Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
130 results about "Ionic impurity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
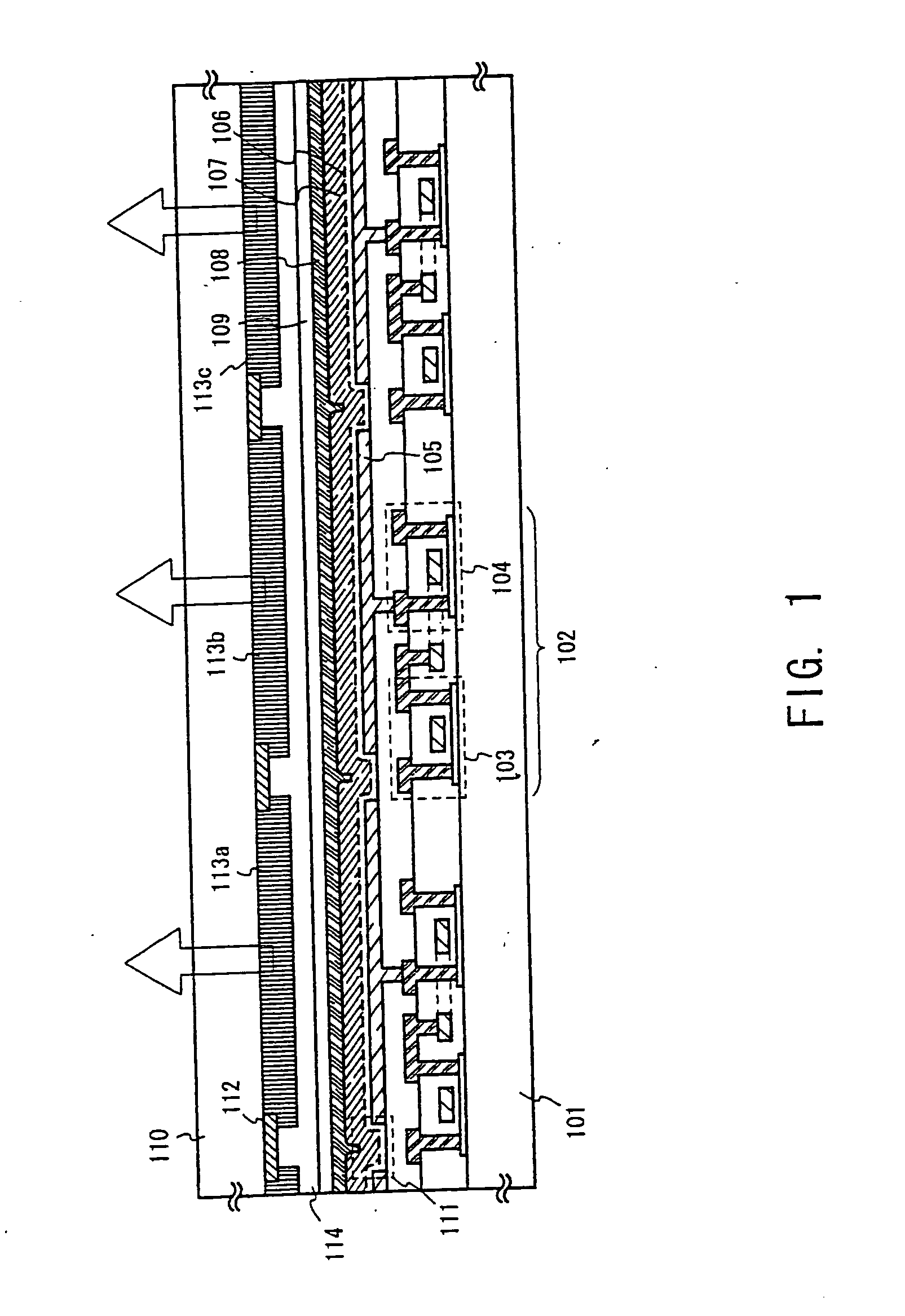
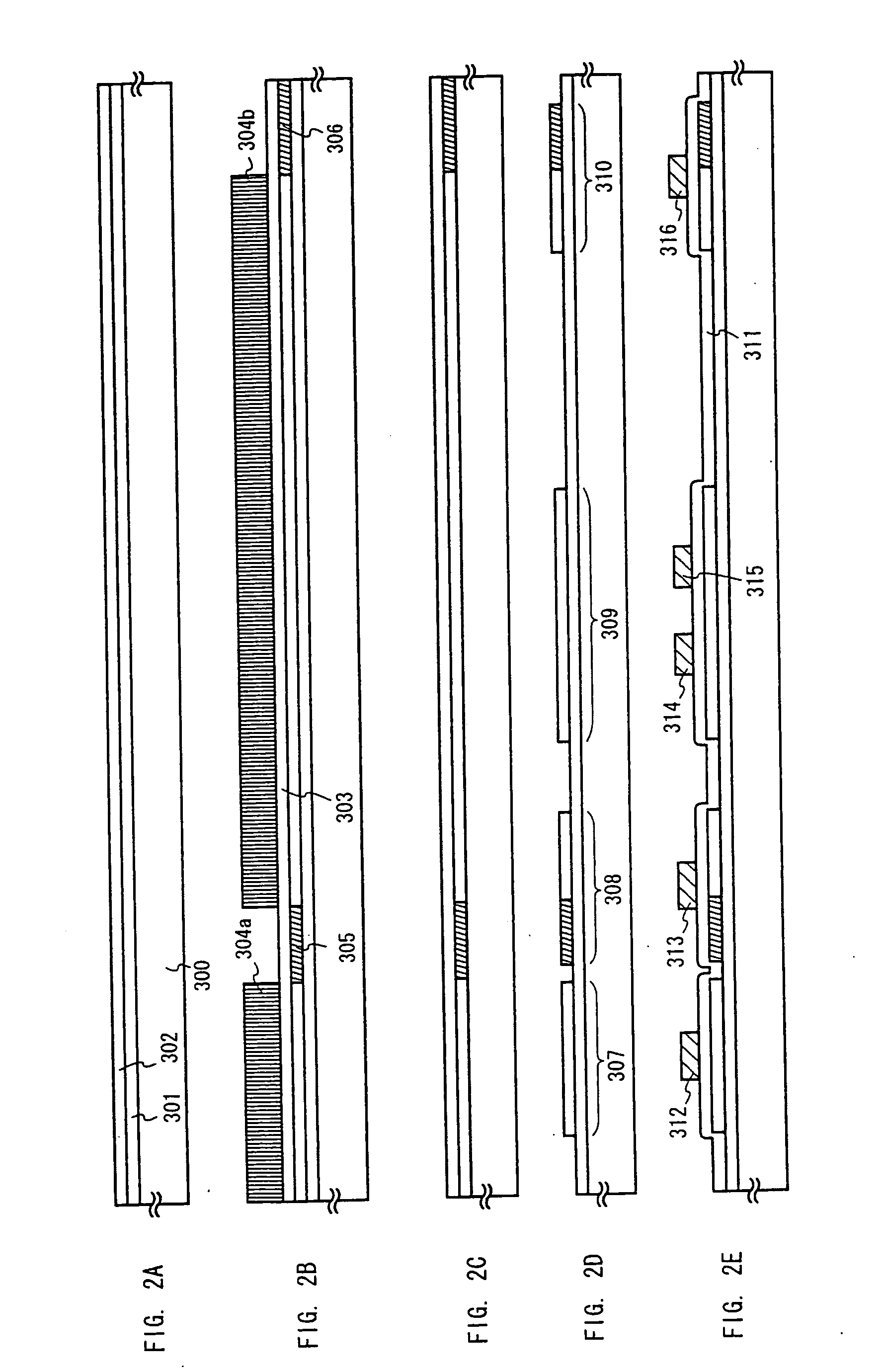
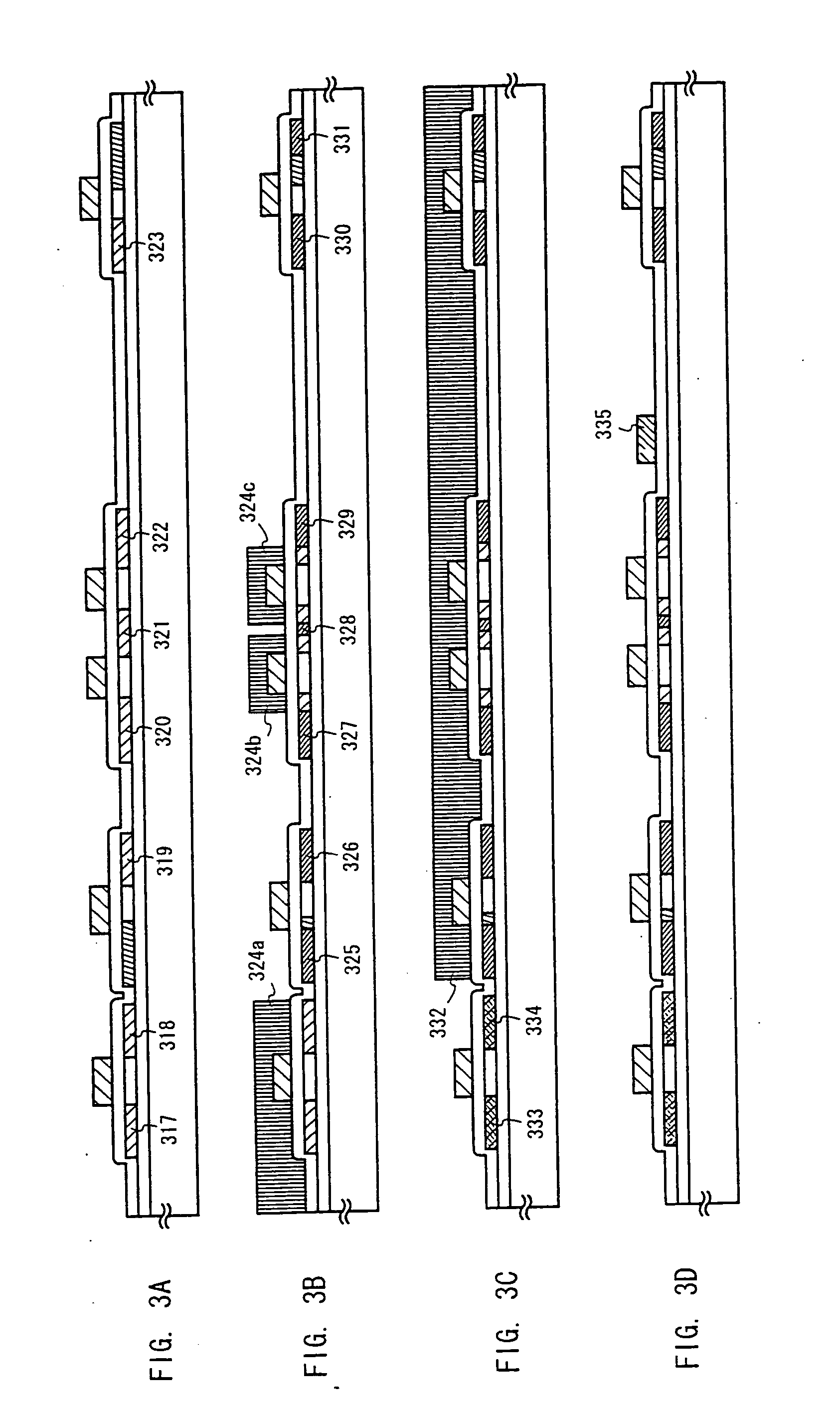
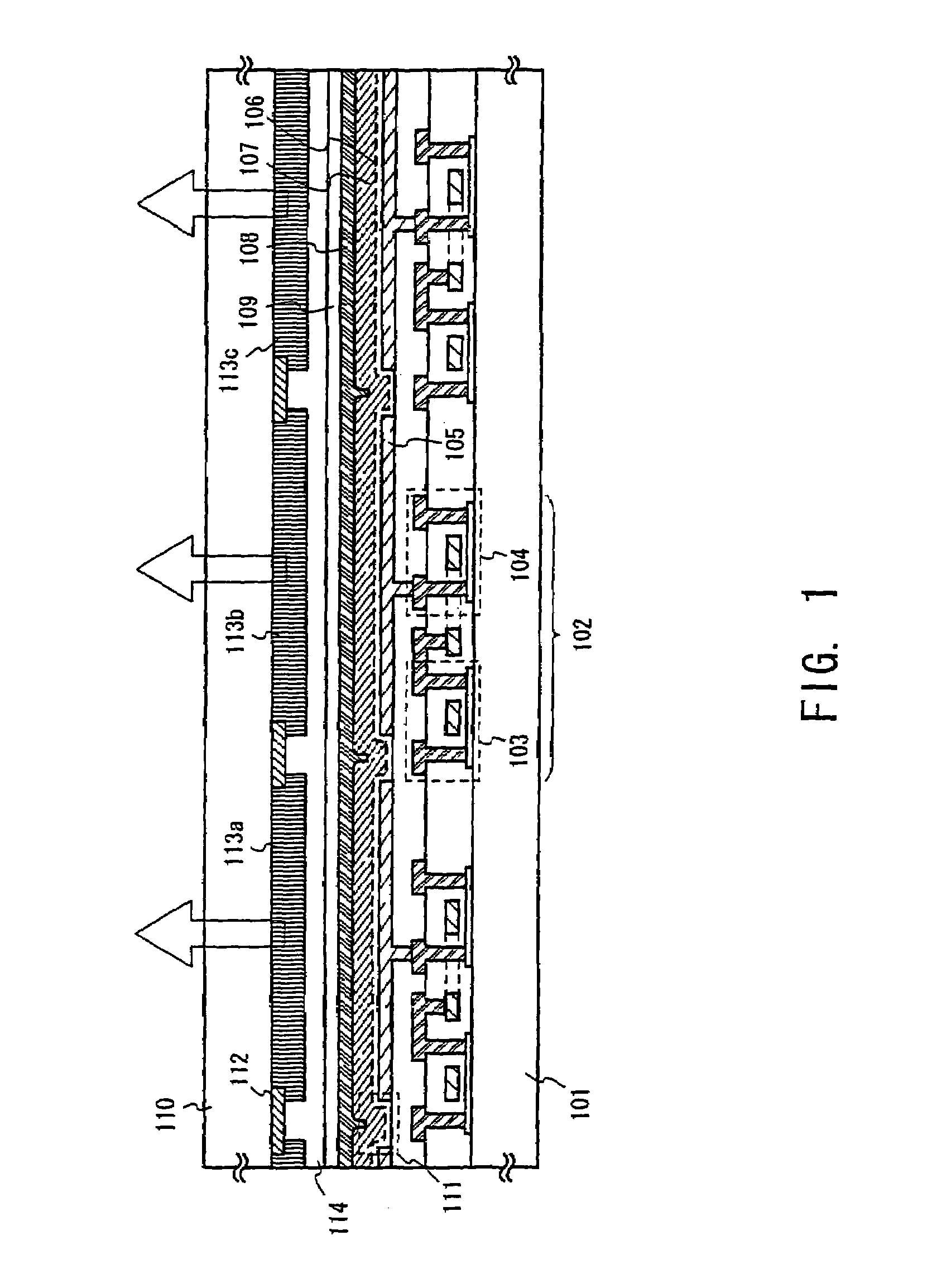
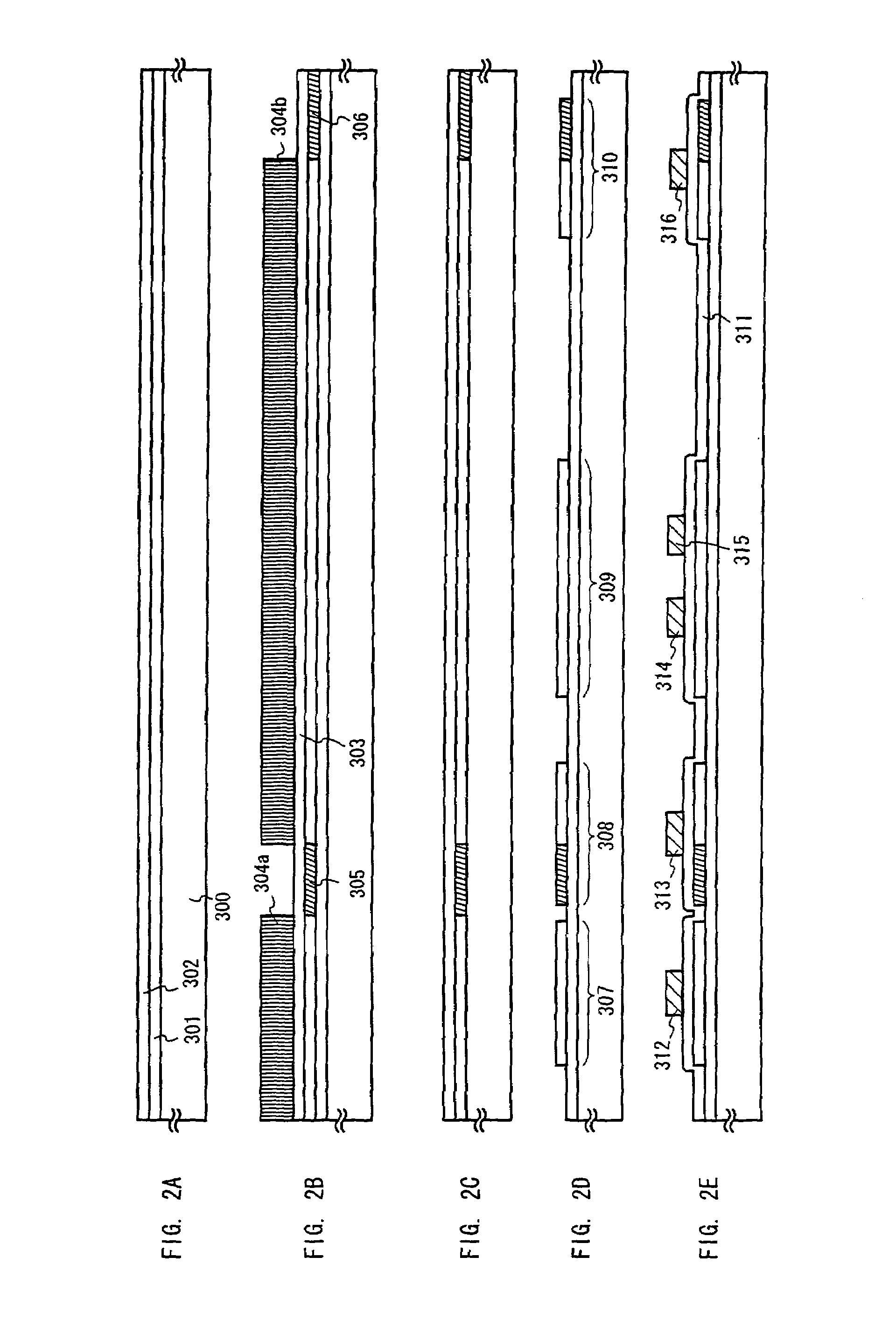
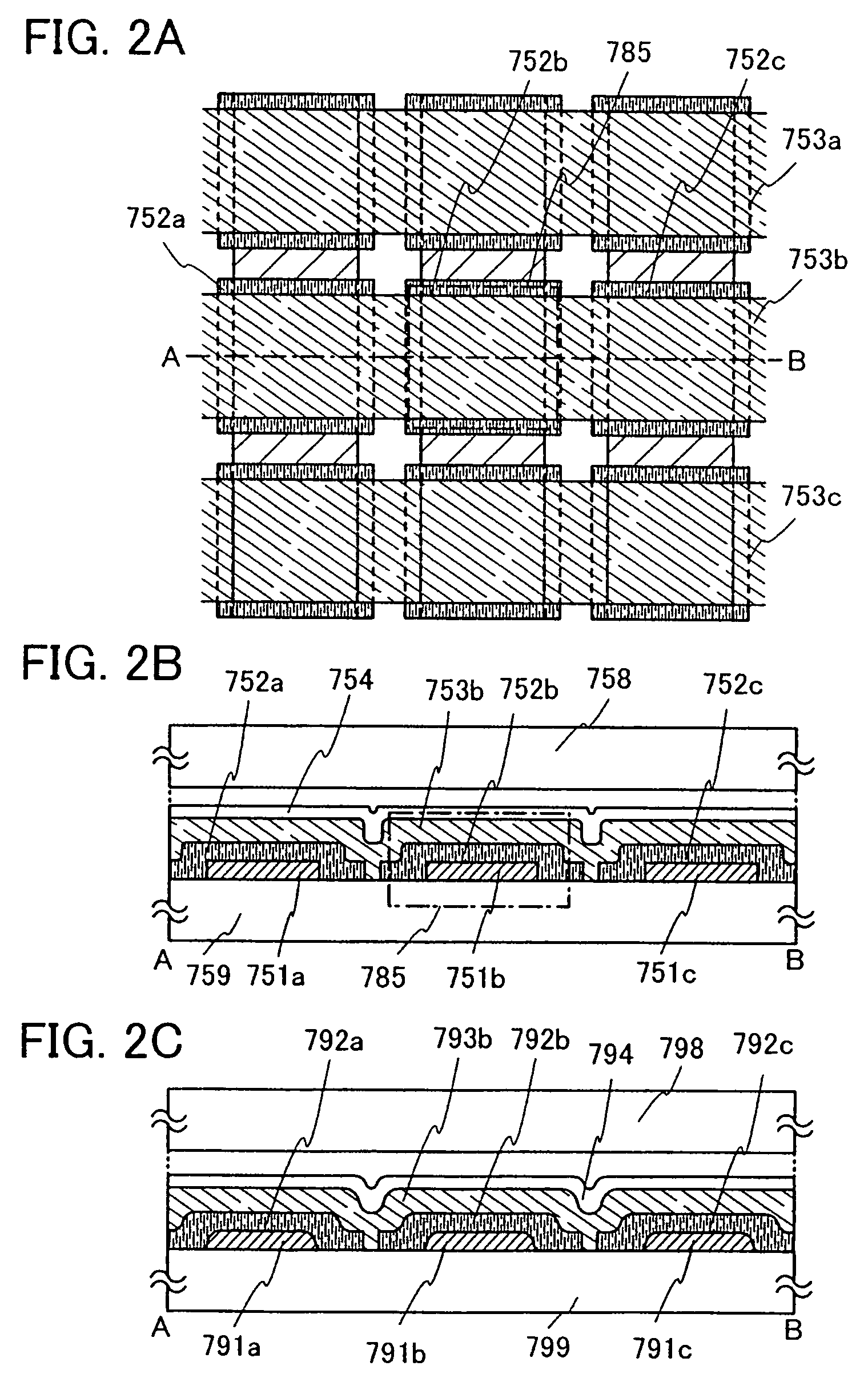
Light-emitting organic compound and EL display device utilizing the same
InactiveUS20070007870A1Improve reliabilityHighly reliable display portionIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensSimple Organic CompoundsDisplay device
By repeating a purification process of a light-emitting organic compound several times, a thin film made of the light-emitting organic compound to be used in an EL display device contains ionic impurities at the concentration of 0.1 ppm or lower and has a volume resistivity in the range of 3×1010 Ωcm or larger. By using such a thin film as a light-emitting layer in the EL device, a current caused by reasons other than the carrier recombination can be prevented from flowing through the thin film, and deterioration caused by unnecessary heat generation can be suppressed. Accordingly, it is possible to obtain an EL display device with high reliability.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
EL display device utilizing light-emitting organic compounds and method for forming the same
InactiveUS7112374B2Improve reliabilityHighly reliable display portionTelevision system detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesCharge carrierDisplay device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Liquid crystal display substrate and method for manufacturing the same, liquid crystal panel and liquid crystal display
ActiveCN102262319AAvoid separationReduce the effect of symmetryNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display substrate and a manufacturing method thereof, a liquid crystal display panel and a liquid crystal display, wherein the liquid crystal display substrate comprises an underlayment substrate and a film layer formed on the underlayment substrate; a box sealing glue groove is formed on the film layer in an edge region of the liquid crystal display substrate; and the box sealing glue groove is used for containing box sealing glue. The embodiment of the invention further provides a liquid crystal display panel, comprising an array substrate and a colour film substrate which are arranged in a folding way, wherein a liquid crystal layer is filled between the array substrate and the colour film substrate; the box sealing glue is filled in an edge region of the liquid crystal display panel; and at least one of the colour film substrate and the array substrate is adopted with the liquid crystal display substrate. The invention further provides a liquid crystal display. The liquid crystal display substrate and the liquid crystal display panel are capable of limiting the box sealing glue in a fixed region so as to effectively prevent the internal part of the box sealing glue from easily separating out ionic impurities, reduce the influence to the symmetrical characteristic of an alternating current power supply in an impurity gathering region and improve the product quality.
