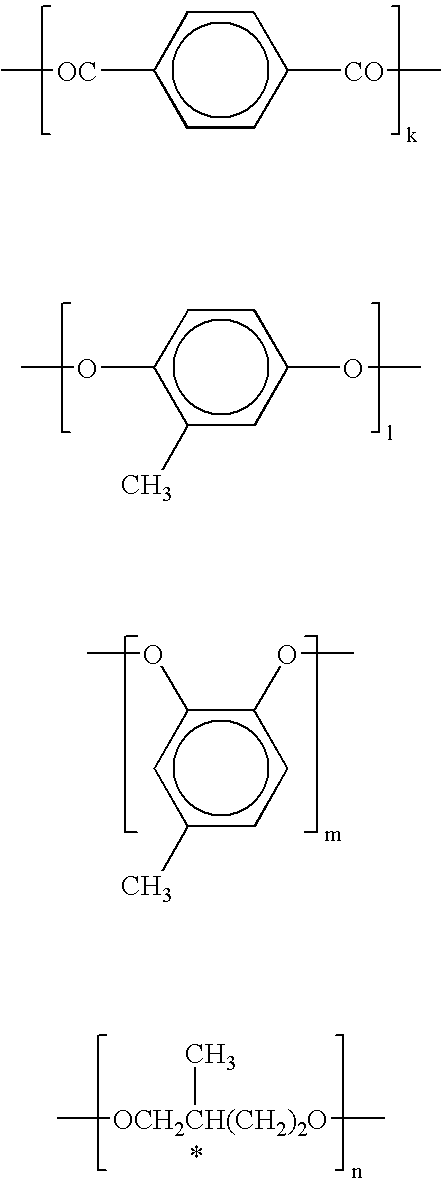
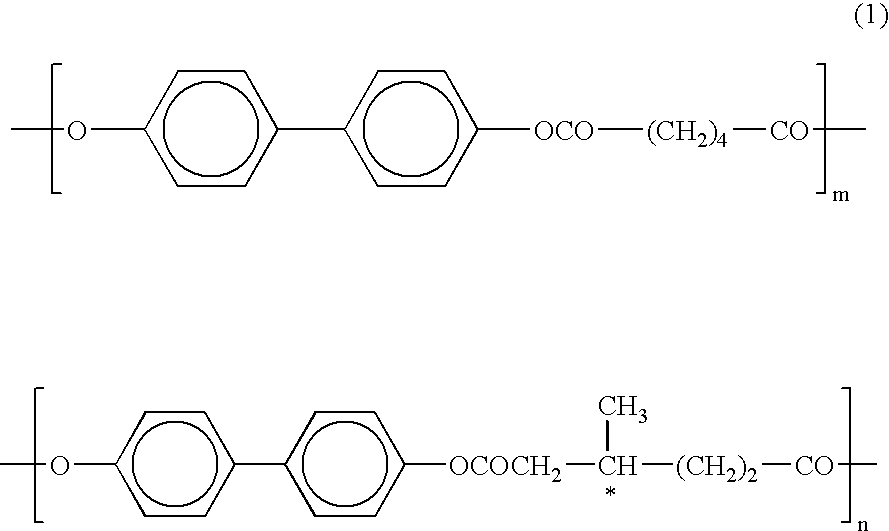
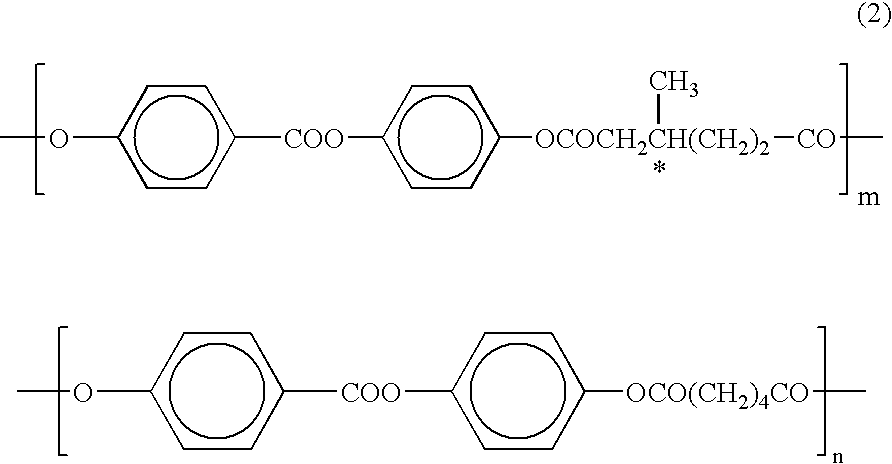
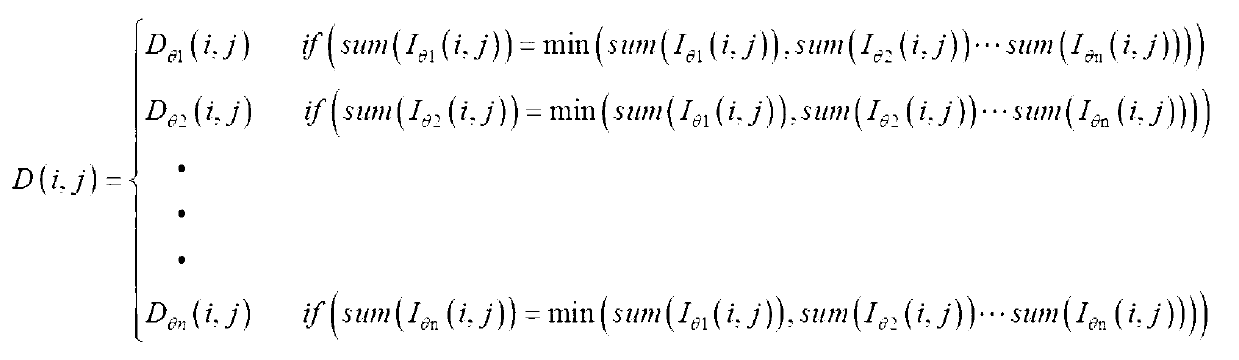Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
250 results about "Brewster's angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
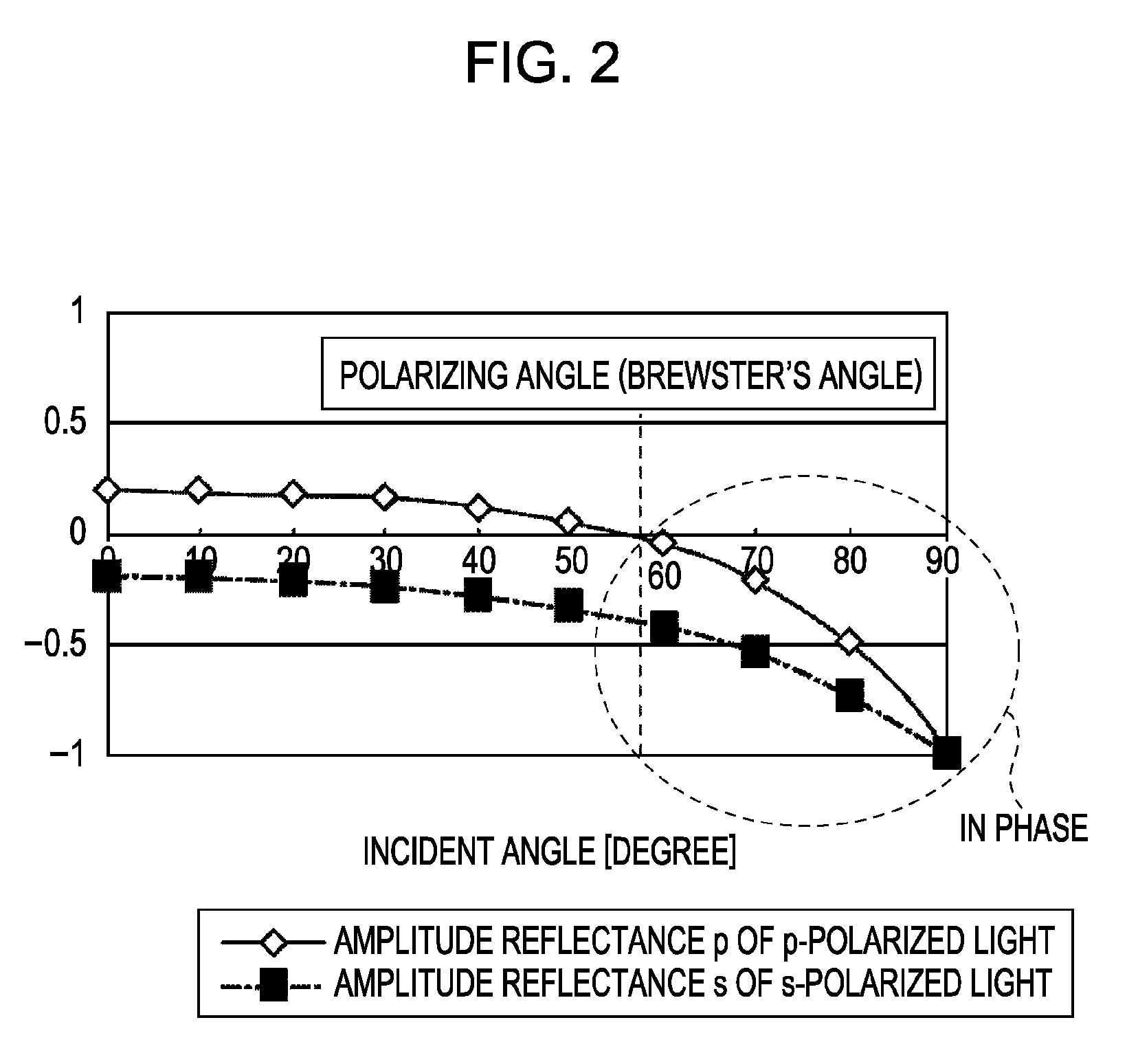
Brewster's angle (also known as the polarization angle) is an angle of incidence at which light with a particular polarization is perfectly transmitted through a transparent dielectric surface, with no reflection. When unpolarized light is incident at this angle, the light that is reflected from the surface is therefore perfectly polarized. This special angle of incidence is named after the Scottish physicist Sir David Brewster (1781–1868).
Heads-up display system with optical rotation layers
A head-up display system comprising a transparent plate. A liquid crystal display generates a display light of information with a plane of polarization inclined by about 45.degree. relative to an image plane vertical axis. A first optical rotation layer is disposed on a first surface of the transparent plate, and receives the display light from the liquid crystal display and optically rotates the plane of polarization of the display light by about 90.degree.. A second optical rotation layer is between the image plane of the liquid crystal display and a second surface of the transparent plate, and optically rotates the plane of polarization of the display light by about 45.degree. and allows S-polarized light to emanate toward the transparent plate at Brewster's angle. The S-polarized light is reflected on the second surface and is directed toward an eye of an operator.
Owner:CENT GLASS CO LTD +1
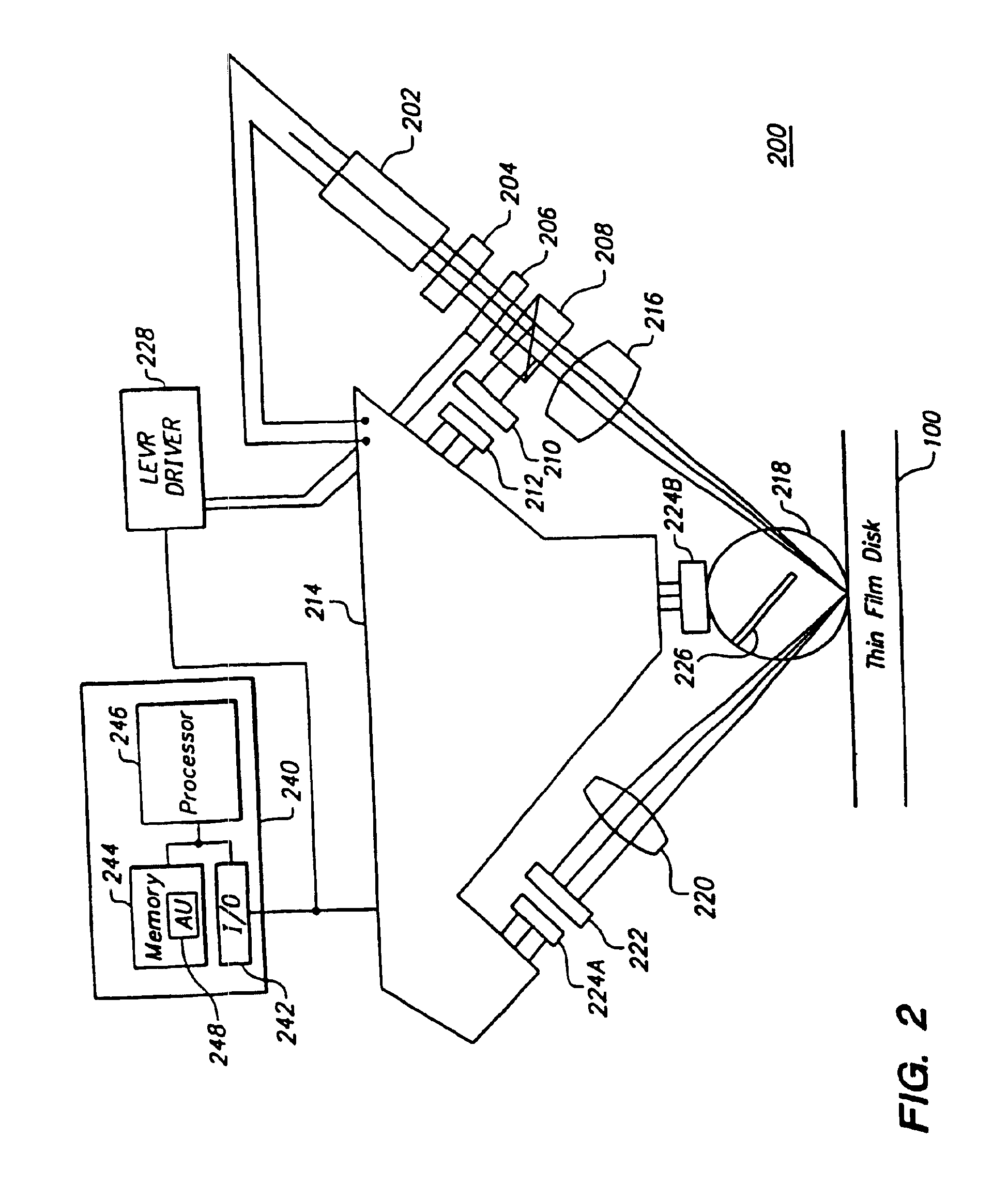
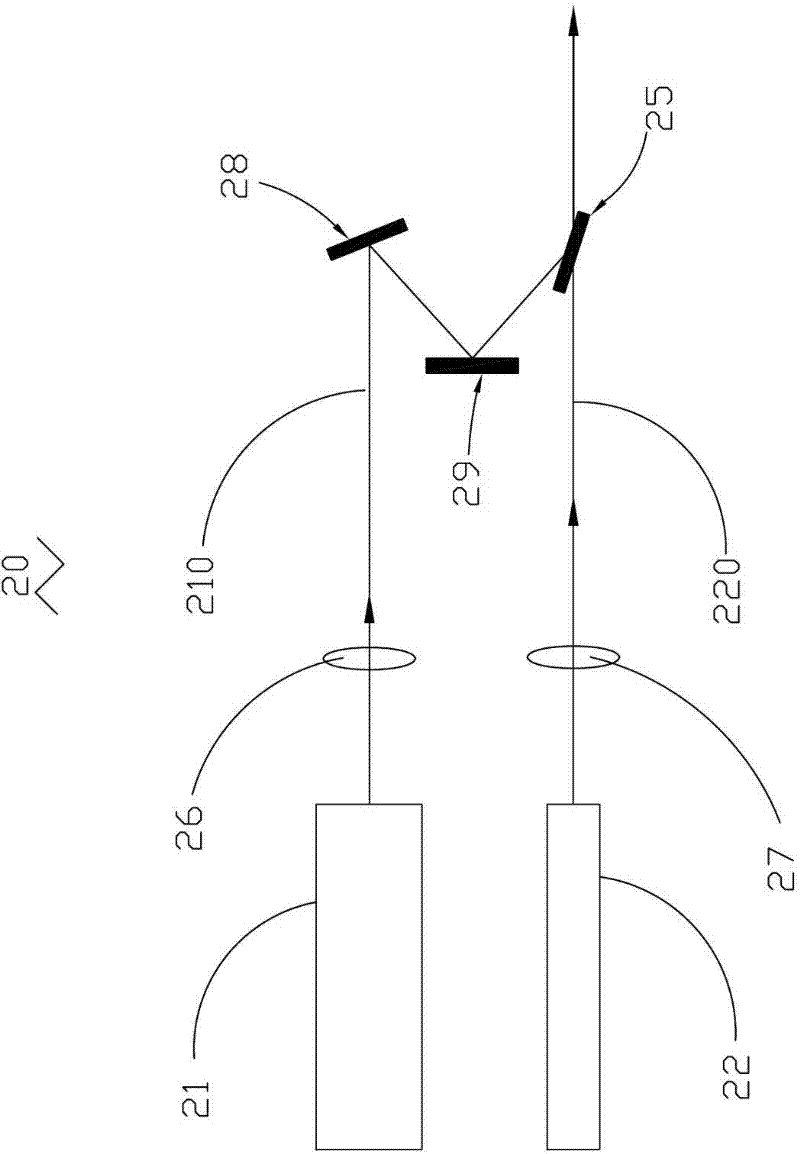
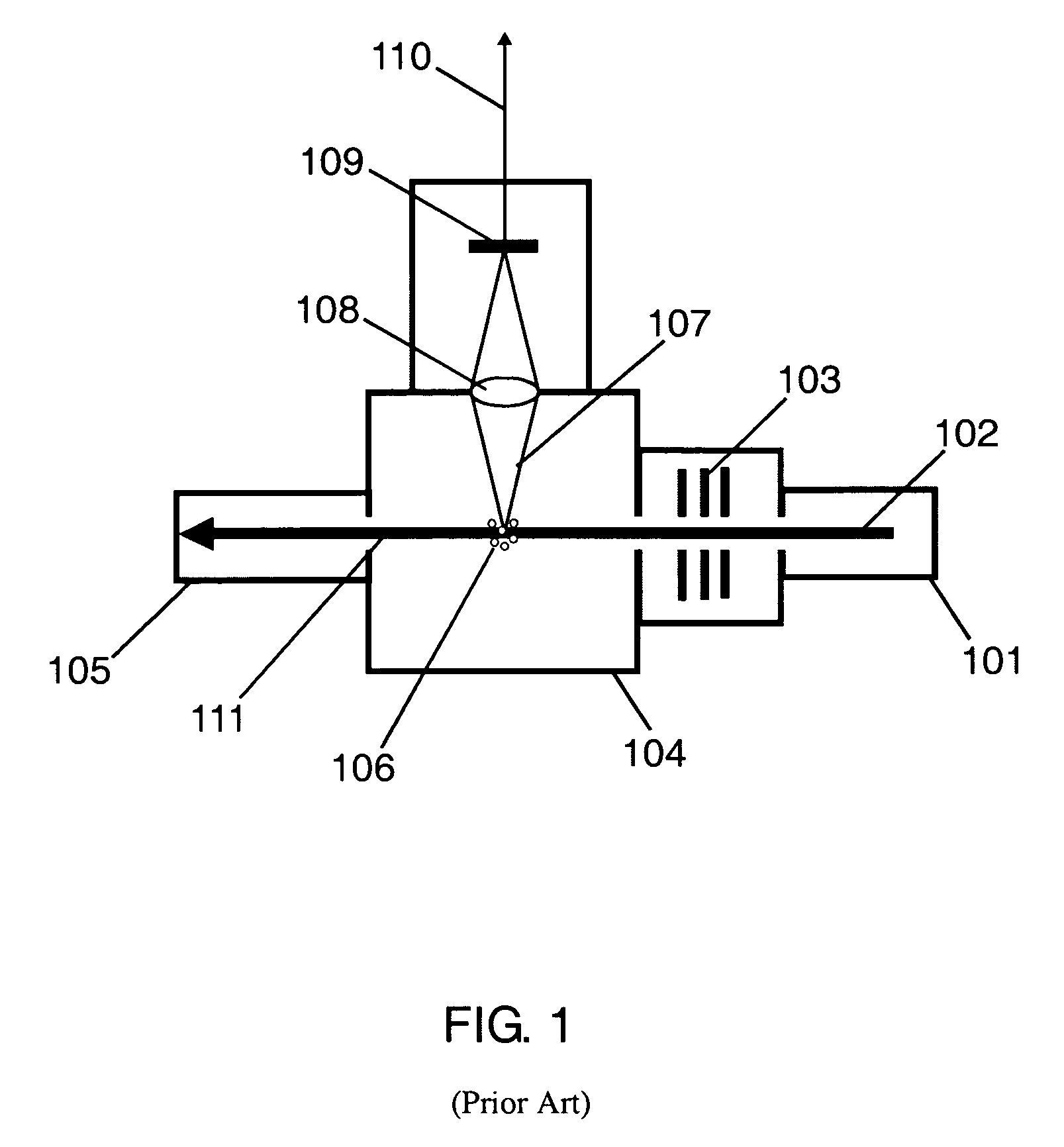
Method and apparatus for locating/sizing contaminants on a polished planar surface of a dielectric or semiconductor material
ActiveUS7002675B2Simple and compact and portableMaximizes capturePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsSemiconductor materialsHigh numerical aperture
To locate / size contaminants at the surface of a dielectric or semiconductor material, a P-polarized beam of light from a monochromatic solid-state source is disposed specifically at Brewster's angle and focused to form an illuminated quasi-elliptical spot on the surface that produces effectively no reflected or scattered light from the surface. The spot is scanned over the entire surface so as to assure multiple passes of any contaminant through the spot. On each pass through the spot a contaminant will produce scattered light. A novel high numerical aperture reflective or refractive system is disposed above the surface to always view the spot and to collect / redirect the bulk of the contaminant scattered light to a detector. Illumination at Brewster's angle combined with the high numerical aperture scattered light collector / redirector maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio from the detector. These core components are packaged with support subsystems as a uniquely compact and portable apparatus.
