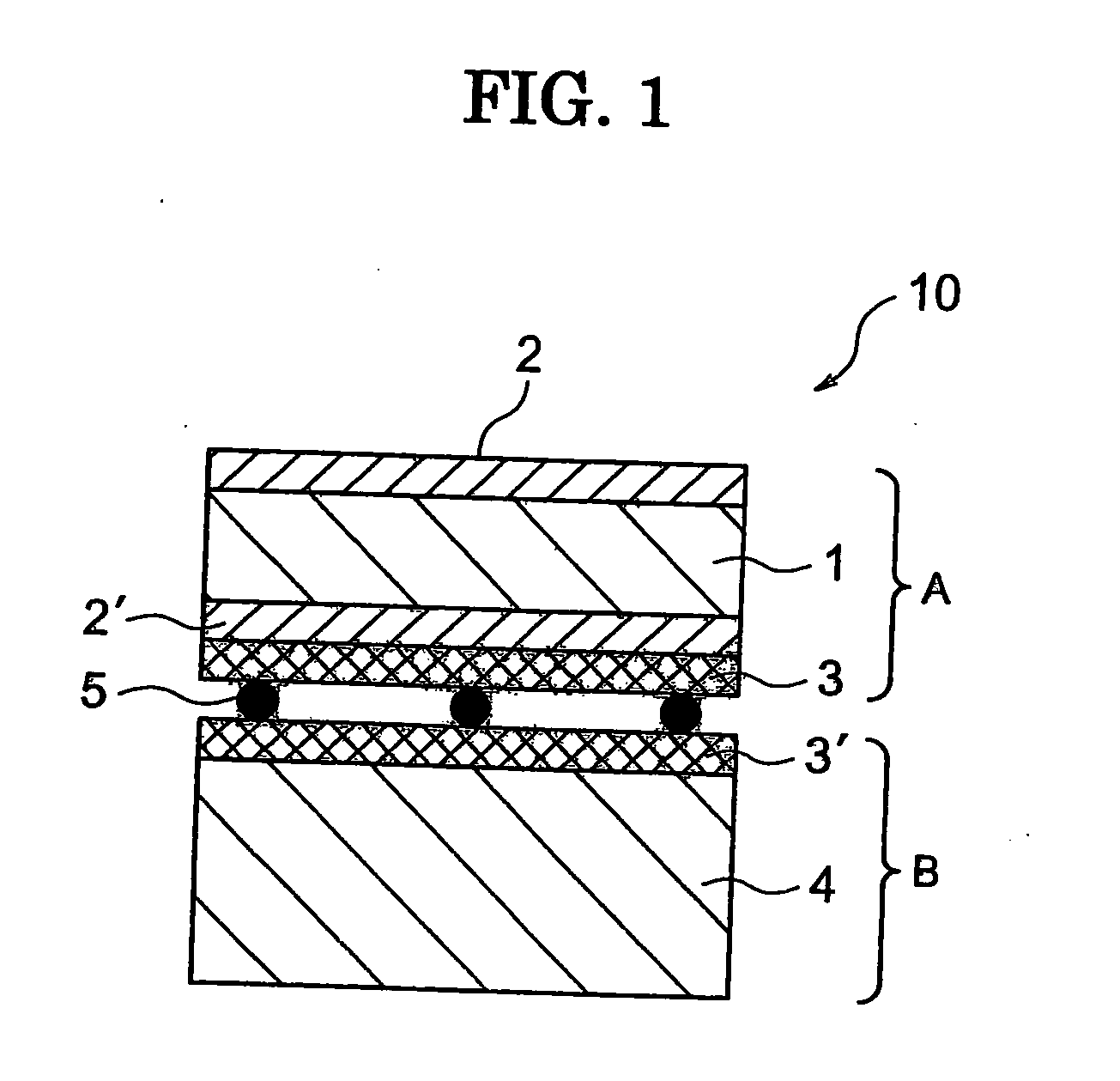
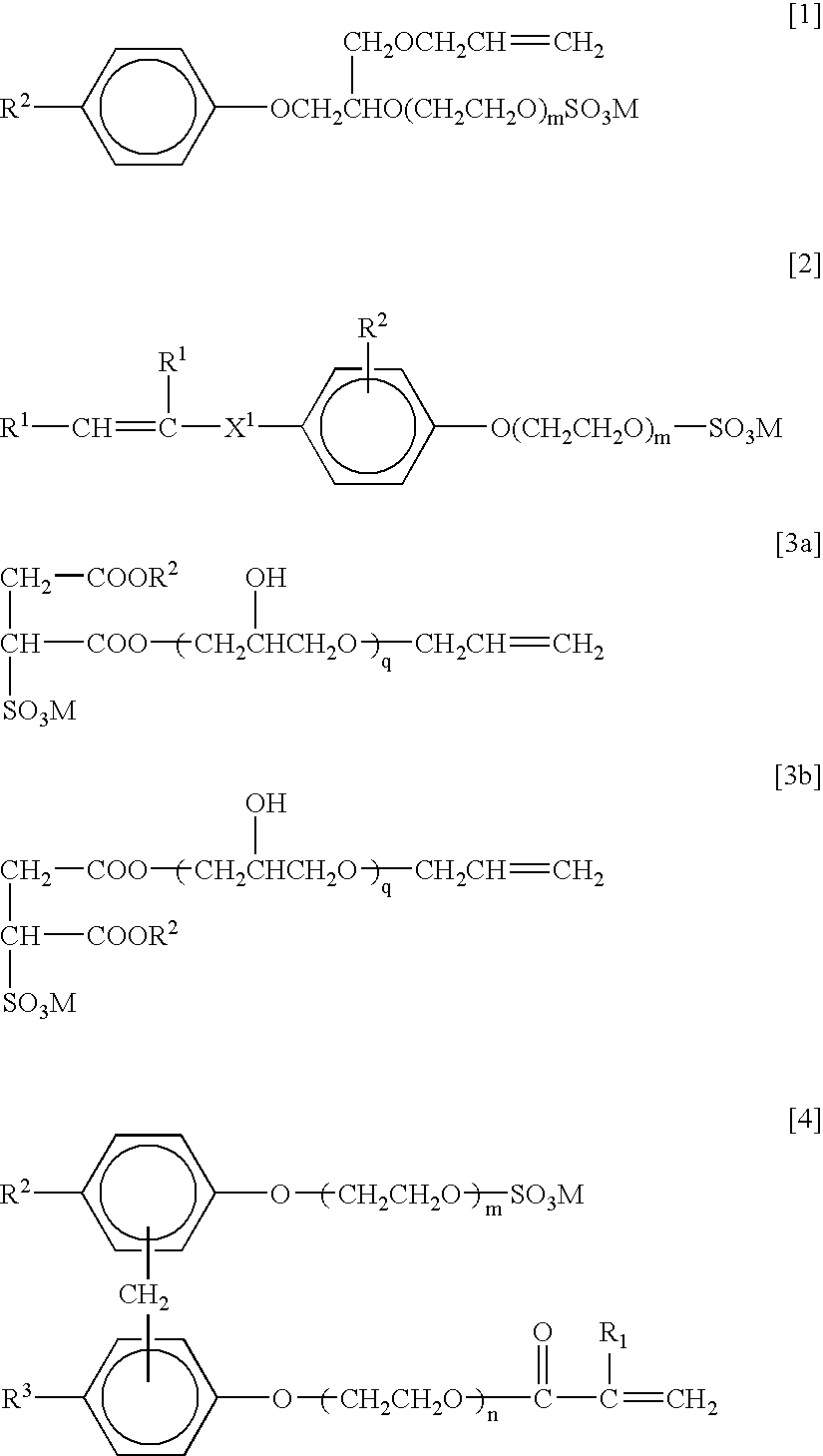
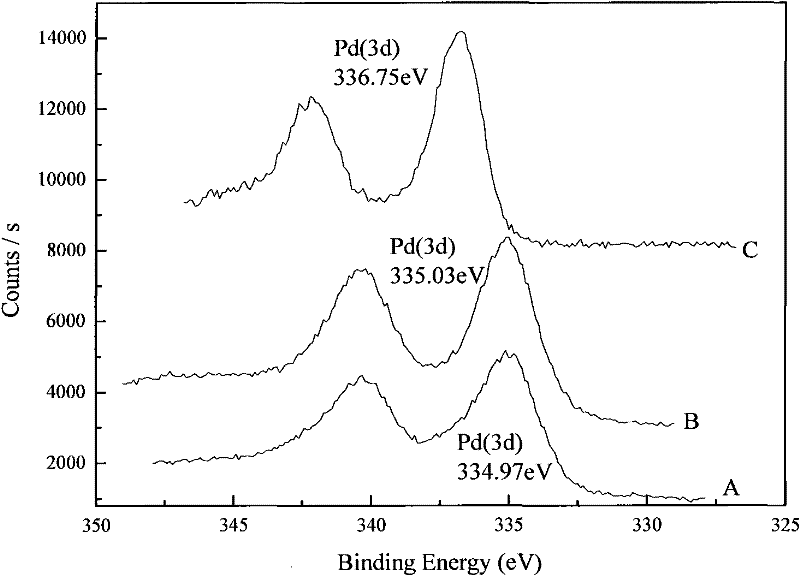
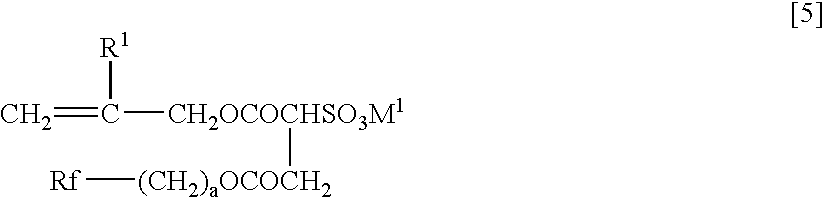Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
567 results about "Ionized radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
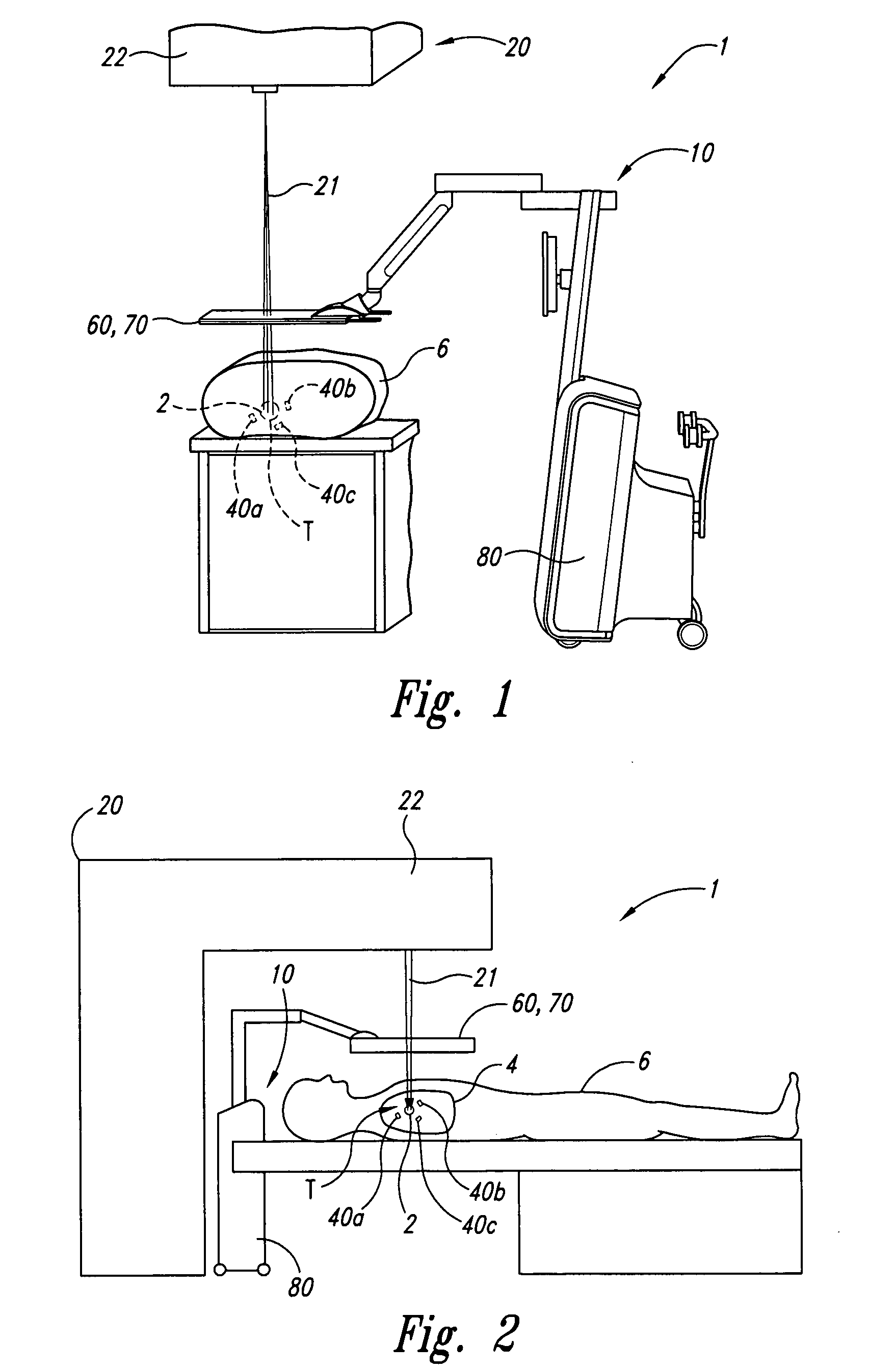
Ionizing radiation is a form of energy that acts by removing electrons from atoms and molecules of materials that include air, water, and living tissue. Ionizing radiation can travel unseen and pass through these materials. It is on the right side of the electromagnetic spectrum in the figure below.
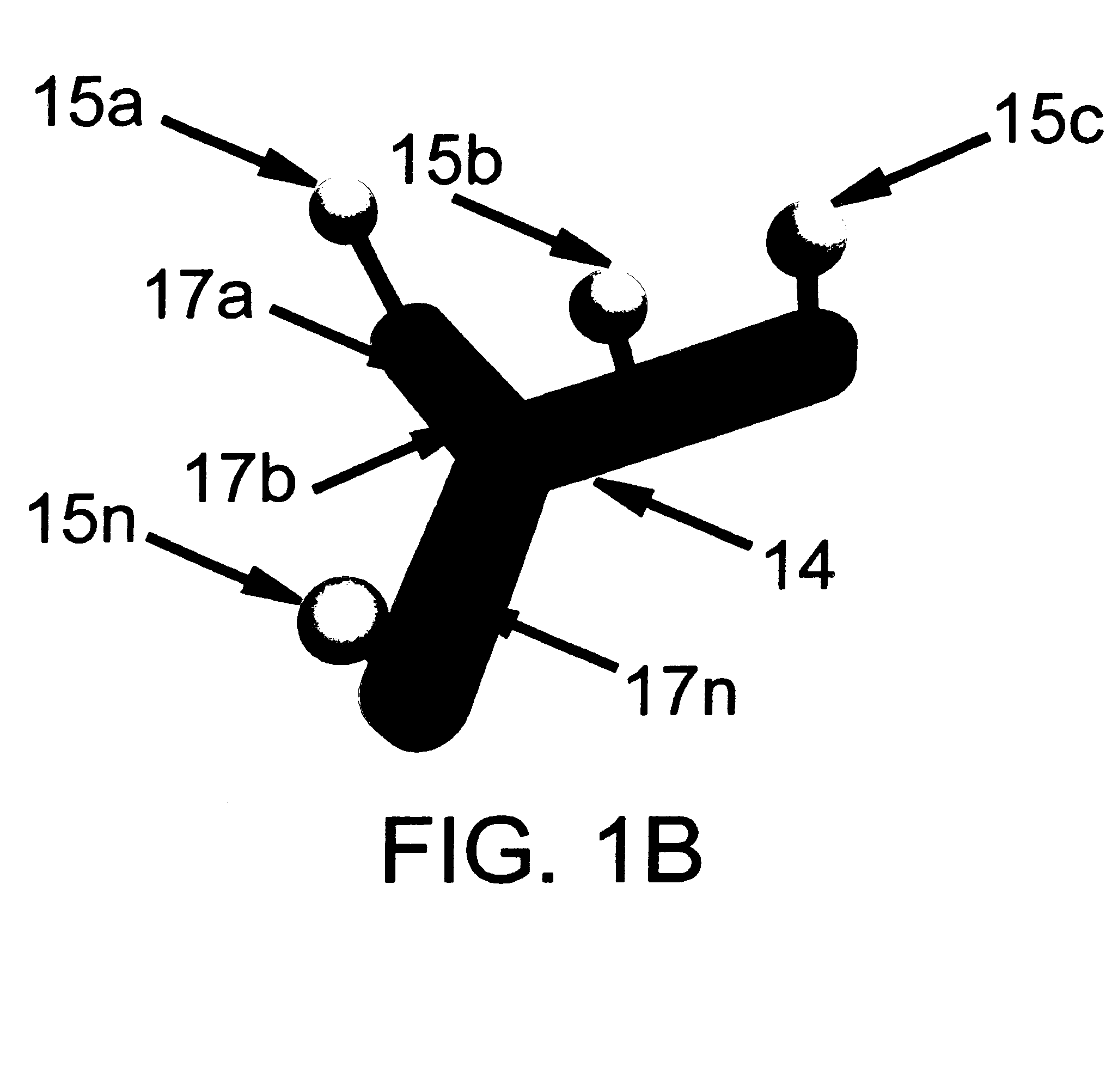
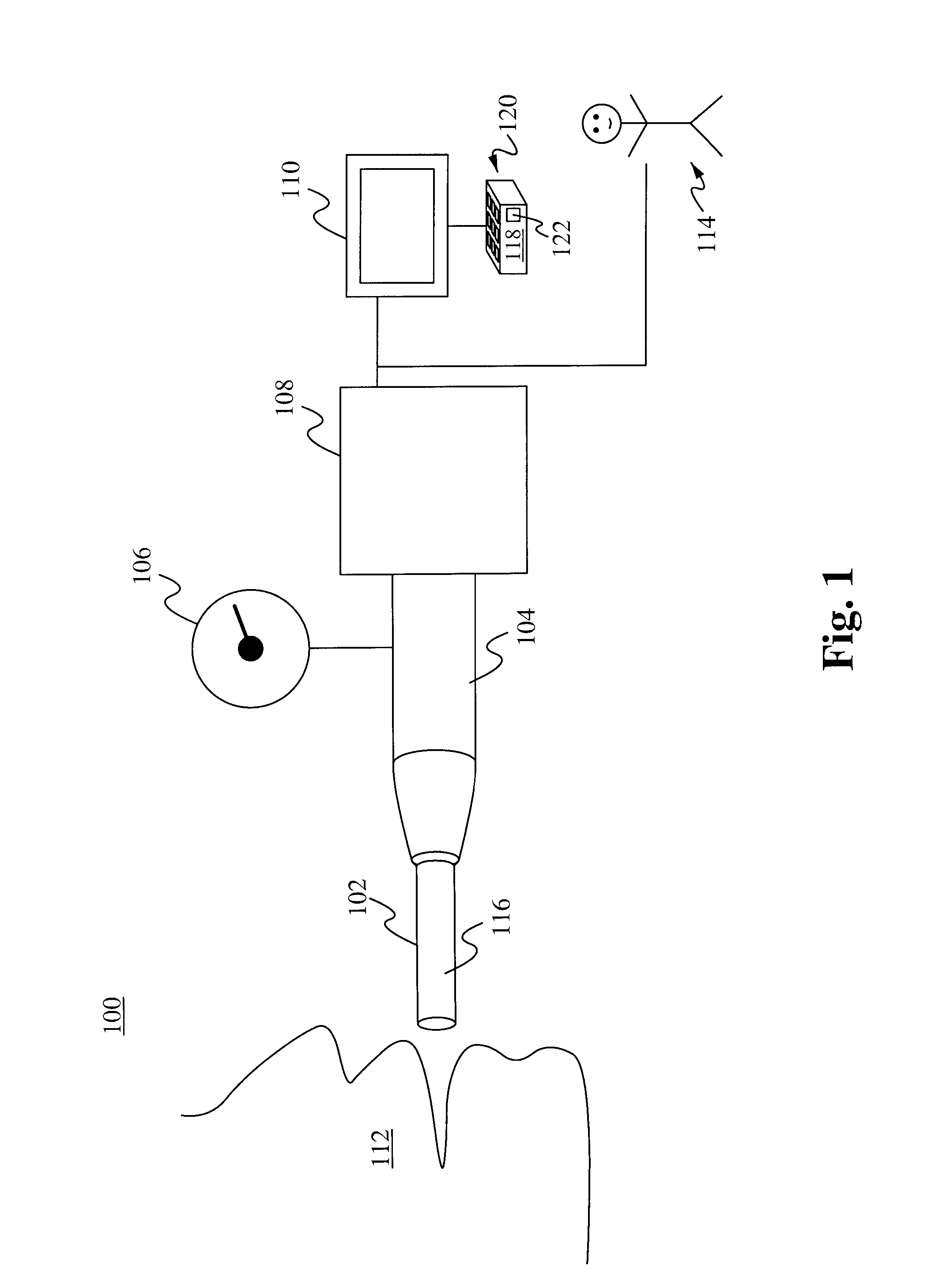
Intraoperative, intravascular, and endoscopic tumor and lesion detection, biopsy and therapy
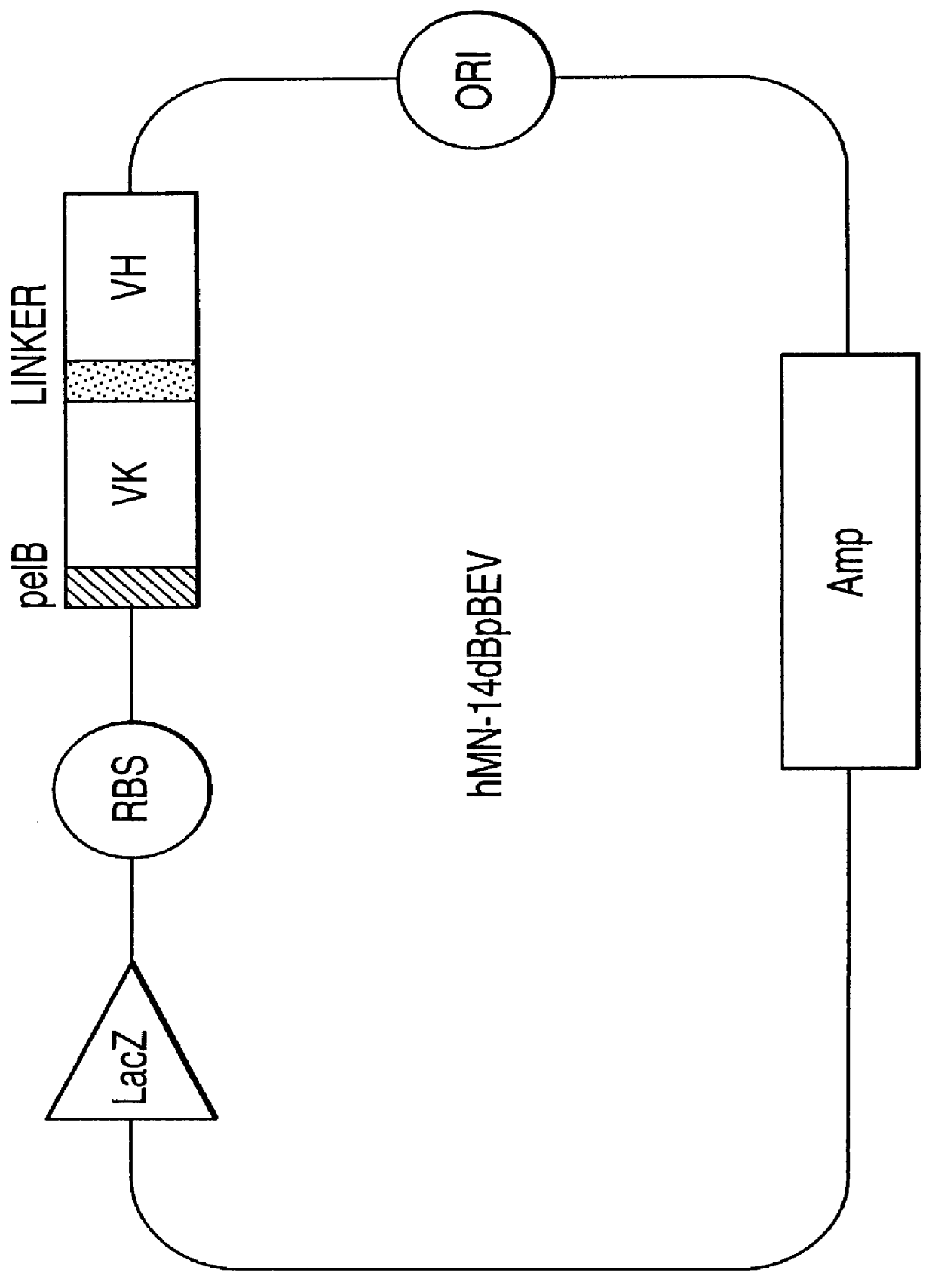
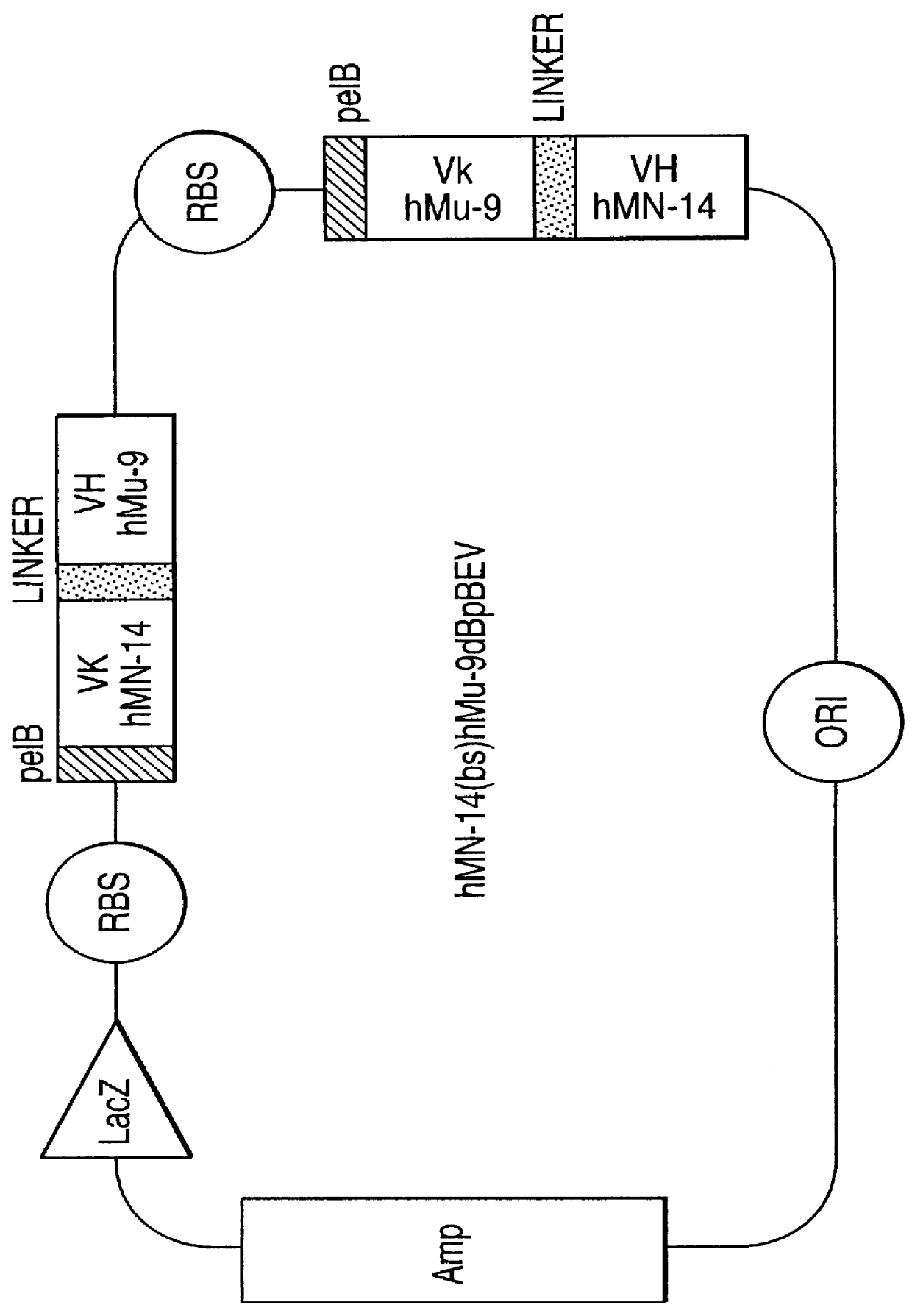
InactiveUS6096289ADiscriminationImprove discriminationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryNon malignantAntibody fragments
Methods are provided for close-range intraoperative, endoscopic and intravascular deflection and treatment of lesions, including tumors and non-malignant lesions. The methods use antibody fragments or subfragments labeled with isotopic and non-isotopic agents. Also provided are methods for detection and treatment of lesions with photodynamic agents and methods of treating lesions with a protein conjugated to an agent capable of being activated to emit Auger electron or other ionizing radiation. Compositions and kits useful in the above methods are also provided.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
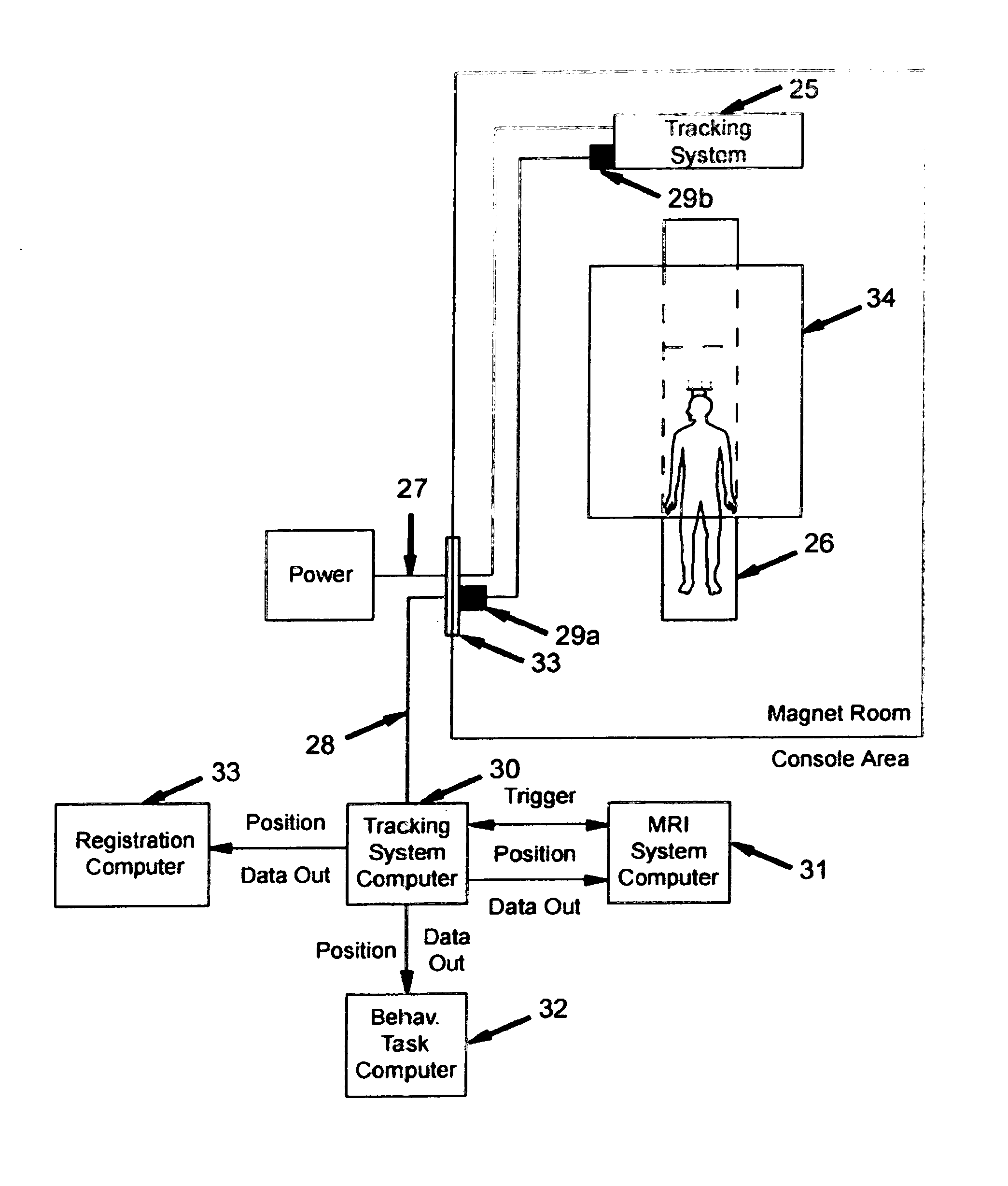
Optical image-based position tracking for magnetic resonance imaging applications
InactiveUS20050054910A1Improve data qualityImprove stress conditionImage analysisMagnetic measurementsThermal energyIonizing radiation
An optical image-based tracking system determines the position and orientation of objects such as biological materials or medical devices within or on the surface of a human body undergoing Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Three-dimensional coordinates of the object to be tracked are obtained initially using a plurality of MR-compatible cameras. A calibration procedure