Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
85 results about "Immunophenotyping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
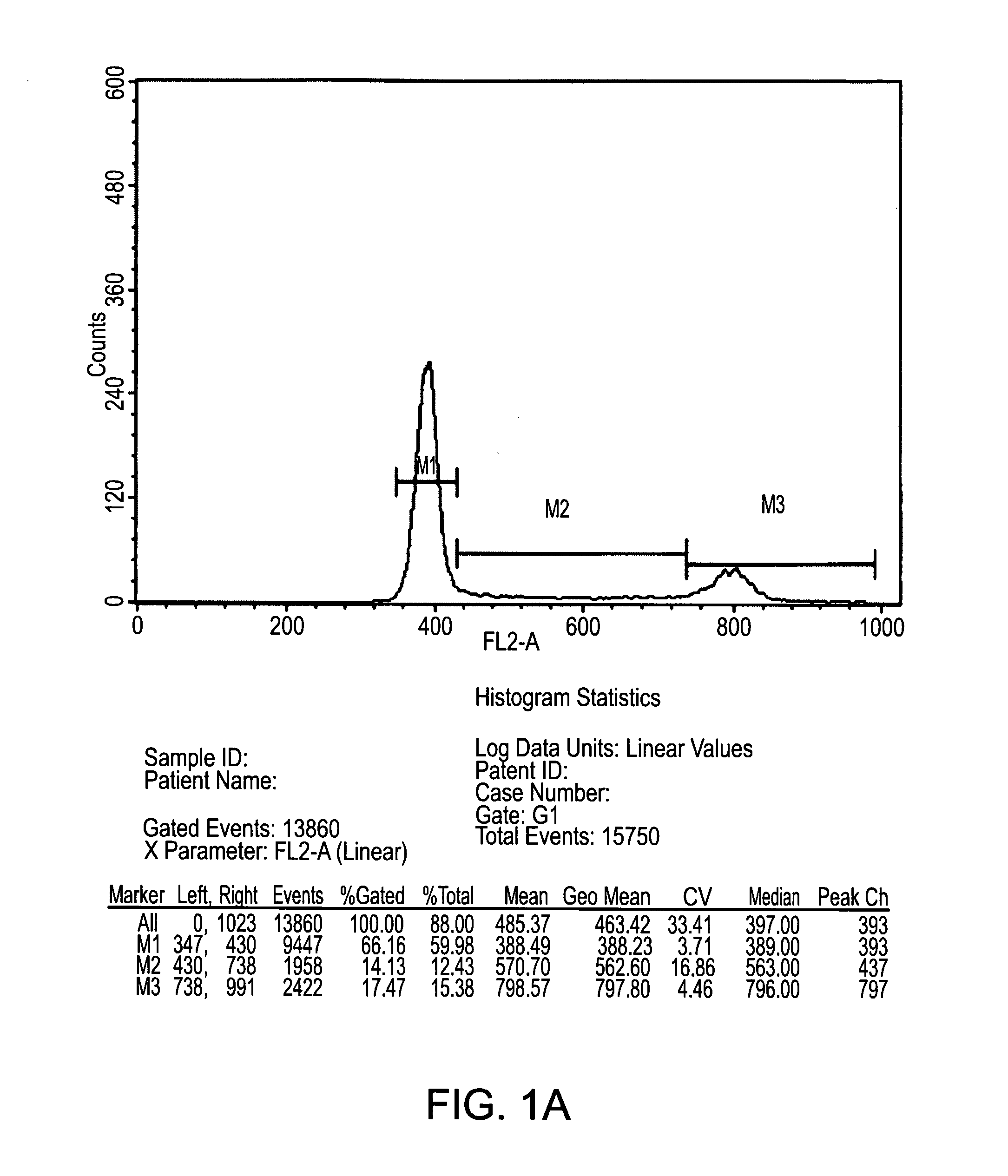
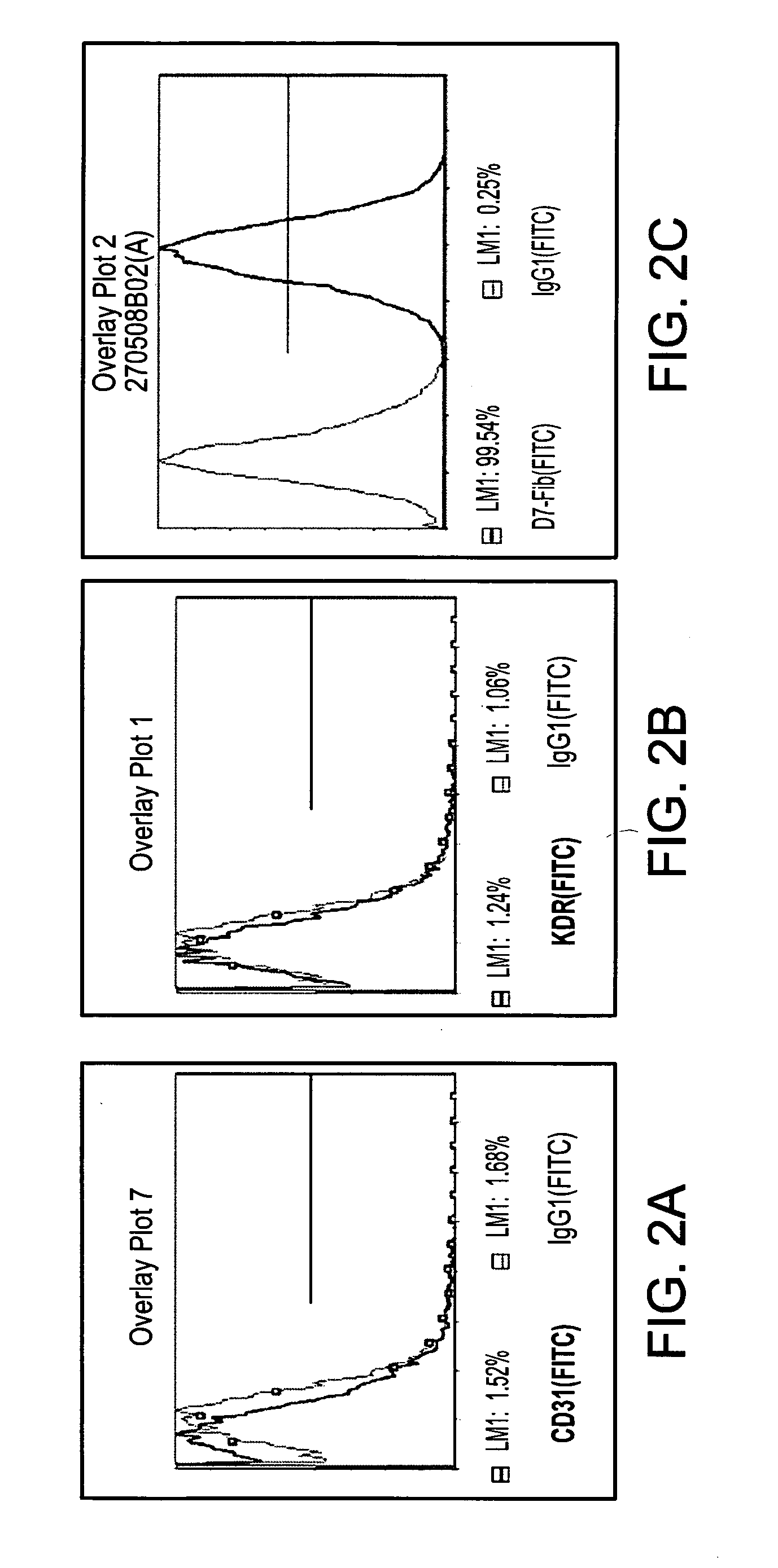
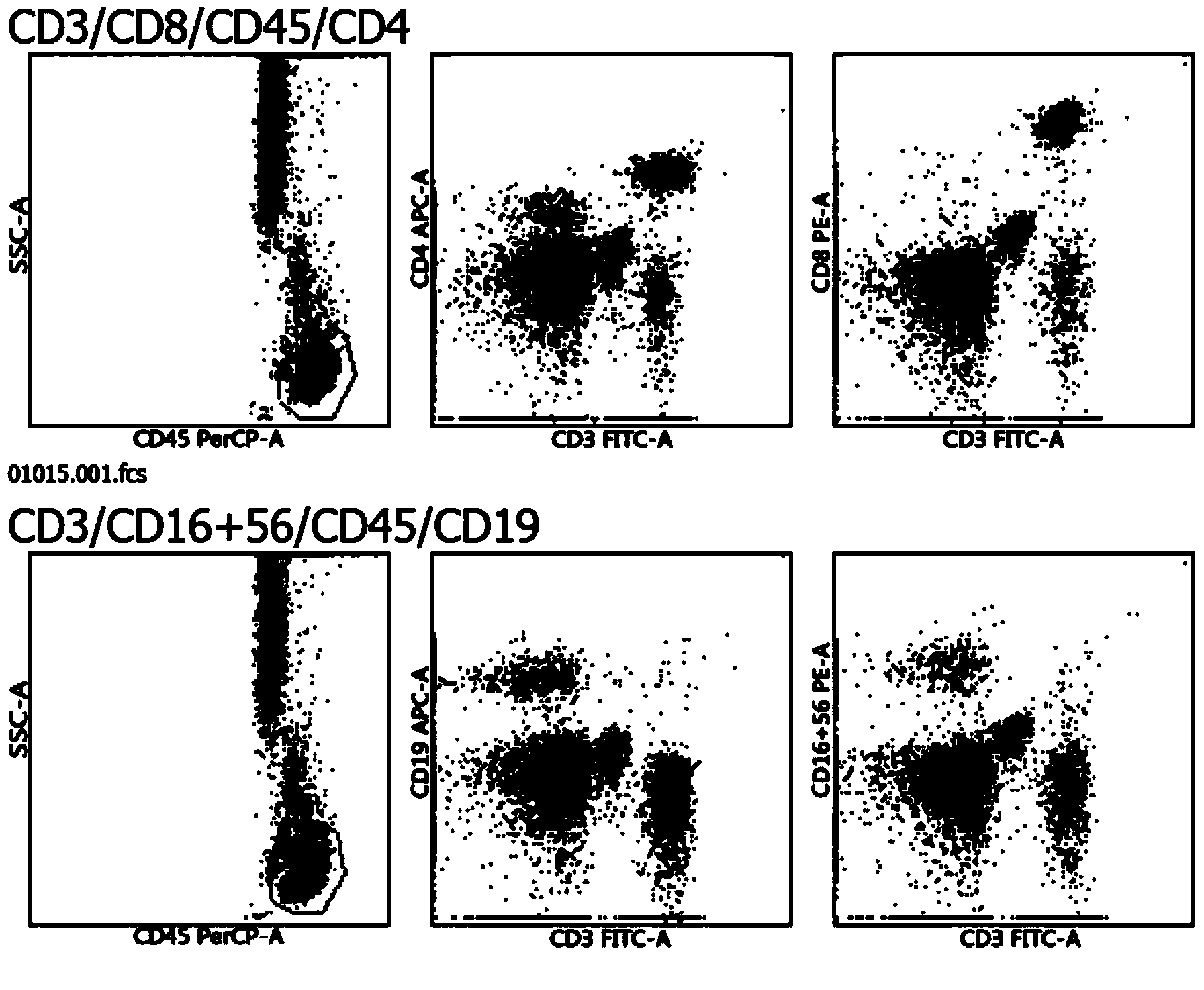
Immunophenotyping is a technique used to study the protein expressed by cells. This technique is commonly used in basic science research and laboratory diagnostic purpose. This can be done on tissue section (fresh or fixed tissue), cell suspension, etc. An example is the detection of tumor marker, such as in the diagnosis of leukemia. It involves the labelling of white blood cells with antibodies directed against surface proteins on their membrane. By choosing appropriate antibodies, the differentiation of leukemic cells can be accurately determined. The labelled cells are processed in a flow cytometer, a laser-based instrument capable of analyzing thousands of cells per second. The whole procedure can be performed on cells from the blood, bone marrow or spinal fluid in a matter of a few hours.
