Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Particle trajectory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
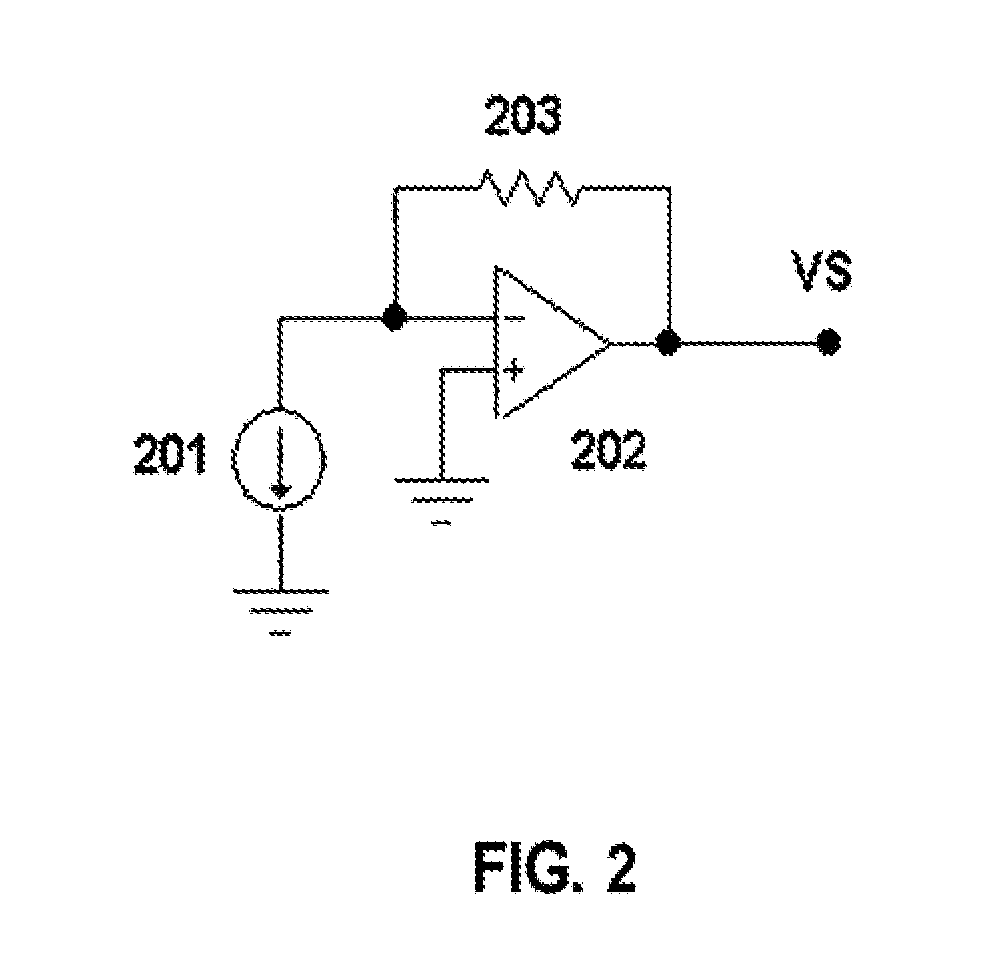
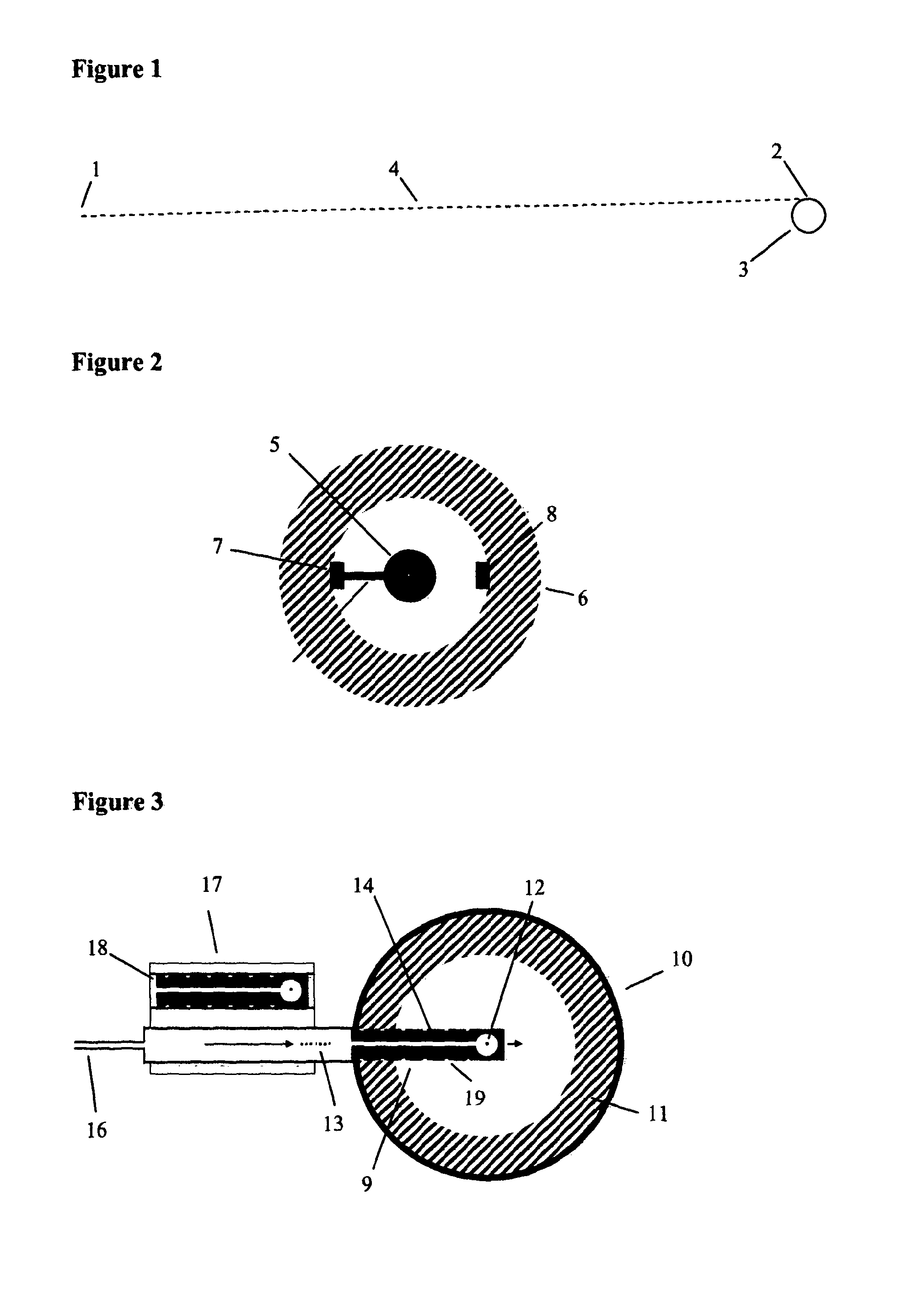
Multi-element deflection aberration correction for electron beam lithography
InactiveUS6180947B1Adjust focusStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsProjection opticsLithographic artist
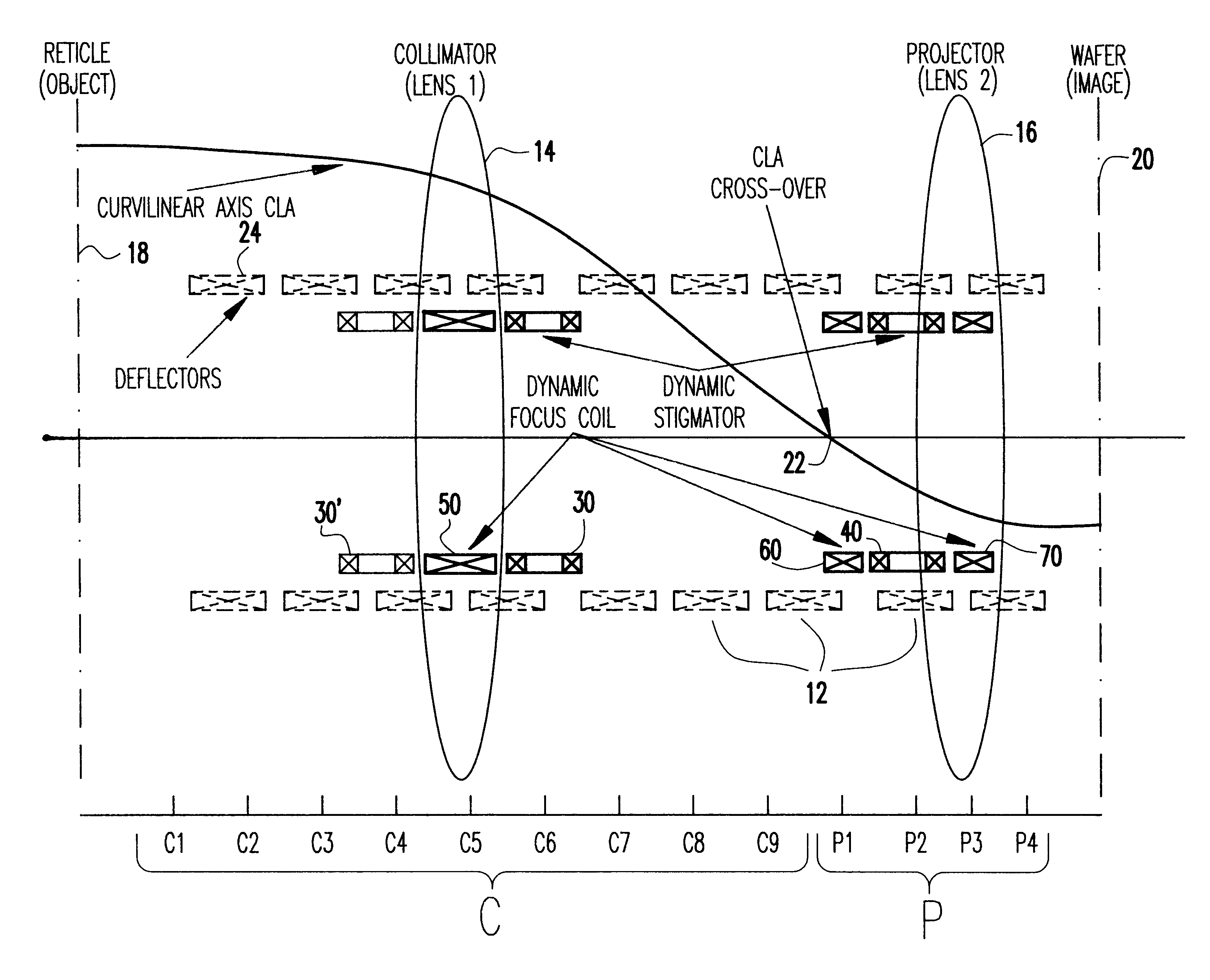
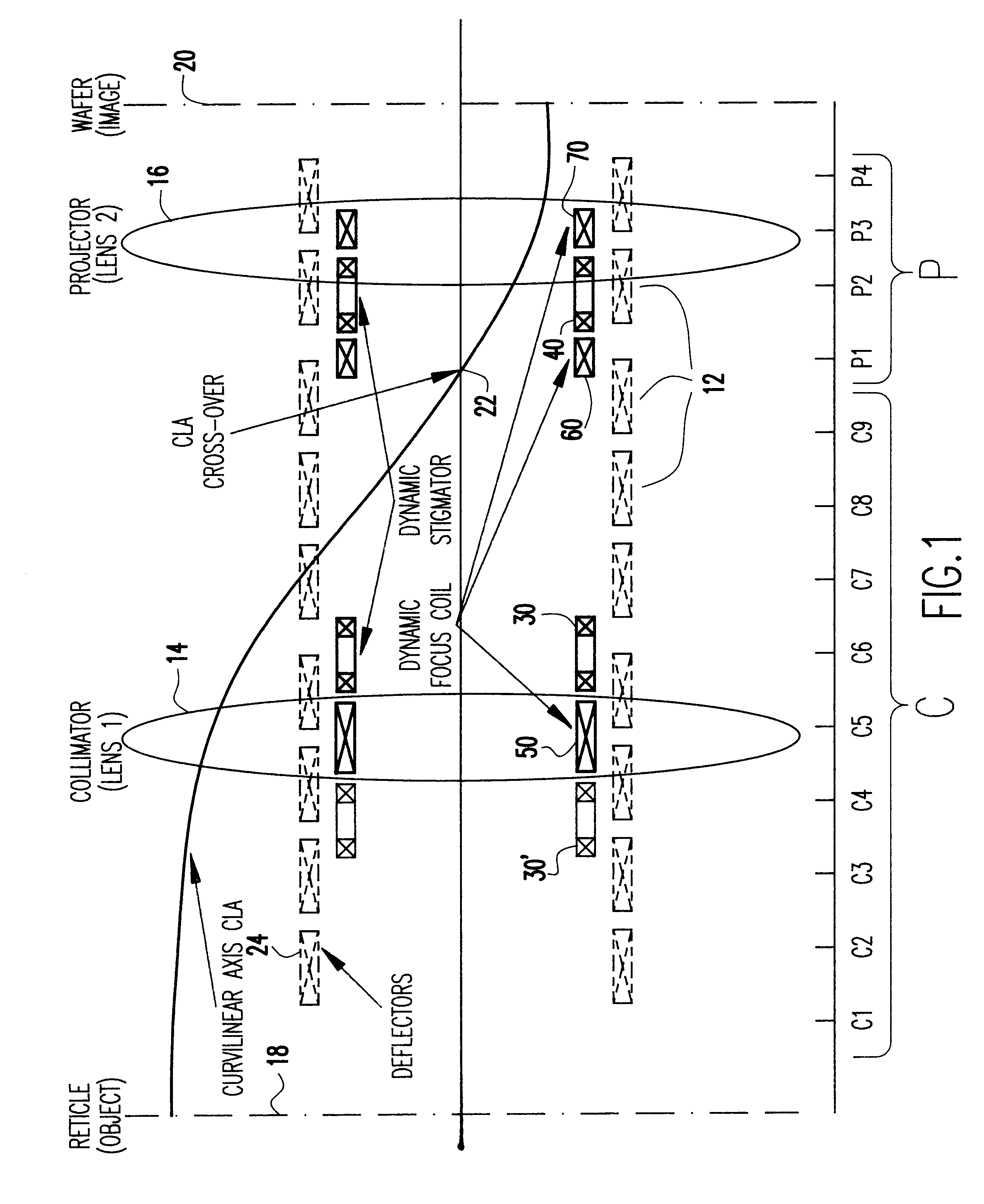
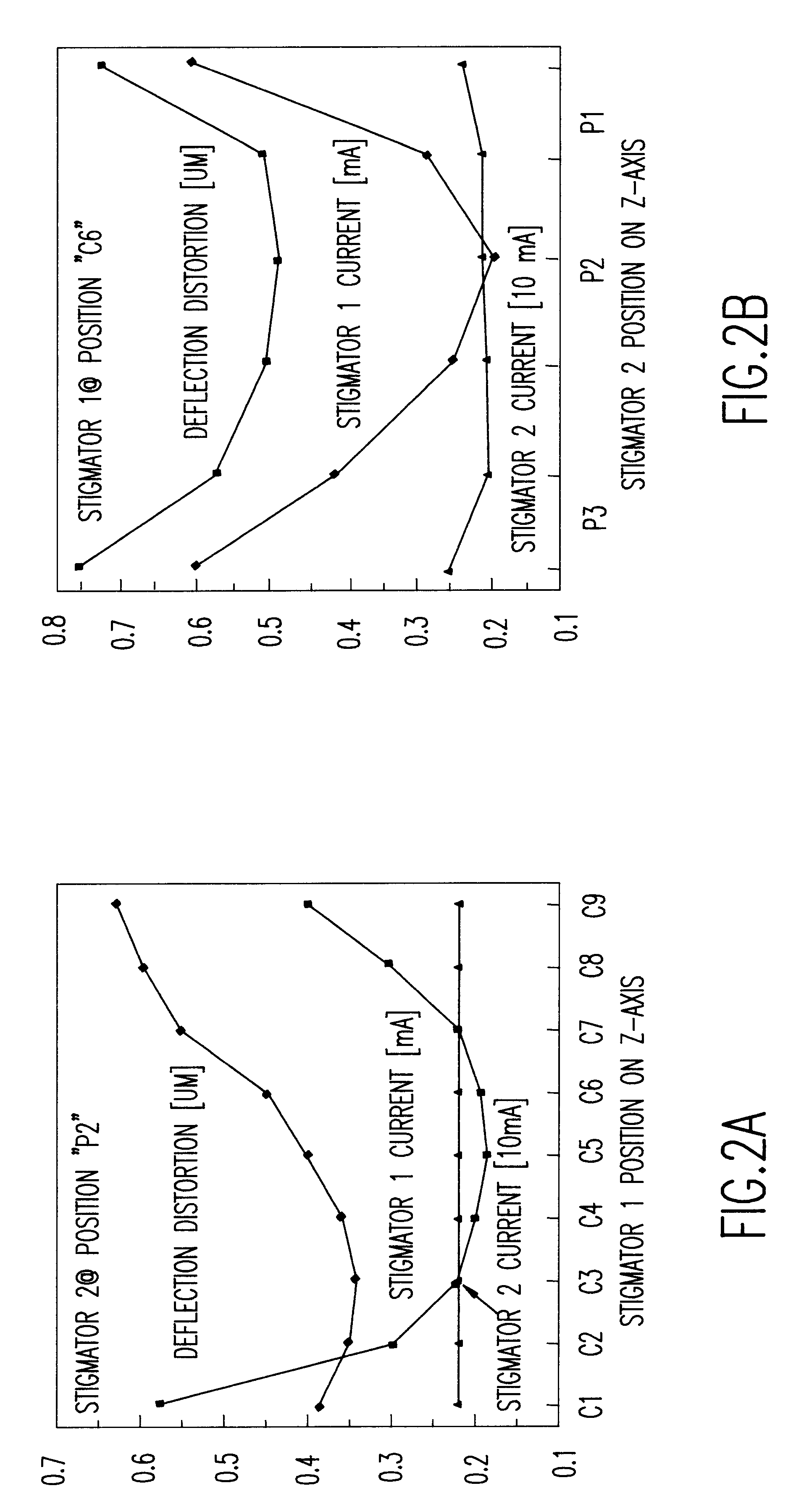
A method of optimizing locations of correction elements of a charged particle beam system determines respective corrector element currents to achieve optimum correction as a function of individual corrector location. Substantially complete dynamic correction of FSD and SFD can be obtained consistent with efficiency of operation and minimization of deflection distortion. In particular, FSD and SFD corrections can be sufficiently separated for substantially complete correction of SFD and FSD simultaneously with two stigmators. Both of these types of correction can be provided in complex charged particle beam systems employing curvilinear axis (CVA) particle trajectories and or large area reduction projection optics (LARPO) which cause complex hybrid aberrations in order to achieve high throughput consistent with extremely high resolution supporting one-tenth micron minimum feature size lithography regimes and smaller.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20050179904A1High sensitivityImprove light collectionComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Method and system for detecting polygon boundaries of structures in images as particle tracks through fields of corners and pixel gradients
