Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
153 results about "Biological hydrogen production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The biological hydrogen production with algae is a method of photobiological water splitting which is done in a closed photobioreactor based on the production of hydrogen as a solar fuel by algae. Algae produce hydrogen under certain conditions. In 2000 it was discovered that if C. reinhardtii algae are deprived of sulfur they will switch from the production of oxygen, as in normal photosynthesis, to the production of hydrogen.
Method for preparing hydrogen with biology and with utilization of organic waste water step
ActiveCN101270368AImprove Coulombic efficiencyHigh process energy conversion rateWater contaminantsFermentationActivated sludgePhosphate
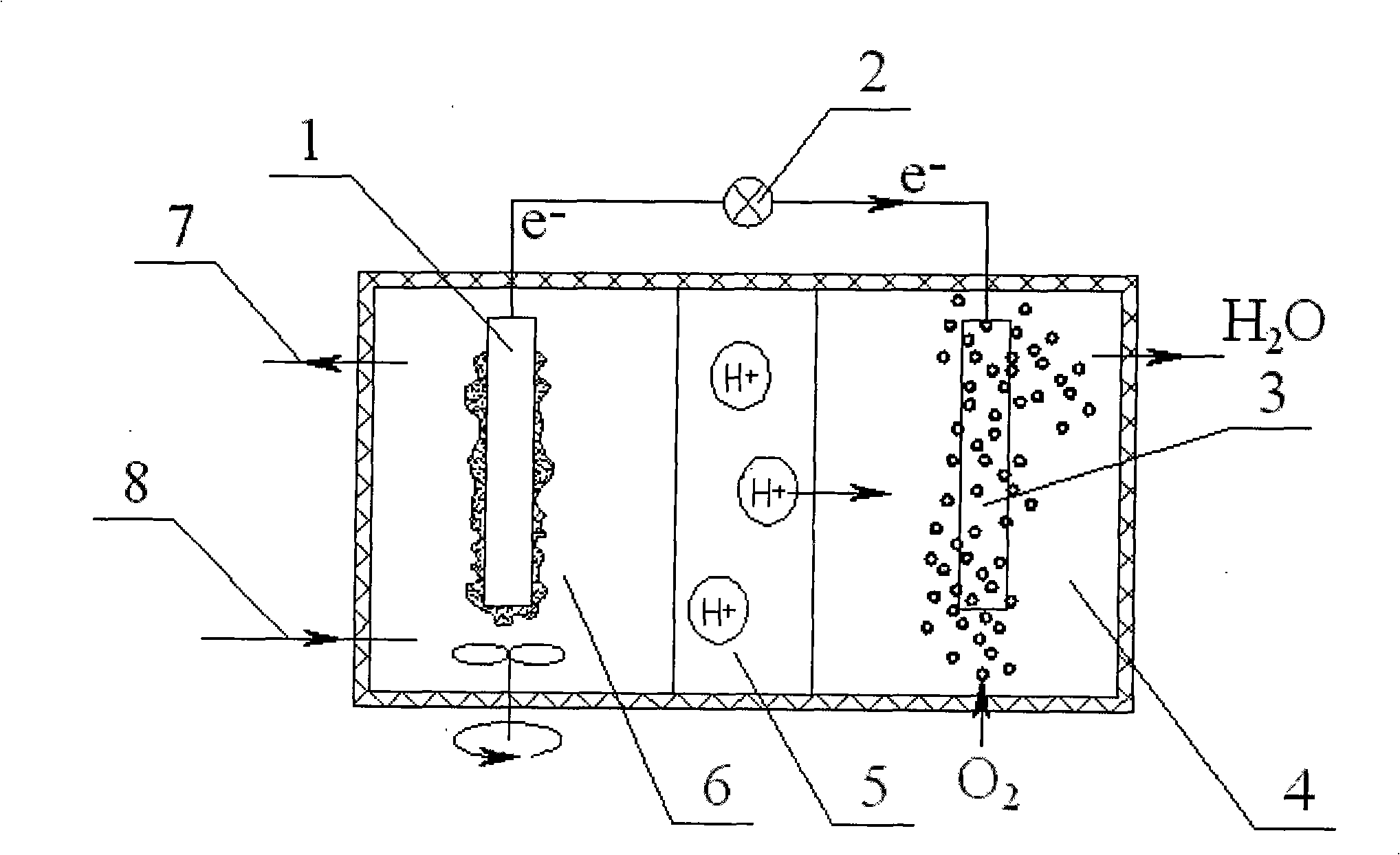
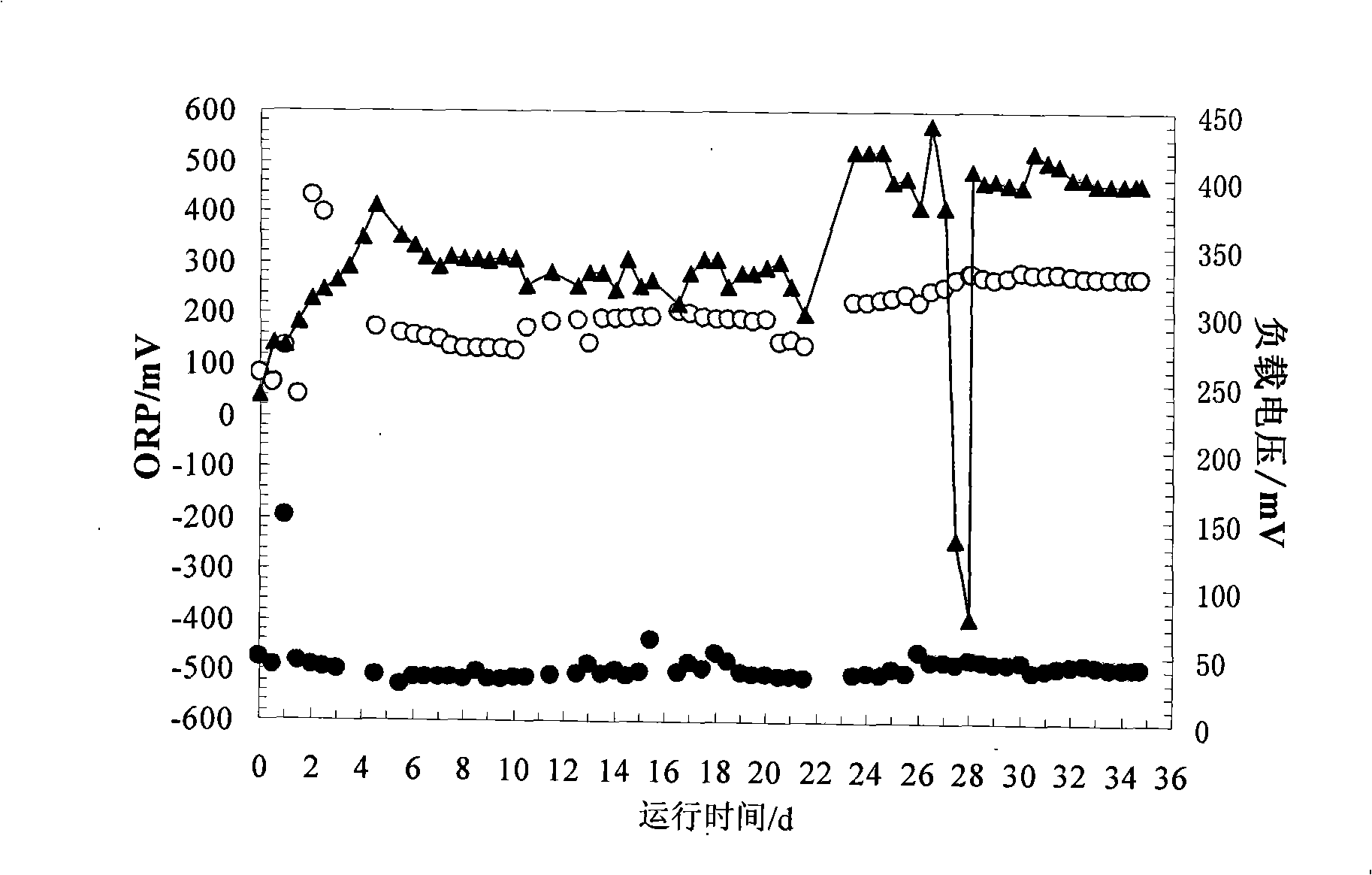
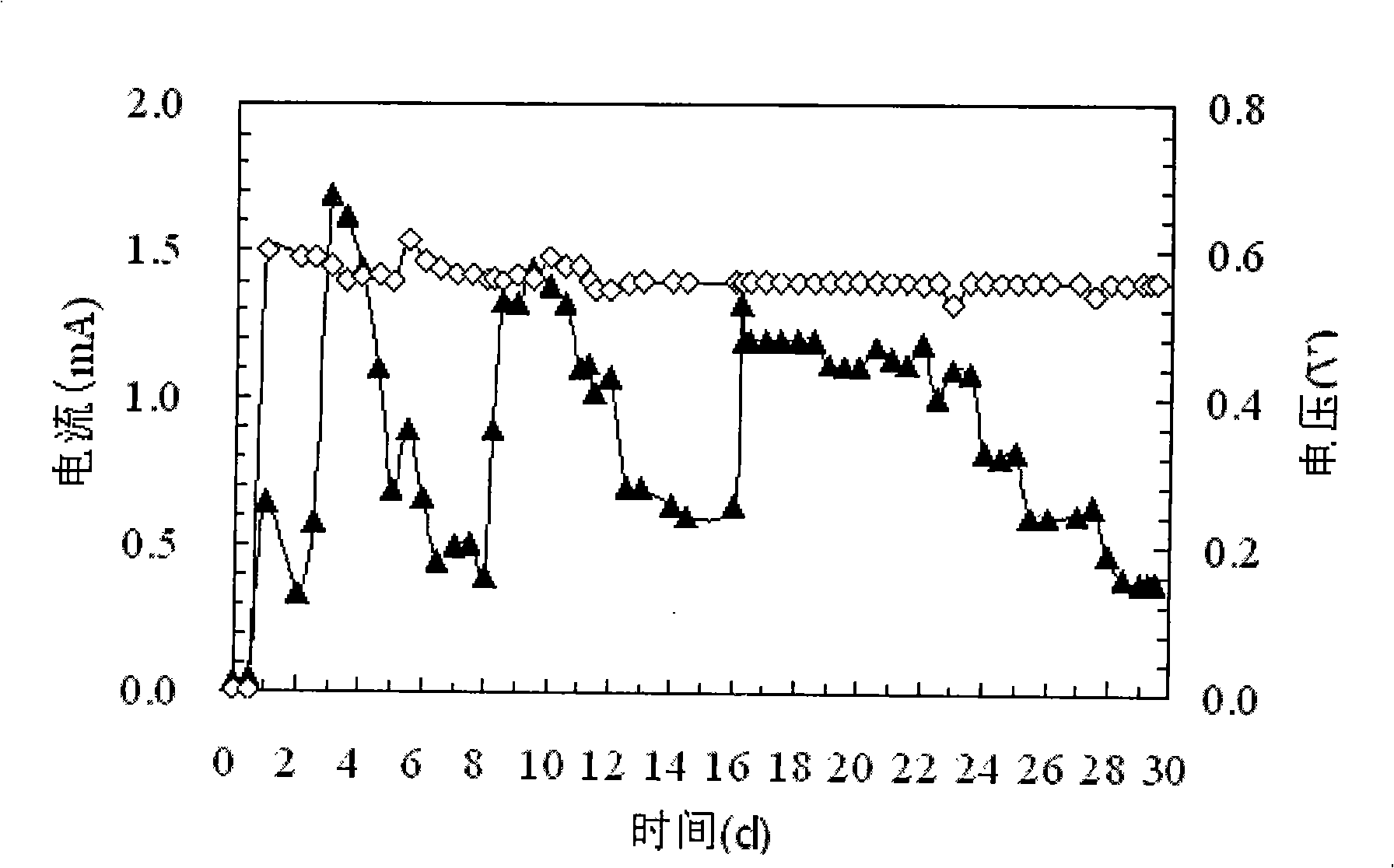
The invention discloses a method of hydrogen production of biological cascade utilization on organic wastewater and relates to a method of producing hydrogen. The invention solves the existing problem of low conversion on biological hydrogen production with organic wastewater fermentation by using anaerobic activated sludge. The hydrogen production method of the invention is carried out as follows: firstly an anode chamber is in the anaerobic condition during startup procedure, anaerobic activated sludge is put into the anode chamber, the nutrient solution with pH value of 6.8 to 7.0 is introduced into the anode chamber, phosphate buffer is added into a cathode chamber, aeration is carried out in the cathode chamber in the previous 28 to 35 days of the startup procedure, startup is successful till the output voltage is continuously and steadily over 400 mV; secondly the organic wastewater is filled into the anode chamber from an inlet of the anode chamber and the organic wastewater is processed in the anode chamber, consequently hydrogen is obtained in the cathode chamber. The coulombic efficiency of the organic substrate conversion of the method reaches as high as over 80 percent, the electron transfer efficiency of transferring the cathode electron into hydrogen approaches to 100 percent, the purity of the hydrogen obtained in the cathode chamber in the entire process reaches 99.5 percent, the energy conversion efficiency of the entire process reaches over 80 percent, and the hydrogen yield calculated based on the input voltage is 288 percent.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optimization design method of anaerobic continuous flow agitator bath type biological hydrogen production reactor
InactiveCN102855342ASimple designSolve engineering problemsSpecial data processing applicationsContinuous flowAgitator
The invention belongs to the field of environment protection, and in particular relates to an optimization design method of an anaerobic continuous flow agitator bath type biological hydrogen production reactor. The method comprises the following steps: researching reactor internal flow field characteristics of different types of stirring paddles under the conditions of different paddle-bath diameter ratios and different agitating speeds and influence on hydrogen production process, by using a numerical simulation software based on computational fluid mechanics technology; obtaining detailed flow field information, such as velocity field, turbulence energy and dissipation rate thereof, biogas integration rate and shearing rate distribution by adopting a two-phase flow model, and analyzing and comparing different flow field information obtained through simulation according to influence on hydrogen production process by the various flow field information, thereby determining an optimal stirring paddle style and agitating speed combination, and providing an effective method for the optimization design of the agitator bath reactor. The optimization design method of the anaerobic continuous flow agitator bath biological hydrogen production reactor is mature in technology, avoids the blindness of hydraulic design of the reactor using an empirical or semiempirical association method, and has the advantages of being visual in optimization cycle effect and short in optimization cycle, saving cost, and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
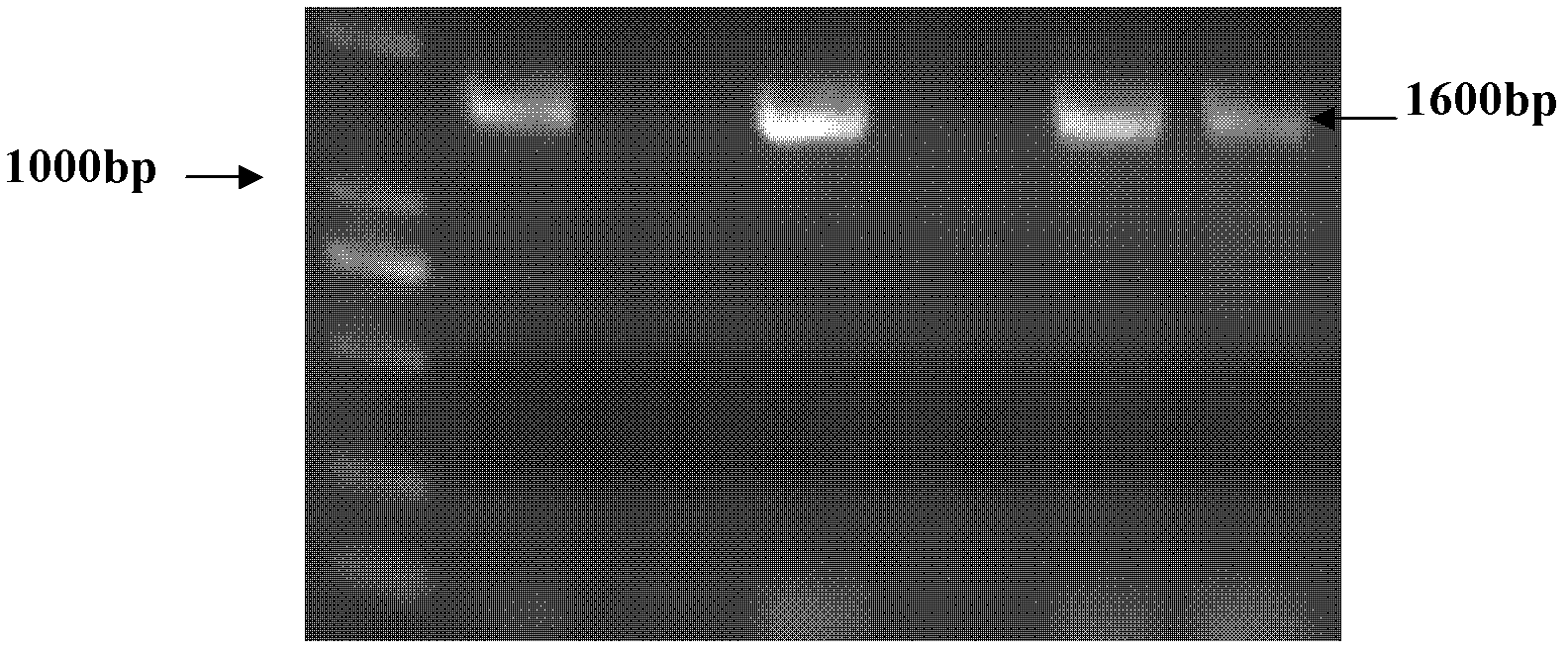
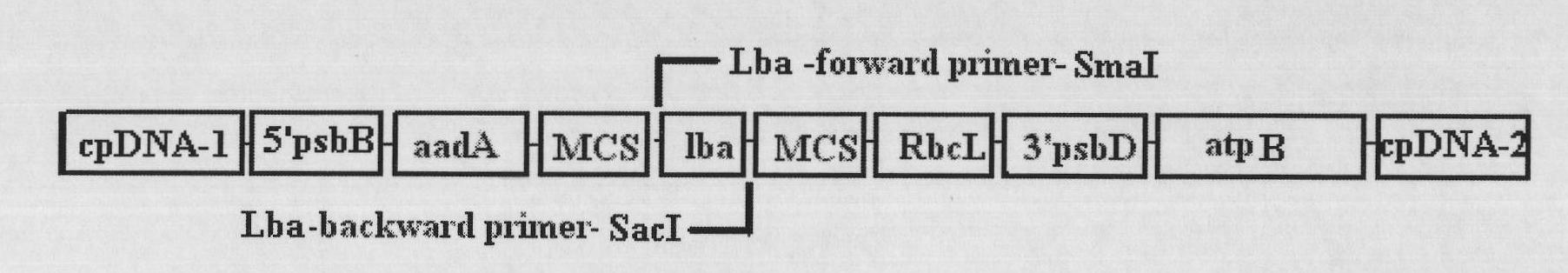
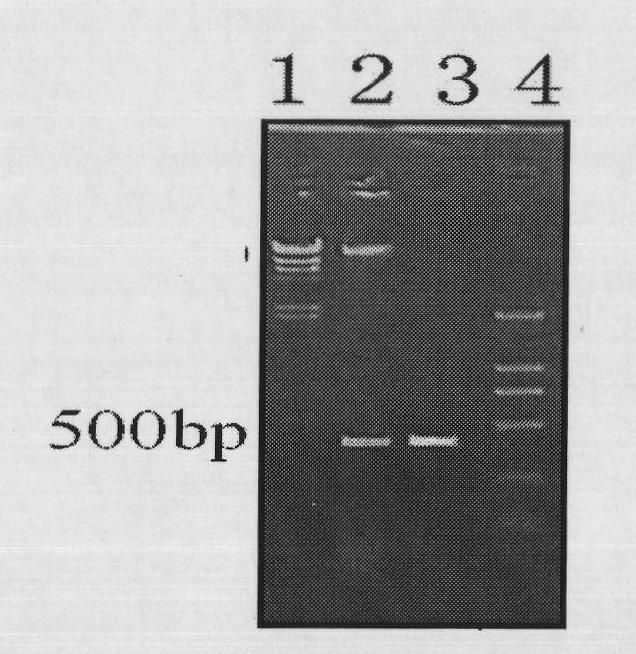
Method for improving chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene
InactiveCN101775407ALower oxygen levelsIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeFermentationEnzyme GeneChlamydomonas reinhardtii
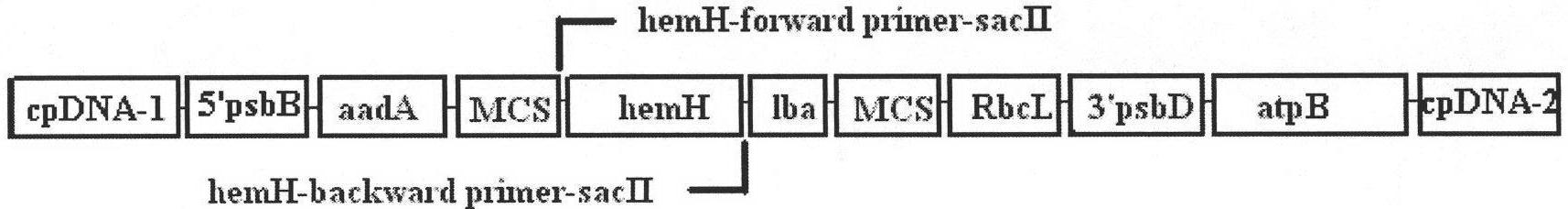
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for improving the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production method has the defects that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen enzymes are sensitive to oxygen and easily restricted by the oxygen to lose activity, and the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production effect is limited. The invention discloses an application of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene and a globulin subunit gene to hydrogen production by constructing the leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene hemH and the globulin subunit gene lba in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, transferring the expression vector in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast and expressing the hemH-lba gene in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The invention has the advantages that the content of oxygen in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is reduced obviously faster than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of an un-transformed gene, the oxygen content is kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen production amount is obviously increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Composite system used for purifying high ammonia nitrogen pig breeding biogas slurry via algae-bacterium symbiosis/ecological floating bed combined technology
