Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1046 results about "Biomass gasification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
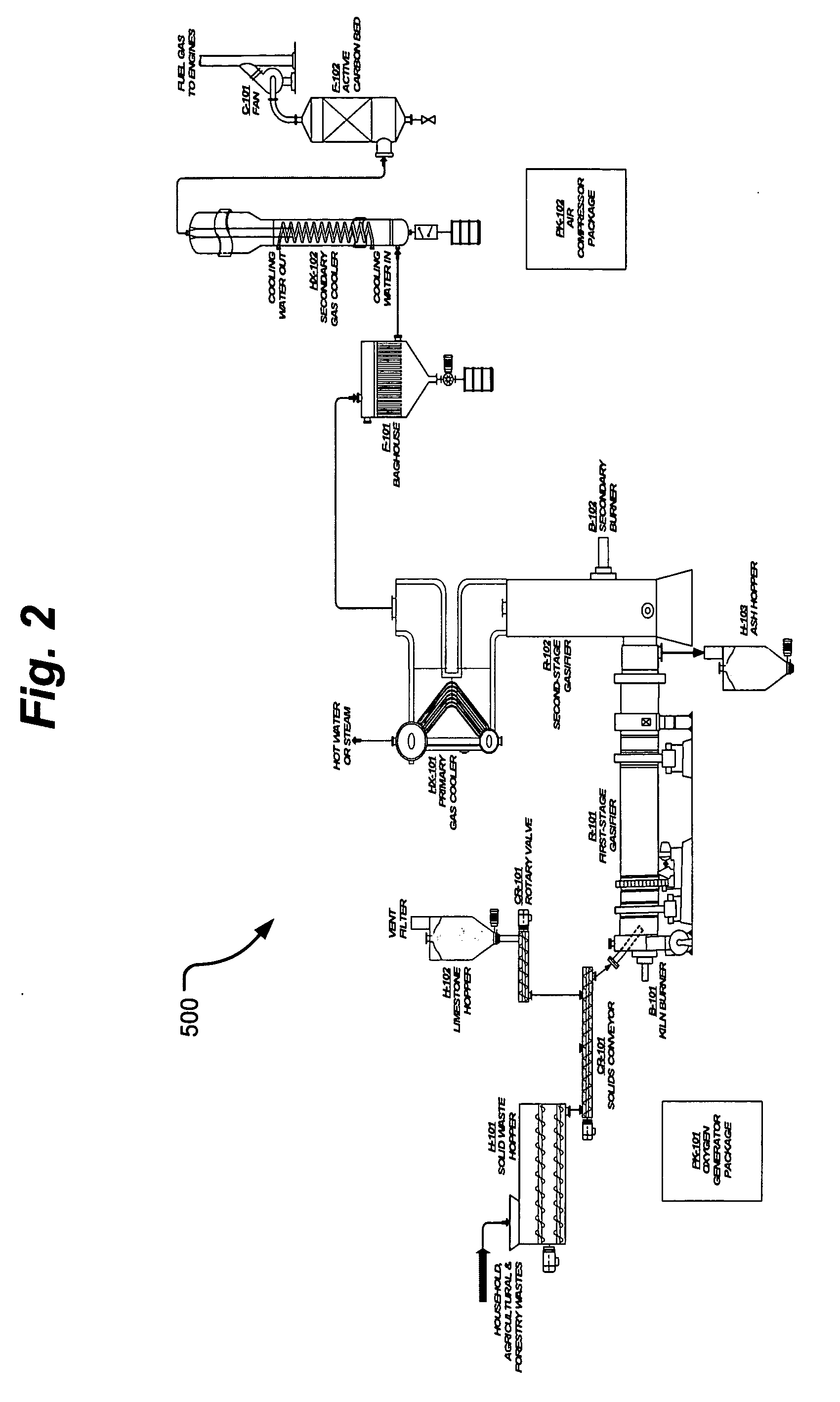
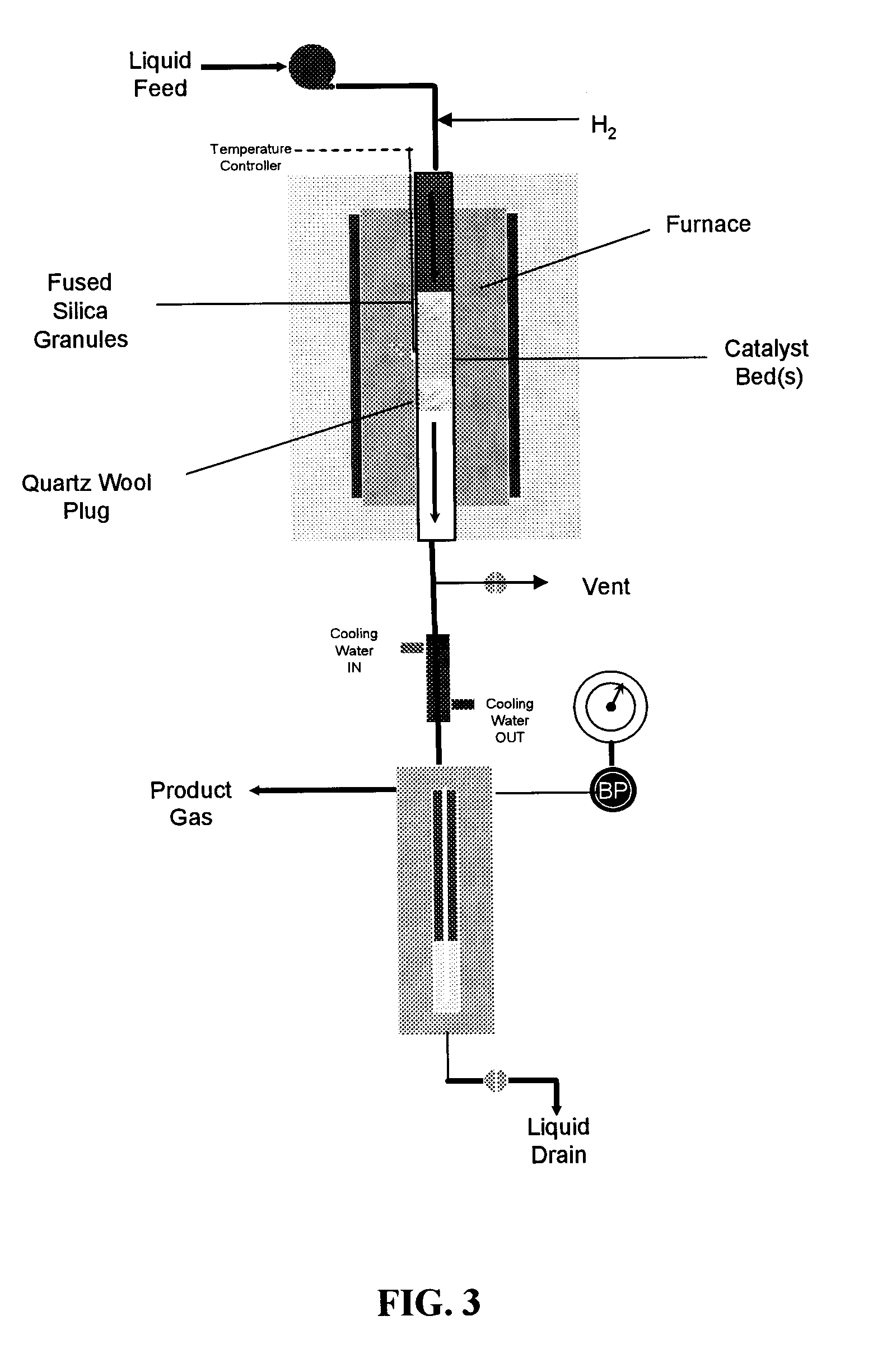
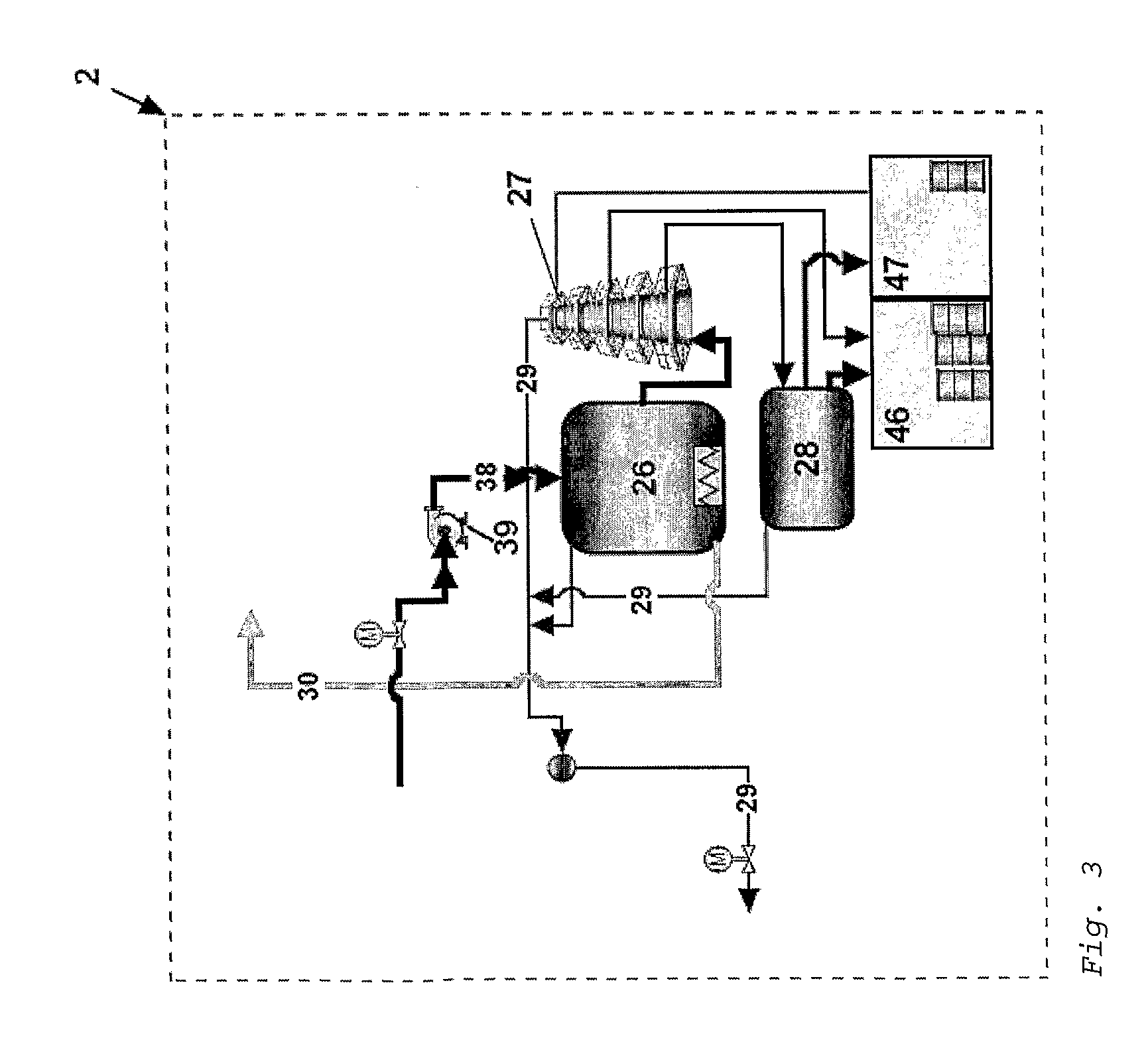
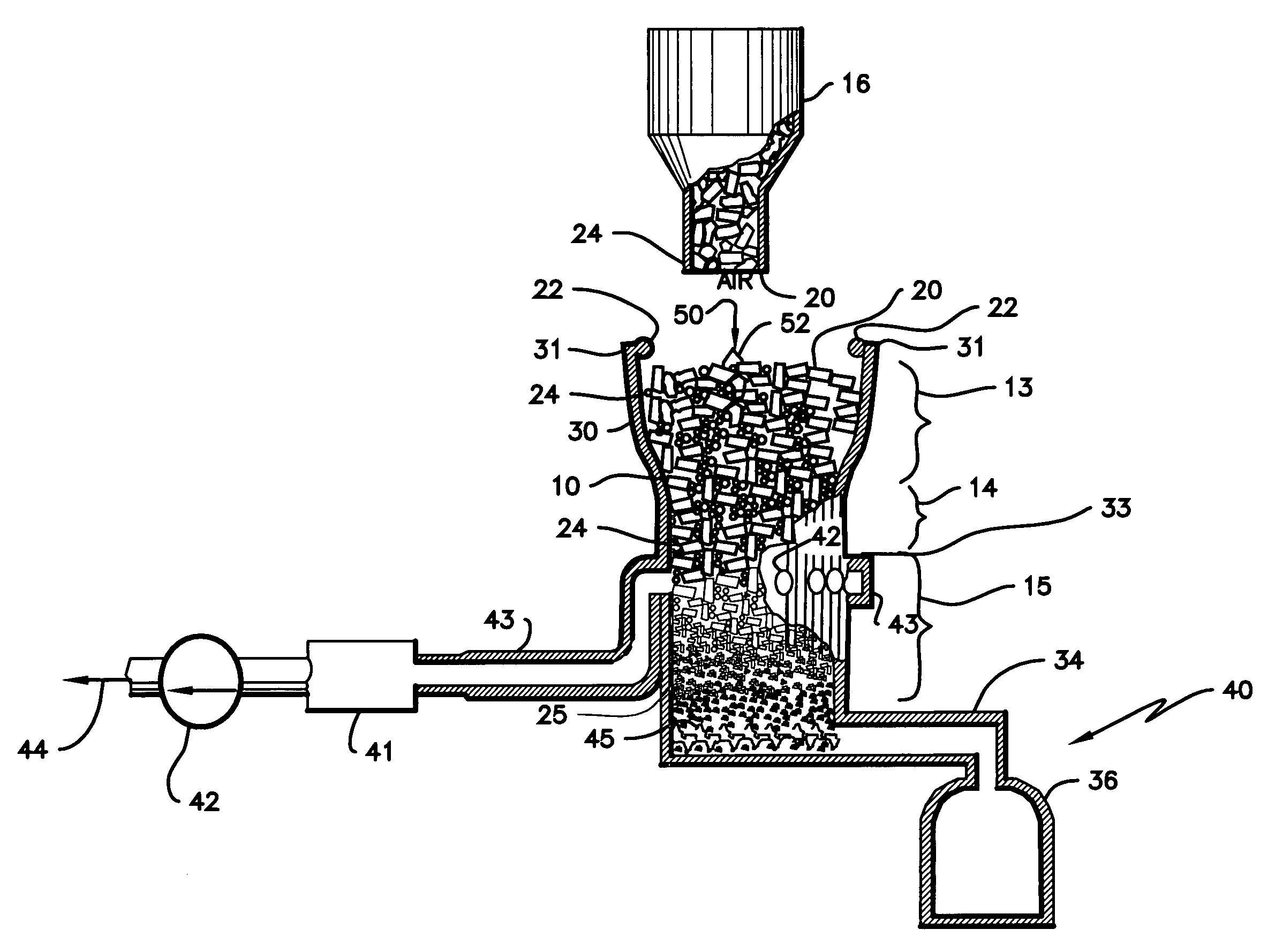
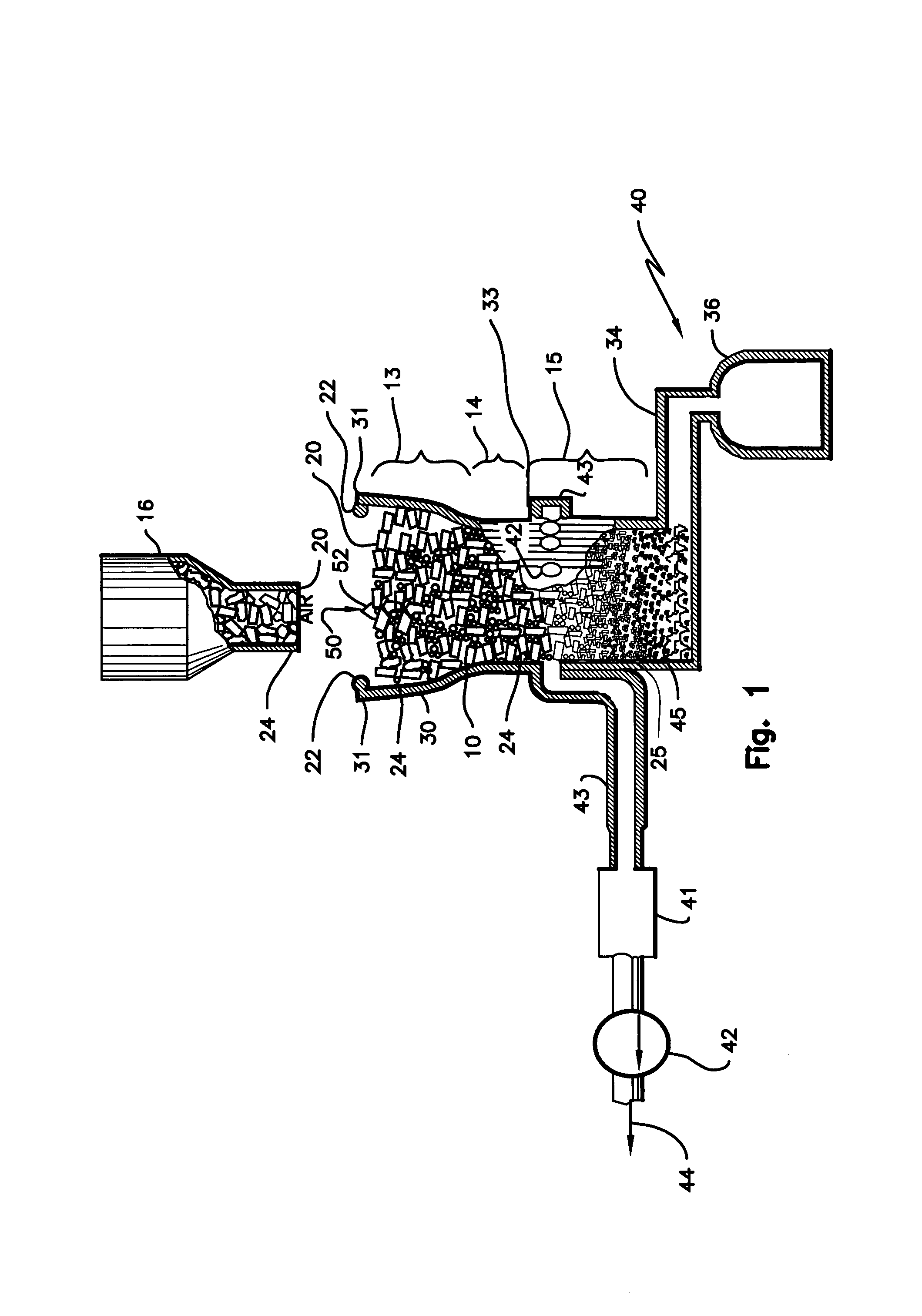
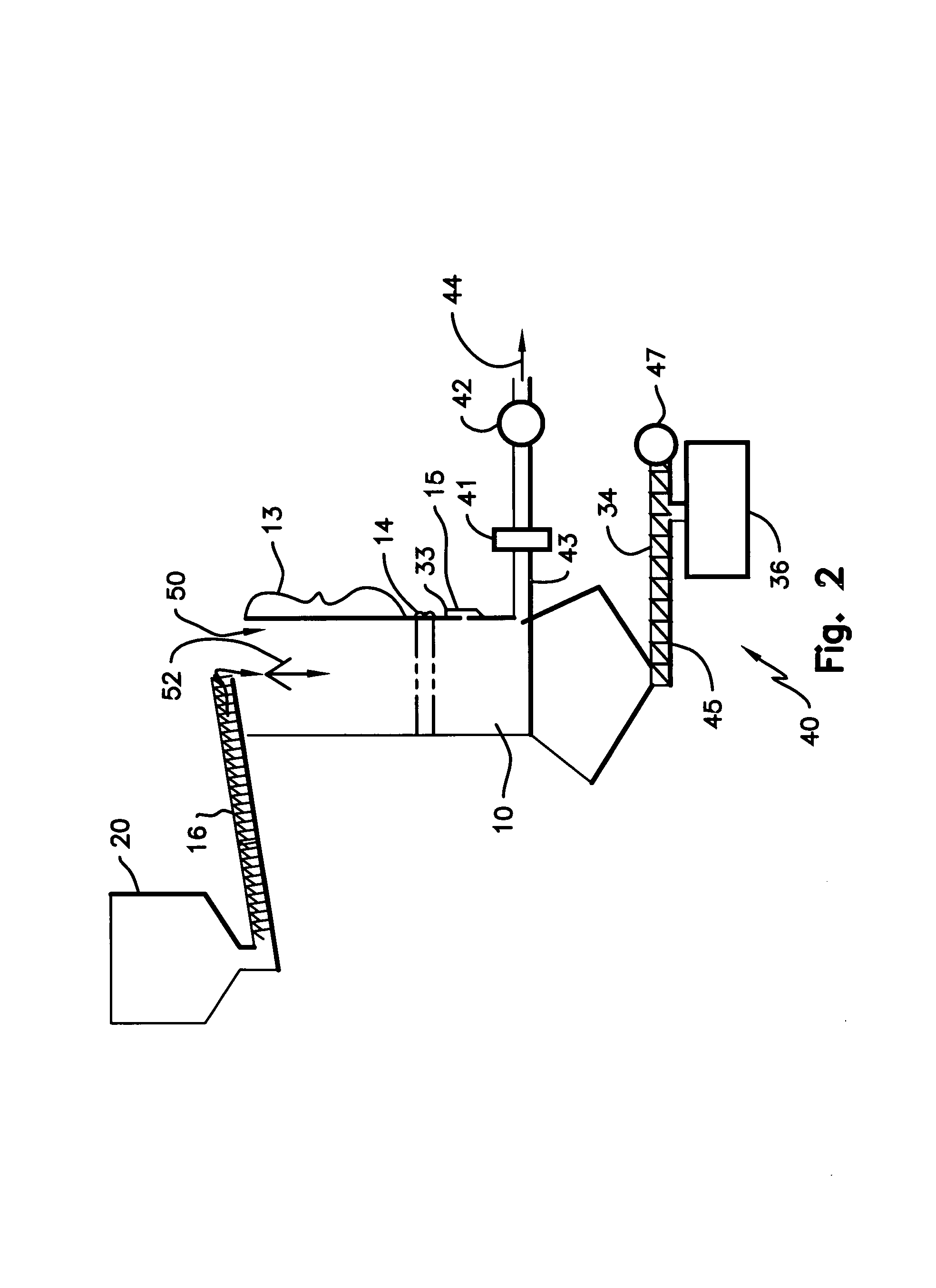
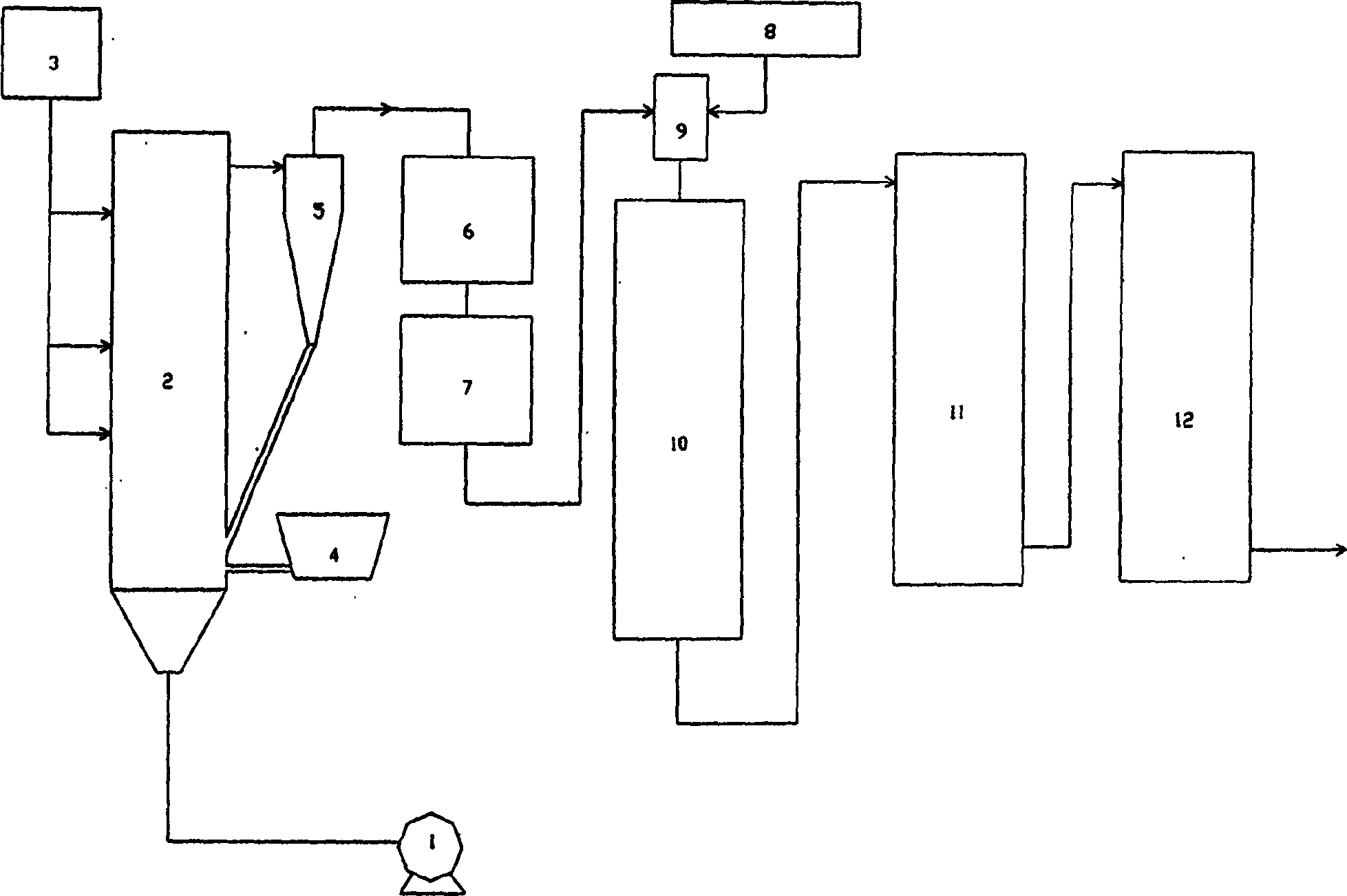
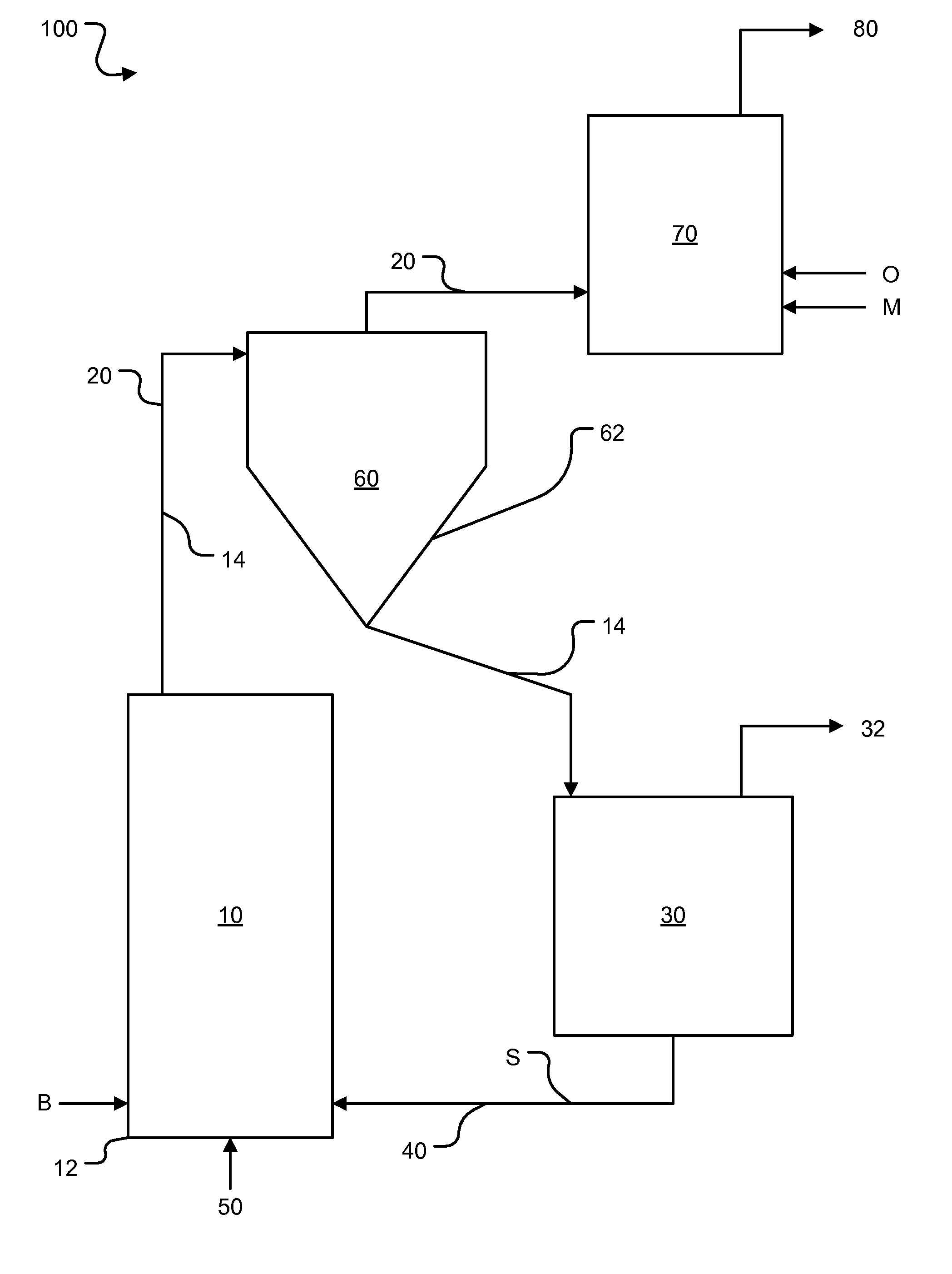
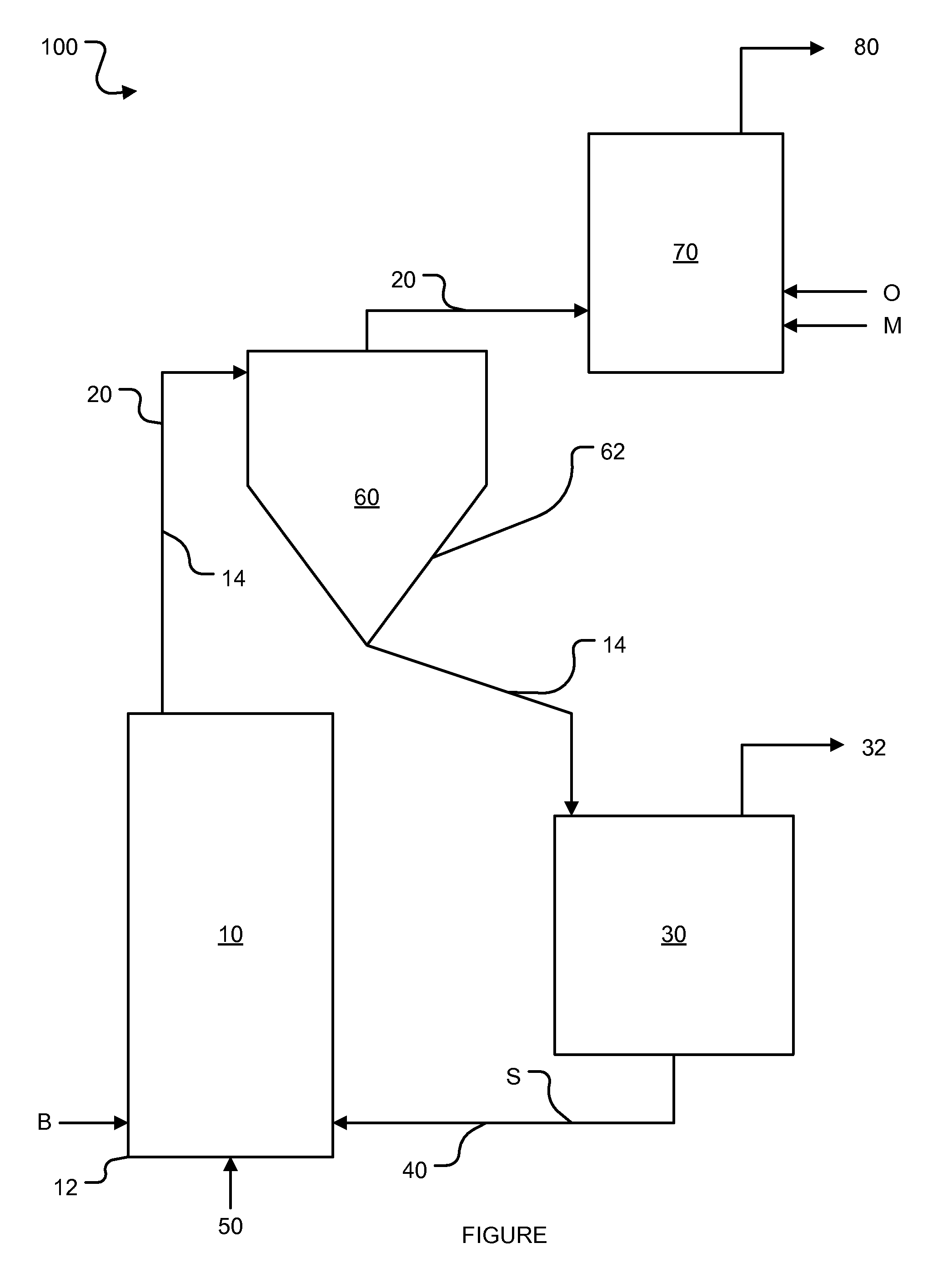
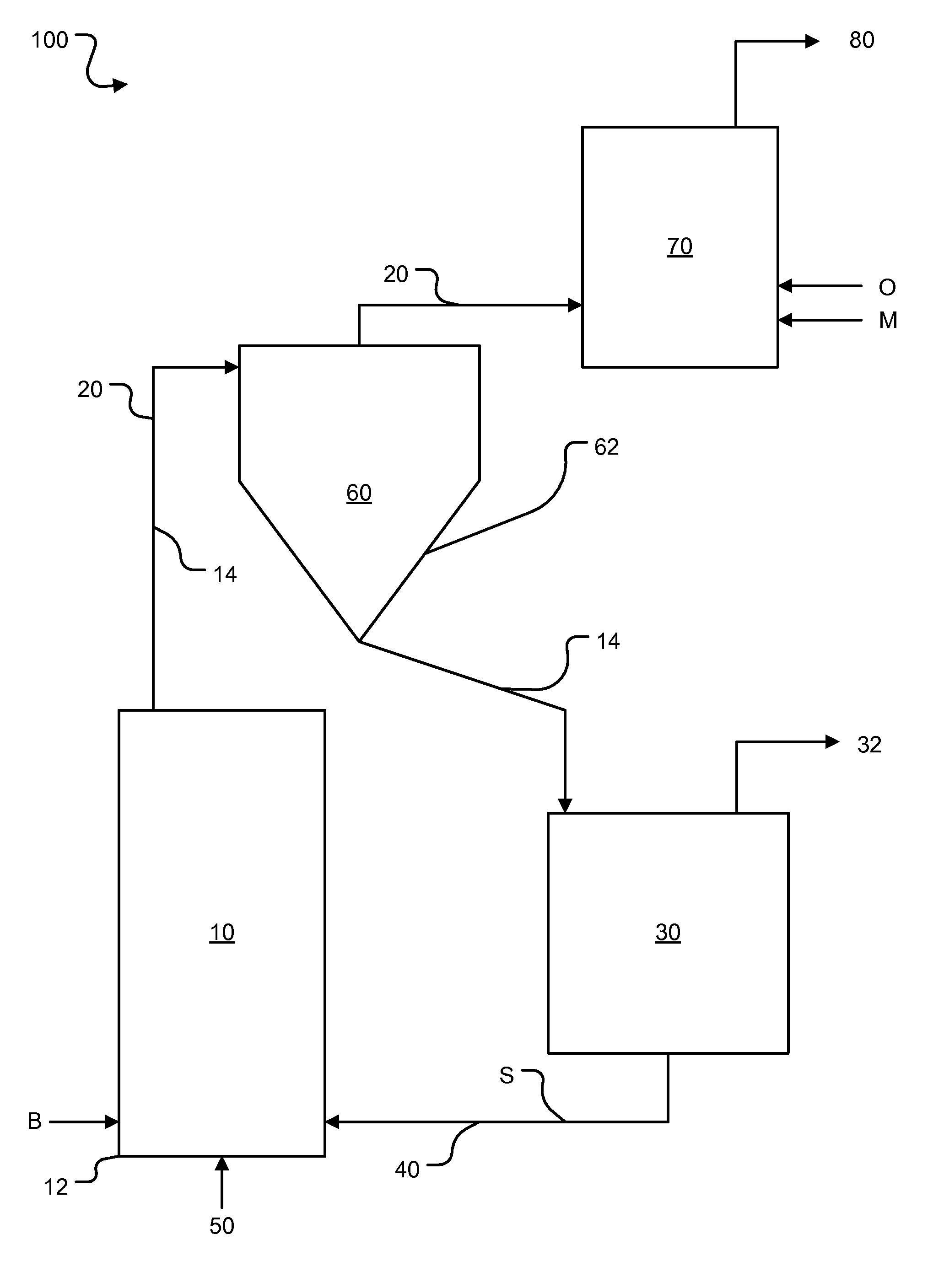
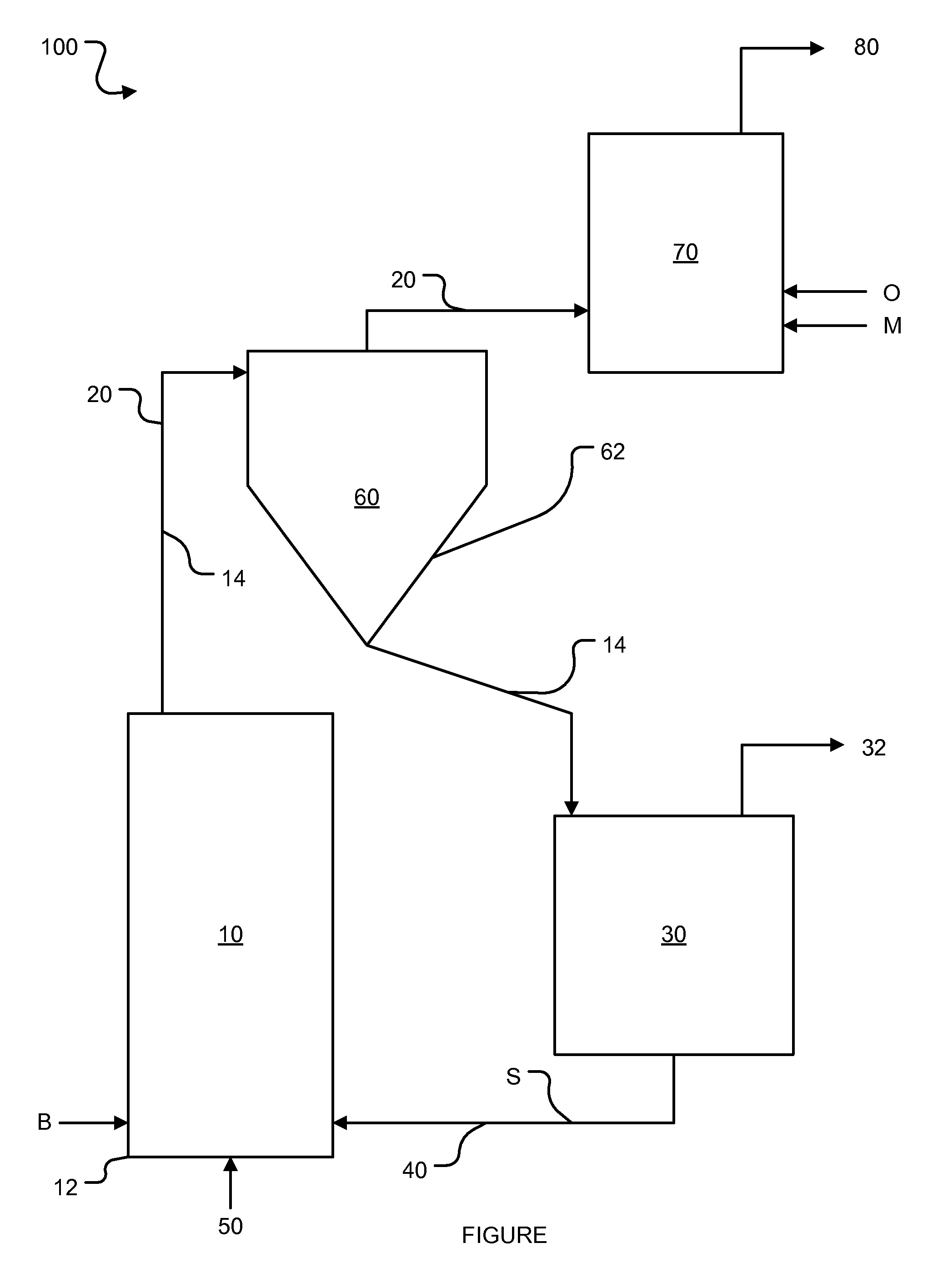
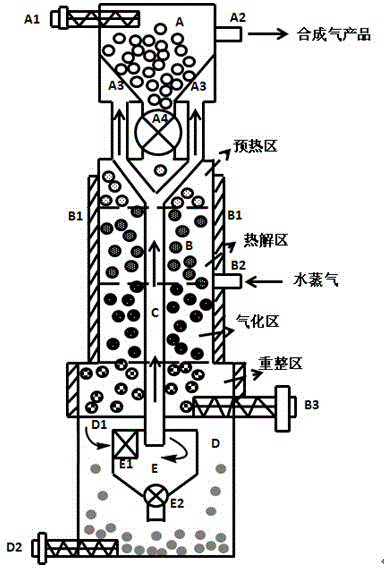
