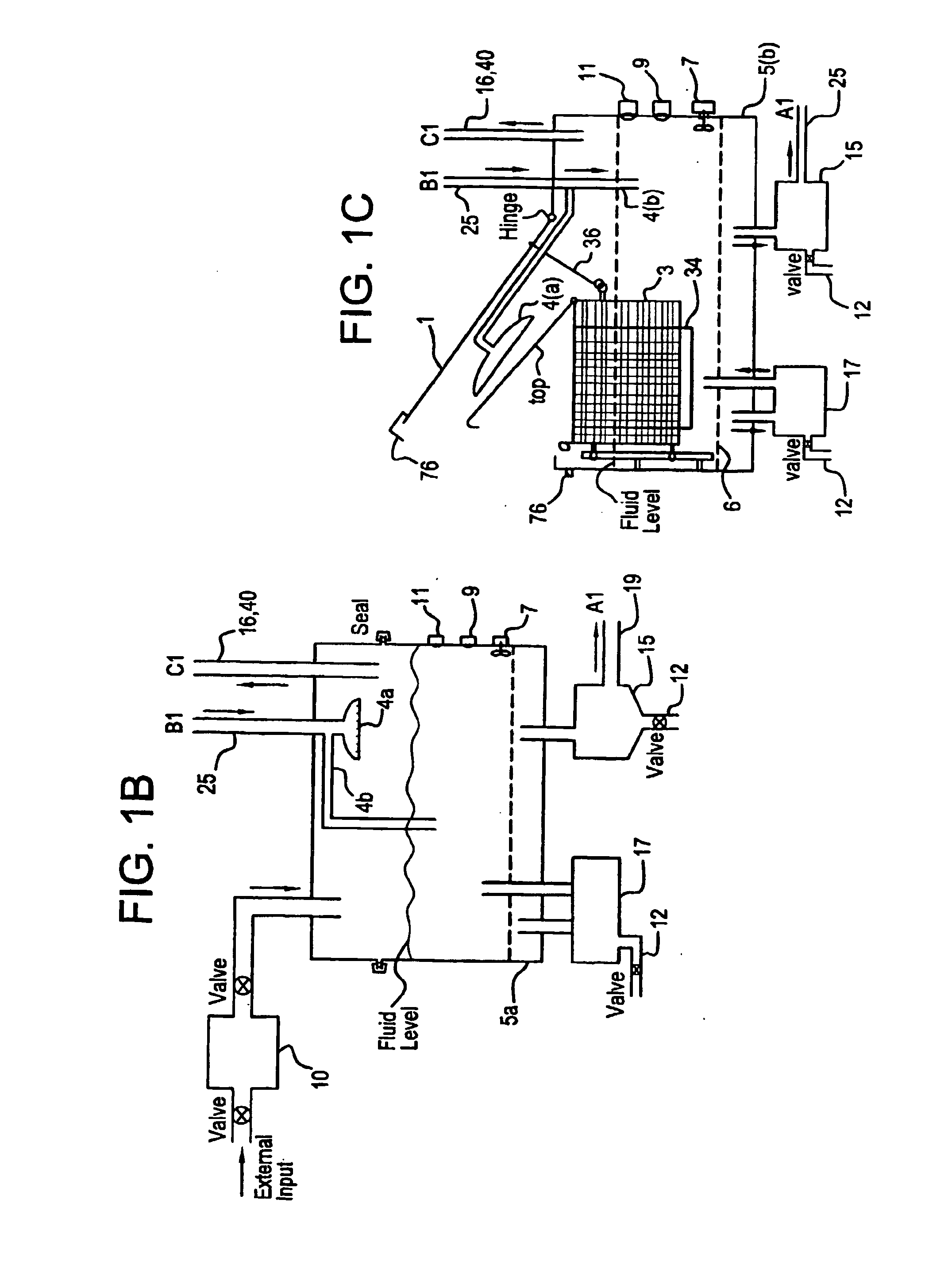
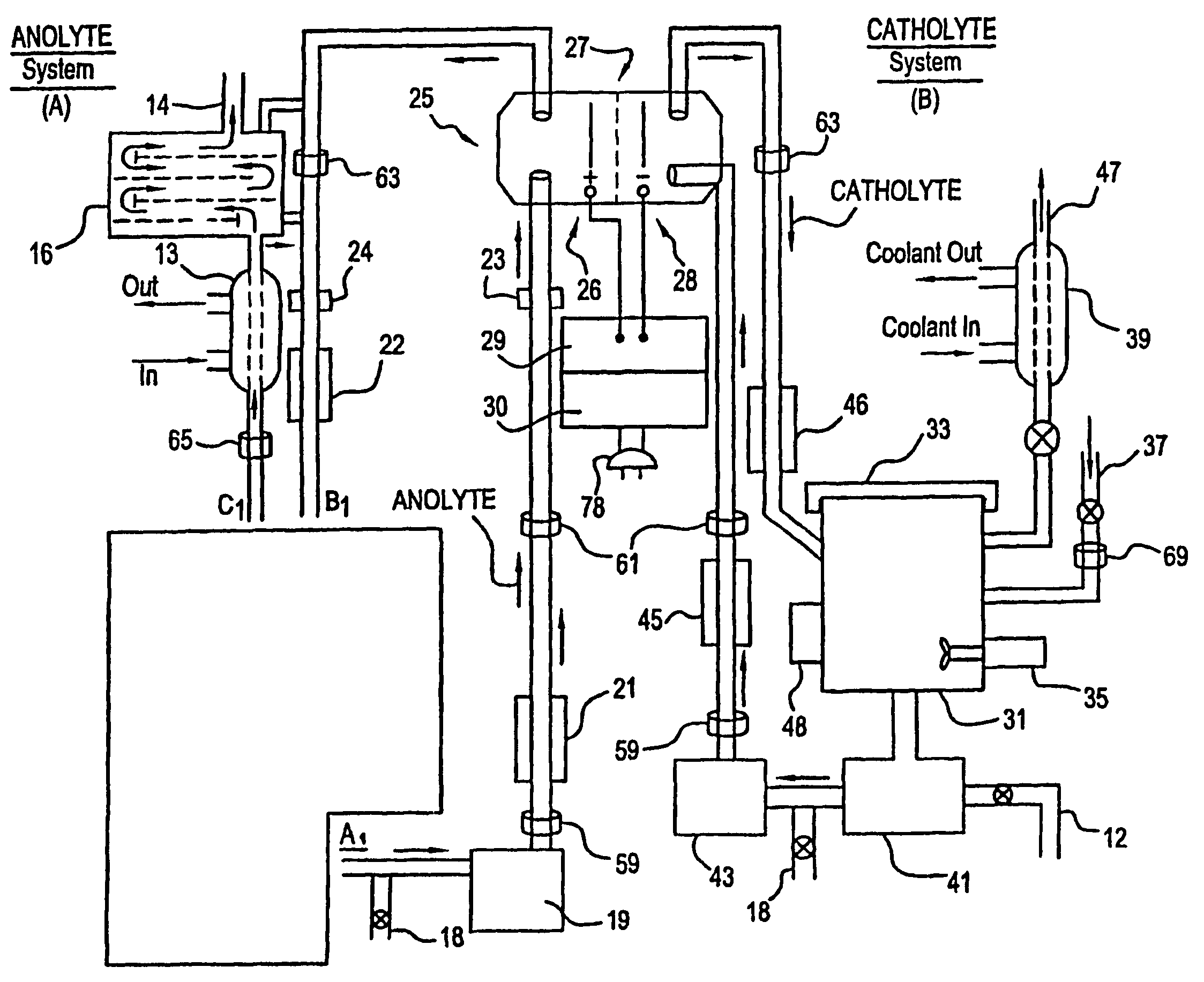
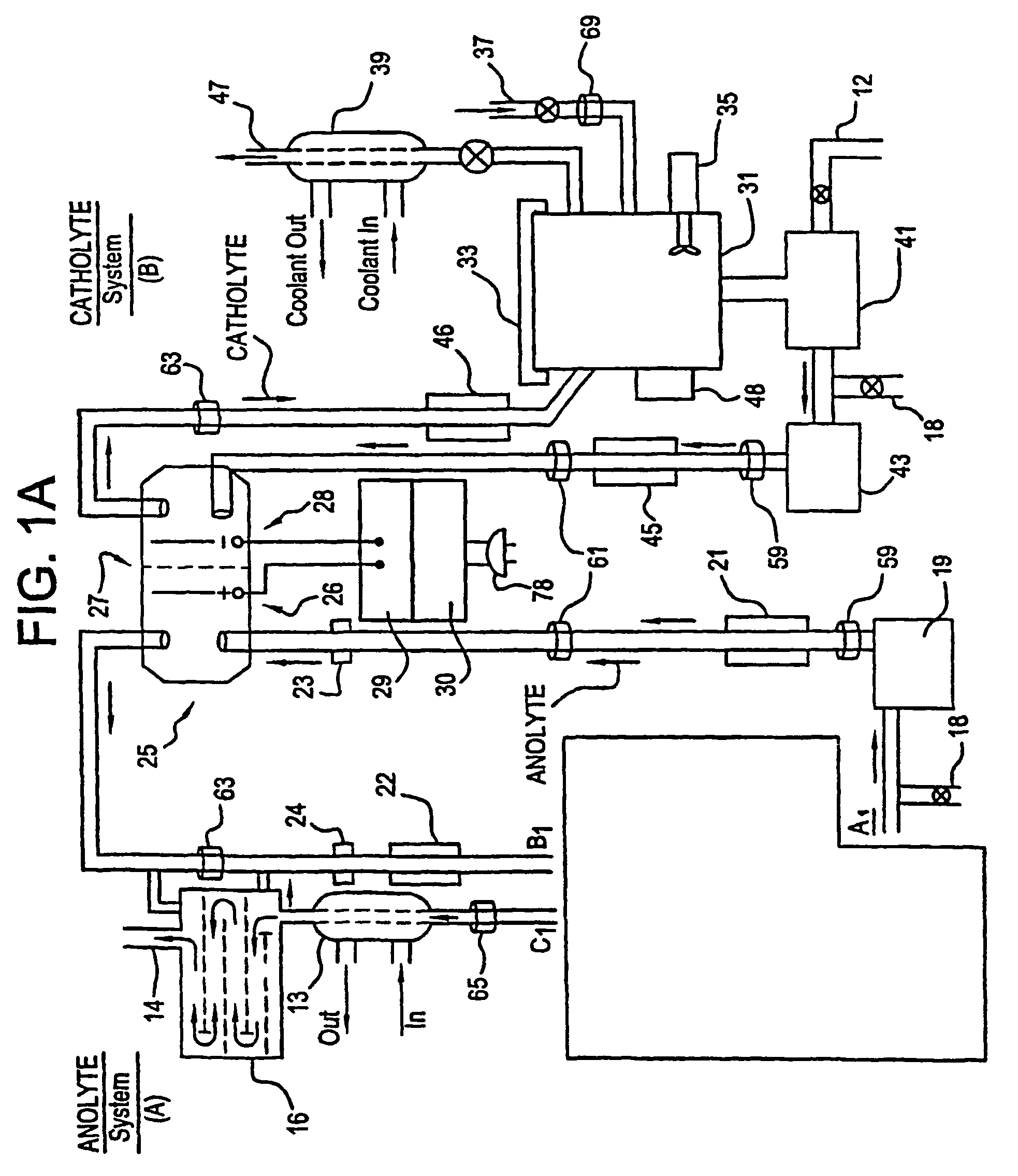
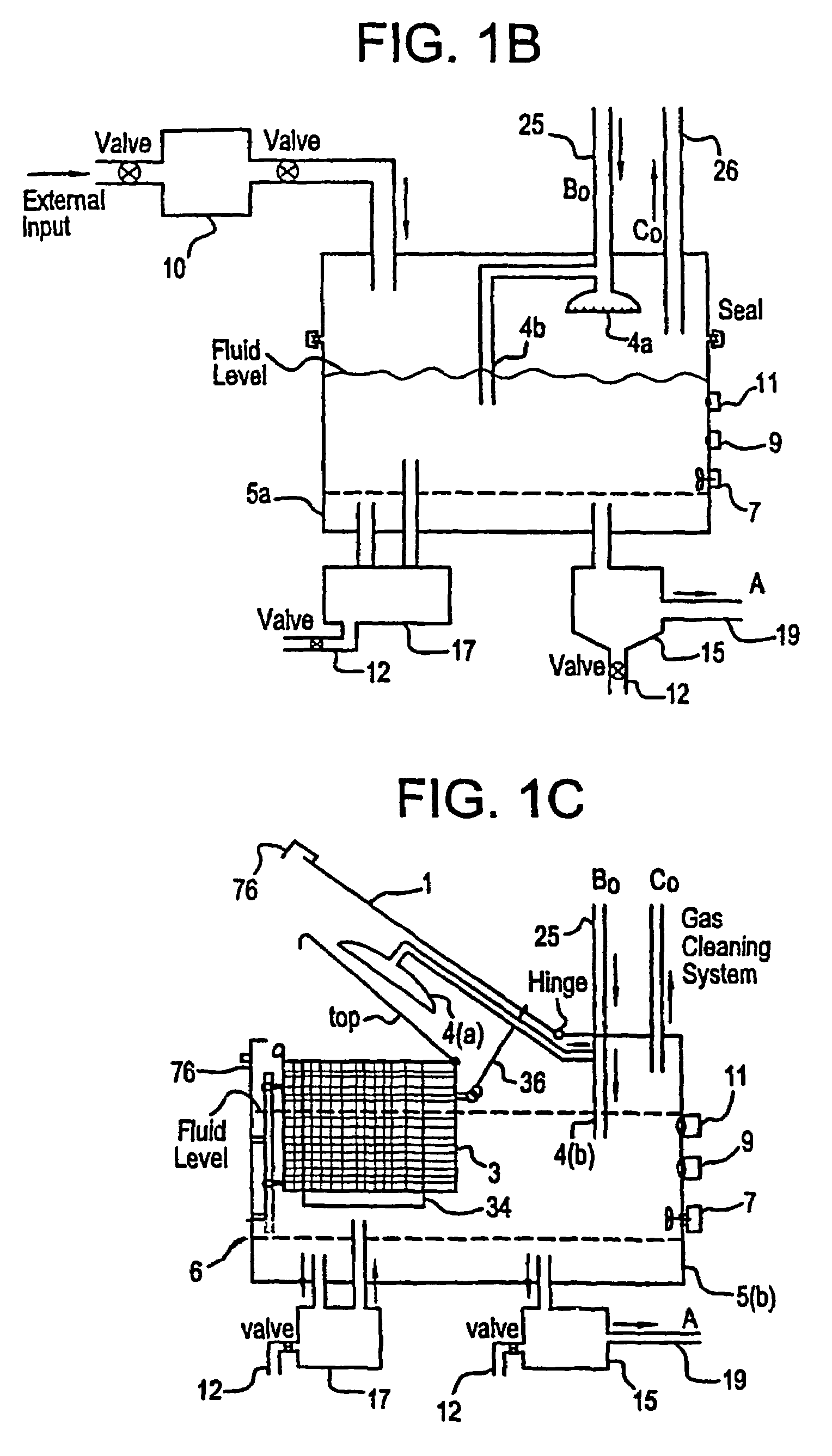
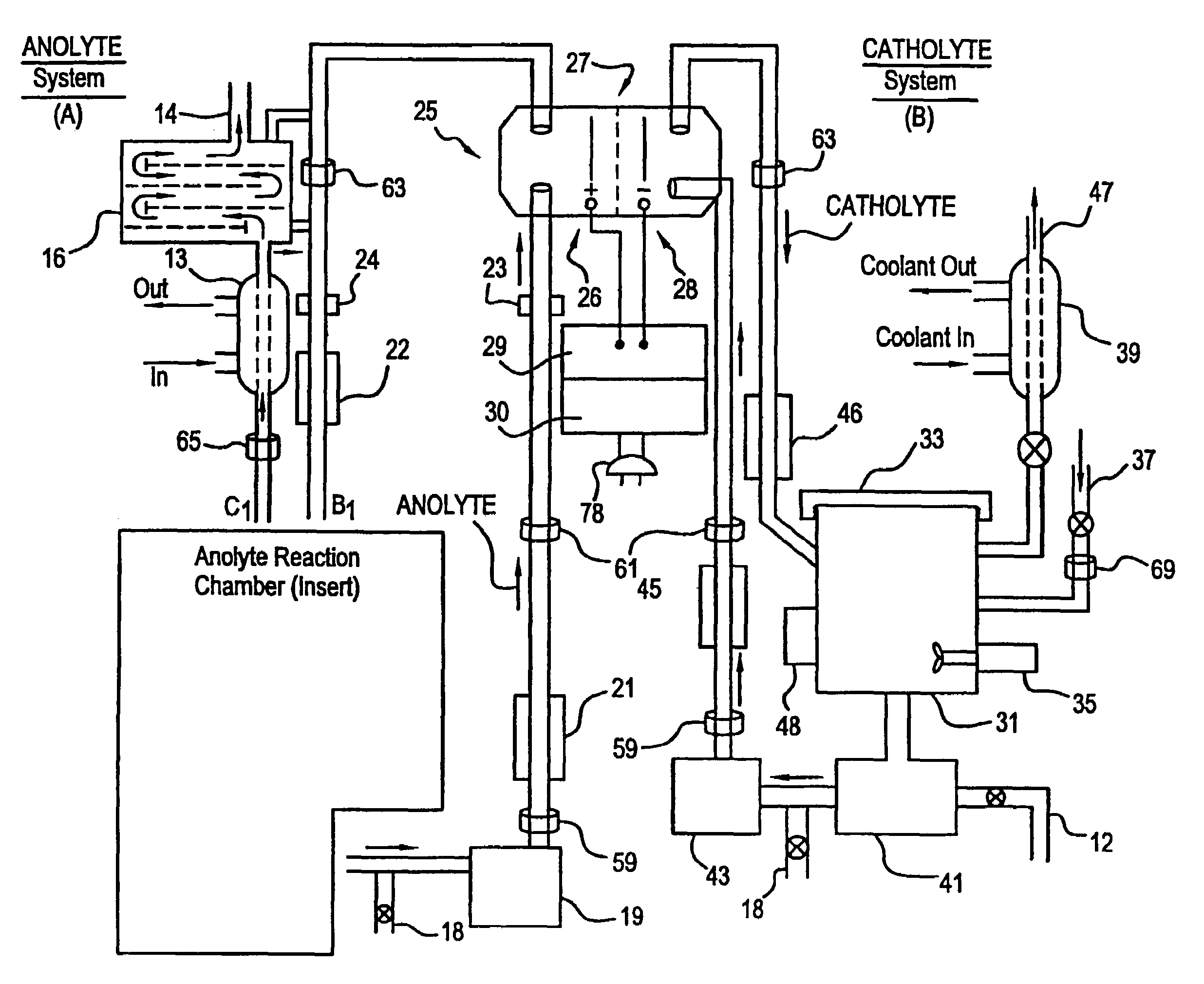
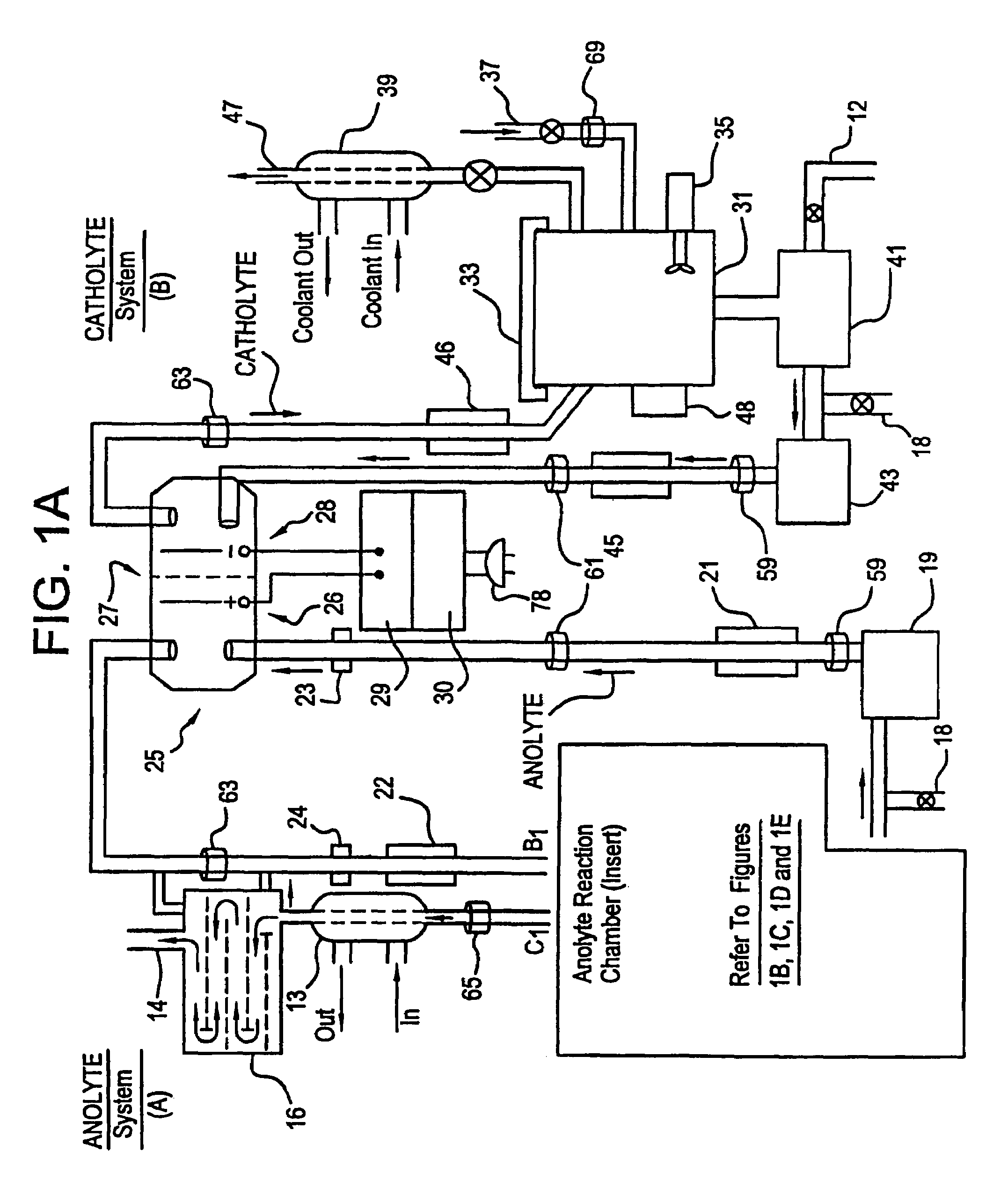
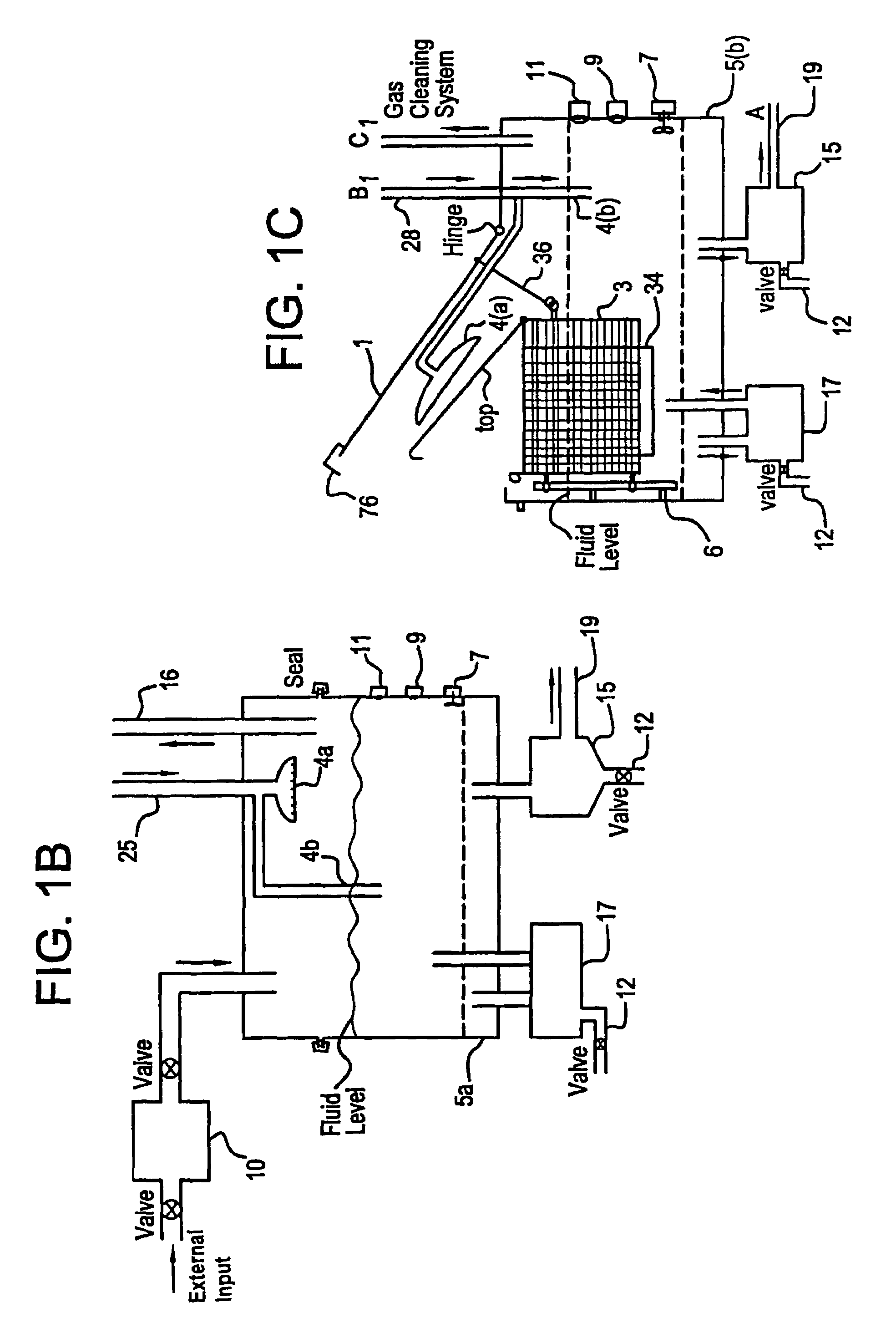
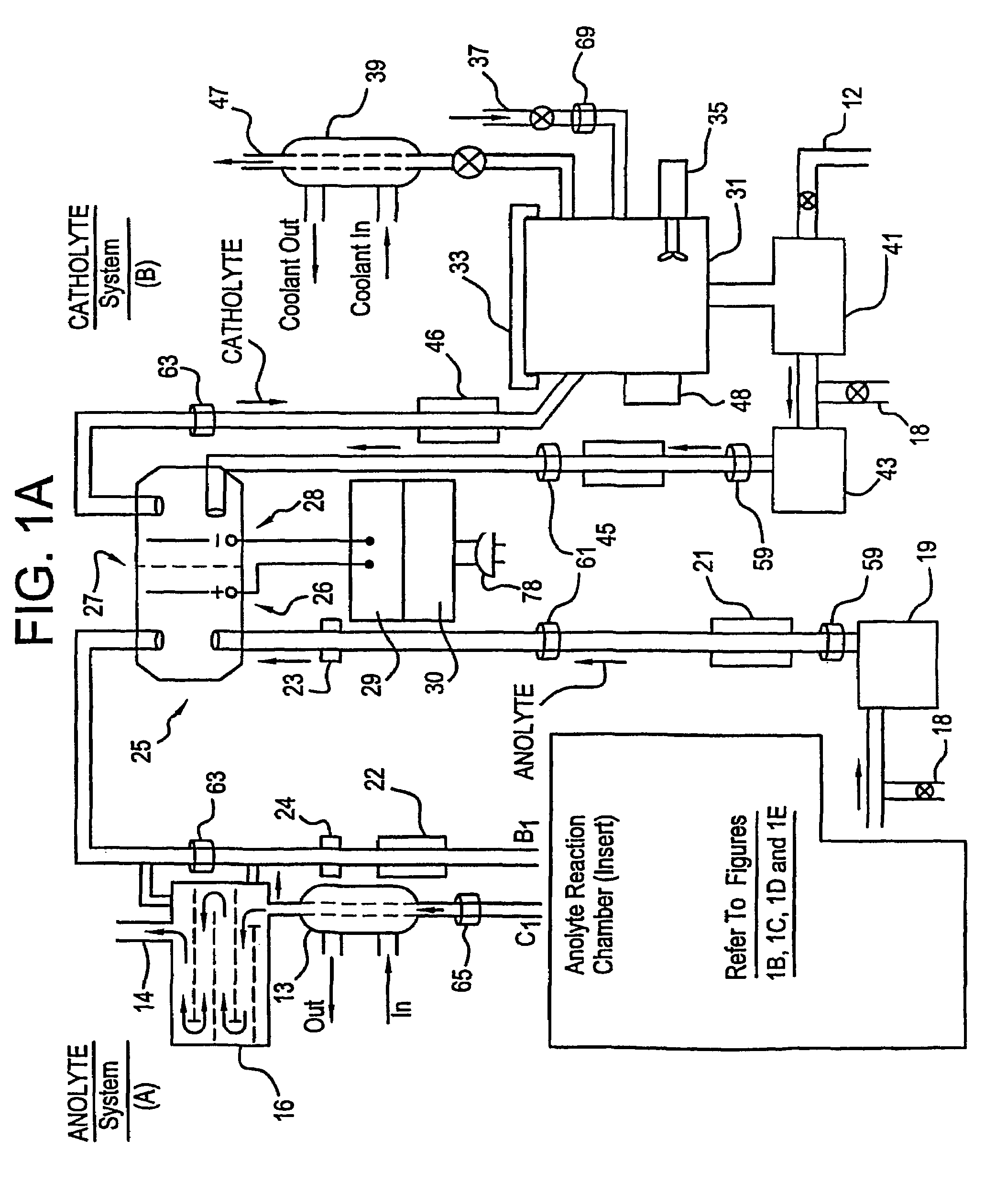
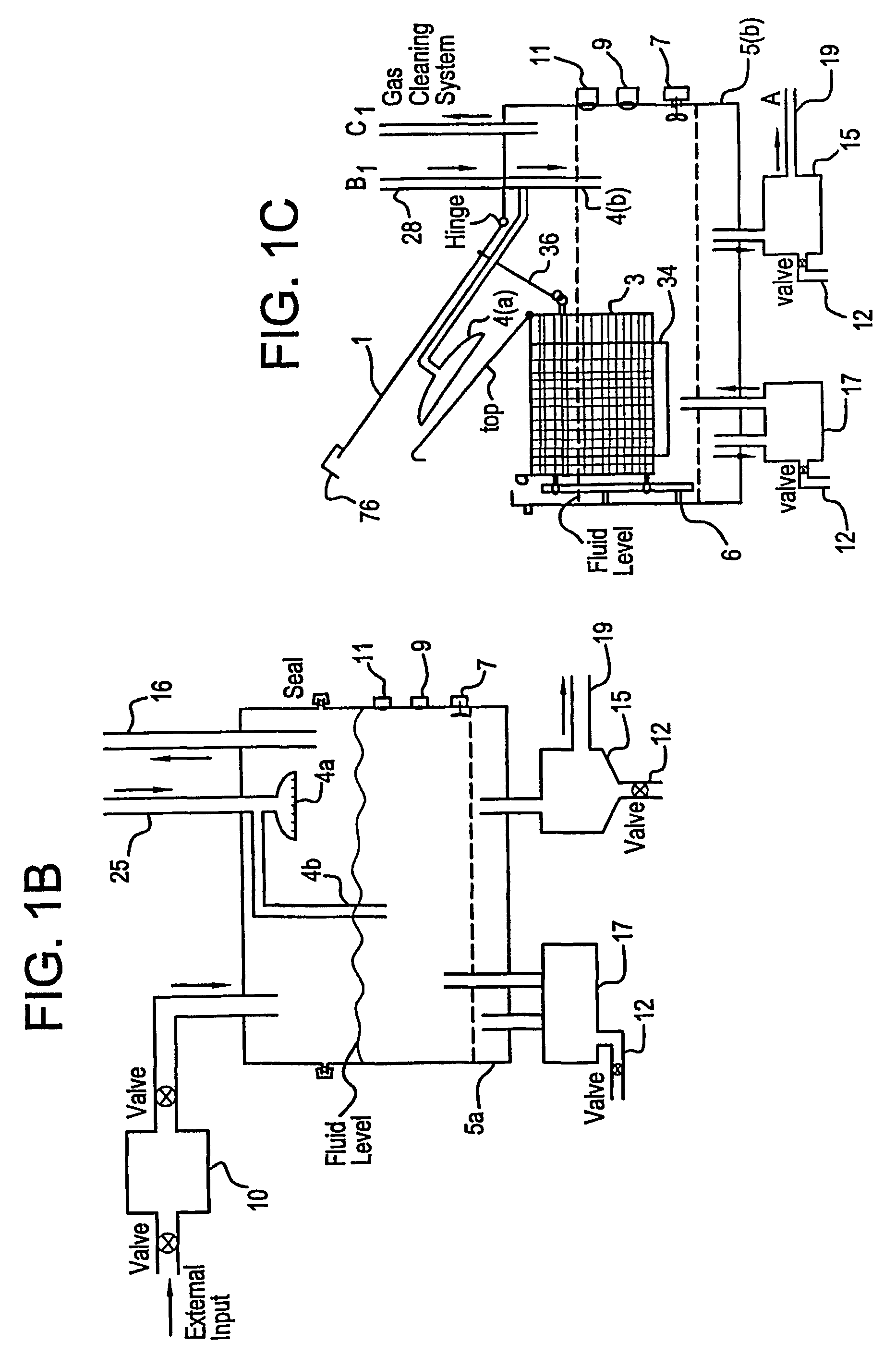
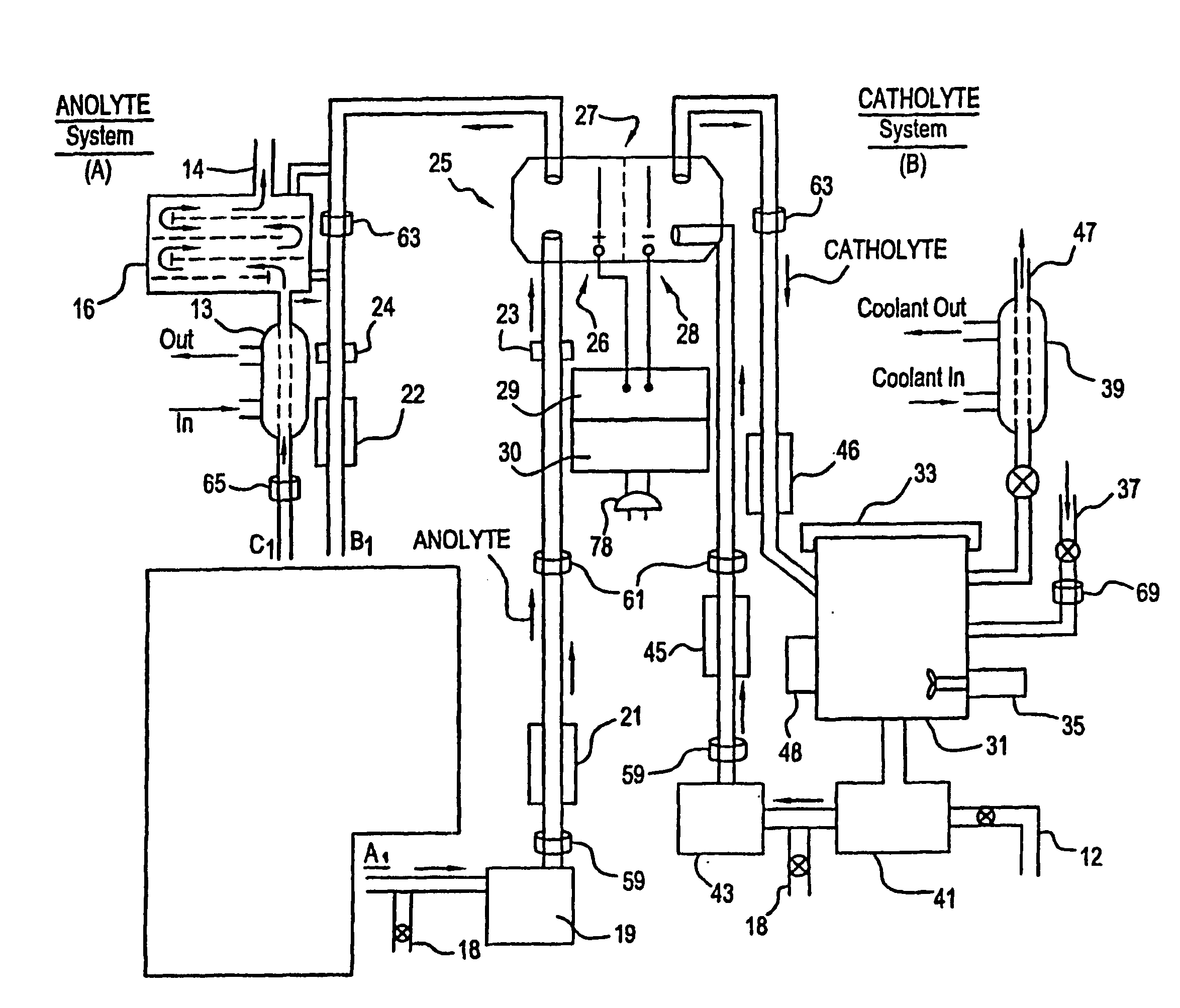
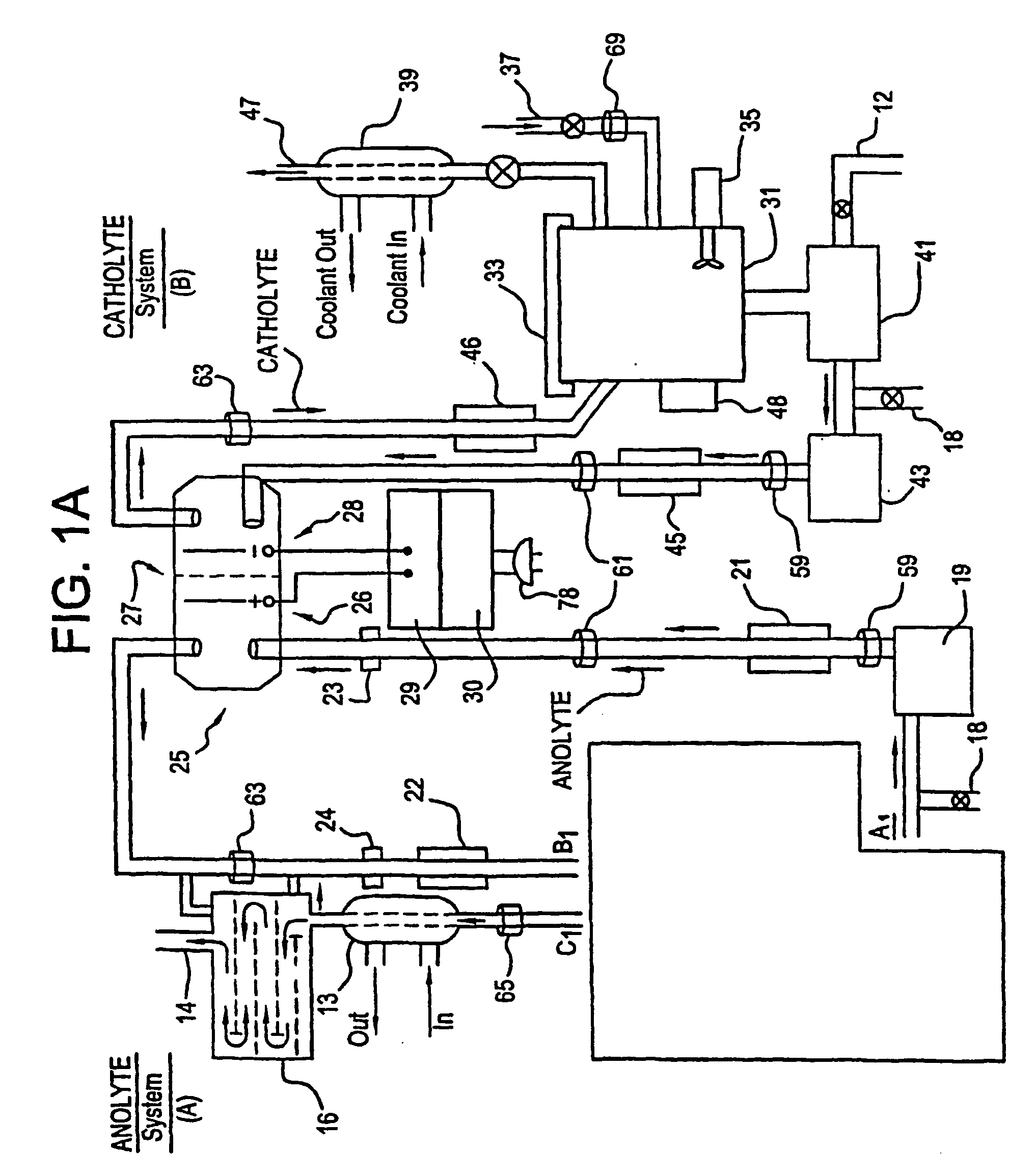
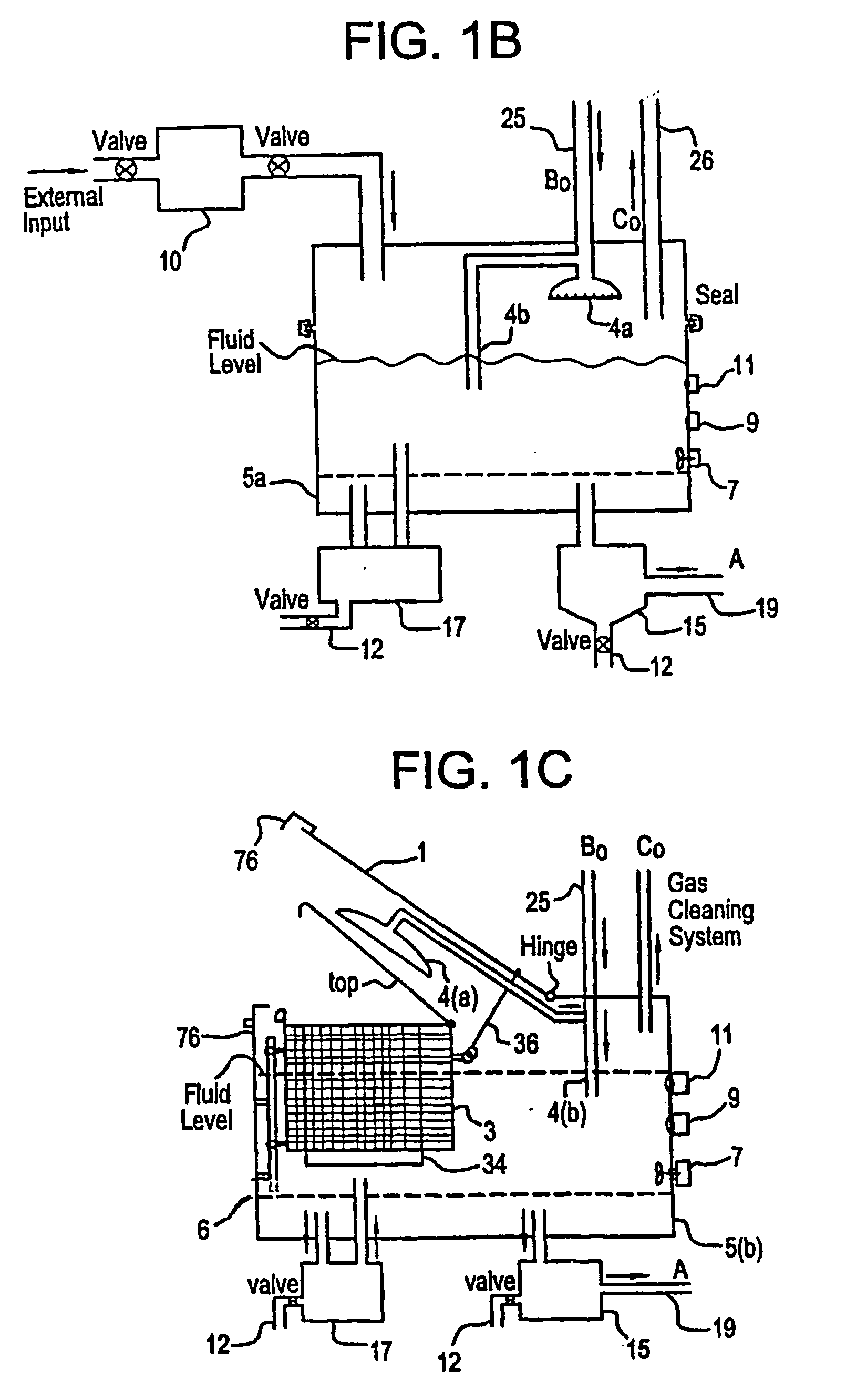
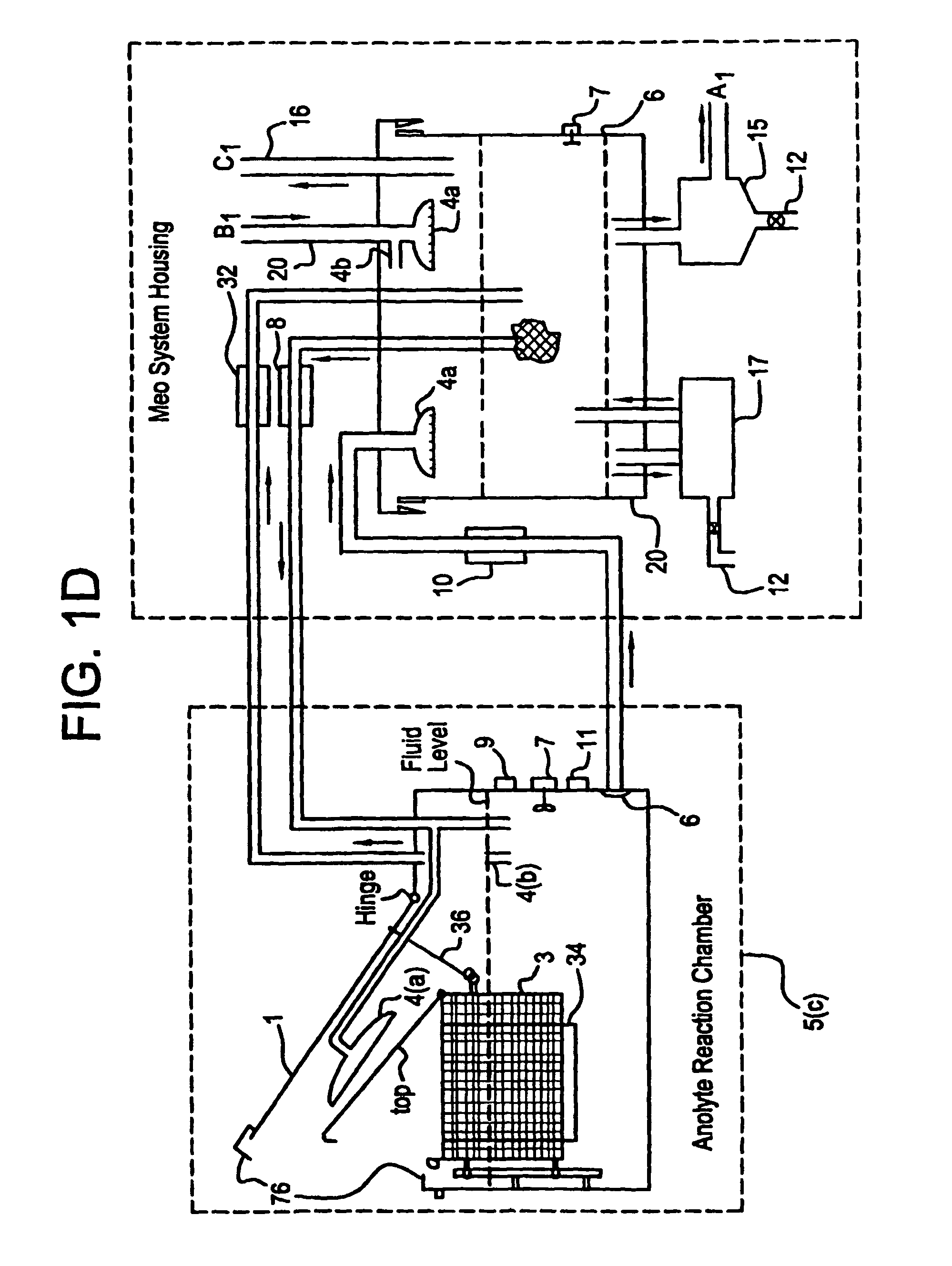
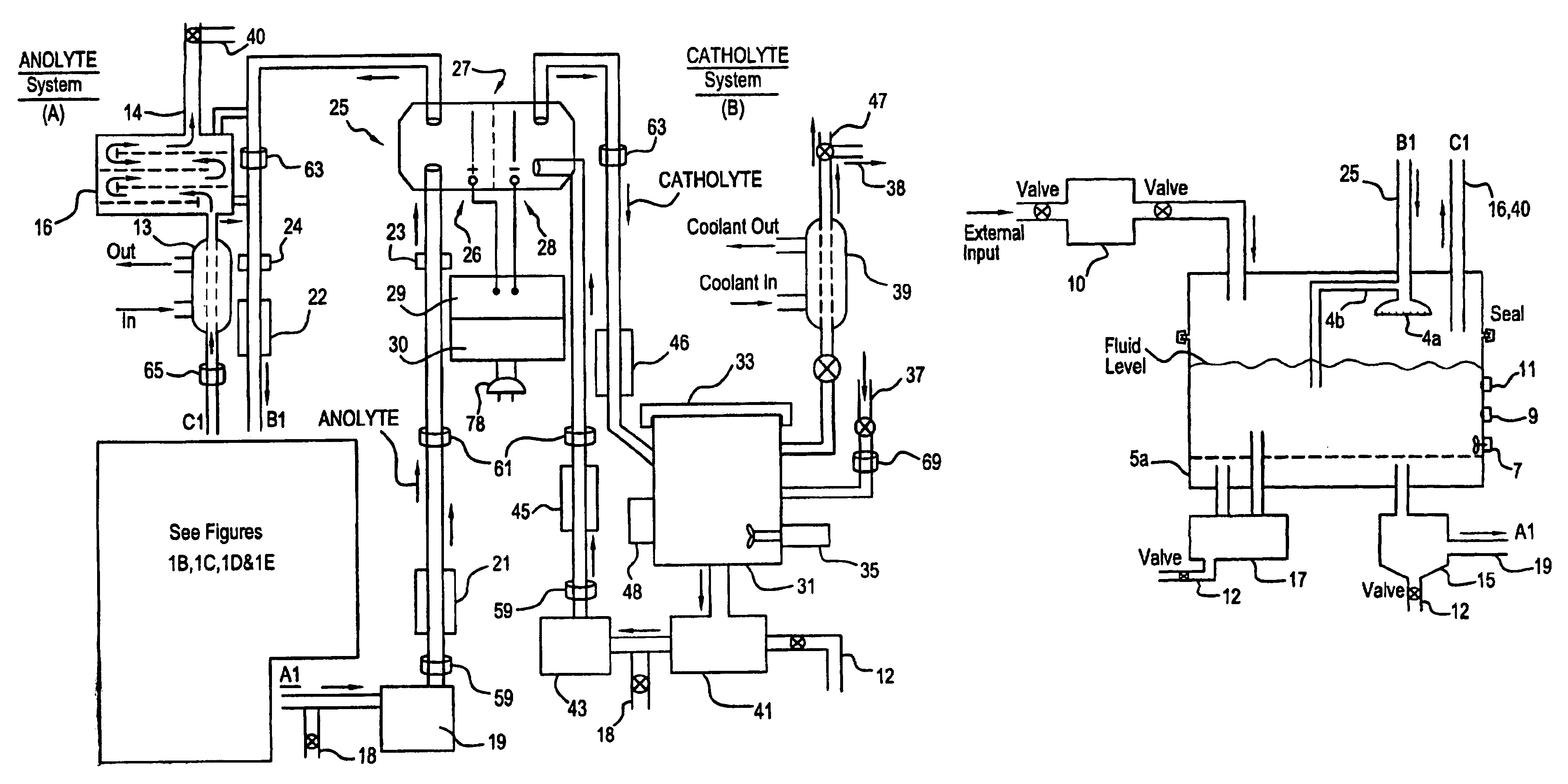
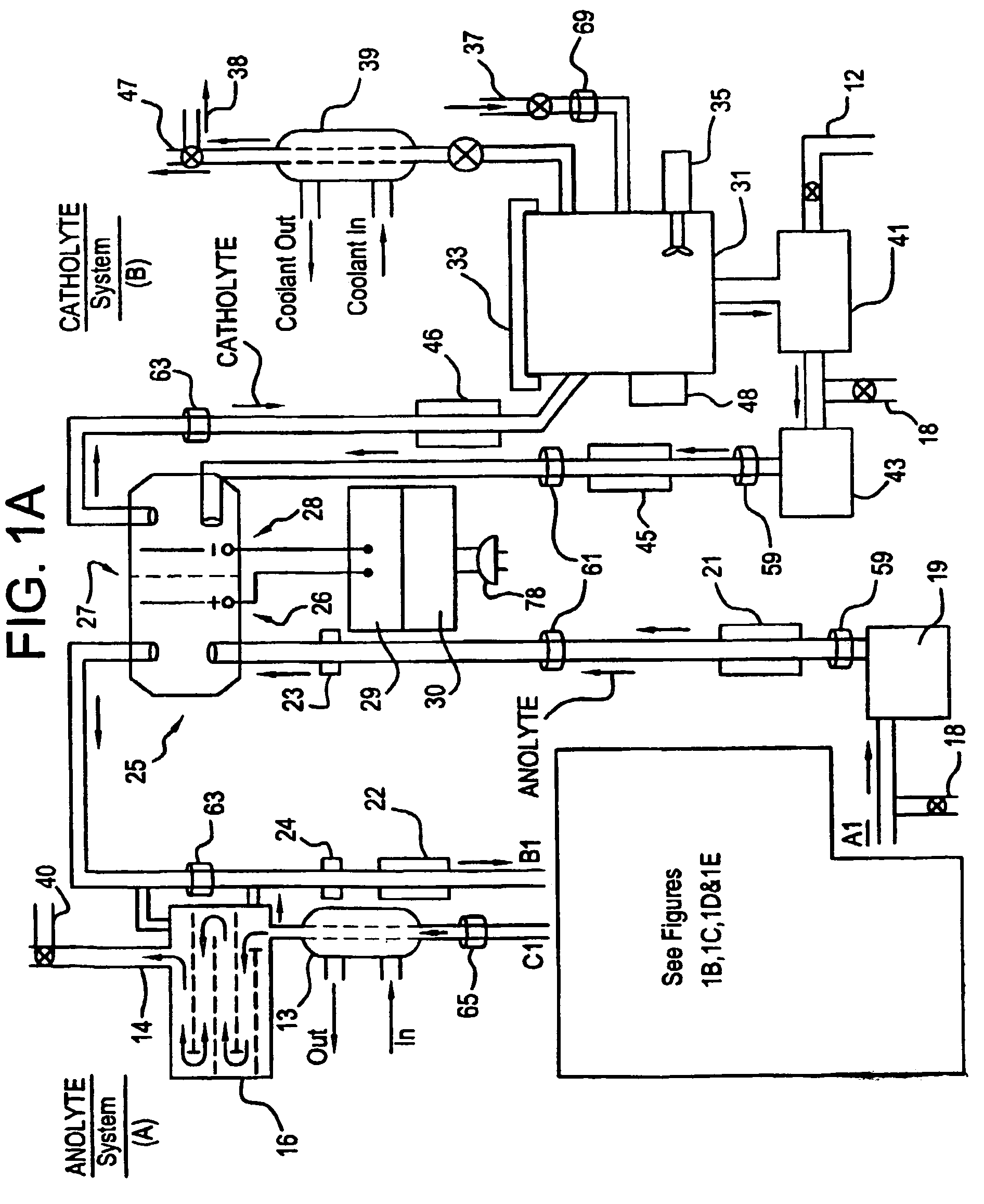
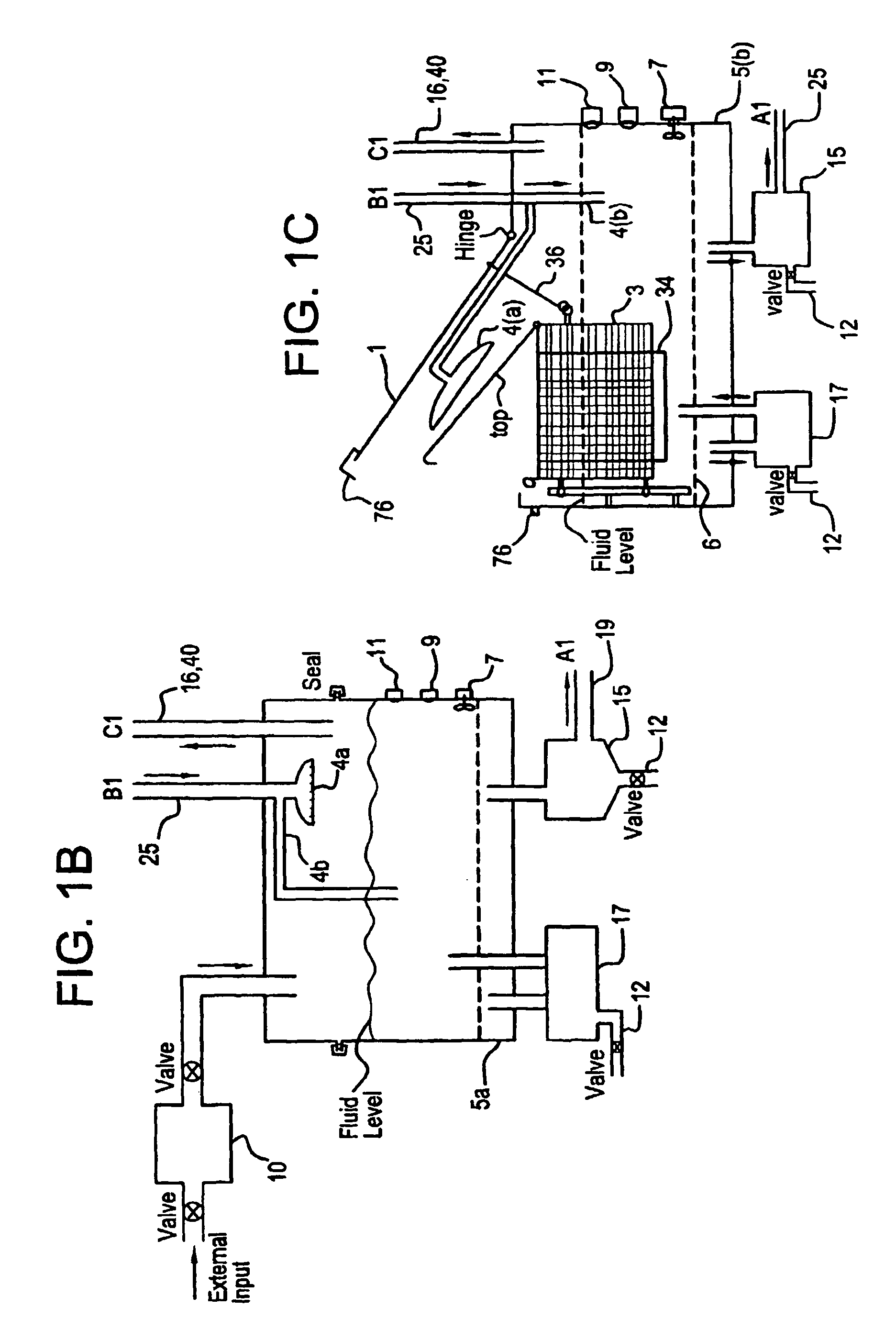
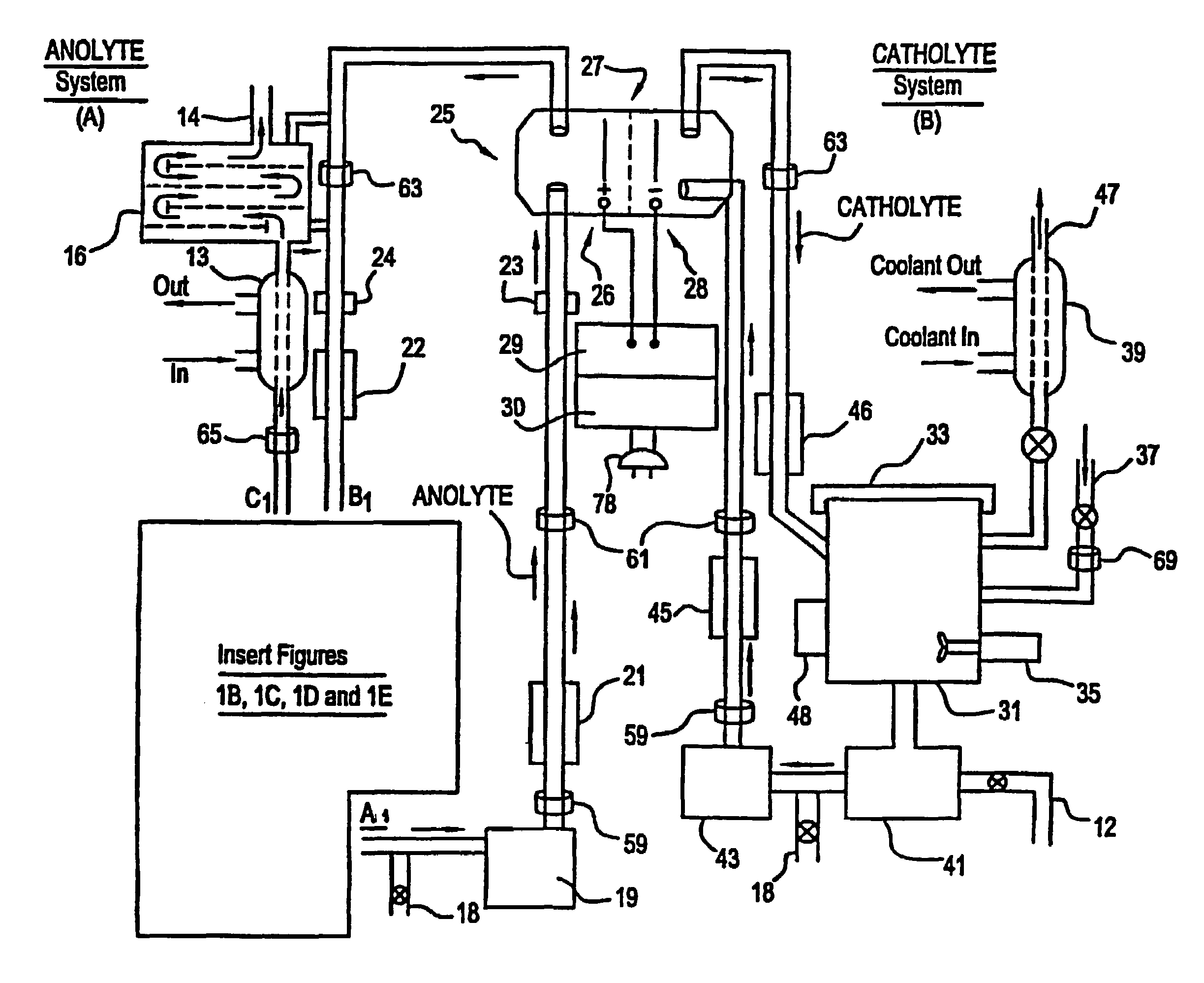
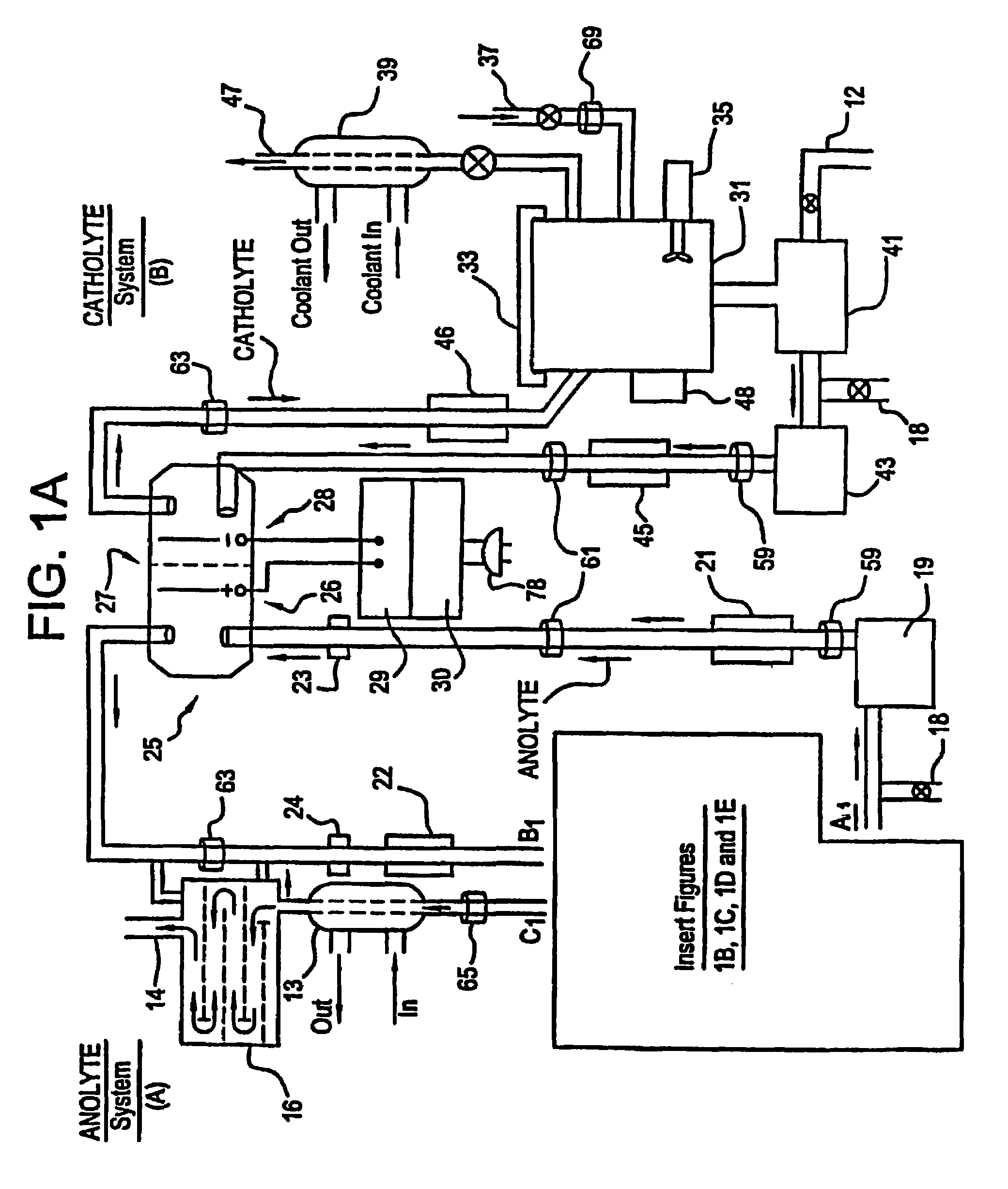
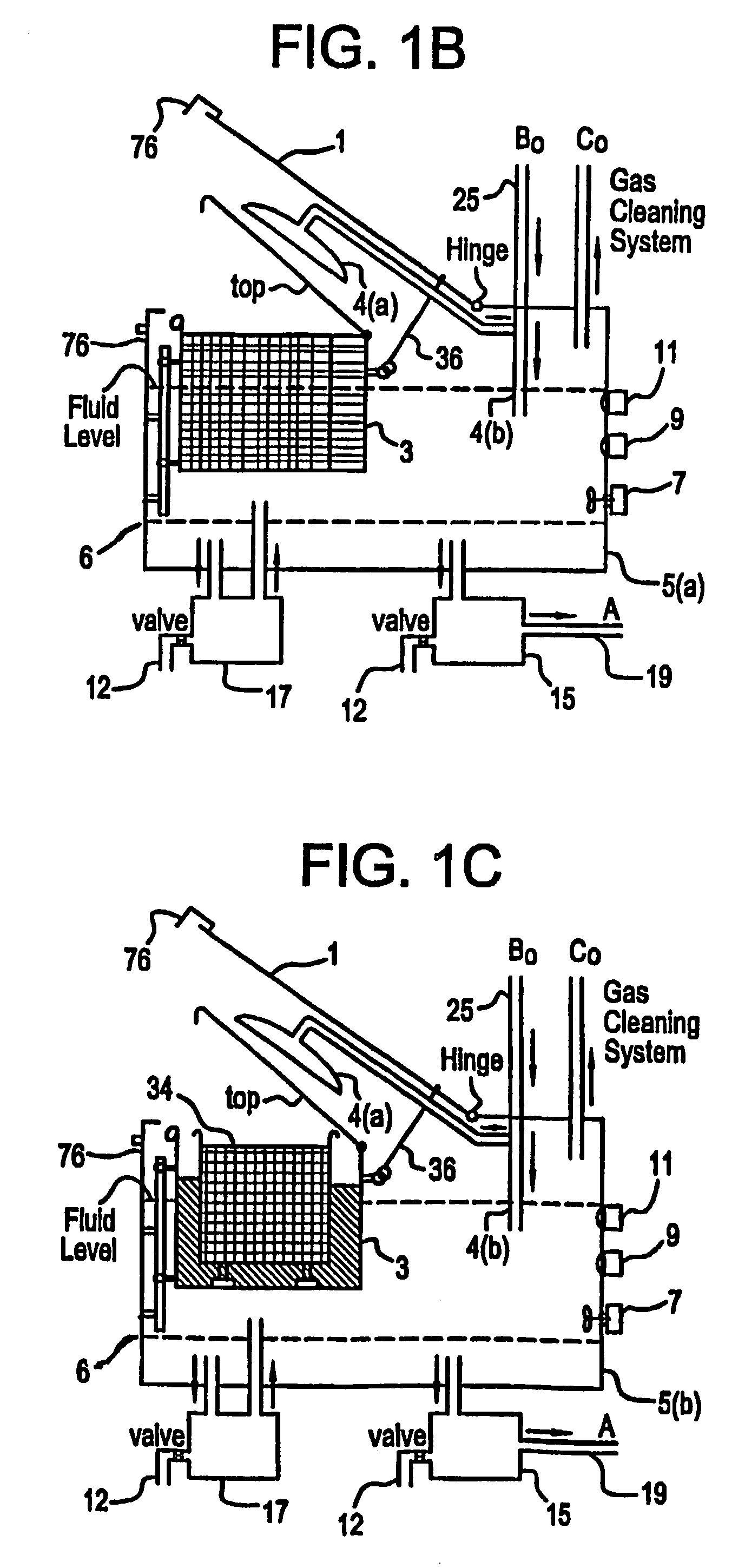
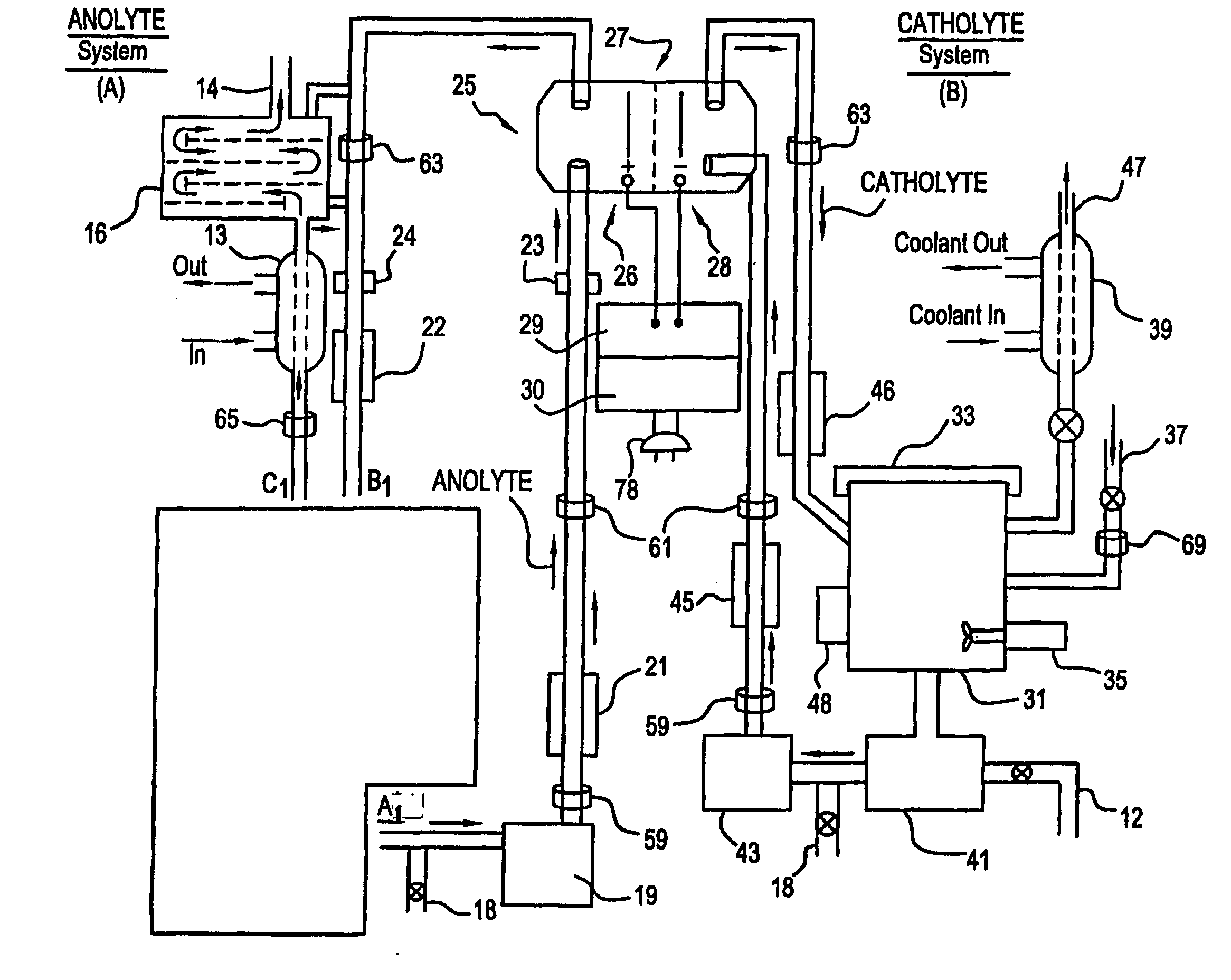
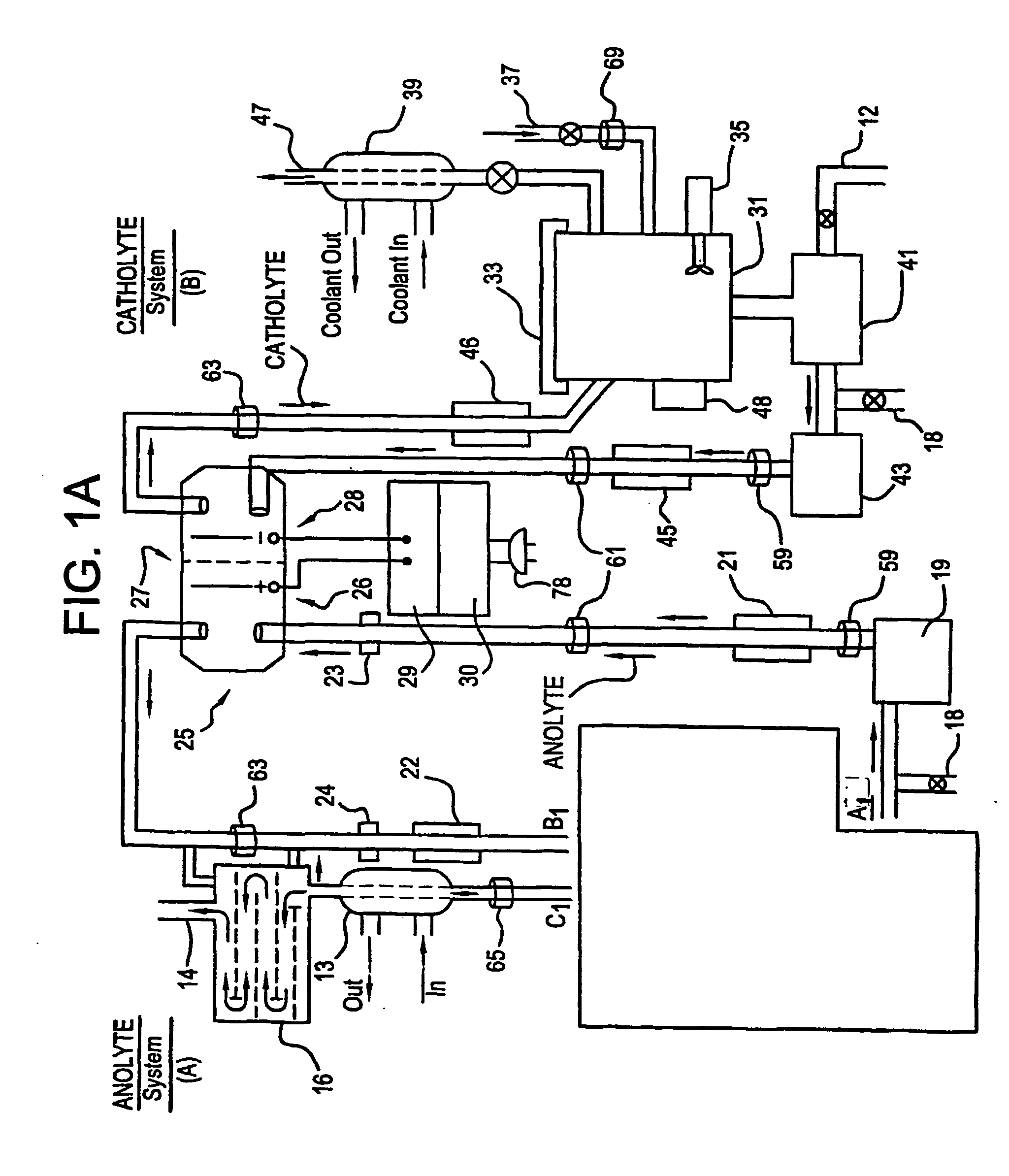
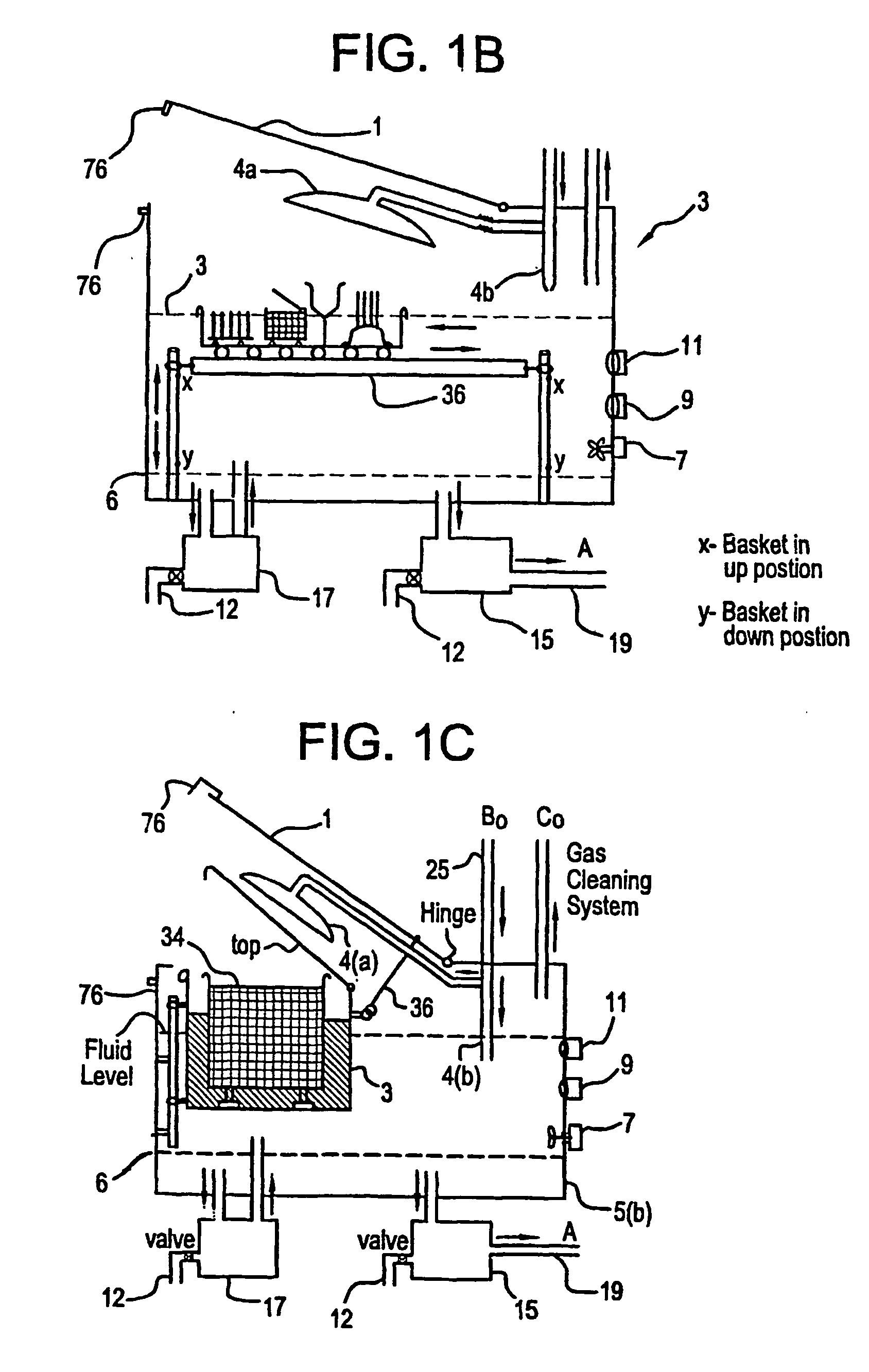
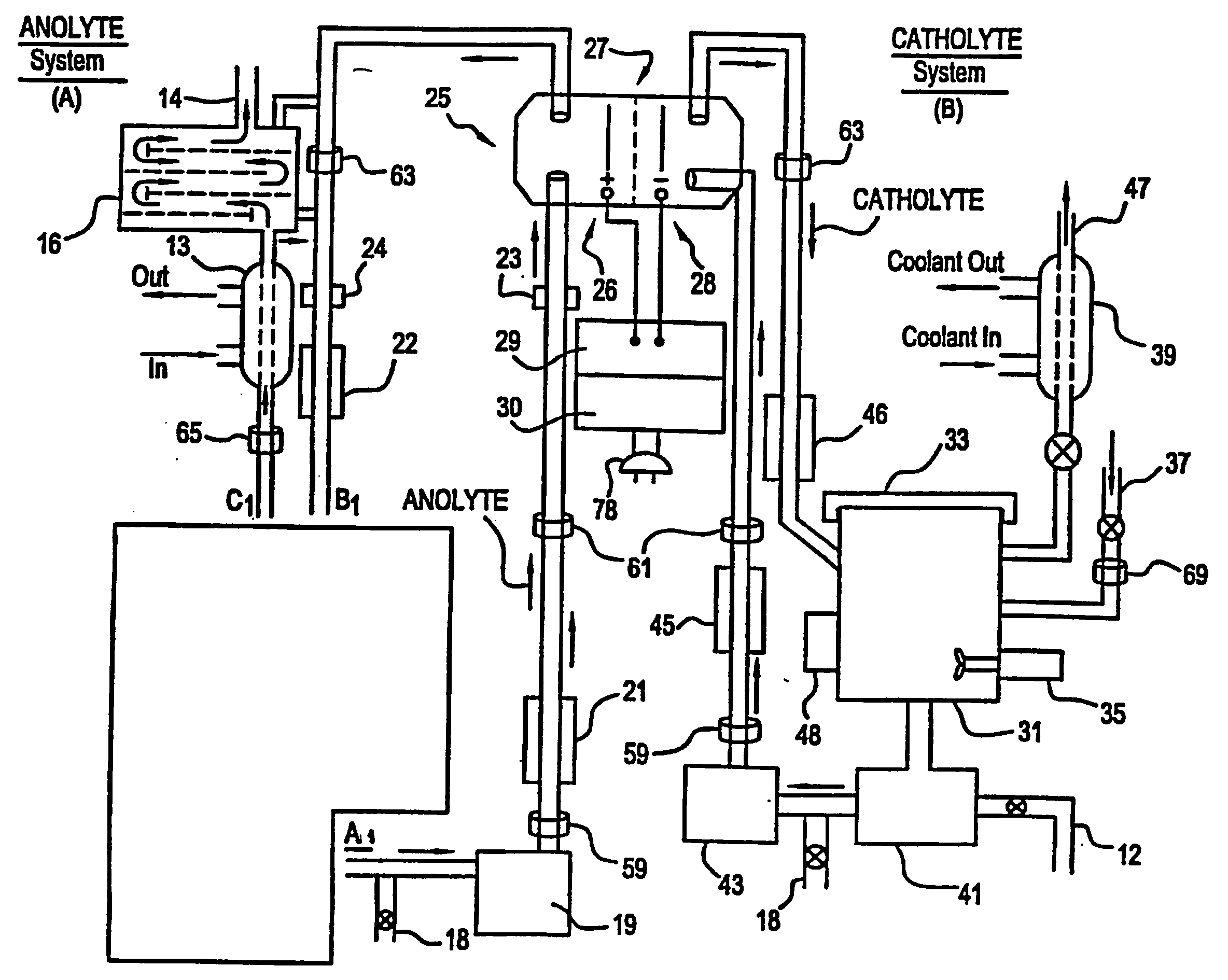
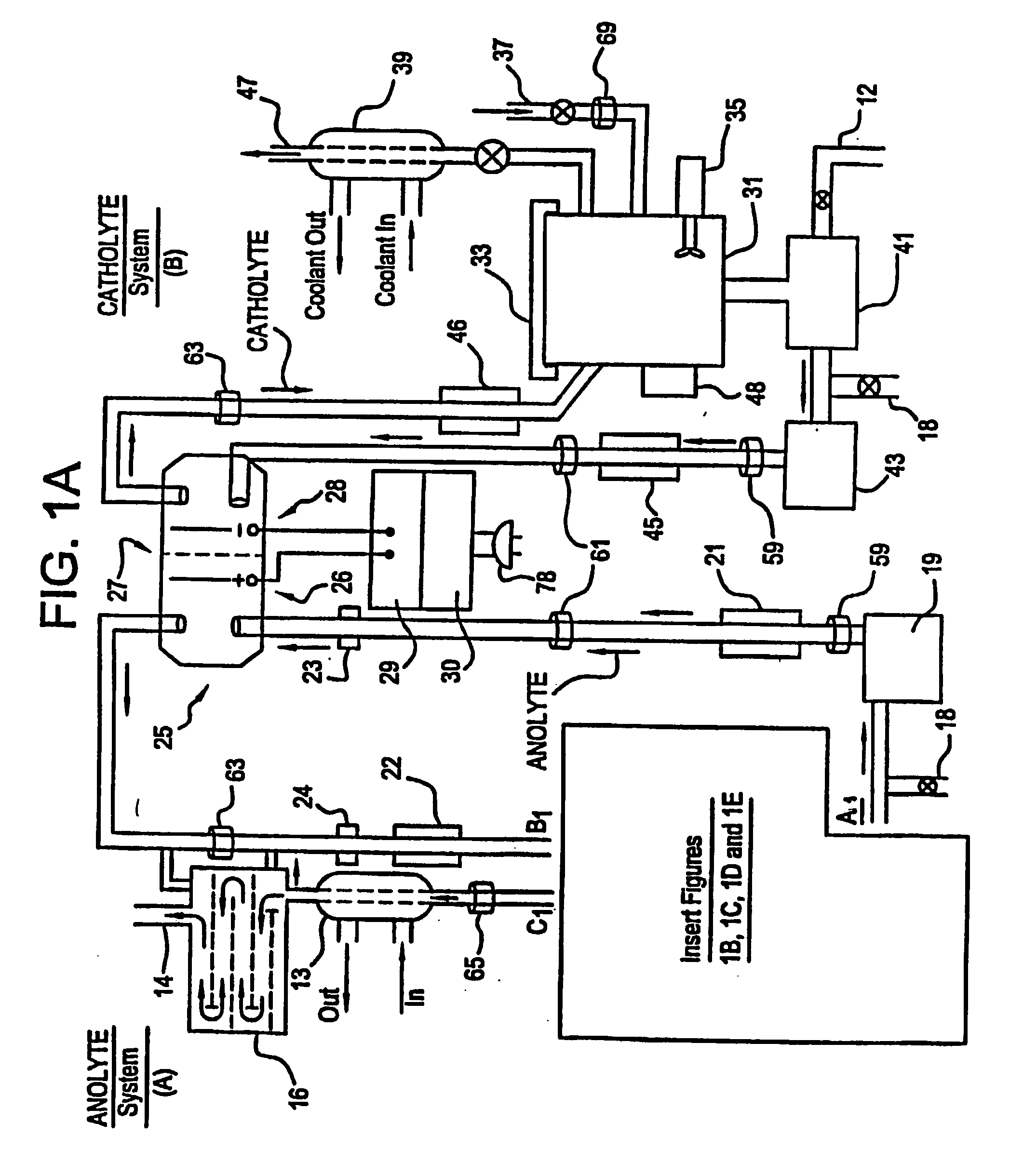