converts the motion information obtained with the optical tracking system coordinates into coordinates of an MR system. A motion information file is acquired for each MRI scan, and each file is then converted into coordinates of the MRI system using a registration transformation. Each converted motion information file can be used to realign, correct, or otherwise augment its corresponding single MR image or a time series of such MR images. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of an interventional treatment system, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal energy, microwaves, laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and like instruments. In other embodiments, the invention is also useful for conventional clinical MRI events, functional MRI studies, and registration of image data acquired using multiple modalities.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK & WOMENS COLLEGE HEALTH SCI CENT
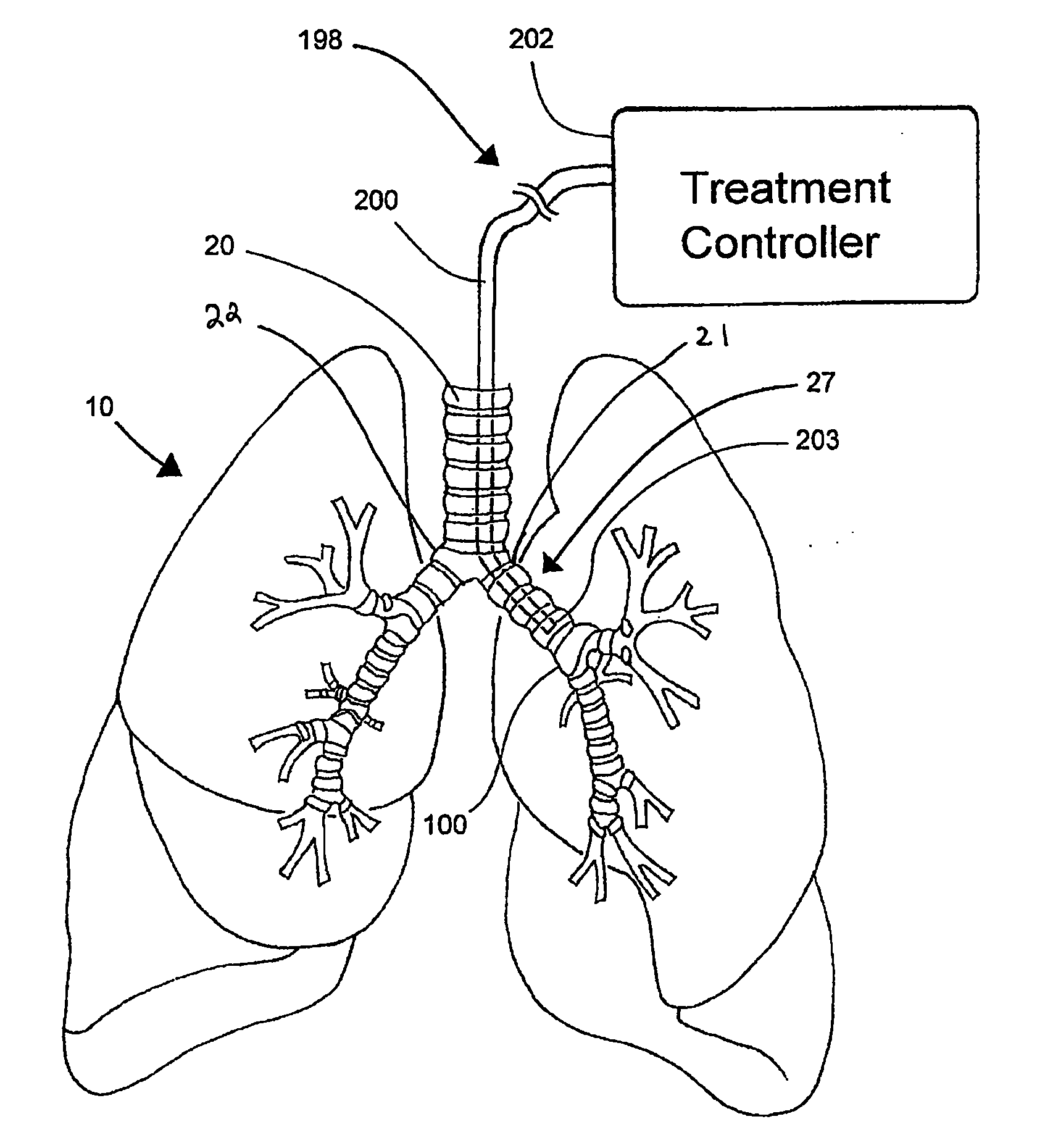
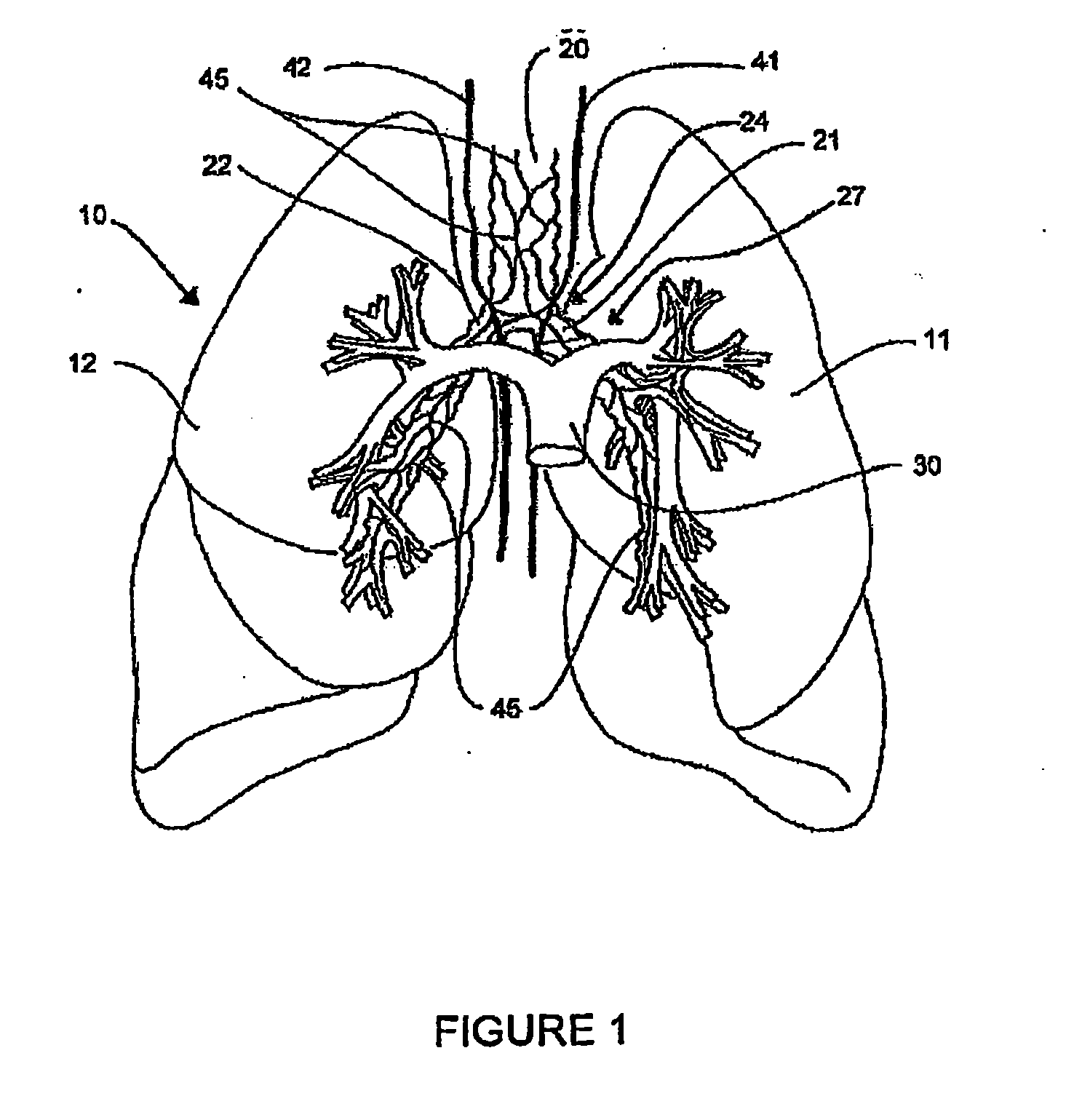
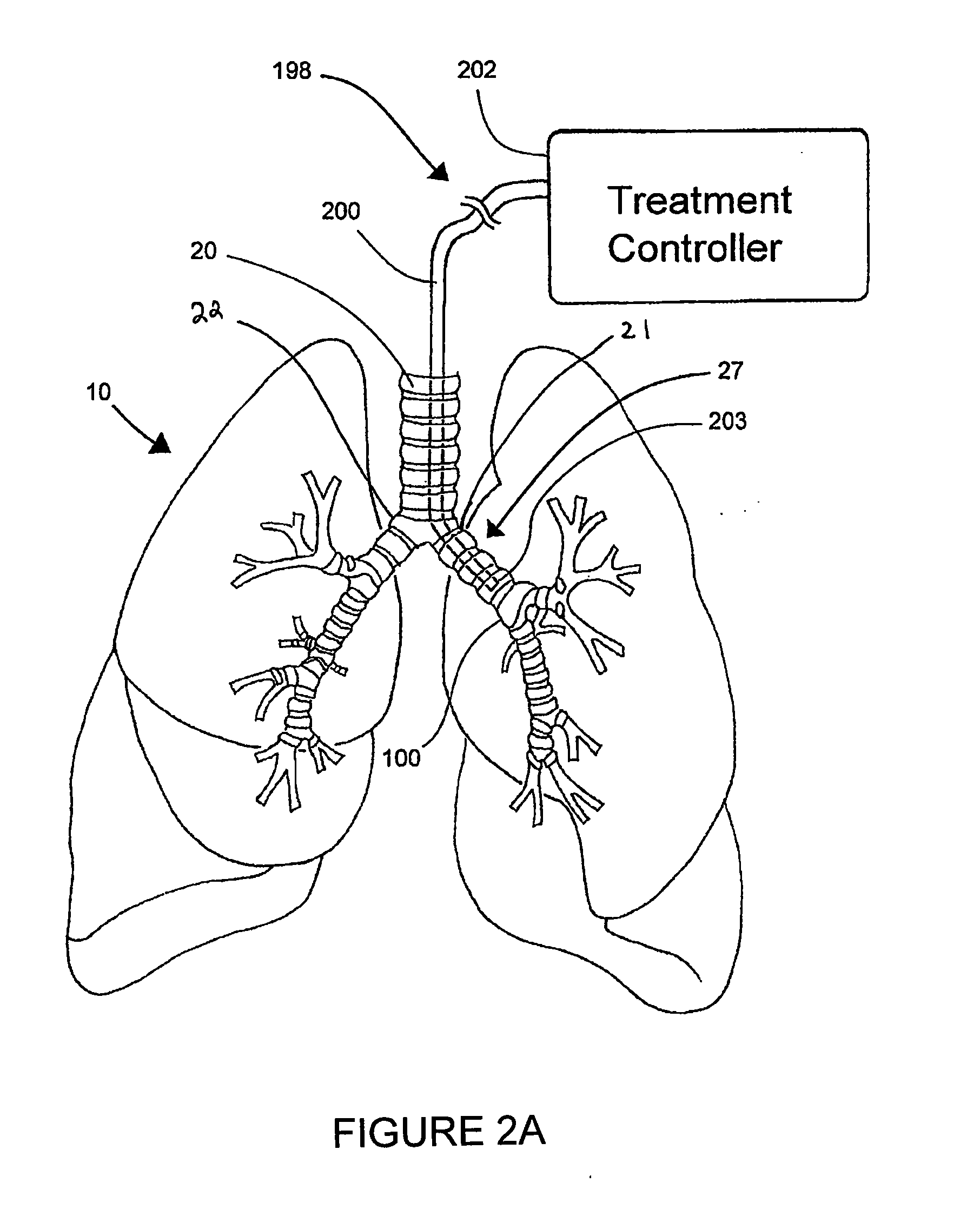
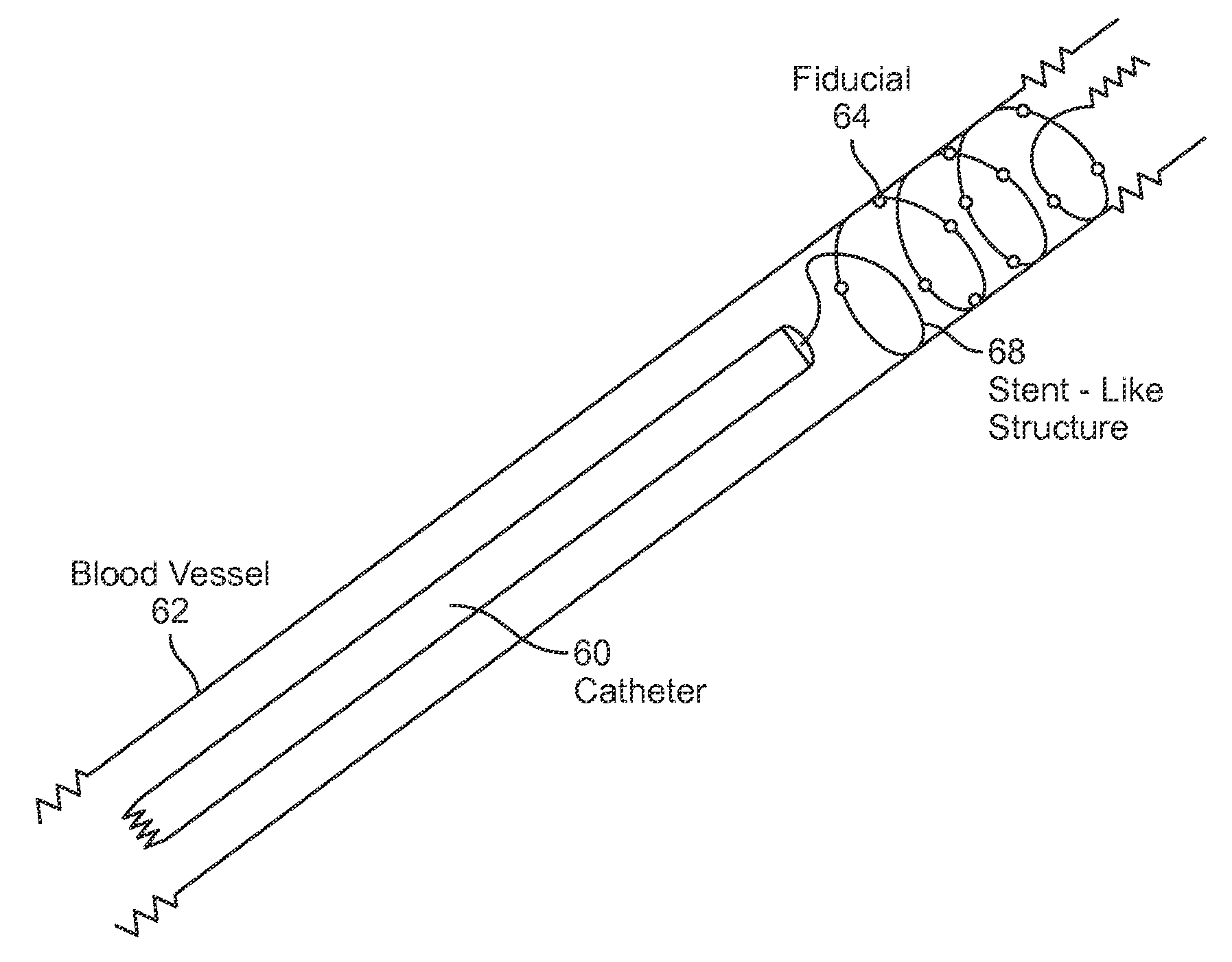
Systems, assemblies, and methods for treating a bronchial tree
ActiveUS20090306644A1Improve the immunityWithout eliminating smooth muscle toneUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsNervous systemCell membrane
Systems, assemblies, and methods to treat pulmonary diseases are used to decrease nervous system input to distal regions of the bronchial tree within the lungs. Treatment systems damage nerve tissue to temporarily or permanently decrease nervous system input. The treatment systems are capable of heating nerve tissue, cooling the nerve tissue, delivering a flowable substance that cause trauma to the nerve tissue, puncturing the nerve tissue, tearing the nerve tissue, cutting the nerve tissue, applying pressure to the nerve tissue, applying ultrasound to the nerve tissue, applying ionizing radiation to the nerve tissue, disrupting cell membranes of nerve tissue with electrical energy, or delivering long acting nerve blocking chemicals to the nerve tissue.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
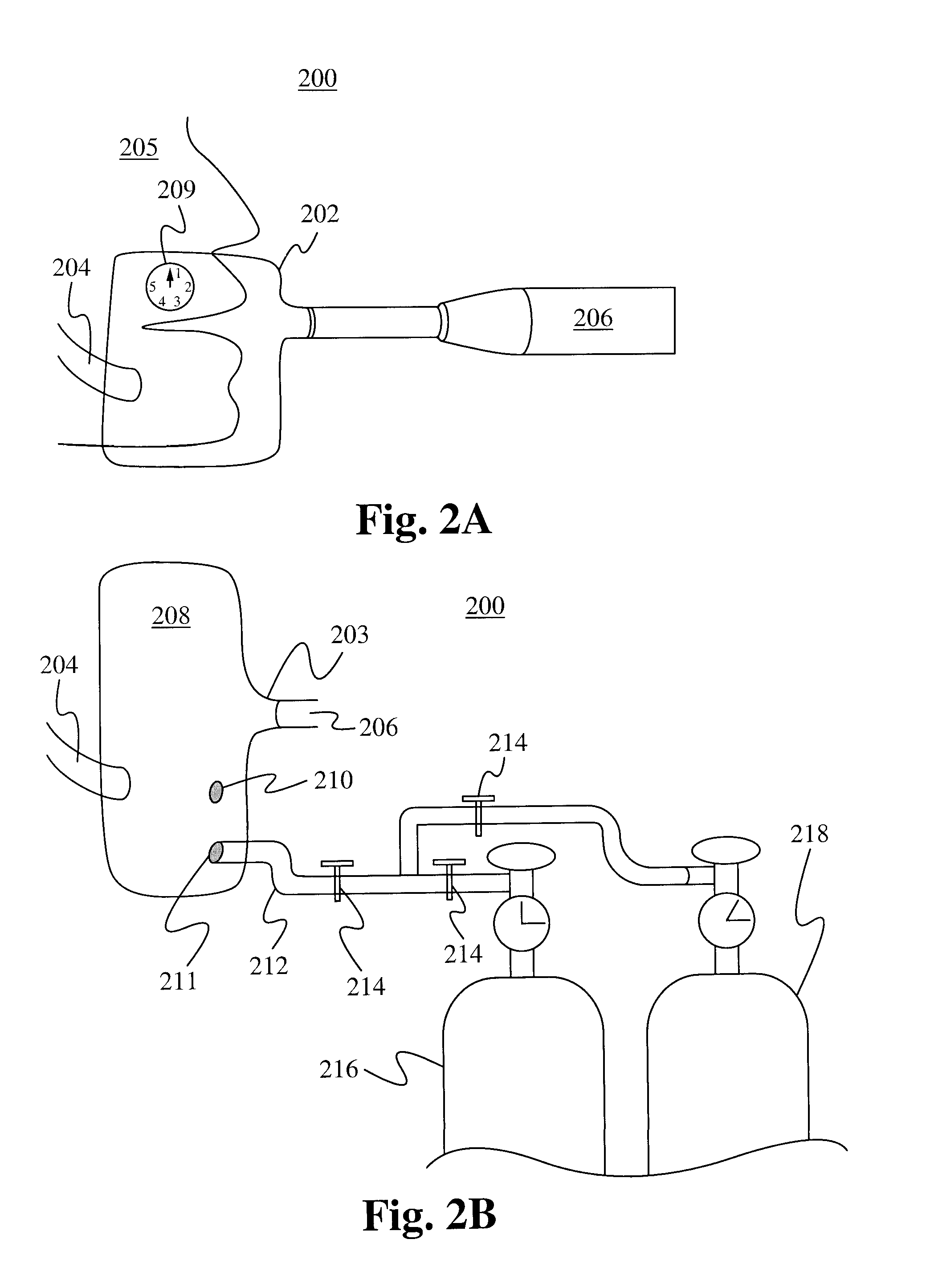
Apparatus and method for treatment of malignant tumors
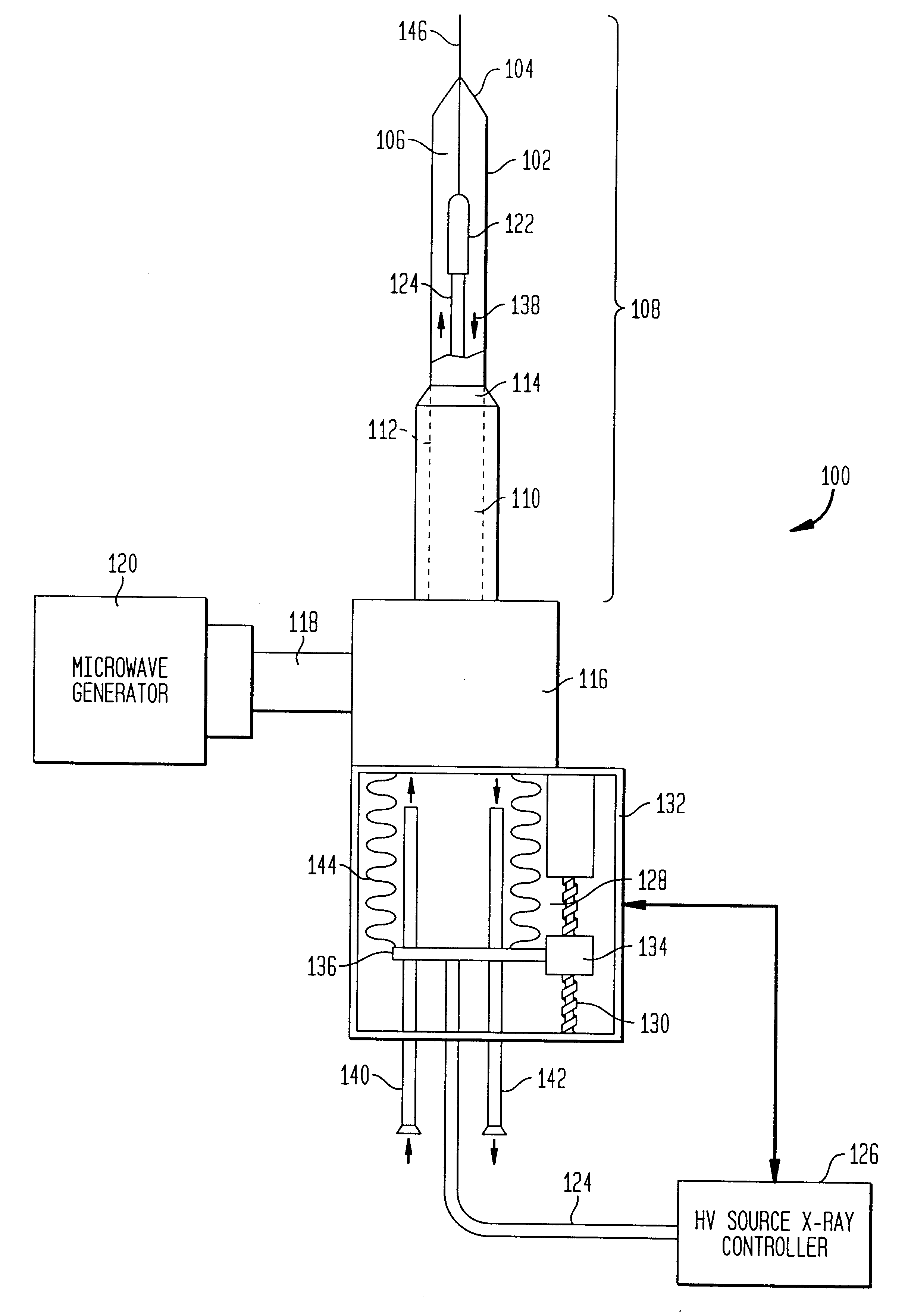