ActiveCN106396112AEasy to handleRealize ecological treatmentWaste water treatment from animal husbandryWaste based fuelBiodieselPig breeding
The invention discloses a composite system used for purifying high ammonia nitrogen pig breeding biogas slurry via algae-bacterium symbiosis / ecological floating bed combined technology. According to the composite system, algae-bacterium symbiosis and ecological floating bed technology is taken as a base, a high-efficiency low-consumption standard treatment system of high ammonia nitrogen pig breeding biogas slurry is constructed, and algae bacterium biomass and plant are obtained at the same time. A purifying method comprises following steps: pig breeding waste water is subjected to solid-liquid separation firstly, and is delivered into an anaerobic fermentation pool; generated high ammonia nitrogen biogas slurry is subjected to pH adjusting and nutritive salt adjusting, and is delivered into the composite system for processing, and biochemical treatment effluent is delivered through a flocculating settling pool and a disinfectant pool so as to realize clear water up-to-standard release. Operation is simple; operation cost is low; pollutant removing efficiency is high; harvested algae bacterium biomass can be taken as a raw material of feed, biological hydrogen production, and biodiesel, and no secondary pollution is caused.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen and/or methane through fermentation of fiber wastes and device thereof
InactiveCN101760481ASolve pollutionWidely used valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingFiberLiquid storage tank
The invention provides a method for producing hydrogen and / or methane through fermentation of fiber wastes and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps: smashing a straw into a certain grain diameter, placing into a hydrogen production reactor, adding a given amount of water and nutrient solution and then mixing with thermophile bacteria seed liquid together for fermentation to prepare the hydrogen; pumping hydrogen fermentation liquid into a liquid storage tank, continuously pumping into the hydrogen production reactor for fermentation to prepare the methane after pH is adjusted. Because of adopting fiber wastes, raw materials used by the invention have rich resource and low cost, effectively solve the resource problem of biological hydrogen production and overcome the problem that the fiber raw materials of the traditional straw are hard to effectively produce the hydrogen when being not subjected to pretreatment; and the semi-continuous hydrogen production is achieved through the fiber waste dynamic immobilization technology. The invention is easier to popularize and apply by adopting a coupled continuous methane production system and has the advantages of simple and highly-efficient method, energy conservation, low cost and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization
InactiveCN102146344AHigh expressionLower oxygen levelsUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to exogenous gene expression and biological hydrogen production technologies, in particular to a method for increasing exogenous gene expression quantity and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity by codon optimization. In the prior art, the expression efficiencies of exogenous leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast are low, thus influencing the increase of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity. The invention discloses a method for respectively optimizing the codon bias of the leghemoglobin genes hemH and lba. The codon-optimized hemHc and lbac genes are transferred into the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast to be expressed. The invention obviously increases the expression quantity of the exogenous recombinant protein; the expression quantity of the exogenous leghemoglobin hemH and Lba in the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast is increased by 6.8 times; and compared with the non-codon-optimized hemH and lba transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production quantity is increased by 22%. The invention is applicable to regulating and controlling the exogenous gene expression of more species having codon bias.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
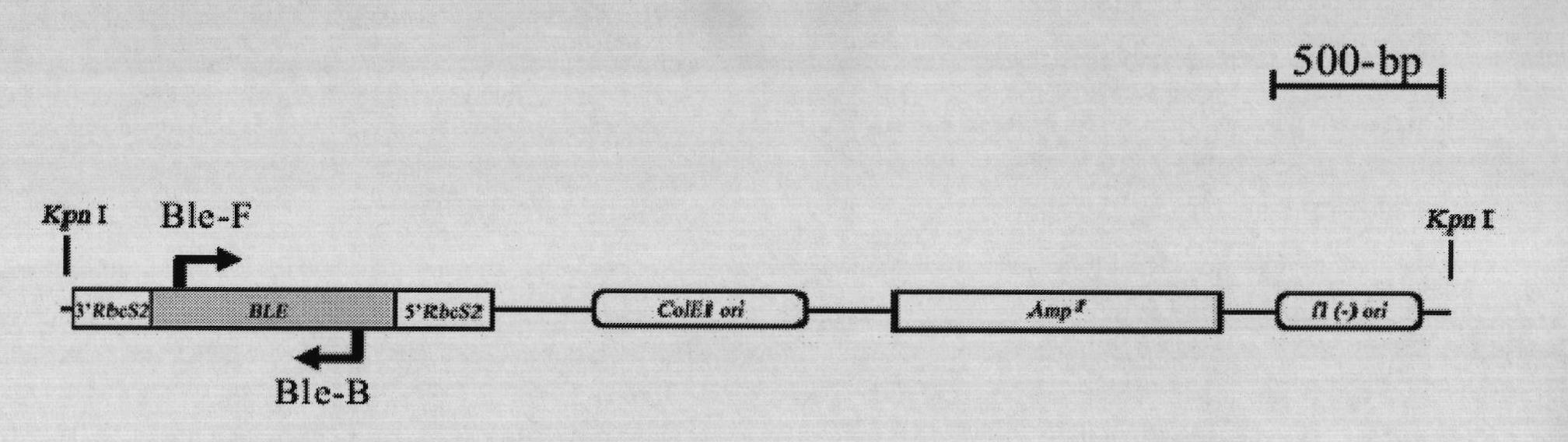
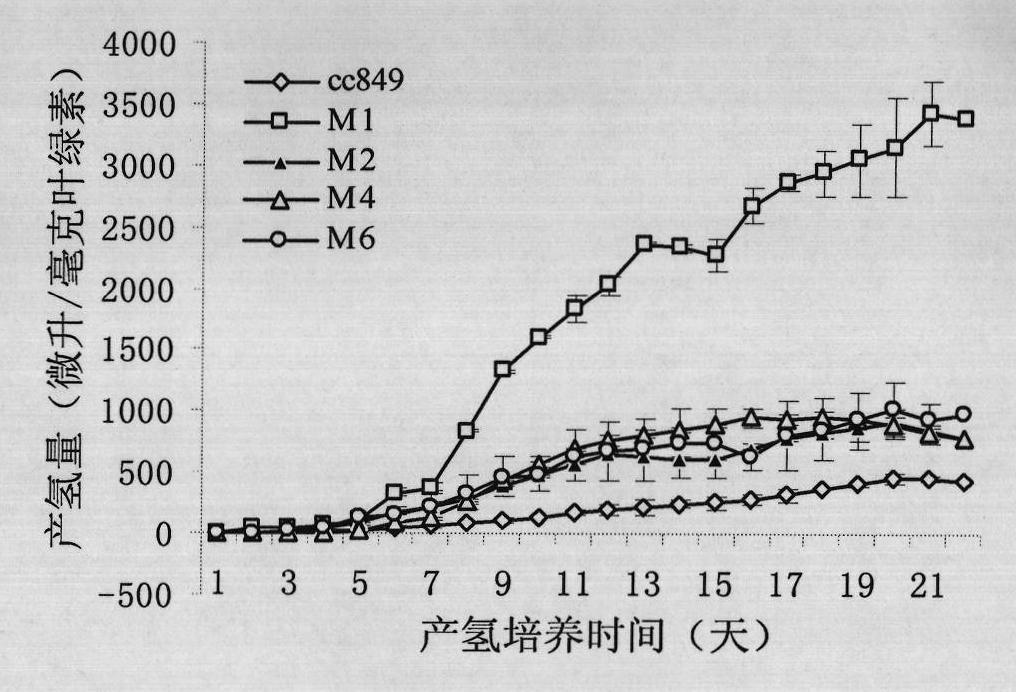
Method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis
InactiveCN101864365AHigh biohydrogen productionGood experimental materialUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChlamydomonas reinhardtii
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for breeding high-yield photosynthetic-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii through cell nucleus insertion mutagenesis. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii has low hydrogen production rate and limits the application and the development of a biological and photosynthetic hydrogen production technology. The method for obtaining a high-hydrogen-production mutant strain through the random insertion mutagenesis of chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nuclei comprises the following steps: cultivation of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii; preparation of a chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation vector and a glass bead; chlamydomonas reinhardtii cell nucleus transformation and transformant screening; analysis of the hydrogen yield and the oxygen consumption of chlamydomonas reinhardtii transformant hydrogen-production cultivation; analysis of the integration and the expression thereof of ble genes in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii mutant strain; and analysis of the influence of recombinant leghemoglobin hemH-1ba on the growth of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The invention has the advantages that the biological hydrogen production yield of the obtained high-hydrogen-production chlamydomonas reinhardtii is 7 times of the original yield; the method provides a good experimental material and a good basic condition for deeply researching the hydrogen-production metabolic mechanism of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