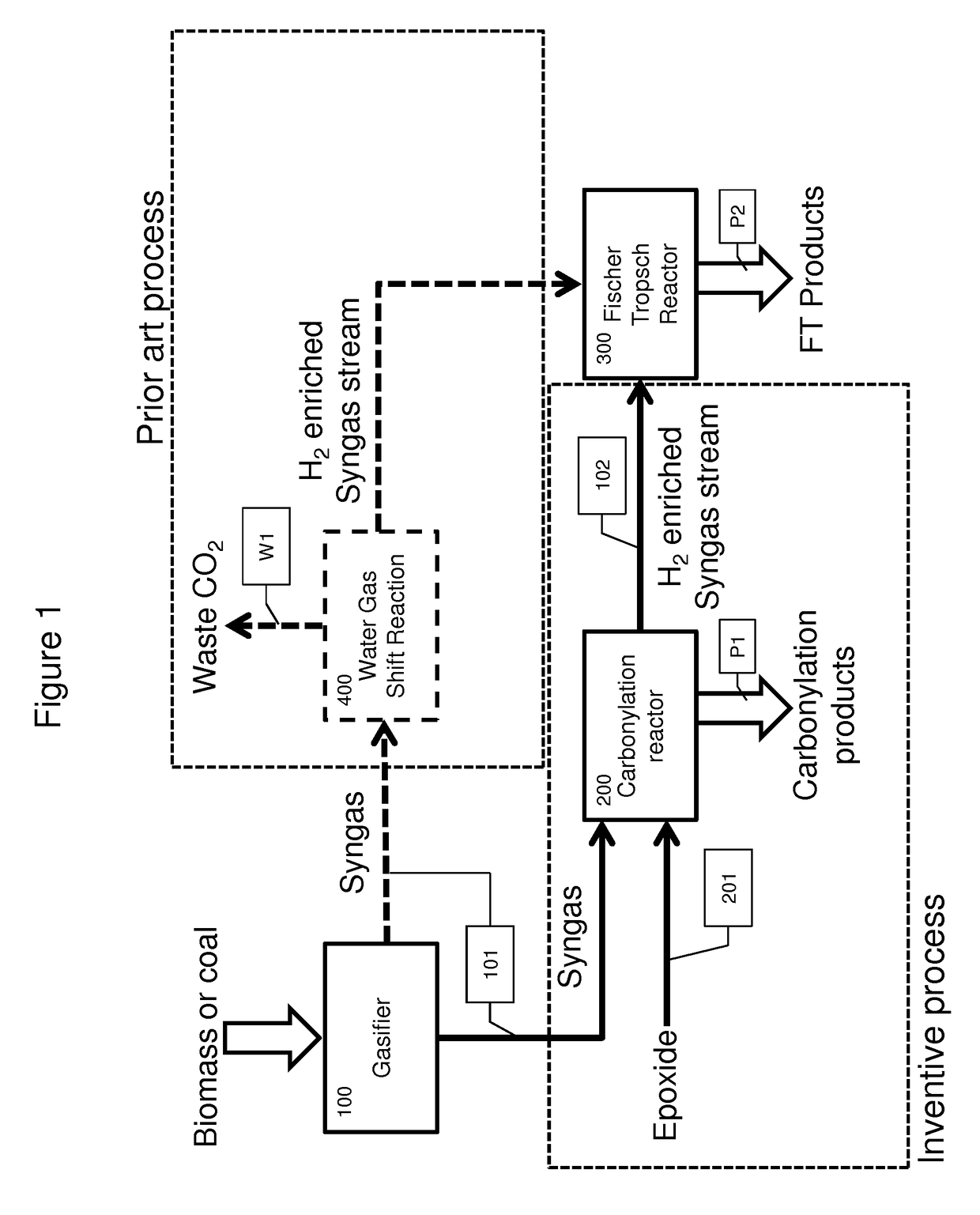
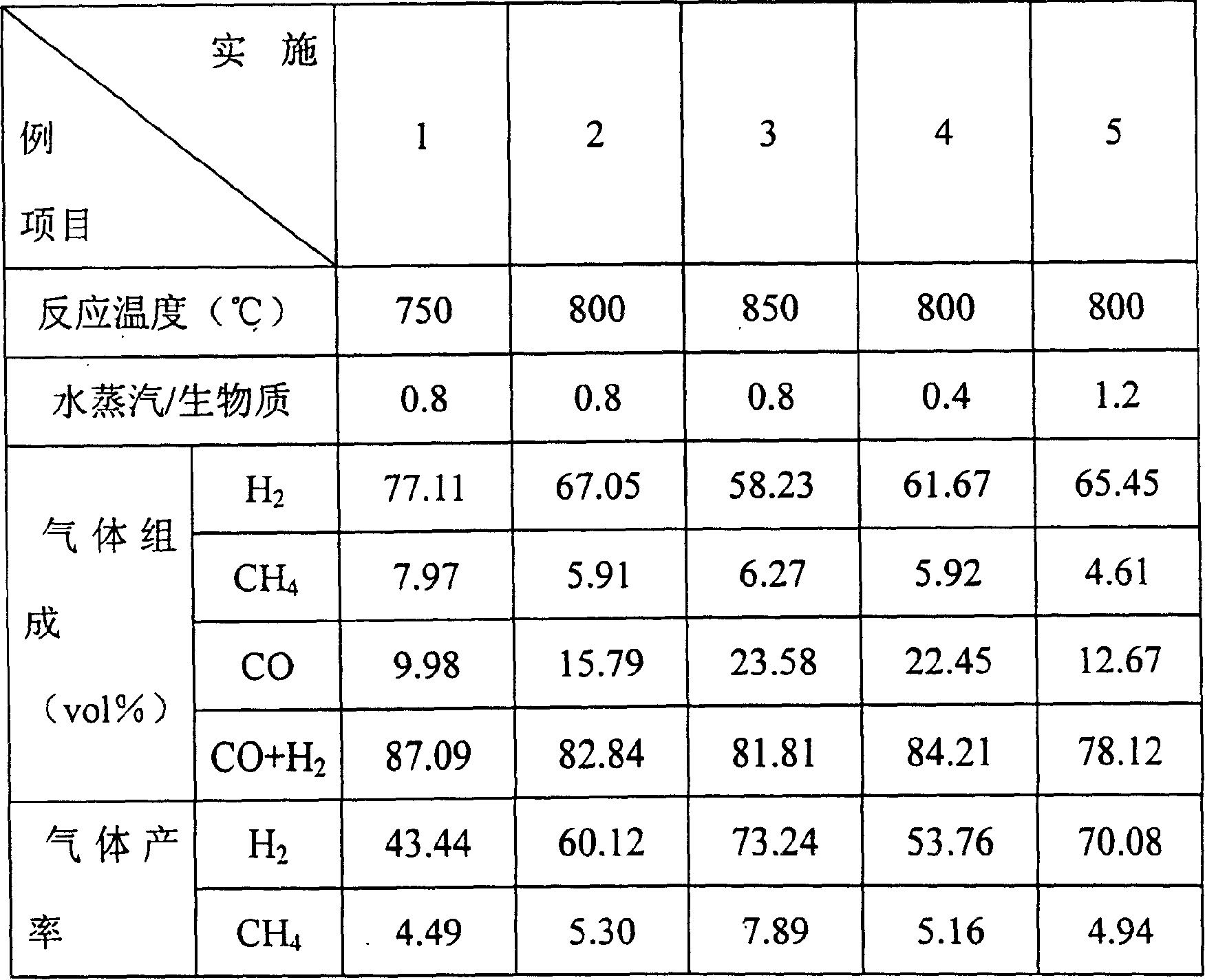
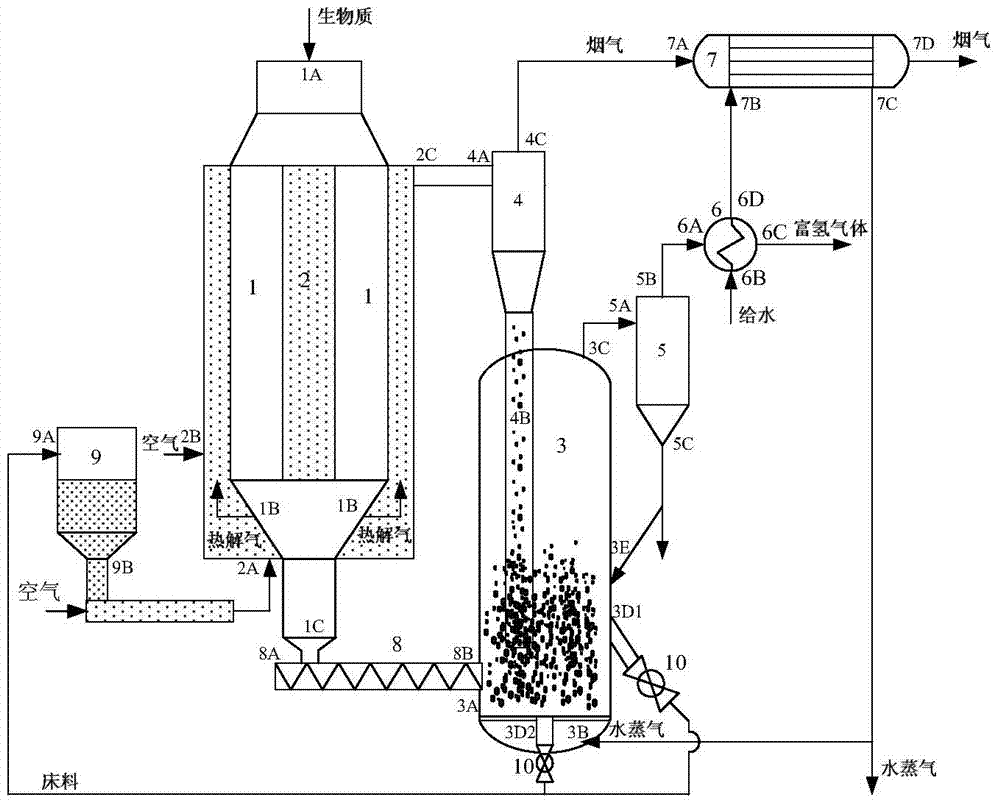
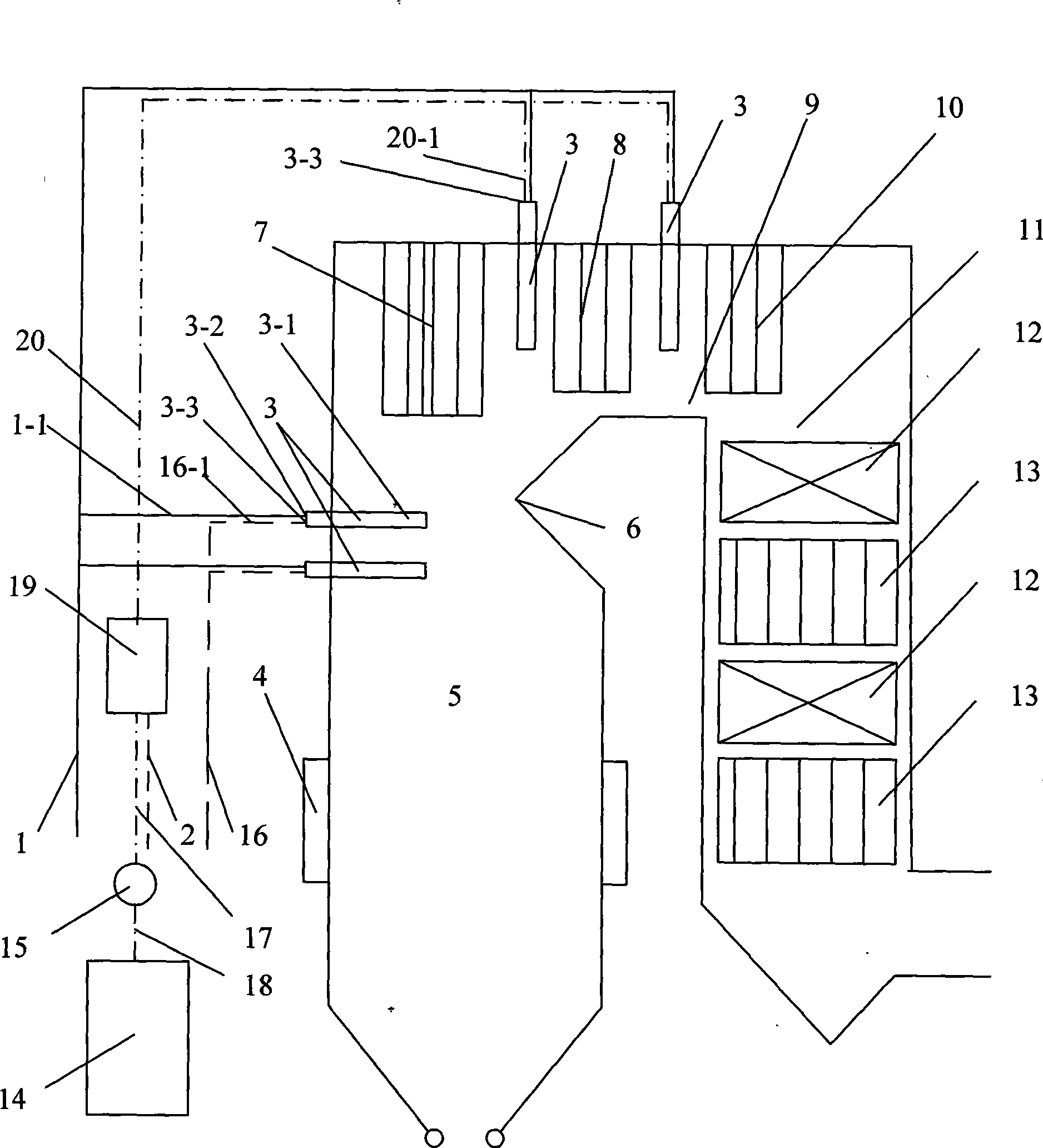
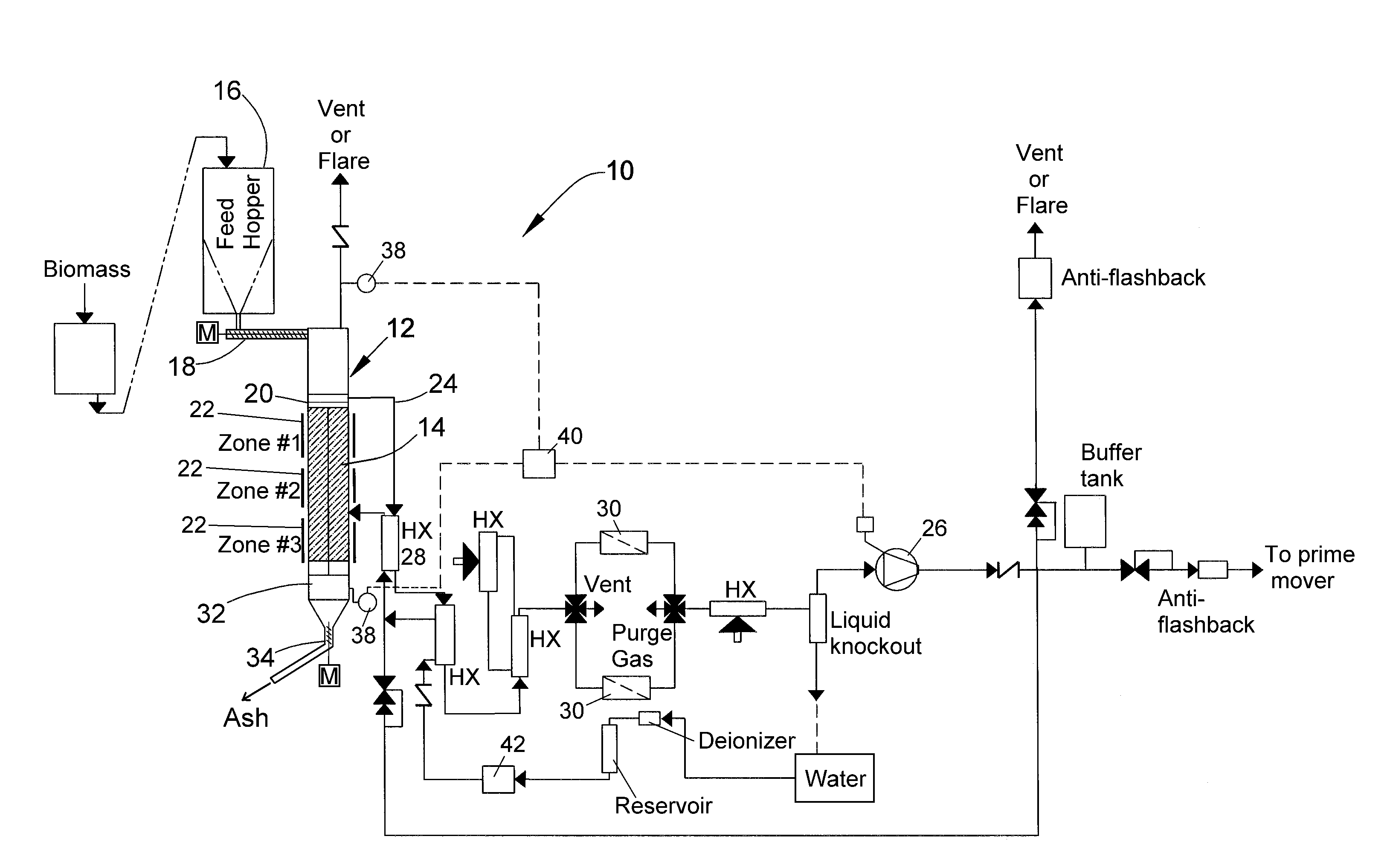
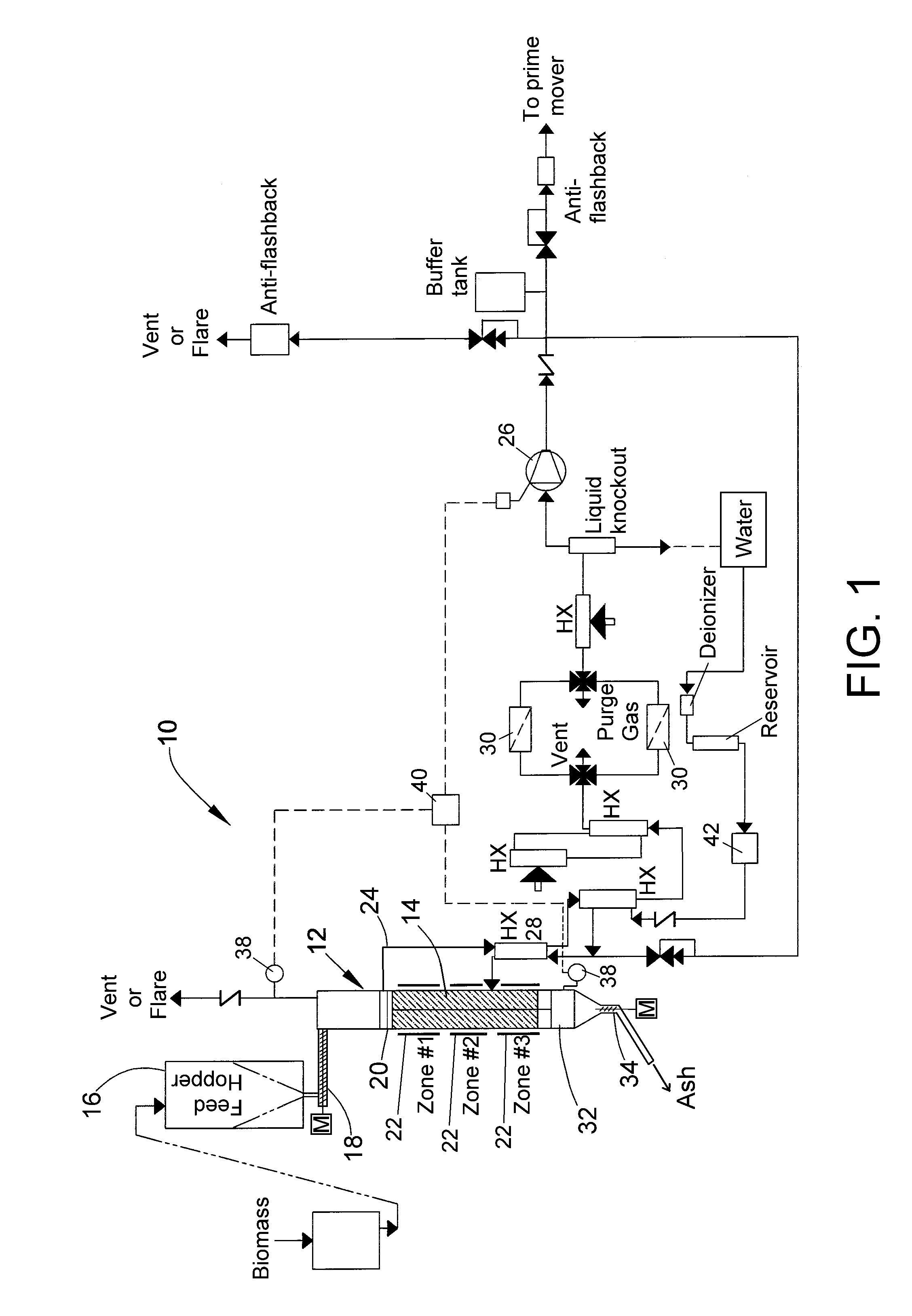
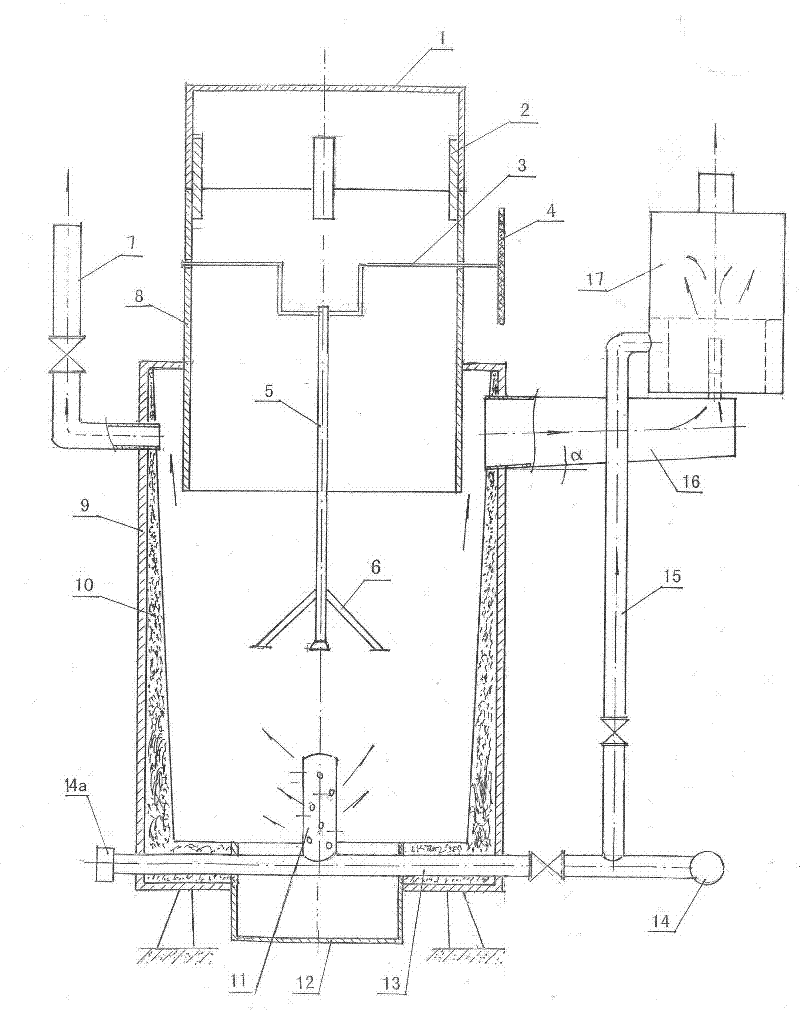
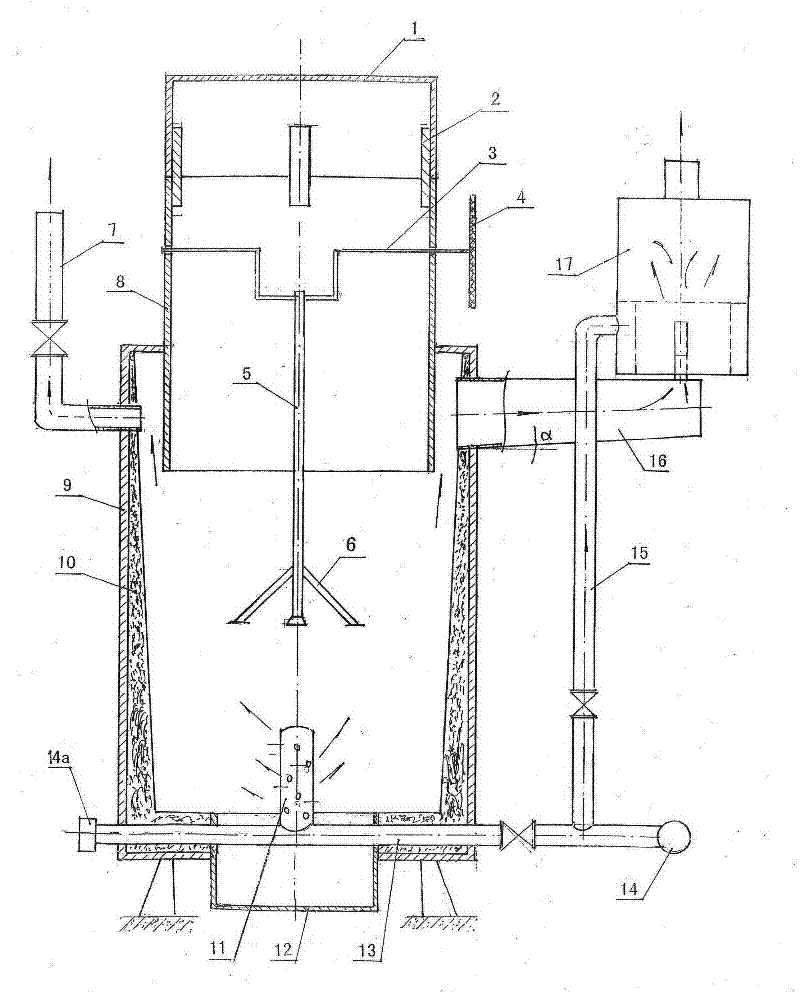
Process and apparatus for biomass gasification
InactiveUS20050095183A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationGasifier mechanical detailsForming gasTar
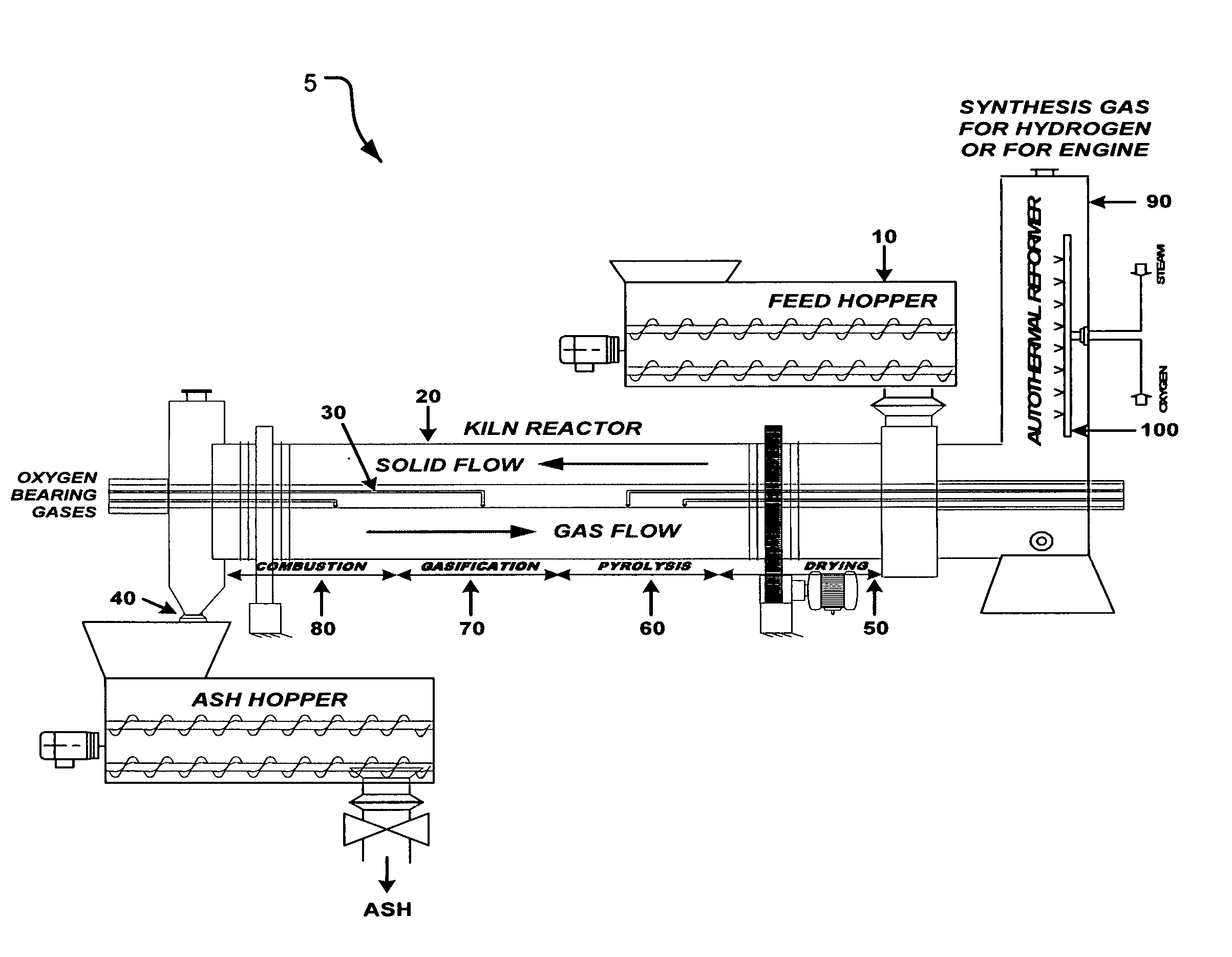
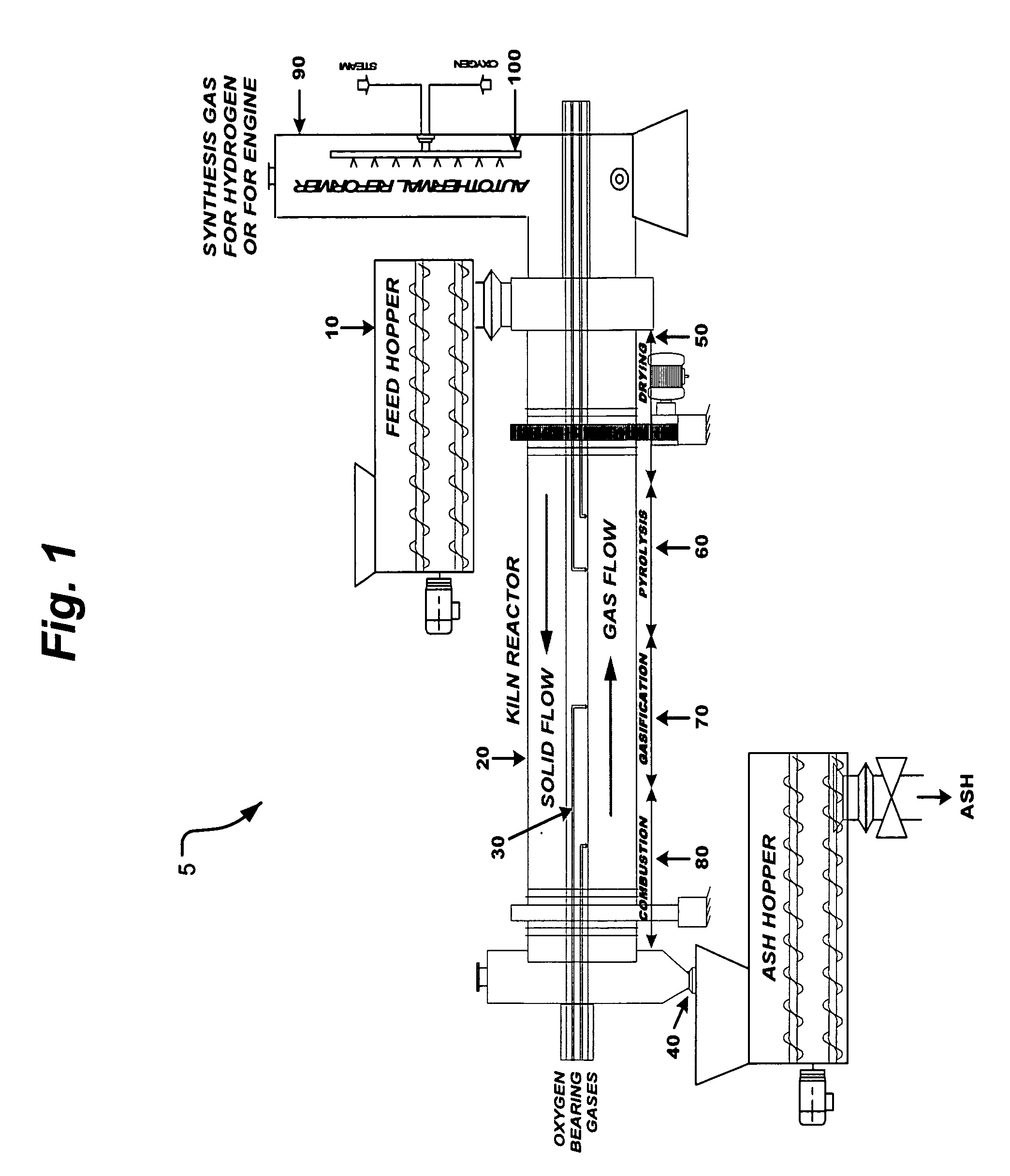
A waste-to-synthesis gas system including: a first gasifier for receiving biomass; a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the first gasifier in a countercurrent direction to the biomass flow and to define a plurality of reaction regions including a drying region, a pyrolysis region, a gasification region and a combustion region; and, a second gasifier for receiving gases from the plurality of regions of the first gasifier and a gas distributor for delivering reactant gas and oxygen into the second gasifier in a concurrent direction to the flow of gases from the first gasifier. As a result, no carbon chars, oils or tars are expected to be present in the synthesis gas produced.