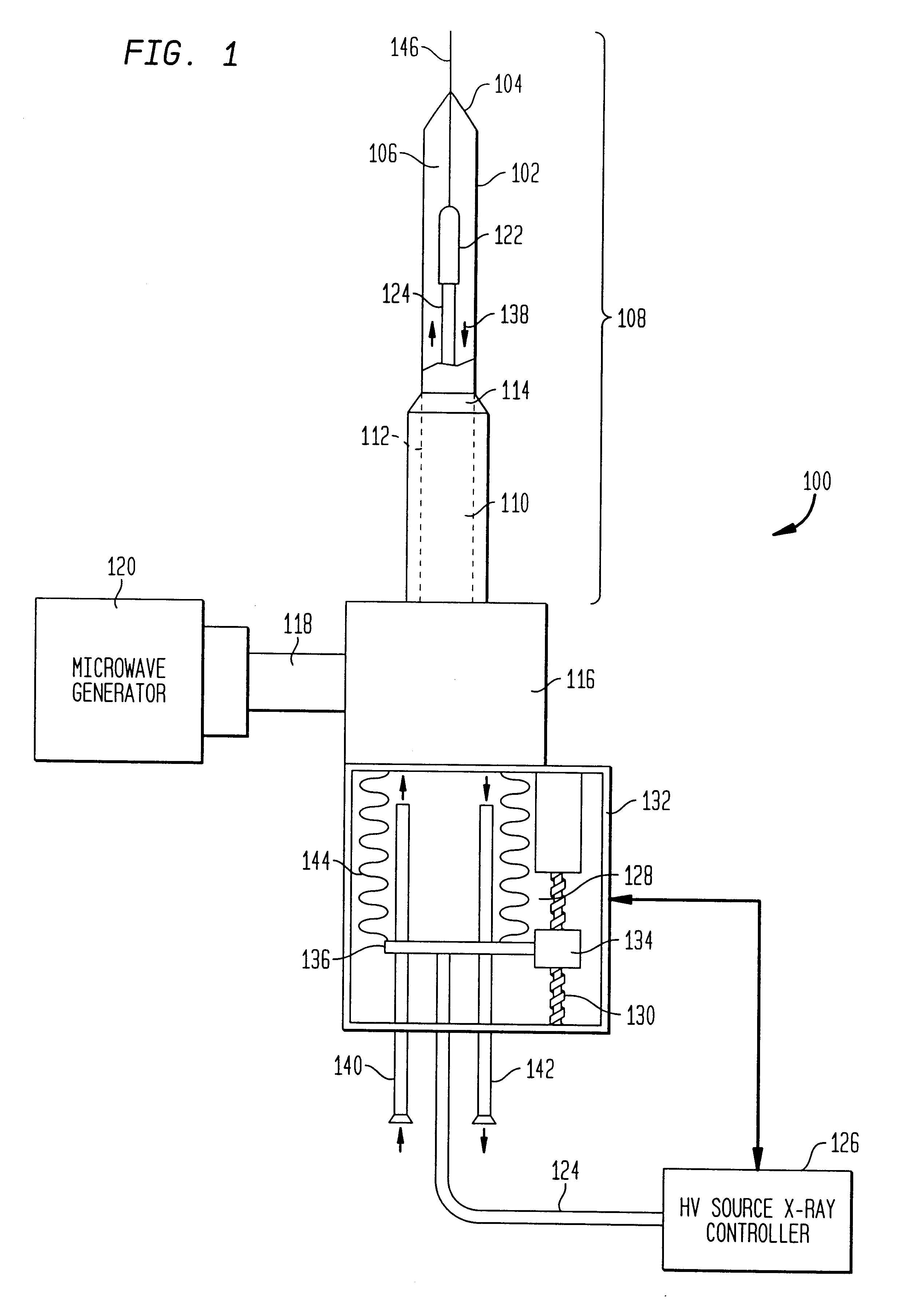
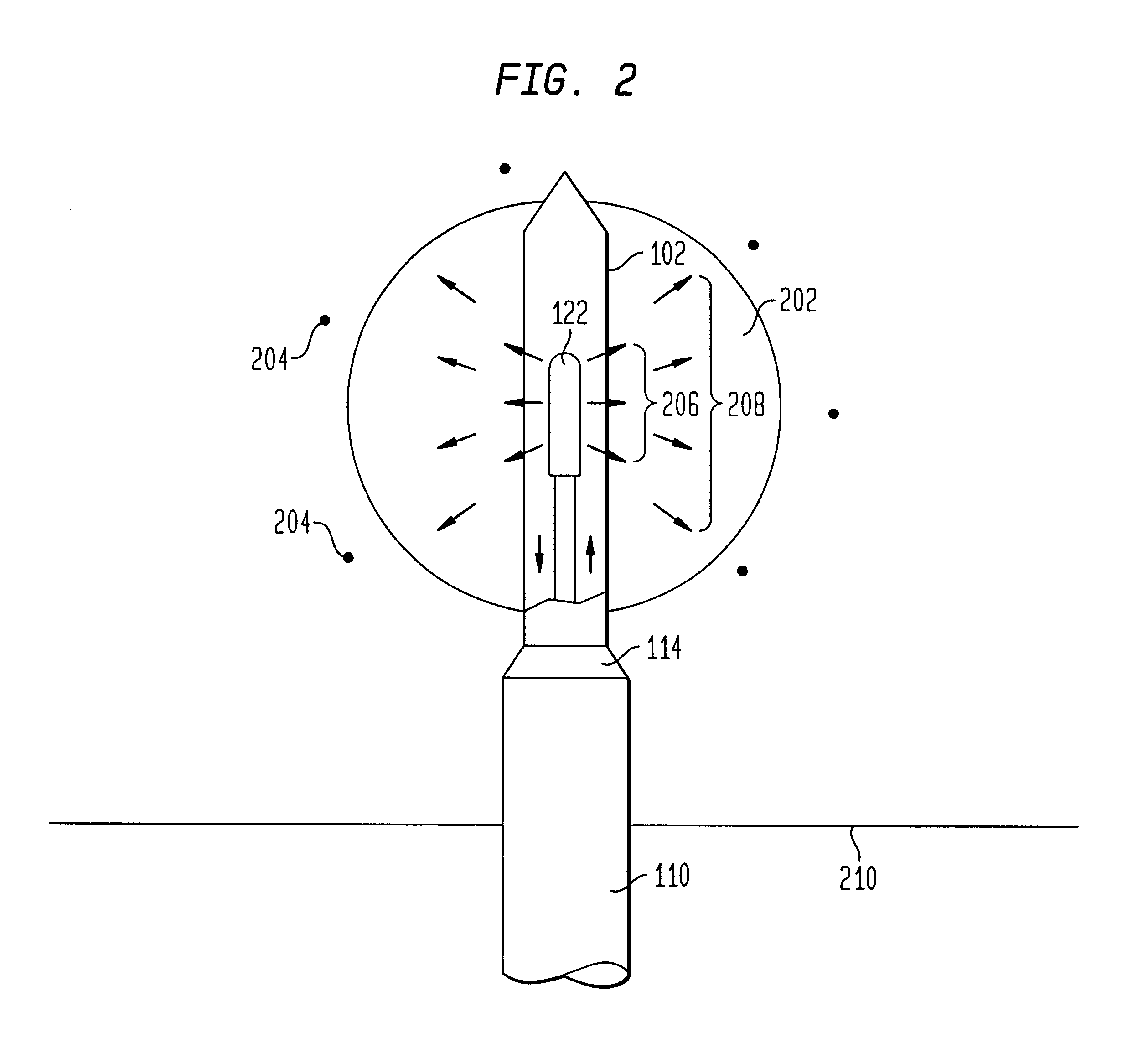
InactiveUS6866624B2Increase powerIncrease temperatureElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyAbnormal tissue growthBrachytherapy
The present invention relates to a device for simultaneously treating a tumor or cancerous growth with both hyperthermia and X-ray radiation using brachytherapy. The device includes a needle-like introducer serving as a microwave antenna. Microwaves are emitted from the introducer to increase the temperature of cancerous body tissue. The introducer is an inner conductor of a coaxial cable. The introducer contains a hollow core which houses an X-ray emitter. The X-ray emitter is connected to a high voltage miniature cable which extends from the X-ray emitter to a high voltage power source. The X-ray emitter emits ionizing radiation to irradiate cancerous tissue. A cooling system is included to control the temperature of the introducer. Temperature sensors placed around the periphery of the tumor monitor the temperature of the treated tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
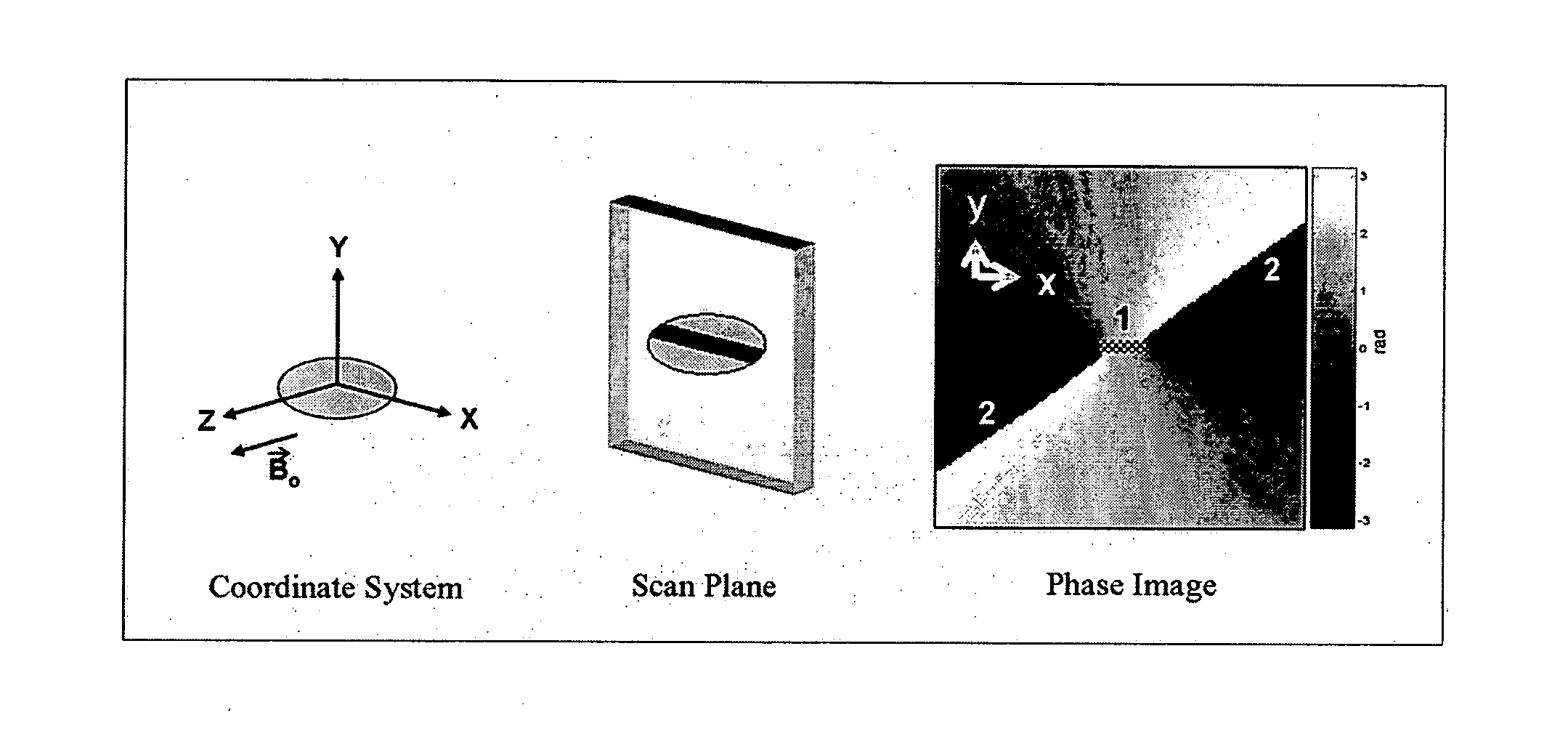
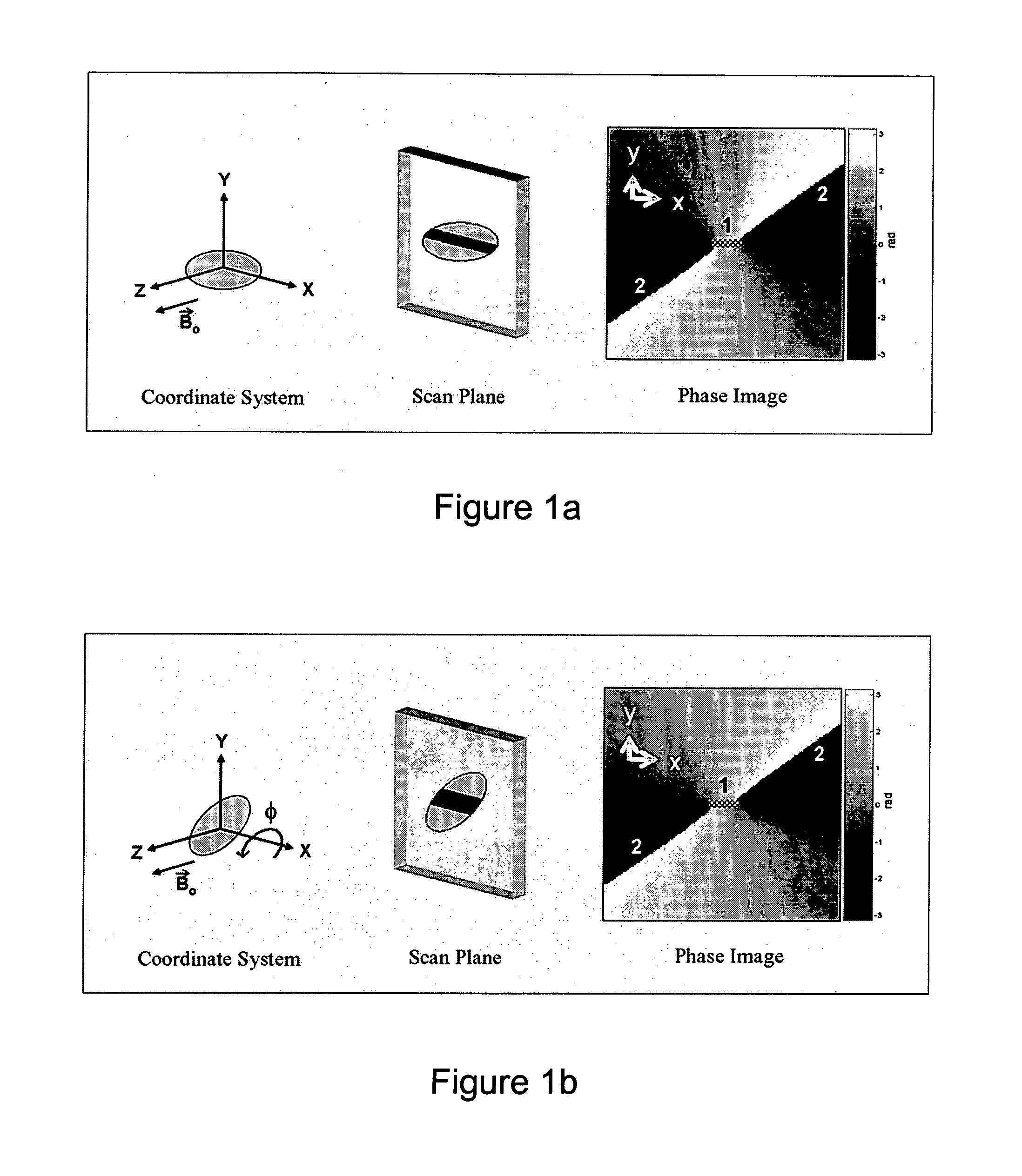
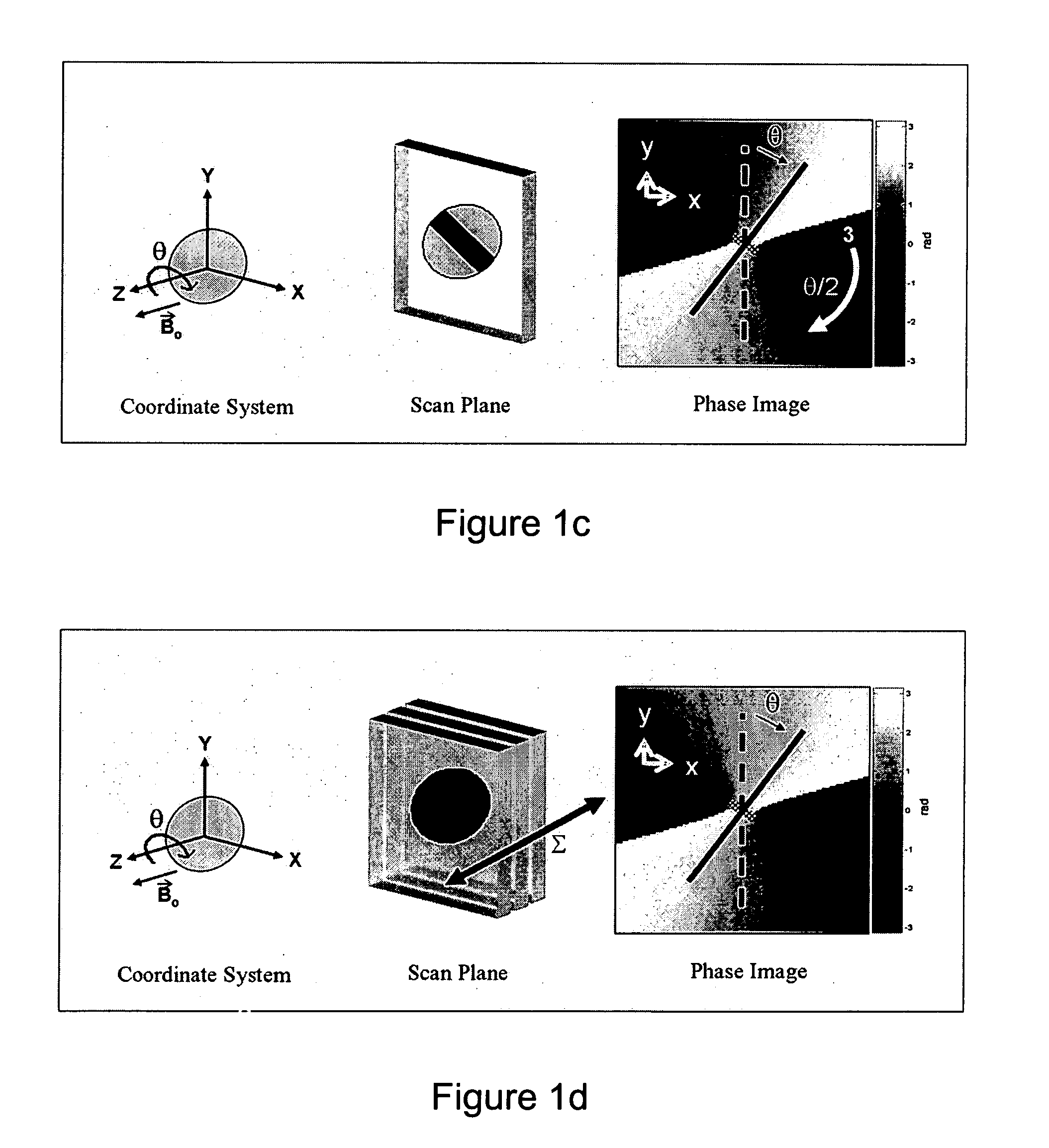
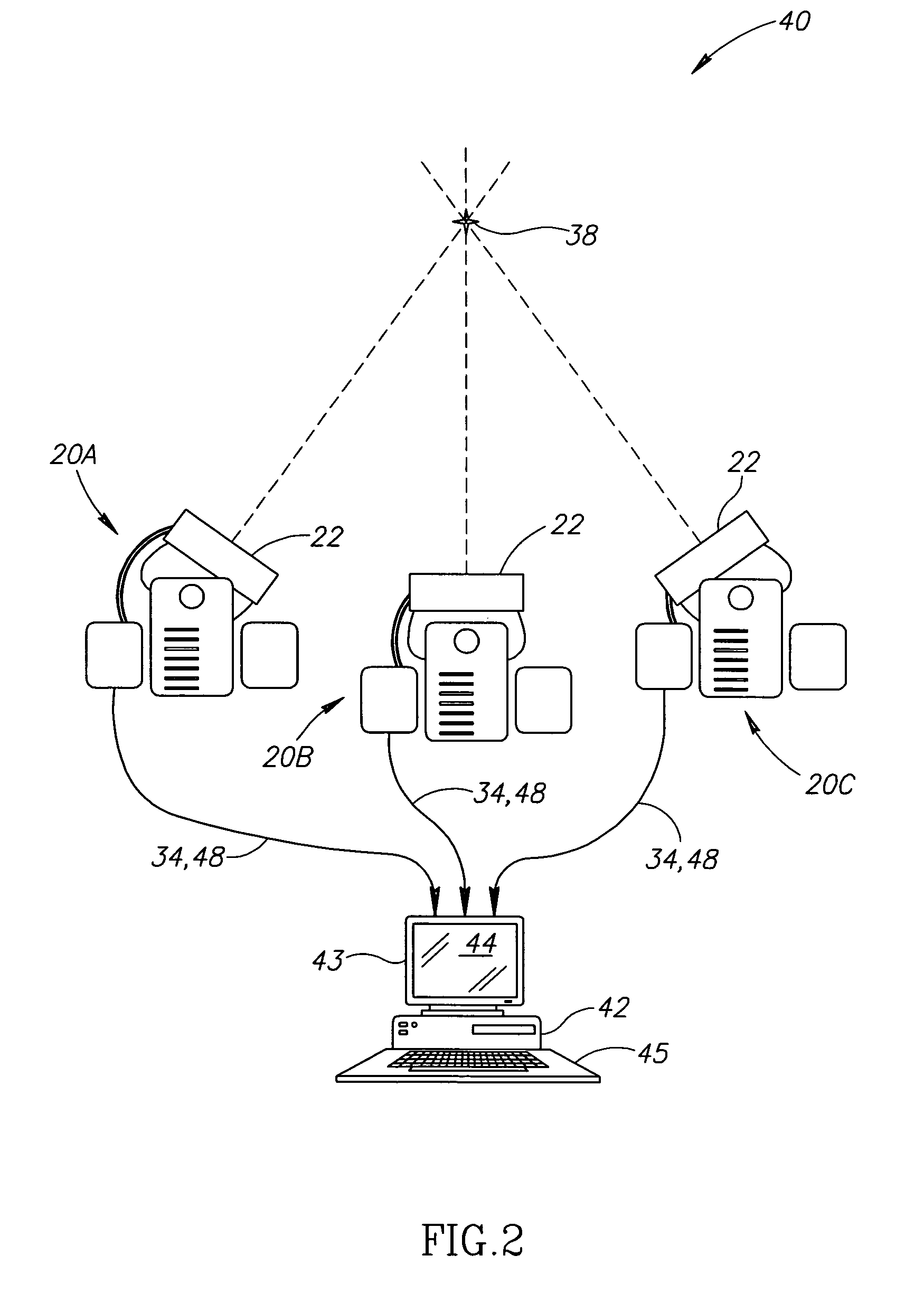
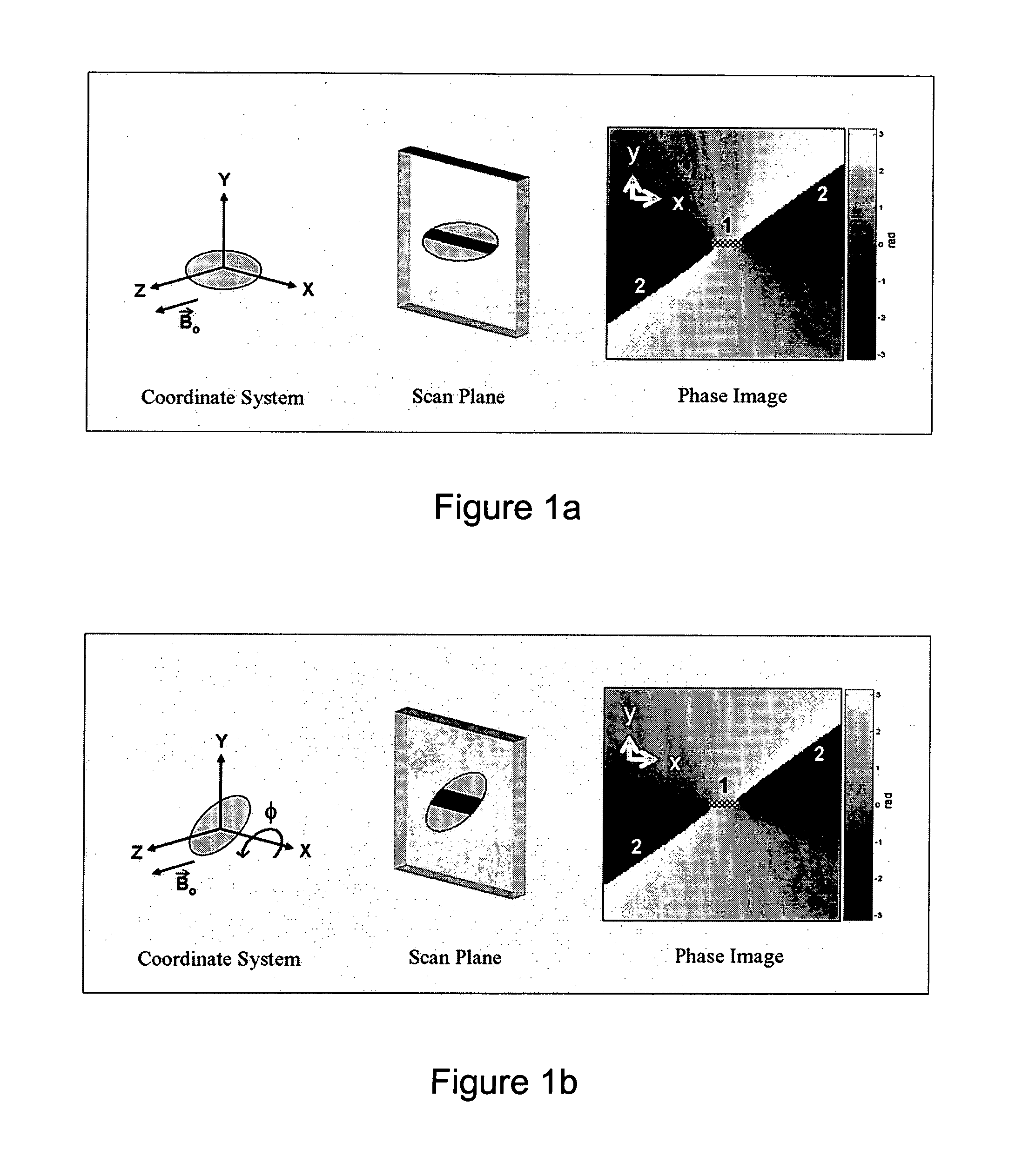
Catheter tracking with phase information
ActiveUS20050245814A1Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesBiopsy
The present invention discloses a method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern and orientation of individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, tracking of interventional devices is performed by one integrated phase image projected onto the axial plane and a second image in an oblique plane through the center of the coil and normal to the coil plane. In another preferred embodiment, the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular access devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
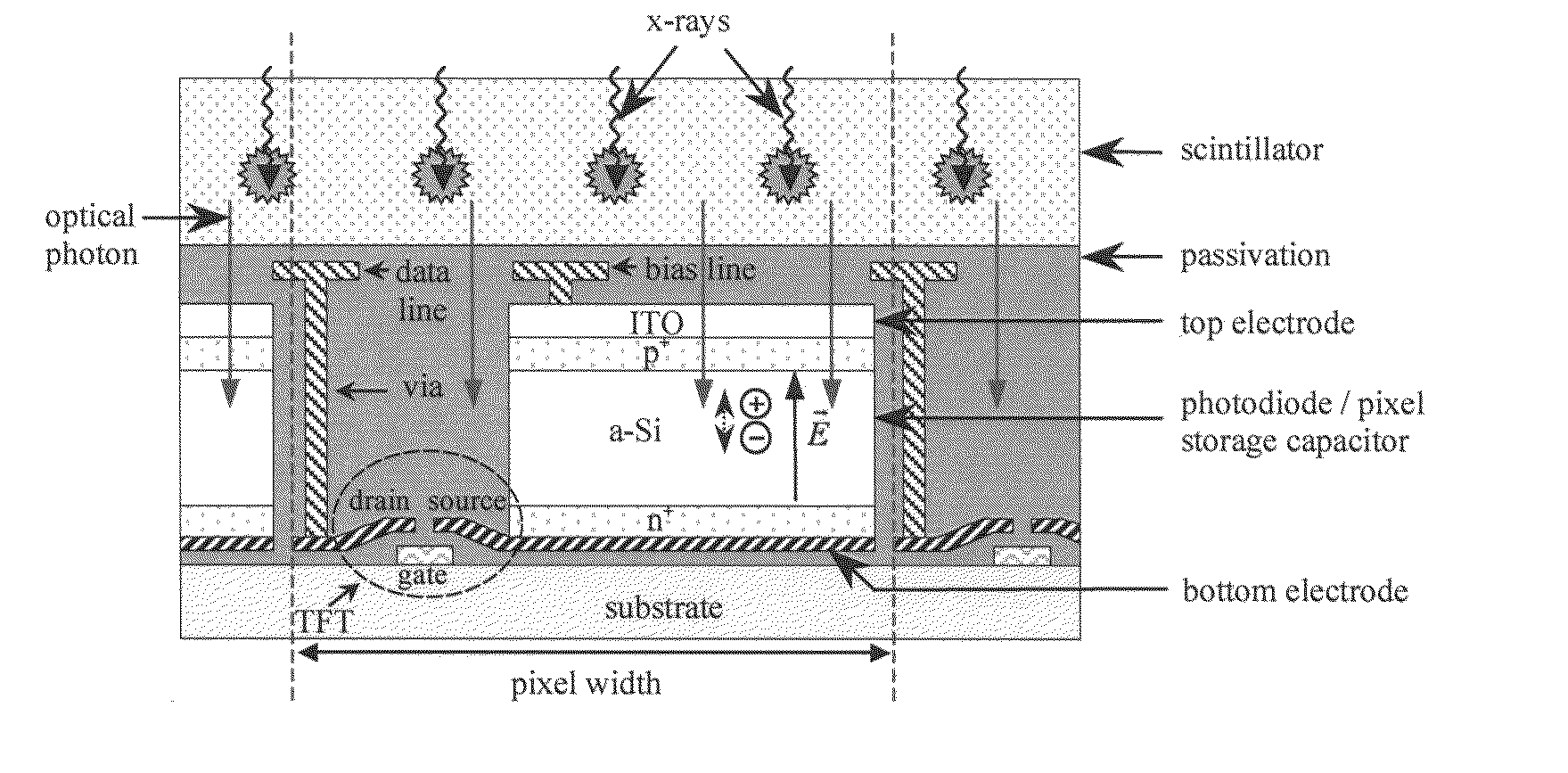
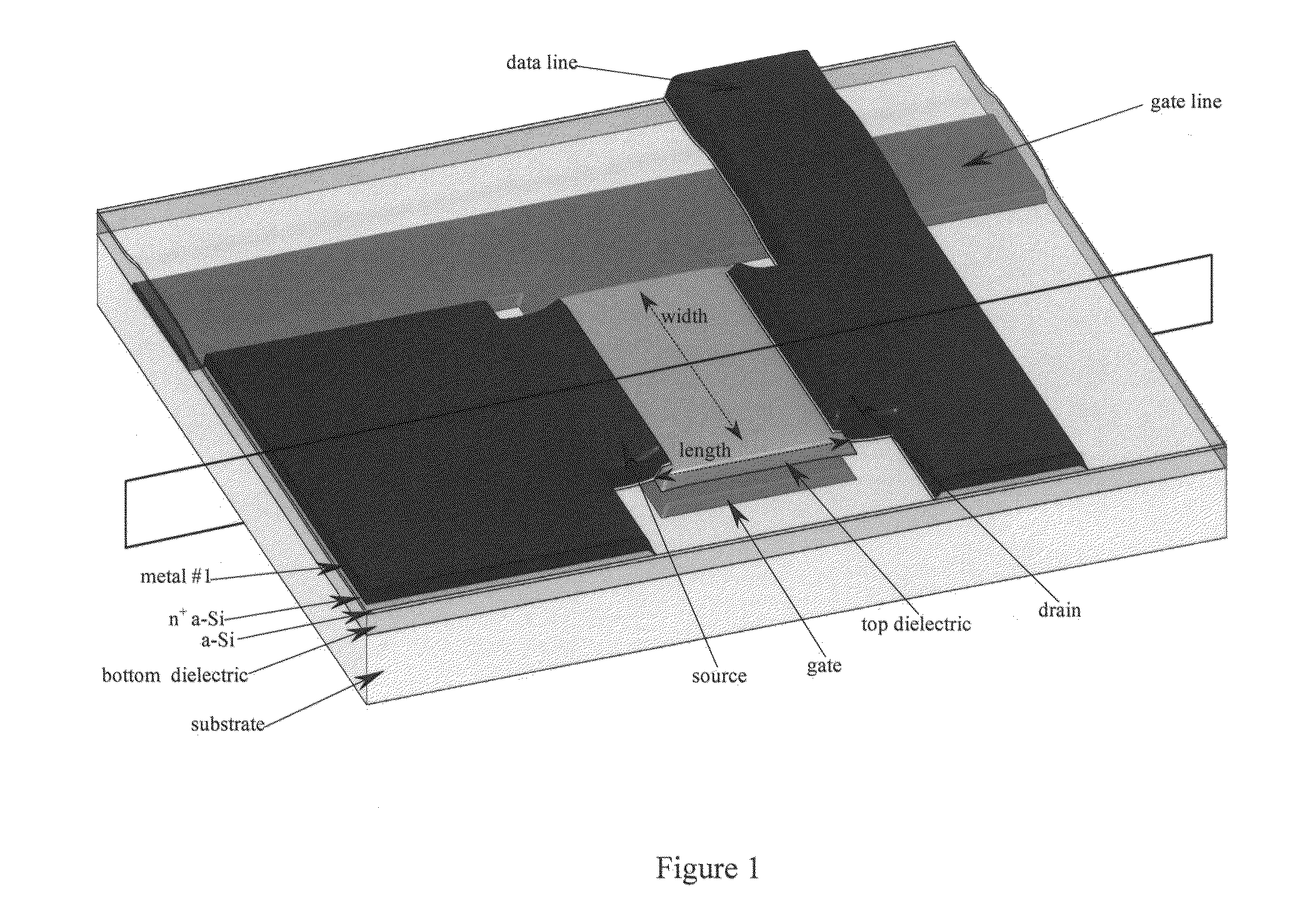
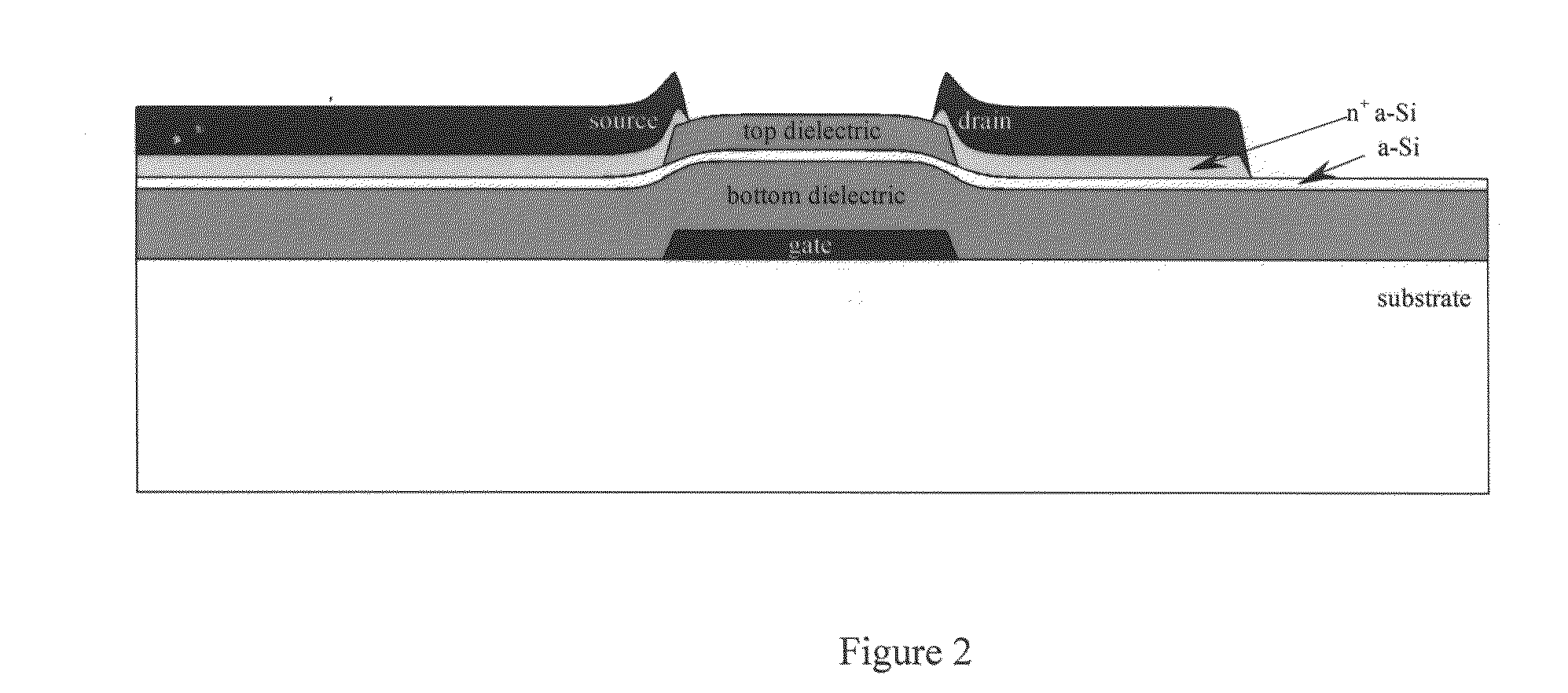
Photodiode and other sensor structures in flat-panel x-ray imagers and method for improving topological uniformity of the photodiode and other sensor structures in flat-panel x-ray imagers based on thin-film electronics
