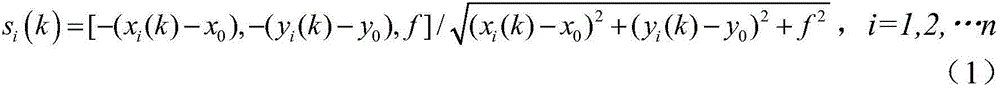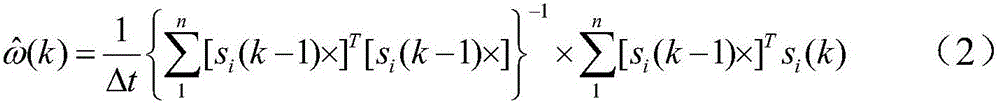Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
92 results about "Guide star" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In astronomy, a guide star is a reference star used to accurately maintain the tracking by a telescope of a heavenly body, whose motion across the sky is primarily due to the rotation of the Earth. Accurate telescope pointing and tracking is critical for obtaining good astronomical images and astrophotographs. However, because the Earth rotates, the sky appears to be in a constant state of motion relative to the Earth. Although this movement appears to be relatively slow when viewed with the naked eye, with the high magnification and consequently smaller field of view provided by even a small telescope this motion becomes apparent on timescales of the order of seconds.
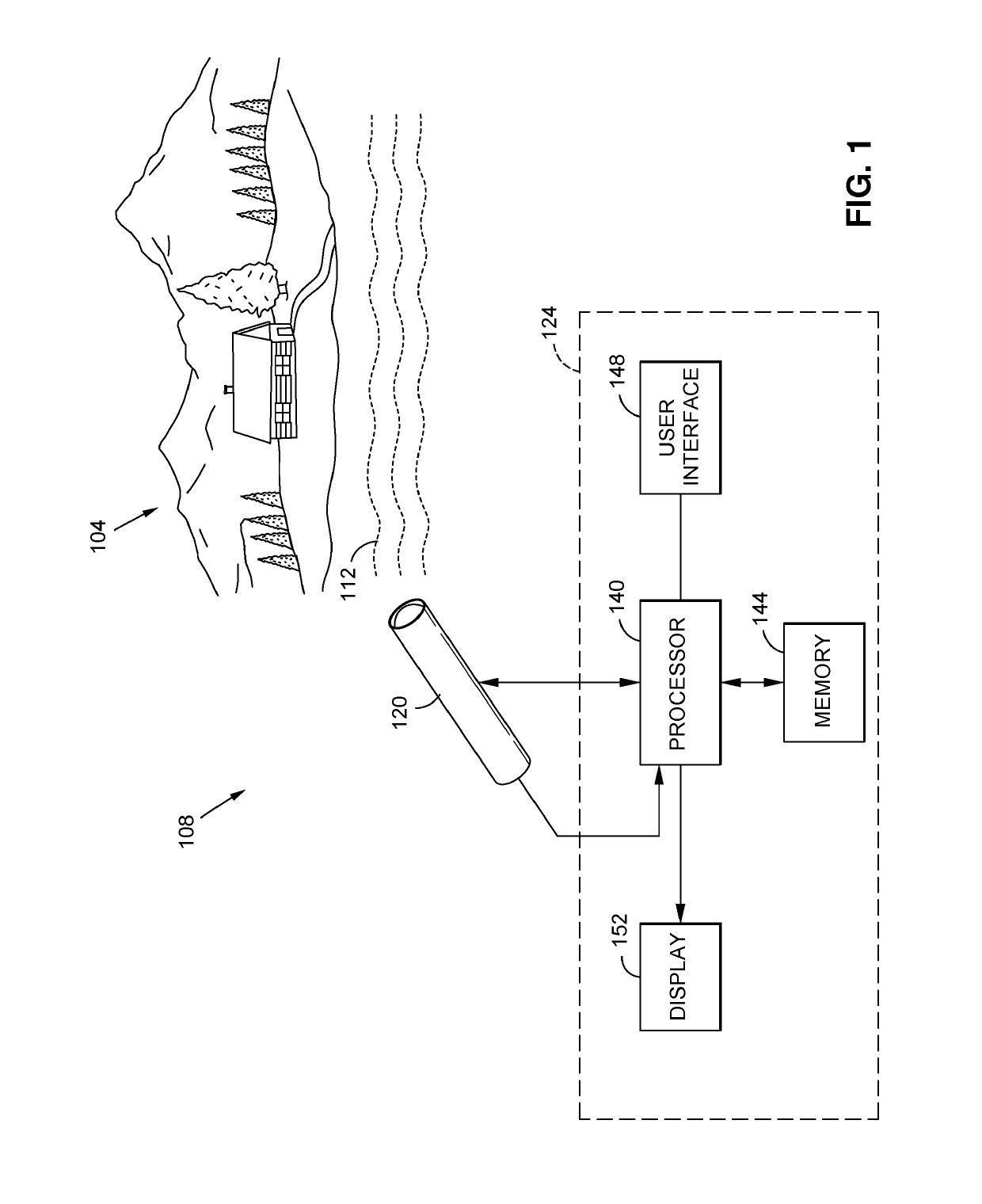
System for measuring atmospheric turbulence
InactiveUS20070077071A1Electromagnetic transmissionElectromagnetic wave reradiationWavefront sensorAngular distance
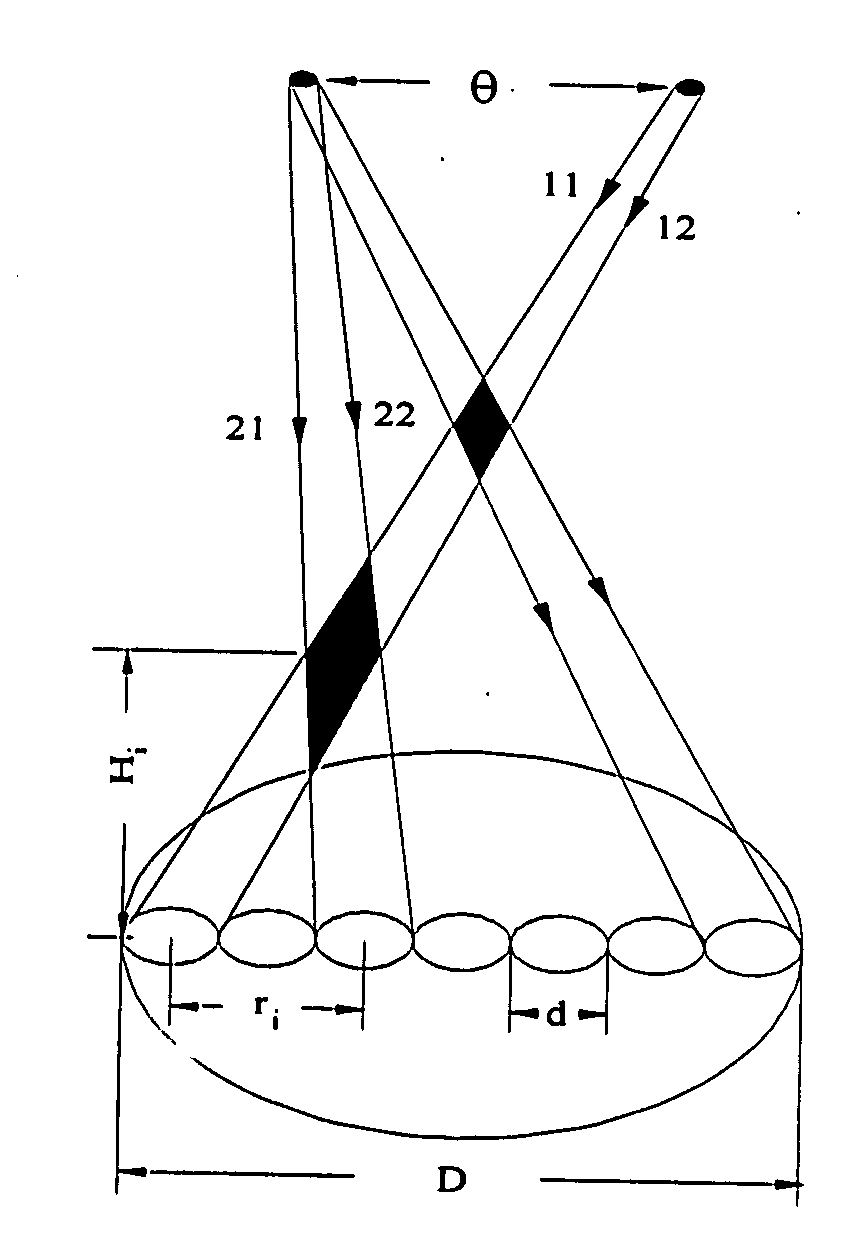
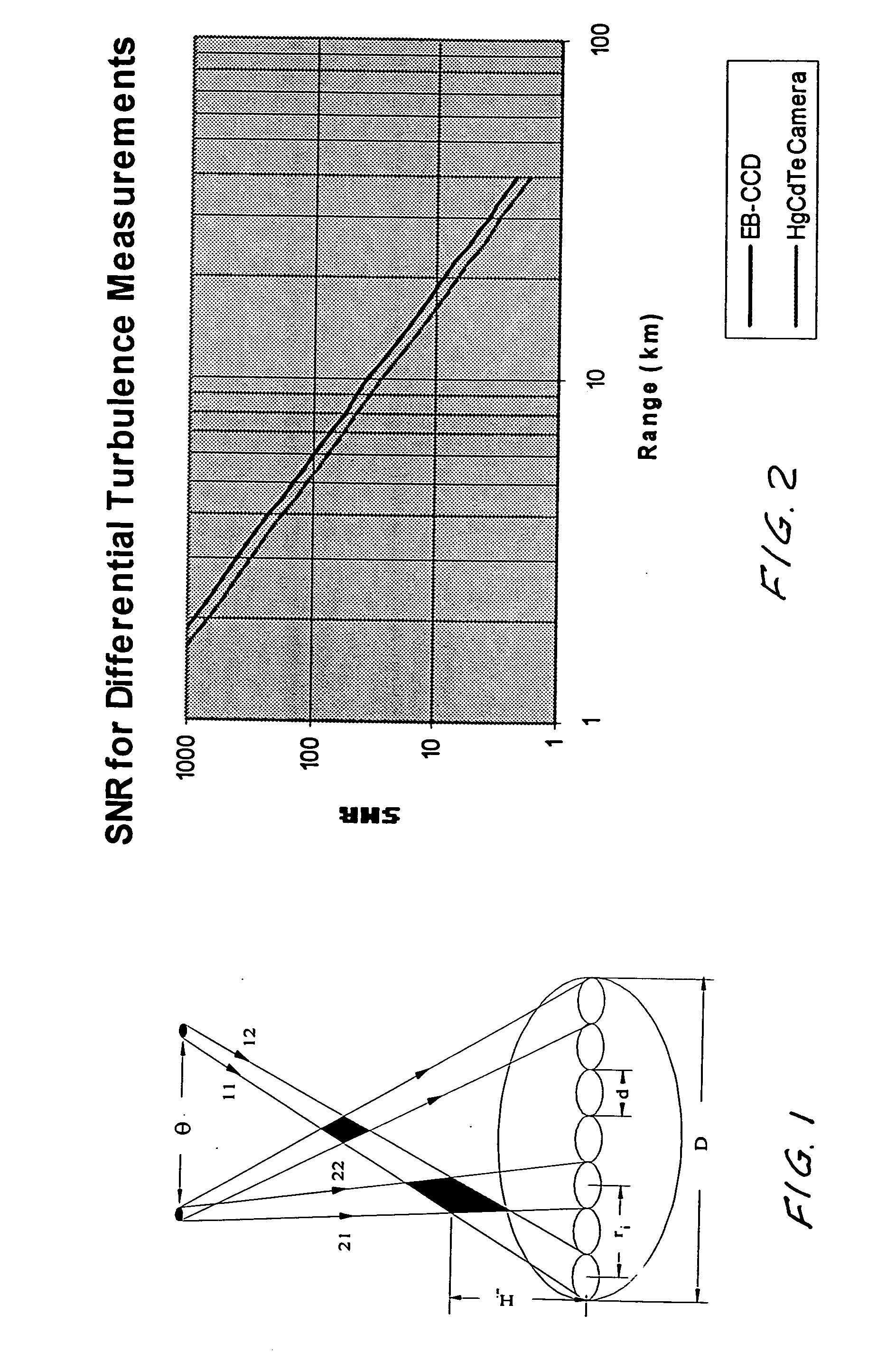
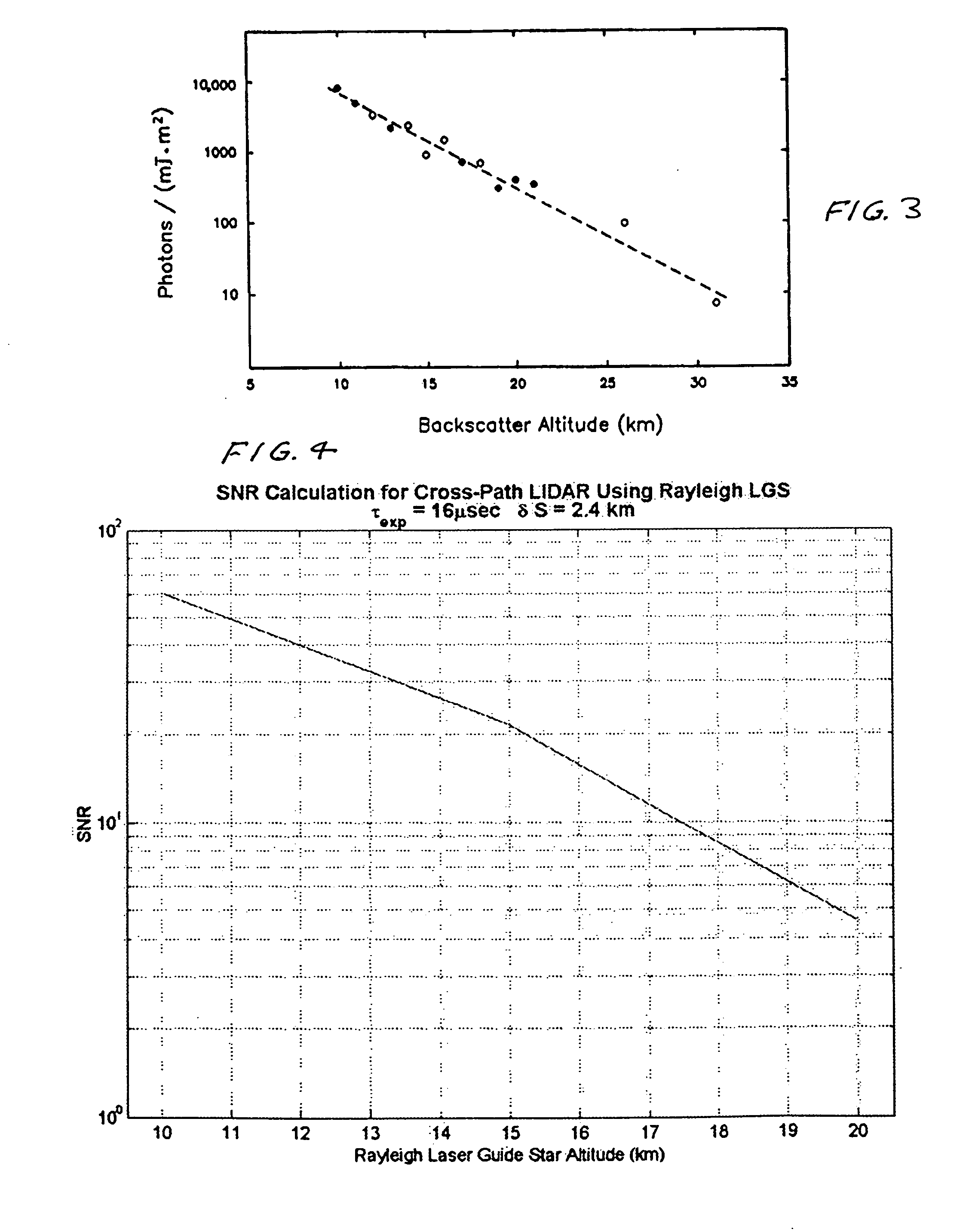
Equipment and techniques for the accurate estimates of the turbulence profile to improve the performance of adaptive optics systems designed to compensate the degradation effects of turbulence on directed energy systems, in astronomy, and in laser communication systems. The present invention is an optical turbulence profiler. The invention includes a cross-path LIDAR. The cross-path LIDAR technique uses laser guide star technology combined with a cross-path wavefront sensing method. In this method, two Rayleigh, or sodium, laser beacons separated at some angular distance are created by using a pulsed laser and a range-gated receiver. In preferred embodiments a Hartmann wavefront sensor measures the wavefront slopes from two laser guide stars. The cross-correlation coefficients of the wavefront slope are calculated, and the turbulence profile of refractive index structure characteristic Cn2(z) is reconstructed from the measured slope cross-correlations.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Robust integrated precision high-speed satellite attitude determination and control system (ADCS)
ActiveUS20150219744A1Robust and efficient satellite attitude determinationRobust and efficient and controlPosition fixationColor television detailsStar trackerControl system
Various embodiments of the present invention provide methods, systems, apparatus, and computer program products for providing integrated attitude determination and attitude control for slewing of a satellite. In one embodiment a method is provided. The method comprises after receiving a repointing request, selecting a guide star sample comprising one or more guide stars from a guide star catalog; determining current attitude information; selecting and retrieving at least one point spread function (PSF) image from a PSF library; estimating an expected position for at least one guide star, the at least one guide star being one of the guide stars of the guide star sample; acquiring at least one star tracker image; calculating a cross-correlation function (CCF) to determine shifts in position of the at least one guide star compared to the expected position; and determining updated current attitude information based at least in part on the determined shifts in position.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Interferometric focusing of guide-stars for direct wavefront sensing
ActiveUS20160003740A1Limited resolutionReduce penetration depthOptical measurementsPhotometryWavefront sensorNear infrared laser
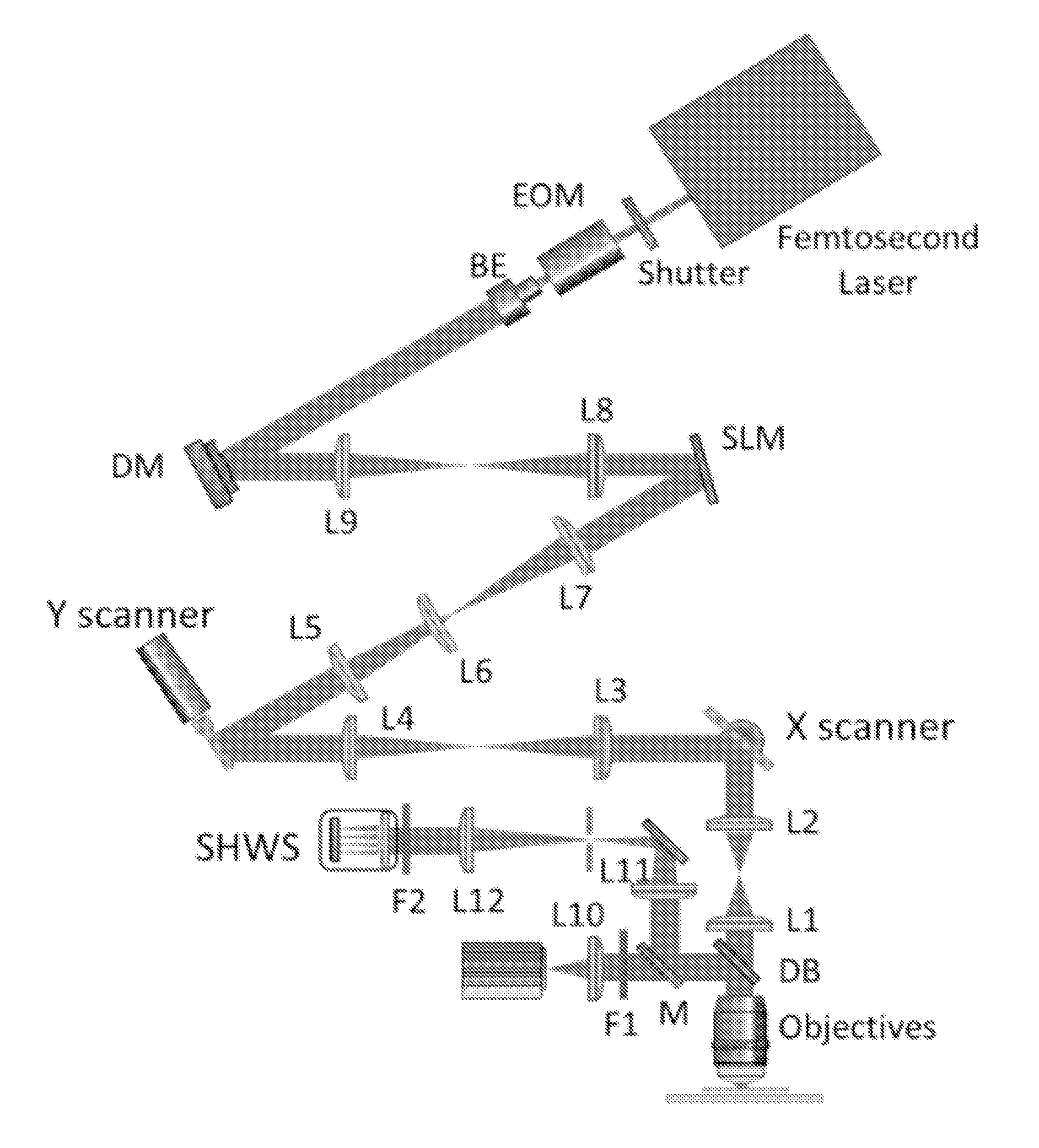
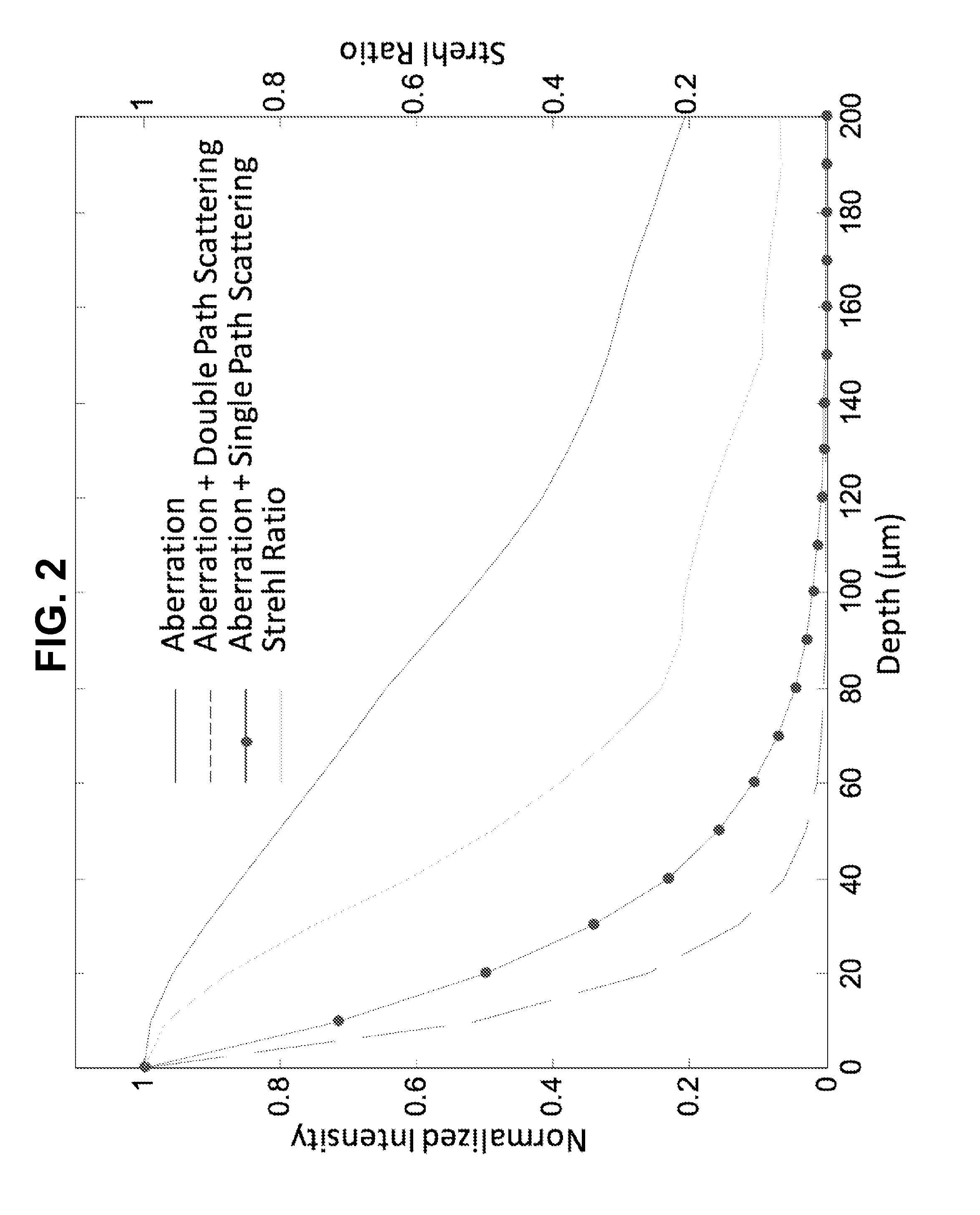
Interferometric focusing (IF), rather than conventional geometric focusing, of excitation light onto a guide-star that is embedded deeply in tissue, increases its fluorescence intensity. The method can extend the depth of wavefront measurement and improve correction inside of tissues because of its ability to suppress both scattering of diffuse light and aberration of ballistic light. The results showed more than two times improvement in SNR and RMS error of the wavefront measurement. Although only ballistic light in the excitation path is corrected, the intensity after wavefront correction increased by 1.5 times. When applying IF to a two-photon microscope with a near infra-red laser, this method would further extend the measurement depth and achieve high SNR for the wavefront sensor.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for making guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors
InactiveCN106595645AGuaranteed completenessGuaranteed even distributionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsSky
