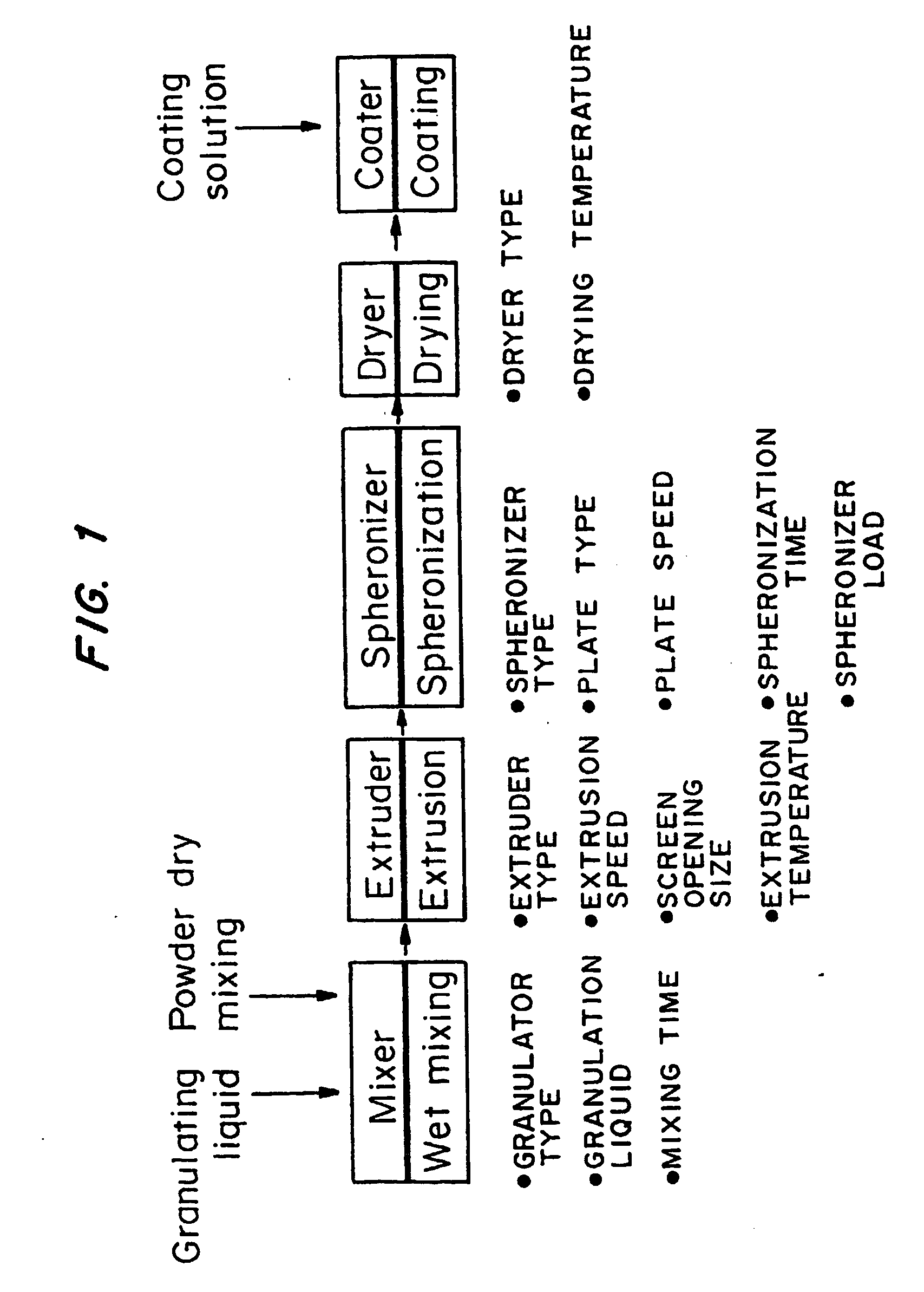
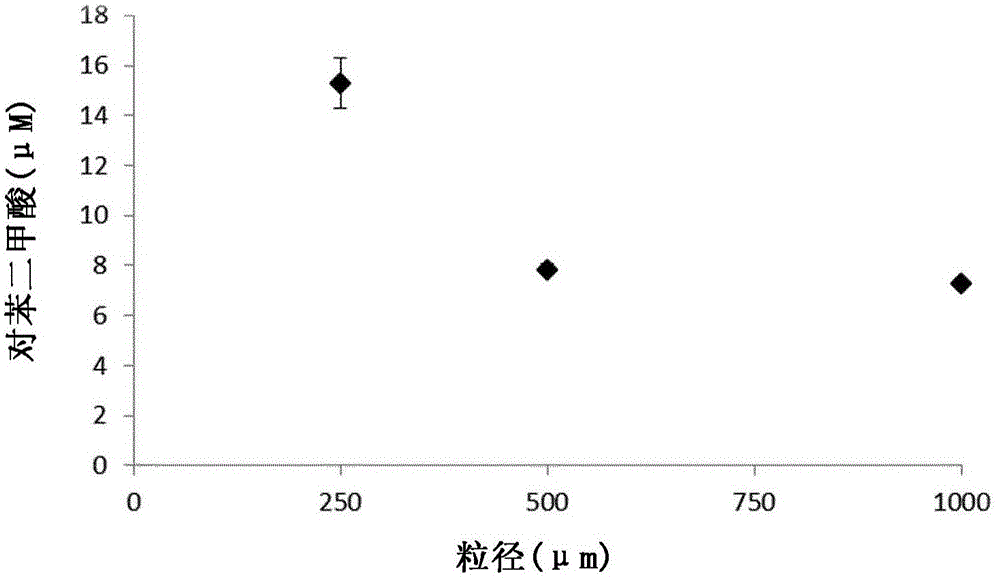
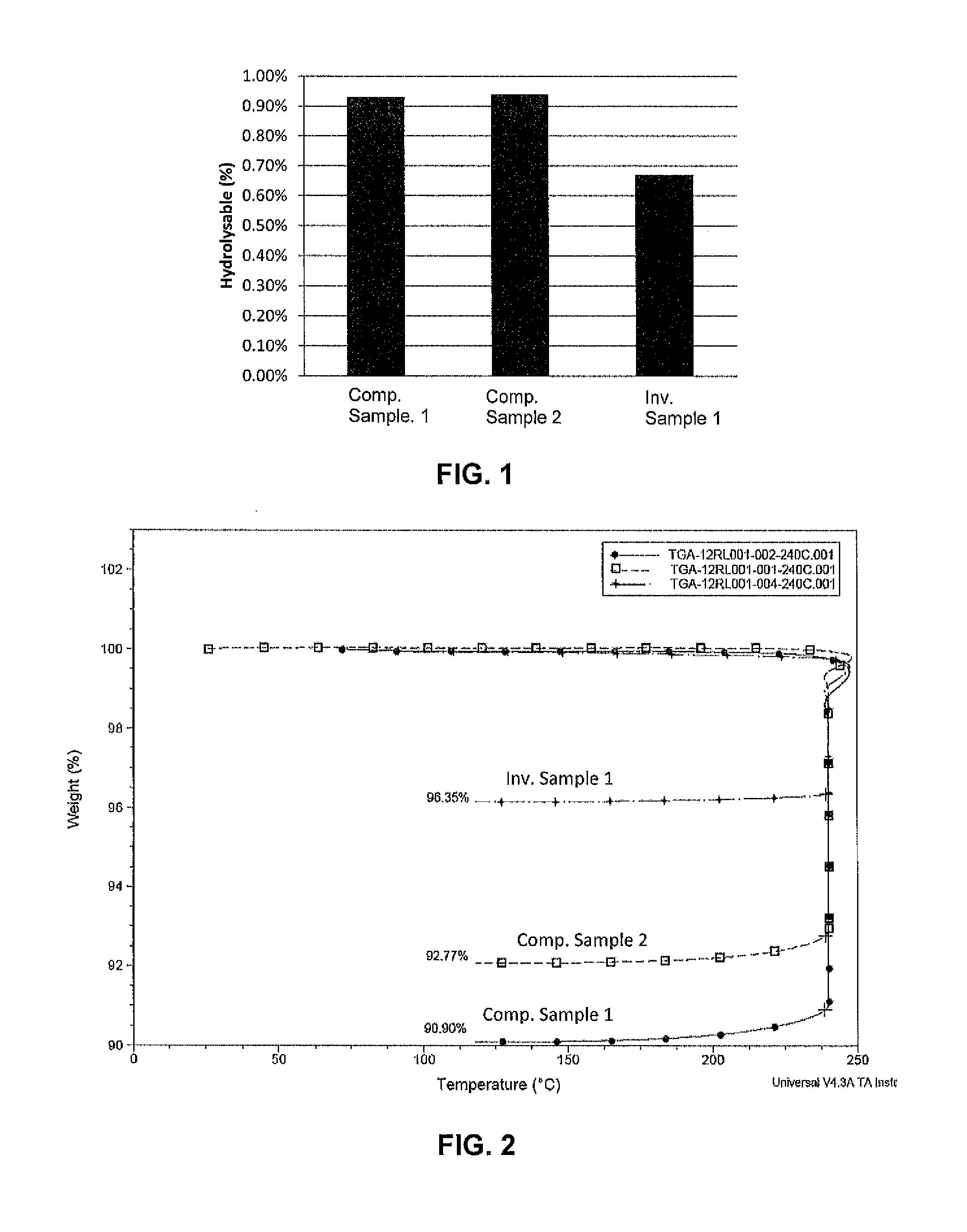
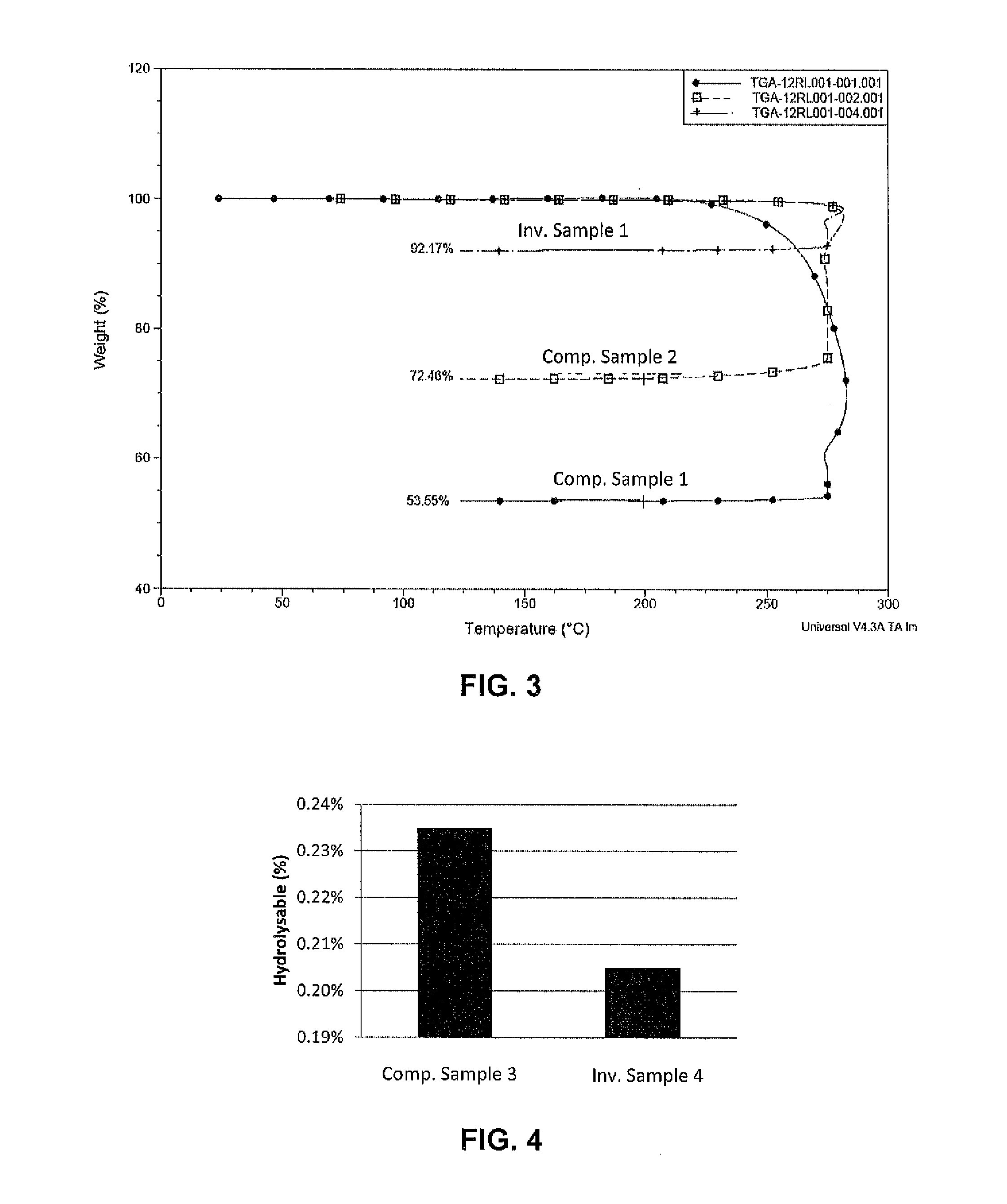
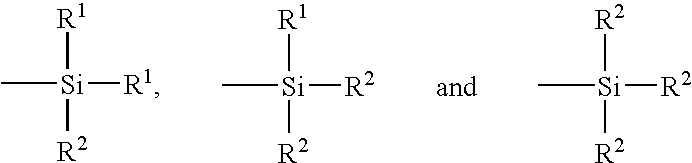Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
173 results about "Polymer degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer degradation is a change in the properties—tensile strength, color, shape, etc.—of a polymer or polymer-based product under the influence of one or more environmental factors such as heat, light or chemicals such as acids, alkalis and some salts. These changes are usually undesirable, such as cracking and chemical disintegration of products or, more rarely, desirable, as in biodegradation, or deliberately lowering the molecular weight of a polymer for recycling. The changes in properties are often termed "aging".