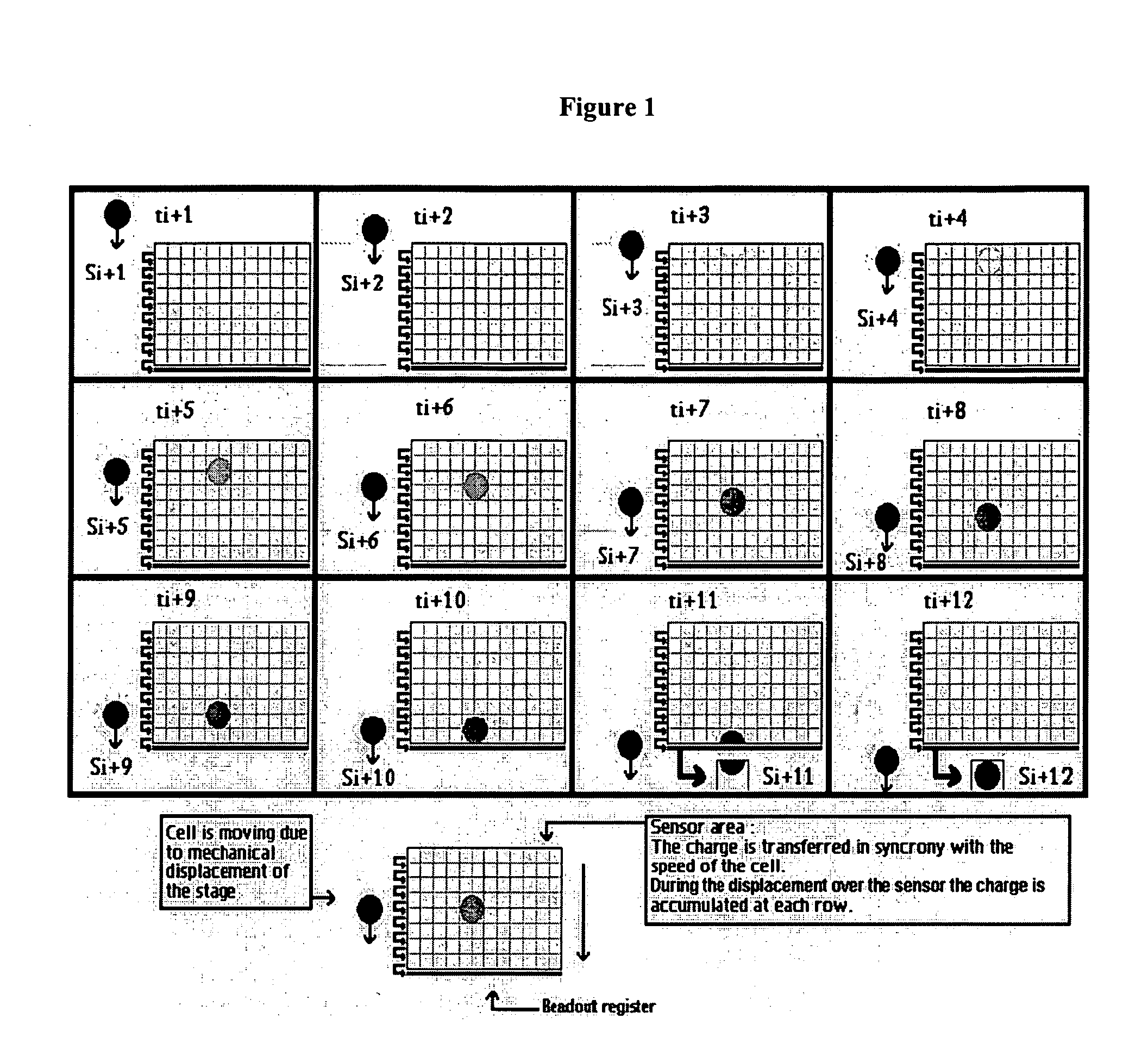
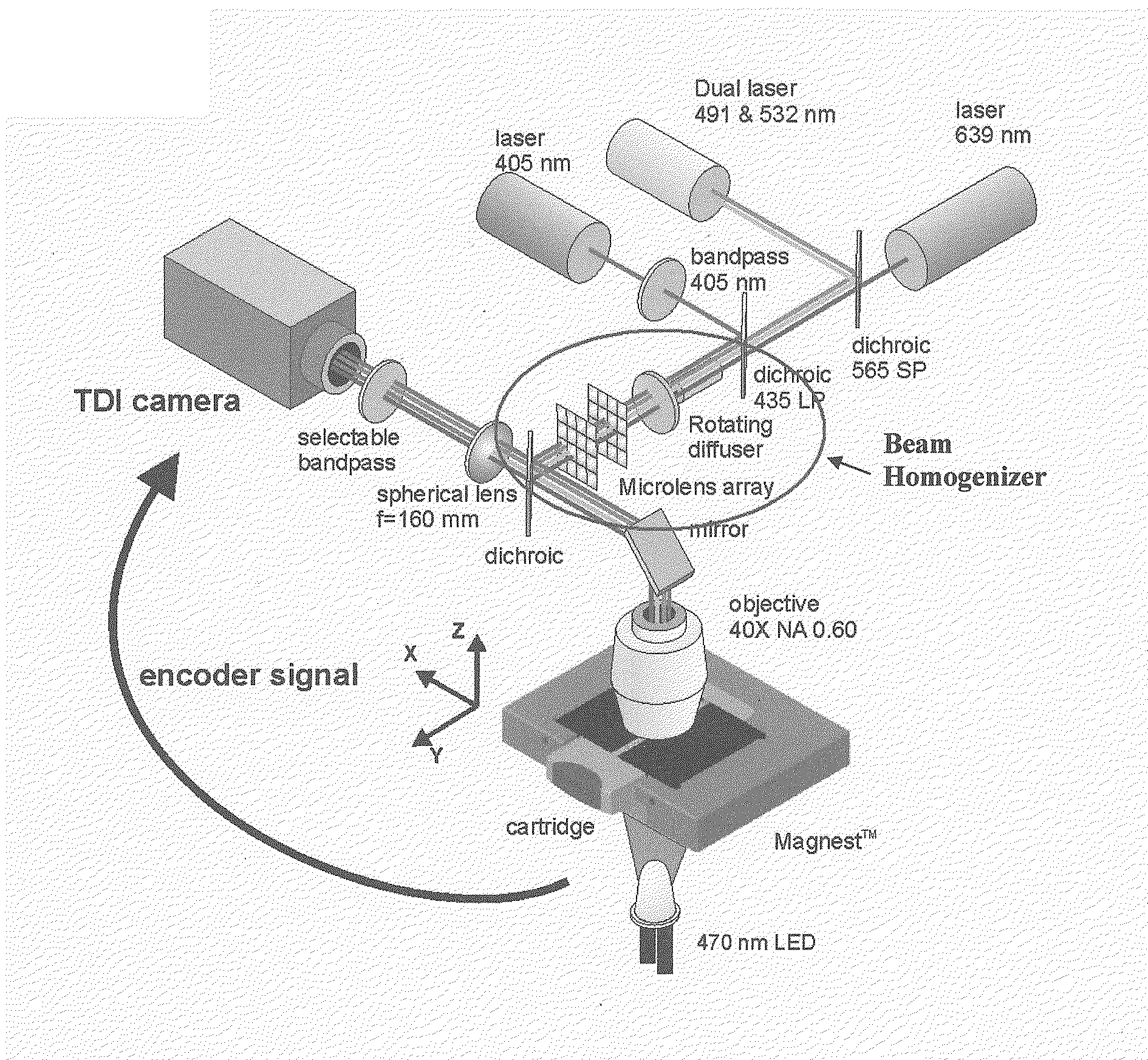
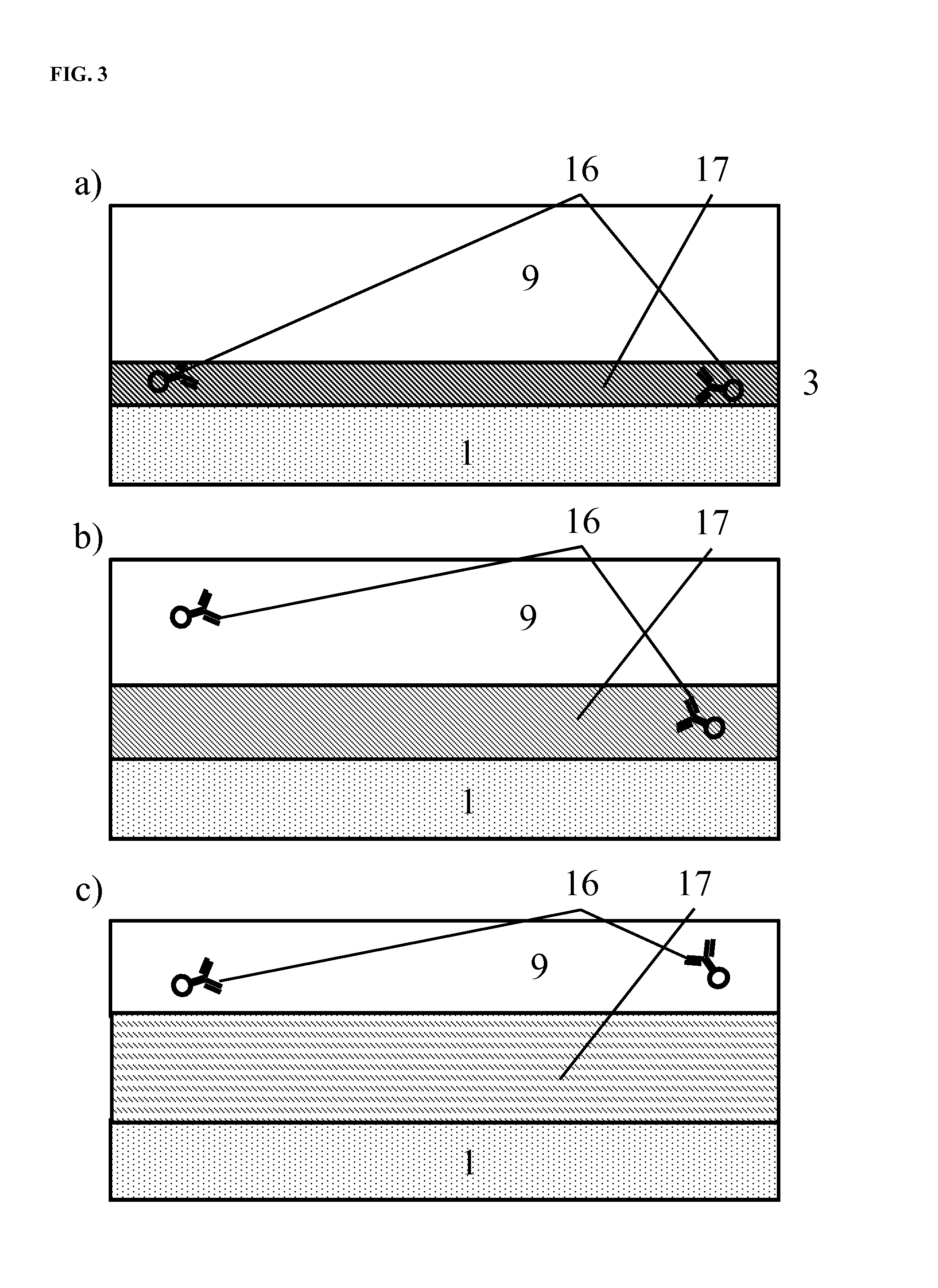
Devices and methods to image objects by time delay integration
InactiveUS20060147901A1Improved detection and enumeration and classificationAvoid lostBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRare cellSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
Devices and methods for automated collection and image analysis are disclosed that enable identification or classification of microscopic objects aligned or deposited on surfaces. Such objects, e.g. detectably labeled rare target cells, are magnetically or non-magnetically immobilized and subjected to Time Delay Integration imaging (TDI). Incorporation of TDI technology into image cytometry analysis, like CellTracks®, makes it possible to image moving objects with very high sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratios. Implementation of TDI camera technology with dual excitation and multispectral imaging of enriched rare cells provides a rapid system for detection, enumeration, differentiation and characterization of imaged rare cells on the basis of size, morphology and immunophenotype.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Detecting disease-correlated clonotypes from fixed samples
InactiveUS20130324422A1Convenient, less invasive, and more accessibleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsSolid tissueLymphocyte
The invention is directed to a method for determining immunophenotypes of tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes in a solid tissue of a patient by (a) generating clonotype profiles from a sample of nucleic acid extracted from a fixed tissue sample from a solid tissue of the patient, where such tissue contains tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes; and (b) determining immunophenotypes of the tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes by (i) obtaining a sample of lymphocytes from peripheral blood of the patient; (ii) sorting the lymphocytes from peripheral blood into at least one subset based on different immunophenotypes of the lymphocytes; (iii) generating a clonotype profile for each of the at least one subset of lymphocytes; and (iv) determining immunophenotypes of lymphocytes in the fixed tissue sample by a correspondence between clonotypes of the fixed tissue sample and clonotypes of the at least one subset.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
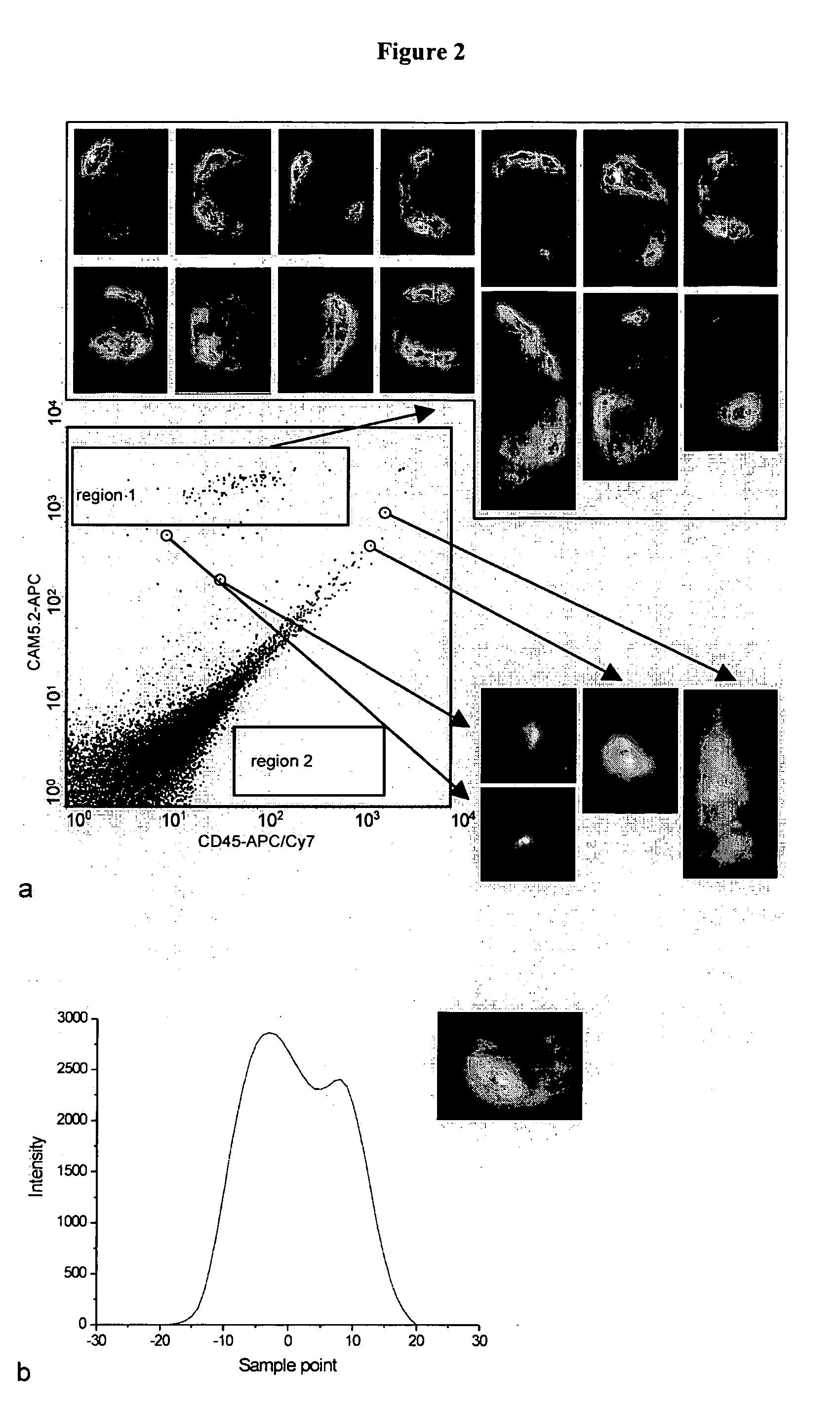
A simple and affordable method for immunophenotyping using a microfluidic chip sample preparation with image cytometry
ActiveUS20140038230A1Simple methodCheap componentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPoint of careFluorescence