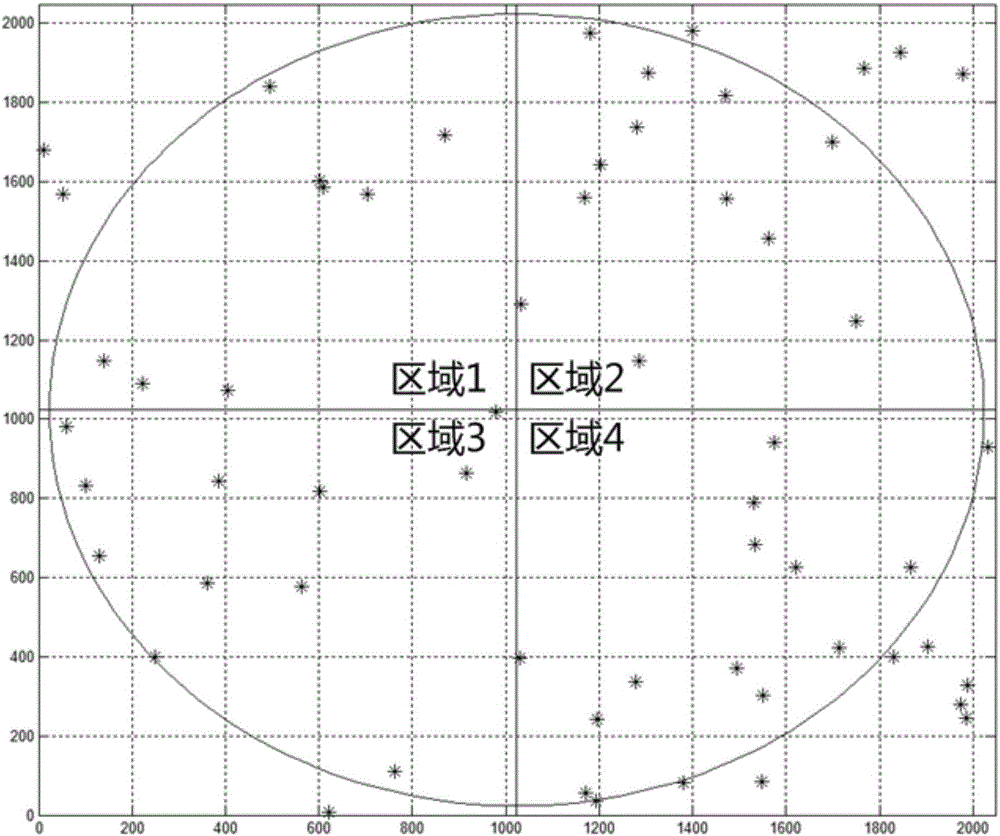
The invention provides a method for making a guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors. The method comprises the following steps: S1, subjecting a basic star database to screening of fixed stars; S2, generating the direction of an optical axis of a test sky area covering the whole celestial sphere; S3, converting the celestial system of coordinates of all the fixed stars in a field of view under the direction of the optical axis into a planar system of image plane projection; S4, dividing an image plane into n regions and arraying fixed stars in each region according to m combination modes; S5, carrying out attitude solution on each combination mode of the fixed stars and removing combination modes with great errors in an accuracy index; S6, searching for fixed stars in the whole view field of the image plane and combination modes of the fixed stars forming polygons with great errors in a mismatching accuracy index; and S7, carrying out steps S2 to S6 on each optical axis direction and combining overlapped fixed star points in each sky area so as to obtain the guide star database. According to the invention, the selection process of guide stars in each field range is optimized, so a fixed star combination eventually chosen is guaranteed to meet requirements of average distribution, and attitude calculation precision is guaranteed to be optimal.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
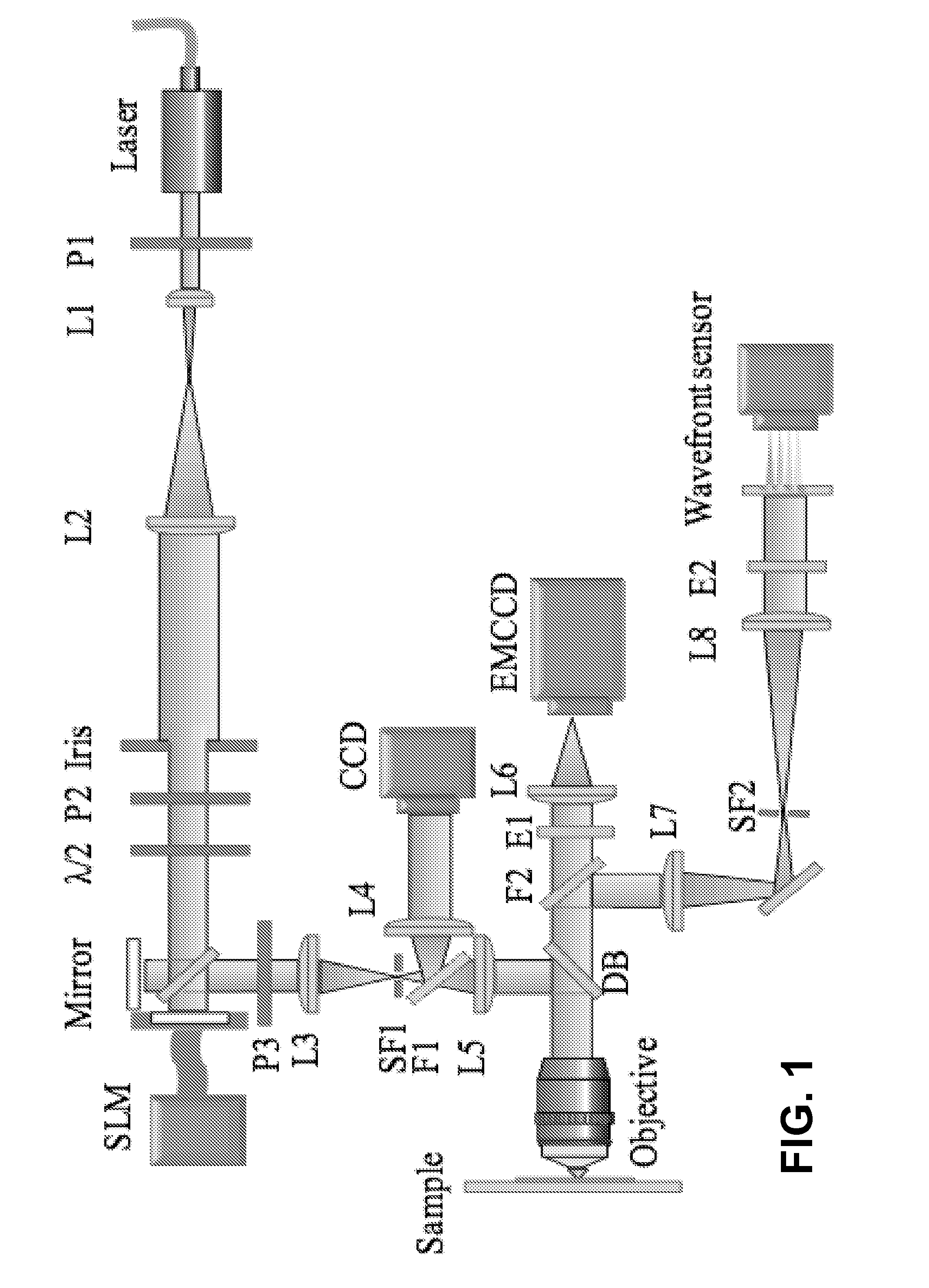
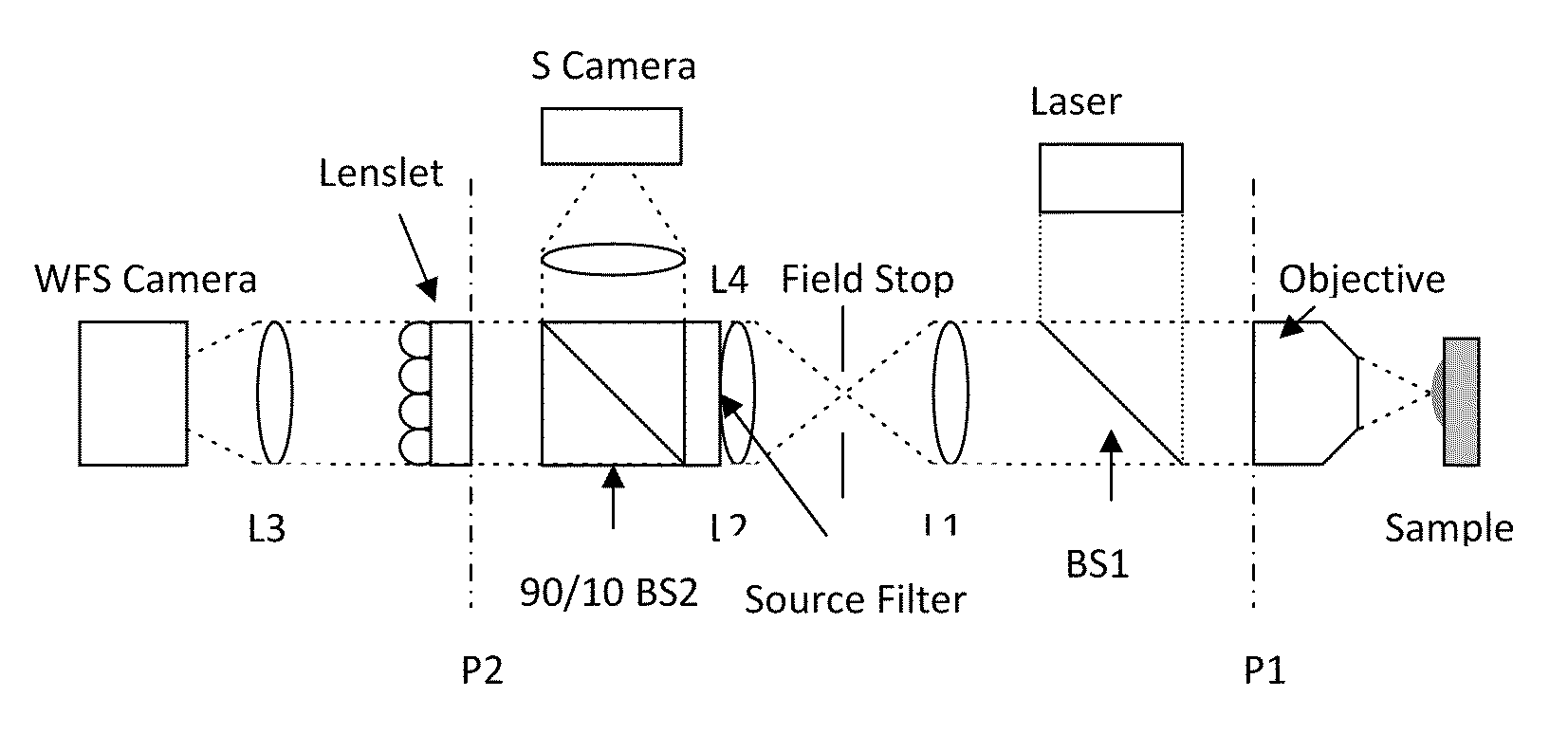
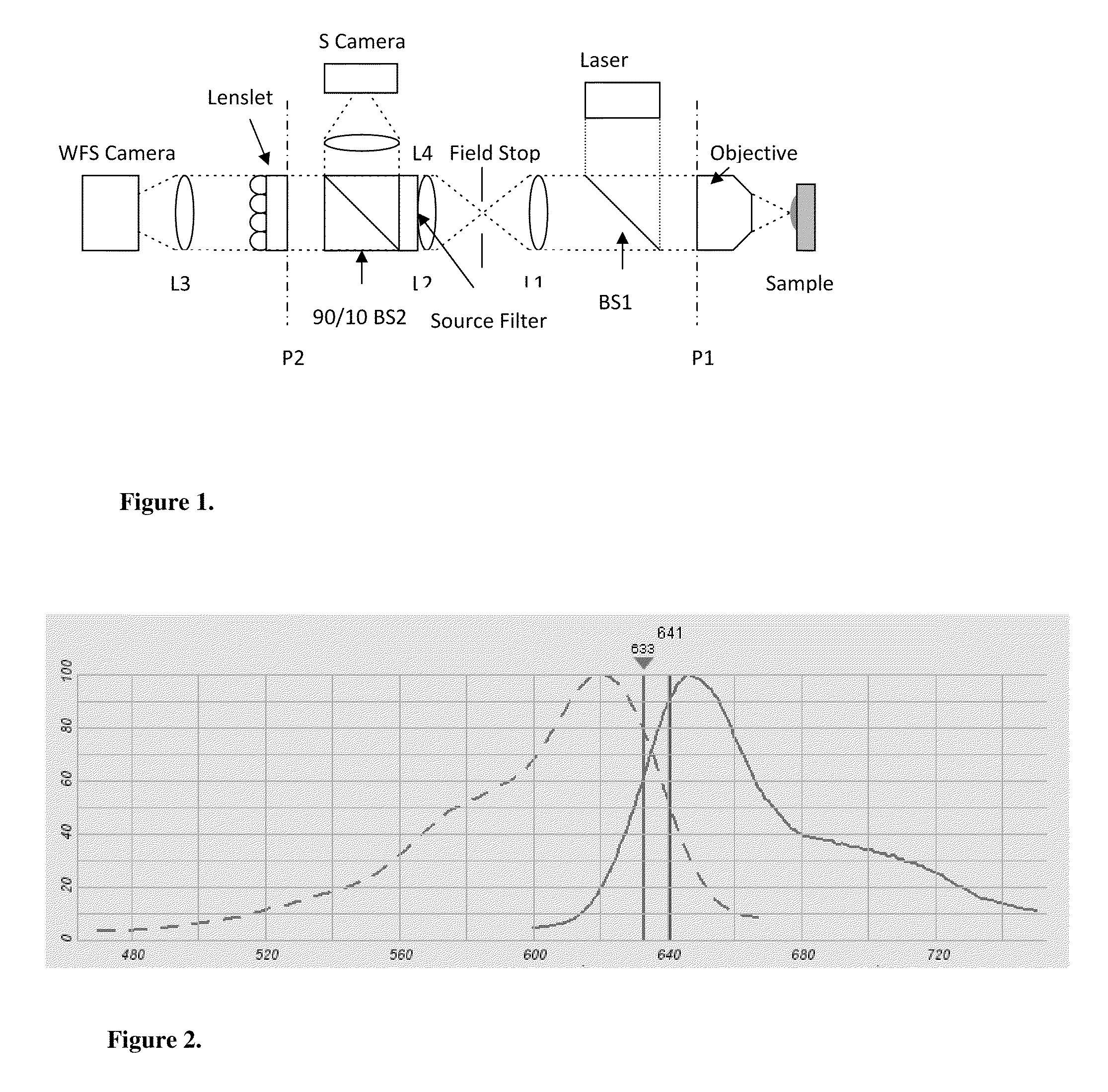
Use of a reference source with adaptive optics in biological microscopy
ActiveUS20100105105A1Raise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicro imagingStrehl ratio
Methods of microscopic imaging of biological tissue using adaptive optics technology to improve the image focus and sharpness. Wavefront measurements are taken by using a novel method of seeding biological tissue by using a fluorescent microsphere as a “guide star” as a natural point-source reference. The current methods are capable of improving the Strehl ratio of modern biological microscopes as much as 15 times.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
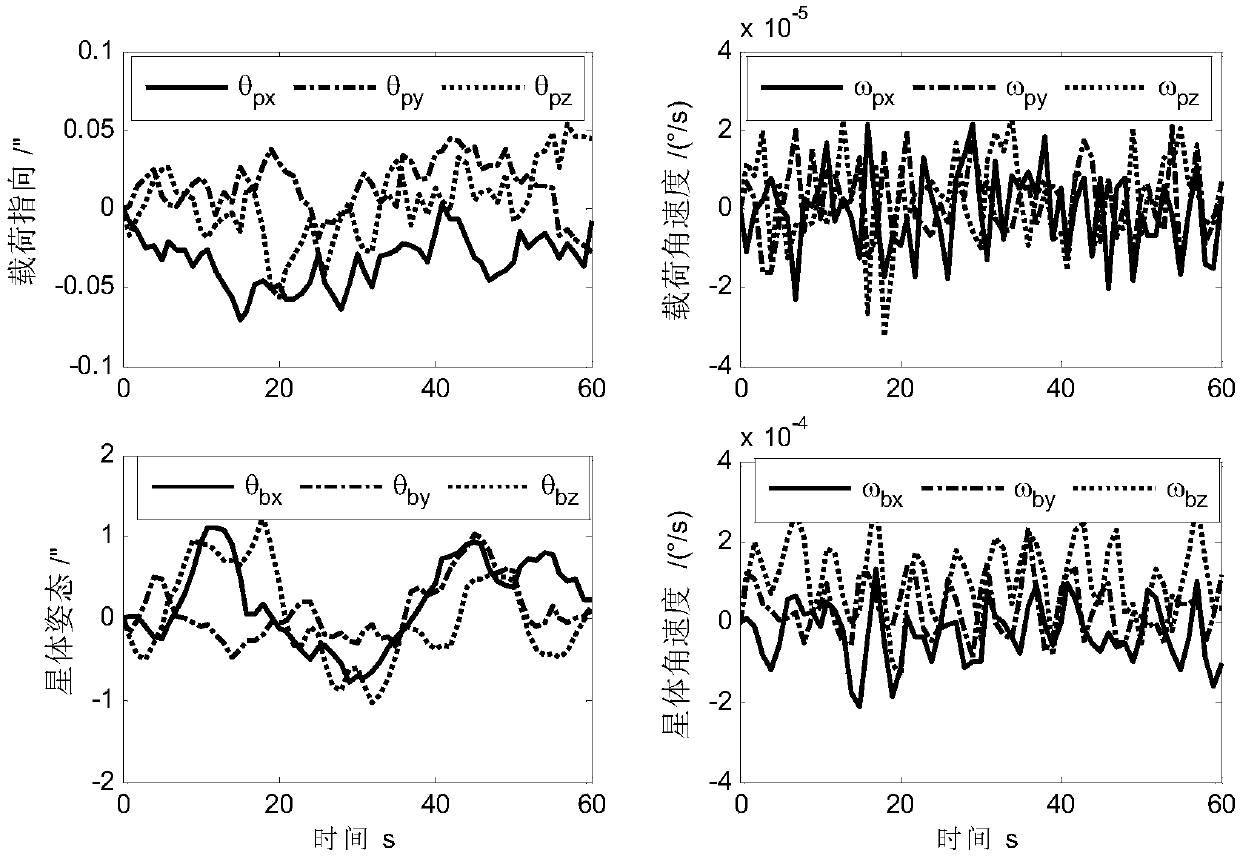
Determining method for ultrahigh-accuracy attitude of spacecraft multi-stage compound control system
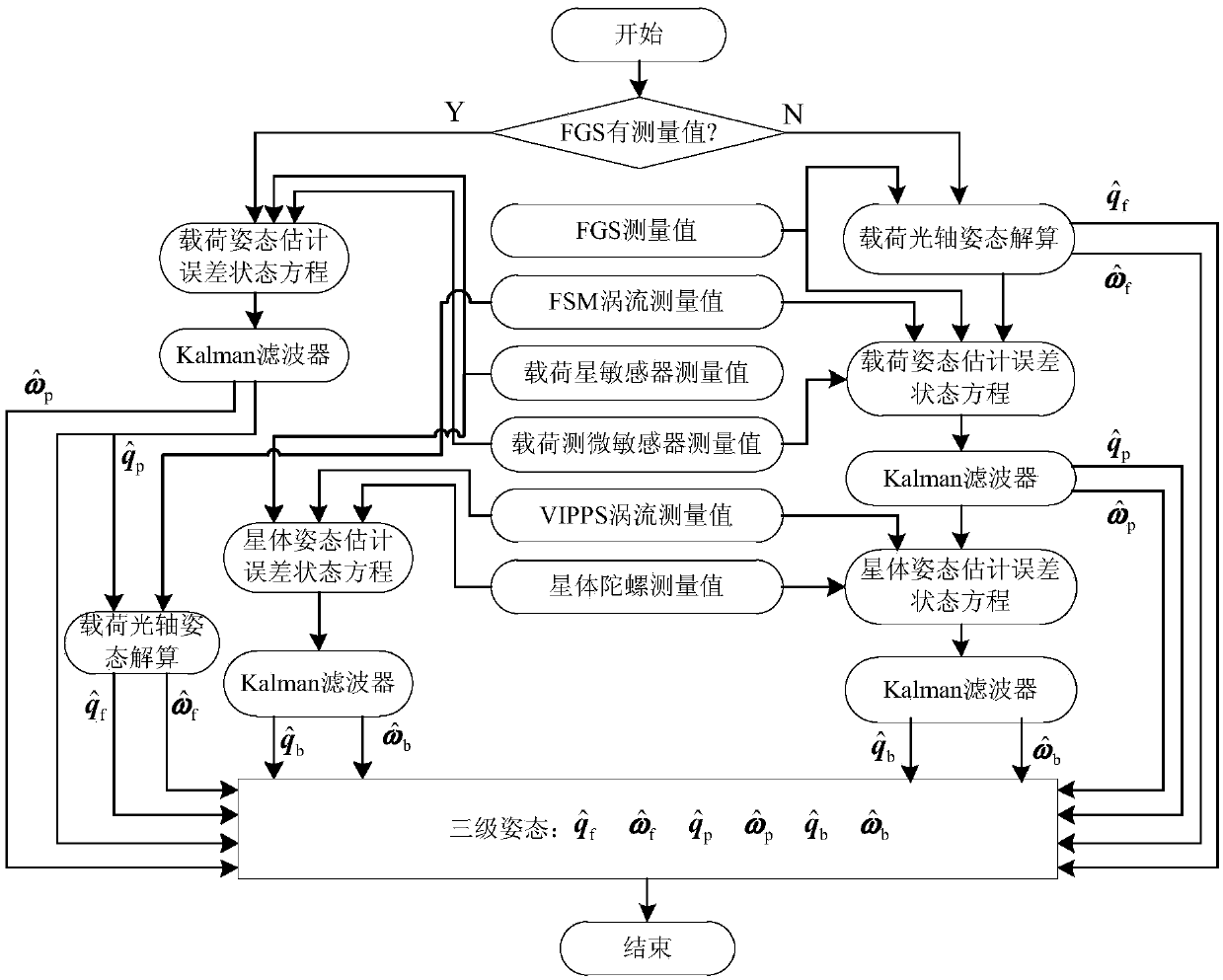
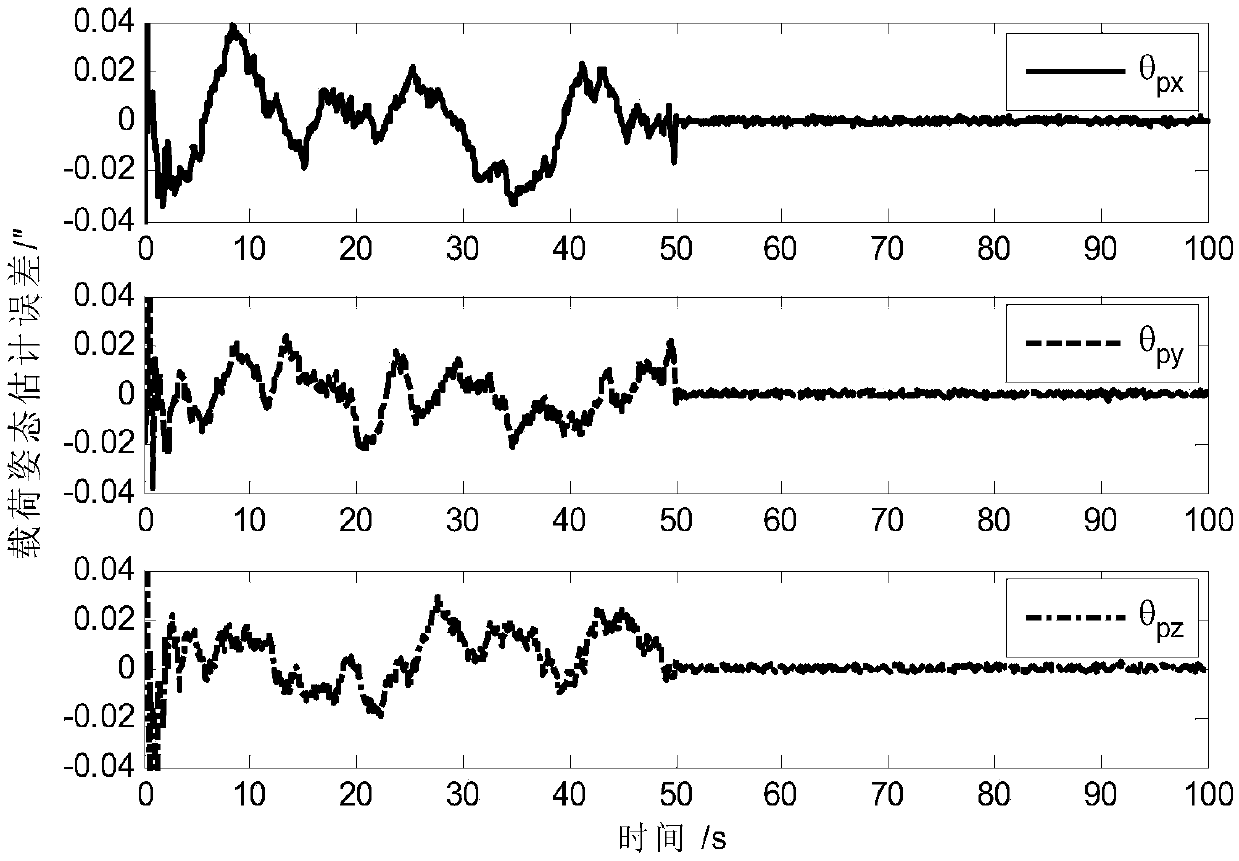
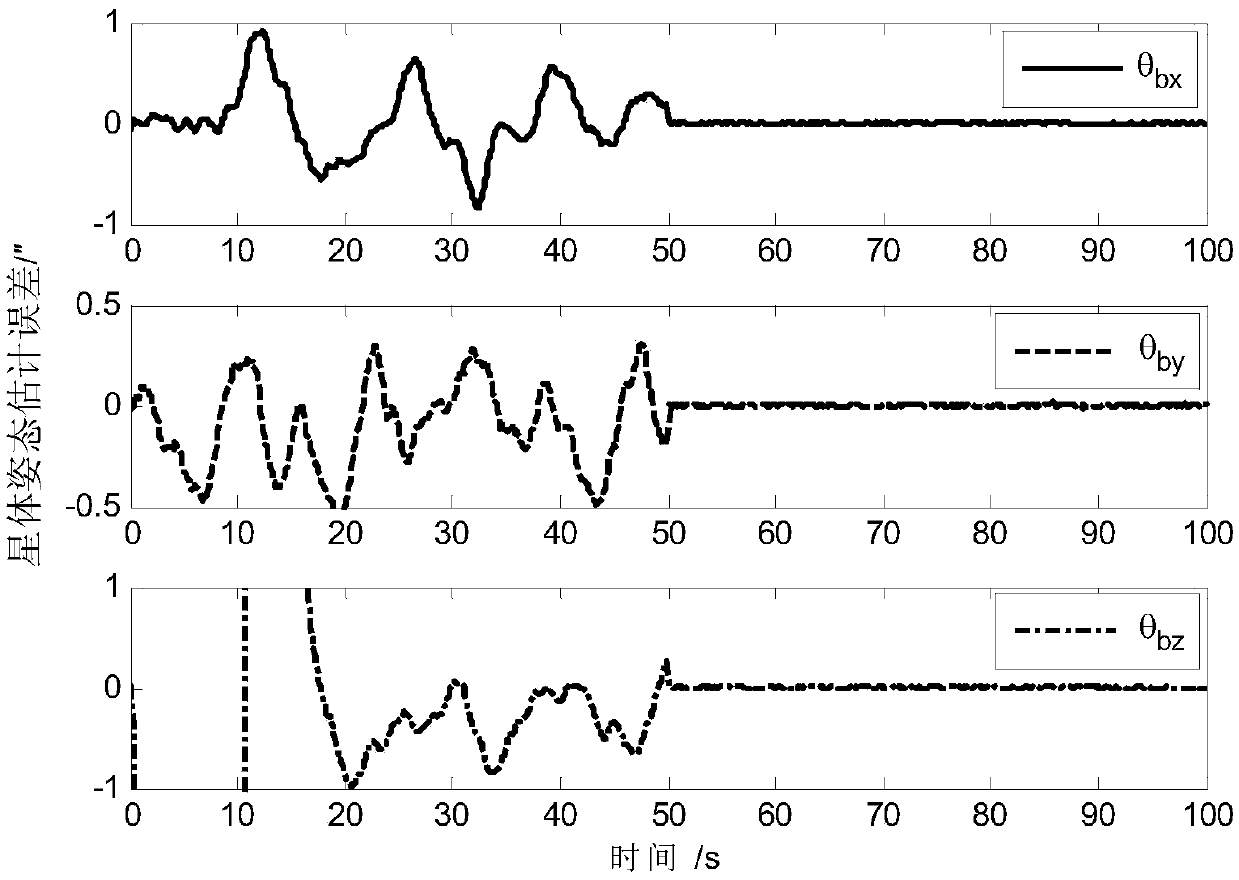
ActiveCN108801270AAchieving High-Precision EstimationImplementing Relative Pose EstimationCosmonautic vehiclesInstruments for comonautical navigationQuaternionControl system
A determining method for ultrahigh-accuracy attitude of a spacecraft multi-stage compound control system. The determining method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an attitude constraintmodel between a star and a load as well as between the load and a fast reflective mirror of the spacecraft multi-stage compound control system; (2) establishing a relative attitude quaternion model between the star and the load as well as between the load and the fast reflective mirror; (3) judging whether a star guiding sensor has a measured value or not; (4) establishing a load attitude estimation error state equation if the star guiding sensor has no the measured value, estimating a load attitude by adopting a Kalman filtering method, and realizing determination on high accuracy of the loadattitude; (5) establishing a star attitude estimation error state equation, and realizing determination on high accuracy of a star attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method; (6) estimating a load sight attitude by adopting a measured value qfm of the star guiding sensor if the star guiding sensor has the measured value; (7) establishing the load attitude estimation error state equation, estimating the load attitude by adopting the Kalman filtering method, and realizing the determination on high accuracy of the load attitude; (8) establishing the star attitude estimation error state equation.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Coarse and fine layered, fast and slow combined and active and passive integrated multi-level composite control method for spacecraft
ActiveCN109002047AImprove load stability indexReduce the stability indexCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsThree levelGyroscope
