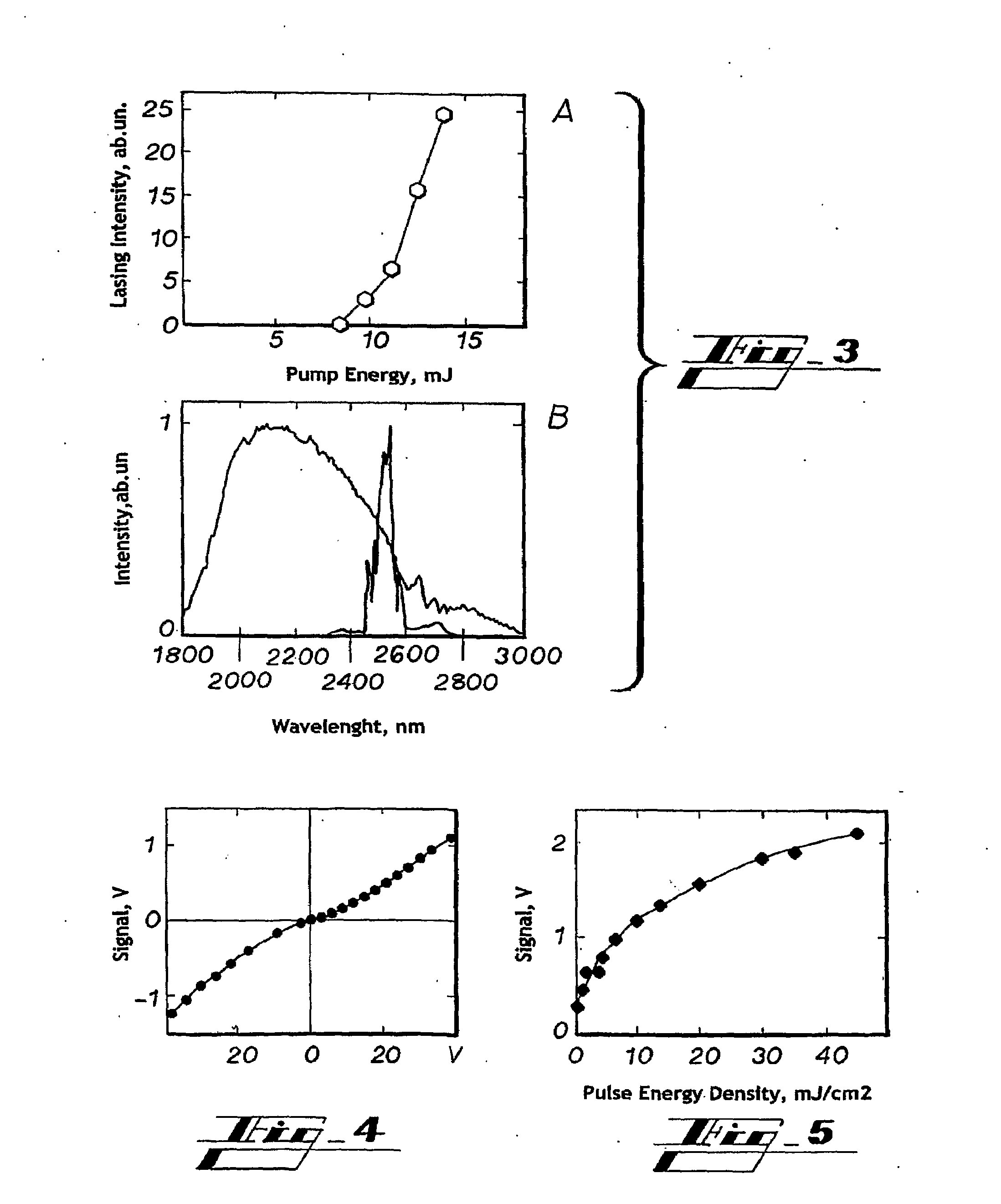
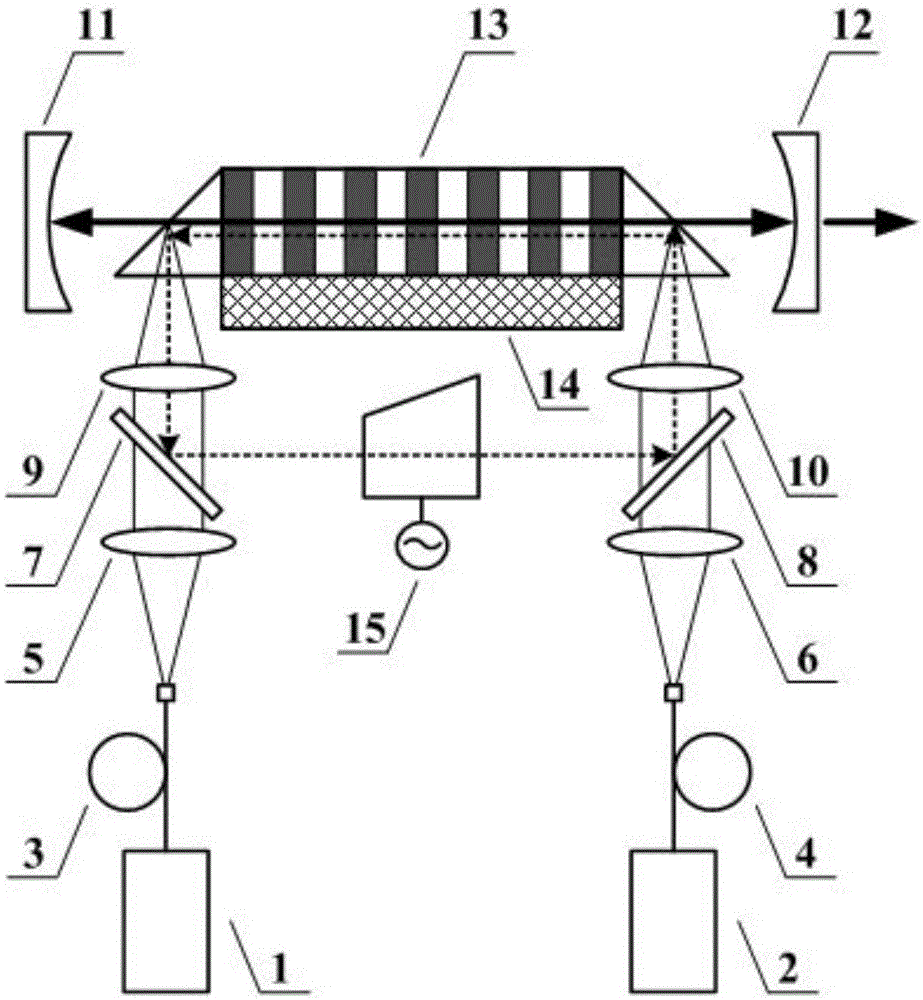
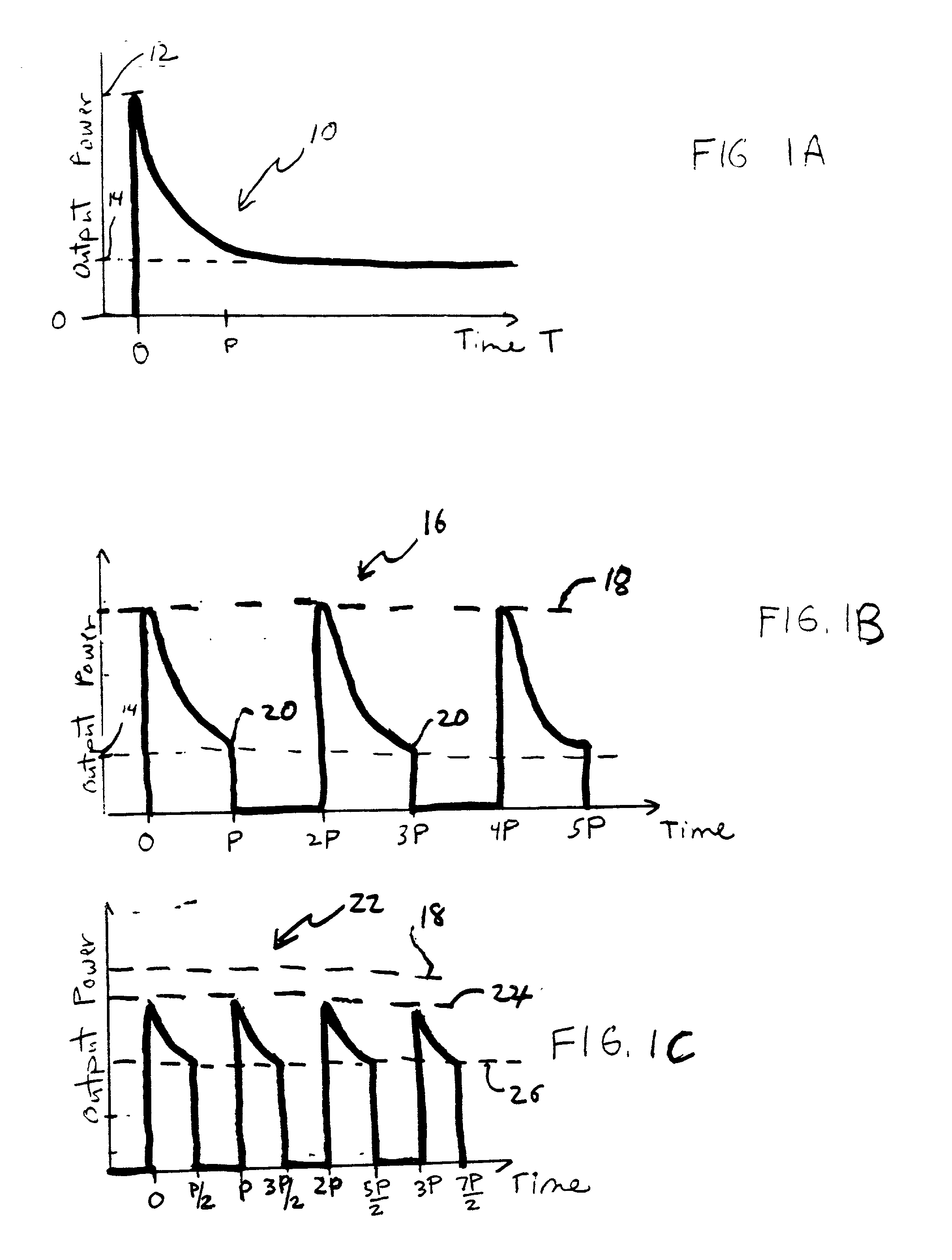
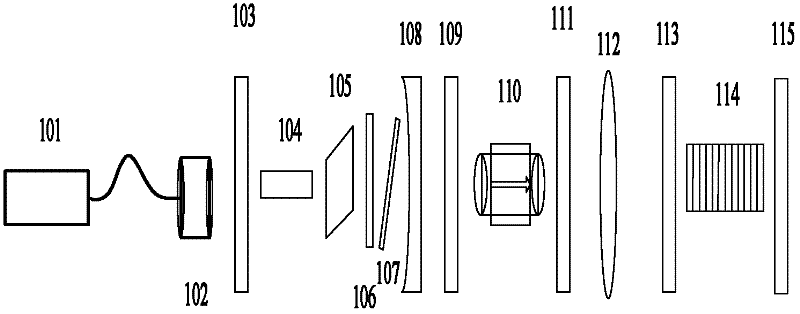
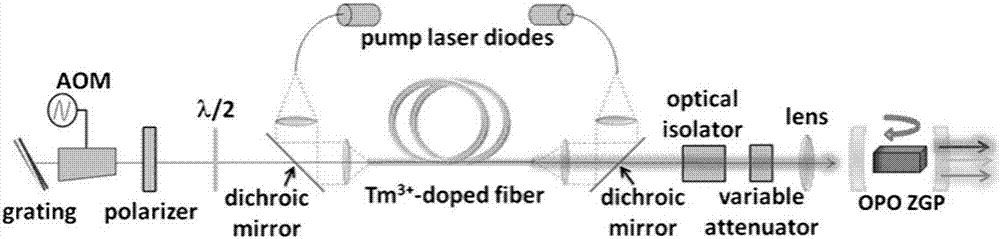
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
111 results about "Mid ir lasers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
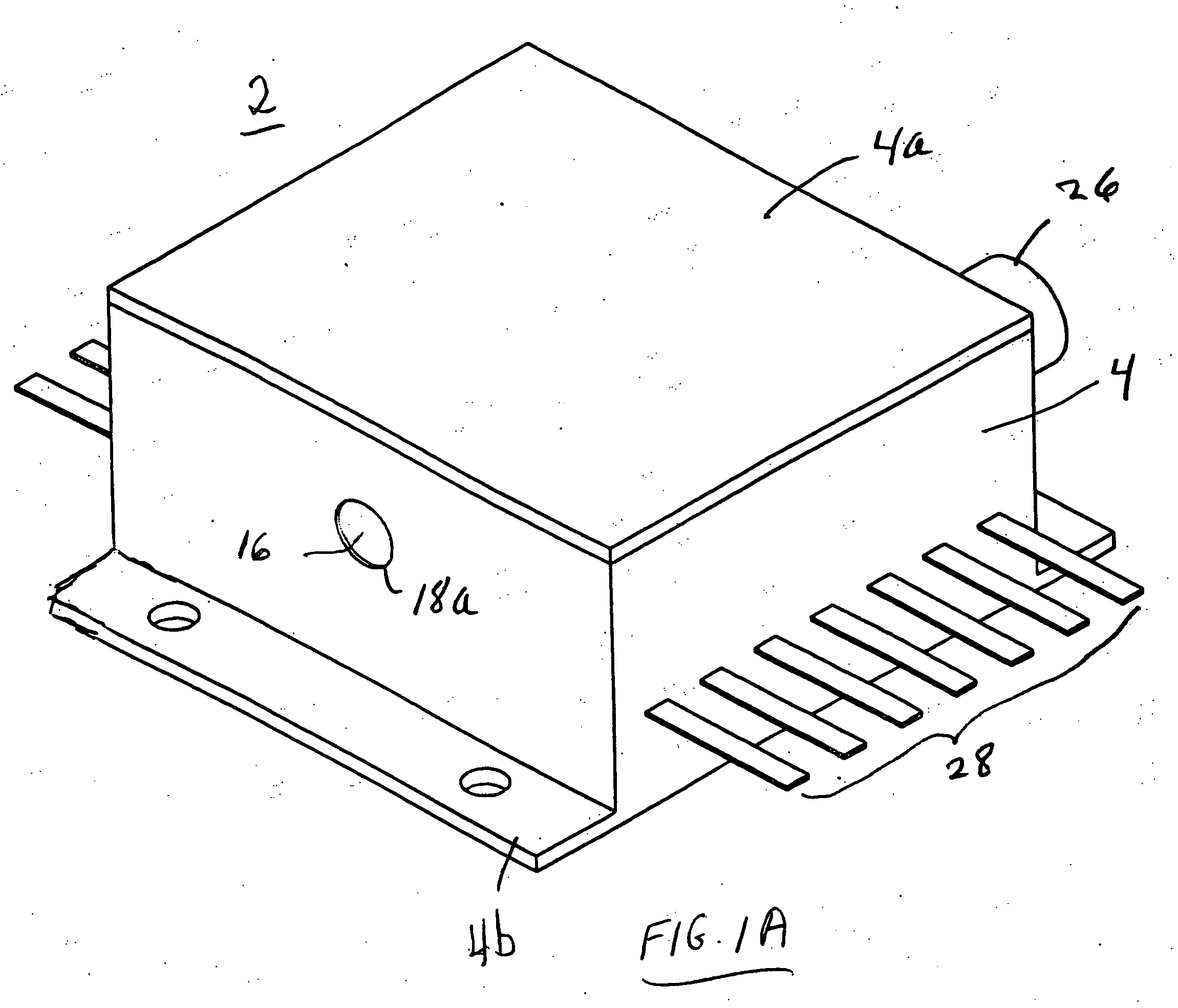
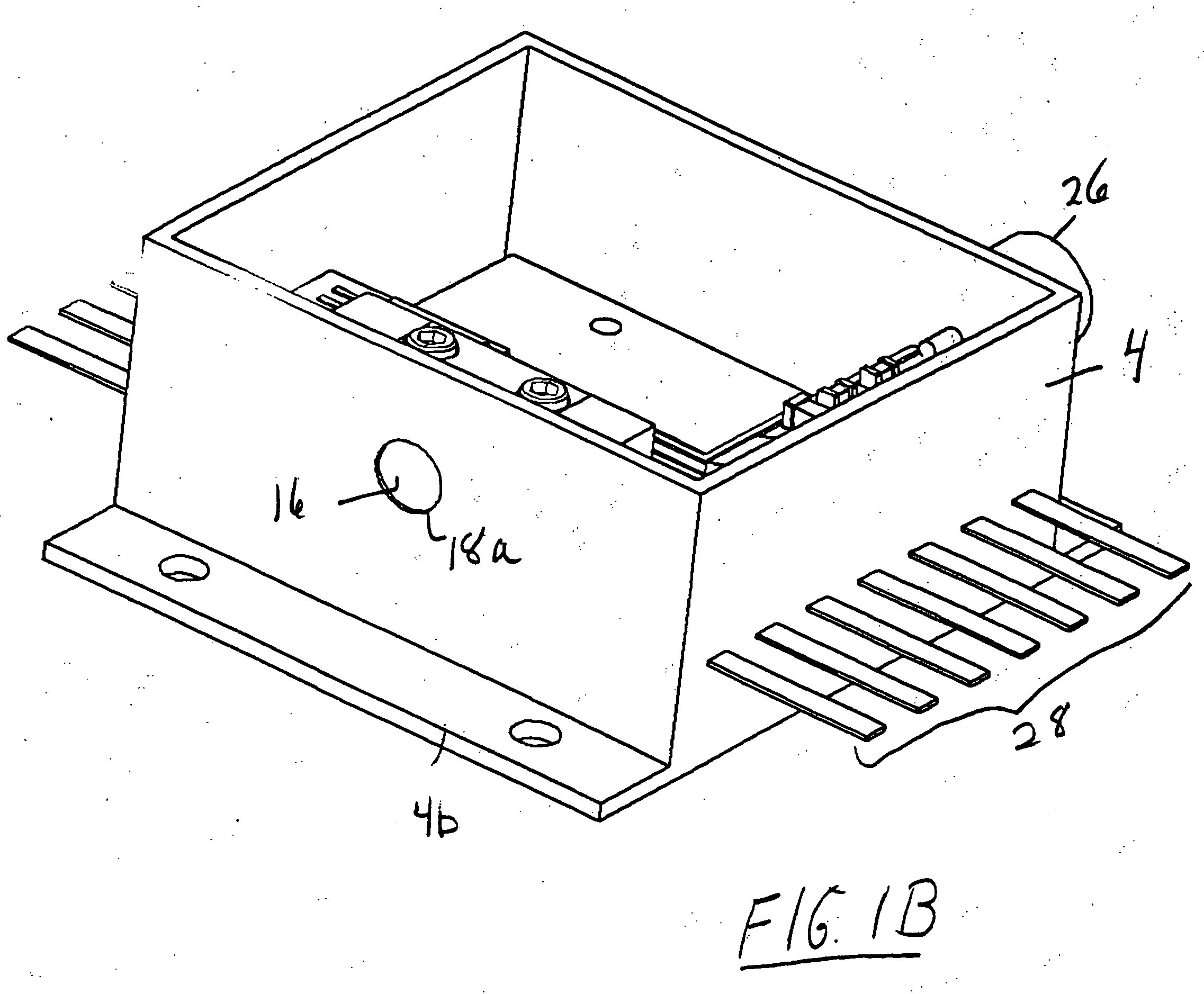
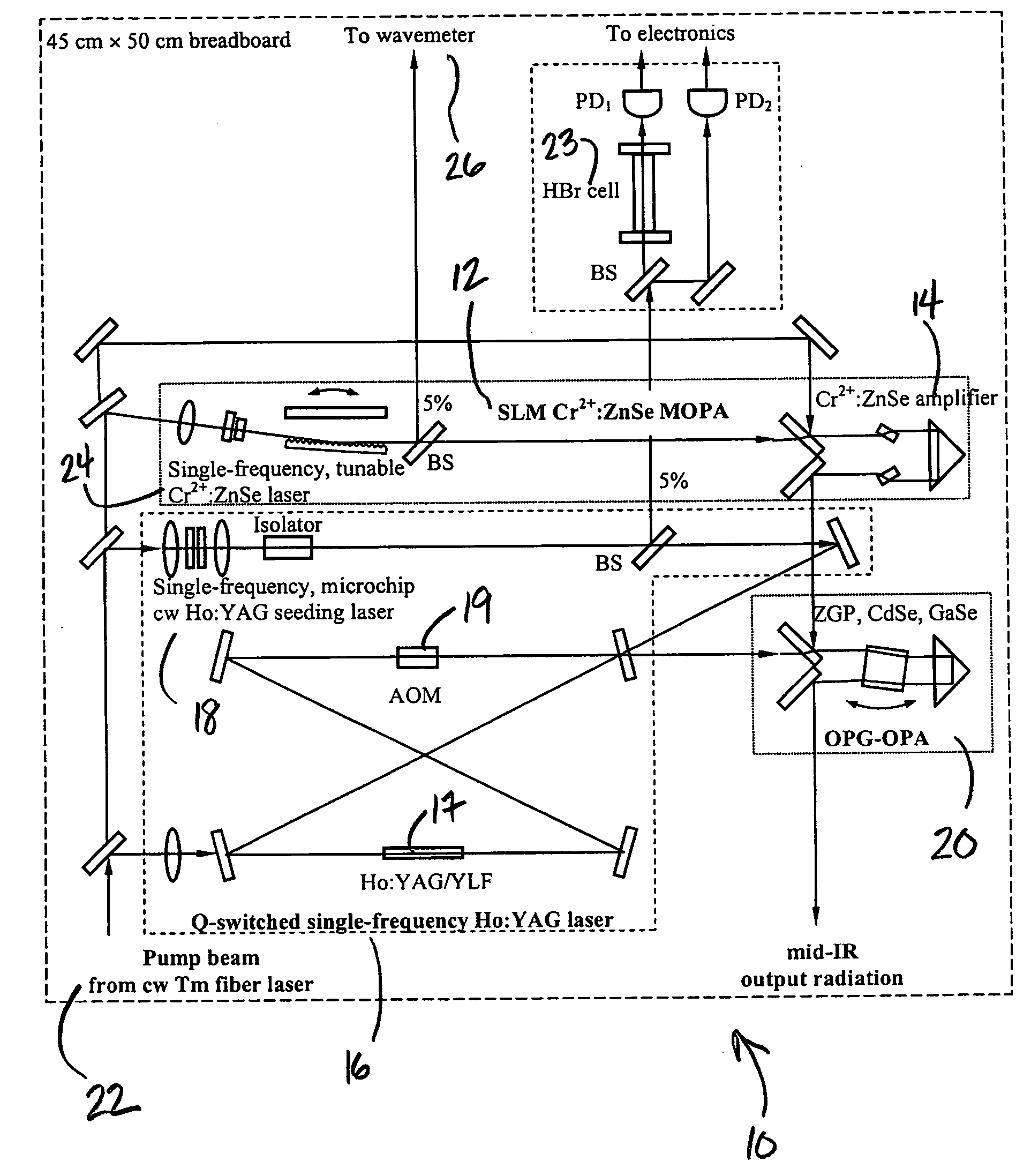
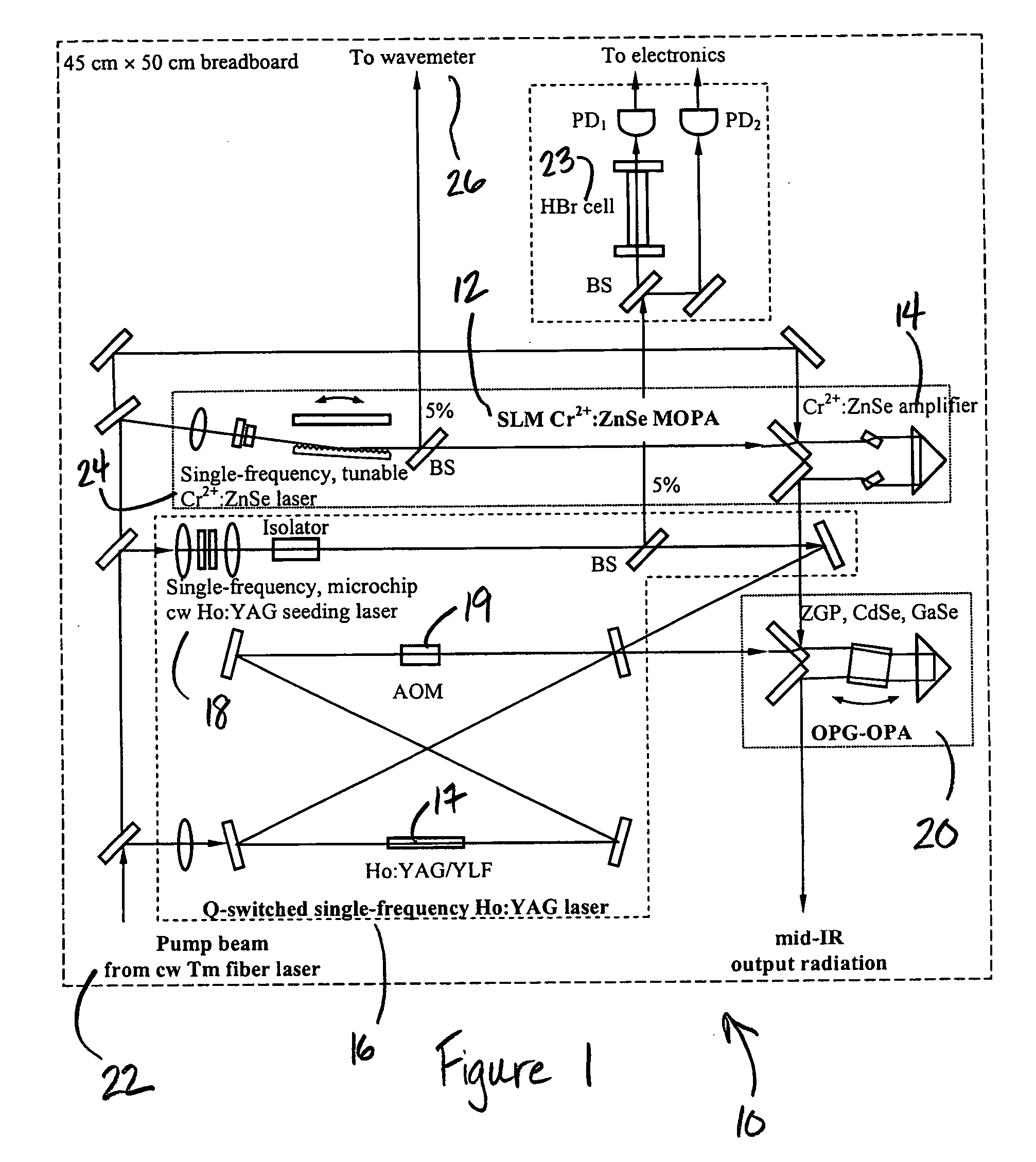
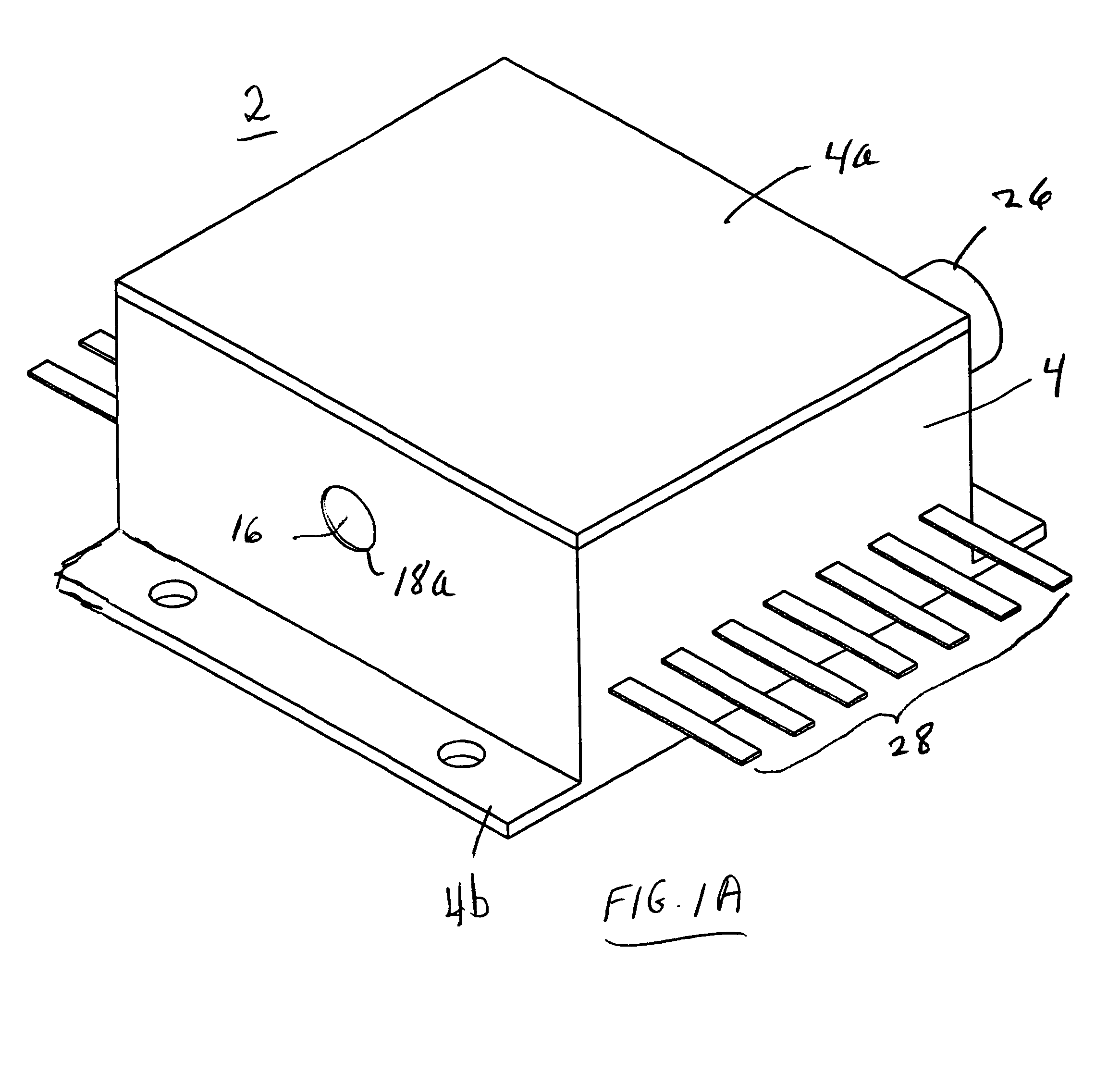
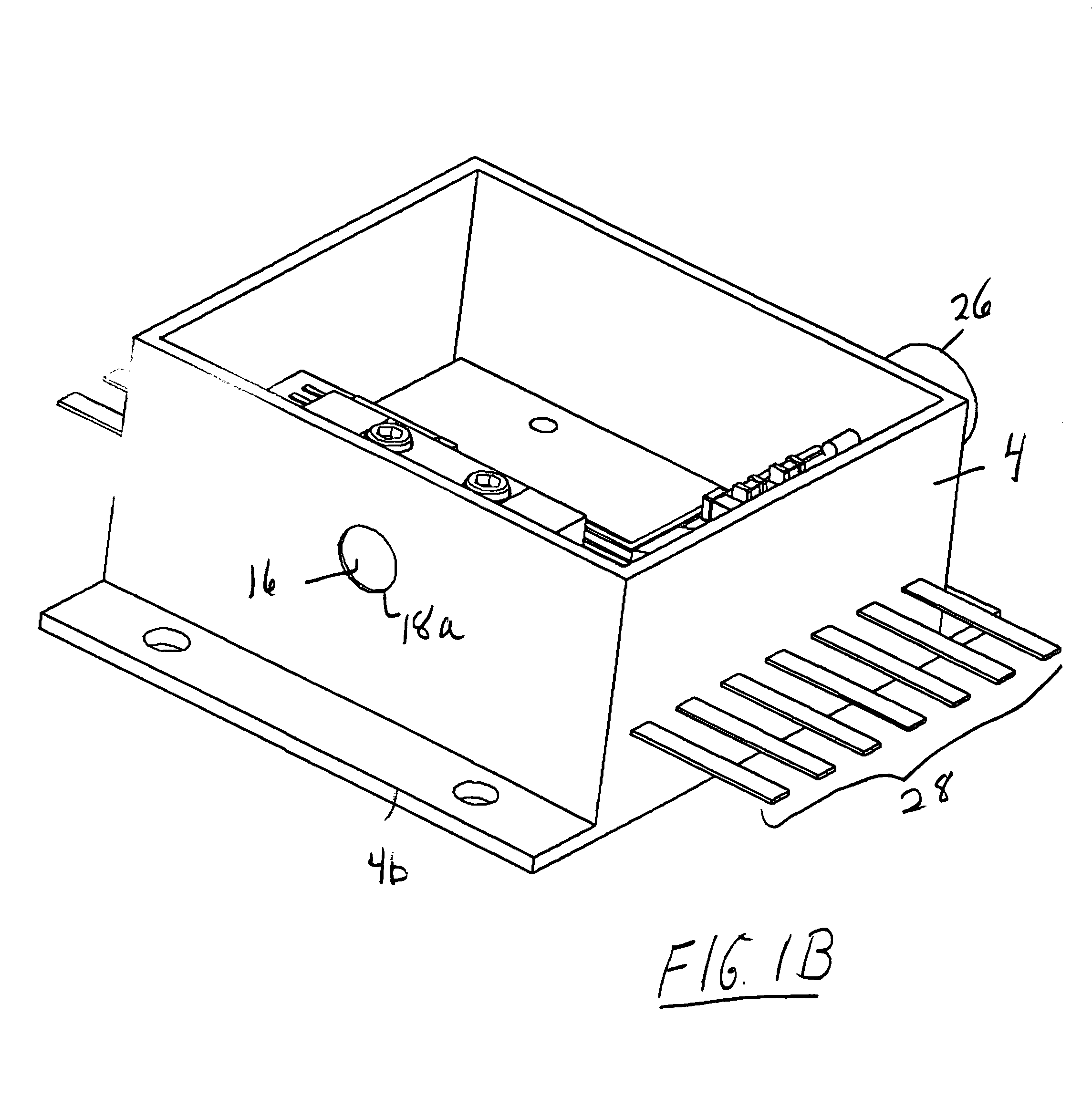
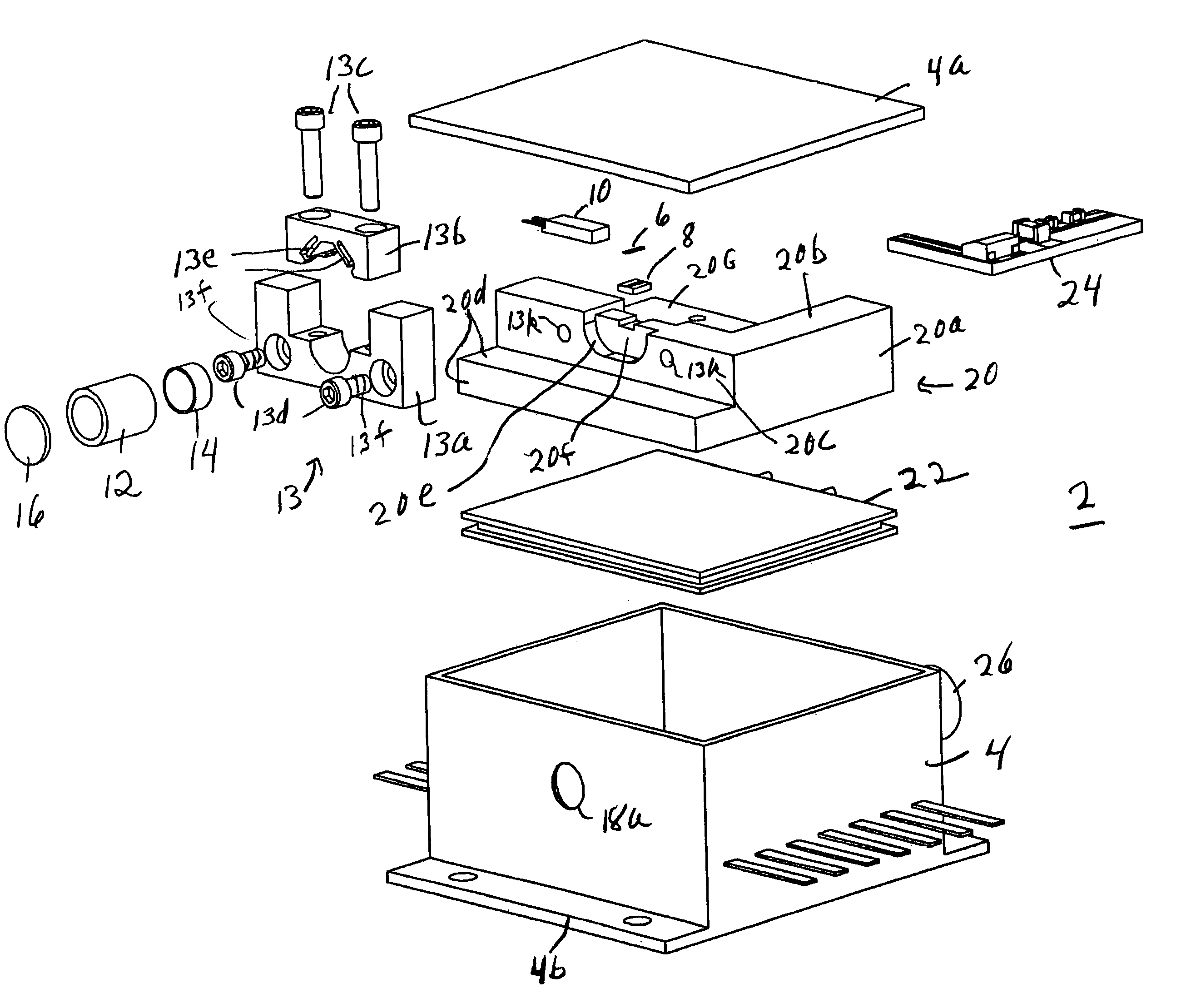
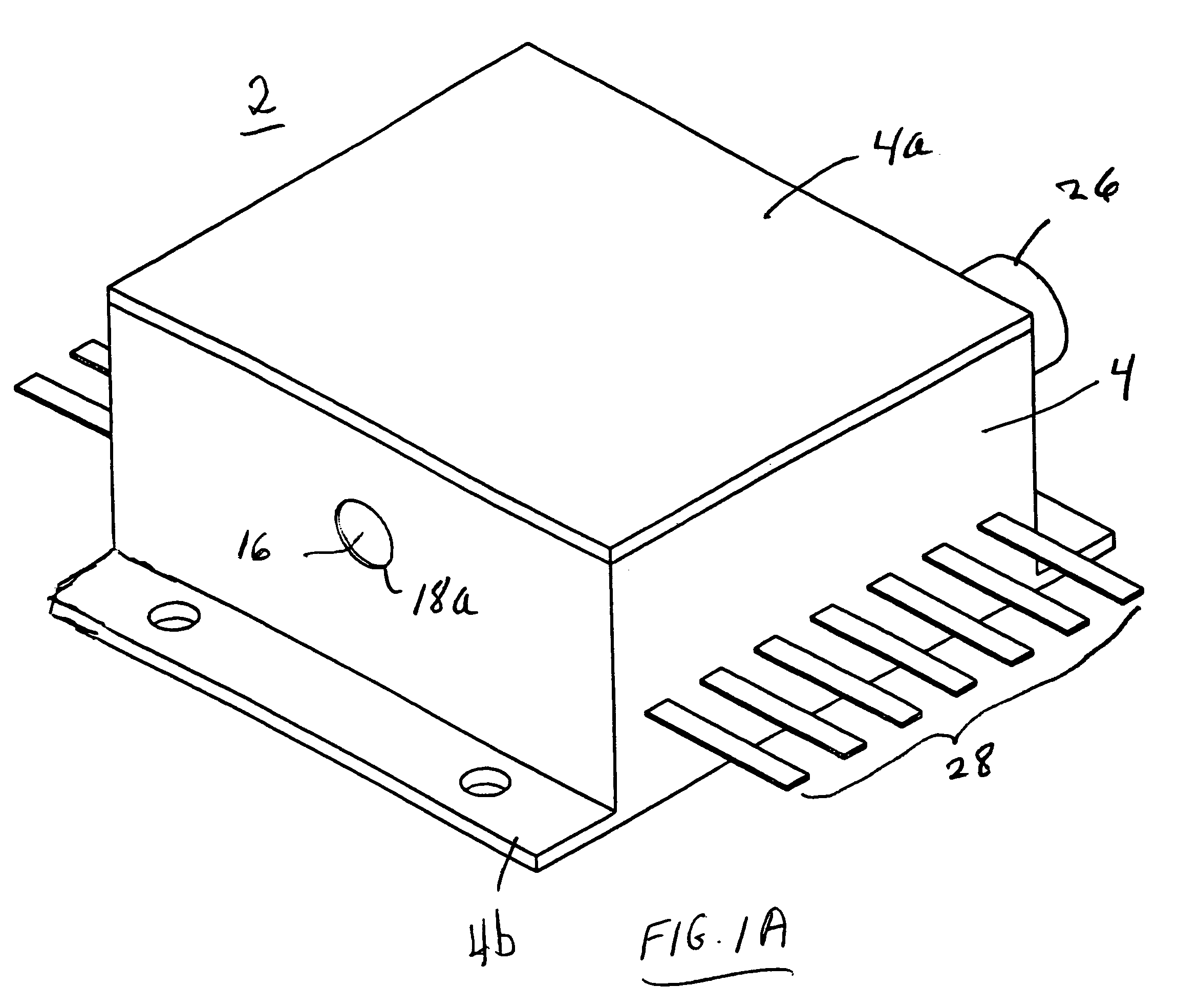
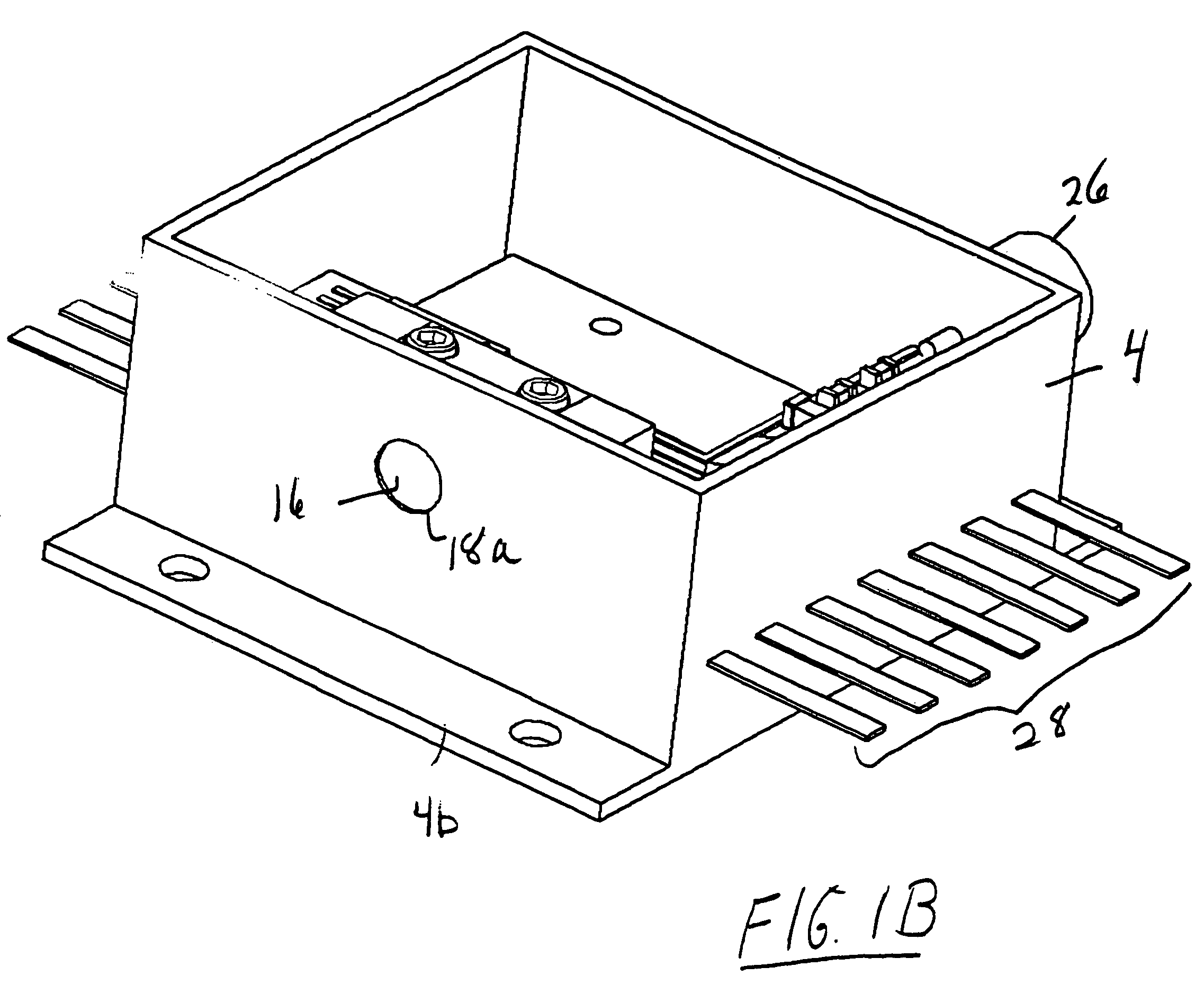
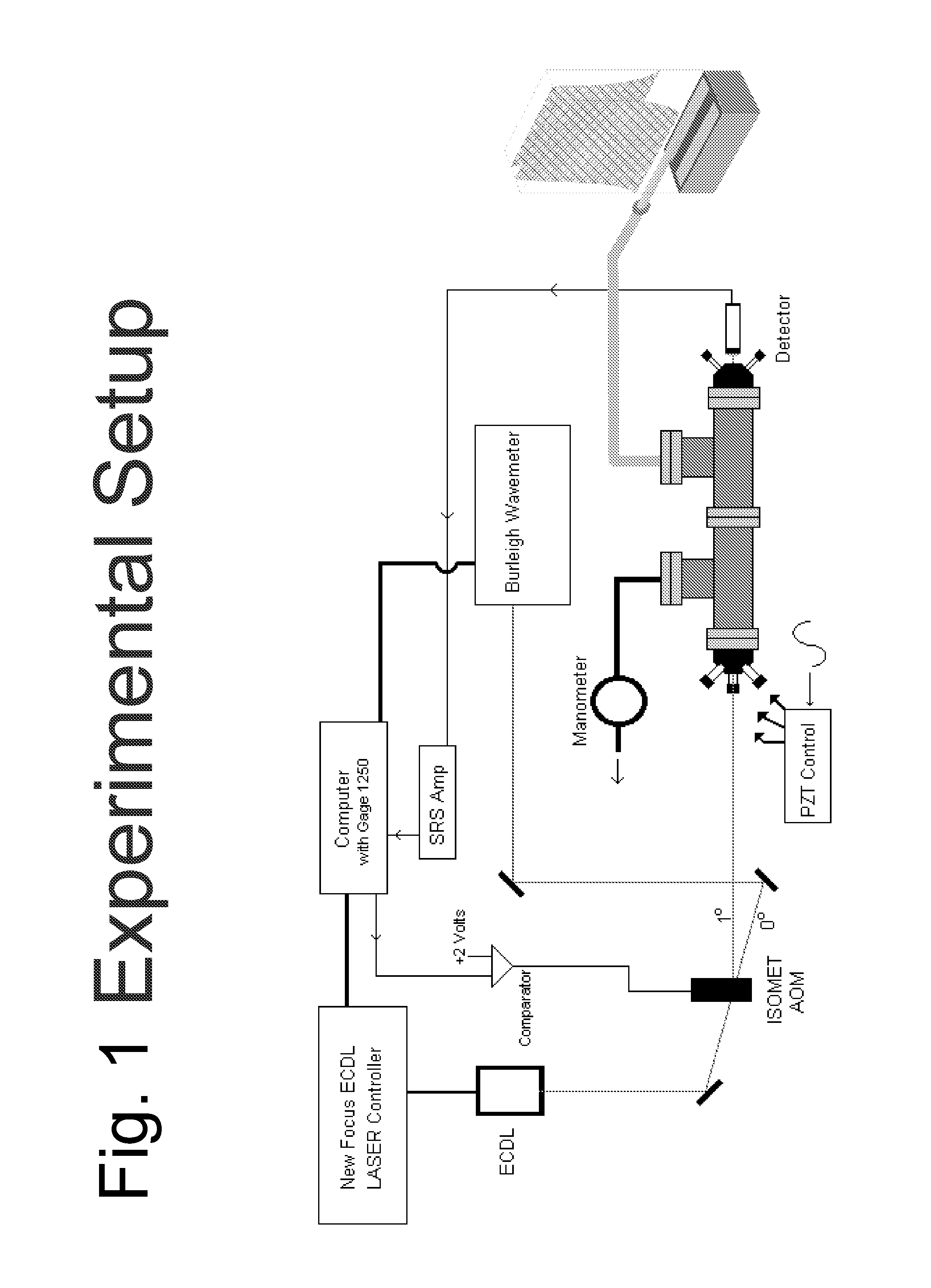
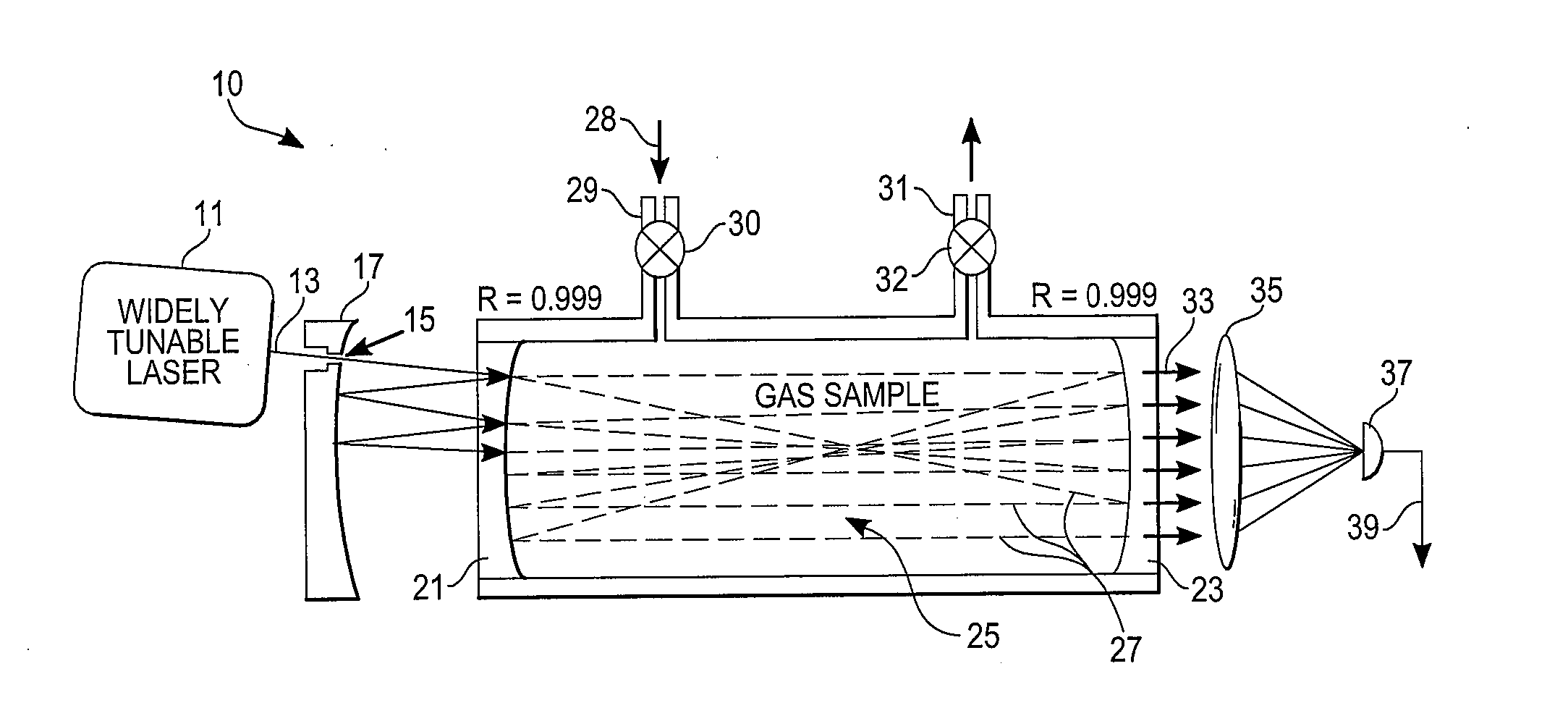
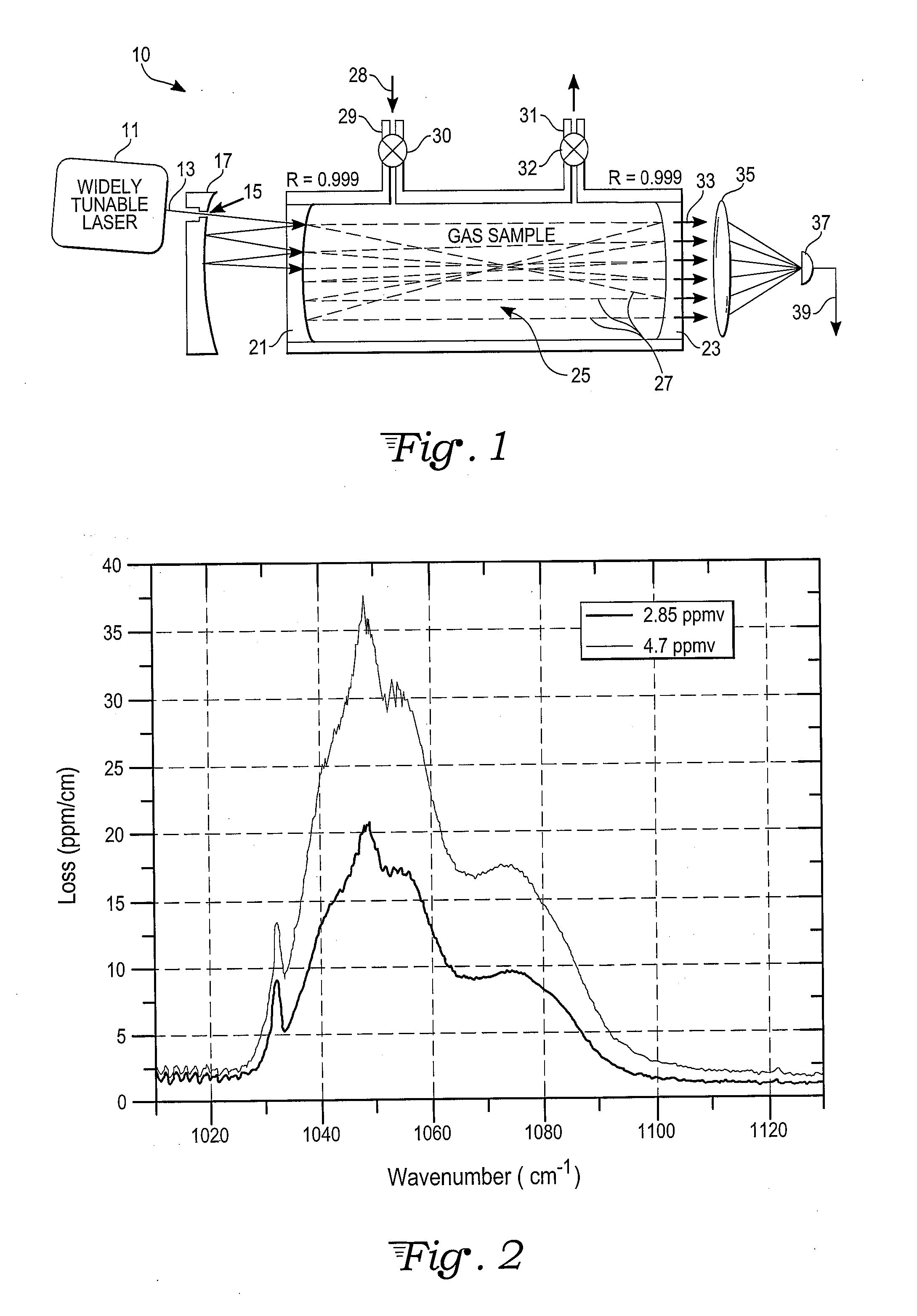
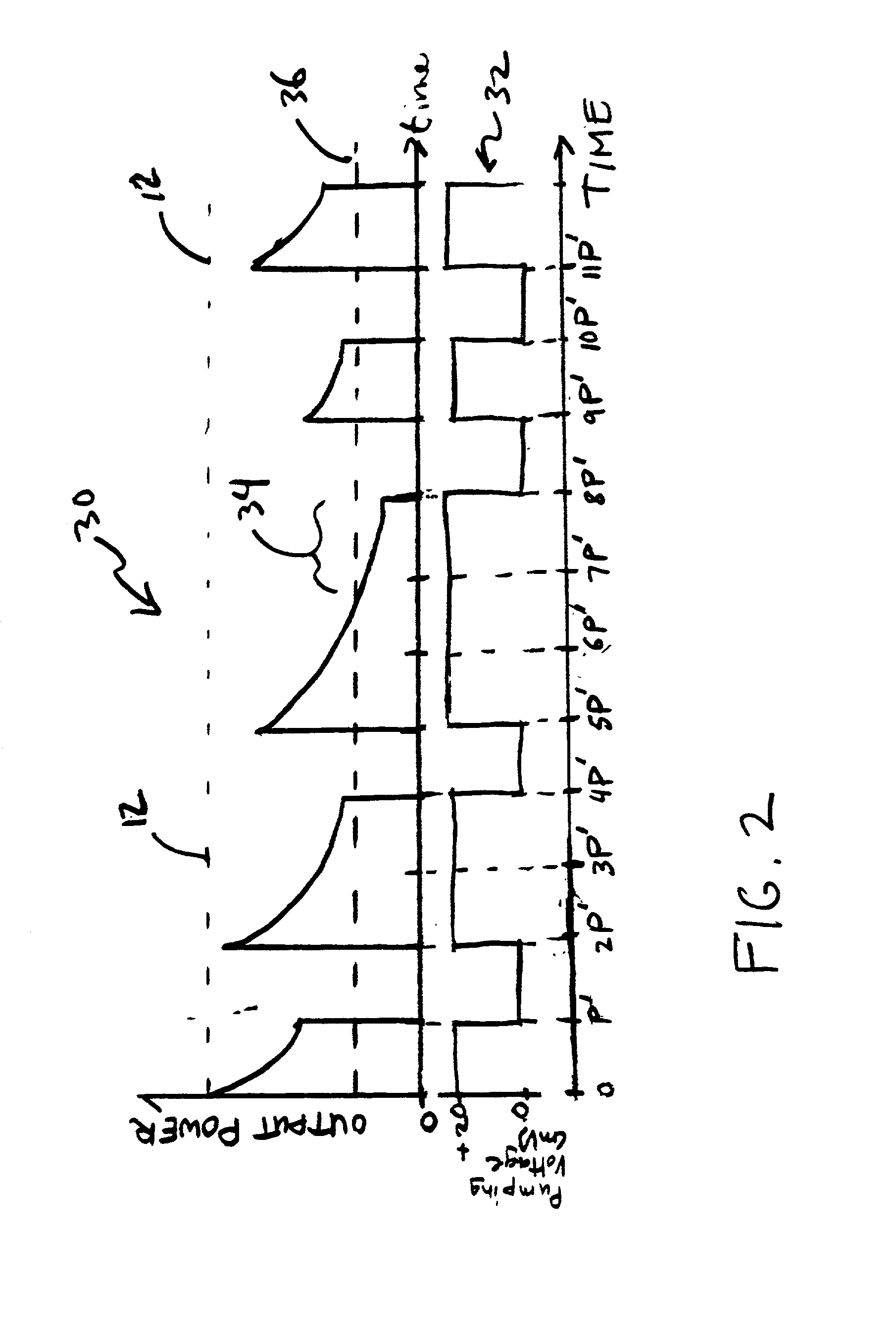
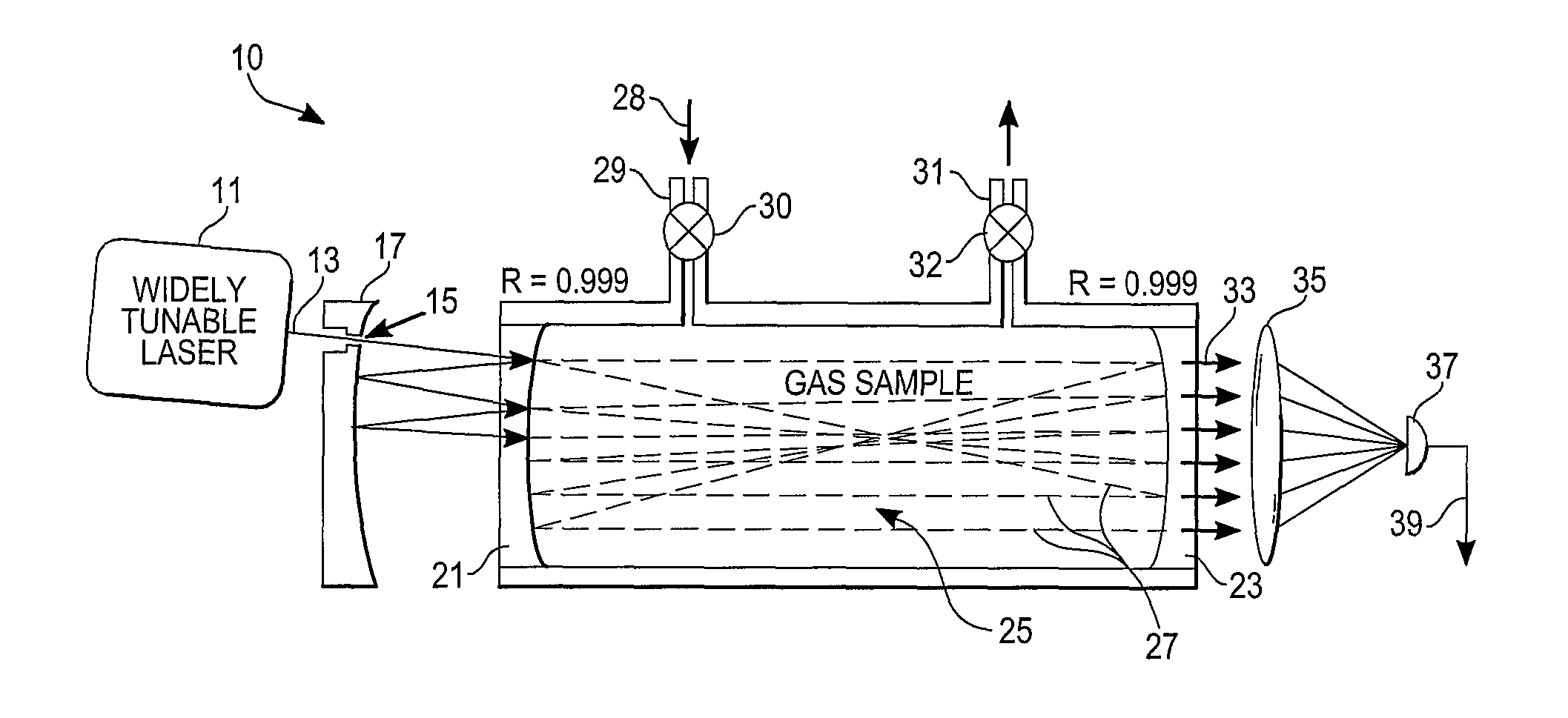
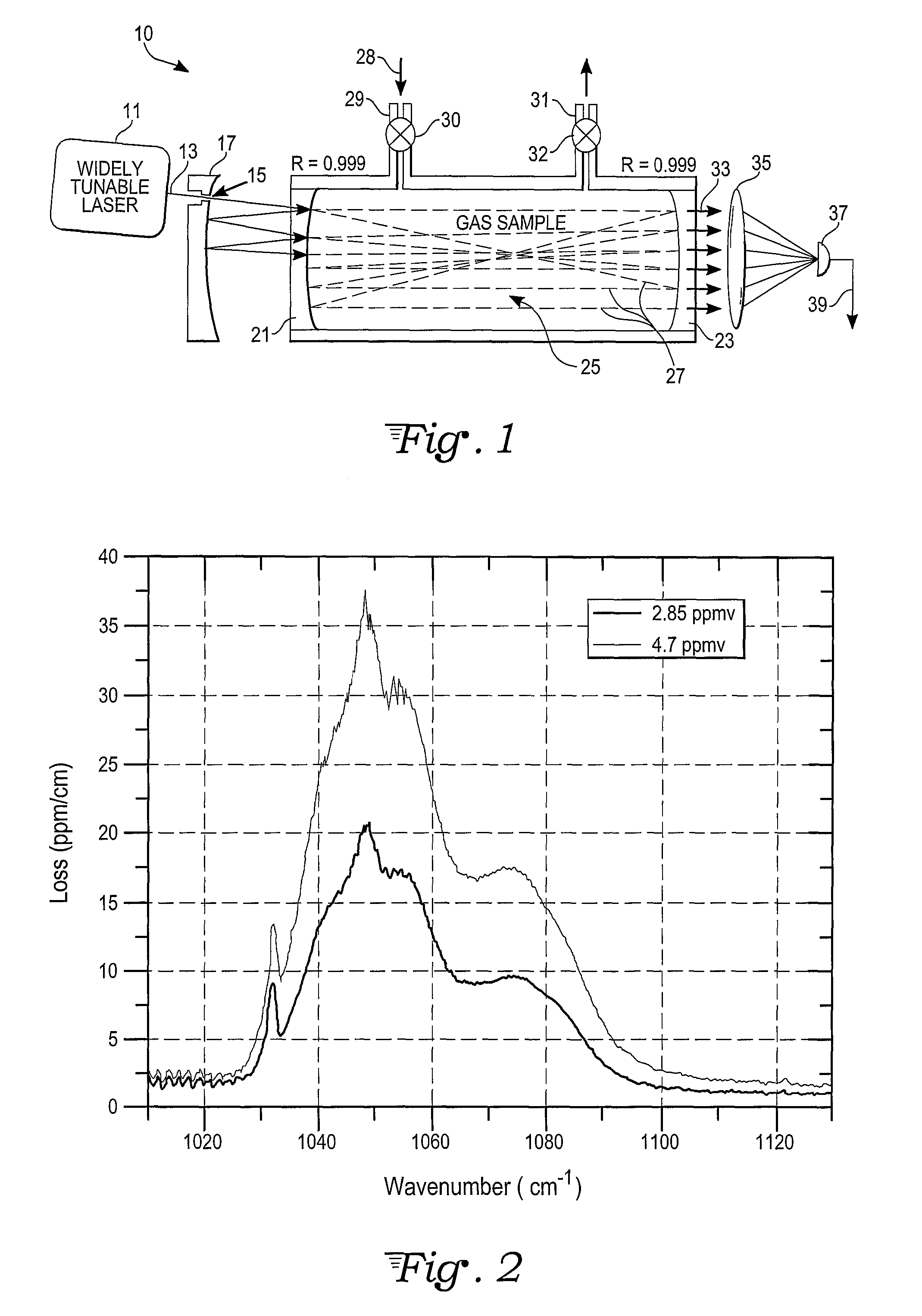
High-Accuracy Mid-IR Laser-Based Gas Sensor
InactiveUS20120287418A1Good choiceImprove accuracyRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsPhotodetectorAmbient pressure
A gas sensor system is provided, comprising: a gas cell operable so as to receive a sample gas; a vacuum system fluidically coupled to the gas cell operable to maintain the sample gas within the gas cell at a sub-ambient pressure; a pressure sensor operable to sense a pressure of the sample gas; a thermally insulated enclosure having the gas cell therein; a heat source or heat exchanger operable to influence an interior temperature of the thermally insulated enclosure; a light source within the thermally insulated enclosure operable to provide a mid-infrared (mid-IR) light into and through the gas cell; a photodetector within the thermally insulated enclosure operable to receive the attenuated mid-IR; and a control system electronically coupled to the vacuum system and to the pressure sensor operable to maintain the sample gas within the gas cell at the predetermined pressure to within one torr (1 Torr).
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
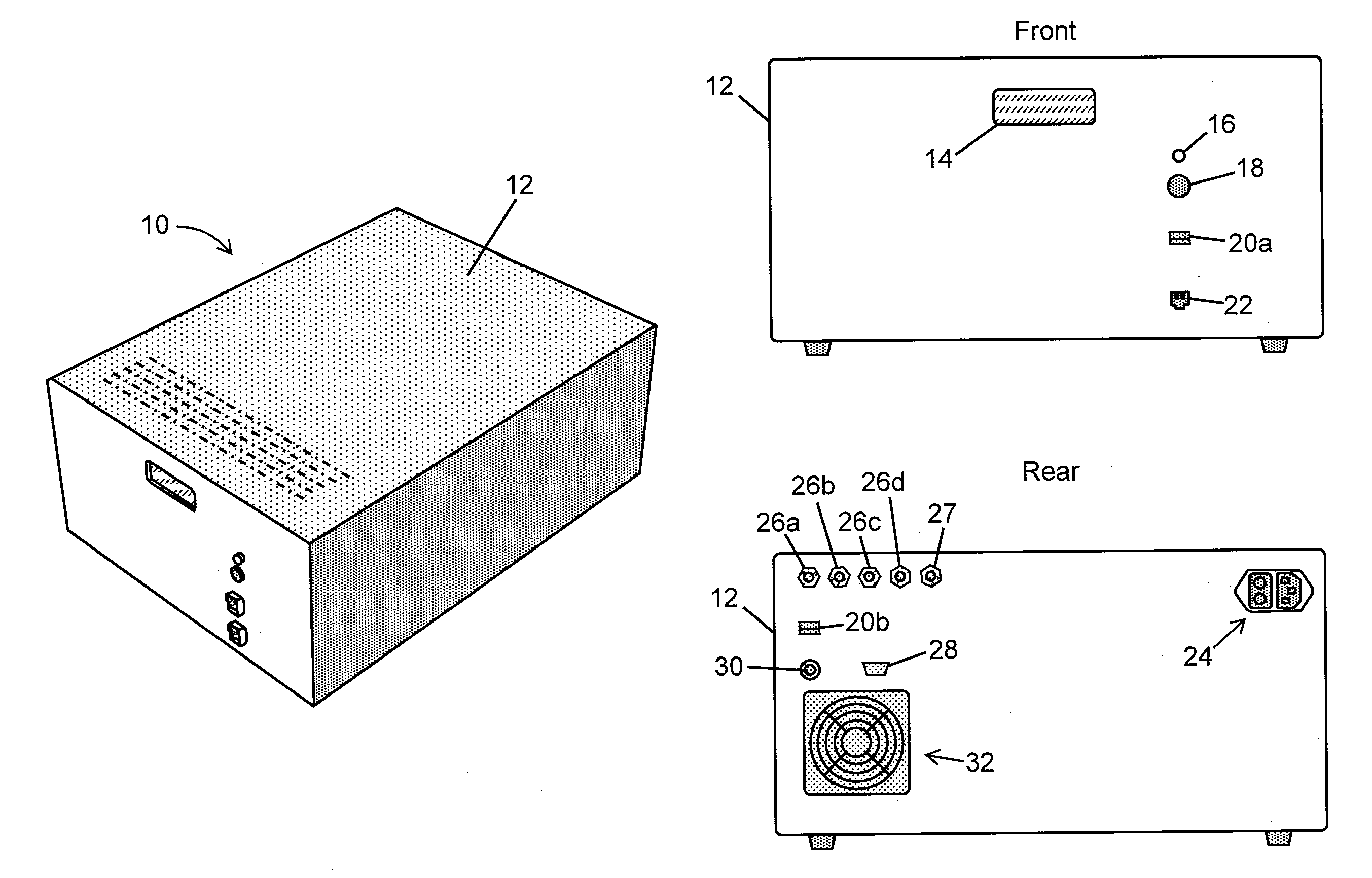
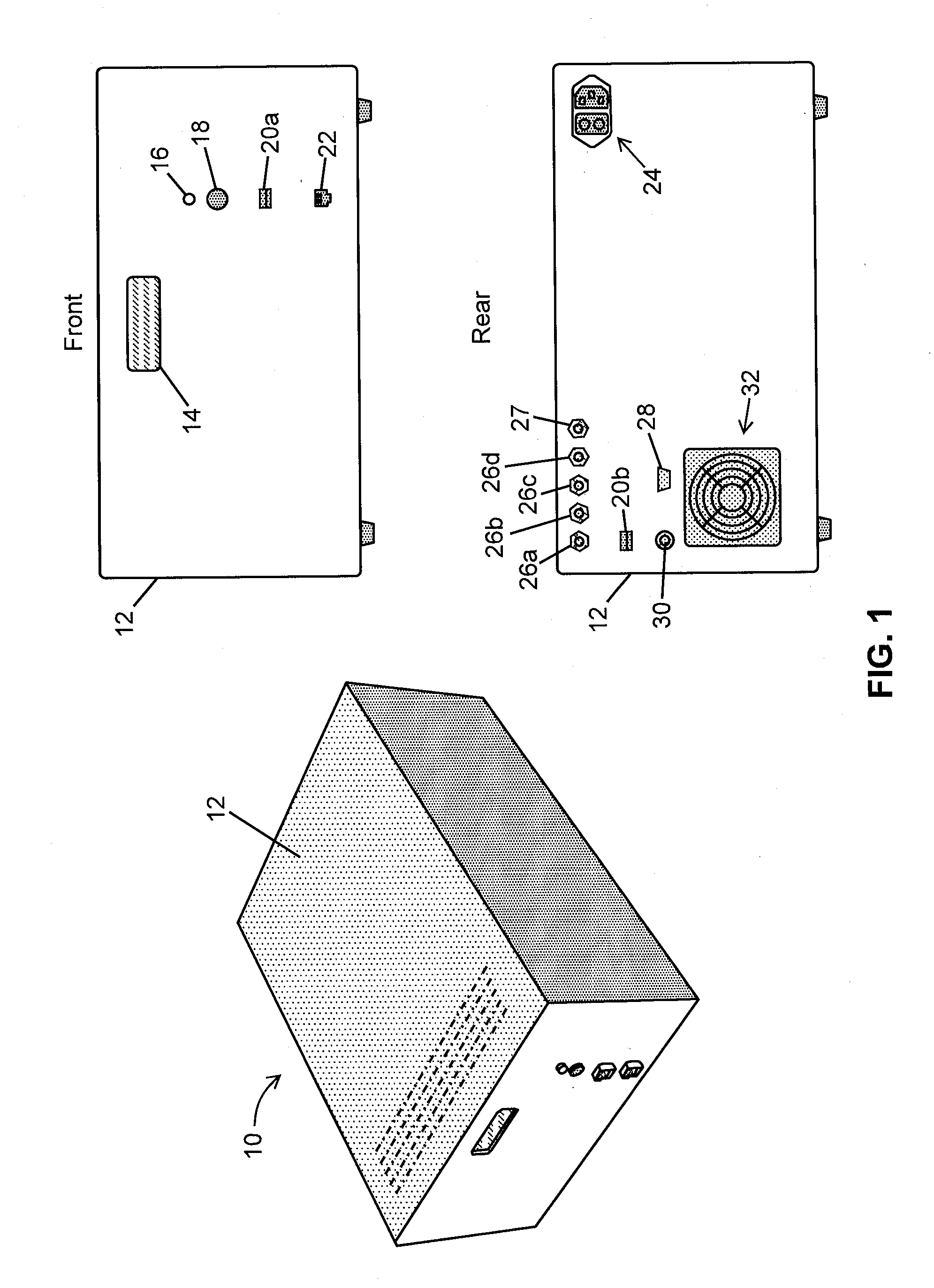
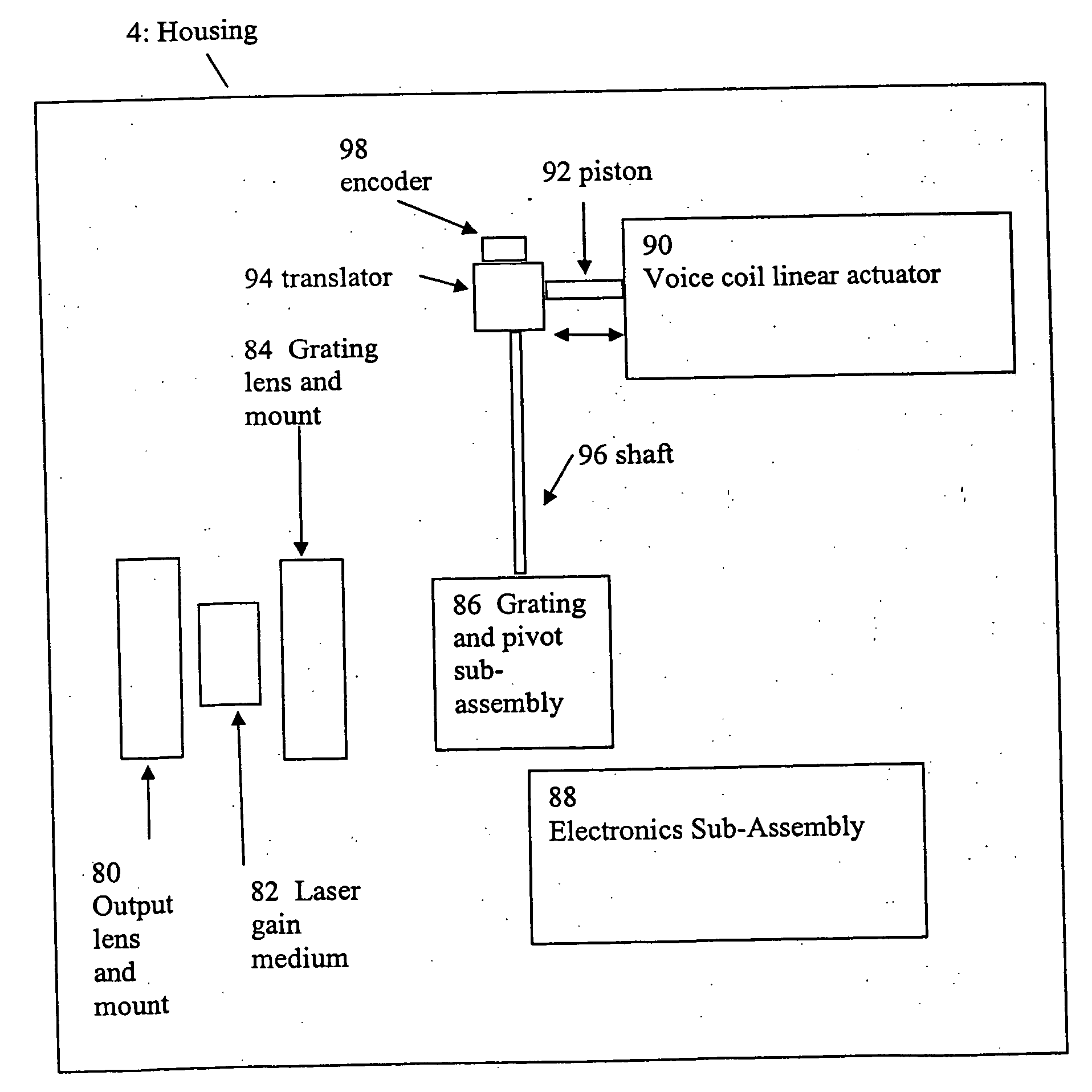
External cavity tunable compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070030865A1Reduce usageImprove cooling effectLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
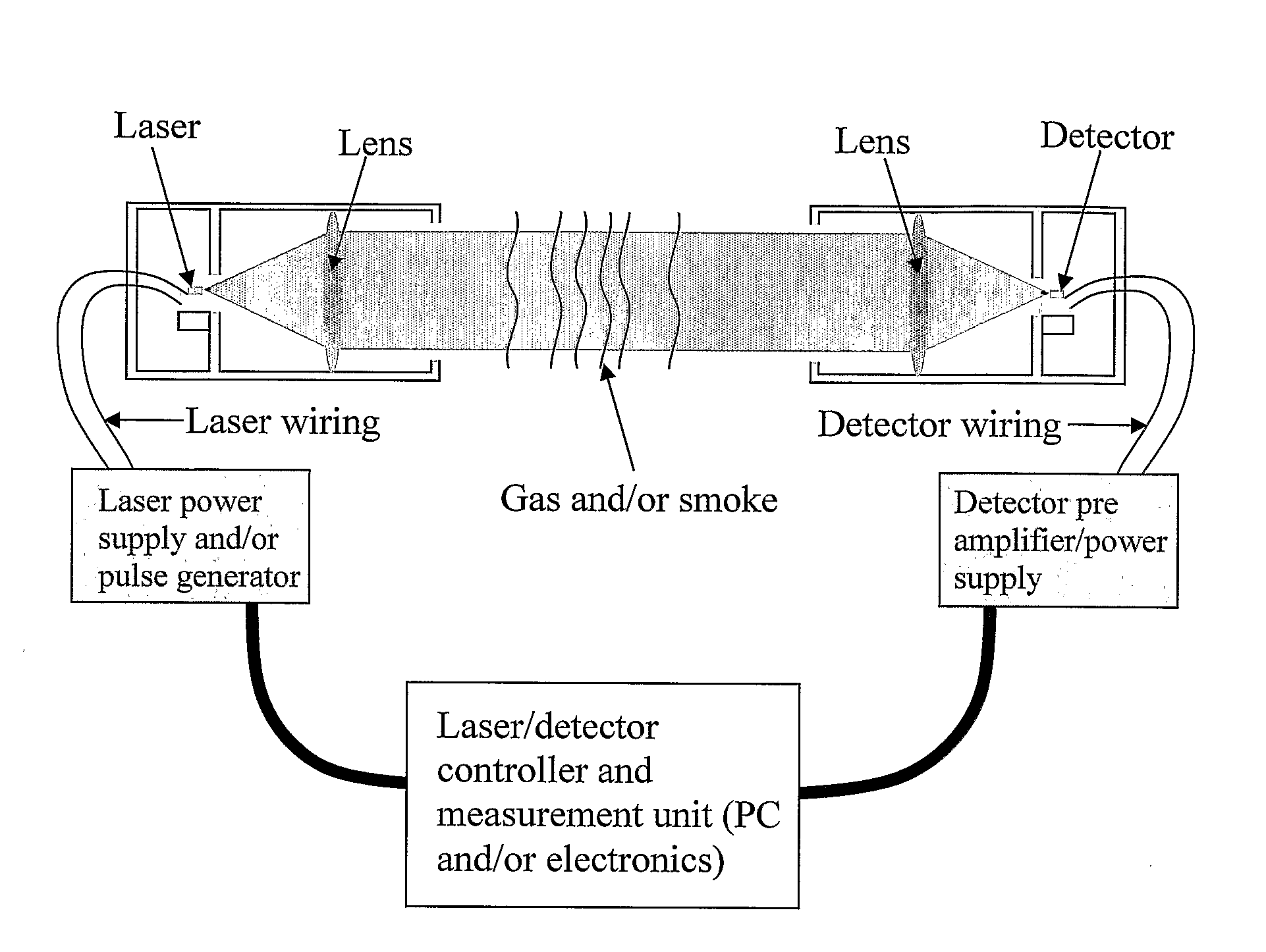
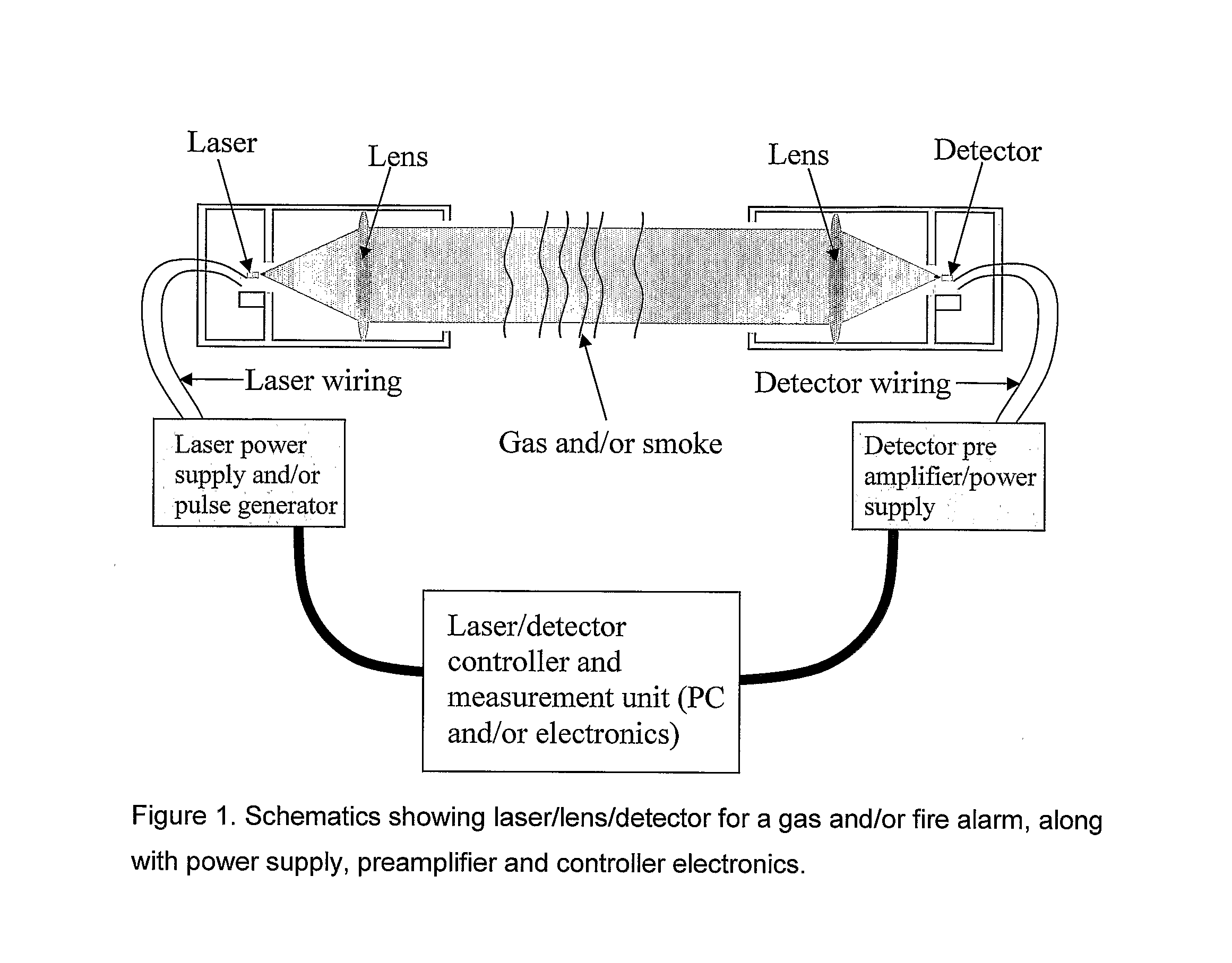
Infrared Laser Based Alarm
InactiveUS20080198027A1Avoid frostAvoid corrosion damageInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsScattering properties measurementsGas compositionParticle density
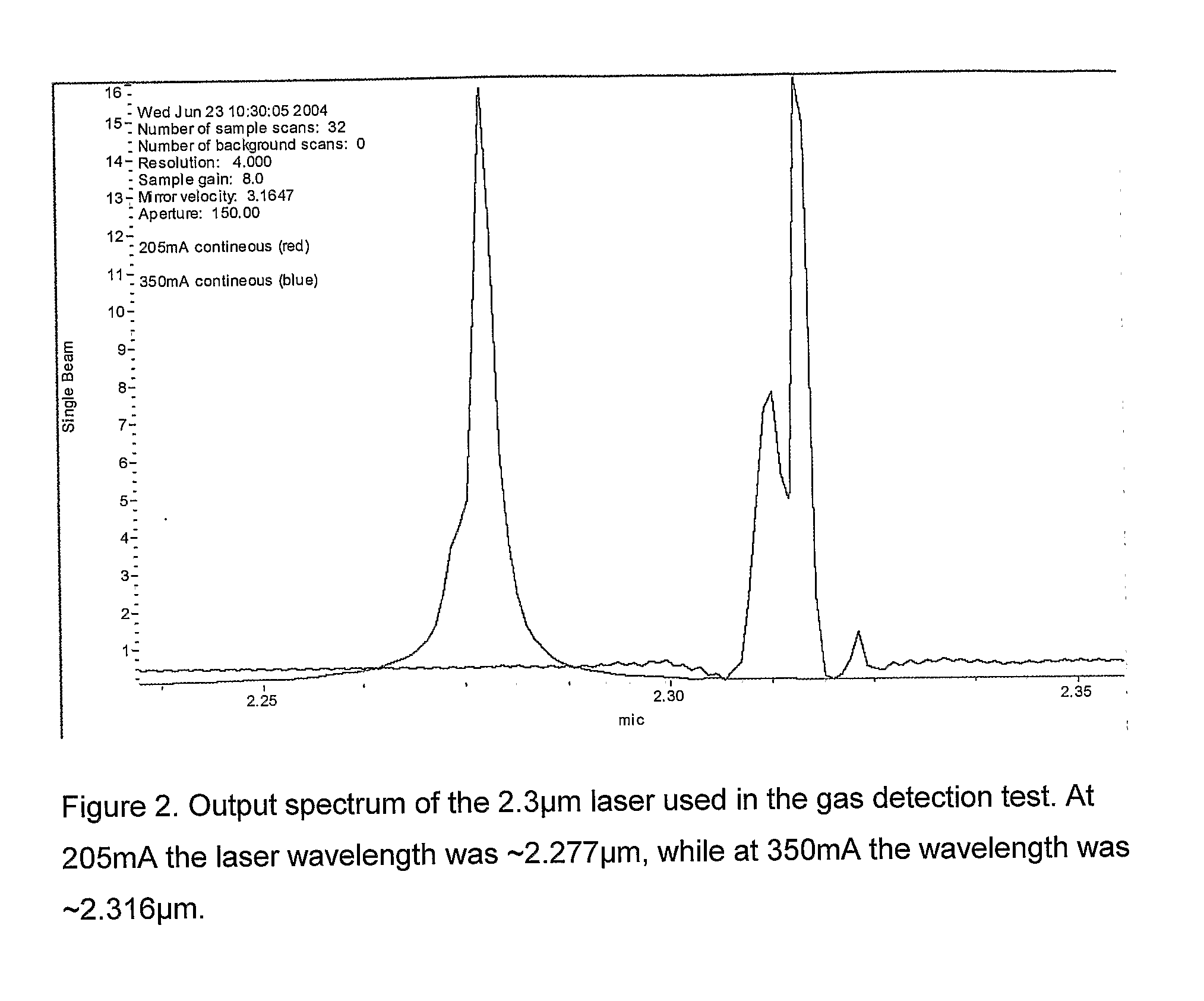
The subject invention relates to a new alarm which is based on using a quarternary tunable Mid-IR laser to measure both particles and gas at the same time. The measurement is done within an area of which the gas of interest will absorb the Mid-IR radiation. By widely tuning the emission wavelength of the laser, several wavelengths can be measured in order to accurately find both gas composition and particle density with one laser based sensor. We tested a new device which use radiation between 2.27 μm and 2.316 μm. Methane gas reduces intensity of the radiation at certain wavelengths in this device, while particles / fog reduce intensity for all wavelengths. In this case, fog should not trigger an alarm, while methane leaks should. This can also be applied for CO and smoke in which one sensor will measure both parameters to sound an alarm instead of just one parameter.
Owner:INTEGRATED OPTOELECTRONICS
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS20070291804A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser using scattering effectsSemiconductor laser optical deviceThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
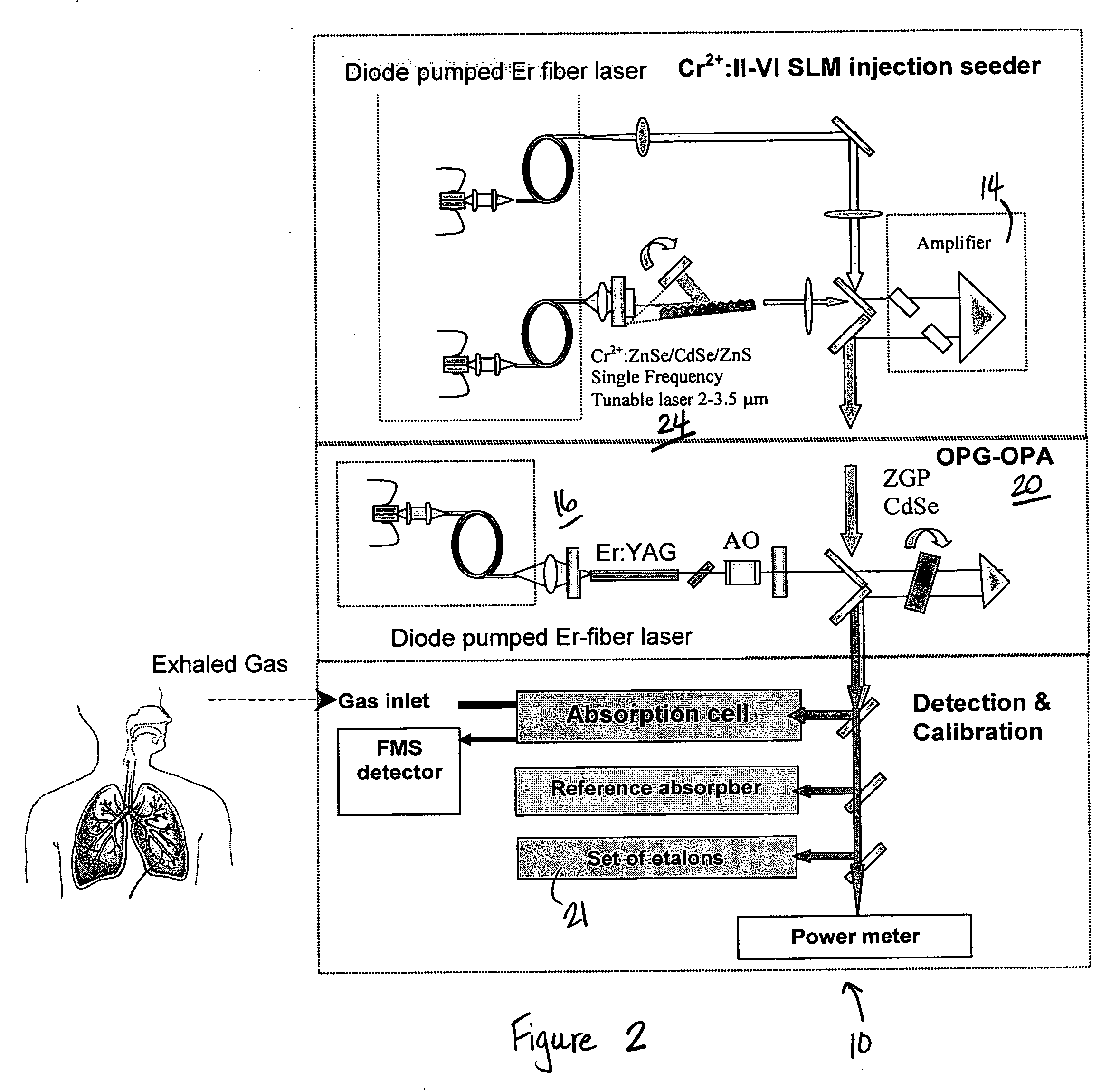
Mid-IR laser instrument for analyzing a gaseous sample and method for using the same
InactiveUS20070064748A1Wide tunabilityRapidly tuned SLM idlerPolycrystalline material growthDiffusion/dopingNoseMicrometer