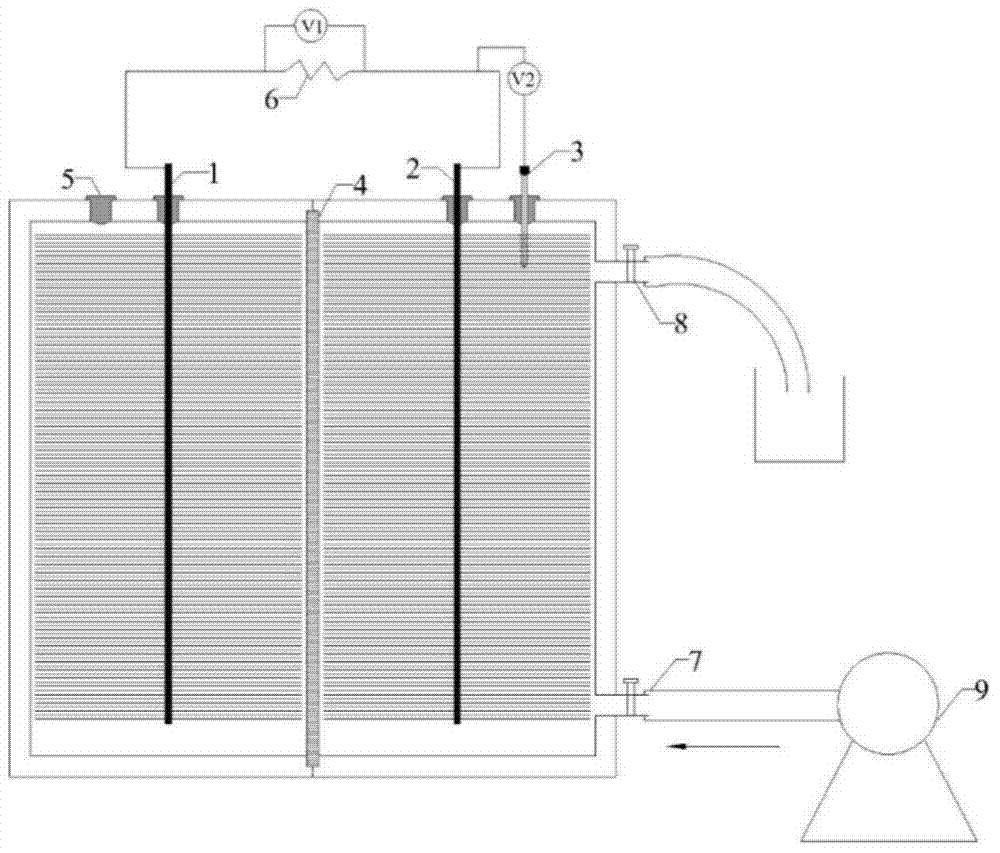
Microorganism electrochemical denitrification method for enhancing bio-hydrogen production
InactiveCN103613206AImprove denitrification effectImprove nitrogen removal rateBiological water/sewage treatmentChemical industryOrganic acid
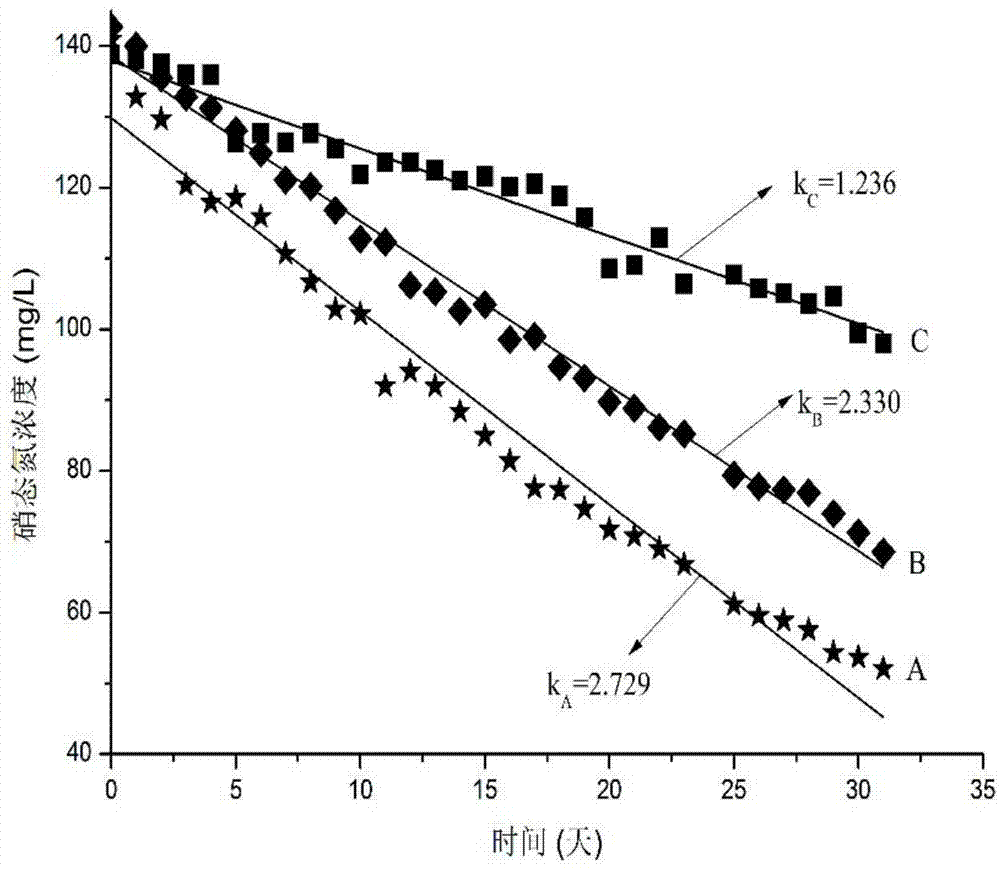
The invention discloses a microorganism electrochemical denitrification method for enhancing the bio-hydrogen production, which belongs to the field of environmental engineering and energy and chemical industry. The method is characterized in that a microorganism electrochemical system is used as a reactor, and denitrification microorganisms are added into a cathode to realize the nitrogen removal by denitrification of a biological cathode. Meanwhile, by adding the hydrogen-production microorganisms in the biological cathode, the BES (knowledge based expert system) denitrification capacity is further improved by utilizing the biological hydrogen production. The denitrification microorganisms can directly utilize the hydrogen generated by the hydrogen-production microorganisms in the biological cathode to carry out the denitrification effect; meanwhile, organic acid generated in the biological hydrogen production process can play a role in buffering pH, so that the BES denitrification rate can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method utilizing hydrogen-producing acetogens and electricigens to enhance biological hydrogen production efficiency
InactiveCN103865957ARealize the effect of catalytic hydrogen productionLow priceFermentationAcetic acidElectron transfer
The invention discloses a method utilizing hydrogen-producing acetogens and electricigens to enhance the biological hydrogen production efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing hydrogen-producing acetogens and electricigens to deeply degrade the organisms, modulating the operation parameters of the dark fermentation technology so as to high efficiently accumulate acetic acid in the end products of the water-generating hydrogen-producing acetogens, taking the generated water as the substrate of an electric catalysis reactor, modulating the additional voltage value, taking the Ni nano particles as the catalyst, the stainless steel as the negative pole, and carbon cloth as the positive pole, and utilizing the extracellular electron transfer effect of the electricigens to further degrade the end products of the hydrogen-producing acetogens to convert the end products into hydrogen gas; thus the phenomenon of fermentation obstacle is weakened, high efficient hydrogen production by utilizing hydrogen-producing acetogens and electricigens is achieved, hydrogen production and pollution treatment are integrated, and the method has the characteristics of cost saving, little energy consumption, and high hydrogen production efficiency.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fossil fuel-free process of lignocellulosic pretreatment with biological hydrogen production
InactiveUS20110136196A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseMicroorganism
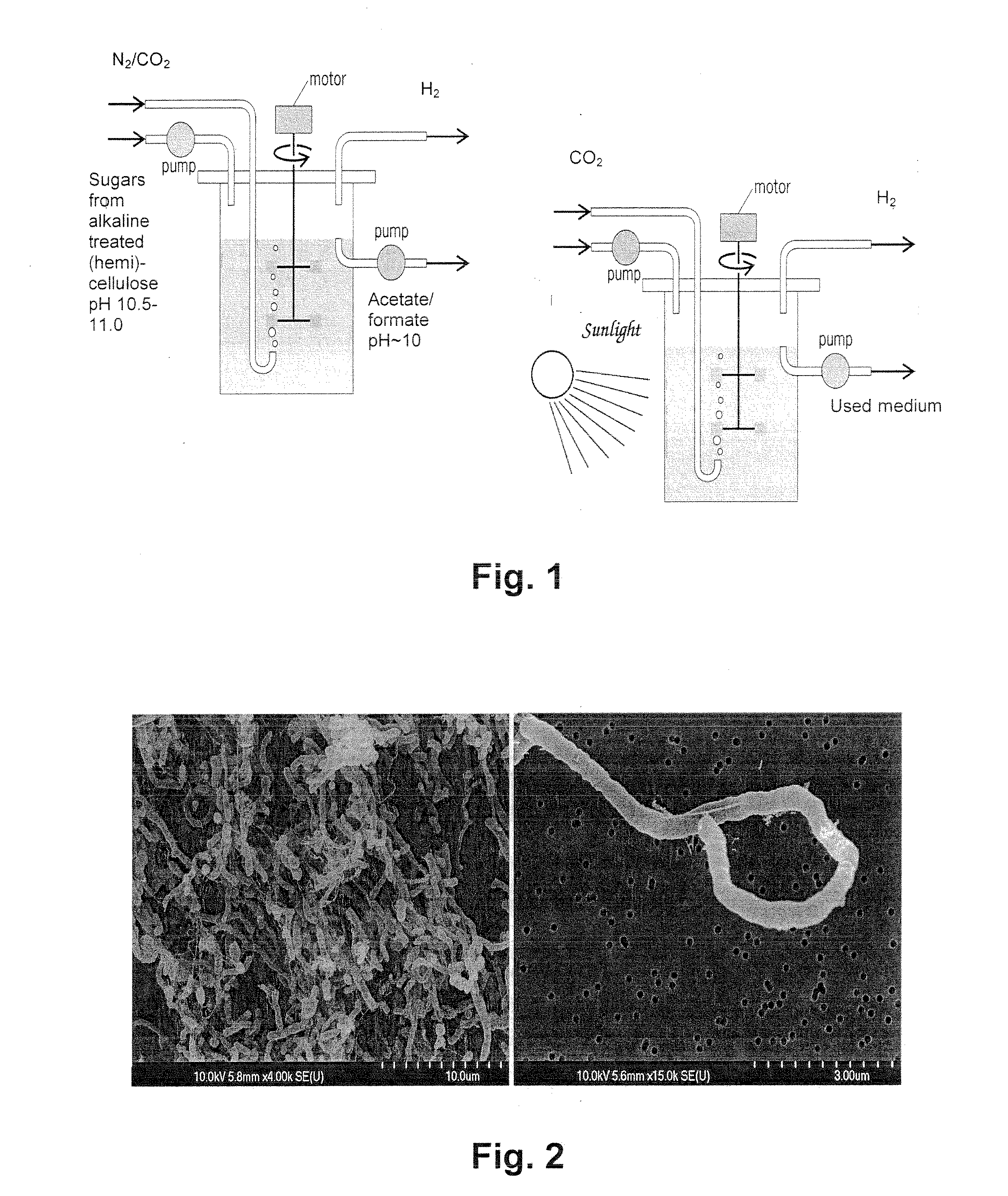
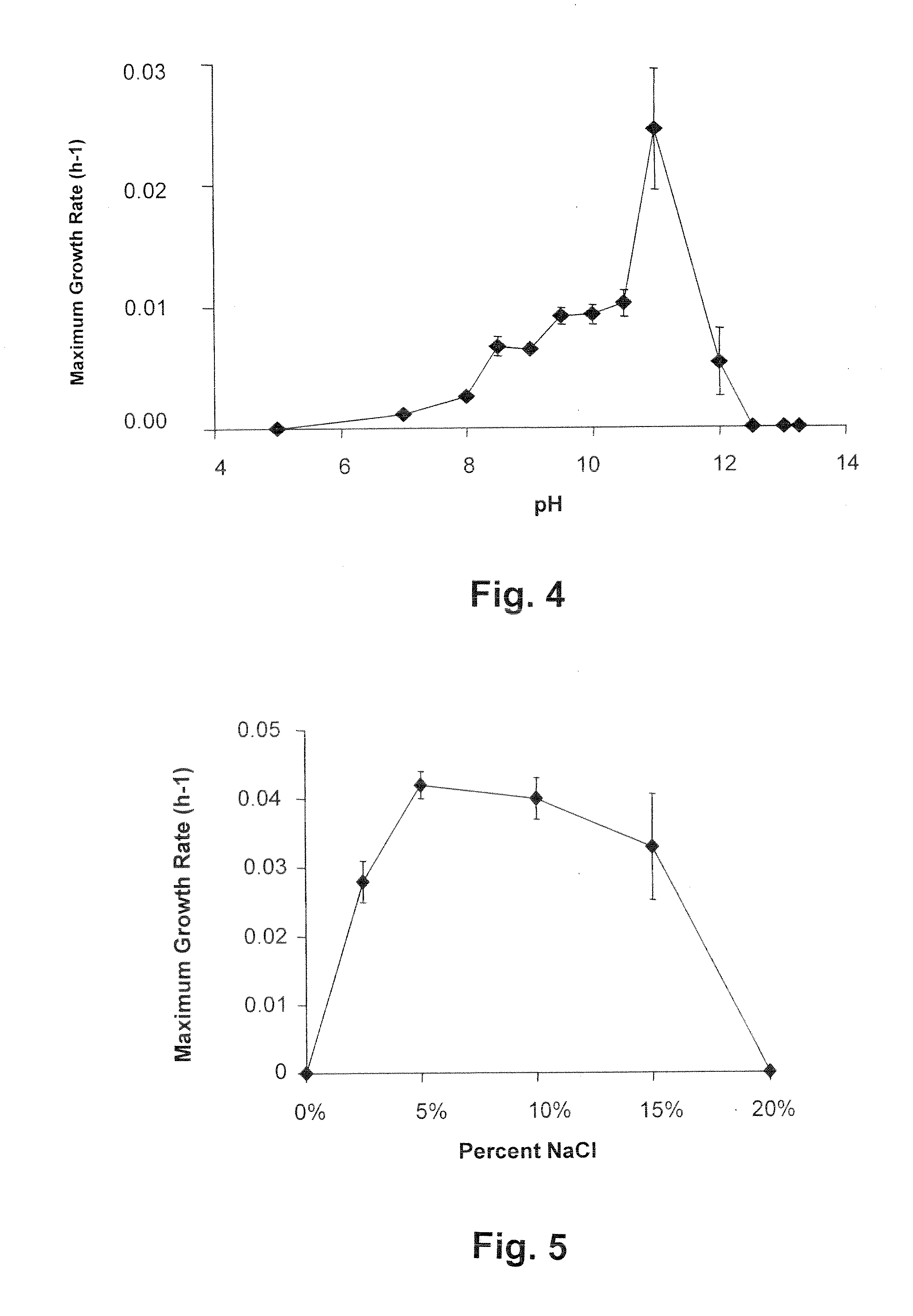
The invention provides an isolated haloalkaliphilic microorganism designated as strain sapolanicus belonging to the genus Halanaerobium, which is capable of producing hydrogen from biomass. Methods of producing biohydrogen comprising the fermentation of the microorganism with alkaline pretreated biomass are also provided. Fermentation is preferably carried out without neutralization of the pretreated biomass and at a pH of greater than or equal to about 10.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Disintegration method for excess sludge and application of disintegrated sludge in hydrogen production through fermentation
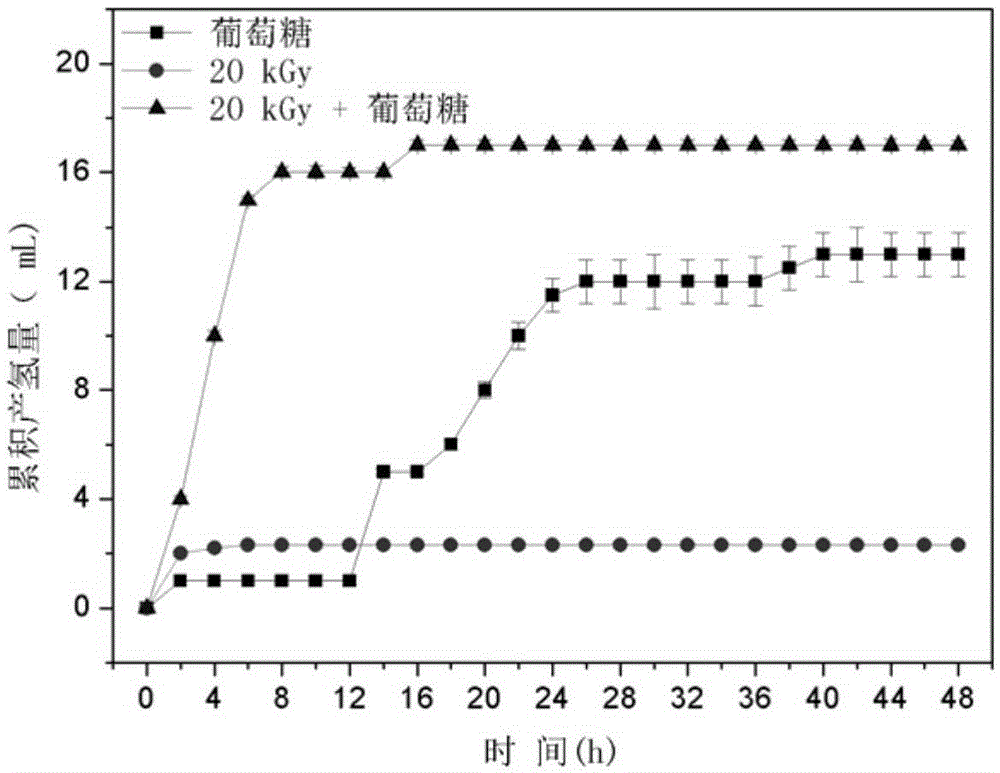
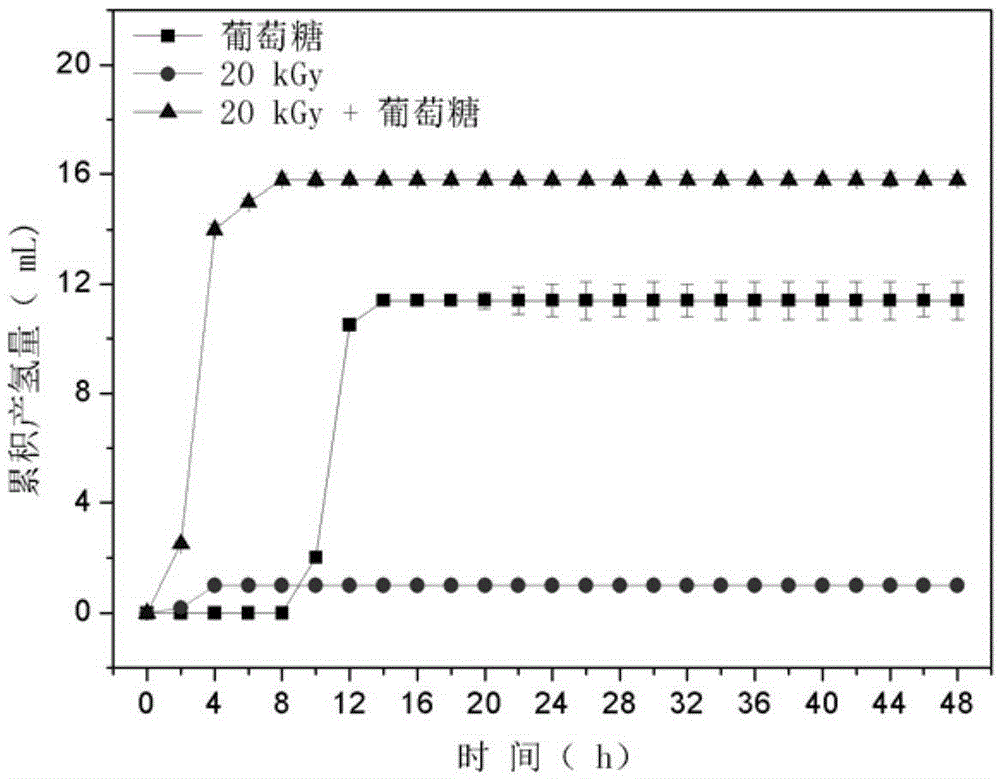
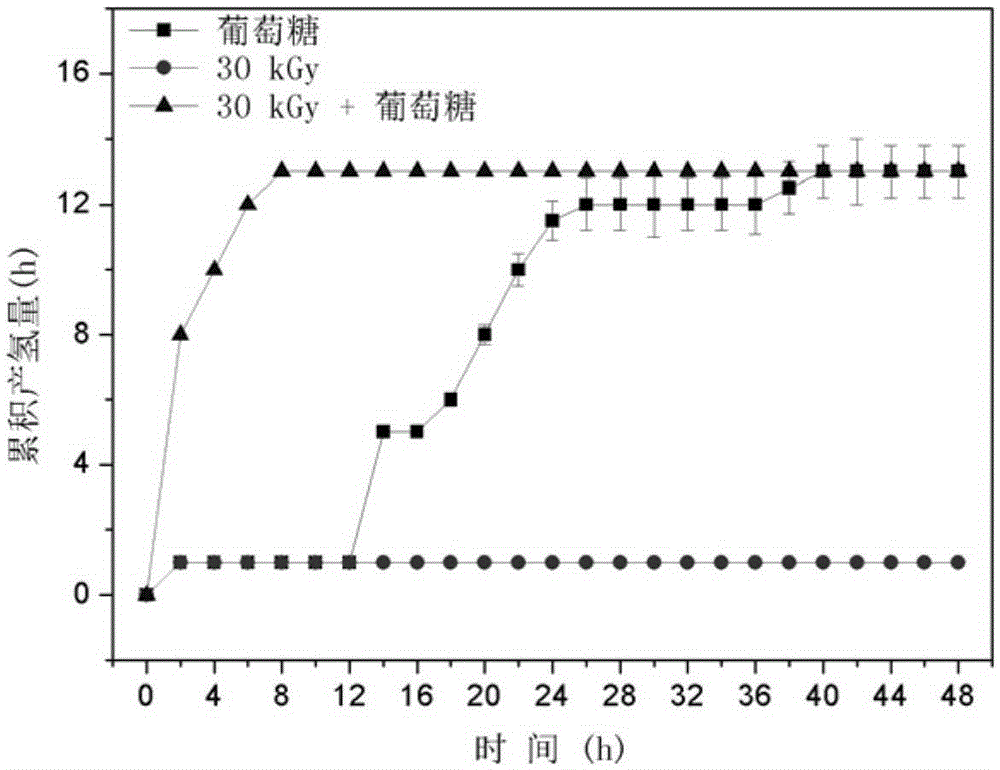
ActiveCN105399291ARelease fullyIncreased concentration of dissolved CODFermentationBiological sludge treatmentSludgeRoom temperature
The invention specifically relates to a disintegration method for excess sludge and application of disintegrated sludge in hydrogen production through fermentation, belonging to the technical field of hydrogen production through biological fermentation. The disintegration method disintegrates the excess sludge through irradiation and alkali coupled treatment and comprises the following concrete steps: adjusting the pH value of the excess sludge to 10 to 12 by using an alkaline solution and carrying out Gamma ray irradiation at room temperature, wherein irradiation dose is 10 to 30 kGy and a radioactive source is 60 Co; and after completion of irradiation, adjusting the pH value of the excess sludge to 7 so as to obtain the disintegrated sludge. According to the invention, through irradiation and alkali coupled treatment, full release of organic components in the excess sludge is promoted; high-efficiency hydrogen production with the disintegrated sludge as a substrate is realized; a cheap and easily available substrate source is provided for the process of biological hydrogen production; and cost for hydrogen production through fermentation is reduced. Compared with the raw sludge, the concentration of soluble COD in a sludge disintegration liquid is increased by 28 to 37 times, the concentration of polysaccharide is increased by 25 to 29 times, and the concentration of protein is increased by 32 to 37 times.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for producing hydrogen by using marsh red pseudomonas