The invention relates to a coarse and fine layered, fast and slow combined and active and passive integrated multi-level composite control method for a spacecraft. A layered control idea in a star-load-fast reflection mirror three-level system includes the following steps: 1) fast reflection mirror third-level control: adopting a guiding star sensor as a measuring component, adopting a fast reflection mirror actuator as an executing mechanism, and adopting a PID controller to realize the ultra-high-precision pointing control of a rolling-pitching axis of a fast reflection mirror; 2) load secondary control: adopting a load star sensor, a micrometer gyroscope and an FSM eddy current as the measuring components, adopting an active pointing ultra-static platform (VIPPS) actuator as the executing mechanism, and adopting the PID controller to realize the high-precision pointing control of the load; and 3) star first-level control: adopting a gyroscope, the load star sensor and a VIPPS eddy current as the measuring components, adopting a momentum wheel as the executing mechanism, and adopting the PID controller to realize the coarse pointing control of the star.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Laser beam optical fiber transmission device in laser sodium guiding technology
InactiveCN101271176AImprove power conversion efficiencyLarge core diameterGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberLight beam
A laser beam optical fiber transmission device of a laser sodium guide star technology is characterized in that: the device uses a cylindrical multimode optical fiber for producing a conical shape by adopting the melt-pulling method for pulling, then a table is formed by grinding, the device comprises: a cylindrical multimode optical fiber part and a conical table optical fiber part, the conical table optical fiber part is formed at the tail end of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber by direct processing, the other end of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber is an input end of a laser beam, the other end of the conical table optical fiber is an output end of the laser beam, the length of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber is equal to 1 to 1.2 times of the distance from a laser to a transmitting telescope; the radius of a fiber core of the conical table optical fiber which is arranged at the thick end is equal to the radius of the fiber core of the cylindrical multimode optical fiber, and the radius of the fiber core of the conical table optical fiber which is arranged at the thin end meets the single-mode condition for transmitting the laser by the optical fiber. The optical fiber transmission device has the advantages of simple and flexible structure and low cost, the quality of the output light beam is close to the diffraction limit, at the same time, the optical fiber transmission device can effectively overcome the non-linear scattering and other effects during the optical fiber transmission, thus achieving the purpose of transmitting the higher laser power.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
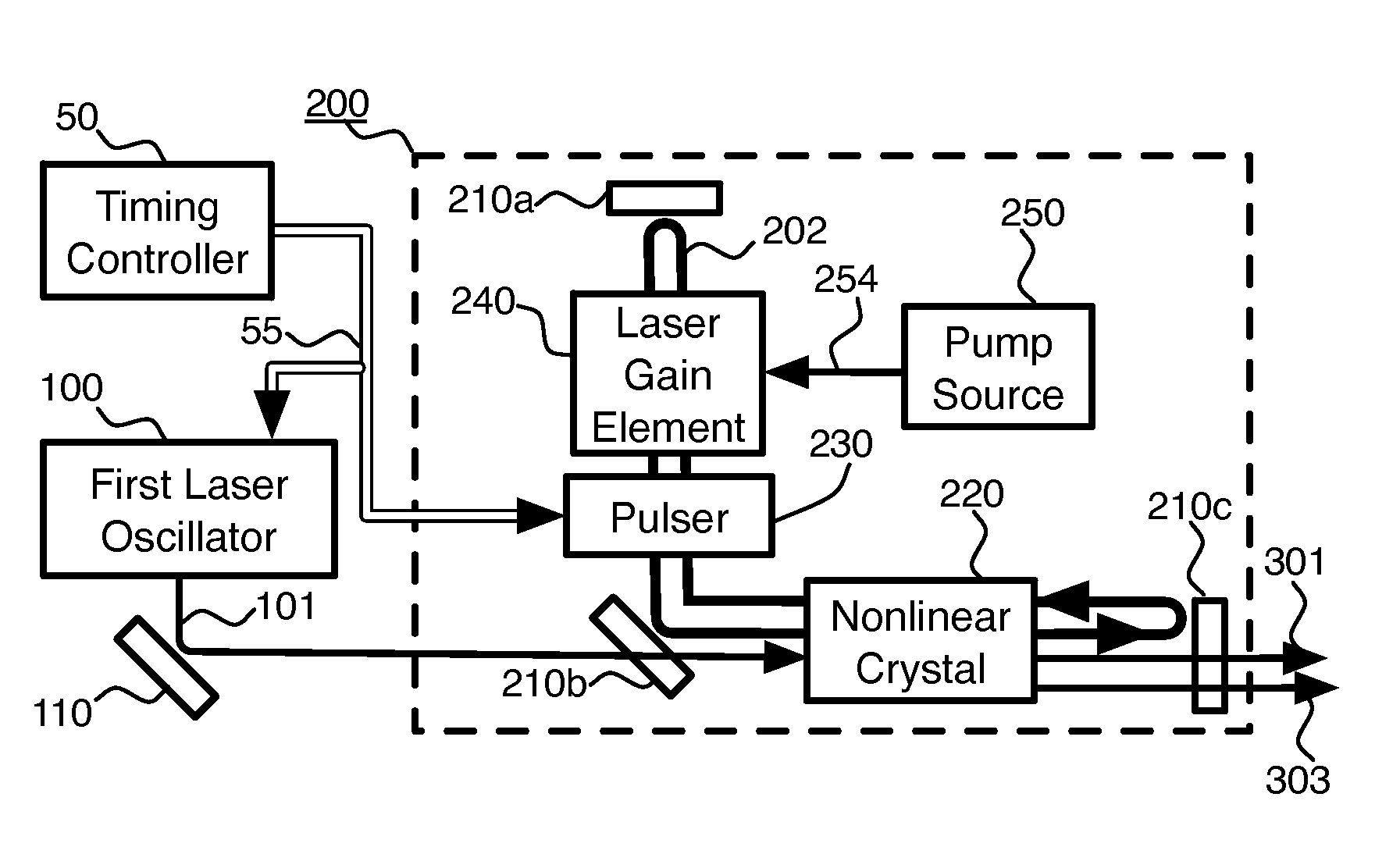
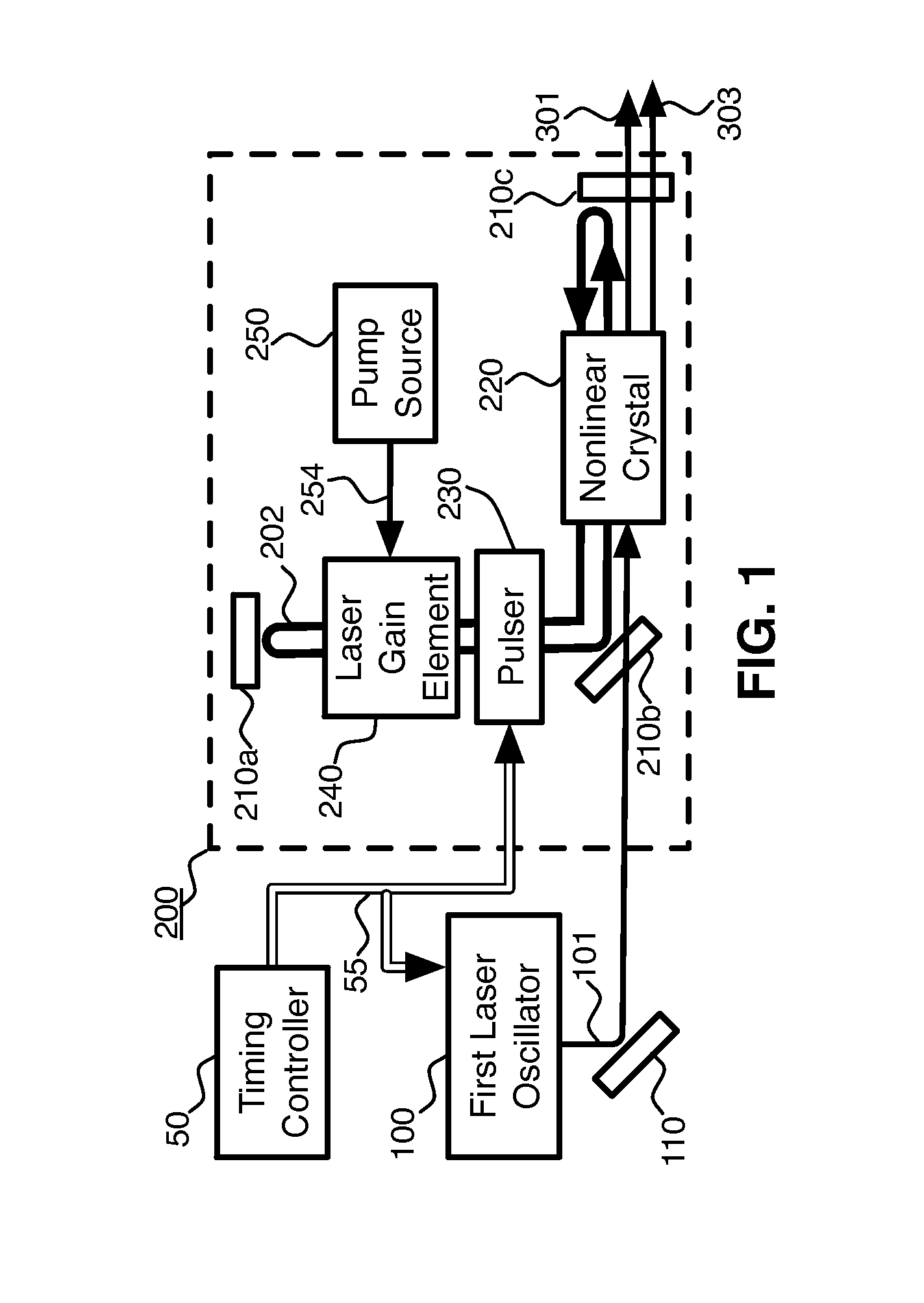
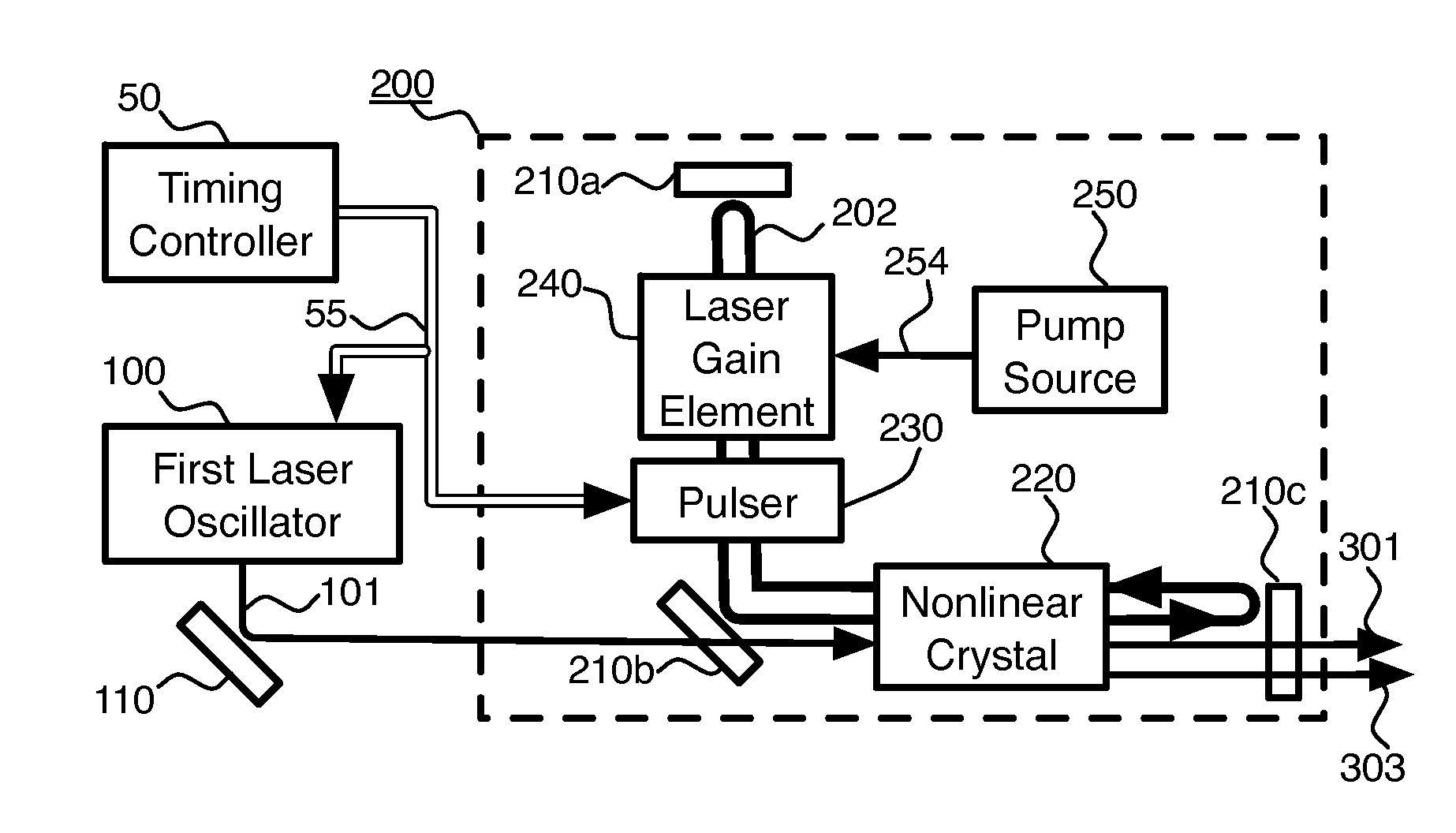
Pulsed, Internal Optical Mixer
InactiveUS20140301417A1Increase powerHigh beam qualityLaser detailsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesOptical parametric amplifierSum-frequency generation
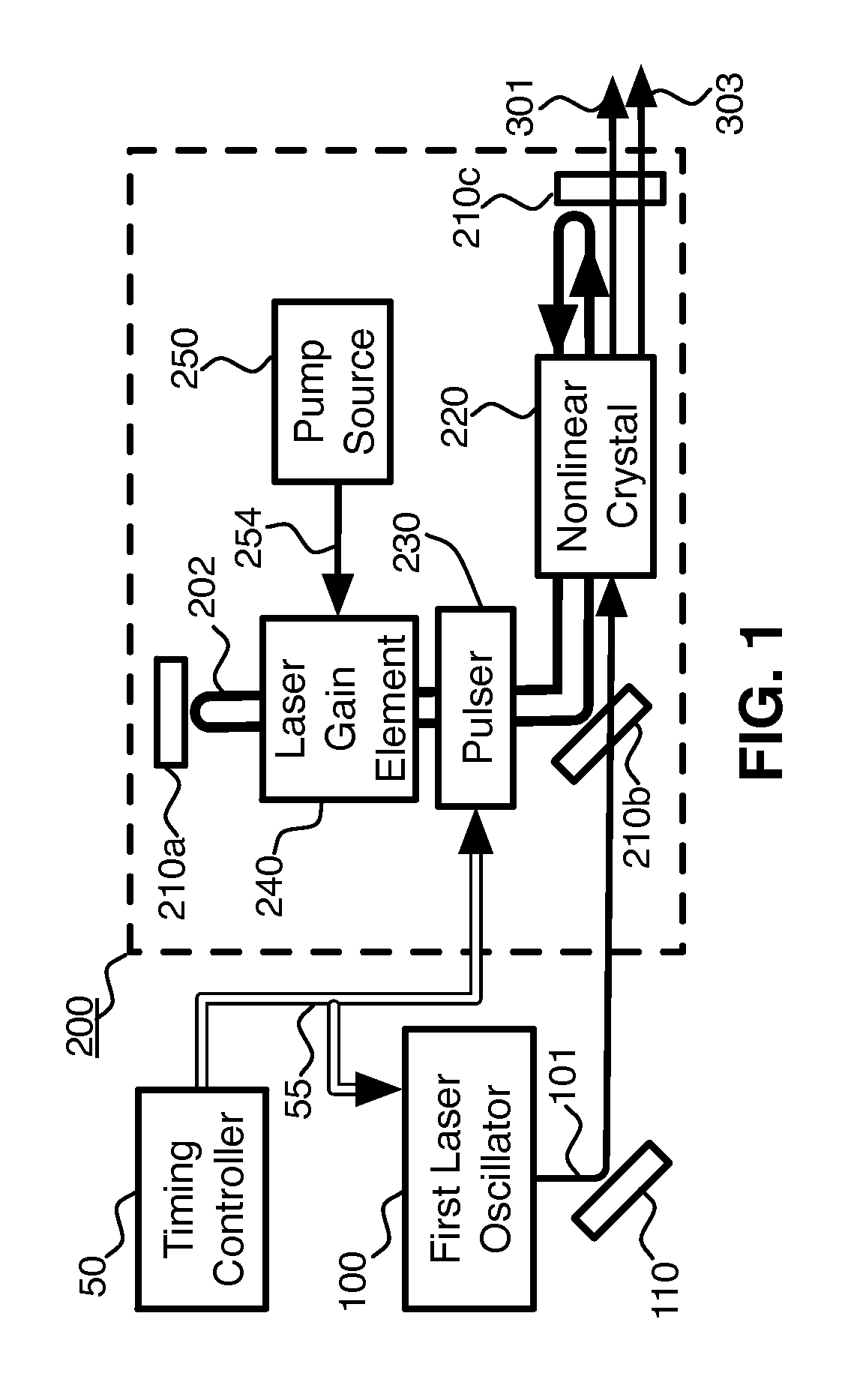
Pulsed, coherent light is generated by optical mixing which takes place inside the resonator of a pulsed laser oscillator. One of the beams to be mixed is generated by the pulsed laser, and the other by a distinct, external laser oscillator. If the light from the external oscillator is modulated, that modulation will be transferred onto the light generated by the optical mixing. This enables modulated light at an expanded range of wavelengths. Using sum frequency generation, light for sodium excitation, such as for a guide star, can be generated with the optimal modulation of spectral and temporal properties. If the type of optical mixing is difference frequency generation, optical parametric amplifiers with improved efficiency and beam quality are enabled.
Owner:FASORTRONICS
Single-frequency solid-state raman laser
ActiveCN105552709AImprove stabilityExtended Laser Wavelength RangeLaser using scattering effectsHigh peakBeam splitter
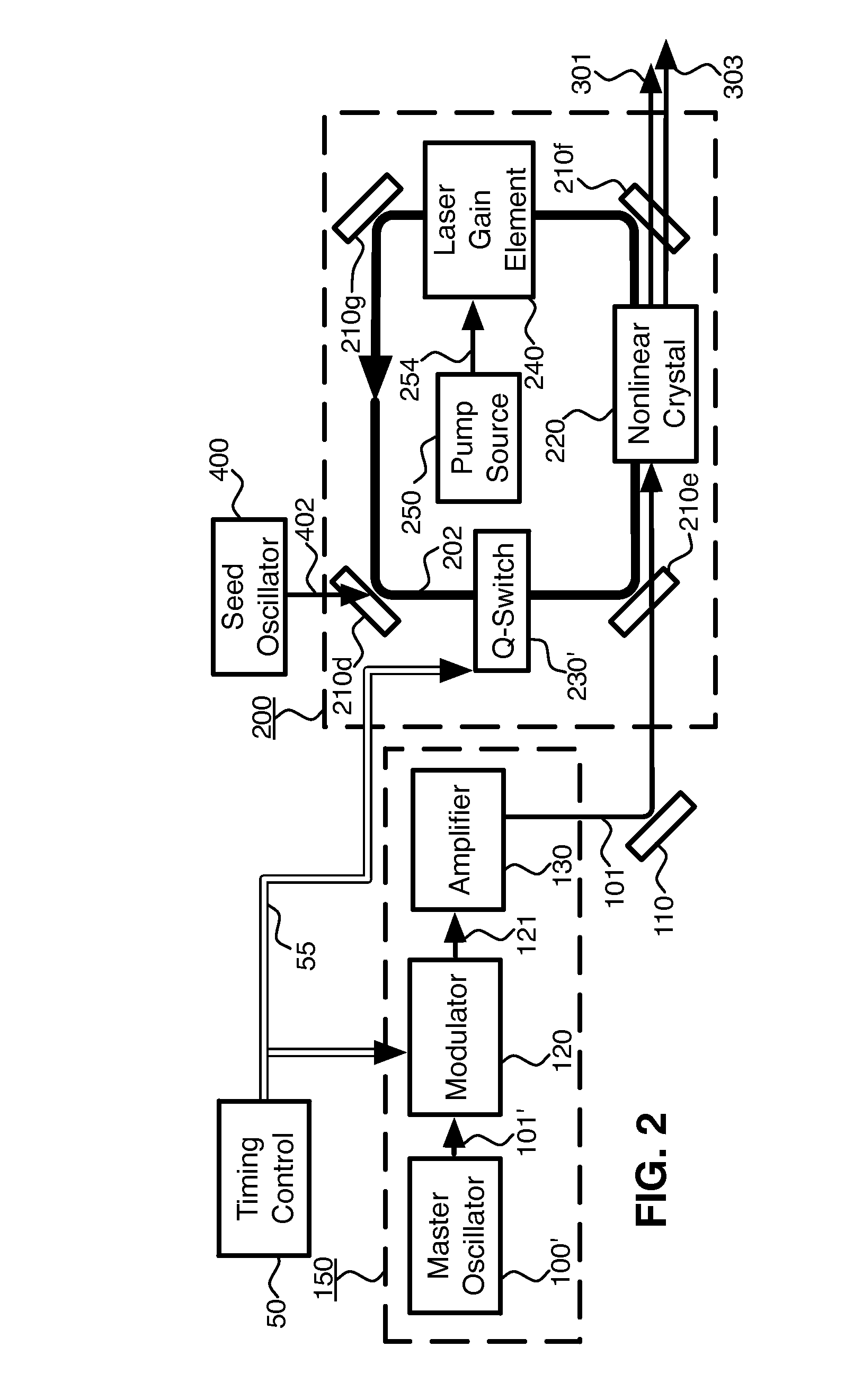
The invention relates to a single-frequency solid-state raman laser, and belongs to the technical field of lasers. The single-frequency solid-state raman laser comprises a pumping source, a coupling lens group, a laser gain medium, a raman crystal, an endoscope M1, an endoscope M3, an endoscope M4, a beam splitter M5 and a temperature control system, wherein the pumping source outputs a pump light; the coupling lens group, the endoscope M1, the laser gain medium, the raman crystal, the endoscope M3, a first FP etalon, a second FP etalon, the endoscope M4 and the beam splitter M5 are arranged along the propagation direction of the pump light; the temperature control system is arranged out of the laser gain medium and the raman crystal, so that stable single-frequency raman laser output with a high-peak power can be achieved; the single-frequency solid-state raman laser can be applied to the fields of a sodium guide star, nonlinear conversion, terahertz generation, laser medical treatment and the like, and has the characteristics of being wide in applicability, compact in structure, good in stability, simple to operate, low in cost, beneficial to industrial production and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Dual-mode electro-optic sensor and method of using target designation as a guide star for wavefront error estimation