Owner:BIOMASS ENERGY SOLUTIONS
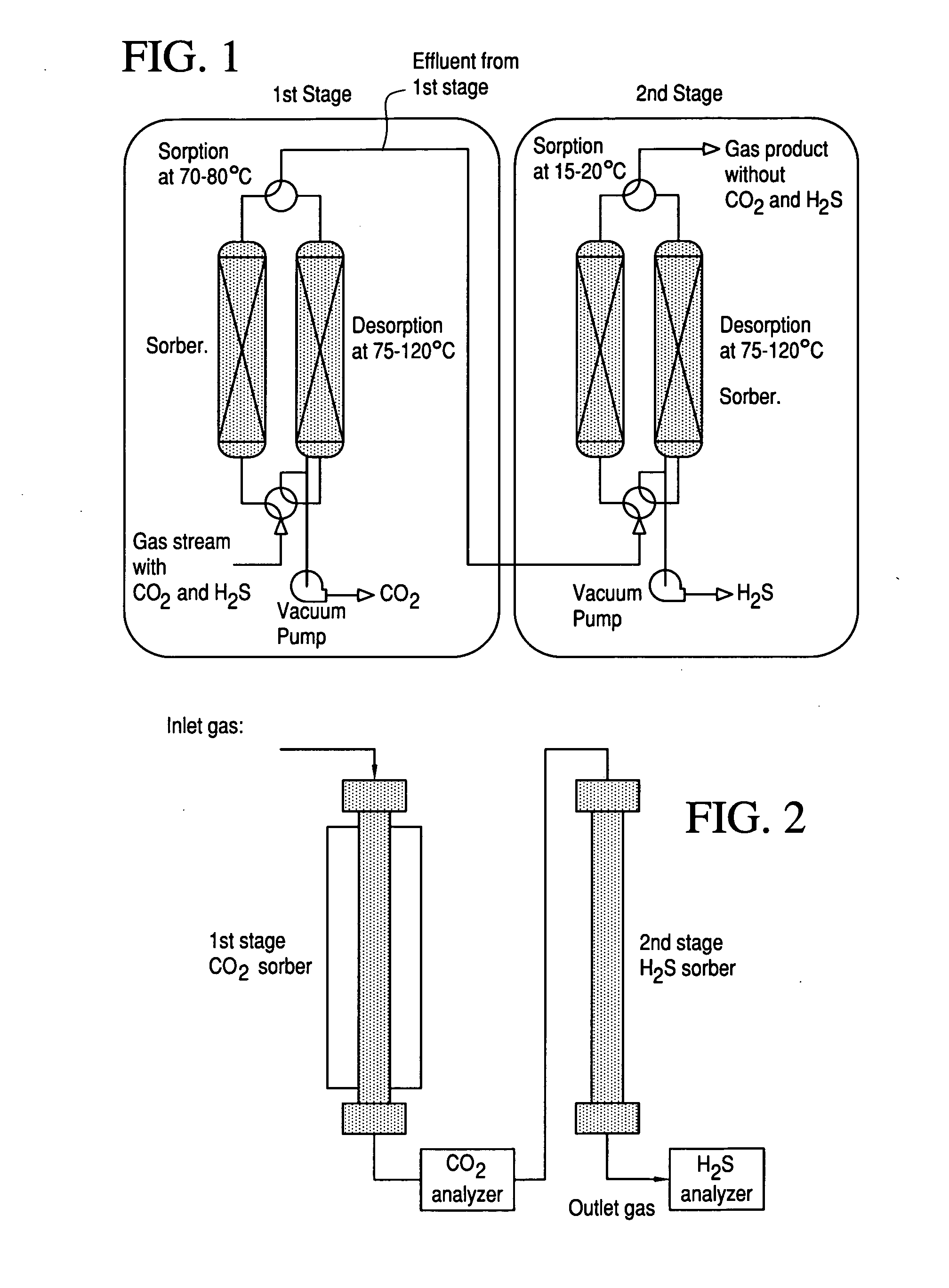
Novel sorbents and purification and bulk separation of gas streams
InactiveUS20080264254A1Large capacityLittle and no corrosive effectNitrous oxide captureGas treatmentSorbentDesorption
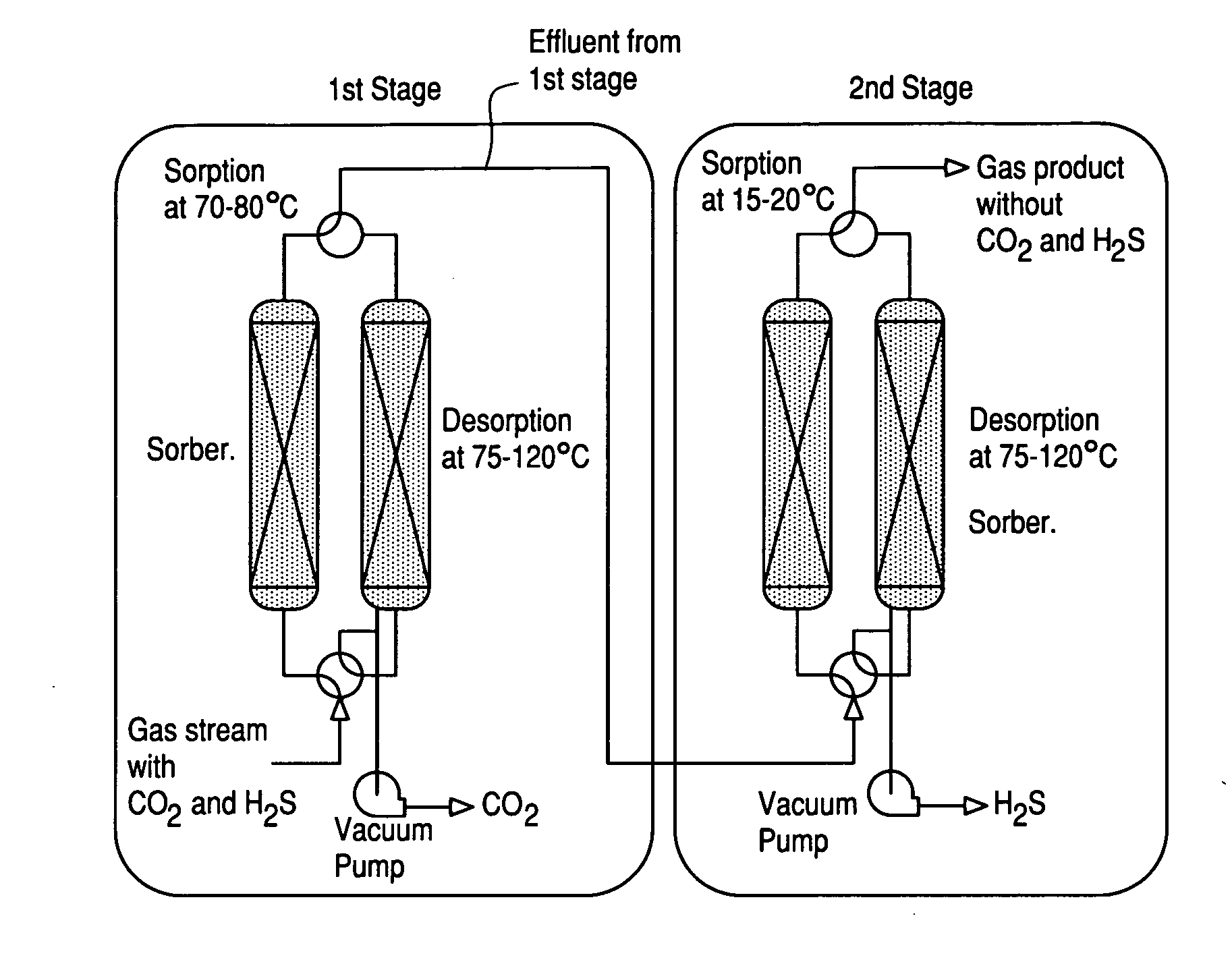
Porous-material-supported polymer sorbents and process for removal of undesirable gases such as H2S, COS, CO2, N2O, NO, NO2, SO2, SO3, HCl, HF, HCN, NH3, H2O, C2H5OH, CH3OH, HCHO, CHCl3, CH2Cl2, CH3Cl, CS2, C4H4S, CH3SH, and CH3—S—CH3 from various gas streams such as natural gas, coal / biomass gasification gas, biogas, landfill gas, coal mine gas, ammonia syngas, H2 and oxo-syngas, Fe ore reduction gas, reformate gas, refinery process gases, indoor air, fuel cell anode fuel gas and cathode air are disclosed. The sorbents have numerous advantages such as high breakthrough capacity, high sorption / desorption rates, little or no corrosive effect and are easily regenerated. The sorbents may be prepared by loading H2S—, COS—, CO2—, N2O, NO—, NO2—, SO2—, SO3—, HCl—, HF—, HCN—, NH3—, H2O—, C2H5OH—, CH3OH—, HCHO—, CHCl3—, CH2Cl2—, CH3Cl—, CS2—, C4H4S—, CH3SH—, CH3—S—CH3-philic polymer(s) or mixtures thereof, as well as any one or more of H2S—, COS—, CO2—, N2O, NO—, NO2—, SO2—, SO3—, HCl—, HF—, HCN—, NH3—, H2O—, C2H5OH—, CH3OH—, HCHO—, CHCl3—, CH2Cl2—, CH3Cl—, CS2—, C4H4S—, CH3SH—, CH3—S—CH3-philic compound(s) or mixtures thereof on to porous materials such as mesoporous, microporous or macroporous materials. The sorbents may be employed in processes such as one-stage and multi-stage processes to remove and recover H2S, COS, CO2, N2O, NO, NO2, SO2, SO3, HCl, HF, HCN, NH3, H2O, C2H5OH, CH3OH, HCHO, CHCl3, CH2Cl2, CH3Cl, CS2, C4H4S, CH3SH and CH3—S—CH3 from gas streams by use of, such as, fixed-bed sorbers, fluidized-bed sorbers, moving-bed sorbers, and rotating-bed sorbers.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
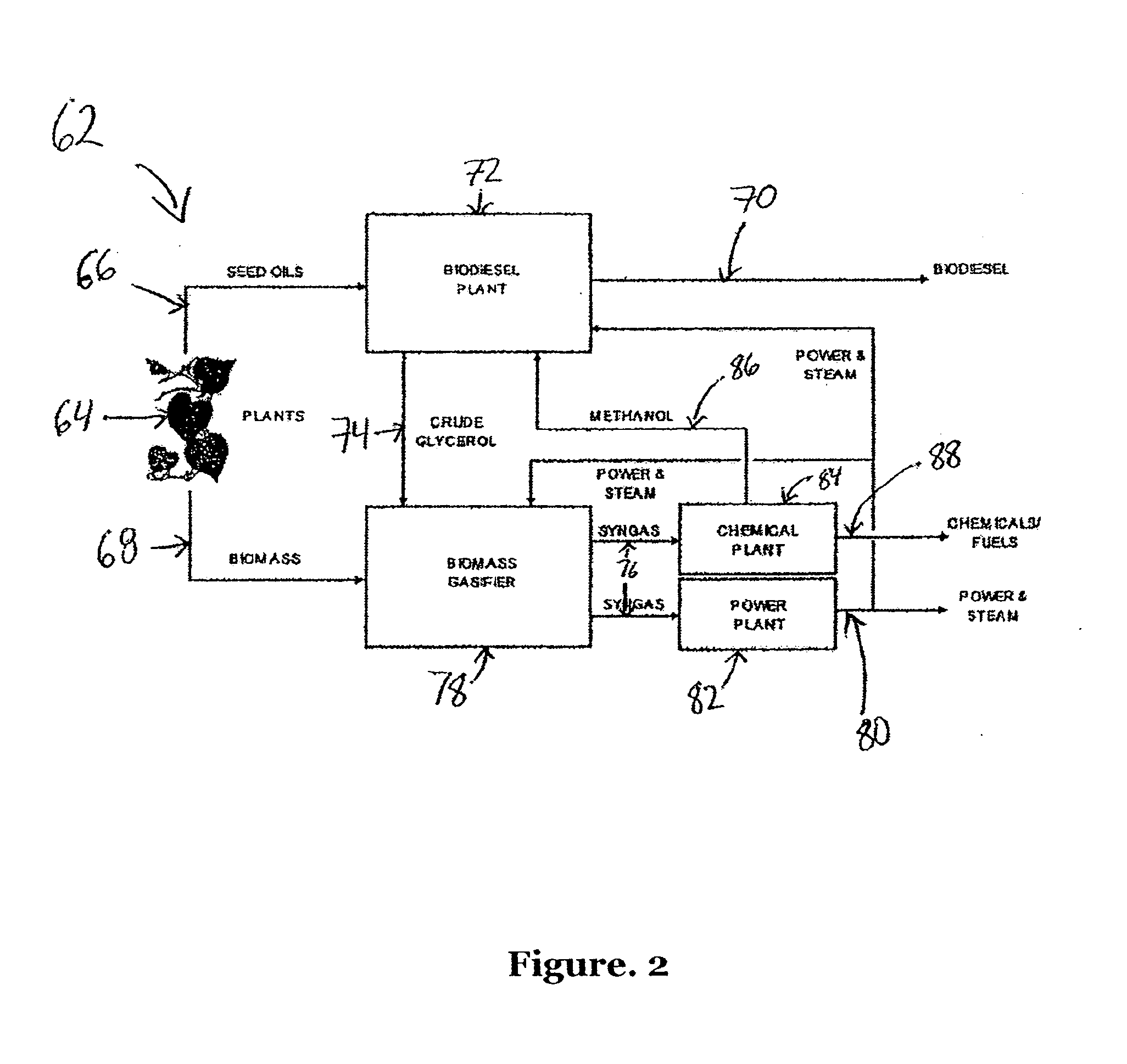
Method for producing bio-fuel that integrates heat from carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions to drive biomass gasification reactions
ActiveUS20070225383A1Improve thermal efficiencyImprove economyCatalytic crackingBiofuelsSyngasBiodiesel
A low-temperature catalytic process for converting biomass (preferably glycerol recovered from the fabrication of bio-diesel) to synthesis gas (i.e., H2 / CO gas mixture) in an endothermic gasification reaction is described. The synthesis gas is used in exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions, such as Fischer-Tropsch, methanol, or dimethylether syntheses. The heat from the exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction is integrated with the endothermic gasification reaction, thus providing an energy-efficient route for producing fuels and chemicals from renewable biomass resources.
Owner:VIRENT +1
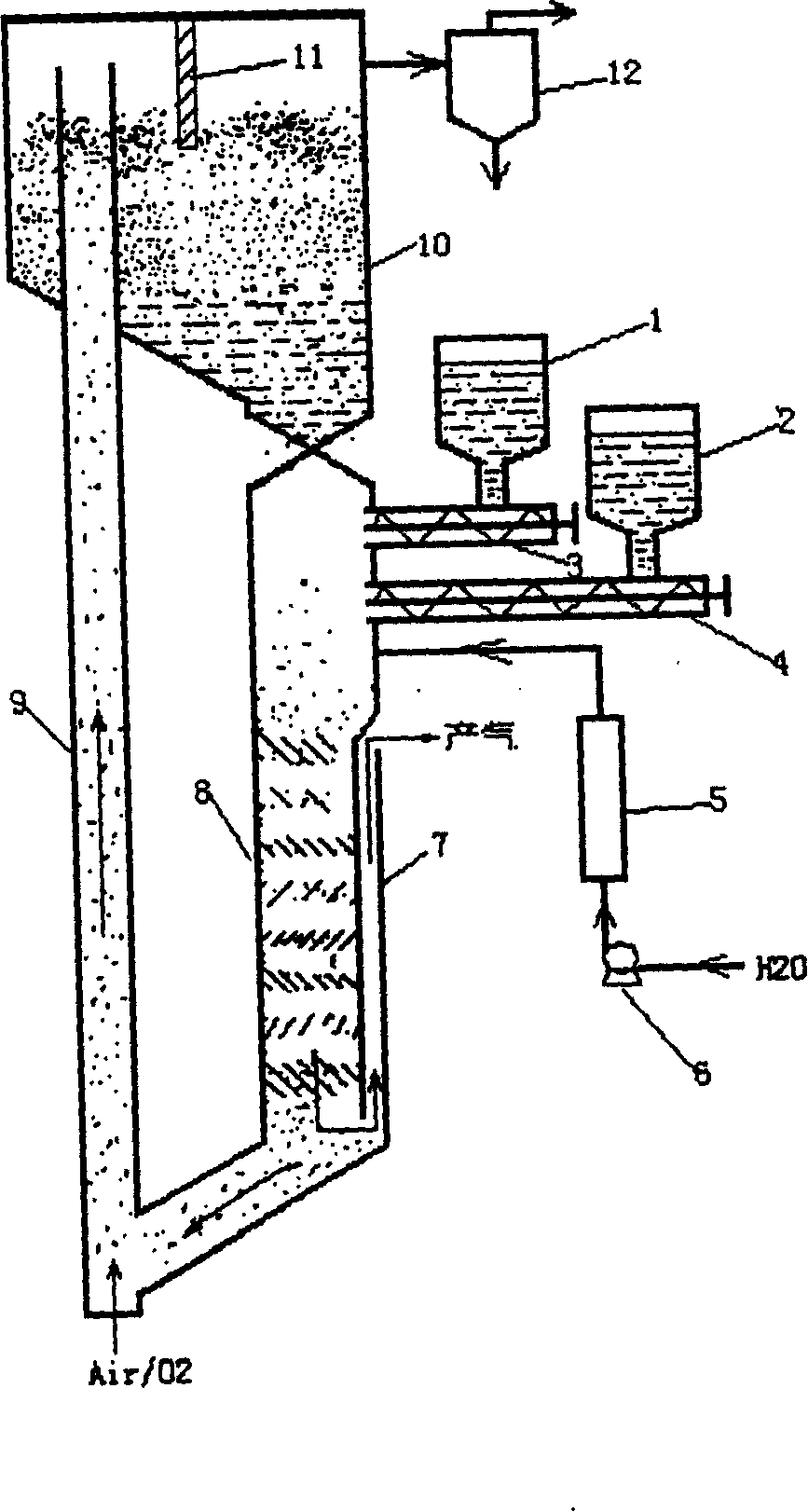
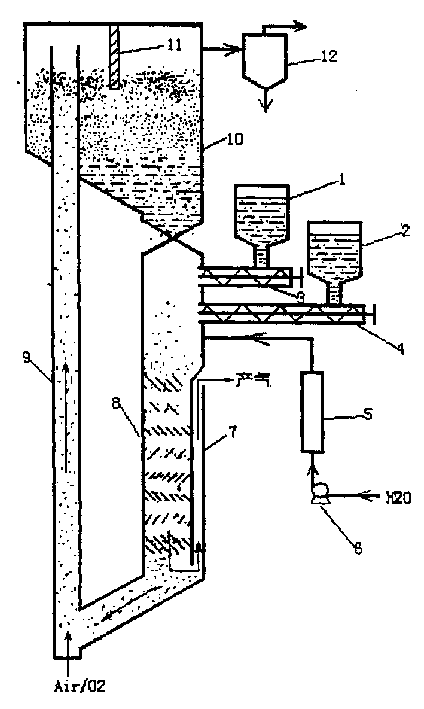
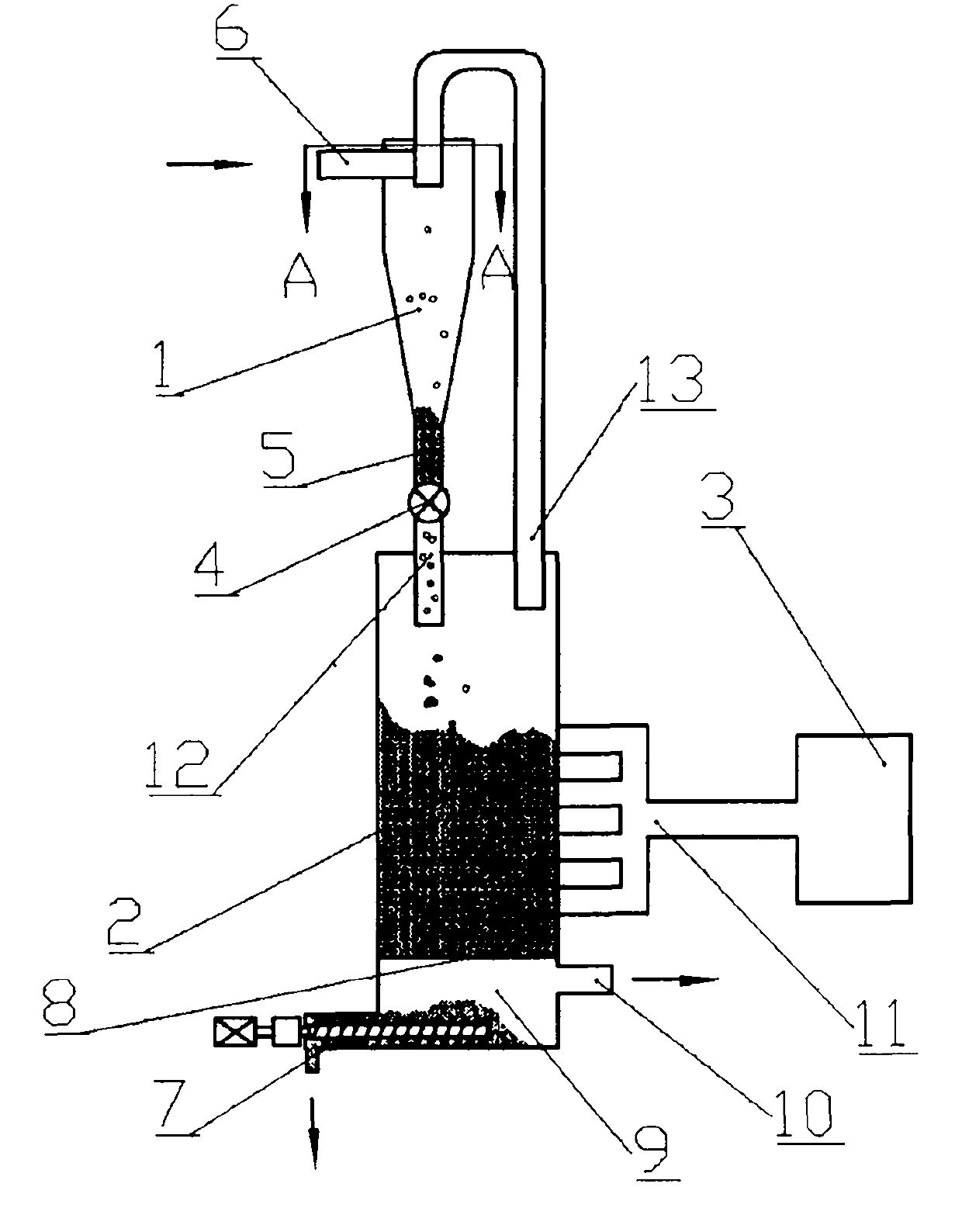
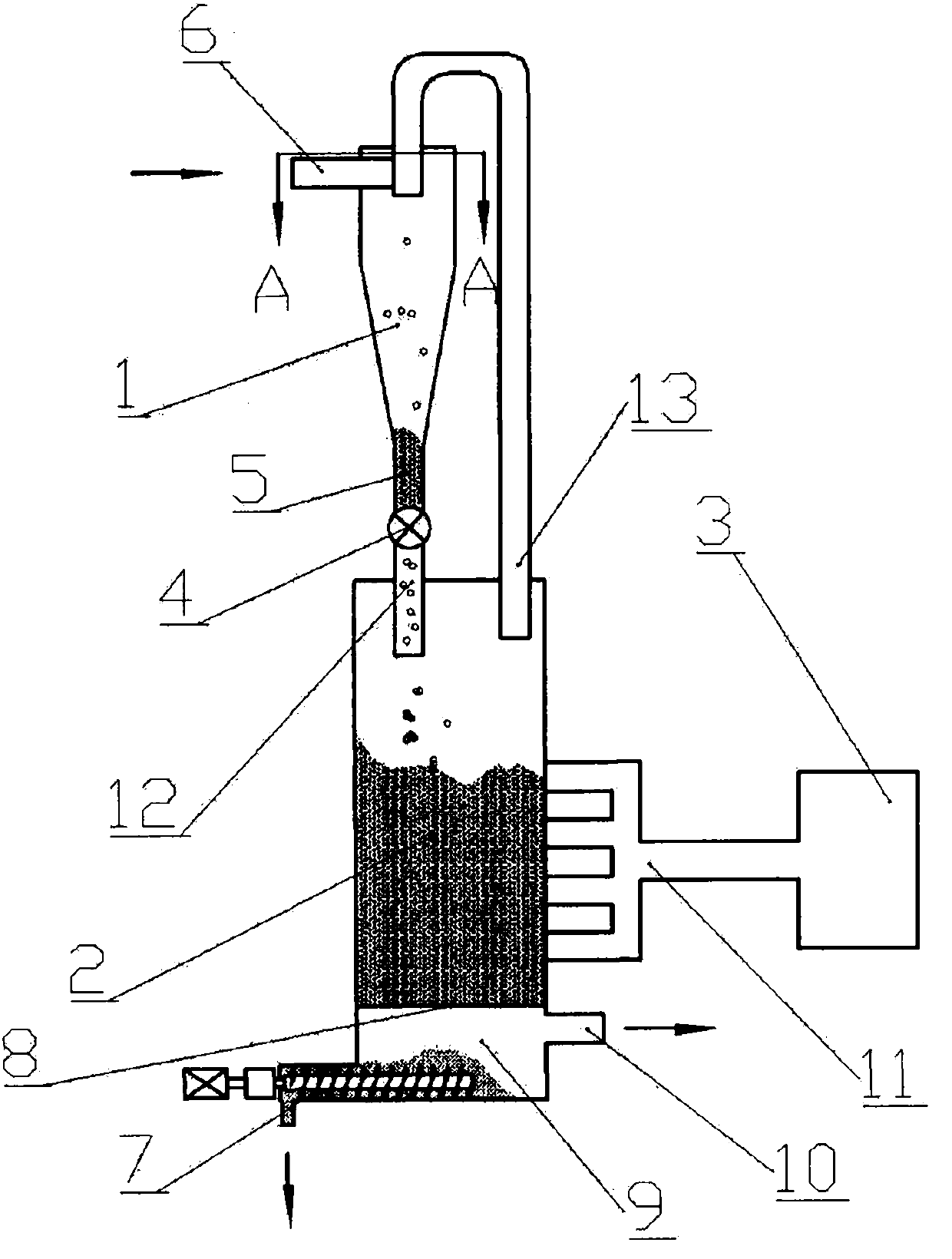
Low-tar biomass gasifying method and apparatus
InactiveCN1710023AWide adaptability of raw materialsSpecial form destructive distillationCarbon layerDecomposition
The invention discloses a kind of biomass gasifying method and device. The technology through separating the two courses of solid biomass pyrogenation and decomposition and gasification of the pyrogenation outcome, then transform the biomass into flammable gas of rather low tar content. Firstly send biomass into the pyrogenation reactor, without oxidant in; have pyrogenation reaction at 400 - 650 Deg. C, the pyrogenation outcome including pyrogenation gas and remaining charcoal gets into pyrogenation carburetor, and have incomplete oxidizing combustion reaction with sent oxidant, to form a high temperature of 900 - 1100 Deg. C. At the time, the heavy hydrocarbon substance of tar decomposes into small molecule gas, and the decomposed gas leaves out of the carburetor after having deoxidizing reaction with the nether blazing carbon layer. The high temperature gas is provided for consumers' use after depurated and cooled. The gas produced by the invention has very low tar content, which makes the following depurating equipment simple, won't produce second pollution and makes the raw materials widely used. The produced fuel gas can be used in civil filed and directly used for generating electricity.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
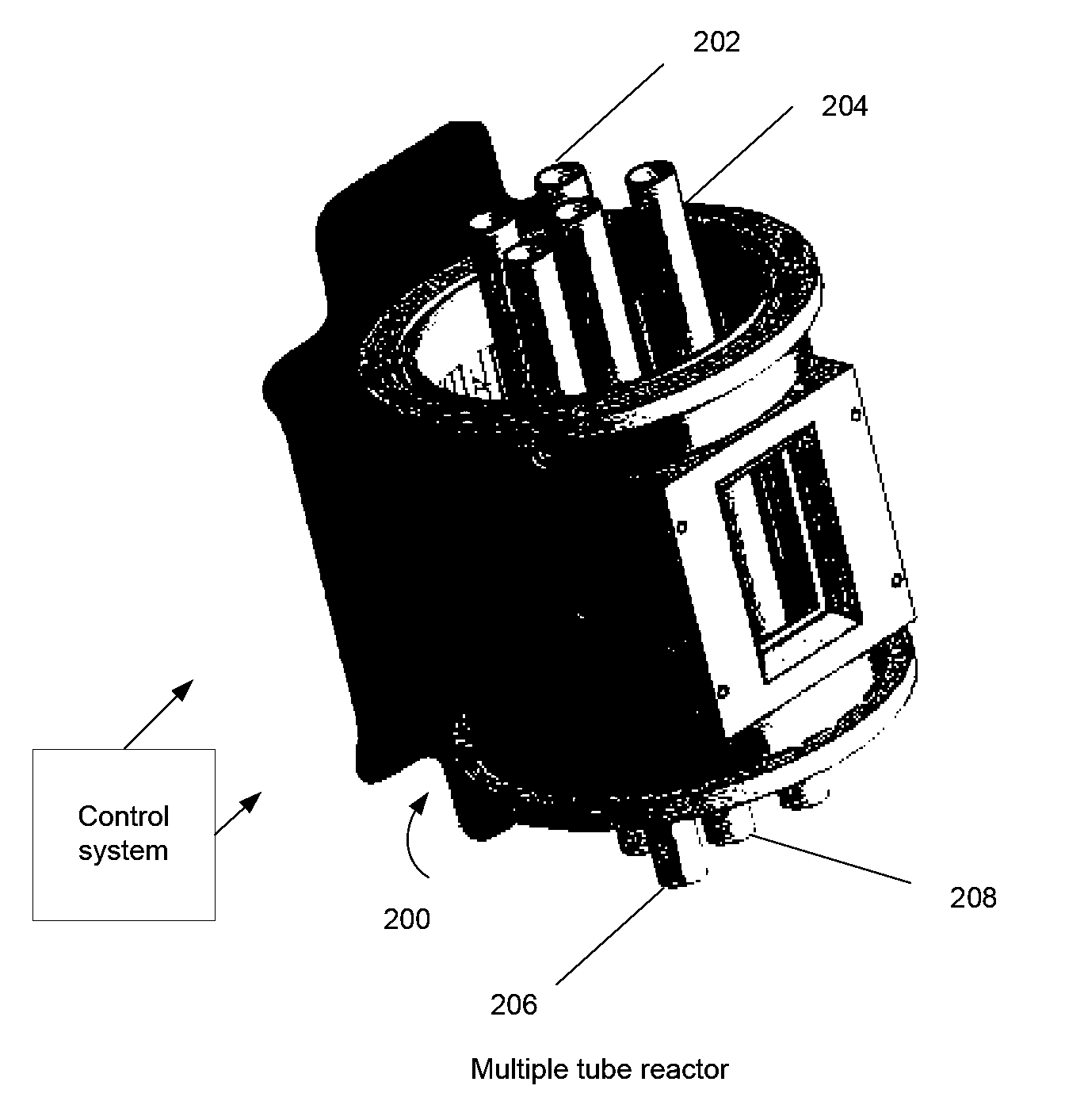
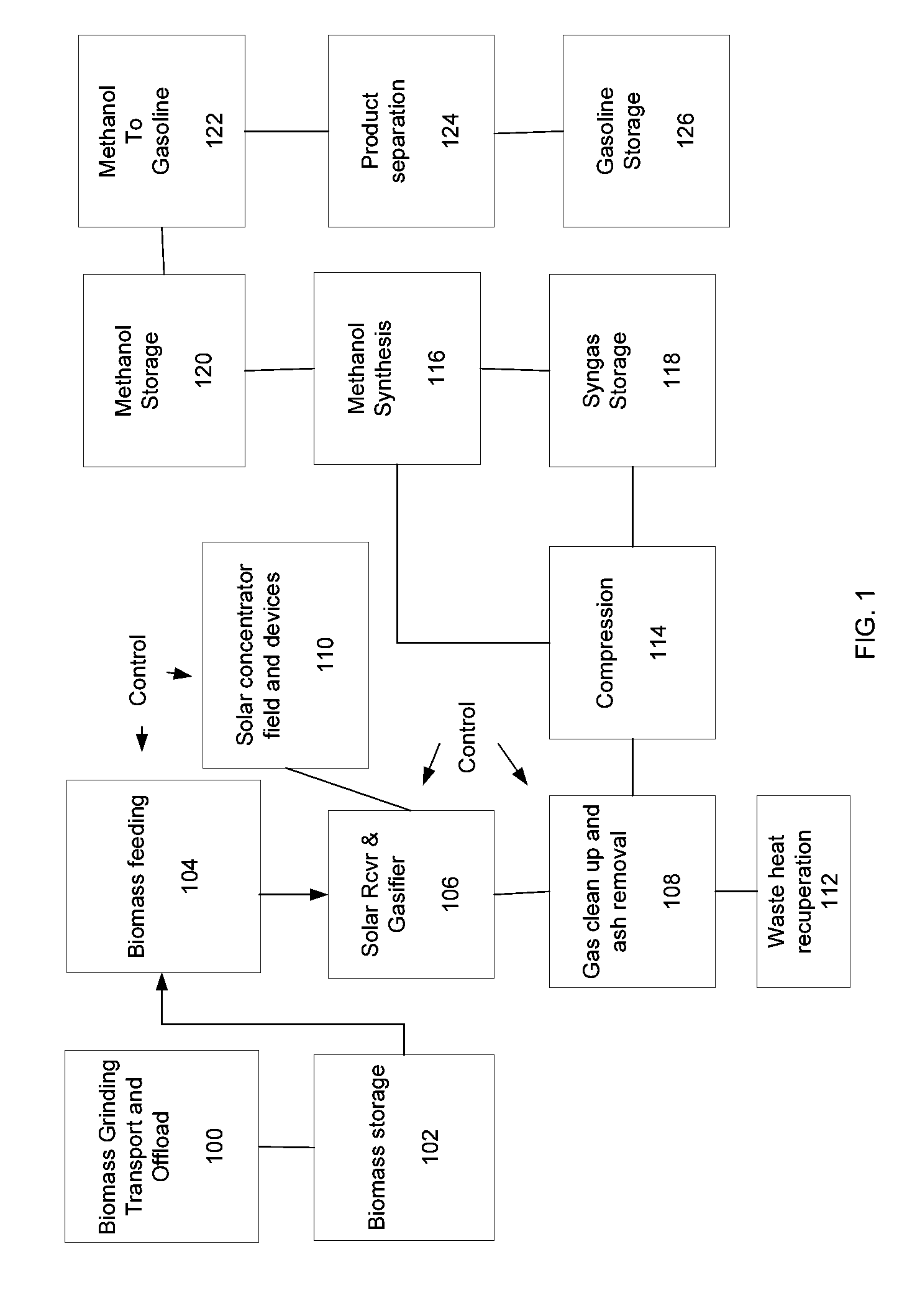
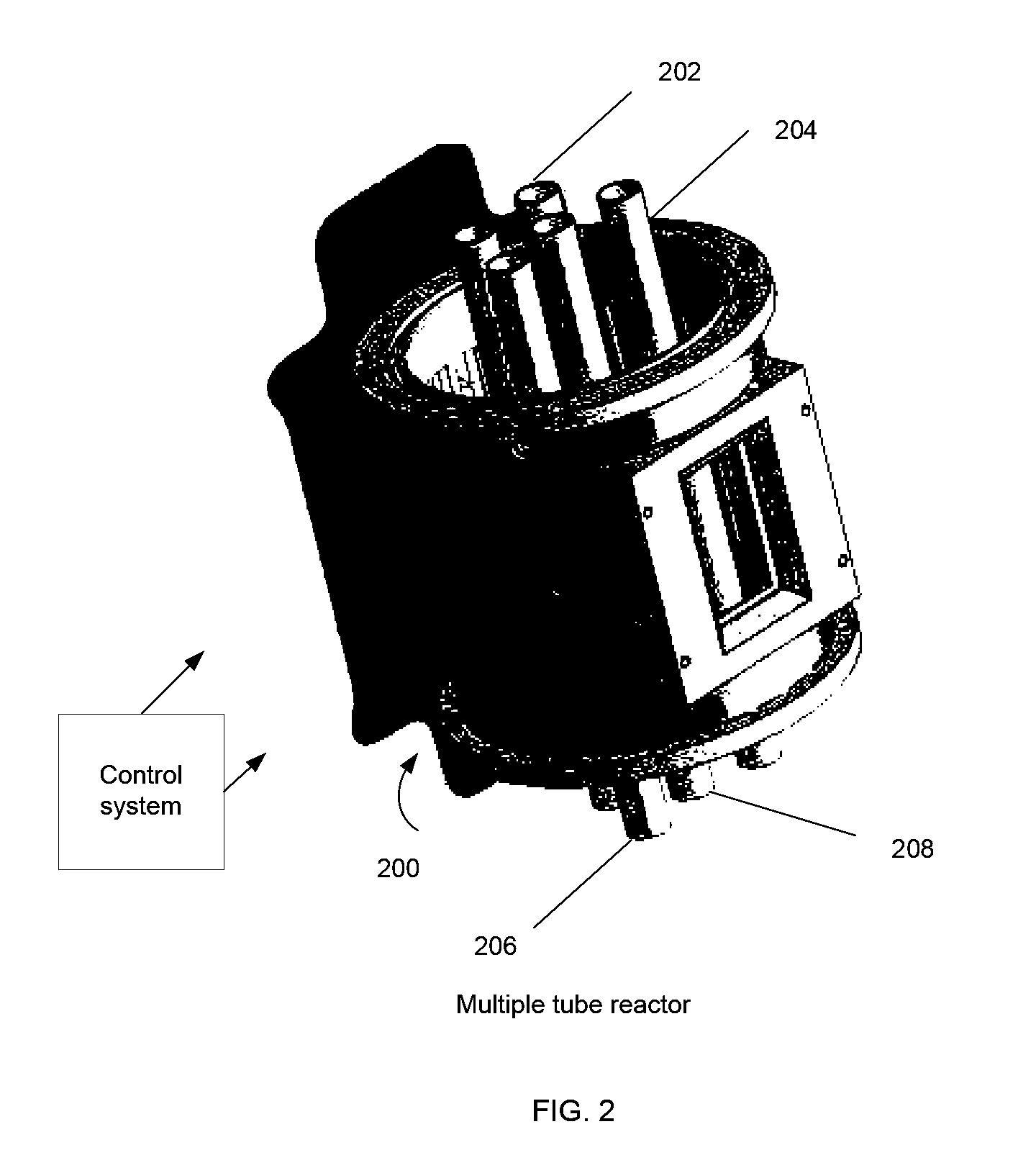