The enumeration of cells in fluids by flow cytometry is widely used across many disciplines such as assessment of leukocyte subsets in different bodily fluids or of bacterial contamination in environmental samples, food products and bodily fluids. For many applications the cost, size and complexity of the instruments prevents wider use, for example, CD4 analysis in HIV monitoring in resource-poor countries. The novel device, methods and system disclosed herein largely overcome these limitations. The system includes a simple system for CD4 and CD8 counting in point-of-care HIV staging within resource poor countries. Unlike previous approaches, no sample preparation is required with the sample added directly to a chip containing dried reagents by capillary flow. A large area image cytometer consisting of an LED module is used to excite the fluorochromes PerCP and APC labeled targets and a monochrome CCD camera with a combination of two macro lenses captures images of 40 mm2 of blood (approximately 1 microliter). CD4 and CD8-T-lymphocyte counts correlate well with those obtained by flow cytometry. The cytometer system described in the present invention provides an affordable and easy-to-use technique for use in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Methods of selection of cells for transplantation
A method of selecting a population of adherent cells of a placenta tissue suitable for transplantation is disclosed. The method comprising: (a) determining prior to transplantation in a candidate population of adherent cells of a placenta tissue at least one of the following parameters: (i) percentage of viable cells in the candidate population; (ii) immune phenotype of cells in the candidate population; (iii) xeno-contamination in the candidate population; (iv) sterility of the candidate population; and (v) immunosuppressive activity of cells in the candidate population; and (b) selecting or excluding the candidate population according to predetermined values of at least one of the parameters, thereby selecting a population of adherent cells of the placenta tissue suitable for transplantation.
Owner:PLURISTEAM LTD
Method for lymphocyte subsets and kit thereof
InactiveCN104360050AEfficient combinationEasy to operateBiological material analysisBiological testingFluorescenceImmunologic Technique
The invention belongs to the field of immunological technique and discloses a method for lymphocyte subsets and a kit thereof. The method of lymphocyte subsets provided by the invention includes T lymphocyte subsets and B lymphocyte subsets. T lymphocyte subsets contain the following steps of: getting different fluorescence labeled antibodies, mixing with a sample to be detected, incubating, detecting by flow cytometry to obtain test data and analyzing the test data. B lymphocyte subsets contain the following steps of: getting different fluorescence labeled antibodies, mixing with a new aforementioned sample to be detected, incubating, detecting by flow cytometry to obtain test data and analyzing the test data. The method provided by the invention is used to realize a more comprehensive fine immunophenotyping of lymphocyte, has advantages of less sample needed to be detected, simple operation, short time needed and high precision, and can be widely applied in immunophenotyping of lymphocyte subpopulation.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and compositions for obtaining hematopoietic stem cells derived from embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050221482A1Good conditionMammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
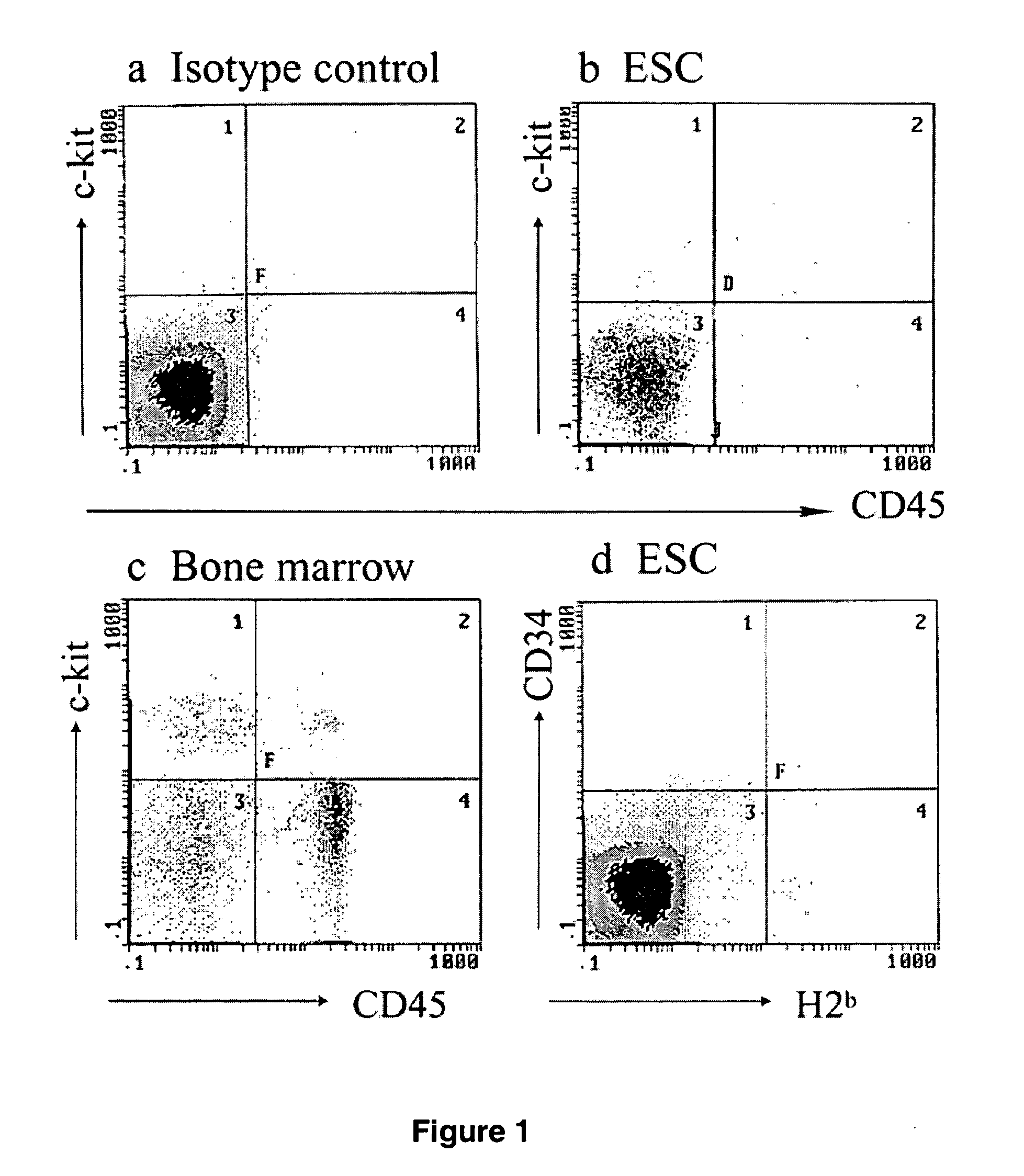
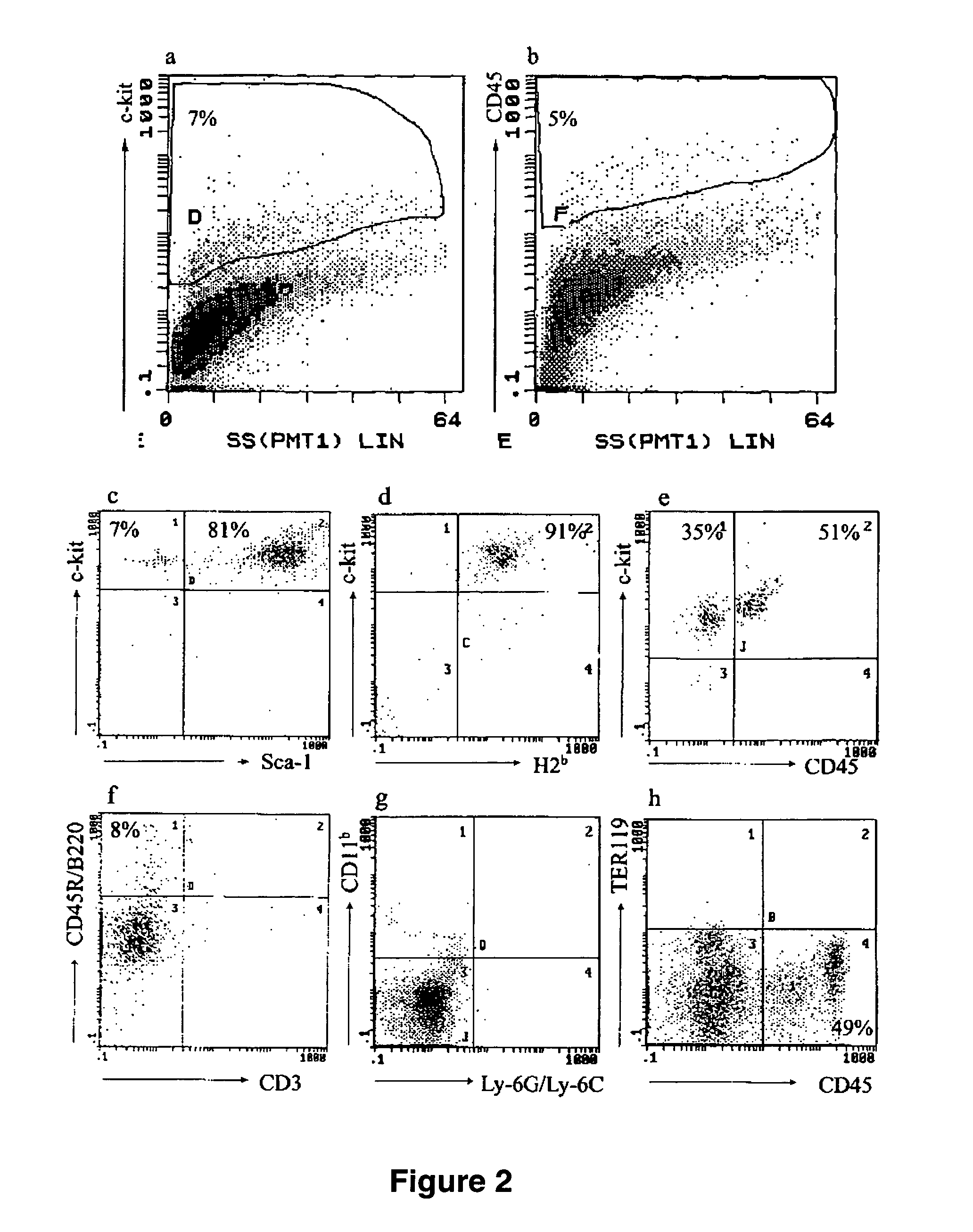
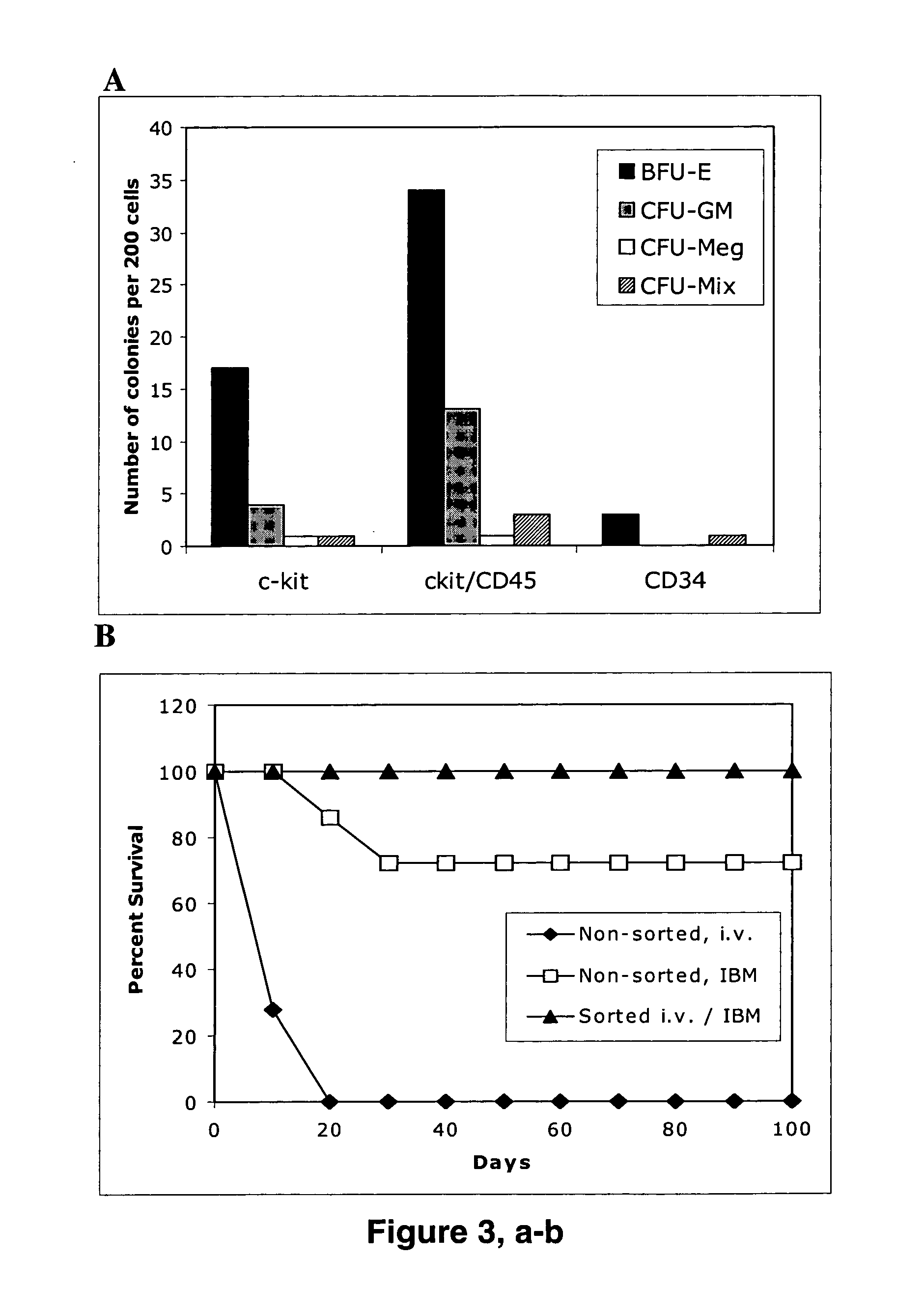
The present invention provides an isolated population of adult hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) derived from embryonic stem cells (ESC) induced to differentiate in vitro by culturing ESCs in a medium with stem cell factor, interleukin (IL)-3, and IL-6. HSC of immunophenotype c-kit+ or c-kit+ / CD45+ from this population are isolated and injected either intra bone marrow or intravenously into myeloablated recipient individuals. This method allows for the establishment of banks of allogeneic ESC-derived adult stem cells for treatments of autoimmune diseases, immune deficiencies and induction of immunotolerance during organ transplantation. These allogeneic ESC-derived adult hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) may be used in reconstituting bone marrow, without the development of teratomas or graft versus host disease, despite crossing histocompatibility barriers. Additionally, allogeneic ESC-derived HSC can be used to prevent the development of autoimmune diseases or organ rejection during transplantation.
Owner:NEWLINK GENETICS +1
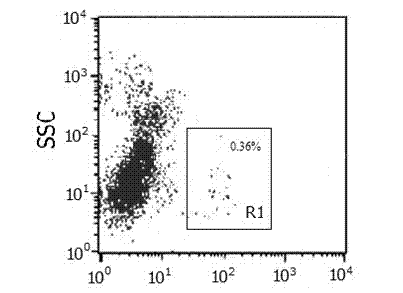
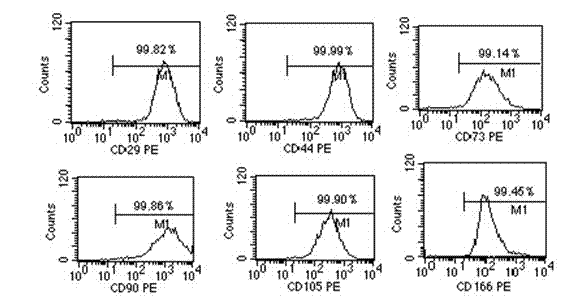
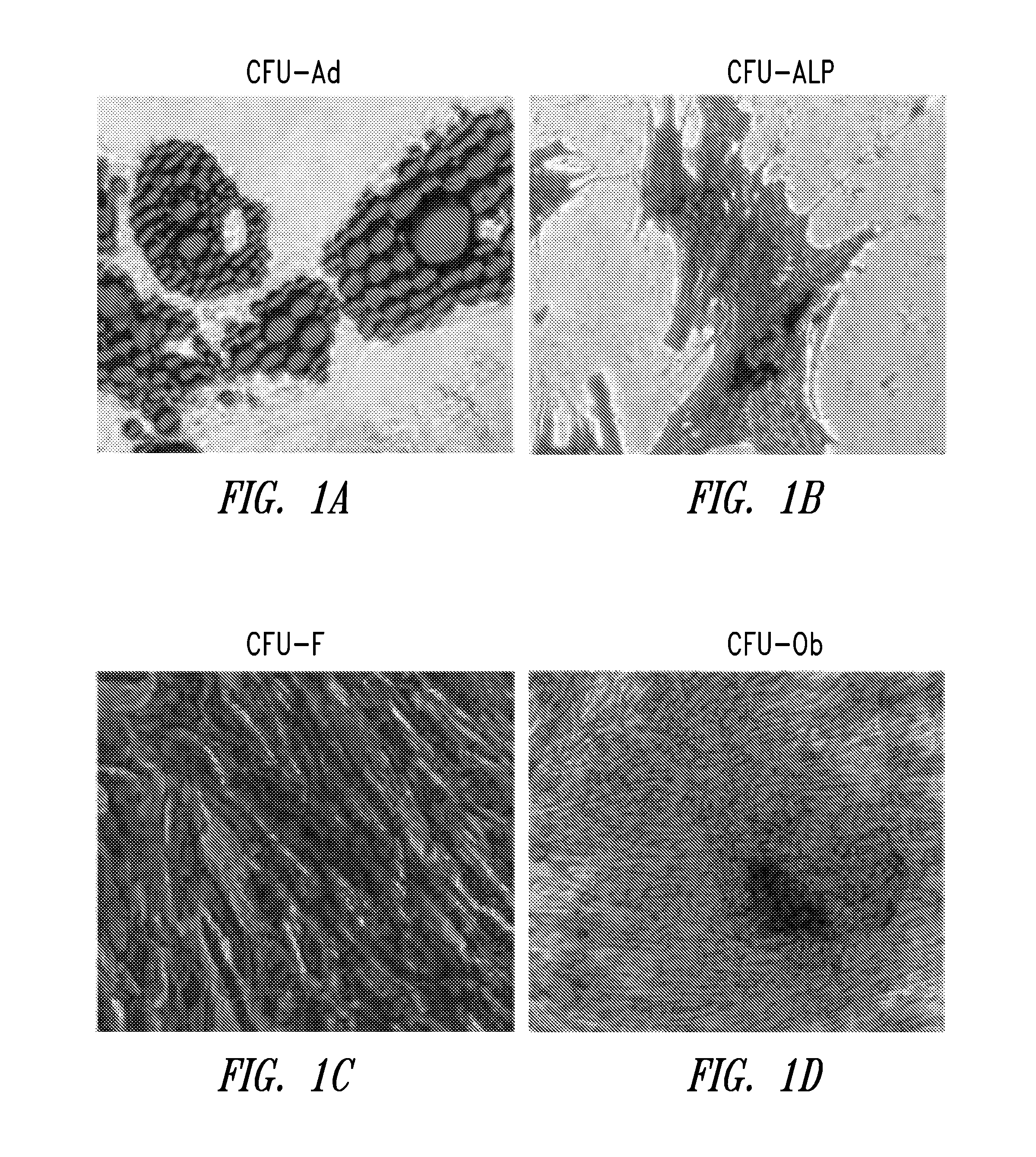
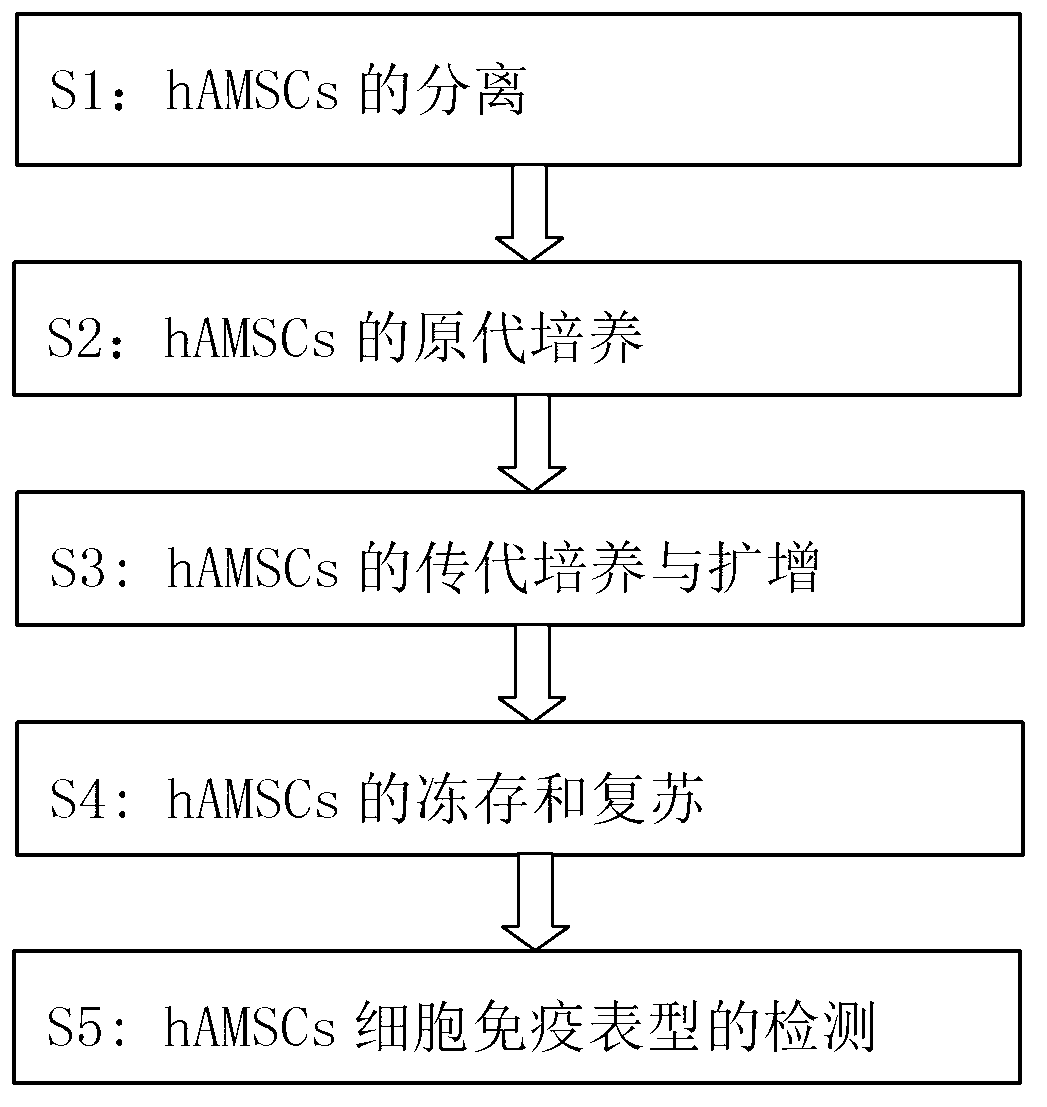
Separation method for human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN103789258AEasy to operatePractical and stableSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEnzyme digestionDigestion
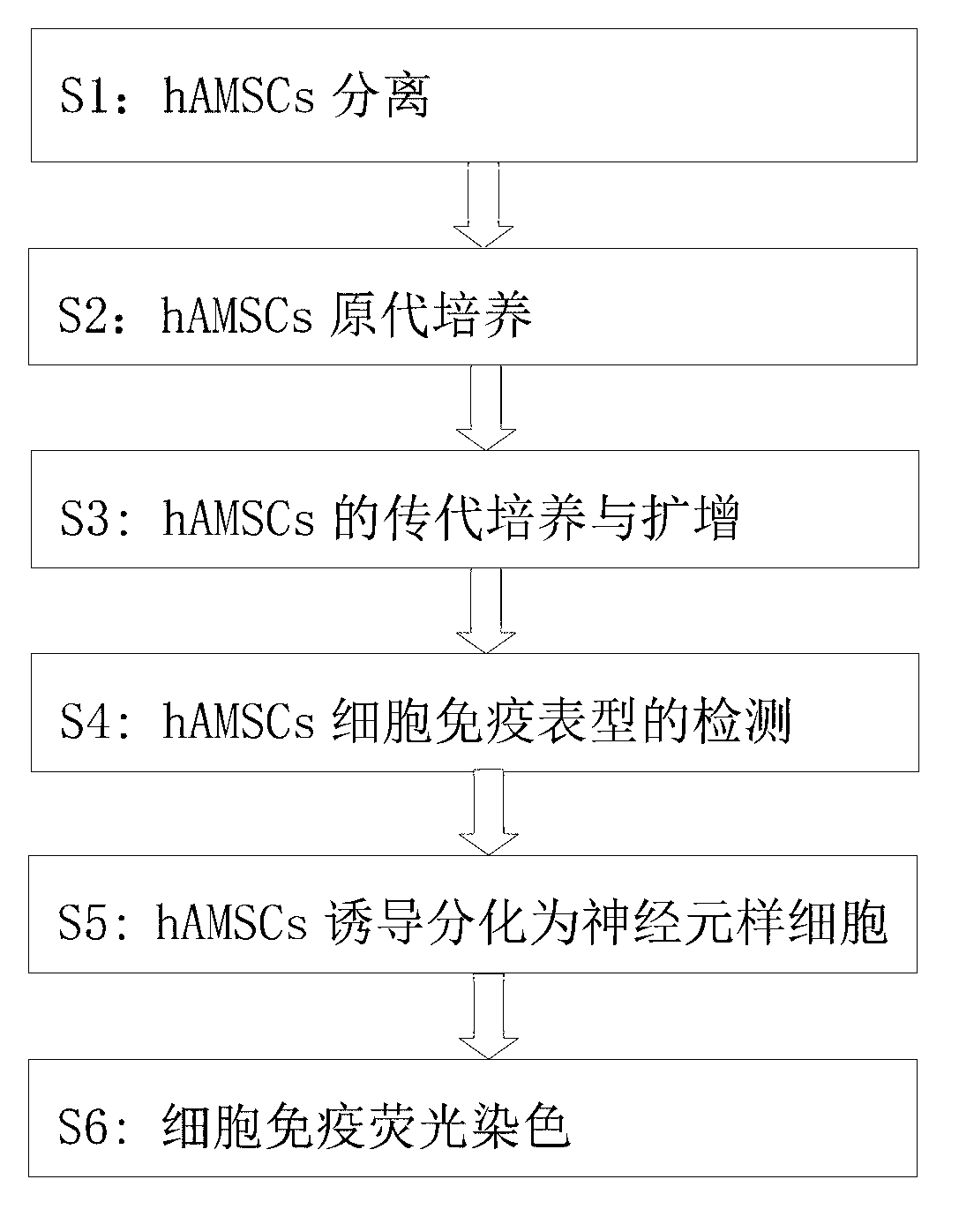
The invention provides a separation method for human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) in a process of cultivating the hAMSCs through enzyme digestion and epidermal growth factor (EGF). The cultivating process comprises the steps of separation of hAMSCs, primary culture of hAMSCs, hAMSCs subculturing and amplification, hAMSCs cryopreservation and recovery, and hAMSCs immunophenotyping detection. According to the method