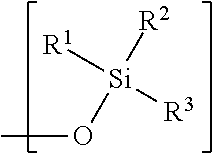
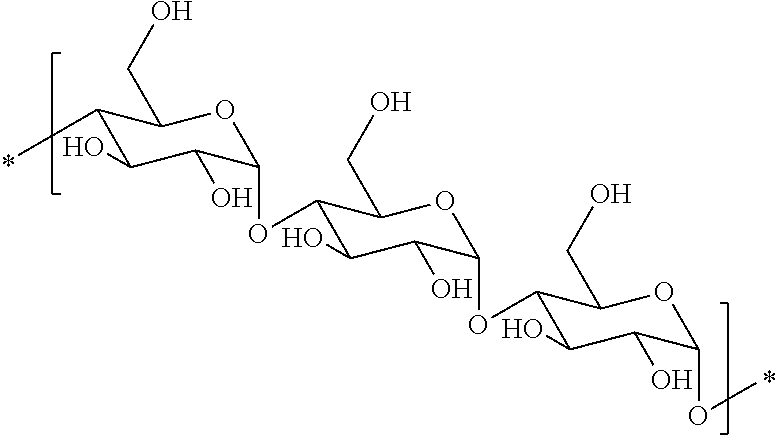
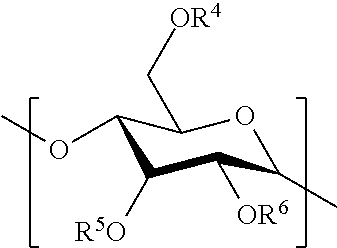
Hydrophobic polysaccharides with silyl ether linkages having enhanced degradation and medical articles made therefrom
ActiveUS8932616B2Improve degradation rateOvercome difficultiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPolymer scienceActive agent
Hydrophobic α(1→4)glucopyranose polymers with enhanced degradation properties are described. Between the α(1→4)glucopyranose polymeric portion and the hydrophobic portion exists a linker portion having a silyl ether chemistry that facilitates degradation of the polymer. Biodegradable matrices can be formed from these polymers, and the matrices can be used for the preparation of implantable and injectable medical devices wherein the matrix is capable of degrading in vivo at an increased rate. Matrices including and capable of releasing a bioactive agent in vivo are also described.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Methods of placing treatment chemicals
Among the methods provided are methods of treating a subterranean formation comprising placing a solid treatment chemical and a tacky polymer onto a solid substrate to create a coated solid substrate; placing the coated solid substrate into a portion of a subterranean formation; and, allowing the tacky polymer to degrade and allowing the solid treatment chemical to be released into the portion of the subterranean formation. Also provided are methods of creating a particulate pack comprising a treatment chemical in a subterranean formation comprising placing a solid treatment chemical and a tacky polymer onto a particulate to create a coated particulate; creating a slurry comprising the coated particulates slurried into a treatment fluid; placing the slurry into a portion of a subterranean formation so as to create a particulate pack; and, allowing the tacky polymer to degrade and allowing the solid treatment chemical to be released into the portion of the subterranean formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
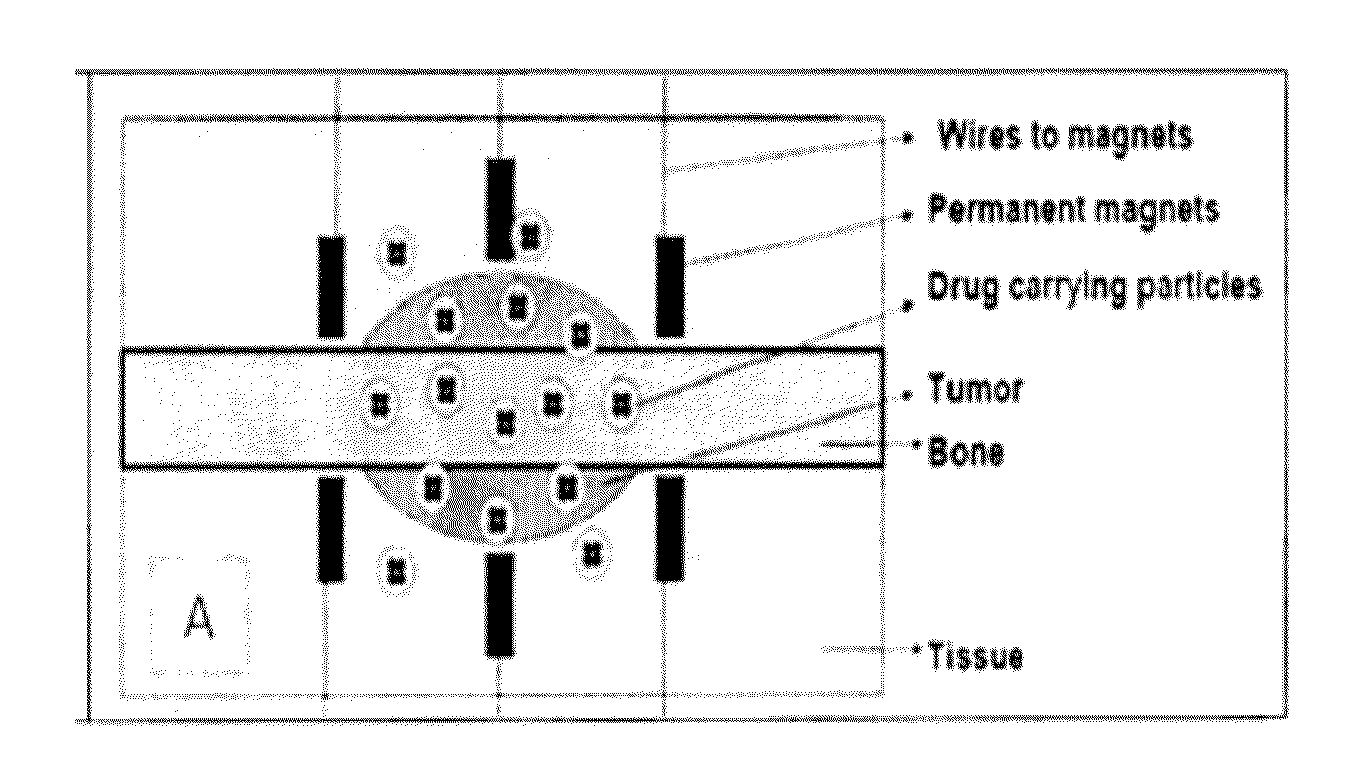
Composite magnetic nanoparticle drug delivery system
ActiveUS20120265001A1Accurate placementLimit deliveryBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseOil emulsion
A composite magnetic nanoparticle drug delivery system provides targeted controlled release chemotherapies for cancerous tumors and inflammatory diseases. The magnetic nanoparticle includes a biocompatible and biodegradable polymer, a magnetic nanoparticle, the biological targeting agent human serum albumin, and a therapeutic pharmaceutical composition. The composite nanoparticles are prepared by oil-in-oil emulsion / solvent evaporation and high shear mixing. An externally applied magnetic field draws the magnetic nanoparticles to affected areas. The biological targeting agent draws the nanoparticles into the affected tissues. Polymer degradation provides controlled time release delivery of the pharmaceutical agent.
Owner:WICHITA STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods of placing treatment chemicals
Methods of treating a subterranean formation comprising placing a solid treatment chemical and a tacky polymer onto a solid substrate to create a coated solid substrate; placing the coated solid substrate into a portion of a subterranean formation; and, allowing the tacky polymer to degrade and allowing the solid treatment chemical to be released into the portion of the subterranean formation. Methods of creating a particulate pack comprising a treatment chemical in a subterranean formation comprising placing a solid treatment chemical and a tacky polymer onto a particulate to create a coated particulate; creating a slurry comprises the coated particulates slurried into a treatment fluid; placing the slurry into a portion of a subterranean formation so a to create a particulate pack; and, allowing the tacky polymer to degrade and allowing the solid treatment chemical to be released into the portion of the subterranean formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
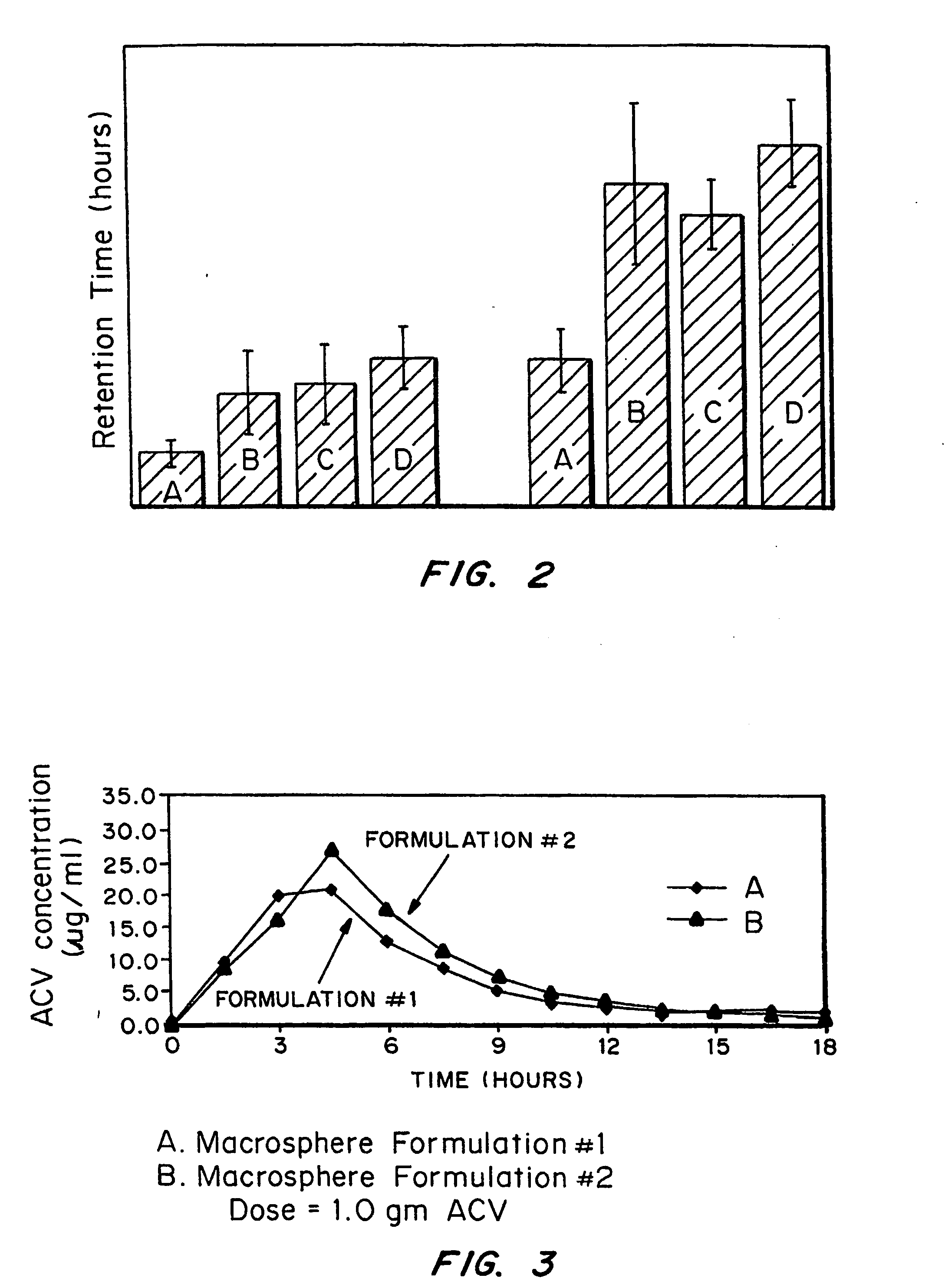
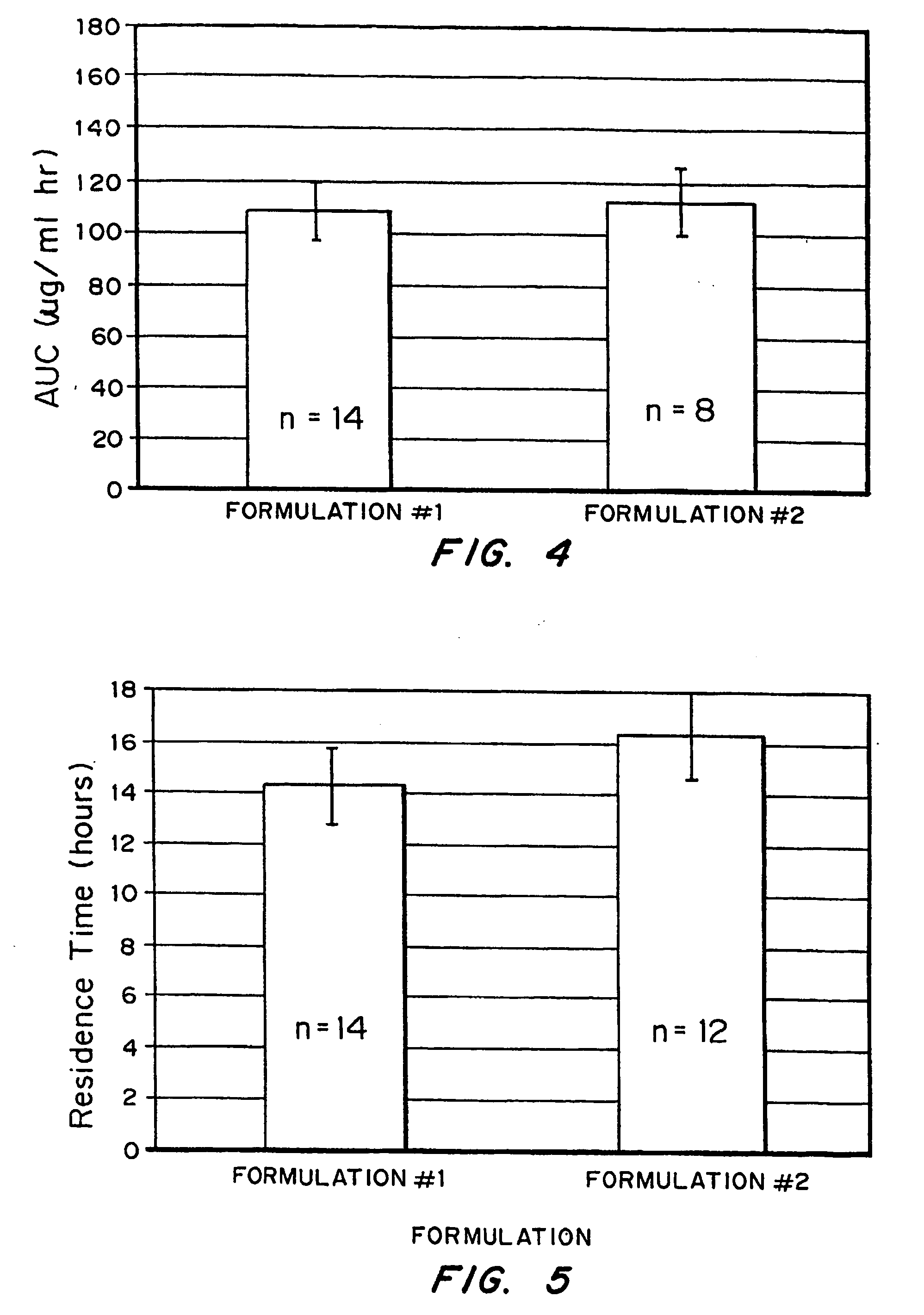
Bioadhesive drug delivery system with enhanced gastric retention