Systems and methods for solar-thermal gasification of biomass
InactiveUS20100237291A1Process control/regulationSolar heating energySteam reformingChemical reaction
A method, apparatus, and system for a solar-driven chemical plant that may include a solar thermal receiver having a cavity with an inner wall, where the solar thermal receiver is aligned to absorb concentrated solar energy from one or more of 1) an array of heliostats, 2) solar concentrating dishes, and 3) any combination of the two. Some embodiments may include a solar-driven chemical reactor having multiple reactor tubes located inside the cavity of solar thermal receiver, wherein a chemical reaction driven by radiant heat occurs in the multiple reactor tubes, and wherein particles of biomass are gasified in the presence of a steam (H2O) carrier gas and methane (CH4) in a simultaneous steam reformation and steam biomass gasification reaction to produce reaction products that include hydrogen and carbon monoxide gas using the solar thermal energy from the absorbed concentrated solar energy in the multiple reactor tubes.
Owner:SUNDROP IP HLDG LLC
Waste to liquid hydrocarbon refinery system
InactiveUS20110158858A1Eliminate concernsReduce dependenceDirect heating destructive distillationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentLiquid wasteCogeneration
A Waste to Liquid Hydrocarbon Refinery System that transforms any municipal solid wastes and hazardous industrial wastes, Biomass or any carbon containing feedstock into synthetic hydrocarbon, particularly, but not exclusively, diesel and gasoline and / or electricity and co-generated heat, comprising three major subsystems: i) the Pyro-Electric Thermal Converter (PETC) (10) and Plasma Arc (PA) waste and biomass gasification subsystem (1); ii) the hydrocarbon synthesis subsystem (2); and iii) the electricity generation and heat co-generation subsystem (3).
Owner:ALVES RAMALHO GOMES MARIO LUIS
Method of producing charcoal, conditioned fuel gas and potassium from biomass
InactiveUS7226566B2Reduce productionSuitable for useLiquid degasificationSolid waste disposalPotassiumProcess engineering
Owner:CSA ENERGY
Method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by adopting biomass indirect liquification one-step process
InactiveCN1477090ASelf-heating reactionOvercoming the deficiency of hydrogen contentEther preparationSyngasPetroleum
The present invention relates to a method for synthesizing dimethyl ether by high-effectively cleanly utilizing biomass. It utilizes the gasified gas produced by catalytic gasification of biomass air-water vapor, and makes the gasified gas undergo the process of methane reformation to prepare synthetic gas, and utilizes the synthetic gas to directly synthesize clean fuel dimethyl ether.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
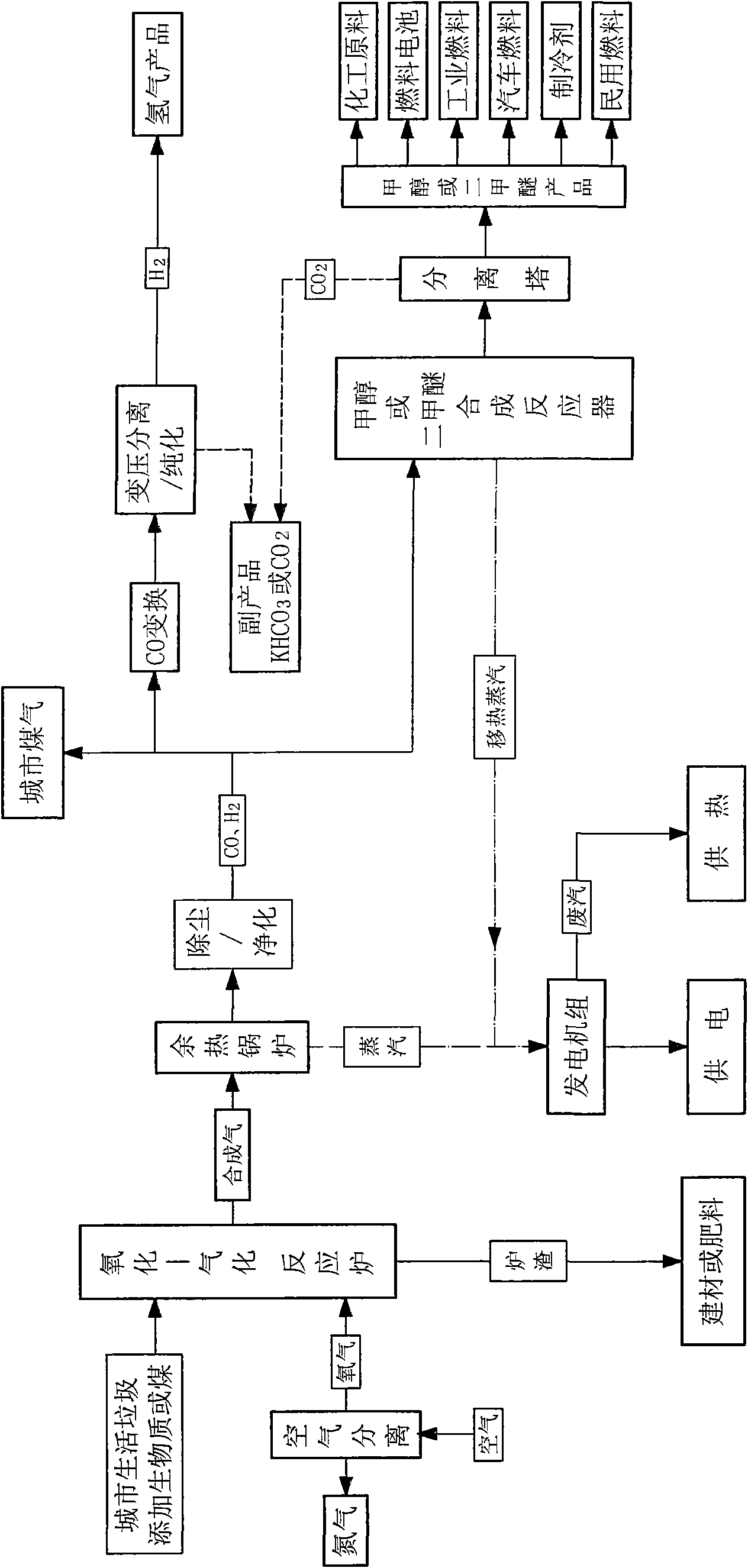
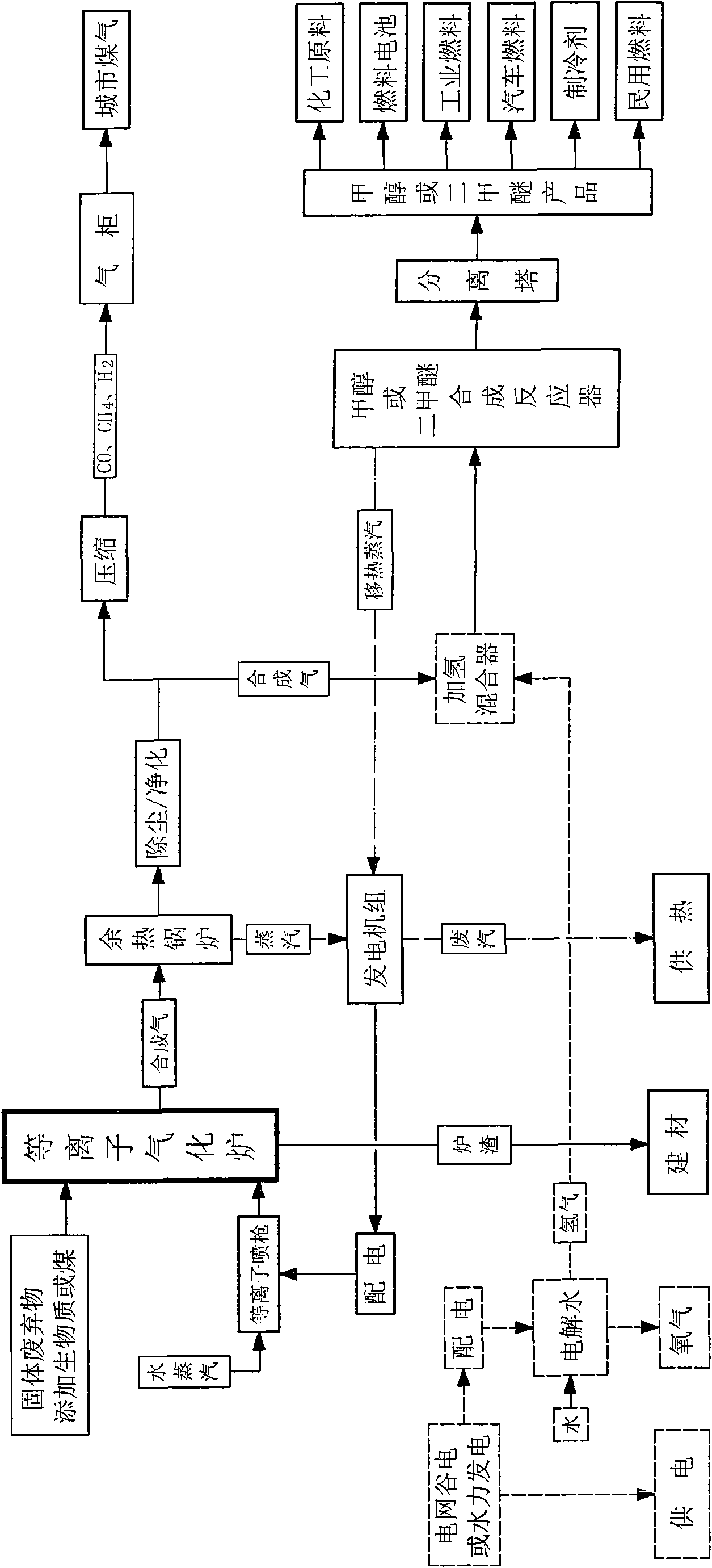
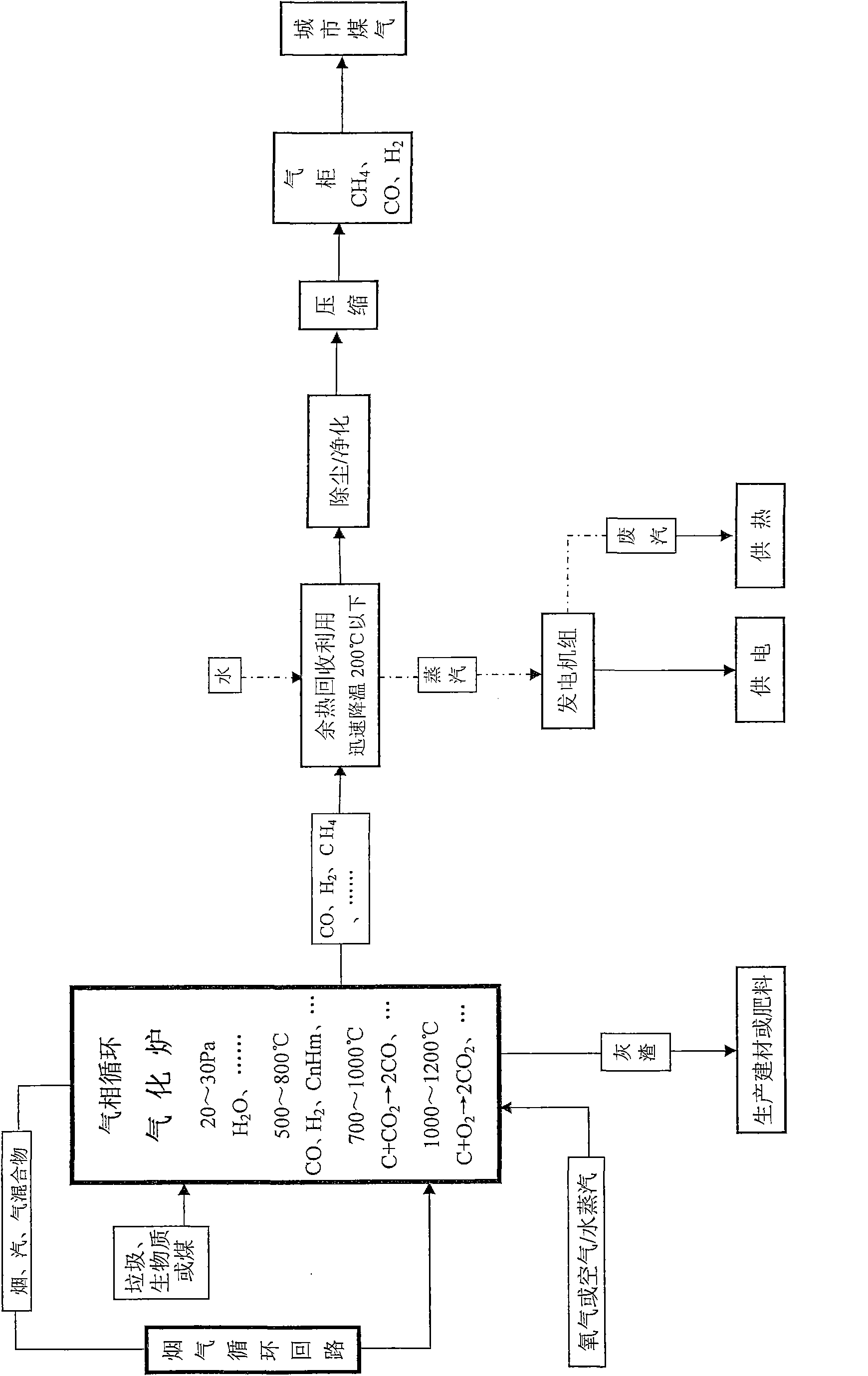
Process, system and device for waste biomass multi-production processing
ActiveCN101565629AEliminate pollutionHarmlessHydrogen separationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentEcological environmentGas phase
The invention relates to a process, a system and a device for waste biomass multi-production processing, in particular to a waste biomass gasification and liquefaction treatment system. The gasification treatment is performed to the waste biomass, the gas is used for producing clean energy and chemical raw materials, the furnace slag is used for producing building materials or fertilizer and the waste heat is used for electric power generation and heat supply so as to realize the environmental-friendly municipal solid waste treatment and the ecological environment protection. The system mainlycomprises a gas-phase circulation gasification furnace, a flue gas circulation air tube, a flue gas circulation fan, a dust-removal / purifying tower and a synthesis reactor and is characterized in that the gas-phase circular reaction is performed to the flue gas in the gasification furnace, the water vapor and the gaseous matter generated during the pyrolysis to obtain hydrogen-rich synthetic gas,and meanwhile, the dioxin (violent in toxicity) is broken up; and the post treatment is performed to the hydrogen-rich synthetic gas to generate city gas, methanol, dimethyl ether or hydrogen. The system has the advantages of full gasification of the solid raw material, no pollutant discharge, extremely low exhaust emission and easy purifying treatment, and the device is flexible in size and is feasible for popularization.