A stochastic method and system for detecting polygon structures in images, by detecting a set of best matching corners of predetermined acuteness α of a polygon model from a set of similarity scores based on GDM features of corners, and tracking polygon boundaries as particle tracks using a sequential Monte Carlo approach. The tracking involves initializing polygon boundary tracking by selecting pairs of corners from the set of best matching corners to define a first side of a corresponding polygon boundary; tracking all intermediate sides of the polygon boundaries using a particle filter, and terminating polygon boundary tracking by determining the last side of the tracked polygon boundaries to close the polygon boundaries. The particle tracks are then blended to determine polygon matches, which may be made available, such as to a user, for ranking and inspection.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
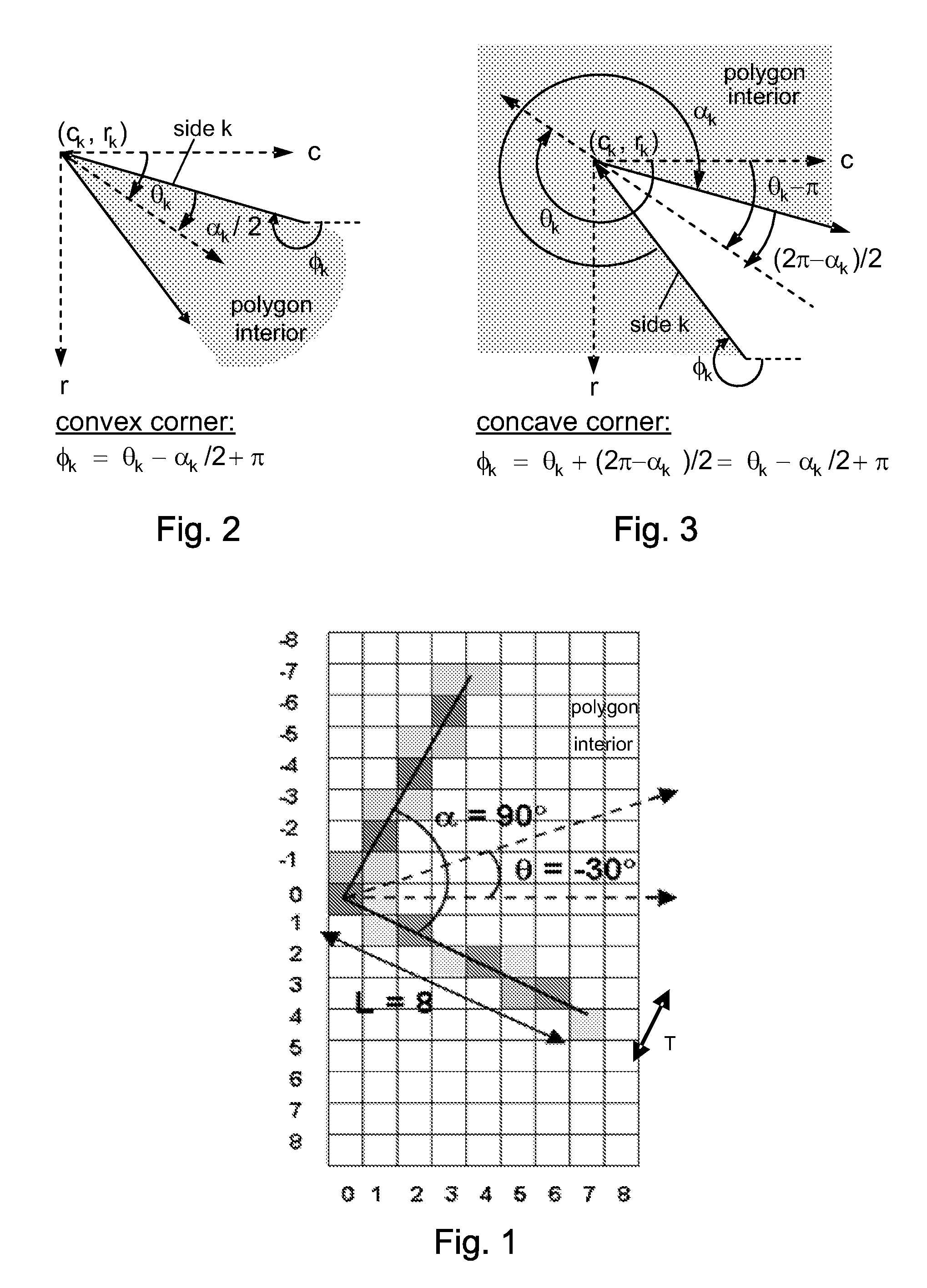
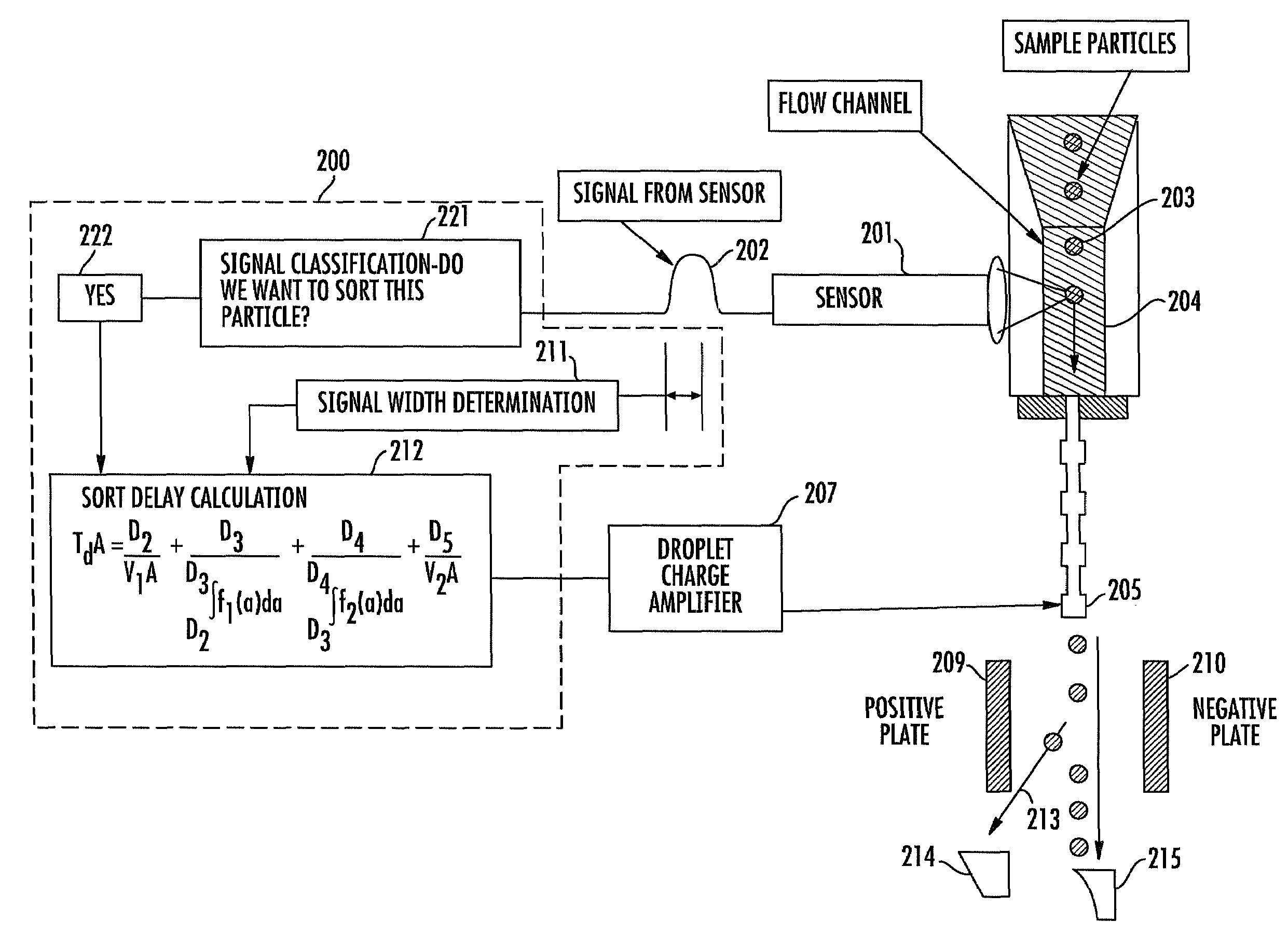
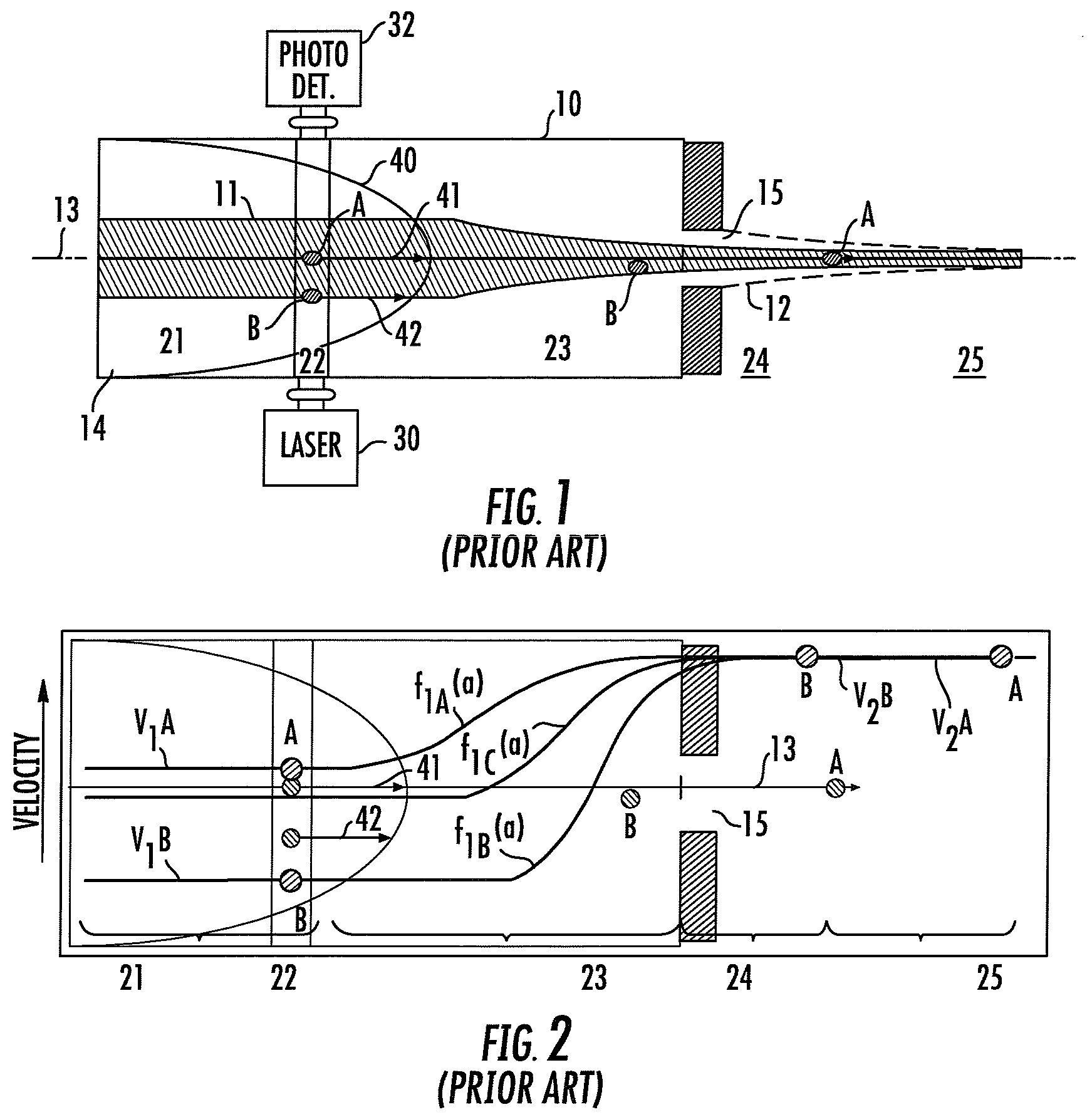
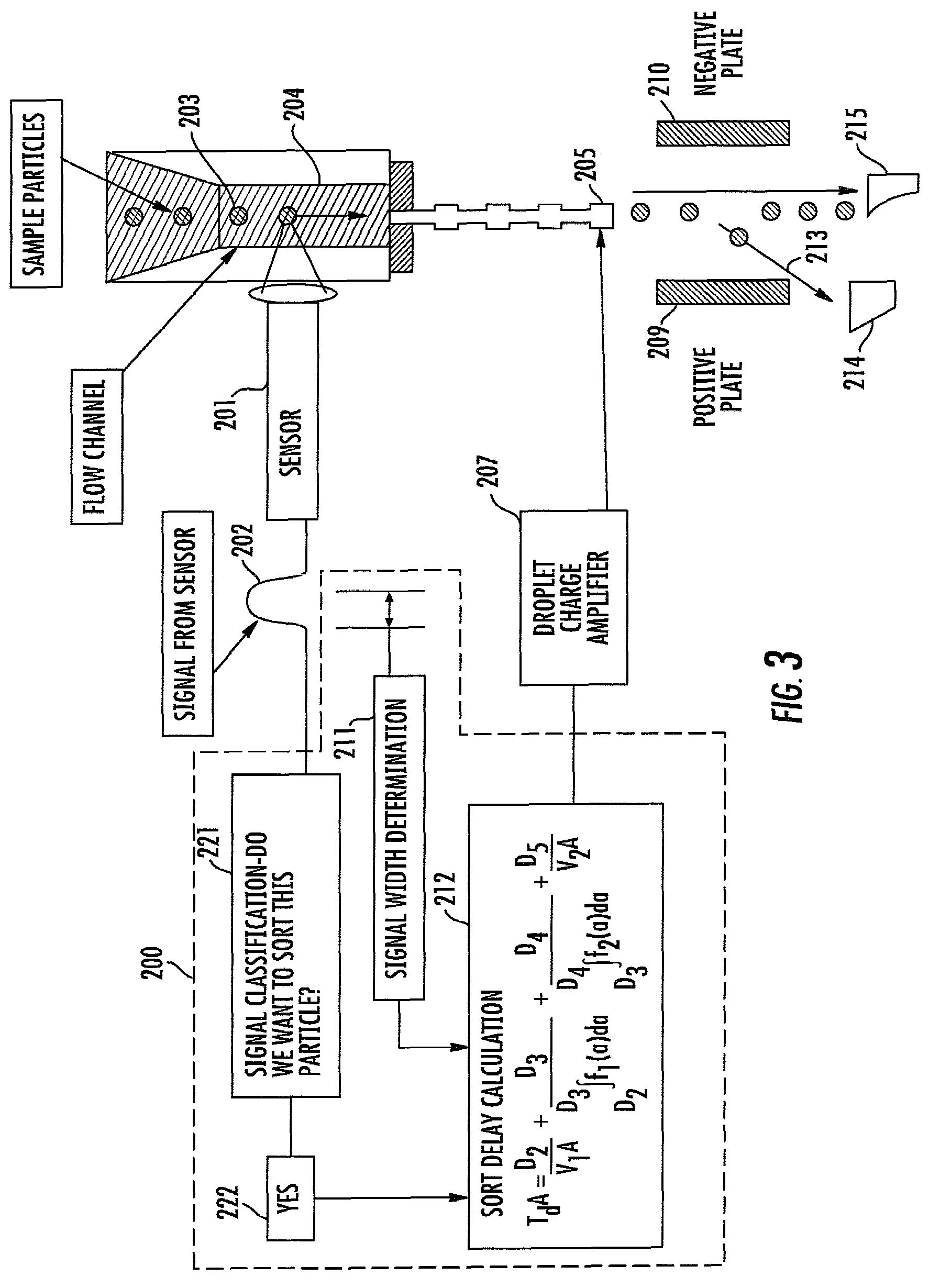
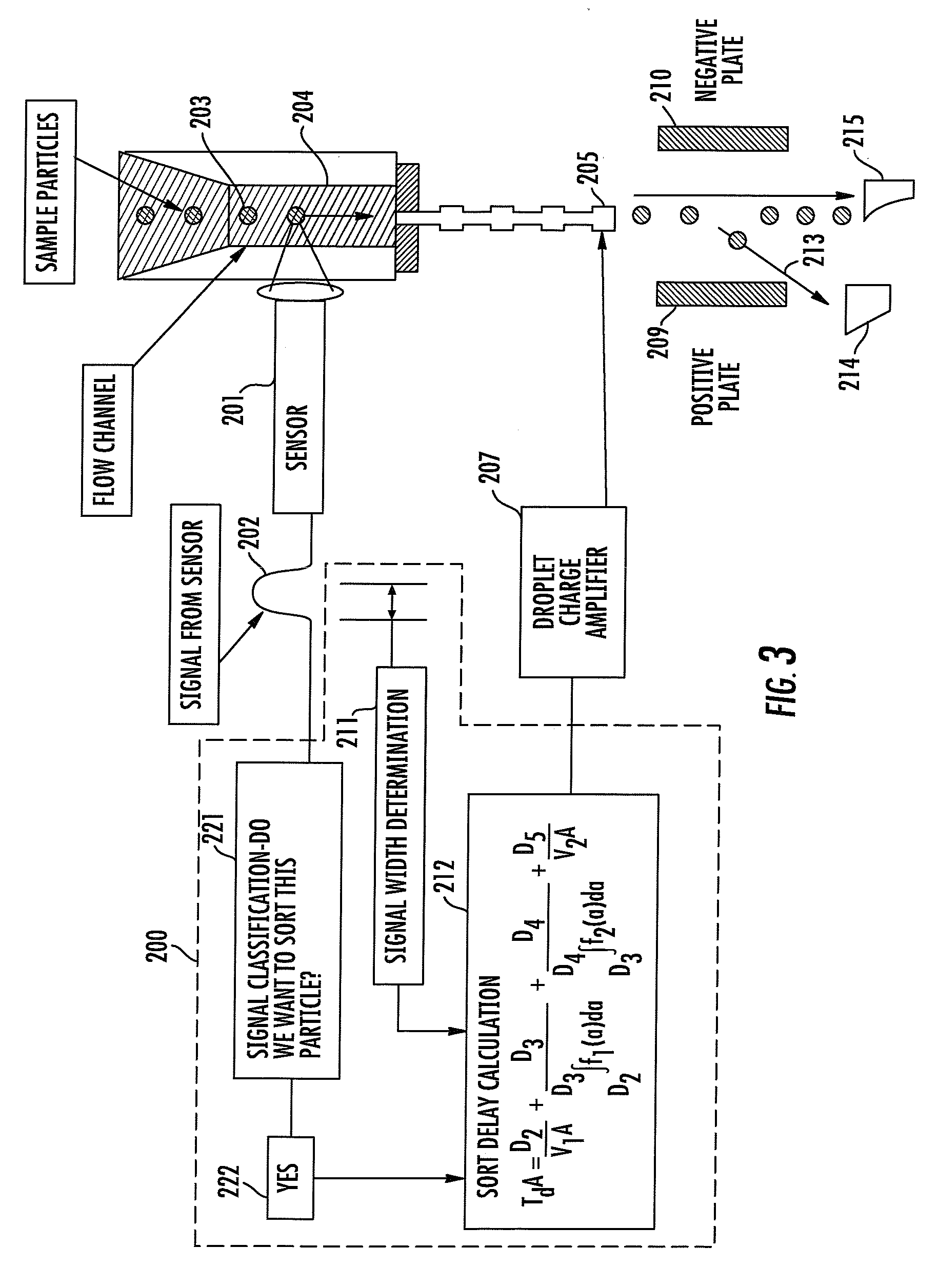
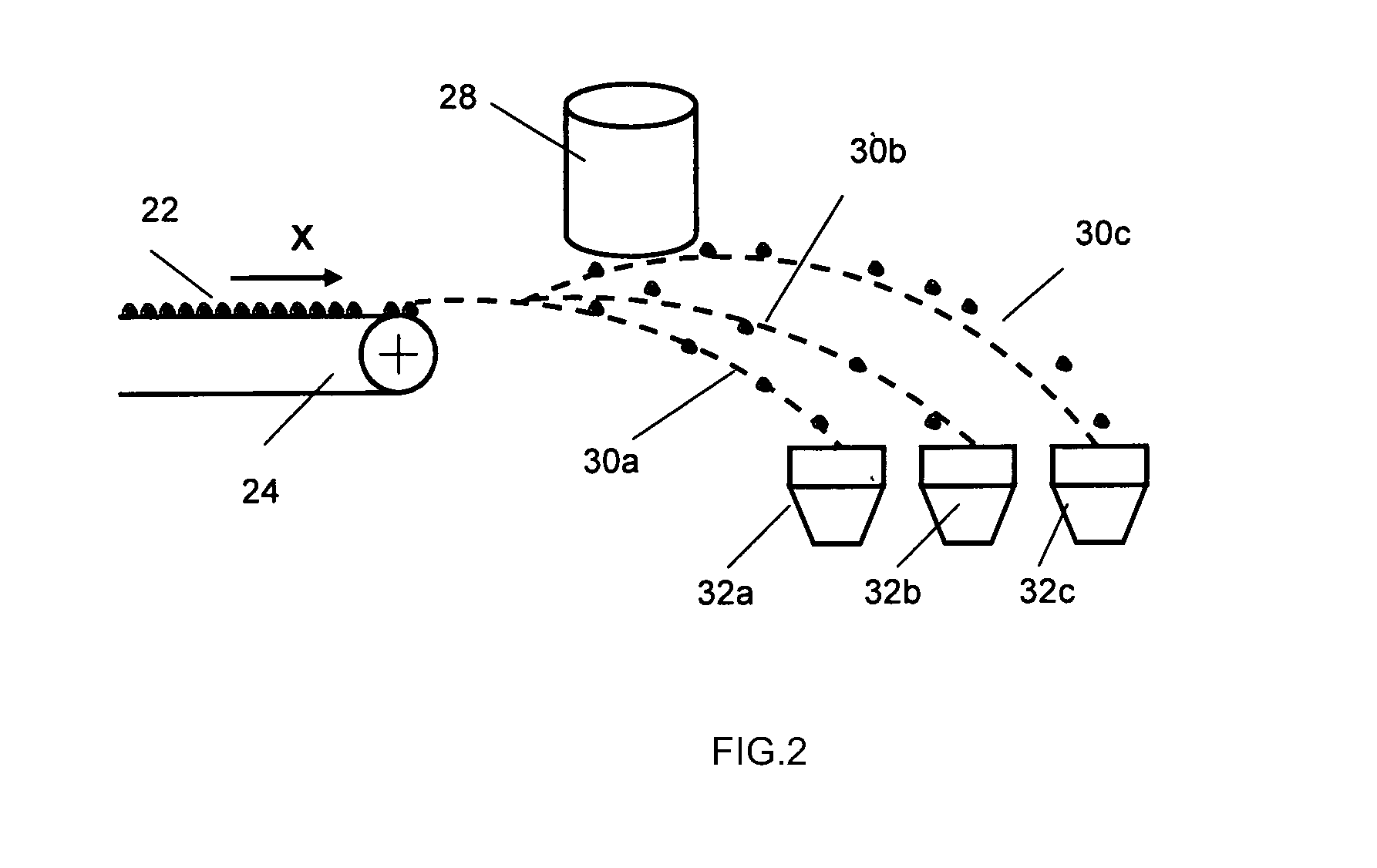
Method and apparatus for compensating for variations in particle trajectories in electrostatic sorter for flowcell cytometer
ActiveUS7691636B2High puritySpeed of travel can be readilyElectrostatic separationCharacter and pattern recognitionFluid transportCarrier fluid
A flow cytometer subsystems monitors a particle sensing zone within a fluid transport chamber for the presence of a particle (e.g., blood cell) traveling therethrough, and produces an output pulse, whose width is representative of the trajectory and thereby the length of time that the particle is within the particle sensing zone as it travels through the fluid transport chamber. This output pulse is then processed in accordance with geometry parameters of successive time delay zones of the particle fluid transport chamber through which the particle passes, in order to derive a composite time delay between the sensing of the particle to the time at which a fluid droplet containing the particle will break off from the carrier fluid. The composite time delay is employed to accurately establish the time at which the particle is controllably charged as the particle breaks off from the carrier fluid.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