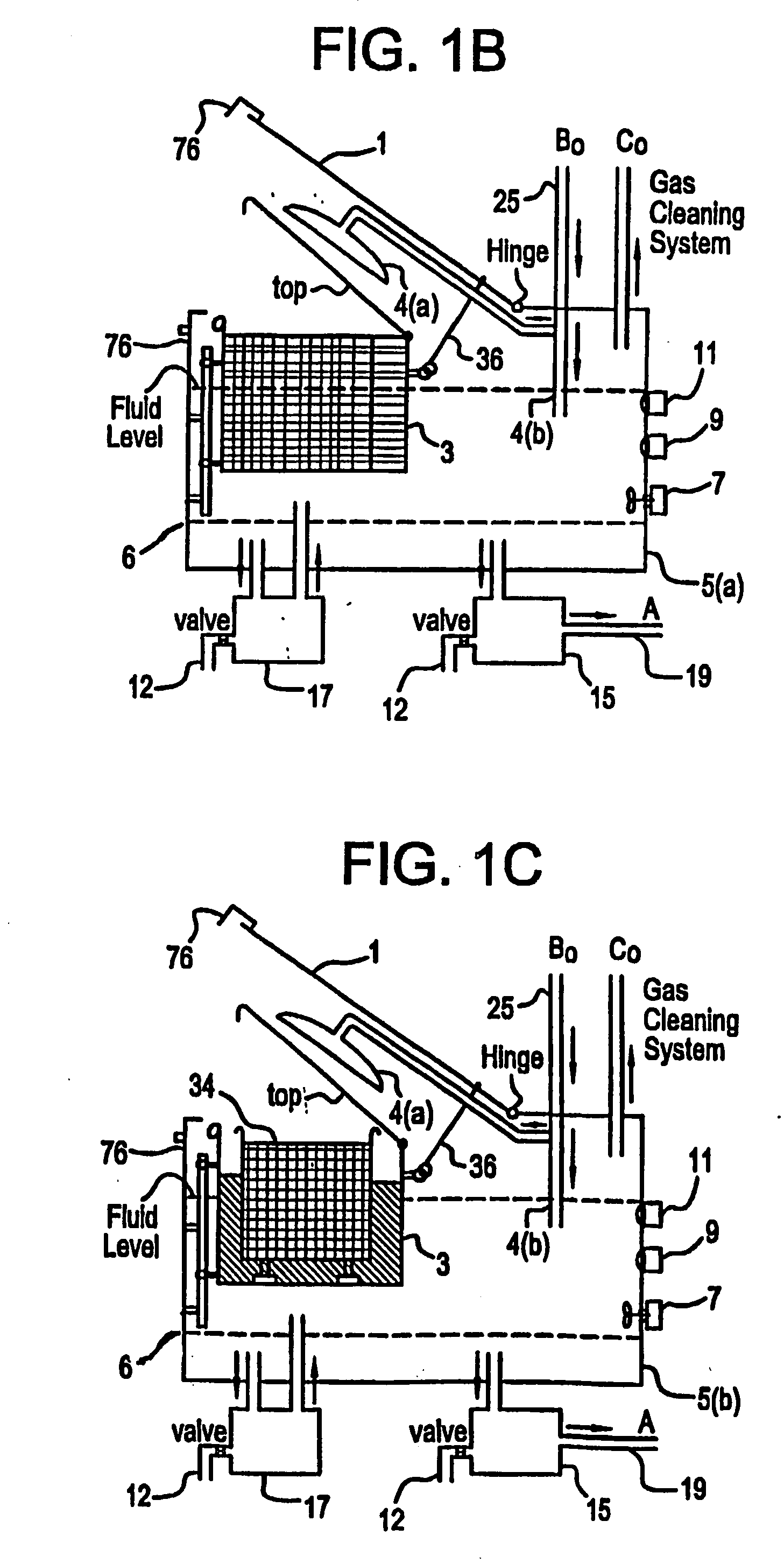
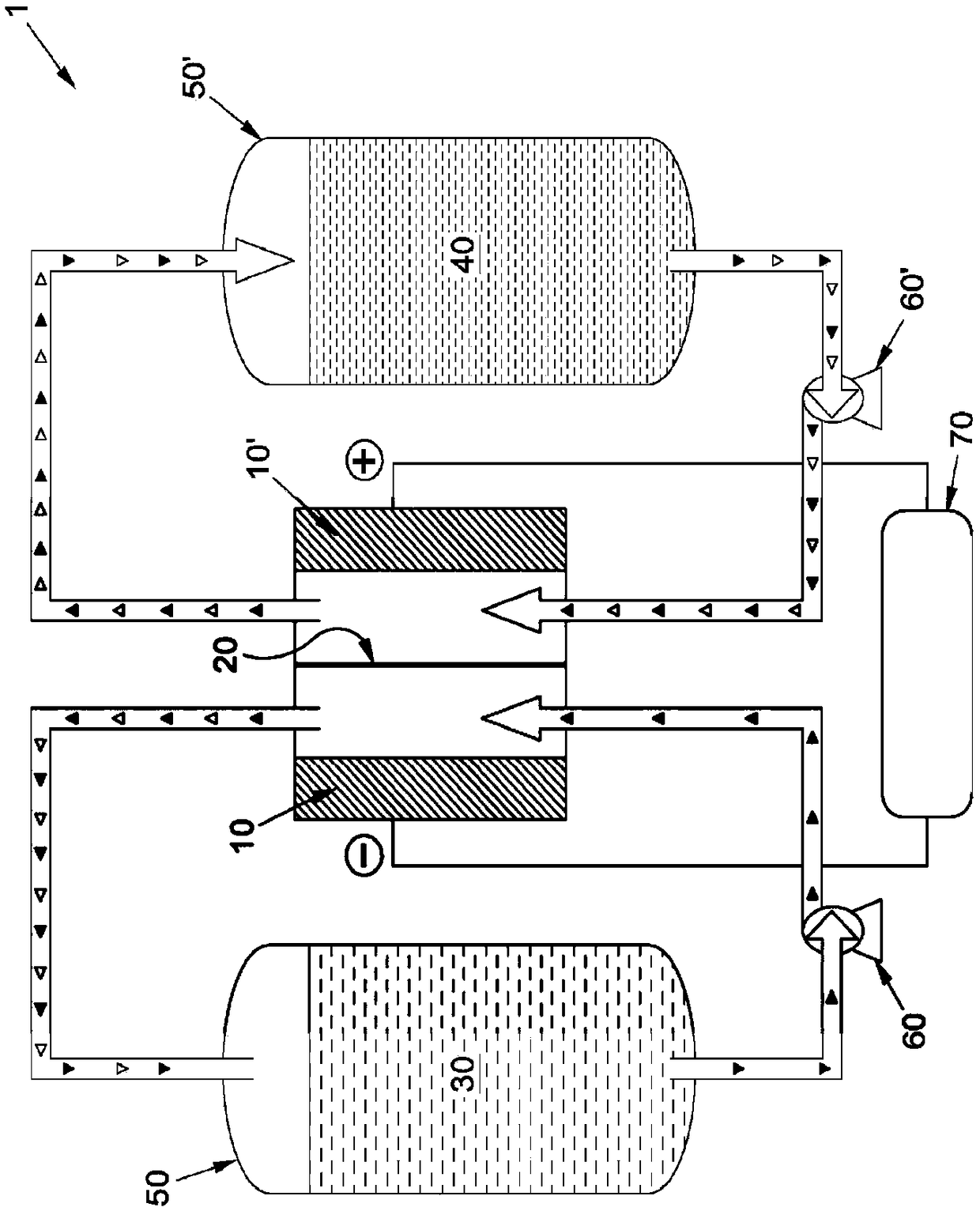
Apparatus and process for mediated electrochemical oxidation of materials
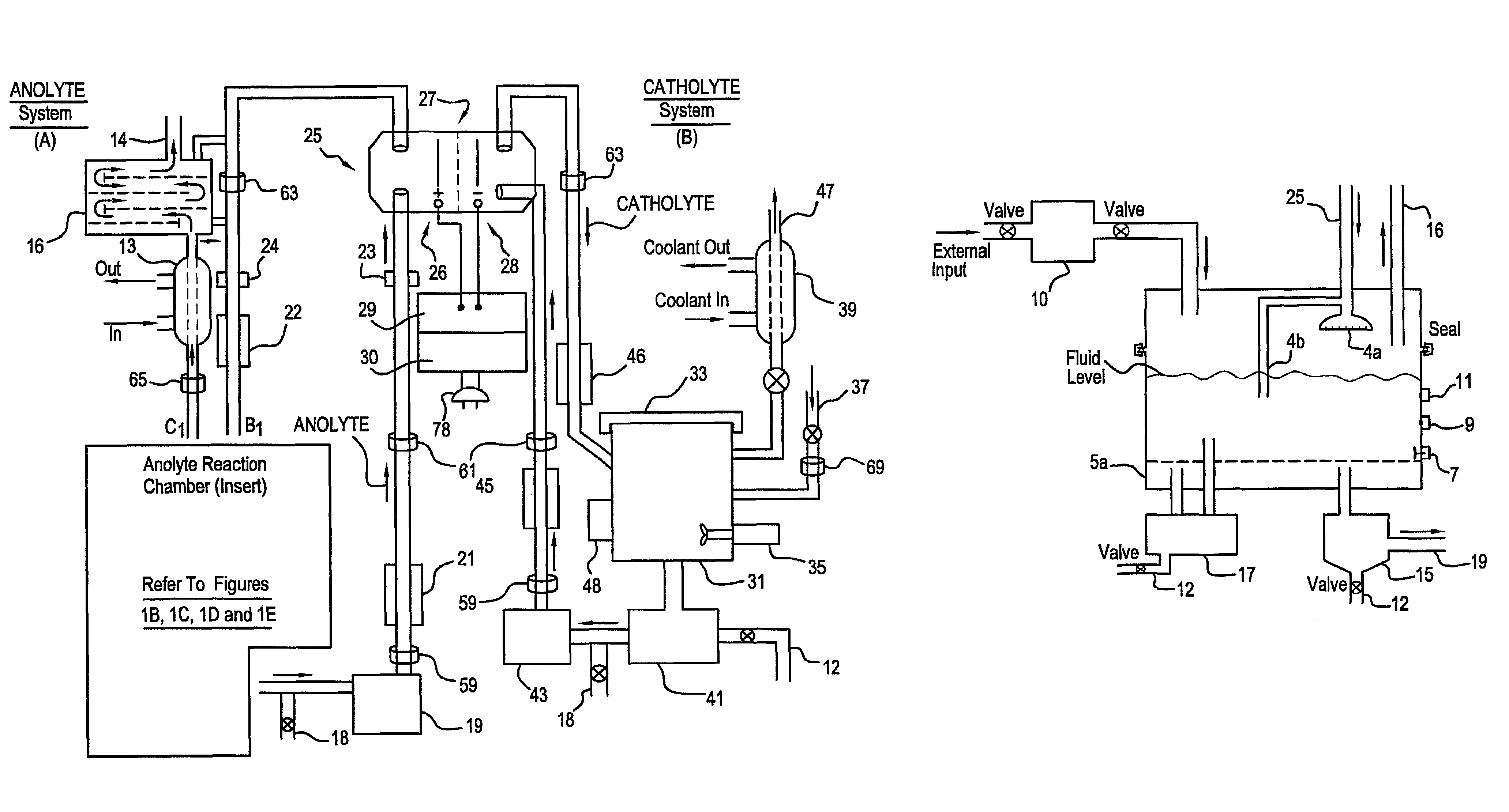
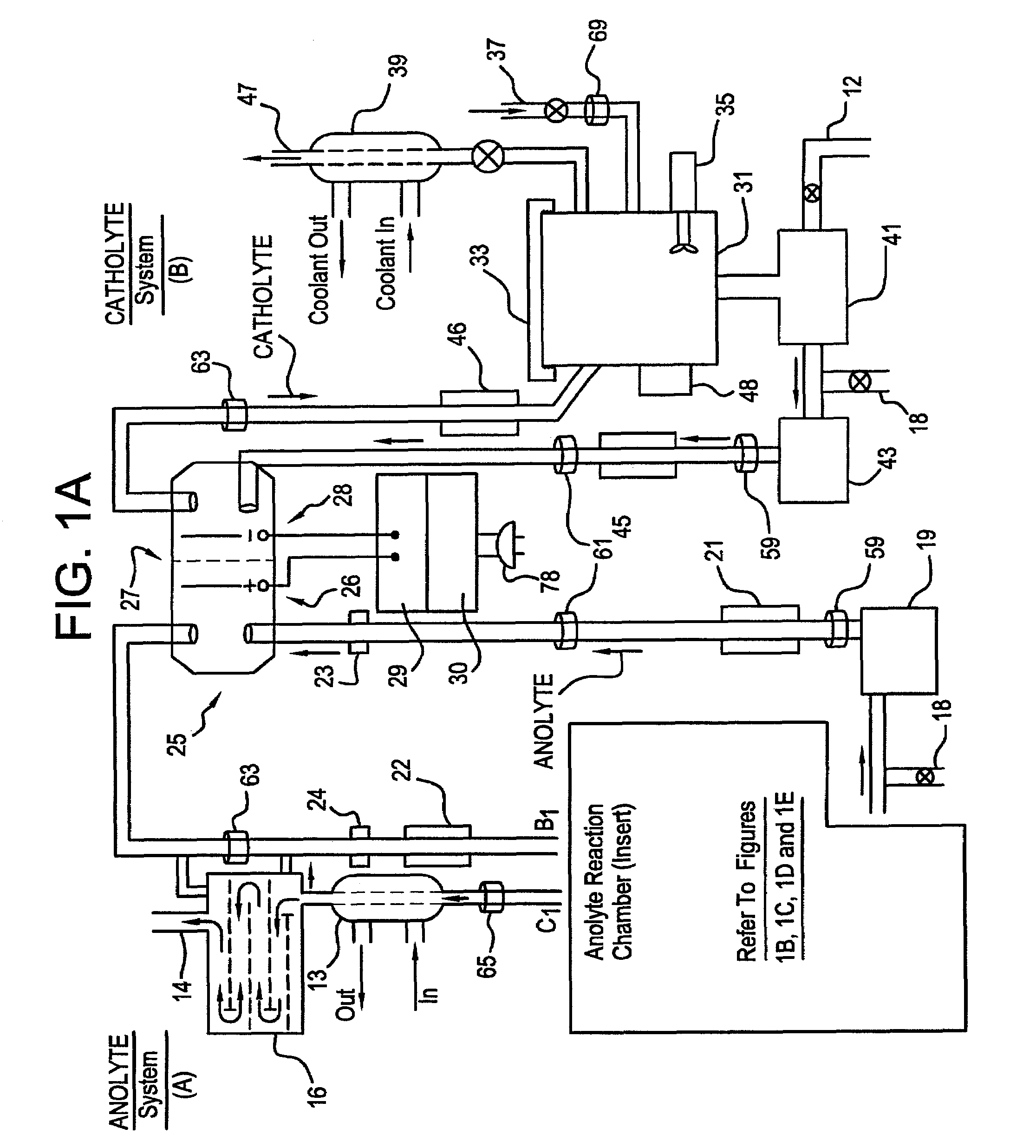
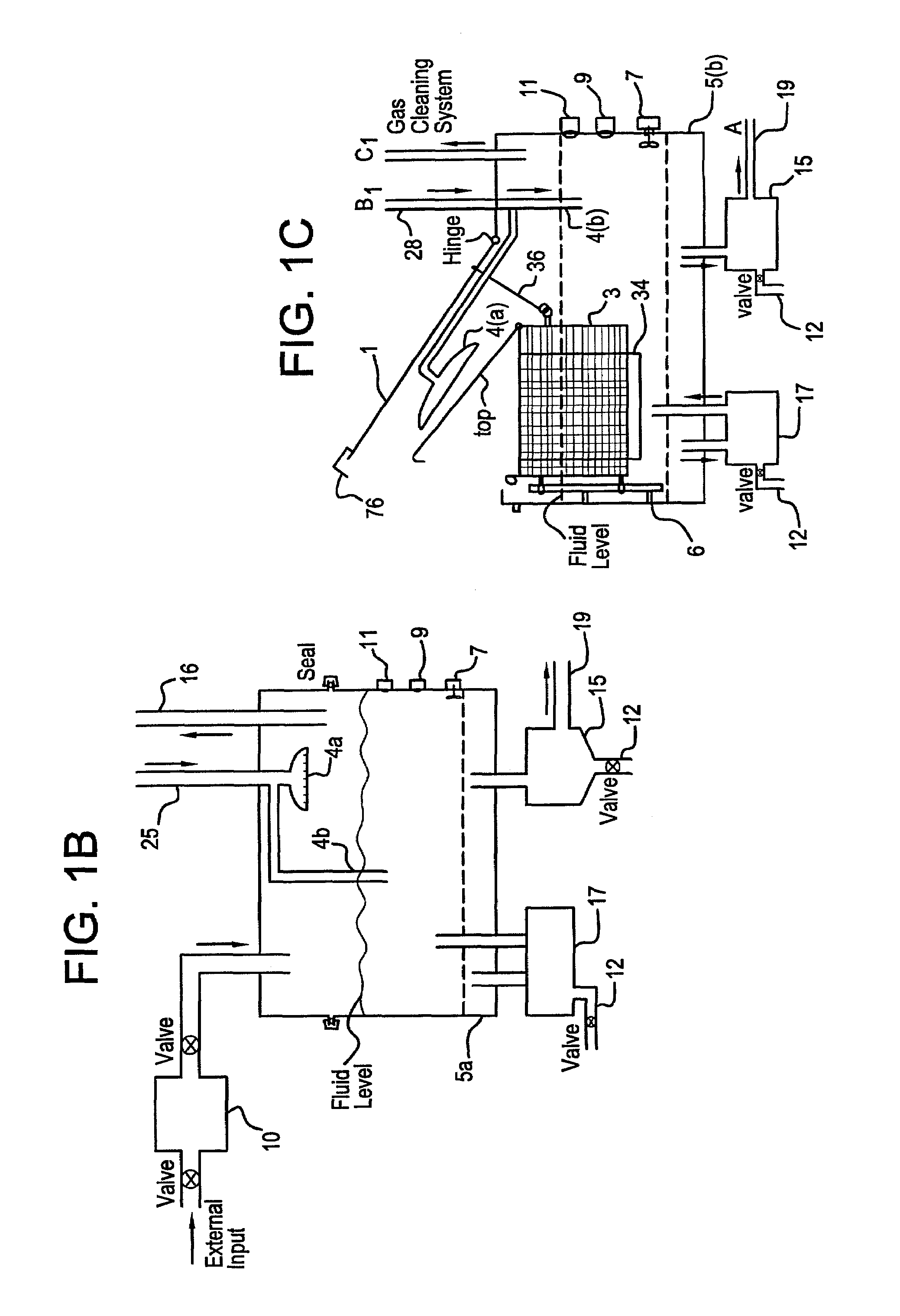
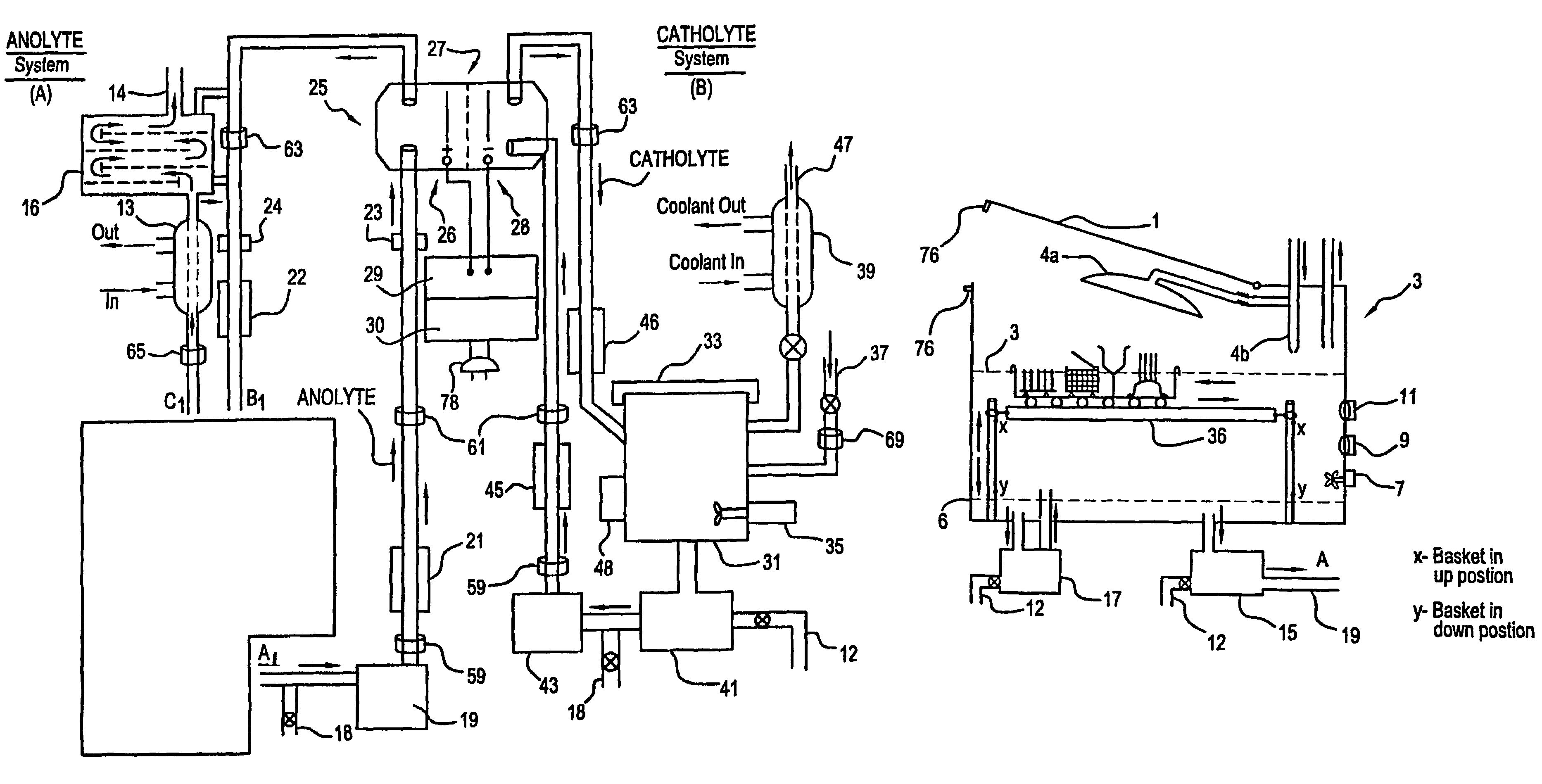
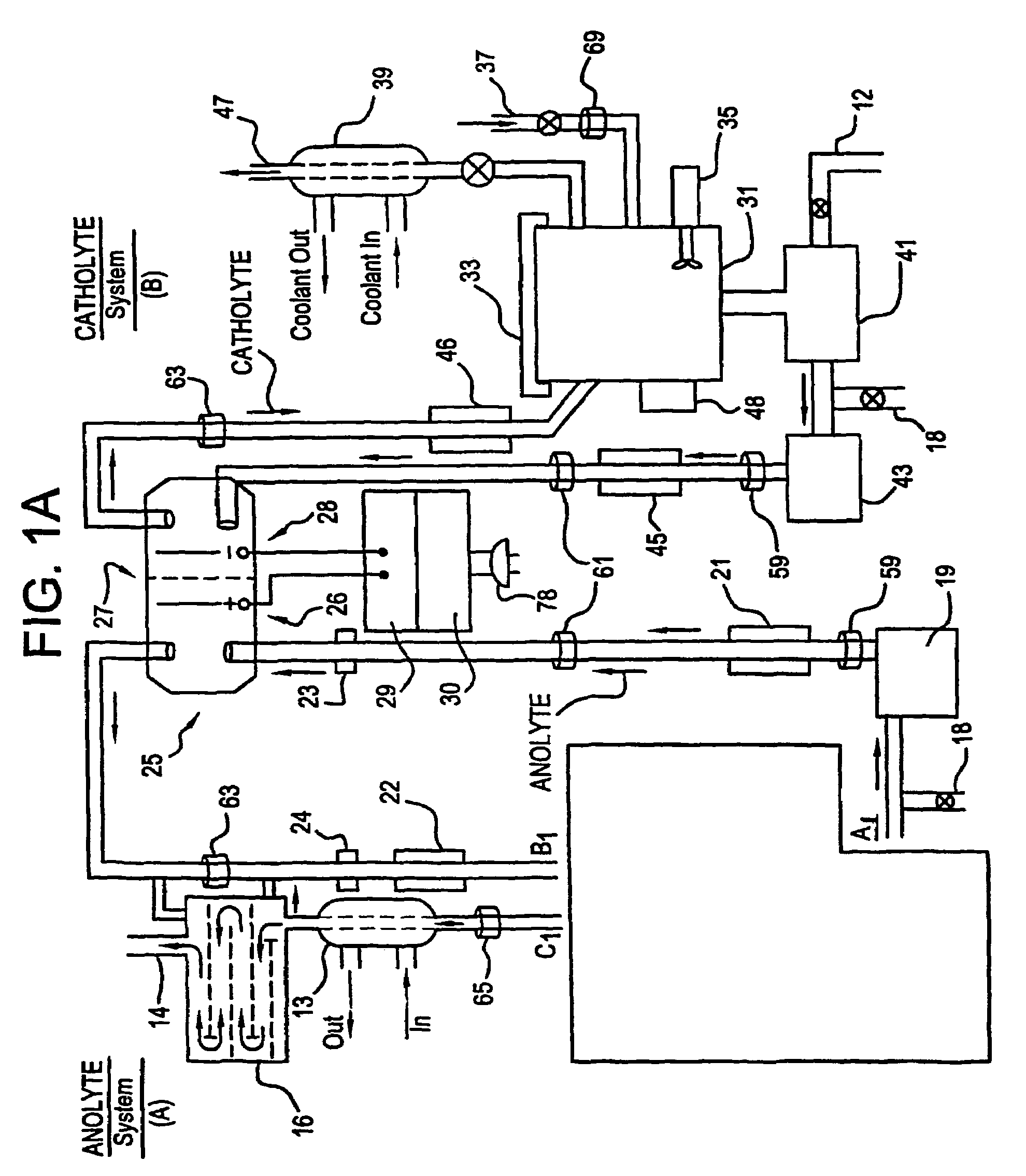
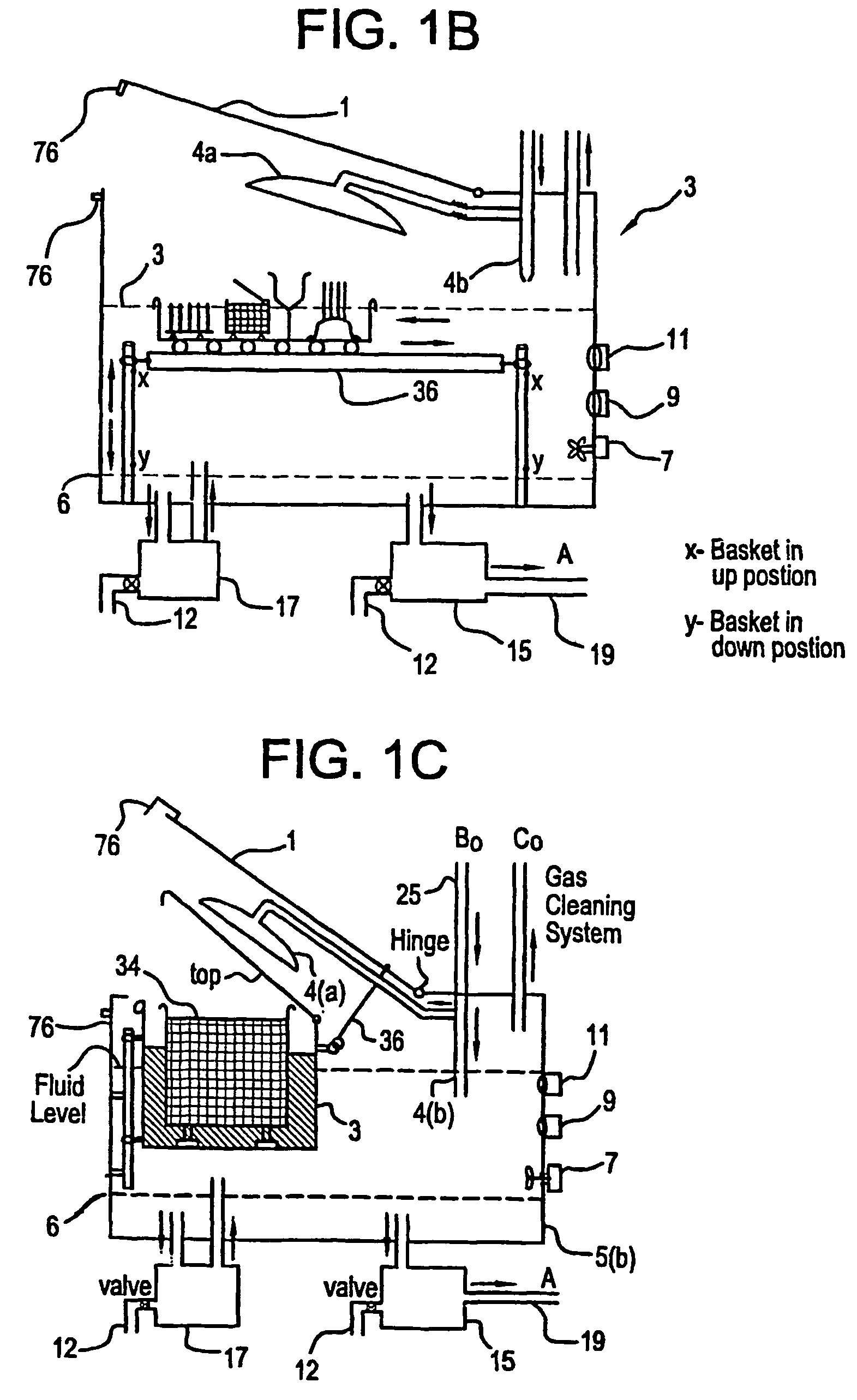
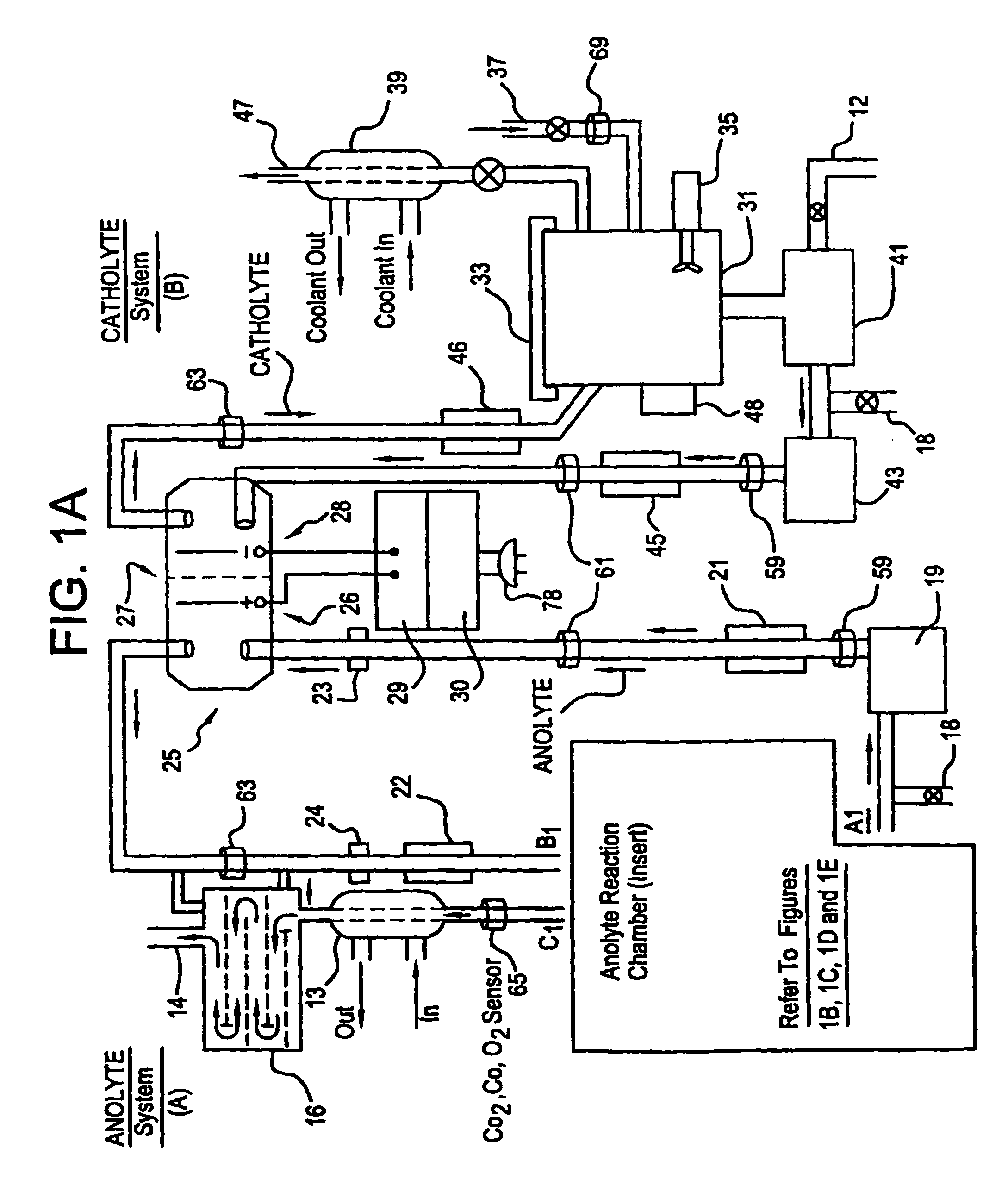
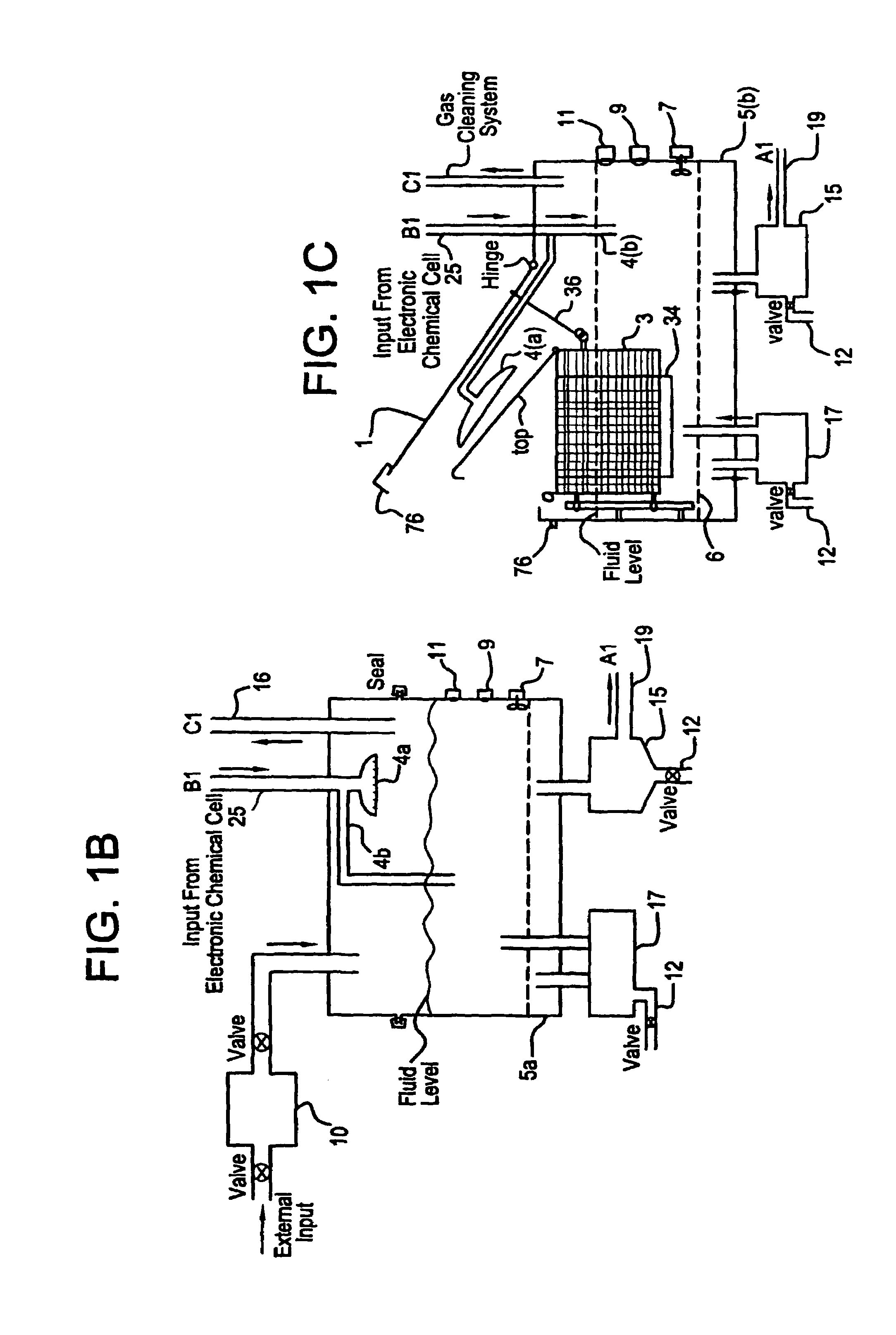
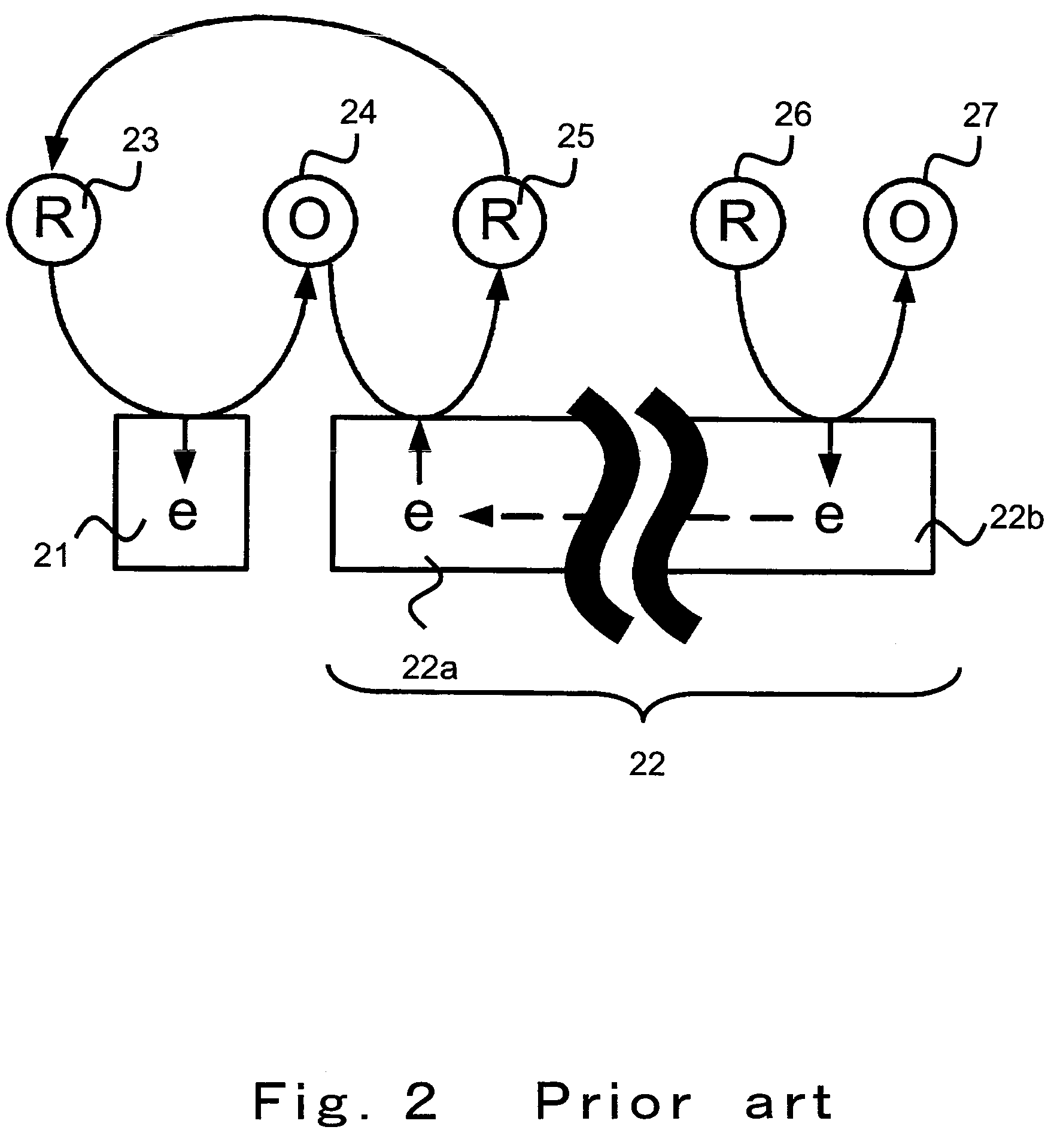
A unique apparatus unique apparatus and process that uses mediated electrochemical oxidation (MEO) for: (1) Destruction of: a) nearly all organic solid, liquid, and gases materials, except fluorinated hydrocarbons; b) all biological solid, liquid, and gases materials; c) and / or dissolution and decontamination (such as cleaning equipment and containers, etc.) of nearly all inorganic solid, liquid, or gas where higher oxidation states