InactiveUS20050064027A1Prolonged gastric retention timeHigh retention rateBiocideCosmetic preparationsWhole bodyRetention time
Bioadhesive macrosphere delivery systems (“BDDS”) having prolonged gastric retention time due to bioadhesion rather than physical density or size are described. In general, the macrospheres have diameters that are greater than 200 microns, more preferably greater than 500 microns. The bioadhesive macrospheres are released in the stomach where they reside in close proximity to the gastric mucosa for a prolonged period of time. Increased residence of BDDS in the upper GI can lead to increased systemic absorption of drug in the preferred site of systemic absorption, namely the upper GI tract (upper to mid-jejunum). The BDDS may be engineered either as a capsule with drug delivery controlled by a diffusion-limited membrane or degradable shell, or as a solid matrix system with drug delivery controlled by a combination of diffusion and polymer degradation kinetics.
Owner:SPHERICS
Degradable therapeutic delivery device
InactiveUS20070243229A1Reduced pHMedical devicesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsVaginal insertPolymer degradation
A biodegradable biodelivery device is disclosed. The biodelivery device is formed from a polymer comprising the reaction product of a polyol and a polyacid. When exposed to water, the polymer degrades through hydrolysis. Of particular advantage, the polymer can be formed so as to be elastic and flexible. In one embodiment, the polymer is formed into a vaginal insert. As the polymer degrades, the polymer releases acid to a vaginal environment for decreasing the pH of the environment.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method and composition for the triggered release of polymer-degrading agents for oil field use
InactiveUS20050130845A1Avoid damageMaintain activityFluid removalFlushingChemical physicsPolymer degradation
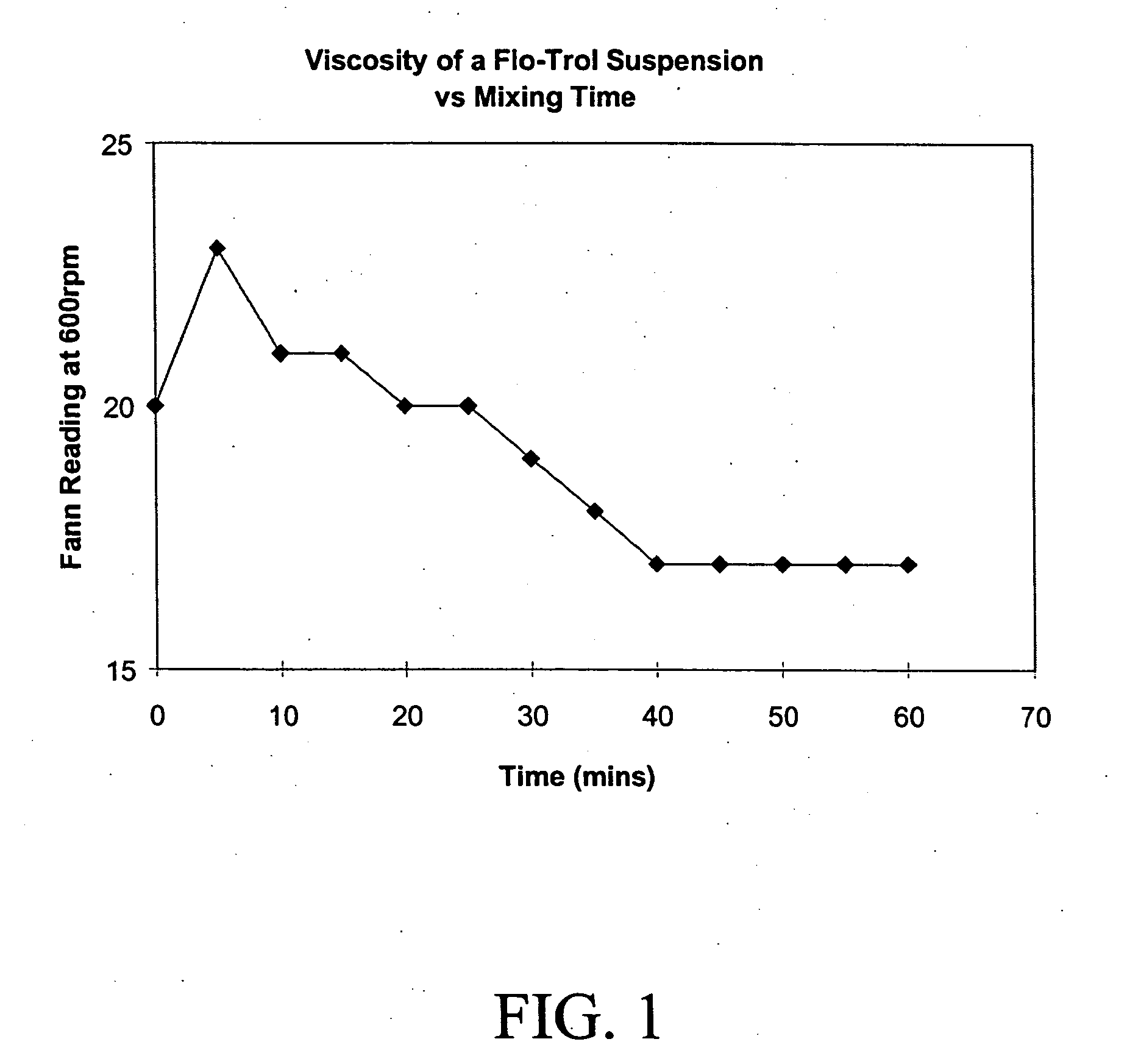
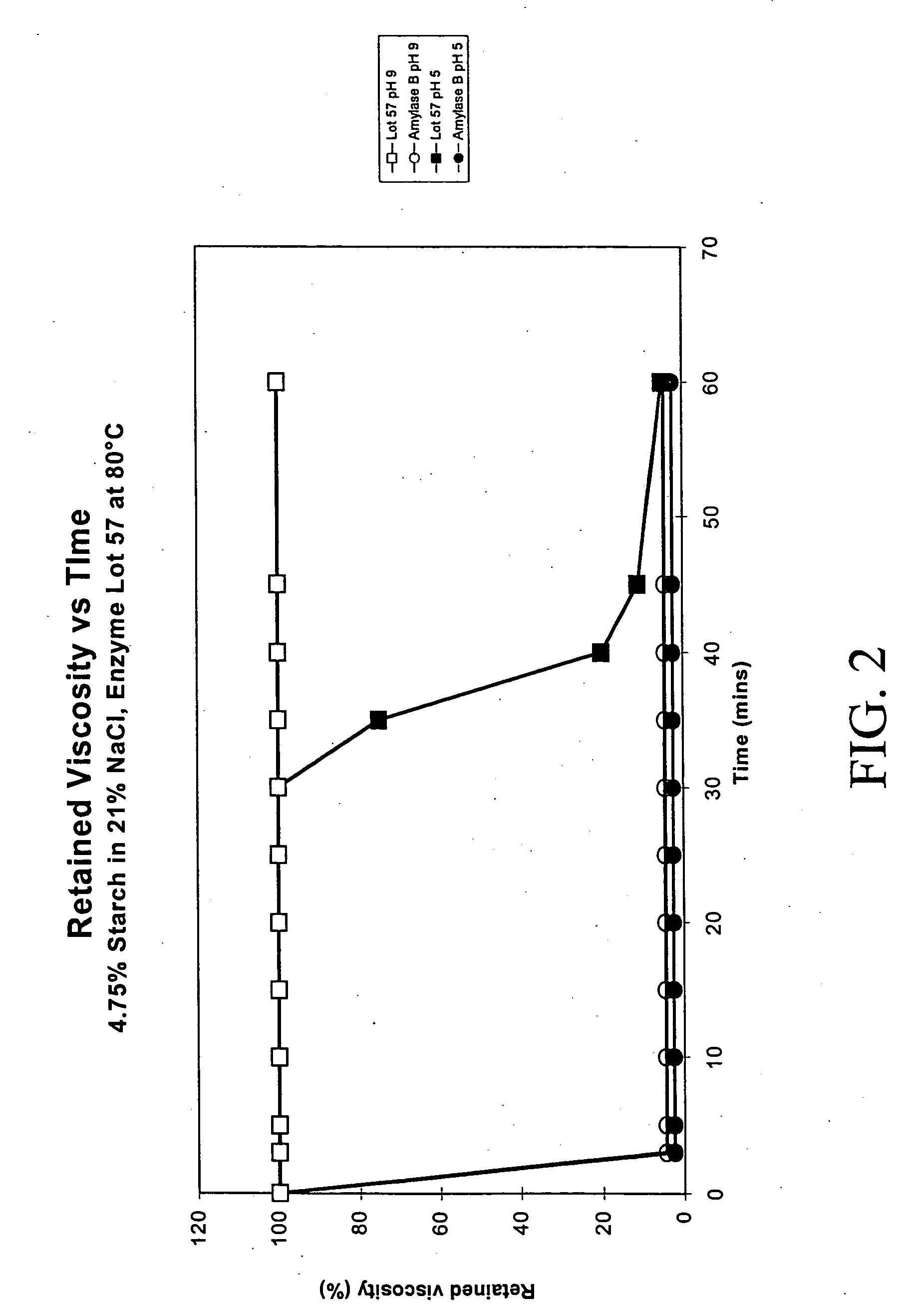
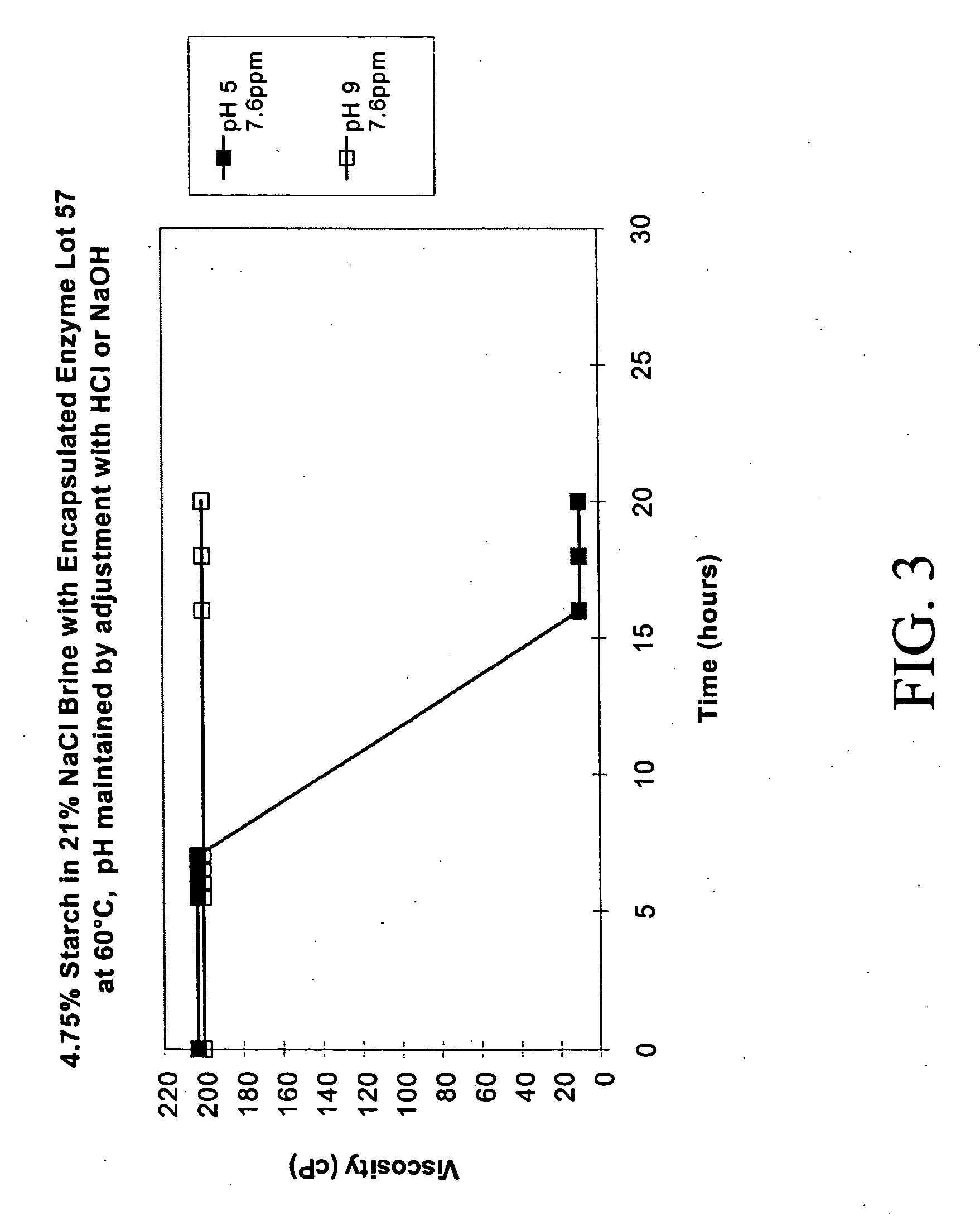
Disclosed are methods and related compositions for altering the physical and chemical properties of a substrate used in hydrocarbon exploitation, such as in downhole drilling operations. In a preferred embodiment a method involves formulating a fluid, tailored to the specific drilling conditions, that contains one or more inactivated enzymes. Preferably the enzyme is inactivated by encapsulation in a pH responsive material. After the fluid has been introduced into the well bore, one or more triggering signals, such as a change in pH, is applied to the fluid that will activate or reactivate the inactivated enzyme, preferably by causing it to be released by the encapsulation material. The reactivated enzyme is capable of selectively acting upon a substrate located downhole to bring about the desired change in the chemical or physical properties of the substrate.
Owner:FREEMAN MICHAEL A +5
Active and adaptive photochromic fibers, textiles and membranes
InactiveCN1942612AElectro-spinningMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentFiberElectrospinning
A process to make a dyed fiber which has the steps of mixing a dye capable of changing color and a polymer into a solution at a temperature below the temperature at which the dye or polymer degrades to form a polymer dye solution and electrospinning said polymer dye solution to form a fiber wherein the dye penetrates more than the surface of the fiber. The invention also relates to the fiber and use of the fiber.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Process for preparing a silica rubber blend
InactiveUS20050022915A1Efficiently and effectively disperseEnhanced interactionSpecial tyresOrganic dyesPolymer scienceEnd-group