An optical nose for detecting the presence of molecular contaminants in gaseous samples utilizes a tunable seed laser output in conjunction with a pulsed reference laser output to generate a mid-range IR laser output in the 2 to 20 micrometer range for use as a discriminating light source in a photo-acoustic gas analyzer.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Compact mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7492806B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
External cavity tunable compact Mid-IR laser
ActiveUS7535936B2Guaranteed uptimeSmall portabilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionThermoelectric coolingGrating
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes an external cavity to tune the laser. The external cavity may employ a Littrow or Littman cavity arrangement. In the Littrow cavity arrangement, a filter, such as a grating, is rotated to provide wavelength gain medium selectivity. In the Littman cavity arrangement, a reflector is rotated to provide tuning. A quantum cascade laser gain medium provides mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens for both the output lens and the external cavity lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser gain medium is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. The small diameter aspheric output and external cavity lens each may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and each lens is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser gain medium. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
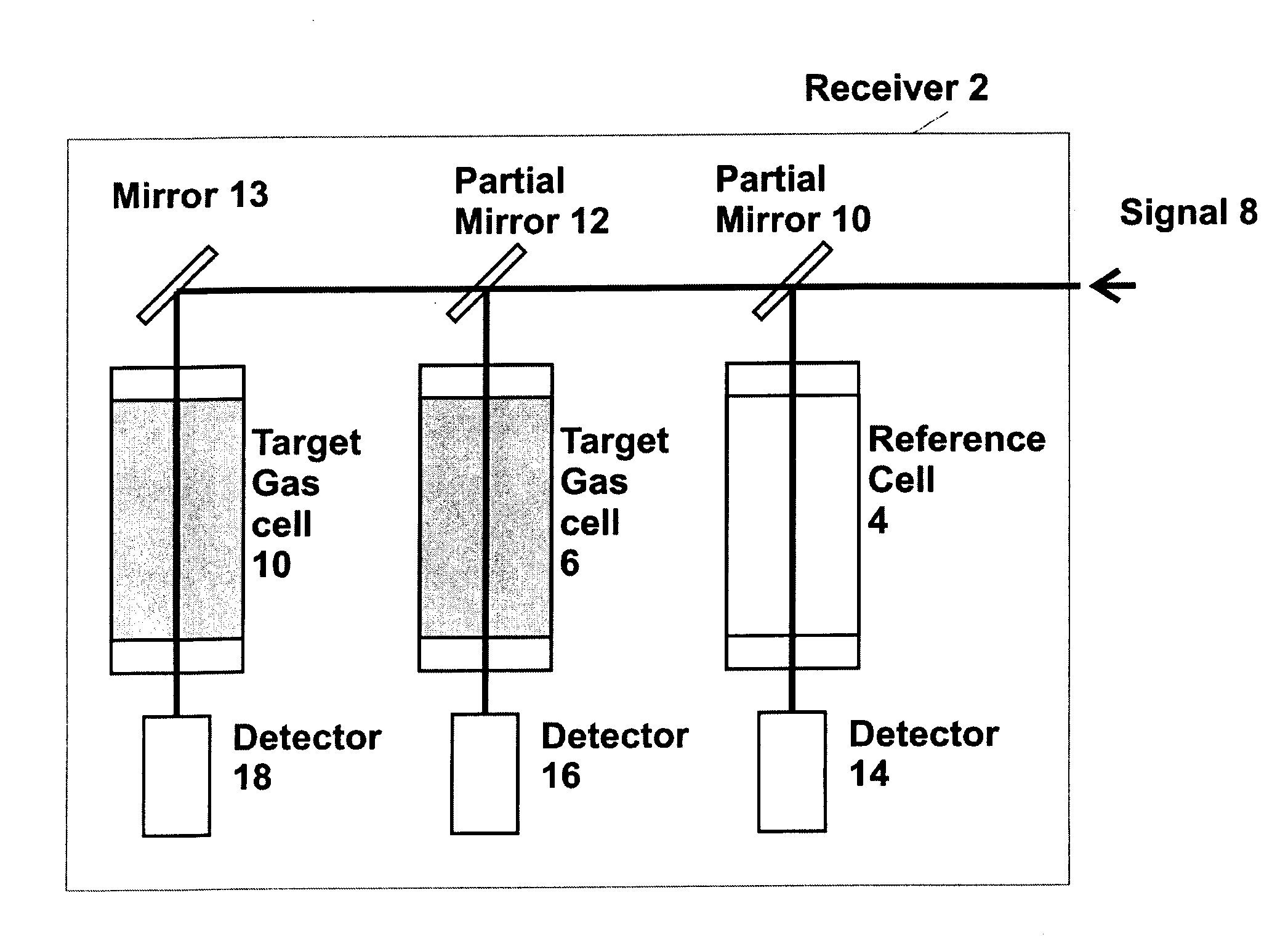
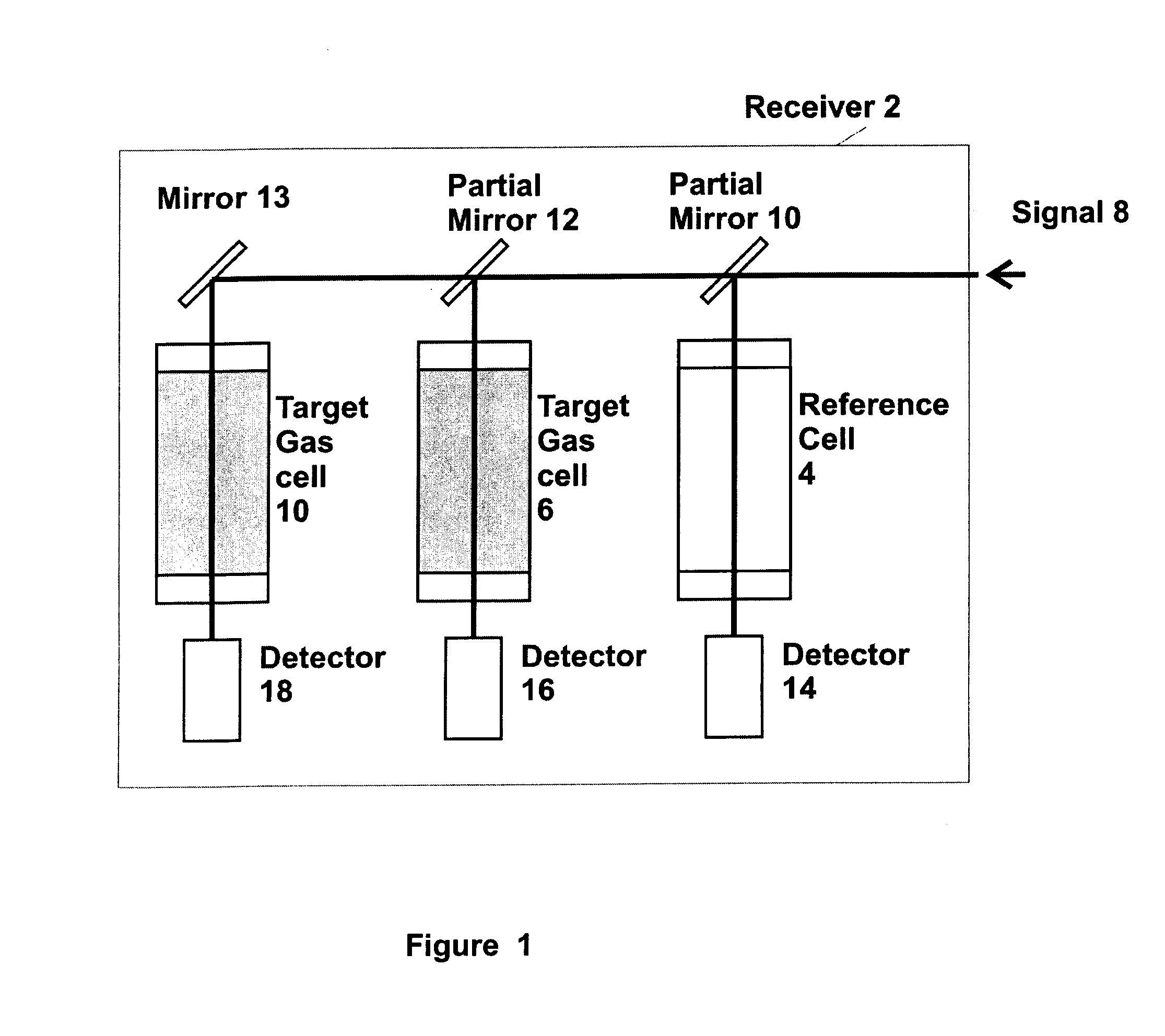
Airborne tunable mid-ir laser gas-correlation sensor
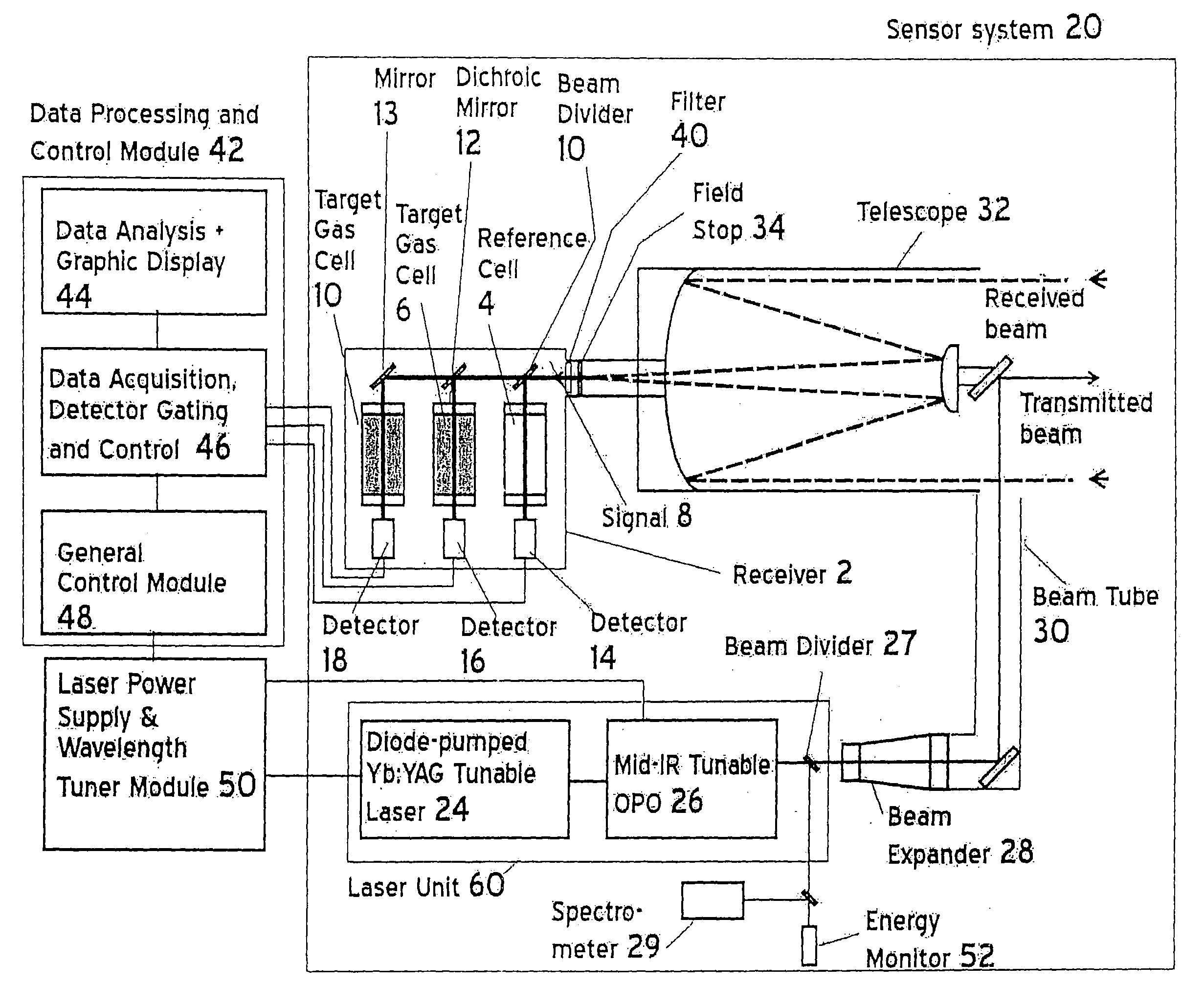
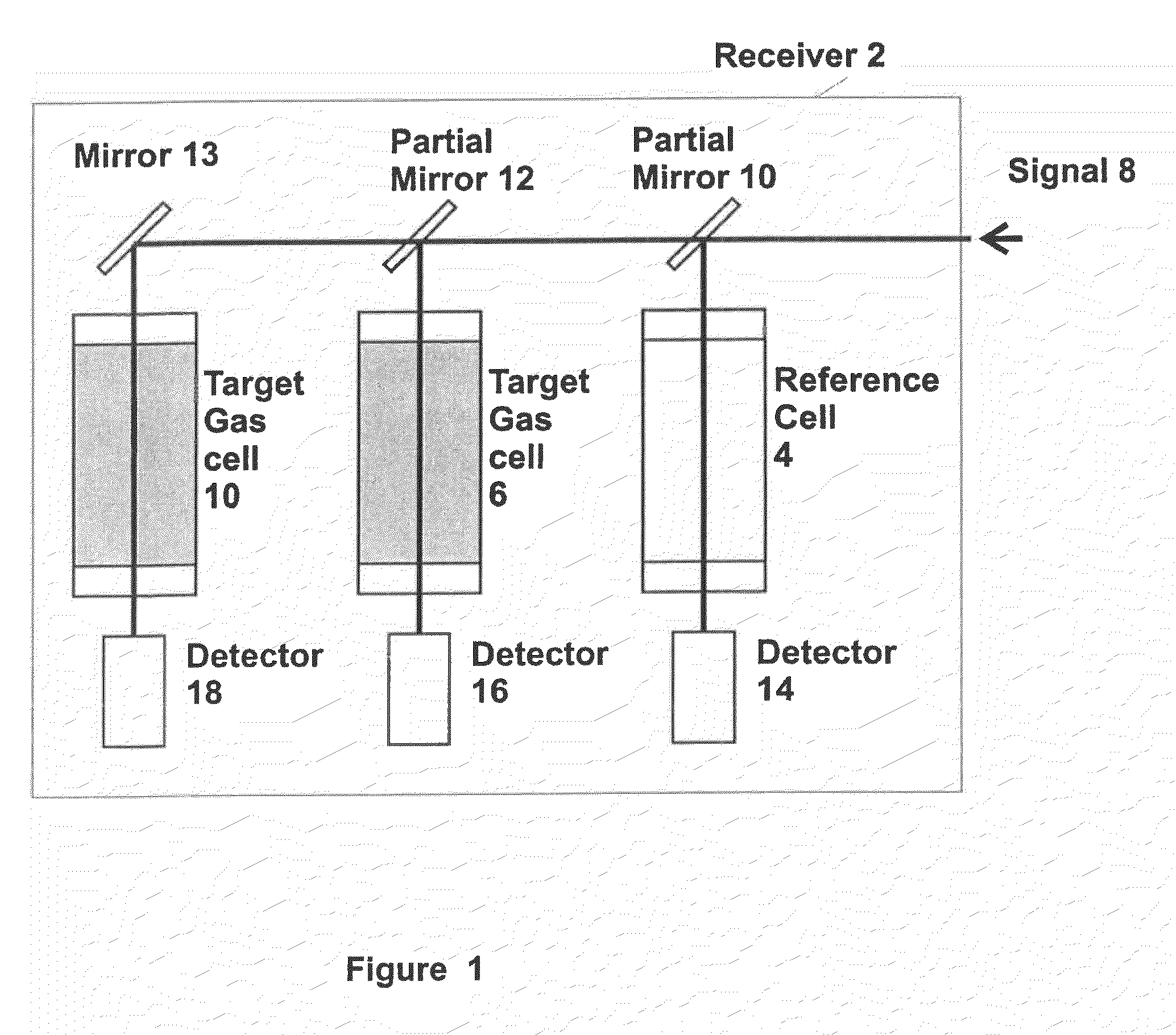
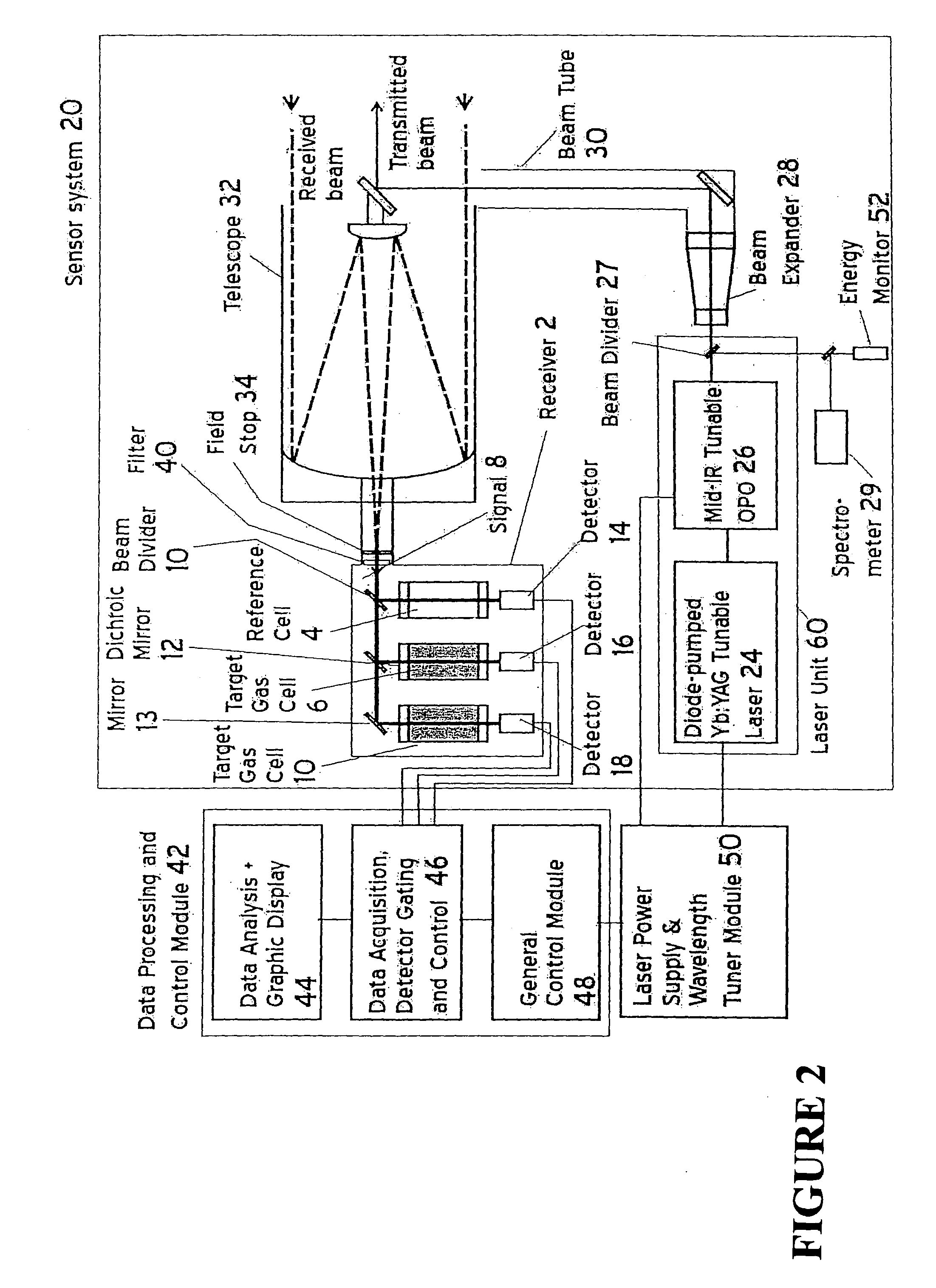
InactiveUS20080259340A1Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMid infrared laserGas concentration
A method and apparatus for measuring target gas concentrations in an atmosphere. The method and apparatus emit in the atmosphere a laser beam tuned to a molecular absorption line of a target gas, receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, divide and direct the received signal into a first optical path and a second optical path including in one of the paths a correlation gas cell filled with a predetermined concentration of the target gas, detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path, and calculate a target gas concentration by comparing a first signal transmitted through the first optical path to a second signal transmitted through the second optical path. The apparatus includes a laser source tunable to a specific molecular absorption line of a target gas and configured to emit in the atmosphere a laser beam having a spectral bandwidth greater than a full width of the molecular absorption line of the target gas, a receiver configured to receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, and at least one detector configured to detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Compact near-ir and mid-ir cavity ring down spectroscopy device
InactiveUS20080111077A1Reduce power consumptionSmall and portableRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsRing downInterquartile range
This invention relates to a compact cavity ring down spectrometer for detection and measurement of trace species in a sample gas using a tunable solid-state continuous-wave mid-infrared PPLN OPO laser or a tunable low-power solid-state continuous wave near-infrared diode laser with an algorithm for reducing the periodic noise in the voltage decay signal which subjects the data to cluster analysis or by averaging of the interquartile range of the data.
Owner:GEORGE WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY
Compact mid-ir laser
InactiveUS20100243891A1Enhanced cooling techniqueLight weightLaser active region structureMaterial analysis by optical meansThermoelectric coolingAspheric lens