A radiation sensor including a scintillation layer configured to emit photons upon interaction with ionizing radiation and a photodetector including in order a first electrode, a photosensitive layer, and a photon-transmissive second electrode disposed in proximity to the scintillation layer. The photosensitive layer is configured to generate electron-hole pairs upon interaction with a part of the photons. The radiation sensor includes pixel circuitry electrically connected to the first electrode and configured to measure an imaging signal indicative of the electron-hole pairs generated in the photosensitive layer and a planarization layer disposed on the pixel circuitry between the first electrode and the pixel circuitry such that the first electrode is above a plane including the pixel circuitry. A surface of at least one of the first electrode and the second electrode at least partially overlaps the pixel circuitry and has a surface inflection above features of the pixel circuitry. The surface inflection has a radius of curvature greater than one half micron.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
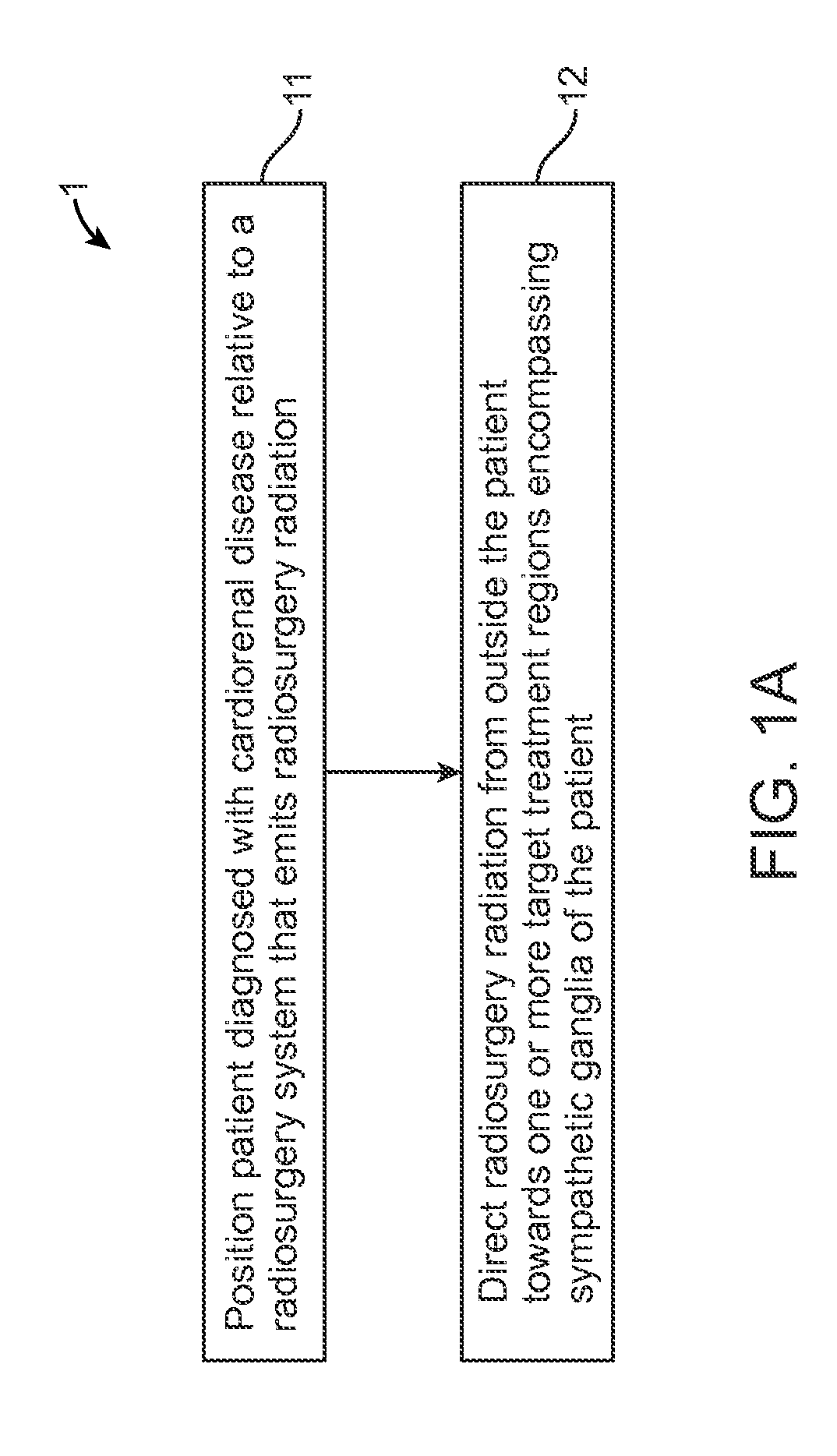
Renovascular treatment device, system, and method for radiosurgically alleviating hypertension
InactiveUS20120323233A1Reduce high blood pressureImprove securitySurgical instruments for heatingX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyRadiosurgeryCardiorenal disease
A radiosurgical method for treating cardiorenal disease of a patient, the method including directing radiosurgery radiation from outside the patient towards one or more target treatment regions encompassing sympathetic ganglia of the patient so as to inhibit the cardiorenal disease. In an exemplary embodiment, the method further includes acquiring three dimensional planning image data encompassing the first and second renal arteries, planning an ionizing radiation treatment of first and second target regions using the three dimensional planning image data so as to mitigate the hypertension, the first and second target regions encompassing neural tissue of or proximate to the first and second renal arteries, respectively, and remodeling the target regions by directing the planned radiation from outside the body toward the target regions.