Owner:SYNETICS SOLUTIONS +2
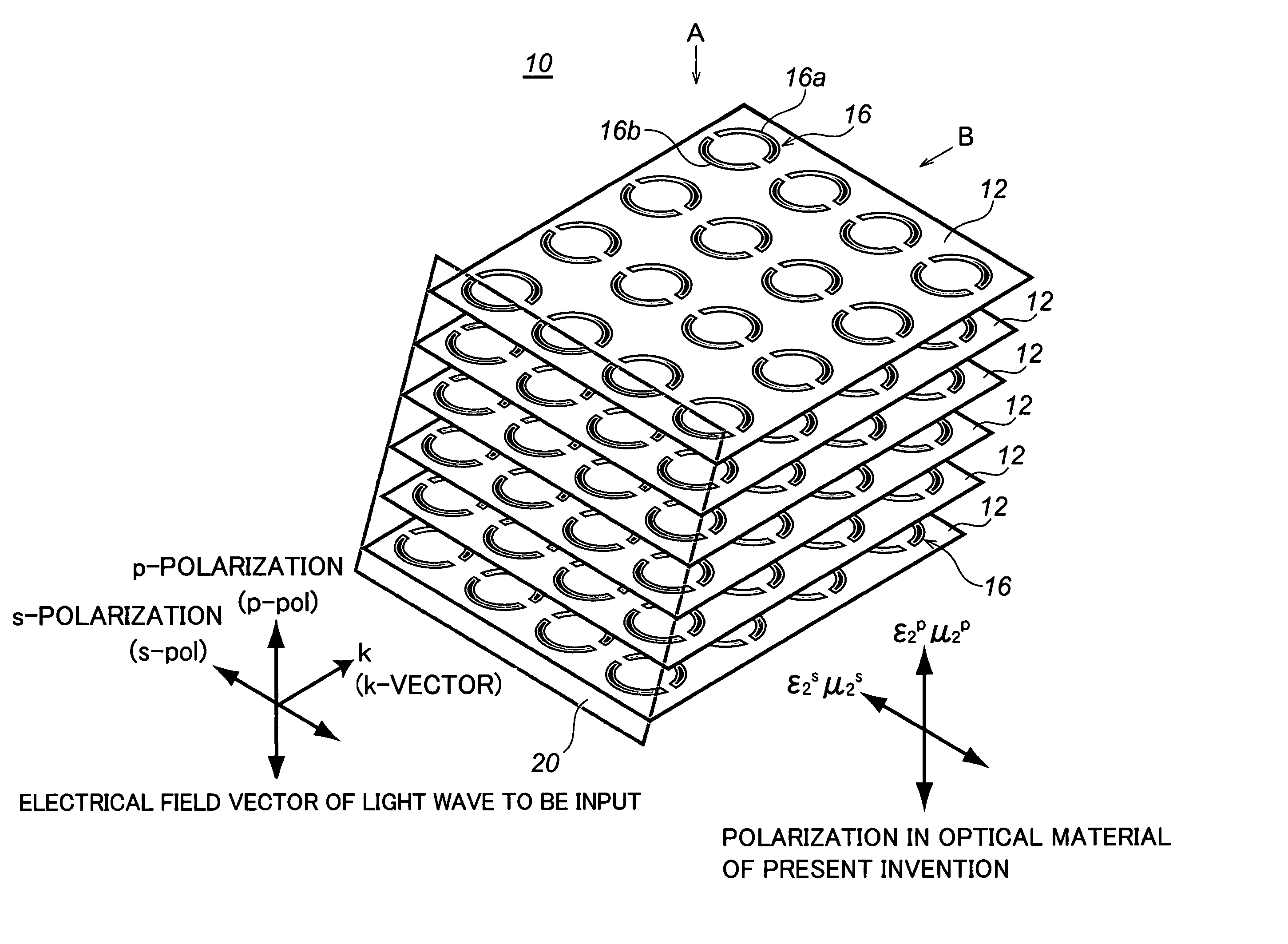
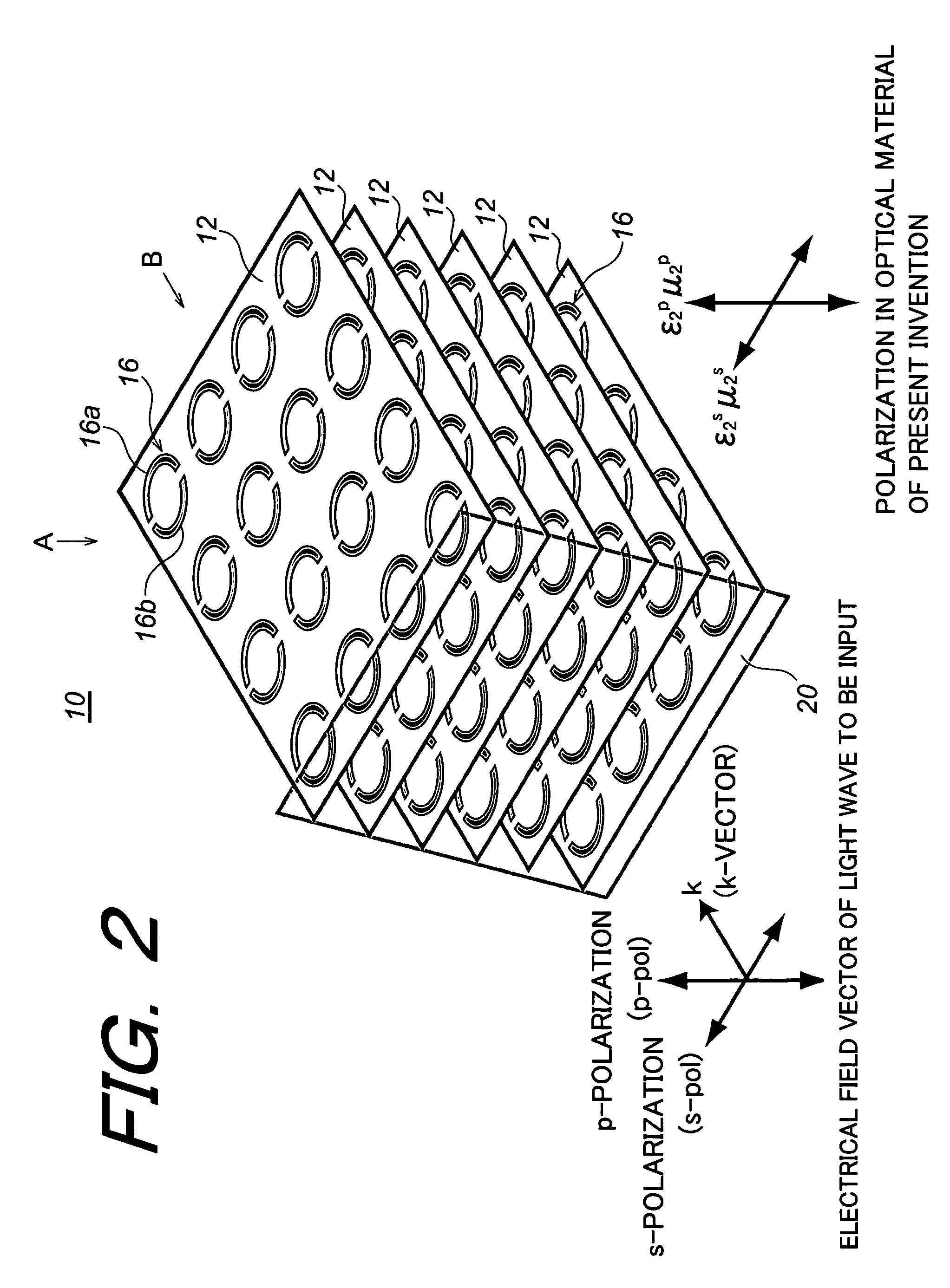
Optical material, optical device fabricated therefrom, and method for fabricating the same
In order to make a reflection coefficient in boundary surface between materials to be zero and permeate 100% of a light independent of a polarization direction, an optical device made of an optical material composed of a metamaterial prepared by arranging a plurality of at least either of electrical resonators or magnetic resonators each being smaller than a wavelength of a light wave in only a predetermined plane, and at least either of the electrical resonators and the magnetic resonators arranged functioning with respect to s-polarization, whereby at least either of the dielectric constant or the magnetic permeability is controlled in response to the function to induce a Brewster phenomenon in the s-polarization wherein the incident plane of a light wave being set out at a Brewster's angle with respect to the p-polarization and further at least either of the dielectric constant and the magnetic permeability of the optical material being controlled with respect to the s-polarization of the optical material, whereby the Brewster condition is independently satisfied in both the p-polarization and the s-polarization at the same time.
Owner:RIKEN
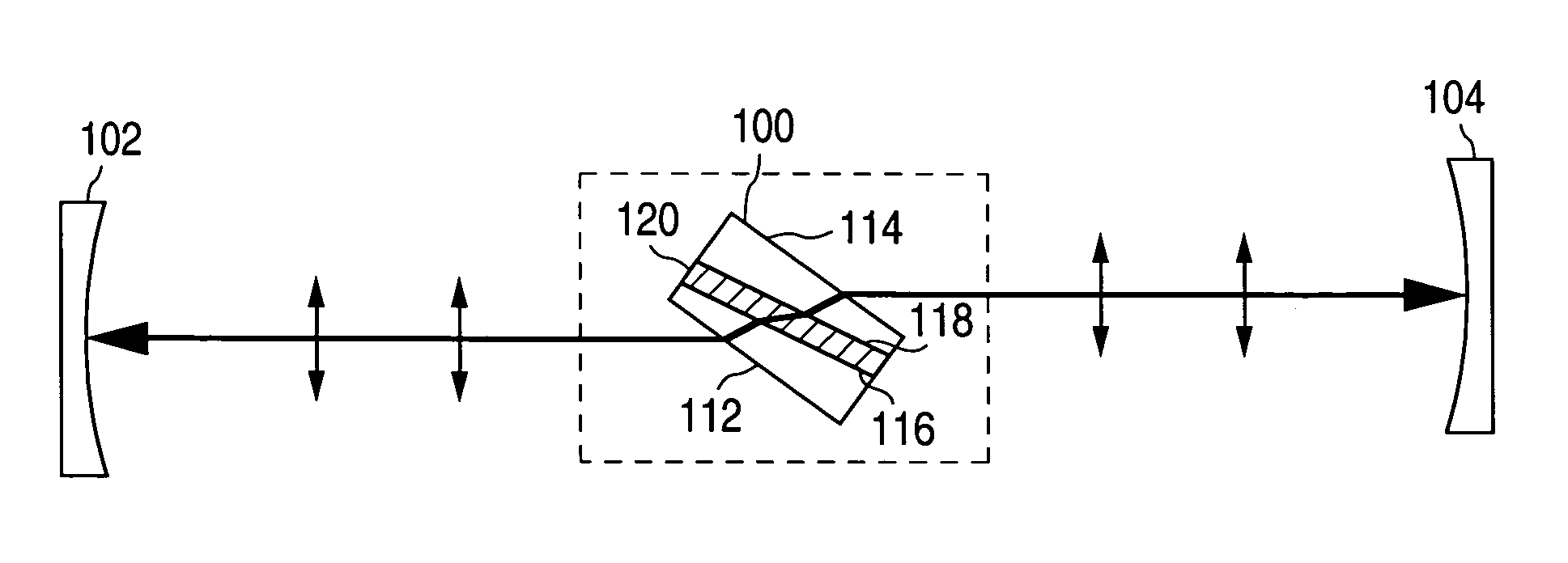
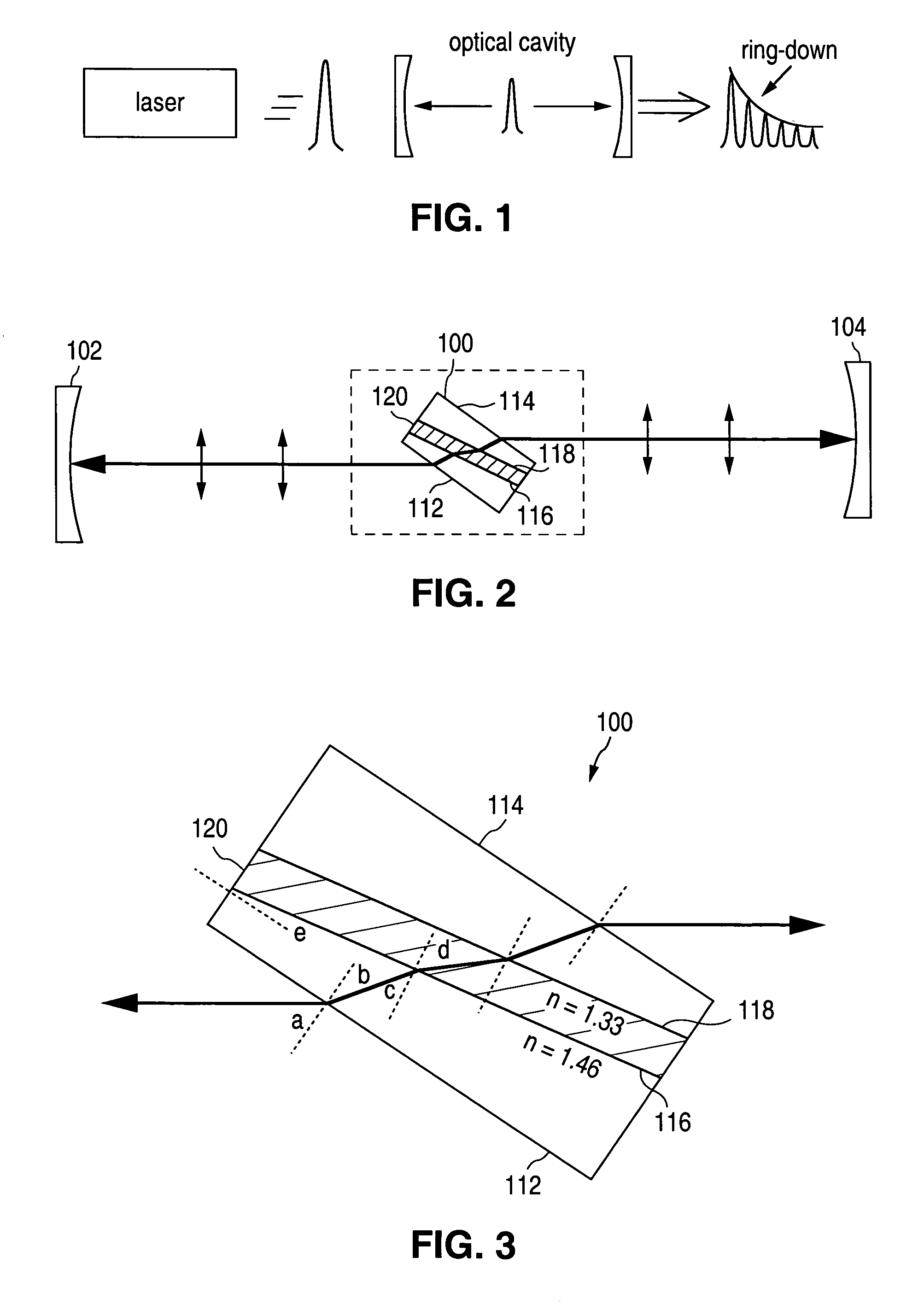
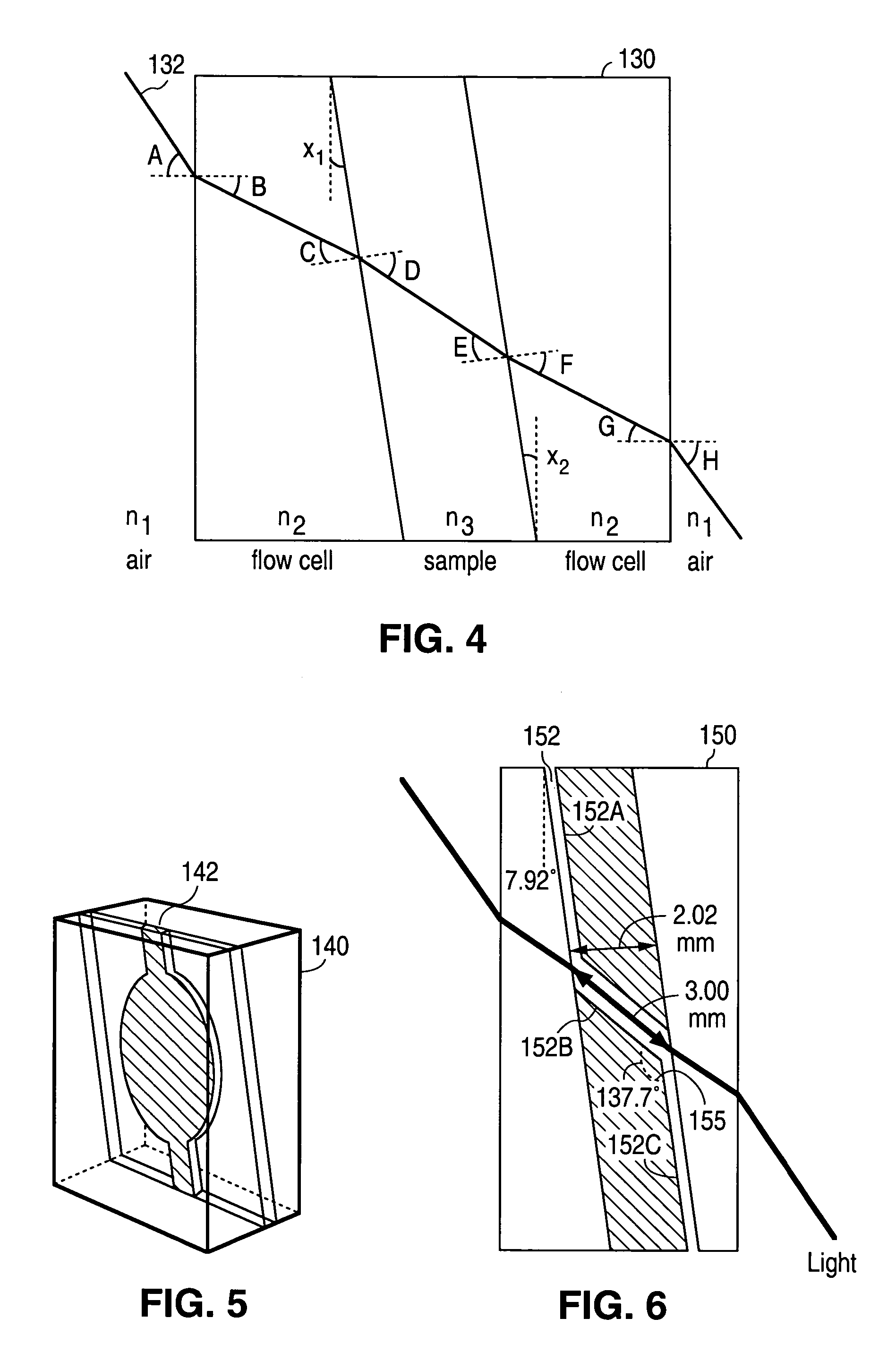
Brewster's angle flow cell for cavity ring-down spectroscopy
InactiveUS7064836B2Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsRing downOptical cavity
A container to be positioned in a ring-down optical cavity for containing a sample includes an outer surface having opposing first and second outer faces and an inner surface forming a void for containing the sample and having opposing first and second inner faces. The container may include a first portion forming the first outer face having a second index of refraction and a second portion forming the second outer face having a third index of refraction. The container may be placed in an optical cavity including a medium. The first and second outer faces of the outer surface and the first and second inner faces of the inner surface are oriented so that the cavity-to-container interfaces and the container-to-sample interfaces of the container transmit and receive a light beam at an incidence angle approximately equal to the Brewster's angle of the respective interface.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
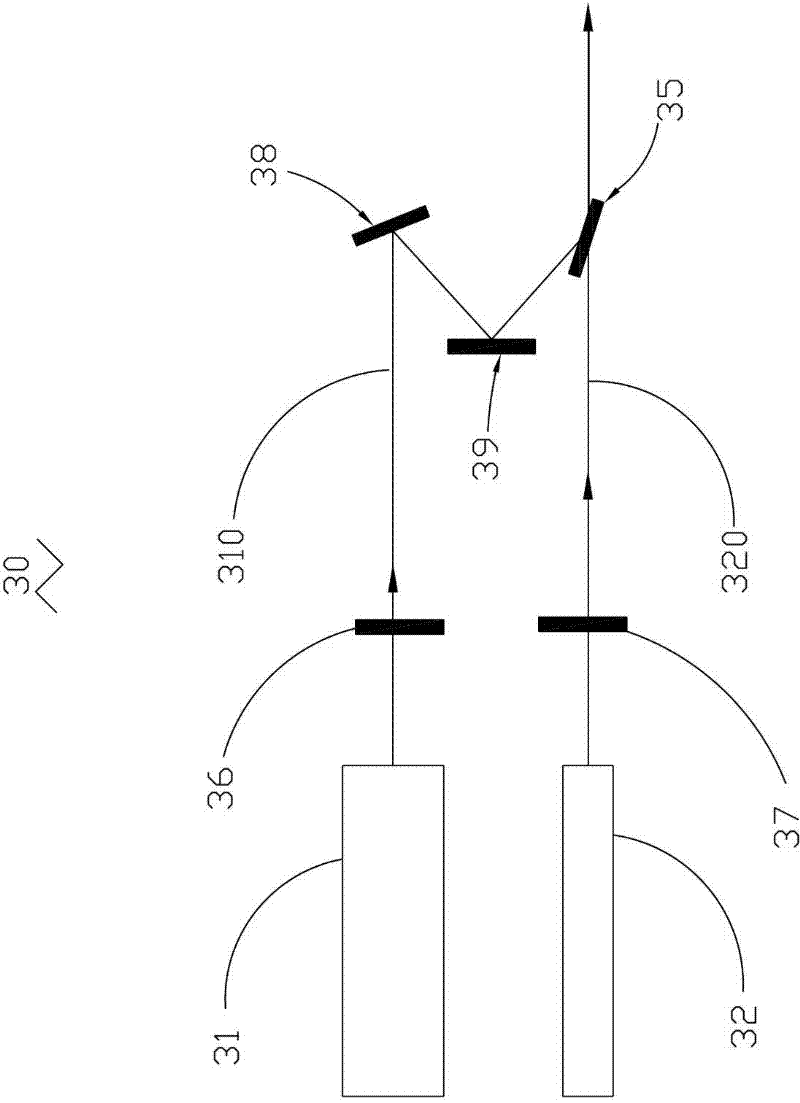
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20050179904A1High sensitivityImprove light collectionComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Laser thermal processing with laser diode radiation
InactiveUS20050045604A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusHigh energyVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for performing laser thermal processing (LTP) using a two-dimensional array of laser diodes to form a line image, which is scanned across a substrate. The apparatus includes a two-dimensional array of laser diodes, the radiation from which is collimated in one plane using a cylindrical lens array, and imaged onto the substrate as a line image using an anomorphic, telecentric optical imaging system. The apparatus also includes a scanning substrate stage for supporting a substrate to be LTP processed. The laser diode radiation beam is incident on the substrate at angles at or near the Brewster's angle for the given substrate material and the wavelength of the radiation beam, which is linearly P-polarized. The use of a two-dimensional laser diode array allows for a polarized radiation beam of relatively high energy density to be delivered to the substrate, thereby allowing for LTP processing with good uniformity, reasonably short dwell times, and thus reasonably high throughput.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