Owner:BEIJING BOE OPTOELECTRONCIS TECH CO LTD
Liquid crystal display panel
InactiveUS6839122B2Avoid it happening againStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
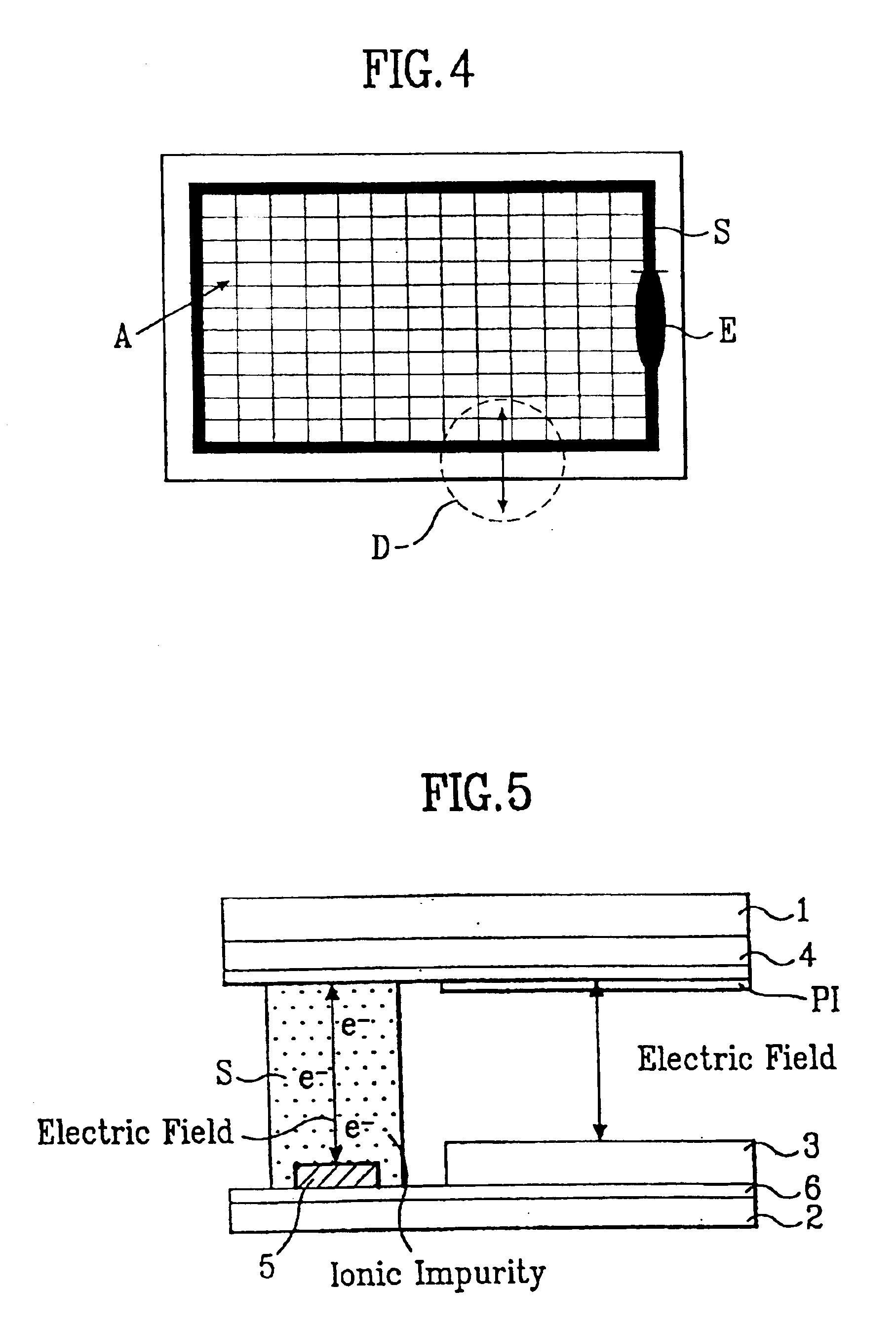
The invention relates to an LCD panel for preventing the generation of blur due to ionic impurities. The LCD panel comprises a first substrate having a common electrode; a second substrate having an active area; a seal pattern along the periphery of said active area between said first substrate and said second substrate; a liquid crystal layer between said first substrate and said second substrate in said active area; and an electrode pattern between said seal pattern and said second substrate. Alternatively, the seal pattern has outwardly projecting corner portions. An electric field is generated between the electrode pattern and the common electrode so that the ionic impurities are prevented from penetrating into the active area, and the ionic impurities in liquid crystal are captured in the seal pattern portion to prevent the generation of blur due to ionic impurities.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Rutile titania nano sols and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060110319A1Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureTitanium tetraisopropoxideHydrolysis
The present invention is related to a process of manufacturing rutile high-purity titania nano sols in a pure aqueous medium having no ionic impurities. In more detail, the present invention is related to a process for manufacturing titania nano sols, in which high-purity rutile titania nano particles are dispersed stably, through the hydrolysis of titanium tetraisopropoxide in an aqueous solution containing hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and simultaneously with the hydrolysis, formation of peroxotitanate precursors, and hydrothermal treatment of them at 50-120° C.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF CHEM TECH
Wet zinc metallurgical ultrasound purification method, device and use
InactiveCN101392328AImprove stabilityHas the prospect of industrializationPurification methodsCopper
The invention relates to an ultrasonic purification method for wet zinc smelting, and a device and application thereof. In the ultrasonic purification device for wet zinc smelting, an ultrasonic field produced by ultrasonic waves is adopted to carry out irreversible ultrasonic irradiation to wet zinc smelting solution to be purified, which causes the concentration of ionic impurities to be decreased irreversibly so as to realize the purpose of removing impurities. The application of the method can realize quick purification of required standards, greatly decreases the consumption of zinc powder, directly produces high-quality copper residue, cadmium residue and cobalt residue, and also is applicable to the treatment of the copper-cadmium residue and cobalt-nickel residue produced by wet zinc smelting purification previously.
Owner:XINGMIN TECH ZHUZHOU
Cleaning sheet and method for cleaning substrate processing apparatus
InactiveUS20060151004A1Good removal effectEliminate pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCleaning using toolsForeign matterTectorial membrane
An aim of the invention is to provide a cleaning member which causes no contamination of a substrate processing equipment by ionic impurities in the removal of foreign matters attached to the interior of the equipment through cleaning by the conveyance thereof into the equipment, a cleaning member which causes little contamination of a substrate processing equipment by metal impurities attributed to a protective film in the removal of foreign matters attached to the interior of the equipment through cleaning by the conveyance thereof into the equipment and a cleaning member which causes no contamination of a substrate processing equipment by metal impurities in the removal of foreign matters attached to the interior of the equipment through cleaning by the conveyance thereof into the equipment. The means for solving the aims of the invention concerns a cleaning sheet comprising a cleaning layer provided on one side of a base material, from which cleaning layer F−, Cl−, Br−, NO2−, NO3−, PO43−, SO42−, Na+, NH4+ and K+ are extractable with pure water each in an amount of not greater than 20 ppm (as extracted under boiling at 120° C. for 1 hour), and a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer provided on the other, a carrying material with cleaning capacity comprising the aforementioned cleaning sheet laminated on a carrying material with a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer and a method for cleaning a substrate processing equipment which comprises conveying the aforementioned carrying material with cleaning capacity into the substrate processing equipment; a cleaning sheet comprising a releasable protective film laminated on a cleaning layer, wherein the protective film is formed by a material from which metal elements such as Na, K, Ca, Mg, Al, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn or compounds thereof are transferred to a silicon wafer each in an amount of not greater than 1×1012 atoms / cm2 as calculated in terms of metal element when the protective film is brought into contact with (the mirror surface of) the silicon wafer at 23° C. for 1 minute, a carrying material with cleaning capacity comprising the aforementioned cleaning sheet laminated on a carrying material with a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer and a method for cleaning a substrate processing equipment which comprises conveying the aforementioned carrying material with cleaning capacity into the substrate processing equipment with the releasable protective film peeled off the cleaning layer; and a cleaning sheet comprising a cleaning layer provided on one side of a base material, which cleaning layer containing metal elements such as Na, K, Mg, Al, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn or compounds thereof each in an amount of not greater than 5 ppm (μg / g) as calculated in terms of metal element, and a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer provided on the other, a carrying material with cleaning capacity comprising the aforementioned cleaning sheet laminated on a carrying material with a pressure-sensitive adhesive layer and a method for cleaning a substrate processing equipment which comprises conveying the aforementioned carrying material with cleaning capacity into the substrate processing equipment.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
ActiveUS20050016929A1Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
A method and system for supplying an ultra-pure fluid to a substrate process chamber using point-of-use filtration and purification. The method and system provide ability to automatically monitor and control contamination levels in fluids in real time and to stop substrate processing when contamination levels exceed predetermined thresholds. In one aspect, the invention is a system comprising: a fluid supply line adapted to supply a fluid to the process chamber; filtration means operably coupled to the fluid supply line for removing positively and negatively charged particles from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; a purifier operably coupled to the fluid supply line in series with the filtration means for removing ionic contaminants from the fluid prior to the fluid passing into the process chamber; sensor means for repetitively measuring particle and ionic impurity levels in the fluid that has passed through the filtration means and the purifier, the sensor means producing signals indicative of the measured particle and ionic impurity levels; a controller electrically coupled to the sensor means for receiving the signals created by the sensor means, the controller adapted to respectively compare the measured particle level and the measured ionic impurity level indicated by the signals to a predetermined particle threshold and a predetermined ionic impurity threshold, wherein upon the controller determining that either the measured particle level is above the predetermined particle threshold and / or that the measured ionic impurity level is above the predetermined ionic impurity threshold, the controller further adapted to (1) activate means to alert a user, (2) cease processing of substrates in the process chamber, and / or (3) prohibit processing of substrates in the process chamber.
Owner:AKRION TECH
Cleaning sheet and method for cleaning substrate processing apparatus
InactiveCN1717285ANo pollution in the processReduce pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDetergent materialsEngineeringCleaning methods
A cleaning member which does not contaminate a substrate processing apparatus with an ionic impurity when conveyed into the apparatus for removing foreign materials within the apparatus is disclosed. A cleaning member which does not contaminate a substrate processing apparatus with a metallic impurity when conveyed into the apparatus for removing foreign materials within the apparatus is also disclosed. Specifically, a cleaning sheet characterized in that a cleaning layer wherein pure water extraction amounts (extracted for one hour while boiling at 120 1 / 2 C) of F<->, Cl<->, Br<->, NO2<->, NO3<->, PO4<3->, SO4<2->, Na<+>, NH4<+>, and K<+> are respectively 20 ppm or less is provided on one surface of a supporting body and an adhesive layer is provided on the other surface is disclosed. A cleaning sheet characterized in that a cleaning layer wherein respective contents of Na, K, Mg, Al, Ca, Ti, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn and compounds thereof are 5 ppm (mug / g) or less when calculated in terms of respective metal elements is provided on one surface of a supporting body and an adhesive layer is provided on the other surface is also disclosed.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
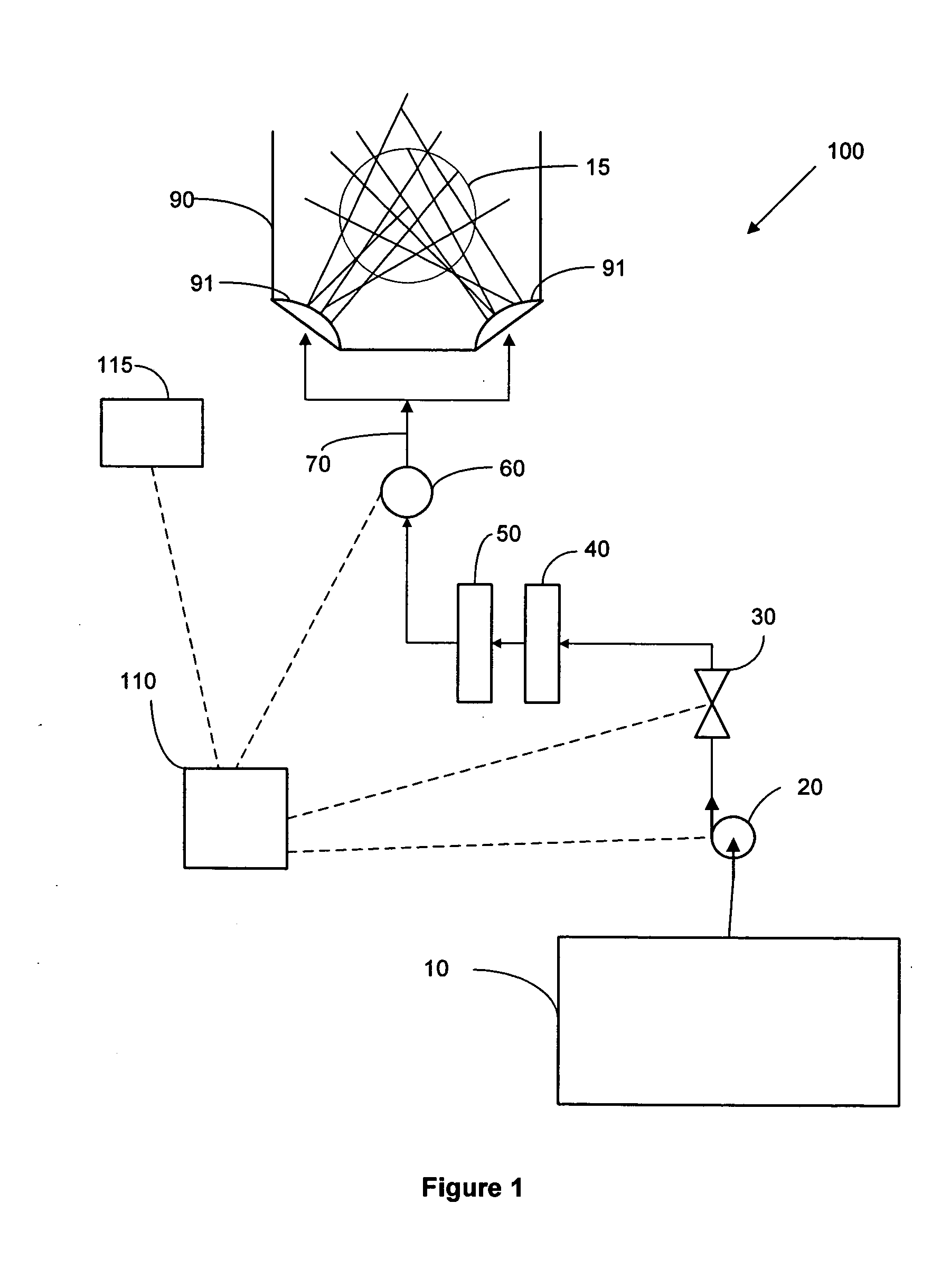
Electrodeionization deionized water producing apparatus
InactiveUS7201832B2Simple structureReduce assemblySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisWater flow
In the electrodeionization deionized water producing apparatus, water is passed through a deionizing chamber(s) packed with an organic porous ion exchange material having a three-dimensional network structure to remove ionic impurities in the water, thereby producing deionized water. At the same time, a DC electric field is applied to the deionizing chamber(s) to discharge ionic impurities adsorbed on the organic porous ion exchange material outside the system, wherein the DC electric field is applied so that the ions to be discharged may electrophoretically move in the direction reverse to the flow of water through the organic porous ion exchange material.