disclosed by the invention, step-by-step digestion is implemented for multiple times through trypsin and collagenase to collect amnion cells, and adherent culture and digestion time control are combined through adding of 4ng / ml of EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor), so as to obtain human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) which are relatively high in both purity and activity. The method disclosed by the invention, which combines enzyme digestion and EGF, has the advantages of being simple to operate, rapid, practical and the like, being an effective method for separating and purifying hAMSCs.
Owner:陆华
Cryopreservation solution for preserving congenital intrathoracic kidney (CIK) cells and application thereof
InactiveCN103210903ANo significant difference in proliferative activityNo significant difference in killing activityDead animal preservationSerum free mediaCD8
The invention discloses a cryopreservation solution for preserving congenital intrathoracic kidney (CIK) cells and application thereof. The cryopreservation solution for preserving the CIK cells is prepared according to the following methods: adding dimethyl sulfoxide and dextran into a lymphocyte serum-free medium, so that the volume percent content of the dimethyl sulfoxide is 5-15 percent, and the volume percent content of the dextran is 5-15 percent. Compared with the cells before cryopreservation, the cells cryopreserved by employing the cryopreservation solution have the following advantages: (1) the cellular morphology does not have obvious difference; (2) immunophenotype (CD3+CD56+CD8+) does not have obvious difference; and (3) the cell proliferation activity and cell killing activity do not have obvious difference.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
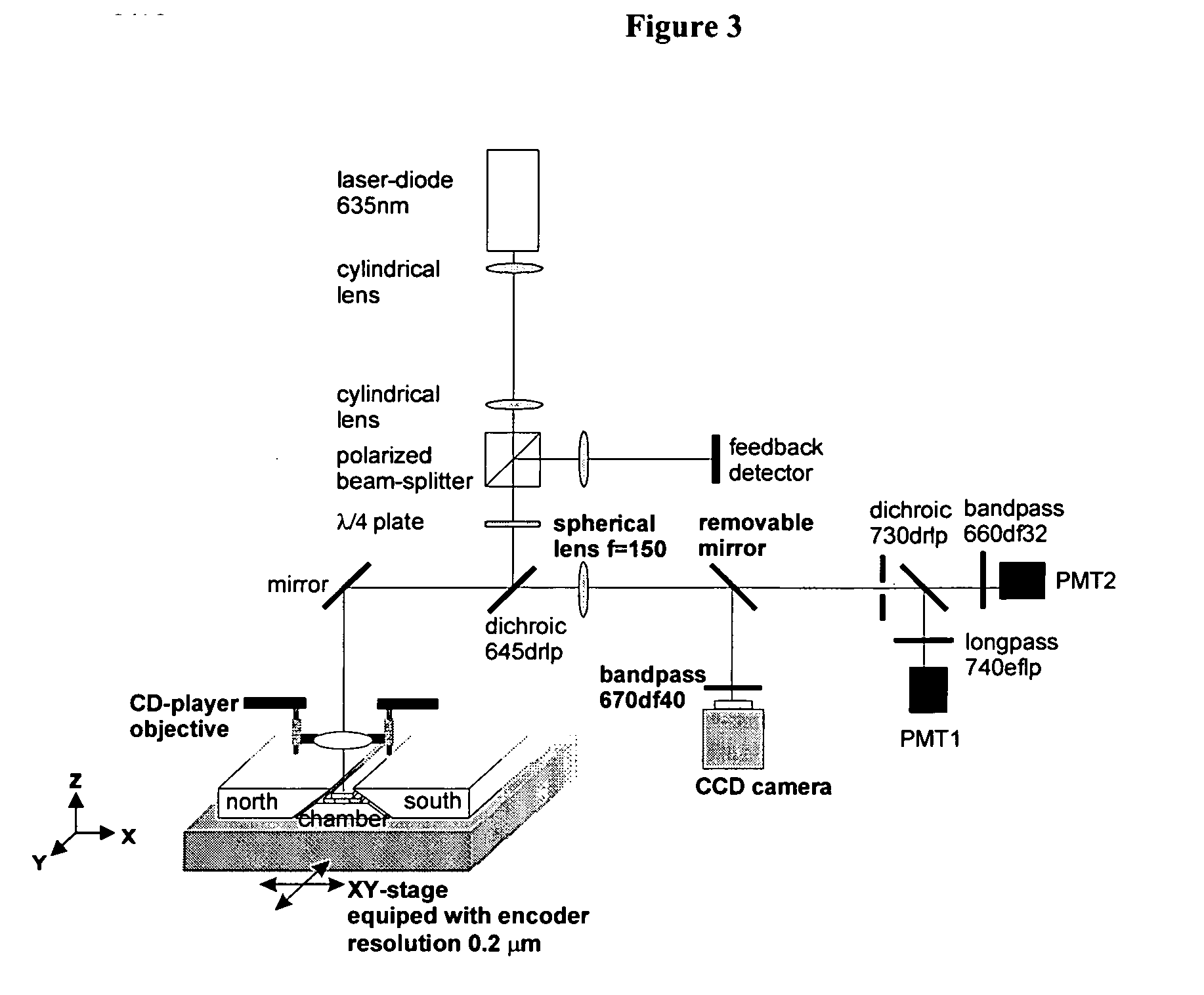
Laser Illumination System in Fluorescent Microscopy
InactiveUS20090311734A1High quality fluorescence imageEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceMicroscopic scale
Devices and methods for automated collection and image analysis are disclosed that enable identification or classification of microscopic objects aligned or deposited on surfaces. Such objects, e.g. detectably labeled rare target cells, are magnetically or non-magnetically immobilized and subjected to Time Delay Integration imaging (TDI). Incorporation of TDI technology into image cytometry analysis, like CellTracks®, makes it possible to image moving objects with very high sensitivity and signal-to-noise ratios. Implementation of TDI camera technology with dual excitation and multispectral imaging of enriched rare cells provides a rapid system for detection, enumeration, differentiation and characterization of imaged rare cells on the basis of size, morphology and immunophenotype.