exist which includes, but is not limited to, halogenated inorganic compounds (except fluorinated), inorganic pesticides and herbicides, inorganic fertilizers, carbon residues, inorganic carbon compounds, mineral formations, mining tailings, inorganic salts, metals and metal compounds, etc.); and d) combined materials (e.g. a mixture of any of the foregoing with each other); henceforth collectively referred to as materials. (2) Sterilization / disinfection of equipment, glassware, etc., by destroying all existing infectious materials. (3) Dissolution of transuranic / actinide materials and / or destruction of the oxidizable components in the hazardous waste portion of mixed waste. (4) Generation of hydrogen and oxygen from MEO of materials. (5) Alteration of organic, biological, and inorganic materials by MEO to produce other compounds from these materials. The materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the materials with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the materials molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable material species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation process used as a hydrogen fuel generator
InactiveUS20050161342A1Improve efficiencyLiquid separation by electricityWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processFuranUltraviolet
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process and apparatus are used to process biological and organic materials to provide hydrogen and oxygen for use as fuel in numerous types of equipment. Waste materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the organic waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures to avoid any possible formation of either dioxins or furans. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
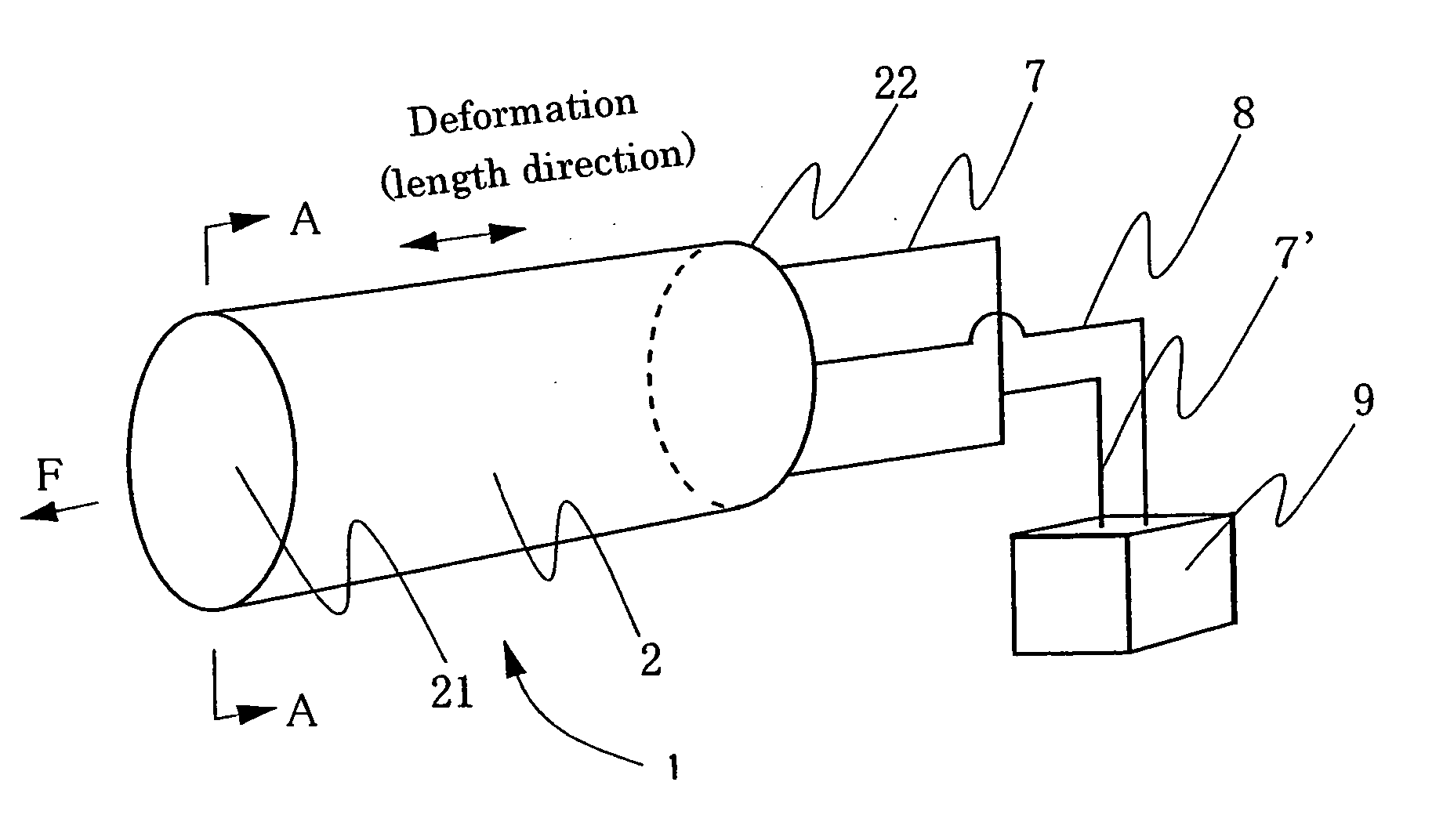
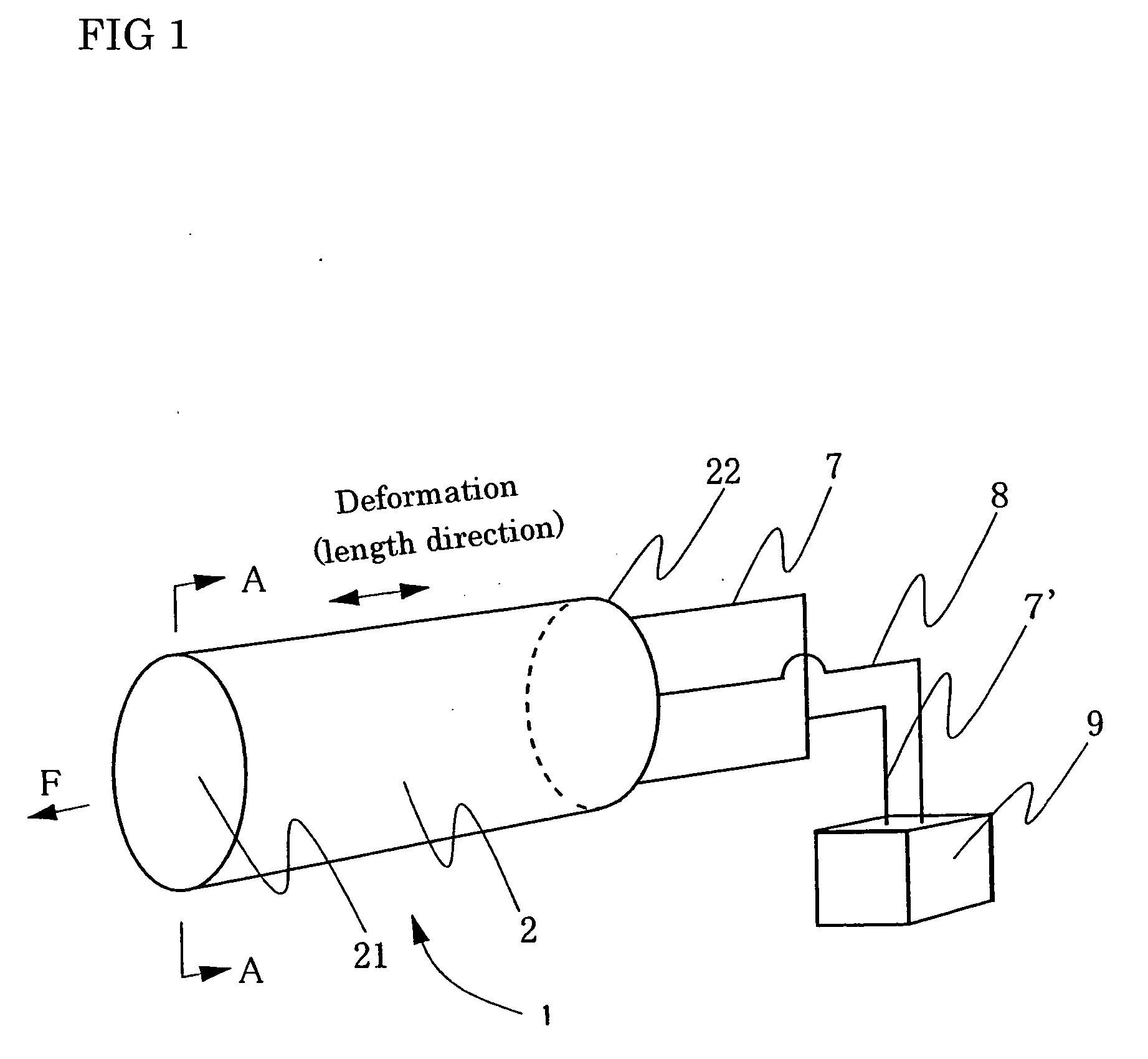
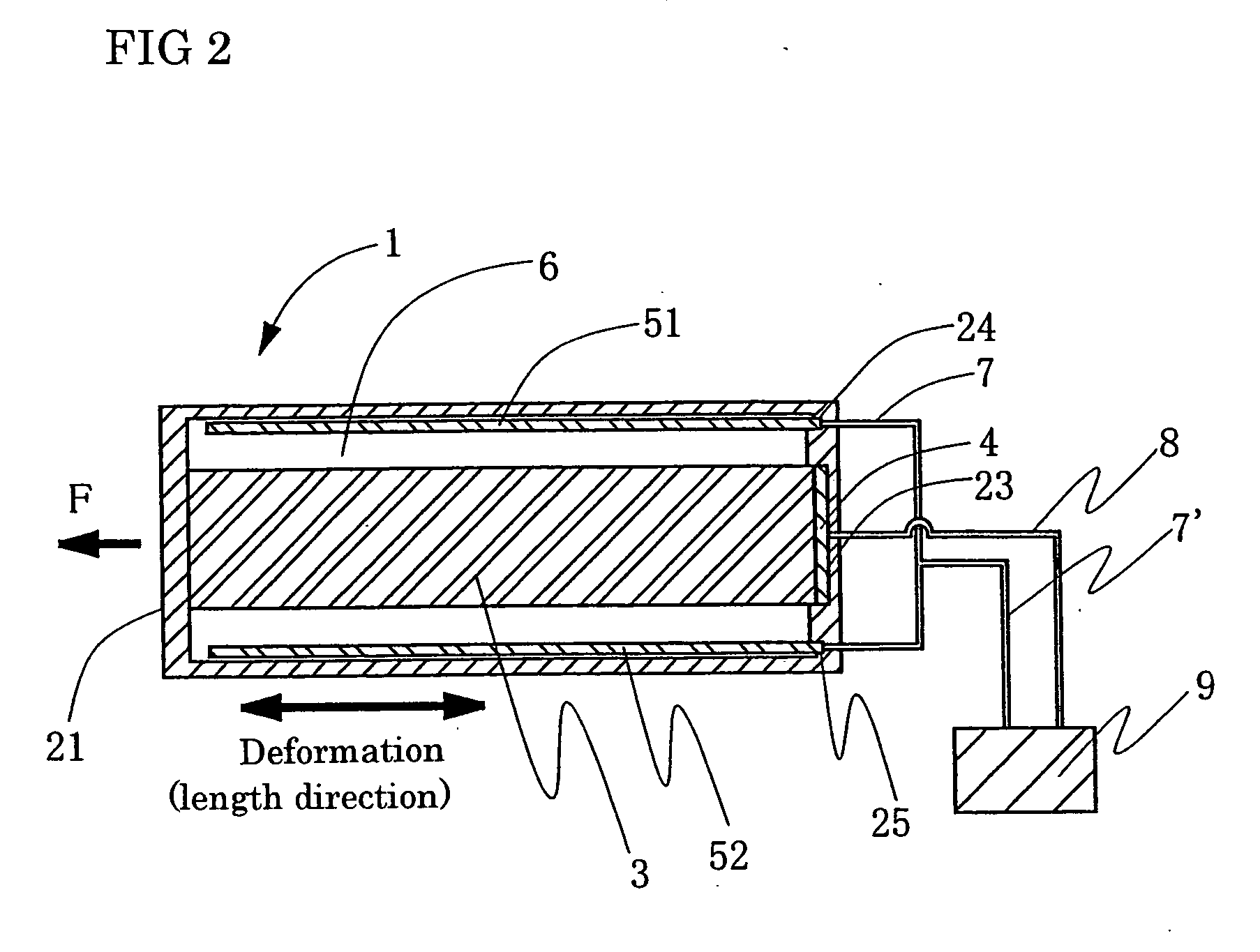
Process for producing conductive polymer
A process for producing conductive polymers with excellent electrochemical strain per redox cycle is provided. A process for producing conductive polymers by an electrochemical polymerization method, wherein said conductive polymers have deformation property by electrochemical redox, said electrochemical polymerization method is a polymerization method using electrolyte including organic compounds as solvents, and wherein said organic compounds include (1) chemical bond species selected at least one from a group composed of the chemical bond consisting of ether bond, ester bond, carbon-halogen bond, and carbonate bond and / or (2) functional groups selected at least one from a group composed of functional groups consisting of hydroxyl group, nitro group, sulfone group, and nitryl group in a molecule, and said electrolyte includes anions which include trifluoromethanesulfonate ion and / or plural of fluorine atoms which bond to central atom is used.