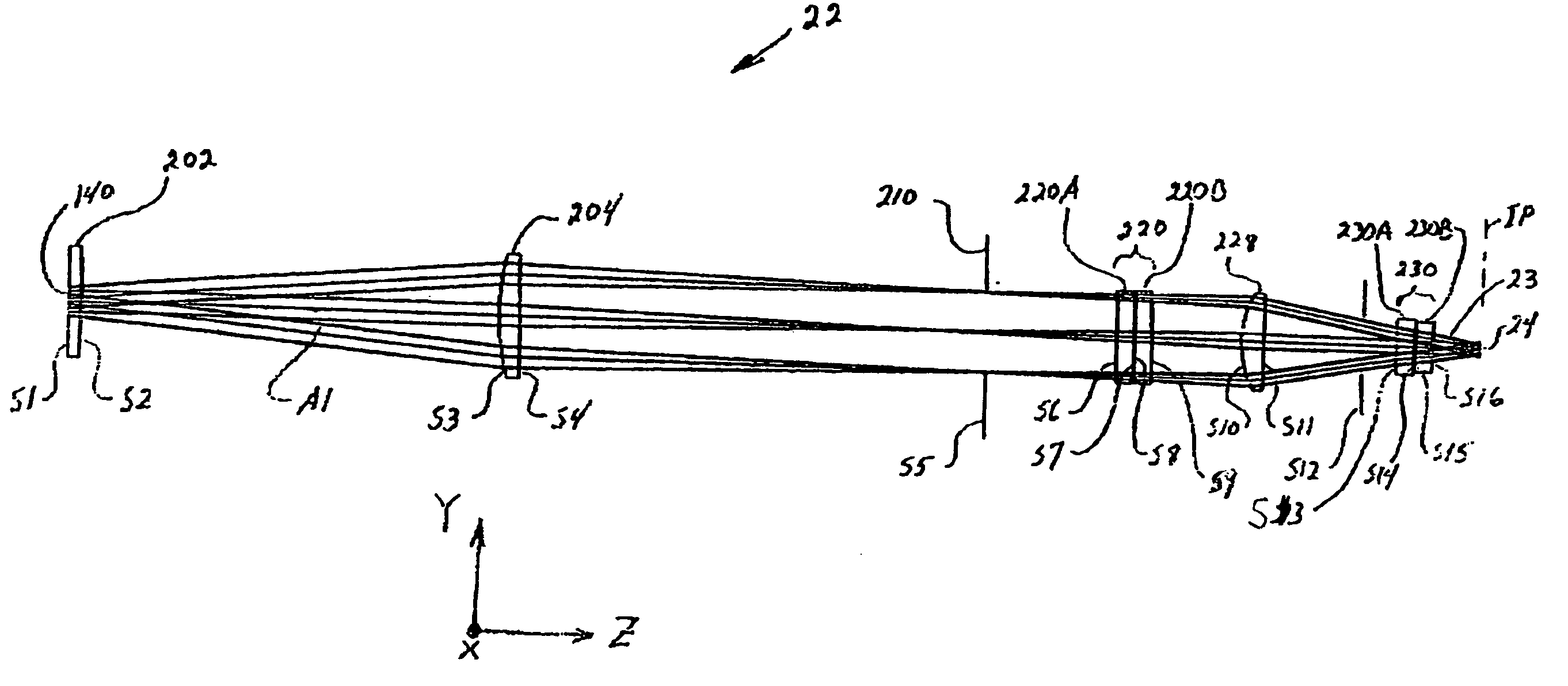
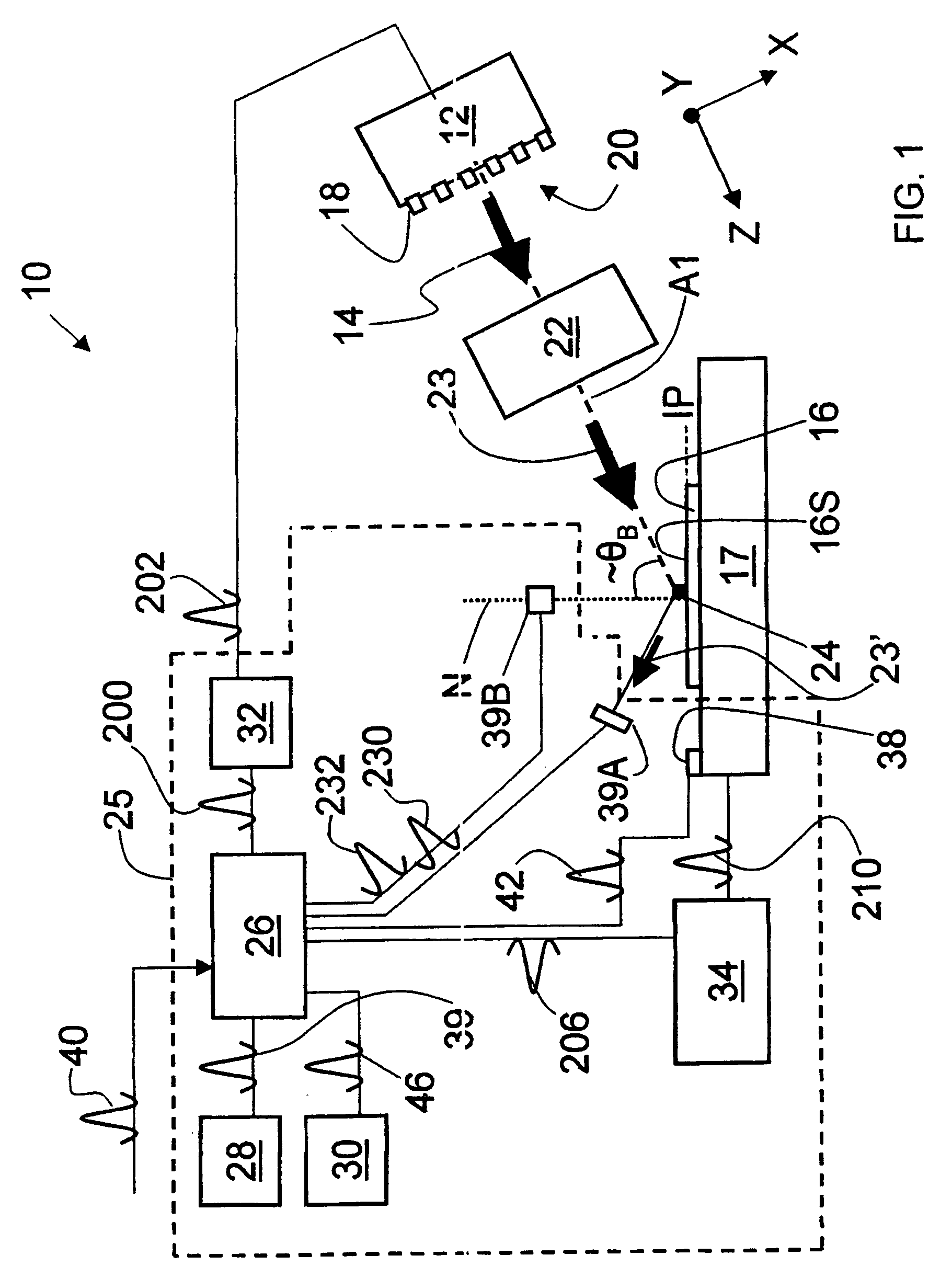
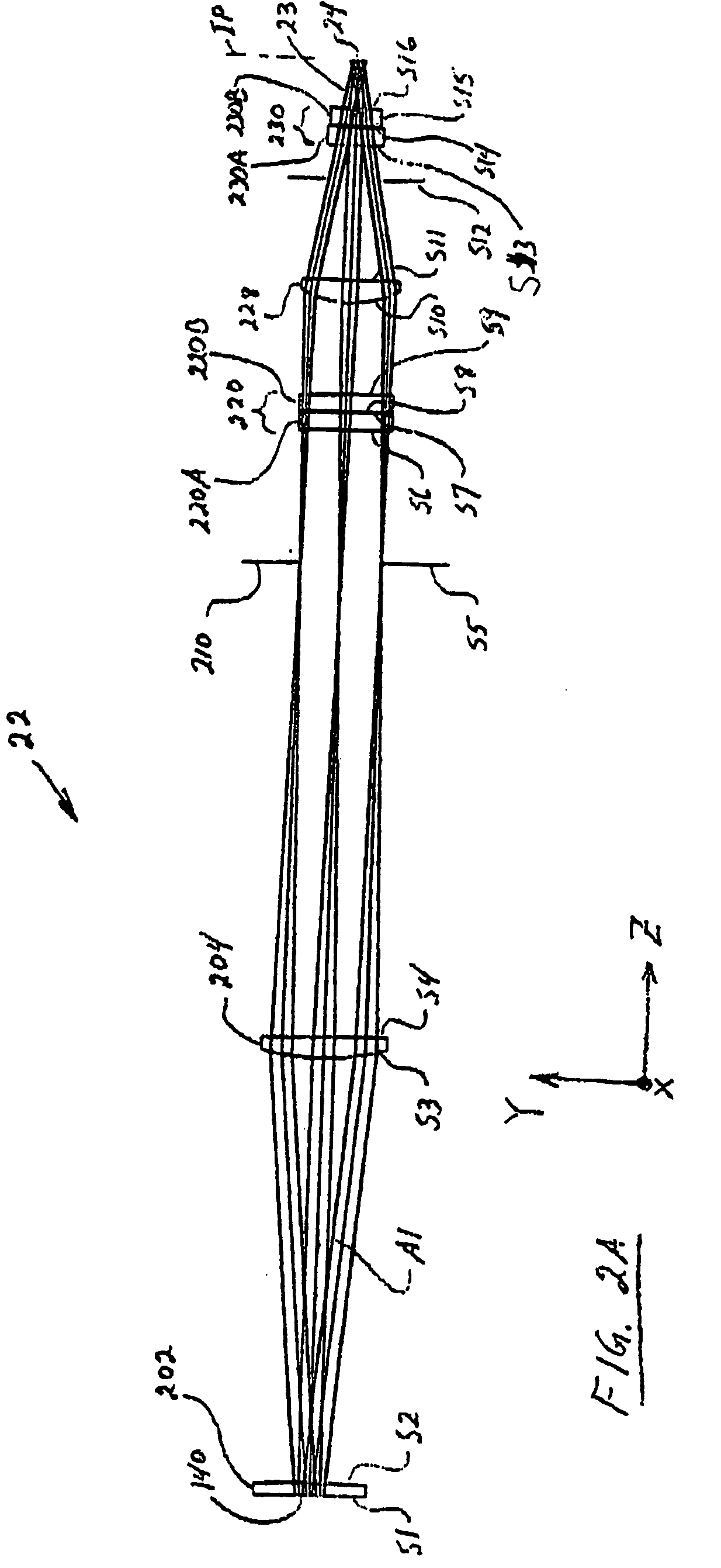
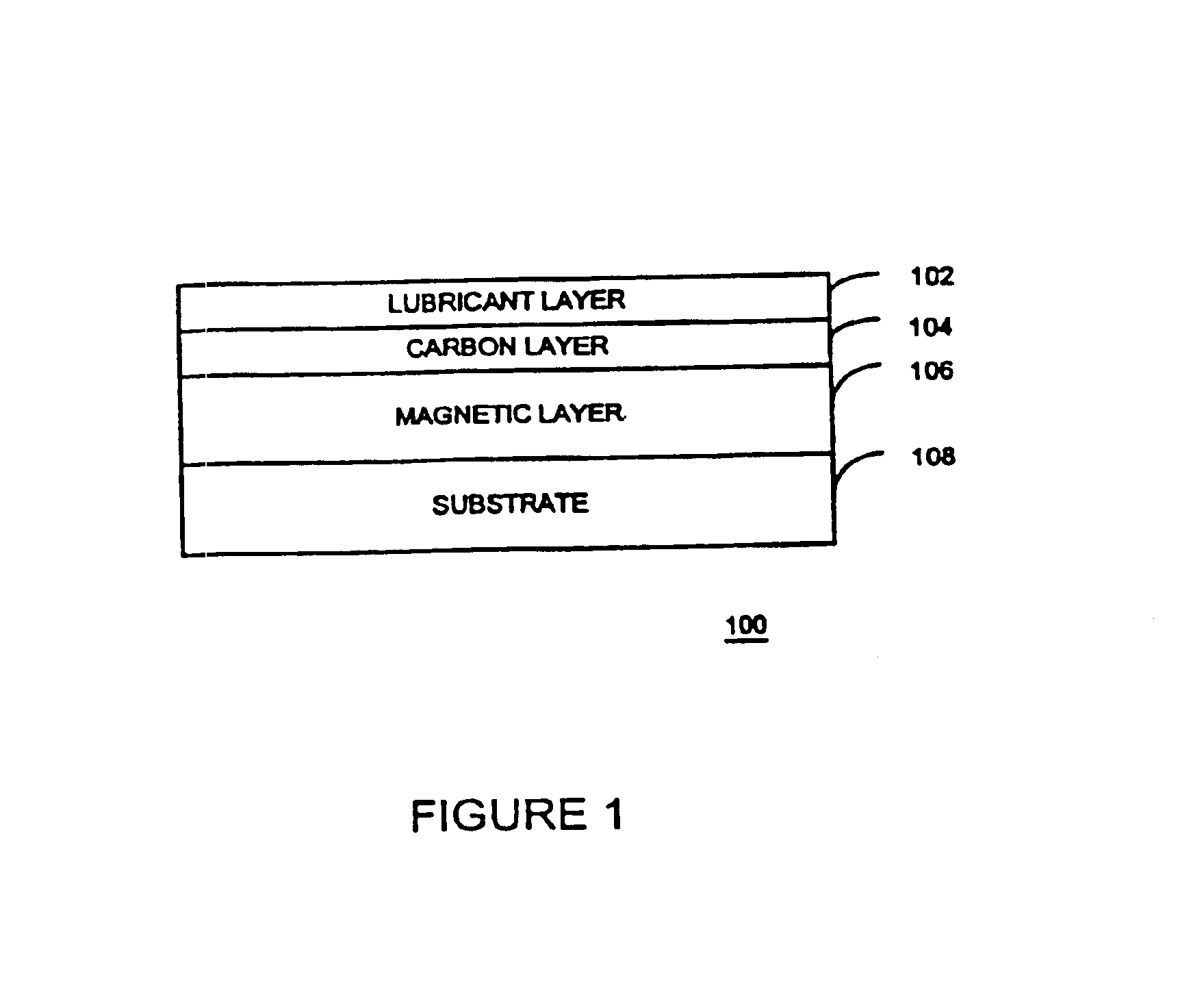
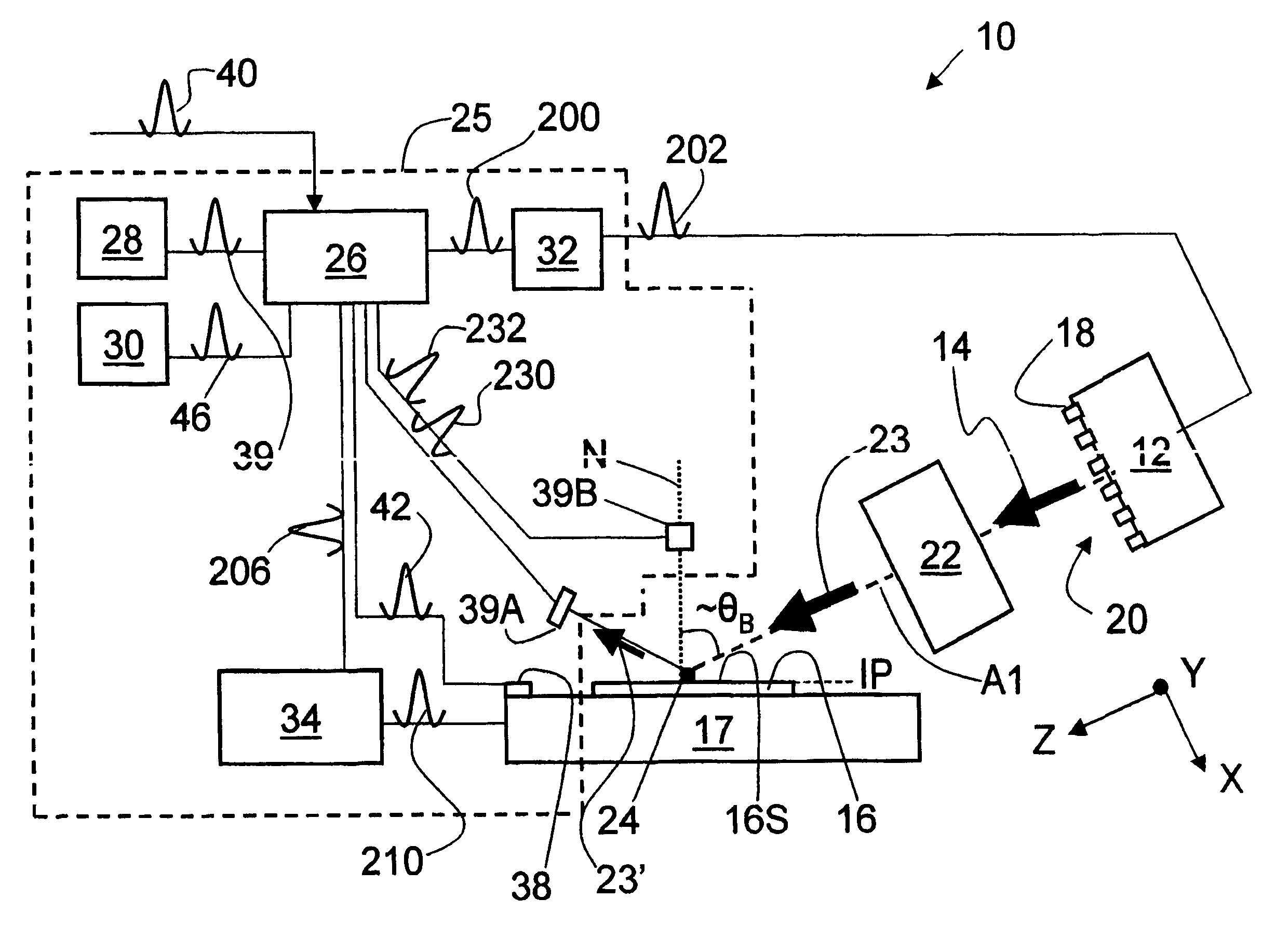
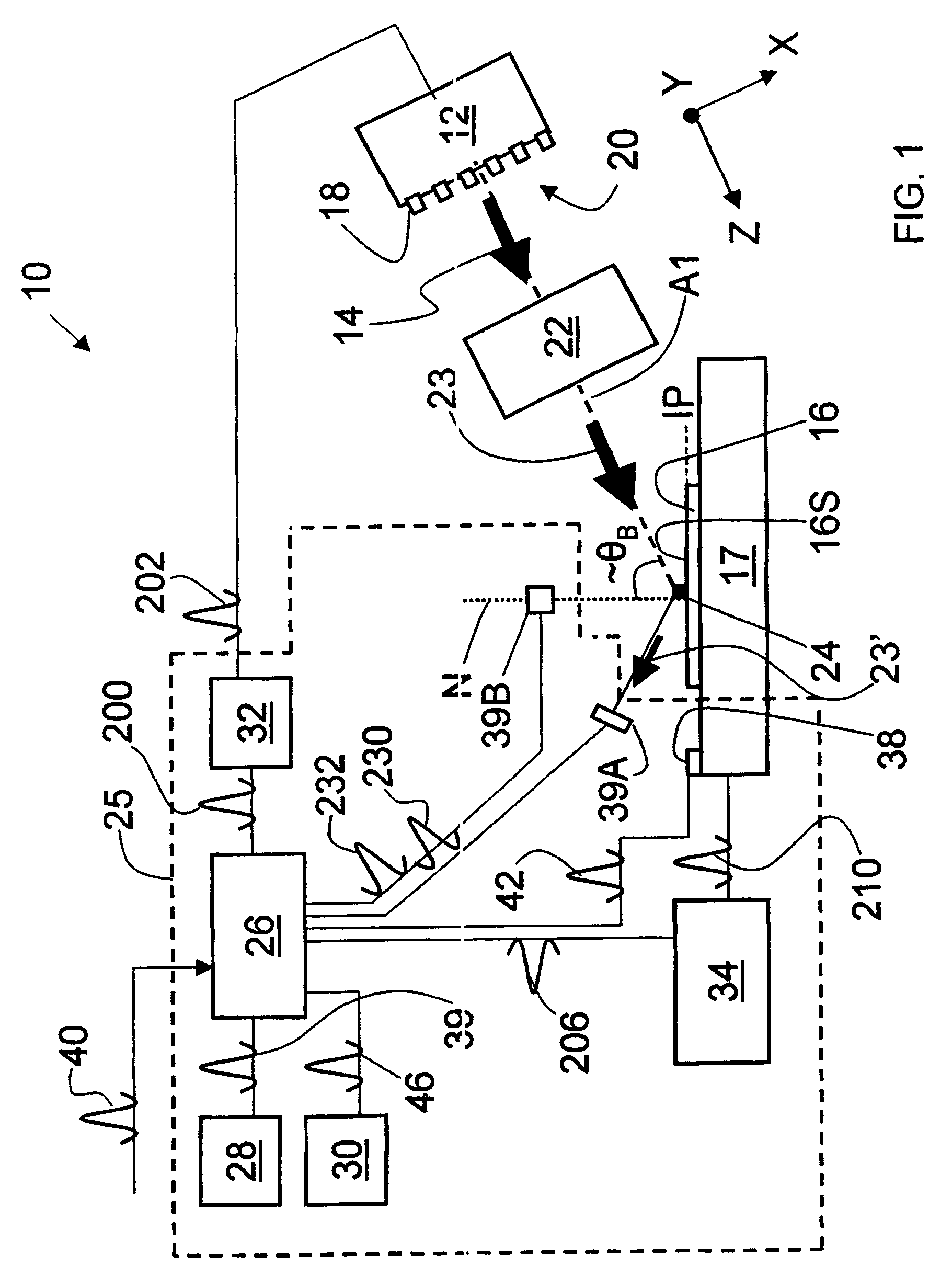
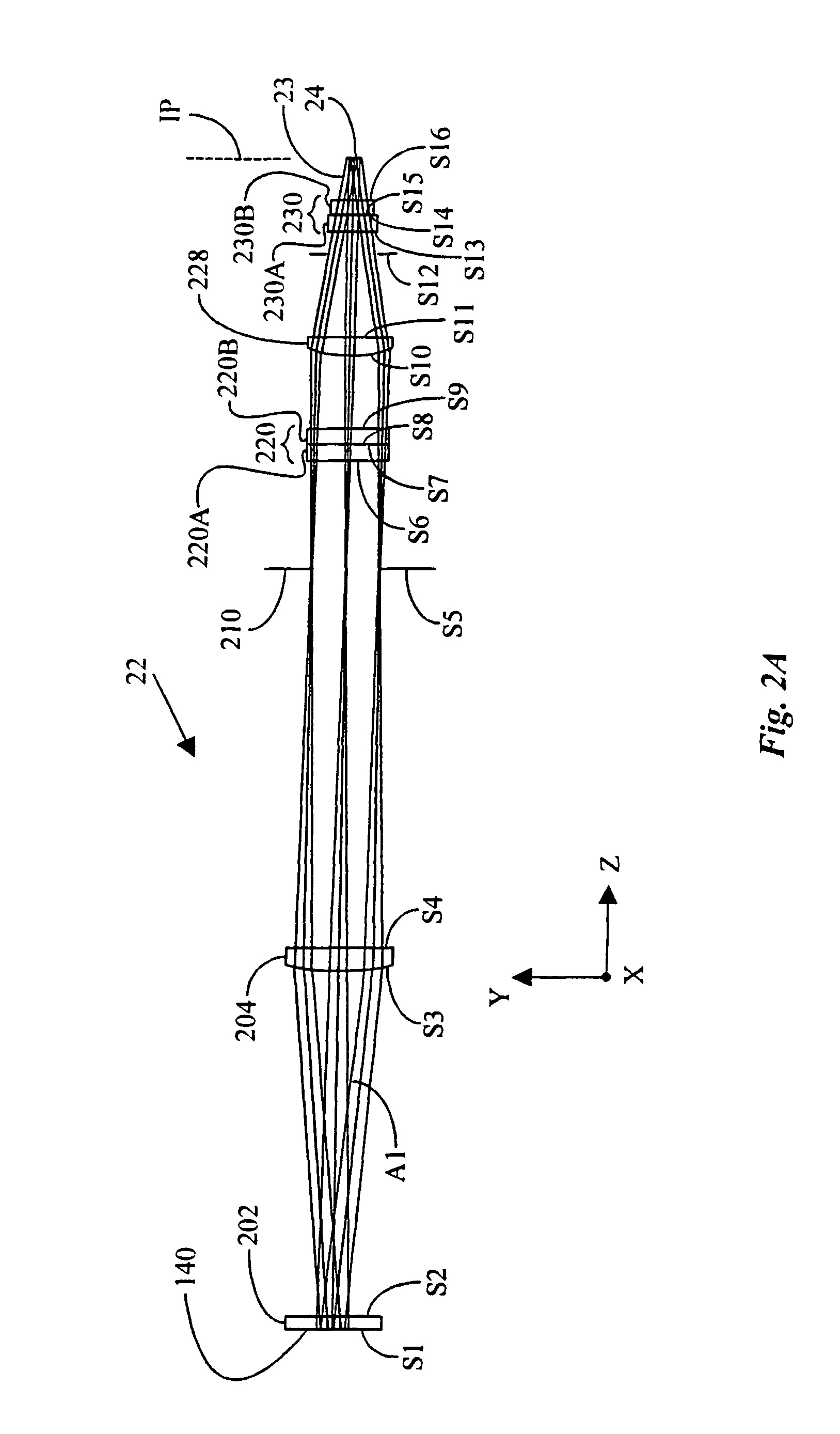
System and method for measuring object characteristics using phase differences in polarized light reflections
InactiveUS6956658B2Easy to measurePolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsPhase differenceLight reflection
A system and method for performing a magnetic imaging, optical profiling, and measuring lubricant thickness and degradation, carbon wear, carbon thickness, and surface roughness of thin film magnetic disks and silicon wafers at angles that are not substantially Brewster's angle of the thin film (carbon) protective overcoat is provided. The system and method involve a focused optical light whose polarization can be switched between P or S polarization is incident at an angle to the surface of the thin film magnetic disk. This generates both reflected and scattered light that may be measured to determine various values and properties related to the surface of the disk, including identifying the Kerr-effect in reflected light for determination of point magnetic properties. In addition, the present invention can mark the position of an identified defect.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Laser thermal processing with laser diode radiation
InactiveUS7763828B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusHigh energyVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for performing laser thermal processing (LTP) using a two-dimensional array of laser diodes to form a line image, which is scanned across a substrate. The apparatus includes a two-dimensional array of laser diodes, the radiation from which is collimated in one plane using a cylindrical lens array, and imaged onto the substrate as a line image using an anomorphic, telecentric optical imaging system. The apparatus also includes a scanning substrate stage for supporting a substrate to be LTP processed. The laser diode radiation beam is incident on the substrate at angles at or near the Brewster's angle for the given substrate material and the wavelength of the radiation beam, which is linearly P-polarized. The use of a two-dimensional laser diode array allows for a polarized radiation beam of relatively high energy density to be delivered to the substrate, thereby allowing for LTP processing with good uniformity, reasonably short dwell times, and thus reasonably high throughput.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
F2-laser with line selection
InactiveUS6345065B1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialDischarge efficiencyRefractive index
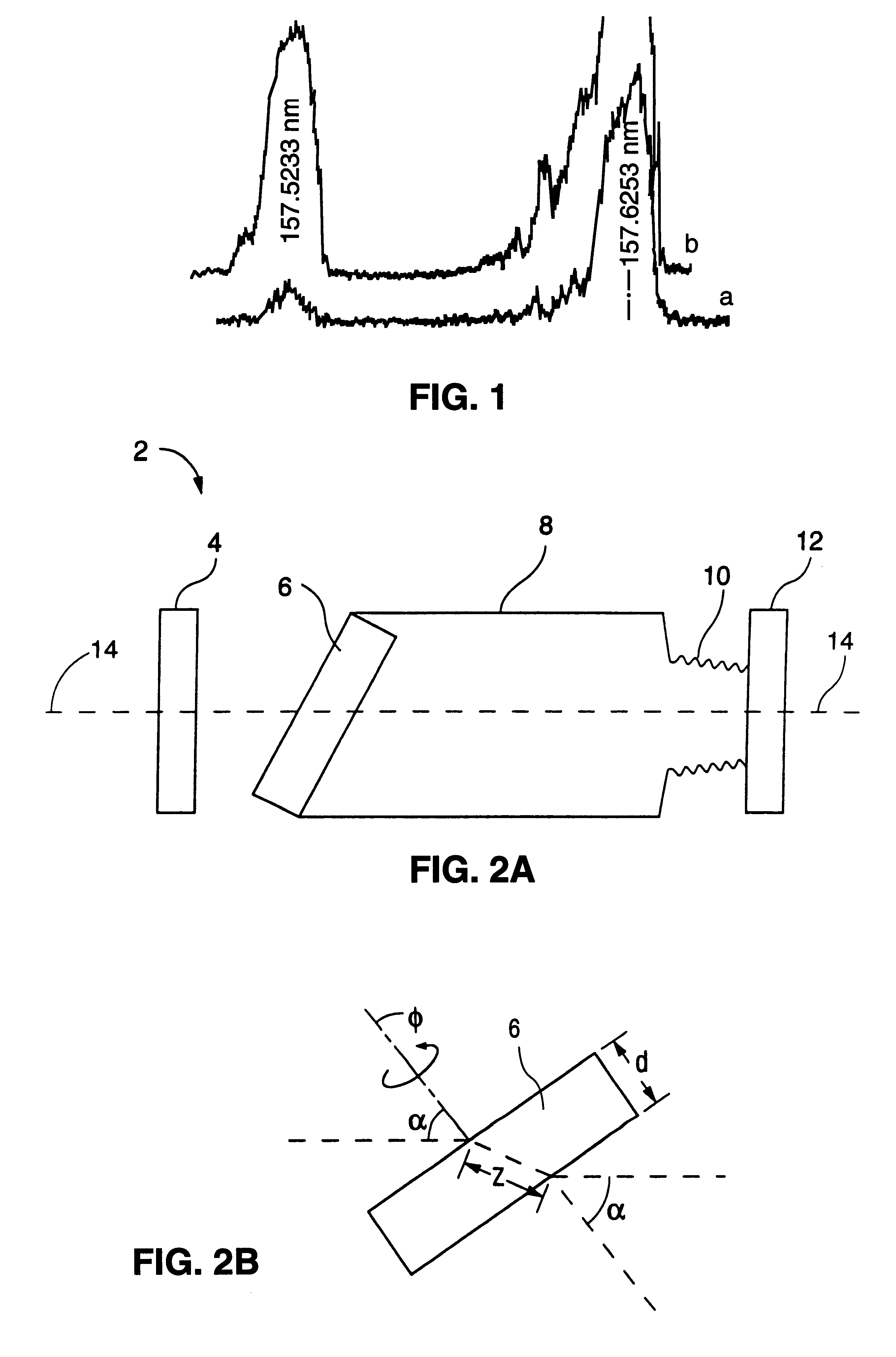
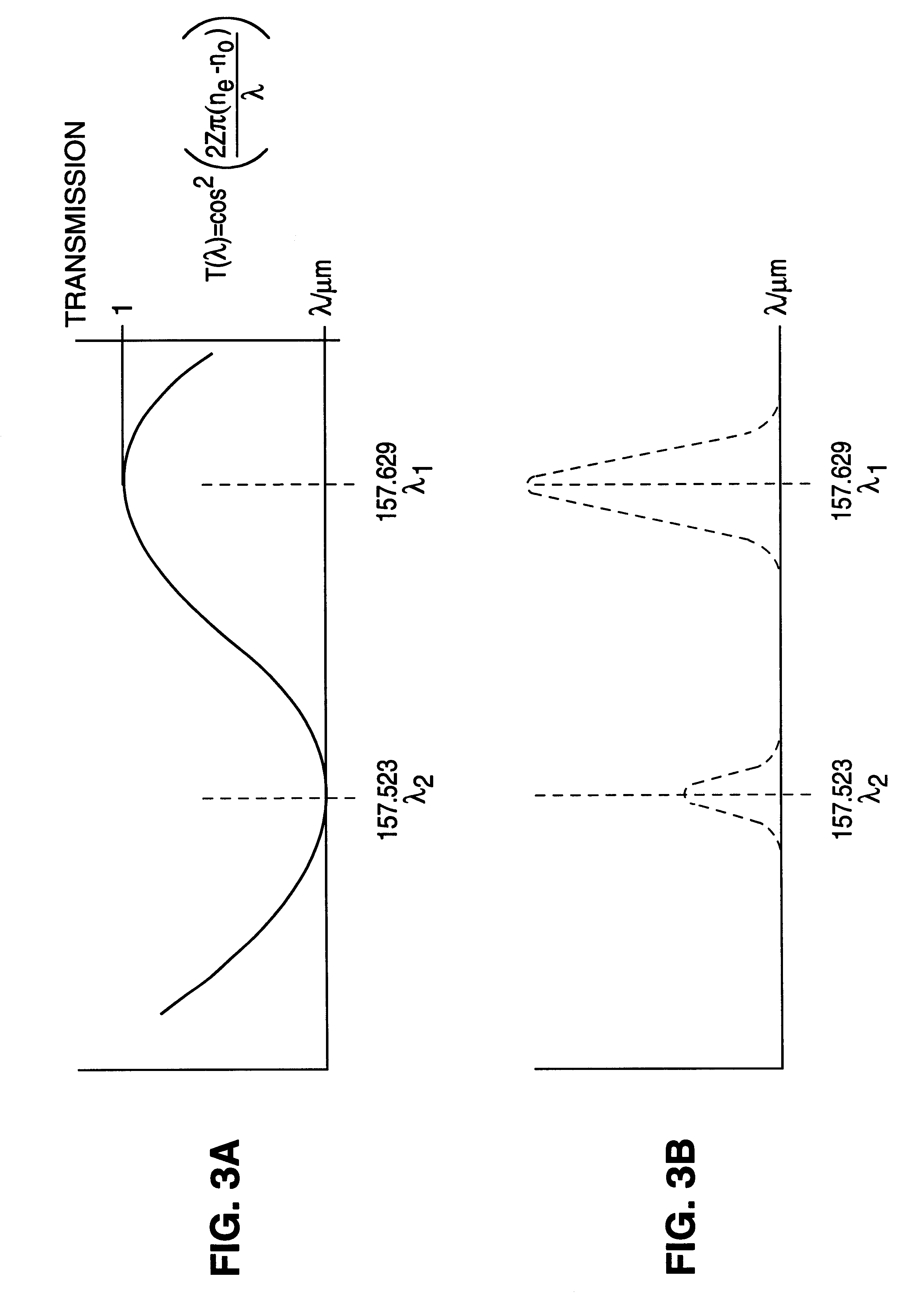
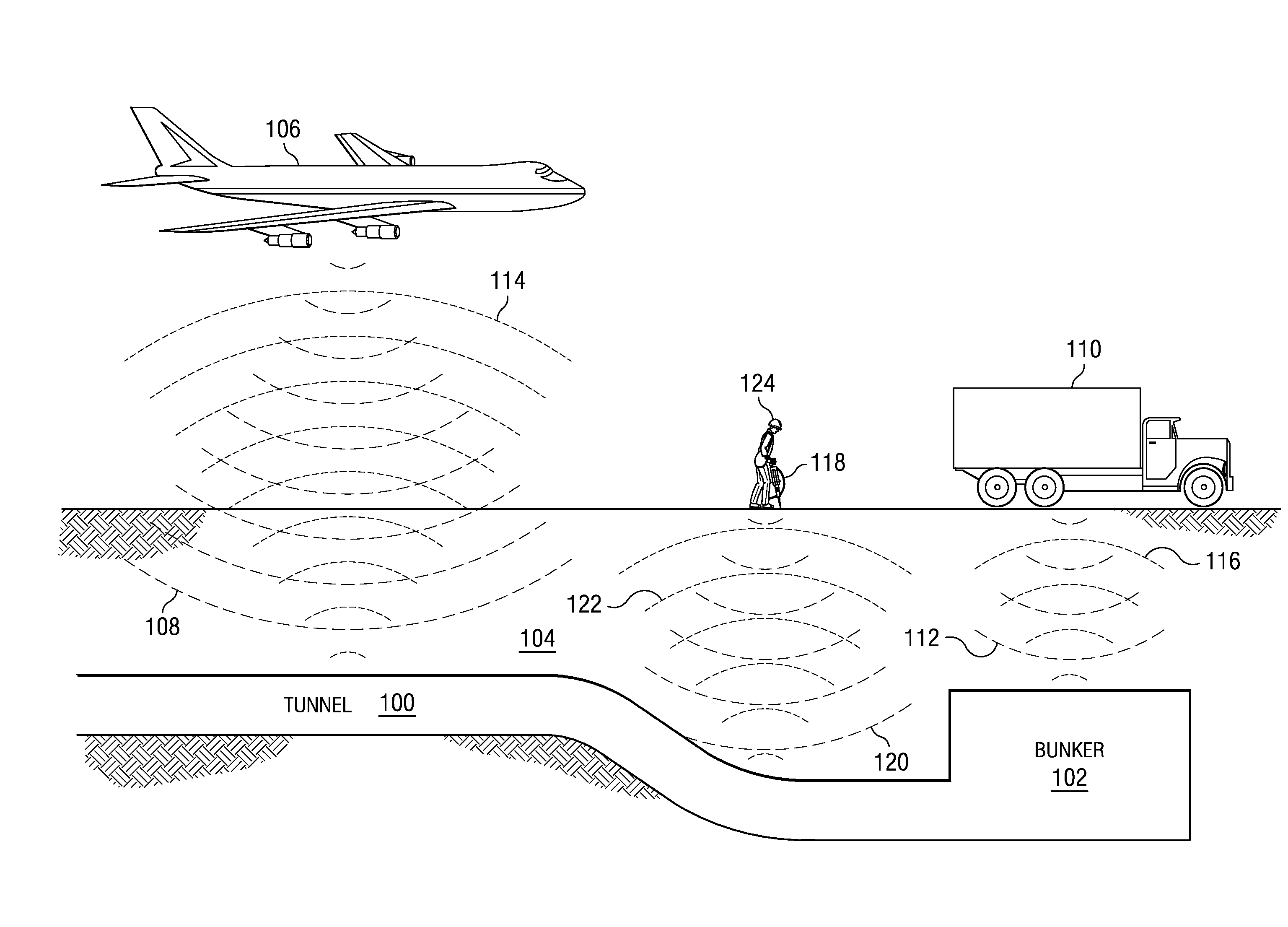
An F2-excimer laser has multiple closely-spaced spectral lines of interest around 157 nm, and one of the lines is selected by wavelength selection optics. The wavelength selection optics of a first preferred embodiment include a birefringent Brewster window enclosing the laser gas volume of the discharge chamber. The window preferably comprises MgF2 and is located at one end of the discharge chamber. One line is selected of the two when the optical thickness of the window is selected in coordination with rotatably adjustable, orthogonal refractive indices of the window. The transmissivity of the window is dependent on the orthogonal refractive indices and the optical thickness of the window. The wavelength selection optics of a