Owner:ORGANO CORP
Process for extracting lithium from lithionite by fluorine chemistry
InactiveCN101885496AReduce production energy consumptionNo pollution hazardLithium compoundsReaction temperatureLiquid solid
The invention provides a process for extracting lithium from lithionite by fluorine chemistry, comprising the following steps: throwing raw materials of lithionite powder, an additive and sulfuric acid based on the weight ratio of 1: (0.1-2): (0.5-5) into a pre-reactor, and then stirring to react or simply stirring and then throwing the raw materials into the reactor to react, wherein, the additive is one or more of a fluorine-containing mineral substance, salt or acid; reaction conditions in the pre-reactor are as follows: preheating the raw materials at the temperature of 50-150 DEG C for 0.1-2 hours, and then transferring into the reactor to react at the temperature of 150-350 DEG C for 0.5-4 hours; immediately evacuating the gas generated during the reaction process; leaching the obtained reaction residue with water and then carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain a sulfate liquor; and adjusting pH into 5.0-10.0 to eliminate ionic impurities such as aluminum, magnesium, calcium, ferrum and the like; and after the liquid-solid separation is carried out, concentrating the sulfate liquor, precipitating lithium ions and then filtering to obtain a crude lithium salt product or the corresponding refined lithium salt product as required. The process of the invention has the advantages of low reaction temperature, small production energy consumption and high lithium extraction efficiency; and various valuable components of the lithionite mineral substance can be comprehensively utilized during the production process of lithium salt.
Owner:江西海汇龙洲锂业有限公司
Display device
InactiveUS20080316410A1Improve reliabilityReduce manufacturing costLiquid crystal compositionsElectroluminescent light sourcesImaging qualityConductive polymer
To provide display devices with improved image quality and reliability or display devices with a large screen at low cost with high productivity, an electrode layer containing a conductive polymer is used as an electrode layer for a display element, and the concentration of ionic impurities contained in the electrode layer containing a conductive polymer is reduced (preferably to 100 ppm or less). Ionic impurities are ionized, and easily become mobile ions, and they deteriorate a liquid crystal layer or an electroluminescent layer, which is used for a display element. Therefore, an electrode layer containing a conductive polymer, in which such ionic impurities are reduced is provided; thus, reliability of the display device can be improved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