A compact mid-IR laser device utilizes a quantum cascade laser to provide mid-IR frequencies suitable for use in molecular detection by signature absorption spectra. The compact nature of the device is obtained owing to an efficient heat transfer structure, the use of a small diameter aspheric lens and a monolithic assembly structure to hold the optical elements in a fixed position relative to one another. The compact housing size may be approximately 20 cm×20 cm×20 cm or less. Efficient heat transfer is achieved using a thermoelectric cooler TEC combined with a high thermal conductivity heat spreader onto which the quantum cascade laser is thermally coupled. The heat spreader not only serves to dissipate heat and conduct same to the TEC, but also serves as an optical platform to secure the optical elements within the housing in a fixed relationship relative on one another. A small diameter aspheric lens may have a diameter of 10 mm or less and is positioned to provided a collimated beam output from the quantum cascade laser. The housing is hermetically sealed to provide a rugged, light weight portable MIR laser source.
Owner:DAYLIGHT SOLUTIONS
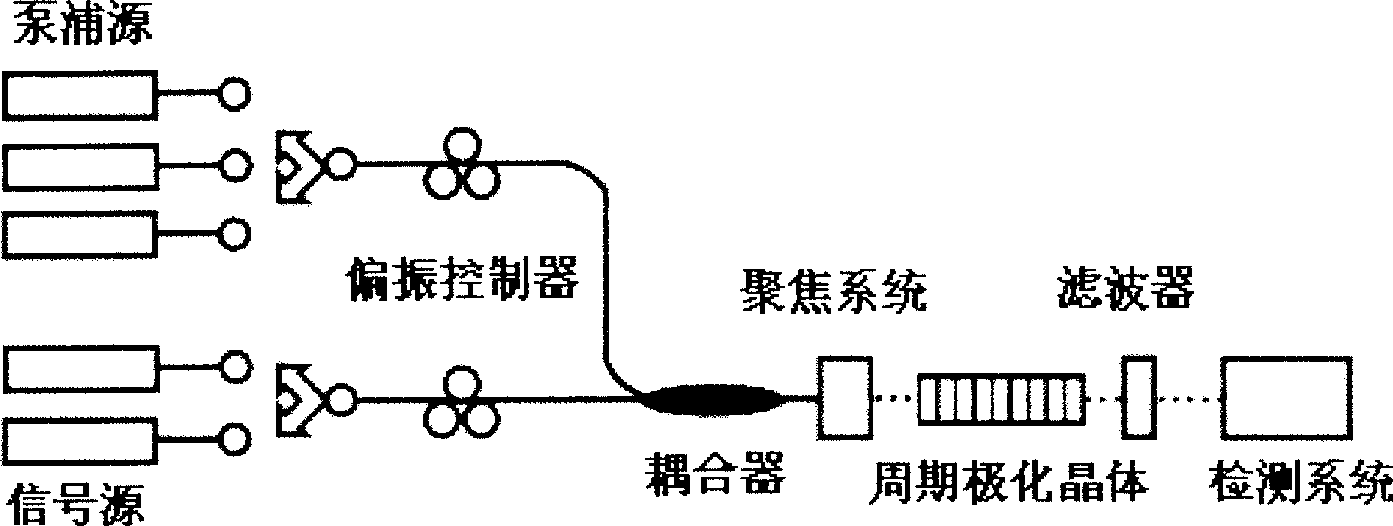
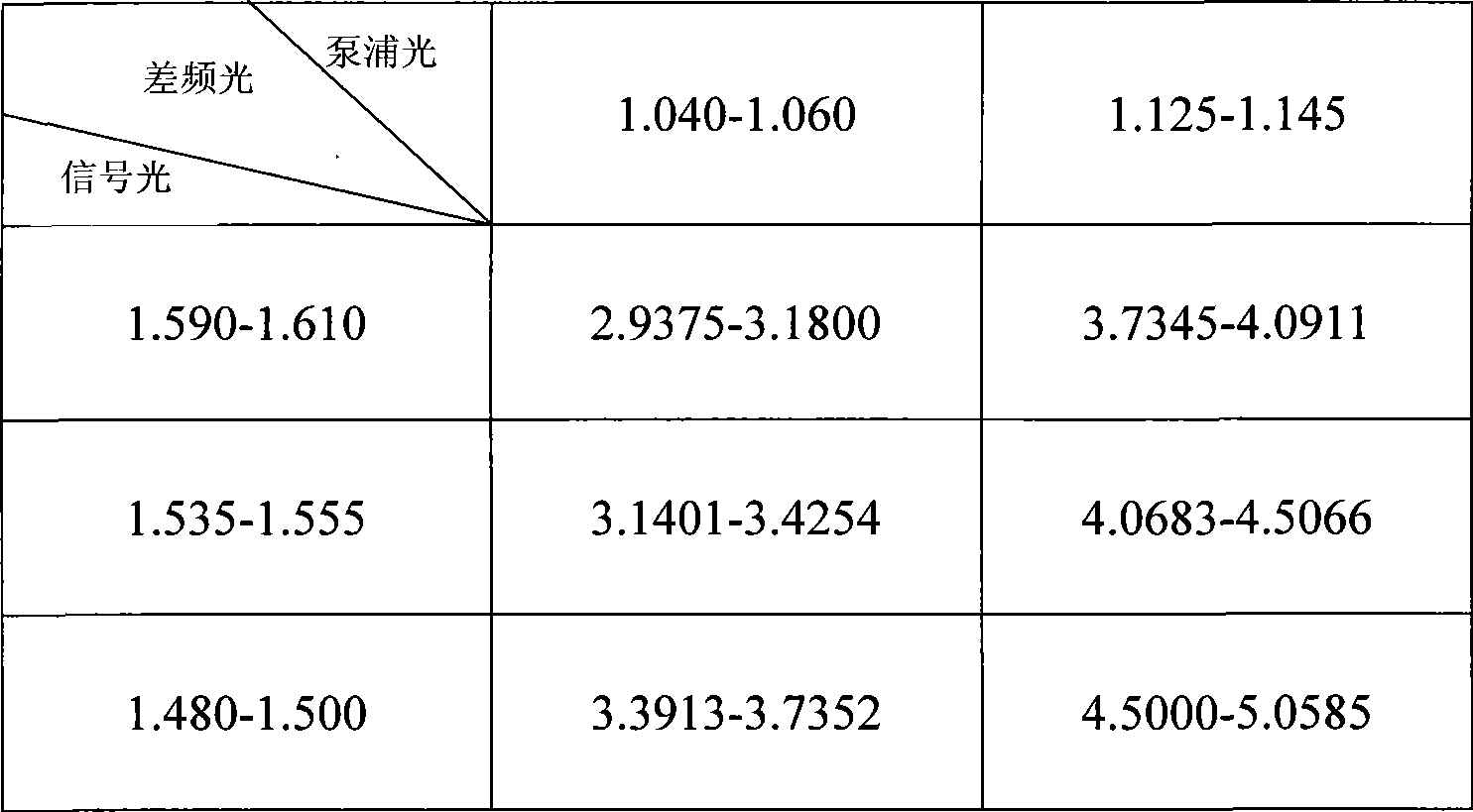
Optical fiber type mid-IR laser source generated by 3-5micrometre continuous wave differential frequency and its implementing method
InactiveCN101504507ASatisfy the broadband phase matching conditionRealize infrared outputNon-linear opticsFiber couplerS-wave
The invention discloses an iraser light source in the generation of an optical fiber type 3-5-micron continuous wave difference frequency and a method for achieving the same, wherein a pump light and a signal light adopt a wavelength sectional combining plan, a rare-earth-doped fiber laser with suitable wavelength is selected, a pump source adopts a ytterbium-doped fiber laser with a wave band of 1,060 nm and wave bands of over 1,100 nm, and the wave bands can be exchanged with each other. The signal light adopts an erbium-doped fiber laser with an S wave band, a C wave band and an L wave band, and the wave bands can be exchanged with each other. The ytterbium-doped fiber laser and the erbium-doped fiber laser emit the pump light and the signal light respectively, the pump light and the signal light are adjusted to be parallel with an optical axis of a crystal by a polarization controller respectively and are combined together by a fiber coupler, then a lens focusing system focuses the two light beams into a periodical polarization lithium niobate crystal; and by adjusting the length of the polarization cycle and the crystal temperature of the periodical polarization lithium niobate crystal, the pump light, the signal light and the difference frequency light meet a phase matching condition to finally achieve the infrared output in the generation of the difference frequency.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
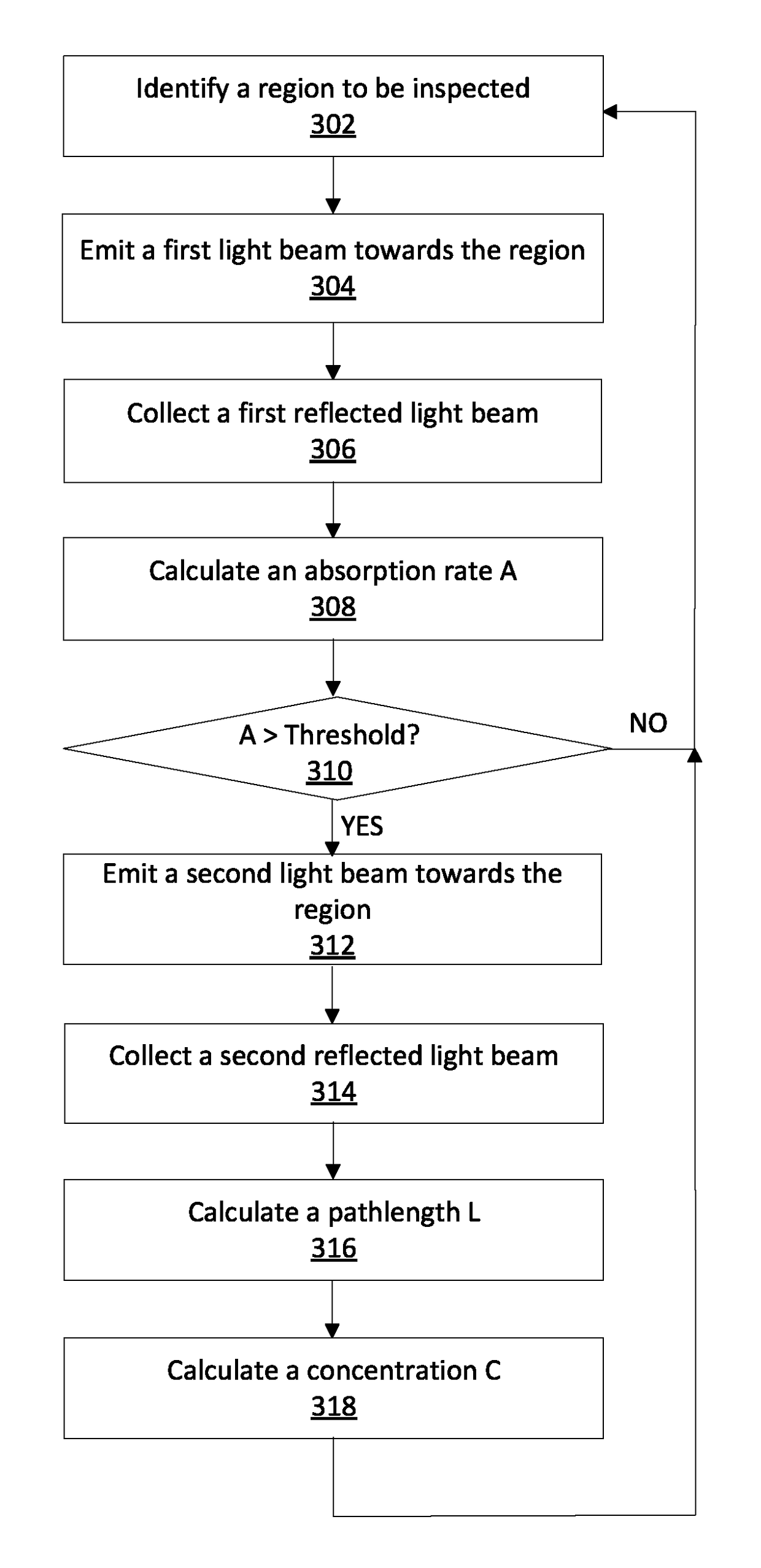
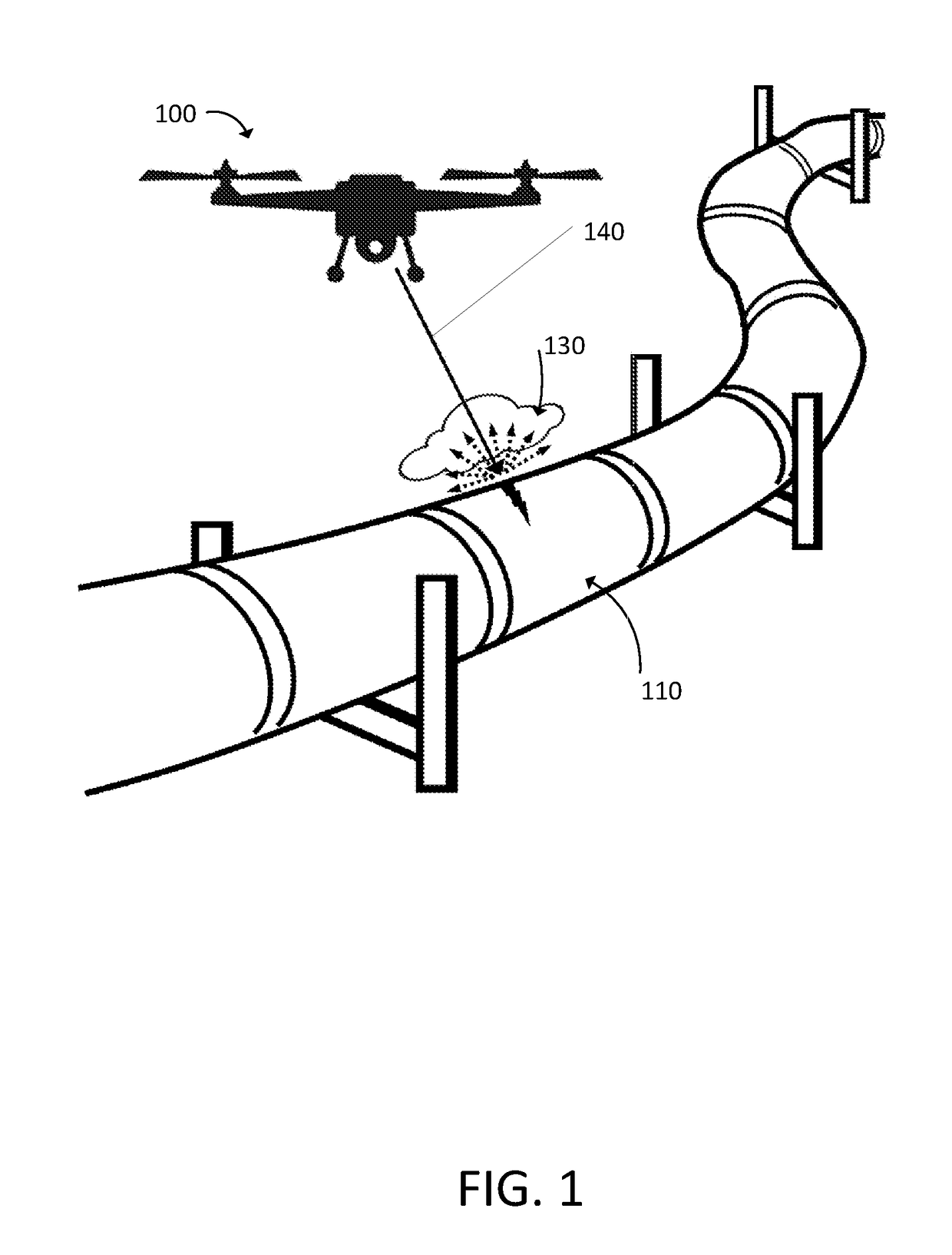
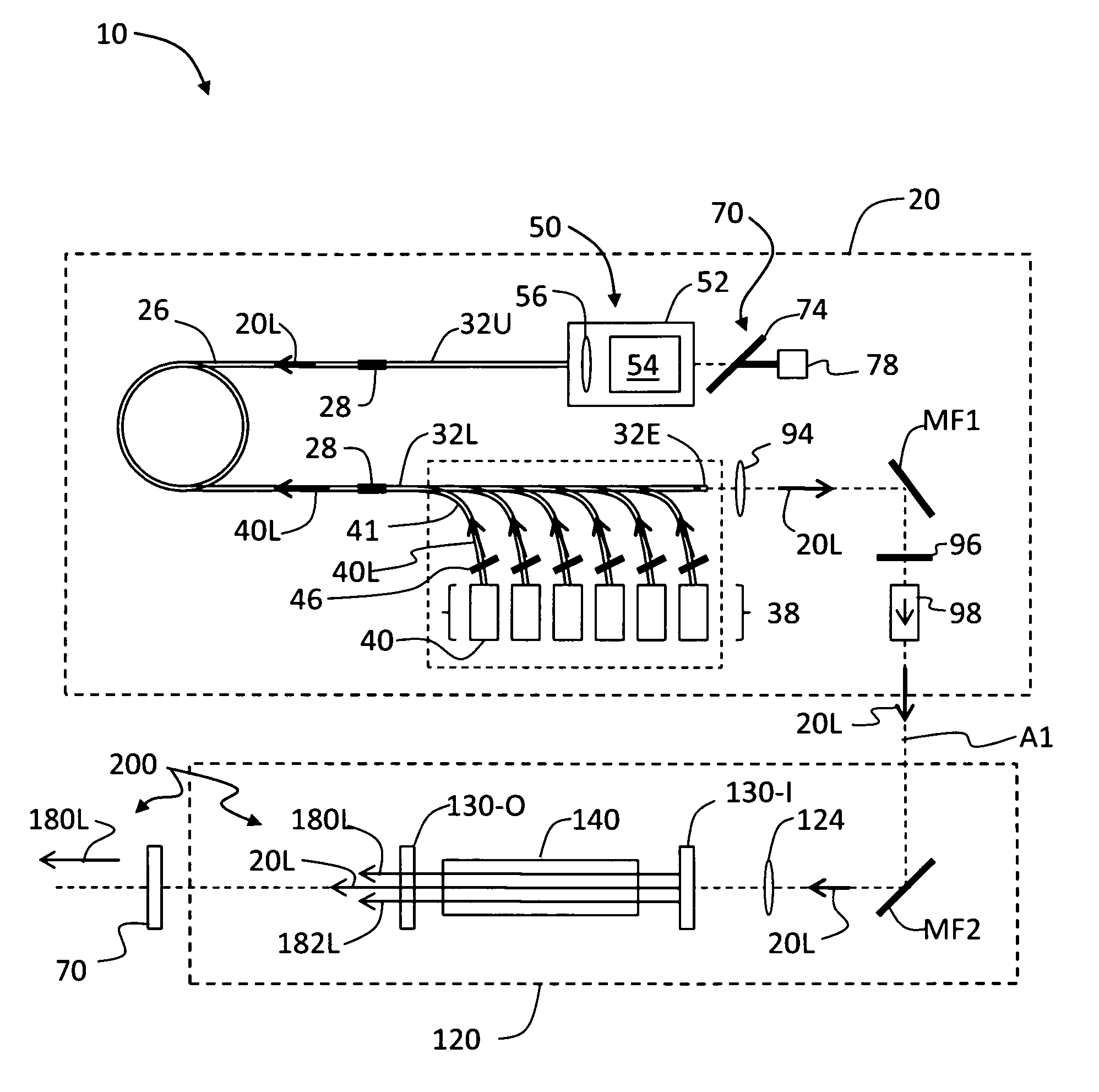
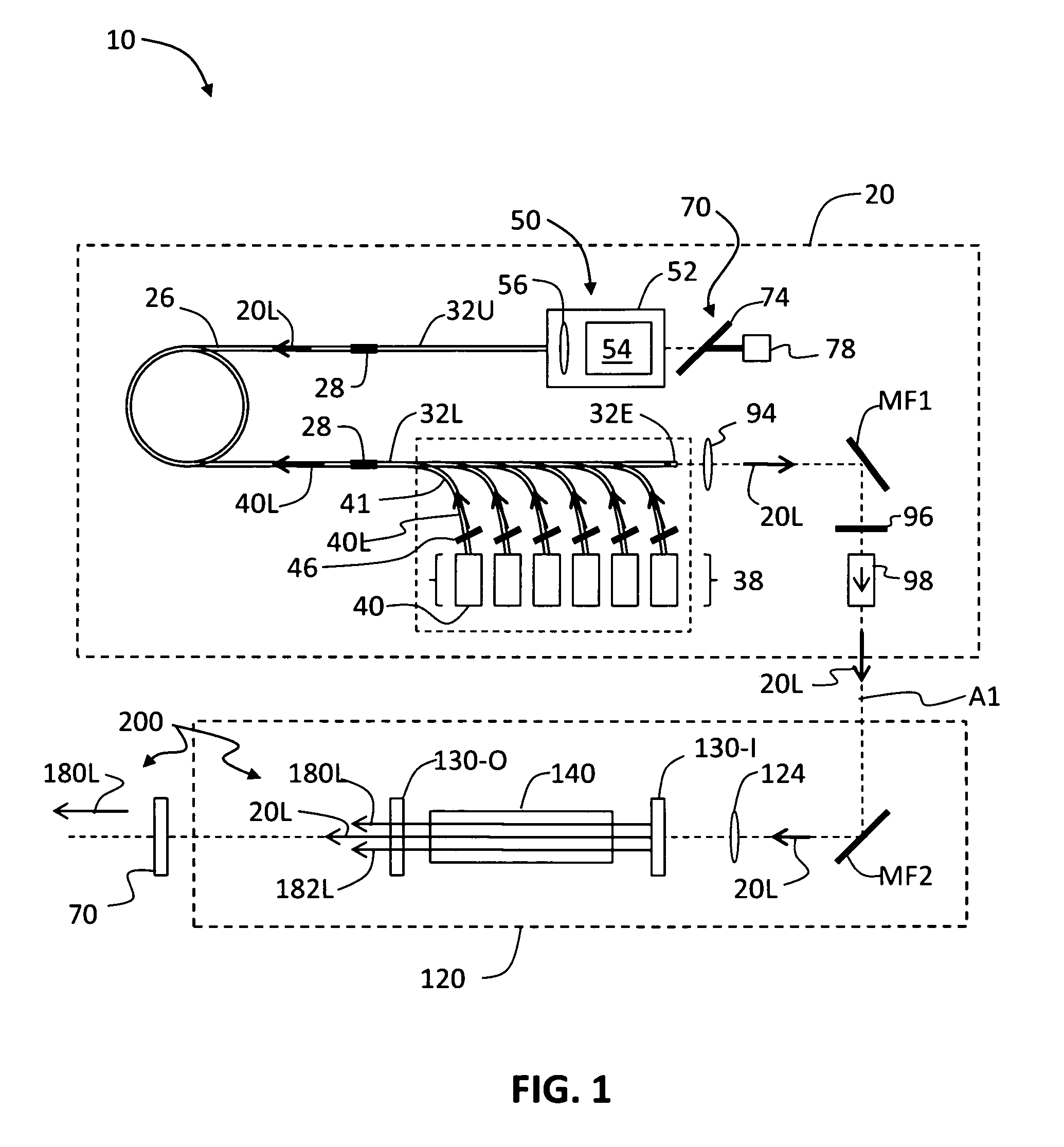
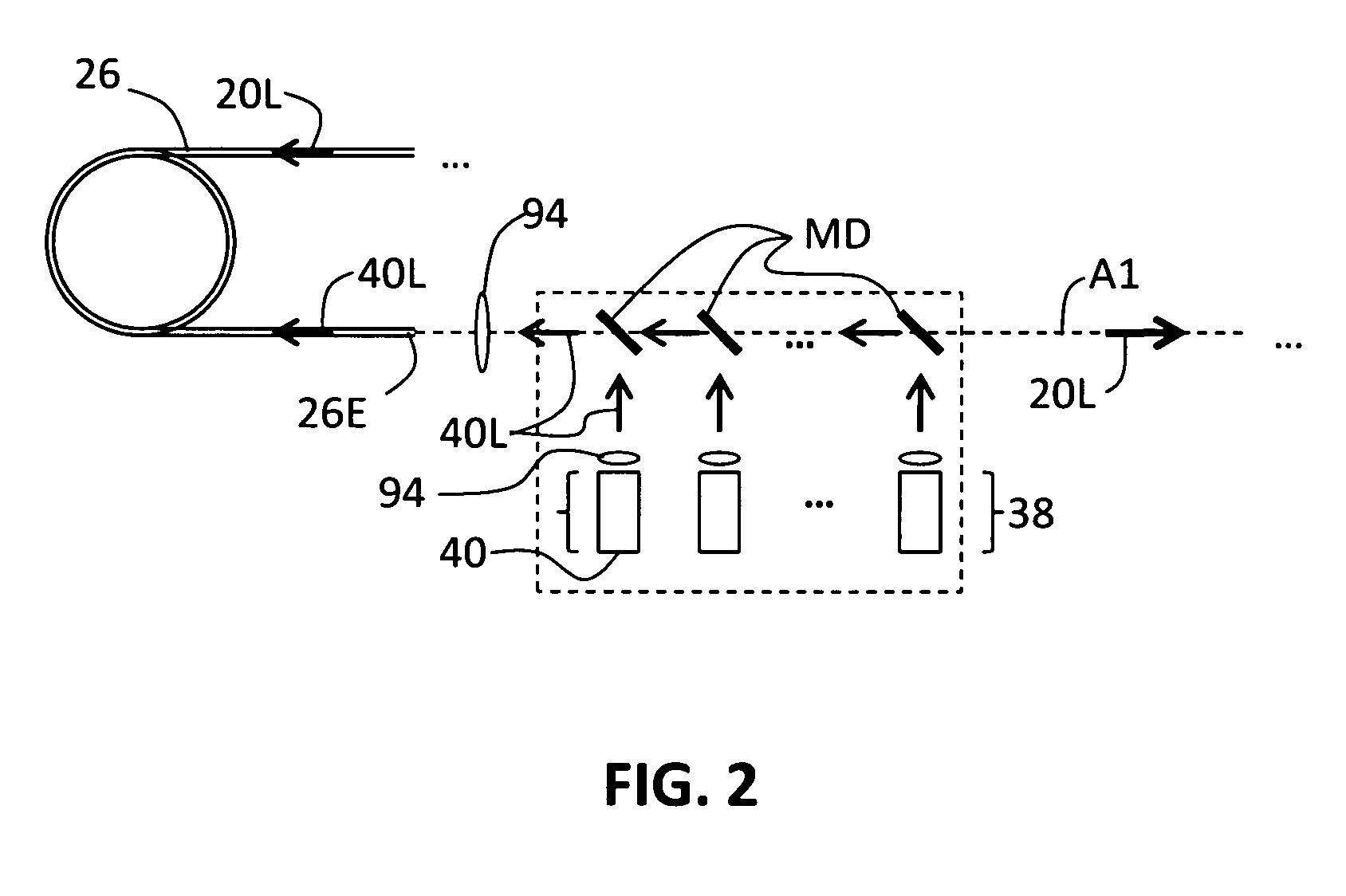
Remote gas leakage detection systems using mid-infrared laser
A system remotely detects a gas leakage from a target in an area. The gas detection system includes two light sources: a mid-infrared (mid-IR) laser for detecting absorbance of the gas in the area, and a visible laser for detecting a pathlength of the mid-IR laser. The absorption is determined based on the relative amplitude difference of the emitted and reflected mid-IR light beams. The mid-IR laser may use wavelength modulation techniques to improve the absorption determination. The pathlength is determined by comparing a phase between the emitted visible light beam and the measured visible light beam. The gas detection system calculates a concentration of the gas in the area using the determined absorption and pathlength. The gas detection system may be attached to an unmanned aerial vehicle.
Owner:AURORA INNOVATIVE TECH LLC
Mid-IR laser employing Tm fiber laser and optical parametric oscillator
A laser system that generates light in the mid-infrared (mid-IR) wavelength range is disclosed. The laser system includes an optical fiber laser having a thulium-doped optical fiber gain medium and that is configured to generate pump light having an optical power of greater than 50 W. The laser system also includes an optical parametric oscillator (OPO) arranged to receive the pump light and configured to generate therefrom, via spontaneous parametric downconversion, mid-IR-wavelength output light. A phase-matching tuning curve is used to select the pump wavelength that provides desired signal and idler wavelengths for the outputted signal and idler light. The laser system is capable of generating high-mode-quality 100 ns optical pulses with about 400 μJ energy at an average power greater than 5 W, in some cases up to several tens of Watts, and in some cases greater than 50 W at the pump wavelength.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Airborne tunable mid-ir laser gas-correlation sensor
