Single-frequency solid-state raman laser
A Raman laser, solid-state technology, applied in the field of lasers, can solve the problems of limited applicability, loss of optical power density, difficulty in Raman light vibration, etc., to reduce thermal effects, optimize output effects, and achieve good stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
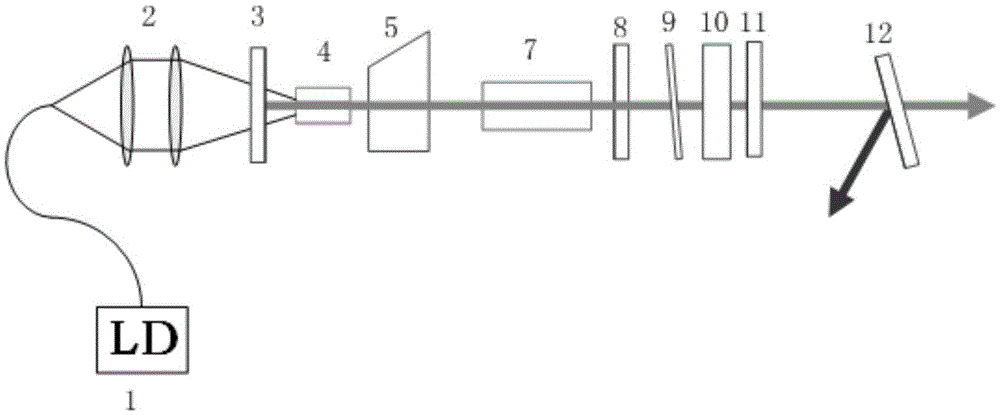
[0052] The laser structure of this embodiment is as figure 1 shown.
[0053] A single-frequency solid-state Raman laser, including a pump source, a coupling lens group, a laser gain medium, a Q-switching device, a Raman crystal, a cavity mirror M1, a cavity mirror M3, a cavity mirror M4, a beam splitter M5 and a temperature control system, The pumping source outputs pumping light, and a coupling lens group, a cavity mirror M1, a laser gain medium, a Q-switching device, a Raman crystal, a cavity mirror M3, a first FP etalon, a second FP etalon, cavity mirror M4, beam splitter M5, laser gain medium, Q-switching device, and Raman crystal are all equipped with a temperature control system. The laser gain medium, Q-switching device, and Raman crystal are all placed in the temperature control system to keep the temperature of the above crystal and the device constant so as to reduce the thermal effect of the crystal in the laser cavity; the cavity mirror M1 and the cavity mirror M3...
Embodiment 2
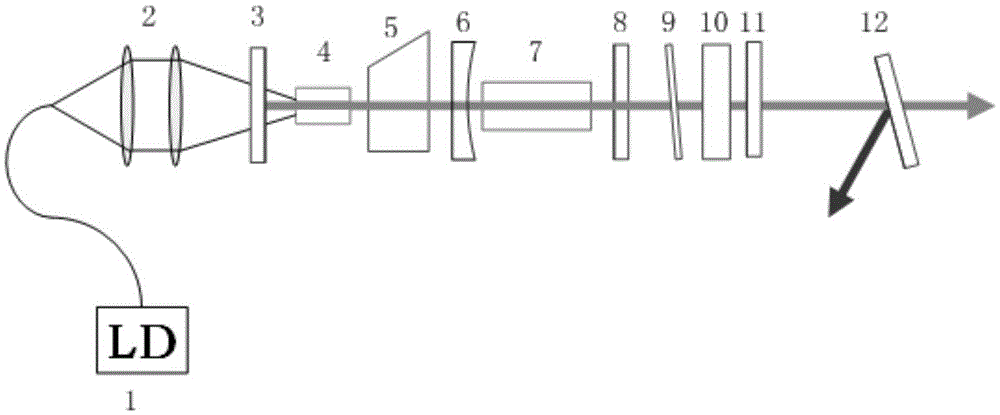
[0055] A single-frequency solid-state Raman laser, its structure is as described in embodiment 1, the difference is that it also includes a cavity mirror M2, and the cavity mirror M2 is located between the laser gain medium and the Raman crystal, such as figure 2 shown. The cavity mirror M2 is added, so that the cavity mirror M1 and the cavity mirror M3 form a fundamental frequency optical resonant cavity, and the cavity mirror M2 and cavity mirror M4 form a Raman optical resonant cavity, thereby forming a coupled-cavity all-solid-state laser structure, which shortens the Raman optical resonance The cavity length of the cavity increases the optical power density in the Raman optical resonant cavity, reduces the loss of the Raman cavity, and makes it easier to realize Raman conversion.