InactiveCN101041832AGreat application potentialReduce organic contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationMarshLiquid medium
The invention discloses a hydrogen preparing method with marsh red pseudomonas, which comprises the following steps: (1) putting fluid medium into autoclave sterilizing pot; sterilizing at 12-15 min; fetching out of the culture medium; cooling to normal temperature; embedding the fluid medium into bioreactor and photo biological hydrogen production reactor separately; setting the initial pH range at 4.5-8.8 and density range of organic subtract at 1.98g / l-45g / l; (2) fetching marsh red pseudomonas colony on solid double layer plate culture medium with inoculating needle; seeding in the cooling culture medium; charging into argon gas to remove air in the biological reactor of fluid medium; forming anaerobic environment; placing the seeding liquid medium at 25-35 deg.c; stewing and culturing at 36-96 h in constant-temperature culture box with illuminance at 1500lx-8000lx; getting the enlargement culture liquid in the subsequent hydrogen producing course.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
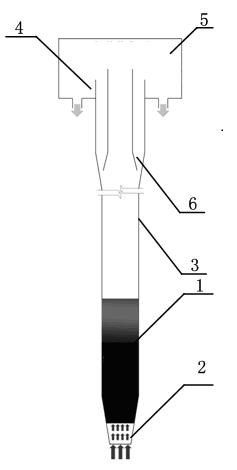
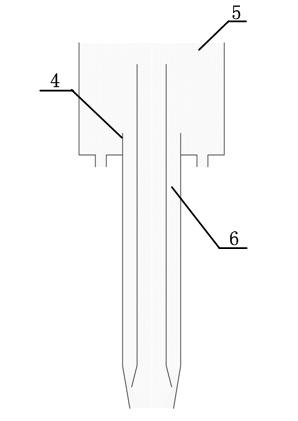
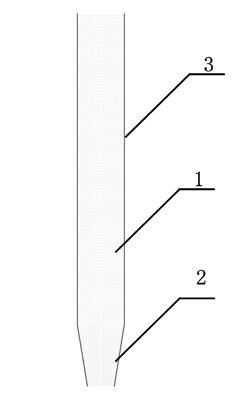
Hydrogen production method and device based on aluminum or magnesium underwater stir friction welding process
InactiveCN101798063ASolve the problem of discontinuous hydrogen productionThe hydrogen production method is simpleHydrogen productionElectrolysisChemical reaction
The invention provides hydrogen production method and device based on an aluminum or magnesium underwater stir friction welding process, relating to hydrogen production method and device. The invention aims to solve the problems of complex process and environmental pollution of the traditional biological hydrogen production method and necessary addition of chemical agents or alloy elements in both the traditional electrolytic water hydrogen production method and the traditional chemical reaction hydrogen production method. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, installing a welded aluminum plate or a welded magnesium plate; secondly, injecting water; thirdly, selecting parameters of a welding tool; fourthly, installing the welding tool; fifthly, installing a hydrogen collection component; sixthly, carrying out stir friction welding on the welded aluminum plate or the welded magnesium plate; and seventhly, generating hydrogen when carrying out chemical reaction on the welded part of the aluminum plate or the magnesium plate and water in the stir friction welding seam forming process, continuously generating the hydrogen, collecting the hydrogen into a collection cover, and finishing hydrogen preparation by introducing the hydrogen into a storage container through an airway. In the device, a stainless steel cushion plate is arranged at the bottom of a water groove, the hydrogen collection component is arranged above the stainless steel cushion plate, and the collection cover is vertical to the stainless steel cushion plate. The invention is used for preparing hydrogen.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamydomonas reinhardtii
InactiveCN102559832AIncrease hydrogen productionReduce the greenhouse effectMicroorganism based processesFermentationChlamydomonas reinhardtiiBradyrhizobium japonicum
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for com-culturing and improving hydrogen output by utilizing bacteria and chlamyodomonas reinhardtii. Through mixing aerobic bacteria represented by bradyrhizobium japonicum with the chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to a certain proportion for culture, the hydrogen output can be remarkably improved. The invention provides a new method for further improving the hydrogen output in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii twp-step-method hydrogen production technology.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF GENOMICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI CHINA NAT CENT FOR BIOINFORMATION
Method for improving yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes
InactiveCN101845461AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiChloroplast
The invention belongs to a biological hydrogen production technology, particularly to a method for improving the yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes. Traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production has the disadvantages that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogenase is sensitive to oxygen and is easily inhabited by the oxygen to inactivate; and the hydrogen production effect of chlamydomonas is limited. The invention discloses application of soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes in chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production, the soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes lba are constructed in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, and the expression vector is transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast, so that the lba genes are expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The decrease of the oxygen content in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is markedly quicker than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of the untransformed genes, the oxygen content can be kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen yield is markedly increased; the method is applicable for all microalgae for hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
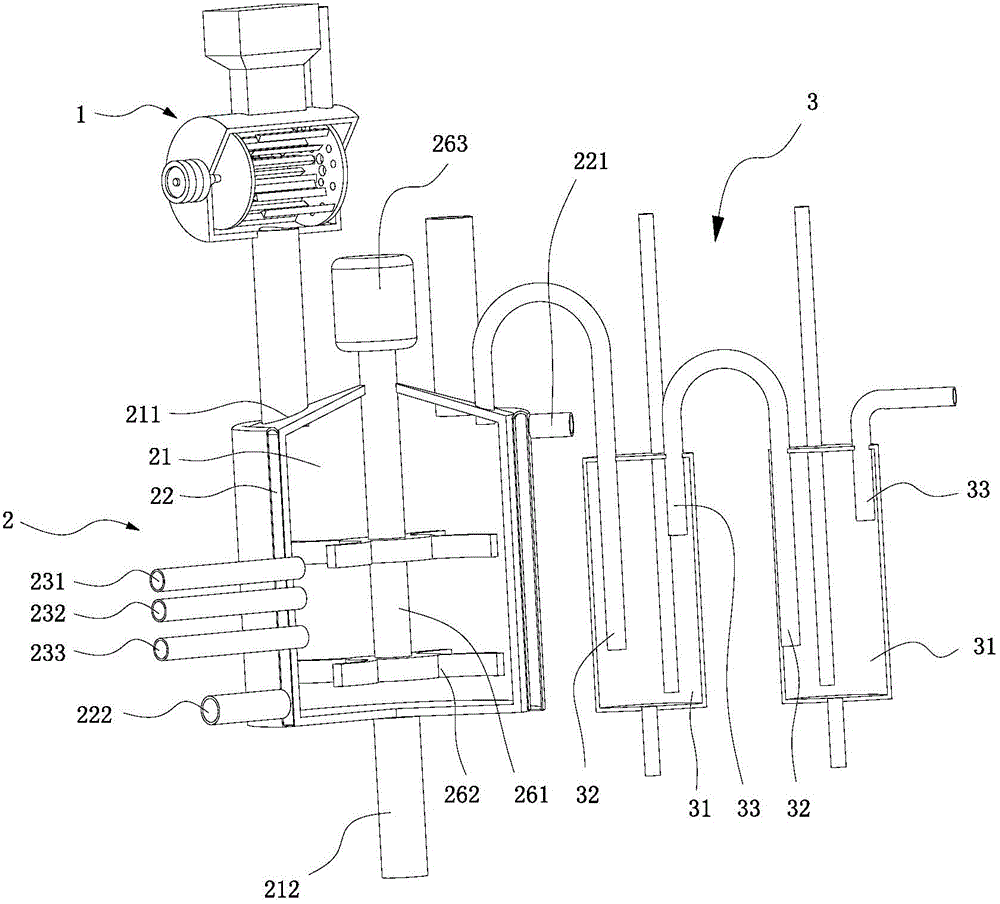