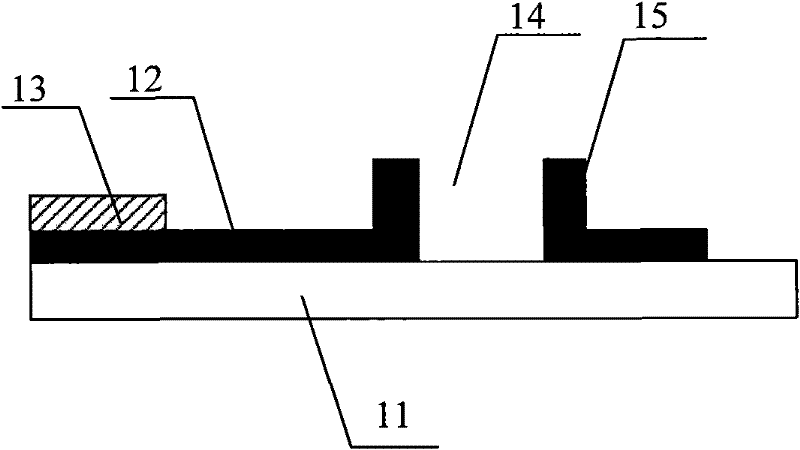
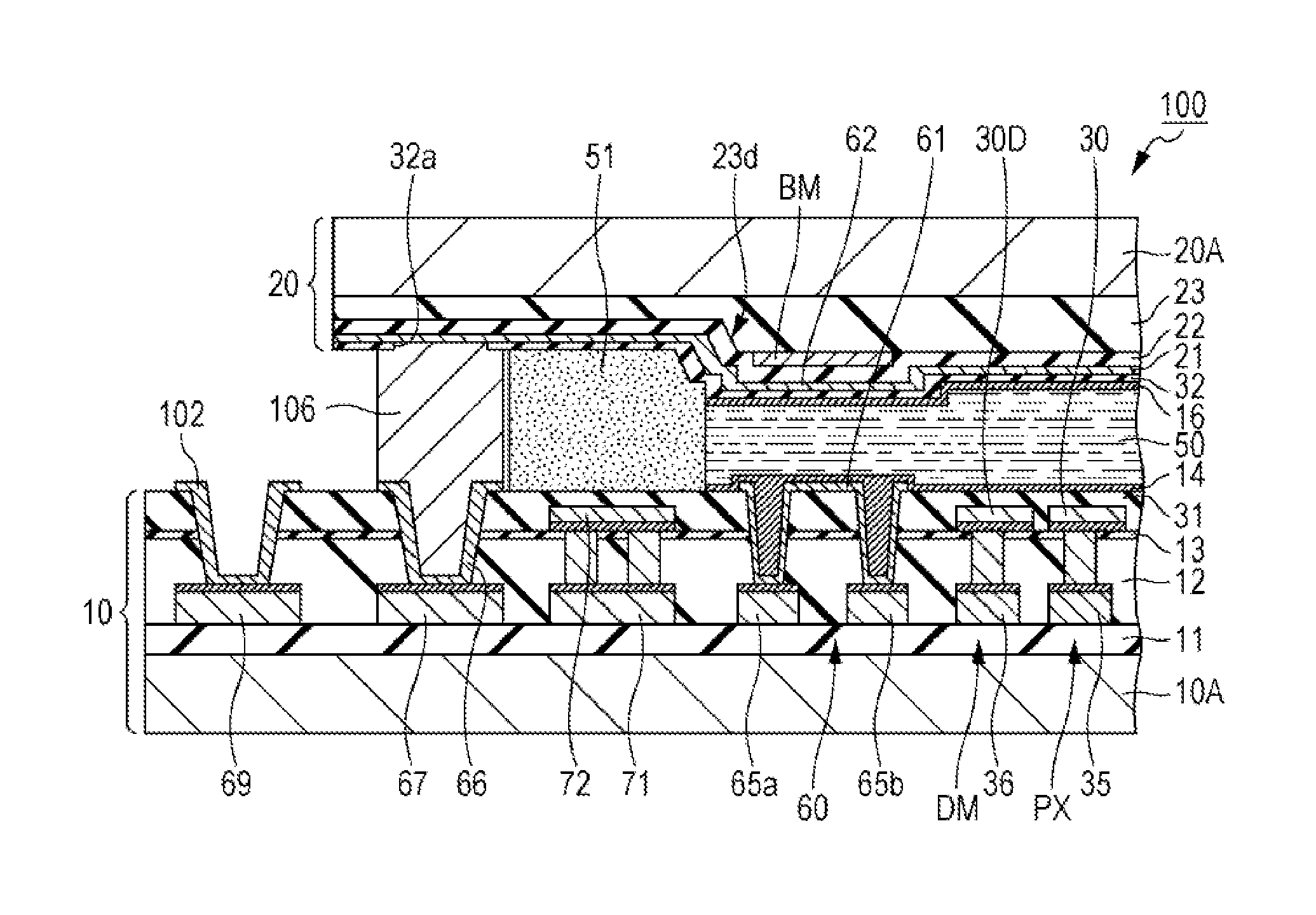
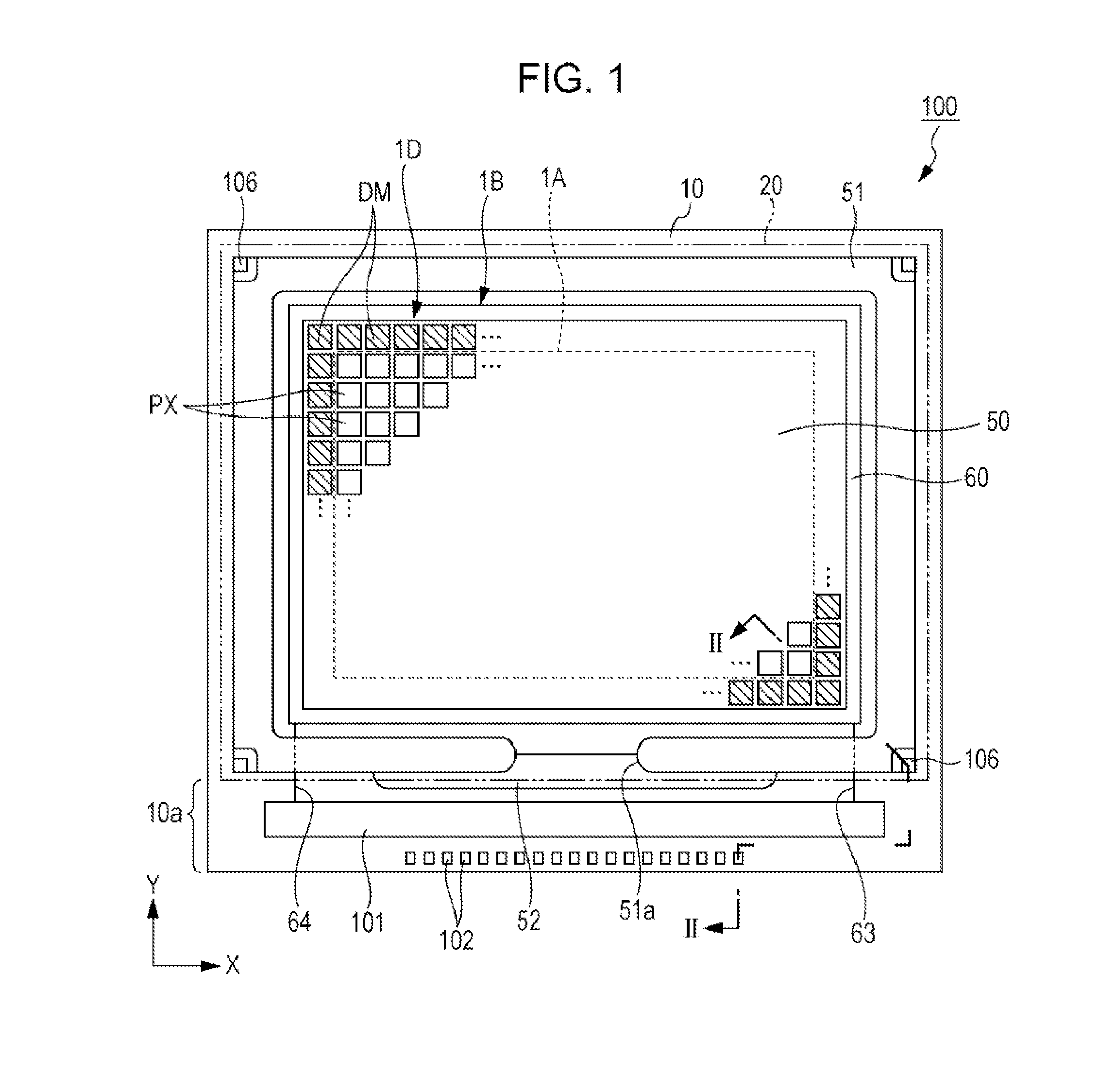
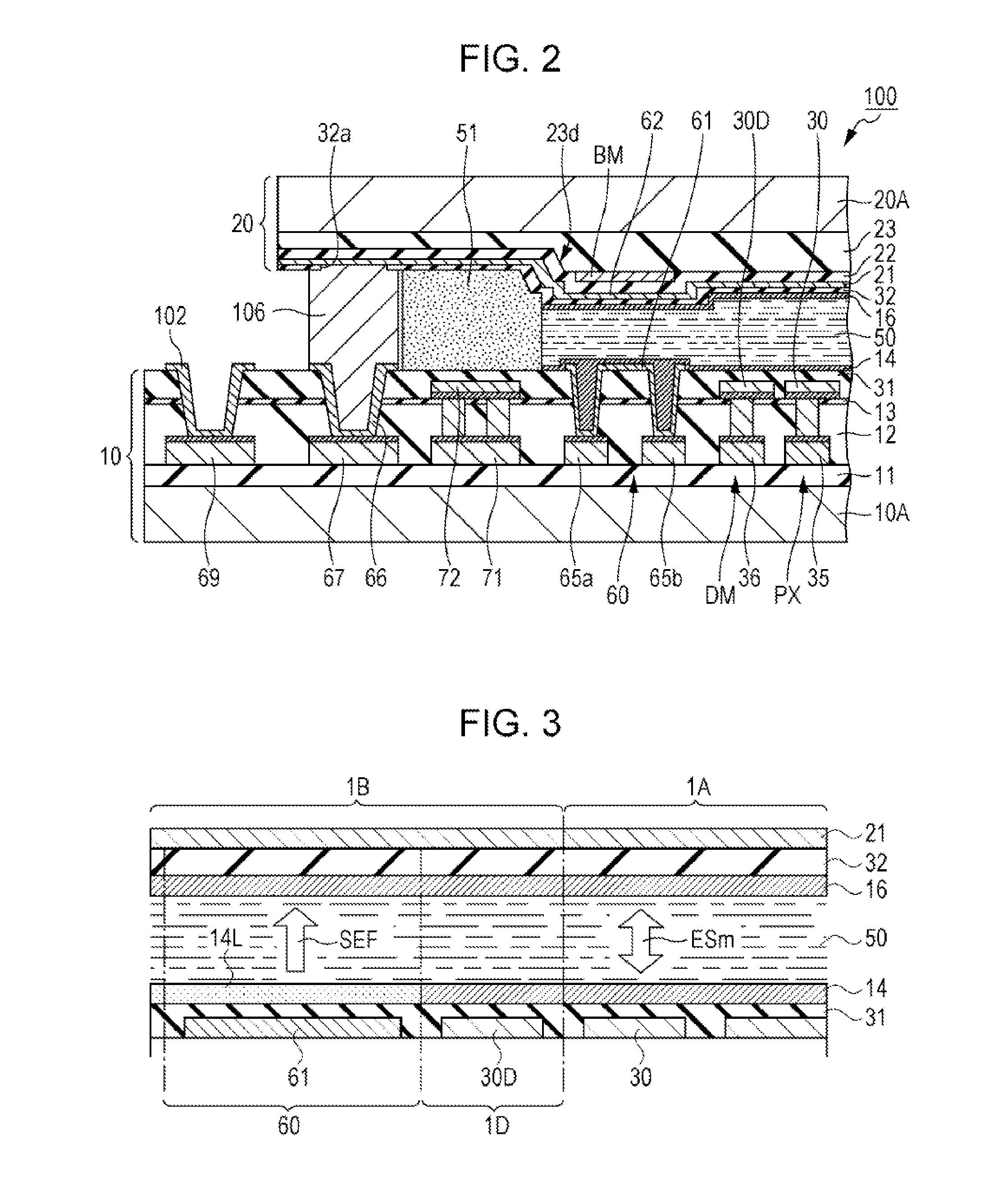
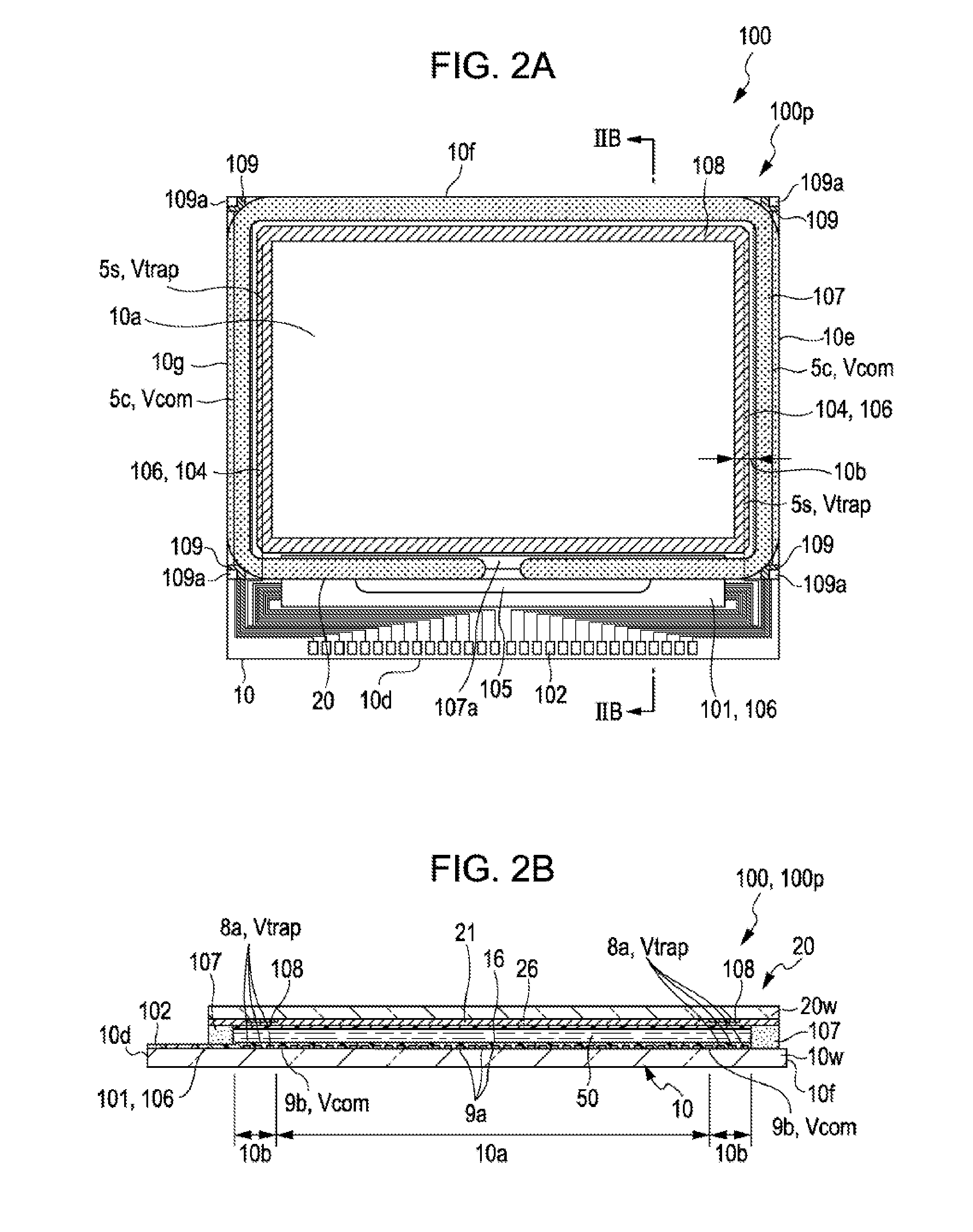
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20140160413A1Long product lifeSimple manufacturing processNon-linear opticsImpurityElectron
An electro-optical device includes a first substrate, a second substrate and a liquid crystal, and has a display region and a peripheral region. The peripheral region of the first substrate has a peripheral electrode and a first orientation film covering the peripheral electrode. Then, since the density of first orientation film in the display region is different from the density of the first orientation film in the peripheral region, it is possible to efficiently capture ionic impurities present in the liquid crystal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
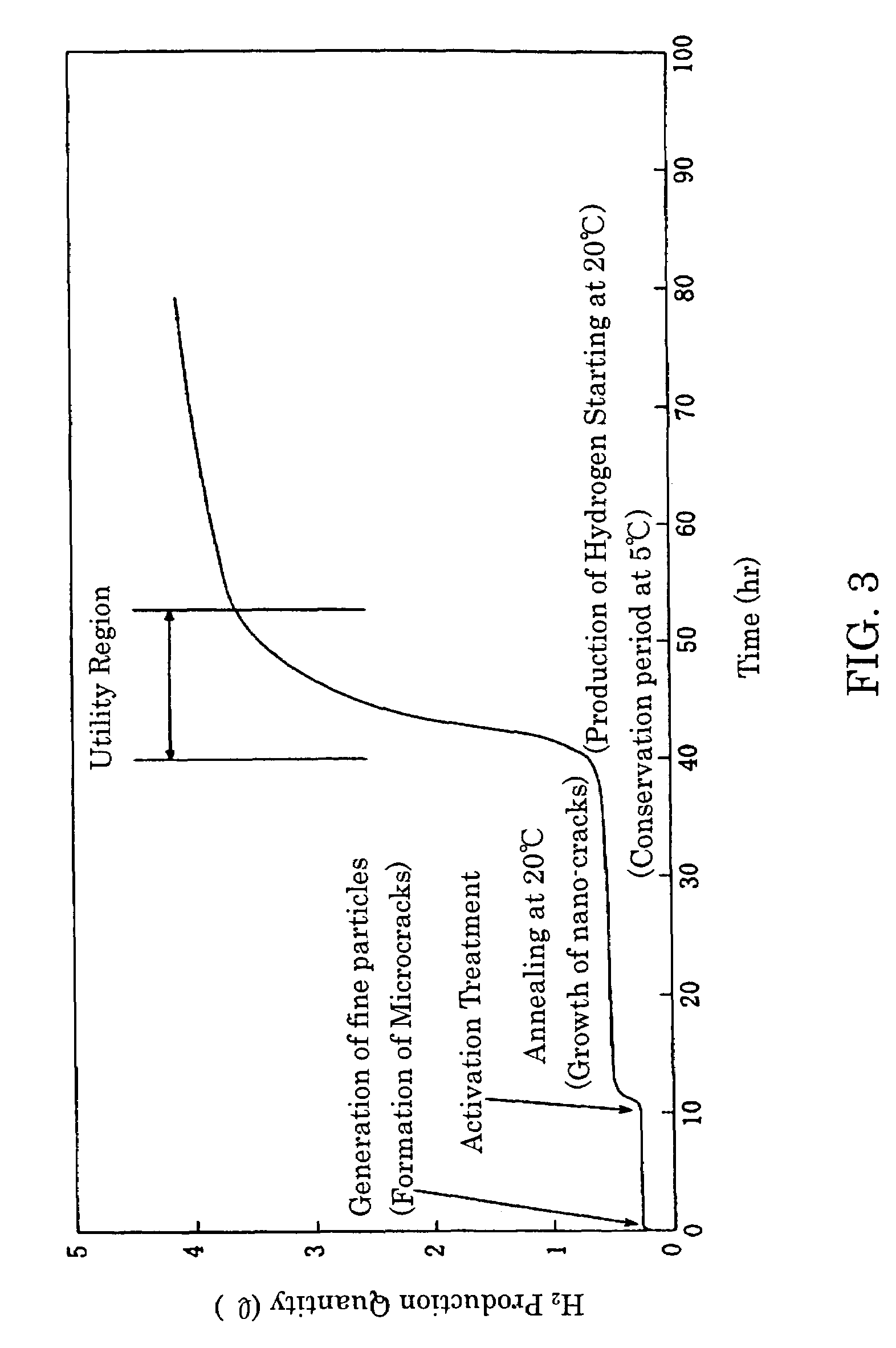
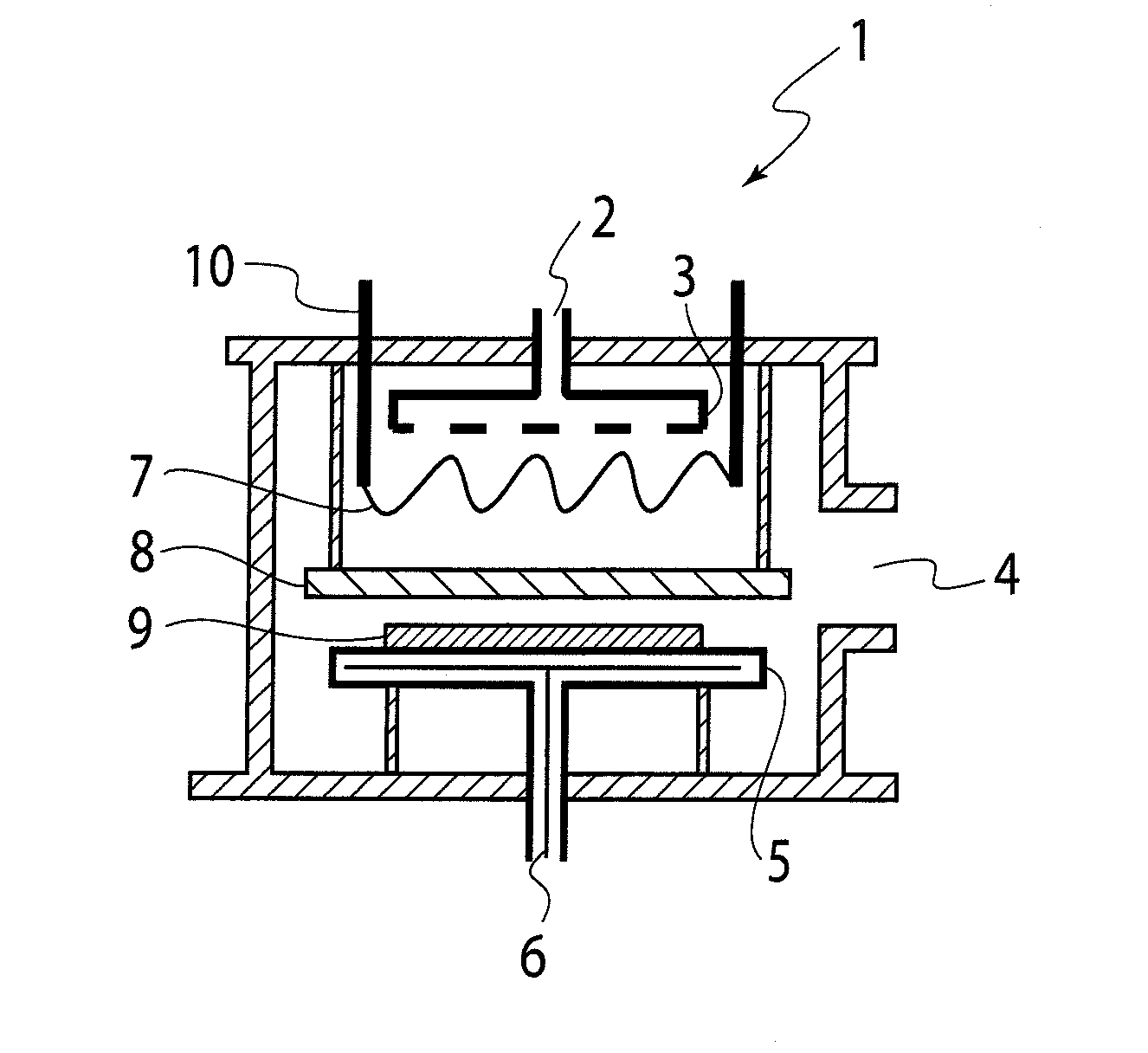
Method for producing hydrogen gas utilizing mechano-corrosive reaction
InactiveUS7008609B2Low costSimple and safe processAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationHydrogen productionCorrosion reactionChemical reaction
There is provided a method of producing hydrogen gas serving as fuel for a portable fuel cell, whereby hydrogen gas can be provided easily, safely, and at a low cost. To that end, the method of producing hydrogen gas comprises the steps of causing friction and mechanical fracture accompanying the friction to occur to a metallic material under water and increasing thereby chemical reactivity of atoms of the metallic material, in close proximity of the surface thereof; wherein water molecules are decomposed by accelerating corrosion reaction of water with the metallic material. Further, for the metallic material, an aluminum or aluminum alloy material is used as industrial waste including refuse and cutting chips (curls) of an industrial aluminum material. Meanwhile, pure water not substantially containing ionic impurities and organic molecules is used for the water.