Owner:上海格灵迈环境科技有限公司
Systems and methods for oxidation of synthesis gas tar
Owner:RES USA LLC
Systems and methods for oxidation of synthesis gas tar
InactiveUS20090090053A1Improve propertiesMuffle furnacesGas purification by catalytic conversionTarProduct gas
Owner:RES USA LLC
Method for preparing synthetic gas through microwave pyrolysis and gasification of biomass
ActiveCN105524662ARelaxed size requirementsReduce preprocessing power consumptionCombustible gas chemical modificationFixed-bed gasificationHigh carbonLiquid fuel
The invention discloses a method for preparing synthetic gas through microwave pyrolysis and gasification of biomass. The method comprises the following steps: a biomass raw material sent to a bunker and a catalyst are introduced into a microwave pyrolysis reactor, and passes through a preheating zone, a pyrolysis zone, a gasification zone and a reforming zone in order for reactions of dehydration, cracking, gasification and reforming, the reformed product is performed with gas-solid separation, gas and a few of carried tar and coke are subjected to a cracking reaction in a gas lifting pipe again, synthetic gas is released from an outlet, and the coke and ash obtained by gas-solid separation can be discharged from a reactor. The method has the advantages of high biomass gasification rate and high carbon conversion rate, the obtained synthetic gas product has high quality, can satisfy synthesis requirement of a liquid fuel, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SINOPEC DALIAN RES INST OF PETROLEUM & PETROCHEMICALS CO LTD +1
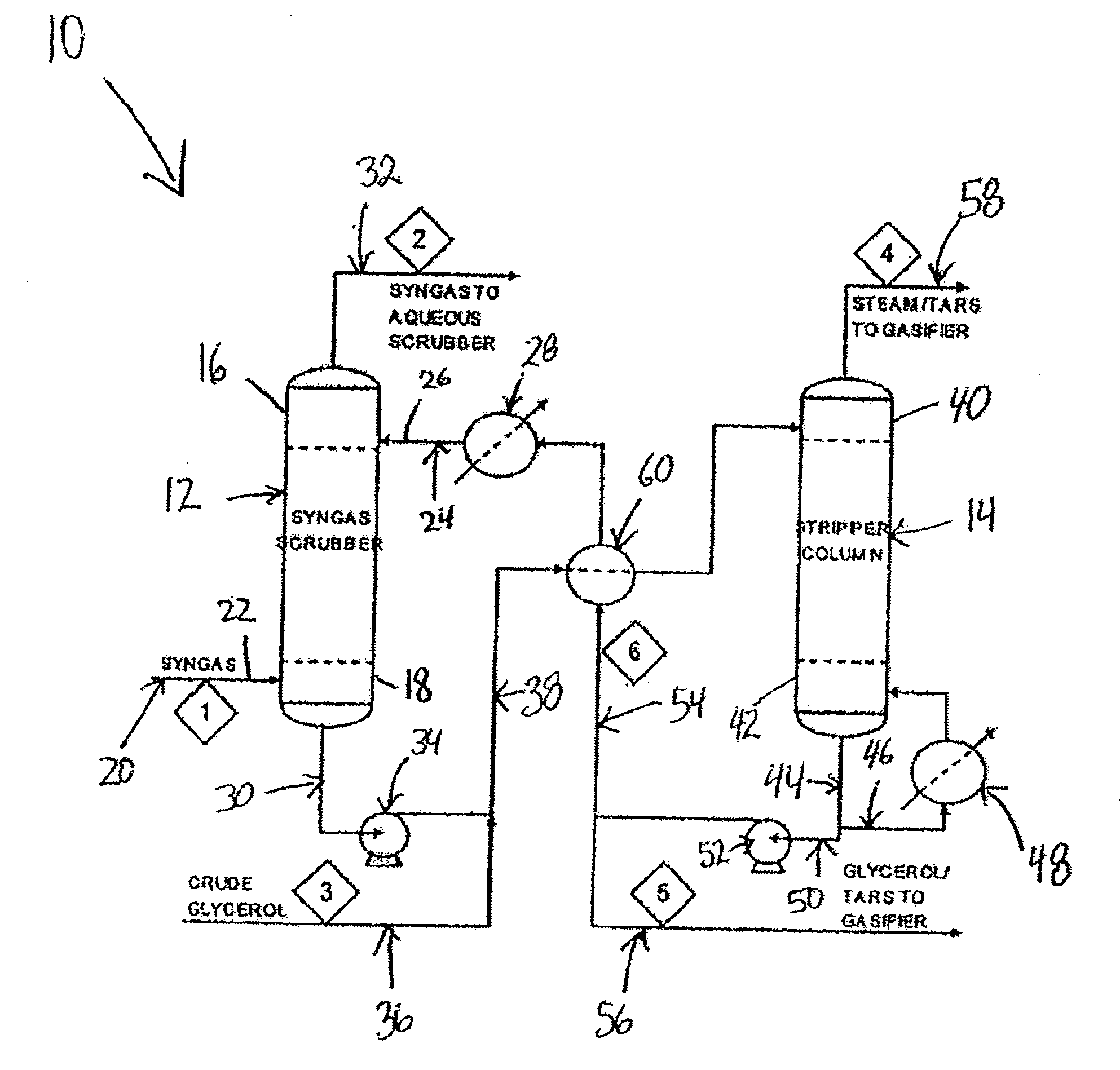
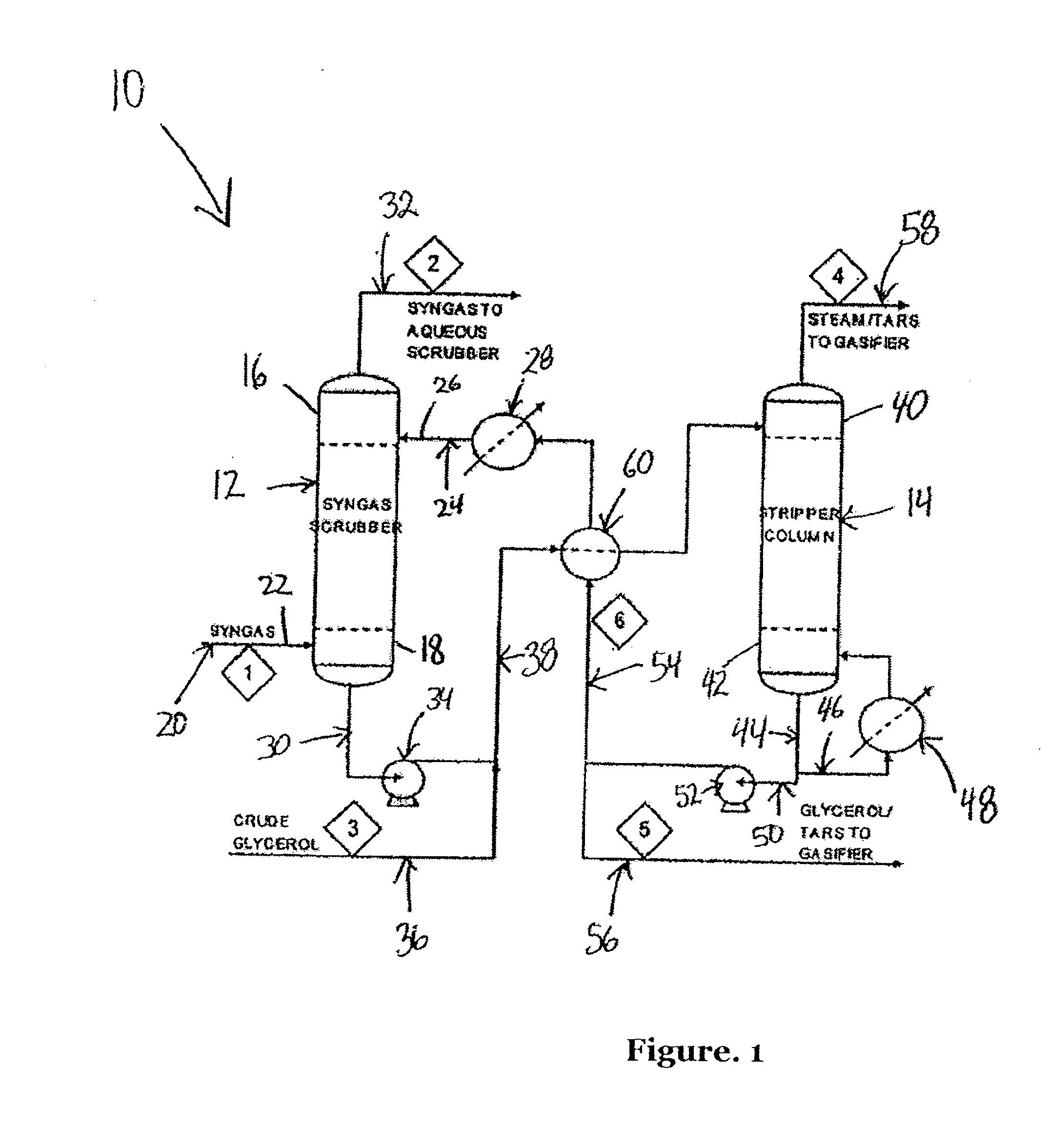
Process for removing tar from synthesis gas
A process and system for removing tars from synthesis gas uses glycerol produced as a byproduct of biodiesel manufacture. The biodiesel may be made from various oil feedstocks such as canola, rapeseed, or soybean oils. Associated with the harvesting of these crops may be the ready availability of byproduct biomass useful as feedstock for gasification. In addition, methanol may be sourced from the gasification of biomass to exploit a potential synergy between biodiesel manufacture and biomass gasification. The present invention develops those synergies further by making use of a byproduct stream from the manufacture of biodiesel to remove tars from the gasifier synthesis gas and to provide a useful end use for the byproduct.
Owner:IHI E&C INT
Method of modifying biomass, modified biomass aqueous biomass sluryy and method of producing the same, modified biomass gas and method of gasifying biomass
InactiveUS20060112638A1Reduce the amount of oxygenImprove efficiencyPressurized chemical processSolid waste disposalCelluloseSolid component
This method of upgrading a biomass comprises: an upgrading step for performing upgrading treatment of a cellulose based biomass with an oxygen / carbon atomic ratio of at least 0.5, in presence of water and under a pressure of at least saturated water vapor pressure, and reducing said oxygen / carbon atomic ratio of said biomass to no more than 0.38, and a separation step for separating an upgraded reactant obtained from said upgrading step into a solid component and a liquid component.
Owner:JGC CORP +1
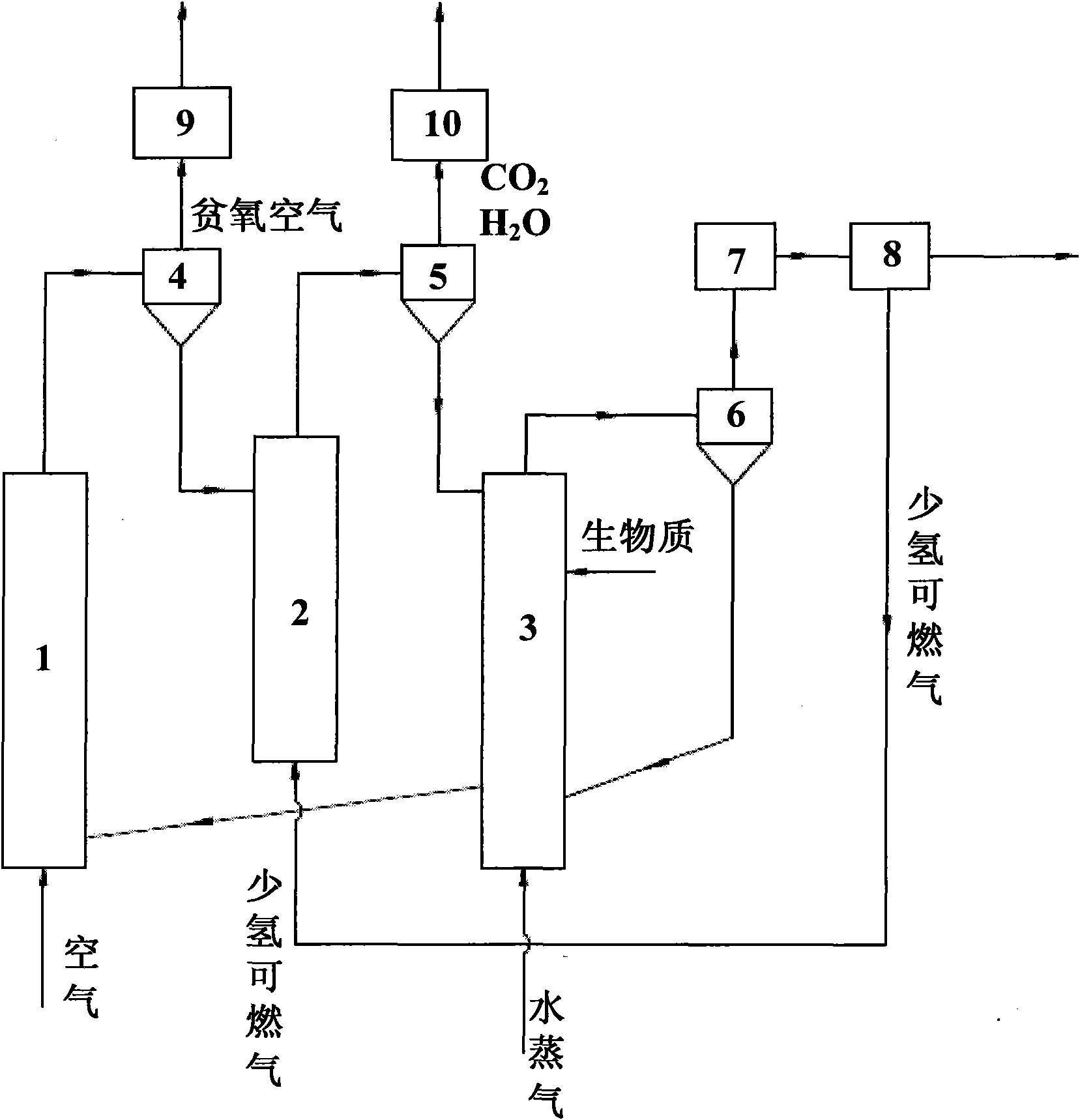
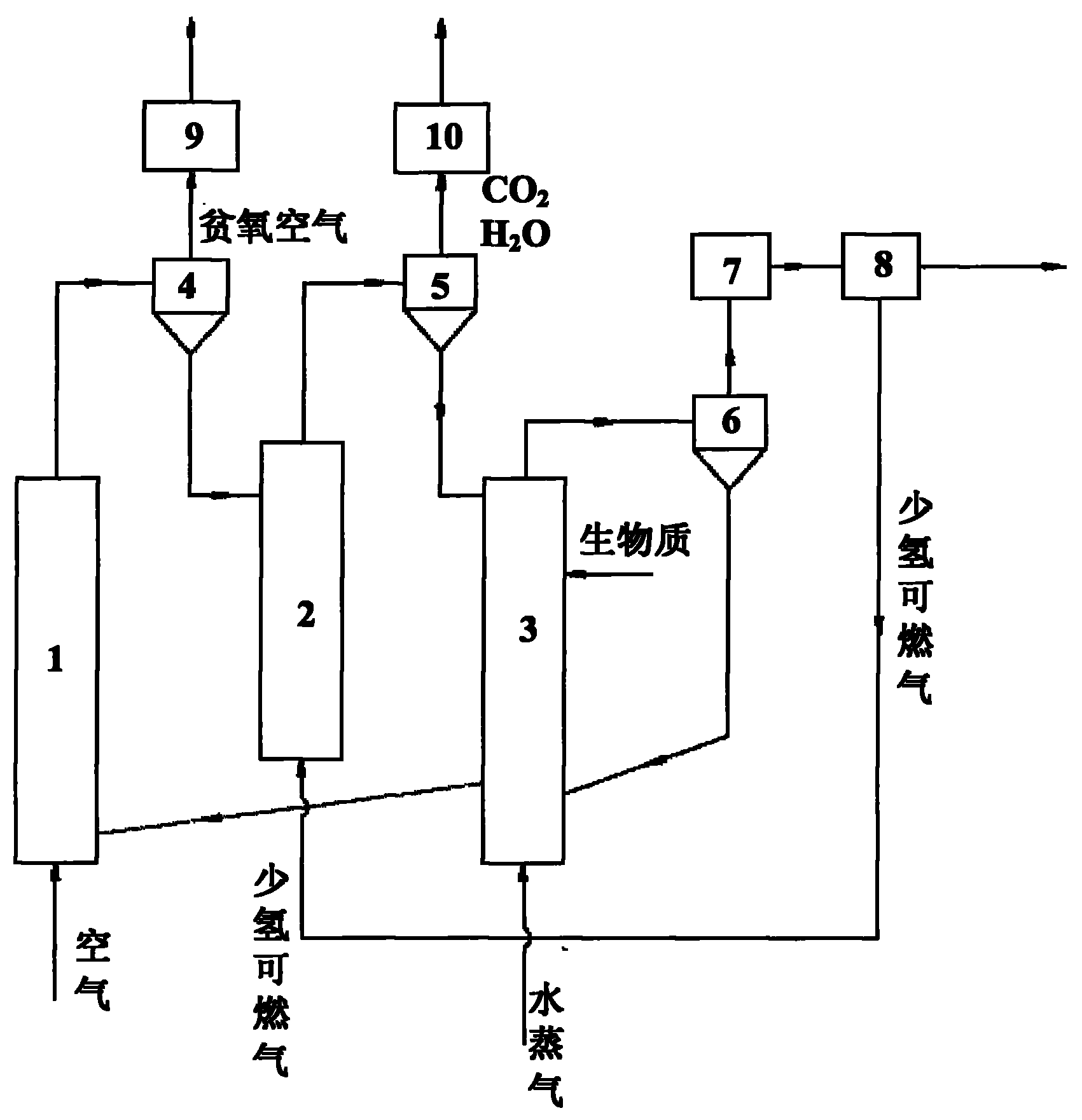
Biomass gasification hydrogen-producing system and method
InactiveCN101774542AReduce utilizationTo achieve hierarchical utilizationHydrogen productionGas solidHeat carrier
The invention discloses a biomass gasification hydrogen-producing system and a method, which belongs to the technical field of hydrogen production. Biomass gasification hydrogen production and chemical-looping combustion are combined to realize low-cost separation of carbon dioxide; and the fractional utilization of matter and energy is realized via the circulation among three beds with metal oxide as a heat carrier and an oxygen carrier. The system mainly comprises an air reactor, a fuel reactor, a moving bed gasifier, a gas-solid separation device, a gas purification device, a hydrogen separation device and a follow-up hydrogen-producing device. The system not only can realize hydrogen production, but also can realize hydrogen production with near zero emission of CO2, thereby realizing efficient cleaning and utilization of biomass.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
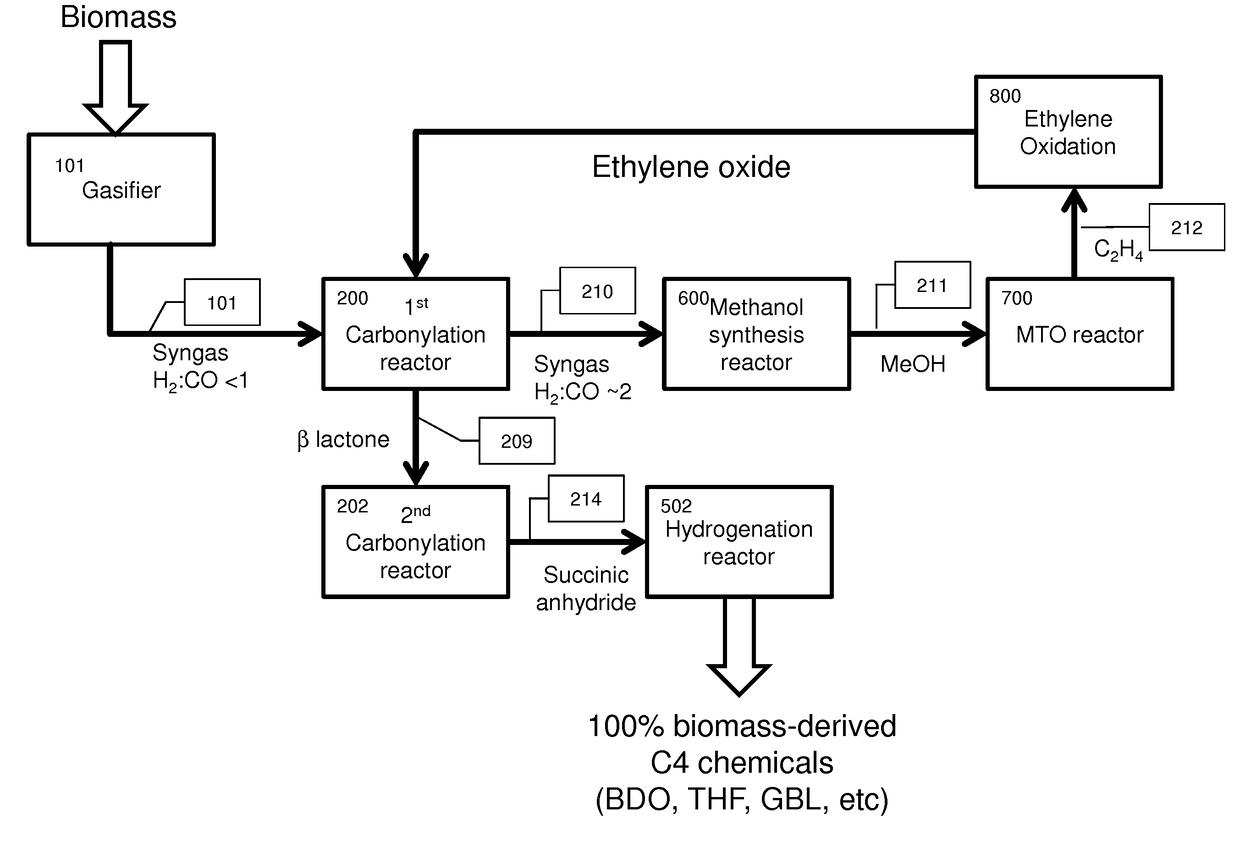
Biomass gasification and integrated processes for making industrial chemicals through an acetic acid intermediate
InactiveUS20130143972A1Raise the ratioCombustible gas catalytic treatmentBiofuelsCarboxylic acidOxygen
The invention relates to integrated processes for producing industrial chemicals, such as alcohols, carboxylic acids, esters, aldehydes, olefins and polymers from biomass. In one embodiment, the invention is to a process comprising the steps of (a) introducing biomass and an oxygen stream to a gasifier and converting the biomass into a product gas, wherein the gasifier is operated at a pressure of at least 10 bar; (b) compressing the product gas at a compression ratio that is less than 5:1 to form compressed product gas; (c) directing a first portion of the compressed product gas to an alcohol synthesis reactor to produce methanol; (d) directing a second portion of the compressed product gas to a gas separator to produce a hydrogen stream and a carbon monoxide stream; (e) reacting the carbon monoxide stream with the methanol to produce acetic acid; and (f) reacting the hydrogen stream with acetic acid to produce ethanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Integrated methods for chemical synthesis
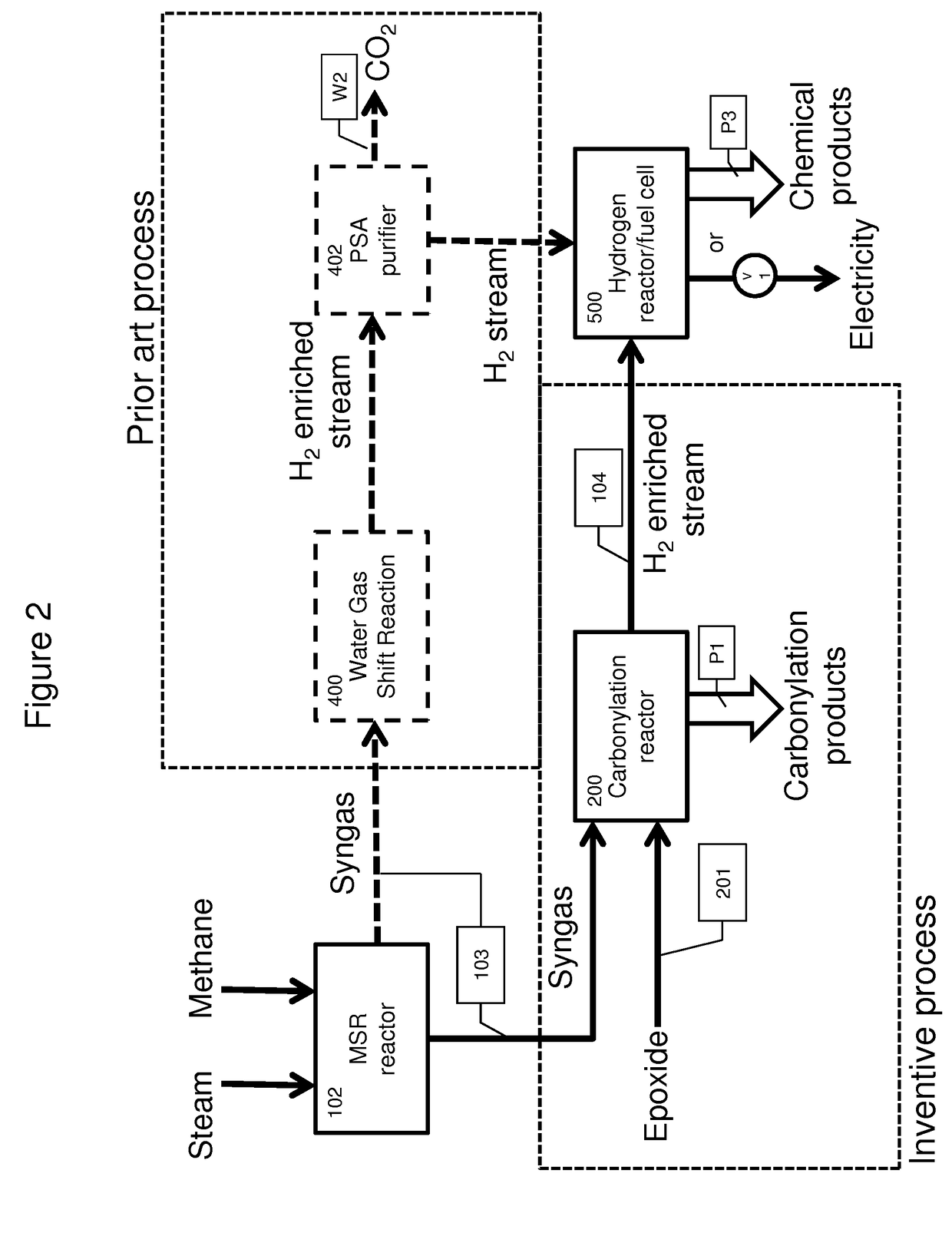
ActiveUS20170107103A1Improve carbon efficiencyQuantity maximizationBiofuelsPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesChemical synthesisSyngas
Among other things, the present invention encompasses the applicant's recognition that epoxide carbonylation can be performed industrially utilizing syngas streams containing hydrogen, carbon monoxide and varying amounts carbon dioxide. Contrary to expectation, the epoxide carbonylation reaction proceeds selectively in the presence of these mixed gas streams and incorporates excess CO in the syngas stream into valuable chemical precursors, resulting in hydrogen streams substantially free of CO. This is economically and environmentally preferable to performing WSGR which releases the excess carbon as CO2. The integrated processes herein therefore provide improved carbon efficiency for processes based on coal or biomass gasification or steam methane reforming.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Process of catalyzing and gasifying fresh substance by solid thermophore for preparing hydrogen-rich gas
InactiveCN1482056AFast pyrolysisRapid mixing and heatingDirect heating destructive distillationHydrogen productionHydrogenHeat carrier
The present invention relates to the method of extracting hydrogen from biomass, and is especially the solid heat carrier catalyzing and gasifying method of preparing hydrogen-rich gas from biomass.The method includes mixed heating of solid heat carrier catalyst and biomass, fast thermolysis of biomass, catalytic gasifying and regeneration circulation of solid catalyst grain. The catalyst as solid heat carrier has accumulated heat for gasifying biomass. The technological apparatus consists of mobile bed reactor, material feeder, regenerating riser tube, catalyst storage tank, etc. The present invention makes the hydrogen in biomass converted into hydrogen gas at most, and the continuous switch-less regeneration of catalyst solves the problem of fast deactivation of catalyst. The present invention has low tar content, simple operation and high gas product purity, and is new technological process with great potential.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Device and method for preparing hydrogen-rich gas by gasifying biomass
ActiveCN103923705AAvoid mixingEfficient use ofEnergy inputGasification with fuel pre-distillationWater vaporGas cooler