ActiveUS8502128B1Reduce wavefront errorGood estimateDirection controllersSpecial data processing applicationsAngle of incidenceDual mode
A dual-mode sensor uses the active guidance radiation as a “guide star” to generate a wavefront error estimate for the primary optical element in-situ without interfering with the generation of either the active guidance or passive imaging guidance signals. An array of optical focusing elements performs the normal function of spatially encoding an angle of incidence of the active guidance radiation at an entrance pupil onto an active imaging detector. The array also performs an additional function of spatially encoding wavefront tilt deviations emanating from sub-pupils of an exit pupil onto the active imaging detector. A processor processes the electrical signals from the imaging detector in accordance with the respective spatial encodings to generate an active guidance signal and the wavefront error estimate for the primary optical element.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
589 nm laser based on raman frequency conversion and laser sum frequency
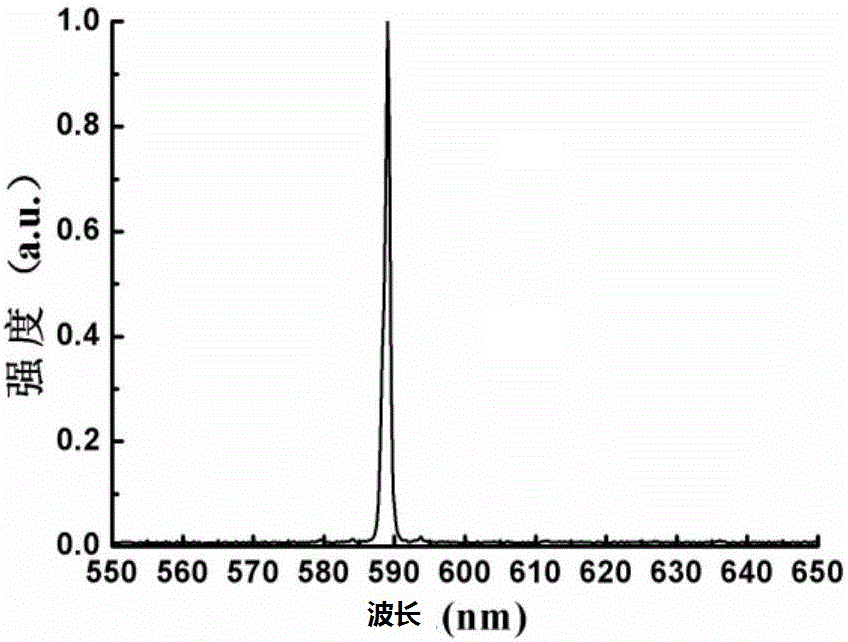
ActiveCN106785881ASimple structureCompact structureLaser using scattering effectsResonant cavityBarium nitrate
Provided is a 589 nm laser based on raman frequency conversion and laser sum frequency. The 589 nm laser based on the raman frequency conversion and the laser sum frequency is composed of a 1064 nm laser source, a faraday isolator, a half slide, a beam split element, a front cavity mirror of a first raman resonant cavity, a tungstic acid gadolinium potassium crystal, a rear cavity mirror of the first raman resonant cavity, a first filtering lens, a first reflecting mirror, a front cavity mirror of a second raman resonant cavity, a barium nitrate crystal, a rear cavity mirror of the second raman resonant cavity, a second filtering lens, a second reflecting mirror, a nonlinear crystal and a third filtering lens. According to the 589 nm laser based on the raman frequency conversion and the laser sum frequency, the structure is simple, synchronization is easy to realize, the obtained 589 nm can be used for generating sodium guide stars, and the 589 nm laser based on the raman frequency and the laser sum frequency has an important significance in fields of astronomy, national defense and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
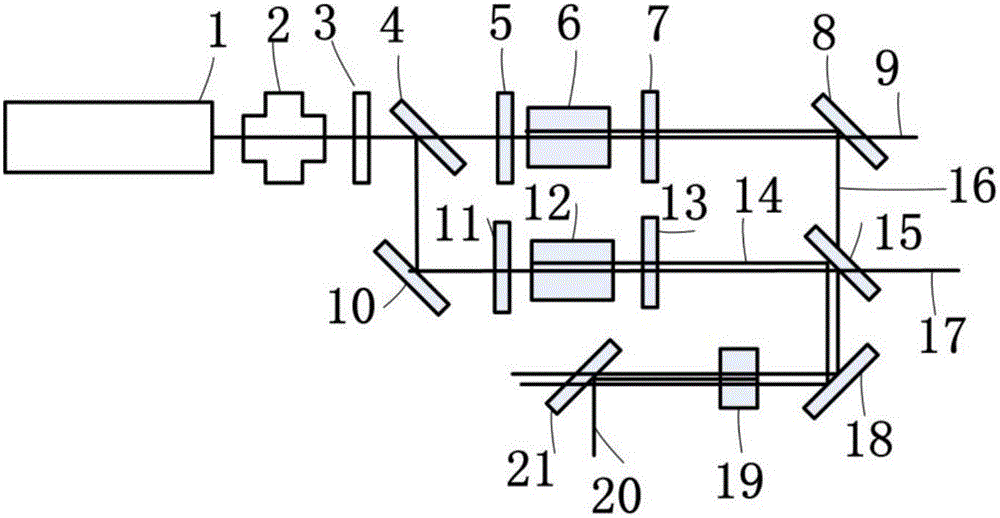
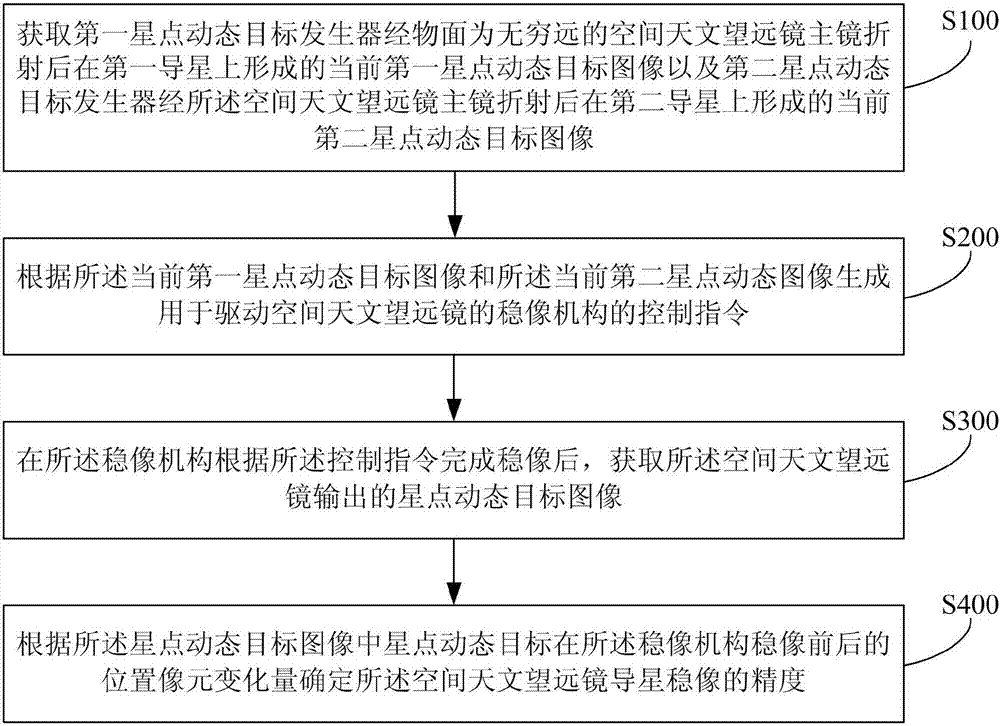
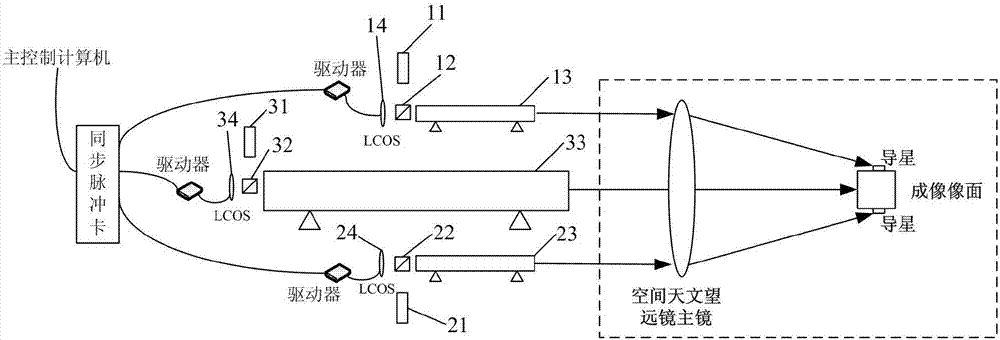
Space astronomical telescope guiding image stabilization precision testing method and apparatus
ActiveCN106872141AImprove accuracyOvercome the defect that it is impossible to accurately measure the image stabilization accuracy of the guide star of the space astronomical telescopeOptical apparatus testingImage stabilizationAstronomical telescopes
The invention relates to a space astronomical telescope guiding image stabilization precision testing method and apparatus, belonging to the technical field of photoelectric test. The space astronomical telescope guiding image stabilization precision testing method and apparatus can simulate the input target for testing the space astronomical telescope guiding image stabilization precision. Under the condition of maintaining the space astronomical telescope and the guiding unmovable, the input target is changed, after the image stabilization mechanism completes the normal image stabilization, the position pixel change of the star point dynamic target is calculated according to the star point dynamic target image output by the space astronomical telescope, and the precision of the space astronomical telescope guiding image stabilization can be determined according to the position pixel change, and after the multitime image stabilization of the image stabilization mechanism, the position pixel changes of the star point dynamic target for multiple times can be compared, so that the accuracy of the guiding image stabilization precision testing result can be improved. A reference method and device is provided for the detection of a large-view-field space astronomical telescope system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Large-aperture large-field-of-view telescope system built-in measurement device and measurement method thereof