The present invention relates to a technique to efficiently and effectively disperse silica throughout a rubbery polymer. By utilizing this technique mechanical mixing procedures that are energy intensive and require large capital investments in mixing equipment can be significantly reduced. By reducing the amount of shearing forces to which the rubber is subjected polymer degradation is also significantly reduced. The utilization of the technique of this invention also results in a uniform blend of the silica throughout the rubber and consequently better interaction between the silica and the rubber. This results in better physical properties, such as higher modulus. The subject invention more specifically discloses a process for preparing a silica / rubber blend which comprises dispersing silica, a silica coupling agent, and a low molecular weight end-group functionalized diene rubber throughout a cement of a conventional rubbery polymer, and subsequently recovering the silica / rubber blend from the organic solvent. The present invention further reveals a tire which is comprised of a generally toroidal-shaped carcass with an outer circumferential tread, two spaced beads, at least one ply extending from bead to bead and sidewalls extending radially from and connecting said tread to said beads, wherein said tread is adapted to be ground-contacting, and wherein said tread is comprised of the silica / rubber blend made by dispersing silica, a silica coupling agent, and a low molecular weight end-group functionalized diene rubber throughout a cement of a conventional rubbery polymer, and subsequently recovering the silica / rubber blend from the organic solvent.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
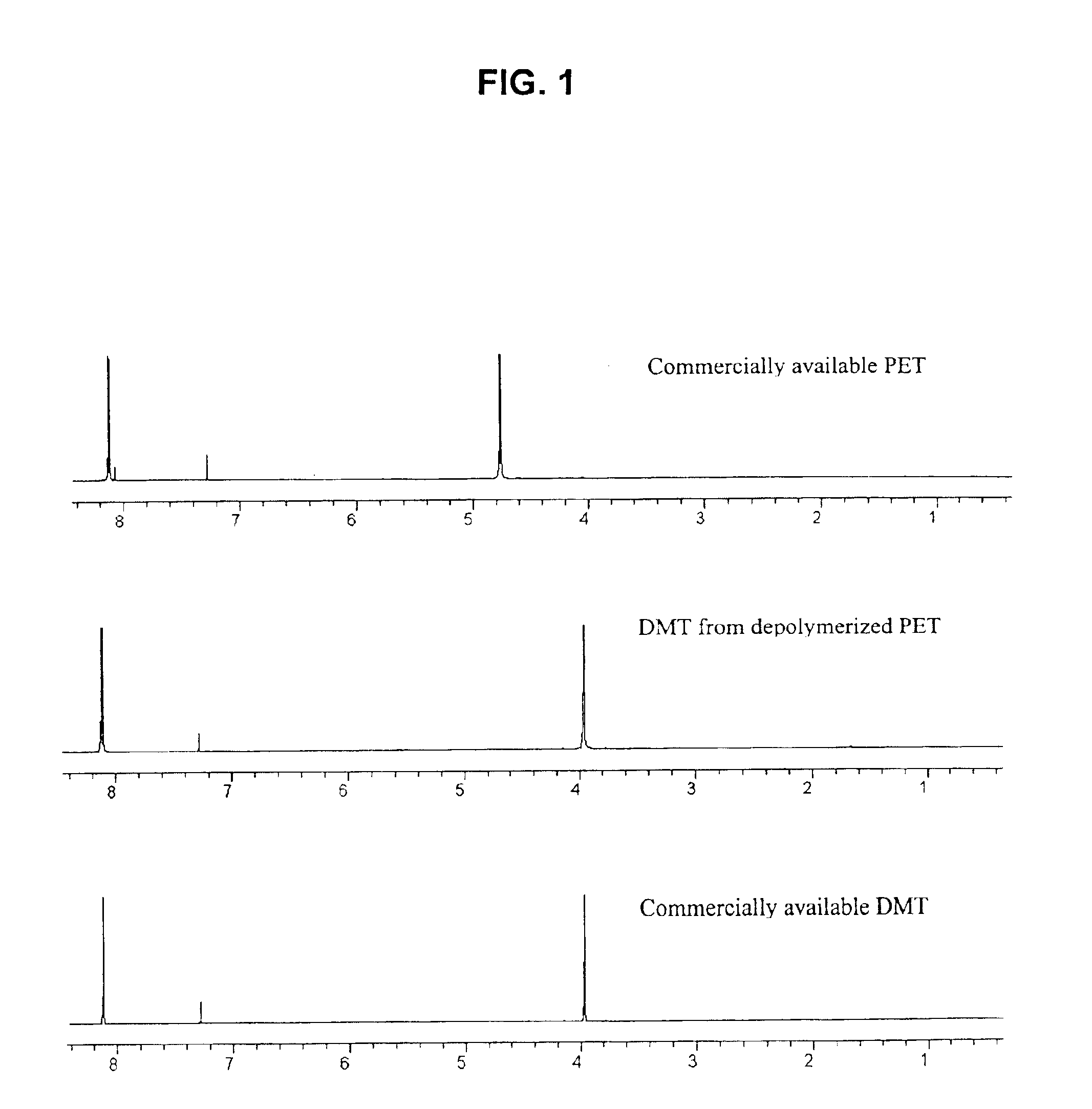
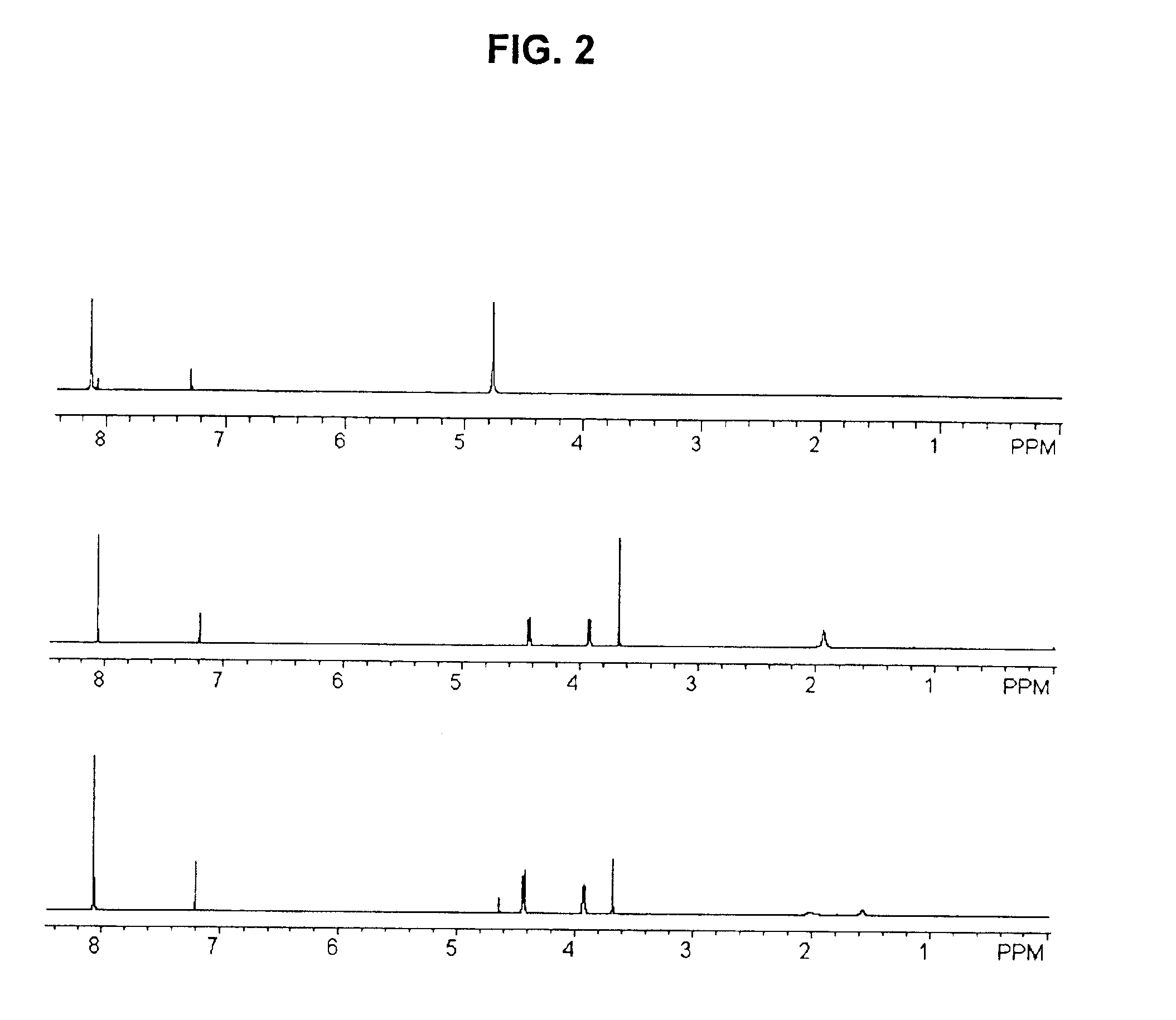
Catalytic depolymerization of polymers containing electrophilic linkages using nucleophilic reagents
InactiveUS6911546B2Minimize resultLightweight productionGroup 1/11 element organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationPolyesterDepolymerization
A method is provided for carrying out depolymerization of a polymer containing electrophilic linkages in the presence of a catalyst and a nucleophilic reagent, wherein production of undesirable byproducts resulting from polymer degradation is minimized. The reaction can be carried out at a temperature of 80° C. or less, and generally involves the use of an organic, nonmetallic catalyst, thereby ensuring that the depolymerization product(s) are substantially free of metal contaminants. In an exemplary depolymerization method, the catalyst is a carbene compound such as an N-heterocyclic carbene, or is a precursor to a carbene compound. The method provides an important alternative to current recycling techniques such as those used in the degradation of polyesters, polyamides, and the like.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method for degrading and recycling unsaturated polyester resin material
ActiveCN104326907AImprove immersionEfficient fractureOrganic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid anhydridesFiberPolyester
The invention provides a method for degrading and recycling an unsaturated polyester resin material. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a reaction solution by a catalyst and a reaction solvent; mixing the reaction solution with an unsaturated polyester material to prepare an unsaturated polyester degrading system; heating the prepared unsaturated polyester degrading system for degradation; adding a separation solvent into the cooled unsaturated polyester degrading system; filtering to obtain solids, namely enhanced fibers and a catalyst; drying and sieving, and recycling; adding water into filtrate so as to separate out a polymer degrading component containing a styrene structure, and filtering; drying and recycling the filtered polymer solids containing the styrene structure; and evaporating filtrate to obtain substances mainly comprising resin degraded products which do not contain the styrene structure. The method for degrading and recycling the unsaturated polyester resin material has the advantages of low cost, moderate recycling conditions and high degrading activity.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for recycling plastic products
ActiveUS20150290840A1Reduce energy consumptionIncrease productionPlastic recyclingFermentationPolymer degradationEnzyme
The invention relates to a method for recycling at least one plastic product, the method comprising degrading at least one polymer of the plastic product to monomers using an enzyme and recovering the resulting monomers. The method of the invention may be used for degrading, simultaneously or sequentially at least two different polymers of the plastic product, and / or for recycling at least two plastic products.