Owner:CYBERHEART
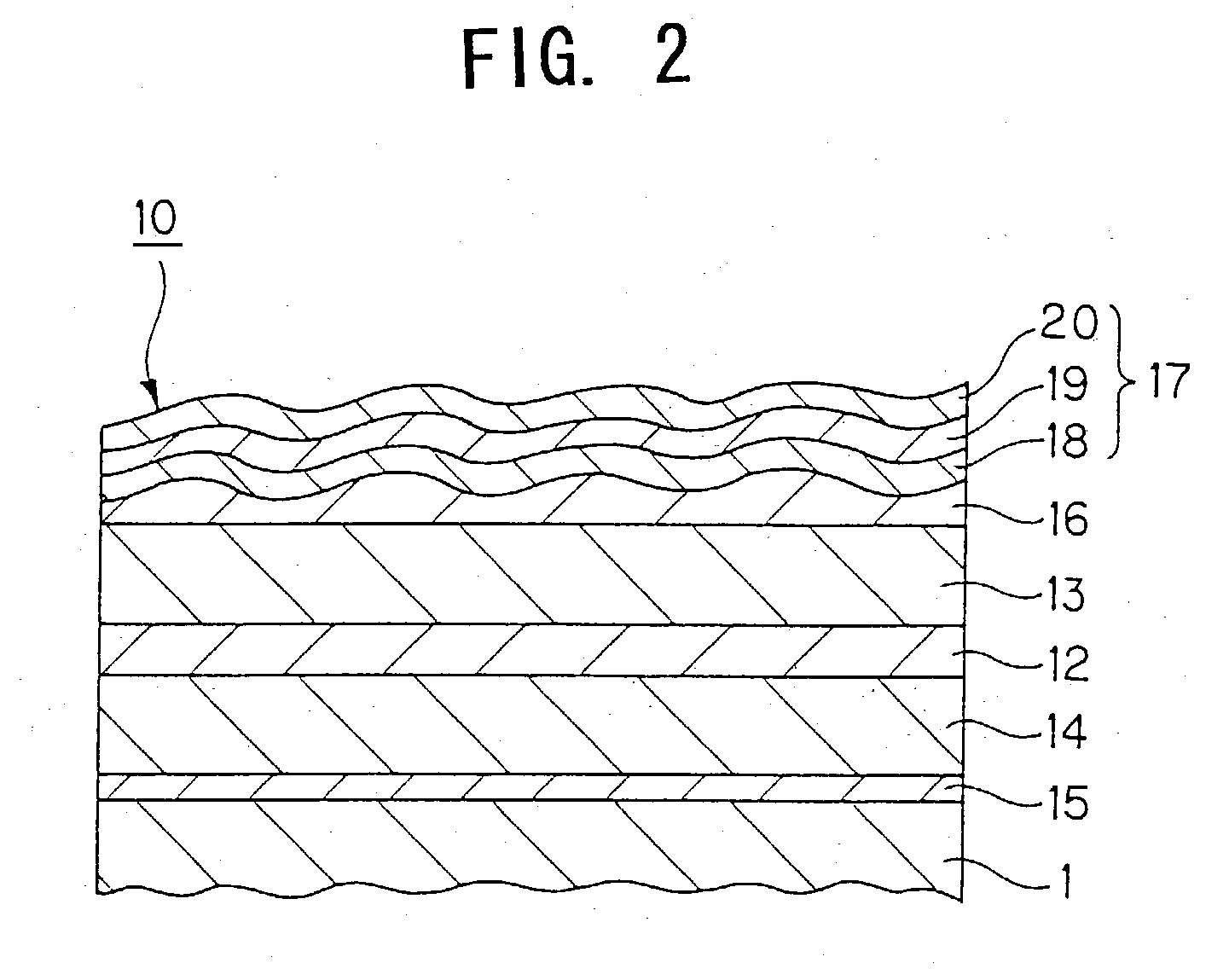
Coating composition, coating formed therefrom, anti-reflection coating, anti-reflection film, and image display device
ActiveUS20050038137A1Low refractive indexImprove adhesionOther chemical processesConductive materialPolymer chemistryReflection function
The present invention provides a coating composition capable of forming a fluorine-containing coating layer having a low refractive index and a high hardness, a coating layer formed by using the coating composition, an anti-reflecting layer using the coating layer and an anti-reflecting film and an image display device to which the anti-reflecting layer is applied. The coating composition according to the present invention comprises (A) a binder system containing a fluorine-containing component (a) having one or both of a functional group which can be cured by ionizing radiation and a polar group which can be heat-cured, and contains both an ionizing radiation-curable group and a heatcurable polar group as a whole and (B) an inorganic superfine particle of the order of submicron in size which can be dispersed in a colloidal state in a liquid medium for preparing a coating liquid. The coating layer formed using this coating composition is preferable for forming a light-transmitting layer, particularly, a low-refractive index layer 20, constituting a monolayer type or multilayer type anti-reflecting layer 17.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
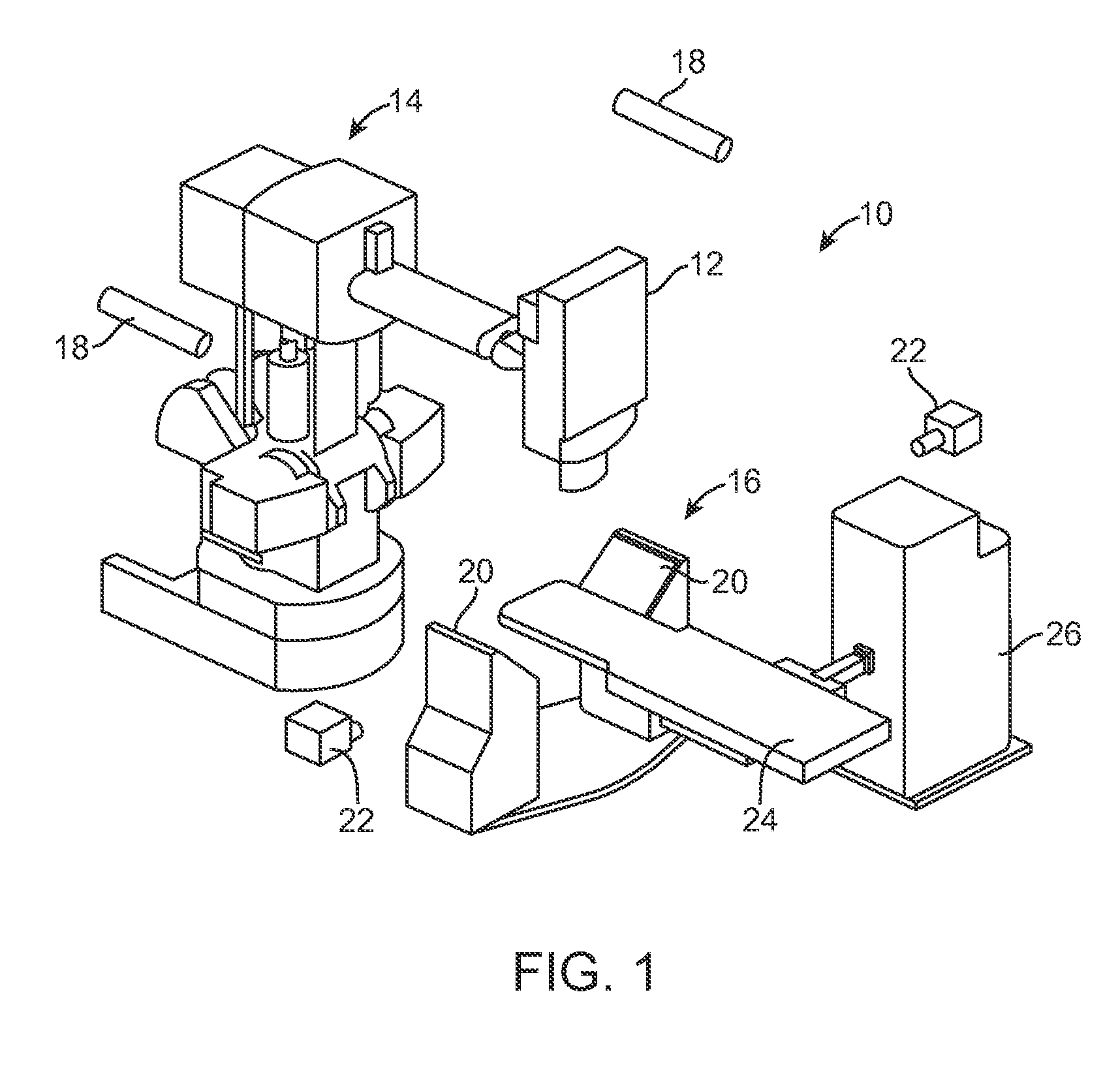
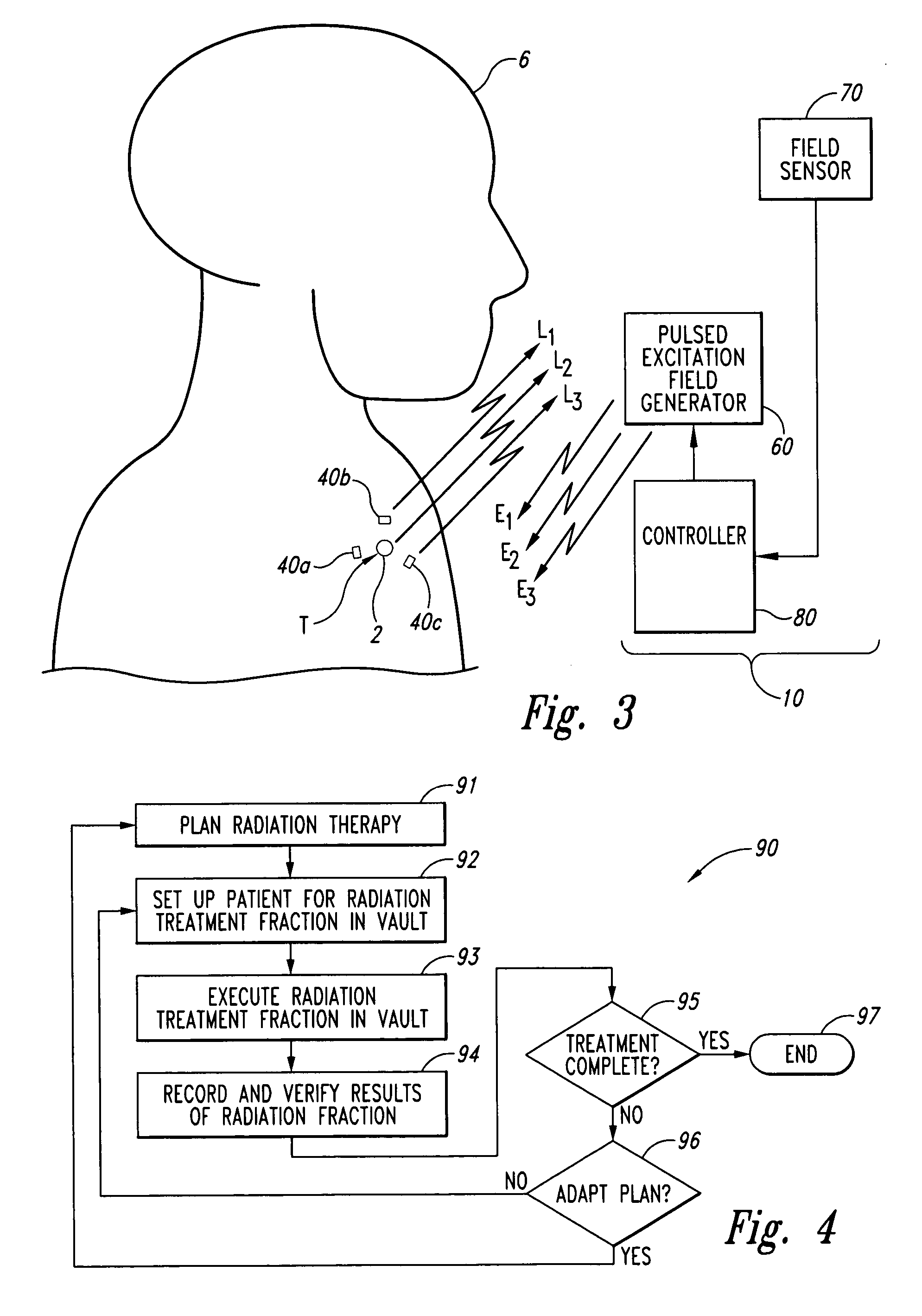
Systems and methods for real time tracking of targets in radiation therapy and other medical applications
InactiveUS20060079764A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsComputer scienceIsocenter
Systems and methods for tracking targets in real time for radiation therapy and other applications. In one embodiment, a method includes collecting position information of a marker implanted within a patient at a site relative to the target at a time tn, and providing an objective output indicative of the location of the target based on the position information collected at time tn. The objective output is provided to a memory device, user interface, and / or radiation delivery machine within 1 ms to 2 seconds of the time tn when the position information was collected. This embodiment of the method can further include providing the objective output at a periodicity of 10-200 ms during at least a portion of a treatment procedure. For example, the method can further include generating a beam of ionizing radiation and directing the beam to a machine isocenter, and continuously repeating the collecting procedure and the providing procedure every 10-200 ms while irradiating the patient with the ionizing radiation beam.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Localization of a radioactive source
InactiveUS7952079B2High sensitivityImprove efficiencySurgical navigation systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansRadioactive sourceAbsorbing element
An angle-responsive sensor, comprising:a radiation detector adapted to detect ionizing radiation;at least one radiation absorbing element arranged to block radiation from reaching said detector in a manner dependent on a relative orientation of a radiation source, said detector and said element, said detector and said element defining an aim for said sensor; andcircuitry coupled to said detector and which generates an output signal which varies as a function of said relative orientation,wherein said detector and said element are arranged to have a working volume of at least 10 cm in depth and having an angular width, such that said signal defines an accuracy of better than 3 mm within one standard deviation, over said working volume.