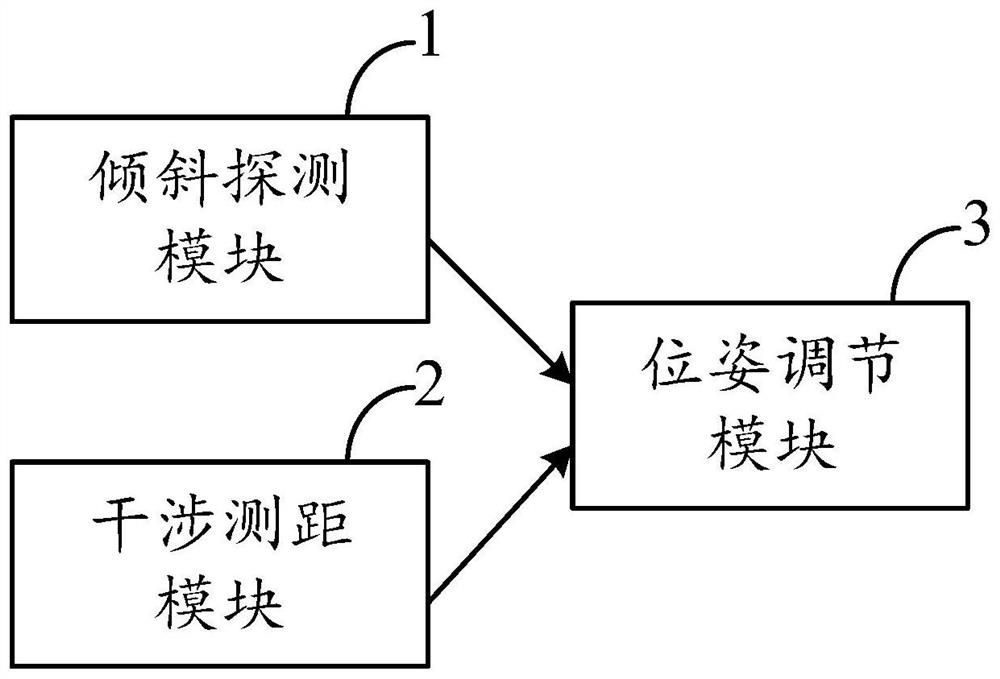
ActiveCN111781719AImprove seating timeAchieve positioningMeasurement devicesControl using feedbackLight spotLight beam
The invention discloses a large-aperture large-field-of-view telescope system built-in measurement device and a measurement method thereof, and the device comprises an inclination detection module which is used for generating and imaging a plurality of laser beams, carrying out the alignment of the formed image, obtaining the wavefront angle information through the deviation of a light spot, and feeding back the wavefront angle information to a pose adjustment module; an interference distance measurement module, located on one side of the inclination detection module and used for measuring distance information of the optical truss and feeding back the distance information to the pose adjustment module; and a pose adjusting module used for driving the executing mechanism to adjust the spatial pose of the optical element according to the received angle information and distance information. An information source of the optical truss is formed by results obtained by angle measurement and distance measurement. The displacement and attitude between optical elements can be effectively monitored, so that continuous correction commands are provided for the system under the condition that the telescope cannot perform wavefront sensing through a guide star, real-time calibration and correction are realized in the operation process of the telescope, and the in-place time of the telescope is greatly prolonged.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Guide star-based large-scale telescope field assembly and adjustment detection device and method
InactiveCN106066239AHigh development costMeet stability requirementsTesting optical propertiesFixed starsWavefront sensor
The invention relates to a guide star-based large-scale telescope field assembly and adjustment detection device and a guide star-based large-scale telescope field assembly and adjustment detection method and belongs to the optical assembly and adjustment detection technical field. The objective of the invention is to solve the problem of poor reliability and the incapability of a fixed star target to satisfy a light source stability requirement of optical system assembly and adjustment detection. The guide star-based large-scale telescope field assembly and adjustment detection device of the invention comprises a high-performance laser, a laser beam expanding telescope, a precision pointing mirror and a wavefront sensor; the wavefront sensor is located behind the focus of a detected large-scale telescope; a laser beam emitted by the high-performance laser is subjected to beam expansion of the laser beam expanding telescope; the expanded laser beam is reflected to a sodium atom layer through the precision pointing mirror, wherein the sodium atom layer is 100km above the ground; the laser beam excites sodium atoms to resonate, so that a sodium laser guide star can be obtained; the sodium laser guide star enters into the center of the detector view field of the wavefront sensor; the optical axis of the laser reflected by the precision pointing mirror is parallel to the visual axis of the detected large-scale telescope; and the star point of the sodium laser guide star enters view field of the detected large-scale telescope system.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
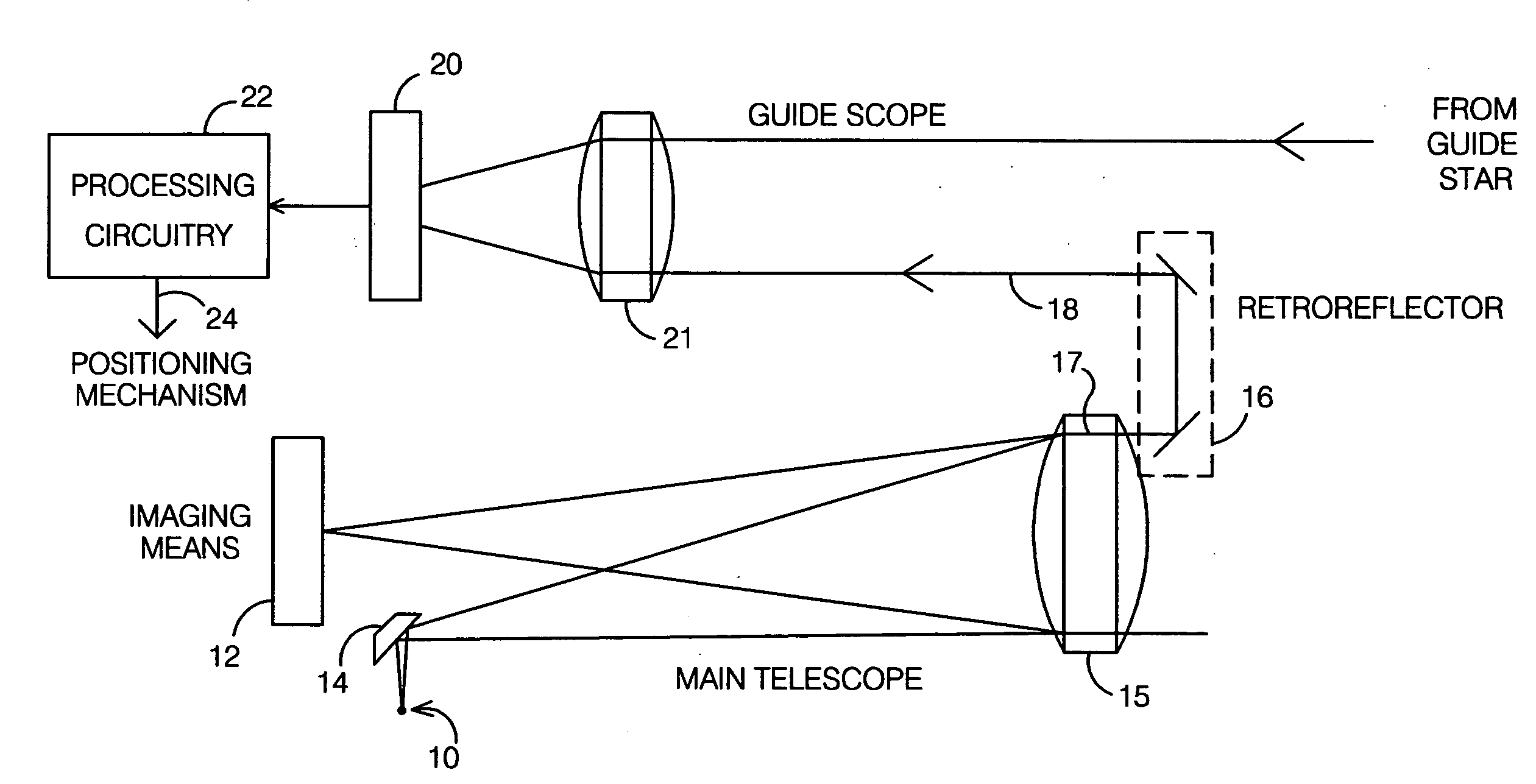
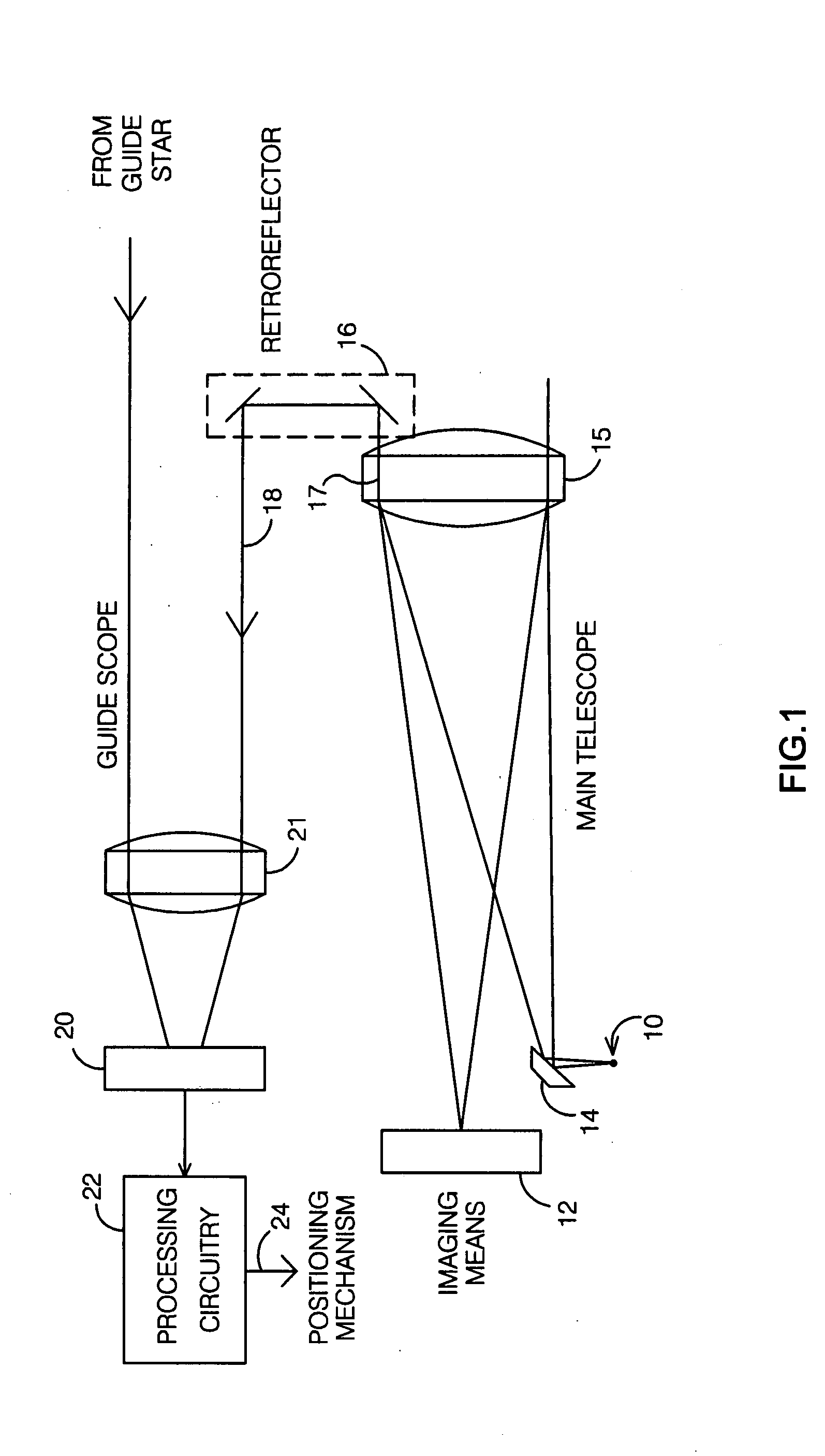
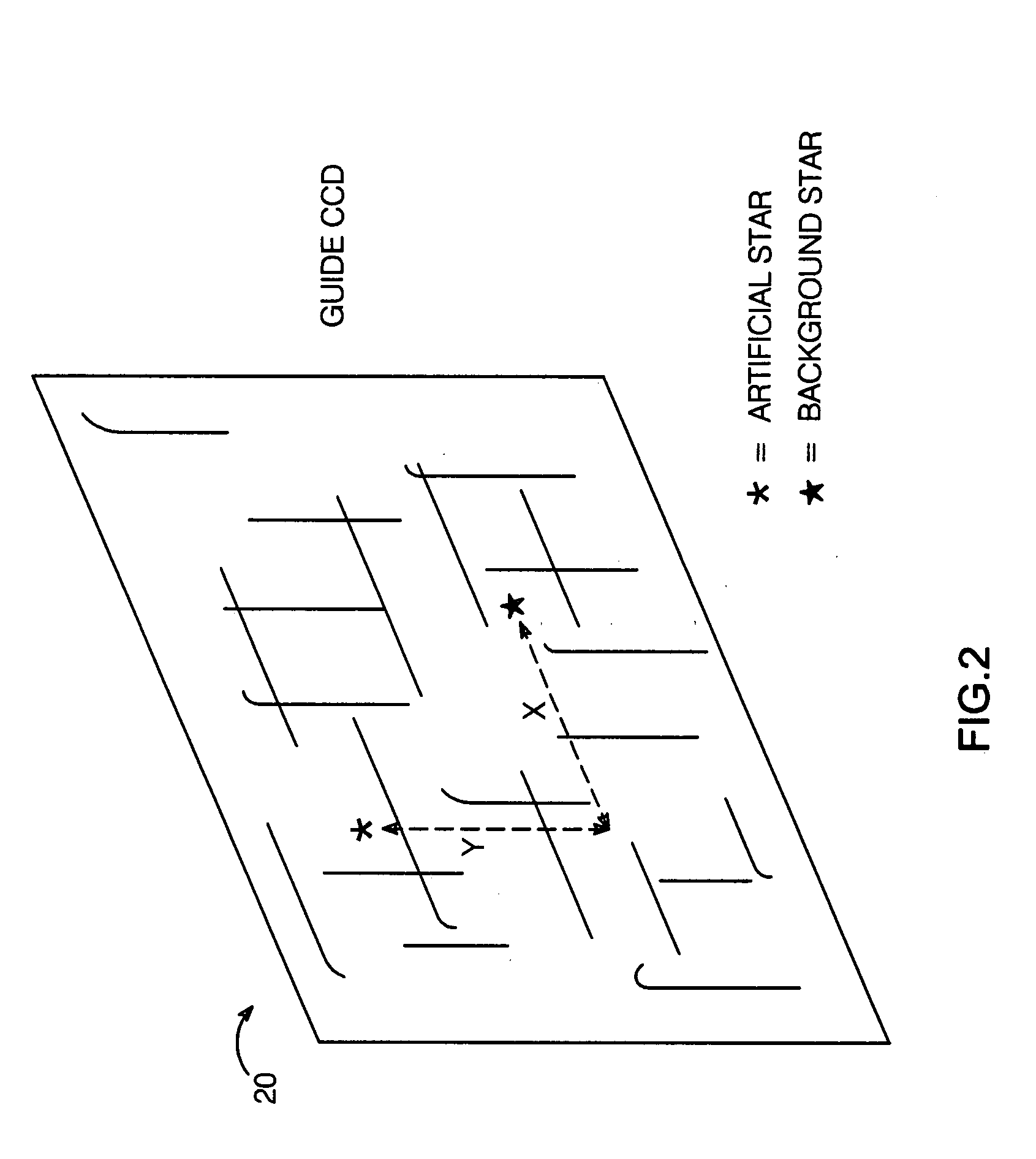
System and method for telescope guiding utilizing an artificial reference star
InactiveUS20080259448A1Effective lockingLimited amountPhotometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationLight beamEngineering
A system and method for telescope guiding requires creating an artificial reference star which is locked to the line of sight of the imaging means of a main telescope in the field-of-view (FOV) of a guide scope. A real guide star is selected using the guide scope, such that both artificial and guide stars are within the FOV of the guide scope. Guiding is accomplished by varying the line of sight such that the positional displacement between the guide and artificial stars on the guide star's focal plane is maintained approximately constant. The artificial star is created by generating a point source of light near the main scope's imaging means, directing the light outside the main scope and retroreflecting it at the same direction angle of the beam exiting the aperture into the guide scope, effectively locking the guide scope to the line of sight of the imaging means.