InactiveUS20100163733A1Radiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsMid infrared laserGas concentration
A method and apparatus for measuring target gas concentrations in an atmosphere. The method and apparatus emit in the atmosphere a laser beam tuned to a molecular absorption line of a target gas, receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, divide and direct the received signal into a first optical path and a second optical path including in one of the paths a correlation gas cell filled with a predetermined concentration of the target gas, detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path, and calculate a target gas concentration by comparing a first signal transmitted through the first optical path to a second signal transmitted through the second optical path. The apparatus includes a laser source tunable to a specific molecular absorption line of a target gas and configured to emit in the atmosphere a laser beam having a spectral bandwidth greater than a full width of the molecular absorption line of the target gas, a receiver configured to receive a reflected signal affected by gas absorption of the target gas in the atmosphere, and at least one detector configured to detect transmitted signals through the first optical path and the second optical path.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of an infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice. By utilizing the optic superlattice of the structure, the structure of the optic superlattice provides two reciprocal lattice vectors simultaneously, wherein one reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in an OPO (optical parametric oscillation) process from near infrared to intermediate infrared, and the other reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in a signal light pump OPA (optical parametric amplification) from the OPO process, in the process, the intermediate infrared laser which is generated in the OPO process can be amplified further, thus more efficient intermediate infrared laser output of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained; and a commensurability ratio double periodic structure is adopted for the optic superlattice, thus the more efficient intermediate infrared laser of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
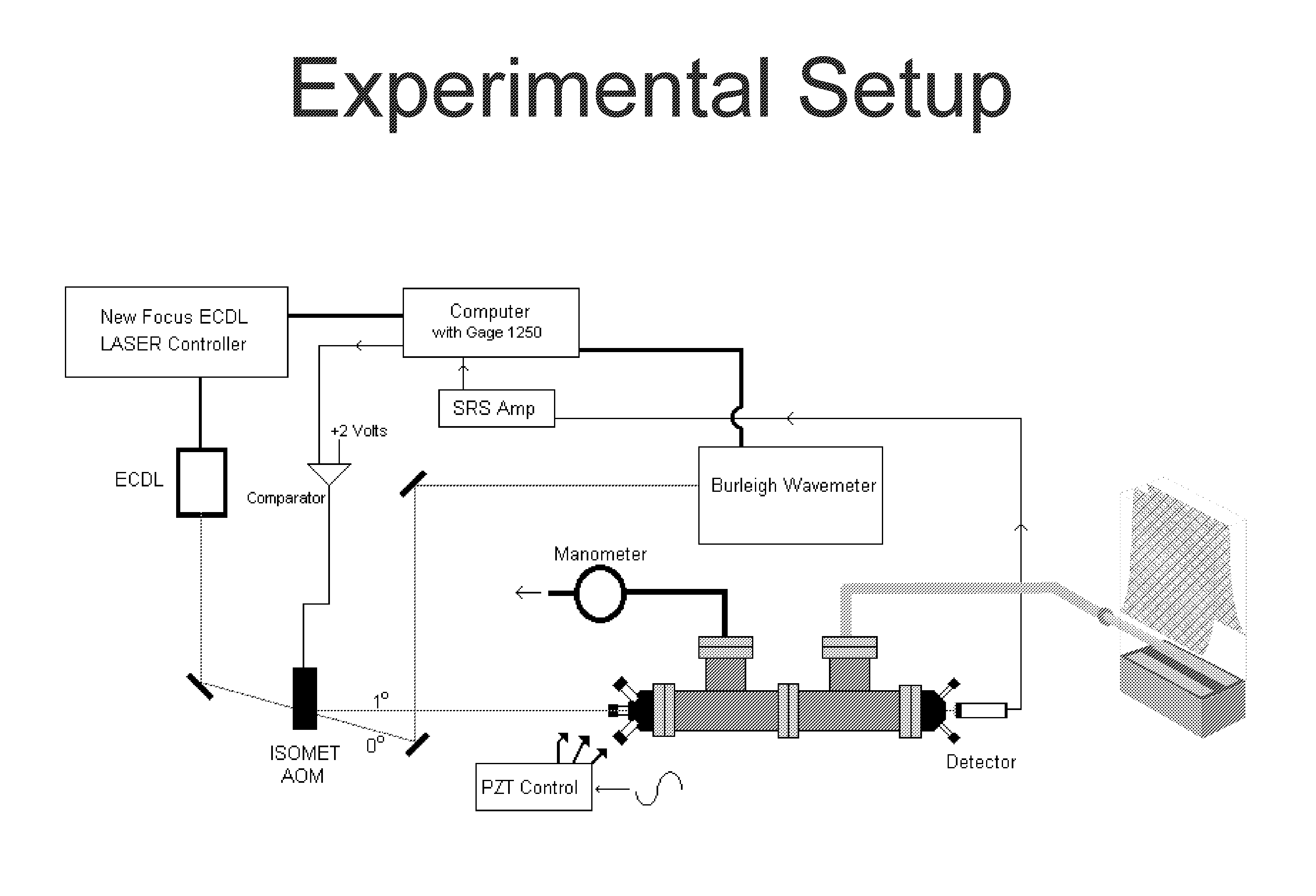
Long-path infrared spectrometer
ActiveUS20140319352A1Improve accuracyLong effective optical path lengthRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsGratingGas composition
A tunable mid-infrared laser operated in a pulsed mode is coupled off-axis into a high-finesse optical cavity to produce a long-path spectrometer. The cavity receives a gas sample. Laser pulses may be wavelength-scanned by stepping an external grating, allowing the grating to mechanically settle, then measuring the ring-down with a set of laser pulses, before moving on the next wavelength. A detector receiving infrared light exiting the cavity supplies a cavity ring-down trace representative of sample absorption of the infrared pulses. A processor determines an absolute absorption spectrum of the gas sample from the ring-down trace and analyzes sample gas composition and trace concentration from that spectrum. The absorption baseline is highly reproducible and stable, improving the accuracy of multivariate fits, and the spectral resolution can be better than 0.001 cm−1 (contingent upon the laser source), allowing for high-resolution measurements of sharp absorption features.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Electrically Pumped Broadly Tunable Mid-Infrared Lasers based on Quantum Confined Transition Metal Doped Semiconductors
ActiveUS20090304034A1Efficient energy transferCapability to luminesceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingActive medium shape and constructionMid infrared laserMid ir lasers