Method and System for detecting polygon Boundaries of structures in images as particle tracks through fields of corners and pixel gradients
A stochastic method and system for detecting polygon structures in images, by detecting a set of best matching corners of predetermined acuteness α of a polygon model from a set of similarity scores based on GDM features of corners, and tracking polygon boundaries as particle tracks using a sequential Monte Carlo approach. The tracking involves initializing polygon boundary tracking by selecting pairs of corners from the set of best matching corners to define a first side of a corresponding polygon boundary; tracking all intermediate sides of the polygon boundaries using a particle filter, and terminating polygon boundary tracking by determining the last side of the tracked polygon boundaries to close the polygon boundaries. The particle tracks are then blended to determine polygon matches, which may be made available, such as to a user, for ranking and inspection.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
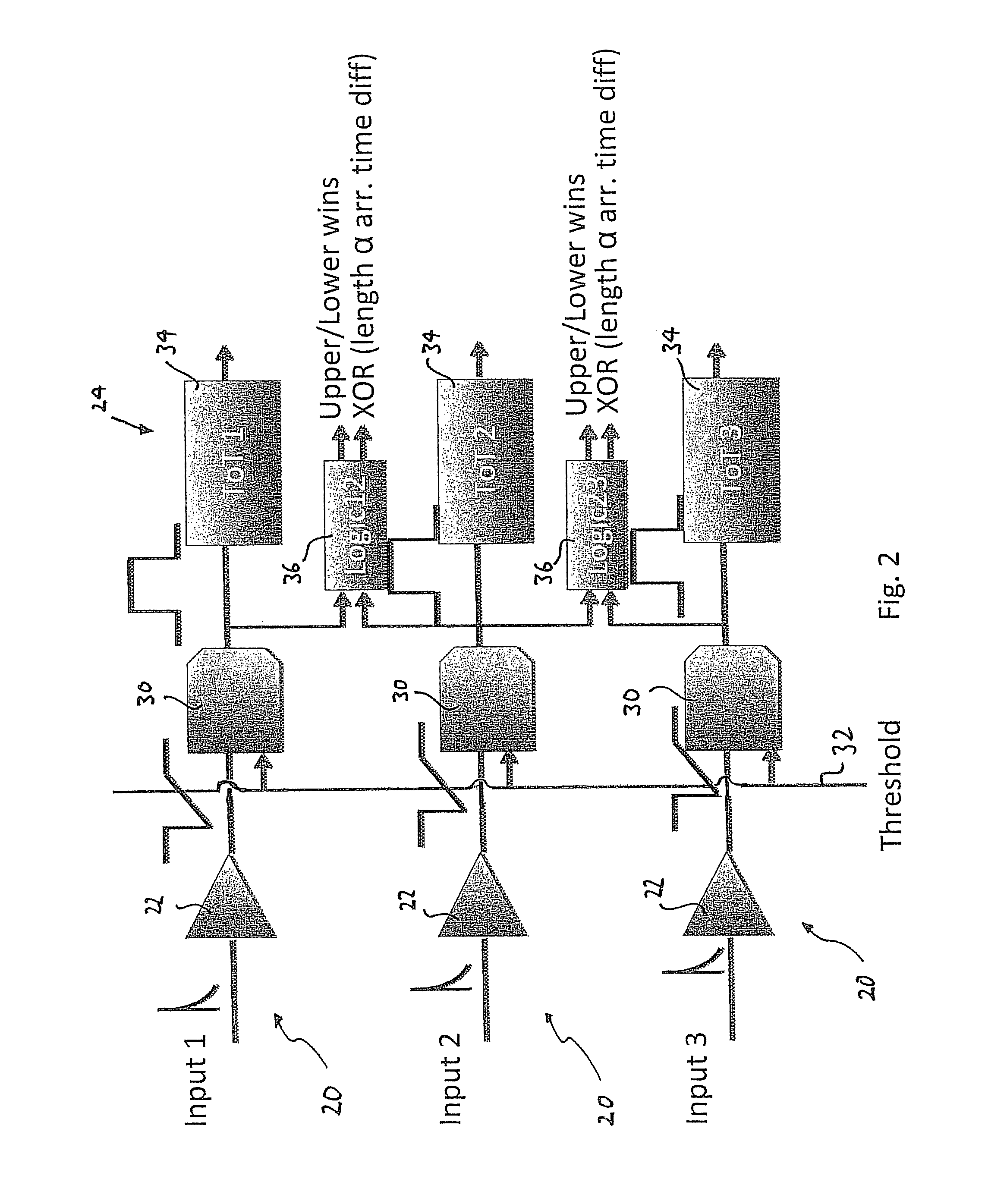
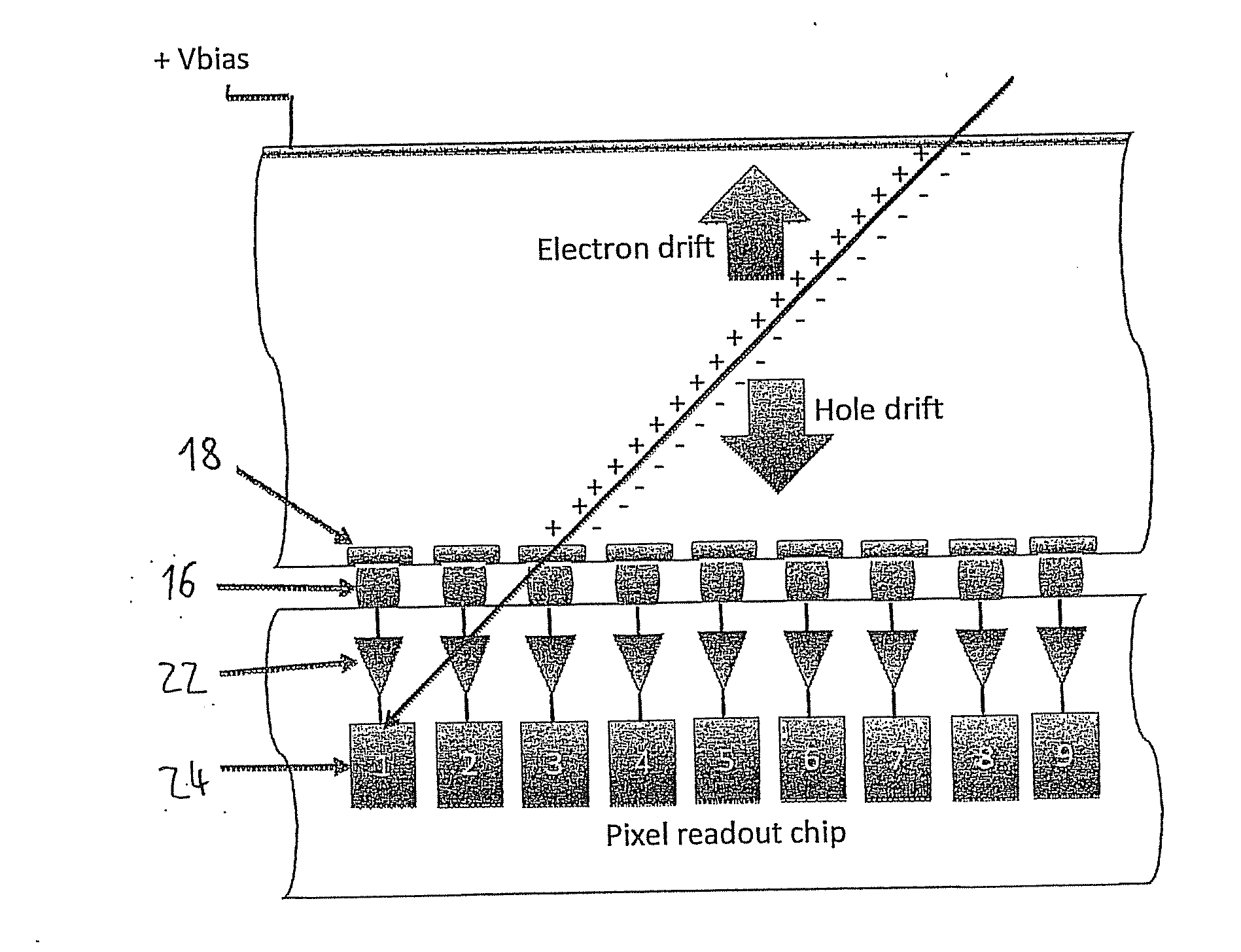
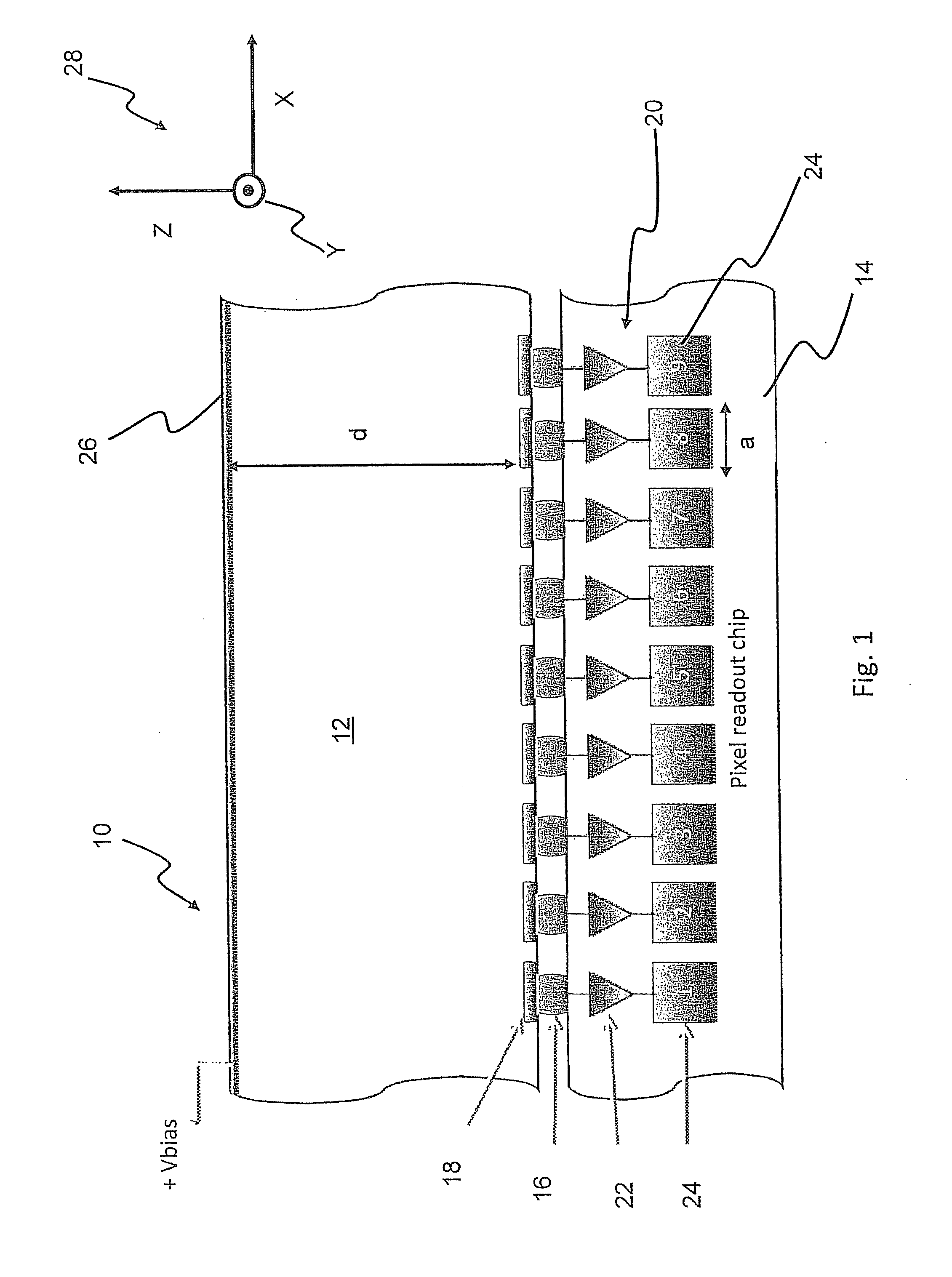
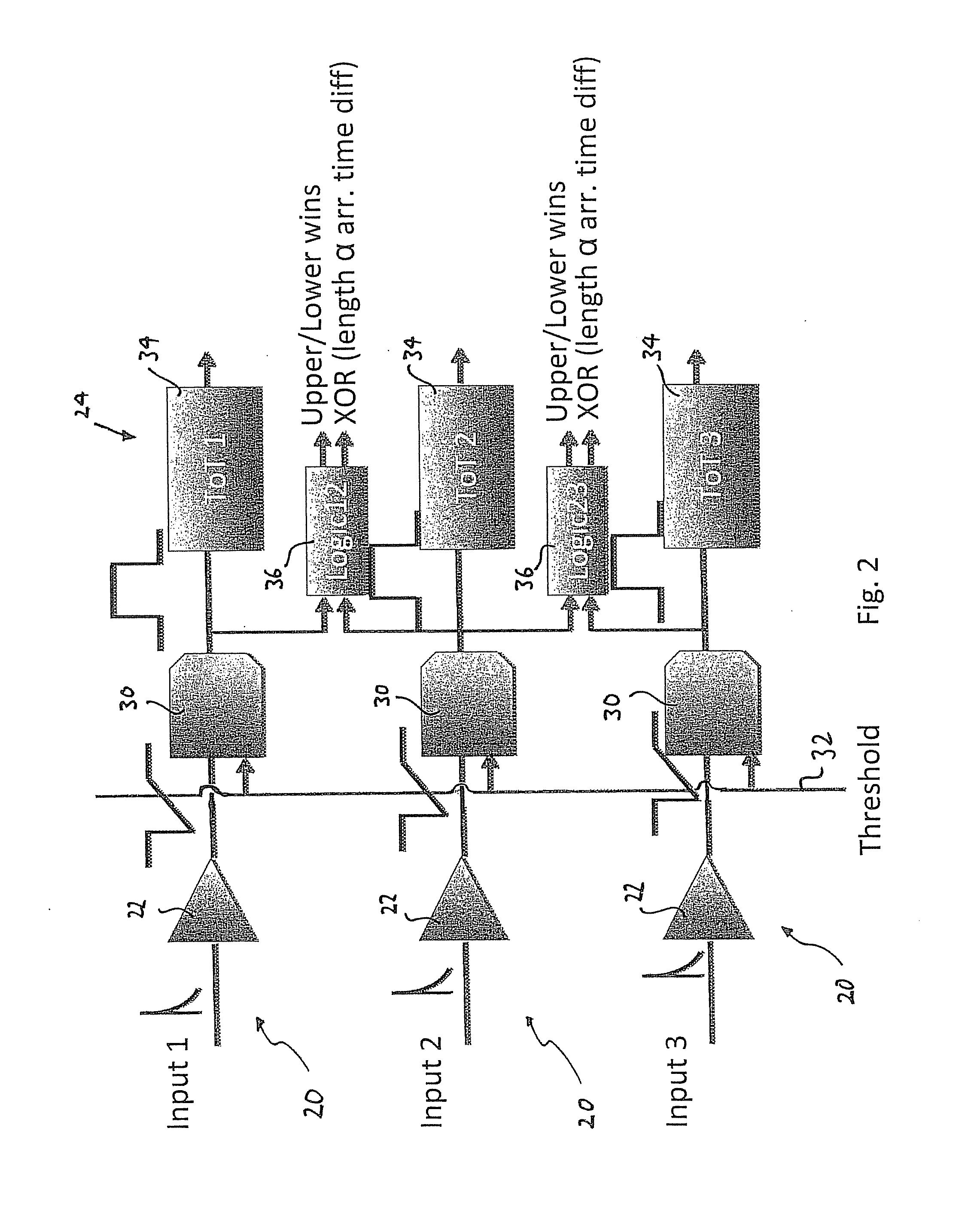
Single layer 3D tracking semiconductor detector
ActiveUS9297912B2Three-dimensional reconstruction more straightforwardModerate power consumptionSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devices3d trackingSemiconductor sensor
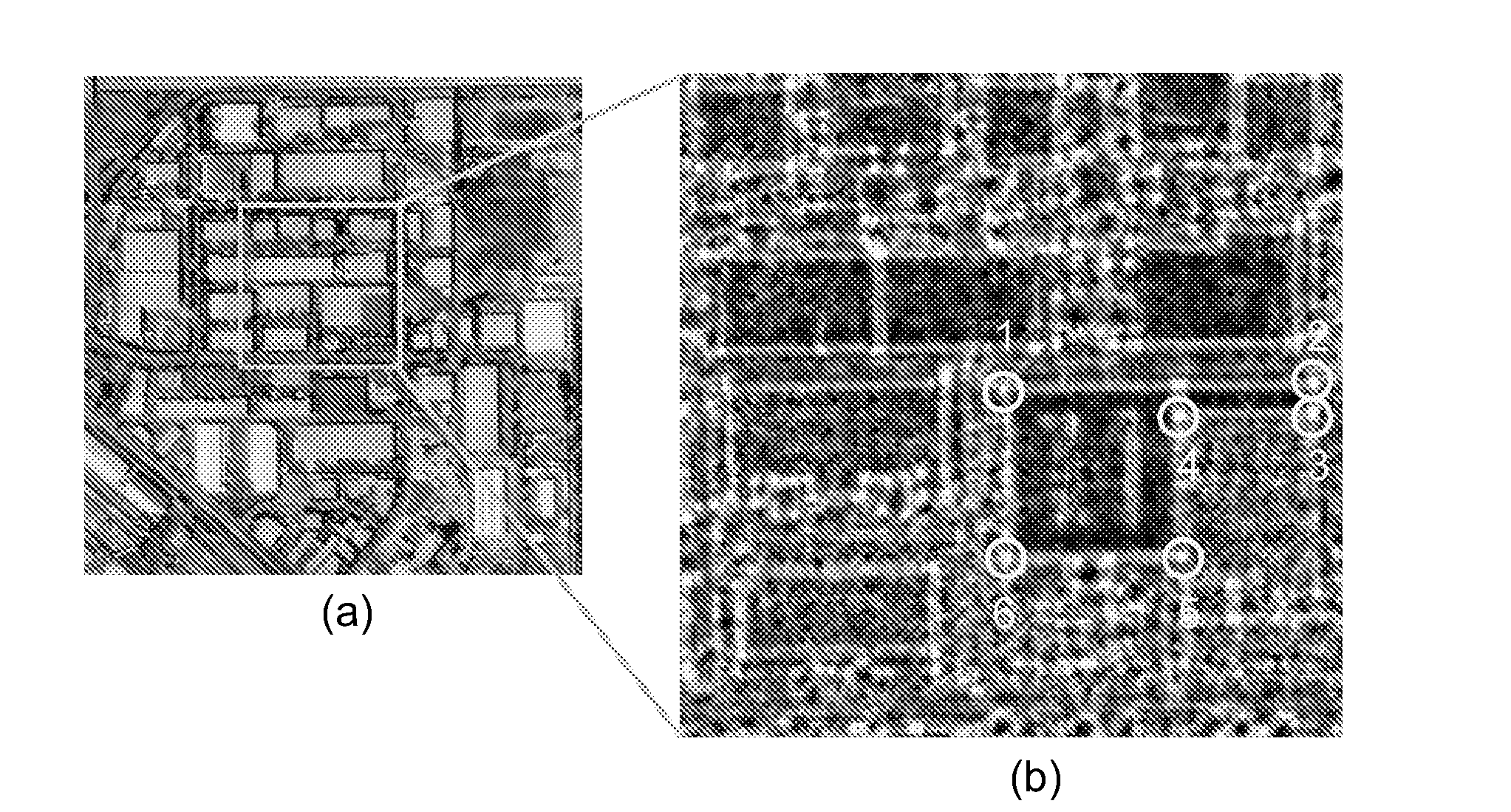
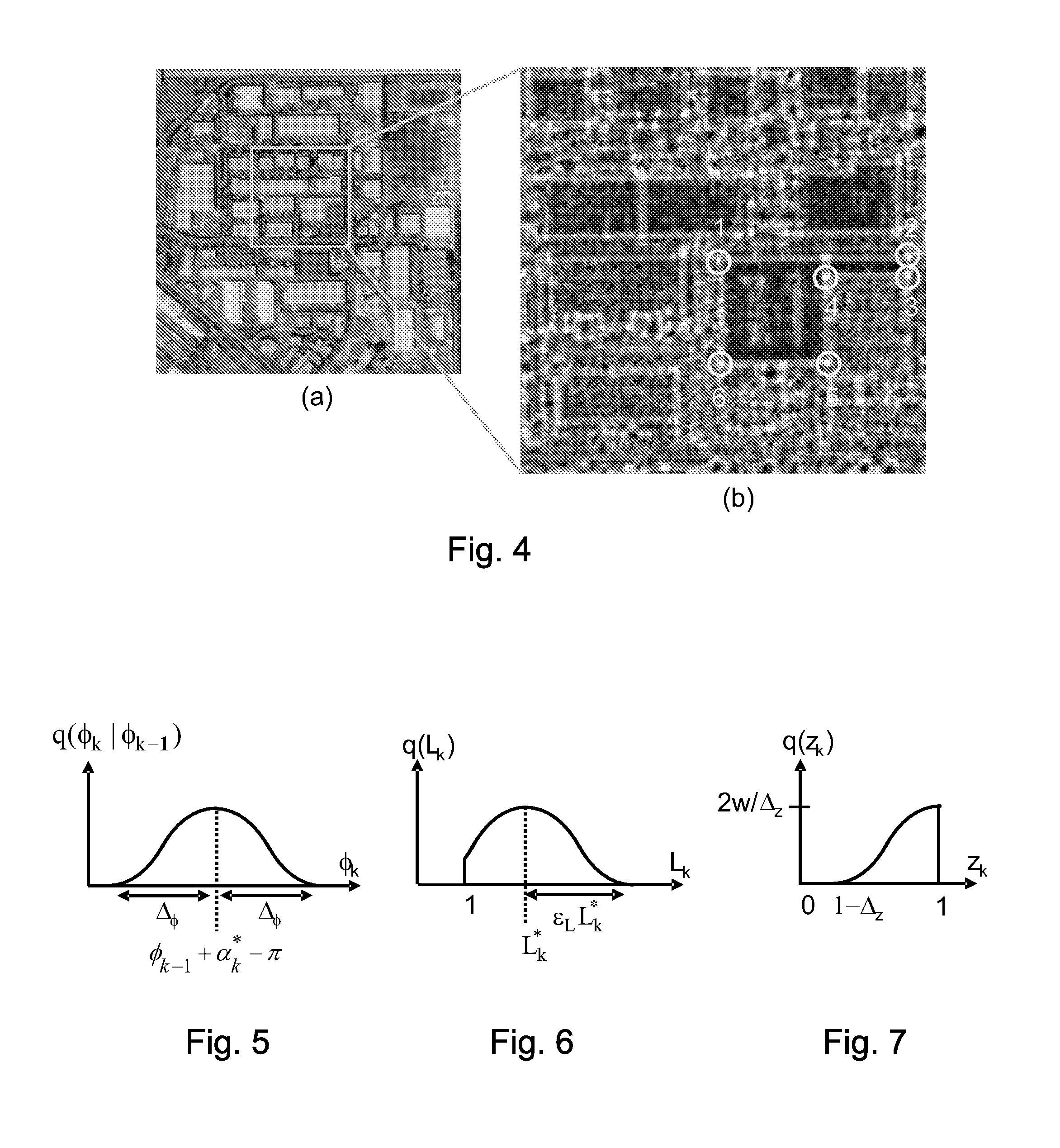
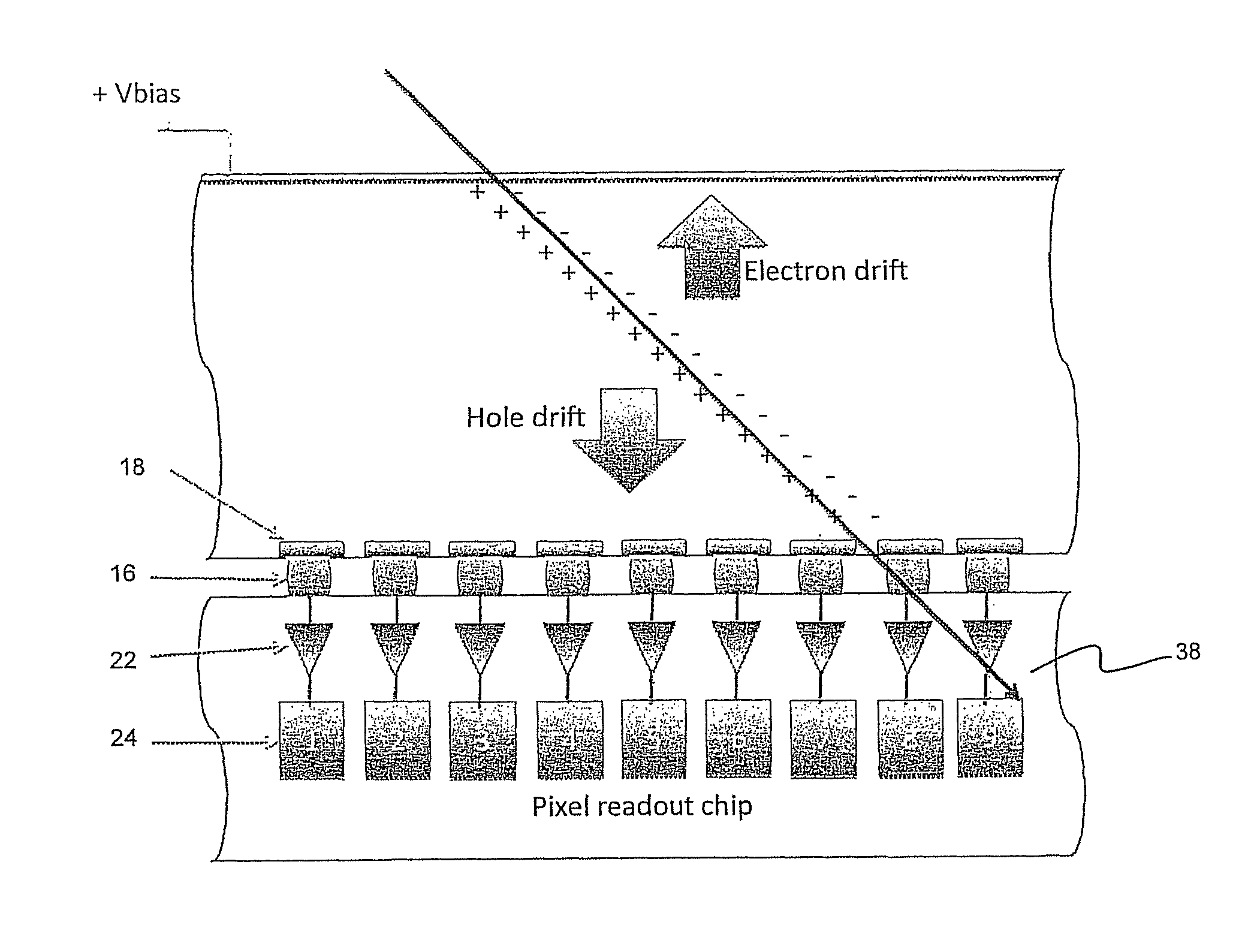
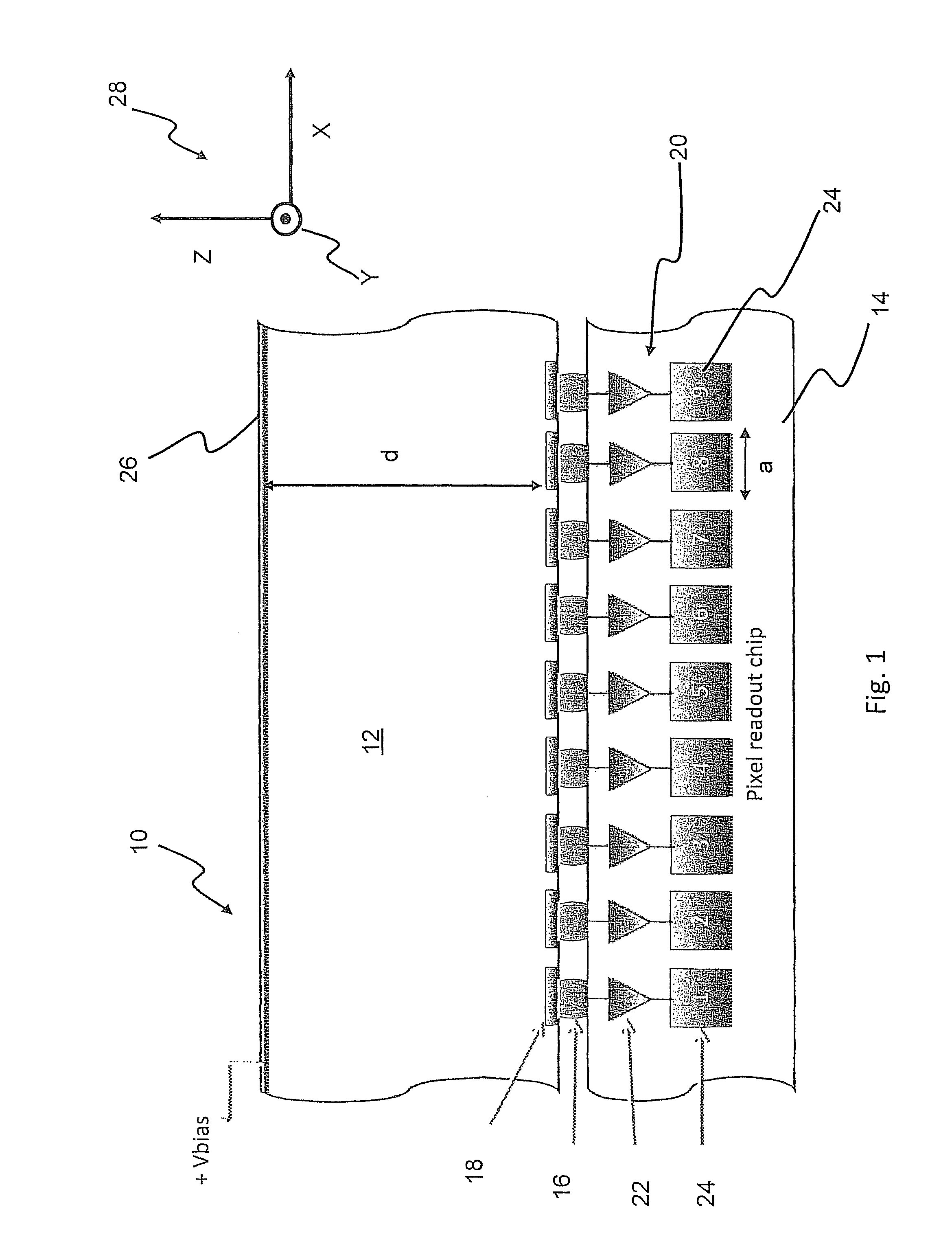
The present invention relates to a pixel detector (10), comprising a semiconductor sensor layer (12), in which charges can be generated upon interaction with particles to be detected. The semiconductor layer defines an X-Y-plane and has a thickness extending in Z-direction. The detector further comprises a read-out electronics layer (14) connected to said semiconductor layer (12), said