Owner:DIFFRACTION
A large-visual-field-angle multilayer conjugate self-adaptive optical focusing and microscopic system and method
The invention discloses a large-visual-field-angle multilayer conjugate self-adaptive optical focusing and microscopic system and method. The light emitted from a laser is incident on three spatial light modulators; the light beam modulated by the spatial light modulators is focused on a scattering medium and then imaged by an imaging lens; the scattering medium is divided into two layers including two conjugate spatial light modulators and a pupil-type spatial light modulator; the two conjugate spatial light modulators are respectively conjugated to the two layers of the scattering medium; and the pupil-type spatial light modulator is arranged among the two conjugate spatial light modulators and the scattering medium. The system and method of the invention use a plurality of guide stars and a plurality of wave-front correctors to correct the aberrations generated at different thicknesses of biological samples at the same time, overcome the disadvantages that the traditional adaptive optical imaging technology has a small viewing angle, a poor non-target point correction effect and a low correction speed, and can realize large-view-field, multi-zone, high-quality focus and high-resolution microscopic imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Astronomical site-selecting instrument guide star device and working method thereof
The invention discloses an astronomical site-selecting instrument guide star device and a working method thereof. The astronomical site-selecting instrument guide star device consists of a lens, a camera and guide star software, wherein an output signal is connected with an equatorial telescope. The astronomical site-selecting instrument guide star device is characterized in that an automatic guide adapter is arranged between the guide star software and the equatorial telescope. The automatic guide adapter is composed of a micro controller and a four-path switch switcher; the camera is used for continuously taking a candid photograph of the target area, and providing the candid photograph to the guide star software through a computer; the guide star software is used for processing the target area image, identifying a target celestial body, and sending the target celestial body position correction amount to the automatic guide adapter which controls the movement of the equatorial telescope. According to the astronomical site-selecting instrument guide star device disclosed by the invention, a star searching function and a star guide function share the same hardware, the device is simple; the target celestial body is automatically identified through an algorithm, and the astronomical site-selecting instrument is assisted to automatically search and point the target celestial body; the correction amount of target celestial body position is calculated in real time through the algorithm, and fed back to the equatorial telescope through the automatic guide adapter, so that the target celestial body is automatically tracked; when a telescope is caused to shake by wind load, the target celestial body also can be tracked.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ASTRONOMICAL OPTICS & TECH NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSE
Splicing method of space astronomical camera guide star CCD and detection CCD
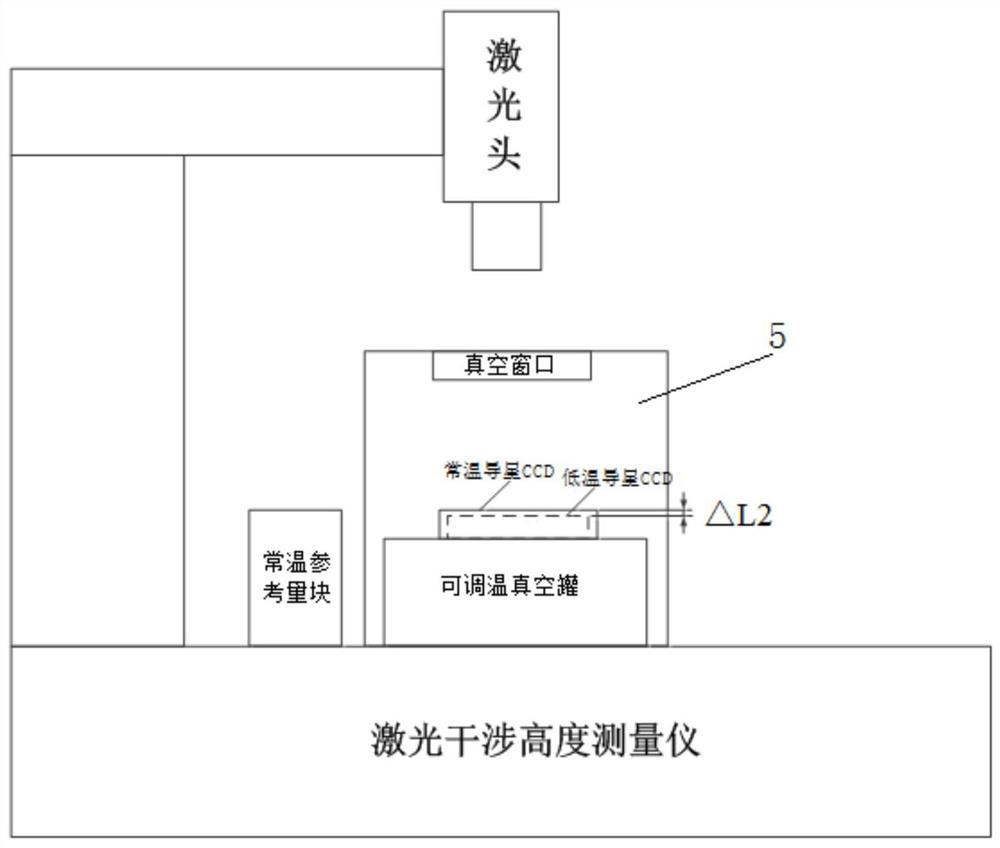
InactiveCN111721266AMeet the depth of focus requirementsImprove stitching accuracyPicture taking arrangementsHeight/levelling measurementThermal deformationGuide star
The invention discloses a splicing method of a space astronomical camera guide star CCD and detection CCD, and aims to solve the technical problem that a back-illuminated guide star CCD and a detection CCD cannot be spliced by using a traditional high-magnification tool microscope imaging method in the prior art. The method sequentially comprises the steps of screening, thermal deformation verification, splicing, initial adjustment, measurement, trimming, fixing and splicing verification. The splicing method can enable the splicing height and collinear error of the guide star CCD and the detection CCD to meet the focal depth requirement of the space astronomical camera, and has the characteristics of simple operation and high splicing precision.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Embedded guiding star processing system
ActiveCN109991900ABig amount of dataEasy to implementProgramme controlTelevision system detailsAstronomical telescopesHandling system
The invention discloses an embedded guiding star processing system, relates to a space target guiding star-oriented embedded processing system, and aims at solving the problem that the existing imageacquisition and processing systems are difficult to answer huge real-time data size and difficult to guide stars so that the main visual fields cannot observe space targets for a long time. The systemcomprises an image acquisition module and a guiding star calculation module, wherein the guiding star calculation module adopts a guiding star processing system constructed by FPGA and DSP heterogeneous processors; the image acquisition module acquires video signals of an sCMOS camera in real time and stores the video signals to a DDR3 SDRAM; and the image data in the DDR3 SDRAM is transmitted tothe guiding star calculation module. According to the system, strong image processing and calculation analysis abilities are provided, space targets can be recognized and accurate mass center positions of the space targets can be obtained, the calculated error vectors are converted into practical miss distances of telescopes, and the practical miss distances are fed back to pointing control systems of the astronomical telescopes. The embedded guiding star processing system is capable of improving the stability and accuracy of the guiding stars and achieving the long-time observation for the targets.