The invention discloses device and method for preparing hydrogen-rich gas by gasifying biomass. The device mainly comprises a pyrolysis reactor, a combustion reactor, a gasification reactor, a gas-solid separator, a gas cooler and an exhaust heat boiler, wherein the pyrolysis reactor is arranged in the combustion reactor. In a process course, the biomass is firstly pyrolyzed in the pyrolysis reactor to generate pyrolysis gas and coke, the pyrolysis gas is directly combusted to provide heat for biomass pyrolysis and gasification, and the coke is subjected to gasification reaction with water vapor to obtain the hydrogen-rich gas. The device and method disclosed by the invention realize the separation of the pyrolysis process and coke gasification process of the biomass and can be used for displacing the hydrogen contained in the water vapor by sufficiently utilizing fixed carbon contained in the biomass. According to the device and method, the obtained hydrogen-rich gas mainly contains H2, CO2 and a small amount of CO, so that the conventionally gasified hydrogen-rich gas product is prevented from being mixed with low-carbon hydrocarbon gas and tar, and the subsequent decontamination and purification utilization are simple, convenient and economic.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Selective non-catalytic reduction method for gasifying and atomizing biomass and used boiler
InactiveCN101433799AWidely distributedWell mixedLighting and heating apparatusDispersed particle separationProcess engineeringMixed gas
The invention relates to a selective non-catalytic reduction method for gasifying and atomizing biomass and a boiler used by the same, which relate to the selective non-catalytic reduction method and the boiler used by the same. The invention solves the problems that the prior selective non-catalytic reduction method has narrow temperature window, low denitration efficiency at a low temperature region and single effective component in synthesis gas of a reaction additive. The inlet of a gas mixer of the boiler is communicated with a gas additive pipeline and a compressed air pipeline respectively, while the outlet of the gas mixer is communicated with an atomizing medium pipeline. The selective non-catalytic reduction method mixes the biomass gasified gas in the gas additive pipeline with the compressed air through the gas mixer, uses the mixed gas as an atomizing medium for an amino reducing agent solution, and sprays the atomizing medium and the amino reducing agent solution together into a furnace chamber and a horizontal flue in a region with a temperature of between 800 and 950 DGE C through nozzles arranged in the furnace chamber and the horizontal flue. The selective non-catalytic reduction method improves the denitration efficiency and enlarges the temperature window. The boiler system of the invention is simple and has high reliability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and device for preparing low-tar combustible gas through biomass gasification
ActiveCN101906323AHigh cracking rateMake up for the problem of low conduction rateGranular/pulverulent flues gasificationFixed bedCombustible gas
The invention discloses a method and a device for preparing a low-tar combustible gas through biomass gasification. The method comprises the followings steps of: pulverizing and gasifying biomass, and rapidly separating obtained gasification gas products and biomass char; heating and activating the biomass char in a microwave field; catalytically cracking tar in the gasification gas products by introducing the gasification gas products to pass through a treated biomass char layer, and carrying out secondary reaction on the gasification gas and the biomass char to produce the combustible gas. The device comprises a spiral-flow gasifier 1, a fixed bed reactor 2 and a microwave generator 3 which are connected through ducts, and the middle part of the fixed bed reactor is connected with the microwave generator 3 through a microwave duct 11. The microwave technology is applied to tar cracking, so that the problem of low heat transfer speed due to porous and loose biomass char is solved. Meanwhile, the cracking rate of tar and the secondary reaction activity between the char and the gasification gas are increased by using the 'hot spot effect' of microwaves. The device has the advantages of strong adaptability, simple and compact structure and easy enlargement.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
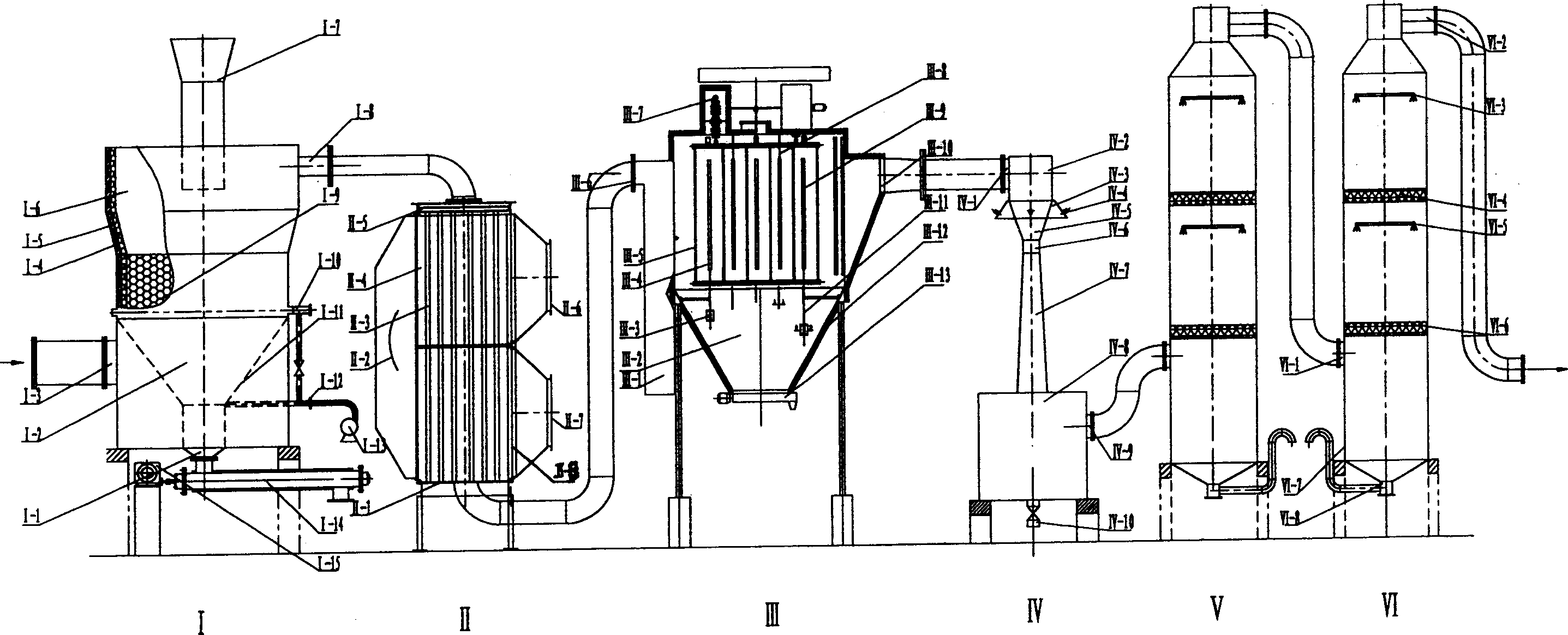
Biomass graded temperature-control slow pyrolysis process and its system
ActiveCN1935941AMeet the requirements of gasification reactionGuaranteed operating conditionsBiofuelsEnergy inputSyngasTemperature control
The invention relates to biomass grading temperature controlling slow speed pyrolysis technology and its system. The technology includes the following steps: dividing the pyrolysis into many independent stages with temperature increasing; processing countercurrent flow for external heat source and biomass; heating the biomass grade by grade to make it pyrolyse; pre-drying and deep drying the material to make sure its water content is 5-10%; pre-charring and charring to gain charcoal, pyrolysis gas, little gas state biological crude oil; processing the secondary decompose for the crude oil at roasting stage to gain the pyrolysis product. The system is made up of external hot gas source and its bypass route, main heat exchanger, multiple-stage pyrolyzer, and multiple-stage heat exchanger. The invention has the advantages of wide material accommodation limit, easy adjustable pyrolysis process, easy controllable pyrolysis product, utilizing waste heat to increase gasification efficiency.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
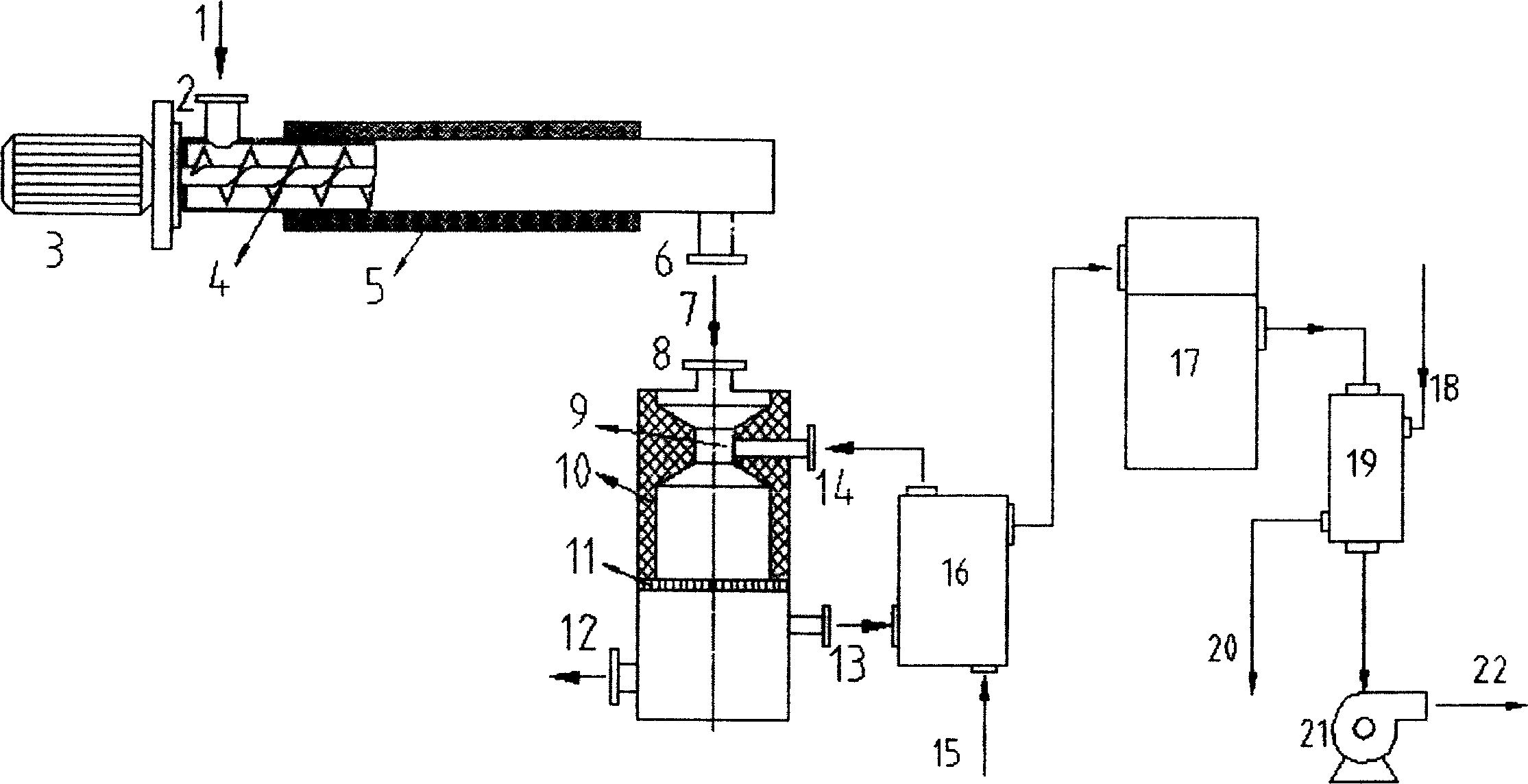
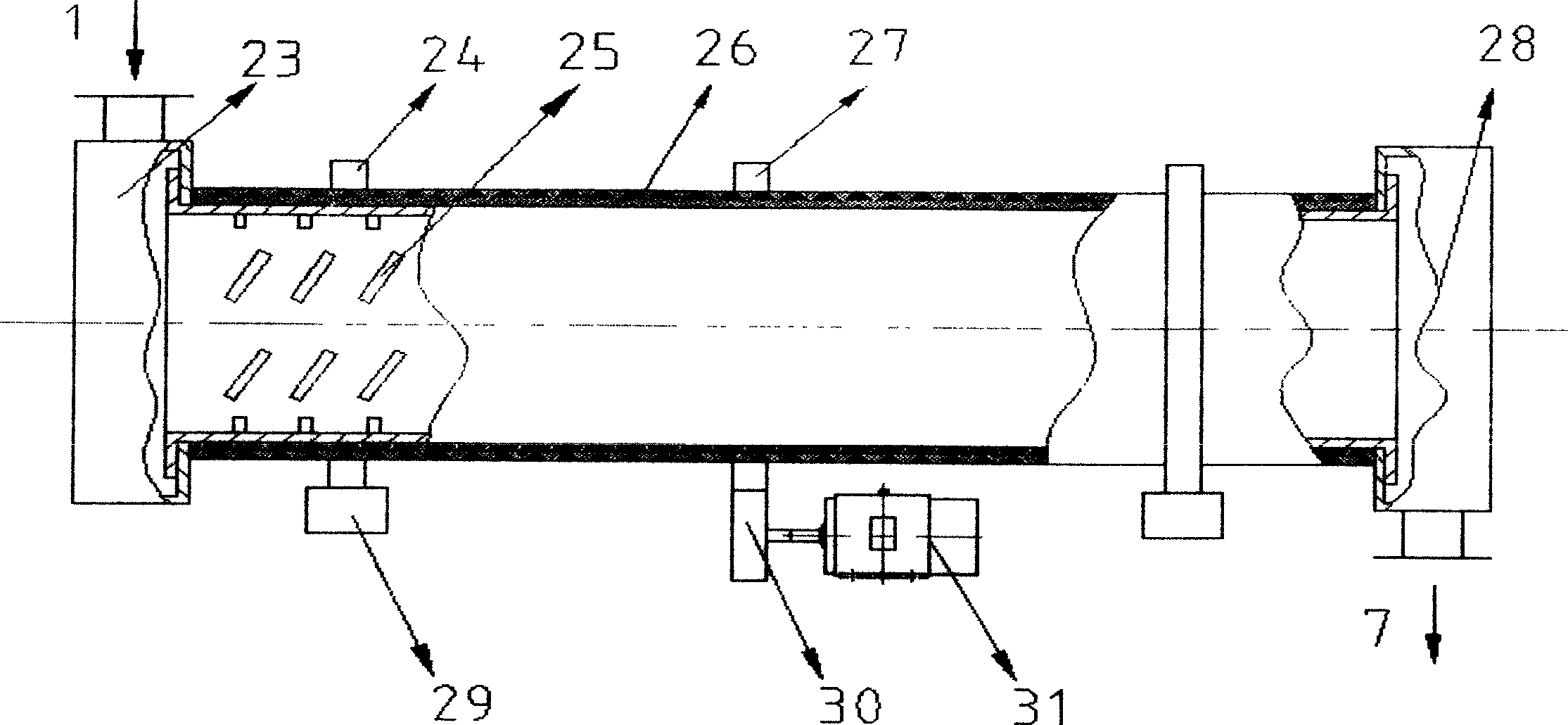
Biomass gasification/pyrolysis system and process
A system and process capable of promoting the energy content of a syngas produced from a biomass material. The system and process entail compacting a loose biomass material and simultaneously introducing the compacted biomass material into an entrance of a reactor tube, and then heating the compacted biomass material within the tube to a temperature at which organic molecules within the biomass material break down to form ash and a fuel gas mixture. The fuel gas mixture is withdrawn from the tube and the ash is removed from the tube through an exit thereof. The entrance and exit of the tube, the compaction step, and the removal step cooperate to inhibit ingress of air into the tube by forming a plug of the biomass material at the entrance of the tube and a plug of ash at the exit of the tube.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Harmless gasification treating process for medical waste
InactiveCN102641880ASave on shipping costsSave on processing costsSolid waste disposalIncinerator apparatusWater vaporExhaust pipe
The invention discloses a harmless gasification treating process for a medical waste. By the process, the water content of a biomass gasification auxiliary material is less than 40 percent, and the particle diameter is controlled to be between 0 and 10mm. The treating process comprises the following steps of: mixing the medical waste with the biomass gasification auxiliary material in volume ratio into a mixture, wherein metal and glass are removed from the medical waste and the medical waste is subjected to solid-liquid separation, adding the mixture into a medical waste treating gasification furnace at the speed of 1 to 50kg / h, operating a balance wheel to compress the mixture, covering a top cover, opening an exhaust pipe and a valve which is arranged on a primary air supply pipe, closing a valve on a secondary air supply pipe, starting a fan, and adjusting the temperature of the medical waste treating gasification furnace; and when flue gas which contains much and steam is exhausted, closing a valve on an exhaust pipe, opening a valve of the secondary air supply pipe, filtering crude gas generated by the medical waste treating gasification furnace through a silk bamboo net in a purified gas conveying pipe, and conveying purified gas into a gas burning tower. The treating process for the medical waste can perform harmless gasification treatment on the medical waste, saves transportation cost and treatment cost, and is obvious in social benefit and environment-friendly benefit.