read-out electronics layer (14) comprising an array of read-out circuits (20) for detecting signals indicative of charges generated in a corresponding volume of said semiconductor sensor layer (12). The neighboring read-out circuits (20) are connected by a relative timing circuit configured to determine time difference information between signals detected at said neighboring read-out circuits (20). The time difference information is indicative of a difference in the Z-components of the locations of charge generations in the corresponding neighboring sensor volumes caused by a particle trajectory that is inclined with respect to the X-Y-plane.
Owner:CZECH TECH UNIV IN PRAGUE
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS7268881B2High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Single layer 3D tracking semiconductor detector
ActiveUS20140332691A1Moderate power consumptionRobust and simple and affordable meanMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devices3d trackingSemiconductor sensor
The present invention relates to a pixel detector (10), comprising a semiconductor sensor layer (12), in which charges can be generated upon interaction with particles to be detected. The semiconductor layer defines an X-Y-plane and has a thickness extending in Z-direction. The detector further comprises a read-out electronics layer (14) connected to said semiconductor layer (12), said read-out electronics layer (14) comprising an array of read-out circuits (20) for detecting signals indicative of charges generated in a corresponding volume of said semiconductor sensor layer (12). The neighbouring read-out circuits (20) are connected by a relative timing circuit configured to determine time difference information between signals detected at said neighbouring read-out circuits (20). The time difference information is indicative of a difference in the Z-components of the locations of charge generations in the corresponding neighbouring sensor volumes caused by a particle trajectory that is inclined with respect to the X-Y-plane.