Owner:CARBIOS
Spinneret plate for melt spinning and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101177793AExtended service lifeReduce stressSpinnerette packsFurnace typesManufacturing cost reductionOrganic solvent
The invention discloses a spinneret plate used for melt spinning. The surface or the inner surface of the spinneret plate is covered by a nano-scaling or hypo-nano scaling oxide film with a thickness of 0.8nm to 28nm or a 0.1mm to 0.25mm metal lamina is embedded in a spinneret orifice in the spinneret plate. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the spinneret plate used for melt spinning. As the surface or the inner surface of the spinneret plate of the invention is covered by the nano-scaling or hypo-nano scaling oxide film or because the metal lamina is embedded in the spinneret orifice , the invention not only can avoid the degradation and degeneration of melten polymer passing through the spinneret plate but also can avoid the damage of corrosive substances and impurities of fused mass to the inner surface of the spinneret orifice, thus prolonging the service life of the spinneret plate and lowering the rejection rate of the fibers. Suspension used in the invention does not use expensive and poisonous organic solvent, thus not only lowering manufacturing cost, but also avoiding environmental pollution.
Owner:德阳科吉高新材料有限责任公司
Highly oriented fluoropolymer films
InactiveUS6465103B2Less likelihoodImprove bindingLayered product treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present invention provides highly oriented multilayer films. They are produced by coextruding or laminating films having at least one layer of a fluoropolymer, at least one layer of a polyolefin homopolymer or copolymer and an intermediate adhesive layer of a polyolefin having at least one functional moiety of an unsaturated carboxylic acid or anhydride thereof. With this structure the polyolefin layer allows the fluoropolymer layer to be stretched up to ten times its original length. Such a high orientation ratio for the fluoropolymer film increases the mechanical strength, toughness, and water vapor barrier properties of the film while using a thinner gauge fluoropolymer film. Coextrusion processing can be done at higher temperatures, i.e. in the range of from at about 280° C. to about 400° C. These temperatures allow films to be produced in the absence of polymer degradation and film melt fracture.
Owner:ALLIED SIGNAL INC
Methods to Improve the Compatibility and Efficiency of Powdered Versions of Microfibrous Cellulose
InactiveUS20110059883A1Improve performanceOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsCellulose fiberPolymer degradation
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
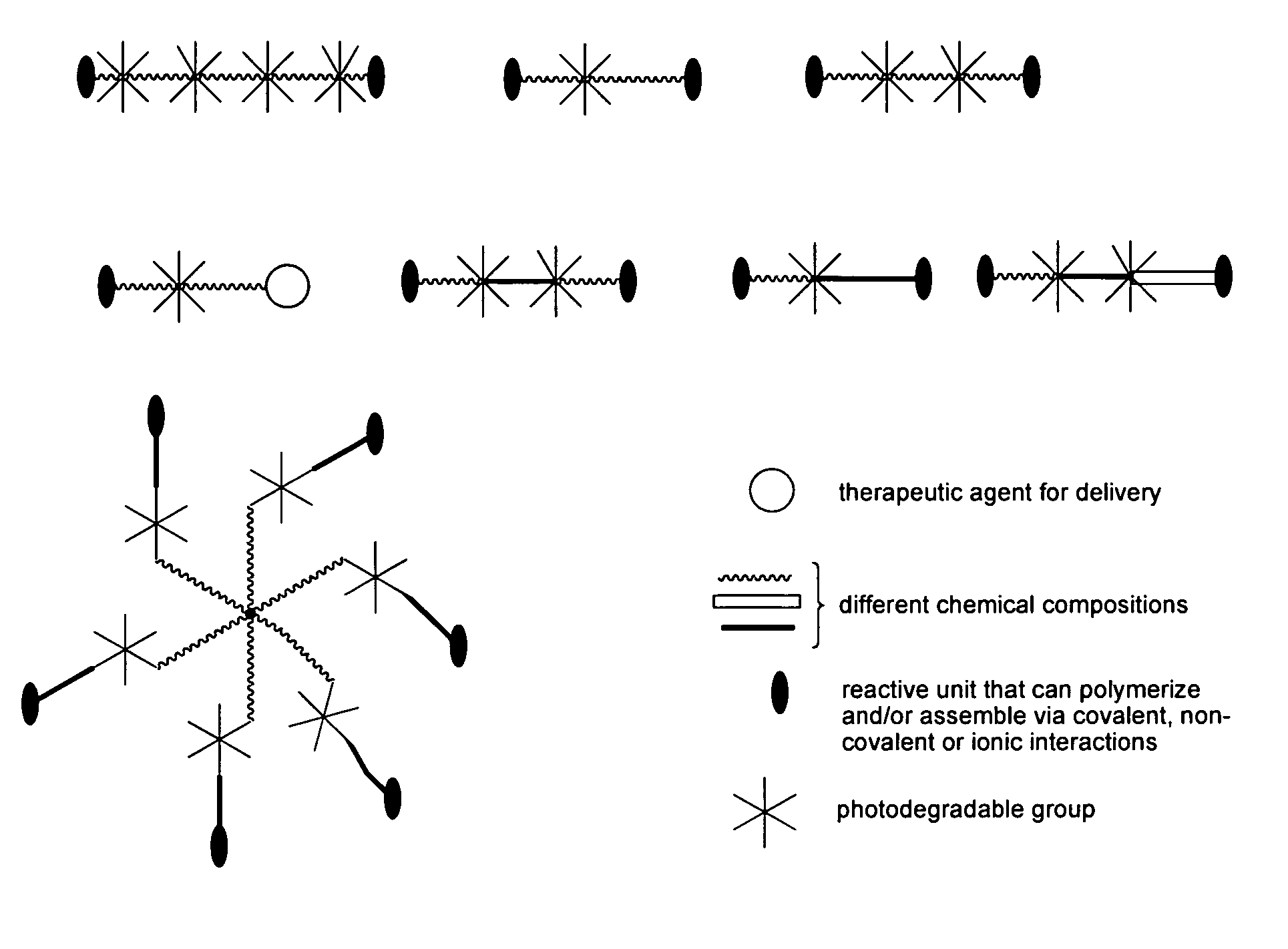
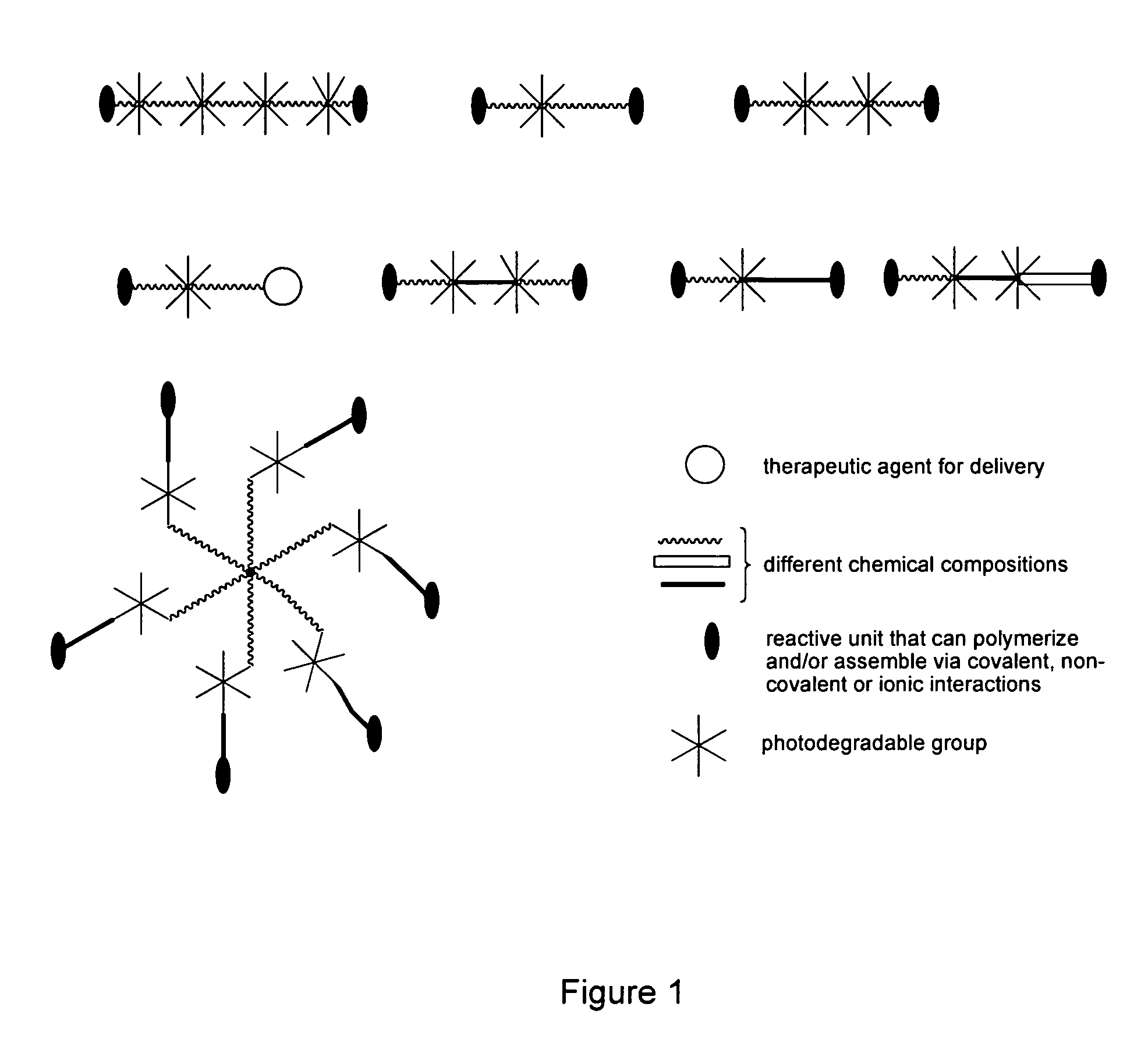
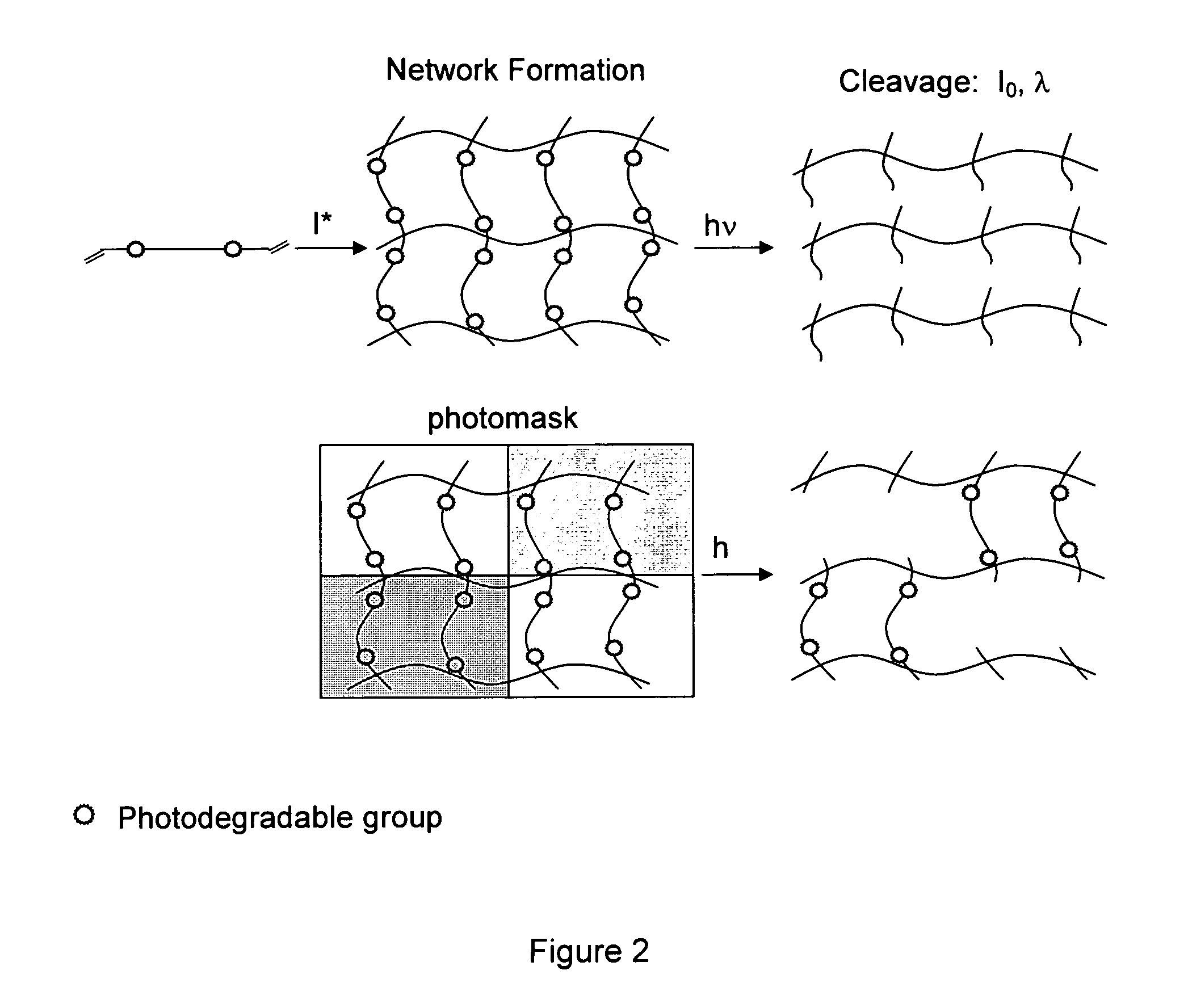
Photodegradable groups for tunable polymeric materials
ActiveUS8343710B1Sure easyEasy to useOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsPolymer scienceEnd-group