second preferred embodiment include are at least partially within the laser active volume. In this way, line selection is performed in a manner which optimizes the combination of optical and discharge efficiency, resonator size and cost. The wavelength selection unit preferably includes a prism having a front surface oriented at Brewster's angle and a back surface oriented to receive and reflect an ordinary refracted ray travelling within the prism at a right angle to the back surface. The back surface also preferably includes a highly reflective coating to serve as the highly reflective surface of the resonator. The wavelength selection unit preferably further comprises an adjustment component for adjusting the orientation of the prism and for enclosing the other end of the housing, opposite the outcoupling end.
Owner:COHERENT GMBH
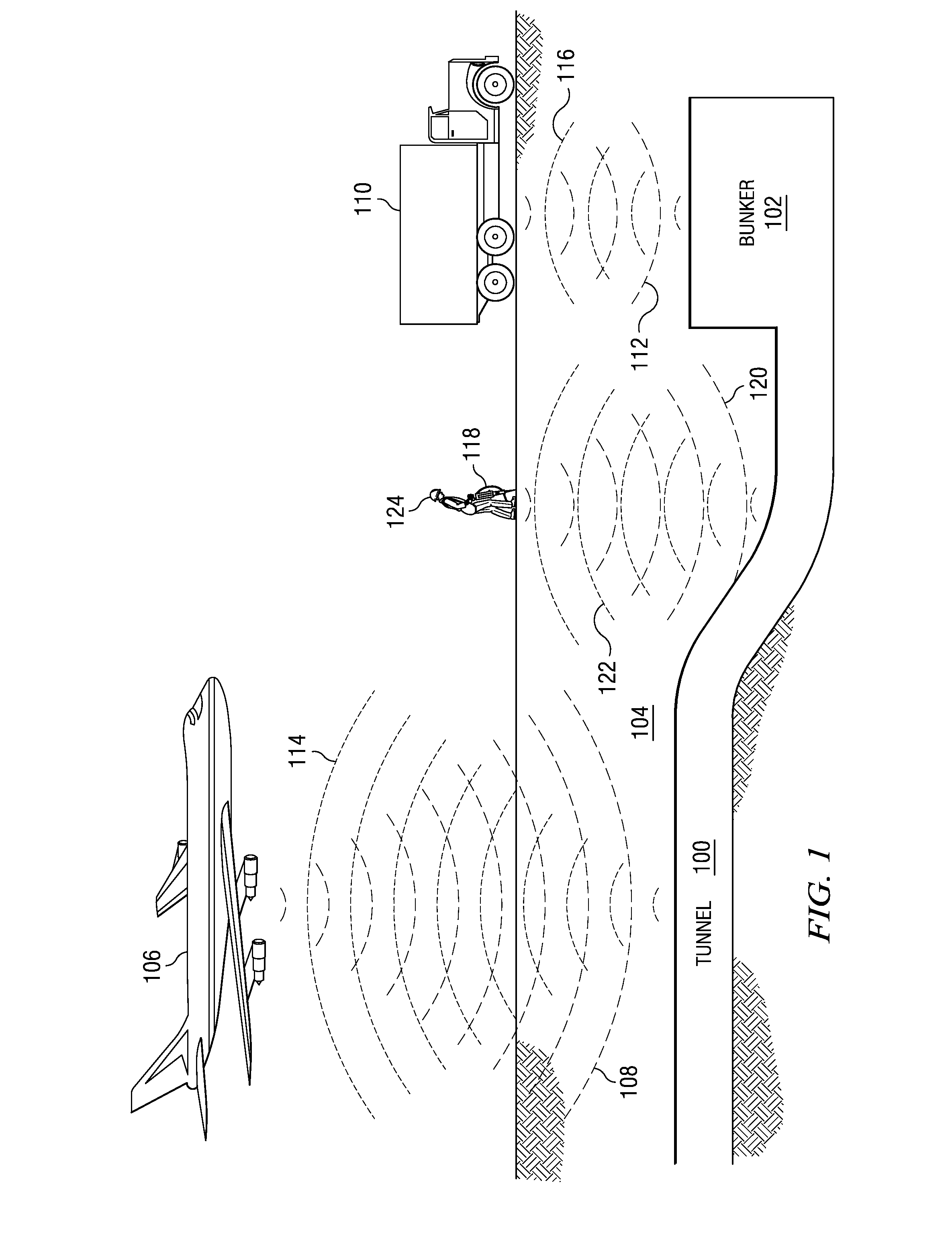
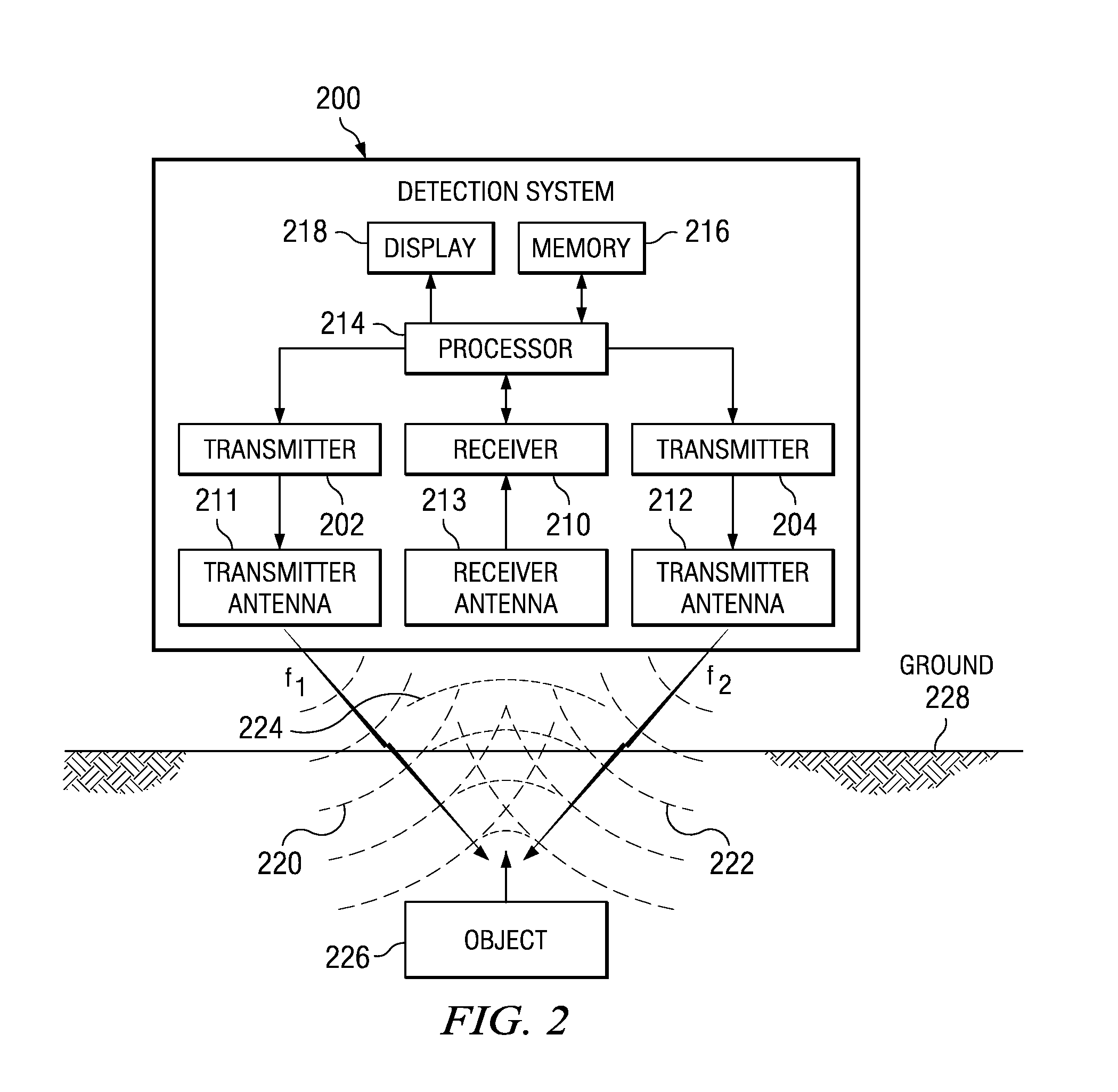
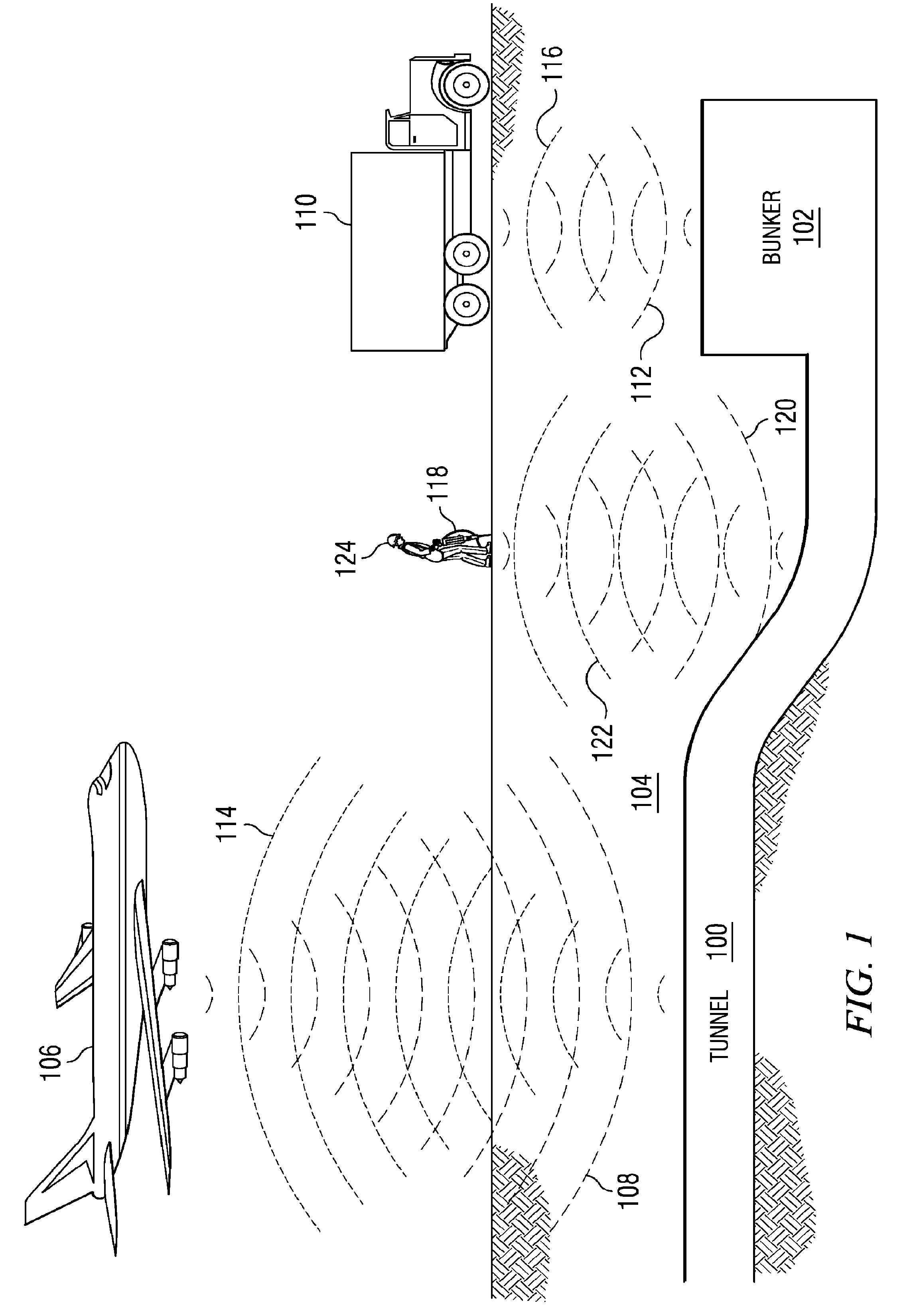
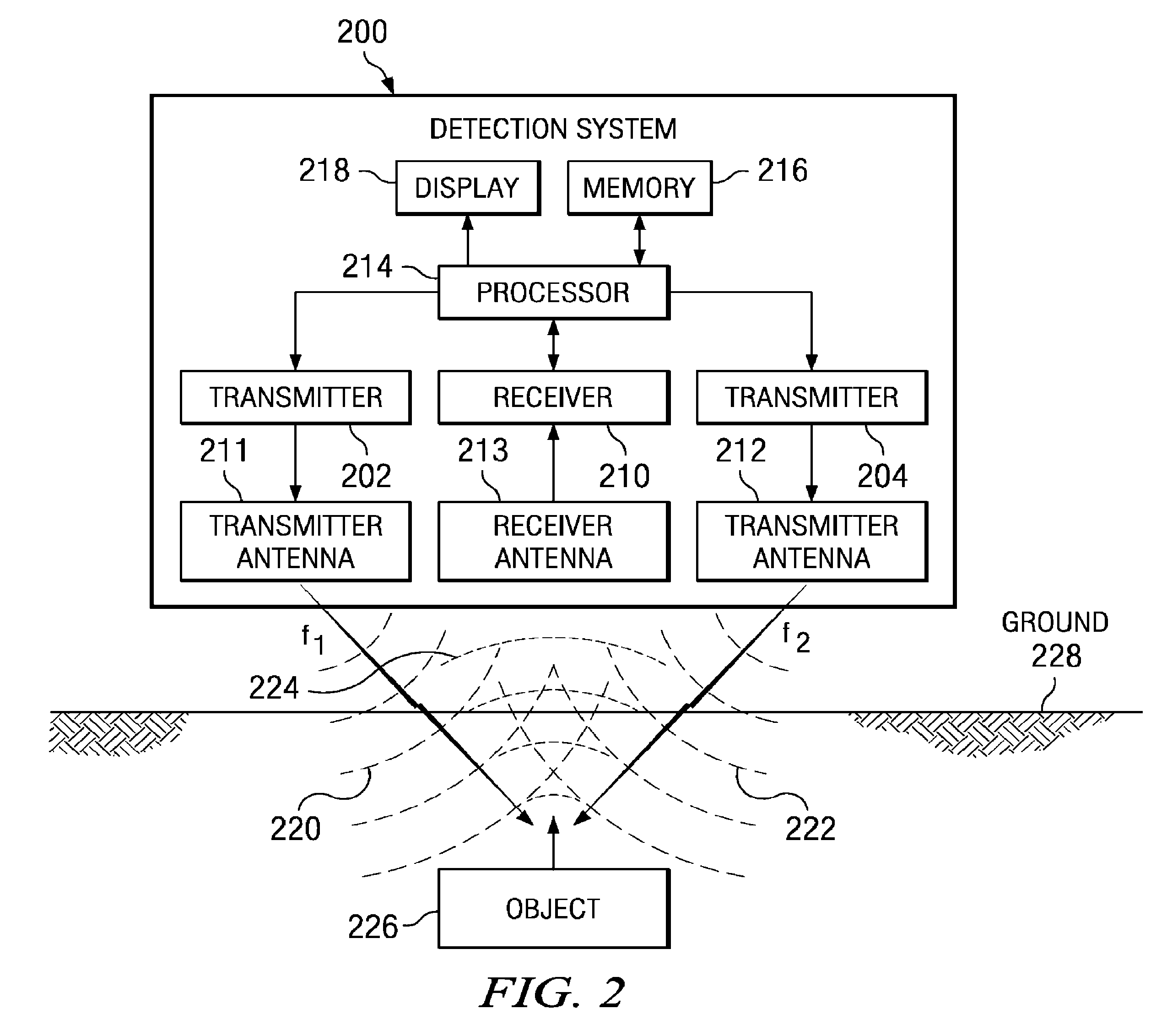
Method and apparatus for using collimated and linearly polarized millimeter wave beams at brewster's angle of incidence in ground penetrating radar to detect objects located in the ground
InactiveUS20090040093A1Defence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio frequency signalLight beam
A detection system comprises a transmitter unit, a receiver, and a processor. The transmitter unit is capable of transmitting a first collimated beam having a first frequency and a second collimated beam having a second frequency into a ground, wherein the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam overlap in the ground. The receiver is capable of monitoring for a response radio frequency signal having a frequency equal to a difference between the first frequency and the second frequency. The response radio frequency signal is generated by an object having non-linear conductive characteristics in response to receiving the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam. The processor is capable of controlling an operation of the transmitter unit and the receiver. The processor is connected to the transmitter unit and the receiver. The object is detected when the response radio frequency signal is detected by the receiver.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
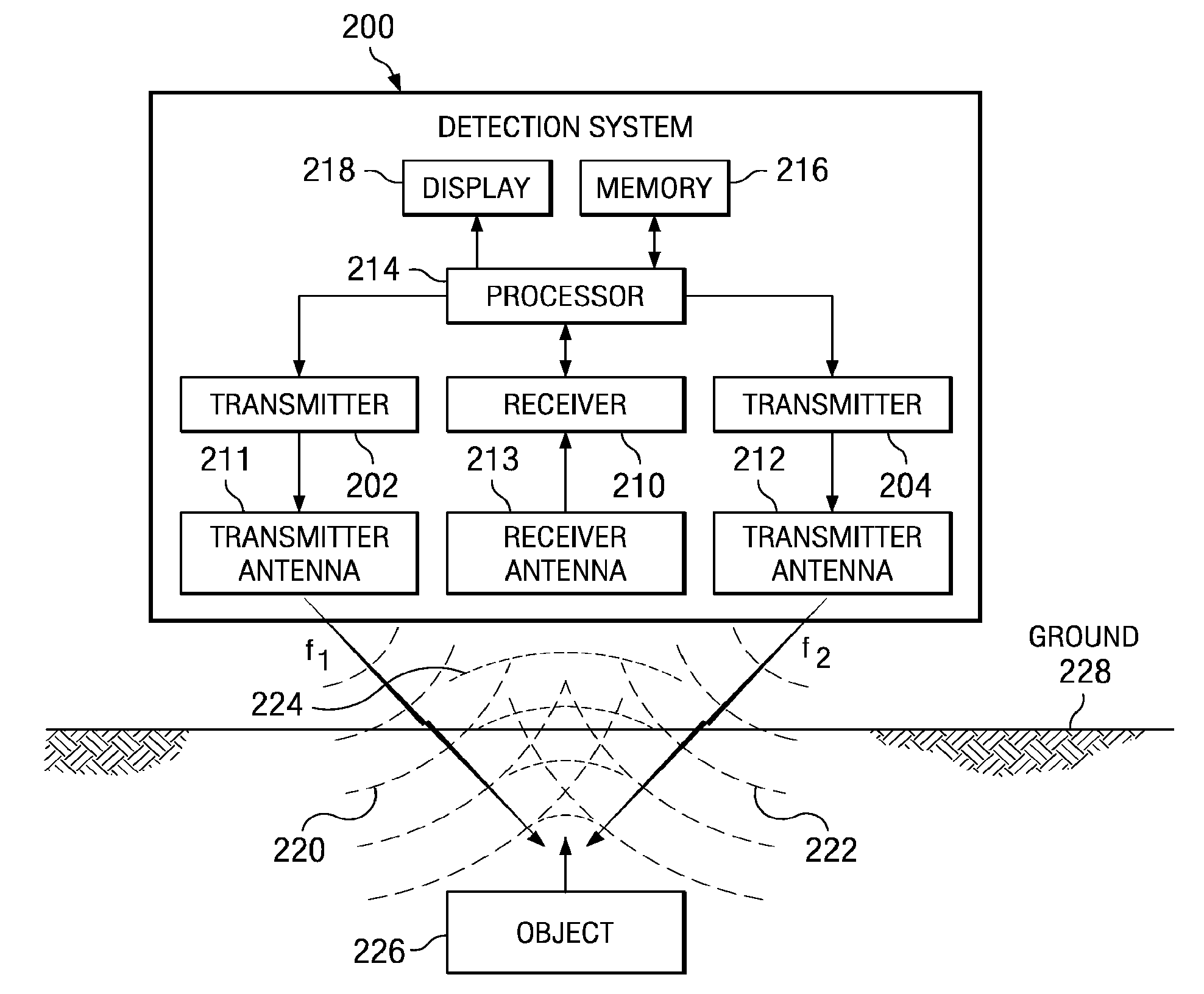
Method and apparatus for using collimated and linearly polarized millimeter wave beams at Brewster's angle of incidence in ground penetrating radar to detect objects located in the ground
InactiveUS7893862B2Defence devicesDetection using electromagnetic wavesRadio frequency signalGround-penetrating radar
A detection system comprises a transmitter unit, a receiver, and a processor. The transmitter unit is capable of transmitting a first collimated beam having a first frequency and a second collimated beam having a second frequency into a ground, wherein the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam overlap in the ground. The receiver is capable of monitoring for a response radio frequency signal having a frequency equal to a difference between the first frequency and the second frequency. The response radio frequency signal is generated by an object having non-linear conductive characteristics in response to receiving the first collimated beam and the second collimated beam. The processor is capable of controlling an operation of the transmitter unit and the receiver. The processor is connected to the transmitter unit and the receiver. The object is detected when the response radio frequency signal is detected by the receiver.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
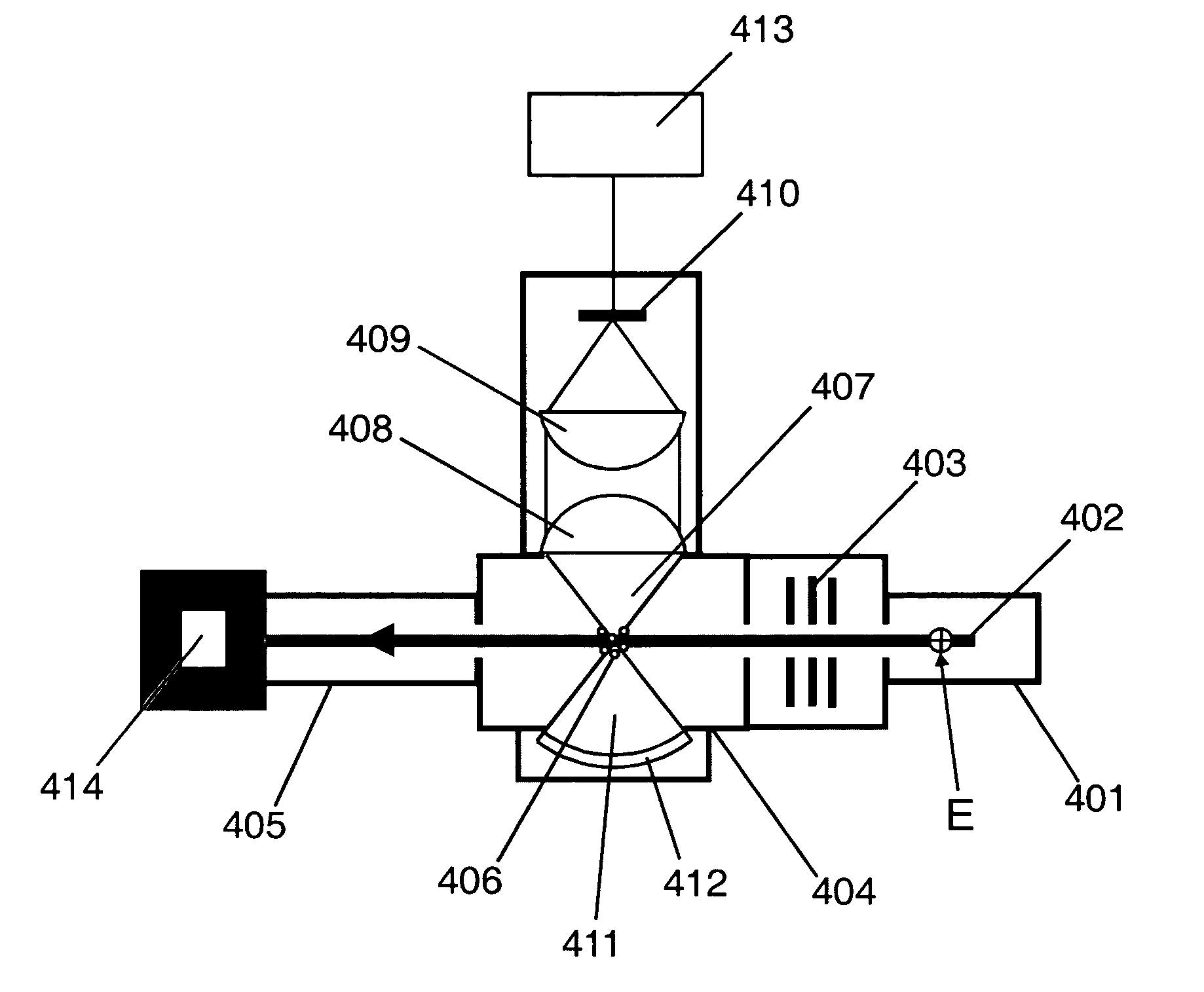
Laser for outputting radial polarized light beam
InactiveCN101552425AHigh beam qualityEasy to processOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical elementsDrift angleRefractive index