Owner:罗江平
Biomass vaporizing combustion coupled type cyclone boiler
InactiveCN101625117ABurn fullyGuaranteed gasification effectChemical industrySolid fuel combustionCycloneCombustion chamber
The invention relates to a biomass vaporizing combustion coupled type cyclone boiler, solving the problems of low thermal efficiency, high tar content in vaporizing gas, easy scorification of a high-temperature heating surface and the like existing in the current biomass boiler, and comprising a jacketed type boiler body and a feeding device thereof, a primary air fan, a secondary air fan, a water circulating pump, an ash slurry pond and a flue water fog deduster. The invention has the technical points that the secondary air fan is connected with the jacket of the boiler body, and an atomizing nozzle is arranged on the inner side of an outer boiler wall; secondary air and water vapour tangential jet holes are distributed on the circumference of an inner boiler wall; one end of a small spiral feeder of the feeding device is connected with the inner cavity of a vaporizing combustion chamber, and the other end is connected with the secondary air fan by a feeding air valve; the vaporizing combustion chamber and a complete combustion chamber are communicated. The invention has reasonable structure design and stable operation and strengthens effects of heat transfer and fuel vaporization, which can increase the transformation efficiency of biomass energy and heat values of biomass fuel vaporizing products, and thus, the biomass fuel is completely and sufficiently burnt, thereby saving energy, increasing the heat efficiency of the boiler, protecting environment and reducing environmental pollution.
Owner:辽宁玺丰新能源科技有限公司
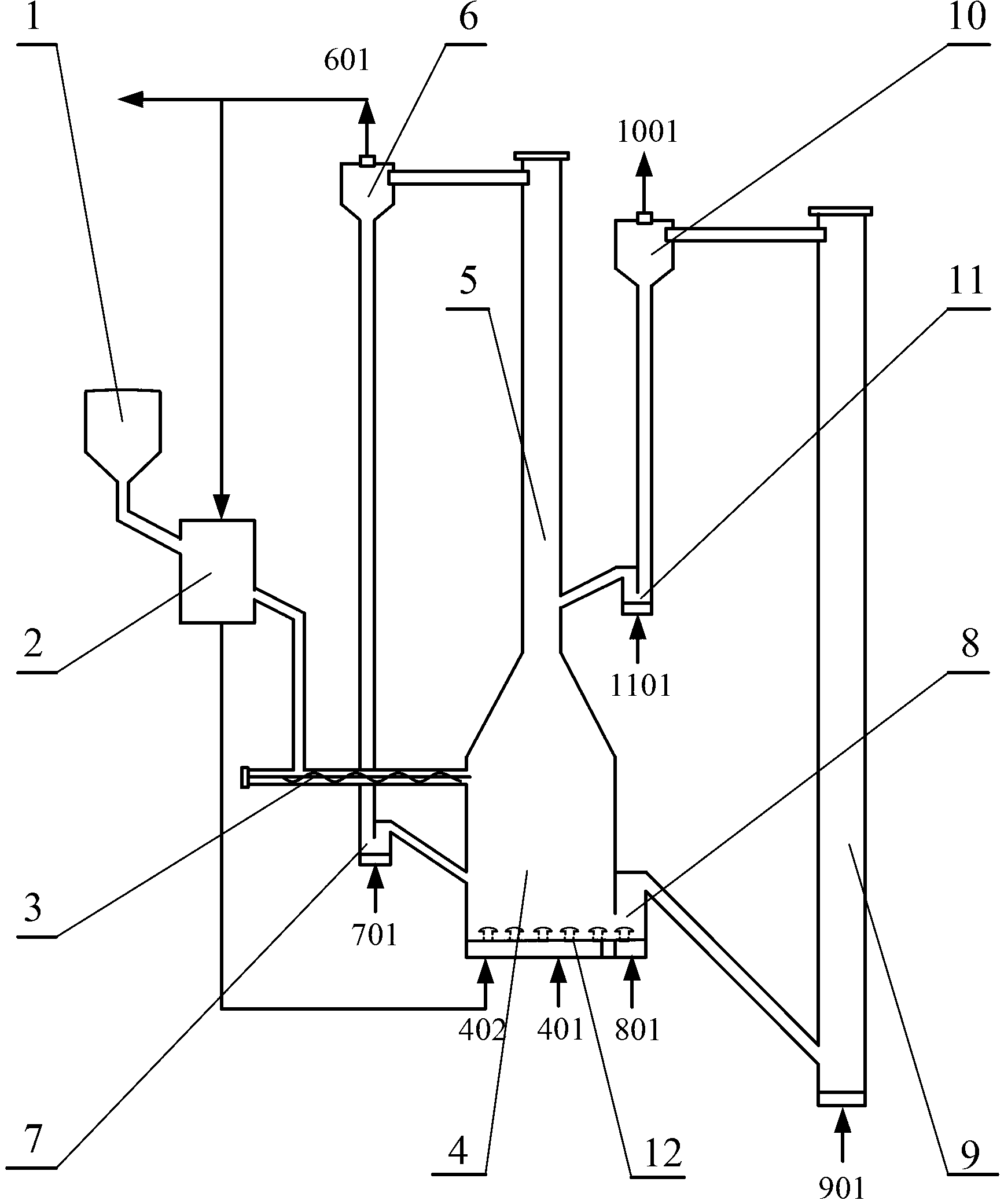
Apparatus for preparing synthesis gas based on dual fluidized bed biomass gasification and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102977927AReduce outputHigh calorific valueBulk chemical productionGranular/pulverulent flues gasificationCycloneGas phase
The present invention discloses an apparatus for preparing synthesis gas based on dual fluidized bed biomass gasification, including a hopper, a dryer, a screw feeder, a pyrolysis fluidized bed, a reforming fluidized bed, a reforming cyclone separator, a calcination fluidized bed, a calcination cyclone separator, a first U-shaped refeeder, a second U-shaped refeeder and a third U-shaped refeeder. The method of the apparatus for preparing synthesis gas includes: feeding biomass into the hopper, feeding the dried biomass to the pyrolysis fluidized bed, pyrolyzing and gasifying, and feeding carbon residue into the calcination fluidized bed. In the calcination fluidized bed, the coke in solid residue is combusted with oxygen to decompose calcium carbonate. The products of gas phase and solid phase are separated by the calcination cyclone separator. The heat-carrying agent calcium oxide is fed into the reforming fluidized bed. The pyrolysis gas carries calcium oxide to increase to promote catalytic cracking of tar. The reformed gas is obtained by reforming the pyrolysis gas. The synthesis gas is obtained from a synthesis gas outlet. The apparatus for preparing synthesis gas can reduce the tar yield, and improve the synthesis gas heat value ?and gasification efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Plasma and calcium oxide cooperation-gasified rubbish biomass gasification method and equipment
InactiveCN101469865AReduce contentHigh calorific valueSpecial form destructive distillationIncinerator apparatusNew energyWater vapor
A method and apparatus for gasifying a plasma and calcium oxide cooperating with gasified rubbish biomass, relating to the rubbish processing and new energy resource field, characterized in that, the rubbish biomass is fed into a suspending fluidized bed thermal decomposition furnace, meanwhile, the heated fluidization material is circularly fed into the thermal decomposition furnace and is mixed with the raw materials to transfer heat, so that the rubbish biomass raw material is heated to decompose, and then the thermal decomposed gas and solid carbocoal is fed into a turbulent fluidized bed gasification furnace, the water vapor is heated over 3100 DEG C and is sprayed into the gasification furnace by a plasma spray gun, the water vapor is reacted with the solid carbocoal to generate carbon monoxide and hydrogen gas, the required heat of the gasification reaction in the gasification furnace can be provided by the plasma spray gun and an exothermal reaction of the calcium oxide absorbing the carbon dioxide. According to the invention, synthesis gas can be produced by rubbish and biomass raw materials under the condition without air or oxygen, the main ingredients of the synthesis gas are hydrogen gas and carbon monoxide which can be directly used for city gas or producing hydrogen gas, methanol and dimethyl ether and so on clean energies.
Owner:衢州市广源生活垃圾液化技术研究所
Multilevel-control polyradical biomass-gasification energy regeneration system
ActiveCN101519604AImprove gasification efficiencyHigh reforming efficiencyBiofuelsEnergy inputOxygenMoisture
The invention provides a multilevel-control free-polyradical biomass-gasification energy regeneration system, which can transform extensive biomass and carbon-containing raw materials, including energy crops, agriculture-forestry byproducts, organic waste, industrial and dangerous waste and the like, into high-grade energy. The system is designed for continuous operation. Gasification comprises the following steps of performing pretreatment, performing pyrolysis, transforming carbon, fusing ash, cracking tar, reforming syngas and utilizing waste heat, wherein the steps are precisely controlled one by one and integrated so as to achieve optimum; moisture from the pretreatment of the materials is led into a carbon-transforming unit so as to realize oxygen-free pyrolysis; gasification gas is in contact with a large number of free polyradicals in a free-polyradical reaction-accelerating unit; and the obtained product is purified and then enters downstream application, such as power generation, hydrogen production and biomass methanol / ethanol production. The system has the advantages of needing no auxiliary fuel, maximizing gasification efficiency and thoroughly cracking tar and clearing pollutants, and is an upstream technique for the application of biomass renewable energy. As energy utilization meets all strict environmental protection standards, the system is also an energy-saving environment-friendly technique for non-incineration harmless treatment.
Owner:浙江瑞拓展泰再生能源有限公司
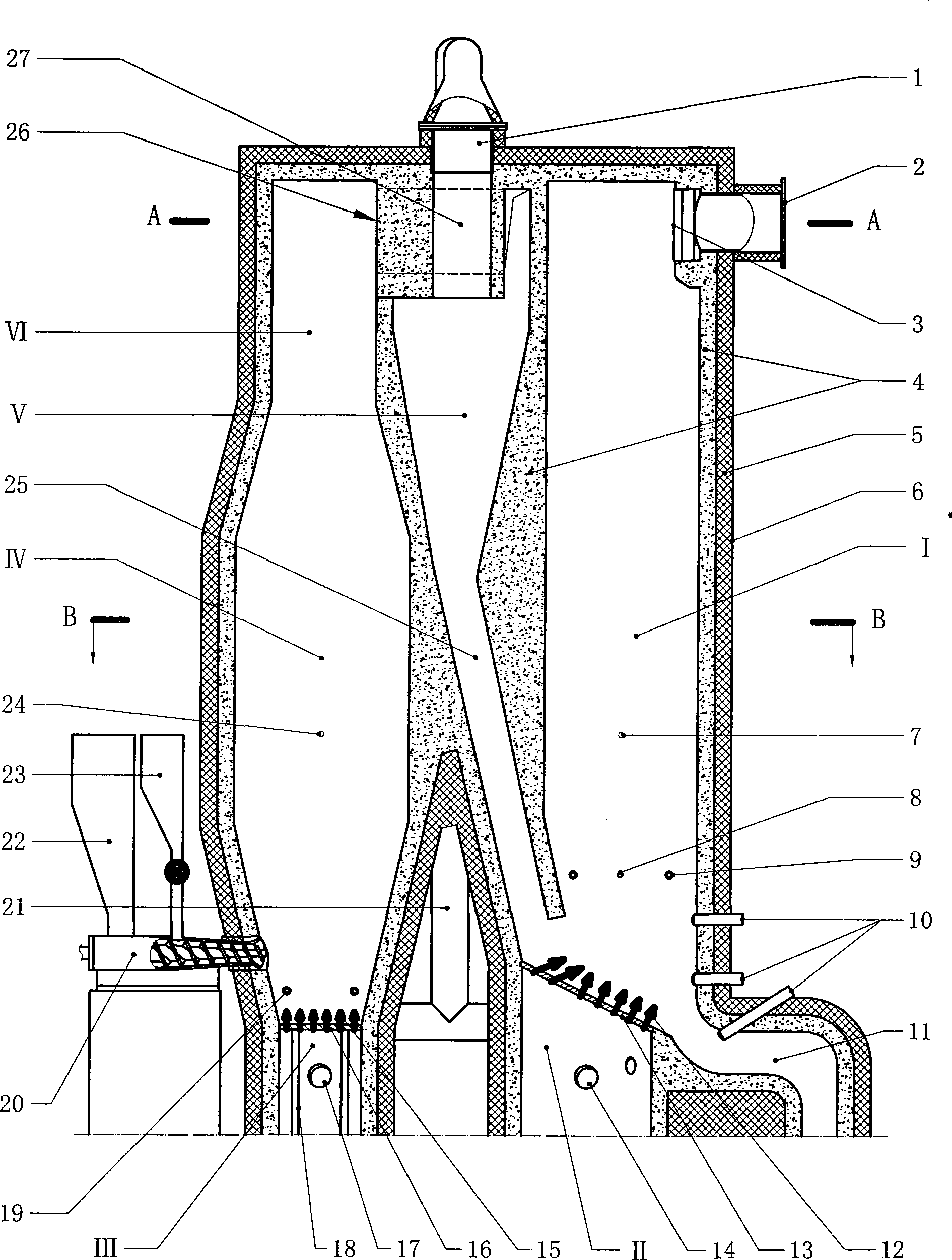
Microwave plasma biomass gasification fixed-bed gasification furnace and process
The invention relates to a microwave plasma biomass gasification fixed-bed gasification furnace and a process, comprising a vertically arranged furnace body; a gasification furnace clearance zone is arranged at the upper part of the furnace body; a fixed bed is arranged at the lowest part of the furnace body; an raw material and fuel inlet, a product gas outlet and an oxygen / steam inlet are arranged on the furnace body; a slag notch is arranged at the bottom of the furnace body, and a synthesis gas monitoring unit is arranged at the position of the product gas outlet. The gasification furnace and the process are characterized in that: at least one microwave plasma generating device is arranged on the furnace body, the characteristics of high dispersion degree and high ionization of microwave plasma are adopted to achieve high-efficiency conversion of biomass fuel chemical energy in the furnace. The cold gas efficiency can be significantly higher than that of the conventional biomass gasification process and can reach more than 85%. Non-equilibrium cleavage reaction is carried out to tar and the like in synthesis gas, so that tar content is very low, direct industrialization utilization can be achieved, and the follow-up process is simple and reliable. No special requirements on the fuel particle size are demanded, simple breaking operation is only needed without complex processing, and the economy is good.
Owner:WUHAN KAIDI ENG TECH RES INST CO LTD
Cracking purification method for combustible gas produced by gasifying crude material
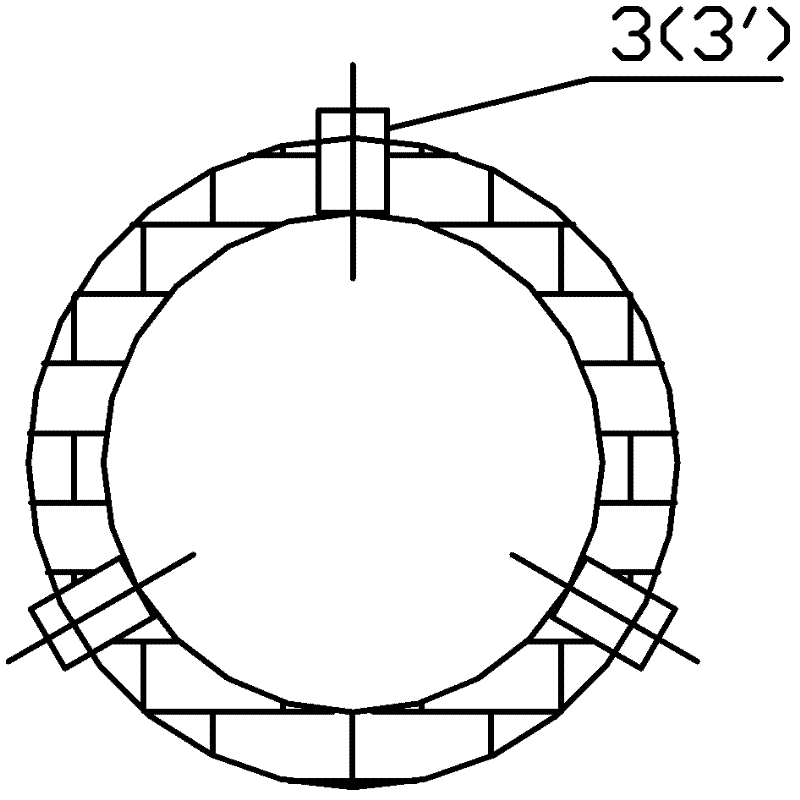
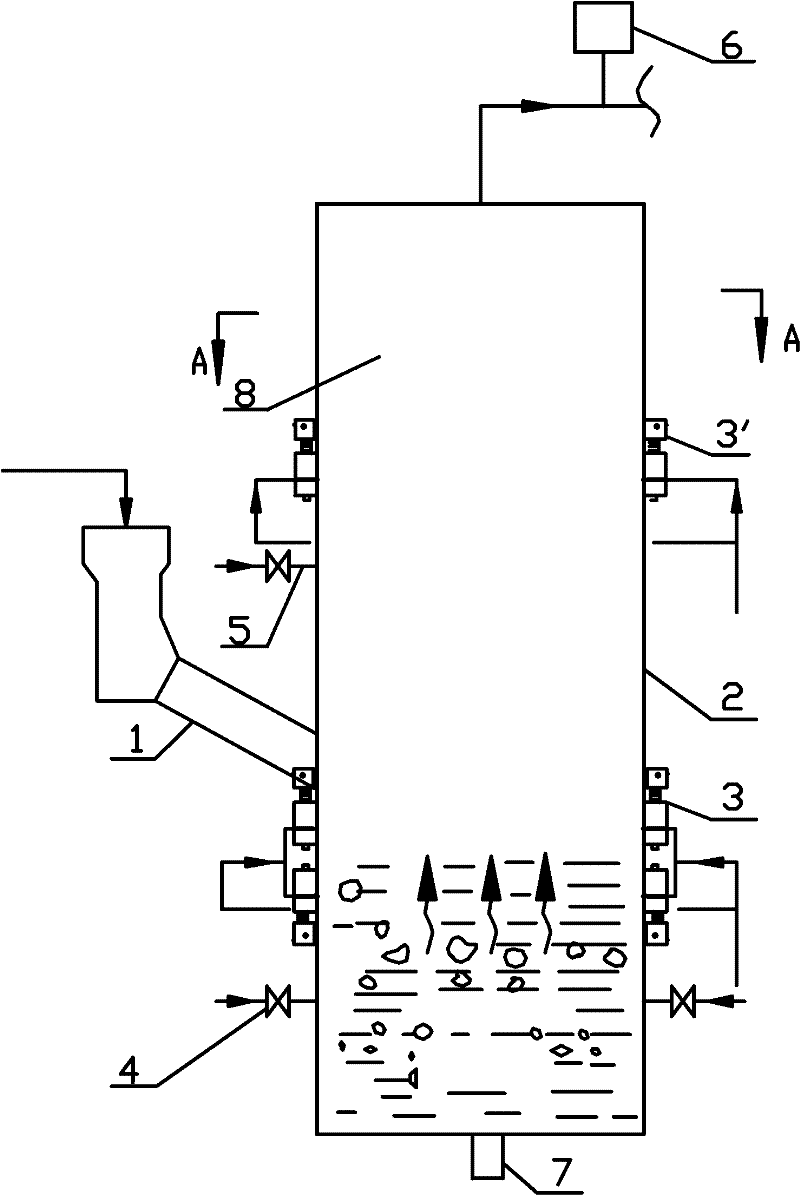
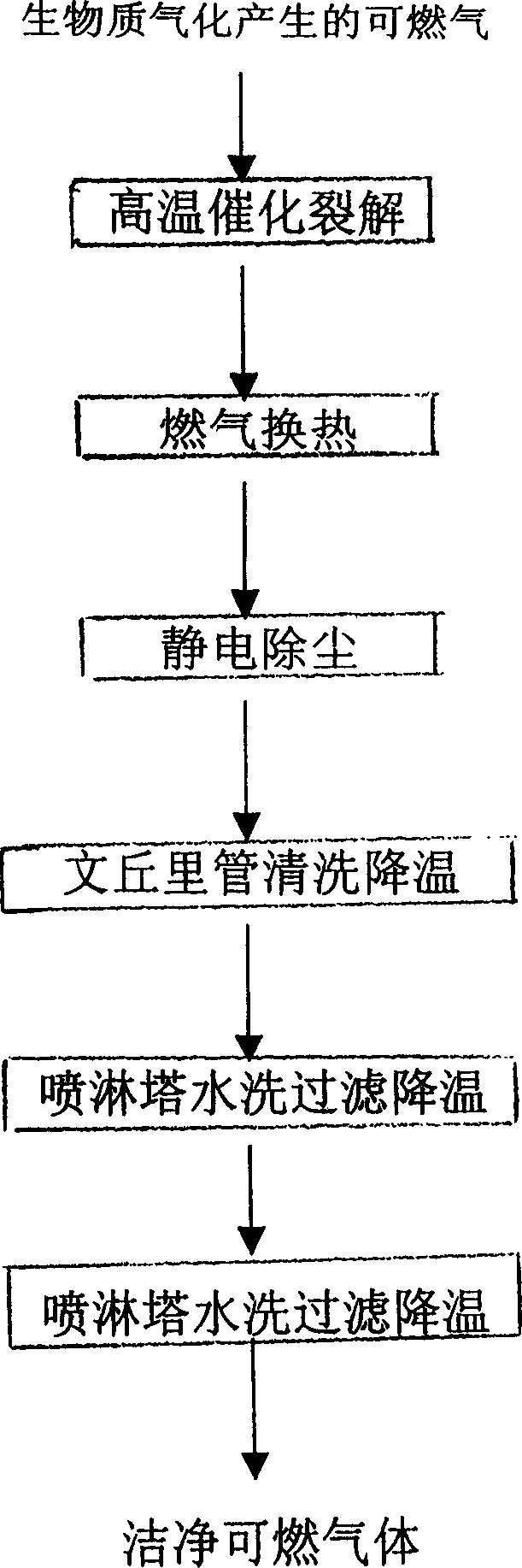
InactiveCN1485415AEfficient recyclingAffect operationCombustible gas catalytic treatmentPurification methodsHigh pressure
A method of degrading and cleansing combustible gases produced during gasifying biological matters. It comprises) passing a cracking machine with a moving bed, the combustible gases will be cracked by high-temperature and catalysis in the charcoal bed at 800-1200degree C, most of tar is removed; b)reducing the temperature of combustible gases from 800degree C to 300-350degree C; c) dedusting by static electricity at a high-voltage electric field of 80000 volts, reducing the temperature to 250-300degree Cú”(d) washed by water, debusting and detarring, reducing the temperature to 60-80degree Cú”(E) washing, filtering and reducing the temperature to below 40degree C, the contents of tar and dust in the combustible gases will be reduced below 50mg / Nm3. The invention could remove completely dust and tar in combustible gases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com