Owner:EAMEX
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of halogenated hydrocarbon waste materials
InactiveUS7479215B2Improve efficiencyLiquid separation by electricityTreatment involving filtrationHalohydrocarbonPhysical chemistry
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of food waste materials
InactiveUS7517445B2Reduce the total massReduce volumeCellulosic pulp after-treatmentLiquid separation by electricityBoiling pointOxidation-Reduction Agent
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process is used to treat, oxidize and destroy food waste materials, such as manure, biological residue, hay, straw, animal byproducts, bones, horns, blood, biological items, pathological waste and combined waste. Food waste is introduced into an apparatus for contacting the waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced by anodic oxidation in an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the organic waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The process takes place at temperatures between zero degrees centigrade and below the boiling point of the electrolyte.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of organic waste materials
InactiveUS7611620B2Easy accessSave energyCellsLiquid separation by electricityFuranElectrochemical anodization
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process is used to treat and destroy organic waste materials. The materials are introduced into an apparatus containing an electrolyte having the oxidized form of one or more redox couples. The oxidized couples oxidize the organic waste materials and are converted into their reduced form. The reduced forms are reoxidized by electrochemical anodic oxidation in the anode compartment of an electrochemical cell or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples. The redox cycle continues until the desired degree of oxidation is reached. The process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C., to avoid the formation of dioxins or furans. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of halogenated hydrocarbon waste materials
InactiveUS20050139486A1Easy accessSave energyLiquid separation by electricityTreatment involving filtrationOxidation-Reduction AgentElectrochemical cell
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process is used to treat, oxidize and destroy halogenated hydrocarbon waste materials. The waste materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the halogenated hydrocarbon waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of animal waste materials
InactiveUS7488409B1Improve efficiencyOxidation process strengthenedCellsLiquid separation by electricityFuranAnimal feces
Animal waste is contacted with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the organic waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms. The redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place between zero degrees centigrade and slightly below the boiling point of the electrolyte, avoiding formation of either dioxins or furans. Ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation provide reaction enhancements.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
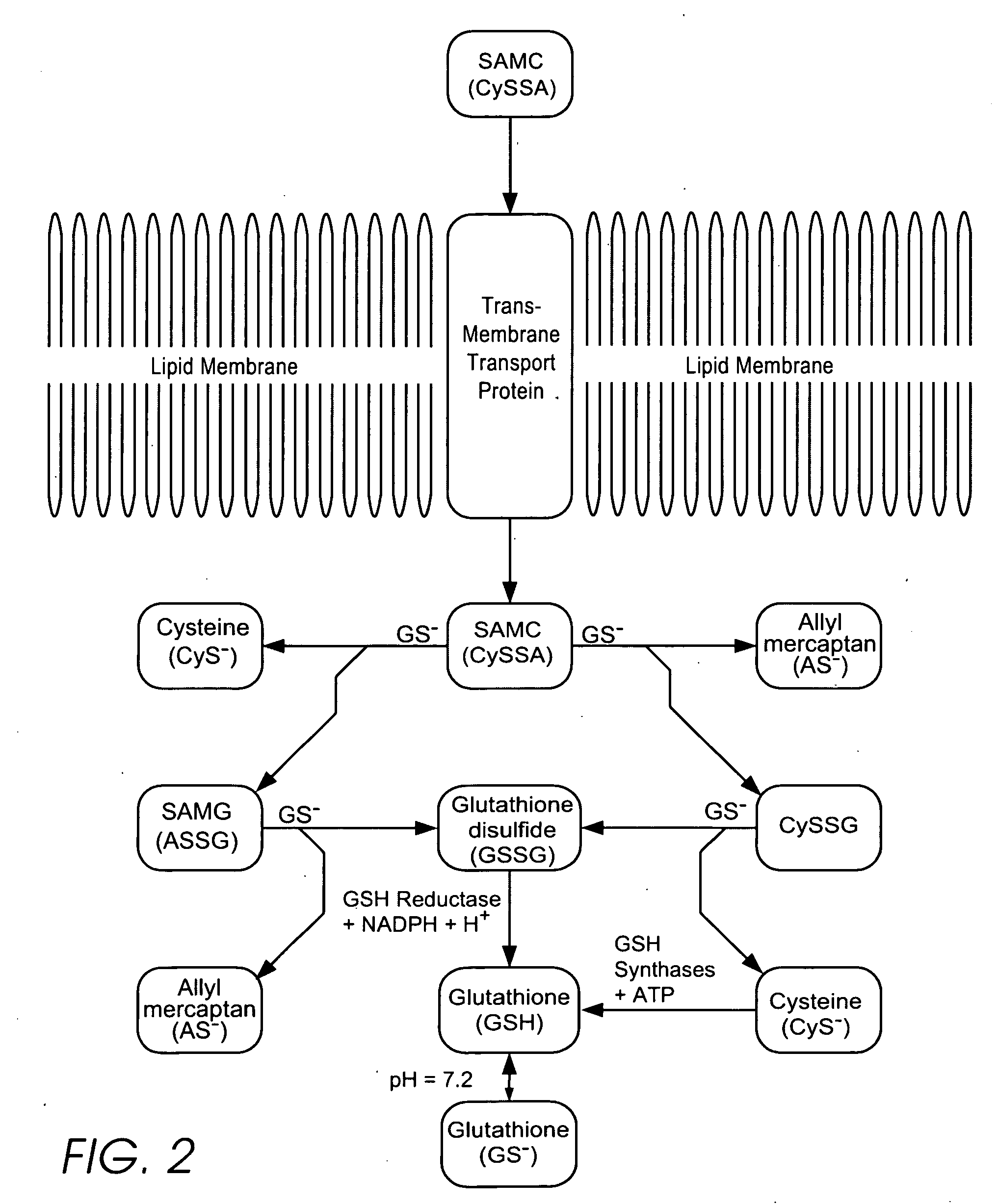
Personal care and medicinal products incorporating bound organosulfur groups
ActiveUS20060269488A1Low techSimple manufacturing processCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsThiosulfinic acidsThiosulfinate
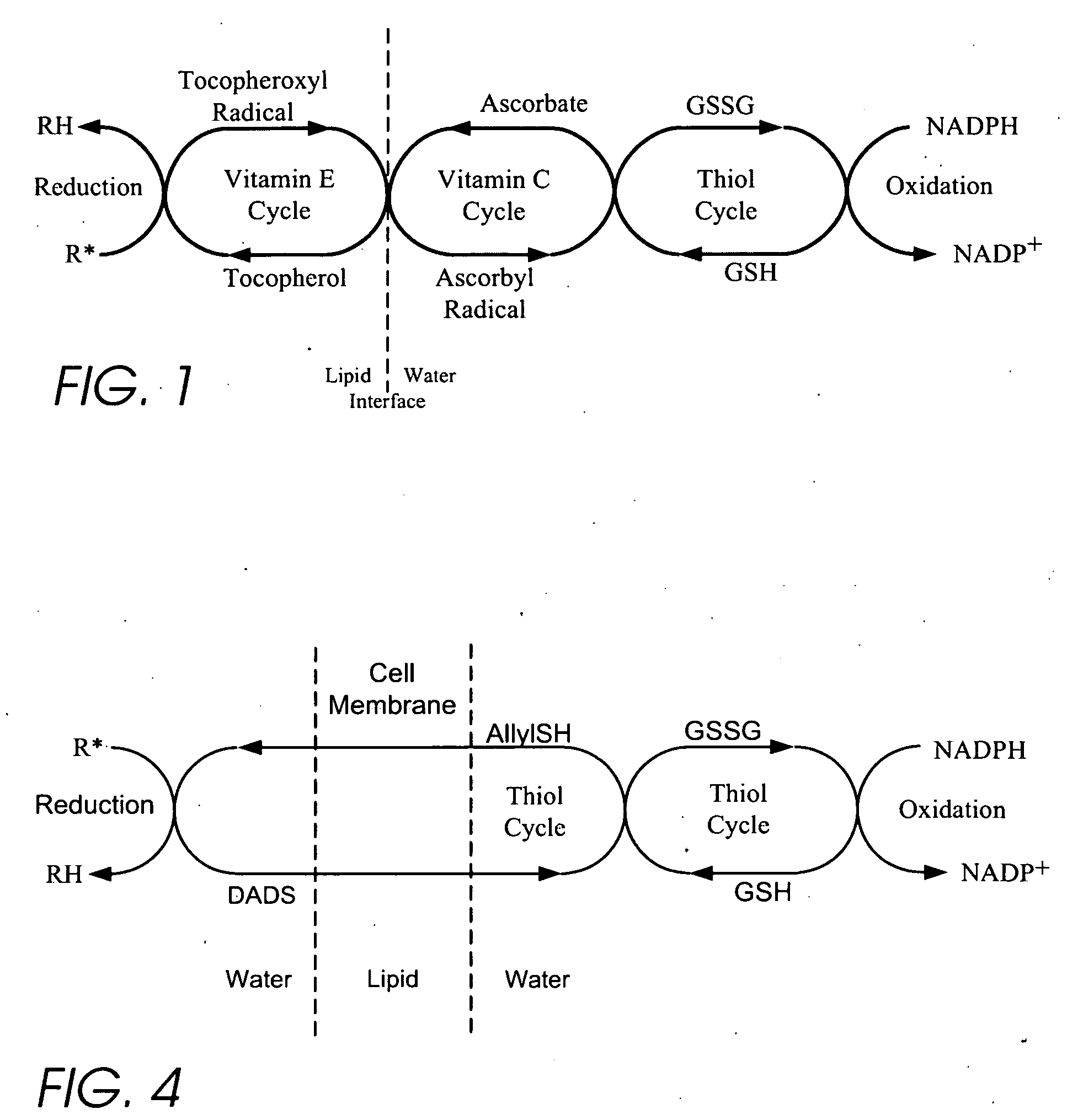
Personal care products useful for the maintenance of personal appearance and good health and minor treatments that do not require professional health care, as well as products that provide a combination of anti-microbial, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging properties and are suitable for use without a prescription. The products utilize a biomembrane permeable organosulfur compound that can redox cycle between thiol, disulfide, and thiosulfinate forms in response to oxidants and antioxidants inside and outside of cells. Example products include an anti-microbial toothpaste with anti-plaque properties, an anti-inflammatory skin lotion with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and deodorant properties, and an anti-toxin skin lotion with anti-arsenicosis properties.
Owner:ALLIUM VITALS
Preconditioning treatment to enhance redox tolerance of solid oxide fuel cells
A high temperature, redox tolerant fuel cell anode electrode and method of fabrication in which the anode electrode is pre-conditioned by application of an initial controlled redox cycle to the electrode whereby an initial re-oxidation of the anode electrode is carried out at temperatures less than or equal to about 650° C.
Owner:VERSA POWER SYST
Mediated electrochemical oxidation used for sterilization/disinfection
InactiveUS7531080B2Improve efficiencyFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityOxidation-Reduction AgentUltraviolet
A medicated electrochemical oxidation process is used for sterilization / disinfection of contaminated instruments and infectious waste. Contaminated instruments and waste are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the infectious waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the infectious waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable infectious waste species have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100 degree celsius. The oxidation process will be enhanced by the addition of reaction of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Method for detecting dopamine on basis of nanoparticle label oxidation-reduction cycle
ActiveCN105044273AChemical analysis using catalysisMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerPlatinum
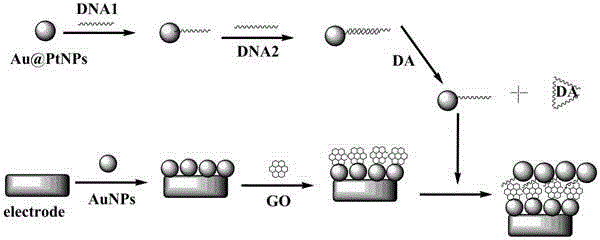
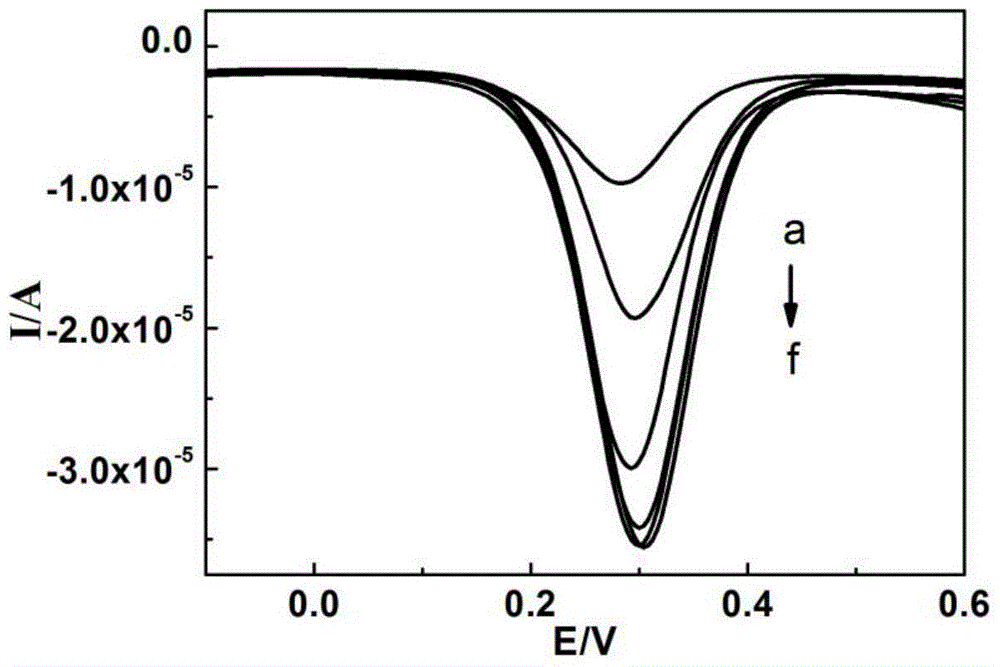
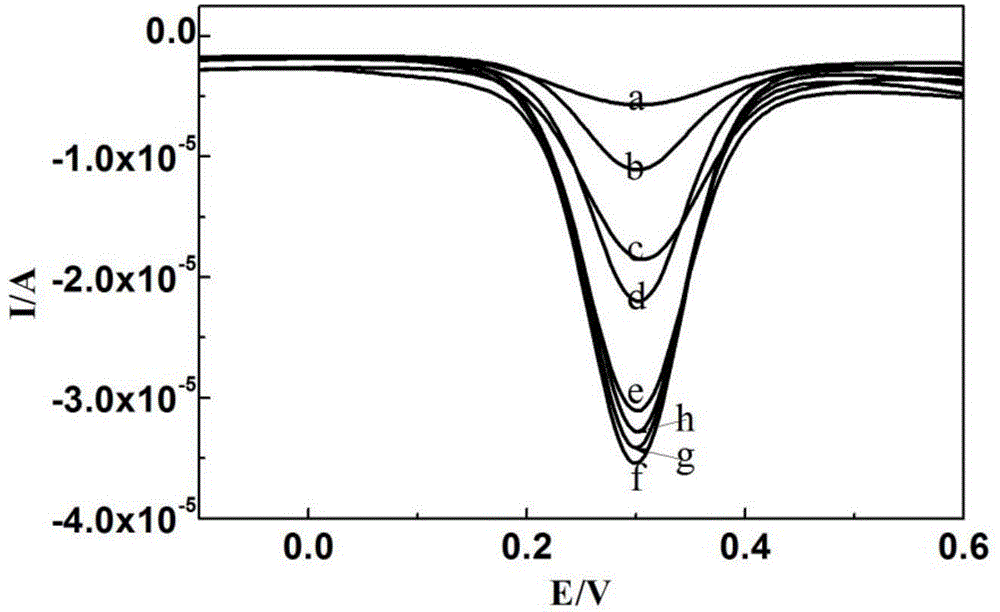
The invention belongs to the field of electrochemical sensors and relates to a method for detecting dopamine on the basis of a nanoparticle label oxidation-reduction cycle. According to the method, gold platinum composite nanoparticles are connected to dopamine aptamer complementary sequence single-stranded DNA to form a probe, the dopamine aptamer is added into the probe, so that double-stranded DNA modified gold platinum composite nanoparticles are obtained, when a dopamine-containing sample solution is added into the double-stranded DNA modified gold platinum composite nanoparticles, dopamine is specifically bonded with the dopamine aptamer and the probe is released; the released probe is captured by gold nanoparticles and a graphene oxide modified gold electrode, and the catalysis effect of gold platinum composite nanoparticles is used to generate an electrochemical signal to realize detection of dopamine. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple and high in sensitivity.