Provided is a method that provides both spatial and temporal control of a polymer degradation process using mono- and multifunctional macromolecular monomers (“macromers”) that degrade via single- and multi-photon photolysis mechanisms over a broad range of wavelengths. The macromers can form or be incorporated into networks via covalent, non-covalent and / or ionic interactions. The spatial and temporal degradation of these networks can be controlled. More specifically, provided is a photodegradable macromer, comprising: (a) a photodegradable group; (b) a backbone structure comprising one or more repeating units that may be the same or different, which backbone structure is attached to the photodegradable group directly or through a linker; (c) one or more reactive end groups at one or more ends of the macromer; and optionally, (d) one or more therapeutic agents; and optionally (e) one or more caged groups. Also provided are polymers and networks incorporating macromers of the invention and optionally other substituents such as other polymeric structures. Also provided is a method of controlled degradation of a polymer comprising: providing a photodegradable polymer as described herein and exposing the photodegradable polymer to photoradiation of the appropriate wavelength and energy to cause one or more of the photodegradable groups to photodegrade.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Method for Increased Production of Biogas
InactiveUS20080124775A1Improve overall utilizationGood curative effectManure treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismAcetic acid
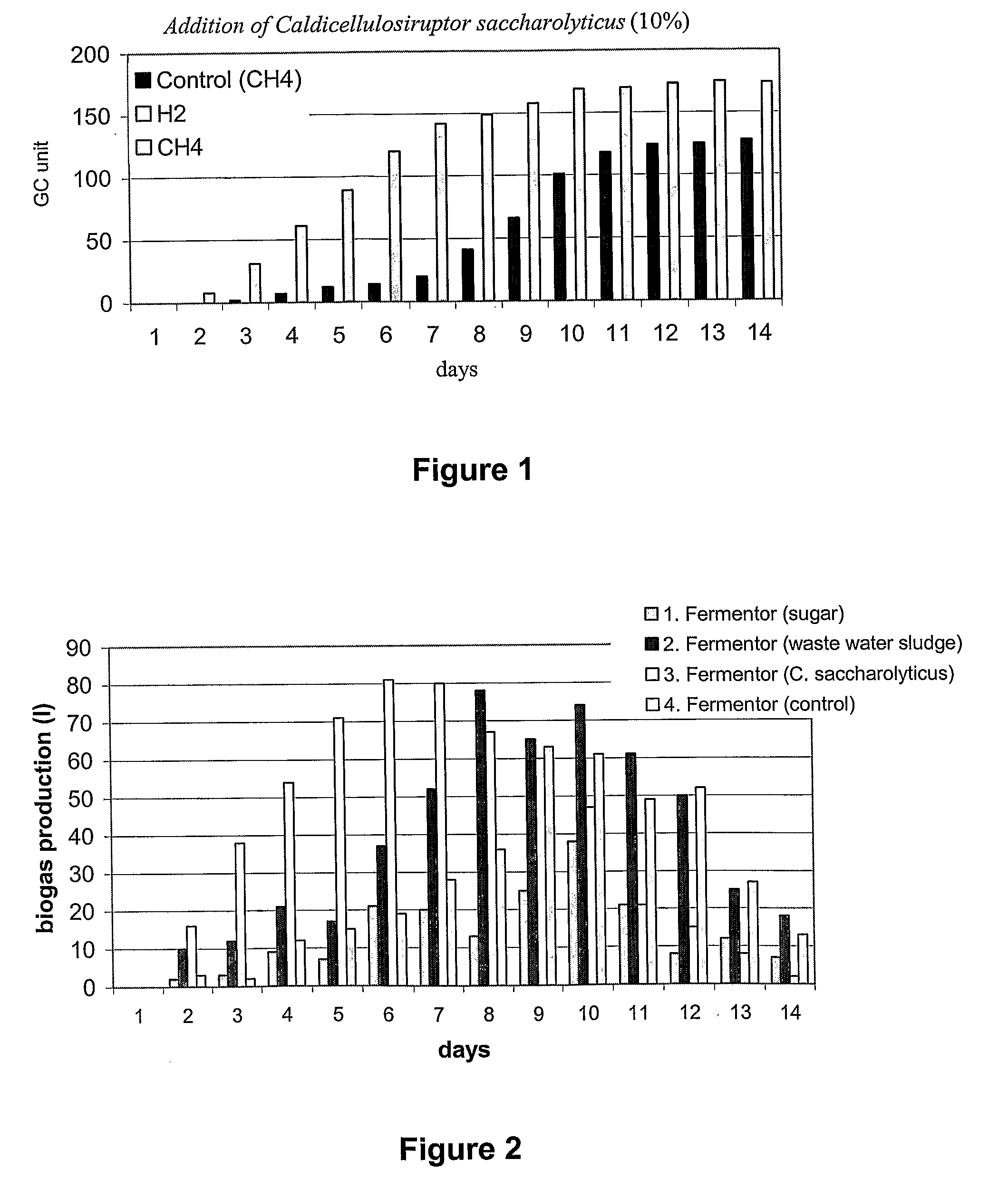
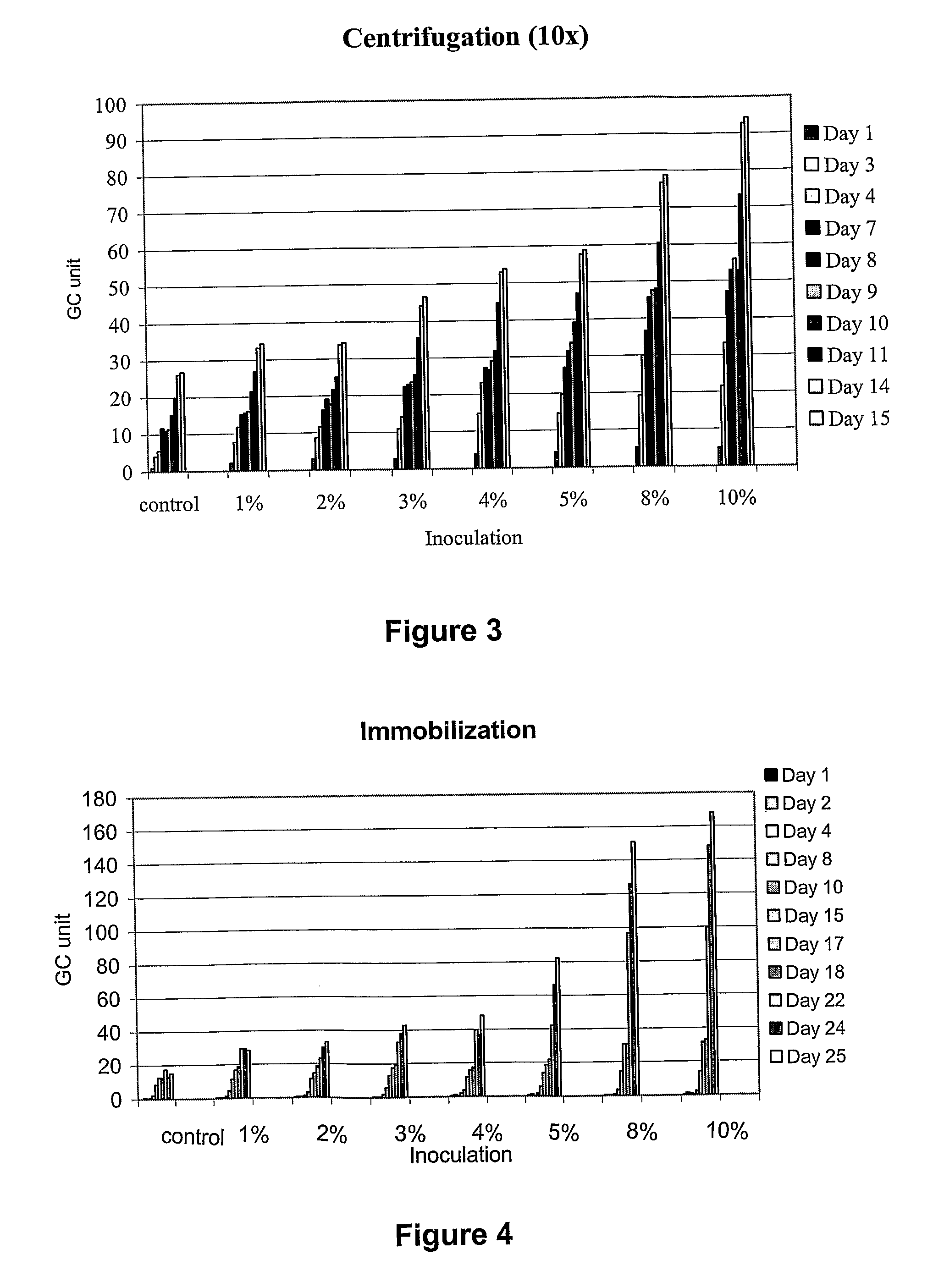
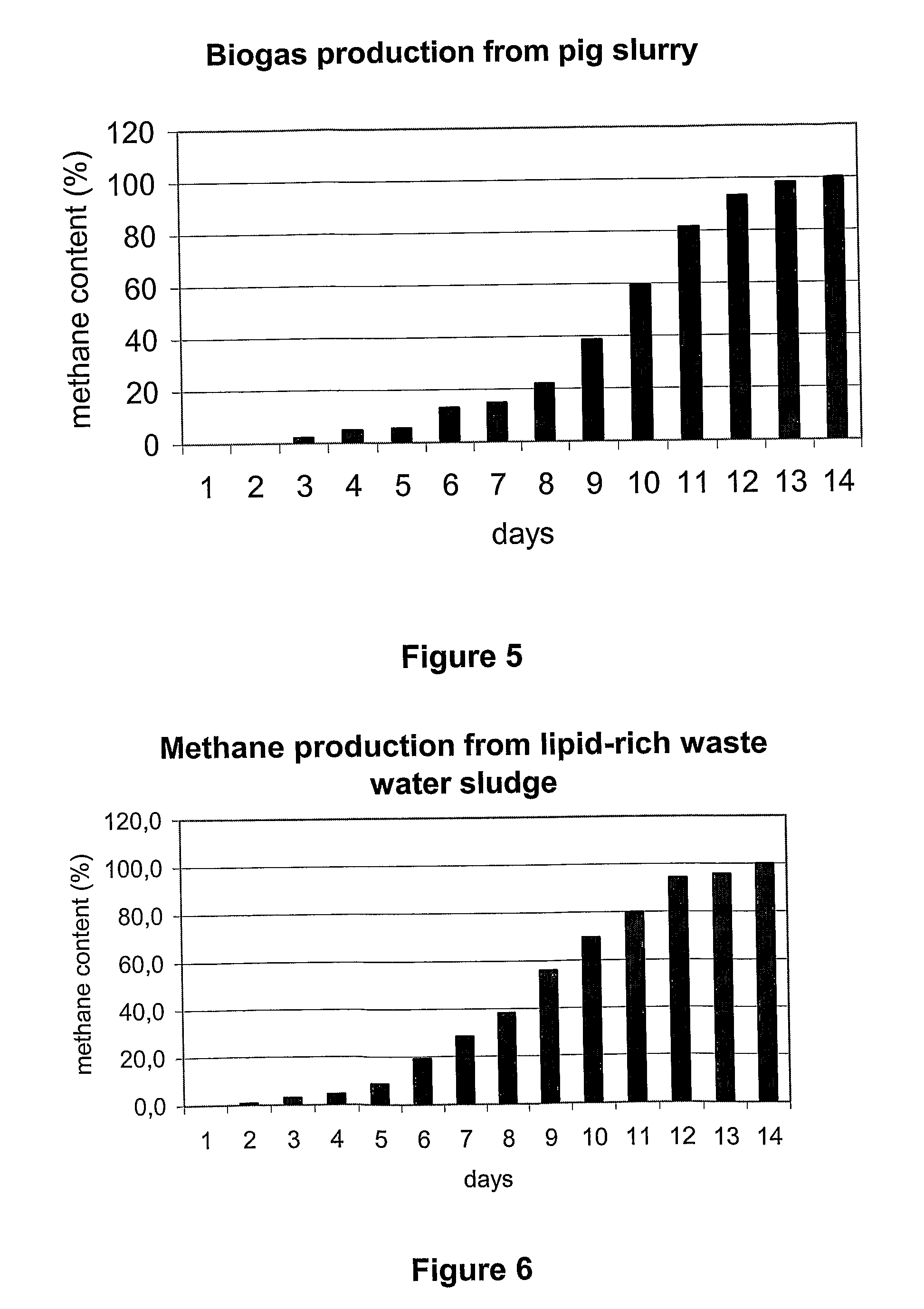
The invention relates to a method for increasing biogas production of thermophilic anaerobe systems. More closely, a biomass containing a consortium comprising polymer-degrading, acetogenic and methanogenic microorganisms is inoculated with a microorganism culture before the start of or during biogas production. Said microorganism is a thermophilic, acetogenic, hydrogen producing bacterium. As an example, Caldicellulosiruptor saccharolyticus is applied. According to the invention production if methane containing biogas is significantly increased.The invention is useful for intensifying biogas production and thereby increasing its feasibility.
Owner:SCHMACK BIOGAS GMBH
Full-dull polyamide 6 fibre and method for producing the same
ActiveCN101463506AAvoid yellowingImprove structural uniformityFilament/thread formingHeating/cooling textile fabricsYarnPolymer science
The invention relates to a chemical fiber and a manufacturing method thereof, in particular to a full-dull daiamid 6 fiber added with titanium dioxide and a manufacturing method thereof. The full-dull daiamid 6 fiber and the manufacturing method thereof which have less polymer degradation, even yarn levelness, less filoplume and uniform dyeing aim at solving the disadvantages of easy degradation of high polymer fusant, poor evenness of the yarn levelness, high fluctuation of oiling rate, easy occurrence of more filoplume, bad uniformity of dyeing, etc. The invention mainly has the technical proposal that daiamid 6 particle with more than or equal to 1.6% of TiO2 is taken as raw material, treated by melt spinning and cross air blasting through twice of rectification and oiling, and is wound; finally, the full-dull daiamid 6 fiber is obtained.
Owner:YIWU HUADING NYLON
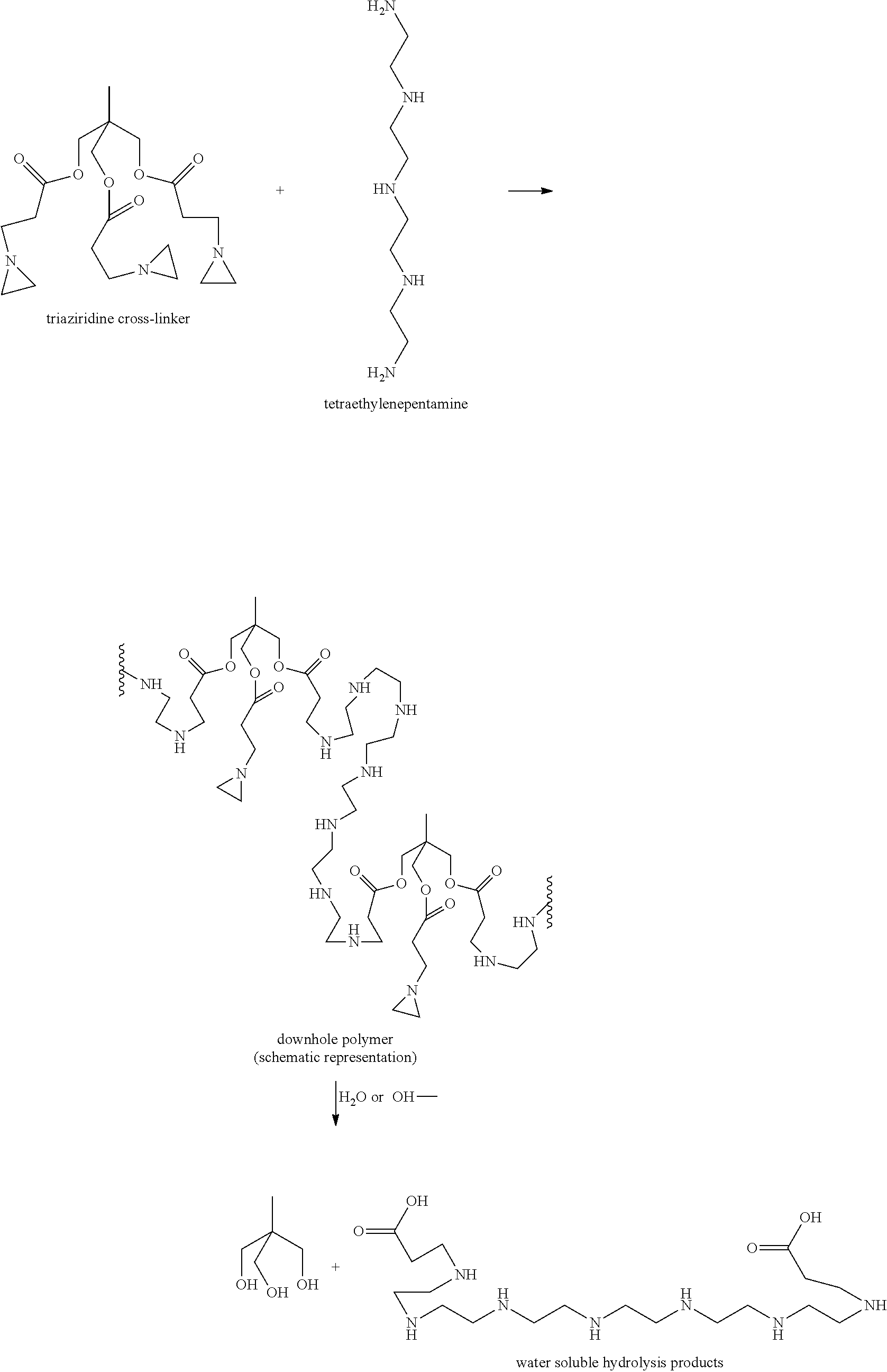
Synthesis of Degradable Polymers Downhole for Oilfield Applications