Electrically pumped mid-IR semiconductor lasers that are operable at room temperature and possess a range of tunability up to 1100 nm, which constitutes a revolutionary (1-2 orders of magnitude) improvement in the range of tunability over existing semiconductor laser technology utilizing Doped quantum confined host material (DQCH) with characteristic spatial dimension of the confinement tuned to enable the overlap of the discrete levels of the host and impurity ions and efficient energy transfer from the separated host carriers to the impurity, wherein: said DQCH material has the formula TM:MeZ and / or MeX2Z4, wherein Me is selected from the group consisting of Zn, Cd, Ca, Mg, Sr, Ba, Hg, Pb, Cu, Al, Ga, In; Z is selected from the group consisting of S, Se, Te, O, N, P, As, Sb and their mixtures; X being selected from the group consisting of Ga, In, and Al; and TM is selected from the group consisting from V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Infrared laser in self-optical parametric oscillation of double-cavity composite unsteady cavity mode selection pump
ActiveCN107528197AGuaranteed non-interferenceImprove output efficiencyActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionFiberBeam splitter
An infrared laser in a self-optical parametric oscillation of double-cavity composite unsteady cavity mode selection pump relates to the laser field. A problem that the infrared laser in a self-optical parameter based on an Nd: MgO: PPLN crystal considers matching of high power and high beam quality base frequency light self-pump and a focusing parameter during a self-optical parameter oscillation process is solved. The laser comprises two laser diode pump sources, two energy transfer fibers, four focusing lenses, two 45 degree beam splitter mirrors, a parameter-oscillation-cavity totally-reflective mirror, a parameter oscillation cavity output mirror, the Nd: MgO: PPLN crystal, a temperature controller and an acousto-optic Q switch. Through adopting a double-cavity composite structure of a base-frequency optical resonant cavity and a parametric optical oscillation cavity, integration compactness is considered and simultaneously the two cavities completely work separately so that cavity-type structure parameter designs of the two cavities do not interfere with each other. Large base mode high beam quality base frequency optical pump can be realized, oscillation parameter light and base frequency light focusing parameters are highly matched, and energy conversion efficiency is high.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
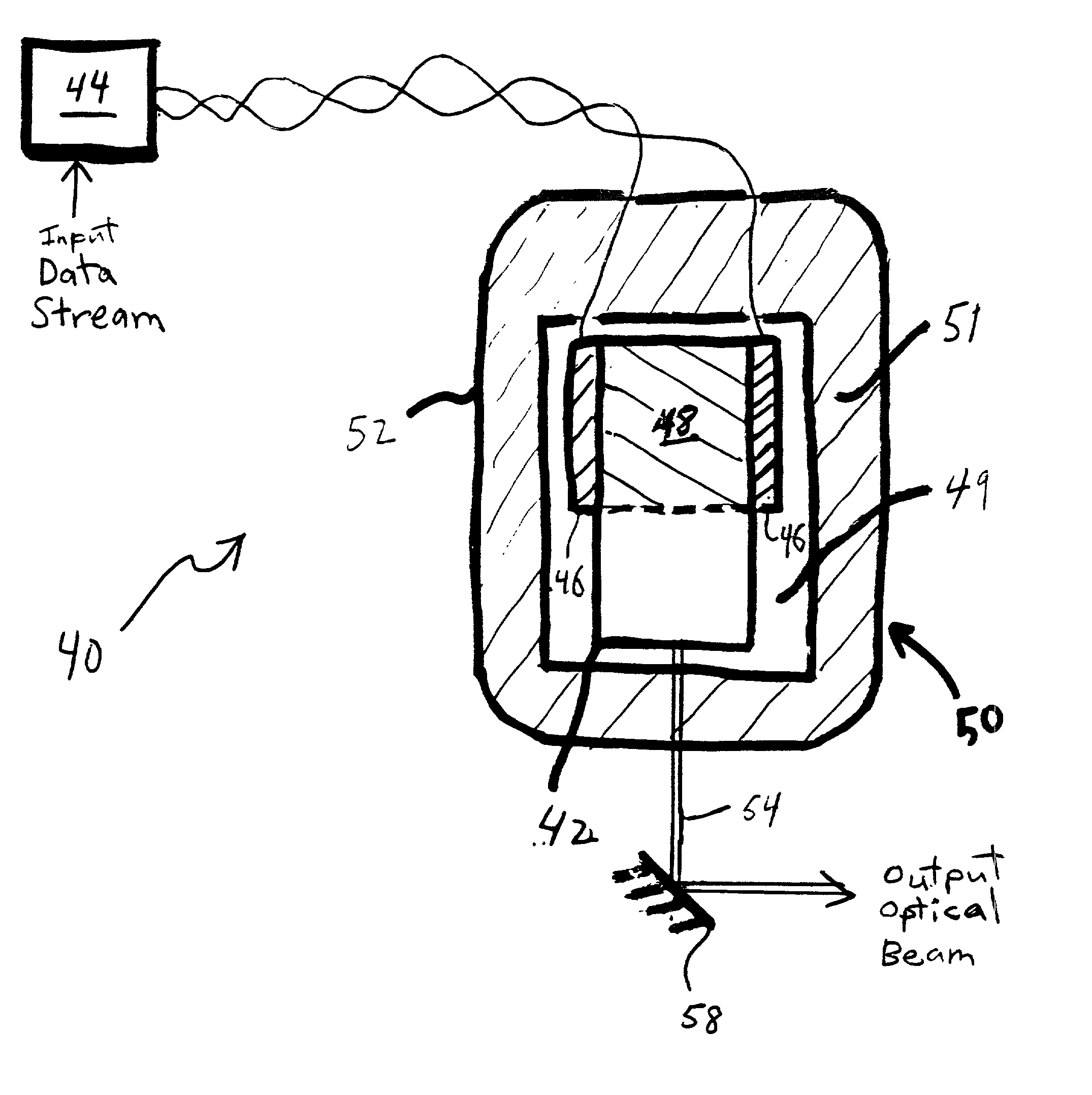
Data transmission via direct modulation of a mid-IR laser
A process for optically transmitting data to a remote receiver includes receiving a stream of input data signals and modulating a mid-IR laser by direct modulation with a waveform whose sequential values are responsive of the data signals of the stream. The direct modulation includes pumping the mid-IR laser to produce high and low optical power levels in response to different ones of the values. The process also includes transmitting output light from the modulated mid-IR laser to the remote receiver via a free space communications channel.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Long-path infrared spectrometer
ActiveUS9097583B2Improve accuracyAvoid short lengthTransmissivity measurementsAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyGratingGas composition
A tunable mid-infrared laser operated in a pulsed mode is coupled off-axis into a high-finesse optical cavity to produce a long-path spectrometer. The cavity receives a gas sample. Laser pulses may be wavelength-scanned by stepping an external grating, allowing the grating to mechanically settle, then measuring the ring-down with a set of laser pulses, before moving on the next wavelength. A detector receiving infrared light exiting the cavity supplies a cavity ring-down trace representative of sample absorption of the infrared pulses. A processor determines an absolute absorption spectrum of the gas sample from the ring-down trace and analyzes sample gas composition and trace concentration from that spectrum. The absorption baseline is highly reproducible and stable, improving the accuracy of multivariate fits, and the spectral resolution can be better than 0.001 cm−1 (contingent upon the laser source), allowing for high-resolution measurements of sharp absorption features.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