Owner:GREVE JAN +1
Serum-free culture medium for human umbilical cord MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells)
InactiveCN107043747AImprove survival rateMaintain propertiesCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUmbilical cordPollution
The invention discloses a serum-free culture medium for human umbilical cord MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells). The serum-free culture medium comprises the major ingredients of amino acid, inorganic salt ingredients, growth factors and albumin ingredients. The serum-free culture medium for human umbilical cord MSCs does not contain any serum ingredients; in addition, the ingredients are clear; the foreign protein pollution and pathogenic microorganism risks are avoided; the biosecurity problem of the MSCs clinic application is solved. When the serum-free culture medium provided by the invention is used for culturing the human umbilical cord MSCs, the high-quantity high-purity safe and high-quality umbilical cord MSCs can be obtained in vitro; meanwhile, the cell survival rate can be improved; the stem cell characteristics are maintained. The problem of insufficient cell quantity can be solved; the cell number, the survival rate and the immunophenotyping in each batch are more stable; the relevant index requirements are met.
Owner:王晓柯
Method for culturing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells through combination of adherence density gradient method and EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor)
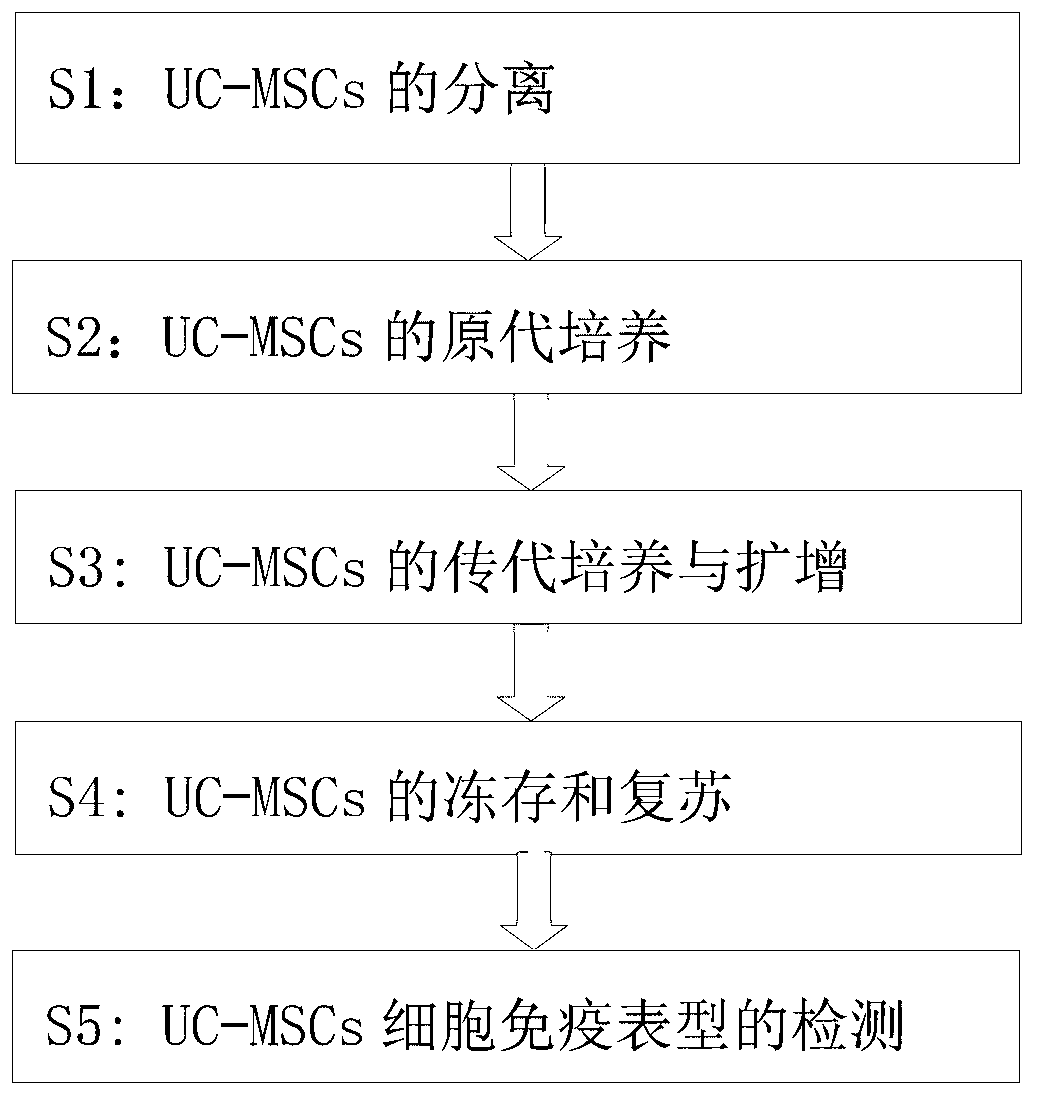
InactiveCN103013911AEasy to operateEffective separation and purification methodSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCryopreservationDigestion
The invention provides a method for culturing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells through combination of an adherence density gradient method and as EGF (Epidermal Growth Factor). The method comprises the following steps of: seperation of the UC-MSCs (Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells), primary culture of the UC-MSCs, subculture and augmentation of the UC-MSCs, cryopreservation and resuscitation of the UC-MSCs and detection of UC-MSCs immunophenotyping. According to the method, 4ng / ml of EGF is added by adopting the adherence density gradient method, adherent culture and digestion time control are combined, so that the UC-MSCs with higher purity and activity is obtained; and the method combining the adherence density gradient method and the EGF has the advantages of simple operation, rapidness, practicability and the like and is an effective method for separating and purifying the UC-MSCs.
Owner:陆华
Immunophenotype and immunogenicity of human adipose derived cells
InactiveUS20070122393A1Improve severityReduce usageBiocideGenetic material ingredientsStromal cellImmunophenotyping
The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for generating an isolated adipose tissue-derived stromal cell exhibiting a low level of immunogenicity. The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for reducing an immune response associated with transplantation by administering the recipient with an amount of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells effective to reduce or inhibit host rejection and / or host versus graft disease.
Owner:ARTECEL +1
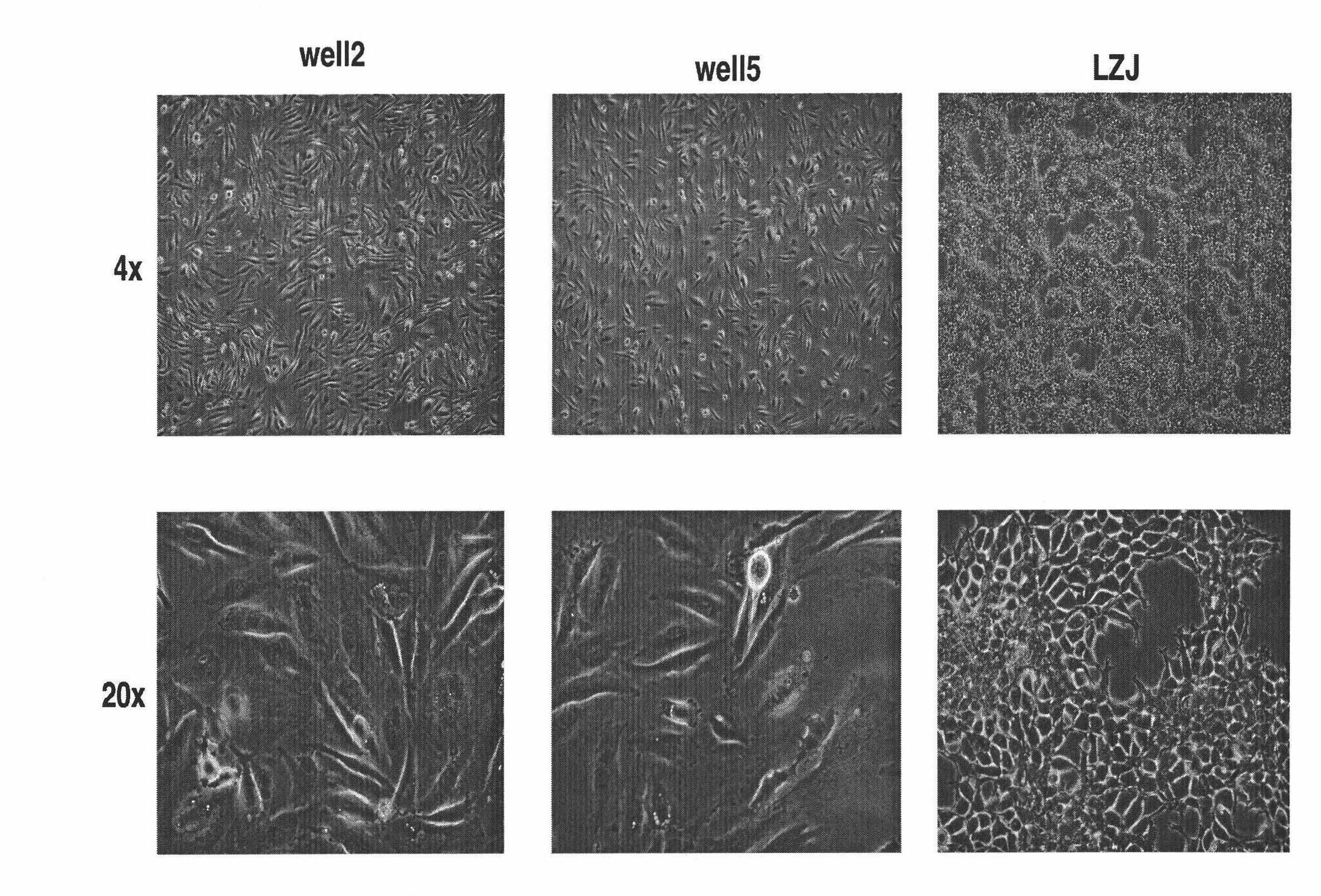
Human osteosarcoma cell line group and mouse in-vivo transplantation model
ActiveCN102051344AKeep activeStable traitsMicroorganism based processesTumor/cancer cellsCombined immunodeficiency diseaseSevere combined immunodeficiency disease
The invention discloses three human osteosarcoma cell lines well2, well 5 and LZJ, the collection numbers of the three human osteosarcoma cell lines are CCTCC C200961, CCTCC C200962 and CCTCC C200963 respectively, and the invention further discloses establishment of a corresponding NOD / SCID (nonobese diabetic / severe combined immunodeficiency disease) mouse in-vivo transplantation model, thereby providing a good and stable experimental subject and a model platform for clinical and fundamental research work of osteosarcoma. The established osteosarcoma cell lines can enable the in-vitro stable passage to be more than two years, have stable characters and enable morphology, have immuno-phenotype, chromosome genetics and other characteristics similar to the common osteosarcoma cell lines. The tumorigenesis of NOD / SCID mice is stable, the pathomorphism of tumor bodies is similar to primary tumor tissues of patients, and the animal model is simultaneously sensitive to common chemotherapeutic drugs for the osteosarcoma and can well simulate clinical retracking for clinical patients with the osteosarcoma.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
CD106-positive cells, and identification and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102539736APrevent rejectionSuppress immune responseSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEmbryonic cellsAdipogenesisAutoimmune disease
The invention discloses an identification and preparation method and application CD106-positive mesenchymal stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: identifying and isolating CD106-positive cells from mononuclear cells isolated from bone marrow, placenta or other tissues through an immunological method, carrying out adherent culture, and collecting adherent CD106-positive cells; or carrying out adherent culture of mononuclear cells isolated from bone marrow, placenta or other tissues, collecting adherent mesenchymal cells, and isolating the CD106-positive mesenchymal stem cells when the count of the obtained cells is large enough. The CD106-positive cells are mesenchymal stem cells with adherent growth, express mesenchymal stem cell-related immunological phenotype, and have osteogenesis, adipogenesis and other differentiation potencies. Compared with CD106-negative mesenchymal stem cells, the CD106-positive cells have higher immunosuppression capacity, can better inhibit proliferation of IFN-gamma (interferon-gamma) secretion of lymphocytes, and can be used for treating graft versus host disease (GVHD) and autoimmune diseases.