A method is given for polymerizing monomers downhole to create well treatment polymers. The monomers each contain two polymerizable groups and a degradable group or groups which allow the polymer to degrade under downhole conditions, for example by hydrolysis. Polymerization downhole allows easier, more precise, placement of polymer. Polymer obtained from monomers pumped downhole may be used, for example, for fluid diversion plugs, isolation plugs, formation consolidation, flowback control, and fluid loss control. Synthesized polymer may form gels, films, solids or other structure in treated wellbores, fractures, and / or formations. After the desired effect is achieved, the deposited polymer degrades and the polymer degradation products dissolve, leaving the wellbore, fracture and / or formation clean, with no damage that might have decreased fluid flow.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Separation method and device of polymer-containing oil sludge
The invention discloses a separation method and a separation device of polymer-containing oil sludge. The separation method comprises the steps of: (1) ultrasonic gel breaking of the polymer-containing oil sludge; (2) ultrasonic cleaning; and (3) standing separation. An ultrasonic device comprises a cylinder, an ultrasonic generation device, an ultrasonic controller arranged in the ultrasonic generation device, and ultrasonic transducers matching the ultrasonic generation device. The ultrasonic transducers are arrayed and are uniformly distributed on the two ends of the cylinder. A feeding port and a discharging port are respectively arranged on the top and the bottom of the cylinder. A feeding direction is perpendicular to an ultrasonic emission direction. According to the invention, polymer degradation is enhanced by using ultrasonic, stabilization of the polymer upon the oil-water-solid phase is reduced, and separation efficiency is improved. The feeding direction is perpendicular to the ultrasonic emission direction, and the ultrasonic device runs on line. Ultrasonic field radiation energy is concentrated, and an irradiation time is short, such that polymer-containing oil sludge can be subjected to large-scale industrial processing.
Owner:WUHAN GLT ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Method for recycling plastic products
The invention relates to a method for recycling at least one plastic product, the method comprising degrading at least one polymer of the plastic product to monomers using an enzyme and recovering the resulting monomers. The method of the invention may be used for degrading, simultaneously or sequentially at least two different polymers of the plastic product, and / or for recycling at least two plastic products.
Owner:卡比欧斯公司
Low Emission Polyoxymethylene
Low VOC emission polyoxymethylene and compositions and products that incorporate the polyoxymethylene are described. The polyoxymethylene is end capped with compound that can prevent degradation of the polymer and subsequent emission of VOC degradation products such as formaldehyde. The end-capped polyoxymethylene can include an inorganic linkage within the polymer backbone that is the reaction product of a terminal hydroxyl group of the polyoxymethylene and a hydrolyzable group of the compound. Also disclosed are products as may be formed from the low VOC emission polyoxymethylene.