A laser for outputting radial polarized light beam comprises a pumping source, is characterized in: a pumping light shaping and coupling apparatus, a front cavity mirror, a laser medium, a Brewster shaft vertebra mirror and a rear cavity mirror are disposed successively along the direction of the pumping light from the pumping source; the centered wavelength of the pumping light from the pumping source is the same with the absorption wavelength of the laser medium; the pumping light passes through the pumping light shaping and coupling apparatus and is focused onto the laser medium; and the Brewster shaft vertebra mirror is made of high refractive index material, has a drift angle twice of the complementary angle of the Brewster angle. The invention achieves the advantages of simple structure, low cost, good quality of outputted radial polarized light beam.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
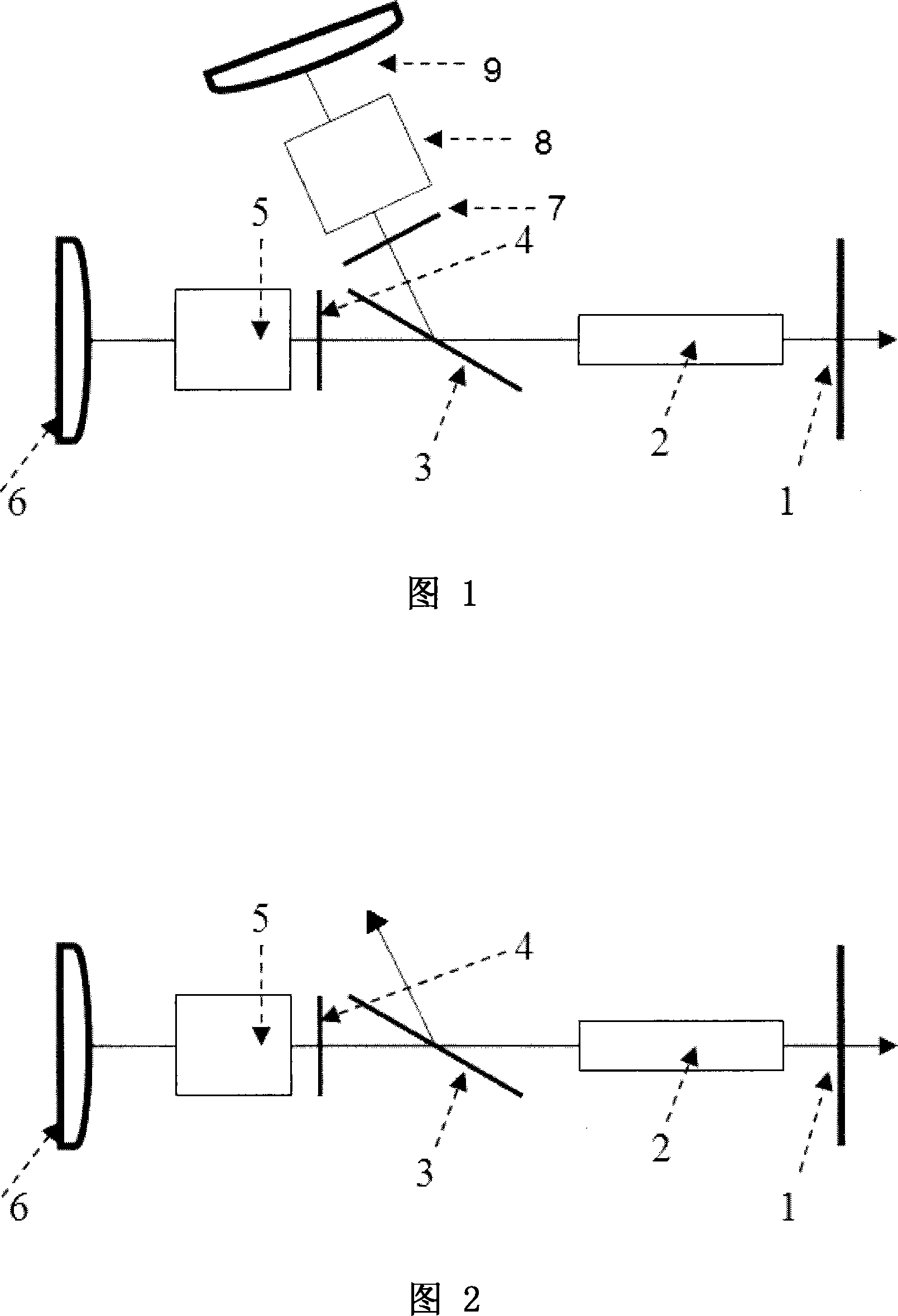
Free-space time-domain method for measuring thin film dielectric properties
InactiveUS6057928AImprove stabilityReduce frequencyPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsDielectricAngle of incidence
A non-contact method for determining the index of refraction or dielectric constant of a thin film on a substrate at a desired frequency in the GHz to THz range having a corresponding wavelength larger than the thickness of the thin film (which may be only a few microns). The method comprises impinging the desired-frequency beam in free space upon the thin film on the substrate and measuring the measured phase change and the measured field reflectance from the reflected beam for a plurality of incident angles over a range of angles that includes the Brewster's angle for the thin film. The index of refraction for the thin film is determined by applying Fresnel equations to iteratively calculate a calculated phase change and a calculated field reflectance at each of the plurality of incident angles, and selecting the index of refraction that provides the best mathematical curve fit with both the dataset of measured phase changes and the dataset of measured field reflectances for each incident angle. The dielectric constant for the thin film can be calculated as the index of refraction squared.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
A laser beam combining system and a laser beam combining method
InactiveCN102289078AStable jobMeets high laser power requirementsOptical elementsLight beamOptoelectronics
The present invention provides a laser beam combining system, comprising a first laser, a second laser, a reflecting mirror, and a beam combining mirror, wherein the beam combining mirror is a thin film polarizer, the beam combining mirror includes a first mirror surface and a second mirror surface, and the first laser outputs A reflector is arranged on the center line of the optical path. After being reflected by the reflector, the laser beam output by the first laser is incident on the first mirror surface of the beam combiner and reflected by the mirror surface. The laser beam emitted by the second laser is at the Brewster angle. Incident to the beam combiner, after the laser beam emitted by the second laser is transmitted through the beam combiner, it overlaps with the laser beam reflected by the first mirror surface of the beam combiner to form a beam. The invention also discloses a laser beam combining method. The laser beam combining system of the present invention can combine laser beams emitted by lasers of the same type. The power of the combined output laser beam is twice that of the single beam laser power, which can meet the requirements of high laser power for processing and use under the premise of ensuring the stable operation of the laser.