Owner:CZECH TECH UNIV IN PRAGUE
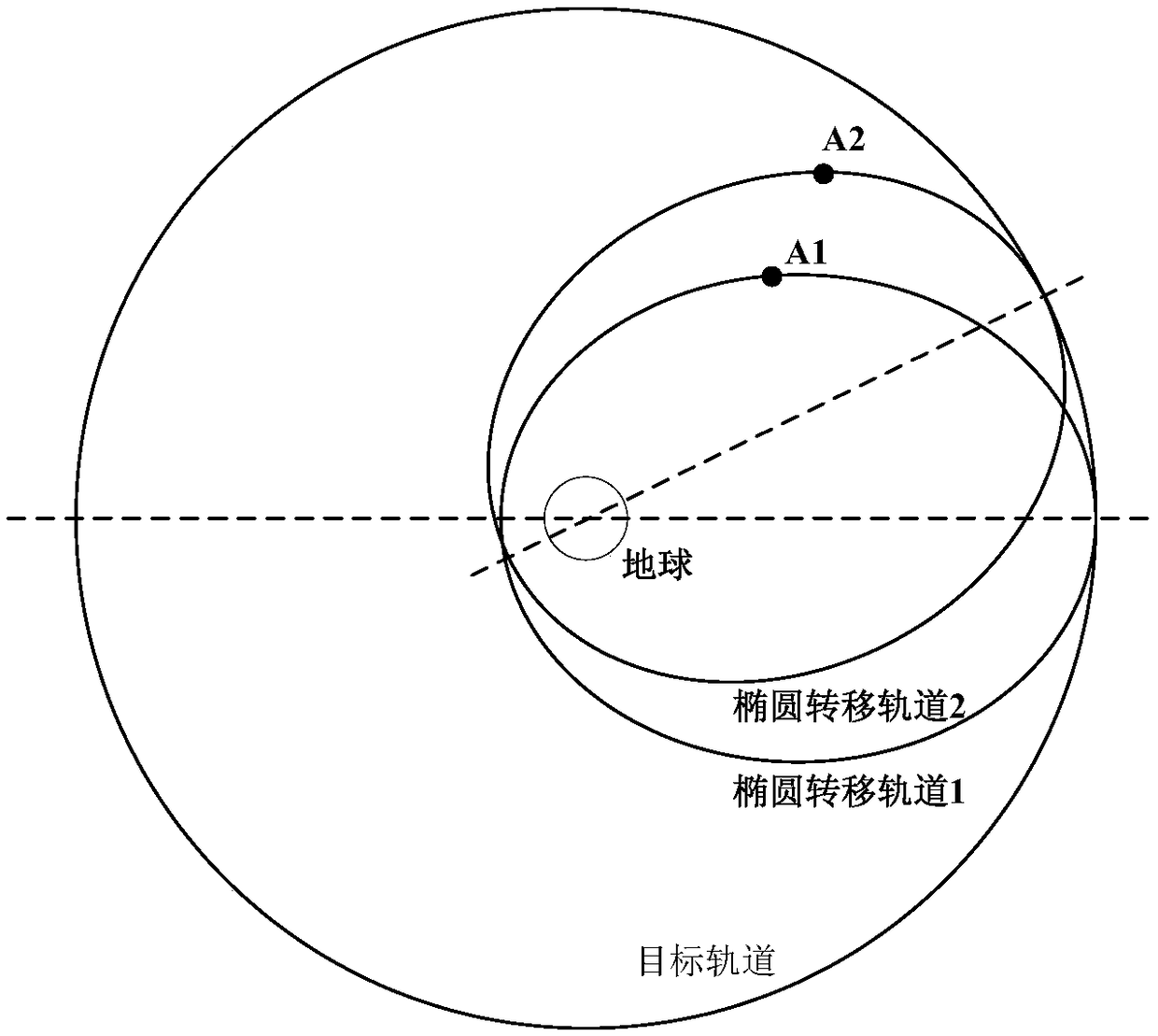
Orbit-injection-type trajectory design method of solid rocket based on elliptical transfer orbit
ActiveCN109398762AAchieve regulationChange properties and shapeCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusThree degrees of freedomEllipse
The invention discloses an orbit-injection-type trajectory design method of a solid rocket based on an elliptical transfer orbit, and relates to the field of carrier rocket trajectory design. The orbit-injection-type trajectory design method comprises the steps that a control variable is initialized; the perigee altitude of the elliptical transfer orbit is fixed by fixing the final-stage second working hour; according to the set carrier rocket fight time sequence, the force-bearing condition in the rock flight process is modeled, the speed and the position are subjected to numerical integration, and three-degree-of-freedom particle trajectory calculation is conducted; the calculated speed and position are converted through a coordinate system, whether the geocentric radius vector magnitude, the absolute speed magnitude, the orbit inclination angle and the current trajectory inclination angle meet the requirements or not is judged, if yes, related trajectory parameters such as the speed, the position, the flight program angle and the height are output, and a launch trajectory is designed; and otherwise, the control variable is adjusted according to the difference between a current value and a target value, and iterative calculation is conducted until the requirements are met. By adopting the orbit-injection-type trajectory design method, the orbit-injection-type trajectory scheme design of the elliptical transfer orbit of the solid rocket can be quickly achieved.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Method And Apparatus For Compensating For Variations In Particle Trajectories In Electrostatic Sorter For Flowcell Cytometer
ActiveUS20080293146A1High purityReduce dilutionElectrostatic separationCharacter and pattern recognitionElectricityFluid transport
A flow cytometer subsystems monitors a particle sensing zone within a fluid transport chamber for the presence of a particle (e.g., blood cell) traveling therethrough, and produces an output pulse, whose width is representative of the trajectory and thereby the length of time that the particle is within the particle sensing zone as it travels through the fluid transport chamber. This output pulse is then processed in accordance with geometry parameters of successive time delay zones of the particle fluid transport chamber through which the particle passes, in order to derive a composite time delay between the sensing of the particle to the time at which a fluid droplet containing the particle will break off from the carrier fluid. The composite time delay is employed to accurately establish the time at which the particle is controllably charged as the particle breaks off from the carrier fluid.
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC
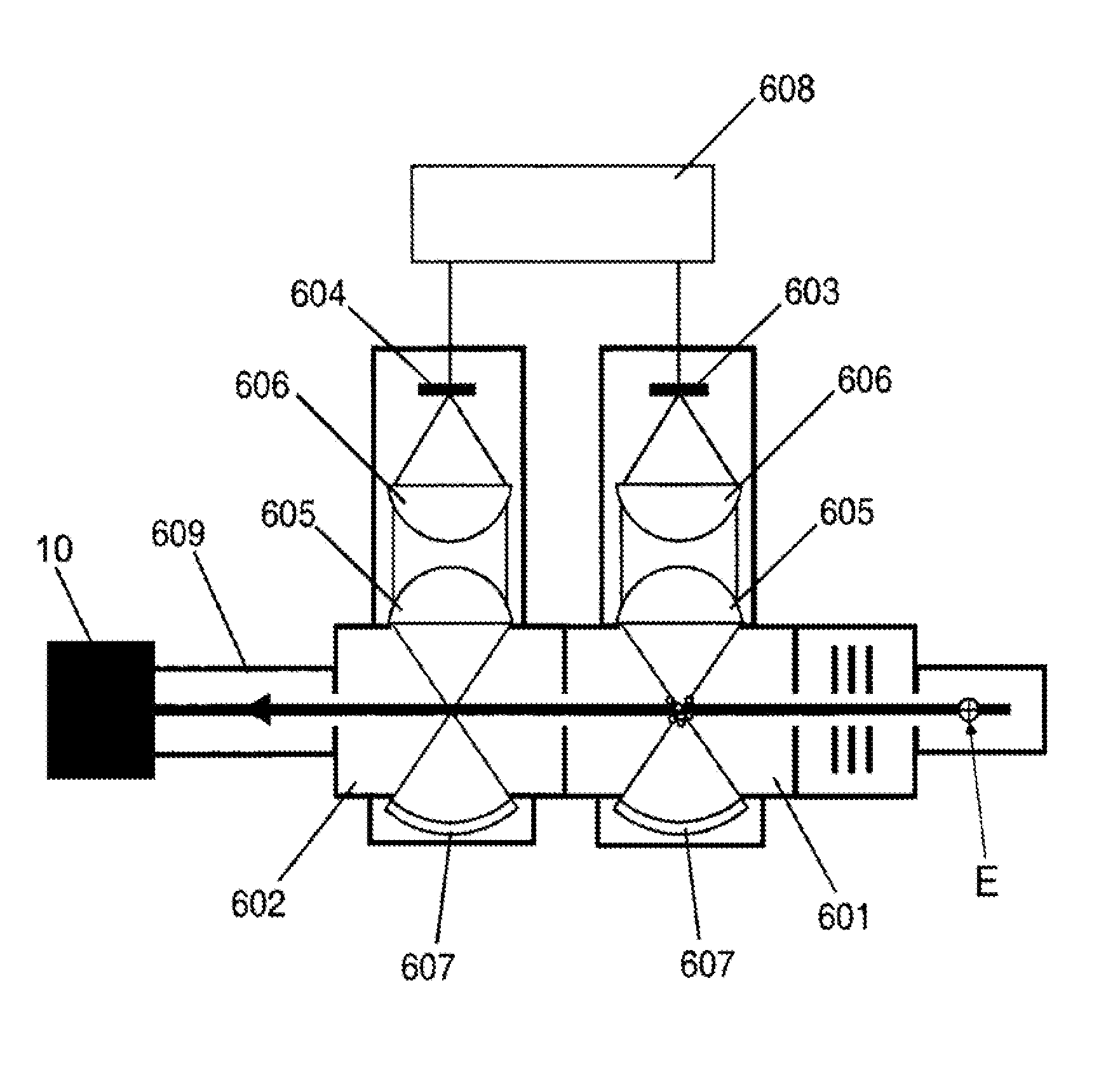
Charged-particle condensing device
ActiveUS20100148062A1Improve utilization efficiencyEfficient extractionTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionPotential wellAxis of symmetry
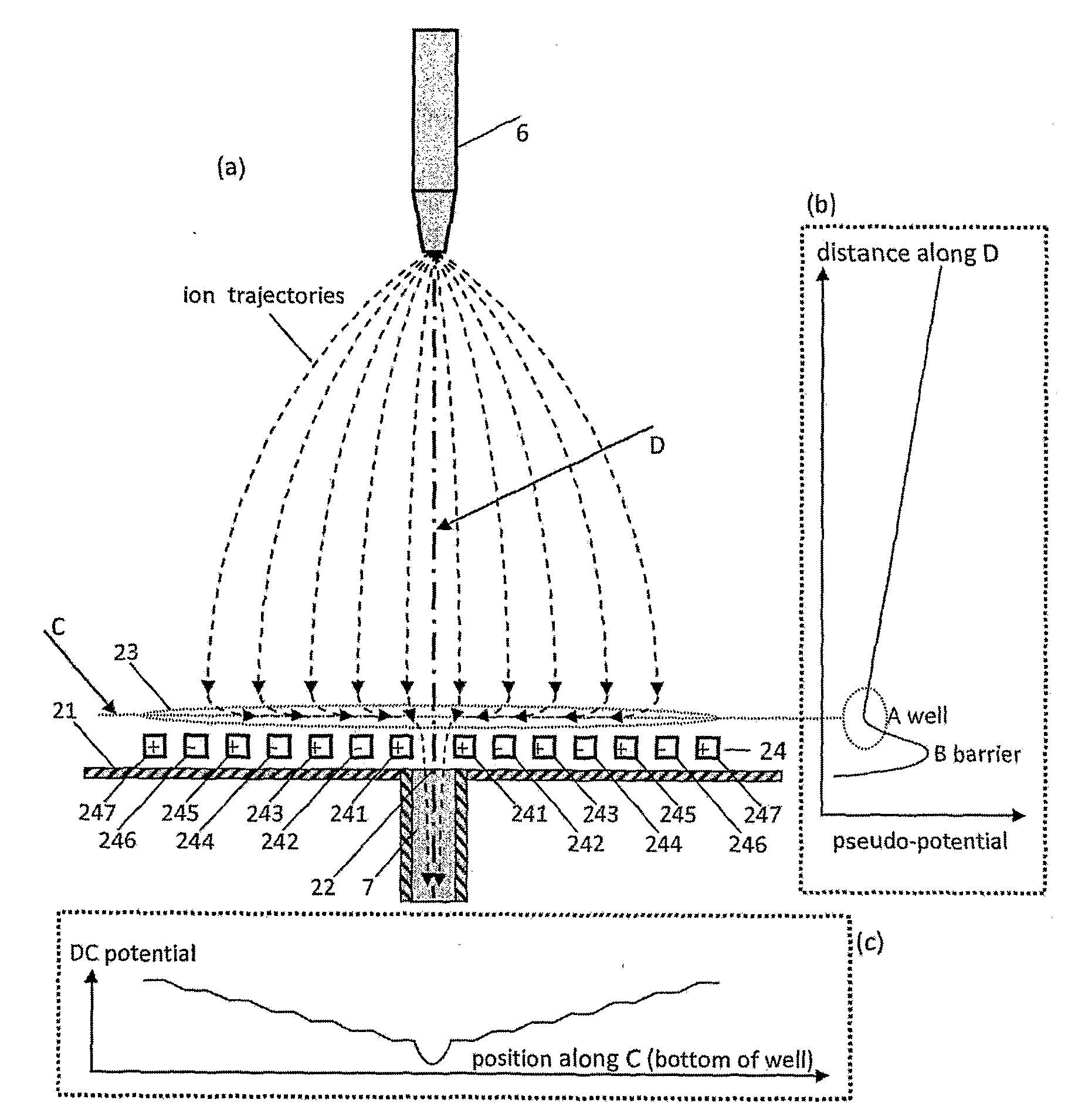
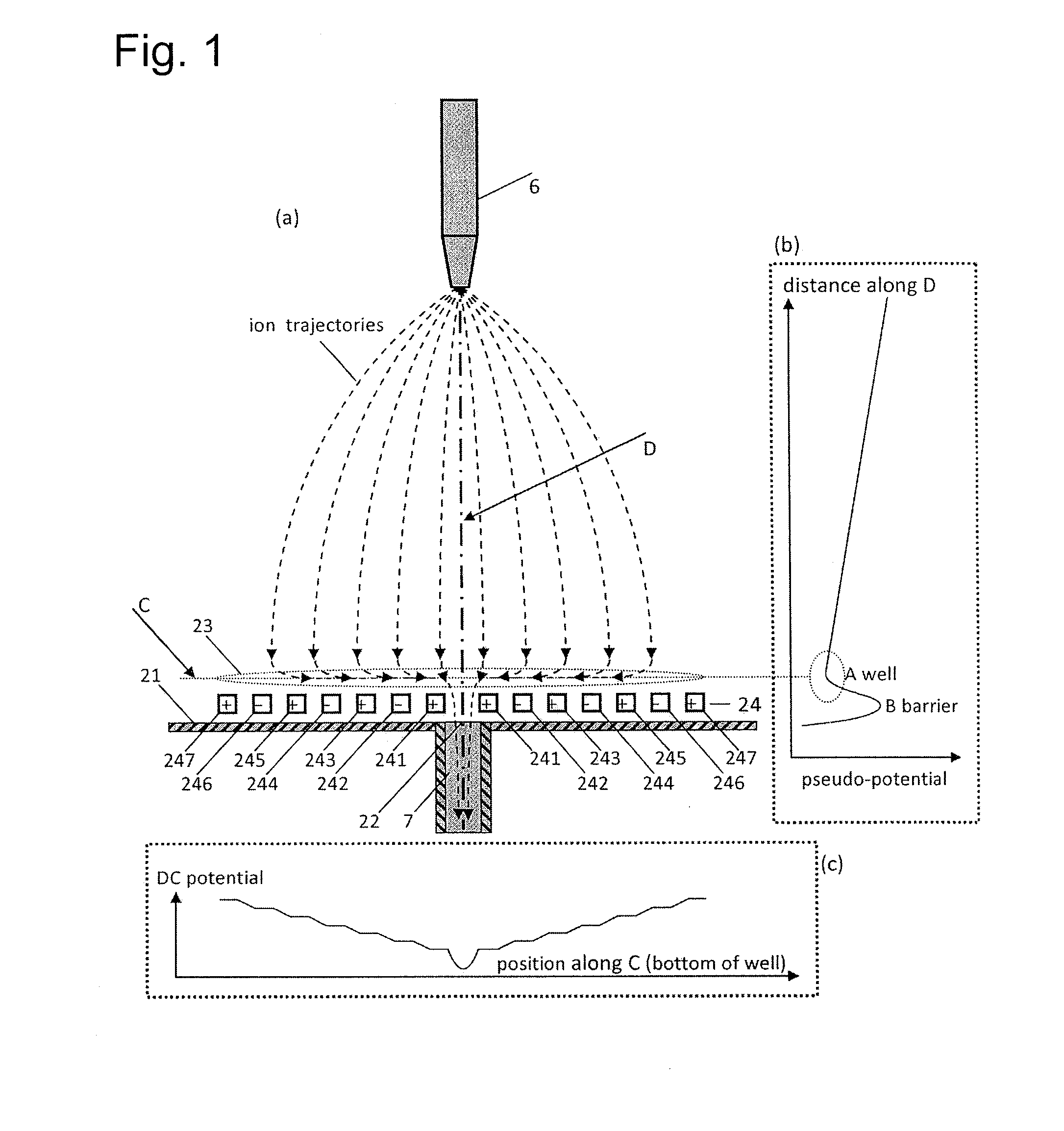
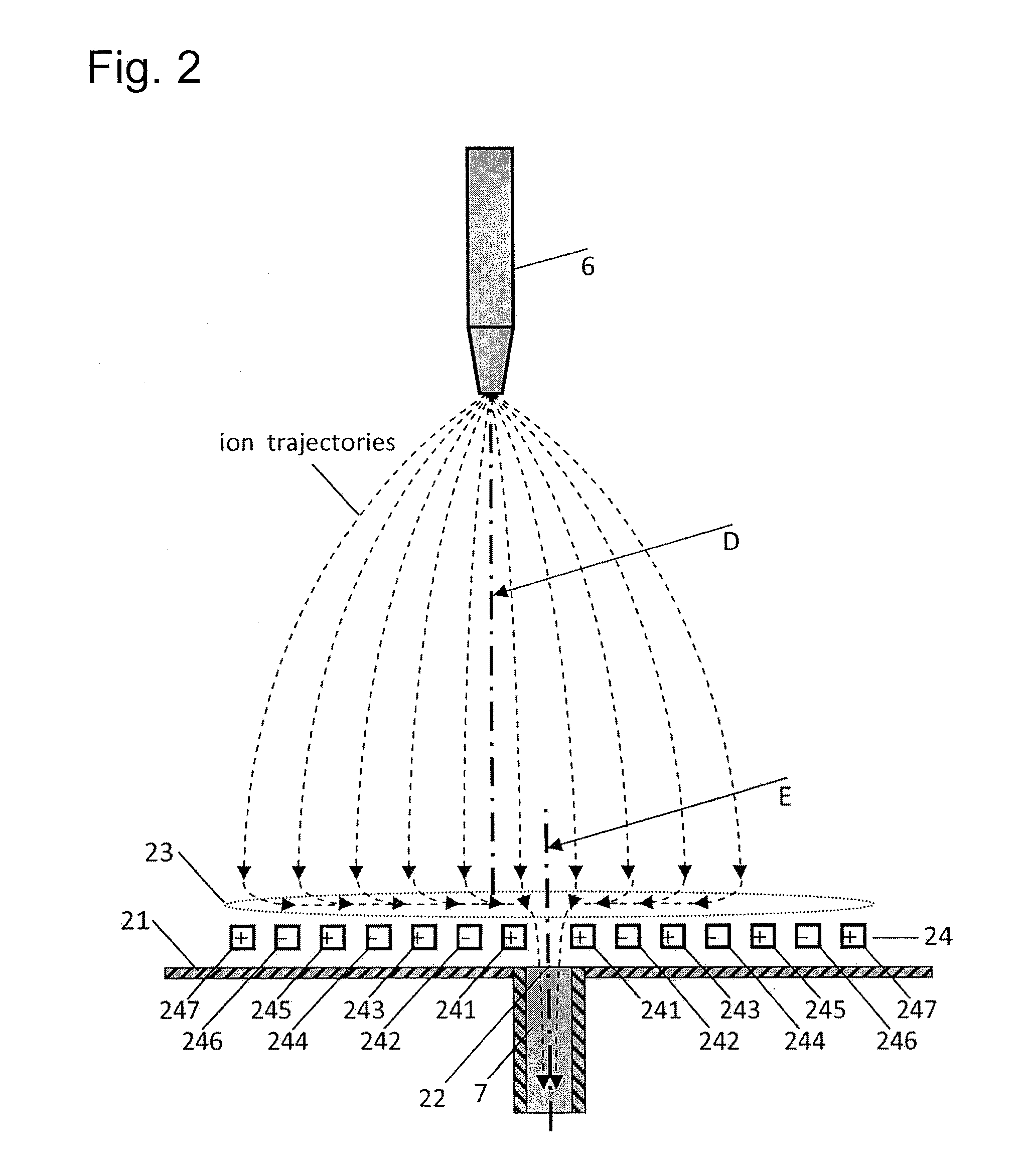