Owner:NAVOTEK MEDICAL
Catheter tracking with phase information
ActiveUS7505808B2Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesIn vivo
A method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern around individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In one embodiment the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
Coating composition, coating film thereof, antireflection coating, antireflection film, image display, and intermediate product
InactiveUS20030096102A1Good dispersibilityGood dispersionSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsMetallurgyRefractive index
A coating material capable of forming a high-quality thin film having a regulated refractive index; a coating film formed from the coating material; an antireflection coating comprising the coating film; an antireflection film to which the antireflection coating is applied; and an image display. The coating composition comprises (1) rutile-form titanium oxide having primary particle diameter of 0.01 to 0.1 mum and coated with an inorganic compound for reducing or eliminating the photocatalytic activity and with an organic compound having an anionic polar group and / or an organometallic compound, (2) a binder ingredient curable with an ionizing radiation, (3) a dispersant having an anionic polar group, and (4) an organic solvent. The coating film formed from the coating composition is suitable for forming a light-transmitting layer constituting or contained in a single- or multi-layer antireflection coating (17), in particular, a medium-refractive-index layer (18), high-refractive-index layer (19), or hard coat layer (16) having a high refractive index.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
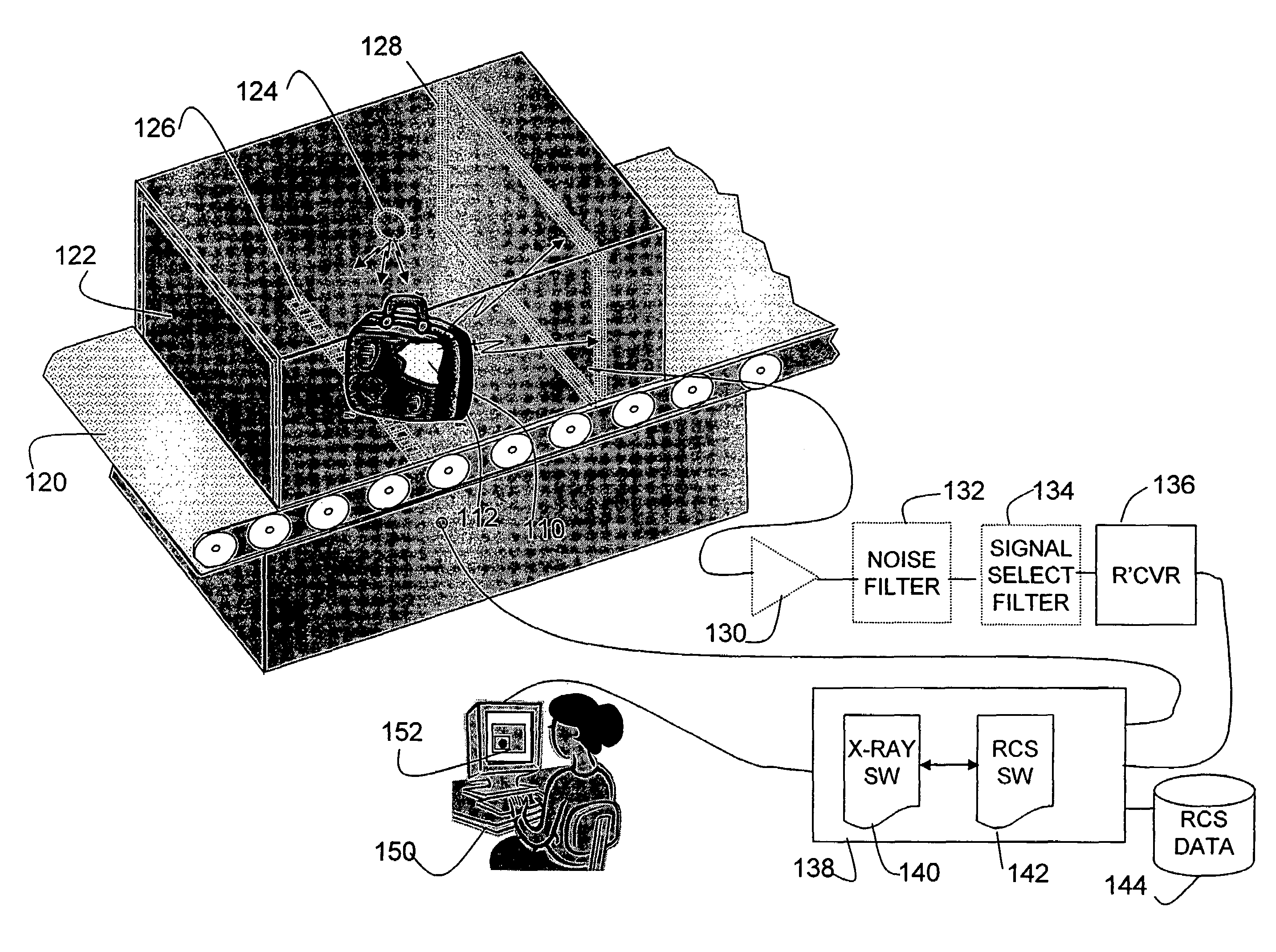
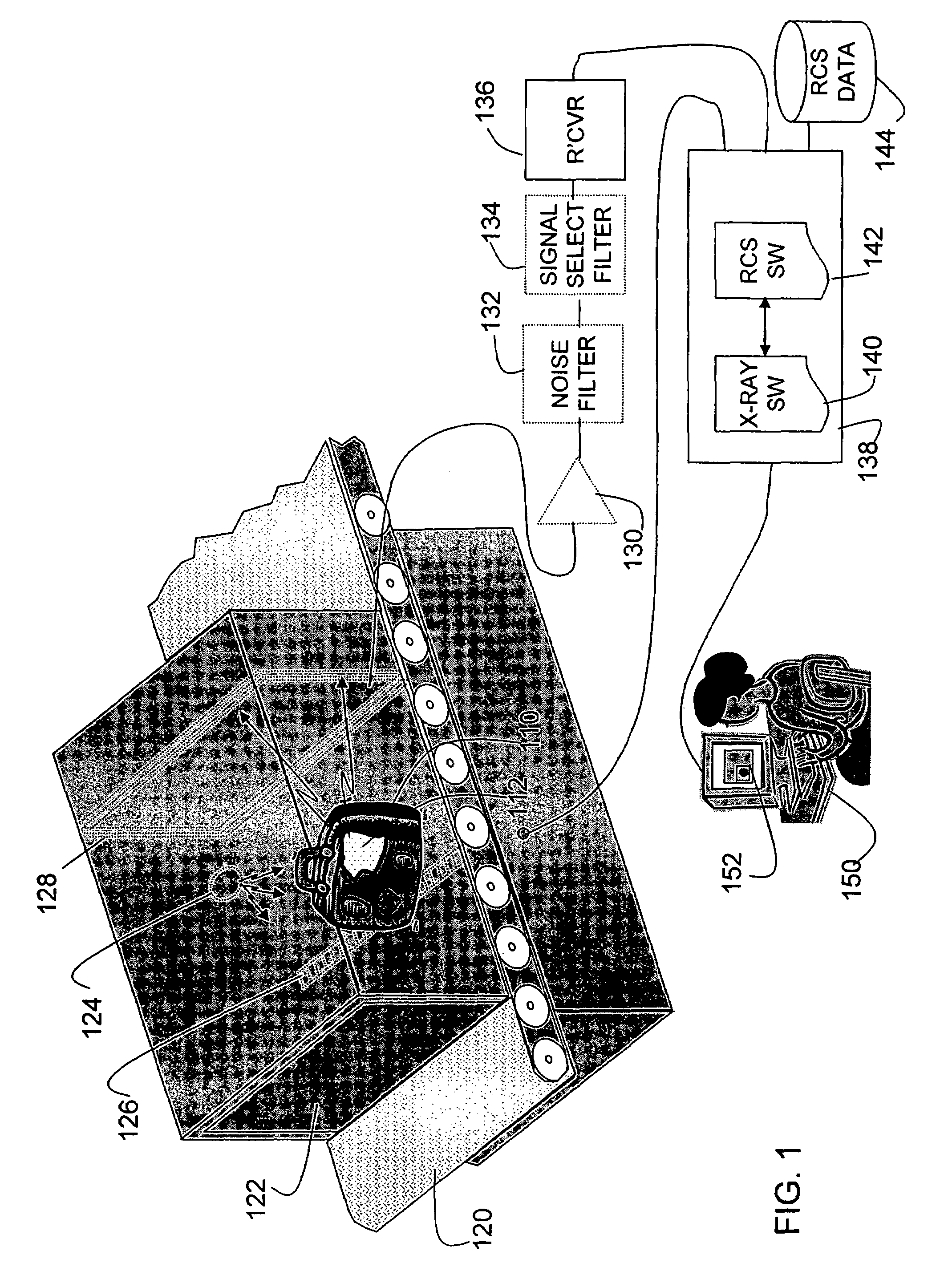
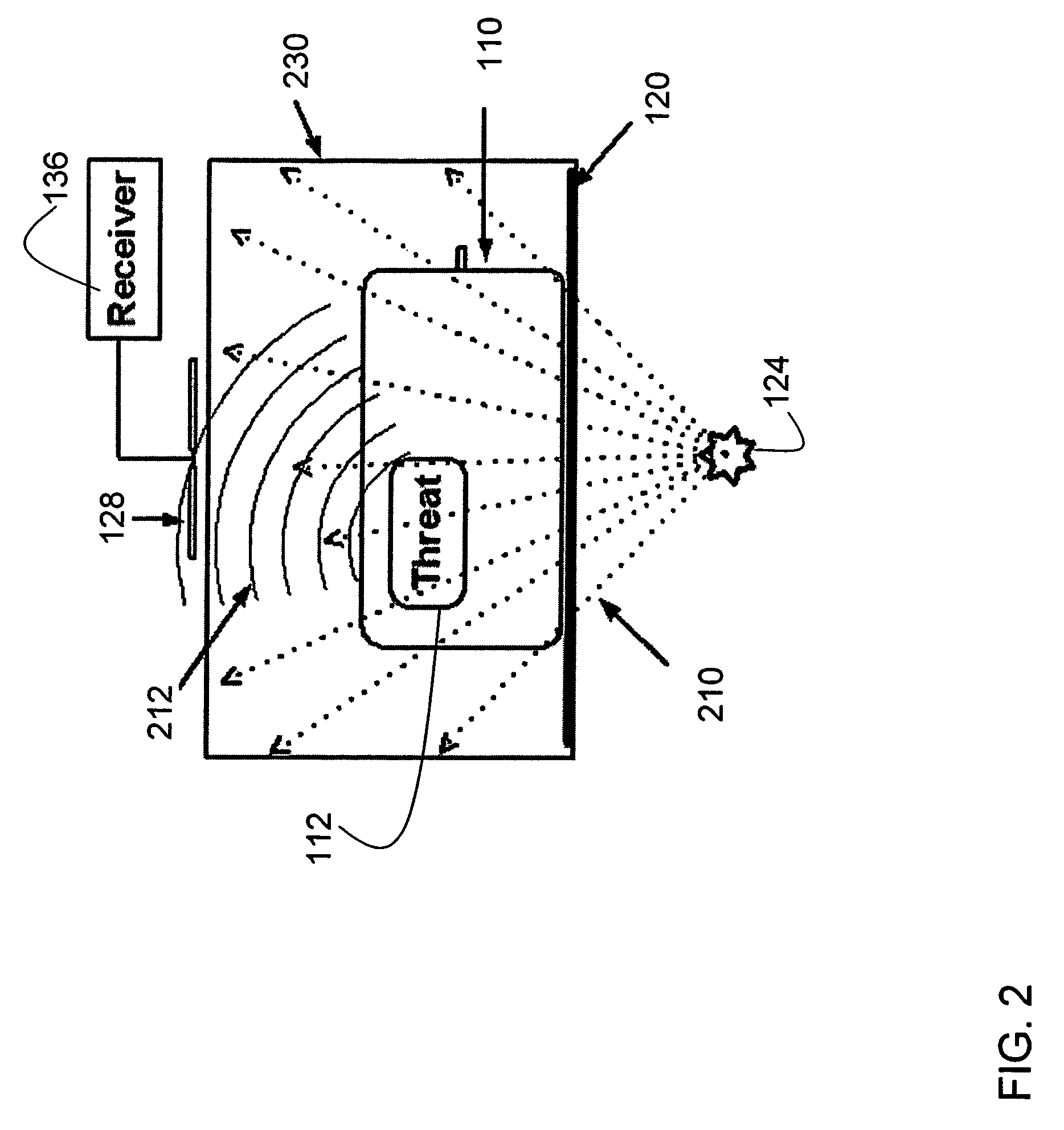
Method and apparatus for detecting contraband using radiated compound signatures
InactiveUS7251310B2Electric/magnetic detectionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSecondary analysisIonization
An system for detecting contraband, particularly explosives or other energetic materials. The system includes a source of ionizing radiation that irradiates an item under inspection. The radiation stimulates the emission of RF energy from objects within the item under inspection. The characteristics of the emitted RF energy reveals information about the material composition of the objects. The system detects this emitted RF energy and comparers it to a signature of RF emissions from contraband objects. Apparatus to detect and analyze RF emissions may be constructed as a stand-alone unit or may be incorporated into an imaging system in which the ionizing radiation is used to form an image of the item under inspection. Similarly, the RF analysis may be used, in the first instance, to determine whether an object contains a contraband item or may be used as a second level analysis to clear alarms generated by analysis of images formed by the imaging system.
Owner:L3 COMMUNICATIONS SECURITY & DETECTION SYSTEMS CORPORATION
Method of luminescent solid state dosimetry of mixed radiations
A method of determining the doses of neutrons, gamma and X-ray photons, beta, alpha and other ionizing radiations using a method of image processing in spatial and frequency domain that produces parameters that are related to the radiation dose absorbed in a luminescent material. Portions of the luminescent material may be covered by different converters to allow for doses of different radiations to be discriminated.
Owner:LANDAUER INC
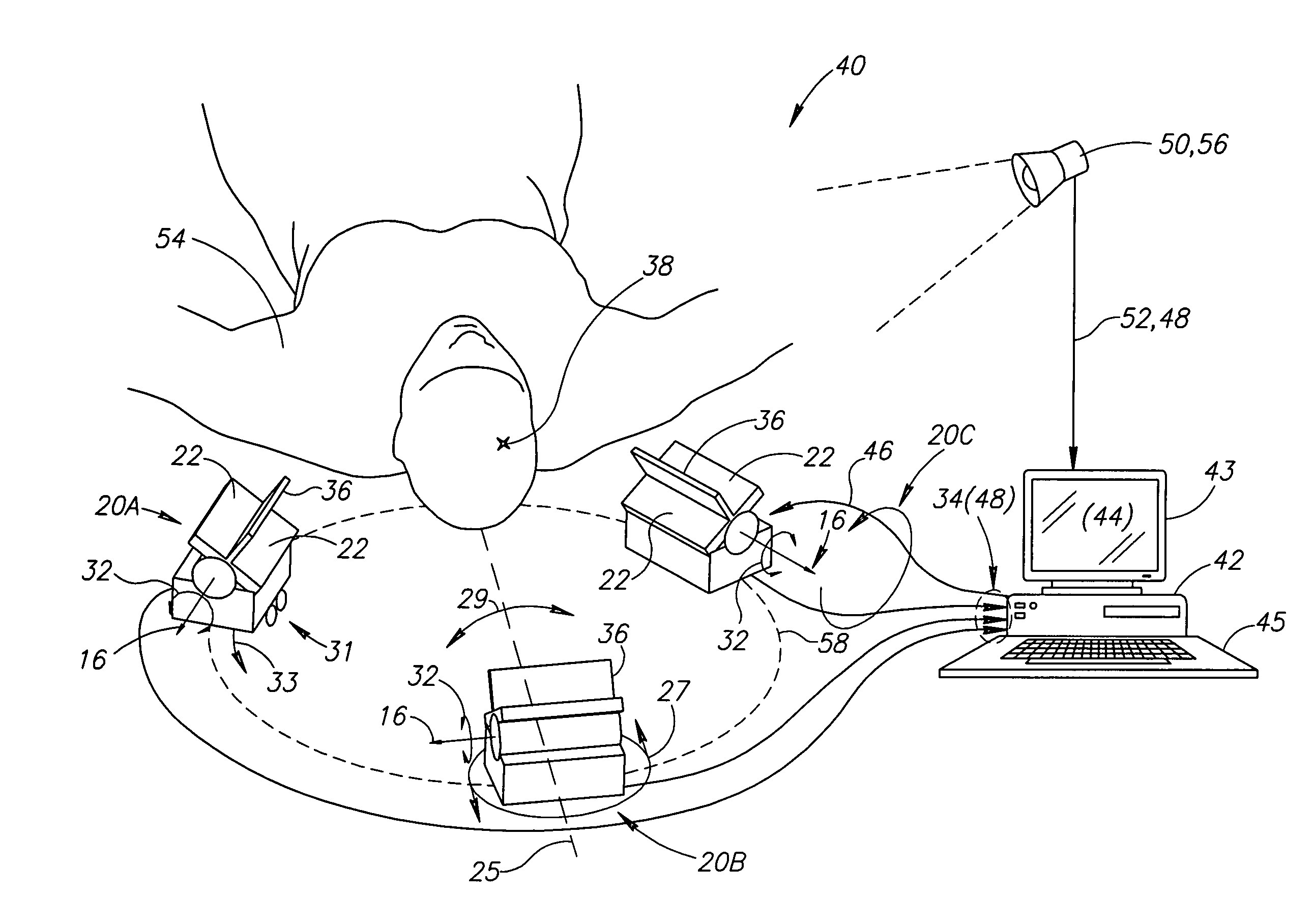
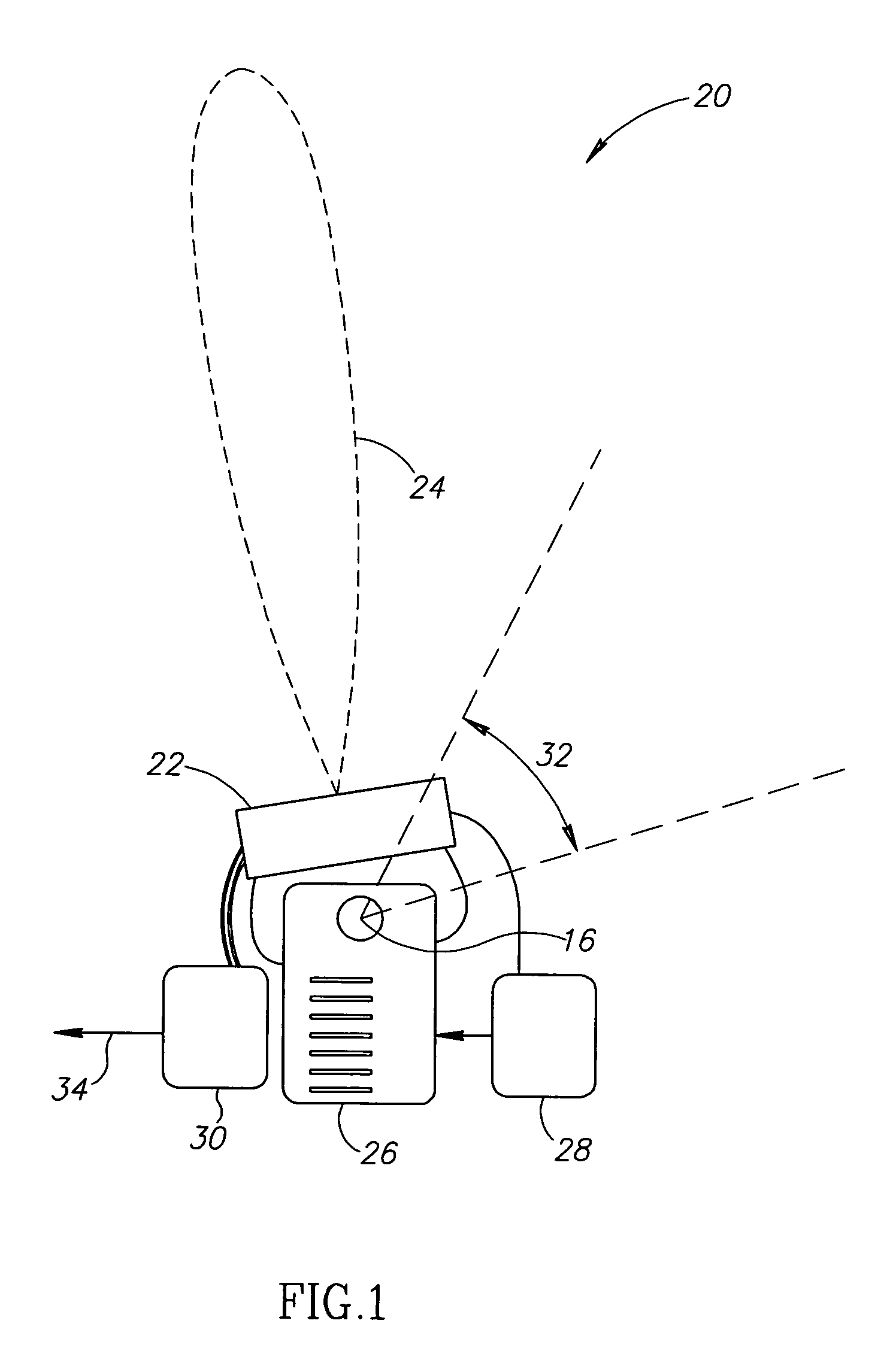
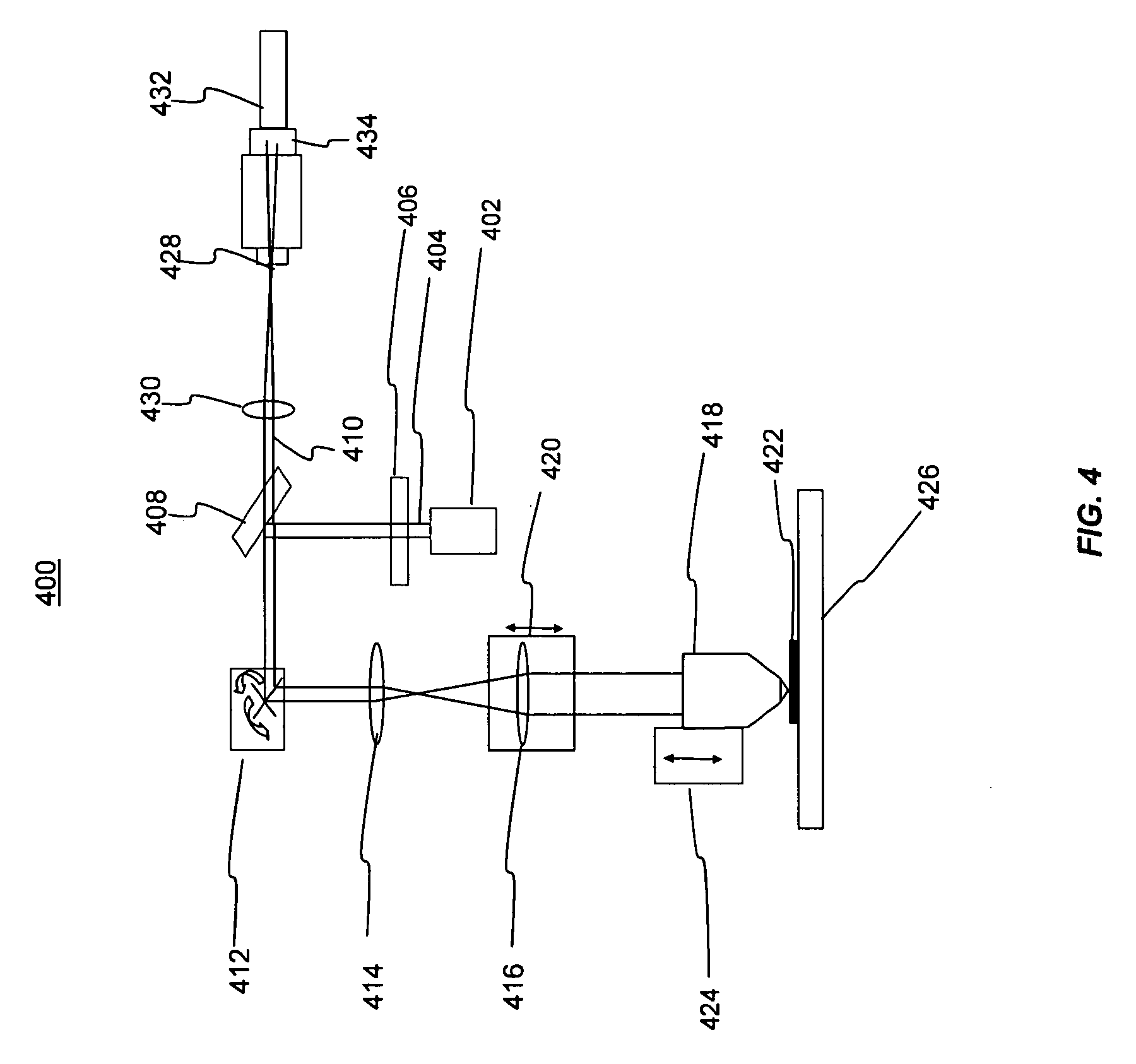
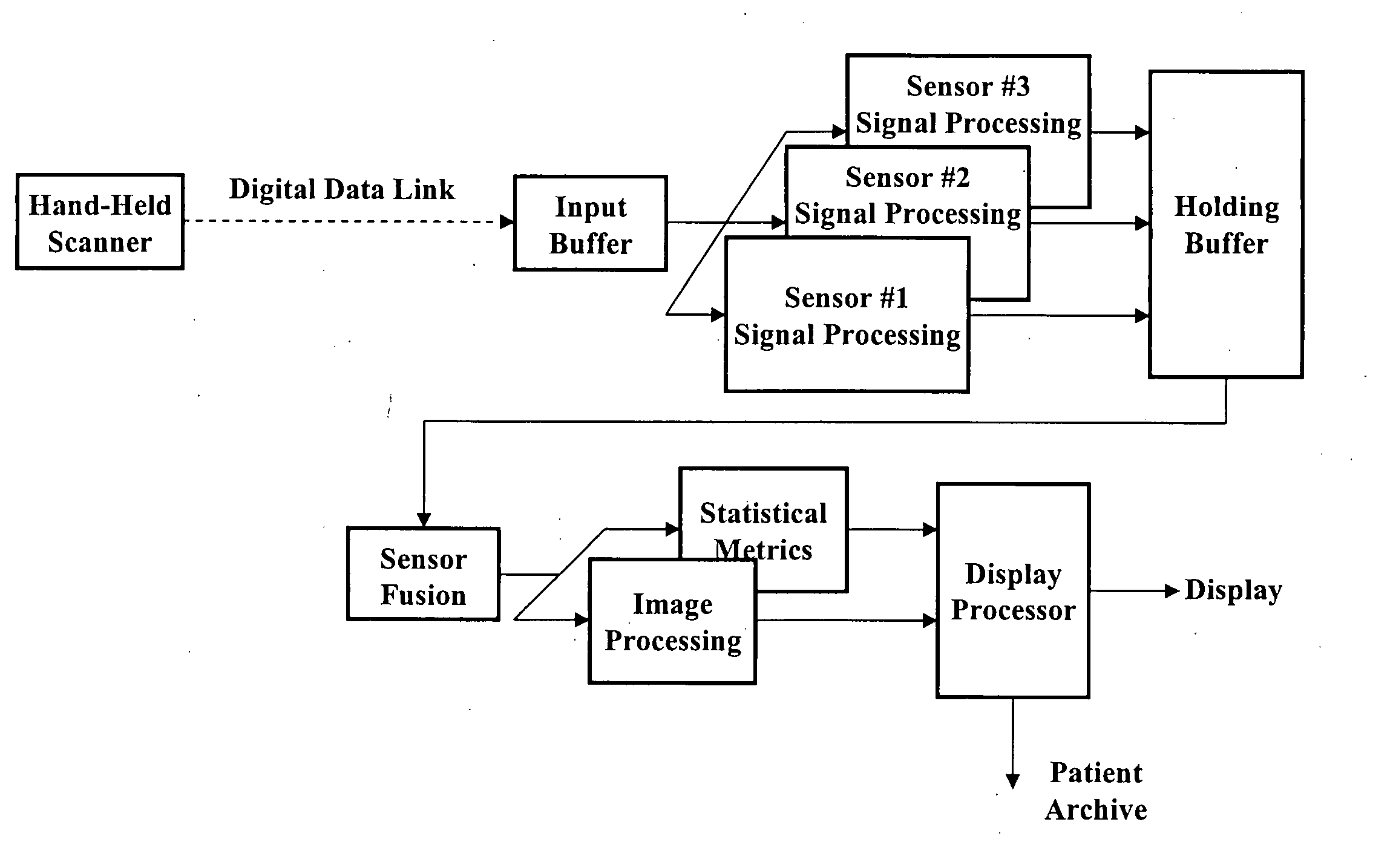
Multi-sensor breast tumor detection
InactiveUS20040220465A1Strong specificityIncrease cost/complexityOrgan movement/changes detectionDiagnostic recording/measuringGeneral practionerBreast cancer screening
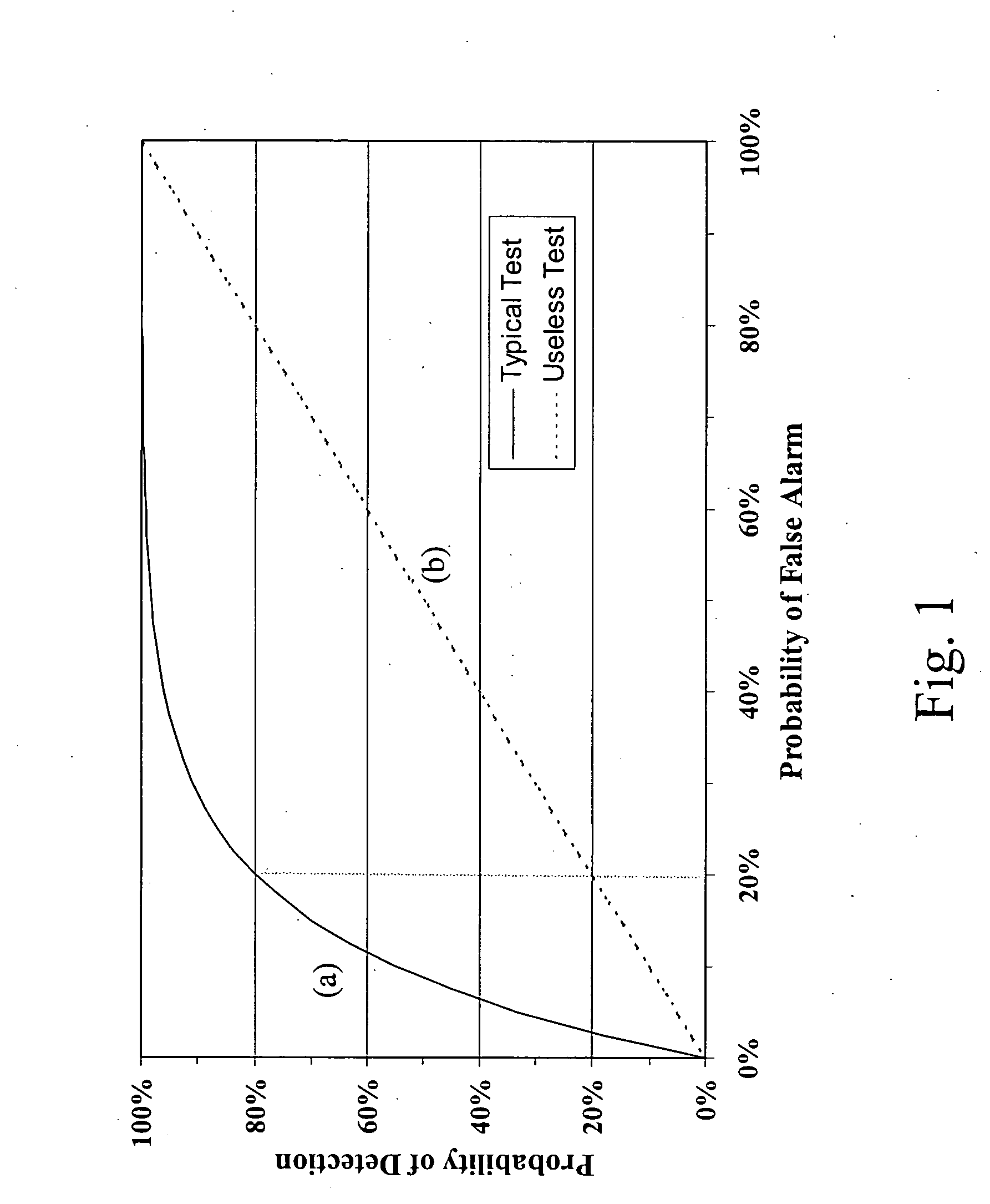
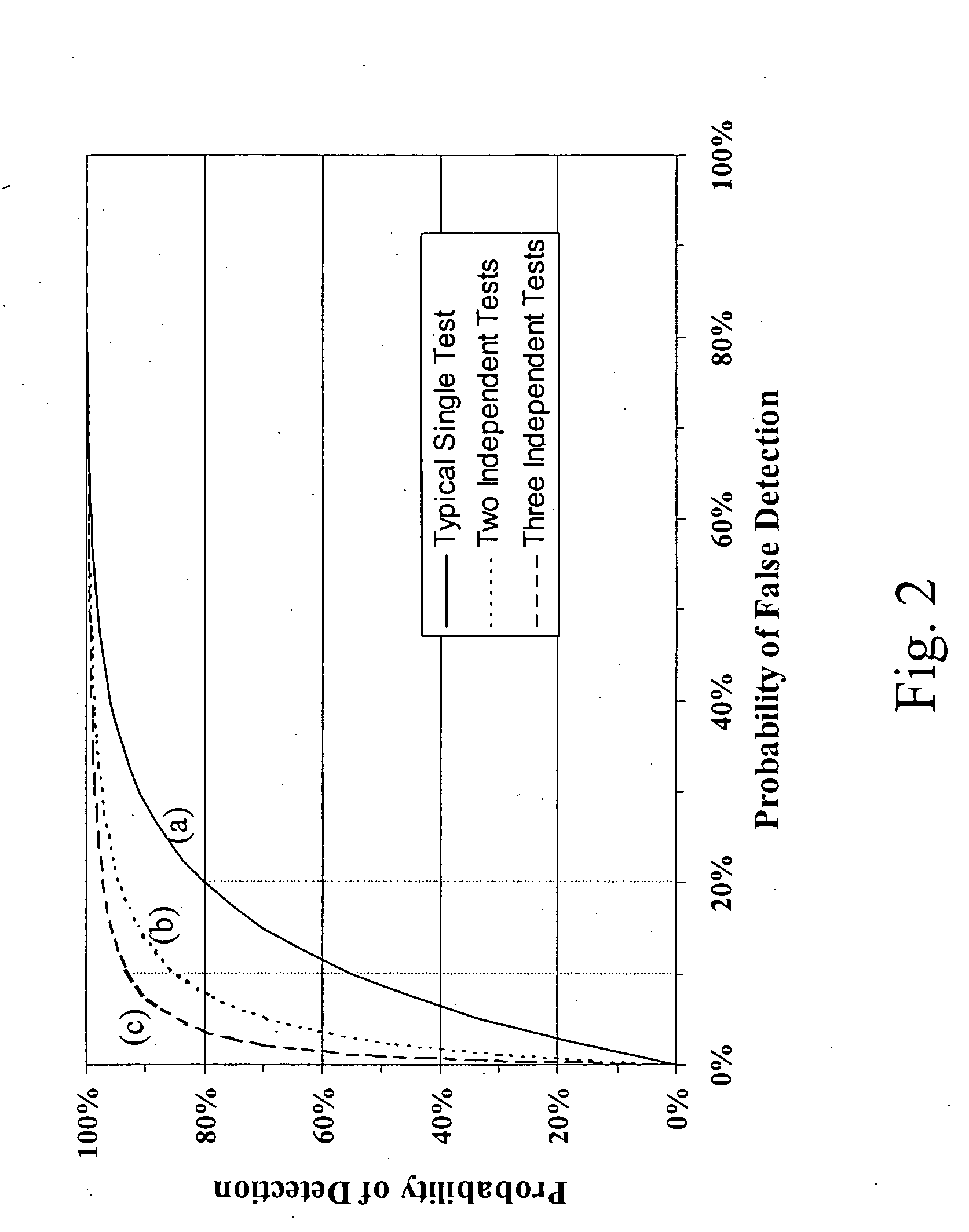
X-ray mammography has been the standard for breast cancer screening for three decades, but offers poor statistical reliability; it also requires a radiologist for interpretation, employs ionizing radiation, and is expensive. The combination of multiple independent tests, performed effectively at the same time and co-registered, can produce substantially more reliable detection performance than that of the individual tests. The multi-sensor approach offers greatly improved reliability for detection of early breast tumors, with few false positives, and also can be designed to support machine decision, thus enabling screening by general practitioners and clinicians; it avoids ionizing radiation, and can ultimately be relatively inexpensive.
Owner:CAFARELLA JOHN H
Hard coat film
InactiveUS20050142362A1Increase resistanceEasy to wearInput/output for user-computer interactionSynthetic resin layered productsDisplay deviceSolvent
A hard coat film exhibits excellent scratch resistance and wear resistance, provides the property for preventing attachment of finger prints and the property for removal of finger prints by a simple operation, is excellent in retaining these properties, exhibits excellent solvent resistance and is advantageously used as the hard coat film for touch panels and the hard coat film for protecting various types of display. The hard coat film comprises a transparent substrate film and a hard coat layer disposed at least on one face of the substrate film, wherein the hard coat layer comprises a cured product of a resin composition sensitive to an ionizing radiation which comprises a polymerizable surfactant.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Separator for secondary battery and porous film made of polyolefin blend and process for preparing the same
InactiveUS20060188786A1Improve wettabilityWettabilities in a battery electrolyte are lowSemi-permeable membranesMembranesPolyolefinElectrical battery