Owner:中国科学院国家天文台长春人造卫星观测站
Satellite-ground same band optical communication adaptive optical correction system and method based on sodium guide star
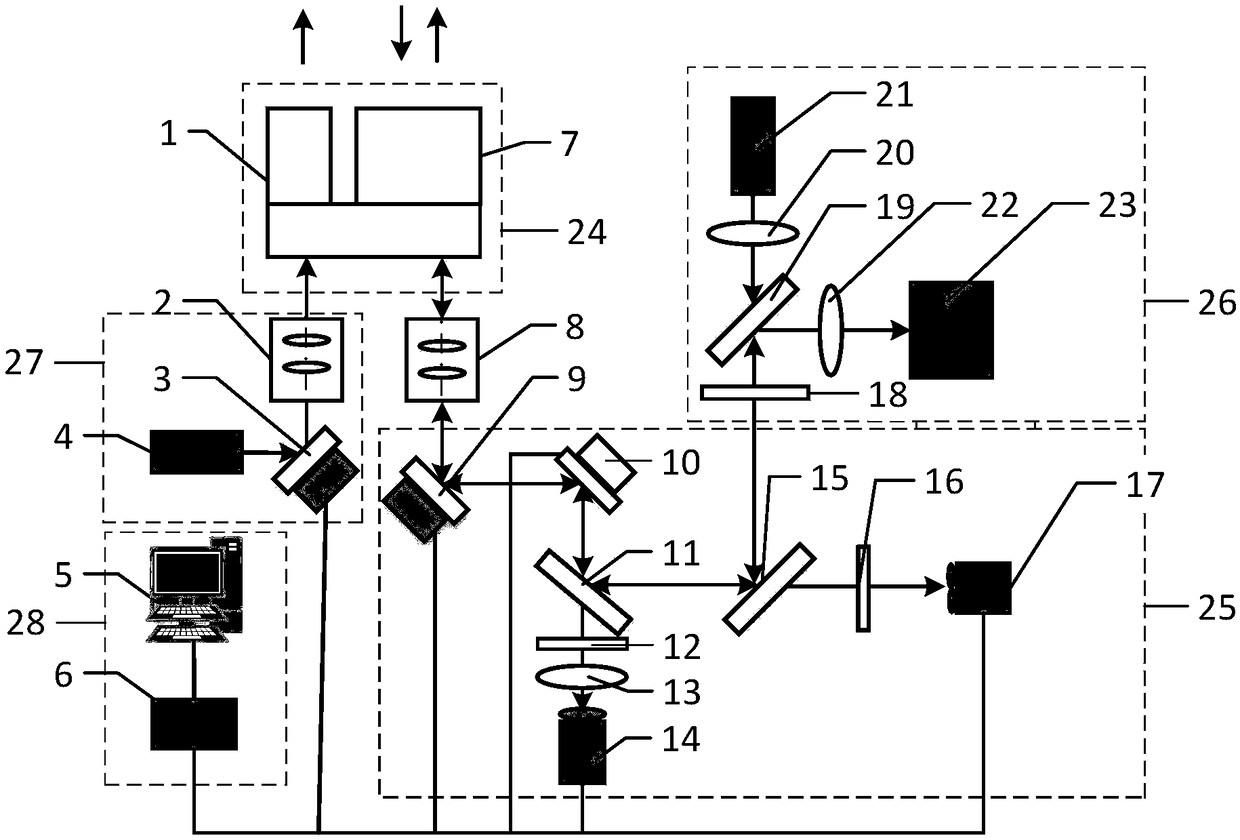
ActiveCN108732742AImprove signal reception efficiencyNon-linear opticsOptical elementsOptical correctionSignal light
The invention discloses a satellite-ground same band optical communication adaptive optical correction system and method based on the sodium guide star. The system comprises a ground station telescope(24), a sodium beacon transmitting unit (27), an adaptive optics unit (25) and a signal transceiving unit (26), wherein the ground station telescope (24) is used for transmitting the sodium beacon laser and receiving the sodium beacon light emitted by the sodium guide star and the downstream communication signal light emitted a target, the sodium beacon light is utilized by the adaptive optics unit (25) for wavefront detection to carry out wavefront correction for the received communication signal light, the corrected communication signal light enters the signal transceiving unit (26) for demodulation, and the signal transceiving unit (26) is used for transmitting the uplink communication signal light which is transmitted through the adaptive optics unit ( 25) and the ground station telescope (24) for realizing uplink communication. The system is advantaged in that an adaptive optical correction method is provided for atmospheric laser communication of a same band beacon-less terminal, and signal reception efficiency of a communication terminal machine is improved.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
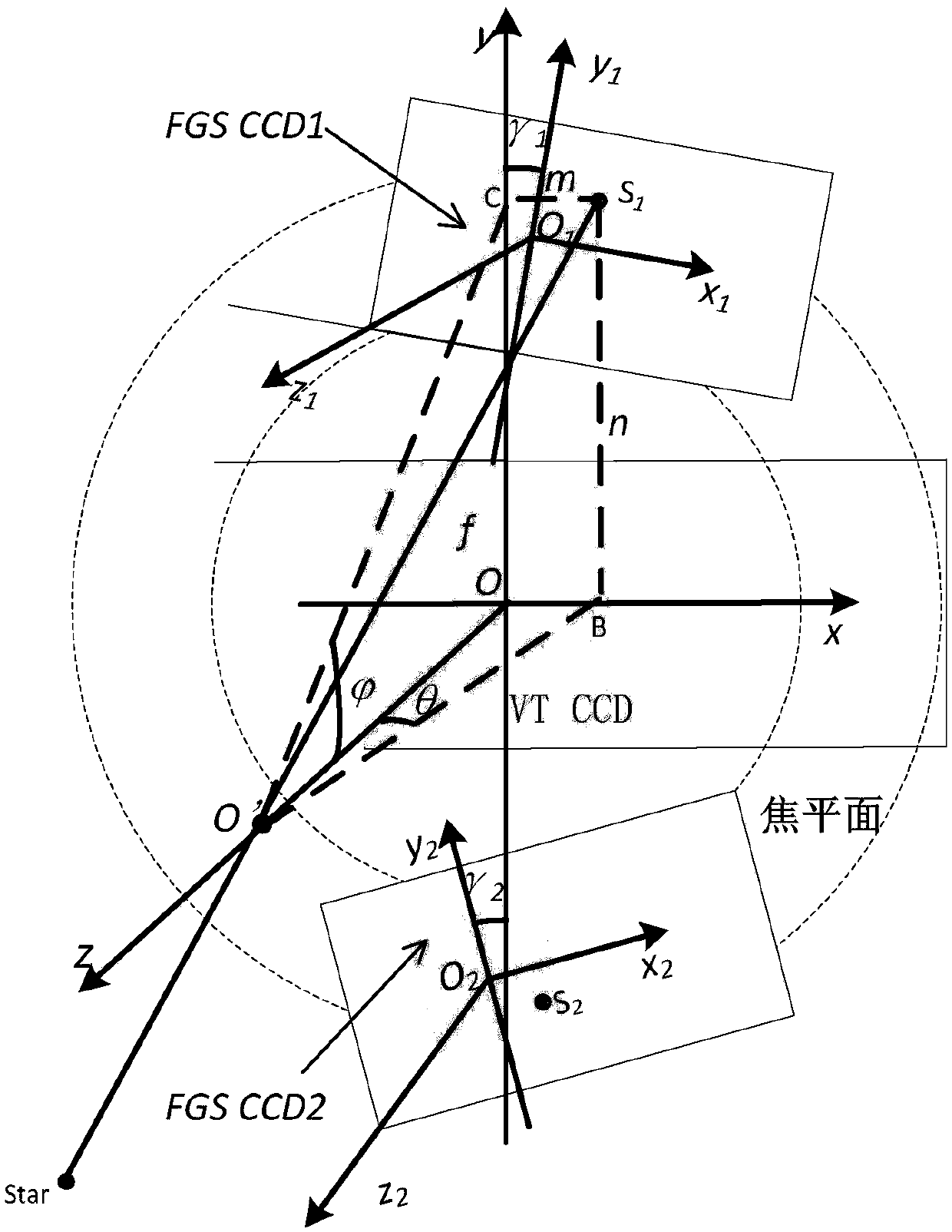
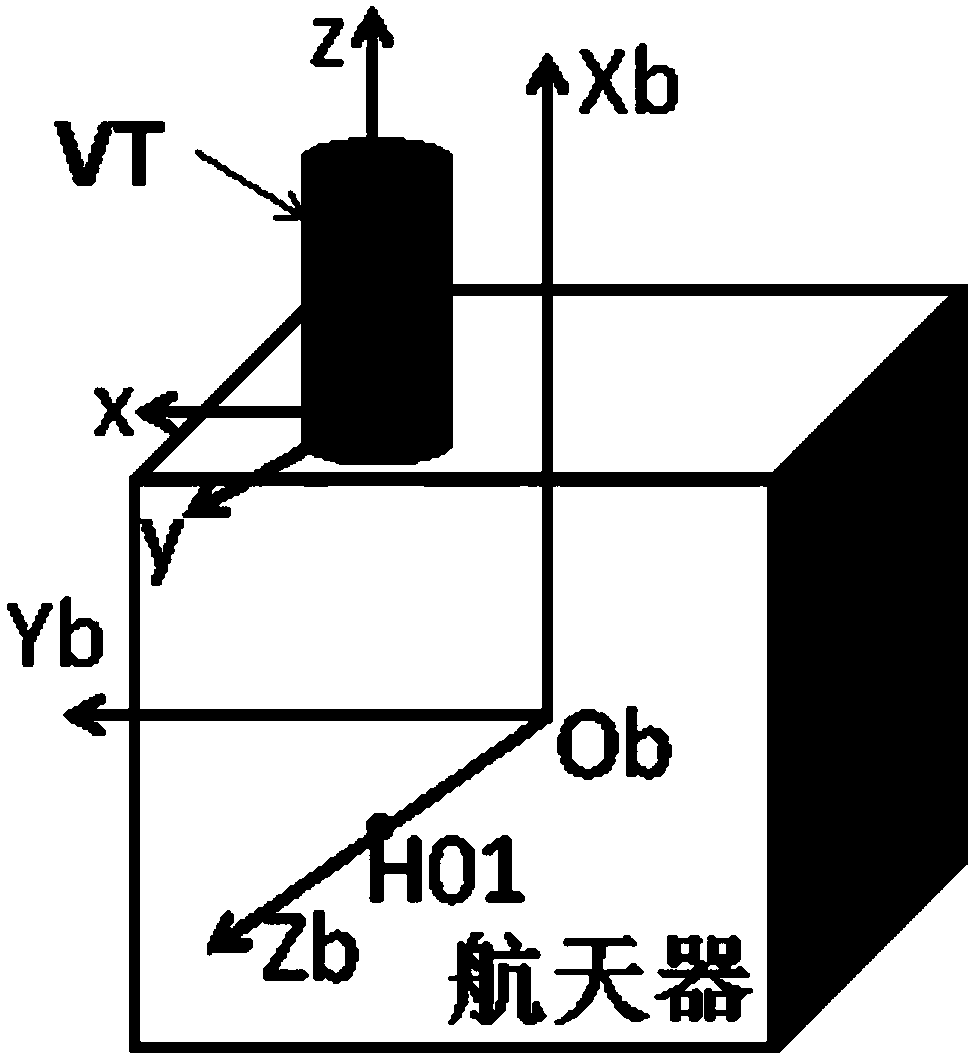
Ultrahigh-precise guide star sensor attitude determination method
The invention relates to an ultrahigh-precise guide star sensor attitude determination method including the steps of: mapping the position of a mass center of an image point of a fixed star on FGSCCDonto a VT coordinate system; calculating attitude deviations in x-axis, y-axis and z-axis directions in the VT coordinate system; calculating relative attitude deviation quaternion; and calculating absolute attitude.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
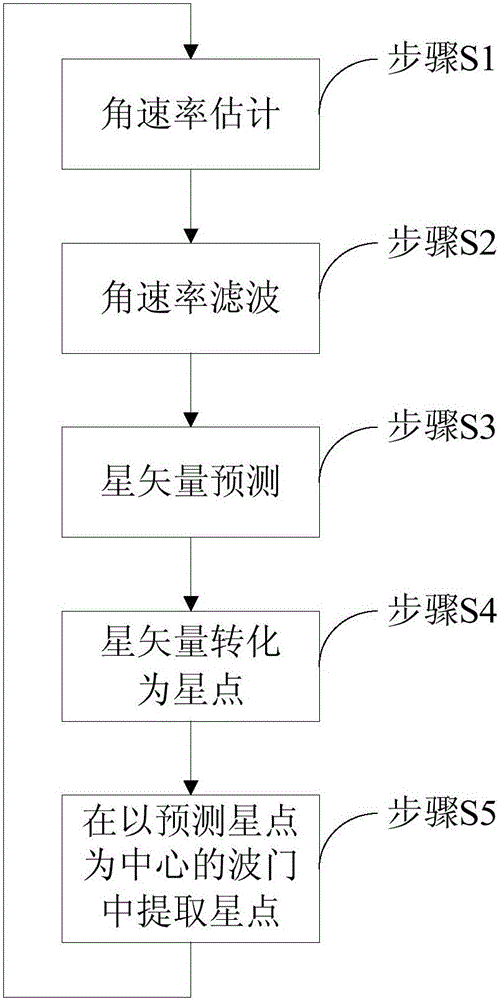
Star sensor based star tracking method
The invention provides a star sensor based star tracking method. The method comprises steps as follows: firstly, angular velocity is estimated and filtered; then, star vectors are predicted and transformed into star points; finally, the star points are extracted from a wave gate with a prediction star point as the center. The method does not depend on attitude information, only the star vector of the star point of each frame is required to be modeled as a whole, and a star point predicted value is obtained on the basis of the star vector and a parameter of a star sensor. The method adopts a simple model and is small in computational amount and easy to implement; different from an existing star tracking method used for calculating angular velocity and recursion based on quaternion differential and adopting a guide star catalogue, the method has the advantages that the angular velocity can be directly computed on the basis of star vector differential for star vector recursion, the star tracking is further realized, and the method can be used as an effective complement to existing star tracking methods.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
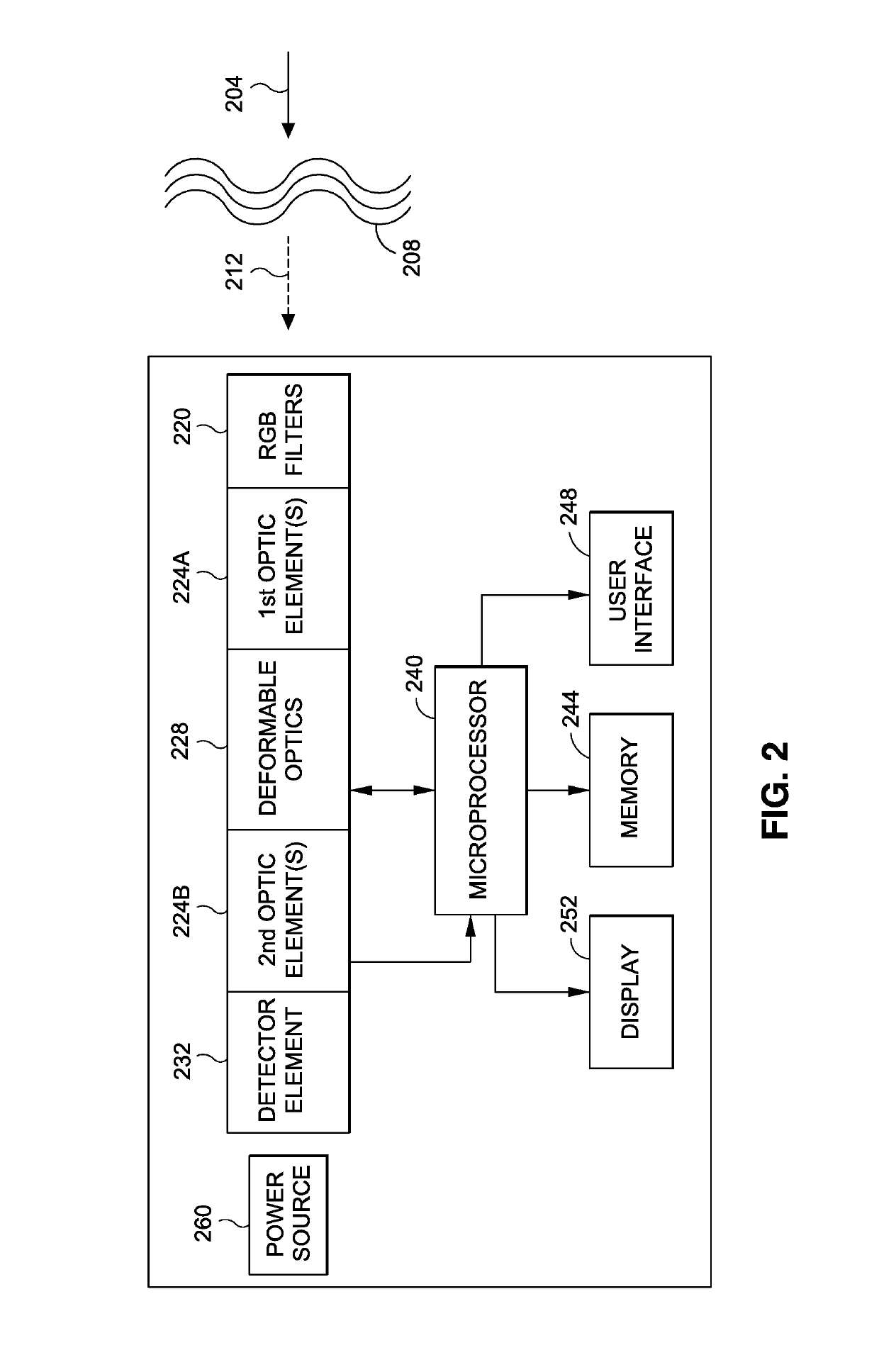
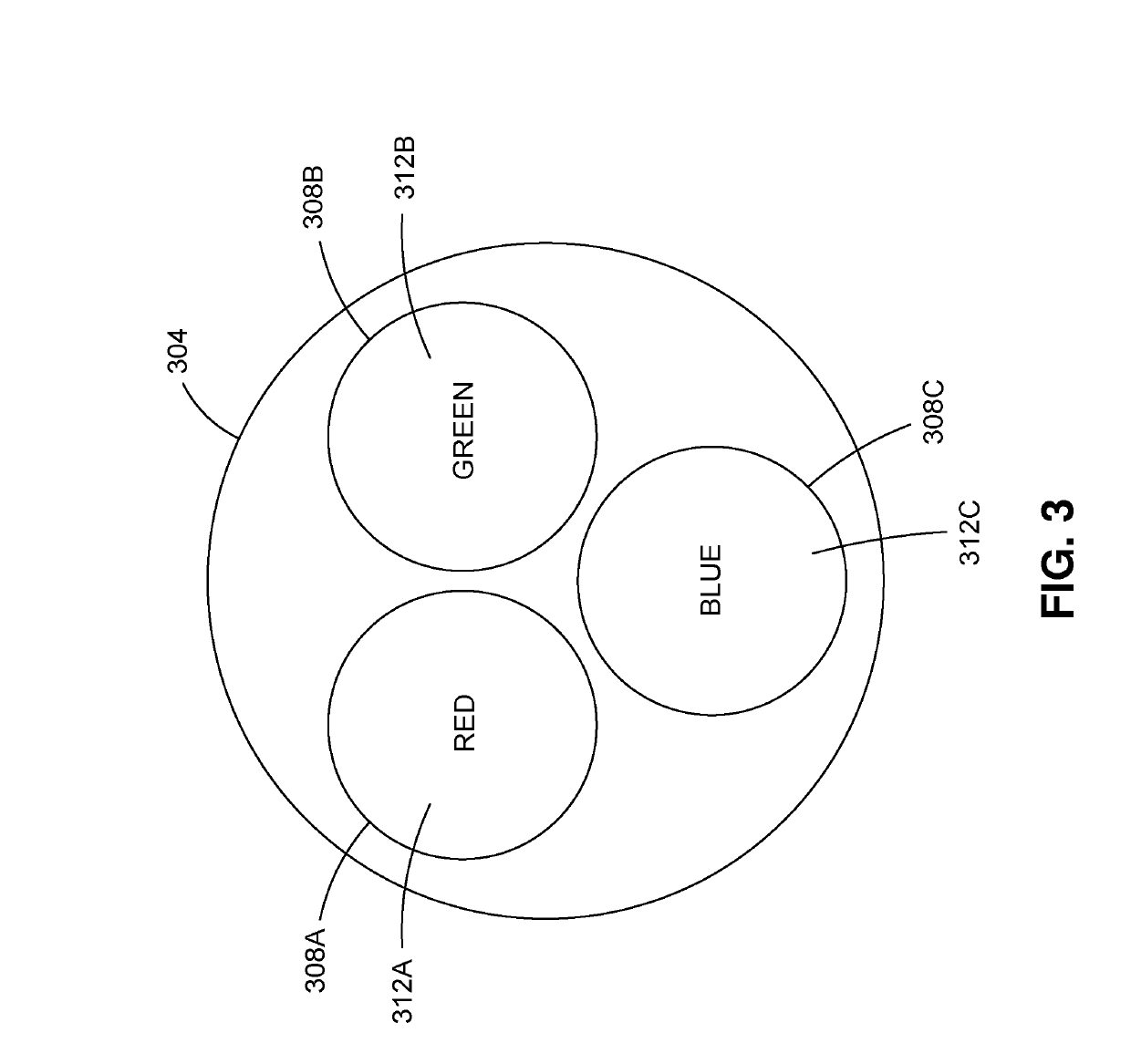
RGB wavefront sensor for turbulence mitigation
ActiveUS20190212552A1Easy to optimizeCorrect optical aberrationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsColor imageWavefront sensor
A compact adaptive optics system for long-range horizontal paths imaging that improves degraded images. The system uses a filter that corresponds to the three colors in a typical color detector element, one or more optic elements, a deformable mirror, and a detector. Focus errors, due to turbulence, in the image recorded by the detector element show up as image shifts in the three distinct color images. The shifts and statistics of these shifts between these simultaneous images are used to create control signals for the deformable mirror resulting in a compact adaptive optic system for horizontal paths without need for a point source located at the distance scene being imaged. Analysis of the relative pixel shifts in various regions of the image provides third order statistics revealing tip / tilt and additional Zernikes modes that are used to control a deformable mirror without the need for a guide star / point-source.
Owner:MISSION SUPPORT & TEST SERVICES LLC
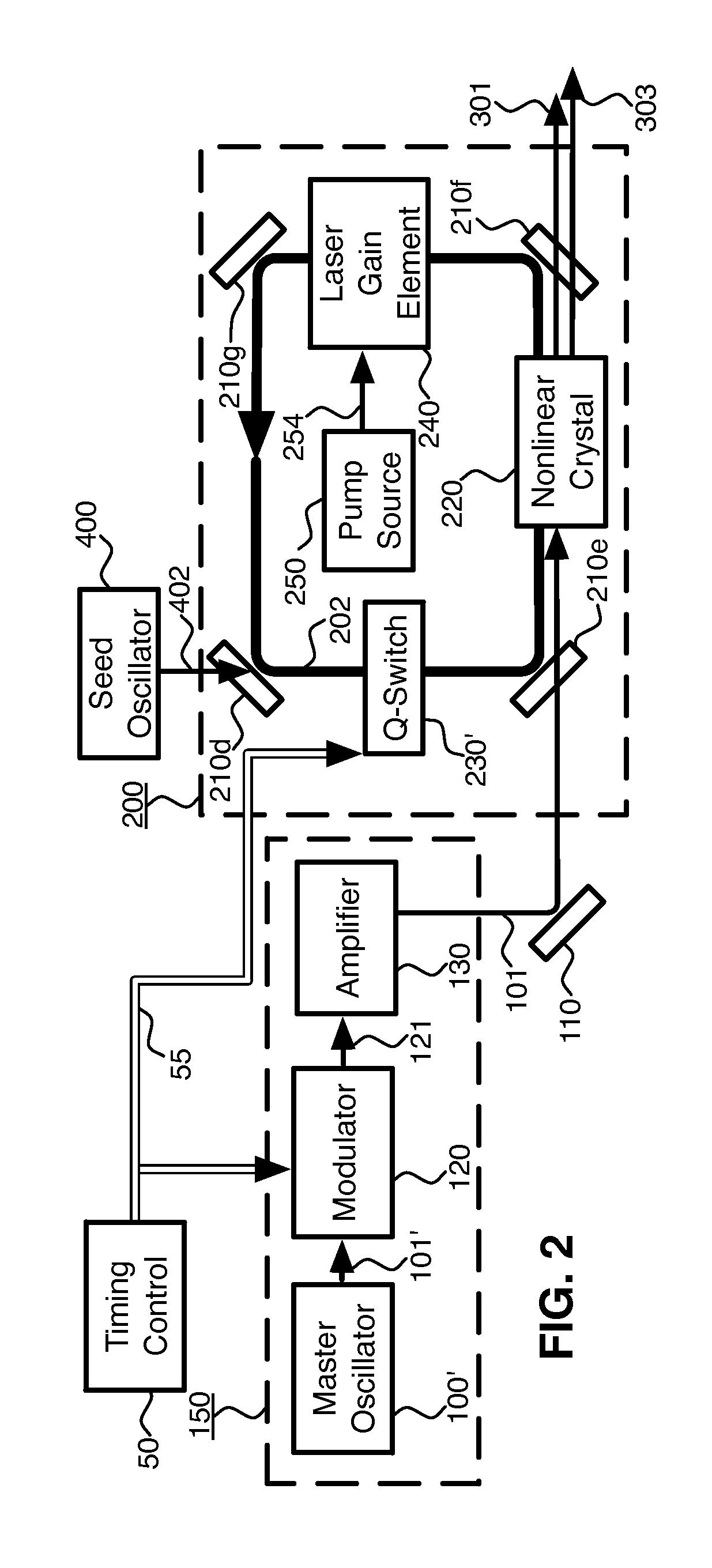
Internal optical mixer pulsed at larmor frequency
Pulsed, coherent light is generated by optical mixing which takes place inside the resonator of a pulsed laser oscillator. One of the beams to be mixed is generated by the pulsed laser, and the other by a distinct, external laser oscillator. If the light from the external oscillator is modulated, that modulation will be transferred onto the light generated by the optical mixing. Using sum frequency generation, light for sodium excitation, such as for a guide star, can be generated with the optimal modulation of spectral and temporal properties. If the pulse repetition frequency is chosen to be at or near the magnetic (Larmor) resonance of the sodium, then the amount of scattered light due to sodium excitation is enhanced, and the magnetic field at the location of the sodium atoms can be measured.