Ions and charged droplets move from the nozzle (6) towards the orifice (22) of a charged-particle transport device or the desolvation pipe (7). This particle motion is governed by the distribution of the pseudo-potential along particle trajectories. There are RF-voltages applied to neighboring electrodes (241-246) of the electrode array (24) cause the charged particles to substantially hover above the electrode array (24). Right before the ions come to the electrode array (24) they thus experience a repelling force “F” perpendicular to the surface of the electrode array (24). This force “F” causes an effective barrier (B) right before the electrode array (24) and consequently a pseudo-potential well (A) where the charged particles stop their motion parallel to the plume axis (D). Thus they accumulate around the center line (C) of this well (A). Applying additionally to the RF-potentials also DC-potentials to neighboring electrodes within the electrode array (24) small DC-fields can be formed within the well area (23). These additional DC-fields drive the charged particles towards the axis of symmetry (C) and thus towards the orifice (22) of a charged-particle transport device or the desolvation pipe (7). Thus, many of the charged particles which would normally impinge on the wall (21) around the orifice (22) can now be analyzed.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
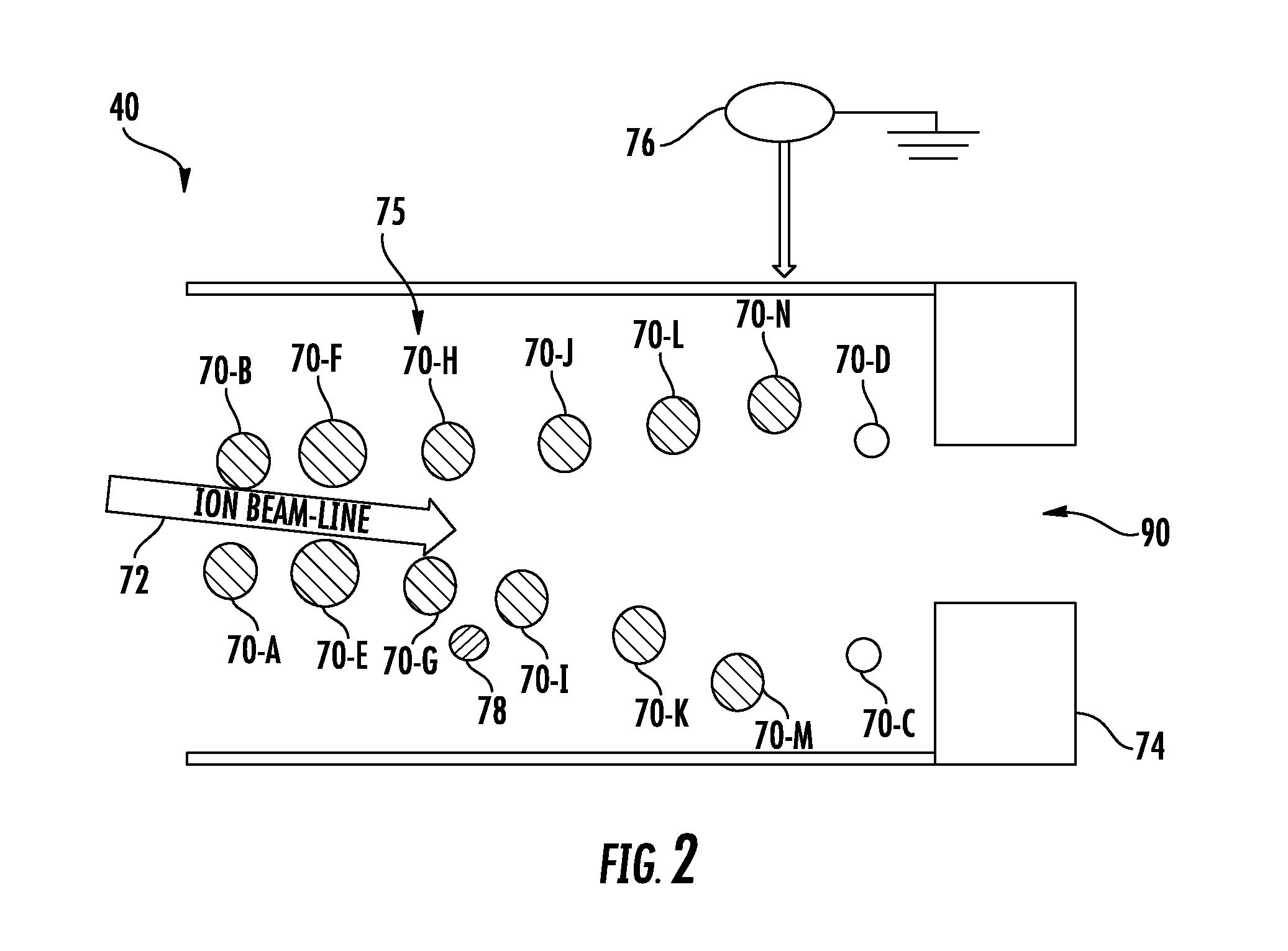
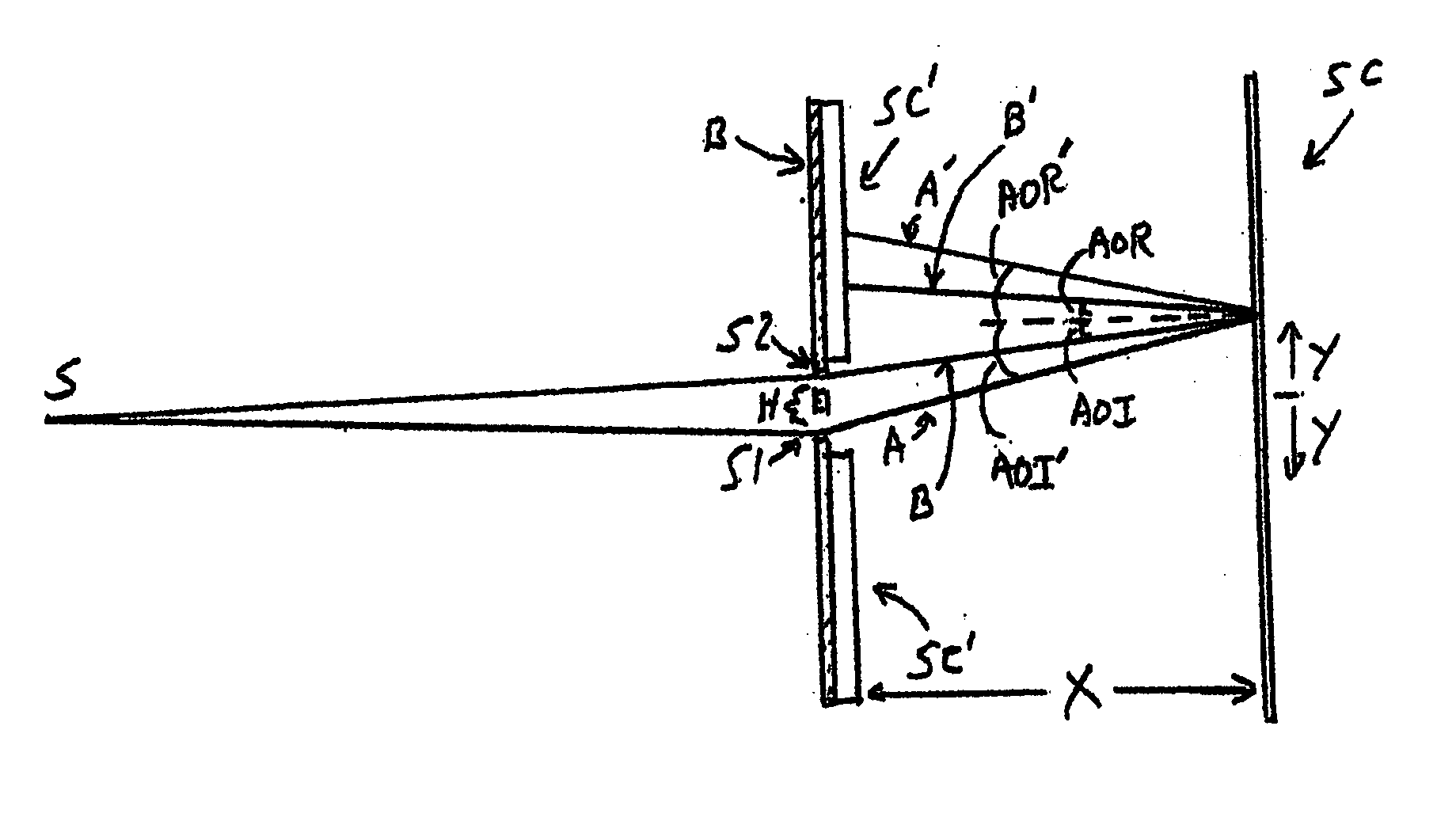
Controlling contamination particle trajectory from a beam-line electrostatic element
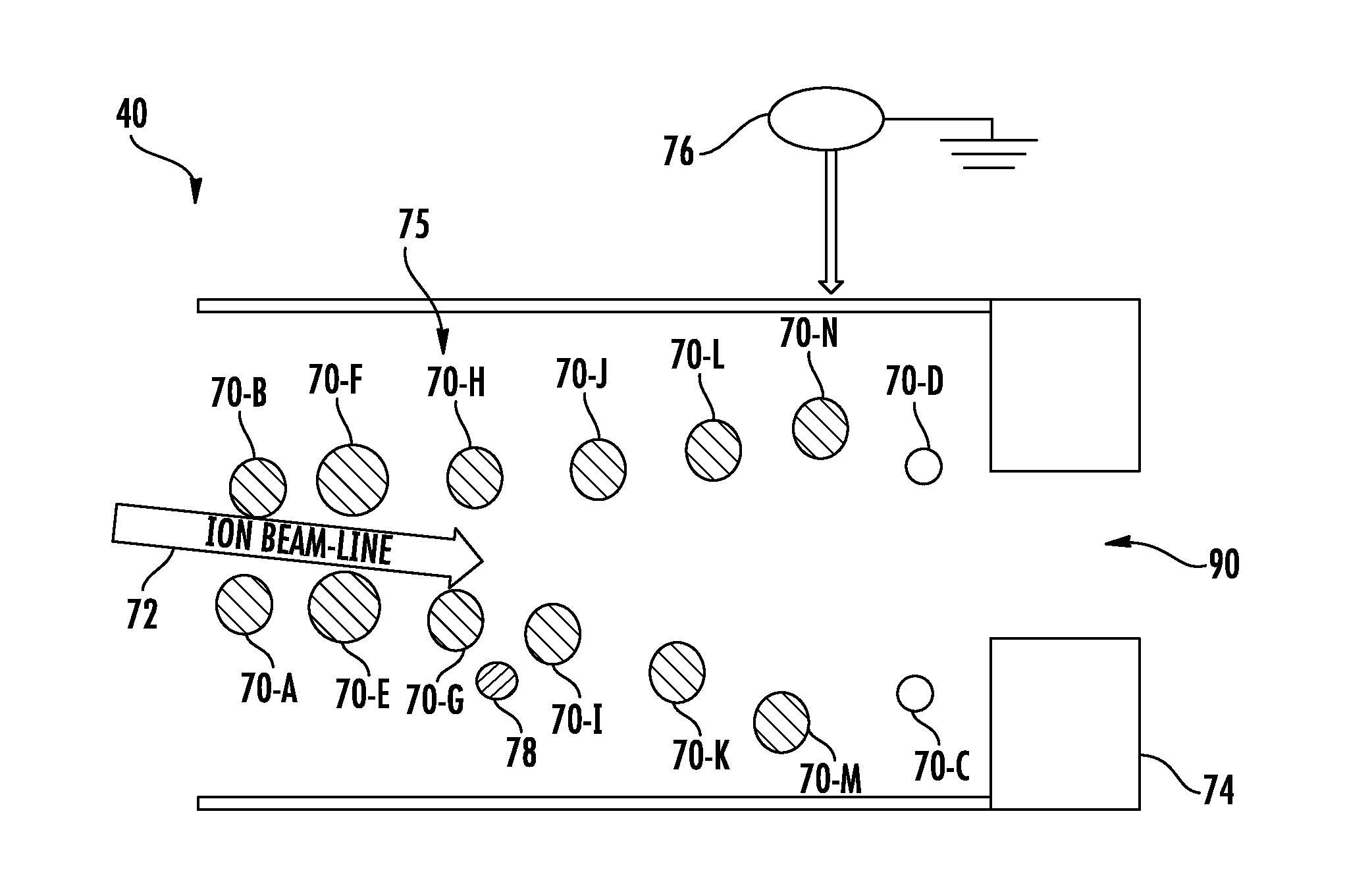
Provided herein are approaches for controlling particle trajectory from a beam-line electrostatic element. In an exemplary approach, a beam-line electrostatic element is disposed along a beam-line of an electrostatic filter (EF), and a voltage is supplied to the beam-line electrostatic element to generate an electrostatic field surrounding the beam-line electrostatic element, agitating a layer of contamination particles formed on the beam-line electrostatic element. A trajectory of a set of particles from the layer of contamination particles is then modified to direct the set of particles to a desired location within the EF. In one approach, the trajectory is controlled by providing an additional electrode adjacent the beam-line electrostatic element, and supplying a voltage to the additional electrode to control a local electrostatic field in proximity to the beam-line electrostatic element. In another approach, the trajectory is influenced by one or more geometric features of the beam-line electrostatic element.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
Multiple numerical aperture electron beam projection lithography system
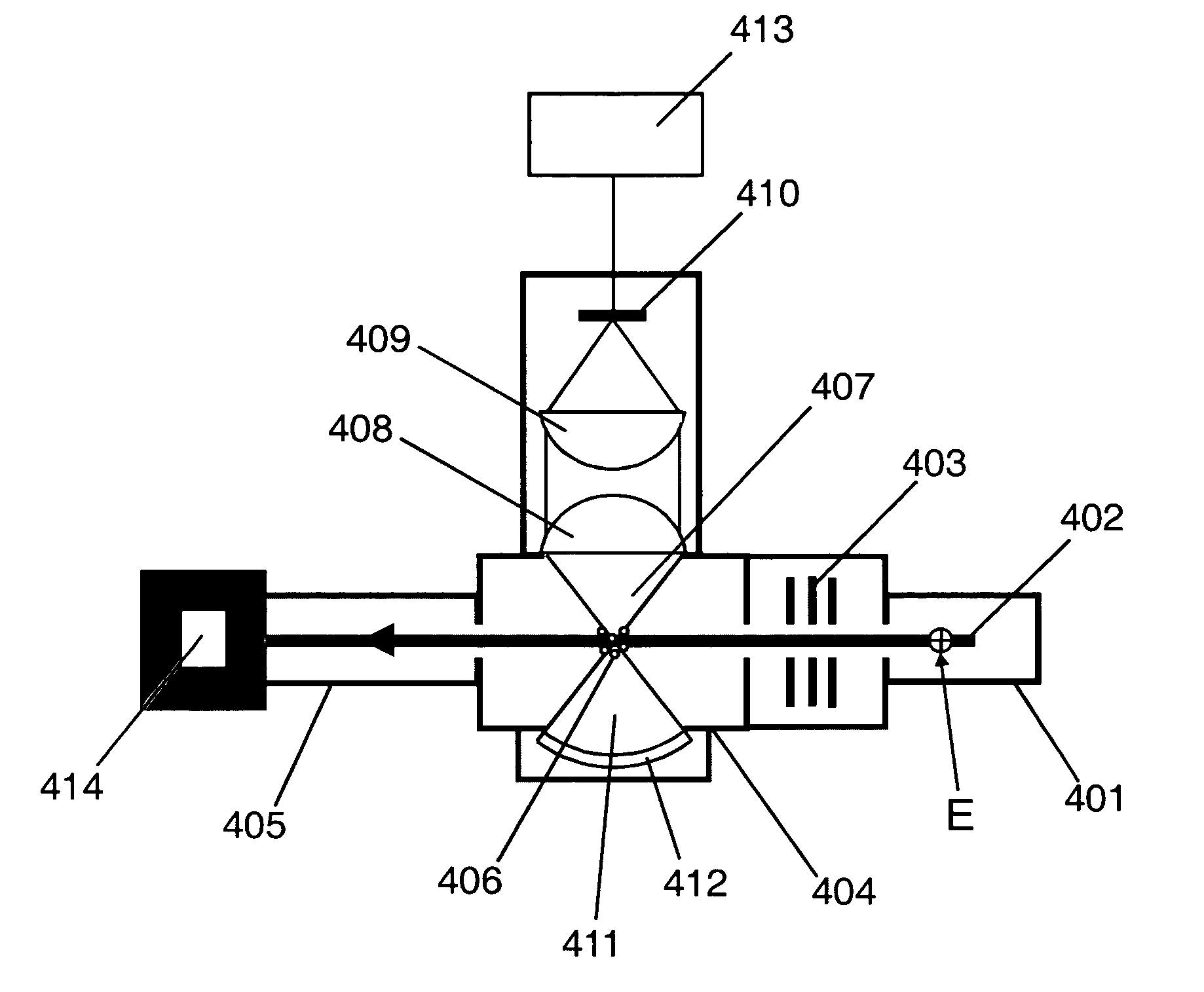
A beam-limiting aperture truncates selected portions of a charged particle beam illuminating portions such as subfields of a patterned reticle of a charged particle beam projection lithography tool and then projects a pattern of charged particles onto a target in a charged particle beam lithography tool. The respective portions of the reticle are patterned in accordance with respective portions of an integrated circuit or other desired pattern and may have differing transmissivities; altering beam current at the target even when source beam current remains substantially constant. The portion of the beam which is truncated, thus altering the particle trajectory semi-angle and numerical aperture of the tool is controlled in accordance with the transmissivity of the reticle portion to enhance resolution to near optimal limits.