Owner:HANS LASER TECH IND GRP CO LTD
Double-electro-optic modulation QNdi:YAG laser
InactiveCN101022203ACompensation for thermal depolarization lossesEfficient outputOptical resonator shape and constructionCouplingPolarizer
A dual-photoelectric Q-switched Nd:YAG laser includes a main optical path on a main oscillation axes composed of an output coupling mirror, a Nd:YAG bar, a polariser, a first 1 / 4 wave plate, a first Q-switched crystal and a first back control mirror arranged orderly, in which, said polarizer is in Brewster angle with the opposite direction of emitted laser, which is charactered that a Q-switched branch is along the direction of depolarization lost of the polarizer and is composed of a second 1 / 4 wave plate, a second Q-switched crystal and a second back cavity mirror. This invention adds a Q-switched branch along the depolarization lost output optical path on the basis of the traditional Q-switched polarization cavity, so that, lost component is fed back to the cavity along the original path via the Q-switched switch to form effective laser output.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
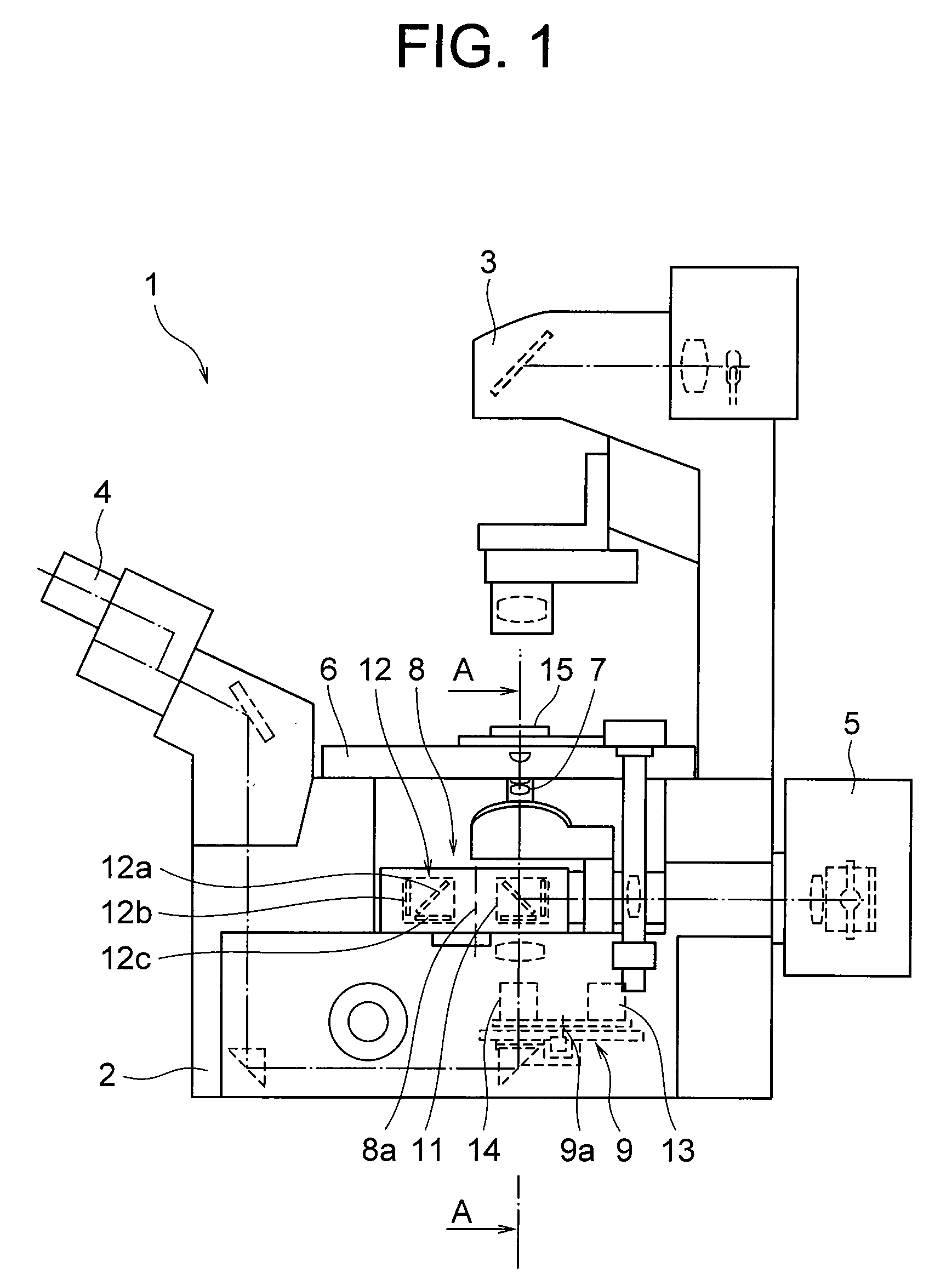
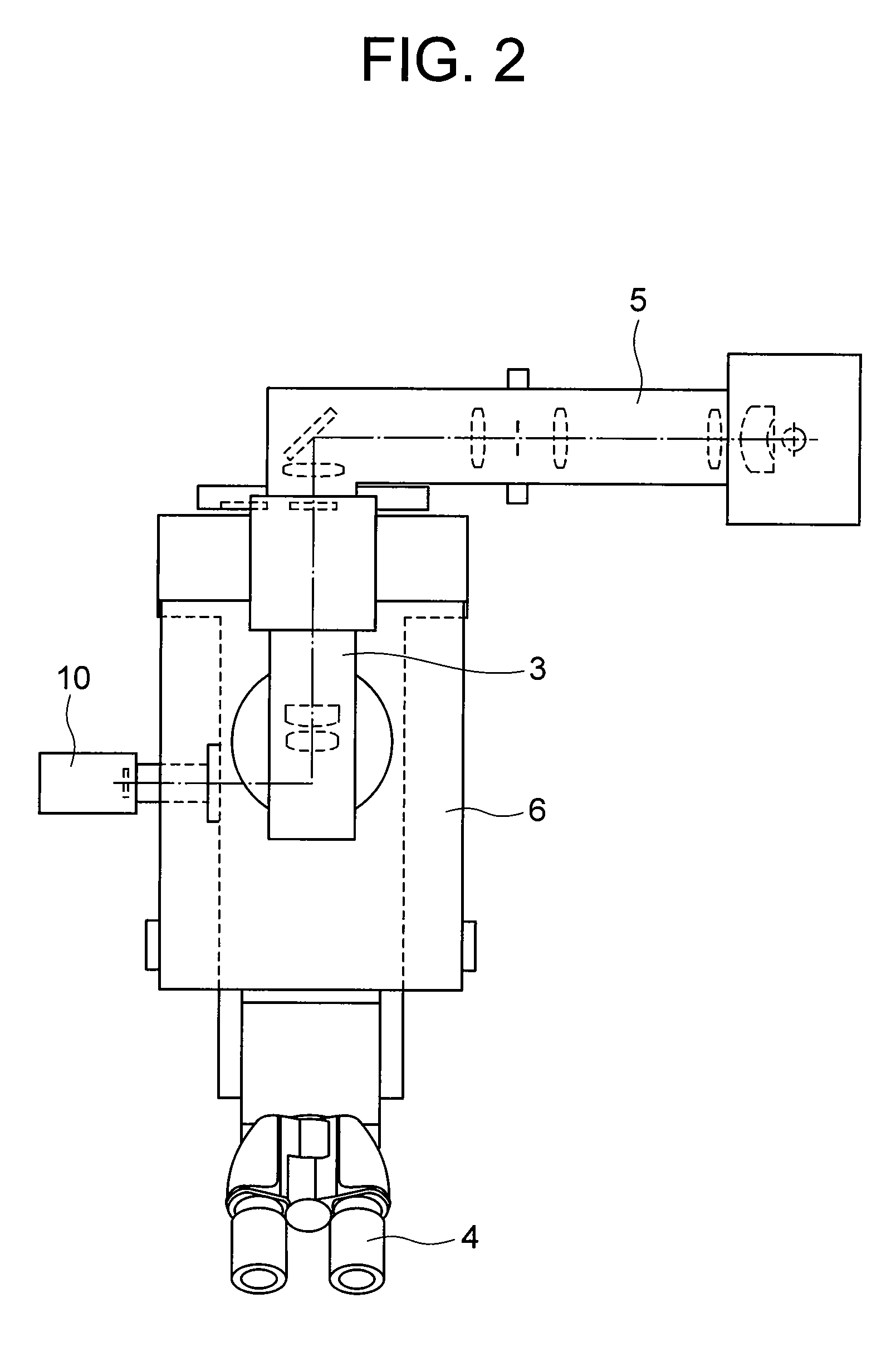
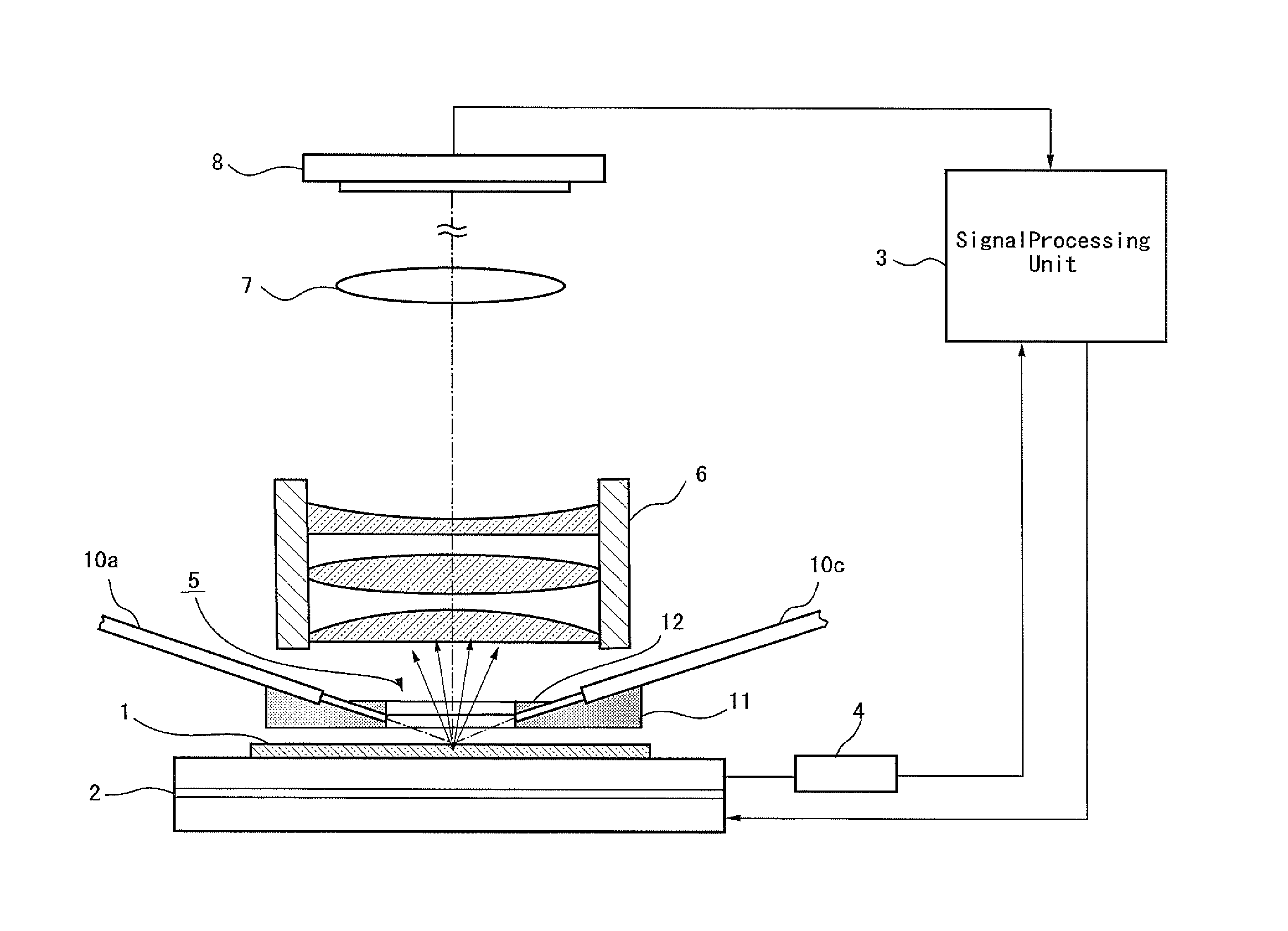
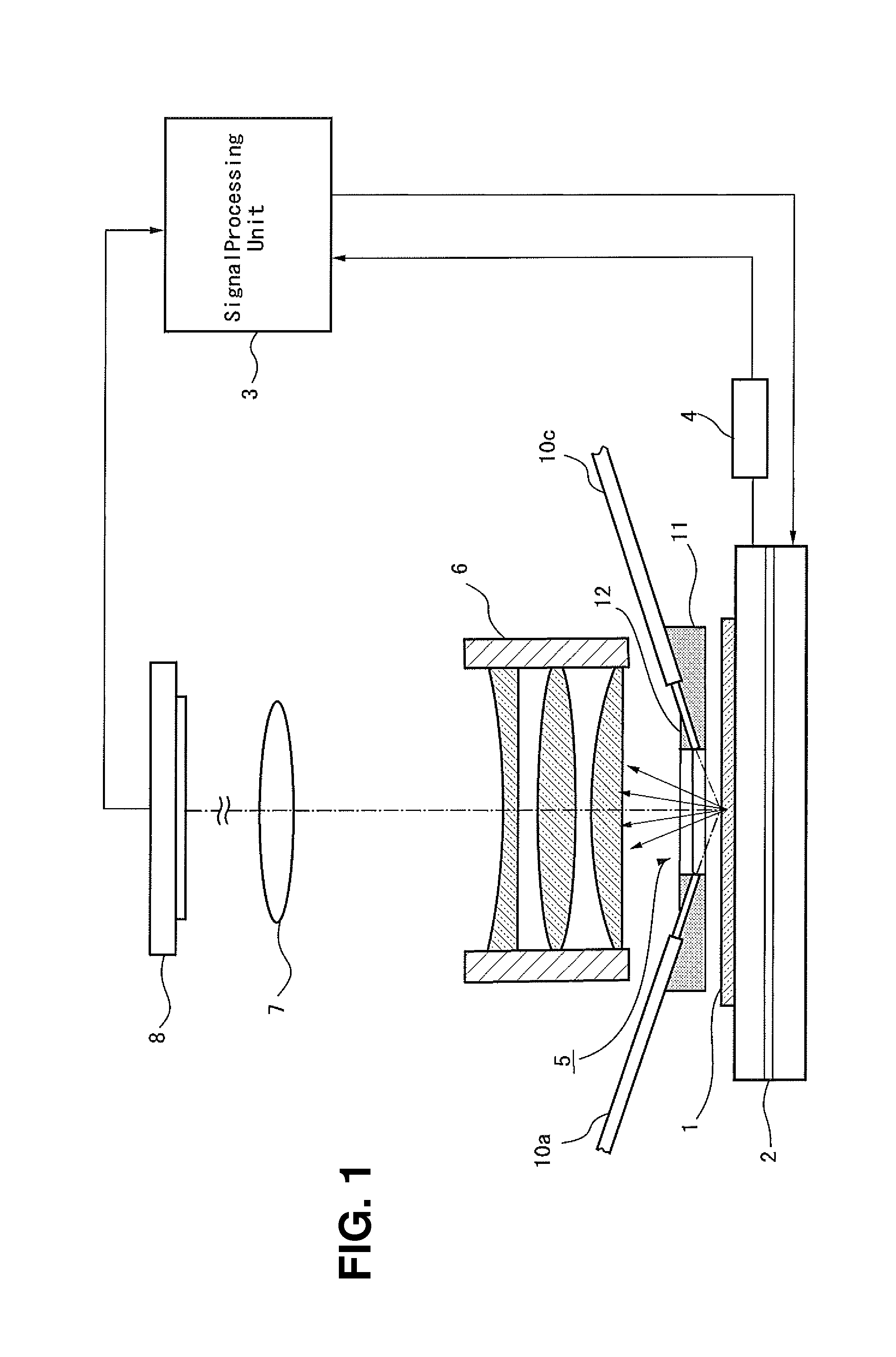
Microscope
A microscope for introducing light from a light source via an objective lens to a sample so that a user observes the sample via the objective lens includes: a minute opening arranged in an optical path between the light source and the objective lens and on a focal plane of the image side of the objective lens or at a position conjugate with its conjugate plane; position adjusting means for adjusting the position of the minute opening so that the light from the light source via the minute opening is incident to the sample at the Brewster's angle; an polarizing element arranged in the optical path between the light source and the objective lens for extracting rectilinear polarized light from the light from the light source and applying the rectilinear polarized light to the sample.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS7268881B2High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
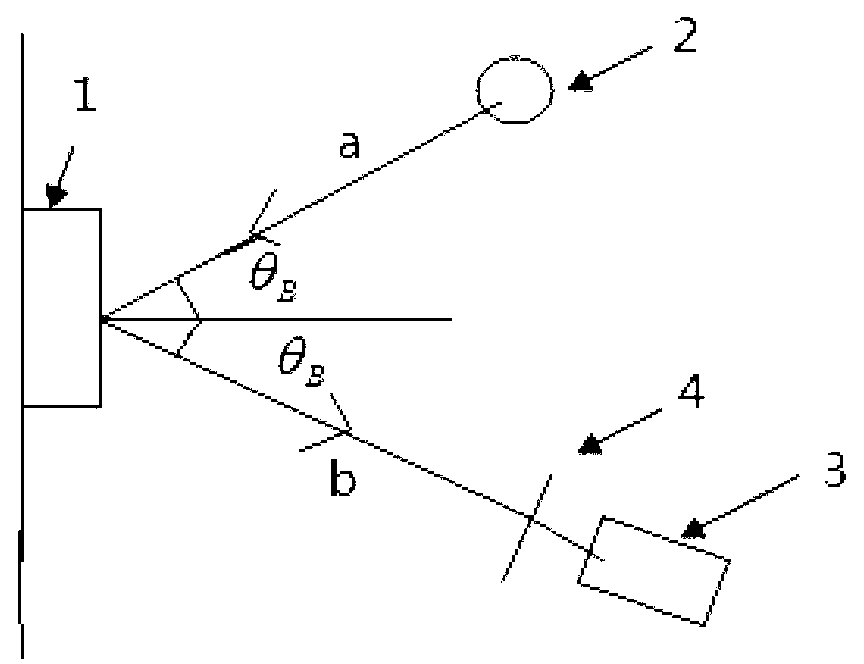
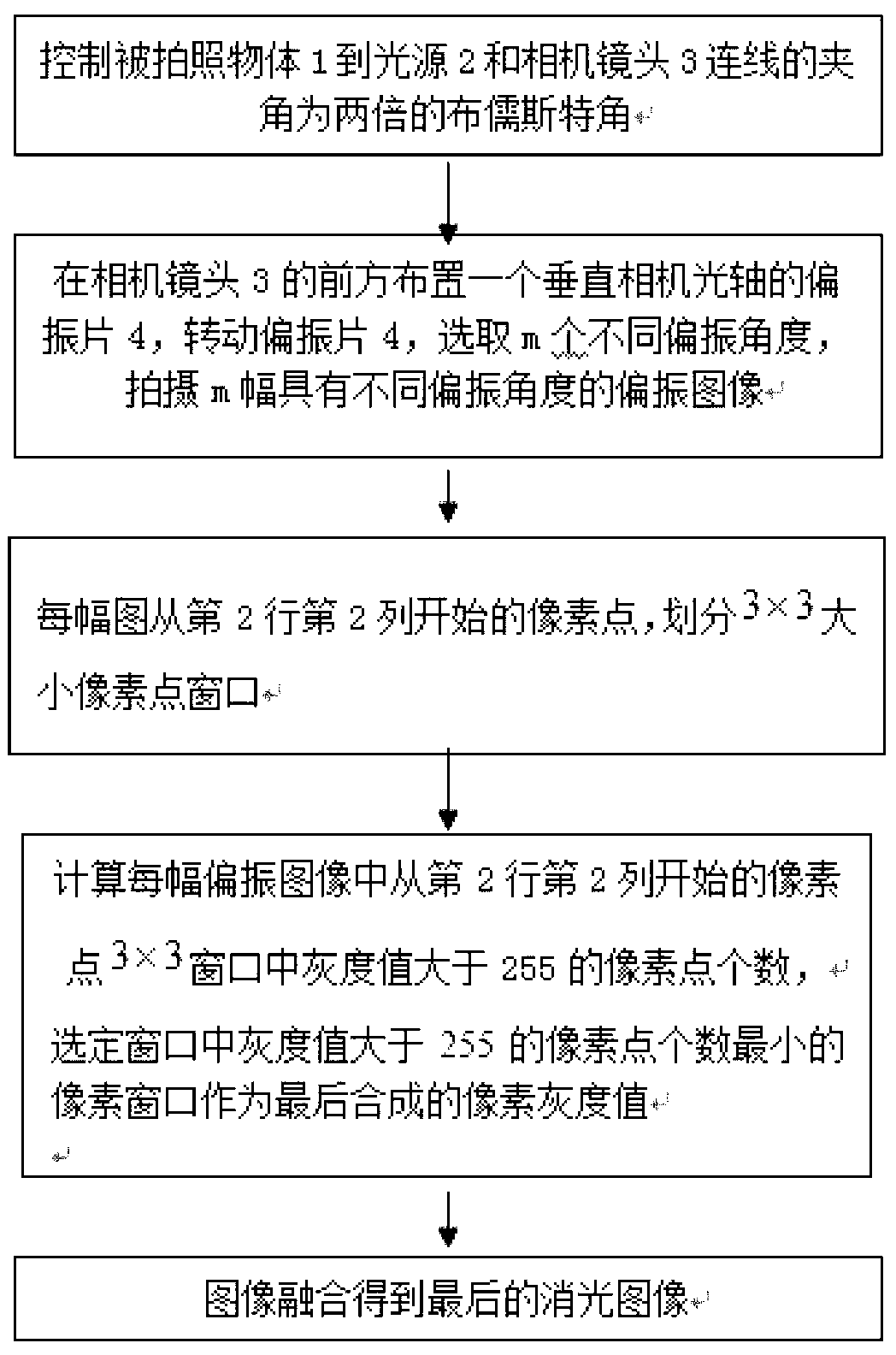
Imaging method based on polarized light extinction
The invention discloses an imaging method based on polarized light extinction to solve the problems of low imaging definition and lacking of instantaneity when a target object is photographed under saturated light in the prior art. The method includes the steps of controlling an included angle between the connecting line from the object to the paragraphed to a light source and the connecting line from the object to be paragraphed to a camera to be twice as large as the Brewster angle, arranging a polarizing film perpendicular to an optical axis of the camera in front of a lens of the camera, paragraphing a plurality of polarization images with different polarization angles through the rotation of the polarizing film, designating a pixel point window for each polarization image, comparing a grey value of each pixel point in each pixel point window with a threshold value, and selecting pixel points in the pixel point window with the minimum number of pixel points of which the grey values are larger than the threshold value to conduct fusion imaging.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
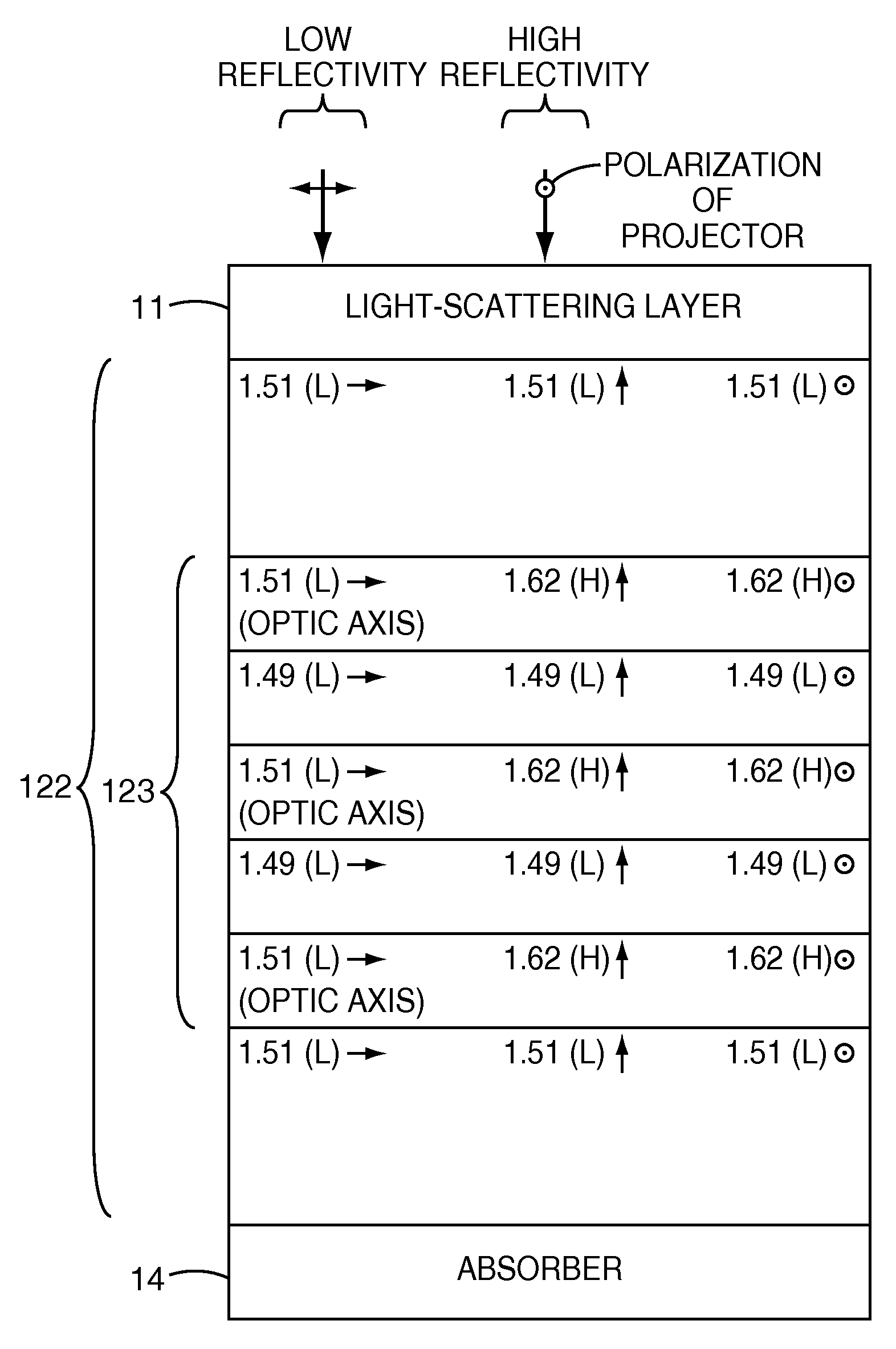
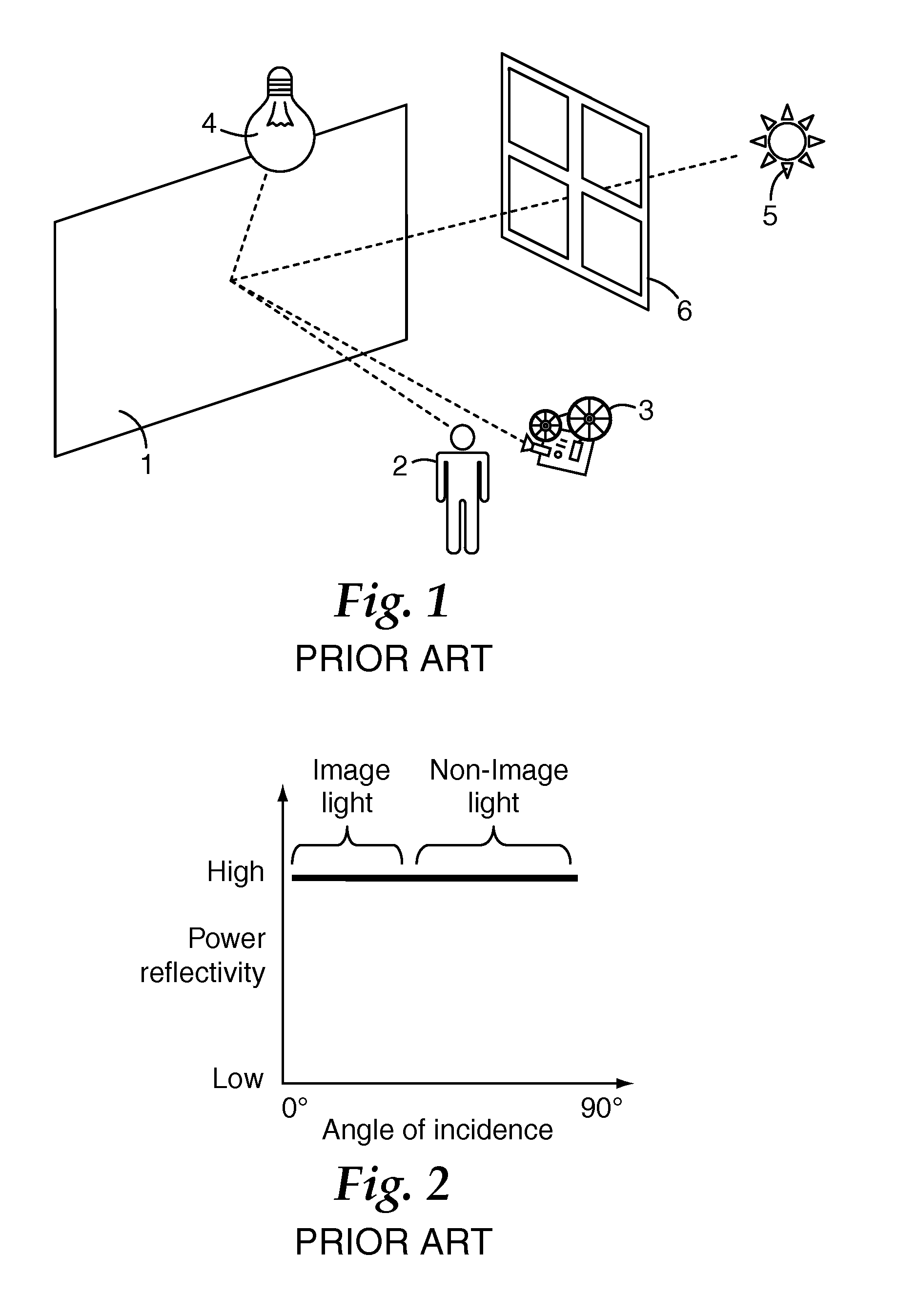
Polarization sensitive front projection screen
A projection system is disclosed, in which a screen may have improved rejection of ambient light by having a high reflectivity at low angles of incidence for a polarization parallel to that of the projector, a low reflectivity at high angles of incidence for a polarization parallel to that of the projector, and a low reflectivity at both low and high angles of incidence for a polarization perpendicular to that of the projector. In some embodiments, for p-polarized light polarized parallel to the projector, the power reflectivity is high at low angles of incidence and decreases to a low value at high angles of incidence. In some embodiments, for p-polarized light polarized perpendicular to the projector, the power reflectivity is low at low angles of incidence. In some embodiments, for s-polarized light polarized perpendicular to the projector, the power reflectivity remains low at all angles of incidence. In some embodiments, the screen includes a thin film structure that has alternating quarter-wave layers of isotropic and birefringent materials, which are refractive-index-matched for light polarized perpendicular to the projector, which form a high reflector at normal incidence for light polarized parallel to the projector, and which exhibit Brewster's angle effects for p-polarized light polarized parallel to the projector at high angles of incidence. The Brewster's angle effect may be reached by use of a light-scattering layer that increases the effective incident refractive index.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
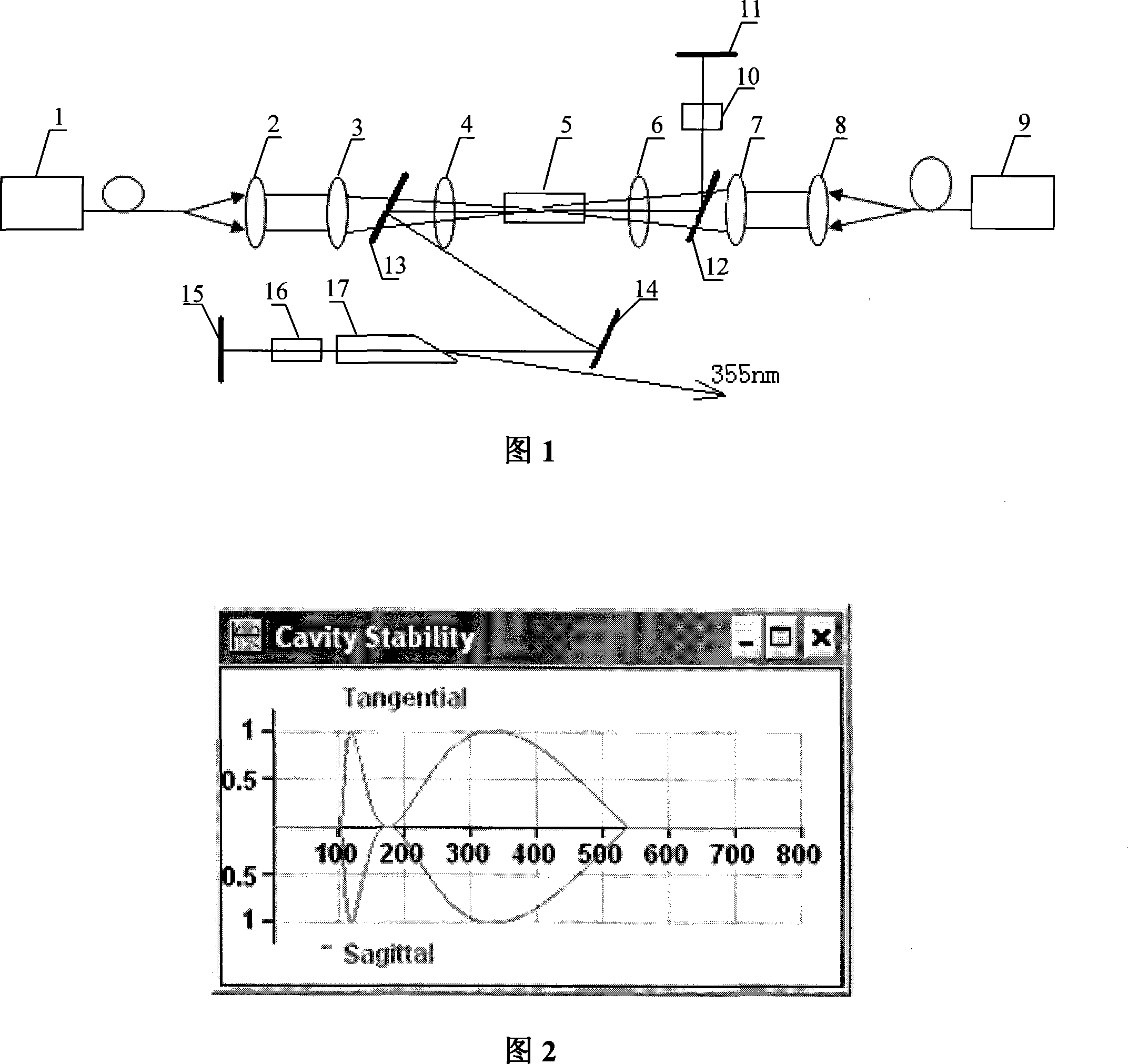
Design method of semiconductor diode both-end pumping high power UV laser
InactiveCN101232148AReduce coupling lossExtend working lifeActive medium materialHigh power lasersPlane mirror
The invention provides a design method of a semiconductor diode double-end-pumped high-power UV laser, which comprises following steps: constituting a double-end-pumped laser crystal by using two semiconductor diodes; outputting a pumped beam with 808 nm; coupling the pumped beam by an aspherical optical coupling system and a lens to a laser crystal to generate a laser beam with 1064 nm; oscillating the laser beam in a resonant cavity consisting of five planar mirrors; modulating with Q switch; converting the modulated fundamental frequency light with 1,064 nm into a frequency-doubled light with 532 nm by a frequency-doubling crystal; mixing the unconverted fundament frequency light with 1,064 nm with the frequency-doubled light with 532 nm by a frequency-tripling crystal to obtain a UV laser with 355 nm; and outputting the UV laser from a surface of the frequency-tripling crystal cut by Brewster angle. According to the scheme, the laser cavity has the advantages of large mode volume, smaller laser spot at the frequency-doubling crystal, greatly reducing intracavity loss by cutting the frequency-tripling crystal with Brewster angle and high power laser output.