Owner:FASORTRONICS
Device and method for outputting solid-state sum-frequency spectrum-continuous laser light for sodium guide stars
ActiveCN108107642AEfficient light returnIncrease brightnessNon-linear opticsOptical elementsFrequency spectrumBeam splitter
The invention relates to a device and a method for outputting solid-state sum-frequency spectrum-continuous laser light for sodium guide stars, and belongs to the technical field of laser light and astronomy adaptive optics. The device comprises a solid-state 1064nm fundamental-frequency laser device, a solid-state 1319nm fundamental-frequency laser device, a plane high-reflectivity mirror, a beamcombiner, a converging ball lens, a sum-frequency crystal, a collimating ball lens and a beam splitter. The device and the method have the advantages that 589nm sum-frequency laser light can be generated by nonlinear sum frequencies of the solid-state 1064nm fundamental-frequency laser device and the solid-state 1319nm fundamental-frequency laser device, acousto-optic frequency-shifted feedback spectrum-continuous laser light can be simultaneously outputted by at least one of the solid-state 1064nm fundamental-frequency laser device and the solid-state 1319nm fundamental-frequency laser device, accordingly, the 589nm sum-frequency laser light can be driven to become spectrum-continuous sum-frequency laser light, atmosphere sodium atoms at all rates can be sufficiently excited and utilized, high-brightness and efficient sodium guide star return light can be implemented, and requirements of astronomy adaptive optics and application such as white light atom cooling and gas detection canbe met; the integral device is simple, compact and small and is convenient to maintain.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Real-time planning method for optimal position of movable guide star of adaptive optical system
ActiveCN110703764APosition/course control in two dimensionsICT adaptationStreaming dataComputational physics
The invention relates to the field of optimal position planning of movable guide stars, and provides a real-time planning method for an optimal position of a movable guide star of an adaptive opticalsystem. The method comprises the steps that: on the basis of sufficient actual measurement atmospheric turbulence profile data accumulation, profile statistical distribution characteristics are obtained through clustering analysis; on the basis of analyzing statistical distribution characteristics, the positions of the guide stars corresponding to different types of profiles are obtained by utilizing a Monte Carlo simulation and optimization algorithm, and the mapping relationship between different turbulence profiles and the optimized positions of the movable guide stars is further obtained through adoption of a machine learning method. The optimal position of the corresponding movable guide star can be quickly calculated according to the actually measured turbulence data in practical application.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
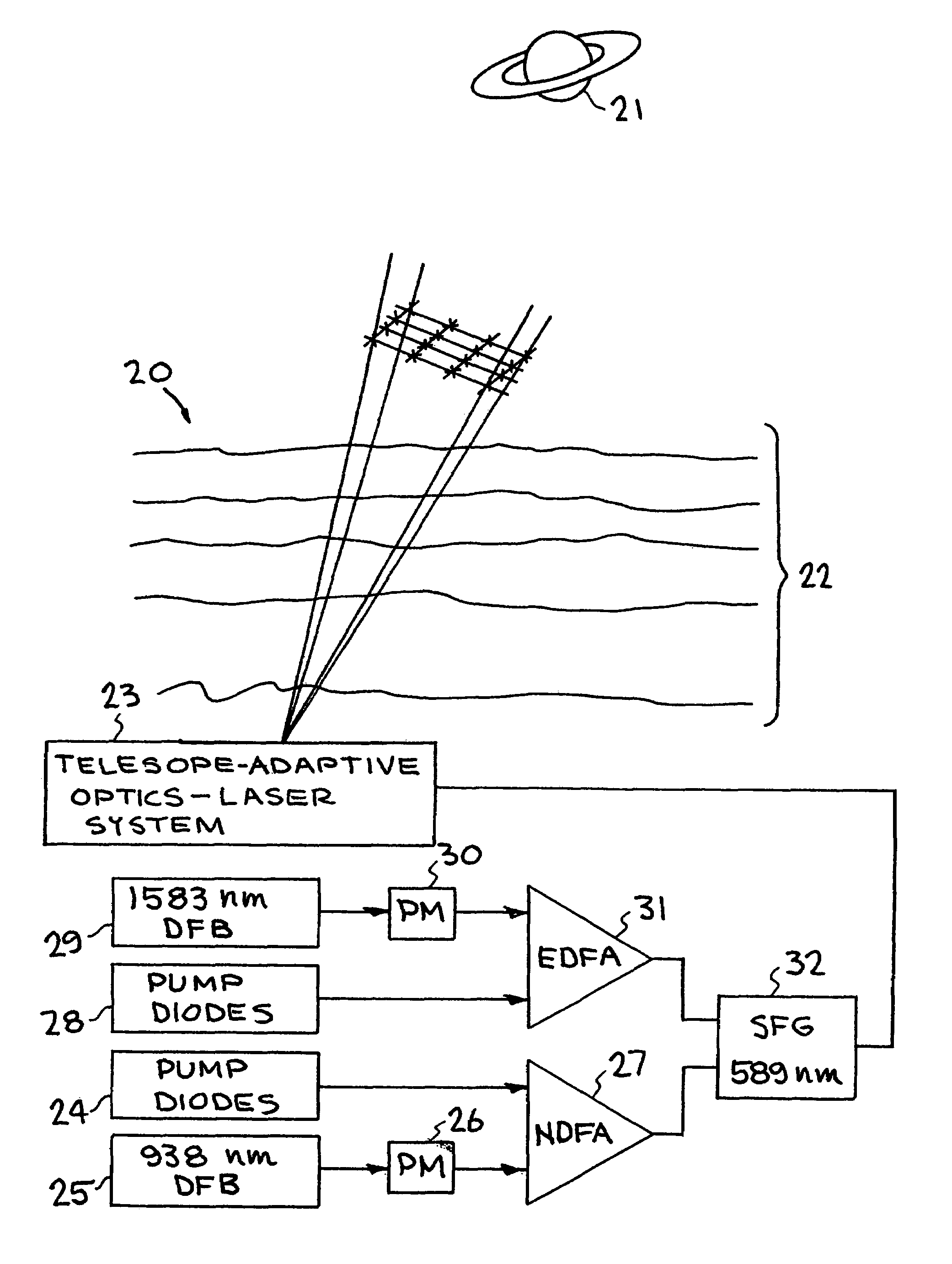
Synthetic guide star generation
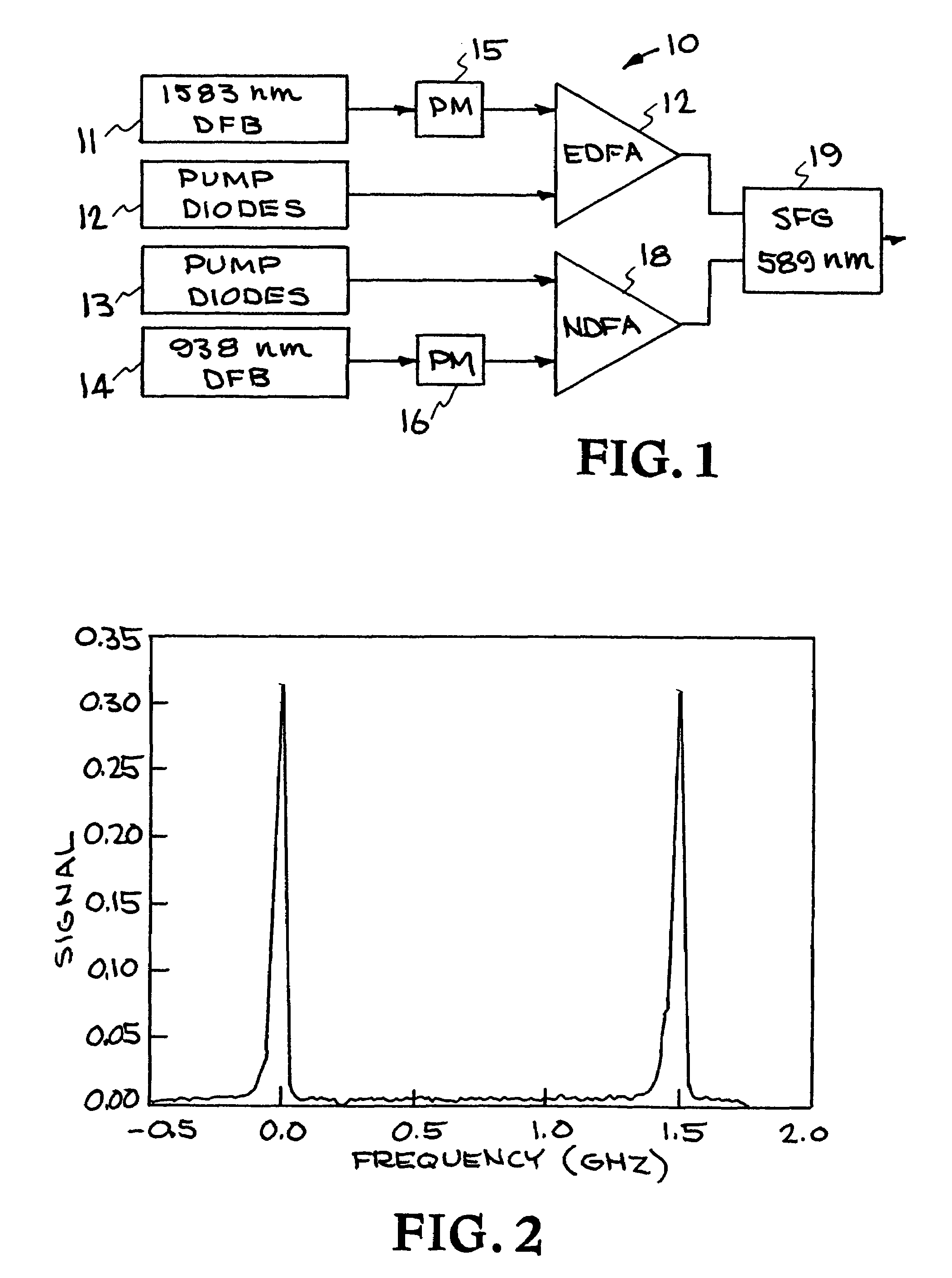
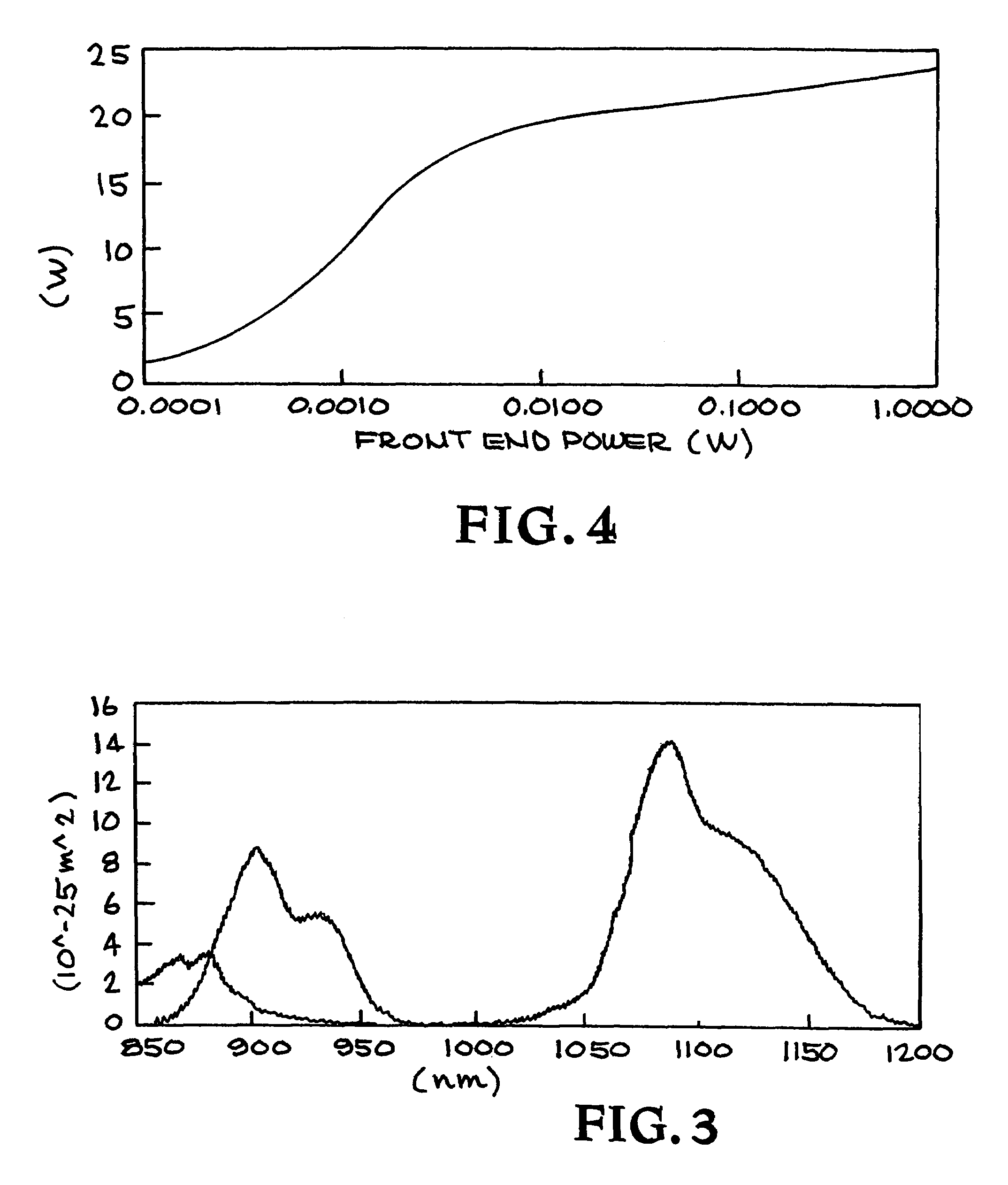
A system for assisting in observing a celestial object and providing synthetic guide star generation. A lasing system provides radiation at a frequency at or near 938 nm and radiation at a frequency at or near 1583 nm. The lasing system includes a fiber laser operating between 880 nm and 960 nm and a fiber laser operating between 1524 nm and 1650 nm. A frequency-conversion system mixes the radiation and generates light at a frequency at or near 589 nm. A system directs the light at a frequency at or near 589 nm toward the celestial object and provides synthetic guide star generation.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Sodium guide star laser atmospheric link compensation system
InactiveCN110045496AReduce measurement errorFlat wavefront distributionOptical elementsAtmospheric layerLight spot
The invention relates to the technical field of a self-adaptive optical system, and in particular to a sodium guide star laser atmospheric link compensation system. The system comprises a first laserbeam expanding system, a second laser beam expanding system, a dichroic mirror, a deformation mirror, a beam combining and expanding system, a wavefront detection and control system, a reflecting mirror and a calibration light source. According to the system, another laser different from the sodium laser wave length and the sodium laser combining beam are emitted in common-caliber and are converged on an atmospheric layer of a sodium laser transmission path to generate atmospheric back scattering; the atmospheric turbulence distortion is measured and compensated by using a back-scattering image; when the sodium laser emits, the phase distortion opposite to the atmospheric turbulence is carried and counteracted when the laser passes through the atmospheric turbulence so that the sodium laser has flat wavefront distributions, smaller light spot diameter and higher energy density when reaching the sodium layer for convergence, thereby being beneficial to reducing the measurement error ofthe self-adaptive optical system of the ground-based optical telescope and improving the imaging correction effect.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid laser source applicable to generation of polychromatic sodium guide star
The present invention relates to a solid laser source applicable to the generation of a polychromatic sodium guide star. The device comprises a semiconductor pump light source, a laser oscillator, a second harmonic generation module and a fourth harmonic generation module; the semiconductor pump light source is used for emitting pump light; the pump light is pulsed light; the repetition frequency of the pulsed light ranges from 200 Hz to 1 KHz; the pulse width of the pulsed light ranges from 80 microseconds to 300 microseconds; the laser oscillator is used for oscillating the pump light emitted from the semiconductor pump light source to generate laser of a first wavelength; the second harmonic generation module is used for converting the laser of the first wavelength into laser of a second wavelength, wherein the second wavelength is smaller than the first wavelength and is larger than 330 nm; and the fourth harmonic generation module is used for converting the laser of the second wavelength into 330-nm laser. Since the front part of a single output pulse has high peak power, a nonlinear attenuation effect appears in atmospheric transmission, and as a result, attenuation of the 330-nm laser caused by atmosphere is weakened; and the rear part of the single output pulse has proper average power which is matched with sodium atom density in the sodium layer of the atmosphere, and a large number of photon echoes can be generated.
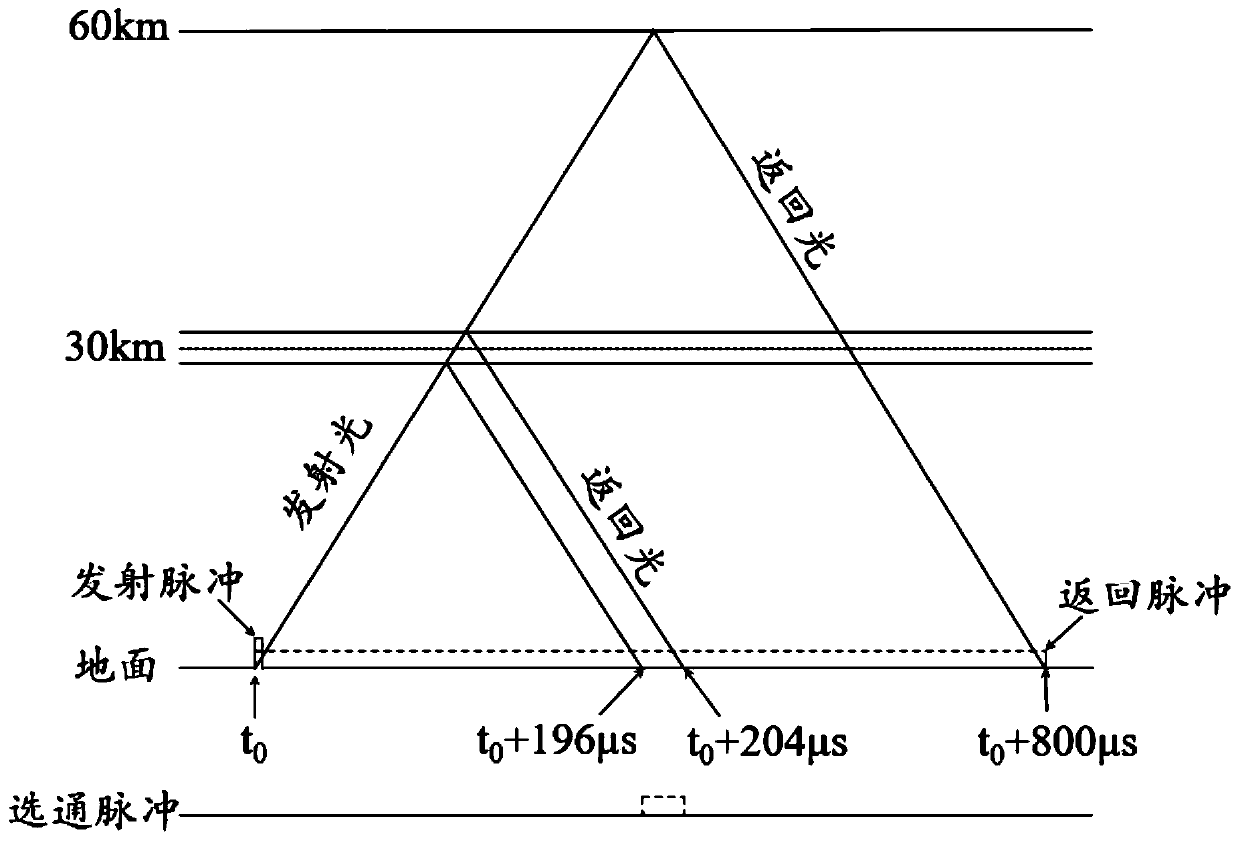
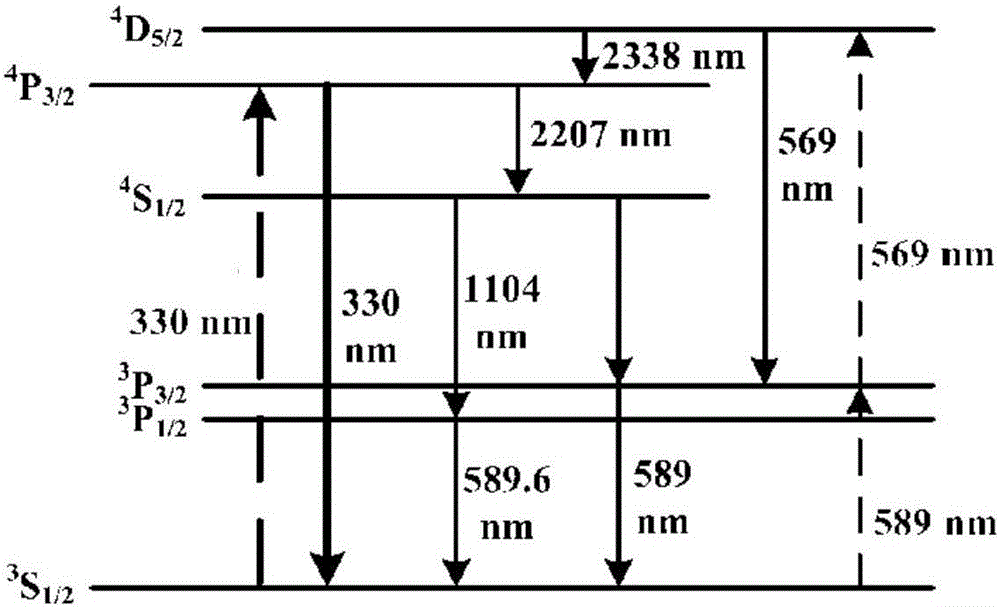
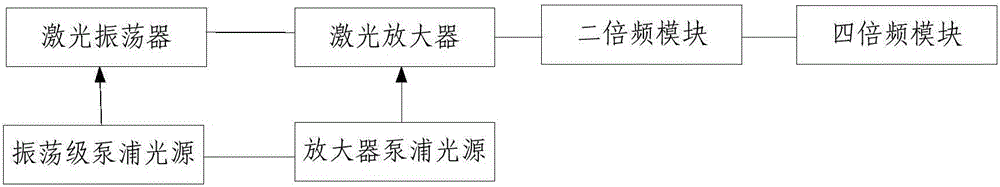
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com