Owner:凯惠睿智生物科技(上海)有限公司
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of inorganic materials
InactiveUS7531710B2Low toxicityImprove efficiencyFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityOxidation-Reduction AgentOxidation state
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process and apparatus for the use of mediated electrochemical oxidation for the oxidation, conversion / recovery, and decontamination of inorganic solids, liquids, and gases where higher oxidation states exist. Inorganic materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the inorganic materials with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the inorganic waste molecules and are converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation process used as a hydrogen fuel generator
InactiveUS7871508B2Improve efficiencyLiquid separation by electricityWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processFuranPhysical chemistry
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process and apparatus are used to process biological and organic materials to provide hydrogen and oxygen for use as fuel in numerous types of equipment. Waste materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the organic waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures to avoid any possible formation of either dioxins or furans. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
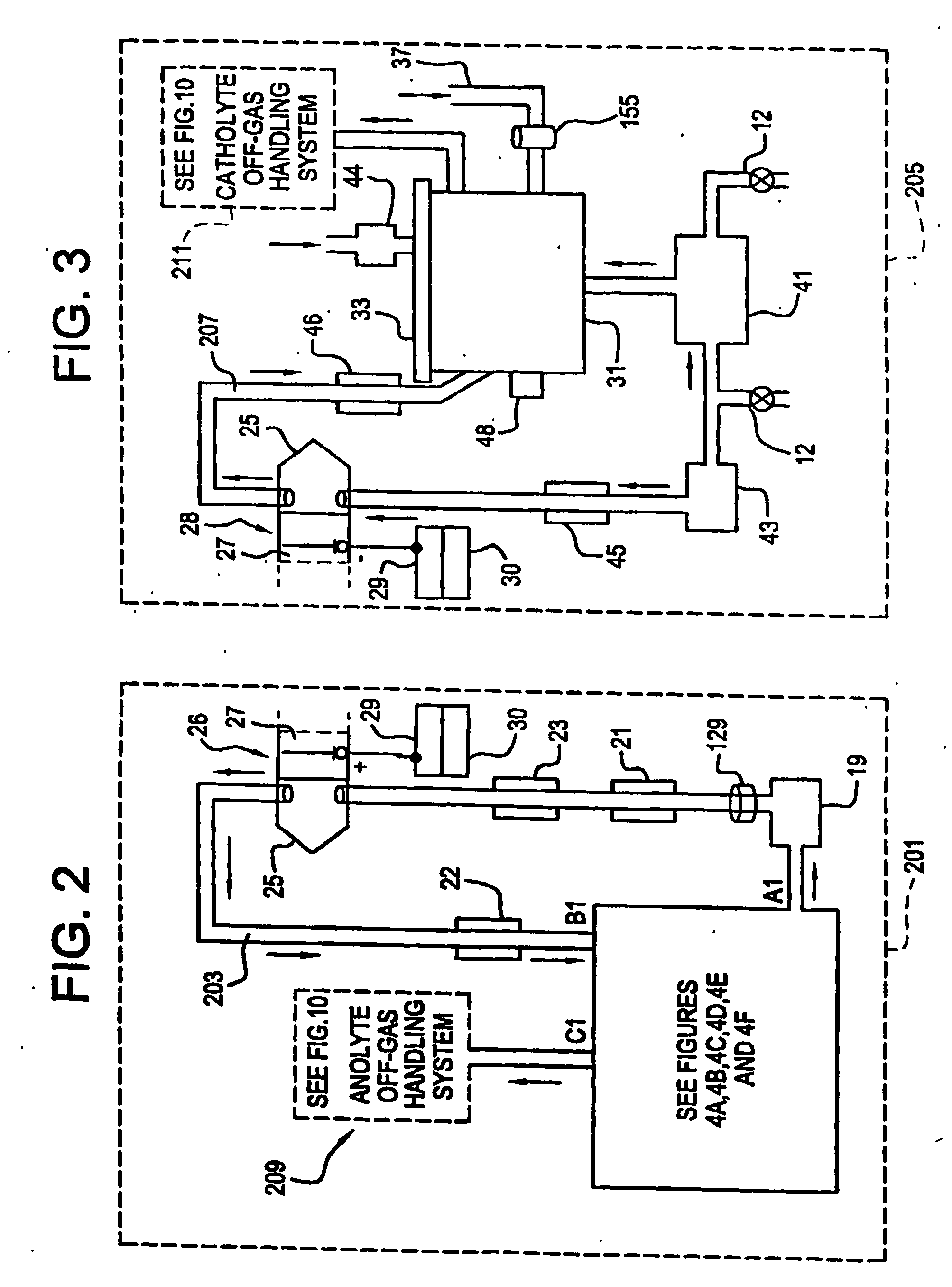
Mediated electrochemical oxidation and destruction of sharps
InactiveUS7691251B2Preventing parasitic reduction of the oxidizing speciesImprove efficiencyCellsSurgical furniturePhysical chemistryBiological waste
Sharps are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the sharps with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized forms of any other redox couples present are produced either by similar anodic oxidation or reaction with the oxidized form of other redox couples present and capable of affecting the required redox reaction. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize sharps and the biological waste on the sharps and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species, including intermediate reaction products, have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100° C. The oxidation process will be enhanced by the addition of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation used for sterilization/disinfection
InactiveUS20050000828A1Promote formationEfficient processingFrom normal temperature solutionsLiquid separation by electricityOxidation-Reduction AgentUltraviolet
A medicated electrochemical oxidation process is used for sterilization / disinfection of contaminated instruments and infectious waste. Contaminated instruments and waste are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the infectious waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the infectious waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized by either of the aforementioned mechanisms and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable infectious waste species have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures between ambient and approximately 100 degree celsius. The oxidation process will be enhanced by the addition of reaction of reaction enhancements, such as: ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
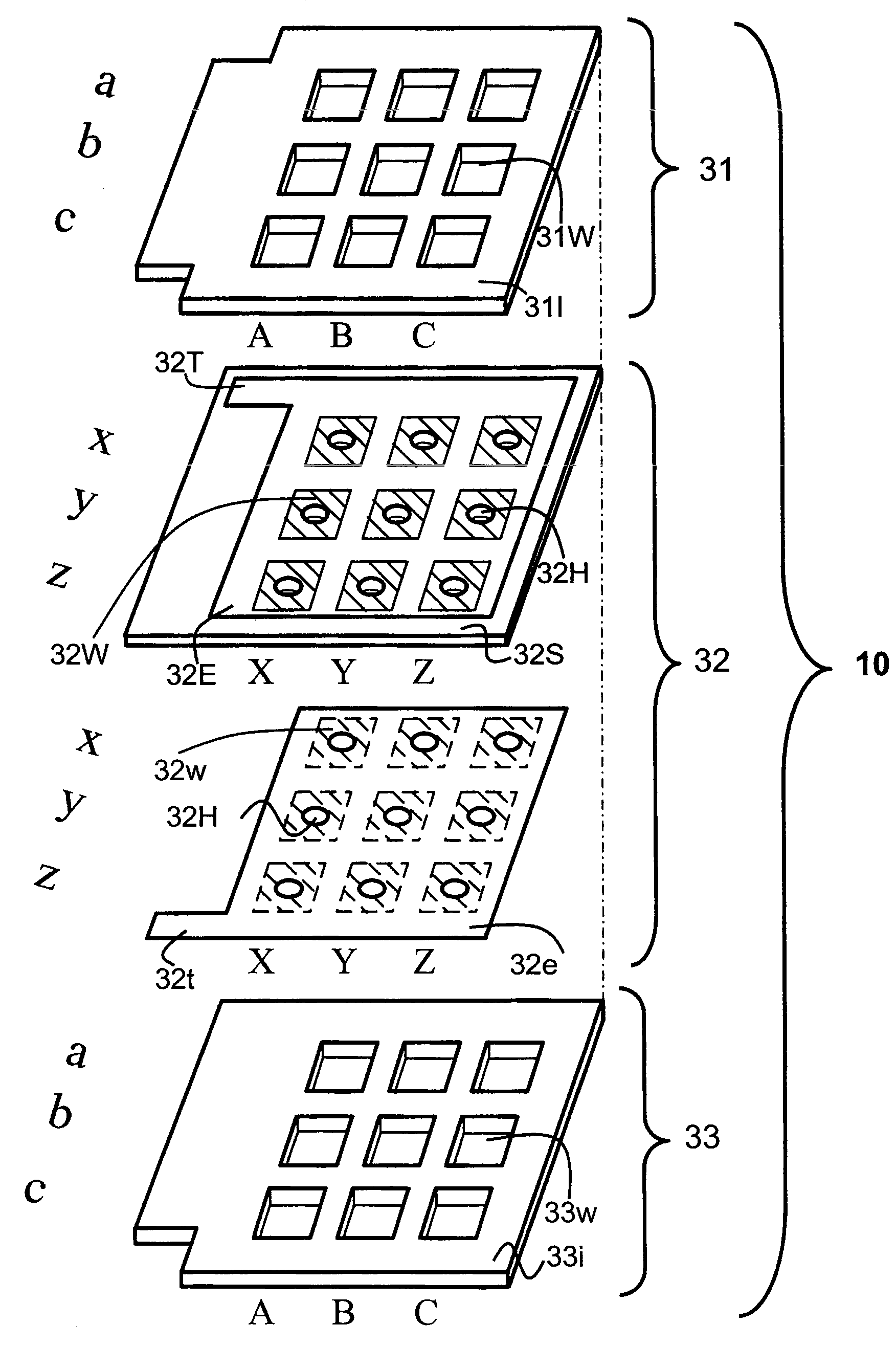
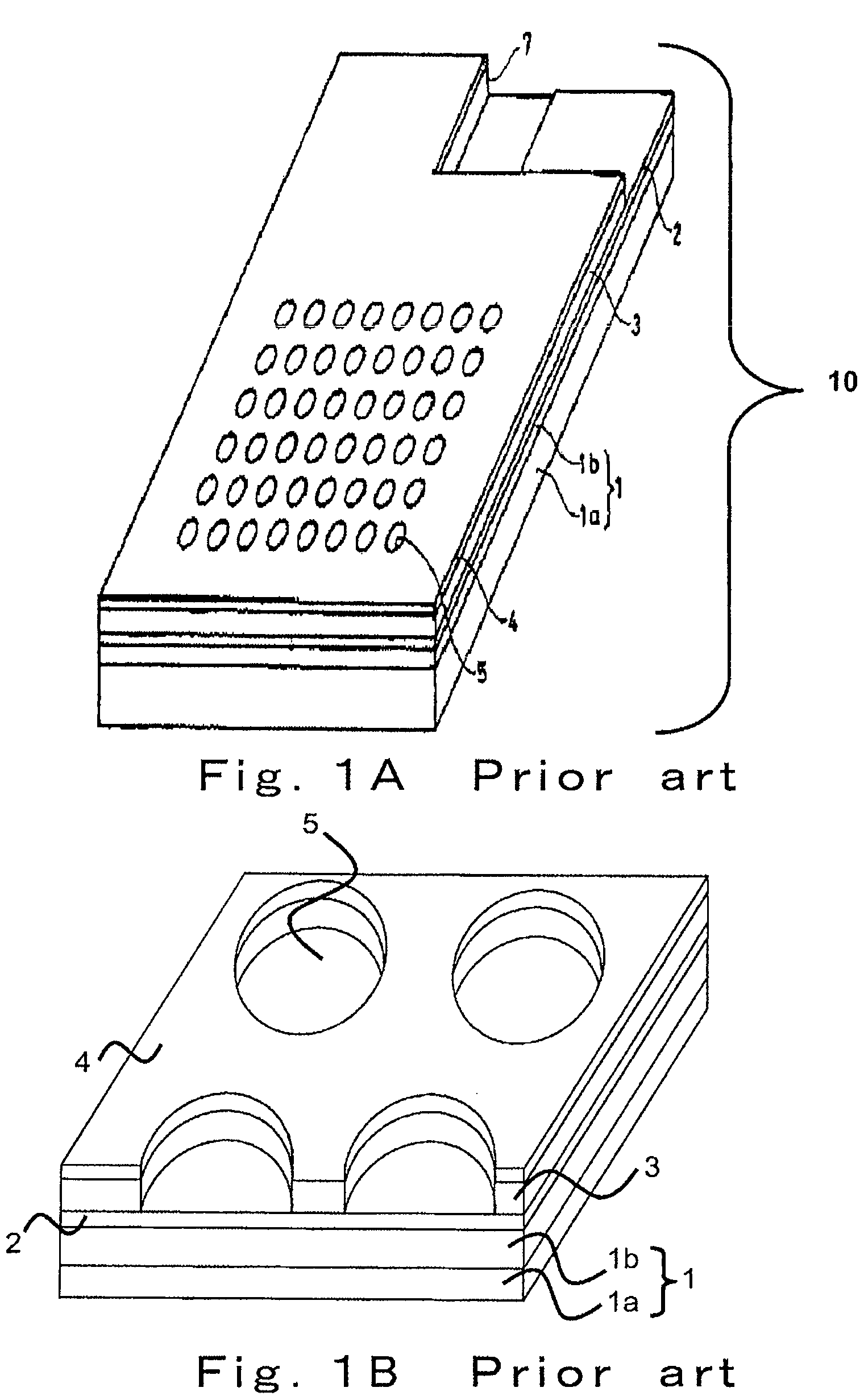
Electrode plate for electrochemical measurements
ActiveUS7638035B2High sensitivityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrochemistryElectrode pair
An object of the invention is to provide an electrode plate for electrochemical measurements for detecting with high sensitivity and determining a substance included in a living body. The electrode plate of the present invention has on both faces of body of the substrate, oxidation electrode and reduction electrode opened respectively at upper layer opening and lower layer opening having the same area; and further has a plurality of through-holes that penetrate through from the face of the oxidation electrode to the face of the reduction electrode, in which electrode pairs are formed which exhibit a redox cycle effect between the oxidation electrode and the reduction electrode by applying the potential which can proceed an oxidative reaction of a reductant on the oxidation electrode, and the potential which can proceed a reductive reaction of an oxidant on the reduction electrode.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Preparation method of high-power external application type lead-carbon battery negative electrode
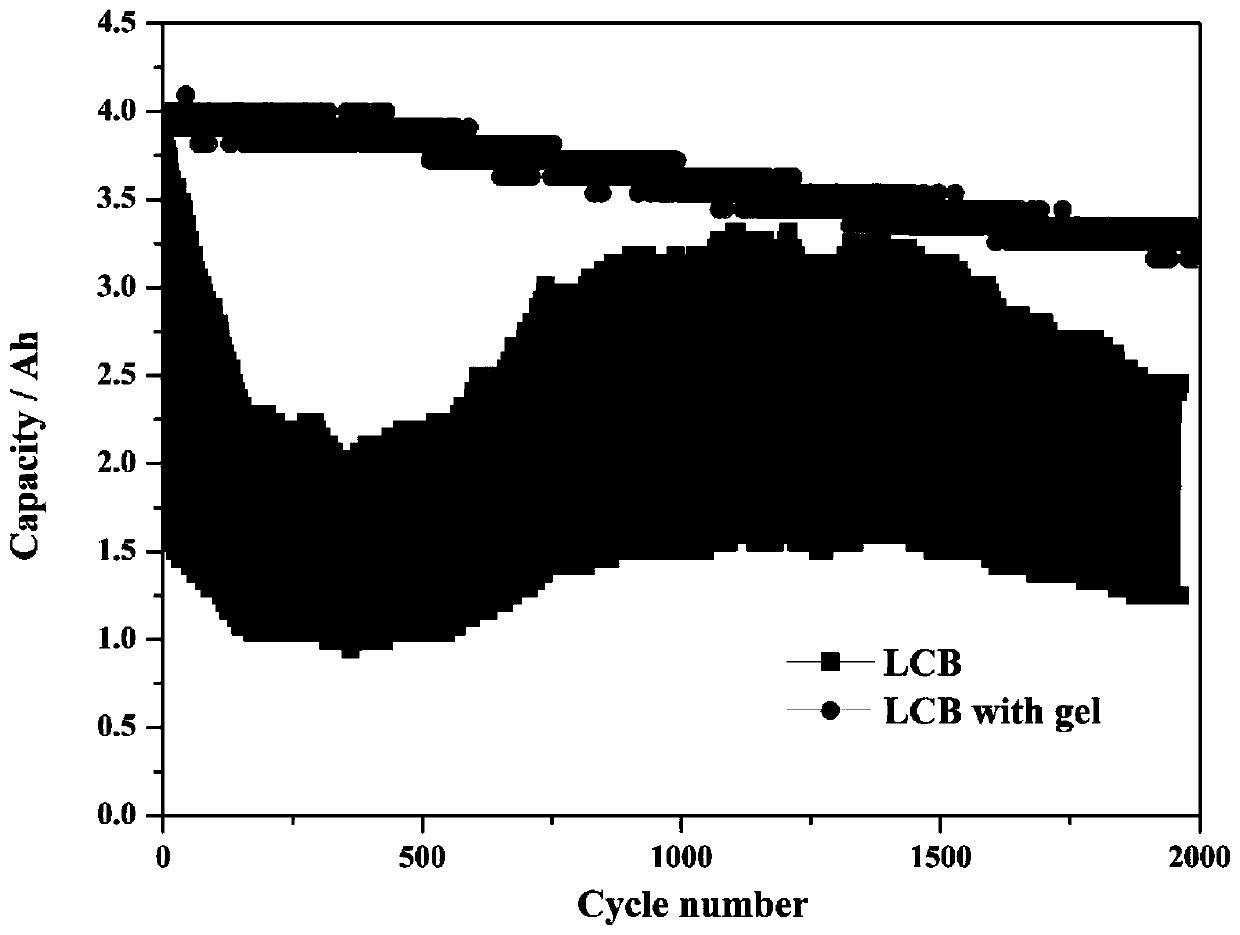
ActiveCN111081986AImprove effective utilizationImprove power densityNegative electrodesLead-acid accumulator electrodesElectrode potentialElectrolytic agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-power external application type lead-carbon battery negative electrode. The negative electrode consists of three parts, namely, lead plaster, a carbon plate and gel. The structure that the carbon plate is attached to the surface of the lead plaster can improve electrode potential distribution, inhibit surface sulfation and improve the effective utilization rate of active substances. When lead ions in an electrolyte contact with the carbon plate of the negative electrode, lead and lead sulfate oxidation-reduction circulation occurs on the surface of the carbon plate under the electrochemical action, sulfation is generated, and the power density and the cycling stability of the electrode are reduced. The gel can inhibit lead ions from contacting the surface of the carbon material, avoid reduction of the lead ions, inhibit sulfation of the surface of the carbon material, ensure normal exertion of beneficial effects of the carbon material, improve the charge-discharge efficiency of the electrode and prolong the cycle service life of the electrode. The external application type lead-carbon battery composed of the negative electrodehas higher large-current bearing capacity and cycling stability, and is suitable for the fields of start-stop automobiles, solar energy, wind energy storage and the like.
Owner:吉林省凯禹电化学储能技术发展有限公司
Catalytic material, preparation method thereof and photocatalyst
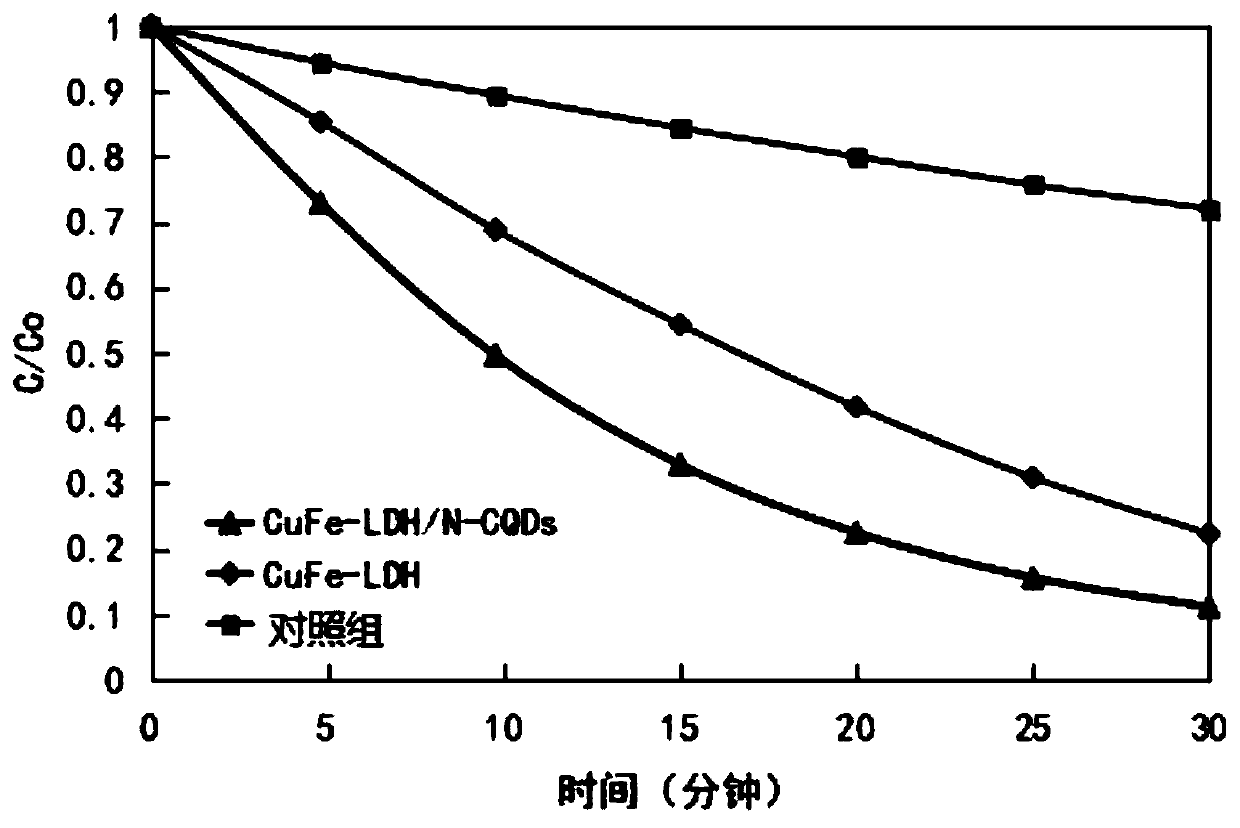
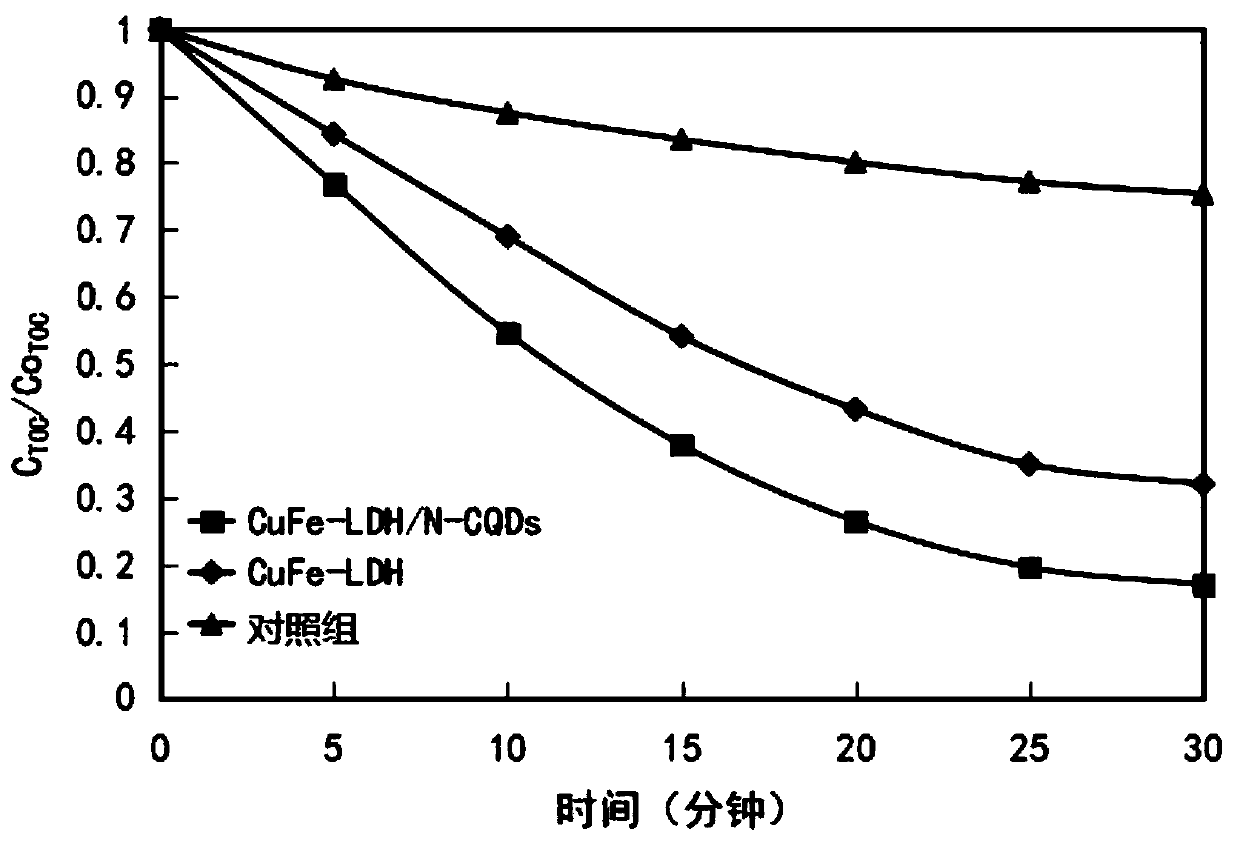
ActiveCN111229286AImprove photocatalytic performanceImprove cycle efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOxidation reductionOrganopónicos
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, and particularly discloses a catalytic material and a preparation method thereof, and a photocatalyst, the catalytic material comprisesthe following raw materials: N-CQDs powder and CuFe-LDH dispersion liquid; wherein the CuFe-LDH dispersion liquid is prepared from the following raw materials: a ferric iron source, a bivalent coppersource and a proper amount of alkaline solution. According to the preparation method, CuFe-LDH and nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots are compounded to obtain the catalytic material; the preparationmethod is simple, the cycle efficiency is high, repeated recycling can be achieved, the pH range of the photo-Fenton reaction is widened, and the problems that an existing layered double hydroxide catalytic material is low in metal redox cycle efficiency and photocatalytic quantum efficiency, the efficiency of degrading organic pollutants in water through the photo-Fenton reaction is low, and thepH application range is narrow are solved. The provided preparation method is simple, the prepared catalytic material promotes the circulation of Fe < 3 + > / Fe < 2 + > and Cu < 3 + > / Cu < 2 + > redoxpairs, and the photocatalytic quantum efficiency is improved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Construction and application of aptamer sensor taking nanogold/zinc oxide-graphene composite material as photoelectric sensitive element
PendingCN111562296AGood biocompatibilityIncrease transfer rateMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrolytic agentElectron donor
The invention relates to construction and application of a photoelectrochemical aptamer sensor taking a nanogold / zinc oxide-reduced graphene oxide ternary composite material as a photoelectric sensitive element. The construction comprises the following steps: by taking conductive glass (ITO) as a substrate electrode, preparing a photoelectrode Au / ZnO-rGO / ITO modified by reduced graphene oxide (rGO), zinc oxide (ZnO) and nanogold (Au), and modifying an aptamer S1 and a complementary strand S2 to form double-stranded DNA (dsDNA); and combining photosensitizer methylene blue (MB) with the dsDNA to construct a sensor for amplifying a detection signal. After a sensing interface senses Cd (II), the S2 specifically recognizes the Cd (II) to form a hairpin structure, and along with dsDNA unwindingand MB separation from the dsDNA, quantitative analysis of the Cd (II) is realized according to the photocurrent response of the recognized sensor. A double-working-electrode method is adopted for testing, a sensor and a glassy carbon electrode serve as a first working electrode and a second working electrode, dopamine (DA) is added into an electrolyte to serve as an electron donor, oxidation-reduction circulation of DA on the surfaces of the double working electrodes is achieved, and signal stability is improved. The method has the advantages of high sensitivity and low detection limit.