Owner:SUZHOU DELPHI LASER
Droplet target control system guided by laser beam
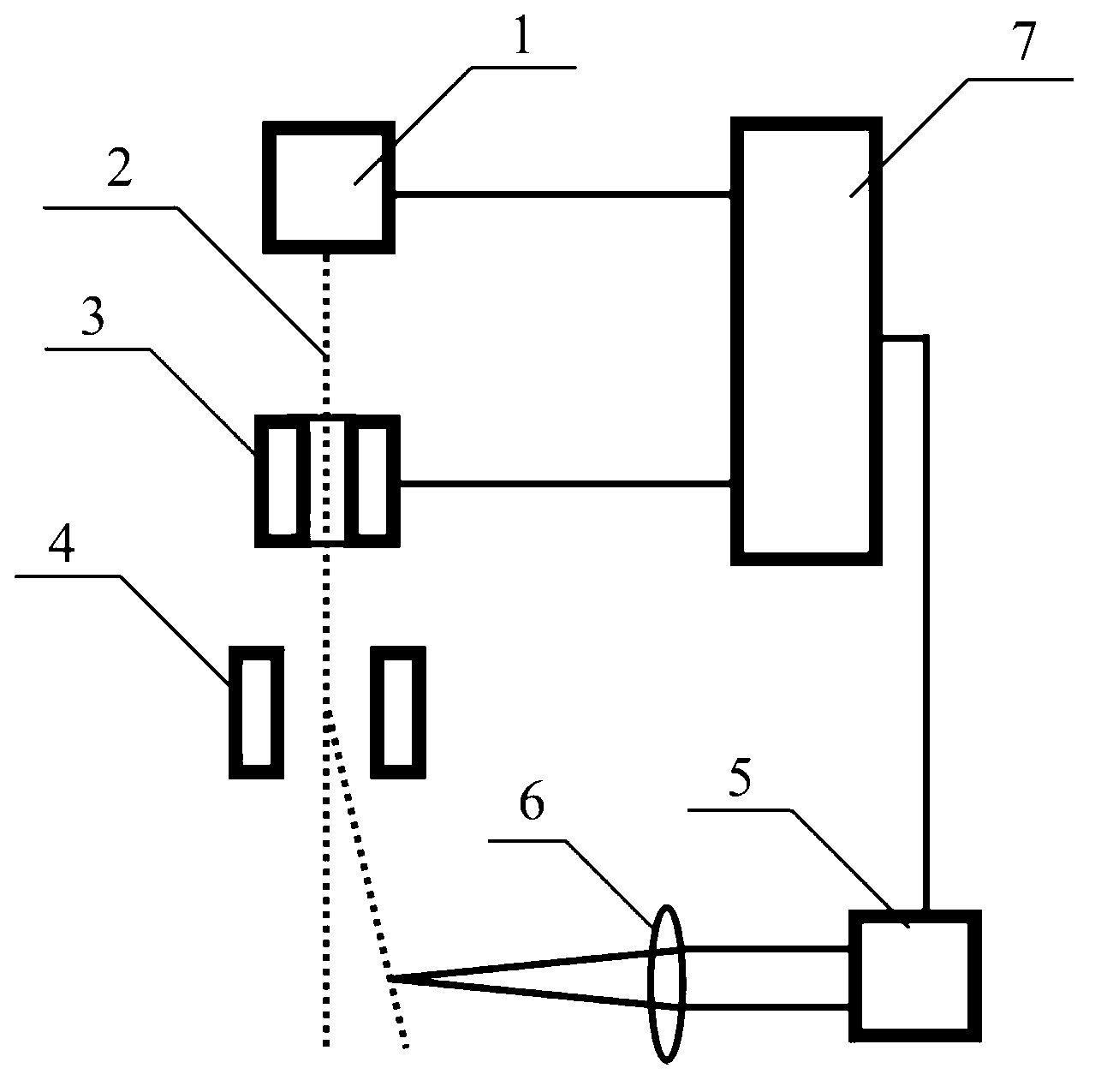
ActiveCN103217870AStrong tractionNo electrification requirementPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusTime delaysMetal droplets
The invention discloses a droplet target control system guided by a laser beam. The droplet target control system comprises a droplet nozzle, a high-power pump laser, a third focusing lens and a time delay pulse generator, and further comprises a laser source, a first reflector, a half valve plate, a Brewster angle polarizing film, a quarter wave plate, a second reflector, a first focusing lens, a vacuum tube, a second focusing lens, an annular plane reflector and an annular focusing lens. A dropping track of metal droplets in 20 micron dimension can be precisely controlled by the droplet target control system, and the dropping speed of the droplets can be regulated. The system is capable of stably working for a long time, the time synchronization and the space coincidence of the droplets and the high-power pump laser are guaranteed.
Owner:上海中科神光光电产业有限公司
Micro-miniature NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) gyroscope with application of oblique-incidence detection light path
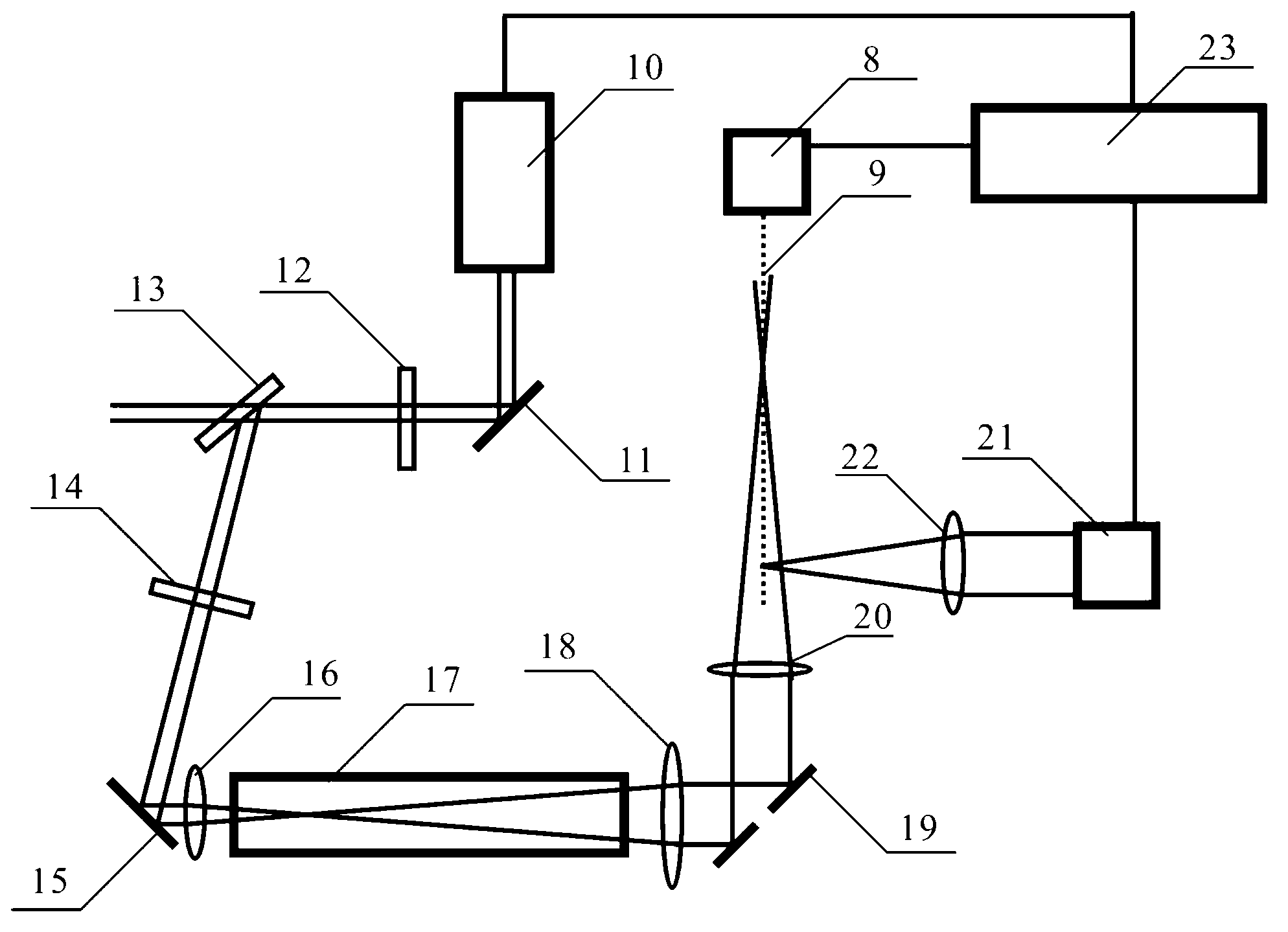
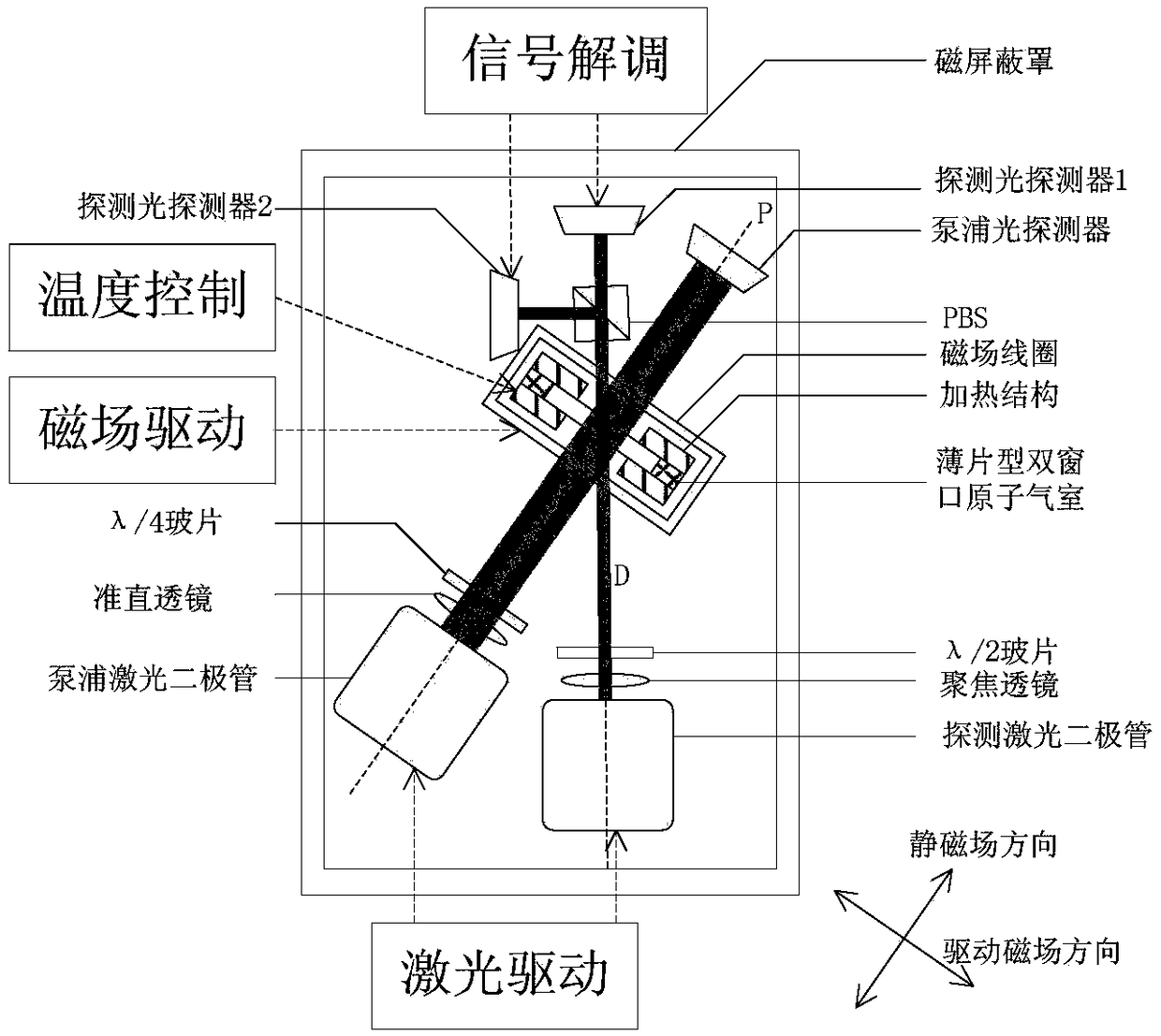
The invention provides a micro-miniature NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) gyroscope with application of an oblique-incidence detection light path. The micro-miniature NMR gyroscope comprises a dual-window atomic gas chamber prepared with an MEMS (micro-electromechanical system) technology, a heating structure for heating the atomic gas chamber, a magnetic field coil, a detection light path assembly, a pumping light path assembly, a photoelectric detection assembly, a signal demodulation module, a temperature control module, a magnetic field drive module and a laser drive module. According to the NMR gyroscope, the thin-sheet dual-window atomic gas chamber prepared with the MEMS bonding technology is adopted, the pumping light path and the detection light path adopt a circularly polarized light vertical window pumping mode and a linearly polarized light oblique-incidence detection mode respectively, the light path structure of the gyroscope is simplified, the overall size of the gyroscope is reduced, and meanwhile, by means of Brewster angle incidence adopted by linearly polarized detection light, high transmittance and high linear polarization degree of the detection light can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
Conductively cooled high-repetition single frequency Nd: YAG Laser
ActiveCN102208742AReduce thermal effectsIncrease powerActive medium shape and constructionHigh energyLine width
A conductively cooled high-repetition single frequency Nd: YAG Laser is disclosed. An improved resonance detection method is used to obtain an injection-seeded single frequency pulse laser. A laser resonator is a u-shaped cavity, which uses two high peak power LD to pump a laser crystal from ends. High-precision TEC is used to control the temperature of the laser crystal. With changes of applied voltage on piezoelectric ceramics, seed lights reflected twice from a Brewster angle polarizing sheet interfere with each other. Interference signals received by photodiodes are processed by a sequential control system and when there is a maximum value, Q-witch is opened by the sequential control system. And then a close-to-diffraction-limited single-rate pulse laser is output. According to changes of light extraction time, system can give a negative feedback so that a cavity length can be maintained stably. The invention possesses a high-repetition frequency, high energy, conduction cooling, narrow linewidth, high frequency stability, and a compact structure and can work stably.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Surface shape measuring apparatus, exposure apparatus, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS20090219499A1Accurate measurementSolving precise measurementsInterferometersPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoelectric conversionWide band
A surface shape measuring apparatus includes an illumination system and a light receiving system. The illumination system splits wide-band light from a light source into measurement light and reference light, illuminates the measurement light to obliquely enter a surface of the film, and illuminates the reference light to obliquely enter a reference mirror. The light receiving system combines the measurement light reflected by the surface of the film and the reference light reflected by the reference mirror with each other and introduces the combined light to a photoelectric conversion element. An incident angle of the measurement light upon the surface of the film and an incident angle of the reference light upon the reference mirror are each larger than the Brewster's angle. S-polarized light and p-polarized light included in the measurement light entering a surface of the substrate have equal intensity on the photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:CANON KK
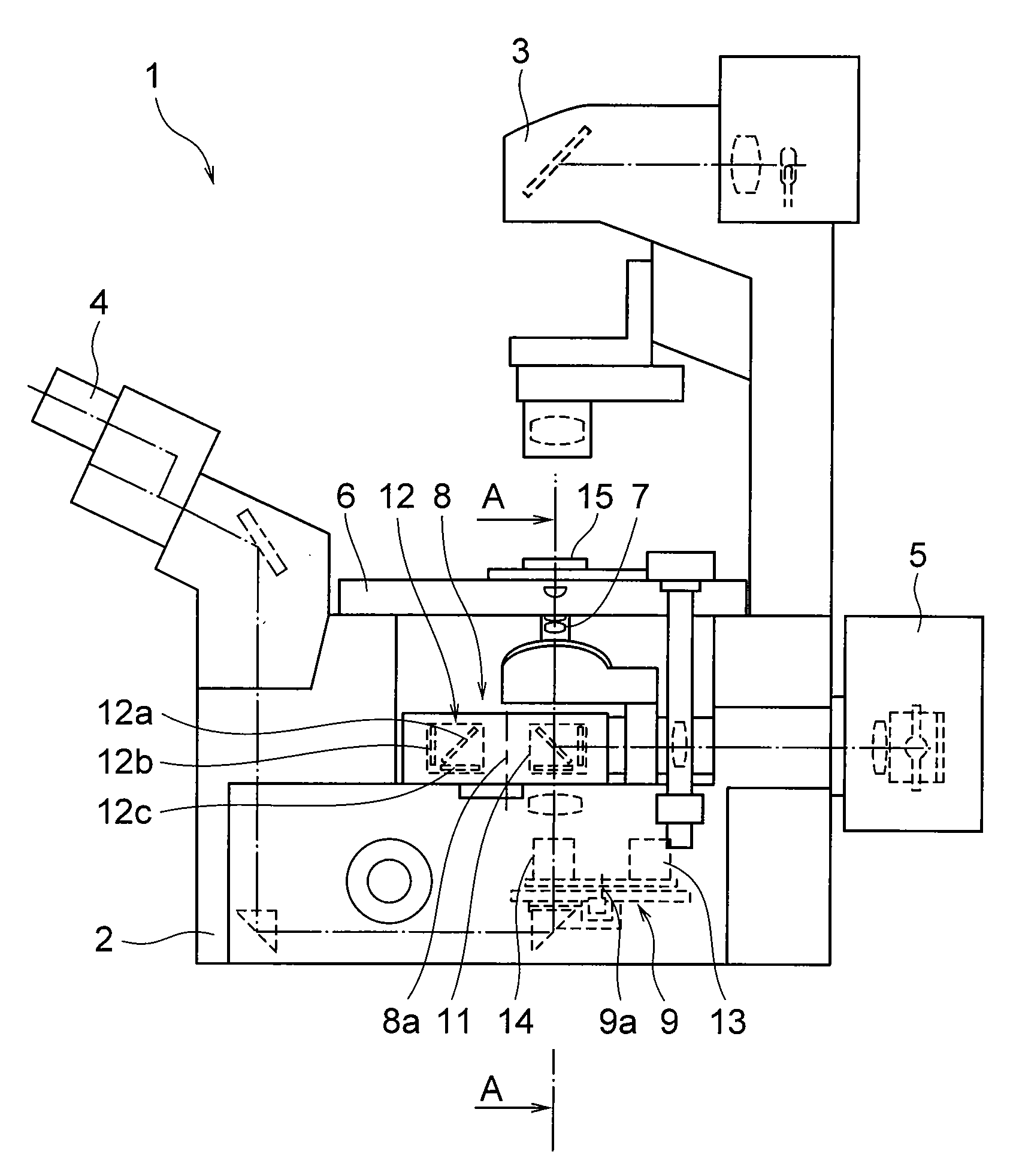
Microscope and inspection apparatus
InactiveUS20130188251A1Accurate detectionUniform brightness distributionMaterial analysis by optical meansFibre light guidesOptical axisLight beam
A system including a microscope and an inspection apparatus in which an objective lens having a large numerical aperture is used for detecting a defect existing inside a sample. A light source apparatus produces linearly polarized light. The polarization maintaining fibers optically coupled to the light source apparatus project the linearly polarized light onto the sample surface as an illumination beam of P-polarized light at an incidence angle substantially equal to the Brewster's angle of the sample. The scattered light generated by the defect existing in the sample is emitted from the sample and is collected by the objective lens whose optical axis is perpendicular to the sample surface. Since the illumination beam of P-polarized light is projected at the incidence angle equal to the Brewster's angle of the sample, no surface reflection occurs and it is possible to use the objective lens having a large numerical aperture.