Owner:HYDRO DEVICE
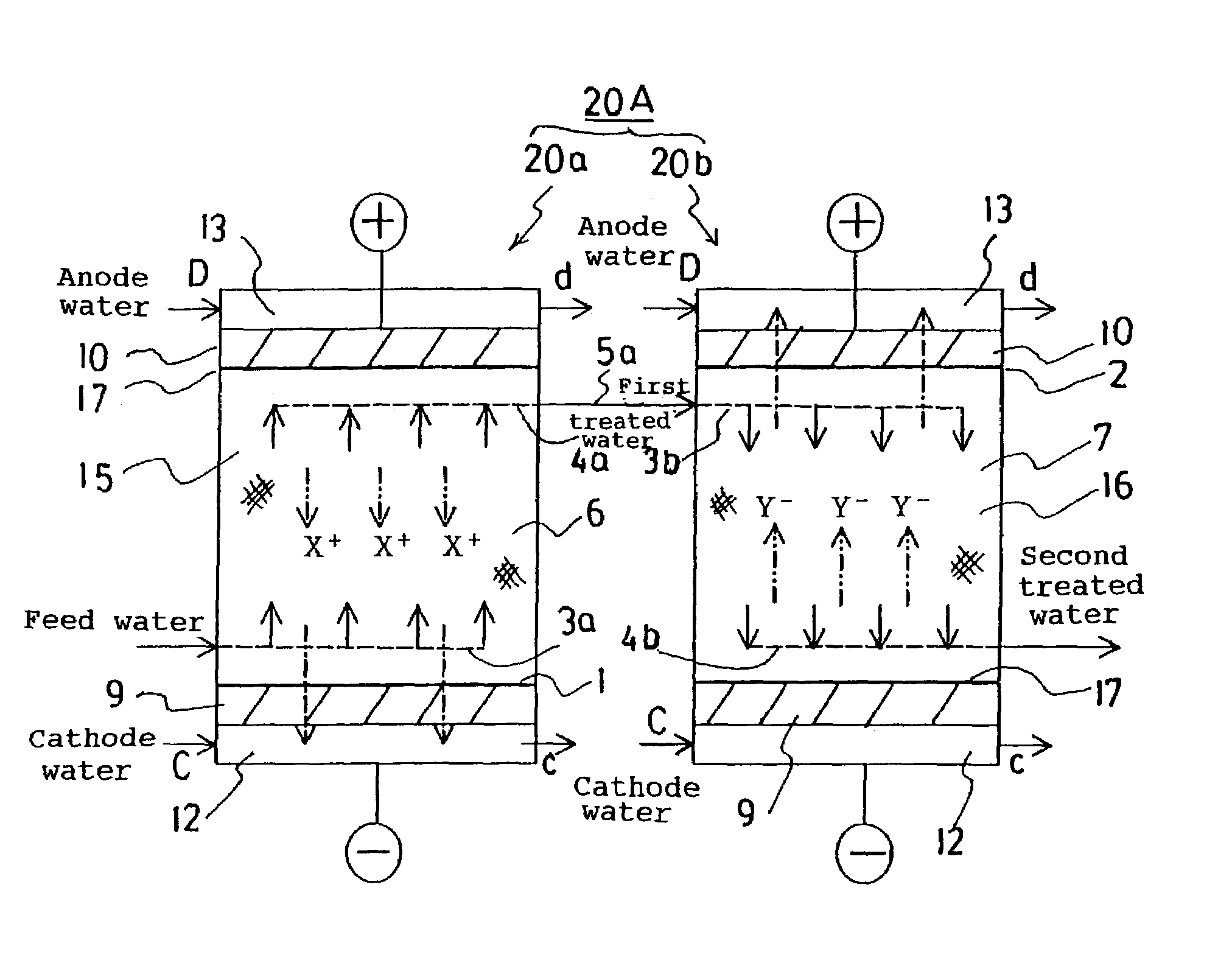
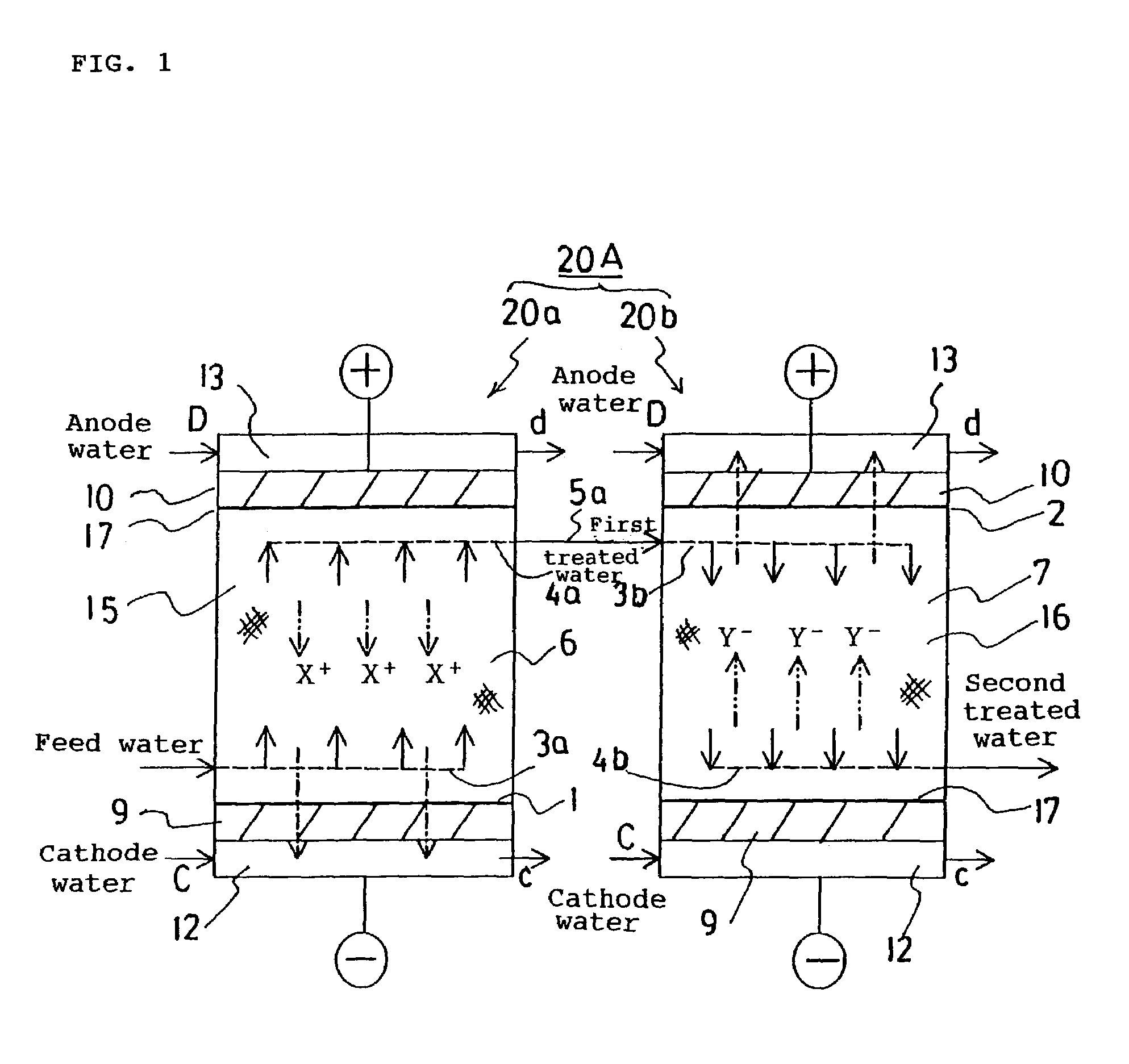
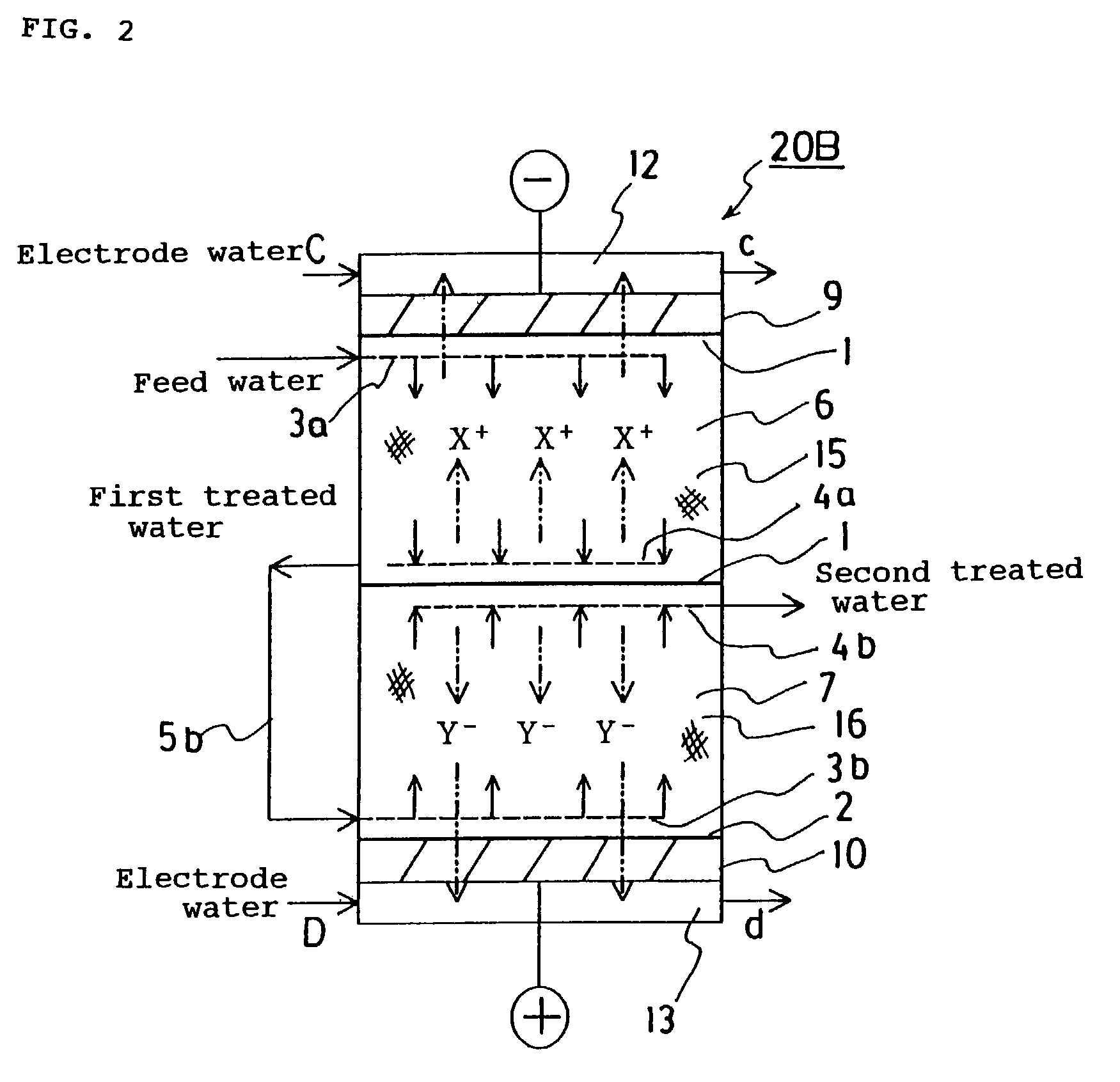
Driving method for liquid crystal device, liquid crystal device, and electronic device
InactiveCN104103250AImprove the display effectStatic indicating devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityEngineering
The invention provides a driving method for a liquid crystal device, a liquid crystal device, and an electronic device with the liquid crystal device, which can effectively capture ion impurities in a liquid crystal layer. In the liquid crystal device (100), pixel electrodes (15) and a common electrode (23) that opposes the pixel electrodes (15) on another side of a liquid crystal layer (50) are formed in a display region (E1) serving as a first region, and dummy pixel electrodes (121, 122) serving as first electrodes are formed in a dummy pixel region (E2) serving as a second region. A driving method for the liquid crystal device (100) applies a voltage that is lower than a threshold voltage at which the transmissibility of liquid crystals changes between the dummy pixel electrodes (121, 122) and the common electrode (23). Accordingly, the dummy pixel electrodes (121, 122) can function as an electricity parting portion (120) and ionic impurities can be pulled from the display region (E1) to the dummy pixel electrodes(121, 122).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Extraction method of monosialotetrahexosylganglioside
InactiveCN102020684AIncrease consumptionSave solventSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationIon exchangeSilica gel
The invention discloses an extraction method of monosialotetrahexosylganglioside. The extraction method mainly comprises the following steps: separating G1S in the total extract of a brain tissue total extract by adopting a macroporous resin for separating a hydrophilic and lipophilic natural product through an adsorptive process, wherein the hydrophilic and lipophilic natural product is sugar and the like; and separating out high-quality monosialotetrahexosylganglioside (GM1) dry power by common silicagel column chromatography. As different metal ionic impurities still exist in the product subject to the silicagel column chromatography, a cation exchange column is used for further ionic exchange. After improving the traditional method, a large amount of solvent and time are saved, the yield is improved, and the cost is lowered to a great extent.
Owner:胡增荣 +1
Printing ink, metal nanoparticles used in the same, wiring, circuit board, and semiconductor package
InactiveCN102549086AGood dispersionDuplicating/marking methodsInksDispersion stabilityTotal solid content
Disclosed is a printing ink comprising Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles, which obtains excellent dispersion properties and successive dispersion stability without using additives such as dispersing agents. Specifically disclosed is a printing ink that comprises Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles and has no more than 2,600 ppm of ionic impurities in the total solid content. The printing ink is obtained by dispersing the Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles, which have no more than 2,600 ppm of ionic impurities in the total solid content, in a dispersion medium.