Biological hydrogen production device
ActiveCN104388305AWell mixedMix thoroughlyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringFermentation
The invention discloses a biological hydrogen production device. The biological hydrogen production device comprises a crushing machine, a fermentation tank and an air washing device, wherein the crushing machine comprises a machine case provided with an inner cavity, a crushing device is arranged in the inner cavity, the inner cavity is divided into a crushing cavity and a blending cavity by virtue of a separating board, a plurality of communicating holes communicating the crushing cavity with the blending cavity are formed in the separating board, the crushing device is arranged in the crushing cavity, a crushing substrate inlet and a blending substrate inlet are respectively formed in the upper ends of the crushing cavity and the blending cavity, a mixed substrate outlet provided with a valve is formed in the lower end of the crushing cavity, the fermentation tank is connected with the crushing machine, the air washing device is connected with the fermentation tank, and the air washing device comprises at least one air washing tank, wherein at least one air washing tanks are sequentially connected. The biological hydrogen production device has the advantages that the blending cavity is arranged in the crushing machine, the crushing substrate and the blending substrate can be fully mixed while the crushing substrate and the blending substrate are crushed, the practice that crushing is firstly carried out and then stirring is carried out in the conventional technology is replaced, hydrogen production time is greatly shortened, the crushing substrate and the blending substrate are mixed more fully and more thoroughly, and a fermentation effect is better.
Owner:SHENZHEN HENG XING SECURITY TESTING TECH
Simulation method of upflow biological hydrogen production reactor flow field
InactiveCN101872379AAvoid blindnessStrong assessmentSpecial data processing applicationsProcess engineeringField data
The invention relates to a simulation method of an upflow biological hydrogen production reactor flow field, and solves the problem of the existing upflow biological hydrogen production reactor that control parameter selection causes a flow state phenomenon which is not beneficial to mass transfer and biological fermentative degradation. The simulation method comprises the following steps: 1, dividing a reactor profile into grid cells; 2, establishing a two-dimensional computed field Euler-Euler three-phase fluid model; 3, establishing a glucose fermentative degradation dynamical model of the profile of the upflow biological hydrogen production reactor; 4, determining a boundary value condition and an initial condition; and 5, solving a coupling model to obtain the flow field data of each grid cell in the profile of the upflow biological hydrogen production reactor. The simulation method is applicable to the design field of the upflow biological hydrogen production reactor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Medium for promoting hydrogen production of HAU-M1 photosynthetic bacteria flora and application thereof
ActiveCN109929897AImprove hydrogen production performanceTo promote metabolismBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTert-leucineYeast extract
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation biological hydrogen production, and particularly relates to a medium for promoting hydrogen production of HAU-M1 photosynthetic bacteria flora and application thereof. The medium comprises 0.1-1g / L of NH4Cl, 0.01-0.5g / L of MgCl2, 0.01-0.2g / L of yeast extract, 0.1-1g / L of K2HPO4, 1-3g / L of NaCl, 1-5g / L of sodium glutamate and 0.3-2.5g / L of hydrogen-producing amino acid. The hydrogen-producing amino acid is one or a mixture of a plurality of L-cysteine, L-alanine, L-threonine, L-leucine and L-serine in any ratio. Based on a general inventive concept, the invention also provides application of the medium in biological hydrogen production, thereby effectively improving the hydrogen production capability of the HAU-M1 photosynthetic bacteria flora.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
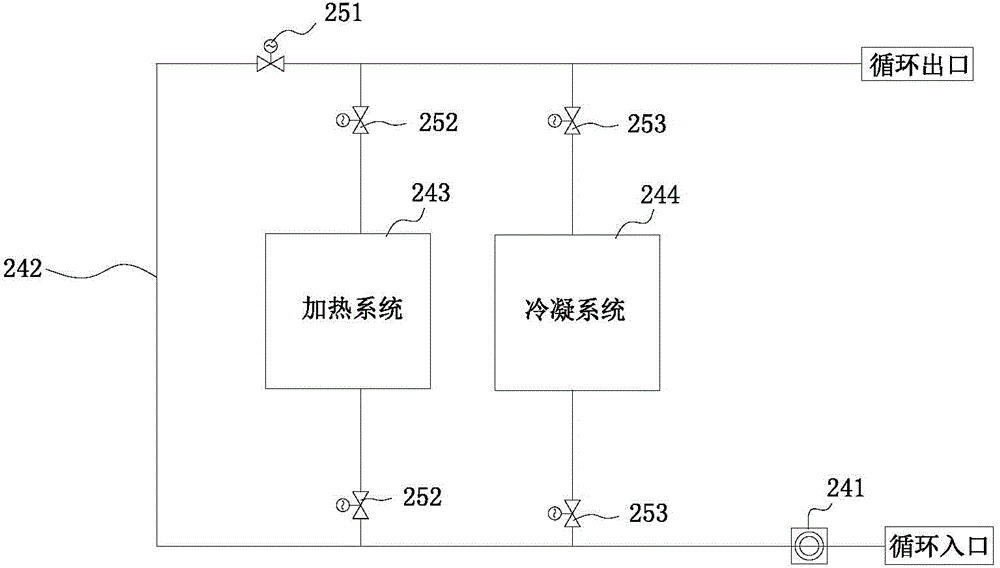
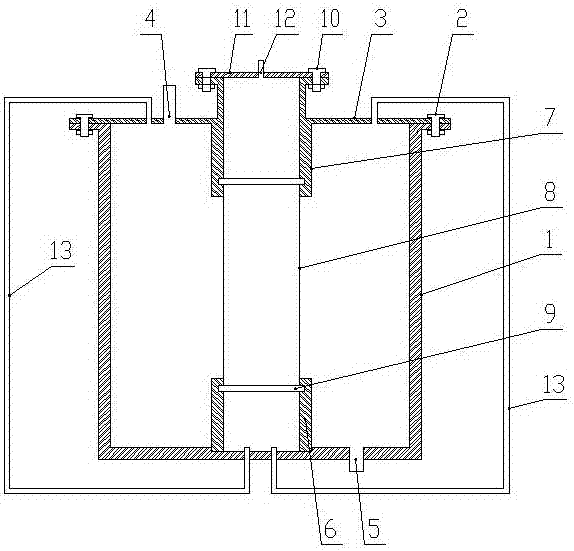
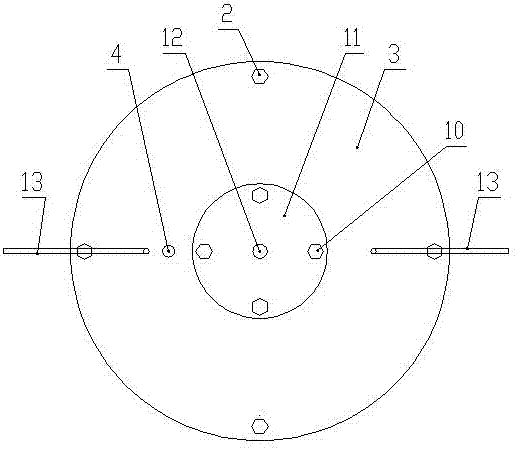
Device and method for temperature-controlled aerobic-anaerobic coupled biological hydrogen production
InactiveCN102827760AStart fastGuaranteed uptimeGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelTemperature controlBiochemical engineering
A device for temperature-controlled aerobic-anaerobic coupled biological hydrogen production comprises a fermentation tank which is installed on a base, wherein the base is provided with a universal wheel which can rotate for 36 degrees and a wheel lock; one side of a fermentation tank body is provided with a feed port, and the other side of the fermentation tank body is provided with a discharge port; the inner part of the fermentation tank is a double-reaction area structure which consists of an aerobic pretreatment chamber and a fermentation hydrogen production chamber, and valves which can be opened from one direction are respectively arranged in the middles of the aerobic pretreatment chamber and the fermentation hydrogen production chamber; a baffle is installed at the inner wall of the fermentation tank; the fermentation tank body is of a double-layer structure, namely two independent interlayers wrapping the aerobic pretreatment chamber and the fermentation hydrogen production chamber; heat transfer liquid is filled in interlayers; the two interlayers are respectively provided with a liquid inlet valve and a liquid discharge valve, and connected by pipelines to form a temperature control layer; and a nanophase ceramic membrane roller penetrates through the center of the tank body, and the gas outlet of the nanophase ceramic membrane roller is connected with a gas collection device. The invention further discloses a method for biological hydrogen production utilizing the device.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