It is an object of the present invention to provide a microporous film made of polyolefin blend having outstanding electrolyte wettability, puncture strength, and shut down characteristics, its manufacturing method, and a secondary battery separator. The present invention provides a microporous film and a method for manufacturing the same characterized in that the microporous film is manufactured by molding a film with a mixed blend containing two or more of polyolefins by using a casting or film blowing, and that a microporous film is manufactured by annealing and stretching the molded film, and the microporous film is surface treated by irradiating it with ionizing radiation either before or after the pore formation in order to achieve the above object. Furthermore, the secondary batteries in which this microporous film is applied as a separator, especially lithium ion secondary batteries or alkali secondary batteries, are safer due to their outstanding puncture strength, shut down characteristics, and separator melt resistance under large external electric current flows, can benefit from a great increase in productivity due to the excellent separator electrolyte wettability during battery assembly, and can achieve high charging density due to their thin separator and high mechanical strength.
Owner:LEE SANG YOUNG +3
C4 selective hydrogenation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102240547AHigh activityHigh crystallinityHydrocarbon purification/separationCatalyst activation/preparationHydrogenActive component
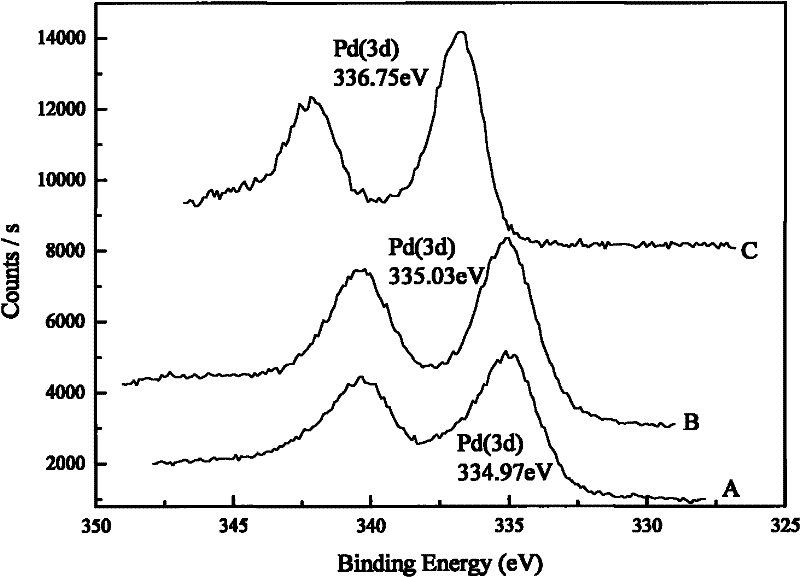
The invention discloses a C4 selective hydrogenation catalyst and a preparation method and use thereof. The saturated hydrocarbon hydrogenation catalyst is prepared by ionizing radiation reduction of a primary metal active component precursor and a secondary metal active component precursor, which are supported by a carrier, wherein the primary metal active component is Pd monomer; and the average diameters of particles of the primary metal active component and the particles of the secondary metal active component are both smaller than 10 nanometers. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has the advantages of avoiding being reduced by hydrogen in advance, along with high activity and selectivity, direct use and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Biomarkers of ionizing radiation
ActiveUS20090289182A1Rapid inexpensiveLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementParticle spectrometer methodsDiseaseMedicine
The present invention provides novel radiation associated markers. The radiation associated markers may be one or more of albumin, LTGF-β, or any protein or peptide listed in any one of Tables 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 provided herein. The present invention also provides methods of assessing exposure to ionizing radiation by determining the presence of one or more radiation associated markers. The methods may optionally include quantifying one or more of the radiation associated markers. The methods may further include comparing the amount of one or more radiation associated markers in the sample determined to be present in the sample with either (i) the amount determined for temporally matched, normal samples or (ii) the amount determined for samples obtained from individuals or subjects that have not been exposed to an elevated level of ionizing radiation. The present invention further provides a method of predicting outcome in a subject after exposure to elevated levels of ionizing radiation. Further, the present invention provides a method of determining the amount of radiation therapy that has been delivered to a particular tissue. Also, the present invention provides kits for assessing the likelihood of significant damage, death, illness or medical complications post exposure to elevated levels of ionizing radiation by determining the presence or absence or by quantifying the amount of one or more radiation associated markers.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Electrophotographic photoreceptor, and image forming apparatus and process cartridge using the same
InactiveUS20070212626A1Improve mechanical durabilityQuality improvementElectrographic process apparatusCorona dischargeImage formationPhotochemistry
An electrophotographic photoreceptor is provided including an electroconductive substrate; a photosensitive layer located overlying the electroconductive substrate; and an outermost layer located overlying the photosensitive layer, wherein the outermost layer is formed by a reaction between a radical polymerizable compound having no charge transport structure including a compound having a specific formula, and a radical polymerizable compound having a charge transport structure, while applying heat, light, or ionizing radiation to the reaction, and wherein at least one of the photosensitive layer and the outermost layer includes at least an arylmethane compound having an alkylamino group or a compound having a specific formula.
Owner:RICOH KK
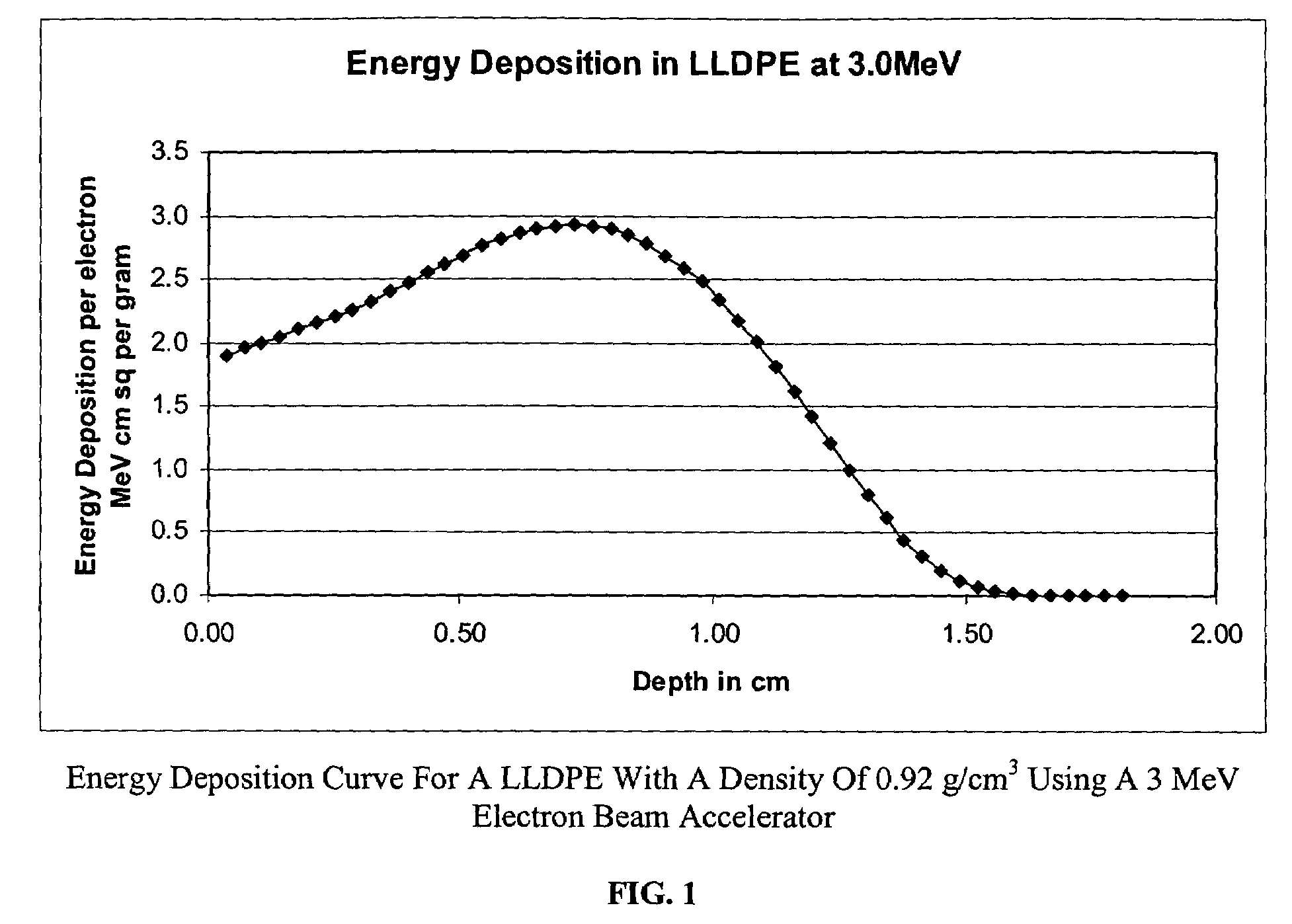
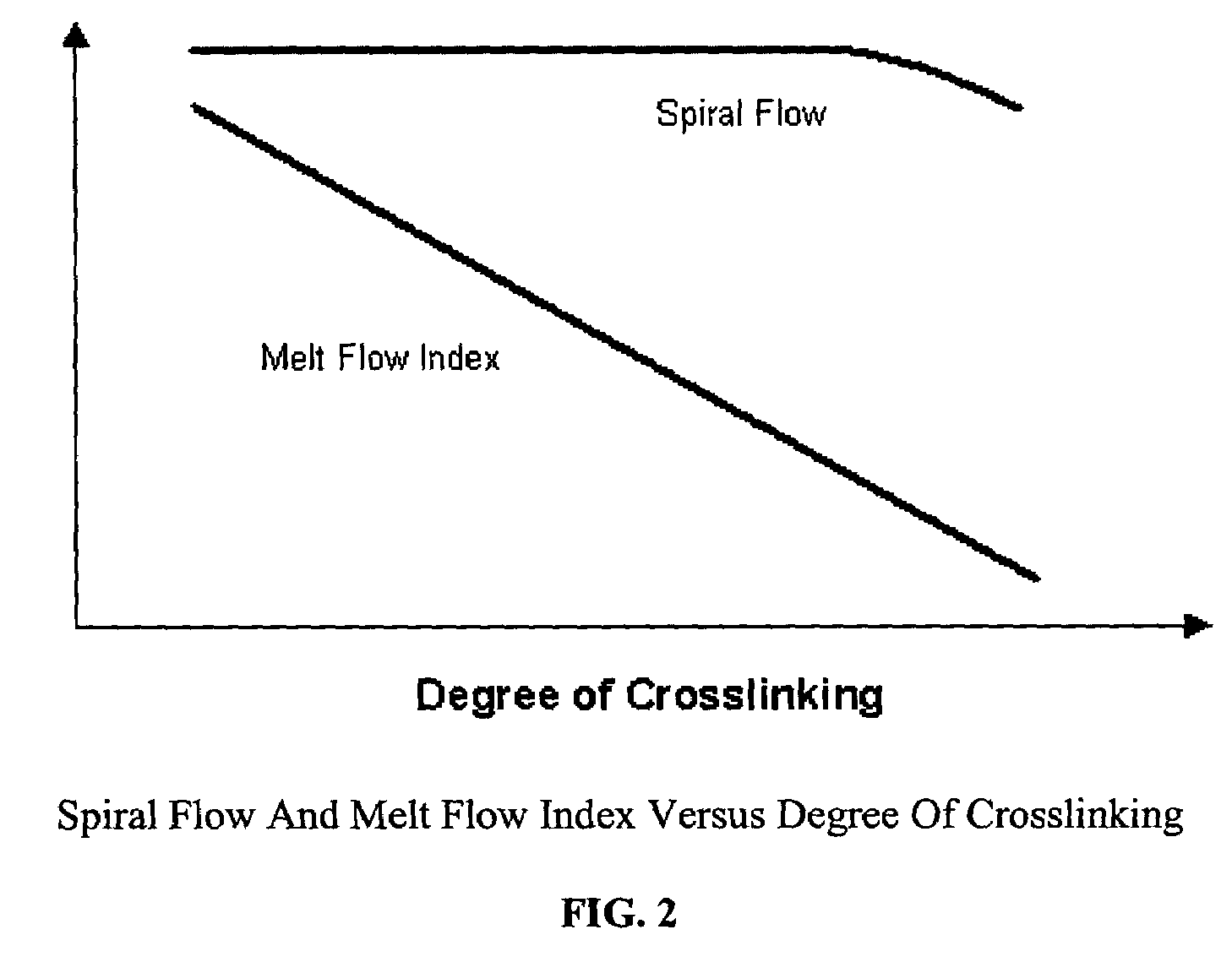
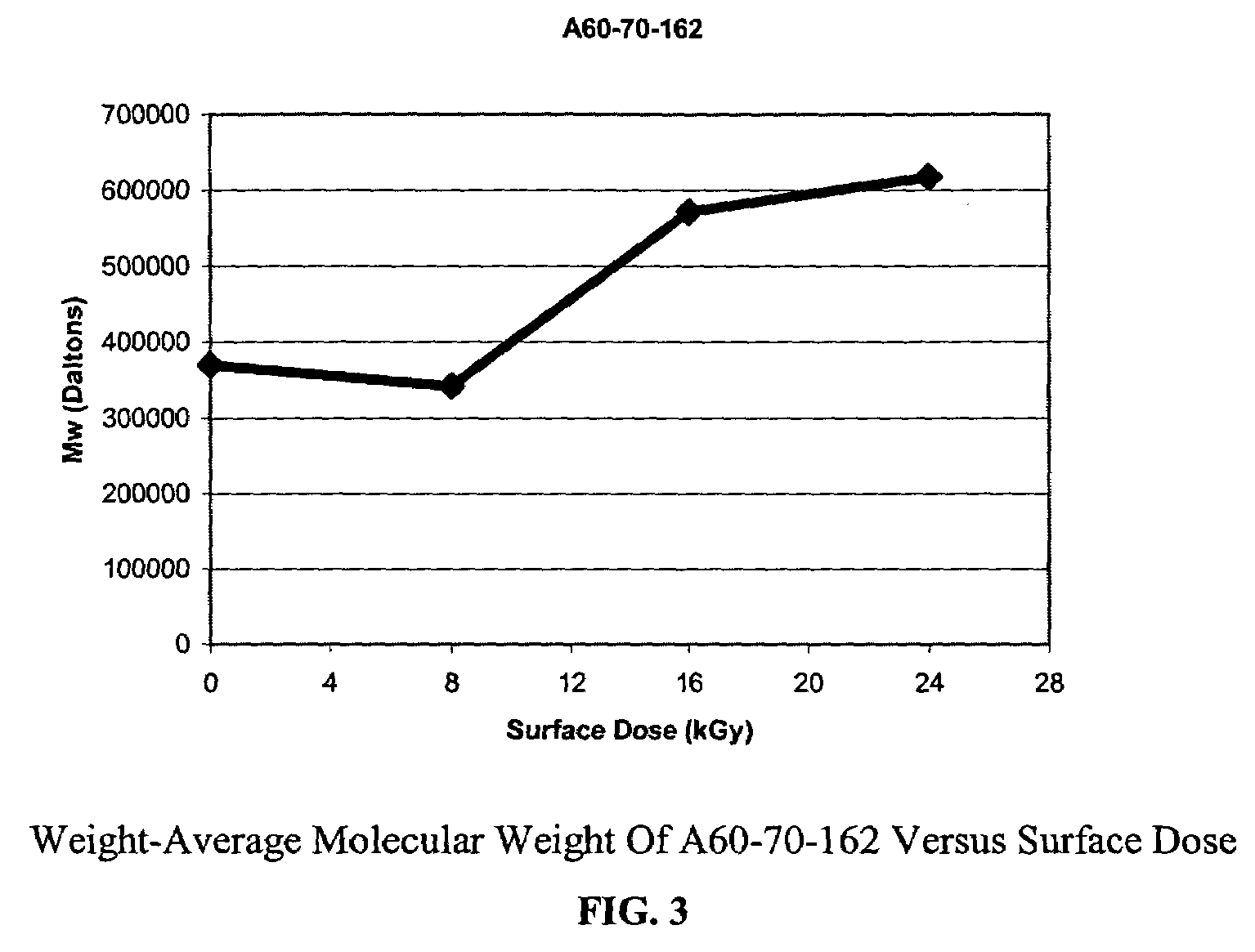
Radiation treated ethylene polymers and articles made from said polymers
InactiveUS7094472B2Improve mechanical propertiesHigh strengthSynthetic resin layered productsGranular deliveryPolymer scienceMelt flow index
Owner:GAMMATRON +1
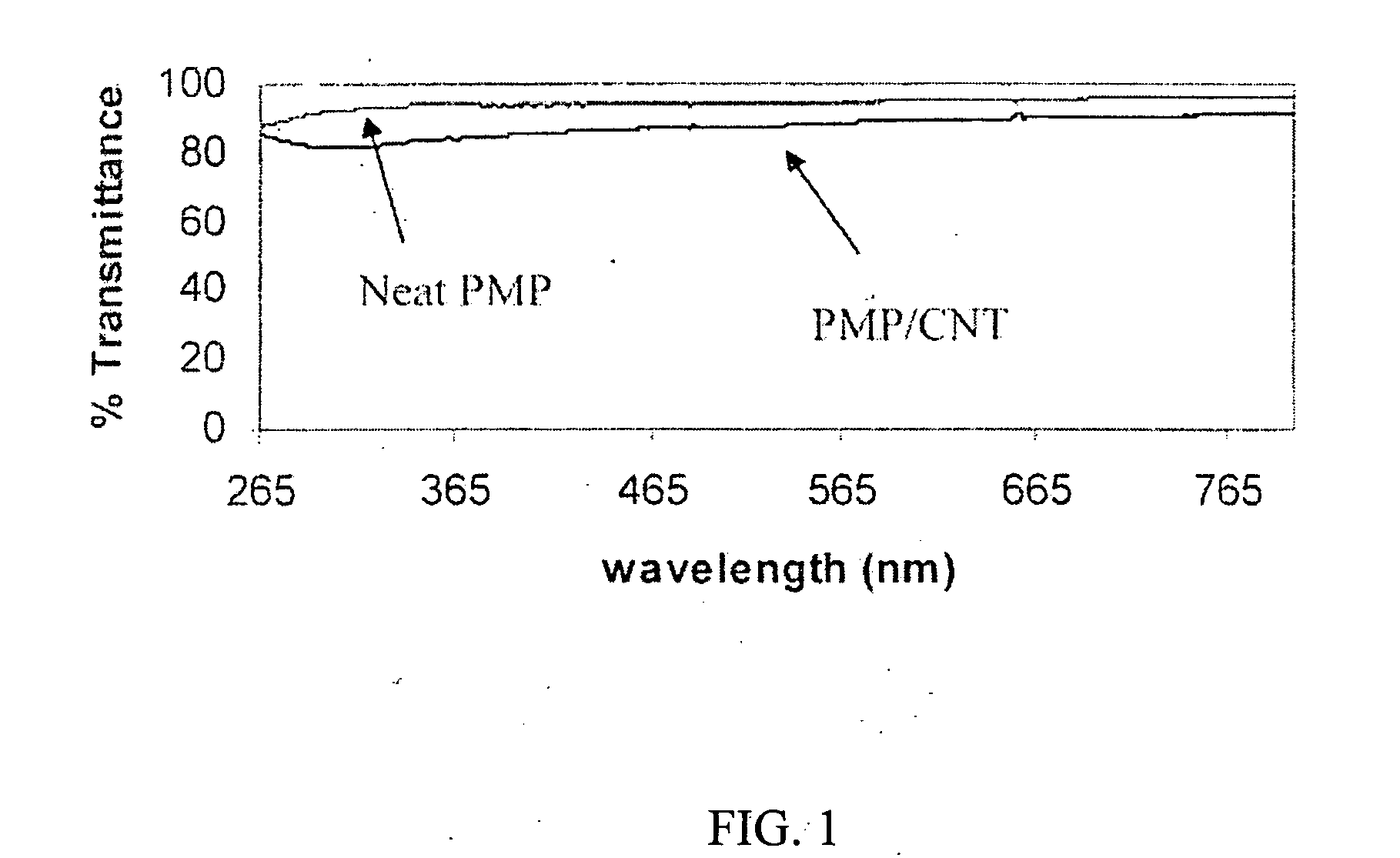
Polymer/carbon nanotube composites, methods of use and methods of synthesis thereof
InactiveUS20050245667A1Good optical performanceMaintain transparencyMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingPolymer scienceOrganic dye
Novel transparent composites composed of single wall carbon nanotubes incorporated into the matrix of a polymer are utilized in services wherein the composites are exposed to ionizing radiation, including galactic cosmic radiation. Accordingly, the composites are useful in deep space applications like space vehicles, space stations, personal equipment as well as applications in the biomedical arts and atom splitting research. The composites can be modified with organic dyes containing at least one phenyl ring and the resulting doped composite is useful as a radiation detector. The preferred polymer is poly(4-methyl-1-pentene).