Owner:北京汉氏干细胞科技有限公司
Immunophenotype and immunogenicity of human adipose derived cells
The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for generating an isolated adipose tissue-derived stromal cell exhibiting a low level of immunogenicity. The present invention encompasses methods and compositions for reducing an immune response associated with transplantation by administering the recipient with an amount of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells effective to reduce or inhibit host rejection and / or host versus graft disease.
Owner:LOUISIANA STATE UNIV +1
Method for culturing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells by enzyme digestion and EGF (epidermal growth factor)
InactiveCN103013913AEasy to operatePractical and stableSkeletal/connective tissue cellsEnzyme digestionDigestion
The invention provides a method for culturing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) by enzyme digestion and EGF (epidermal growth factor). The method comprises the following steps of hAMSCs separation, hAMSCs primary culture, hAMSCs sub-culture and amplification, hAMSCs cryopreservation and recovery, and detection of hAMSCs cytometric immunophenotyping. According to the method, amniotic extracells are collected by digesting trypsin and collagenase for multiple times step by step, and adherent culture and digestion time control are combined by addition of 4ng / ml EGF, so that human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) with high purity and high activity can be obtained. The enzyme digestion and EGF adopted in the method have the advantages of simpleness in operation, quickness and practicality and the like, so that the method is capable of effectively separating and purifying hAMSCs.
Owner:陆华
Method for inducing human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into neuron-like cells
InactiveCN103013917ANervous system cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsGerm layerGlial fibrillary acidic protein
The invention provides a method for inducing differentiating human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs) to differentiate into neuron-like cells by adopting all-trans retinoic acids, a basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and an epidermal growth factor (EGF). The method comprises the following steps of: separating the hAMSCs, carrying out primary culture of the hAMSCs, subculturing and amplifying the hAMSCs, detecting hAMSCs immunophenotyping, inducing the hAMSCs to differentiate into the neuron-like cells and carrying out cellular immunity fluorescence staining. According to the inducing method provided by the invention, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells are induced to differentiate into neutral stem cells by using the all-trans retinoic acids in combination of the bFGF and the EGF; the neural stem cells not only have the typical morphology of nerve cells, but also express neuron marker antigen neuron-specific emolase and astrocyte marker antigen glial fibrillary acidic proteins; and the capability of a mesenchymal cell trans-germinal layer differentiating into non mesenchymal cells is realized so that the mesenchymal cells are likely to turn into more ideal seed cells for clinical application in further.
Owner:陆华
T lymphocyte immunophenotyping method and kit
InactiveCN104360049AEfficient combinationEasy to operateBiological material analysisBiological testingFluorescenceCD8
The invention belongs to the field of immunological technique and discloses a T lymphocyte immunophenotyping method and a kit. The T lymphocyte immunophenotyping method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: taking different fluorescently-labeled antibodies and mixing the antibodies with a sample to be tested, carrying out incubation, carrying out flow cytometry detection to obtain test data, and analyzing the test data. The antibodies contain an anti-TCR alpha beta antibody, an anti-TCR gamma Delta antibody, an anti-CD3 antibody, an anti-CD4 antibody, an anti-CD8 antibody, an anti-CD27 antibody and an anti-CD45RA antibody. By the above method, more comprehensive fine T lymphocyte immunophenotyping is realized. Few samples to be tested are required. The method is simple to operate. Required time is short. And the method has high accuracy and can widely be applied in lymphocyte subpopulation immunophenotyping.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Application of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of medicines for treating joint diseases
InactiveCN103550256AGood differentiation potentialInhibit inflammationAntipyreticAnalgesicsArticular cavityJoint disease
The invention relates to an application of autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in preparation of medicines for treating joint diseases. The application is characterized in that adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (Ad-MSCs) separated and extracted from autologous adipose tissues of the patient are injected to the diseased articular cavity in a large dose once. The adopted mesenchymal stem cells have immunophenotyping and representing biological marks of Ad-MSC through flow cytometry authentication, and can be directionally induced and differentiated to osteoblast and chondrocyte. Primary cells are directly injected to the articular cavity of the diseased joint to treat various joint diseases. With the adoption of the autologous adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells as the primary cells, the cells have better differentiative potential and the ability of inhibiting inflammation and immunoregulation ability. The adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplant provides a novel effective means for treating osteoarticular diseases. The method is simple and feasible, and the quantity of cells collected is great and the trauma is small. The autologous mesenchymal stem cells of the patient are applied without invading related ethics, so that the risk of immunological rejection, infectious diseases and the like is avoided.
Owner:南京优而生物科技发展有限公司
Antibody composition for leukemia/lymphoma immunotyping preliminary screening and application thereof
ActiveCN113777327ATo achieve the purpose of confirming the diagnosisHigh precisionIndividual particle analysisBiological testingAntigenDisease
The invention provides a reagent composition for leukemia / lymphoma typing. The reagent composition comprises 19 kinds of antibodies. According to the optimized antibody combination, the fluorescence labeling combination of the corresponding antibody and the result interpretation method, the AML, the ALL-B, the ALL-T, the MPAL, the NHL-B, the NHL-T, the PCN, the NHL-NK and the chronic myeloid tumors can be preliminarily screened comprehensively and efficiently only by using 19 antibodies and one-tube cell one-time sample loading, and the aim of clearly diagnosing the AML, the ALL-B, the ALL-T, the MPAL, the NHL-B, the NHL-T and the PCN is achieved. The 19 antibody combinations are used for analyzing the expression of tumor cell antigens in a sample, and leukemia-related immunophenotypes (LAIP) which can be used for monitoring post-treatment trace residual disease (MRD) in the antibody combinations are determined.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Acute B-lymphocyte leukemia initiated cell phenetic classification kit and application thereof
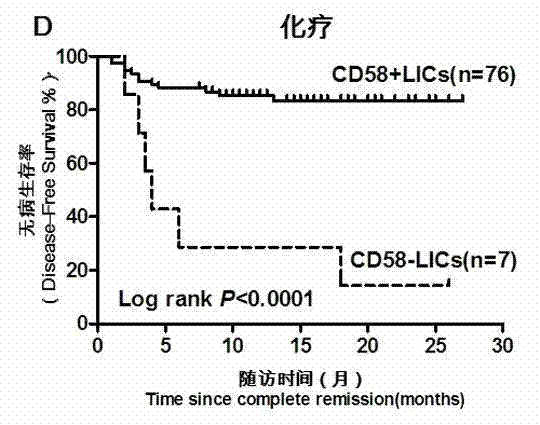
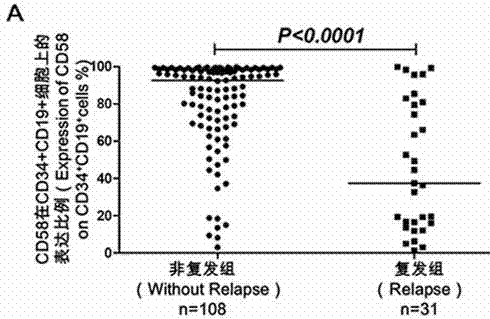
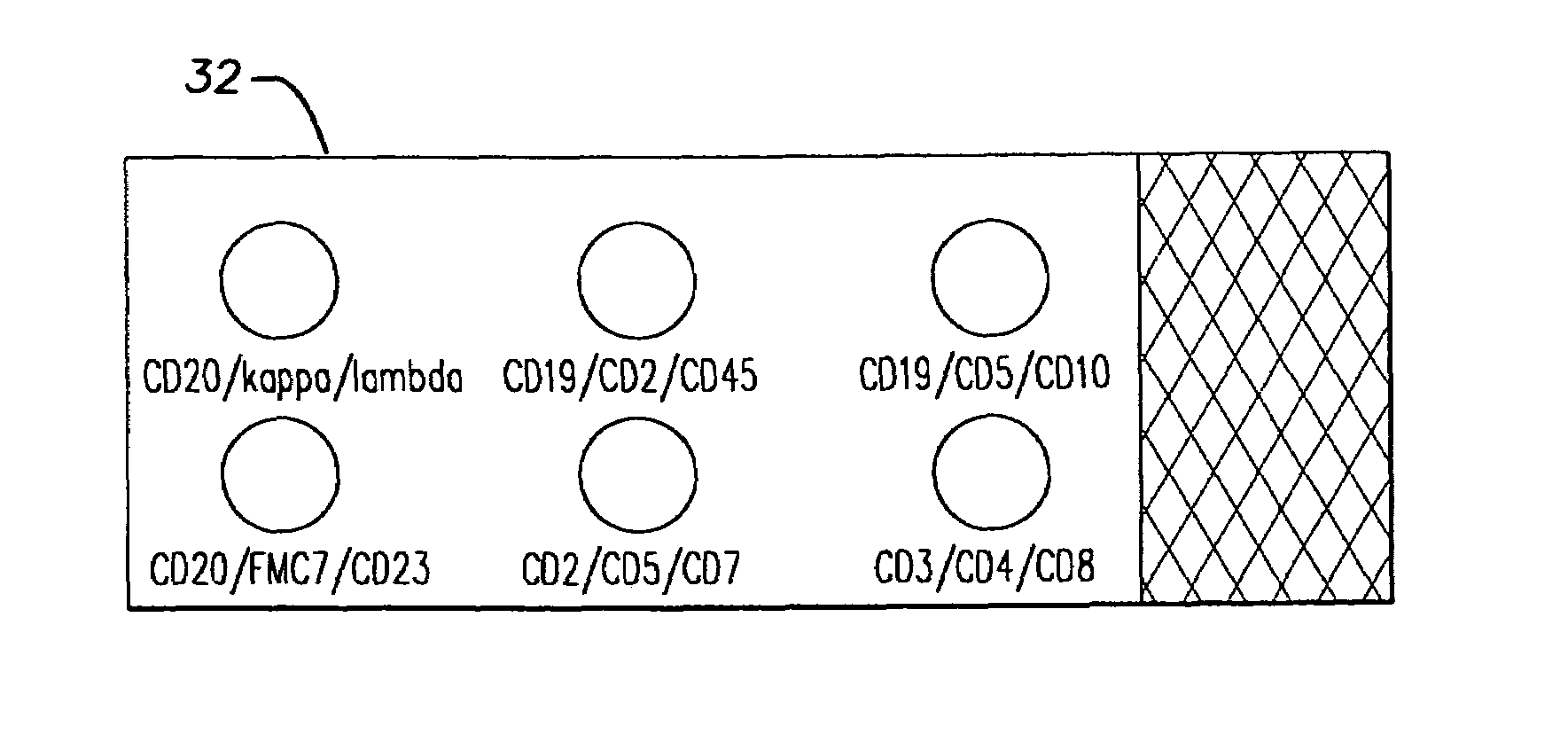
ActiveCN103175966AAccurate typingRapid TypingMaterial analysisCell phenotypeAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses an acute B-lymphocyte leukemia initiated cell phenetic classification kit. The kit is used in cooperation with a sever-color flow cytometer. The structure of the kit is configured with the following fluorescently-labeled monoclonal antibody: CD58FITC, CD10PE, CD34PerCP, CD38APC, CD19APC-Cy7 and CD45PacificBlue. The kit disclosed by the invention can be used for fast and accurately detecting the immunophenotype of the leukemia initiated cell of a B-ALL patient in first visit; and the CD58 expression proportion on the leukemia initiated cell tested by the kit provided by the invention can be used as one of the prognostic indicators of the B-ALL patient, and the indicator has important guiding significance in the prognosis of the B-ALL patient and the decision of a clinic treatment scheme.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL PEKING UNIV
Products and methods for single parameter and multiparameter phenotyping of cells
InactiveUS7364906B2Withdrawing sample devicesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCell bindingMicrosphere
A method of single parameter and multiparameter characterizing of cells, particularly immunophenotyping of cells, is provided. The method preferably uses antibody-coated microspheres which are adapted to bind to specific types of cells. One or more sets of coated microspheres are contacted simultaneously or sequentially with a suspension of cells and bind the cells they are adapted to bind to form bead-cell complexes. Cells may bind to one or more microspheres. The bead-cell complexes are then separated from the suspension The complexes are preferably stained and then examined to characterize the cells, preferably the cells bound to the microspheres. A method of quantitating a specific cell type is provided. A kit and apparatus for performing the method are also provided.