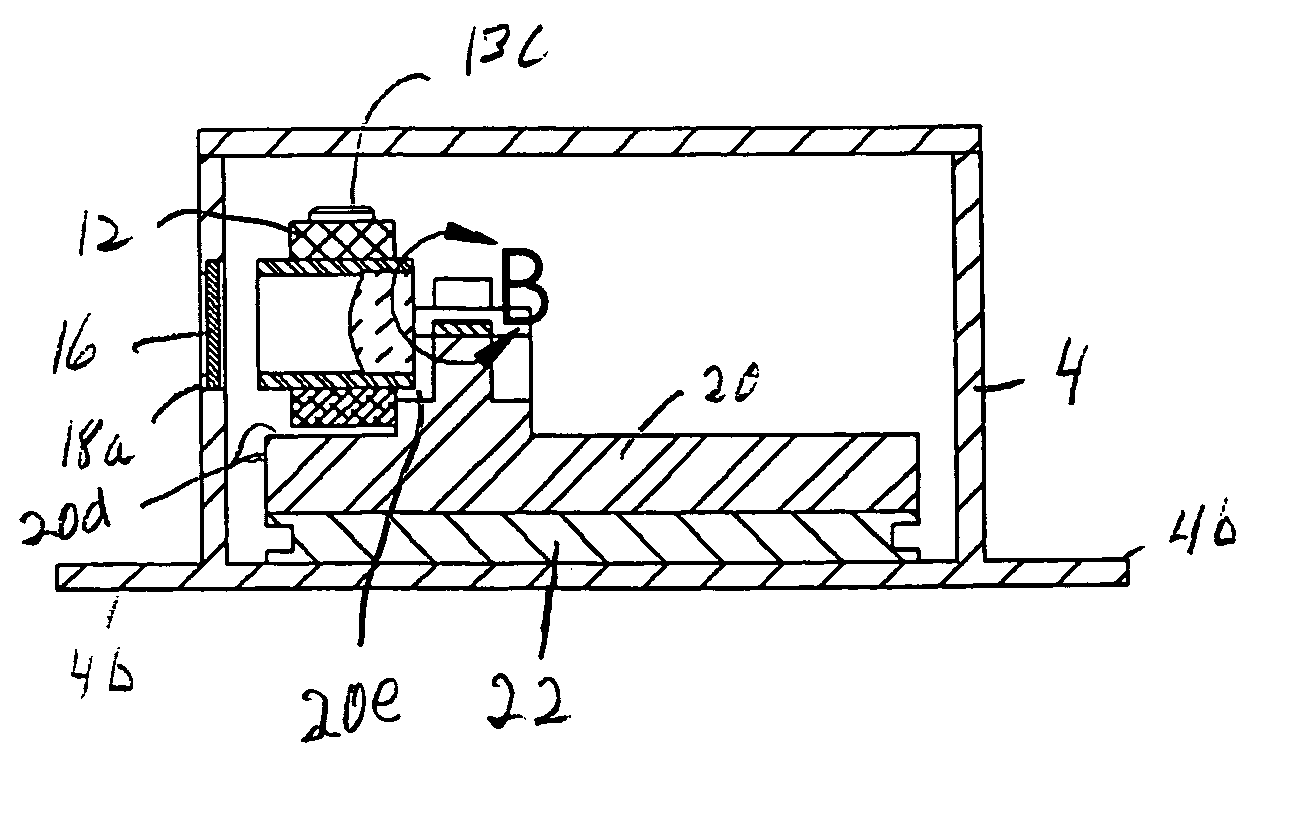
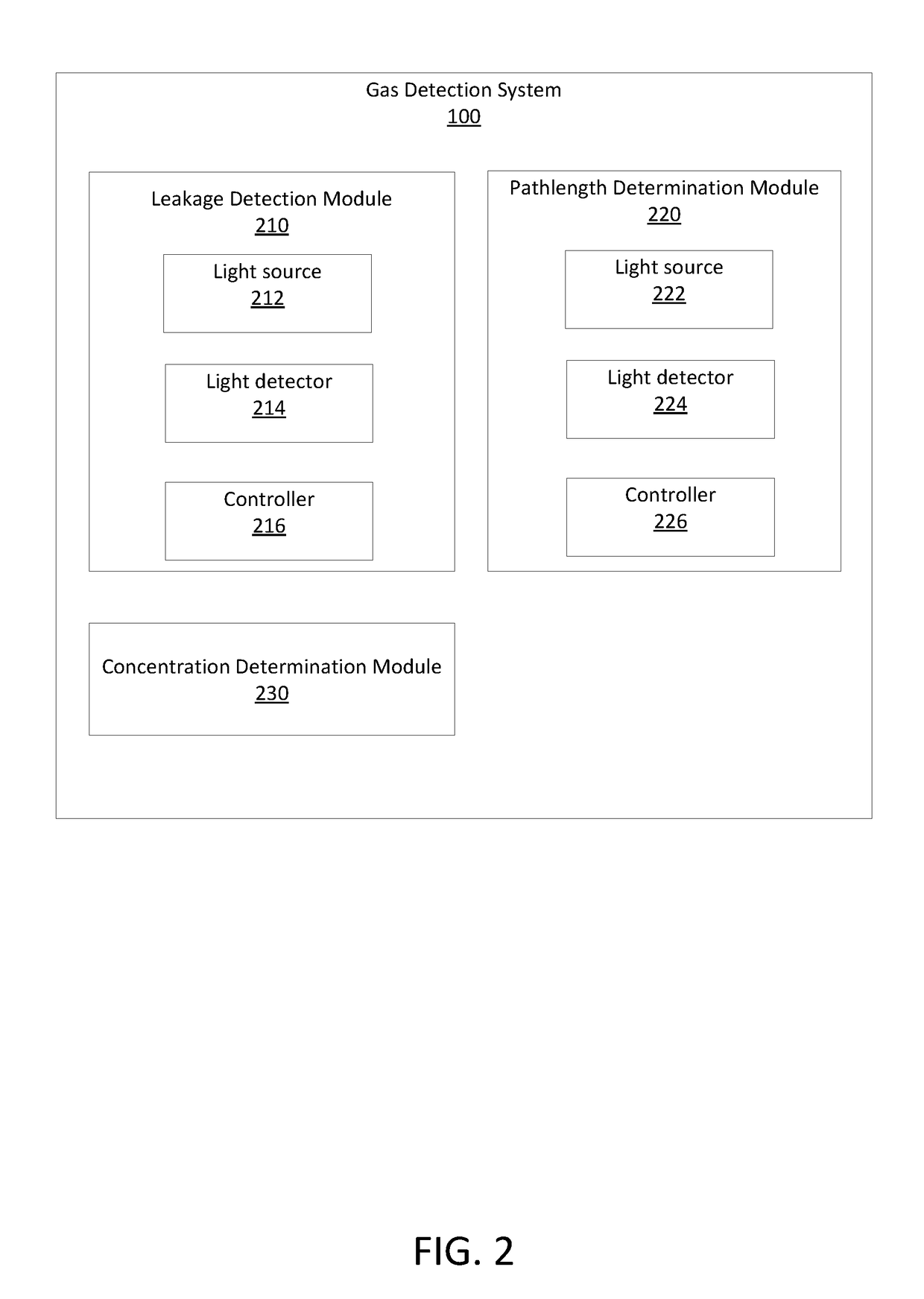
High-accuracy mid-IR laser-based gas sensor
InactiveUS9651488B2Good choiceImprove accuracyRadiation pyrometryTransmissivity measurementsPhotodetectorAmbient pressure
A gas sensor system is provided, comprising: a gas cell operable so as to receive a sample gas; a vacuum system fluidically coupled to the gas cell operable to maintain the sample gas within the gas cell at a sub-ambient pressure; a pressure sensor operable to sense a pressure of the sample gas; a thermally insulated enclosure having the gas cell therein; a heat source or heat exchanger operable to influence an interior temperature of the thermally insulated enclosure; a light source within the thermally insulated enclosure operable to provide a mid-infrared (mid-IR) light into and through the gas cell; a photodetector within the thermally insulated enclosure operable to receive the attenuated mid-IR; and a control system electronically coupled to the vacuum system and to the pressure sensor operable to maintain the sample gas within the gas cell at the predetermined pressure to within one torr (1 Torr).
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
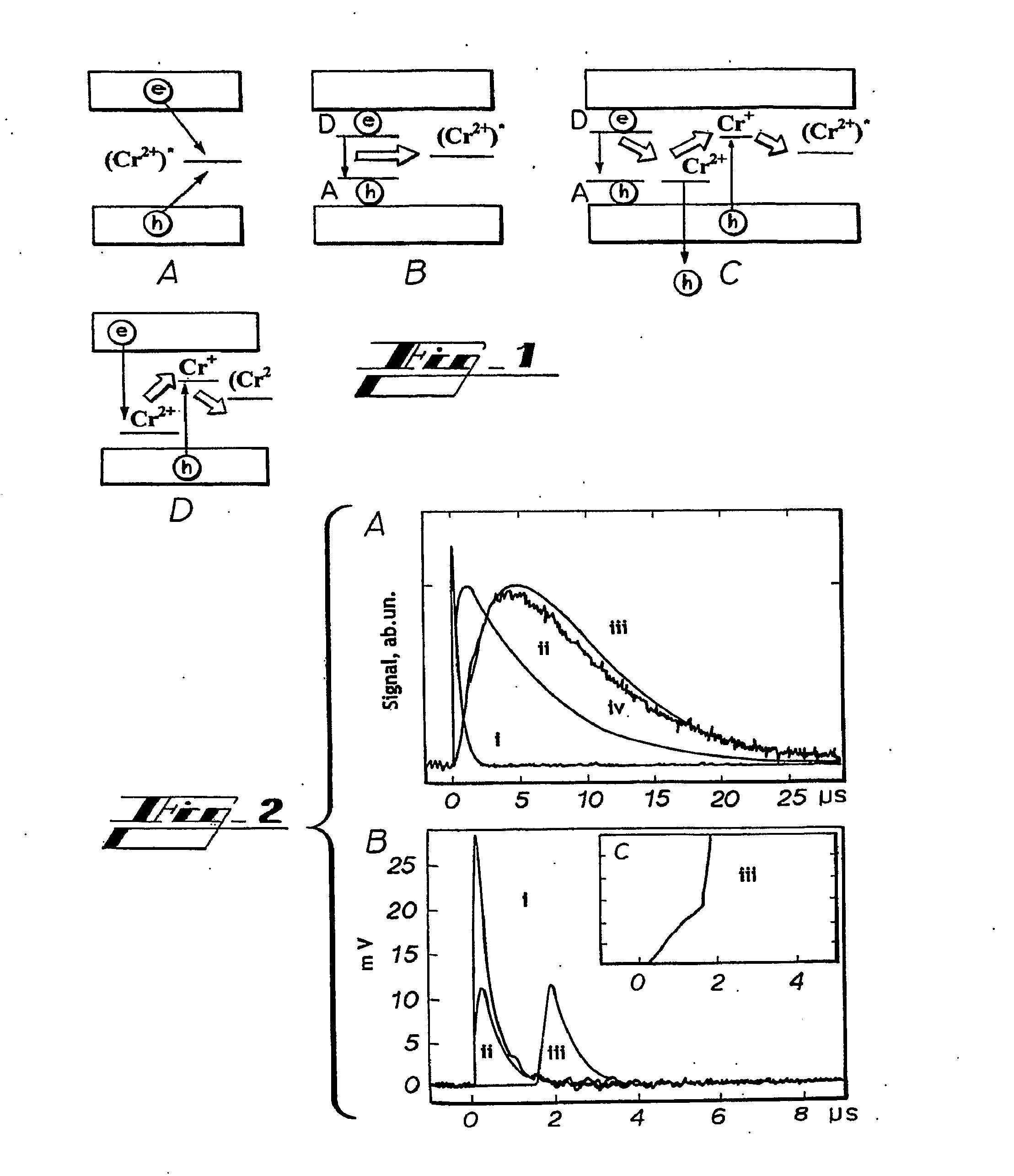
Method for measuring thickness of chromium film on photomask
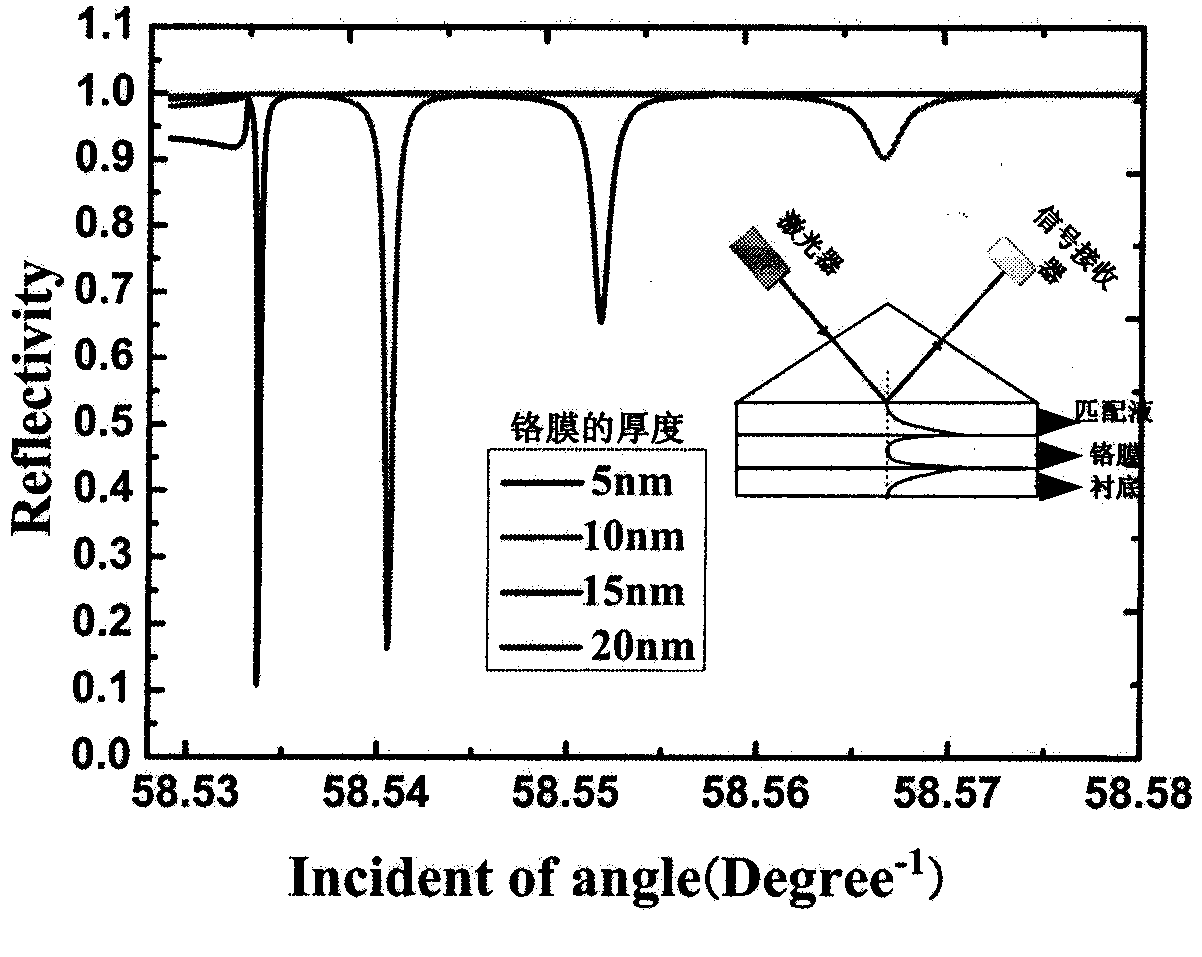
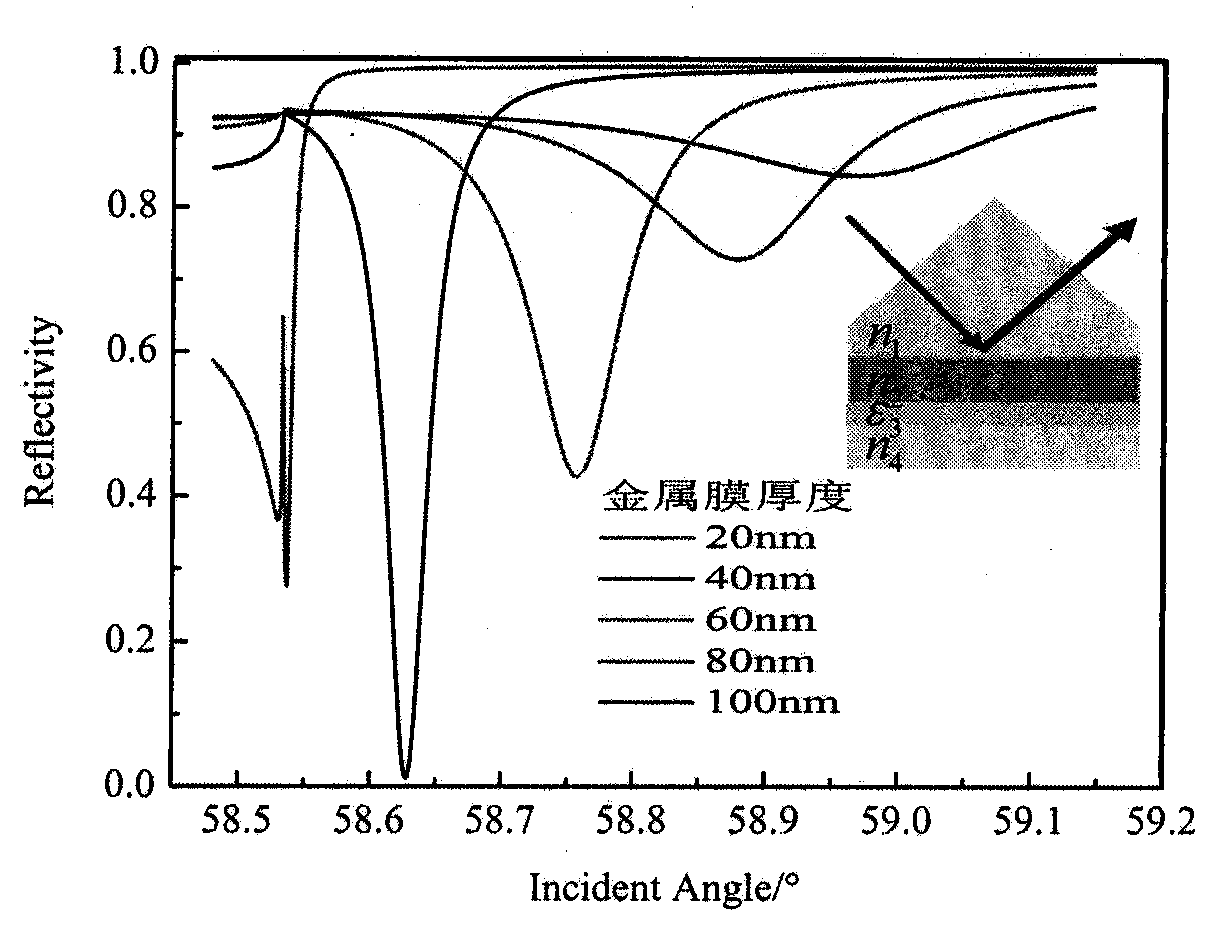
The invention belongs to the field of physical measurement and relates to a method for measuring thickness of a chromium film on a photomask. The method is characterized in that a prism-coupled long-range surface plasmon resonance sensor is provided and used for measuring the thickness of the chromium film on a quartz substrate, under the two ranges, from 5nm to 20nm and from 20nm to 100nm; a mid-infrared He-Ne laser transmit parallel beams which become TM (transverse magnetic) polarized light after passing a polarizer; the TM polarized light enters the prism-coupled long-range surface plasmon resonance sensor; reflected light, carrying the thickness information of the chromium film, projects to a thermal radiation detector. The method has the advantages that mid-infrared He-Ne laser Lambada, being 3.391 micrometers, is used to trigger resonance of the chromium film and long-range surface plasmon on a dielectric interface, ATR (attenuated total reflection) absorption peaks are generated, the angle positions of the ATR absorption peaks are functions sensitive to the thickness of the chromium film, and thus, the thickness of the chromium film can be determined according to the angle positions of the ATR absorption peaks of a reflectivity-incident angle curve; the two measuring ranges, from 5nm to 20nm and from 20nm to 100nm, are available, and resolutions, 0.001 DEG / nm and 0.003 DEG / nm, are available; measuring equipment is simple in structure, convenient to operate and low in cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI OPTICAL LITHOGRAPHY ENG
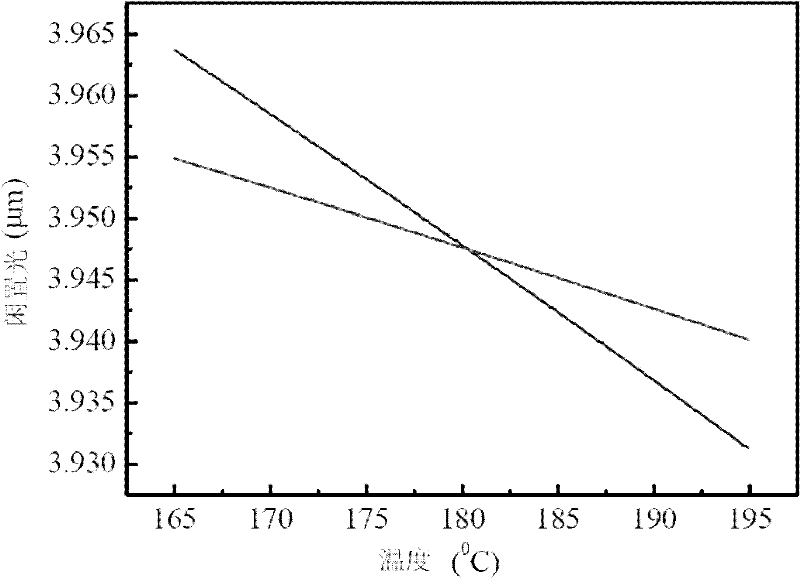
3.9 mu m mid infrared laser
InactiveCN102801102ASimple structureReduce the difficulty of adjustmentOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialSpectroscopyOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a 3.9 mu m mid infrared laser, relates to a laser, and in particular relates to a 889nm LD pump 3.9 mu m Ho:BYF laser. By adoption of an LD pump high doping concentration Ho:BYF crystal mode, 3.9 mu m mid infrared laser output is obtained in a resonant cavity. Due to the overall design, the structure is greatly simplified, the loss brought by the up-conversion effect and ion sensitization is avoided, and the beam quality and stability of the laser output are improved. The laser is applied to technical research of mid infrared lasers, and the application fields comprise photoelectric countermeasure, environmental monitoring, laser radar, laser medical treatment and spectroscopy research.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
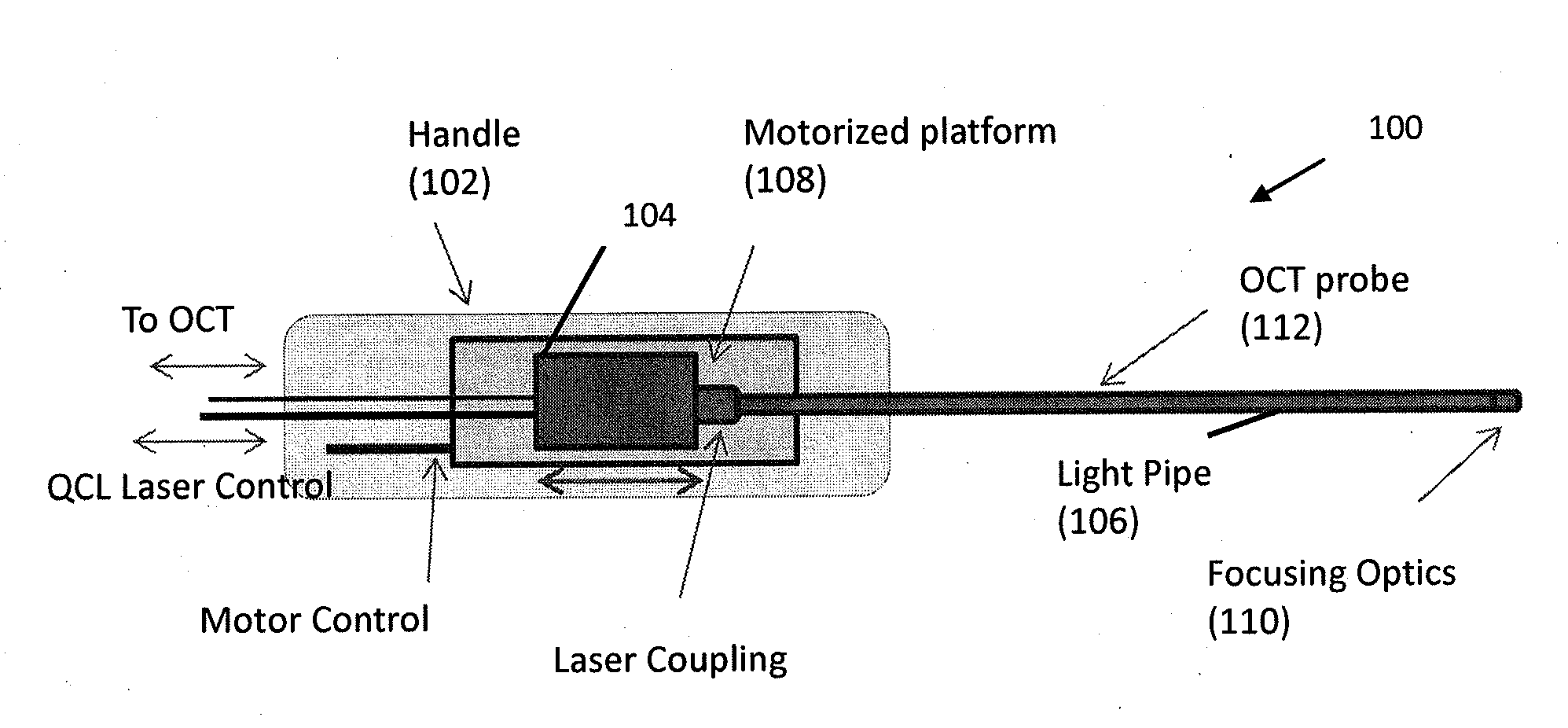
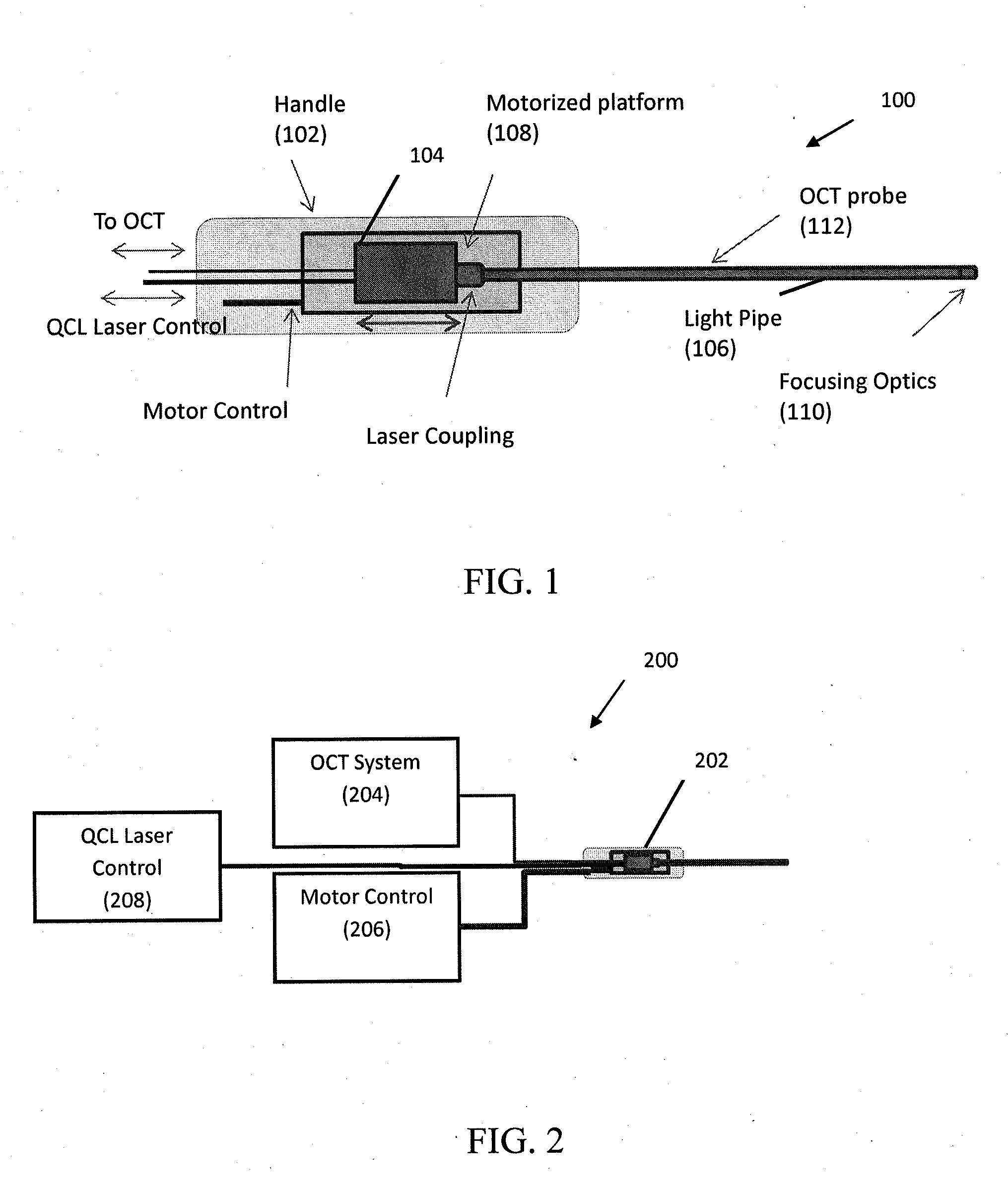
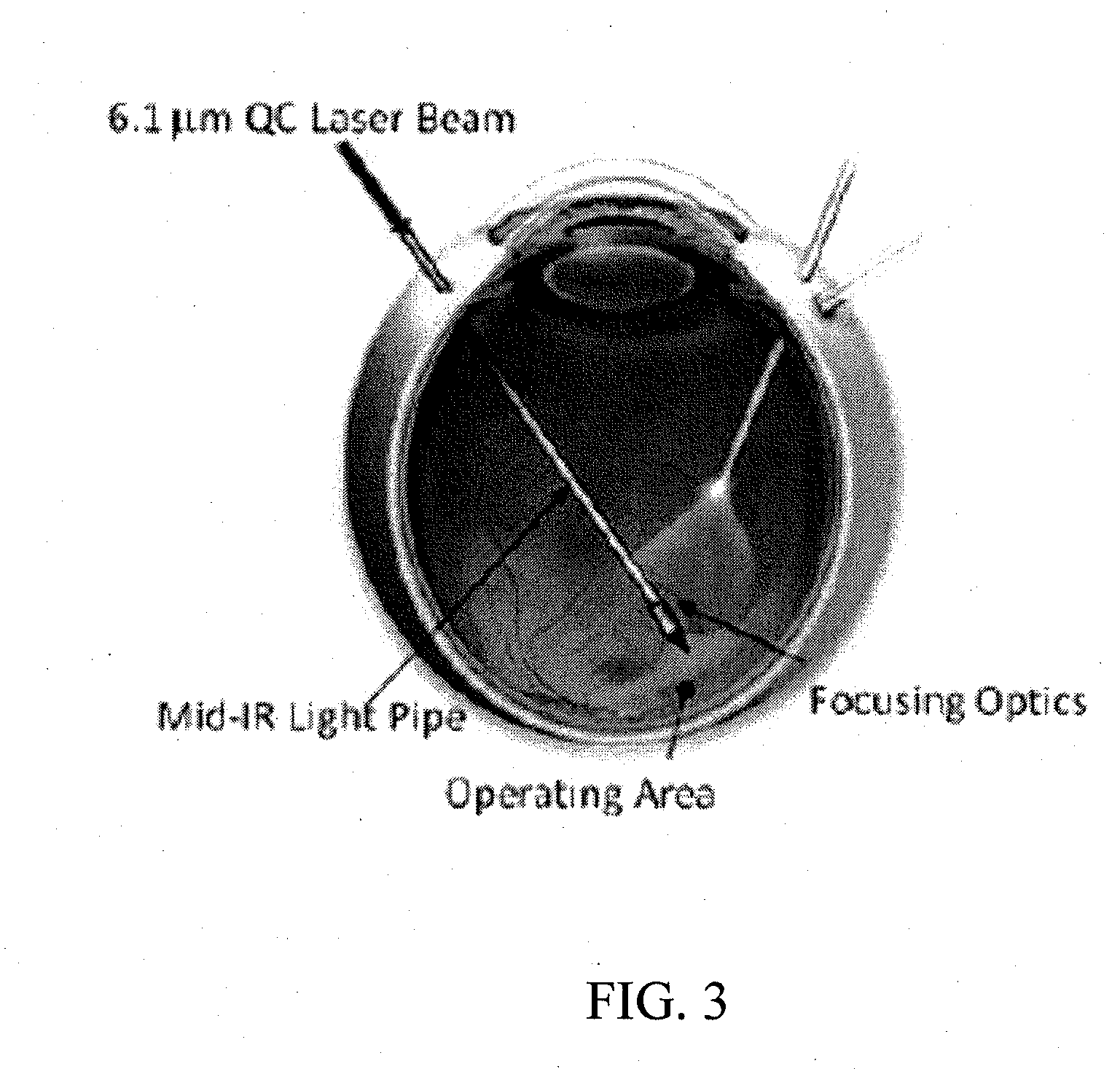
Mid-infrared laser therapy device and system