Owner:RESONAC CORPORATION
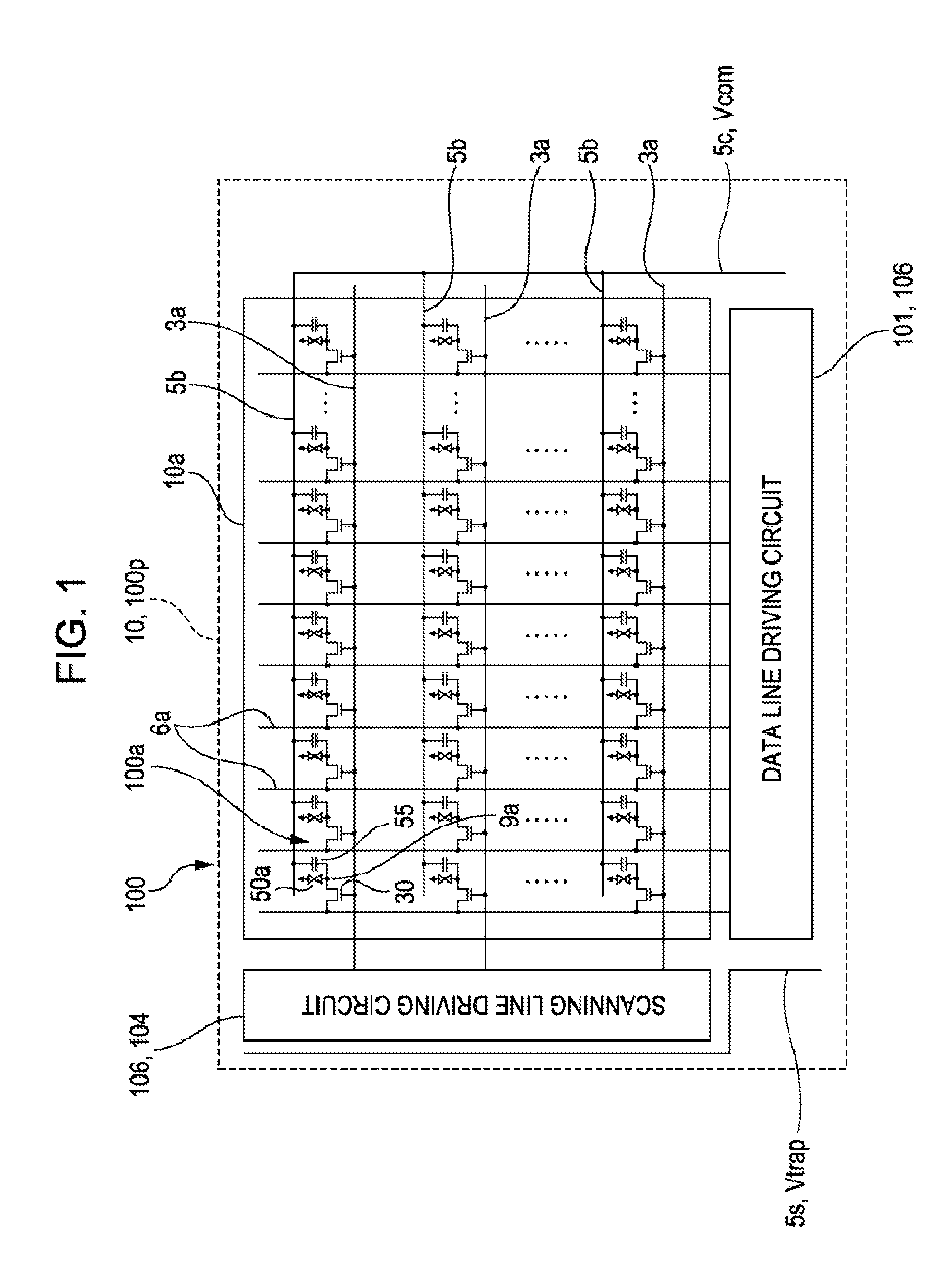
Liquid crystal display device
Right end portions of upper half lines in the scanning signal lines are connected to a semiconductor integrated circuit device via leading lines provided on a right side thereof, and left end portions of lower half lines in the scanning signal lines are connected to a semiconductor integrated circuit device via leading lines provided on a left side thereof. Therefore, the size of a liquid crystal display device in a widthwise direction thereof can be reduced. Also, since crossing points of the leading lines connected to the scanning signal lines are arranged outside the right side edge portion and a left side edge portion of a light shielding film, such a drawback can be prevented from occurring that ionic impurities eluted from the sealing member due a potential difference between the leading lines and the light shielding film corrode the leading lines.
Owner:CASIO COMPUTER CO LTD
Polyamide resin, epoxy resin compositions, and cured articles thereof
InactiveUS20090081466A1Sufficient flexibilityImprove electrical performanceSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentEpoxyPolyamide
Provided herein are a phenolic hydroxyl group-containing aromatic polyamide resin and a resin composition containing the resin, such as an epoxy resin composition containing an epoxy resin. The phenolic hydroxyl group-containing aromatic polyamide resin has a structure represented by the following formula (1):wherein m and n are average values satisfying the following formula: 0.005≦n / (m+n)<0.05, m+n is a positive value of 2 to 200, Ar1 is a bivalent aromatic group, Ar2 is a phenolic hydroxyl group-containing bivalent aromatic group, and Ar3 is a bivalent aromatic group. Such a phenolic hydroxyl group-containing aromatic polyamide resin has a low ionic impurity content and improved adhesive properties as well as excellent properties inherent in conventional phenolic hydroxyl group-containing aromatic polyamide resins, such as the ability to allow a cured epoxy resin composition to have excellent flexibility, electrical properties, flame retardancy, and the like.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD
Method for refining polyglutamic acid in biologic fermentation broth by using ultrafiltration and nanofiltration techniques
ActiveCN103665371AOvercome the difficult problem of removing bacteriaReduce usageUltrafiltrationPaper document
The invention discloses a method for refining polyglutamic acid in biologic fermentation broth by using ultrafiltration and nanofiltration techniques, which belongs to the technique field of biologic synthesis and purification. Aiming at the distribution characteristics of target extracts and molecular weights of impurities in the fermentation broth, the method is used for effectively separating gamma-PGA of different molecular weights with the combination of modern film separation techniques, and the method mainly comprises the following steps: reducing the viscosity of kieselguhr, filtering and sterilizing, heating to be combined with ultrafiltration decontamination proteins and macromolecule active organisms, removing metal ions and impurities with positive charges by using a cation exchange resin, decoloring, subsequently removing micromolecule and ionic impurities in a nanofiltration mode, performing ultrafiltration and extraction at different stages so as to obtain refined gamma-PGA of different molecular weights. The extraction yield is kept greater than 92%, which is higher than the highest yield of 90.6% reported in documents, high market pertinence is achieved, production can be performed according to demands, and the economic benefits are professionally improved as gamma-PGA of different molecular weights are refined with the combination of ultrafiltration and nanofiltration techniques.
Owner:天津北洋百川生物技术有限公司
Aqueous dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene and process for its production
InactiveUS20070015857A1Low viscosityImprove frictional stabilityFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationCooking & bakingCarboxylic acid
An aqueous dispersion of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) comprising from 55 to 70 mass % of PTFE fine particles having an average particle diameter of from 0.1 to 0.5 μm, from 0.0001 to 0.02 mass %, based on PTFE, of a specific C8 fluorine-containing carboxylic acid salt (APFO) such as ammonium perfluorooctanoate, from 1 to 20 mass %, based on PTFE, of a specific nonionic surfactant and from 0.01 to 0.3 mass %, based on PTFE, of a specific C5-7 fluorine-containing carboxylic acid salt such as ammonium perfluorohexanoate. The aqueous dispersion of PTFE has excellent properties which can form crack-resistant coatings which do not undergo coloration during baking or form problematic ionic impurities by improving the friction stability of aqueous PTFE dispersions even at APFO concentrations without viscosity increase.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Process for producing latent catalyst and epoxy resin composition
InactiveUS20090234080A1High yieldGood fluidityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEpoxyPhosphonium
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Printing ink, metal nanoparticles used in the same, wiring, circuit board, and semiconductor package
InactiveUS20120170241A1Satisfactory dispersibilityMaterial nanotechnologyCircuit arrangements on support structuresDispersion stabilityTotal solid content
Disclosed is a printing ink comprising Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles, which obtains excellent dispersion properties and successive dispersion stability without using additives such as dispersing agents. Specifically disclosed is a printing ink that comprises Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles and has no more than 2,600 ppm of ionic impurities in the total solid content. The printing ink is obtained by dispersing the Cu- and / or CuO-containing metal nanoparticles, which have no more than 2,600 ppm of ionic impurities in the total solid content, in a dispersion medium.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
Process for extracting lithium from lithium pyroxene concentrate by using fluorine chemistry
InactiveCN102417995AReduce production energy consumptionHigh Lithium Extraction RateProcess efficiency improvementSlagPotassium
The invention provides a process for extracting lithium from lithium pyroxene concentrate by using fluorine chemistry. The process comprises the following steps of: firstly, uniformly mixing raw materials, such as alpha-lithium pyroxene concentrate powder, an additive and sulfuric acid according to weight ratio of 1:(0.1-2):(0.5-5); secondly, feeding the uniformly-mixed raw materials into a reactor and finishing the reaction and timely extracting gas generated in the reaction process; thirdly, leaching reaction slag retained in the reactor with water and carrying out solid-liquid separation on the reaction slag to obtain a sulfate solution and remove ionic impurities in the solution, such as potassium, sodium, aluminum, magnesium, calcium, ferrum and the like; and fourthly, after the impurities are filtered, concentrating residual solution to obtain a precipitation containing lithium ions, filtering to obtain a rough lithium salt product and producing refined lithium salt according to the requirement. The process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of low reaction temperature, low production energy consumption and high lithium extraction rate; the lithium can be directly extracted from alpha-lithium pyroxene without crystal form transformation; and various valuable components of the lithium pyroxene can be integrally utilized while the lithium salt is produced.
Owner:SHANDONG RUIFU LITHIUM IND
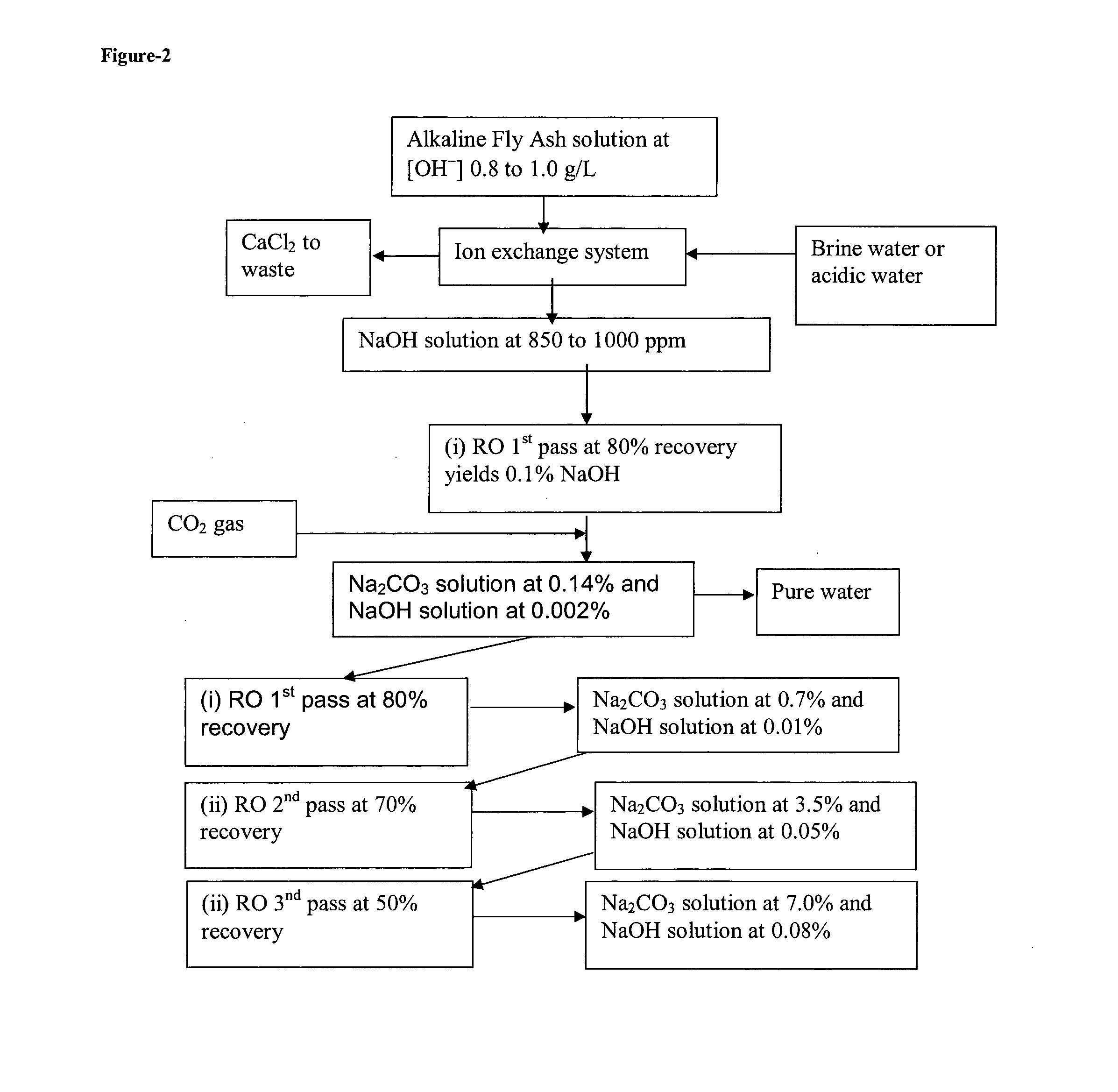
Using alkaline fly ash and similar byproducts in an ion-exchange/reverse osmosis process for the production of sodium carbonate
Owner:OLFI MOHAMMED +1
Purification continuous production process for high-purity hydrogen peroxide
InactiveCN1699144AOvercoming utilizationOvercoming separationPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesIon exchangeCarbon adsorption
The invention relates to a purification continuous production process for high-purity hydrogen peroxide, which comprises preparing technical grade hydrogen peroxide raw material, feeding into macroporous adsorption resin column through pumps, carrying out organic carbon adsorption, feeding hydrogen peroxide into separate anion and cation exchange resin columns for ion exchange, inputting the hydrogen peroxide into anionic and cationic ion-exchange resin mixing column, carrying out ion exchange again, removing detrimental ionic impurities, inputting into polyvinylidene fluoride microfilter with a bore diameter of 0.05um to 0.1um, to as to remove the impurity substance.