Owner:TICONA LLC
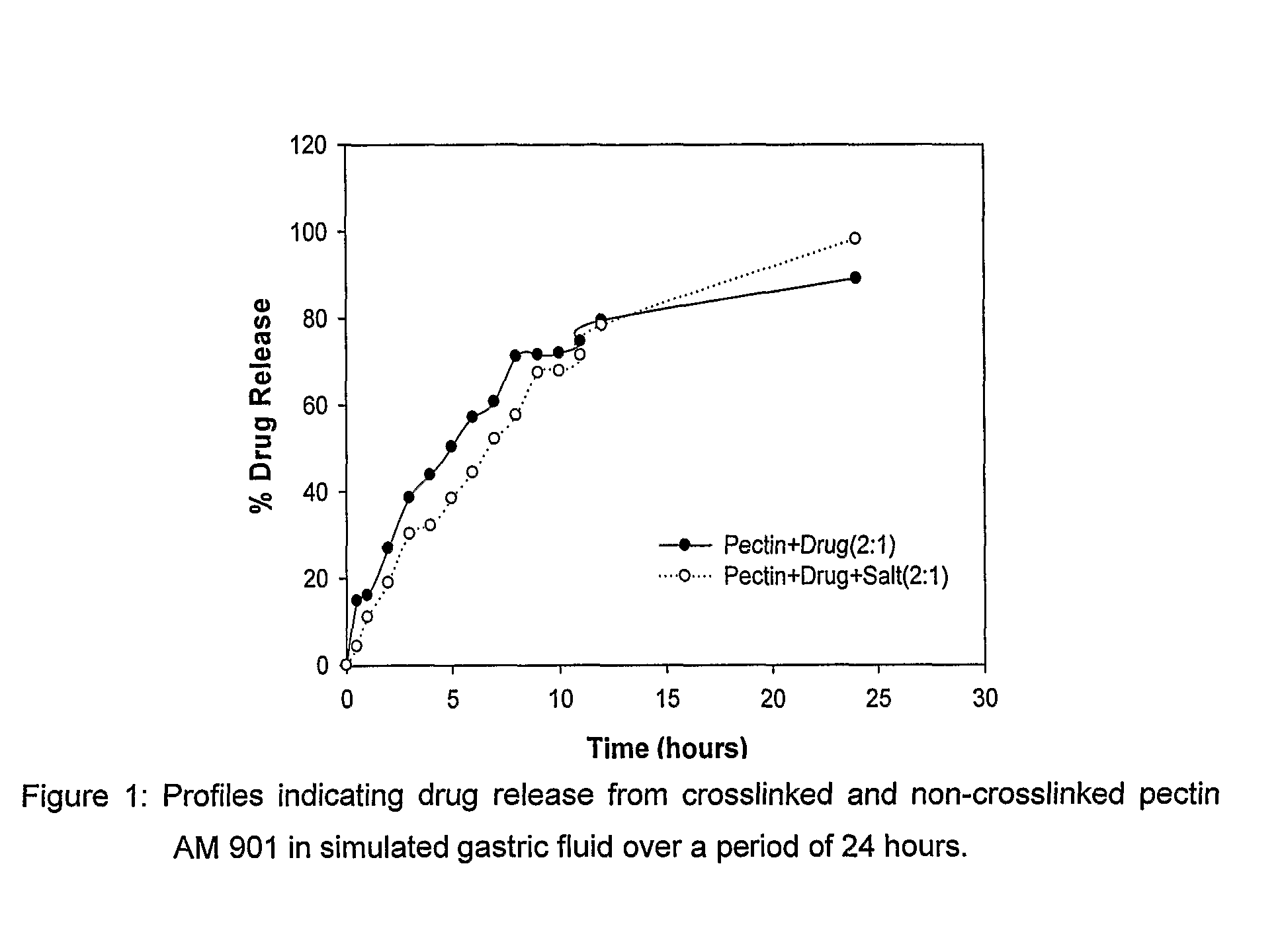
Pharmaceutical dosage form for the site-specific delivery of more than one active pharmaceutical ingredient
InactiveUS20110182987A1Facilitate optimumImproving enzymatic responsivenessBiocideDigestive systemIntestinal structureAdditive ingredient
This invention relates to a pharmaceutical dosage form for the site specific delivery of more than one active pharmaceutical ingredient to different sites in the human or animal body in the gastrointestinal tract. The dosage form has an outer polymeric layer incorporating a first active pharmaceutical ingredient which reacts to stimuli specific in the stomach, degrades, and releases the first active pharmaceutical ingredient in the stomach for absorption. The dosage form also has at least one inner polymeric layer incorporating a second active pharmaceutical ingredient which, once the outer layer has degraded, passes into the intestine where the polymers of the second layer degrade to release the second active pharmaceutical ingredient. The dosage form may have additional layers each incorporating active pharmaceutical ingredients for release in different portions of the intestine depending on the nature of the polymers.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF THE WITWATERSRAND
Extrusion process for polyethylene polymers
A method for the improved extrusion of polyethylene polymers comprising passing polyethylene through a single stage, twin screw extruder comprising a solid polymer conveying zone, a polymer melting zone, a dispersive mixing zone, and a distributive mixing / pumping zone, in which the throughput and screw speed are optimized to reduce the number of gels present, ensure complete polymer melting within the polymer melting zone, and to minimize polymer degradation.
Owner:NOVA CHEM (INT) SA
Masterbatch composition comprising a high concentration of biological entities
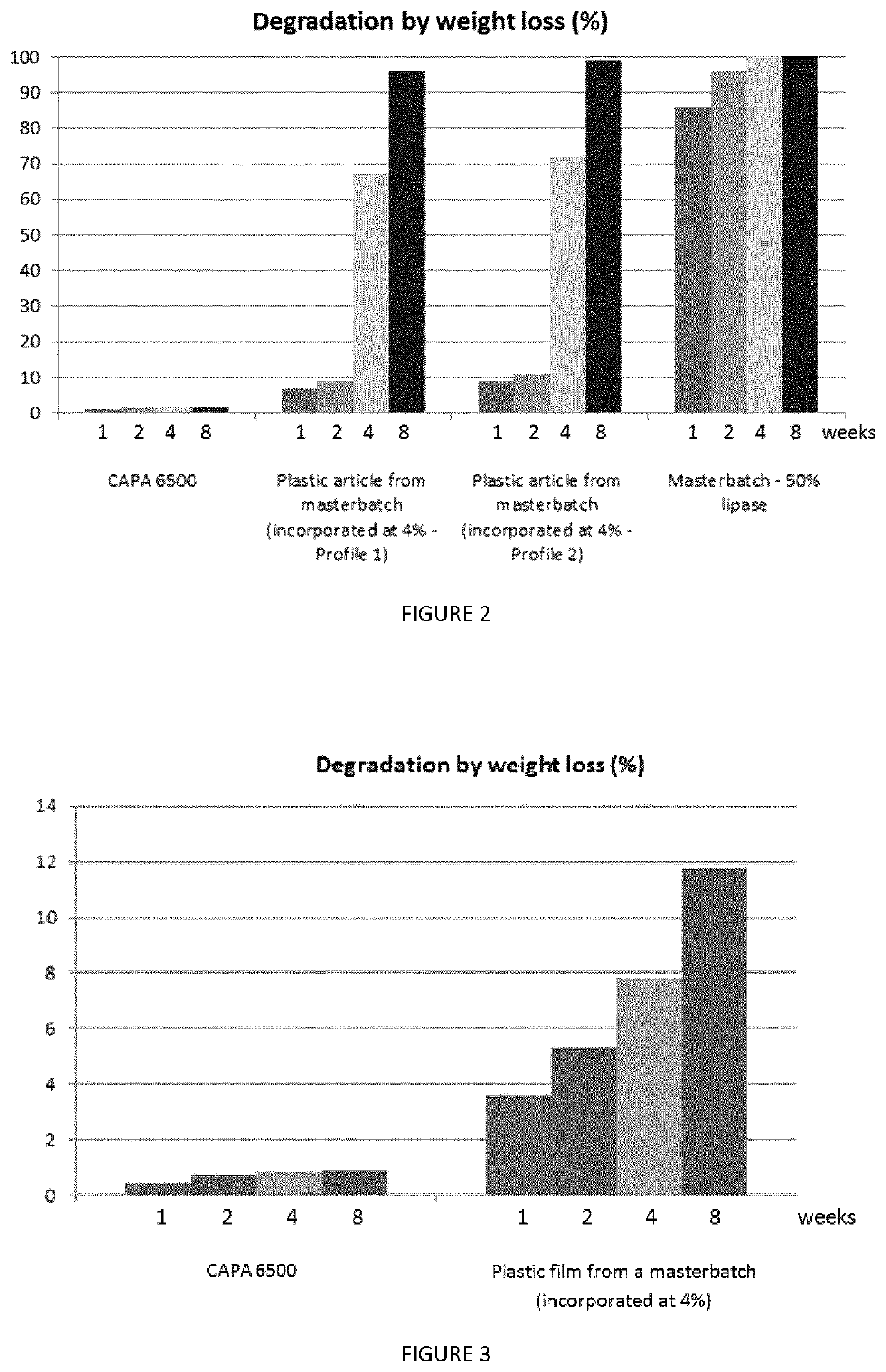
ActiveUS10723848B2Efficient productionEffective degrading activityPlastic recyclingOxidoreductasesMasterbatchEngineering
The present invention relates to a masterbatch composition comprising high concentration of biological entities having a polymer-degrading activity and uses thereof for manufacturing biodegradable plastic articles.
Owner:CARBIOS
Glaucoma valve, a casing for containing a glaucoma valve, and a glaucoma drainage device comprising the valve and/or the casing
Various embodiments of the invention relate to a glaucoma valve, a casing for containing a glaucoma valve and a glaucoma drainage device comprising the glaucoma valve and / or the casing. The valve includes a flow channel having an inlet and an outlet and a valve member connected to the outlet of the flow channel. The valve member may be formed from a degradable polymer or a combination of degradable polymer and non-degradable polymer. Various embodiments of the invention relate to a glaucoma valve, the valve having a first flow channel. The interior of the first flow channel may be coated with a degradable polymer, such that in use, the polymer degrades to allow a greater flow of fluid through the flow channel. In some embodiments, the valve includes a second flow channel, which may be arranged in parallel to the first flow channel. The first flow channel may be completely sealed with the polymer such that in use, the polymer degrades to allow fluid to flow through the first flow channel. Various embodiments relate to a casing for containing a glaucoma valve. The casing may be formed from a degradable polymer, such as a biodegradable polymer.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Preparation method of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) composite mesoporous membrane
InactiveCN103861476AAperture adjustableHigh hydrothermal stabilitySemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisOrganic solventPolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of composite membranes, and relates to a preparation method of a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) mesoporous membrane, and the method includes the following steps: dissolving polyvinylidene fluoride powder in an organic solvent, adding a pore forming agent, stirring evenly to prepare a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane casting solution; adding SBA-15 to obtain a mixed solution, heating and stirring the mixed solution to prepare a polyvinylidene fluoride-silica membrane casting solution; sealing, standing for defoaming; using an automatic coating machine to coat a glass substrate with the PVDF-SBA-15 membrane casting solution, and immersing the glass substrate in a solidification liquid to obtain a polyvinylidene fluoride-silica composite membrane. The preparation method is simple in operation, the membrane is prepared at low temperature, the polymer degradation can be reduced, the strength of the membrane is ensured, the prepared PVDF-SBA-15 can effectively improve the hydrophilic ability and water flux of the membrane, and the membrane has good application prospects in the field of water pollutant removal.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Additives for Improving Polyurethane Foam Performance
ActiveUS20120071576A1Ambient physical propertyImprove stabilityOther chemical processesGuanidine derivativesHardness
Polyurethane foam compositions and processes to make flexible polyurethane foams are disclosed. Polyurethane foam is produced in the presence of additives comprising guanidine derivatives. Improvements in physical properties such as air flow, dimensional stability, tensile, tear, elongation and foam hardness is observed when these additives are present in polyurethane formulations. In addition, these additives can minimize polymer degradation under humid ageing conditions resulting in foam products with better mechanical properties.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Method of preparing simvastatin sustained-release microsphere carried series
InactiveCN101219119ARelease stabilityLarge adjustment rangeOrganic active ingredientsSurgeryMicrospherePolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a method that a functional drug is enveloped into a polymeric material with biodegradability to form a nano-micron microsphere system. The method comprises that the polymeric material and simvastatin are dissolved in an organic liquor to form uniform dispersion which is then added into an liquor containing emulsifier Tween 80 and biologically nontoxic electrolytic polyvinyl alcohol or sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS), and then the obtained liquor is stirred, evaporated at a reduced pressure, centrifugalized, washed and vacuum dried, finally the simvastatin-contained delayed-release microsphere system is obtained. The surface of the microsphere is smooth and round, the granule thereof is regular without conglutination, and the granule diameter, the drug-loading rate (1-10 percent) and the encapsulation rate (above 40 percent) are all controllable, and the delayed-release time exceeds 2 months. The prepared simvastatin-contained delayed-release microsphere system can be processed into various preparations used in bony tissue absorption or bony defect parts, the microsphere system is degraded at a proper speed, thus the simvastatin can be further released; the degradation of the polymer can provide bony tissue with subsequent recuperating space to complete the repair of the bony defect parts.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Environment-protection energy-saving gas for welding and cutting
InactiveCN101139535ARaise the combustion temperatureBurn fasterGaseous fuelsForeign matterEngineering
The invention relates to a fuel gas for welding cut that is environmental friendly and energy saving, in particular to a fuel gas that can substitute acetylene gas. The fuel gas comprises a propane gas, which is characterized in that synergist is added in certain proportion in the propane gas; the content of the propane gas is 97-99%; the content of the synergist is 5 per mill-1%, the content of the liquefiable foreign matter of gas is less than 2.5% by weight; the synergist is a mixed solution comprising combustion catalyst, smoke-removing agent, polymer degrading agent, solvent, solution assistant, and combustion assistant, etc.; the fuel gas is used as combustion gas in place of acetylene gas to weld and cut metals. The flame of the fuel gas is of high temperature, is free from reverse (return) combustion; the fuel gas is of very low explosion limit and low toxicity, free from harm to human bodies, of low comprehensive cost, high efficiency, is safe, environmental friendly and energy saving.
Owner:周尧
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com