A mid-infrared laser therapy tool includes a handle, a mid-infrared laser contained within the handle, and a light pipe optically coupled to the mid-infrared laser. The mid-infrared laser emits at a wavelength within a wavelength band from about 6.0 μm to about 6.5 μm. A mid-infrared laser therapy system includes a mid-infrared laser therapy tool, an optical coherence tomography system adapted to communicate with the mid-infrared laser therapy tool, and a motorized-platform control system adapted to communicate with the mid-infrared laser therapy tool and the optical coherence tomography system. The mid-infrared laser therapy tool comprises a mid-infrared laser emits at a wavelength within a wavelength band from about 6.0 μm to about 6.5 μm.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Forest fire early warning system based on intermediate infrared laser
InactiveCN103956022AEffective Early Fire PreventionGuaranteed flexibilityClimate change adaptationFire alarm radiation actuationSquare kilometerMid infrared laser
The invention discloses a forest fire remote early detection warning system based on an intermediate infrared laser. The forest fire remote early detection warning system comprises a intermediate infrared laser radar device, a signal processing and wireless transmitting module, a monitoring system and a monitoring and dispatching center. The forest fire remote early detection warning system has the advantages that the intermediate infrared laser is adopted as a laser radar light source, safe, low-loss, remote and high-precision detection is achieved, the effective detection range reaches the radius being 6 km, effective early fire prevention is carried out on forest coverage within 100 square kilometers, remote control, intelligentization, flexibility and the like of forest fire detection are ensured, and fire early warning is improved to the maximum extent; due to the intermediate infrared laser capable of generating three wavelengths at the same time, accuracy and precision of fire detection are improved, and reliability is high.
Owner:苏州镭创光电技术有限公司
Intermediate infrared laser
InactiveCN102570268AImprove conversion efficiencyWavelength adjustmentLaser detailsAcousto-opticsMid infrared laser
The invention discloses an intermediate infrared laser. The intermediate infrared laser is characterized in that: a semiconductor laser with the wavelength of 790nm is used for pumping a thulium doped lithium yttrium fluoride (Tm:YLF) crystal to obtain 1.9 mu m laser; and 1.9 mu m pulsed laser is generated in an acousto-optical Q-switching way. Two quartz etalons unplated with a dielectric film are arranged in a Tm:YLF laser, so that the spectrum width of the output 1.9 mu m laser is decreased to less than 1nm, and the output laser is stabilized at the central wavelength of 1,907.5nm, and can be prevented from being absorbed by water molecules in the atmosphere; and the laser is used as a pump source for pumping a magnesium oxide (MgO) doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO:PPLN) crystal, and stable intermediate infrared laser output with the wavelengths of 3 to 5 mu m is obtained in an optical parametric oscillation way. The intermediate infrared laser has the characteristics of simple structure, high conversion efficiency, high tunability and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wavelength-adjustable efficient high-power mid-infrared laser
ActiveCN106911060AImprove conversion efficiencyHigh peak powerActive medium shape and constructionMid infrared laserPulsed laser
The invention discloses a wavelength-adjustable efficient high-power mid-infrared laser, which belongs to the technical field of lasers. According to the wavelength-adjustable mid-infrared laser, the conversion efficiency of a band-adjustable mid-infrared laser is improved. The wavelength-adjustable efficient high-power mid-infrared laser comprises a resonant cavity, a cascade amplification system, a collimating focusing system and an OPO, wherein the resonant cavity uses a ring-shaped full polarization-maintaining mixed dissipation resonant soliton lock mode to produce thalcium-doped fiber laser. A pumping source generates laser through a two-way pumping thulium-doped gain optical fiber. The laser oscillates back and forth in the resonant cavity and outputs nanosecond square wave pulse laser through an output coupler. The nanosecond square wave pulse laser is coupled into the OPO through the cascade amplification system and the collimating focusing system in order. Under the effect of the pulse laser and an OPO crystal, nanosecond pulse mid-infrared fiber laser is finally output through a filter and a dichroic mirror. The invention provides the mid-infrared laser.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Mid-infrared luminescent chalcohalide glass and preparation technology thereof