Owner:HAINAN NORMAL UNIV
Mediated electrochemical oxidation of destruction of sharps
InactiveUS20050103642A1Improve efficiencyCellsSurgical furnitureBiological wasteElectrochemical cell
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
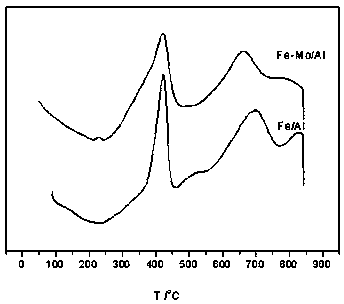
Oxygen carrier for chemical looping hydrogen production and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN107539948BImprove stabilityImprove thermal stabilityHydrogen productionIron oxideHigh activity
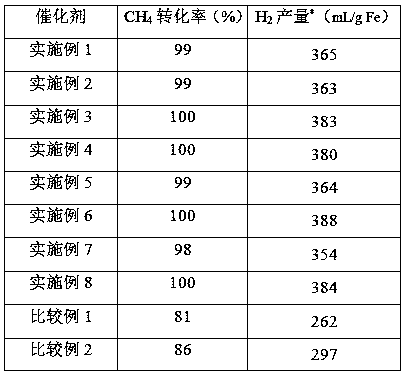
The present invention provides an oxygen carrier for chemical looping hydrogen generation, a preparation method and applications thereof. According to the present invention, the oxygen carrier comprises, by mass, 5-65% of Fe2O3, 5-35% of MoO3 and 30-90% of Al2O3; the oxygen carrier is prepared through a dipping method and can be used for chemical looping hydrogen generation, wherein an alumina carrier is dipped in a soluble solution containing iron and molybdenum, and drying and roasting are performed to prepare the oxygen carrier; molybdenum oxide as the auxiliary agent is added to the oxygencarrier, and the conversion between Mo<6+> and Mo<3+> forms a redox cycle, such that the redox reaction can be promoted, and the reducibility of the active component iron oxide can be easily improved; the dispersity of iron oxide can be improved with molybdenum oxide, such that the particle of the iron oxide can be reduced so as to improve the stability of the oxygen carrier; and the oxygen carrier is suitable for carrying out the reaction at the high temperature, has advantages of good thermal stability, cheap and easily available raw materials and simple preparation method, and is suitablefor industrial applications.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Manganese dioxide-porous carbon composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
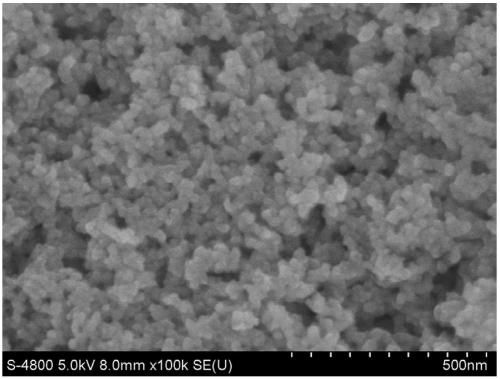
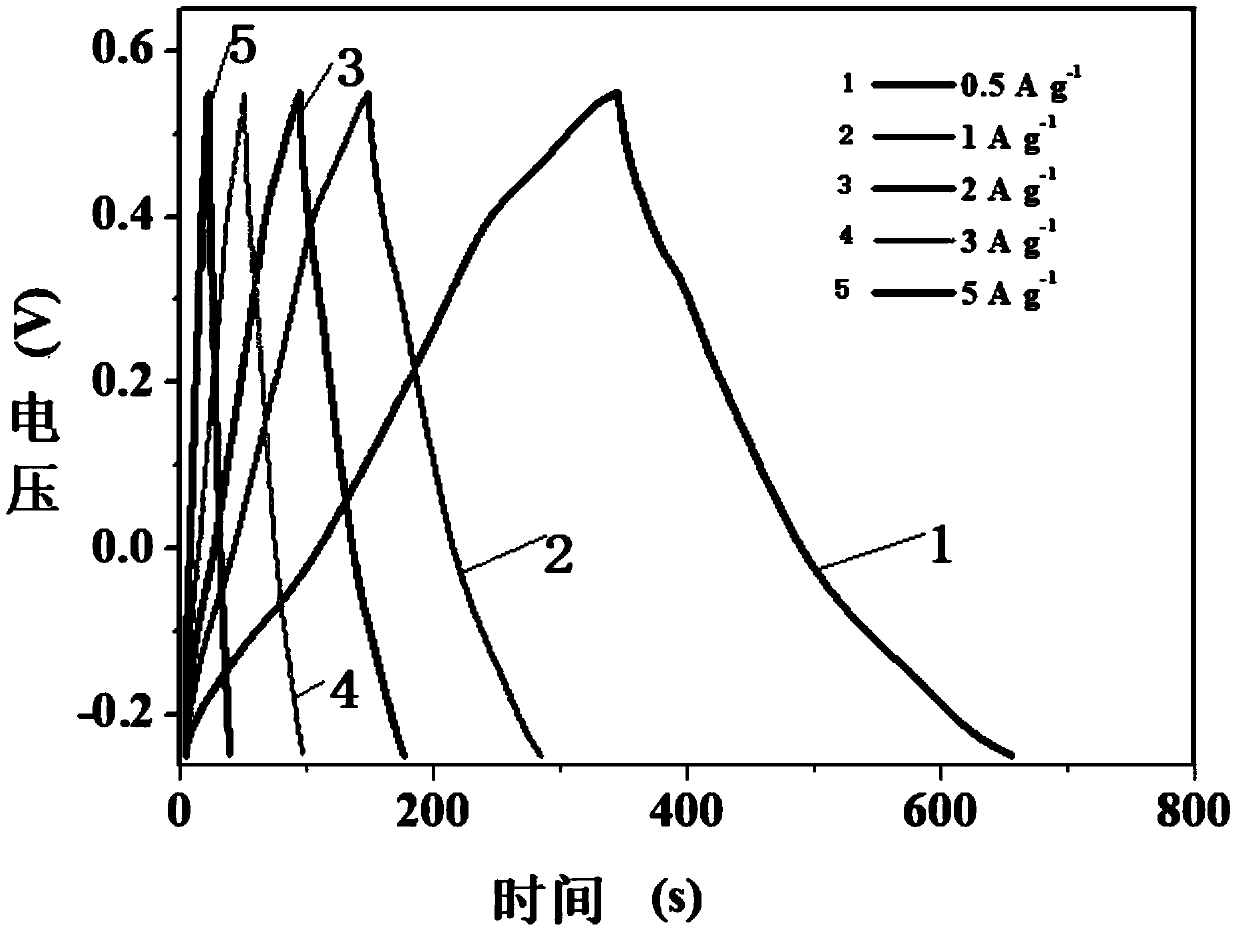
InactiveCN111048324ACoated evenlyThe experimental method is simpleMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesCarbon compositesPorous carbon
The invention discloses a manganese dioxide-porous carbon composite material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. KMnO4 is reduced by utilizing porous carbon, and uniform MnO2 nanoparticles are obtained on the surface of the porous carbon, so that the conductivity of MnO2 is further improved, and the structural damage of MnO2 in an electrochemical cycle process is reduced. Under the current density of 0.5Ag<-1>, the capacity can be stabilized at 215F g<-1>. The method effectively improves the low conductivity of the traditional supercapacitor electrode material MnO2 and thepulverization shedding phenomenon caused by the stress generated in the oxidation-reduction cycle process. Therefore, the MnO2 / porous carbon composite material has a wide application prospect in theaspect of improving the conductivity and the stability of the supercapacitor electrode material.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
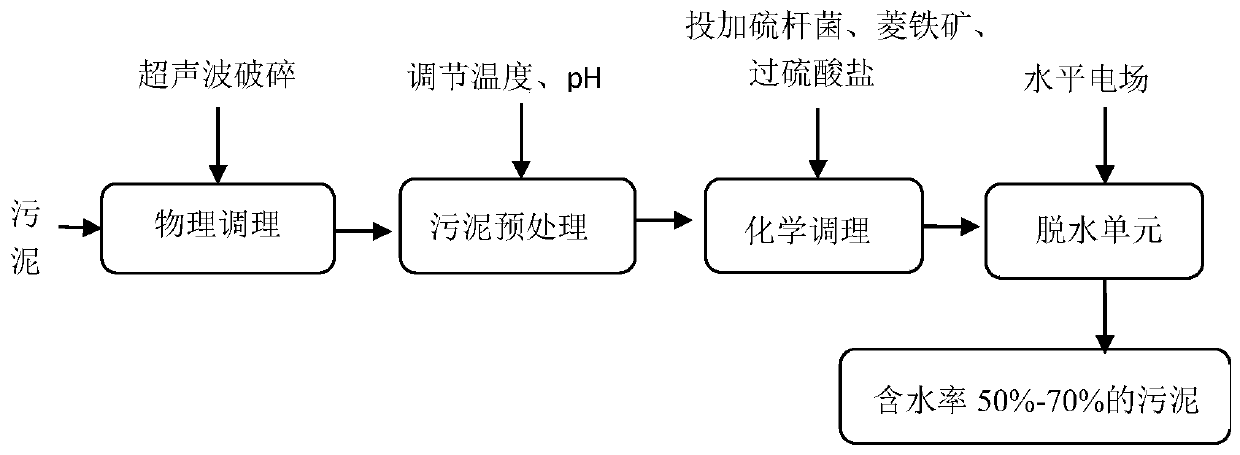
High-efficiency sludge conditioning and dehydrating method
InactiveCN110467332AAdvantages of dehydration methodAchieve deep dehydrationSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSpecific water treatment objectivesSulfate radicalsPersulfate
The invention discloses a sludge conditioning-horizontal electric field dehydration method. The method comprises the following main steps: (1) carrying out ultrasonic treatment on sludge; (2) adjusting the temperature and pH value of the sludge; (3) adding thiobacillus, siderite and persulfate into the sludge, carrying out uniform mixing, and then performing a reaction for a certain period of time; and (4) introducing a mixture obtained in the previous step into a horizontal electric field for dehydration. According to the invention, ultrasonic damage of microbial cells and promotion of an oxidation reaction of siderite with persulfate via thiobacillus are combined together, so the generation of sulfate radical free radicals is activated, a Fe (II) redox cycle is formed, and a sludge structure is disintegrated; the horizontal electric field is cooperatively used for dehydration; and thus, respective advantages are give to full play, synergistic effect is generated, and the moisture content of the conditioned sludge is reduced to 50-70%. The conditioning method is clear in steps and easy to operate, avoids generation of excessive <Fe> due to feeding of excessive siderite, saves cost, and has obvious dehydration effect and no secondary pollution.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
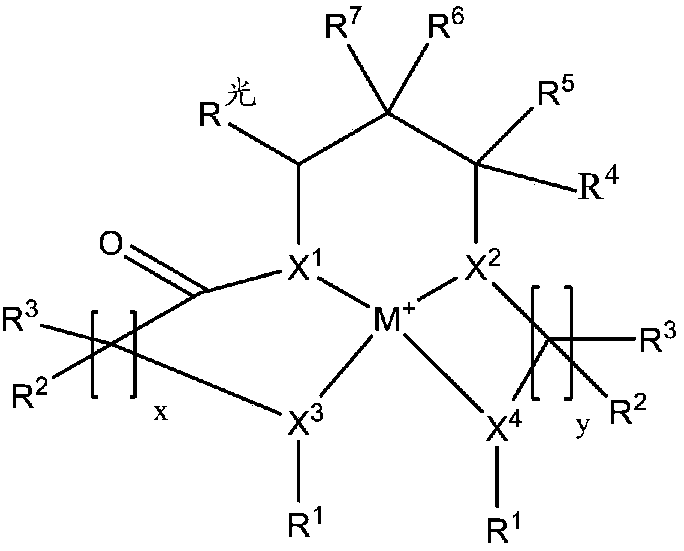
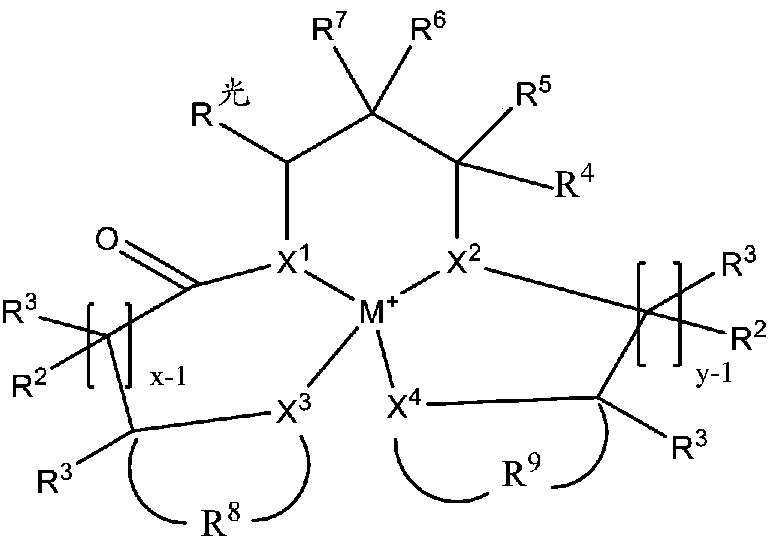
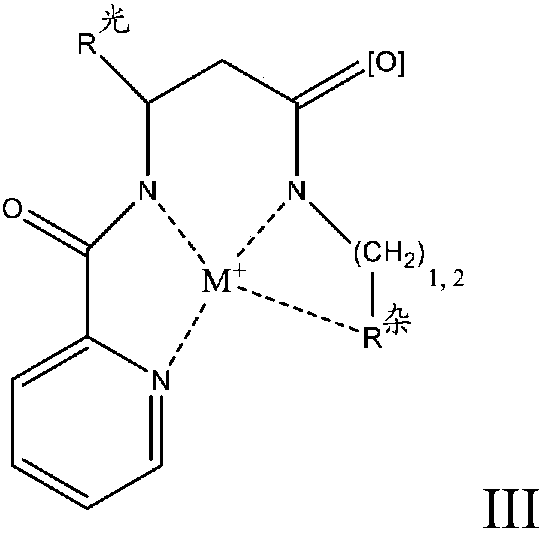
Redox polymerizable composition with photolabile transition metal complexes
ActiveCN108348403AImpression capsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsRedox cyclingMetal
Polymerizable compositions comprising a redox initiator system is disclosed. The redox initiator system comprises a photolabile transition metal complex that photolyzes and initiates the redox cycle.Dental compositions comprising dental resins and the photolabile redox initiator system are also described.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
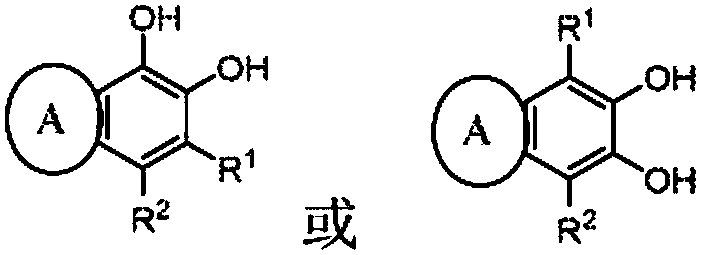
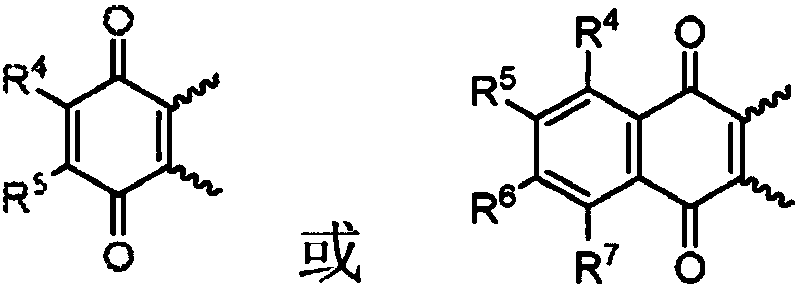
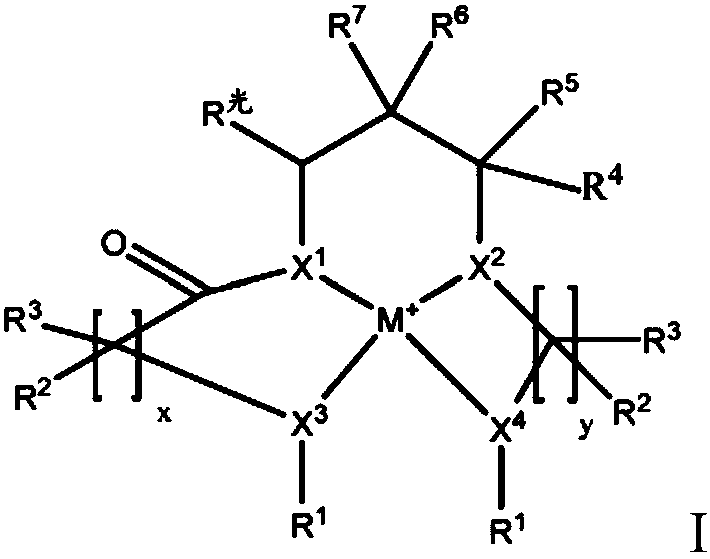
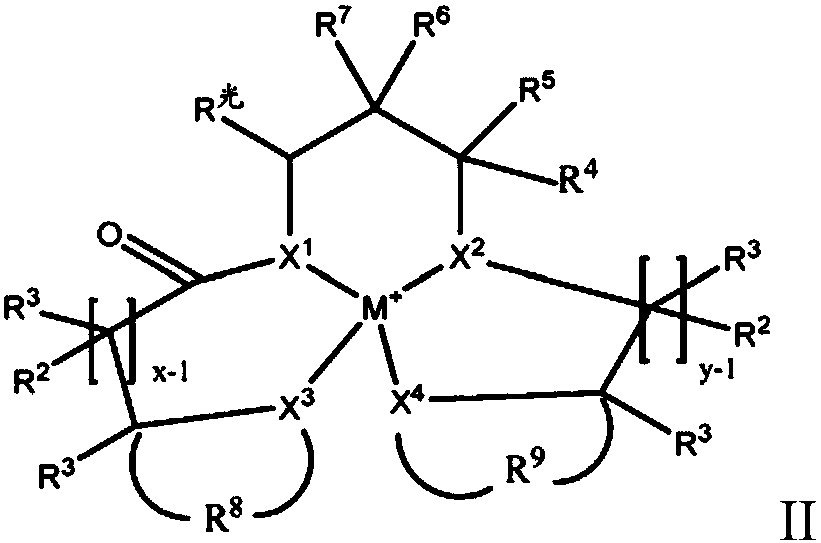
Coordination compounds having redox non-innocent ligands and flow batteries containing the same
Electrolyte solutions for flow batteries and other electrochemical systems can contain an active material capable of transferring more than one electron per oxidation-reduction cycle. Such active materials can include coordination compounds containing a metal center and at least one redox non-innocent ligand. Accordingly, flow batteries can include a first half-cell having a first electrolyte solution therein, where the first electrolyte solution contains a coordination compound having at least one redox non-innocent ligand coordinated to a metal center. Particular redox non-innocent ligands can include those bearing a quinone functional group, such as substituted catecholates bearing a quinone functional group. Some active materials can include compositions containing a coordination compound having at least one redox non-innocent ligand coordinated to a metal center, where the at least one redox non-innocent ligand is a substituted catecholate or a salt thereof bearing a quinone functional group.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ADVANCED ENERGY STORAGE
Redox polymerizable dental composition with photolabile transition metal complexes
Polymerizable dental compositions comprising a redox initiator system is disclosed. The redox initiator system comprises a photolabile transition metal complex that photolyzes and initiates the redoxcycle.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Preconditioning treatment to enhance redox tolerance of solid oxide fuel cells
ActiveUS20100028747A1Improve toleranceCell electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsFuel cellsPre-condition
Owner:VERSA POWER SYST
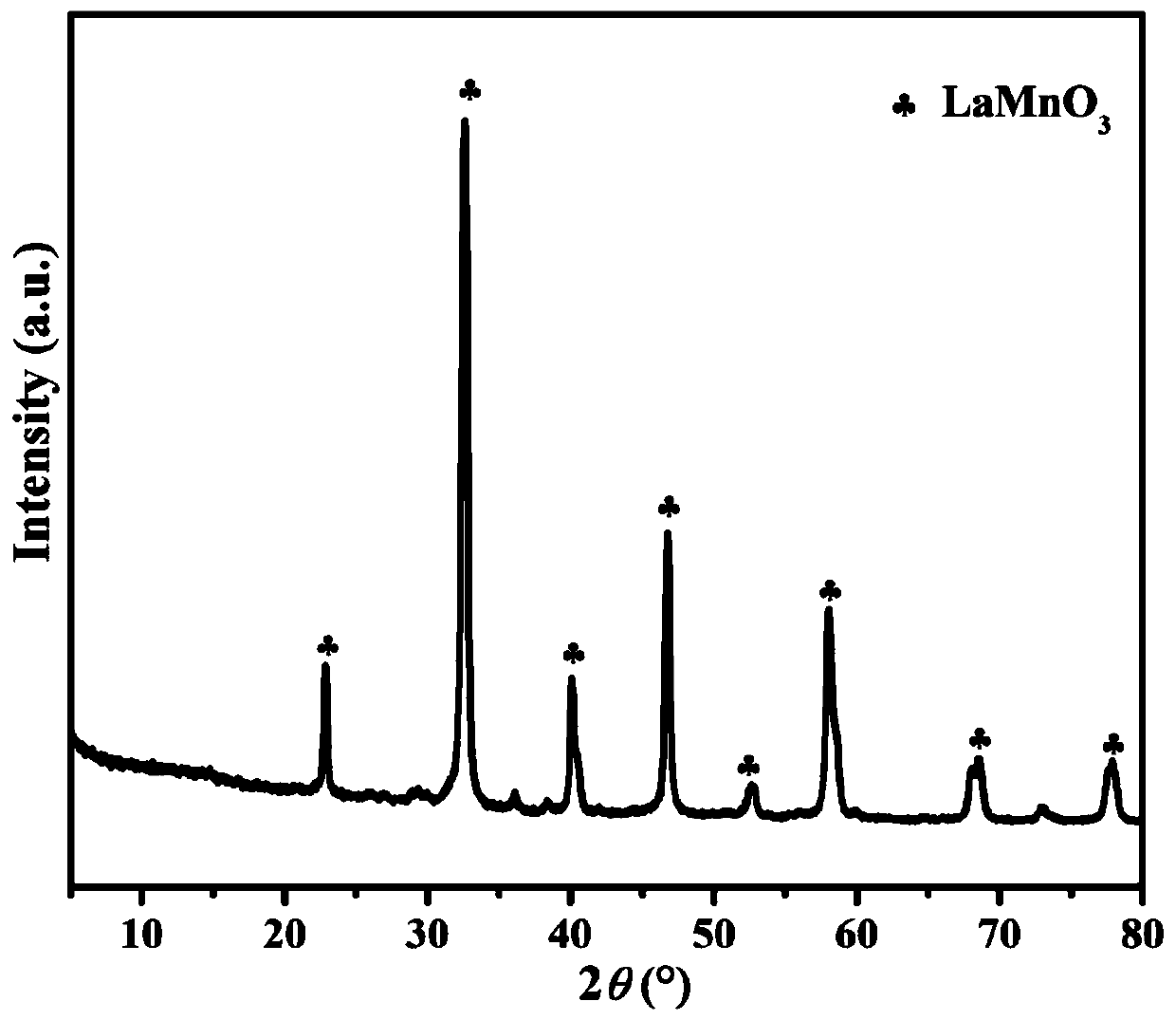
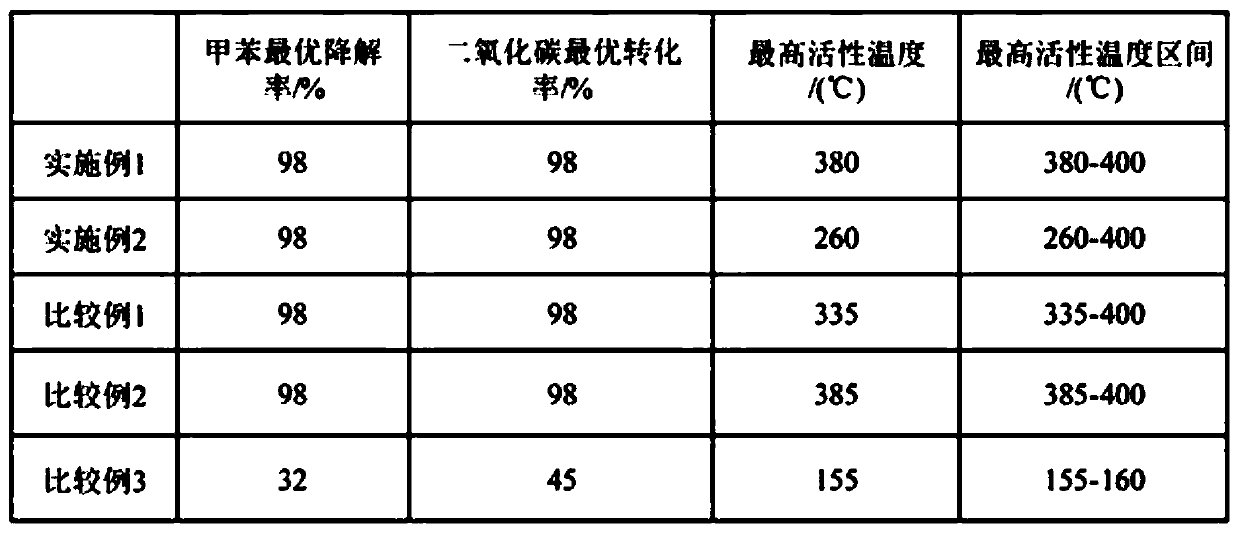
Ce-doped LaMnO3 catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109999796ALow priceSimple preparation processGas treatmentDispersed particle separationHeterojunctionLattice oxygen
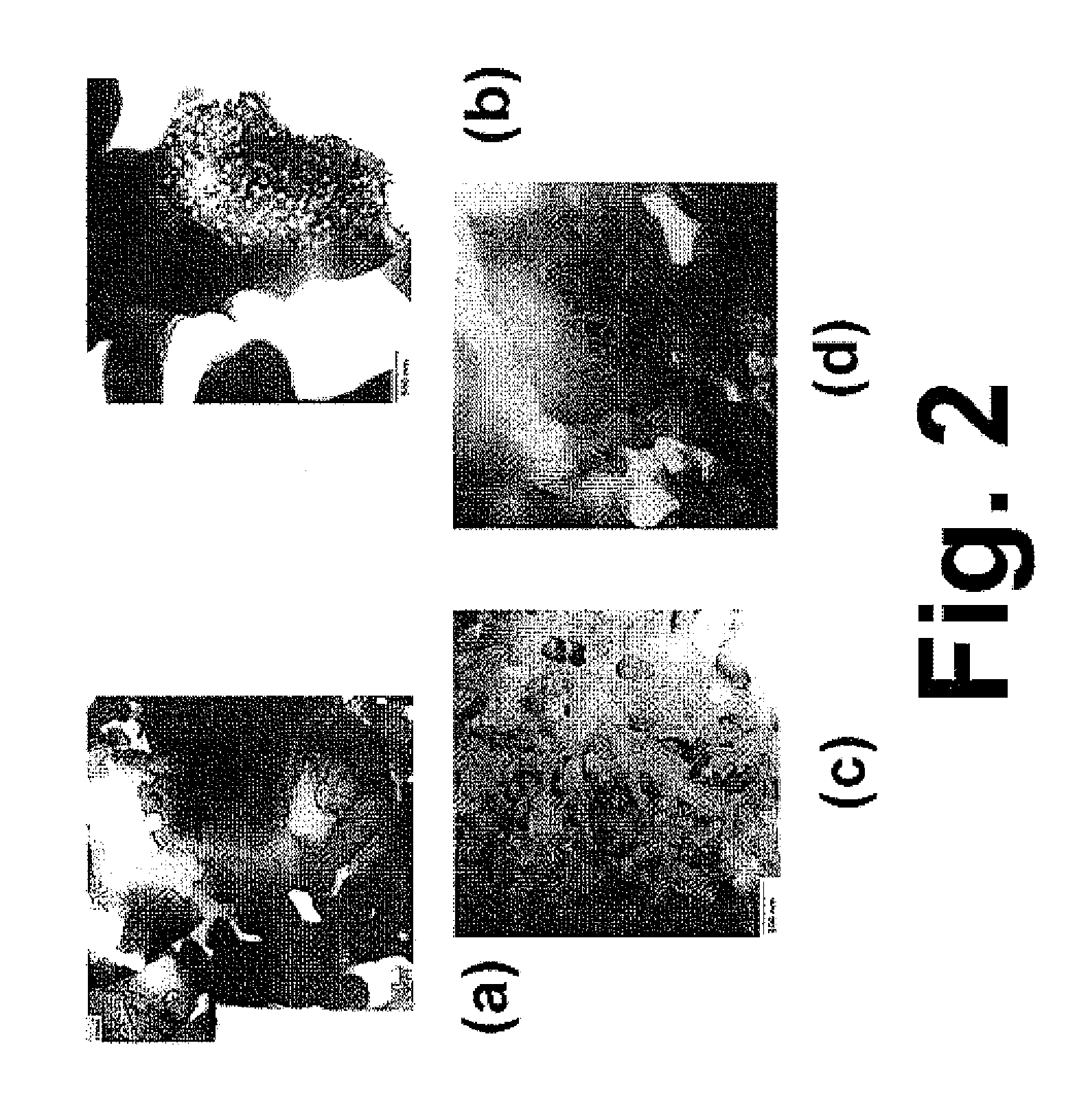
The invention belongs to the field of VOC degradation, and particularly relates to a Z-type La1-xCexMnO3 catalyst used for photothermal degradation of toluene. According to the Ce-doped LaMnO3 catalyst and a preparation method thereof, a series of Ce-doped LaMnO3(La1-xCexMnO3) is prepared by adopting a sol-gel method and is subjected to gaseous toluene oxidation test in order to study the effect of Ce doping in LaMnO3 on the activity of LaMnO3 under photothermal conditions. The Ce-doped LaMnO3 can form the coexistence of the La1-xCexMnO3 and CeO2, the reaction of CeO2 / La1-xCexMnO3 under the photothermal condition follows the Mars-van Krevelen redox cycle mechanism, the prepared CeO2 / La1-xCexMnO3 can form an efficient Z-Scheme heterojunction, and the electron transfer speed of the catalystin a high-temperature region can be improved. Moreover, in photothermal catalytic degradation, lattice oxygen is the most important active substance, and the lattice oxygen content of perovskite and the reaction activity can be increased by doping a small amount of cerium doping. The optical and thermal activity are enhanced by the Ce doped LaMnO3 perovskite and the Ce-doped LaMnO3 catalyst is a promising catalyst.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
A kind of cobalt-cerium/sepiolite catalyst and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109847759BRaw materials are easy to getSimple methodHydrogenMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystCerium(IV) oxide
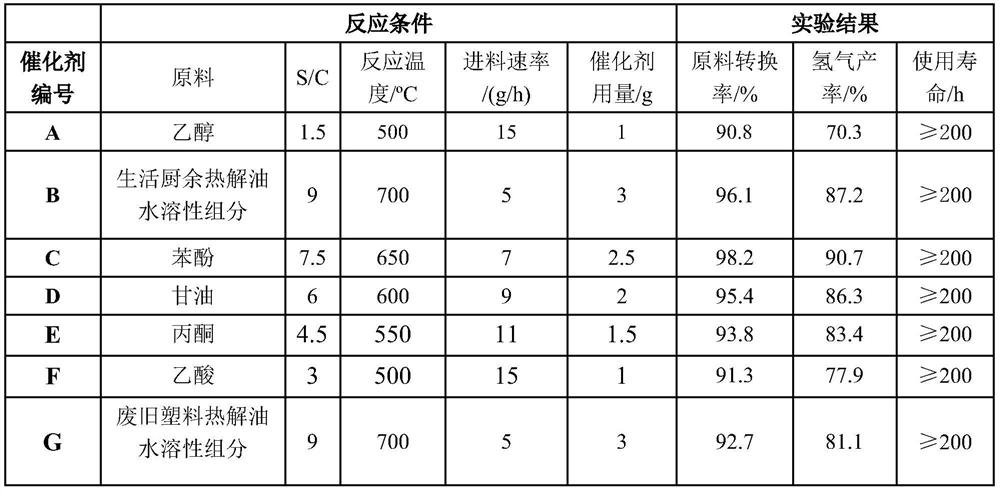
The invention discloses a cobalt-cerium / sepiolite catalyst and its preparation method and application. The catalyst comprises sepiolite as a carrier and cobalt and cerium as active components loaded on the sepiolite. The cobalt-cerium / sepiolite catalyst of the present invention utilizes cerium oxide as an auxiliary component to interact with cobalt during the calcination and reduction process, thereby improving the conversion rate of bio-oil and its model, hydrogen production rate and stability. At the same time, ceria, as an auxiliary agent, undergoes a rapid redox cycle for oxygen transfer during the reforming process, improving the conversion rate of carbon-containing species and hydrogen production efficiency, avoiding the formation of carbon deposits covering metal sites, and thus enhancing catalyst life.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com