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
System for performing a therapeutic procedure
InactiveUS20170165503A1Reduce the possibilitySurgical navigation systemsX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyMedicineBrachytherapy
The invention relates to a system for performing a therapeutic procedure like a HDR brachytherapy. An elongate introduction element is introduced into a body (2), a temperature is determined along the introduction element, and it is determined which part of the introduction element is within the body based on the determined temperature. A therapeutic procedure is performed by using the introduction element depending on the determination which part of the introduction element is within the body (2). This can ensure that the therapeutic procedure is only performed within the body, thereby reducing the likelihood of involuntary affecting, for instance, a patient's outer skin, especially by ionizing radiation which may be used during a HDR brachytherapy.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Treatment screening methods
InactiveUS20060073099A1Unwanted reactionCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsControl subjectsMedicine
The invention includes a method to identify a method to enhance survival of a subject that has been exposed to a biological insult such as an ionizing radiation dose of LD50 / 30 by treating the exposed subject with a test compound an optically comparing the results to that obtained using control subjects that had been treated with 3β,17β-dihydroxyandrost-5-ene or other disclosed compounds.
Owner:NEURMEDIX +2
Methods of and devices for monitoring the effects of cellular stress and damage resulting from radiation exposure
ActiveUS20110035158A1Easy to determineRadiation pyrometryWithdrawing sample devicesDiseaseNitric oxide
Methods of and devices for detecting a measurable characteristic of the gas sample. The methods and devices are able to detect a value of or a change of measurable characteristic (e.g., such as chemical concentrations), a change of chemical compositions and / or biological responses of a living organism that are induced by a stressor. The biological responses are able to include cellular stress, damage, and immune responses. The stressor is able to include an exposure to ionizing radiation. The effects of the stressors are able to be monitored in terms of changes in the chemical concentrations and chemical compositions in an exhaled breath. The chemicals are able to function as bio-markers. The chemicals that are to be monitored are able to include nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, ethane, and other molecules related to specific disease resulting from the stressor.
Owner:BANOS PETER THEOPHILOS
In vivo panning for ligands to radiation-induced molecules
InactiveUS20030130190A1Increase choiceReduced flexibilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementIn vivoTargeting ligands
A method for identifying a molecule that binds an irradiated tumor in a subject and molecules identified thereby. The method includes the steps of: (a) exposing a tumor to ionizing radiation; (b) administering to a subject a library of diverse molecules; and (c) isolating from the tumor one or more molecules of the library of diverse molecules, whereby a molecule that binds an irradiated tumor is identified. Also provided are therapeutic and diagnostic methods using targeting ligands that bind an irradiated tumor.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
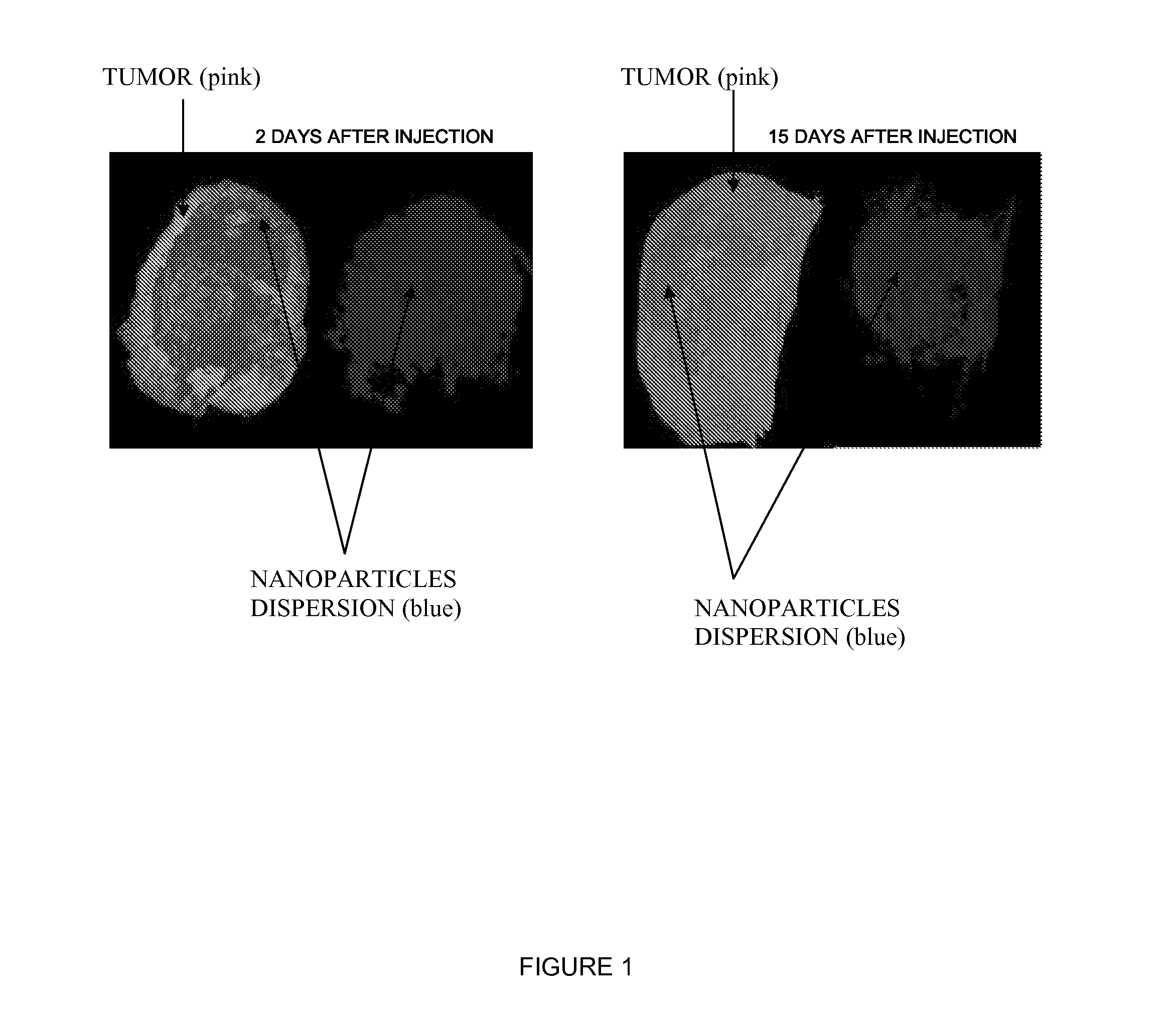
Inorganic Nanoparticles of High Density to Destroy Cells In-Vivo
ActiveUS20110213192A1Safely employedEfficient emissionsBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsHigh energy photonIsotope
The present application relates to novel excitable particles which can be used in the health sector. It more particularly relates to particles which can generate electrons and / or high energy photon when excited by ionizing radiations such as X- Rays, γ-Rays, radioactive isotope and / or electron beams, and to the uses thereof in health, in particular in human health. The inventive particles are made of an inorganic material comprising oxygen, in particular an oxide, said material having an adequate density, and can be activated in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo, by controllable external excitation, in order to disturb, alter or destroy target cells, tissues or organs. The invention also relates to methods for the production of said particles, and to pharmaceutical or medical device compositions containing same.
Owner:NANOBIOTIX SA
Film for optical applications
ActiveUS20050238879A1Inhibits the formation of defectsImprove crack resistanceSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsCarbamateCrack resistance
A hard coat film for optical applications which suppresses formation of defects on the surface derived from roughness of the surface of the substrate film, exhibits excellent scratch resistance and crack resistance and suppresses curling of the substrate film is provided. The film for optical applications comprises (A) a layer of a cured resin 2 which comprises 70% by weight or more of a cured resin derived from a difunctional urethane acrylate-based oligomer having a weight-average molecular weight of 3,000 or greater and has a thickness of 5 to 25 μm and (B) a hard coat layer 3 which comprises a resin cured by irradiation with an ionizing radiation and has a thickness of 1 to 15 μm, layers (A) and (B) being successively laminated on one face of a substrate film 1.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the IR wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
ActiveUS8029501B2Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyThermal dilatationHeat deposition
The present invention provides a method of laser processing of materials, specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material particularly important in medical and dental applications in which the laser removal of material should be done in such a way as to not damage any of the surrounding soft or hard biomaterial. The ablation process is achieved by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation process under prescribed time and wavelength conditions for laser irradiation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion that otherwise would lead to excess heat related damage. The result is that all the deposited laser energy is optimally channelled into the ablation process in which the inertially confined stresses from both photomechanical expansion forces and thermally driven phase transitions and associated volume changes constructively interfere to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects. By choosing a specific range of wavelengths, spatial and temporal shaping of infrared laser pulses, the energy can be optimally deposited in a manner that further increases the efficiency of the ablation process with respect to minimizing collateral damage.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION INC
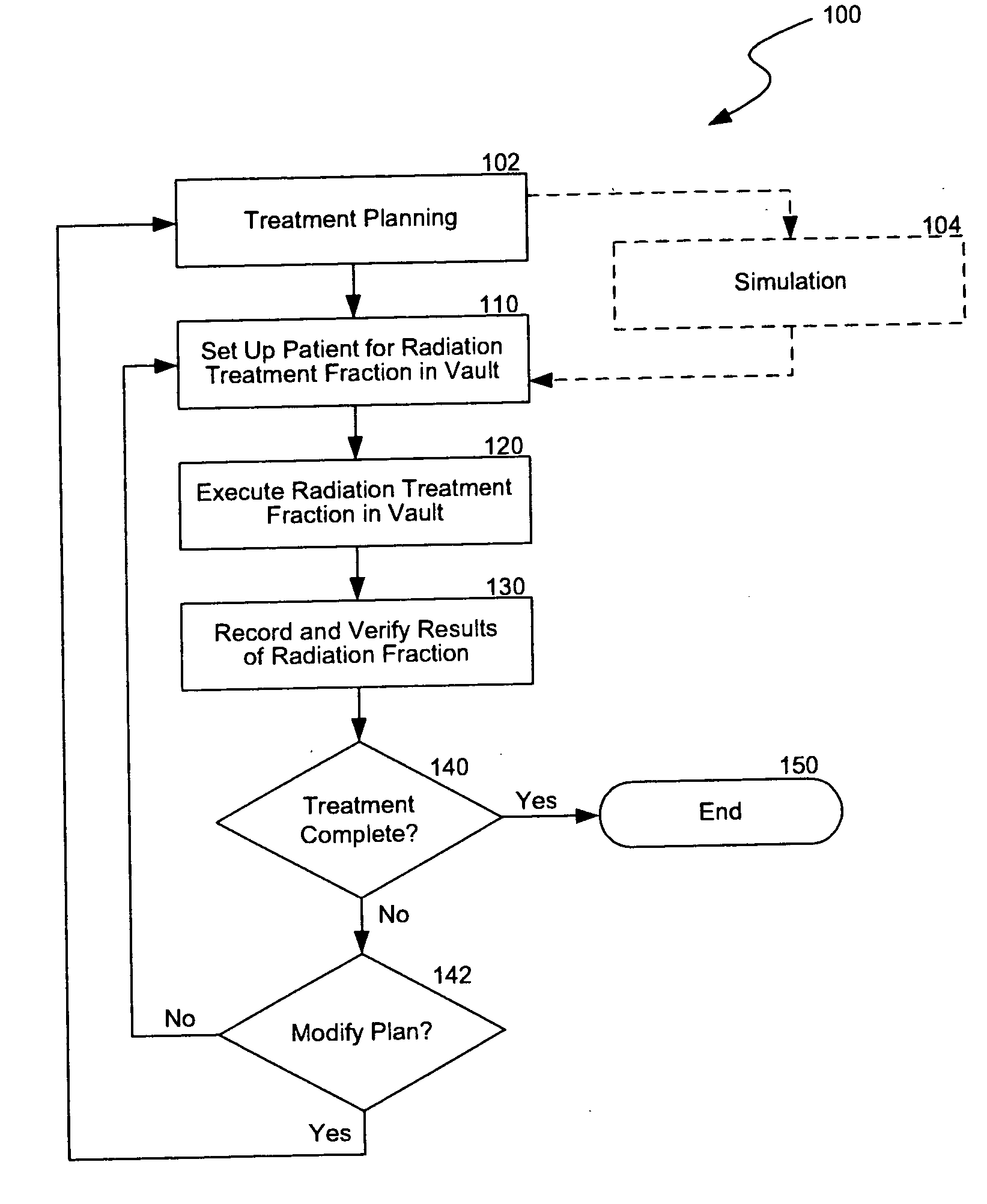
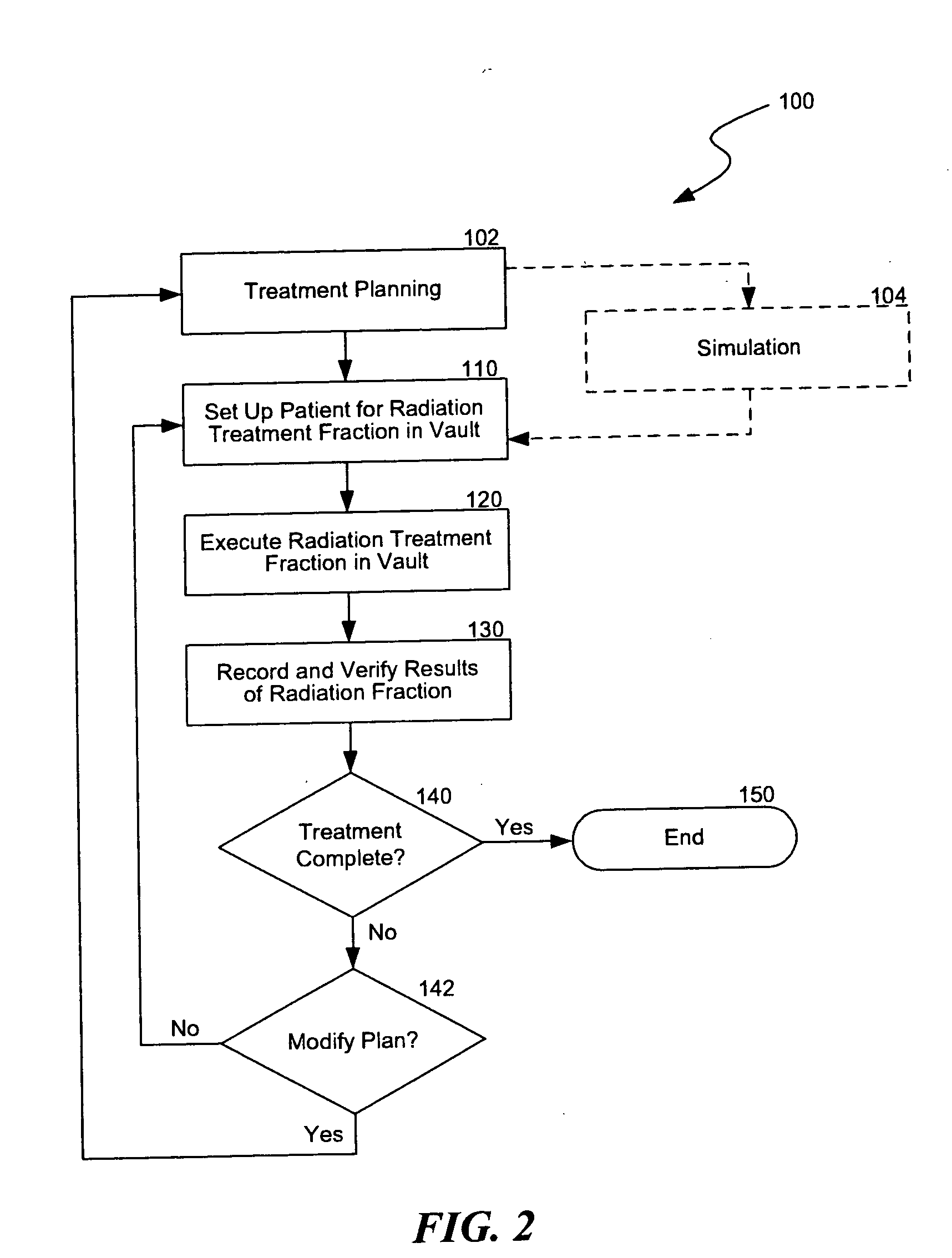
Integrated radiation therapy systems and methods for treating a target in a patient
An integrated radiation therapy process comprises acquiring first objective target data related to a parameter of a target within a patient by periodically locating a marker positioned within the patient using a localization modality. This method continues with obtaining second objective target data related to the parameter of the target by periodically locating the marker. The first objective target data can be acquired in a first area that is apart from a second area which contains a radiation delivery device for producing an ionizing radiation beam for treating the patient. The localization modality can be the same in both the first and second areas. In other embodiments, the first objective target data can be acquired using a first localization modality that uses a first energy type to identify the marker and the second objective target data can be obtained using a second localization modality that uses a second energy type to identify the marker that is different than the first energy type.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com