Owner:NIKON CORP
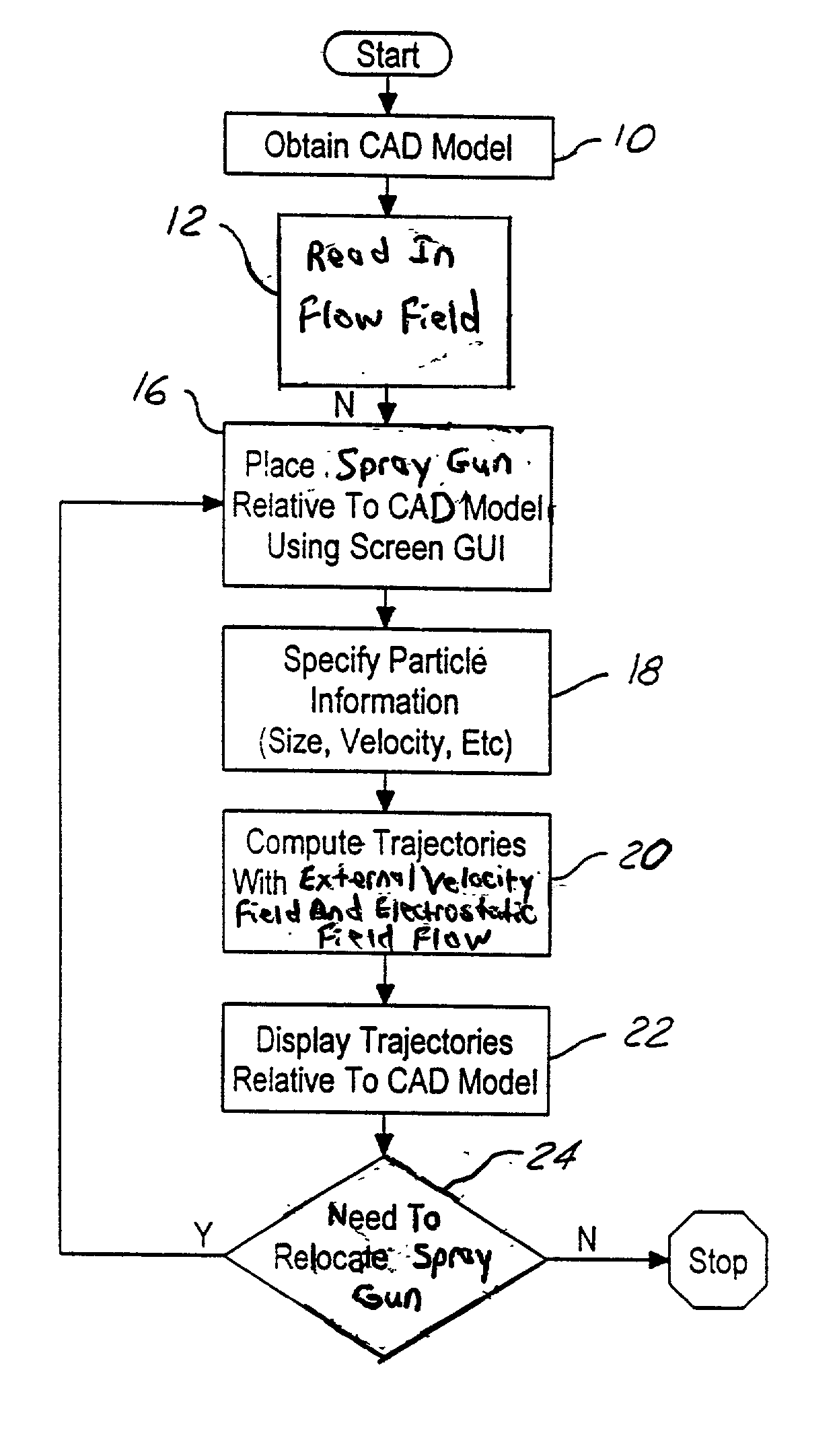
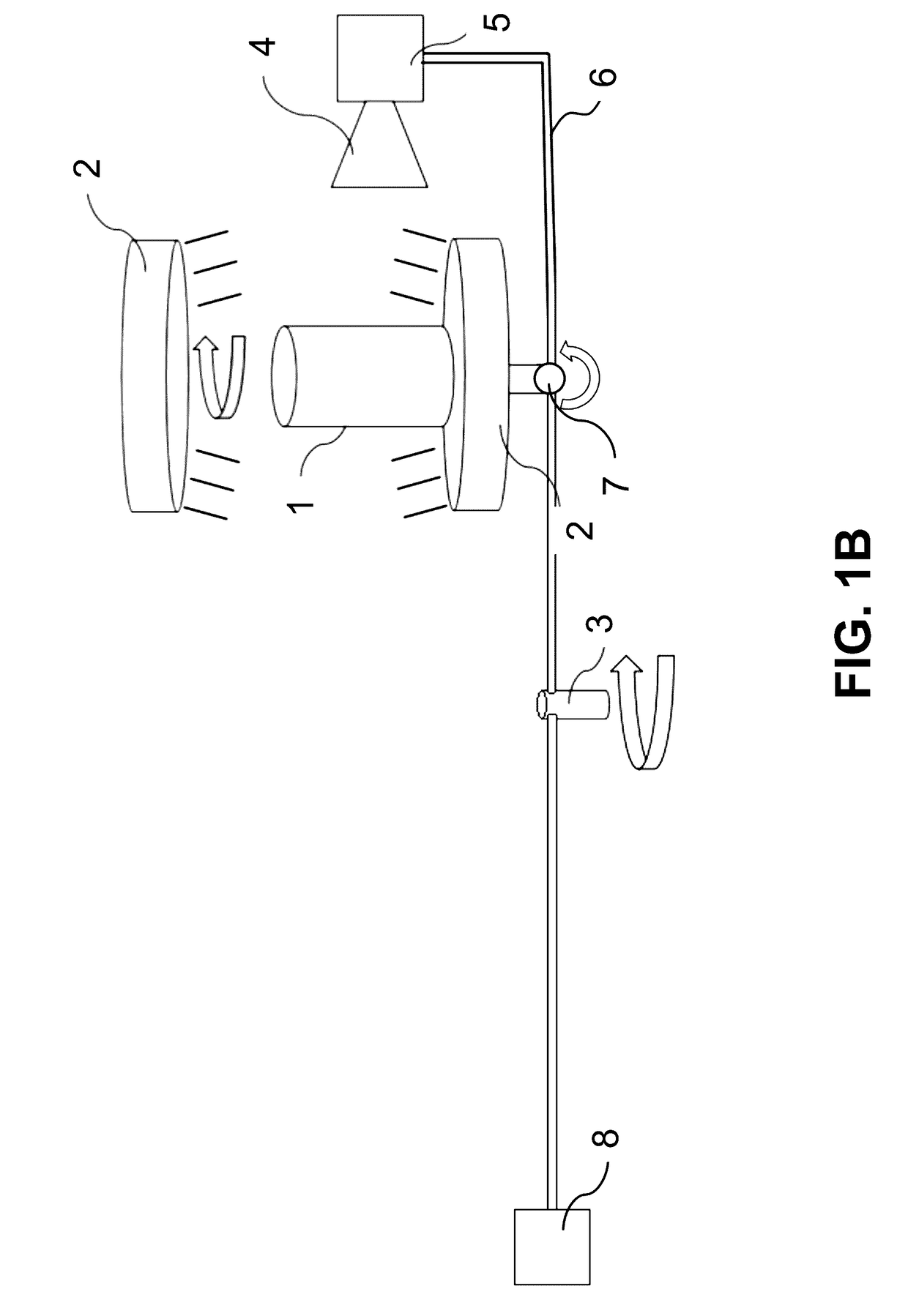
Paint spray particle trajectory analysis method and system
A system and method of analyzing paint spray particle trajectory on a vehicle with a computer aided design (CAD) model representative of the vehicle. The method includes the steps of preparing a CAD model of a desired portion of the vehicle and placing a paint spray gun at a desired location with respect to the desired portion of the vehicle. The method also includes the steps of specifying a set of particle information describing particles to be sprayed from the paint spray gun and computing a trajectory for a particle stream emanating from the paint spray gun. The method further includes the steps of displaying the trajectory relative to the desired portion of the vehicle on a display to permit visual observation thereof and relocating the paint spray gun if necessary to achieve a desired trajectory.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Light scattering detector
InactiveUS20070296971A1High sensitivityEffective guidanceComponent separationWithdrawing sample devicesAngle of incidenceCurrent mode
The invention concerns high sensitivity light scattering detection and its application to evaporative light scattering detection in liquid chromatography. The exemplary embodiment includes a detection cell to accept particles suspended in a gas stream and permit a polarized light beam to pass through a trajectory of the particles and gas stream. A sample light detector is disposed to detect light scattered in the detection cell. A light trap accepts the polarized beam after it passes through the detection cell. The light trap includes an elongated housing through which the polarized beam passes, and light absorptive material within the elongated housing. An absorptive filter is aligned such that the angle of incidence of the light beam upon the filter approximates Brewster's angle and the electric field vector of the beam is aligned with the plane of incidence between the beam and the filter. Other embodiments of the invention provide increased light collection. Embodiments of the invention include temperature-controlled entrance and exit ports that control particle trajectory. Embodiments of the invention include a reference cell disposed between a detection cell and a light trap, and the reference cell includes lensing and a spherical mirror to direct light toward a reference light detector. The reference light detector provides a reference signal that may be used with noise cancellation circuitry, operating in either voltage or current mode, to reduce light source noise in the sample signal.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Detection method of crowd flow anomaly events in monitoring video of congested scenes
ActiveCN106778688AImprove stabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionHierarchical cluster algorithmVisual technology
The invention provides a detection method of crowd flow anomaly events in monitoring a video of congested scenes, and relates to the technical field of computer vision. The method comprises the steps of firstly, obtaining a short trajectory segment of particle motion through correlating the light streams between multiple continuous frames; using the hierarchical clustering algorithm to cluster the unstable light stream trajectory segments to make adjacent and similar trajectory segments concentrate to become small areas with statistical significance and enhance the reliability of motion description; finally, detecting crowd flow anomaly events through calculating the main direction and motion scope of the particles in the small areas to provide pre-warning to potential safety accidents. According to the detection method of crowd flow anomaly events in monitoring video of congested scenes, the clustering of the particle trajectory segments can make a single unreliable particle trajectory able to be co-used with peripheral similar particle trajectory to describe the crowd flow motion and enhance the stability of motion description. Tests are carried out on monitoring videos of actual scenes, the result indicates that the method can effectively detect the crowd flow anomaly events, and the results of the clustering of divided trajectory segments have a strong adaptability.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
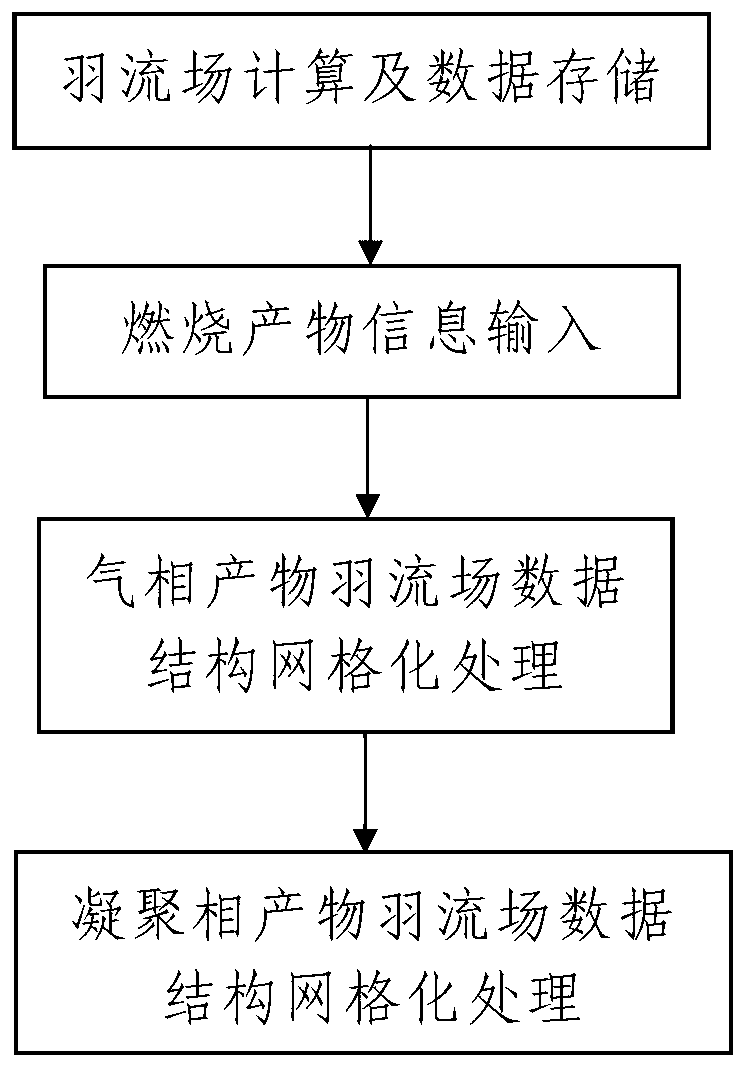
Structure gridding processing method of plume field data for formula design of solid propellant
ActiveCN103218504AThe method steps are simpleReasonable designSpecial data processing applicationsJet flowGas phase
The invention discloses a structure gridding processing method of plume field data for a formula design of solid propellant. The method comprises the steps of: 1, plume field calculation and data storage; 2, combustion product information input; 3, structure gridding processing of gaseous product plume field data, wherein the processing process comprises the following steps of: reading gaseous product plume field data in a jet flow area, building a structure grid chart, and carrying out structure gridding processing of the gaseous product plume field data; and 4, structure gridding processing of condensed product plume field data, wherein the processing process comprises the following steps of: setting initial parameters, reading particle trajectory data, obtaining the quantity of rectangular grids at nozzle inlets of a motor, confirming upper and lower boundaries of the rectangular grids of each nozzle inlet, and carrying out the structure gridding processing of the condensed product plume field data. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple steps, reasonable design, convenience in realization, good using effect and capability of simply, conveniently and rapidly converting an unstructured grid based flow field data into a structured grid based corresponding data for subsequent calculation use.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Fabrication and Operation of Multi-Function Flexible Radiation Detection Systems
ActiveUS20170200762A1Enhanced signalMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesSpectroscopySemiconductor
Curved, flexible arrays of radiation detectors are formed by using standard silicon semiconductor processing materials and techniques and additional functionalization through integration of conversion and shielding materials. The resulting flexible arrays can be handled, integrated, further functionalized and deployed for a wide variety of applications where conventional sensors do not provide the desired functionality, form factors and / or reliability. The arrays can be stacked and include multiple types and thicknesses of conversion layers, enabling the detector to simultaneously detect multiple radiation types, and perform complex, simultaneous functions such as energy discrimination, spectroscopy, directionality detection, and particle trajectory tracking of incident radiation.
Owner:MPOWER TECH
Method of sorting particulate matter
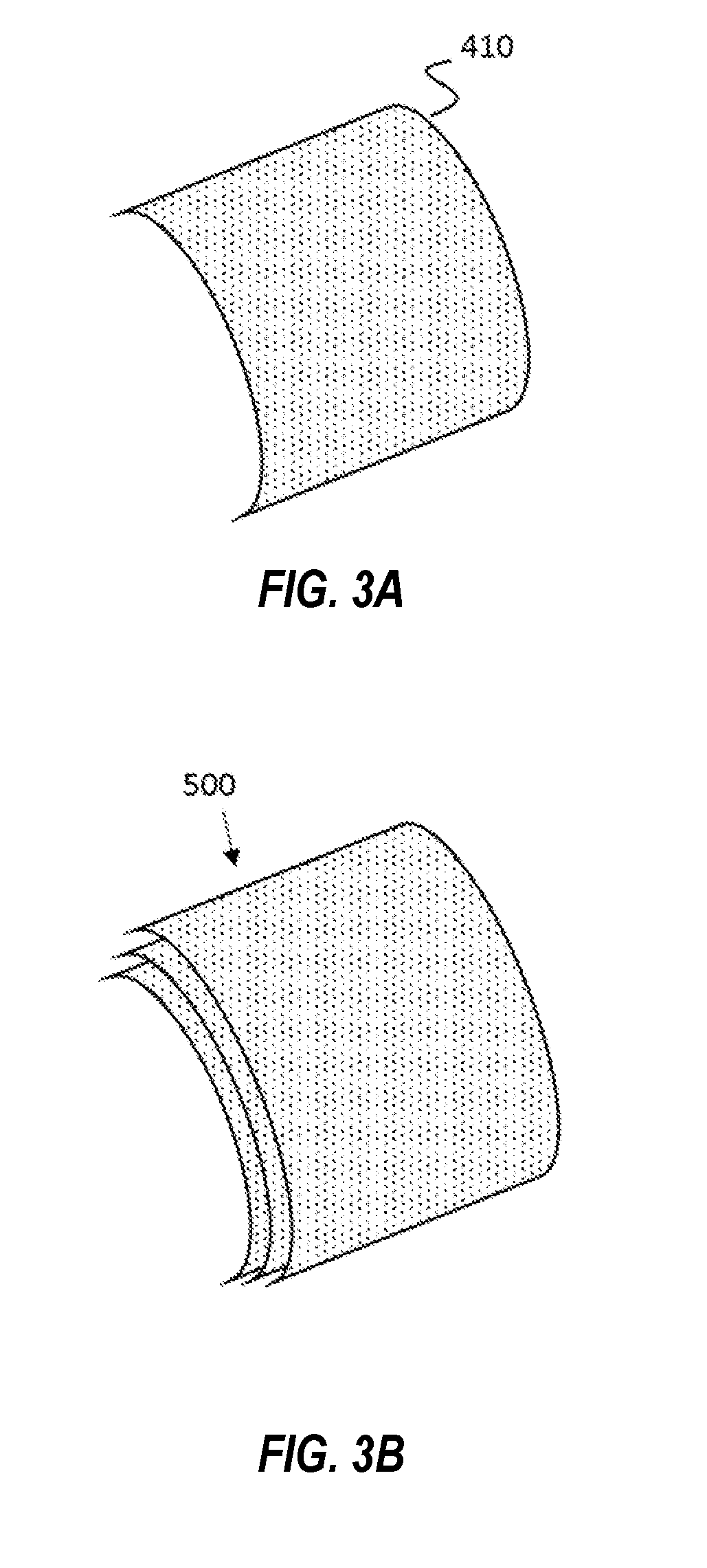
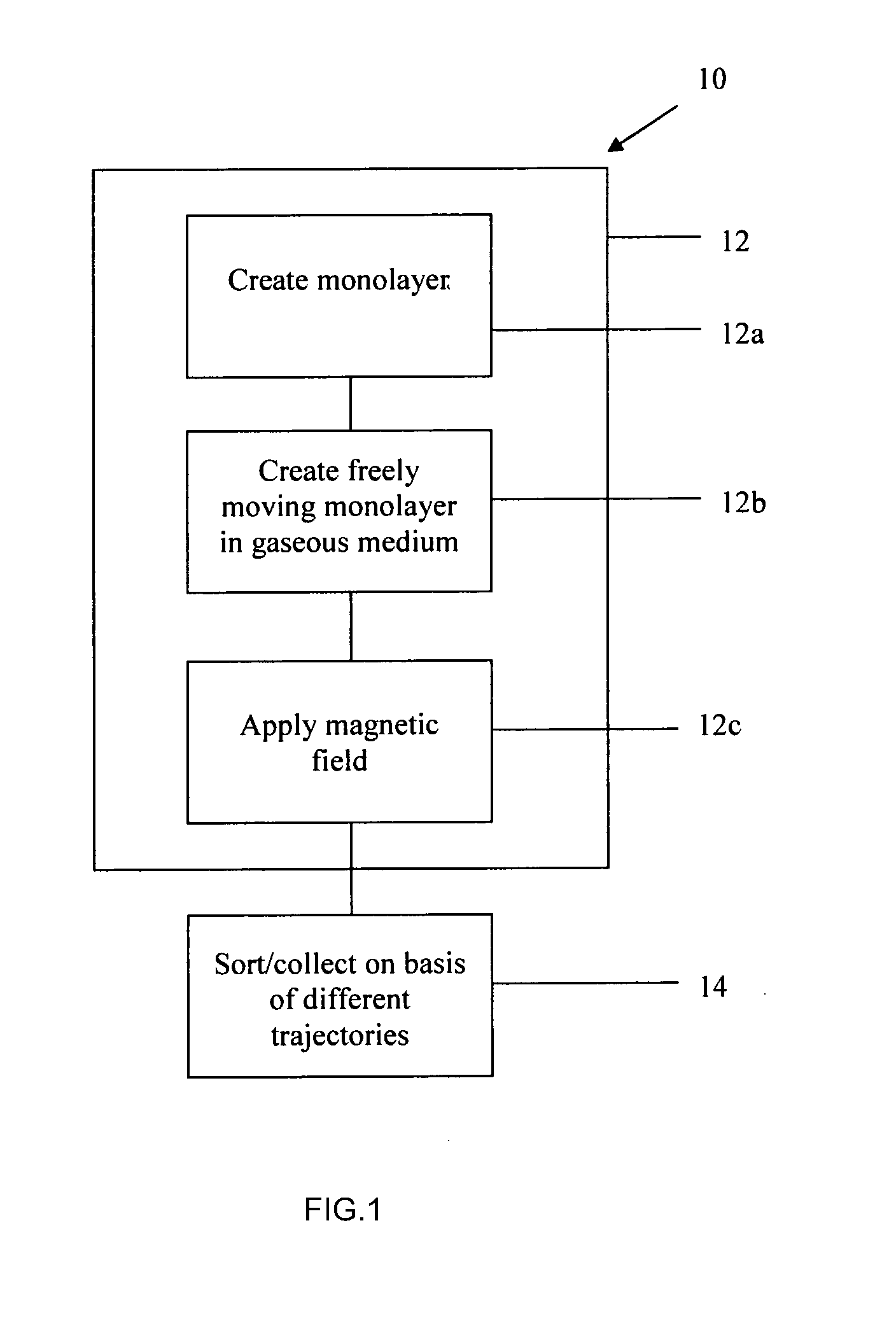
InactiveUS8919566B2Advantageously producedDifference in magnetic susceptibilityHigh gradient magnetic separatorsSortingParticulatesParticle physics
A method of sorting particulate matter comprises creating an unconstrained monolayer feed stream of particulate matter moving with an initial first trajectory in a gaseous medium, and subjecting the monolayer feed stream while in the gaseous medium to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to influence the trajectory of at least some particles in the feed stream to cause a spread of particle trajectories from the first trajectory. The particles are subsequently sorted and / or collected on the basis of their trajectories.