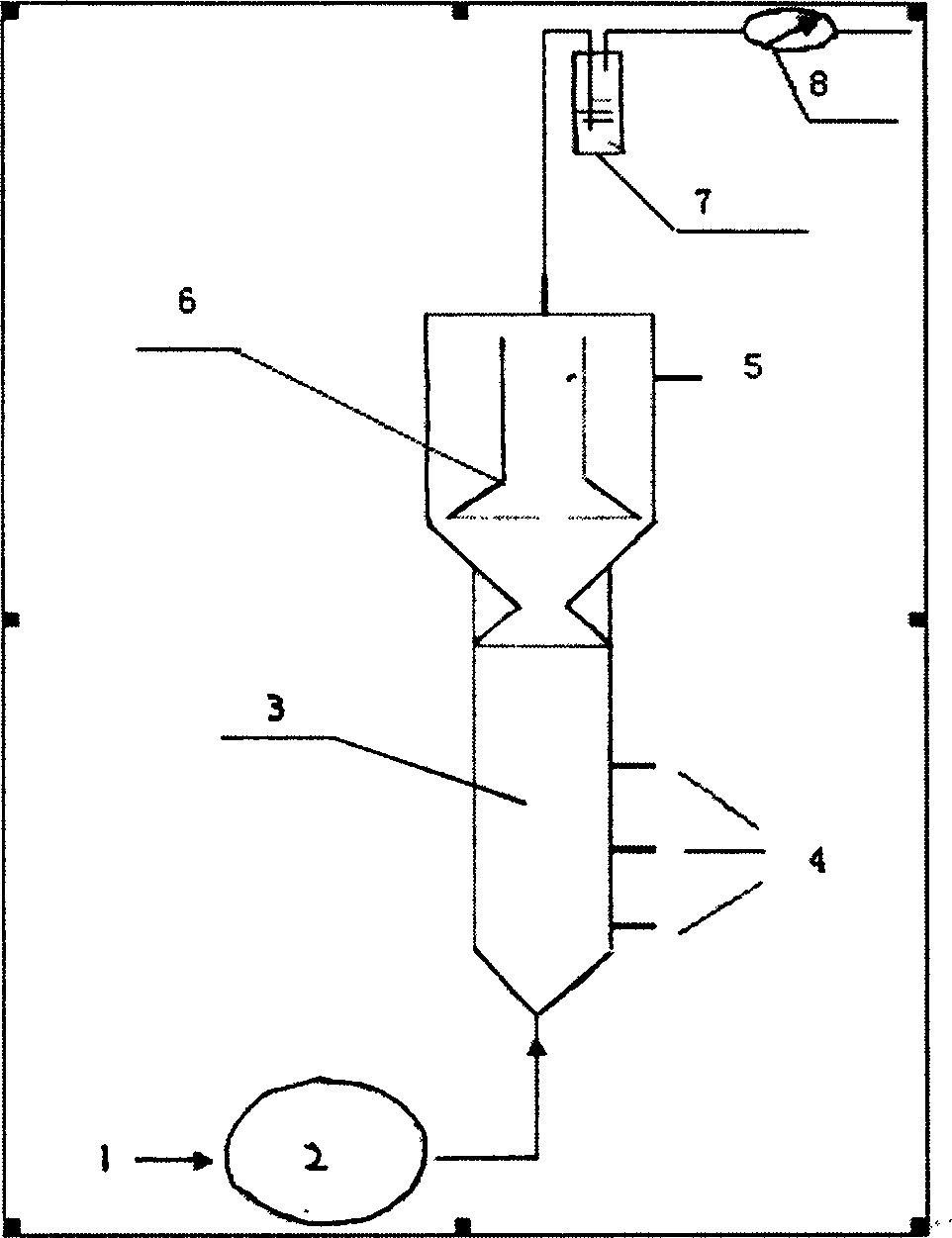
Method for preparing hydrogen by using organic wastes, and apparatus thereof
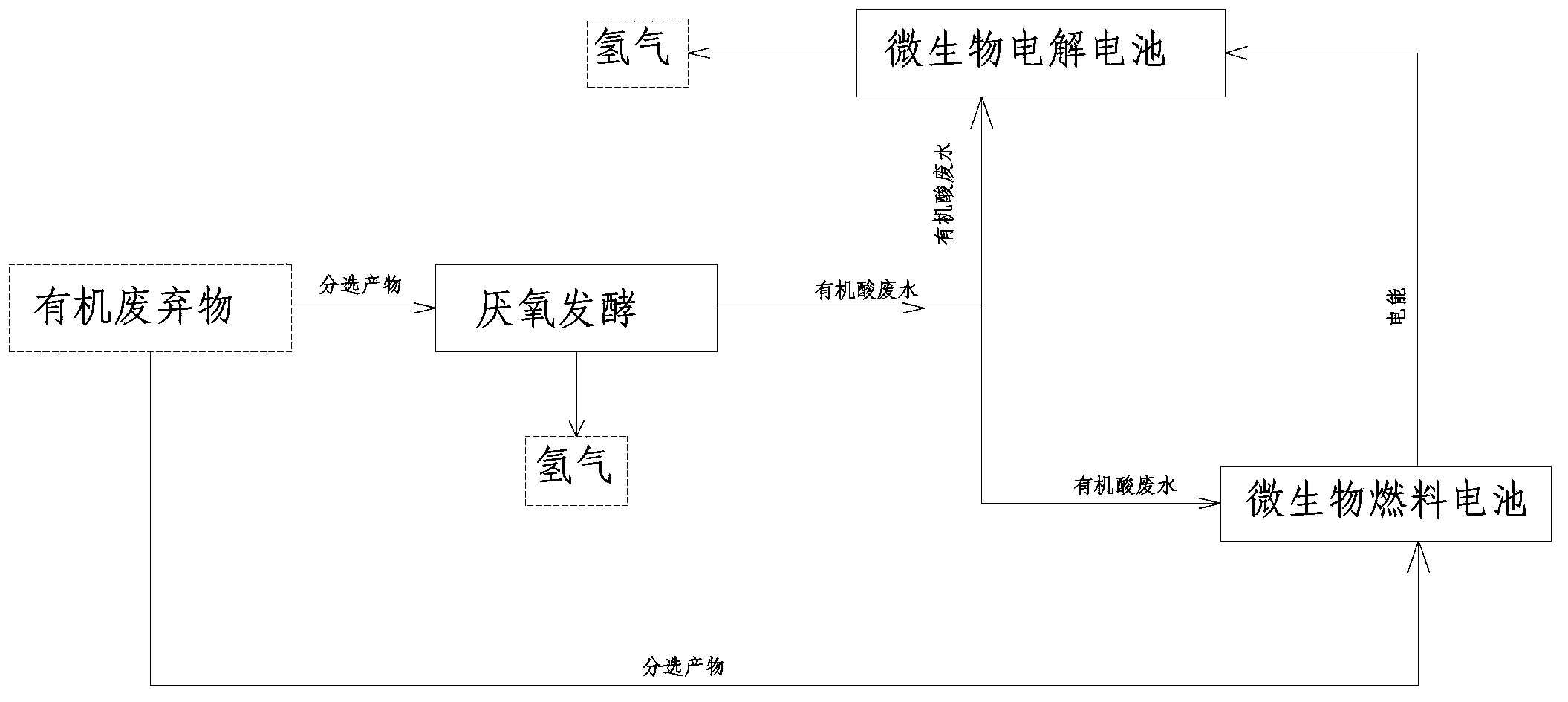
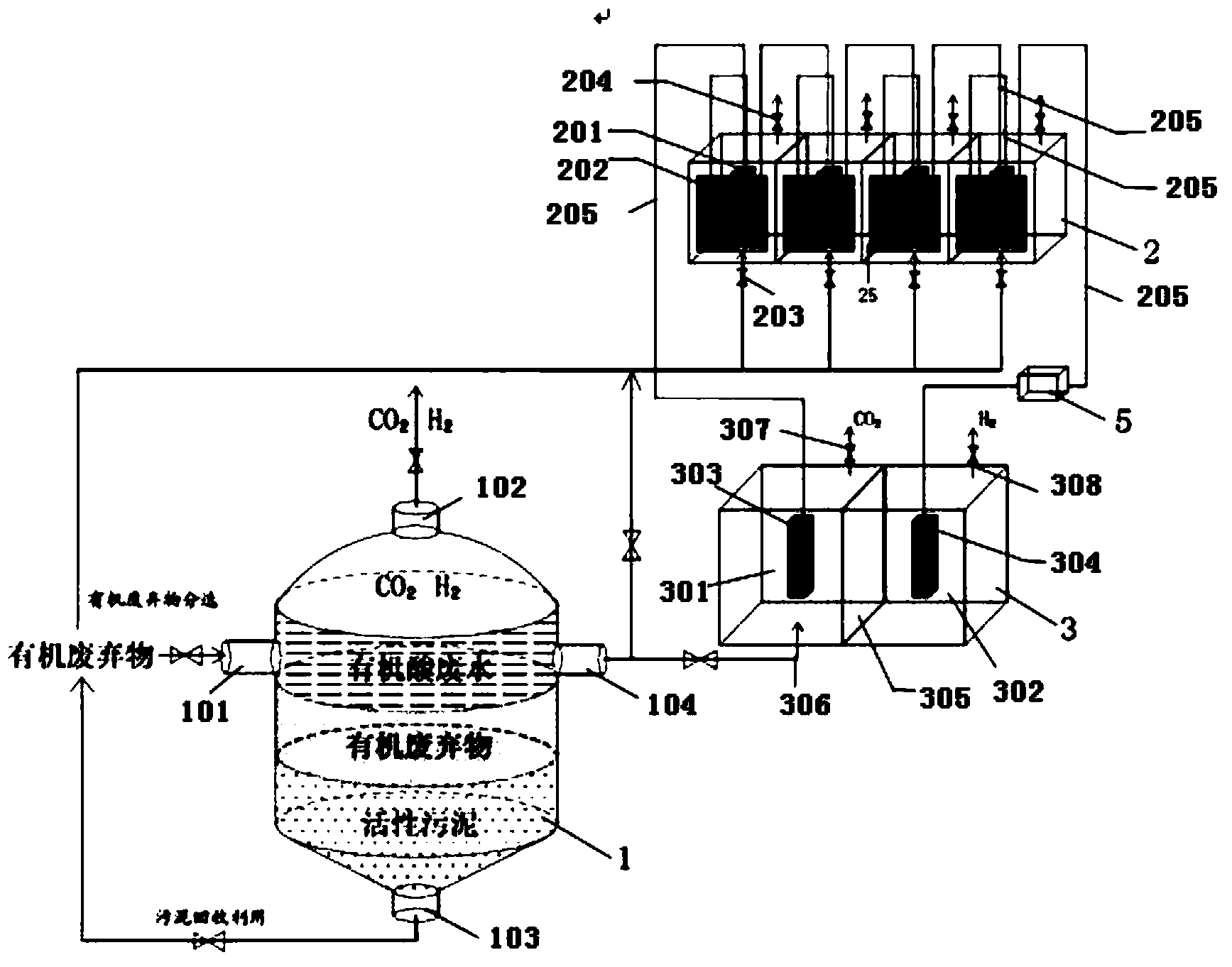
A method for preparing hydrogen by using organic wastes comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing organic matters; 2, mixing the preprocessed organic wastes obtained in step 1 with a hydrogenogen-containing inoculum, placing the above obtained mixture in an anaerobic fermentation reactor, and carrying out anaerobic fermentation; and 3, introducing parts of the preprocessed organic wastes obtained in the step 1 and parts of an organic acid waste liquid generated in the step 1 to an anode chamber of a microbiological fuel cell in order to produce an electrogenesis effect, introducing parts of an organic acid waste liquid obtained in step 2 to an anode chamber of a microbial electrolysis cell, and generating hydrogen by protons permeating an exchange membrane and electrons on a cathode under the catalysis under a voltage applied by the microbiological fuel cell in order to realize microbial electrolysis hydrogen production. The method and the apparatus have the advantages of energy consumption reduction, full recycling and pollution reduction in the biological hydrogen production process of the organic wastes by utilizing an MFC-MEC self-power system to provide energy needed by hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI HIGH SCHOOL
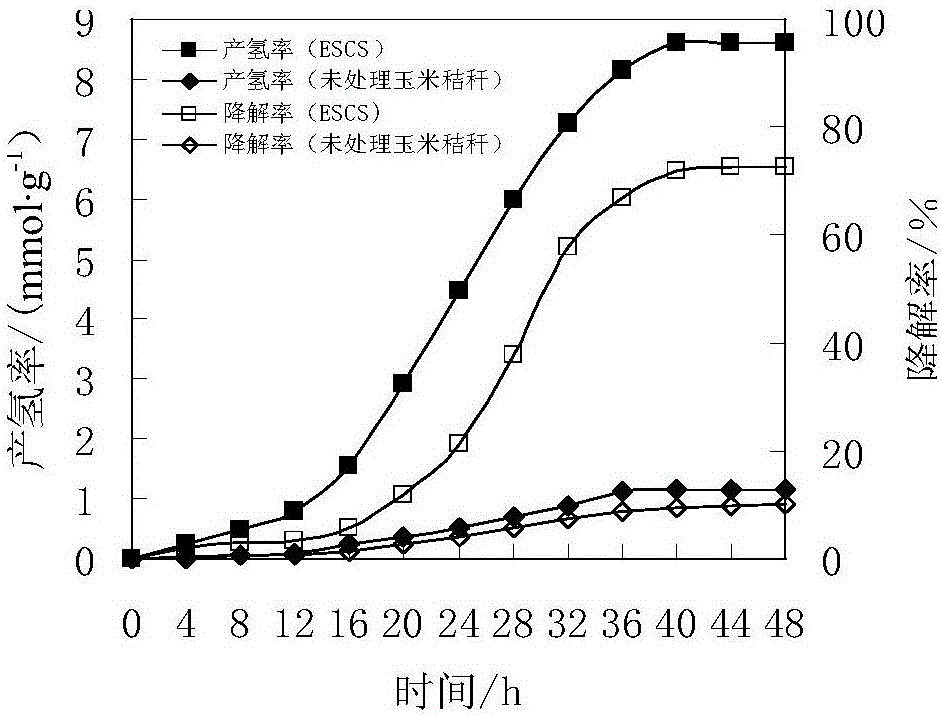
Combined pretreatment method for synergically degrading straw cellulose through compound florae and producing hydrogen through fermentation
InactiveCN106119289ARealize resourcesHigh hydrogen production rateFermentationCellulosePretreatment method
The invention relates to a combined pretreatment method for synergically degrading straw cellulose through compound florae and producing hydrogen through fermentation, belonging to the technical field of processing of solid waste. The combined pretreatment method for combining the compound florae with the combined pretreatment of sodium hydroxide and acidification steam explosion is utilized for carrying out efficient anaerobic fermentation biological hydrogen production for the first time. The method comprises the steps of firstly grinding straws into 30-60-mesh powder, carrying out sodium hydroxide pretreatment, finally carrying out acidification steam explosion pretreatment to obtain pretreated straw powder, adding the compound florae, culturing the mixture in an intermittent fermentation hydrogen production testing device, and carrying out the efficient anaerobic fermentation biological hydrogen production. According to the combined pretreatment method, by virtue of the combined pretreatment of sodium hydroxide and acidification steam explosion, the hydrogen production rate and the cellulose degradation rate of the straw fermentation hydrogen production are increased, and the recycling and the energy regeneration of lots of straws are realized.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
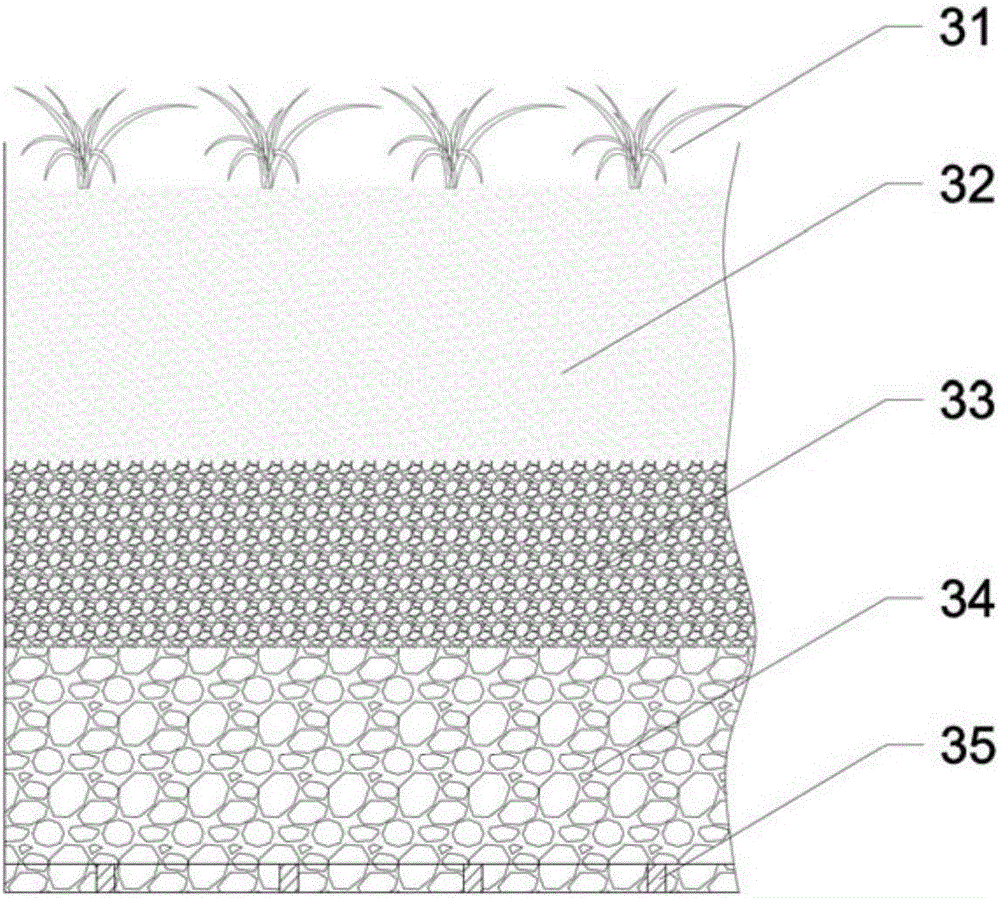
Biological treatment device and process for high ammonia-nitrogen pig-raising biogas slurry
ActiveCN106430820AEasy to handleRealize ecological treatmentMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiodieselSlurry
The invention discloses a biological treatment device and process for high ammonia-nitrogen pig-raising biogas slurry. A body of the biological treatment device is a runway type photo-bioreactor, an efficient and low-consumption standard treatment process for the high ammonia-nitrogen pig-raising biogas slurry is constructed based on a microalgae, photosynthetic bacteria and plant compound ecological system, and meanwhile, algae bacteria biomasses and plants are harvested. The process comprises the following specific steps: pig-raising wastewater is subjected to solid-liquid separation and is introduced into an anaerobic fermentation tank, produced high ammonia-nitrogen biogas slurry is subjected to pH value regulation and nutritive salt regulation and is introduced into the photo-bioreactor to be treated, biochemical effluent is treated by virtue of a flocculation settling tank and a disinfecting tank, and clean water reaches the standard and is discharged. The biological treatment device and the biological treatment process have the advantages that the operation is simple, the removal efficiencies of nitrogen and phosphorus are high, the operation cost is low, the separated algae bacteria biomasses can be taken as the raw materials for feeds, biological hydrogen production or biodiesel, and the secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
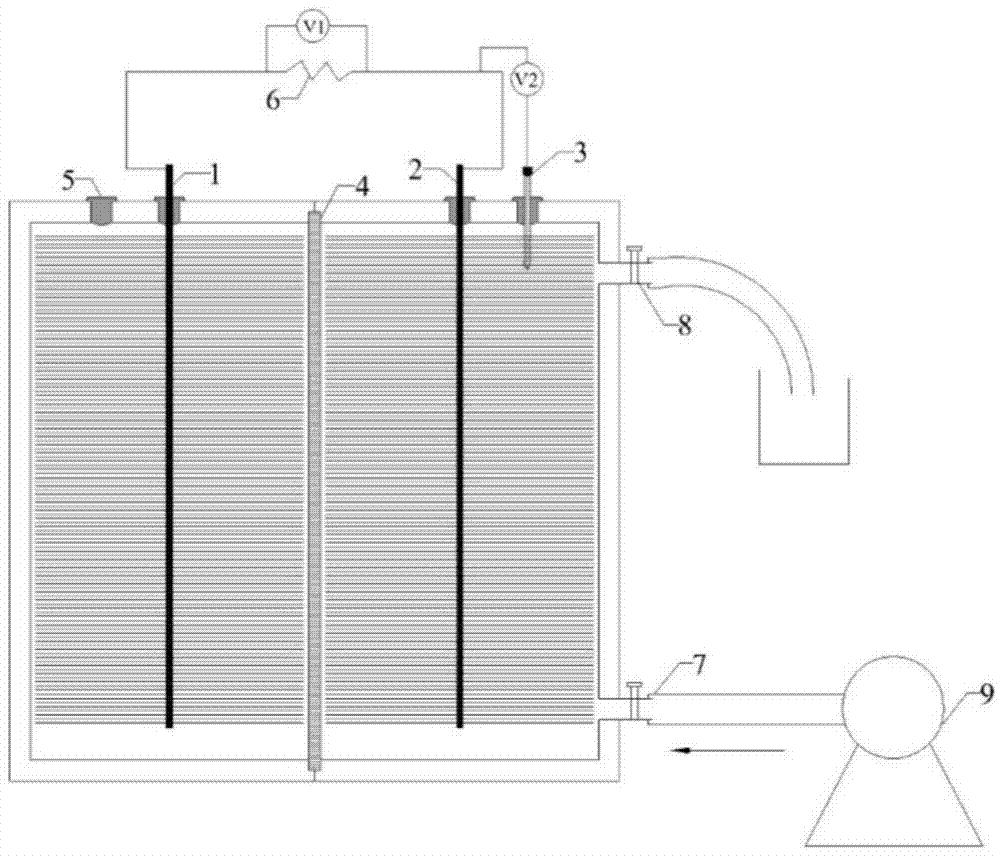
Dark-l fermentation integrated biological hydrogen production device
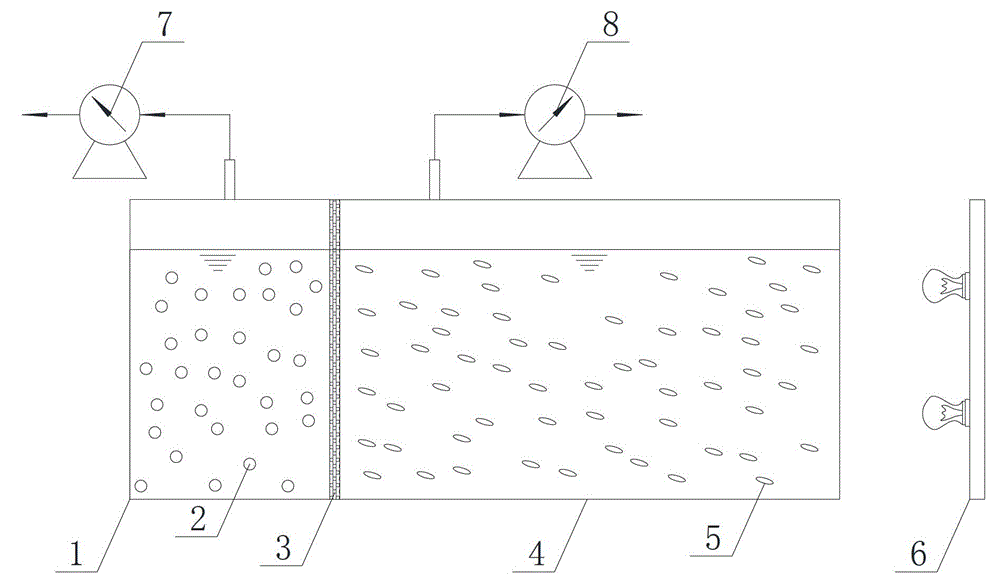
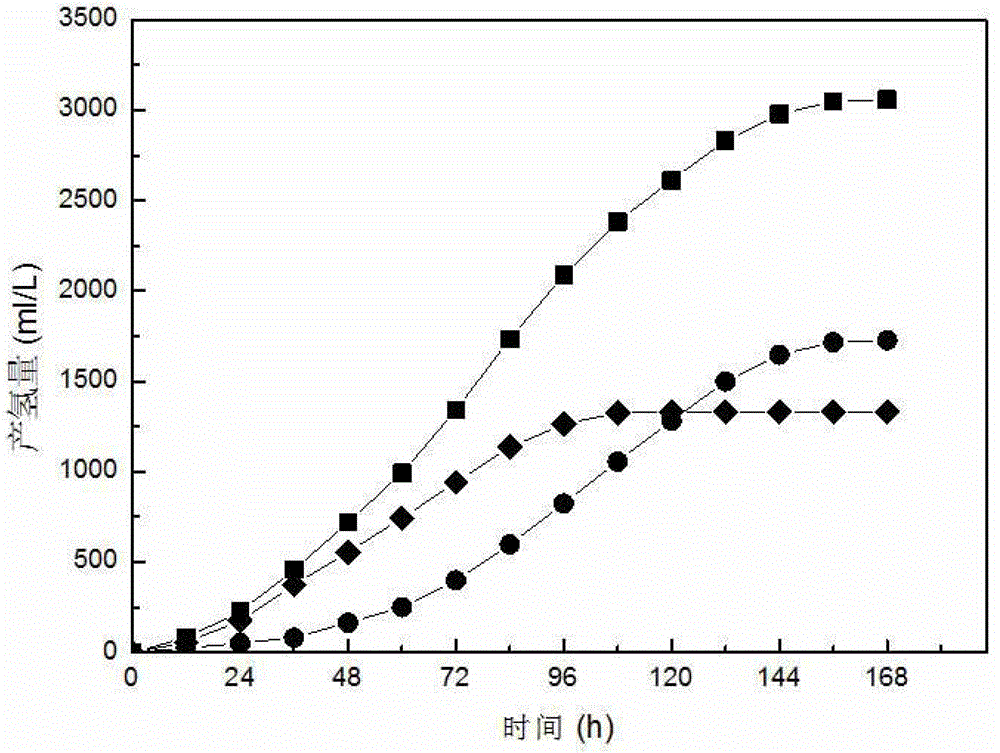
ActiveCN103146568ARich electron donorImprove hydrogen production efficiencyGas production bioreactorsMicroorganism based processesHydrogenGeneration rate