Owner:HEMATOTYPES
Three-color reagent for measurement of CD4 positive lymphocytes by flow cytometry
InactiveUS20040110122A1Easy to exciteMore accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisWhite blood cellPhycoerythrin
The developed reagent is three-color immunophenotyping reagent for measurement of CD4 positive lymphocytes in peripheral blood. The reagent contains 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD) which intercalates into double stranded DNA and is easily excited at 488 nm. The fluorescence emission of 7-AAD has peak at 670 nm that can be detected with FL3 detector of flow cytometer. The 7-AAD, therefore, stains white blood cells and discriminates it from red blood cells. The reagent also contains fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) labeled CD4 monoclonal antibody and phycoerythrin (PE) labeled CD14 monoclonal antibody which are detected with FL1 and FL2 detectors of flow cytometer, respectively. The developed reagent can be used to measure number of CD4 positive lymphocytes in lymphocyte population and monitor monocyte contamination simultaneously. This reagent therefore provides more accuracy results of CD4 positive lymphocyte enumeration.
Owner:NAT SCI & TECH DEV AGENCY +1
Method for easily and efficiently preparing human gamma/deltaT cells
The invention belongs to the technical field of cellular immunology, in particular to a method for amplifying human peripheral blood gamma / deltaT cells massively and preferentially in vitro. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing tubercle bacillus heat stable antigen by using the cultured tubercle bacillus; (2) stimulating to amplify the gamma / deltaT cells by combining the prepared tubercle bacillus heat stable antigen and cell factors rhIL-2 and rhIL-21; and (3) performing morphologic observation through a microscope, performing purity and immunophenotyping analysis by using a flow cytometry, and performing cytotoxicity detection through MTT assay. The method has the advantages that: culture conditions and operation are simple, a large number of gamma / deltaT cells with high purity and high cytotoxicity can be prepared in short time, and the cost is low.
Owner:SHENZHEN HORNETCORN BIOTECH
Serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN110257328APromote in vitro proliferationCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSodium bicarbonateLithium chloride
The invention provides a serum-free culture medium for mesenchymal stem cells. The serum-free culture medium specifically comprises a lipid mixture, glutamine, hydrocortisone, zinc sulfate, sodium butyrate, ferric citrate, vitamin C, recombinant epidermal growth factors, recombinant alkaline fibroblast growth factors, RGD oligopeptides, palmitoyl tripeptide-5, palmitoyl tetrapeptide-7, lithium chloride, L-glutathione, a soybean pancreatin inhibitor, beta-mercaptoethanol, ethanolamine, sodium selenite, Hepes, sodium bicarbonate and a basic culture medium. The serum-free culture medium is free of human and animal resources, clear in chemical component, rich in nutrition, capable of achieving UC-MSCs rapid proliferation, and capable of solving the problem of cells number insufficiency and maintaining the biological features and immunophenotyping stability of the mesenchymal stem cells.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Serum-free medium for large-scale culture of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
InactiveCN109370985AMaintain propertiesSufficient quantityCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSerum free mediaBiology
The invention discloses a serum-free medium for large-scale culture of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The medium mainly includes amino acid, an inorganic salt component, a growth factorand an albumin component. The serum-free medium does not contain any serum component, has clear components, overcomes the danger of heterologous protein contamination and pathogenic microorganisms, and solves the biosafety problem of MSCs clinical application. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can be cultured invitro in large scale by using the serum-free medium. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with high volume, high purity, safety and high quality can be obtained. At the same time, the cell survival rate can be improved, and the characteristics of stem cells can be maintained. The serum-free medium can solve the problem of insufficient cell number, the cell number, the survival rate and the immunophenotype of each batch are more stable, and the requirements for relevant indexes can be met.
Owner:YOCON BIOLOGY TECH CO
Flow cell intelligent immunophenotyping method and device, and electronic equipment
ActiveCN109580458AImprove accuracyImprove efficiencyBiological particle analysisIndividual particle analysisAntigenDividing cell
The invention provides a flow cell intelligent immunophenotyping method and device, and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps that: obtaining the position coordinate of each cell in a flow sample in a coordinate system which takes different antigen molecular weights on the surface of the cell as a coordinate axis; according to the position coordinate, dividing cells in theflow sample into a plurality of cell groups; identifying the respective cell category of the plurality of cell groups; judging whether the position coordinates of cells in each cell group are positioned in a preset range corresponding to the cell category of the cell group or not; and when a judgment result shows that the position coordinates of the cells in the cell group are not positioned in the preset range corresponding to the cell category of the cell group, determining that the cell group is an exceptional group. By use of the method, cell grouping is realized by artificial intelligence, the judgment of the exceptional group is realized through a neural network model, the labor intensity of professionals is greatly lowered, and meanwhile, the accuracy and the efficiency of flow cell immunophenotyping are improved.
Owner:天津深析智能科技发展有限公司
Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102127522BActivity without lossHigh puritySkeletal/connective tissue cellsFreeze and thawDigestion
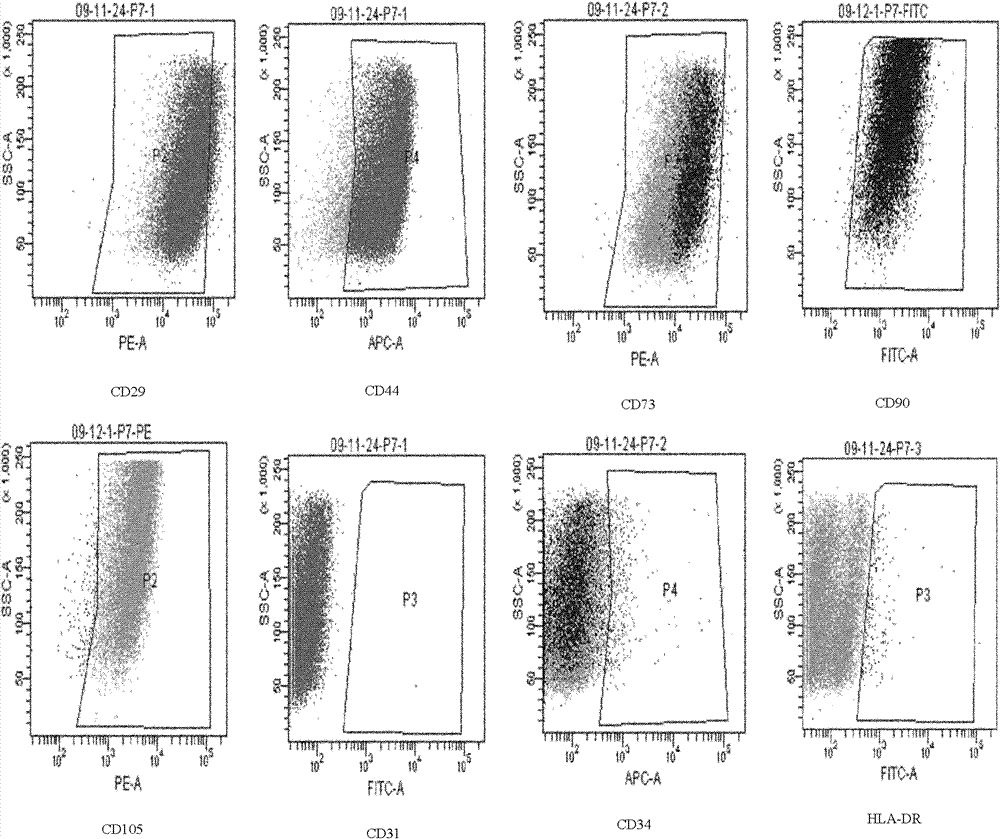
The invention discloses a human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell and a preparation method thereof. The human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell is prepared by carrying out aseptic treatment, mechanical shearing, Wharton jelly exposure, collagenase digestion and isolated culture on an umbilical stalk of a healthy fetus by a term abdominal delivery. After freezing and thawing, the cell activity does not decline dramatically, thereby ensuring that the human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell is an ideal seed cell for cellular therapy. The invention also relates to a primitive mesenchymal stem cell prepared by the method, and the primitive mesenchymal stem cell is confirmed as the mesenchymal stem cell by the identification of morphology, immunophenotype and invitro differentiation experiments in accordance with the mesenchymal stem cell standards established by International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). The cell count, cell activity, purity, doubling time and multiplication capacity of the human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell are apparently higher than those of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Simple and affordable method for immunophenotyping using a microfluidic chip sample preparation with image cytometry
ActiveUS9442106B2Simpler and cheap and robustIntuitive imagePreparing sample for investigationBiological particle analysisPoint of careFluorescence
The system includes a simple system for CD4 and CD8 counting in point-of-care HIV staging within resource poor countries. Unlike previous approaches, no sample preparation is required with the sample added directly to a chip containing dried reagents by capillary flow. A large area image cytometer consisting of an LED module is used to excite the fluorochromes PerCP and APC labeled targets and a monochrome CCD camera with a combination of two macro lenses captures images of 40 mm2 of blood (approximately 1 micro liter). CD4 and CD8-T-lymphocyte counts correlate well with those obtained by flow cytometry. The cytometer system described in the present invention provides an affordable and easy-to-use technique for use in remote locations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TWENTE
Method for identifying malignant pleural effusion
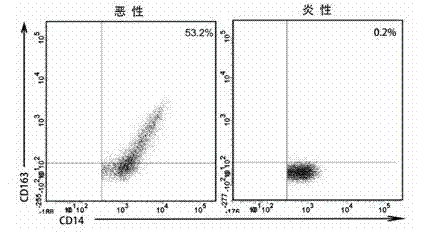
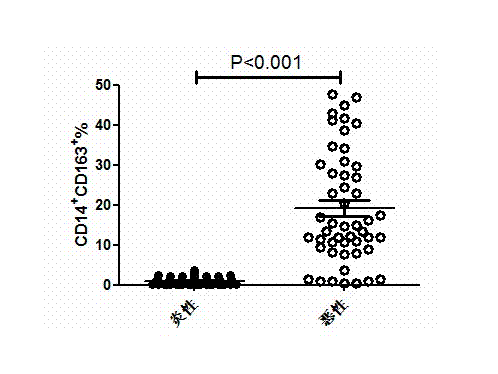
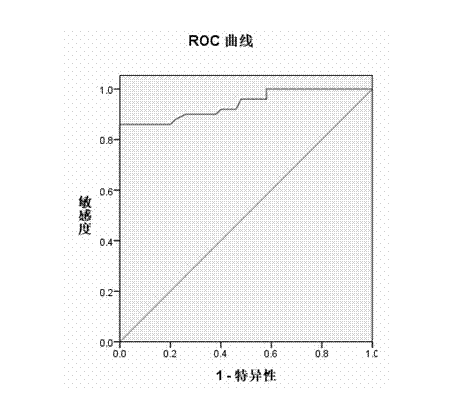
ActiveCN103760349AReduce distractionsHigh sensitivityDisease diagnosisIntervention treatmentOncology
The invention belongs to the technical field of malignant pleural effusion detection methods, and specifically relates to a method for identifying the malignant pleural effusion by using CD14+CD163+cells. The method comprises the following steps of extracting mononuclear cells, labeling antibodies, and performing immunophenotyping analysis by using a flow cytometry. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantages that the method is simple and convenient and rapid, the sensitivity is high, the specificity is high, meanwhile, the interference of man-made subjective factors is reduced by using the method, the method is objective, judgment and identification can be made for the potential malignant pleural effusion patient as soon as possible, and convenience is provided for the subsequent in-time intervention treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com