Owner:李祥庆
Method for preparing lithium oxalyldifluoroborate
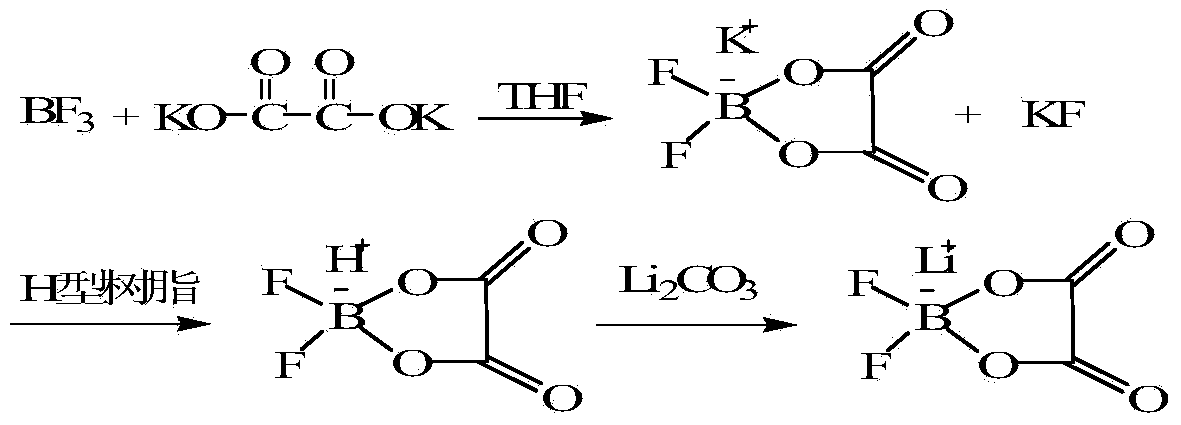
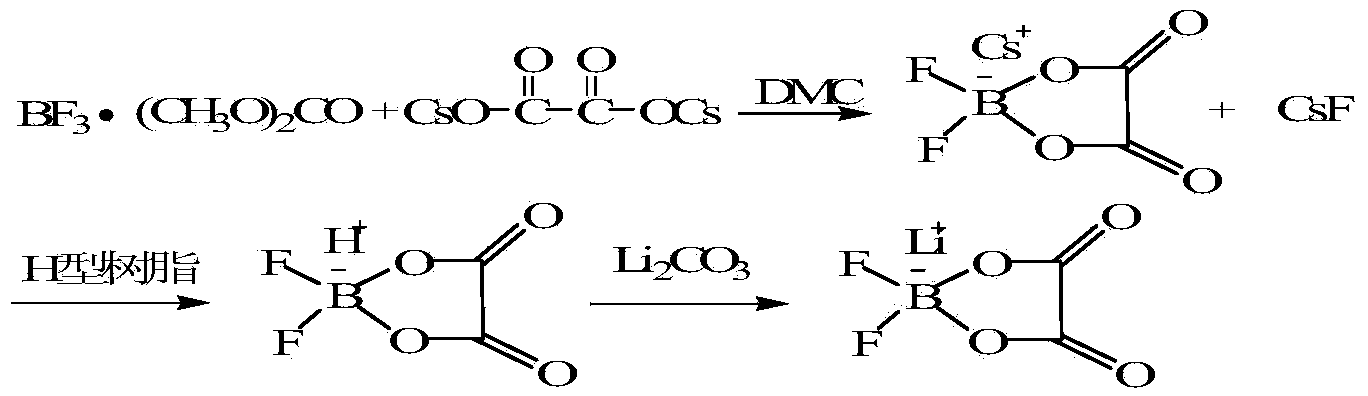
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium oxalyldifluoroborate. According to the method, first, a boracic compound reacts with potassium oxalate (rubidium or cesium) to form difluoro oxalic acid potassium borate (rubidium or cesium) through synthesis; then, a difluoro oxalic acid potassium borate (rubidium or cesium) water solution slowly flows through superacidulated cationic resin for exchange, and an appropriate amount of Li2CO3 or LiOH is added into a collected difluoro oxalic acid boric acid water solution for the neutral reaction to obtain a crude lithium oxalyldifluoroborate product; high-purify lithium oxalyldifluoroborate is obtained through recrystallization purification. The method has the advantages that operation steps are simple, preparation conditions are moderate, cost is low, ionic impurities can be effectively controlled, and the method is suitable for industrialized mass production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TINCI MATERIALS TECH +1
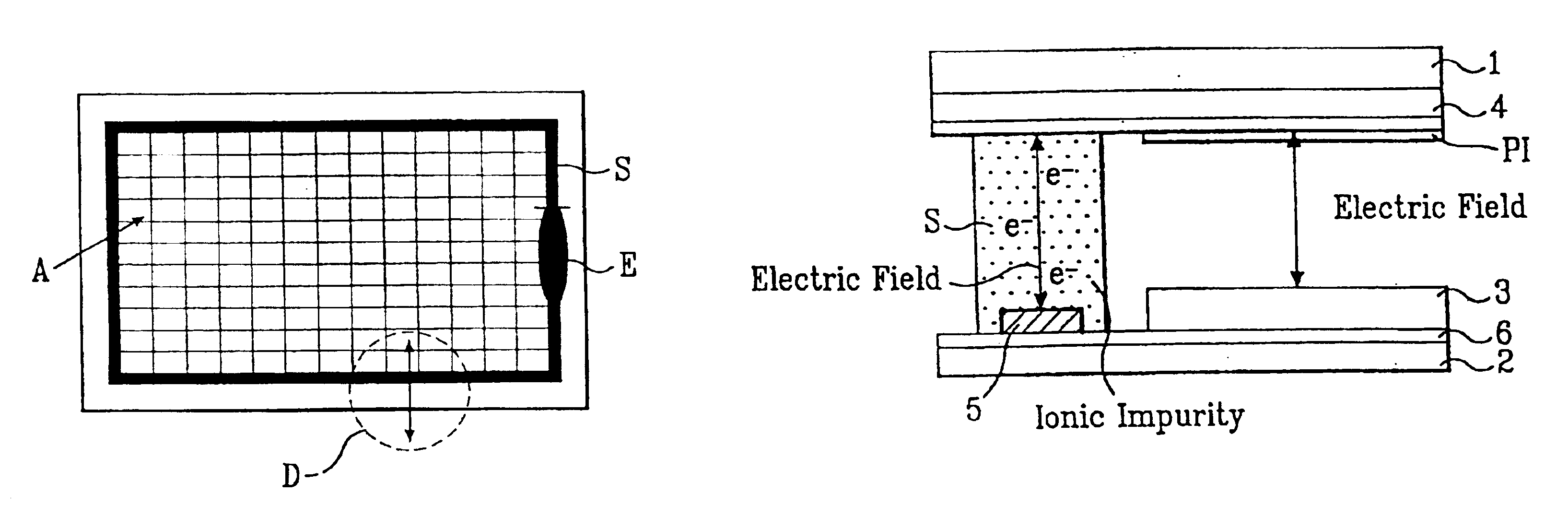
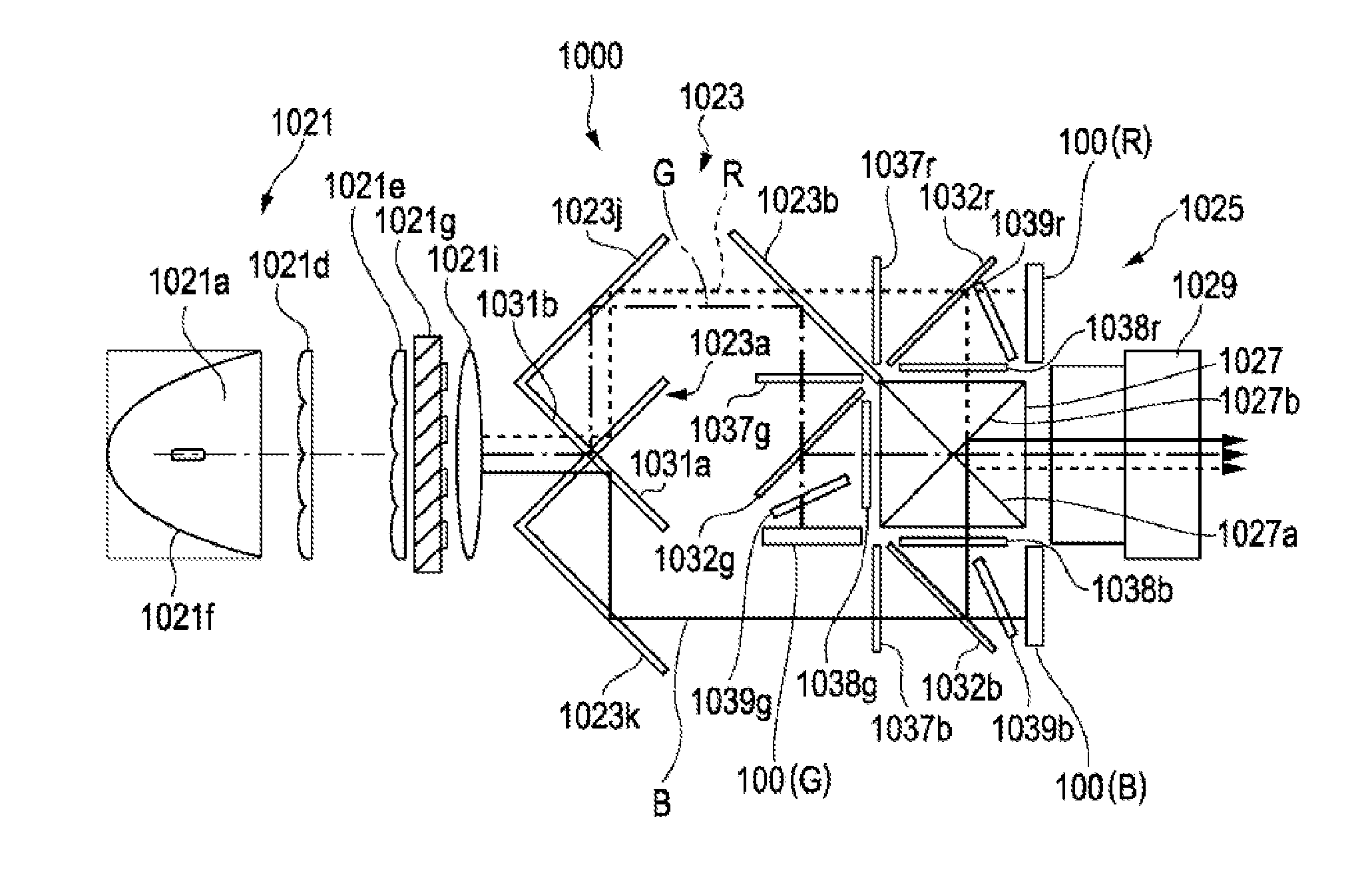
Liquid crystal device and projection-type display apparatus
In an element substrate of a liquid crystal device, in a peripheral region interposed between an image display region and a seal material, a peripheral electrode to which a potential is applied for trapping ionic impurities which is different from a common potential applied to a dummy pixel electrode or the like is formed. In the peripheral electrode, an electrode width of a first portion opposing a sealing material provided at a liquid crystal injection opening of the seal material is set to be greater than electrode widths of the other portions.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
System and method for point-of-use filtration and purification of fluids used in substrate processing
ActiveUS7311847B2Reduce and eliminate particleReduce and eliminate and ionicIon-exchanger regenerationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectricityFiltration
Owner:AKRION TECH
Method for preparing rhodium chloride hydrate from oxo synthesis waste rhodium catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing rhodium chloride hydrate from oxo synthesis waste rhodium catalyst through recycling rhodium, comprising the steps of adding certain amount of carbon into oxo synthesis reaction waste rhodium catalyst and then putting the catalyst into high temperature furnace, burning the catalyst based on certain temperature control program under the aerobic condition, keeping the temperature constant for certain time at the end of procedure to ensure the basic carbonization of the material, turning into anaerobic high temperature roasting,isolating the air and cooling the temperature to the room temperature after high-temperature roasting to obtain the active rhodium ashes, adding concentrated hydrochloric acid, dropping hydrogen peroxide while stirring, dissolving the active rhodium therein to obtain the coarse rhodium chloride acid solution,using the ion exchange method well known in this field to remove such ionic impurities as Fe, Ni and Ca in the coarse rhodium chloride acid solution, and then obtaining the rhodium chloride hydrate after concentration and drying. The filter residues generated from filtration are the carbon residues and used after being returned. This method is characterized by high efficiency, simple operation and small rhodium loss with rhodium yield exceeding 99%.
Owner:CNOOC TIANJIN CHEM RES & DESIGN INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com