Owner:CURTAIN UNIV OF TECH
Method of Sorting Particulate Matter
InactiveUS20120199520A1Advantageously producedDifference in magnetic susceptibilityMagnetic separationSortingParticulatesParticle physics
A method of sorting particulate matter comprises creating an unconstrained monolayer feed stream of particulate matter moving with an initial first trajectory in a gaseous medium, and subjecting the monolayer feed stream while in the gaseous medium to a magnetic field of sufficient strength to influence the trajectory of at least some particles in the feed stream to cause a spread of particle trajectories from the first trajectory. The particles are subsequently sorted and / or collected on the basis of their trajectories
Owner:CURTAIN UNIV OF TECH
Controlling contamination particle trajectory from a beam-line electrostatic element
Provided herein are approaches for controlling particle trajectory from a beam-line electrostatic element. In an exemplary approach, a beam-line electrostatic element is disposed along a beam-line of an electrostatic filter (EF), and a voltage is supplied to the beam-line electrostatic element to generate an electrostatic field surrounding the beam-line electrostatic element, agitating a layer of contamination particles formed on the beam-line electrostatic element. A trajectory of a set of particles from the layer of contamination particles is then modified to direct the set of particles to a desired location within the EF. In one approach, the trajectory is controlled by providing an additional electrode adjacent the beam-line electrostatic element, and supplying a voltage to the additional electrode to control a local electrostatic field in proximity to the beam-line electrostatic element. In another approach, the trajectory is influenced by one or more geometric features of the beam-line electrostatic element.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
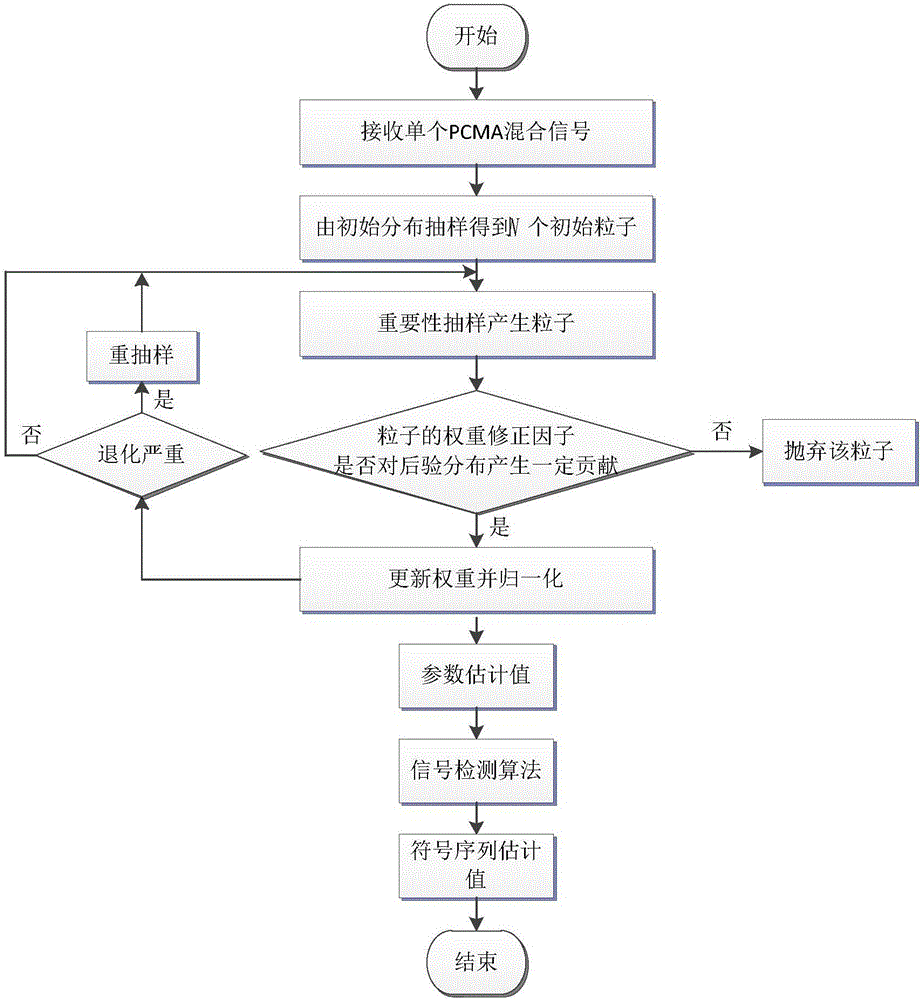
PCMA signal single-channel blind separation method based on improved particle filter
InactiveCN105791183AReduce calculation precisionSmall amount of calculationChannel estimationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation processMinimum mean square error
The invention provides a PCMA signal single-channel blind separation method based on an improved particle filter and belongs to the technical field of signal processing. The method is characterized by carrying out framing processing on a received single PCMA signal, determining parameter value range and distribution and initializing particles; carrying out updating according to a significance sampling function and a particle trajectory before the current time to obtain new particles; calculating particle importance weight values and setting a threshold value to discard particles, which contribute little to posteriori distribution, so that calculation is simplified by dynamically adjusting the total number of the particles; after obtaining parameter estimation values of two paths of uplink signals by utilizing a linear minimum mean square error criterion, designing a parameter-known signal separation method, and in the recursive calculation process of a likelihood function, discarding trajectories, the quality of which is poor, to further reduce calculation amount; and finally, obtaining symbol sequence estimation values of the two paths of uplink signals by utilizing a maximum likelihood criterion. Compared with the original algorithm, which adopts a state exhaustive method, the method can obviously reduce the calculation amount; and the method discards the poor-quality particles, so that computation accuracy required by real-time realization of the algorithm is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Charged-particle condensing device
InactiveUS8013296B2Improve utilization efficiencyAdd additional massStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersPotential wellAxis of symmetry
Ions and charged droplets move from the nozzle (6) towards the orifice (22) of a charged-particle transport device or the desolvation pipe (7). This particle motion is governed by the distribution of the pseudo-potential along particle trajectories. There are RF-voltages applied to neighboring electrodes (241-246) of the electrode array (24) cause the charged particles to substantially hover above the electrode array (24). Right before the ions come to the electrode array (24) they thus experience a repelling force “F” perpendicular to the surface of the electrode array (24). This force “F” causes an effective barrier (B) right before the electrode array (24) and consequently a pseudo-potential well (A) where the charged particles stop their motion parallel to the plume axis (D). Thus they accumulate around the center line (C) of this well (A). Applying additionally to the RF-potentials also DC-potentials to neighboring electrodes within the electrode array (24) small DC-fields can be formed within the well area (23). These additional DC-fields drive the charged particles towards the axis of symmetry (C) and thus towards the orifice (22) of a charged-particle transport device or the desolvation pipe (7). Thus, many of the charged particles which would normally impinge on the wall (21) around the orifice (22) can now be analyzed.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method of Providing Impact in Vacuum
InactiveUS20140233687A1Increase vacuumEasily be made sufficiently coldNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorGreat circleLarge distance
In space, a linear accelerator firing charged pellets can be situated at a large distance from a target at which the pellets are aimed. The accelerator can fire a graduated-speed train of pellets over a period of seconds or longer which arrive at the target simultaneously, and impart a large pulse of energy. An accelerator of modest power can thus provide a pulse in the megajoule range, sufficient to ignite fusion. It is necessary to provide course corrections to the pellets, to bring them together with very high precision as they approach the target. An ideal siting is to place the accelerator at the Earth-Moon L1 or L2 Lagrange point, and the fusion target at a point on the surface of the Moon where the pellets will strike at grazing incidence, i.e. on a great circle intersecting the lunar poles. Length of the particle trajectory is over 60000 km
Owner:JACK COLIN
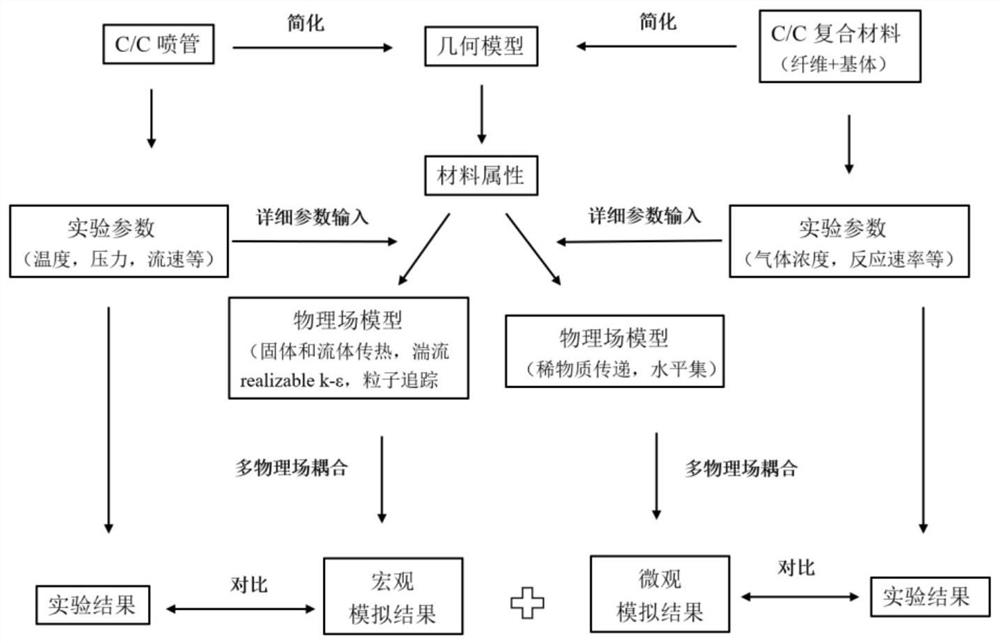
Modeling simulation method for ablation behavior of C/C composite material nozzle of solid rocket engine
The invention discloses a modeling simulation method for an ablation behavior of a C / C composite material nozzle of a solid rocket engine, which comprises the following steps of: establishing a multi-scale ablation model of the C / C composite material nozzle, comprehensively considering the processes of gas flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, mechanical erosion of particles, chemical reaction of gas and the like, and obtaining the temperature field, flow field and pressure distribution conditions of the nozzle; analyzing and judging the mechanical erosion degree of each part of the nozzle according to a particle trajectory result, stimulating the retreat and morphology of the microscopic surface of the C / C composite material by utilizing a level set method, and revealing the thermochemical ablation rule of fibers and a matrix. According to the method, the ablation condition of the C / C composite nozzle is comprehensively analyzed from the macroscopic angle and the microscopic angle, and the method has important value for thermal performance research and fine design of the nozzle.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
High-definition particle detection during centrifugation
InactiveUS20170153431A1Quick identificationAvoid blurHigh-speed photographyMicroscopesAxis of symmetryCentrifugation
High-definition particle detection during centrifugation of a pharmaceutical liquid is provided. Centrifugation of fluid containers drives particles to the interior surface of the container if the particles are denser than the fluid and to the middle of the container if the particles are less dense than the fluid. The imager can then be focused directly on the particle itself for rapid identification without the need for computing complex particle trajectories. If the centrifugation of the container is carried out at an angle to the axis of symmetry of the container, particles can be driven to a single line on the interior surface of the container by the centrifugal force, making the identification of the particles even more straightforward than in two dimensions. The particle imager can also be attached to the rotating container to prevent blurring of the particle image due to the relative motion of the container and imager.
Owner:ZEBRASCI
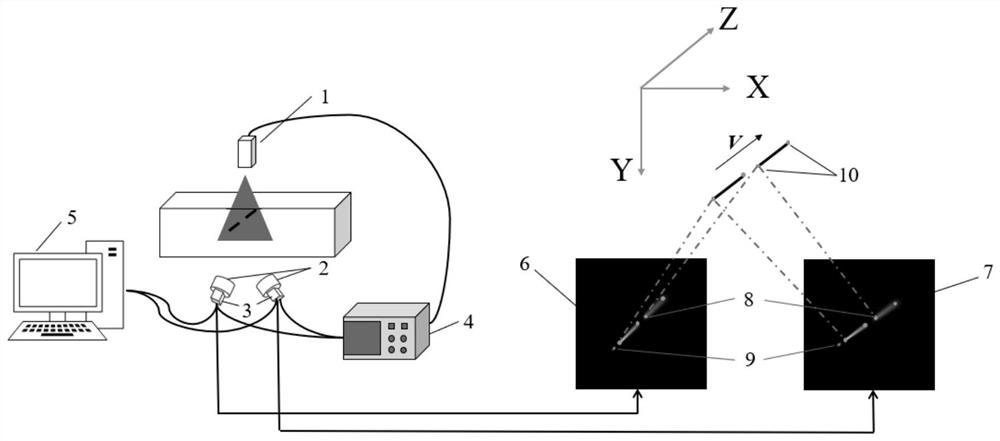
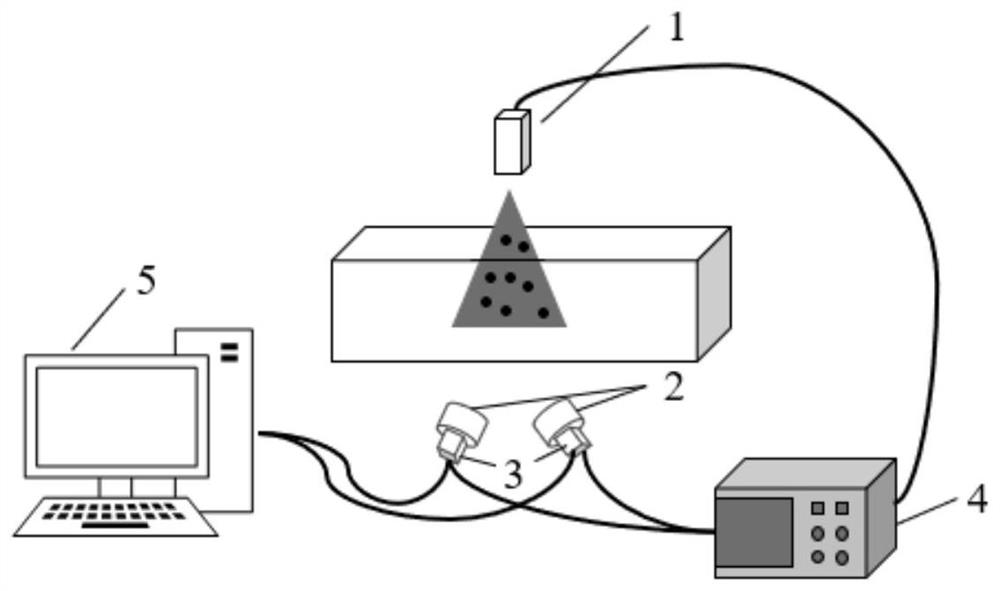
Particle trajectory speed measurement device and method combining compound blur and binocular imaging
PendingCN112710864AImprove recognition accuracyEasy to handleImage enhancementAcceleration measurement using interia forcesLight signalSignal generator
The invention relates to a particle trajectory speed measurement device and method combining compound blur and binocular imaging. A light source illuminates a to-be-measured flow field, double lenses and double cameras are fixedly connected with each other in a one-to-one correspondence manner; the constructed two sets of lenses and cameras are arranged at a fixed angle, and the two sets of lenses can observe the to-be-measured flow field at the same time; a signal generator provides a stroboscopic signal for the light source, single-frame multi-exposure combining long exposure and short exposure is achieved; and the signal generator provides a synchronous trigger signal for the double cameras and the light source; the double cameras shoot flow field images and send the flow field images to a computer; and the computer obtains single-frame multi-exposure images of a binocular vision system under two different visual angles, and calculates the three-dimensional flowing speed and acceleration of particles of the to-be-measured flow field. With a three-dimensional flow field motion information acquisition technology combining particle trajectory speed measurement, compound blur and binocular imaging adopted, a microscopic flow field and a high-speed flow field are tested; a measurement system is simplified, a data processing process is optimized; and three-dimensional flow field measurement of the microscopic flow field or the high-speed flow field can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for investigating photon or particle trajectory and interference pattern formation in double slit experiments
Owner:WELCH JAMES D
Fabrication and operation of multi-function flexible radiation detection systems
ActiveUS10483316B2Enhanced signalMeasurement with semiconductor devicesSolid-state devicesSpectroscopySemiconductor
Curved, flexible arrays of radiation detectors are formed by using standard silicon semiconductor processing materials and techniques and additional functionalization through integration of conversion and shielding materials. The resulting flexible arrays can be handled, integrated, further functionalized and deployed for a wide variety of applications where conventional sensors do not provide the desired functionality, form factors and / or reliability. The arrays can be stacked and include multiple types and thicknesses of conversion layers, enabling the detector to simultaneously detect multiple radiation types, and perform complex, simultaneous functions such as energy discrimination, spectroscopy, directionality detection, and particle trajectory tracking of incident radiation.
Owner:MPOWER TECH
Paint spray particle trajectory analysis method and system
A system and method of analyzing paint spray particle trajectory on a vehicle with a computer aided design (CAD) model representative of the vehicle. The method includes the steps of preparing a CAD model of a desired portion of the vehicle and placing a paint spray gun at a desired location with respect to the desired portion of the vehicle. The method also includes the steps of specifying a set of particle information describing particles to be sprayed from the paint spray gun and computing a trajectory for a particle stream emanating from the paint spray gun. The method further includes the steps of displaying the trajectory relative to the desired portion of the vehicle on a display to permit visual observation thereof and relocating the paint spray gun if necessary to achieve a desired trajectory.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com