The invention discloses a dark-photo fermentation integrated biological hydrogen production device, relates to a dark-photo fermentation integrated biological hydrogen production device and aims at the problem that the efficiency of hydrogen generation through coupling of the dark fermentation bacteria and the photo fermentation bacteria is low in the prior art. The biological hydrogen production device comprises a dark fermentation reaction region, a filter membrane, a photo fermentation region, an illumination system, a dark fermentation gas flow meter and a photo fermentation gas flow meter, wherein a biological hydrogen production reaction container is divided into the dark fermentation reaction region and the photo fermentation reaction region through the filter membrane; a dark fermentation gas flow meter is arranged on the dark fermentation reaction region; the photo fermentation gas flow meter is arranged on the photo fermentation reaction region; the illumination system is arranged at one side of the photo fermentation reaction region; and the working volume of the dark fermentation reaction region is smaller than that of the photo fermentation reaction region. The dark-photo fermentation integrated biological hydrogen production device disclosed by the invention has hydrogen yield of 3048.45ml H2 / L working volume and hydrogen generation rate of 4.08 mol H2 / mol glucose. The dark-photo fermentation integrated biological hydrogen production device is mainly applied to the biological hydrogen production field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Biological hydrogen production method for improving hydrogen generation efficiency and stability
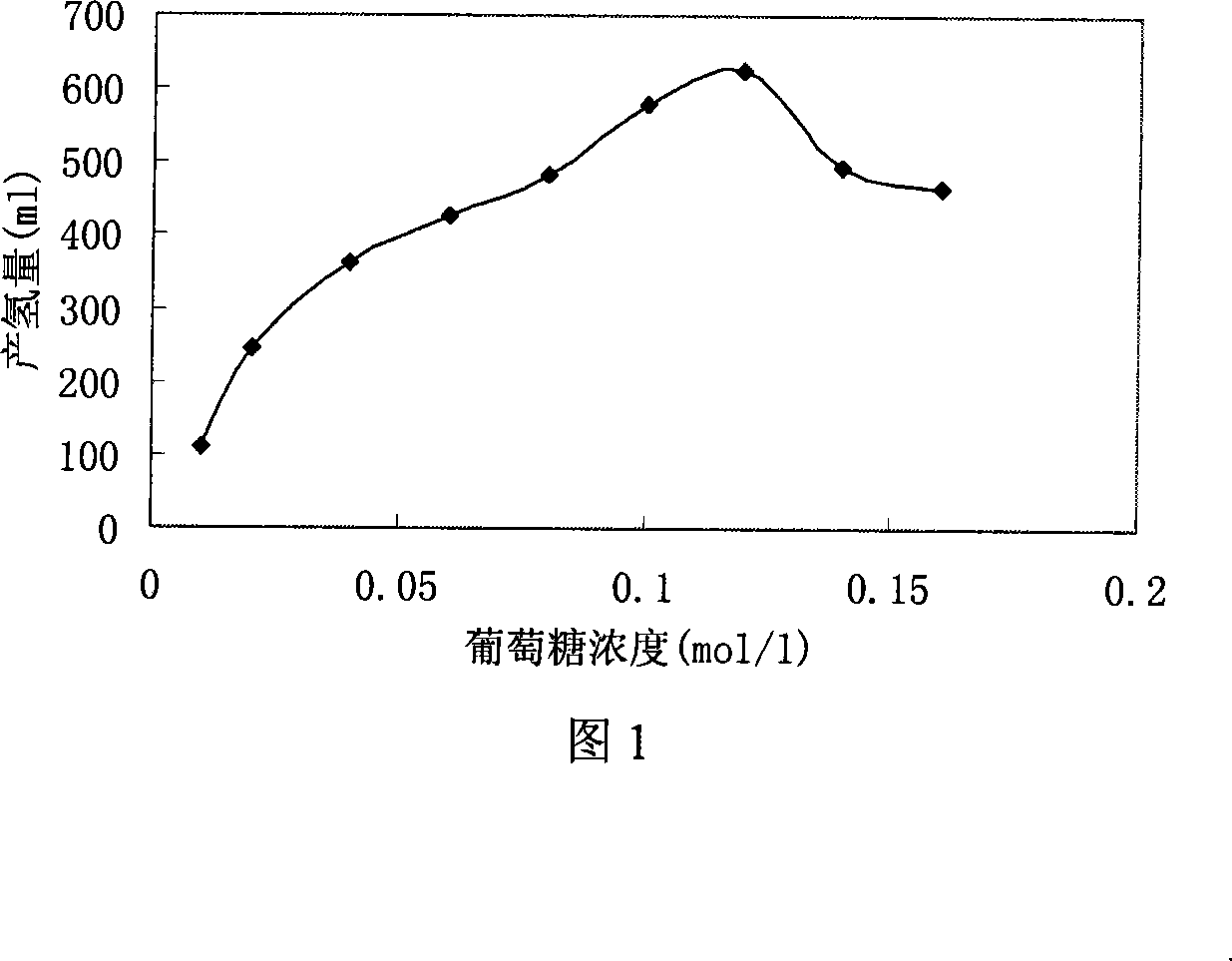
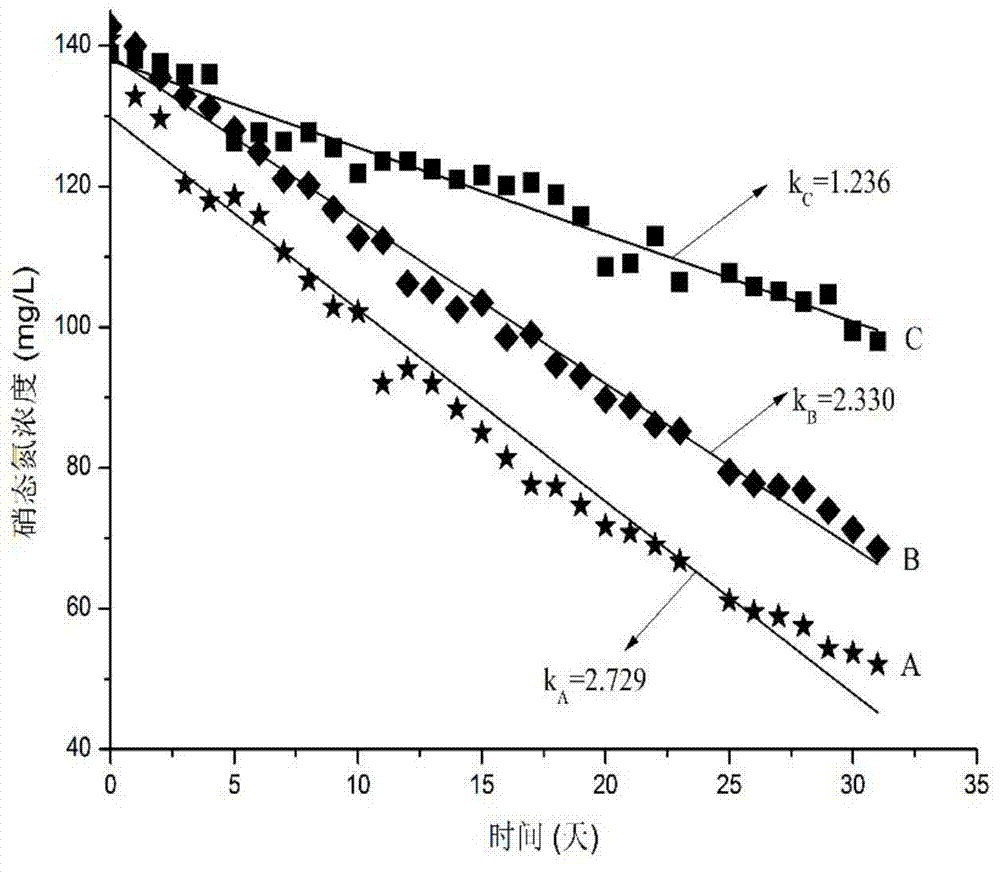
The invention discloses a biological hydrogen production method by culturing hydrogen production granular sludgesto to improve the hydrogen production efficiency and stability characterized in charging methane floccule sludges into the reactor to make the volatile suspended solid density be 3-7g / L in the reactor, controlling the flow rate of the organic wastewater flowing through the reactor to make the organic wastewater stay in the reactor for 5-20 hours; regulating the solution pH to 4.0-4.5 in the reactor, and the hydraulic loading to 15-30g / (L.d) from 2-5g(L.d) by increasing 0.1-0.5g(L.d) day by day; steadily operating till a hydrogen production granular sludge containing bultyric acid bacillus mainly and coccus forms in the reactor, then steadily operating till the volume of the hydrogen production granular sludges is 50-70% of the reacting area volume in the reactor. The invention solves the problems of low hydrogen production efficiency by floccule sludges, no steady and continuous hydrogen production existing in known biological hydrogen production method using organic wastewater, and the hydrogen production efficiency can be 1.22-1.37molH.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Fermentation-separation coupling biological hydrogen-producing method for improving hydrogen-producing fermentation efficiency
InactiveCN102492725ARaise the pHReduce loss rateDispersed particle separationFermentationBiotechnologyOrganic acid
The invention relates to a fermentation-separation coupling biological hydrogen-producing method for improving hydrogen-producing fermentation efficiency. By the biological hydrogen-producing method, the problem of low efficiency and the like in the conventional process for producing hydrogen biologically by a fermentation method is solved. The fermentation-separation coupling biological hydrogen-producing method comprises the following steps of: introducing organic wastewater into a reactor into which anaerobic hydrogen-producing bacteria are added to perform anaerobic hydrogen-producing fermentation, collecting gaseous products, and separating to obtain the hydrogen; pumping biological hydrogen-producing fermentation liquor in a dilution chamber of a bipolar membrane electrodialyzer circularly; pumping a diluted acetic acid solution in a concentration chamber of the bipolar membrane electrodialyzer circularly; pumping an electrode solution in an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, performing bipolar membrane electrodialysis, and separating organic acid from the biological hydrogen-producing fermentation liquor; and returning the separated fermentation liquor to the reactor for fermenting. By the fermentation-separation coupling biological hydrogen-producing method, the yield of hydrogen can be improved by 1.3 to 1.5 times, the pH value can be controlled to 4.8 to 5.5 without addition of alkali, the utilization rate of substrates is improved by over 50 percent to reach 100 percent, the biomass is improved by 80 percent, the specific hydrogen-producing rate can reach 2.54 molH2 / mol glucose, and by the biological hydrogen-producing method, hydrogen production can be promoted greatly.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Microorganism electrochemical denitrification method for enhancing bio-hydrogen production
InactiveCN103613206BImprove denitrification effectImprove nitrogen removal rateBiological water/sewage treatmentChemical industryNitrogen removal
The invention discloses a microorganism electrochemical denitrification method for enhancing the bio-hydrogen production, which belongs to the field of environmental engineering and energy and chemical industry. The method is characterized in that a microorganism electrochemical system is used as a reactor, and denitrification microorganisms are added into a cathode to realize the nitrogen removal by denitrification of a biological cathode. Meanwhile, by adding the hydrogen-production microorganisms in the biological cathode, the BES (knowledge based expert system) denitrification capacity is further improved by utilizing the biological hydrogen production. The denitrification microorganisms can directly utilize the hydrogen generated by the hydrogen-production microorganisms in the biological cathode to carry out the denitrification effect; meanwhile, organic acid generated in the biological hydrogen production process can play a role in buffering pH, so that the BES denitrification rate can be further increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Sequencing-batch simultaneous saccharified photosynthetic biological hydrogen production reactor and hydrogen production operation method thereof
ActiveCN107012089AIncrease contact areaImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess engineeringCellulase