Owner:LASERTEC CORP
Optical method for detecting discerptible medium skin layer and deep layer information
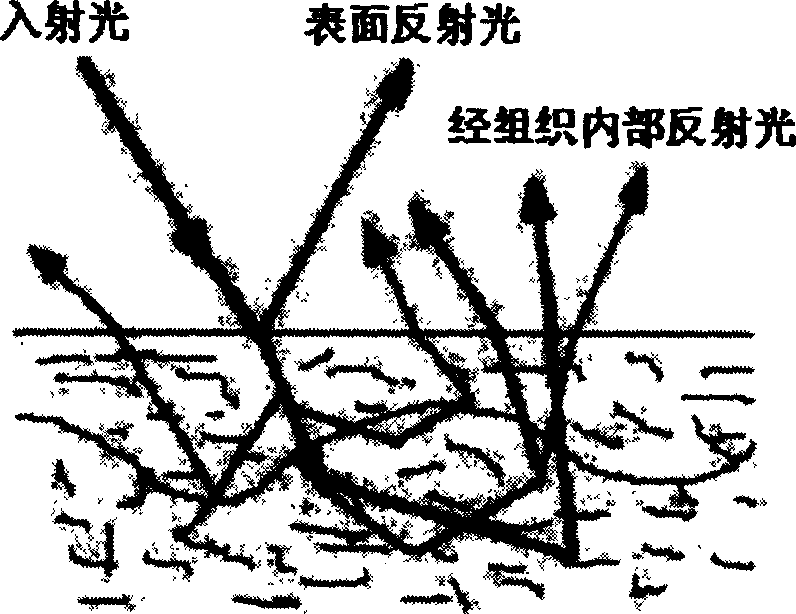
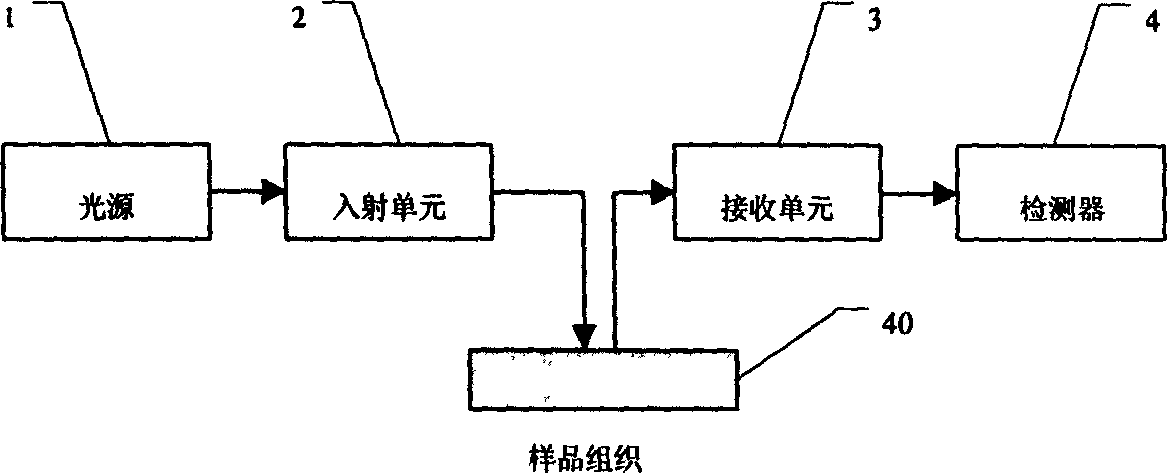
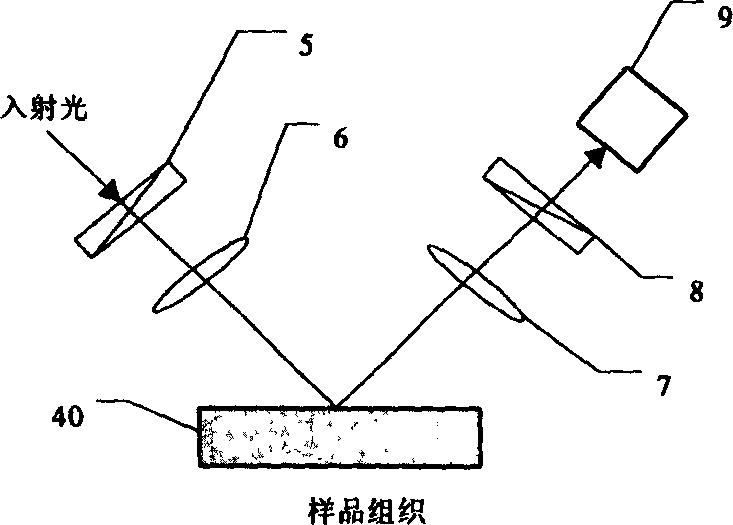
InactiveCN1485605ADiagnostics using lightPolarisation-affecting propertiesTest sampleComputational physics
An optical detecting method of the disintegrating dielectric superficial coat and deep layer information, wherein the illuminating source irradiates on the tested sample structure through an incidence unit, which is then processed by the receiving unit and detected by the detector, the instrumentation system is used for accomplishing the separation of the dielectric skin layer and the deep layer information, and the optical gauge head and the test sample structure are non-contacting.
Owner:TIANJIN SUNRISE TECH DEV
Refractive index measuring instrument for transparent material with Brewster angle
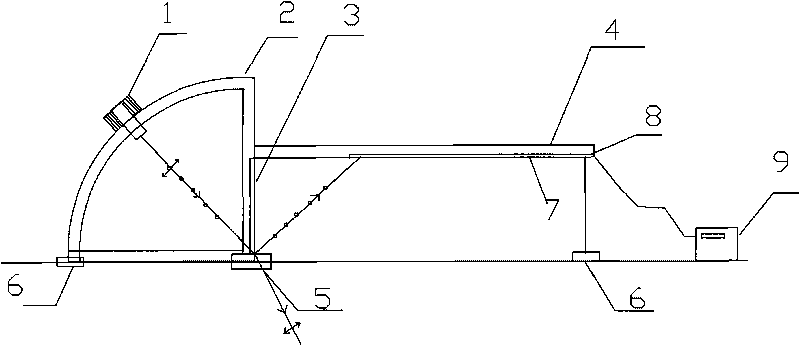
InactiveCN101706426AEasy to confirmSimplified Refractive Index Detection MethodPhase-affecting property measurementsLaser transmitterMeasuring instrument
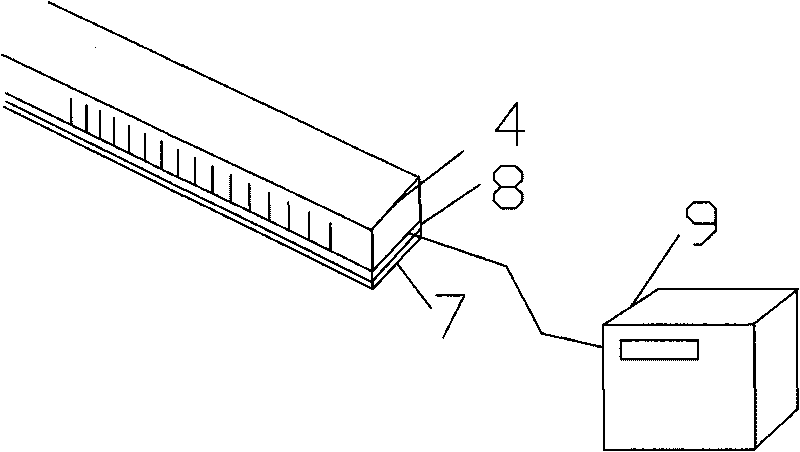
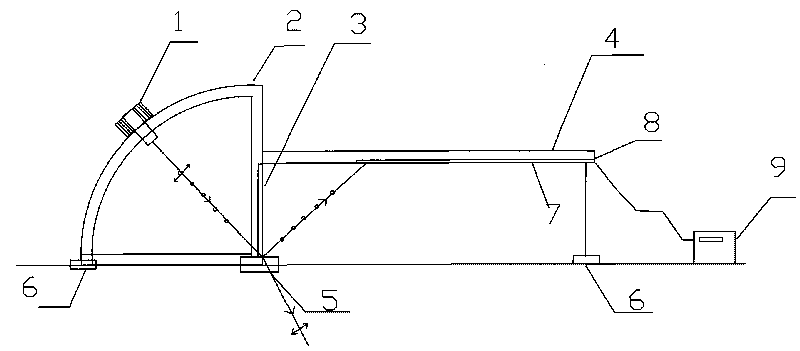
The invention discloses a refractive index measuring instrument for transparent material with the Brewster angle, comprising an upright post and a one-fourth circular arc guide rail taking the upright post as the radius. The guide rail is provided with a laser emitter which can slide along the circular arc direction of the guide rail and is opposite to the direction of the center of a circle of the circular arc guide rail, and an objective table is arranged at the center position of the circle of the circular arc guide rail; the upright post is vertically provided with a scale beam below which a polarization film strip is arranged, and a photoelectric sensor is arranged between the polarization film strip and the scale beam and connected with a digital display indicator. The method simplifies a traditional complex refractive index detecting method, can conveniently and simply confirm the components of the transparent material, can accurately measure the refractive index when the three-dimensional surface of the transparent material is not regular without polishing the surface, and can measure the refractive index only by finding a small reflecting surface on a measured object without damaging original ore.
Owner:GD SOLAR +2
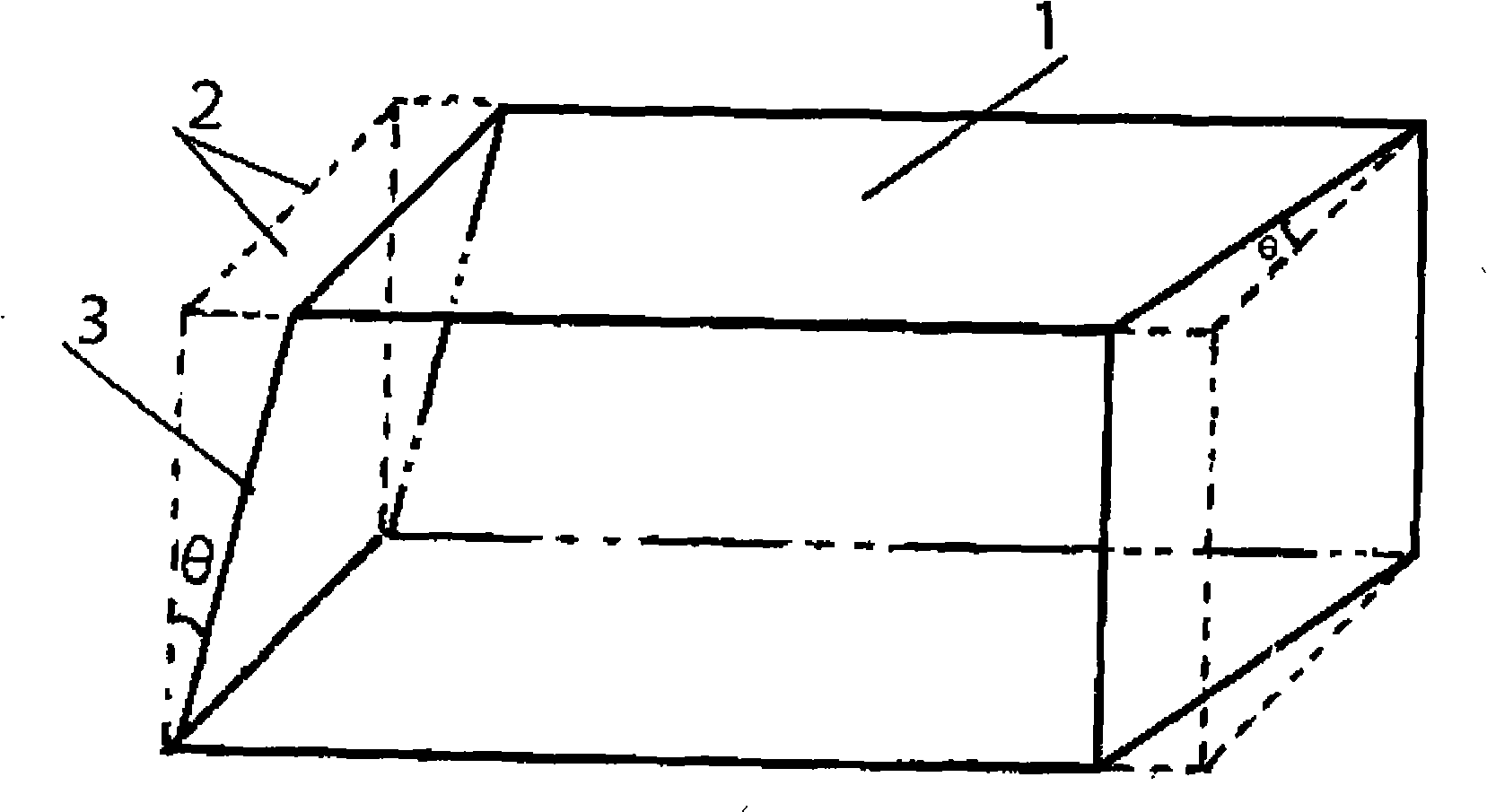
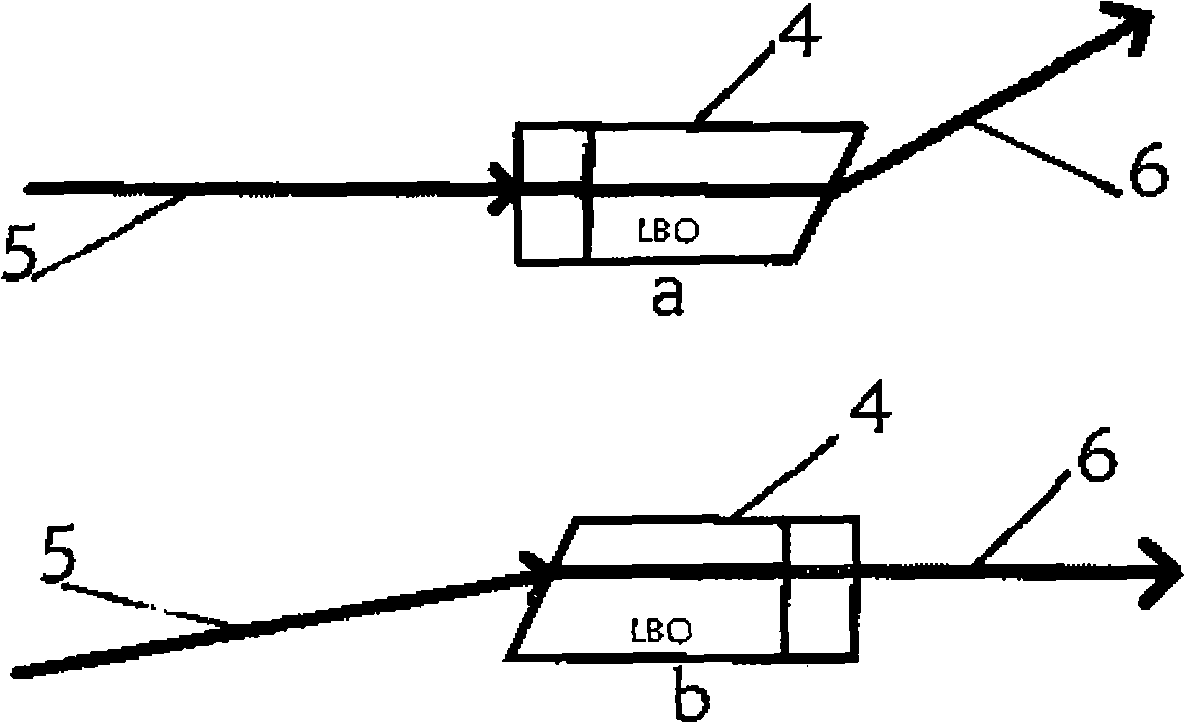
Double Brewster's angle nonlinear optical crystal and cutting method thereof
InactiveCN101276126AAvoid platingAvoid surface damageNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalLaser technology
The present invention provides a dual-brewster angle nonlinear optical crystal belonging to laser technical field, and its cutting method. The dual-brewster angle nonlinear optical crystal includes an aperture entrance plane, an aperture exiting plane; the aperture entrance plane and the aperture exiting plane aim at the design of the emitting light to be transformed and the emergent light obtained by the non-linear optical transform respectively, the aperture entrance plane and the aperture existing plane process cut to the non-linear optical crystal according to the brewster angle, so as to meet incident angle as a brewster angle when the input light to be transformed emits on the light entrance plane and the exiting light produced by the non-linear transformation outputs by the light exiting plane, the aperture entrance plane and the aperture exiting plane without plating antireflection coatings ensure the incident light to be transformed pass through the entrance plane without loss, the emitting light obtained by transformation passes through the exiting end without loss, the antireflection effect of the emitting light by the exiting plane enhances anti-damaging ability of the nonlinear crystal, avoiding the loss of the nonlinear crystal.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
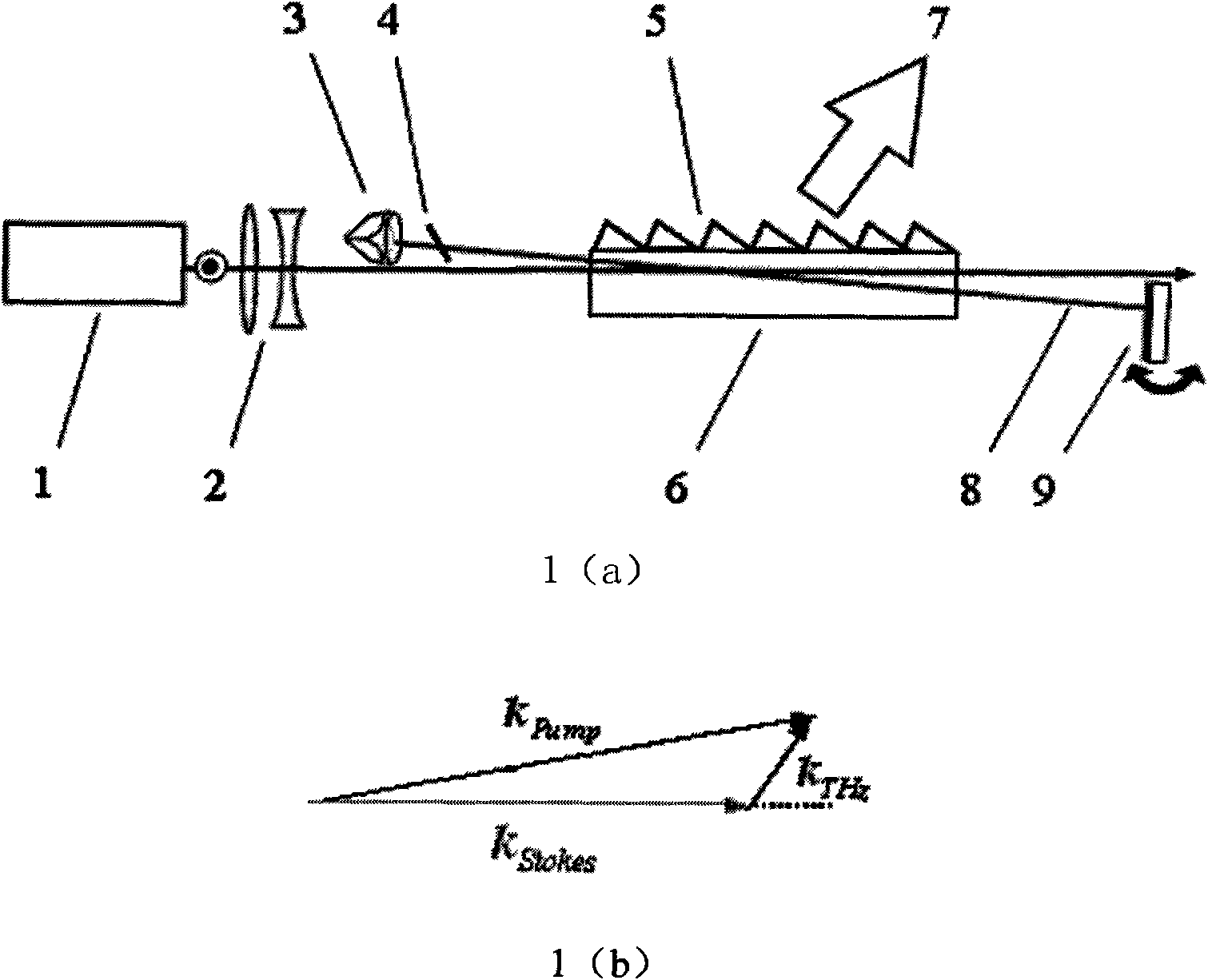
Terahertz-wave parametric oscillator based on corner-cube prism resonant cavity
InactiveCN101609243ATuning method is simpleQuick and easy way to tuneNon-linear opticsPrismMedical diagnosis
The invention provides a terahertz-wave parametric oscillator based on a cube-corner prism resonant cavity, which is characterized in that the resonant cavity is formed by a right-angle trihedral cube-corner prism and an output mirror; the right-angle trihedral cube-corner prism can rotate around a cavity axis of the resonant cavity; the resonant cavity is internally provided with a MgO: LiNbO3 crystal; a silicon prism array is put on the surface of the MgO: LiNbO3 crystal; and a polarizer is arranged between the right-angle trihedral cube-corner prism and the MgO: LiNbO3 crystal according to a Brewster angle; pumplight is incident to the resonant cavity to simulate the MgO: LiNbO3 crystal to generate terahertz-wave which is sent out by the silicon prism array. Frequency tuning output of terahertz-wave is realized by rotating the output mirror without needing integrally rotating the resonant cavity. The oscillator is a continuously tunable full-solid state terahertz-wave coherent radiation source with small volume, compact structure, and high working stability and can be widely applied to terahertz-wave photoelectronic technique fields such as medical diagnosis, fine spectral analysis, biomedical Imaging, terahertz-wave communication, etc.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20070296971A1High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com