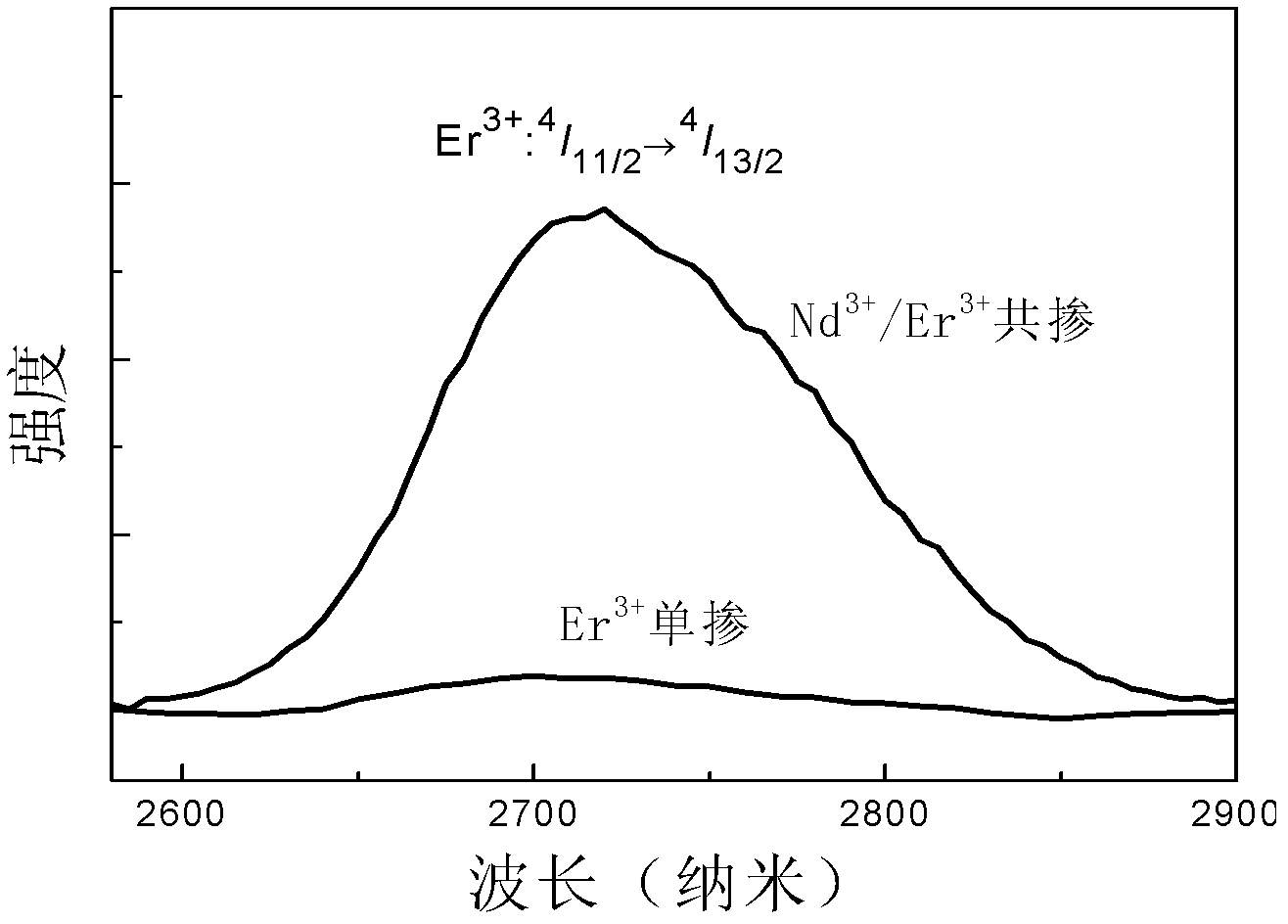
The invention discloses a 2.7 mu m mid-infrared luminescent chalcohalide glass and a preparation technology thereof. The glass is prepared by using a melt quenching method and comprises the following components expressed in mole percent: 50 to 70 mol% of GeS2, 15 to 35 mol% of Ga2S3, 5 to 15 mol% of CsCl, 0.1 to 0.5 mol% of Er2S3 and 0 to 0.15 mol% of Nd2S3 (wherein the total content of all the components is 100 mol%). Since the mid-infrared luminescent chalcohalide glass has extraordinary infrared transmittance and good thermal and mechanical performances, the mid-infrared luminescent chalcohalide glass is expected to be applied in fabrication of 2.7 mu m mid-infrared lasers.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Epitaxial structure of GaSb group infrared laser having electron barrier layer
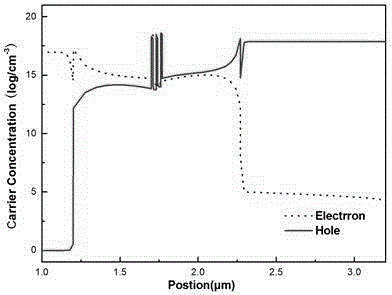
InactiveCN105281201AInhibition of Auger complexReduce crystal defectsLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersConduction bandMid infrared
The present invention provides an epitaxial structure of a GaSb group infrared laser having an electron barrier layer, and relates to the field of the semiconductor laser epitaxial technology. The epitaxial structure provided by the invention comprises a GaSb substrate, a buffer layer, a n-type limitation layer, a n-type ducting layer, an active region, a p-type ducting layer, an electron barrier layer and p-type limitation layer. The electron barrier layer is arranged between the p-type ducting layer and the p-type limitation layer, and the conduction band potential of the electron barrier layer is higher than the conduction band potential of the p-type limitation layer. Compared with the prior art, the epitaxial structure of a GaSb group infrared laser having an electron barrier layer may reduce the Auger recombination in a quantum well, restrain the overflow of the conduction band electrons in the quantum well to the p-type limitation layer, and effectively improve the performance of the GaSb group infrared semiconductor laser.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
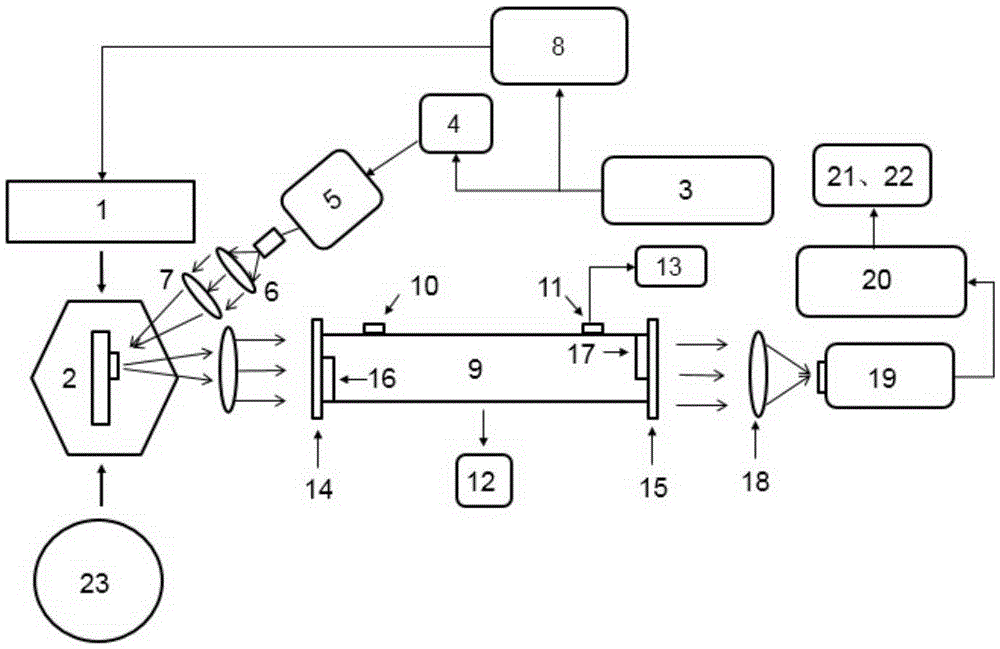
Quantum cascade laser-based high-speed infrared frequency modulation laser spectrum gas detection system and method
ActiveCN105424650AFast spectral scanHigh-speed frequency modulation implementationColor/spectral properties measurementsFrequency modulation spectroscopyMid infrared
The invention relates to a quantum cascade laser-based high-speed infrared frequency modulation laser spectrum gas detection system and method. The system comprises a quantum cascade laser spectrum scanning module, a high-speed frequency modulation module, a synchronization module, a gas multi-returning cavity and a frequency modulation spectrum acquisition module. On the basis of a conventional gas detection system, a distributed feedback quantum cascade laser is used, and a mid-infrared laser is utilized to generate intensity-modulated modulated light for irradiating and pulsating an emergent end face of the quantum cascade laser, thus realizing all-optical modulation on the quantum cascade laser; control and quantitative detection on a gas sample are completed by the gas multi-returning cavity; an all-optical modulation gas absorption spectrum is collected by a high-speed mid-infrared detector, a high-speed lock-in amplifier, a high-speed signal collection card and a computer, thus realizing high-speed high-accuracy gas detection. The high-speed infrared frequency modulation laser spectrum gas detection system can be applied to a high-sensitivity infrared laser spectrum technology and trace gas detection.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com