The invention provides a sequencing-batch simultaneous saccharified photosynthetic biological hydrogen production reactor. The reactor comprises a photosynthetic hydrogen production unit and an enzymolysis reaction unit arranged inside the photosynthetic hydrogen production unit, wherein the photosynthetic hydrogen production unit comprises a transparent container; a first seal cap is arranged at the top of the transparent container, and is provided with a charging hole; a discharging hole is formed in the bottom of the transparent container; the enzymolysis reaction unit comprises a lower cylinder, an upper cylinder and a permeable membrane cylinder; a second seal cap is arranged at the upper end of the upper cylinder; and a hydrogen outlet is formed in the second seal cap. The invention further discloses a hydrogen production operation method of the reactor. According to the method, the enzymolysis reaction unit and the hydrogen production reactor are combined together, carbohydrate generated in cellulase hydrolysis is permeated to the hydrogen production part through the permeable membrane cylinder, photosynthetic bacteria are utilized to produce hydrogen by utilizing the permeated carbohydrate, so that enzymolysis and hydrogen production are performed at the same time, and substrate cannot be accumulated, so that the inhibiting effect of carbohydrate on cellulase can be eliminated, the number of reactors can be reduced, and the reaction cost can be reduced.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
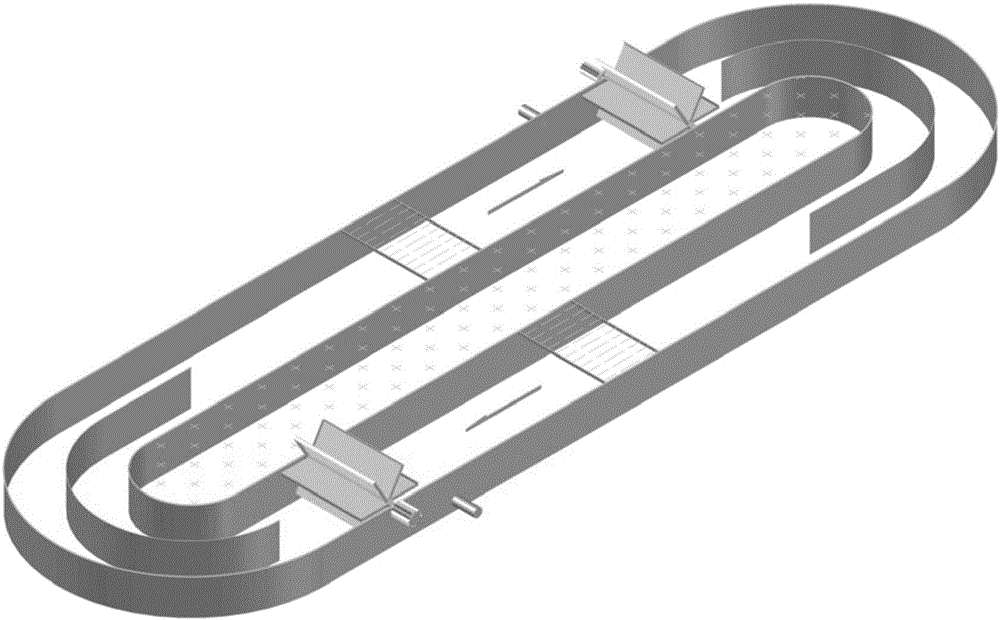
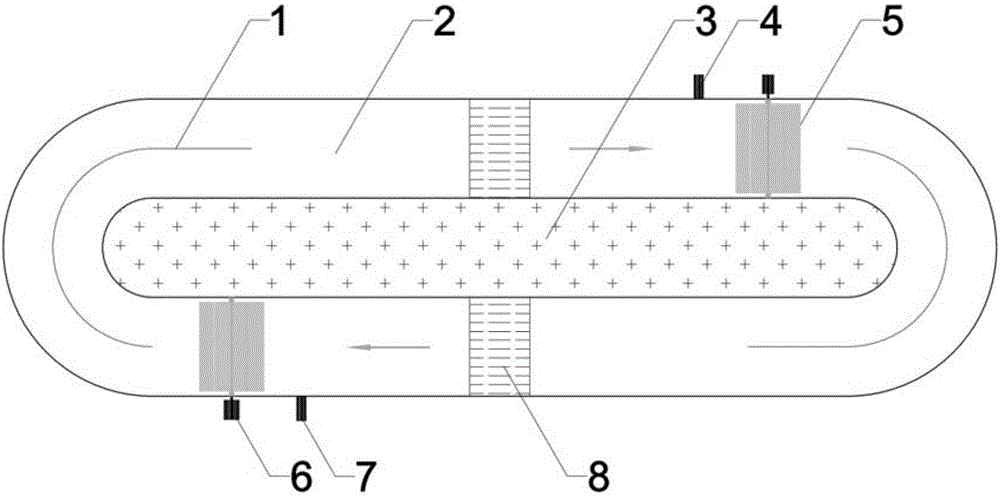
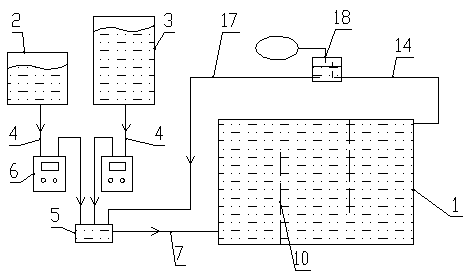
Novel optical channel photosynthetic biological hydrogen production device
ActiveCN103627626AShort stayWell mixedGas production bioreactorsBiomass after-treatmentRefluxProcess engineering
The invention discloses a novel optical channel photosynthetic biological hydrogen production device which comprises a feeding unit, a hydrogen production reactor and a gas-liquid separation unit, wherein the feeding unit comprises a photosynthetic bacteria tank, a hydrogen production substrate tank and a feeding premix box; an outlet of the photosynthetic bacteria tank and an outlet of the hydrogen production substrate tank are respectively connected with an inlet of the feeding premix box through liquid conveying pipes; a constant flow pump is arranged on each liquid conveying pipe; an outlet of the feeding premix box is connected with an inlet of the hydrogen production reactor; an outlet of the hydrogen production reactor is connected with an inlet of the gas-liquid separation unit through a liquid inlet pipe. The device has the advantages that the flow on a flow isolation box is combined with hydrogen production substrate reflux on the basis of summary about the development situations of a conventional photosynthetic bacteria hydrogen production reactor, the flow isolation box is creatively taken as a light box, daylighting area maximization and subtle temperature change are realized, and a technical support is provided for environment-friendly and high-efficiency hydrogen production.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing hydrogen by biomass cascade fermentation
InactiveCN101392269ASolve the problem of low hydrogen conversion rateImprove hydrogen conversionFermentationActivated sludgeSulfonate
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen by the step fermentation of biomass, which relates to a method for producing hydrogen and solves the problem that the transformation rate of the current fermentation method for biological hydrogen production is relatively low. The method comprises the steps: firstly, the shake culture of aerobic granular sludge is carried out, thus obtaining aerobic activated sludge; and then heat treatment is carried out; secondly, water of biological hydrogen production by the fermentation method and disodium bromoethane sulfonate are taken as the bottom materials of reaction equipment, and then the aerobic activated sludge after heat treatment is mutated; and thirdly, nitrogen gas is continuously pumped into the reaction equipment, thus obtaining hydrogen after running. The hydrogen transformation rate of a unit base material in the invention is improved to be more than 2.5molH 2 / mol of hexose.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria
ActiveCN110607337AReduce metabolic inhibitionReduce competitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteElectron transfer
The invention relates to a method for producing hydrogen by syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria, in particular to a method for realizinghigh-efficiency hydrogen production by utilizing syntrophism and interaction of fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria and electroactive bacteria and inter-specific electron transfer, and belongs tothe technical field of hydrogen production by fermentation. The method aims to solve problems that the existing anaerobic biological hydrogen production process is inhibited by bacterial metabolism,substrate is not completely utilized, and then hydrogen production efficiency is influenced. According to the method, Ethanoligenens harbinense W1 and Geobacteria PCA are co-cultured, terminal metabolites such as acetic acid and ethanol produced by the hydrogen-producing bacteria in the fermentation system are consumed by the electroactive bacteria, so that metabolic inhibition among the bacteriain a closed fermentation system is reduced, and continuous and efficient hydrogen production is promoted. In addition, glucose can be used as a carbon source in the method, and the glucose only can beutilized only by the fermentative hydrogen-producing bacteria, so that substrate competition is reduced, and the produced hydrogen has higher yield and higher purity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com