[0056] The laser structure of this embodiment is as figure 2 As shown, the settings along the propagation direction of the pump light are coupling lens group, cavity mirror M1, laser gain me...
Embodiment 3
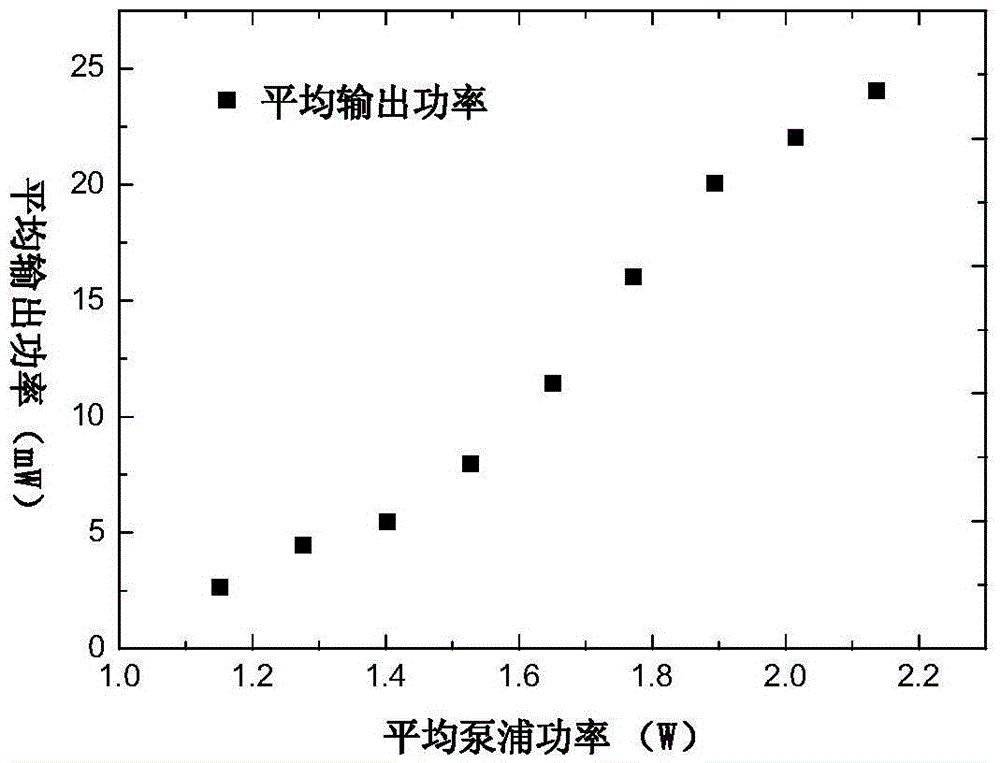
[0072] A kind of single-frequency solid-state Raman laser, its structure is as shown in embodiment 2, difference is that the first FP etalon thickness is 1.5mm, and the second FP etalon thickness is 15mm; Laser gain medium is ceramic Nd:YAG, Nd : The length of YAG is 50mm, and the doping concentration is 10%; the Raman crystal is diamond, and the length of diamond is 0.5mm; the cavity mirror M1 is a plano-convex mirror, and the cavity mirror M2 is a plano-convex mirror.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com